International Encyclopedia of Rehabilitation
|
|
|
- Brett Snow
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 International Encyclopedia of Rehabilitation Copyright 2010 by the Center for International Rehabilitation Research Information and Exchange (CIRRIE). All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced or distributed in any form or by any means, or stored in a database or retrieval system without the prior written permission of the publisher, except as permitted under the United States Copyright Act of Center for International Rehabilitation Research Information and Exchange (CIRRIE) 515 Kimball Tower University at Buffalo, The State University of New York Buffalo, NY [email protected] Web: This publication of the Center for International Rehabilitation Research Information and Exchange is supported by funds received from the National Institute on Disability and Rehabilitation Research of the U.S. Department of Education under grant number H133A The opinions contained in this publication are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of CIRRIE or the Department of Education.
2 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Jennie Walker Carpal tunnel syndrome is an upper limb entrapment neuropathy which may result in motor and sensory disturbance of the median nerve. It is one of the most common entrapment neuropathies and can be managed with varying conservative approaches or with surgical decompression. Lasting impairment may be evident in severe cases and may require intervention from members of the allied health professions to assist with optimum performance in work and leisure activities. What is carpal tunnel syndrome? The carpal tunnel is an anatomical compartment at the base of the wrist. It is bound on three sides by the carpal bones which form an arch and is enclosed by the flexor retinaculum. The retinaculum is attached to the pisiform and hamate on the ulnar side and to the scaphoid and trapezium on the radial side (Abrahams et al. 2005). The median nerve and the nine extrinsic flexors of the fingers and thumb pass through the carpal tunnel beneath the Palmaris longus tendon. The median nerve supplies sensation to the palmer aspect of the radial 3.5 digits and the ends of the fingers on the dorsal aspect of the same digits. The median nerve also provides motor innervation to the muscles of the thenar eminence, particularly the abductor pollicis brevis (abducts the thumb) and the opponens pollicis (flexes, adducts and medially rotates the thumb) (Abrahams et al. 2005, Barnardo, 2004). Carpal tunnel syndrome is a collection of symptoms that occur when there is compression of the median nerve. Intermittent or sustained high pressure within the carpal tunnel due to reduced dimensions of the tunnel, or the increased volume of its contents may result in ischaemia of the median nerve. This results in the impairment of the median nerve conduction and consequently causes paraesthesia and pain within the median nerve distribution. Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is one of the most common upper limb neuropathies and accounts for approximately 90% of entrapment neuropathies (Aroori and Spence 2008). Prolonged pressure on the median nerve may lead to focal demyelination and result in more constant/severe symptoms such as weakness and wasting within the affected hand. If axonal damage occurs due to prolonged ischaemia then nerve dysfunction may become irreversible. Lasting nerve damage may result in permanent loss of function to the median nerve and consequently may have significant impact on work and leisure activities. Prevalence CTS occurs more frequently in those aged over 40 years (Tiedeman, 2004) and is reported by to have an annual incidence of 139 cases per 100,000 females and 67 per 100,000 males (Bland et al. 2003). CTS is also commonly experienced by women during
3 their menopause and during pregnancy due to water retention. Although CTS symptoms generally resolve following childbirth, Mondelli et al. (2007) have noted that approximately 50% of these women may still have mild symptoms 3 years following childbirth. Characteristics CTS produces a range of symptoms that can range from mild to severe and is characterized by tingling, pins and needles, numbness, pain or burning sensations along the median nerve distribution. Pain may often be reported as being worse at night and cause waking; this can be caused by the position of the hands during sleep, which consequently may provoke the symptoms. Relief from symptoms may be obtained by changing hand position or shaking the wrist. The use of a wrist splint at night helps to maintain the wrist in a neutral position without applying direct pressure to the carpal tunnel and consequently reduces the potential to stretch the nerve and therefore alleviates the symptoms (Kanaan and Sawaya 2001; Bland 2007). The dominant hand is more frequently affected by CTS although it is not uncommon for both hands to be affected, especially if there is a constitutionally narrow canal. Symptoms are often exacerbated by sustained hand/arm positions or repetitive actions of the hand and wrist. Other symptoms of CTS may include a dull aching or discomfort in the hand or forearm. Patients may report a weak grip or clumsiness of fine finger movement and/or reduced manual dexterity which may cause the individual to drop things. In severe cases there may also be apparent weakness particularly of the thumb. Physical examination of the hand may be normal, although there may be sensory loss in the median nerve distribution and in some cases dry skin of the thumb, index and middle fingers, although no changes in sensation to the hypothenar element of the palm, as this area is not supplied by the median nerve. As the median nerve carries both motor and sensory fibres there may be noticeable weakness and/or wasting of the thenar eminence. It should be noted that thenar atrophy is a late sign and indicates significant functional loss. On examination thenar atrophy is more readily noticed when comparing both palms together. Special tests for CTS may include Phalen s test or Tinnels sign. Phalen s test causes compression of the median nerve through flexion of the wrist; in a positive test this reproduces the patient s symptoms such as pain and paraesthesia in the median nerve distribution. Similarly, a positive Tinnel s sign causes tingling or discomfort within the digits supplied by the median nerve when the site of the median nerve is percussed at the wrist. What causes CTS? Any condition, trauma or injury which increases the pressure on the median nerve within the carpal tunnel may cause CTS. There is a strong genetic predisposition towards CTS (Hakim et al. 2002) and a positive family history in parents or siblings in 1 in 4 people with CTS (Clinical Knowledge Summaries 2008, Barnardo 2004). Non-specific tenosynovitis is one of the most common causes of increased canal contents (Teidman,
4 2004); however, there are many others factors which may be associated with CTS. Conditions which may be associated with CTS include inflammatory diseases (e.g. rheumatoid arthritis), connective tissue disorders (e.g. systemic lupus erythematosus) or metabolic causes (e.g. hypothyroidism, diabetes mellitus) which should be excluded prior to making the diagnosis of CTS. Other underlying contributory causes may include trauma such as a Colles fracture or a fracture dislocation of the radiocarpal, carpal or carpometacarpal joints. Increased canal volume due to oedema may also occur as a direct result of trauma to the local area. In many cases the cause of CTS in unknown (Clinical Knowledge Summaries, 2008). The routine screening for coexisting disease in people with a new diagnosis of CTS is not recommended despite the higher prevalence of diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism and rheumatoid arthritis in people with CTS (Van Dijk et al. 2003; Clinical Knowledge Summaries, 2008). Practitioners should however have a low index of suspicion before obtaining random blood sugars or thyroxine tests in new cases of CTS. Differential diagnosis for CTS may include cervical radiculopathy particularly at the level C6/7, or generalized peripheral neuropathies. Multiple sclerosis, syringomyelia or brachial plexus injuries should also be excluded, although these are less common neurological conditions. Common vascular conditions to exclude are Raynaud s phenomenon, vibration white finger or cerebral infarction. Osteoarthritis of the metacarpophalengeal joint should also considered as a potential differential diagnosis Diagnostic studies Clinical diagnosis of CTS depends on the presence of median nerve signs and symptoms, although the use of electrodiagnositic studies such as nerve conduction studies or electromyography (EMG) may be beneficial to exclude neuropathy or other nerve entrapments (Bland, 2007, Katz and Simmons 2002). In nerve conduction studies a delay in the latency of the median nerve at the point of suspected compression signifies the compression or demyelination of the nerve. EMG testing can also be utilized to ascertain if there is a delay in latency of the motor unit action potential (muscle). If it is suspected that a tumor, fracture or arthritis are considered to be possible causes of median nerve compression then X-rays should be obtained. Management Symptoms may spontaneously resolve in some individuals, particularly if the individual is under 30 years of age and with short duration of symptoms, or if they are pregnant (Clinical Knowledge Summaries, 2008). Spontaneous remission of CTS was noted in 35% of patients after an average time of 6 months (Futami et al. (1997). The presence of a positive Phalen s test or bilateral symptoms is considered to be poor prognostic signs for a natural recovery (Padua et al. 2001). The purpose of treatment is to alleviate symptoms and where possible prevent the worsening of the condition. Treatment focuses on the decompression of the median nerve within the canal. Conservative management of CTS can simply involve eliminating, or greatly reducing the movements and tasks which seem to exacerbate the symptoms, for example repetitive
5 movements of the wrists and fingers or extremes of flexion/extension of the wrist; although this may not be possible in some types of occupation. The use of a wrist splint to maintain the wrist in a neutral plain is one of the initial steps which can be taken to address CTS symptoms. Wrist splinting is effective in many patients and improvement is usually evident by 8 weeks (Clinical Knowledge Summaries, 2008). There is limited evidence in support of ergonomic adjustments within the workplace to help relieve CTS symptoms (Verhagen et al. 2006), however appropriate modifications may include altering the users or the object position in order to reduce excessive wrist flexion or extension. The use of ergonomic equipment may similarly facilitate the use of correct posturing and alignment to assist with this. Using a relaxed grip and avoidance of gripping too hard when driving, writing or using hand tools again may help alleviate the symptoms of CTS and regular breaks should be encouraged when performing repetitive tasks. Non steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or diuretics are not effective in the ongoing management of CTS and therefore routine uses of these drugs are not recommended. If CTS is attributed to an inflammatory arthritis such as rheumatoid arthritis then management of the underlying condition should relieve the carpal tunnel symptoms (Katz and Simmons, 2002). Local corticosteroid injections to the carpal tunnel may provide short term improvement in symptoms and are often of great benefit to patients, providing significant improvement of symptoms for up to three months (Marshall et al. 2007). At present there is little evidence to support the use of more than one corticosteroid injection (Marshall et al. 2007) as patients often demonstrate no further clinical improvement when compared to those who had the singular injection (Wong 2005). The main risk associated with local corticosteroid injection is the potential for the median nerve to be injected, which may lead to axonal and myelin degeneration (Haase, 2007). The risk of median nerve damage from intraneural injection is however very small and has been estimated to be <0.1% when performed by an experienced health care professional (Bland, 2007). Whilst conservative treatments can be very effective in relieving CTS symptoms, in severe cases or where conservative treatments have been unsuccessful in relieving symptoms, surgical intervention may be necessary. Although splinting has been reported to have a success rate of 37% at 18 months, surgery is more successful in relation to general improvement, severity of symptoms and number of nights waking up due to symptoms (Gerritsen et al. 2002). Operative management involves the decompression of the carpal tunnel by dividing the retinaculum. This decreases the pressure within the carpal tunnel and reduces the pressure on the median nerve. Following surgery the symptoms should resolve, however in severe cases where damage has occurred to the median nerve there may be lasting paraesthesia or weakness. Surgery may be carried out by standard open carpal tunnel release or with the use of less invasive endoscopic technique. Scholten et al. (2007) report that both methods are effective procedures for the short and long term relief of symptoms, however, endoscopic carpal tunnel release allows an earlier return to normal activities of daily living and facilitates an earlier return to work.
6 Complications of surgery may include incomplete release of the retinaculum, injury to the median nerve, reflex sympathetic dystrophy, finger stiffness, weakness, infection and scar tenderness (Tiedman, 2004).Post operative complications such as infection, hypertrophic scar and scar tenderness are noted to be more common in patients who have undergone an open carpal tunnel release, whereas neuropraxia, numbness and paraesthesia are more likely to be experienced by those who undergo an endoscopic carpal tunnel decompression (Gerritsen et al. 2002). The most commonly used method to quantify the effectiveness of treatment involves the use of self reported questionnaires such as the short form-36 (SF-36) to measure generic quality of life, or the Boston Carpal Tunnel Questionnaire which assesses function, activity and outcome measures (Aroori and Spence 2008). CTS may pose many problems for patients, especially if work involves repetitive tasks, or tasks which provoke CTS symptoms. Close liaison with occupational health will assist the individual to adapt the work place to reduce provoking factors, or may be able to help with regards to returning to work following carpal tunnel surgery. In severe cases of CTS where lasting damage is thought to have occurred to the median nerve a thorough assessment of the patients activities of living should be carried out involving the appropriate members of the Allied Health Professions. Reduced grip strength may benefit from advice from occupational therapists and physiotherapists with regards to improving function and finding appropriate adaptations to manage with activities of daily living. Conclusion CTS is a problem which occurs due to compression of the median nerve within the carpal tunnel. Symptoms may be relived through appropriate conservative management which may include ergonomic arrangement of equipment, reduction of repetitive motion and splinting. If conservative management is unsuccessful or medial nerve compression is severe then surgical decompression offers successful management of CTS symptoms. An understanding of what the carpal tunnel is and how carpal tunnel syndrome may be managed allows patients to self-manage the condition where appropriate and enables health care professionals to offer appropriate care and reassurance to patients in different occupational and health care settings. References Abrahams A, Craven J, Lumley J Illustrated clinical anatomy. London: Hodder Arnold. Aroori S, Spence R Carpal tunnel syndrome. Ulster Medical Journal 77(1):6-17. Barnardo J Carpal tunnel syndrome. Arthritis Research Council. Bland J Carpal tunnel syndrome. British Medical Journal :
7 Bland J, Rudolpher S Clinical surveillance of carpal tunnel syndrome in two areas of the United Kingdom Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry 74: Clinical Knowledge Summaries Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. Retrieved from Futami T, Kobayashi A, Ukita T, et al Carpal tunnel syndrome: a natural history. Hand Surgery 2(2): Gerritsen A, de Vet H, Scholten R Splinting vs surgery in the treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome: a randomized control trial. Journal of the American Medical Association 288(10): Haase J Carpal tunnel syndrome a comprehensive review. Advances and Technical Standards in Neurosurgery 32: Hakim A, Cherkas L, El-Zayat S, et al The genetic contribution to carpal tunnel syndrome in women: a twin study. Arthritis and Rheumatism 47(3): Kanaan N, Sawya R Carpal tunnel syndrome: modern diagnostic and management techniques. British Journal of General Practice 51(465): Katz J, Simmons B Carpal tunnel syndrome. New England Journal of Medicine 346(23): Marshall S, Tardif G, Ashworth N Local corticosteroid injection for carpal tunnel syndrome: Cochrane Review. Cochrane Library Issue 2. John Wiley & Sons Ltd. Mondelli M, Rossi S, Monti E, et al Long term follow up with carpal tunnel syndrome during pregnancy: a cohort study and review of the literature. Electromyography and Clinical Neurophysiology 47(6): Pauda L, Pauda R, Aprile I, et al Multiperspective follow up of untreated carpal tunnel syndrome: a multicentre study. Neurology 56(11): Scholten R, Mink van der Molen A, Uitehaag B, et al Surgical treatment options for carpal tunnel syndrome: Cochrane review. Cochrane library Issue 4. John Wiley & Sons Ltd. Tiedman T Nerve entrapments of hand and wrist. In: D Brown, R Neuman, editors. Orthopaedic secrets. 3rd ed. Philidelphia: Hanley and Belfus. Van Dijk M, Reitsma J, Fischer J, Sanders, G Indications for requesting laboratory tests for concurrent diseases in patients with carpal tunnel syndrome: a systematic review. Clinical Chemistry 49(9):
8 Verhagen A, Karels C, Bierma-Zeinstra S, et al Ergonomic and physiotherapeutic interventions for treating work related complaints of the arm, neck or shoulder in adults: Cochrane review. Cochrane Library Issue 3. John Wiley & Sons Ltd. Wong S, Hui A, Lo S, et al Single vs two steroid injections for carpal tunnel syndrome: a randomized clinical trial. International Journal of Clinical Practice 59(12)
Informed Patient Tutorial Copyright 2012 by the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
 Informed Patient Tutorial Copyright 2012 by the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Informed Patient - Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery Introduction Welcome to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons'
Informed Patient Tutorial Copyright 2012 by the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Informed Patient - Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery Introduction Welcome to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons'
A Patient s Guide to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
 A Patient s Guide to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 [email protected] DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a
A Patient s Guide to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 [email protected] DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a
Most active and intricate part of the upper extremity Especially vulnerable to injury Do not respond well to serious trauma. Magee, 2008. pg.
 PTA 216 Most active and intricate part of the upper extremity Especially vulnerable to injury Do not respond well to serious trauma Magee, 2008. pg. 396 28 bones Numerous articulations 19 intrinsic muscles
PTA 216 Most active and intricate part of the upper extremity Especially vulnerable to injury Do not respond well to serious trauma Magee, 2008. pg. 396 28 bones Numerous articulations 19 intrinsic muscles
Proximal border = palmar wrist crease Distal border = Kaplan + ring finger axis
 FPL FCR Proximal border = palmar wrist crease Distal border = Kaplan + ring finger axis Thenar motor branch Kaplan s cardinal line: distal TCL thenar branch Superficial palmar arch superficial arch Originates
FPL FCR Proximal border = palmar wrist crease Distal border = Kaplan + ring finger axis Thenar motor branch Kaplan s cardinal line: distal TCL thenar branch Superficial palmar arch superficial arch Originates
THE WRIST. At a glance. 1. Introduction
 THE WRIST At a glance The wrist is possibly the most important of all joints in everyday and professional life. It is under strain not only in many blue collar trades, but also in sports and is therefore
THE WRIST At a glance The wrist is possibly the most important of all joints in everyday and professional life. It is under strain not only in many blue collar trades, but also in sports and is therefore
Hand Injuries and Disorders
 Hand Injuries and Disorders Introduction Each of your hands has 27 bones, 15 joints and approximately 20 muscles. There are many common problems that can affect your hands. Hand problems can be caused
Hand Injuries and Disorders Introduction Each of your hands has 27 bones, 15 joints and approximately 20 muscles. There are many common problems that can affect your hands. Hand problems can be caused
Repetitive Strain Injury (RSI)
 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and Other Musculoskeletal Problems in the Workplace: What s the Solution? by Richard N. Hinrichs, Ph.D. Dept. of Kinesiology Arizona State University Repetitive Strain Injury (RSI)
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and Other Musculoskeletal Problems in the Workplace: What s the Solution? by Richard N. Hinrichs, Ph.D. Dept. of Kinesiology Arizona State University Repetitive Strain Injury (RSI)
A Patient s Guide to Guyon s Canal Syndrome
 A Patient s Guide to DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources. It may not be complete or timely. It does not cover all diseases, physical conditions, ailments or
A Patient s Guide to DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources. It may not be complete or timely. It does not cover all diseases, physical conditions, ailments or
Mini Medical School: Focus on Orthopaedics
 from The Cleveland Clinic Mini Medical School: Focus on Orthopaedics Common Disorders of the Hand and Wrist Jeffrey Lawton, MD Associate Staff, Department of Orthopaedic The Cleveland Clinic Appointments:
from The Cleveland Clinic Mini Medical School: Focus on Orthopaedics Common Disorders of the Hand and Wrist Jeffrey Lawton, MD Associate Staff, Department of Orthopaedic The Cleveland Clinic Appointments:
Symptoms and Signs of Irritation of the Brachial Plexus in Whiplash Injuries
 1 Symptoms and Signs of Irritation of the Brachial Plexus in Whiplash Injuries J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 2001 Mar;83(2):226-9 Ide M, Ide J, Yamaga M, Takagi K Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kumamoto University
1 Symptoms and Signs of Irritation of the Brachial Plexus in Whiplash Injuries J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 2001 Mar;83(2):226-9 Ide M, Ide J, Yamaga M, Takagi K Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kumamoto University
NERVE COMPRESSION DISORDERS
 Common Disorders of the Hand and Wrist Ryan Klinefelter, MD Associate Professor of Orthopaedics Department of Orthopaedics The Ohio State University Medical Center NERVE COMPRESSION DISORDERS 1 Carpal
Common Disorders of the Hand and Wrist Ryan Klinefelter, MD Associate Professor of Orthopaedics Department of Orthopaedics The Ohio State University Medical Center NERVE COMPRESSION DISORDERS 1 Carpal
CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME A PATIENT GUIDE TO THE NURSE-LED CARPAL TUNNEL SERVICE
 CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME A PATIENT GUIDE TO THE NURSE-LED CARPAL TUNNEL SERVICE Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What is carpal tunnel syndrome? It is entrapment of a nerve at the
CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME A PATIENT GUIDE TO THE NURSE-LED CARPAL TUNNEL SERVICE Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What is carpal tunnel syndrome? It is entrapment of a nerve at the
CONSTRUCTION WORK and CUMULATIVE TRAUMA DISORDERS
 Connecticut Department of Public Health Environmental and Occupational Health Assessment Program 410 Capitol Avenue MS # 11OSP, PO Box 340308 Hartford, CT 06134-0308 (860) 509-7740 http://www.ct.gov/dph
Connecticut Department of Public Health Environmental and Occupational Health Assessment Program 410 Capitol Avenue MS # 11OSP, PO Box 340308 Hartford, CT 06134-0308 (860) 509-7740 http://www.ct.gov/dph
APPENDIX F INTERJURISDICTIONAL RESEARCH
 Ontario Scheduled Presumption: Bursitis, listed in Schedule 3, of the Ontario Workers Compensation Act, entry number 18 Description of Disease Bursitis Process Any process involving constant or prolonged
Ontario Scheduled Presumption: Bursitis, listed in Schedule 3, of the Ontario Workers Compensation Act, entry number 18 Description of Disease Bursitis Process Any process involving constant or prolonged
THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME
 THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME The Problem The term thoracic outlet syndrome is used to describe a condition of compression of the nerves and/or blood vessels in the region around the neck and collarbone, called
THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME The Problem The term thoracic outlet syndrome is used to describe a condition of compression of the nerves and/or blood vessels in the region around the neck and collarbone, called
Differentiating Cervical Radiculopathy and Peripheral Neuropathy. Adam P. Smith, MD
 Differentiating Cervical Radiculopathy and Peripheral Neuropathy Adam P. Smith, MD I have no financial, personal, or professional conflicts of interest to report Radiculopathy versus Neuropathy Radiculopathy
Differentiating Cervical Radiculopathy and Peripheral Neuropathy Adam P. Smith, MD I have no financial, personal, or professional conflicts of interest to report Radiculopathy versus Neuropathy Radiculopathy
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients Therapy Services Phone no: 01625 661481 www.eastcheshire.nhs.uk @eastcheshirenhs Ref: 11437 Review: 06/2015 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Ref: 11437 Page 1 Review:
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients Therapy Services Phone no: 01625 661481 www.eastcheshire.nhs.uk @eastcheshirenhs Ref: 11437 Review: 06/2015 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Ref: 11437 Page 1 Review:
Hand & Plastics Physiotherapy Department Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Hand & Plastics Physiotherapy Department Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients page 2 What is the Carpal Tunnel? The carpal tunnel is made up of the bones
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Hand & Plastics Physiotherapy Department Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients page 2 What is the Carpal Tunnel? The carpal tunnel is made up of the bones
Carpal Tunnel Release. Relieving Pressure in Your Wrist
 Carpal Tunnel Release Relieving Pressure in Your Wrist Understanding Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a problem that affects the wrist and hand. If you have CTS, tingling and numbness
Carpal Tunnel Release Relieving Pressure in Your Wrist Understanding Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a problem that affects the wrist and hand. If you have CTS, tingling and numbness
GUIDANCE AND PROCEDURE FOR HAND ARM VIBRATION
 Department of Human Resources GUIDANCE AND PROCEDURE FOR HAND ARM VIBRATION 1.0 What is Hand-Arm Vibration Syndrome (HAVS)? Hand-Arm Vibration Syndrome (HAVS) is a widespread industrial disease. The Health
Department of Human Resources GUIDANCE AND PROCEDURE FOR HAND ARM VIBRATION 1.0 What is Hand-Arm Vibration Syndrome (HAVS)? Hand-Arm Vibration Syndrome (HAVS) is a widespread industrial disease. The Health
Chapter 7 The Wrist and Hand Joints
 Chapter 7 The Wrist and Hand Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS Many Archery, Relate wrist require sports require precise functioning of flexion, & hand & hand functional combined
Chapter 7 The Wrist and Hand Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS Many Archery, Relate wrist require sports require precise functioning of flexion, & hand & hand functional combined
Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck)
 Copyright 2009 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Neck pain is extremely common. It can be caused by many things, and is most often related to getting
Copyright 2009 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Neck pain is extremely common. It can be caused by many things, and is most often related to getting
Temple Physical Therapy
 Temple Physical Therapy A General Overview of Common Neck Injuries For current information on Temple Physical Therapy related news and for a healthy and safe return to work, sport and recreation Like Us
Temple Physical Therapy A General Overview of Common Neck Injuries For current information on Temple Physical Therapy related news and for a healthy and safe return to work, sport and recreation Like Us
Radiculopathy vs. Peripheral Neuropathy. What to do with arm pain? Defining Arm Pain. Arm Pain
 Radiculopathy vs. Peripheral Neuropathy What to do with arm pain? Miriana G. Popadich RN, MSN Clinical Care Coordinator Brachial Plexus Program Department of Neurosurgery University of Michigan Timing
Radiculopathy vs. Peripheral Neuropathy What to do with arm pain? Miriana G. Popadich RN, MSN Clinical Care Coordinator Brachial Plexus Program Department of Neurosurgery University of Michigan Timing
.org. Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis) Anatomy. Cause
 Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis) Page ( 1 ) Tennis elbow, or lateral epicondylitis, is a painful condition of the elbow caused by overuse. Not surprisingly, playing tennis or other racquet sports can
Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis) Page ( 1 ) Tennis elbow, or lateral epicondylitis, is a painful condition of the elbow caused by overuse. Not surprisingly, playing tennis or other racquet sports can
by joe muscolino body mechanics
 by joe muscolino body mechanics carpal tunnel syndrome The word carpal means wrist. Therefore, the carpal tunnel is a tunnel that is formed by the structural configuration of the wrist (carpal) bones.
by joe muscolino body mechanics carpal tunnel syndrome The word carpal means wrist. Therefore, the carpal tunnel is a tunnel that is formed by the structural configuration of the wrist (carpal) bones.
Work-related upper extremity disorders associated
 Nerve entrapments of the wrist Early treatment preserves function Nerve entrapment syndromes may affect as many as one in four office workers. Prompt diagnosis is critical to the selection of an appropriate
Nerve entrapments of the wrist Early treatment preserves function Nerve entrapment syndromes may affect as many as one in four office workers. Prompt diagnosis is critical to the selection of an appropriate
Fact Sheet: Occupational Overuse Syndrome (OOS)
 Fact Sheet: Occupational Overuse Syndrome (OOS) What is OOS? Occupational Overuse Syndrome (OOS) is the term given to a range of conditions characterised by discomfort or persistent pain in muscles, tendons
Fact Sheet: Occupational Overuse Syndrome (OOS) What is OOS? Occupational Overuse Syndrome (OOS) is the term given to a range of conditions characterised by discomfort or persistent pain in muscles, tendons
Hand & Plastics Physiotherapy Department Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Hand & Plastics Physiotherapy Department Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients This leaflet has been developed to answer any questions you may have regarding
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Hand & Plastics Physiotherapy Department Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients This leaflet has been developed to answer any questions you may have regarding
Ergonomics Monitor Training Manual
 Table of contents I. Introduction Ergonomics Monitor Training Manual II. Definition of Common Injuries Common Hand & Wrist Injuries Common Neck & Back Injuries Common Shoulder & Elbow Injuries III. Ergonomics
Table of contents I. Introduction Ergonomics Monitor Training Manual II. Definition of Common Injuries Common Hand & Wrist Injuries Common Neck & Back Injuries Common Shoulder & Elbow Injuries III. Ergonomics
Basic Concepts. Focal and Entrapment Neuropathies and EMG. Pathophysiology. Median Nerve. A Clinical Approach
 Basic Concepts Focal and Entrapment Neuropathies and EMG A Clinical Approach Nerves predisposed by a narrow anatomic pathway or superficial course are most susceptible May occur acutely, intermittantly,
Basic Concepts Focal and Entrapment Neuropathies and EMG A Clinical Approach Nerves predisposed by a narrow anatomic pathway or superficial course are most susceptible May occur acutely, intermittantly,
The wrist and hand are constructed of a series of complex, delicately balanced joints whose function is essential to almost every act of daily living.
 TOPIC OUTLINE 9- THE WRIST AND HAND. Introduction. The wrist and hand are constructed of a series of complex, delicately balanced joints whose function is essential to almost every act of daily living.
TOPIC OUTLINE 9- THE WRIST AND HAND. Introduction. The wrist and hand are constructed of a series of complex, delicately balanced joints whose function is essential to almost every act of daily living.
Medical Report Checklist: Upper Extremities Peripheral Nerve Disorders Impairments (PND)
 http://www.pdratings.com/ Craig Andrew Lange [email protected] California Workers Compensation Certified AMA Guides Impairment & Disability Rating Specialists Voice: (415) 861-4040 / Fax: (415) 276-3741
http://www.pdratings.com/ Craig Andrew Lange [email protected] California Workers Compensation Certified AMA Guides Impairment & Disability Rating Specialists Voice: (415) 861-4040 / Fax: (415) 276-3741
Diagnosis and Treatment of Cervical Root and Peripheral Nerve Lesions of the Upper Extremity: Carpal and Cubital Tunnel Syndromes
 A Quarterly Publication for Continuing Medical Education Diagnosis and Treatment of Cervical Root and Peripheral Nerve Lesions of the Upper Extremity: Carpal and Cubital Tunnel Syndromes Ann R. Stroink,
A Quarterly Publication for Continuing Medical Education Diagnosis and Treatment of Cervical Root and Peripheral Nerve Lesions of the Upper Extremity: Carpal and Cubital Tunnel Syndromes Ann R. Stroink,
Evaluation of Disorders of the Hands and Wrists
 Evaluation of Disorders of the Hands and Wrists Case 27 yo female with 6 month history of right forearm and hand pain Works as secretary, symptoms are interfering with her job duties Complains that she
Evaluation of Disorders of the Hands and Wrists Case 27 yo female with 6 month history of right forearm and hand pain Works as secretary, symptoms are interfering with her job duties Complains that she
Eric M. Kutz, D.O. Arlington Orthopedics Harrisburg, PA
 Eric M. Kutz, D.O. Arlington Orthopedics Harrisburg, PA 2 offices 805 Sir Thomas Court Harrisburg 3 Walnut Street Lemoyne Mechanism of injury Repetitive overhead activities Falls to the ground Falls with
Eric M. Kutz, D.O. Arlington Orthopedics Harrisburg, PA 2 offices 805 Sir Thomas Court Harrisburg 3 Walnut Street Lemoyne Mechanism of injury Repetitive overhead activities Falls to the ground Falls with
Hand and Upper Extremity Injuries in Outdoor Activities. John A. Schneider, M.D.
 Hand and Upper Extremity Injuries in Outdoor Activities John A. Schneider, M.D. Biographical Sketch Dr. Schneider is an orthopedic surgeon that specializes in the treatment of hand and upper extremity
Hand and Upper Extremity Injuries in Outdoor Activities John A. Schneider, M.D. Biographical Sketch Dr. Schneider is an orthopedic surgeon that specializes in the treatment of hand and upper extremity
Elbow Injuries and Disorders
 Elbow Injuries and Disorders Introduction Your elbow joint is made up of bone, cartilage, ligaments and fluid. Muscles and tendons help the elbow joint move. There are many injuries and disorders that
Elbow Injuries and Disorders Introduction Your elbow joint is made up of bone, cartilage, ligaments and fluid. Muscles and tendons help the elbow joint move. There are many injuries and disorders that
Treatment Guide Understanding Elbow Pain. Using this Guide. Choosing Your Care. Table of Contents:
 Treatment Guide Understanding Elbow Pain Elbow pain is extremely common whether due to aging, overuse, trauma or a sports injury. When elbow pain interferes with carrying the groceries, participating in
Treatment Guide Understanding Elbow Pain Elbow pain is extremely common whether due to aging, overuse, trauma or a sports injury. When elbow pain interferes with carrying the groceries, participating in
.org. Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Anatomy. Cause
 Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Page ( 1 ) Neck pain can be caused by many things but is most often related to getting older. Like the rest of the body, the disks and joints in the neck (cervical
Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Page ( 1 ) Neck pain can be caused by many things but is most often related to getting older. Like the rest of the body, the disks and joints in the neck (cervical
Below is a diagram showing the main bones together with written text on their order of compilation.
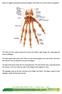 Below is a diagram showing the main bones together with written text on their order of compilation. The hand and wrist contain twenty-seven bones and tendons, eight carpals, five metacarpals and fourteen
Below is a diagram showing the main bones together with written text on their order of compilation. The hand and wrist contain twenty-seven bones and tendons, eight carpals, five metacarpals and fourteen
THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME & BRACHIAL PLEXUS INJURIES
 THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME & BRACHIAL PLEXUS INJURIES I. THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME TOS is a compression of nerves or blood vessels, or both, in the thoracic outlet region, which is the space between the collarbone
THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME & BRACHIAL PLEXUS INJURIES I. THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME TOS is a compression of nerves or blood vessels, or both, in the thoracic outlet region, which is the space between the collarbone
Adult Forearm Fractures
 Adult Forearm Fractures Your forearm is made up of two bones, the radius and ulna. In most cases of adult forearm fractures, both bones are broken. Fractures of the forearm can occur near the wrist at
Adult Forearm Fractures Your forearm is made up of two bones, the radius and ulna. In most cases of adult forearm fractures, both bones are broken. Fractures of the forearm can occur near the wrist at
Multifocal Motor Neuropathy. Jonathan Katz, MD Richard Lewis, MD
 Multifocal Motor Neuropathy Jonathan Katz, MD Richard Lewis, MD What is Multifocal Motor Neuropathy? Multifocal Motor Neuropathy (MMN) is a rare condition in which multiple motor nerves are attacked by
Multifocal Motor Neuropathy Jonathan Katz, MD Richard Lewis, MD What is Multifocal Motor Neuropathy? Multifocal Motor Neuropathy (MMN) is a rare condition in which multiple motor nerves are attacked by
AN EDUCATION BASED ERGONOMIC INTERVENTION PROGRAMME FOR GAUTENG CALL CENTRE WORKERS WITH UPPER EXTREMITY REPETITIVE STRAIN INJURIES.
 AN EDUCATION BASED ERGONOMIC INTERVENTION PROGRAMME FOR GAUTENG CALL CENTRE WORKERS WITH UPPER EXTREMITY REPETITIVE STRAIN INJURIES. Sancha Eliot Johannesburg 2010 DECLARATION I SANCHA ELIOT declare that
AN EDUCATION BASED ERGONOMIC INTERVENTION PROGRAMME FOR GAUTENG CALL CENTRE WORKERS WITH UPPER EXTREMITY REPETITIVE STRAIN INJURIES. Sancha Eliot Johannesburg 2010 DECLARATION I SANCHA ELIOT declare that
CERVICAL DISC HERNIATION
 CERVICAL DISC HERNIATION Most frequent at C 5/6 level but also occur at C 6 7 & to a lesser extent at C4 5 & other levels In relatively younger persons soft disk protrusion is more common than hard disk
CERVICAL DISC HERNIATION Most frequent at C 5/6 level but also occur at C 6 7 & to a lesser extent at C4 5 & other levels In relatively younger persons soft disk protrusion is more common than hard disk
Aetna Nerve Conduction Study Policy
 Aetna Nerve Conduction Study Policy Policy Aetna considers nerve conduction velocity (NCV) studies medically necessary when both of the following criteria are met: 1. Member has any of the following indications:
Aetna Nerve Conduction Study Policy Policy Aetna considers nerve conduction velocity (NCV) studies medically necessary when both of the following criteria are met: 1. Member has any of the following indications:
CUMMULATIVE DISORDERS OF UPPER EXTIMITY DR HABIBOLLAHI
 CUMMULATIVE DISORDERS OF UPPER EXTIMITY DR HABIBOLLAHI Definition Musculoskeletal disorder (MSD) is an injury or disorder of the muscles, nerves, tendons, joints, cartilage,ligament and spinal discs. It
CUMMULATIVE DISORDERS OF UPPER EXTIMITY DR HABIBOLLAHI Definition Musculoskeletal disorder (MSD) is an injury or disorder of the muscles, nerves, tendons, joints, cartilage,ligament and spinal discs. It
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, an overview
 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, an overview Jim Lewis, R.NCS.T. Learning Objectives: Median nerve compression at the wrist is the most common entrapment seen in the electrodiagnostic laboratory. Although it is
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, an overview Jim Lewis, R.NCS.T. Learning Objectives: Median nerve compression at the wrist is the most common entrapment seen in the electrodiagnostic laboratory. Although it is
INFLUENCE OF SELECTED PHYSICAL EXERCISES TO IMPROVE OUTCOMES IN PATIENTS OPERATED FOR CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME IN OWN MATERIAL
 Central European Journal of Sport Sciences and Medicine : 47 51 INFLUENCE OF SELECTED PHYSICAL EXERCISES TO IMPROVE OUTCOMES IN PATIENTS OPERATED FOR CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME IN OWN MATERIAL Zbigniew Deskur,
Central European Journal of Sport Sciences and Medicine : 47 51 INFLUENCE OF SELECTED PHYSICAL EXERCISES TO IMPROVE OUTCOMES IN PATIENTS OPERATED FOR CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME IN OWN MATERIAL Zbigniew Deskur,
Lean-Ergonomic methods to reduce workers compensation costs (Part 2 of 2) Cumulative trauma disorders can be classified as: What is CTD?
 #425 Lean-ergonomic methods to reduce workers compensation costs, Part 2 of 2 Lean-Ergonomic methods to reduce workers compensation costs (Part 2 of 2) Govid Bharwani, Ph.D, Biomedical Engineering Thursday,
#425 Lean-ergonomic methods to reduce workers compensation costs, Part 2 of 2 Lean-Ergonomic methods to reduce workers compensation costs (Part 2 of 2) Govid Bharwani, Ph.D, Biomedical Engineering Thursday,
CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME
 CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME Background 1. Definition: Entrapment neuropathy of median nerve as it courses through carpal tunnel o Stage I: Predominantly nocturnal symptoms of numbness and /or tingling in fingers
CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME Background 1. Definition: Entrapment neuropathy of median nerve as it courses through carpal tunnel o Stage I: Predominantly nocturnal symptoms of numbness and /or tingling in fingers
INJURIES OF THE HAND AND WRIST By Derya Dincer, M.D.
 05/05/2007 INJURIES OF THE HAND AND WRIST By Derya Dincer, M.D. Hand injuries, especially the fractures of metacarpals and phalanges, are the most common fractures in the skeletal system. Hand injuries
05/05/2007 INJURIES OF THE HAND AND WRIST By Derya Dincer, M.D. Hand injuries, especially the fractures of metacarpals and phalanges, are the most common fractures in the skeletal system. Hand injuries
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: No-Stitch Endoscopic Surgery as a Treatment Option by Scott R. Gibbs, MD, Kyle O. Colle, DO, & Christine M.
 Scientific Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: No-Stitch Endoscopic Surgery as a Treatment Option by Scott R. Gibbs, MD, Kyle O. Colle, DO, & Christine M. Byrd, MSN Since the 1980s, CTS has become one of the most
Scientific Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: No-Stitch Endoscopic Surgery as a Treatment Option by Scott R. Gibbs, MD, Kyle O. Colle, DO, & Christine M. Byrd, MSN Since the 1980s, CTS has become one of the most
Wrist Fracture. Please stick addressograph here
 ORTHOPAEDIC UNIT: 01-293 8687 /01-293 6602 UPMC BEACON CENTRE FOR ORTHOPAEDICS: 01-2937575 PHYSIOTHERAPY DEPARTMENT: 01-2936692 GUIDELINES FOR PATIENTS FOLLOWING WRIST FRACTURE Please stick addressograph
ORTHOPAEDIC UNIT: 01-293 8687 /01-293 6602 UPMC BEACON CENTRE FOR ORTHOPAEDICS: 01-2937575 PHYSIOTHERAPY DEPARTMENT: 01-2936692 GUIDELINES FOR PATIENTS FOLLOWING WRIST FRACTURE Please stick addressograph
Muscles of the Forearm and Hand
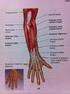 8 Muscles of the Forearm and Hand 132 PRONATOR TERES Strengthening exercises Pronation with strength bar Self stretches Weight of stick increases supination via gravity PRONATOR TERES 133 Latin, pronate,
8 Muscles of the Forearm and Hand 132 PRONATOR TERES Strengthening exercises Pronation with strength bar Self stretches Weight of stick increases supination via gravity PRONATOR TERES 133 Latin, pronate,
BEFORE THE APPEALS BOARD FOR THE KANSAS DIVISION OF WORKERS COMPENSATION
 BEFORE THE APPEALS BOARD FOR THE KANSAS DIVISION OF WORKERS COMPENSATION BARBARA SHEREE HUTSON ) Claimant ) ) VS. ) Docket No. 1,035,700 ) CUSTOM CAMPERS, INC. ) Self-Insured Respondent ) ORDER Claimant
BEFORE THE APPEALS BOARD FOR THE KANSAS DIVISION OF WORKERS COMPENSATION BARBARA SHEREE HUTSON ) Claimant ) ) VS. ) Docket No. 1,035,700 ) CUSTOM CAMPERS, INC. ) Self-Insured Respondent ) ORDER Claimant
.org. Arthritis of the Hand. Description
 Arthritis of the Hand Page ( 1 ) The hand and wrist have multiple small joints that work together to produce motion, including the fine motion needed to thread a needle or tie a shoelace. When the joints
Arthritis of the Hand Page ( 1 ) The hand and wrist have multiple small joints that work together to produce motion, including the fine motion needed to thread a needle or tie a shoelace. When the joints
How To Know If You Can Get A Carpal Tunnel Injury Compensation
 U. S. DEPARTMENT OF LABOR Employees Compensation Appeals Board In the Matter of BARBARA SNYDER and DEPARTMENT OF THE TREASURY, INTERNAL REVENUE SERVICE, Germansville, PA Docket No. 03-1467; Submitted on
U. S. DEPARTMENT OF LABOR Employees Compensation Appeals Board In the Matter of BARBARA SNYDER and DEPARTMENT OF THE TREASURY, INTERNAL REVENUE SERVICE, Germansville, PA Docket No. 03-1467; Submitted on
Neck Pain Overview Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment Options
 Neck Pain Overview Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment Options Neck pain is one of the most common forms of pain for which people seek treatment. Most individuals experience neck pain at some point during
Neck Pain Overview Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment Options Neck pain is one of the most common forms of pain for which people seek treatment. Most individuals experience neck pain at some point during
Sciatica Yuliya Mutsa PTA 236
 Sciatica Yuliya Mutsa PTA 236 Sciatica is a common type of pain affecting the sciatic nerve, which extends from the lower back all the way through the back of the thigh and down through the leg. Depending
Sciatica Yuliya Mutsa PTA 236 Sciatica is a common type of pain affecting the sciatic nerve, which extends from the lower back all the way through the back of the thigh and down through the leg. Depending
Wrist and Hand. Patient Information Guide to Bone Fracture, Bone Reconstruction and Bone Fusion: Fractures of the Wrist and Hand: Carpal bones
 Patient Information Guide to Bone Fracture, Bone Reconstruction and Bone Fusion: Wrist and Hand Fractures of the Wrist and Hand: Fractures of the wrist The wrist joint is made up of the two bones in your
Patient Information Guide to Bone Fracture, Bone Reconstruction and Bone Fusion: Wrist and Hand Fractures of the Wrist and Hand: Fractures of the wrist The wrist joint is made up of the two bones in your
Systemic condition affecting synovial tissue Hypertrohied synovium destroys. Synovectomy. Tenosynovectomy Tendon Surgery Arthroplasty Arthrodesis
 Surgical Options for Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Wrist Raj Bhatia Consultant Hand & Orthopaedic Surgeon Bristol Royal Infirmary & Avon Orthopaedic Centre Rheumatoid Arthritis Systemic condition affecting
Surgical Options for Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Wrist Raj Bhatia Consultant Hand & Orthopaedic Surgeon Bristol Royal Infirmary & Avon Orthopaedic Centre Rheumatoid Arthritis Systemic condition affecting
Repetitive strain injury (RSI) in the workplace
 AbilityNet Factsheet September 2015 Repetitive strain injury (RSI) in the workplace This factsheet looks at repetitive strain injury (RSI) the term most often used to describe the pain felt in muscles,
AbilityNet Factsheet September 2015 Repetitive strain injury (RSI) in the workplace This factsheet looks at repetitive strain injury (RSI) the term most often used to describe the pain felt in muscles,
Get Rid of Elbow Pain
 Get Rid of Elbow Pain Self Regional Healthcare Optimum Life Center 115 Academy Avenue Greenwood, SC 29646 Office: (864) 725-7088 Self Regional Healthcare Physical Therapy Savannah Lakes 207 Holiday Road
Get Rid of Elbow Pain Self Regional Healthcare Optimum Life Center 115 Academy Avenue Greenwood, SC 29646 Office: (864) 725-7088 Self Regional Healthcare Physical Therapy Savannah Lakes 207 Holiday Road
Treatment Guide Understanding Hand and Wrist Pain. Using this Guide. Choosing Your Care
 Treatment Guide Understanding Hand and Wrist Pain With how much we rely on our hands, there s no wonder hand and wrist pain can be so disabling and frustrating. When this pain interferes with typing on
Treatment Guide Understanding Hand and Wrist Pain With how much we rely on our hands, there s no wonder hand and wrist pain can be so disabling and frustrating. When this pain interferes with typing on
Standard of Care: Carpal Tunnel Release
 Department of Rehabilitation Services Physical Therapy Case Type / Diagnosis Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is certainly the most common and frequently diagnosed nerve entrapment, and as such, carpal tunnel
Department of Rehabilitation Services Physical Therapy Case Type / Diagnosis Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is certainly the most common and frequently diagnosed nerve entrapment, and as such, carpal tunnel
Elbow Examination. Haroon Majeed
 Elbow Examination Haroon Majeed Key Points Inspection Palpation Movements Neurological Examination Special tests Joints above and below Before Starting Introduce yourself Explain to the patient what the
Elbow Examination Haroon Majeed Key Points Inspection Palpation Movements Neurological Examination Special tests Joints above and below Before Starting Introduce yourself Explain to the patient what the
The Numb Hand. James T. Mazzara, M.D. Shoulder and Elbow Surgery Sports Medicine Occupational Orthopedics
 The Numb Hand James T. Mazzara, M.D. Shoulder and Elbow Surgery Sports Medicine Occupational Orthopedics Patient Education Disclaimer This presentation describes information to educate consumers on various
The Numb Hand James T. Mazzara, M.D. Shoulder and Elbow Surgery Sports Medicine Occupational Orthopedics Patient Education Disclaimer This presentation describes information to educate consumers on various
United States Department of Labor Employees Compensation Appeals Board DECISION AND ORDER
 United States Department of Labor Employees Compensation Appeals Board P.L., Appellant and U.S. POSTAL SERVICE, POST OFFICE, Santa Clarita, CA, Employer Appearances: Richard Heavey, Esq., for the appellant
United States Department of Labor Employees Compensation Appeals Board P.L., Appellant and U.S. POSTAL SERVICE, POST OFFICE, Santa Clarita, CA, Employer Appearances: Richard Heavey, Esq., for the appellant
Electrodiagnostic Testing
 Electrodiagnostic Testing Electromyogram and Nerve Conduction Study North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Electrodiagnostic Testing? The term electrodiagnostic testing covers a
Electrodiagnostic Testing Electromyogram and Nerve Conduction Study North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Electrodiagnostic Testing? The term electrodiagnostic testing covers a
6/3/2011. High Prevalence and Incidence. Low back pain is 5 th most common reason for all physician office visits in the U.S.
 High Prevalence and Incidence Prevalence 85% of Americans will experience low back pain at some time in their life. Incidence 5% annual Timothy C. Shen, M.D. Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Sub-specialty
High Prevalence and Incidence Prevalence 85% of Americans will experience low back pain at some time in their life. Incidence 5% annual Timothy C. Shen, M.D. Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Sub-specialty
.org. Distal Radius Fracture (Broken Wrist) Description. Cause
 Distal Radius Fracture (Broken Wrist) Page ( 1 ) The radius is the larger of the two bones of the forearm. The end toward the wrist is called the distal end. A fracture of the distal radius occurs when
Distal Radius Fracture (Broken Wrist) Page ( 1 ) The radius is the larger of the two bones of the forearm. The end toward the wrist is called the distal end. A fracture of the distal radius occurs when
EMG and the Electrodiagnostic Consultation for the Family Physician
 EMG and the Electrodiagnostic Consultation for the Family Physician Stephanie Kopey, D.O., P.T. 9/27/15 The American Association of Neuromuscular & Electrodiagnostic Medicine (AANEM) Marketing Committee
EMG and the Electrodiagnostic Consultation for the Family Physician Stephanie Kopey, D.O., P.T. 9/27/15 The American Association of Neuromuscular & Electrodiagnostic Medicine (AANEM) Marketing Committee
Your Body, Your Job. Preventing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and Other Upper Extremity Musculoskeletal Disorders
 Your Body, Your Job Preventing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and Other Upper Extremity Musculoskeletal Disorders Your Body, Your Job Preventing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and Other Upper Extremity Musculoskeletal
Your Body, Your Job Preventing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and Other Upper Extremity Musculoskeletal Disorders Your Body, Your Job Preventing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and Other Upper Extremity Musculoskeletal
OVERVIEW. NEUROSURGICAL ASSESSMENT CERVICAL PROBLEMS Dirk G. Franzen, M.D. WHAT IS THE MOST IMPORTANT PART OF THE PHYSICAL EXAM?
 NEUROSURGICAL ASSESSMENT CERVICAL PROBLEMS Dirk G. Franzen, M.D. Neurological Surgery Bluegrass Orthopaedics and Hand Care OVERVIEW SCOPE OF THE PROBLEM PREVALENCE PATHOLOGY ANATOMIC CONSIDERATIONS ASSESSMENT
NEUROSURGICAL ASSESSMENT CERVICAL PROBLEMS Dirk G. Franzen, M.D. Neurological Surgery Bluegrass Orthopaedics and Hand Care OVERVIEW SCOPE OF THE PROBLEM PREVALENCE PATHOLOGY ANATOMIC CONSIDERATIONS ASSESSMENT
LATE RESPONSES IN MEDIAN NERVE ENTRAPMENT NEUROPATHY IN THE CARPAL TUNNEL
 Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Series VI: Medical Sciences Vol. 7 (56) No.2-2014 LATE RESPONSES IN MEDIAN NERVE ENTRAPMENT NEUROPATHY IN THE CARPAL TUNNEL A. M. GALAMB 1 I. D. MINEA
Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Series VI: Medical Sciences Vol. 7 (56) No.2-2014 LATE RESPONSES IN MEDIAN NERVE ENTRAPMENT NEUROPATHY IN THE CARPAL TUNNEL A. M. GALAMB 1 I. D. MINEA
Body Mechanics for Mammography Technologists
 Body Mechanics for Mammography Technologists Diane Rinella RT(R)(M)(BD)RDMS(BR)CDT Objectives Recognize causes and risk factors for Musculoskeletal Disorders (MSDs) for mammography technologists Understand
Body Mechanics for Mammography Technologists Diane Rinella RT(R)(M)(BD)RDMS(BR)CDT Objectives Recognize causes and risk factors for Musculoskeletal Disorders (MSDs) for mammography technologists Understand
Repetitive Strain Injury
 Page1 Repetitive Strain Injury Repetitive strain injury (RSI) is an injury caused by repetitive use of muscles. For the purpose of this article I will refer to repetitive strain injury as RSI. It usually
Page1 Repetitive Strain Injury Repetitive strain injury (RSI) is an injury caused by repetitive use of muscles. For the purpose of this article I will refer to repetitive strain injury as RSI. It usually
WRIST EXAMINATION. Look. Feel. Move. Special Tests
 WRIST EXAMINATION Look o Dorsum, side, palmar- palmar flex wrist to exacerbate dorsal swellings o Deformity e.g. radial deviation after colles, prominent ulna o Swellings e.g. ganglion o Scars, muscle
WRIST EXAMINATION Look o Dorsum, side, palmar- palmar flex wrist to exacerbate dorsal swellings o Deformity e.g. radial deviation after colles, prominent ulna o Swellings e.g. ganglion o Scars, muscle
Scaphoid Fracture of the Wrist
 Page 1 of 6 Scaphoid Fracture of the Wrist Doctors commonly diagnose a sprained wrist after a patient falls on an outstretched hand. However, if pain and swelling don't go away, doctors become suspicious
Page 1 of 6 Scaphoid Fracture of the Wrist Doctors commonly diagnose a sprained wrist after a patient falls on an outstretched hand. However, if pain and swelling don't go away, doctors become suspicious
Upper Arm. Shoulder Blades R L B R L B WHICH SIDE IS MORE PAINFUL? (CERVICAL PAIN SIDE) RIGHT LEFT EQUAL NOT APPLICABLE (N/A) CERVICAL.
 1 NECK PAIN Patient Name In order to properly assess your condition, we must understand how much your NECK/ARM problems has affected your ability to manage everyday activities. For each item below, please
1 NECK PAIN Patient Name In order to properly assess your condition, we must understand how much your NECK/ARM problems has affected your ability to manage everyday activities. For each item below, please
Low Back Injury in the Industrial Athlete: An Anatomic Approach
 Low Back Injury in the Industrial Athlete: An Anatomic Approach Earl J. Craig, M.D. Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Epidemiology
Low Back Injury in the Industrial Athlete: An Anatomic Approach Earl J. Craig, M.D. Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Epidemiology
Beware! your mouse can bite your hand!
 Beware! your mouse can bite your hand! Pradnya R. Malandkar K. Munshi When a typical form of work is extensively performed repeatedly over a large time span (years) it causes R.S.I. (Repetitive Stress
Beware! your mouse can bite your hand! Pradnya R. Malandkar K. Munshi When a typical form of work is extensively performed repeatedly over a large time span (years) it causes R.S.I. (Repetitive Stress
Entrapment and Compressive Neuropathies
 Entrapment and Compressive Neuropathies Barbara E. Shapiro, MD, PhD*, David C. Preston, MD KEYWORDS Entrapment neuropathy Compressive neuropathy Entrapment and compressive neuropathies of the upper and
Entrapment and Compressive Neuropathies Barbara E. Shapiro, MD, PhD*, David C. Preston, MD KEYWORDS Entrapment neuropathy Compressive neuropathy Entrapment and compressive neuropathies of the upper and
Upper Extremity MMI and Impairment Rating
 Upper Extremity MMI and Impairment Rating 1 How to Determine Maximum Medical Improvement 1. Understand the definition of MMI 2. Review the DWC Form-032, Request for Designated Doctor Examination 3. Review
Upper Extremity MMI and Impairment Rating 1 How to Determine Maximum Medical Improvement 1. Understand the definition of MMI 2. Review the DWC Form-032, Request for Designated Doctor Examination 3. Review
Return to same game if sx s resolve within 15 minutes. Return to next game if sx s resolve within one week Return to Competition
 Assessment Skills of the Spine on the Field and in the Clinic Ron Burke, MD Cervical Spine Injuries Sprains and strains Stingers Transient quadriparesis Cervical Spine Injuries Result in critical loss
Assessment Skills of the Spine on the Field and in the Clinic Ron Burke, MD Cervical Spine Injuries Sprains and strains Stingers Transient quadriparesis Cervical Spine Injuries Result in critical loss
The Hand Exam: Tips and Tricks
 The Hand Exam: Tips and Tricks Nikki Strauss Schroeder, MD Assistant Clinical Professor, UCSF Department of Orthopaedic Surgery November 4, 2013 Outline Surface Anatomy Hand Anatomy Exam Management of
The Hand Exam: Tips and Tricks Nikki Strauss Schroeder, MD Assistant Clinical Professor, UCSF Department of Orthopaedic Surgery November 4, 2013 Outline Surface Anatomy Hand Anatomy Exam Management of
How To Treat Musculoskeletal Injury In Sonographers
 MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDERS IN SONOGRAPHERS: ARE WE DOING ENOUGH? Many terms are used to refer to work related injuries among sonographers. Musculosketetal injury (MSI) Repetitive motion injury (RMI) Repetitive
MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDERS IN SONOGRAPHERS: ARE WE DOING ENOUGH? Many terms are used to refer to work related injuries among sonographers. Musculosketetal injury (MSI) Repetitive motion injury (RMI) Repetitive
The Carpal Tunnel CTS. Stålberg 1. Dysfunction of median nerve in the carpal tunnel resulting in
 The Carpal Tunnel CTS Dysfunction of median nerve in the carpal tunnel resulting in 1 Symptoms in CTS pain and numbness in the abd worse on finger activity aggravated by forceful gripping g symptoms more
The Carpal Tunnel CTS Dysfunction of median nerve in the carpal tunnel resulting in 1 Symptoms in CTS pain and numbness in the abd worse on finger activity aggravated by forceful gripping g symptoms more
.org. Rotator Cuff Tears. Anatomy. Description
 Rotator Cuff Tears Page ( 1 ) A rotator cuff tear is a common cause of pain and disability among adults. In 2008, close to 2 million people in the United States went to their doctors because of a rotator
Rotator Cuff Tears Page ( 1 ) A rotator cuff tear is a common cause of pain and disability among adults. In 2008, close to 2 million people in the United States went to their doctors because of a rotator
Welcome to the July 2012 edition of Case Studies from the files of the Institute for Nerve Medicine in Santa Monica, California.
 Welcome to the July 2012 edition of Case Studies from the files of the Institute for Nerve Medicine in Santa Monica, California. In this issue, we focus on a 23-year-old female patient referred by her
Welcome to the July 2012 edition of Case Studies from the files of the Institute for Nerve Medicine in Santa Monica, California. In this issue, we focus on a 23-year-old female patient referred by her
A Hidden Challenge in WORKERS COMPENSATION
 Published by the Public Risk Management Association www.primacentral.org A Hidden Challenge in WORKERS COMPENSATION APRIL 2015 A Hidden Challenge in WORKERS COMPENSATION By Dr. John Robinton 2 PUBLIC RISK
Published by the Public Risk Management Association www.primacentral.org A Hidden Challenge in WORKERS COMPENSATION APRIL 2015 A Hidden Challenge in WORKERS COMPENSATION By Dr. John Robinton 2 PUBLIC RISK

 Full version is >>> HERE
Full version is >>> HERE  Full version is >>> HERE
Full version is >>> HERE