An Oracle White Paper December Setting Up a Virtual Network Automatically Using Oracle Solaris 11 Express Project Crossbow
|
|
|
- Laura Hoover
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 An Oracle White Paper December 2010 Setting Up a Virtual Network Automatically Using Oracle Solaris 11 Express Project Crossbow
2 Introduction... 1 Description of the Scripts for an Automated Installation... 2 Network Topology... 3 Prerequisites for Using the Scripts... 4 Using the Scripts to Set Up a Virtual Network Automatically... 4 Using the Scripts to Remove or Re-create a Virtual Network... 5 Post-Installation Steps... 6 Setting Up a Virtual Network Interactively... 6 Overview of the Manual Steps... 7 Create vnics, vswitches, and Oracle Solaris ZFS Pool and File System... 7 Create szone (Template Zone)... 8 Create zone Create zone Create zone Create zone Create zgwhost (Gateway Host) Conclusion Appix: Code for the Scripts and var.init File The os_mk_crossbow.sh Script The exec_os_mk_crossbow.sh Script The nv_mk_crossbow.sh Script The exec_nv_mk_crossbow.sh Script... 43
3 The cl_crossbow.sh Script The exec_cl_crossbow.sh Script The var.init File For More Information... 50
4 Introduction This paper is a step-by-step guide on how to set up a virtual network automatically within a single box using Project Crossbow technology and the Bourne shell scripts supplied with this paper. Using the scripts, you can set up a virtual network with no manual intervention. Note: This paper does not explain how Oracle Solaris 11 Express Project Crossbow works. There are many resources on opensolaris.org about virtual networking using Project Crossbow. For example, for more information about Oracle Solaris networking, Project Crossbow network virtualization, and related topics, see the PDF presentation linked to from this page: The scripts provided with this paper can help system administrators, solution architects, and systems engineers perform a quick setup of Project Crossbow for test, demo, or JumpStart installation purposes. This paper also presents an interactive (manual) installation so you can better understand how to customize the scripts, for example, by exting them to use network address translation (NAT) and IP ltering. By customizing the scripts, you can ext them for your own requirements and delve more deeply into Oracle Solaris Containers, Project Crossbow, routing, NAT, and IP ltering. 1
5 Description of the Scripts for an Automated Installation The Bourne shell scripts for setting up a virtual network in a fully automated fashion consist of two shell functions, one for creating the network and one for removing the network. You execute these functions by running two small exec scripts. There is also a variable declaration script for effectively controlling the parameters of the scripts. The shell scripts functions can help you encapsulate and group common tasks into many easily manageable, customizable executable modules. Here is a description of the six scripts and two associated les: Note: See the appix for a code listing of all the scripts and the var.init le. The scripts and associated les were tested with Oracle Solaris 11 Express and with Solaris Express Community Edition Build 130. os_mk_crossbow.sh This script is a collection of function modules to perform a creation of etherstubs, vnics, zones, and so on. This is a script for Oracle Solaris 11 Express based systems. For Solaris Express Community Edition based systems, use nv_mk_crossbow.sh instead. exec_os_mk_crossbow.sh To execute and control a function of interest, use this script. If, for example, you want to create zones but not etherstubs, you just comment out the appropriate function. This is a script for Oracle Solaris 11 Express based systems. For Solaris Express Community Edition based systems, use exec_nv_mk_crossbow.sh instead. nv_mk_crossbow.sh This script is a collection of function modules to perform a creation of etherstubs, vnics, zones, and so on. This is a script for Solaris Express Community Edition based systems. For Oracle Solaris 11 Express based systems, use os_mk_crossbow.sh instead. exec_nv_mk_crossbow.sh To execute and control a function of interest, use this script. If, for example, you want to create zones but not etherstubs, you just comment out the appropriate function. This is a script for Solaris Express Community Edition based systems. For Oracle Solaris 11 Express based systems, use exec_os_mk_crossbow.sh instead. cl_crossbow.sh This script is a collection of function modules to remove the entire virtual network or just part of its conguration. exec_cl_crossbow.sh Use this script to execute the cl_crossbow.sh script. 2
6 var.init All user-denable variables are initialized within this le. Note: The following line is commented out in the var.init le: RPW=`cat /etc/shadow grep root awk -F":" '{print $2}'` Then, the next line contains a hard-coded, encrypted password. The password used to generate the encrypted password was newroot. If you prefer to extract the password from your system, uncomment the commented-out line and then comment out the next line. site.xml This le is useful for enabling or disabling Oracle Solaris Service Management Facility (SMF) services. In our case, we need IPv4 routing and PIv4-forwarding enabled on the gateway host. You can extract this le from any system using the following commands, or you can use the site.xml le provided in the crossbow_scripts.zip le that is associated with this paper: global svccfg extract > site.xml global cp -p site.xml /zones/zgwhost/root/var/svc/prole/site.xml Here is an excerpt from the site.xml le showing the relevant lines for our setup: <service name='network/ipv4-forwarding' type='service' version='0'> <instance name='default' enabled='true'/> </service> <service name='network/routing/route' type='service' version='0'> <instance name='default' enabled='true'/> </service> Network Topology The virtual network will run on a single system using Project Crossbow as a virtual wire. (My system is an Oracle Sun Ultra 24 workstation with quad Q8200 CPUs and 8 GBytes ECC RAM.) As shown in Figure 1, the network consists of hosts (zones), vswitches (etherstubs), and a router. The virtual network is created using Oracle Solaris 11 Express Project Crossbow technology and the hosts are created using Oracle Solaris Zones. Every step necessary to achieve the virtual topology is shown in this paper. 3
7 Figure 1: Network Topology Prerequisites for Using the Scripts All you need is a single host running Oracle Solaris 11 Express or Solaris Express Community Edition (preferably one of the newer builds, for example, 130). Using the Scripts to Set Up a Virtual Network Automatically Note: Before you use the scripts, it is a good idea to become familiar with what the scripts do by reading the Setting Up the Virtual Network Interactively section, which describes how to set up a virtual network interactively (manually). 1. Create a base directory called /repository/crossbow-build for $CFG. Note: You can use a different name for the base directory. If you do, be sure you perform Step 4 to change the default parameter setting for $CFG in the var.init le. 2. Download the crossbow_scripts.zip le that is associated with this paper, which contains the scripts. 3. Copy the scripts to the base directory you created in Step 1. 4
8 4. If you used a name other than /repository/crossbow-build for the base directory or if you want to use a pool other than rpool for the zpool, edit the var.init le and change the value of the parameter settings for $CFG and $MZNPL, respectively. 5. Set the appropriate le permissions for the scripts (for example, 755). 6. Edit exec_os_mk_crossbow.sh (for an Oracle Solaris 11 Express system) or exec_nv_mk_crossbow.sh (for a Solaris Express Community Edition based system) to uncomment all functions so all functions are activated. For example:../os_mk_crossbow.sh verify_user mketherstub mkvnics prepare_templatezone prepare_gzone mk_template_les mkzones Note: The rst time you use the scripts, you need to execute all functions including the template zone creation function. Retain the template zone for later in case you need to remove or recreate the virtual network. Retaining the template zone saves a lot of time, because the other zones are cloned from the template zone. 7. Execute exec_os_mk_crossbow.sh (for an Oracle Solaris 11 Express system) or exec_nv_mk_crossbow.sh (for a Solaris Express Community Edition based system). 8. Go to the Post-Installation Steps section. Using the Scripts to Remove or Re-create a Virtual Network To remove a virtual network: 1. Check the exec_cl_crossbow.sh script to ensure the following lines look like this:../cl_crossbow.sh verify_user cleanup_zones cleanup_vinterfaces 2. Execute exec_cl_crossbow.sh. 3. If necessary, delete the mountpoints of every removed zone manually. 5
9 Note: After I successfully removed all zones including the template zone, I attempted to recreate the zones, but it did not work. The ZFS le systems are mounted out of order, and I got an error message that indicated this problem: cannot mount /.../... directory not empty. This happens only on Oracle Solaris 11 Express, not on Solaris Express Community Edition. The workaround (for Oracle Solaris 11 Express only): Prior to recreation, delete the mountpoints of every removed zone. (This workaround is integrated into the exec_cl_crossbow.sh cleanup script.) To re-create a virtual network: 1. Comment out the prepare_templatezone function in the exec_os_mk_crossbow.sh script (if you have an Oracle Solaris 11 Express based system) or the exec_nv_mk_crossbow.sh script (if you have a Solaris Express Community Edition based system). 2. Execute exec_os_mk_crossbow.sh (if you have an Oracle Solaris 11 Express based system) or exec_nv_mk_crossbow.sh (if you have a Solaris Express Community Edition based system). 3. Go to the Post-Installation Steps section. Post-Installation Steps All the necessary steps for conguring this simple network are done by the scripts. After installation, just try to ping the hosts, or do any network communications from any to any host within the virtual network. Feel free to ext the scripts for use in more complex networking environments and for implementing more networking features. Setting Up a Virtual Network Interactively If you want to create a virtual network interactively (manually), use the information in this section. Note: All the manual conguration steps presented in this section are integrated into the shell scripts. Therefore, to understand what the scripts do, you should become familiar with these manual steps. 6
10 Overview of the Manual Steps The starting point for creating a virtual network comprising hosts, switches, and routers is creating the necessary networking interfaces and setting up a template zone from which the other zones will be cloned. The virtual network is created using Oracle Solaris 11 Express Project Crossbow technology, and the hosts are created using Oracle Solaris Zones. The general steps necessary for creating a virtual network interactively are as follows (see also Figure 1, Network Topology): Congure vswitches for layer-two communication of all networked hosts. Congure a virtual network consisting of three subnetworks that are connected via a virtual router based on Project Crossbow. Set up Oracle Solaris Zones for the internal network and congure the global zone as a public network interface. Create vnics, vswitches, and Oracle Solaris ZFS Pool and File System The following sections show how to create vnics, vswitches, and an Oracle Solaris Zettabyte File System (ZFS) pool and le system. Congure the Etherstubs (vswitches) Global dladm create-etherstub etherstub0 Global dladm create-etherstub etherstub1 Global dladm create-etherstub etherstub2 Congure vnics Within etherstub0 Global dladm create-vnic -l etherstub0 vnic1 Global dladm create-vnic -l etherstub0 vnic4 Global dladm create-vnic -l etherstub0 vnic6 Congure vnics Within etherstub1 Global dladm create-vnic -l etherstub1 vnic2 Global dladm create-vnic -l etherstub1 vnic3 Global dladm create-vnic -l etherstub1 vnic5 Congure vnics Within etherstub2 Global dladm create-vnic -l etherstub2 vnic7 Global dladm create-vnic -l etherstub2 vnic8 7
11 Congure ZFS Pool and File System for the Oracle Solaris Zones Global zfs create -o compression=on -o mountpoint=/zones rpool/zones Create szone (Template Zone) The following sections show how to create the template zone. Congure Oracle Solaris Zone File for szone Note: Exercise caution if you use Oracle Solaris 11 Express, because Solaris Express Community Edition and Oracle Solaris 11 Express use different packaging systems (IPS and SVR4). With Oracle Solaris 11 Express, you cannot set up a native zone with inherited and shared directories. Instead, Oracle Solaris 11 Express downloads the directories directly from the appropriate repository or publisher using the ipkg brand. Therefore, if you are using Oracle Solaris 11 Express, you must delete all lines that include the following: set dir= xxx I provided two scripts for creating the virtual network: one for Solaris Express Community Edition (nv_mk_crossbow.sh) and one for Oracle Solaris 11 Express (os_mk_crossbow.sh). Both are shown in their entirety in the appix. Global cat > /repository/crossbow-build/szone << create -b set zonepath=/zones/szone set ip-type=exclusive set autoboot=false set dir=/lib set dir=/platform set dir=/sbin set dir=/usr set dir=/opt 8
12 commit Set Up szone global zonecfg -z <zone name> -f </path/to/cong/le> global zonecfg -z szone -f /repository/crossbow-build/szone global zoneadm -z <zone name> install global zoneadm -z szone install Create zone1 The following sections show how to create the zone1. Zone Conguration File for zone1 Global cat > /repository/crossbow-build/zone1 << create b set zonepath=/zones/zone1 set ip-type=exclusive set autoboot=true set dir=/lib set dir=/platform set dir=/sbin set dir=/usr set dir=/opt add net set physical=vnic1 commit 9
13 Set Up zone1 global zonecfg -z <zone name> -f </path/to/cong/le> global zonecfg -z zone1 -f /repository/crossbow-build/zone1 global zoneadm -z <zone name> install global zoneadm -z zone1 install Create sysidcfg for zone1 cat > /zones/zone1/root/etc/sysidcfg << terminal=vt100 system_locale=c timezone=us/pacic nfs4_domain=dynamic security_policy=none root_password=i.93fnimc3xc. network_interface=vnic1 {primary hostname=zone1 ip_address= netmask= protocol_ipv6=no default_route=none } timeserver=localhost name_service=none global zoneadm -z zone1 boot 10
14 Create zone2 The following sections show how to create the zone2. Zone Conguration File for zone2 Global cat > /repository/crossbow-build/zone2 << create b set zonepath=/zones/zone2 set ip-type=exclusive set autoboot=true set dir=/lib set dir=/platform set dir=/sbin set dir=/usr set dir=/opt add net set physical=vnic2 commit Set Up zone2 global zonecfg -z <zone name> -f </path/to/cong/le> global zonecfg -z zone2 -f /repository/crossbow-build/zone2 global zoneadm -z <zone name> install global zoneadm -z zone2 install 11
15 Create sysidcfg for zone2 cat > /zones/zone2/root/etc/sysidcfg << terminal=vt100 system_locale=c timezone=us/pacic nfs4_domain=dynamic security_policy=none root_password=i.93fnimc3xc. network_interface=vnic2 {primary hostname=zone2 ip_address= netmask= protocol_ipv6=no default_route=none} security_policy=none timeserver=localhost name_service=none global zoneadm -z zone2 boot Create zone3 The following sections show how to create the zone3. Zone Conguration File for zone3 Global cat > /repository/crossbow-build/zone3 << create b set zonepath=/zones/zone3 set ip-type=exclusive set autoboot=true set dir=/lib set dir=/platform set dir=/sbin 12
16 set dir=/usr set dir=/opt add net set physical=vnic3 commit Set Up zone3 global zonecfg -z <zone name> -f </path/to/cong/le> global zonecfg -z zone3 -f /repository/crossbow-build/zone3 global zoneadm -z <zone name> install global zoneadm -z zone3 install Create sysidcfg for zone3 cat > /zones/zone3/root/etc/sysidcfg << terminal=vt100 system_locale=c timezone=us/pacic nfs4_domain=dynamic security_policy=none root_password=i.93fnimc3xc. network_interface=vnic3 {primary hostname=zone3 ip_address= netmask= protocol_ipv6=no default_route=none} security_policy=none timeserver=localhost name_service=none global zoneadm -z zone3 boot 13
17 Create zone4 The following sections show how to create the zone4. Zone Conguration File for zone4 Global cat > /repository/crossbow-build/zone4 << create b set zonepath=/zones/zone4 set ip-type=exclusive set autoboot=true set dir=/lib set dir=/platform set dir=/sbin set dir=/usr set dir=/opt add net set physical=vnic4 commit Set Up zone4 global zonecfg -z <zone name> -f </path/to/cong/le> global zonecfg -z zone4 -f /repository/crossbow-build/zone4 global zoneadm -z <zone name> install global zoneadm -z zone4 install 14
18 Create sysidcfg for zone4 cat > /zones/zone4/root/etc/sysidcfg << EOF terminal=vt100 system_locale=c timezone=us/pacic nfs4_domain=dynamic security_policy=none root_password=i.93fnimc3xc. network_interface=vnic4 {primary hostname=zone4 ip_address= netmask= protocol_ipv6=no default_route=none} security_policy=none timeserver=localhost name_service=none EOF global zoneadm -z zone4 boot Create zgwhost (Gateway Host) The following sections show how to create the gateway host and enable IPV4 forwarding and IPV4 routing. Zone Conguration File for zgwhost cat > /repository/crossbow-build/zgwhost << create b set zonepath=/zones/zgwhost set ip-type=exclusive set autoboot=true set dir=/lib set dir=/platform set dir=/sbin 15
19 set dir=/usr set dir=/opt add net set physical=vnic5 add net set physical=vnic6 add net set physical=vnic7 commit Set Up Zone zgwhost global zonecfg -z <zone name> -f </path/to/cong/le> global zonecfg -z zgwhost -f /repository/crossbow-build/zgwhost global zoneadm -z <zone name> install global zoneadm -z zgwhost install Create sysidcfg for zgwhost cat > /zones/zgwhost/root/etc/sysidcfg << terminal=vt100 system_locale=c timezone=us/pacic nfs4_domain=dynamic security_policy=none root_password=i.93fnimc3xc. network_interface=vnic5 {primary hostname=zgwhost ip_address= netmask= protocol_ipv6=no default_route=none} 16
20 network_interface=vnic6 {primary hostname=zgwhost1 ip_address= netmask= protocol_ipv6=no default_route=none} network_interface=vnic7 {primary hostname=${zgwhn} ip_address= netmask= protocol_ipv6=no default_route=none} security_policy=none timeserver=localhost name_service=none Enable IPV4 Forwarding and IPV4 Routing global svccfg extract > site.xml global cp -p site.xml /zones/zgwhost/root/var/svc/prole/site.xml global zoneadm -z zgwhost boot Conclusion This paper described how to set up a virtual network automatically, with no manual intervention, using Project Crossbow technology and Bourne shell scripts provided with the paper. This paper also described how to set up the same virtual network interactively (manually). These methods were provided to help you better understand how network virtualization using Project Crossbow technology works and to make it easier for you to ext the scripts for use with more complex network features. 17
21 Appix: Code for the Scripts and var.init File The following sections show the content of the six scripts and the var.init le that are supplied in the crossbow_scripts.zip le associated with this paper. Note: See the Description of the Scripts for an Automated Installation section for more information about the scripts, the var.init le, and the site.xml le supplied in the crossbow_scripts.zip le. The os_mk_crossbow.sh Script This script is a collection of function modules to perform a creation of etherstubs, vnics, zones, and so on. This is a script for Oracle Solaris 11 Express based systems. For Solaris Express Community Edition based systems, use nv_mk_crossbow.sh instead.!/bin/sh -x DIR="`/bin/dirname $0`" export DIR. ${DIR}/var.init ========================================================================= Verify you can only run this script as a root ========================================================================= verify_user() { Verify we can only run as root RUSER=0 EUSER=`id -u` if [ ${RUSER} -ne ${EUSER} ]; then echo "you must be a root user; Exiting..." } ========================================================================= Function to check the existence of pool or lesystem for the zones, then create the template zone to clone the production zones ========================================================================= mketherstub() { 18
22 ========================================================================= Create etherstub for the virtual network ========================================================================= for i in do eval DEST=`dladm show-etherstub grep -v LINK grep -i etherstub$i` eval MESTS=`echo $MEST$i` if [ -n "$MESTS" ]; then eval EST=`echo $MESTS` eval EST=`echo $DEST` if [ -z "$DEST" ]; then echo "Etherstub does not exists" dladm create-etherstub $EST echo "please make sure the same etherstub does not exist" echo " " dladm show-etherstub echo " " done } mkvnics() { ========================================================================= Create VNIC for the rst subnetwork vswitch0 ========================================================================= DEST=`dladm show-etherstub grep -v LINK grep -i $MEST0` if [ -n "$DEST" ]; then for i in do 19
23 eval DVNIC=`dladm show-vnic grep -v LINK grep -i vnic$i awk '{print $1}'` eval MVNICS=`echo $MVNIC$i` if [ -n "$MVNICS" ]; then eval VNIC=`echo $MVNICS` eval VNIC=`echo $DVNIC` if [ -z "$DVNIC" ]; then echo "VNIC does not exists" dladm create-vnic -l $DEST $VNIC echo "please make sure the same VNIC does not exist" echo " " dladm show-vnic echo " " done ========================================================================= Create VNIC for the second subnetwork vswitch1 ========================================================================= DEST=`dladm show-etherstub grep -v LINK grep -i $MEST1` if [ -n "$DEST" ]; then for i in do eval DVNIC=`dladm show-vnic grep -v LINK grep -i vnic$i awk '{print $1}'` eval MVNICS=`echo $MVNIC$i` if [ -n "$MVNICS" ]; then eval VNIC=`echo $MVNICS` eval VNIC=`echo $DVNIC` if [ -z "$DVNIC" ]; then echo "VNIC does not exists" dladm create-vnic -l $DEST $VNIC 20
24 echo "please make sure the same VNIC does not exist" echo " " dladm show-vnic echo " " done ========================================================================= Create VNIC for the third subnetwork vswitch2 ========================================================================= DEST=`dladm show-etherstub grep -v LINK grep -i $MEST2` if [ -n "$DEST" ]; then for i in 7 8 do eval DVNIC=`dladm show-vnic grep -v LINK grep -i vnic$i awk '{print $1}'` eval MVNICS=`echo $MVNIC$i` if [ -n "$MVNICS" ]; then eval VNIC=`echo $MVNICS` eval VNIC=`echo $DVNIC` if [ -z "$DVNIC" ]; then echo "VNIC does not exists" dladm create-vnic -l $DEST $VNIC echo "please make sure the same VNIC does not exist" echo " " dladm show-vnic echo " " done } prepare_gzone() 21
25 { DVNIC=`dladm show-vnic grep -v LINK grep -i vnic8 awk '{print $1}'` echo " " echo " conguring the Global Zone..." echo " " if [ -n "$DVNIC" ]; then echo "Conguring gzone..." ifcong ${MVNIC8} plumb ifcong ${MVNIC8} ${VNIC8IP} netmask ${NM} up routeadm -e ipv4-forwarding routeadm -e ipv4-routing routeadm -u echo "VNIC does not exists" echo "please make sure the VNIC exists" echo " " routeadm echo " " } prepare_templatezone() { ========================================================================= Create a template zone to clone the other zones from Check the template zone is not used ========================================================================= DZNFS=`zfs list grep -v "${ZZFS}" grep ${MZNFS} awk -F"/" '{print $NF}'` DZNPL=`zfs list grep -v "${ZZFS}" grep ${MZNFS} awk -F"/" '{print $1}'` ZZ=`zoneadm list -c grep -c ${SZHN}` if [ ${ZZ} -gt 0 ]; then echo "${SZHN} exists" if [ -n "${MZNFS}" ] && [ -n "${MZNPL}" ]; then ZNFS="${MZNFS}" 22
26 ZNPL="${MZNPL}" ZNFS="${DZNFS}" ZNPL="${DZNPL}" if [ -z "${DZNFS}" ]; then echo " " echo " Filesystem does not exist... " echo " Creating ZFS Filesystem... " echo " " zfs create -o compression=on -o mountpoint=/${znfs} ${ZNPL}/${ZNFS} cat > ${CFG}/${SZHN} << create -b set zonepath=${pathsz} set ip-type=exclusive commit zonecfg -z ${SZHN} -f ${PATHSZCFG} zoneadm -z ${SZHN} install echo "Please delete this lesystem" } mk_template_les() { ========================================================================= Create template le to create the zones cloned out of the template zone ========================================================================= for i in do DVNIC=`dladm show-vnic grep -v LINK grep -i vnic$i awk '{print $1}'` eval MVNICS=`echo $MVNIC$i` if [ -z "$DVNIC" ]; then echo " prior creating template les VNIC must exist, exiting..." echo " Please please make sure VNIC is properly congured" cat > ${CFG}/${ZGWHN} << 23
27 create -b set zonepath=${zpathgwhost} set ip-type=exclusive set autoboot=true add net set physical=${mvnic5} add net set physical=${mvnic6} add net set physical=${mvnic7} commit cat > ${CFG}/${Z1HN} << create -b set zonepath=${zpathzone1} set ip-type=exclusive set autoboot=true add net set physical=${mvnic1} commit cat > ${CFG}/${Z2HN} << create -b set zonepath=${zpathzone2} set ip-type=exclusive set autoboot=true add net set physical=${mvnic2} commit cat > ${CFG}/${Z3HN} << 24
28 create -b set zonepath=${zpathzone3} set autoboot=true set ip-type=exclusive add net set physical=${mvnic3} commit cat > ${CFG}/${Z4HN} << create -b set zonepath=${zpathzone4} set autoboot=true set ip-type=exclusive add net set physical=${mvnic4} commit done } mkzones() { ========================================================================= create the zone ${ZGWHN} which acts as a router ========================================================================= DZGWFS=`zfs list grep ${ZGWHN} awk -F"/" '{print $NF}'` if [ -n "${DZGWFS}" ]; then echo " Filesystem exists, exiting..." echo " Please delete this lesystem" zonecfg -z ${ZGWHN} -f ${ZPATHGWTMP} zoneadm -z ${ZGWHN} clone ${SZHN} 25
29 cat > ${ZPATHGWSYSIDCFG} << terminal=vt100 system_locale=c timezone=us/pacic nfs4_domain=dynamic security_policy=none root_password=${rpw} network_interface=${mvnic7} {primary hostname=${zgwhn} ip_address=${vnic7ip} netmask=${nm} protocol_ipv6=${ipv6} default_route=${drgw}} network_interface=${mvnic5} {hostname=${zgwhn1} ip_address=${vnic5ip} netmask=${nm} protocol_ipv6=${ipv6} default_route=${dr}} network_interface=${mvnic6} {hostname=${zgwhn2} ip_address=${vnic6ip} netmask=${nm} protocol_ipv6=${ipv6} default_route=${dr}} security_policy=none timeserver=localhost name_service=none cat > ${MZNGWFS}/root/etc/ipf/ipf_set.conf << map vnic /24 -> /32 portmap tcp/udp auto map vnic /24 -> /32 map vnic /24 -> /32 portmap tcp/udp auto map vnic /24 -> /32 cp -p ${LSITE} ${RSITE} zoneadm -z ${ZGWHN} boot ========================================================================= create the zone ${Z1HN} ========================================================================= DZ1FS=`zfs list grep ${Z1HN} awk -F"/" '{print $NF}'` if [ -n "${DZ1FS}" ]; then echo " Filesystem exists, exiting..." echo " Please delete this lesystem" zonecfg -z ${Z1HN} -f ${ZPATH1TMP} zoneadm -z ${Z1HN} clone ${SZHN} 26
30 cat > ${ZPATH1SYSIDCFG} << terminal=vt100 system_locale=c timezone=us/pacic nfs4_domain=dynamic security_policy=none root_password=${rpw} network_interface=${mvnic1} {primary hostname=${z1hn} ip_address=${vnic1ip} netmask=${nm} protocol_ipv6=${ipv6} default_route=${dr1}} security_policy=none timeserver=localhost name_service=none zoneadm -z ${Z1HN} boot ========================================================================= create the zone ${Z2HN} ========================================================================= DZ2FS=`zfs list grep ${Z2HN} awk -F"/" '{print $NF}'` if [ -n "${DZ2FS}" ]; then echo " Filesystem exists, exiting..." echo " Please delete this lesystem" zonecfg -z ${Z2HN} -f ${ZPATH2TMP} zoneadm -z ${Z2HN} clone ${SZHN} cat > ${ZPATH2SYSIDCFG} << terminal=vt100 system_locale=c timezone=us/pacic nfs4_domain=dynamic security_policy=none root_password=${rpw} network_interface=${mvnic2} {primary hostname=${z2hn} ip_address=${vnic2ip} netmask=${nm} protocol_ipv6=${ipv6} default_route=${dr2}} security_policy=none timeserver=localhost 27
31 name_service=none zoneadm -z ${Z2HN} boot ========================================================================= create the zone ${Z3HN} ========================================================================= DZ3FS=`zfs list grep ${Z3HN} awk -F"/" '{print $NF}'` if [ -n "${DZ3FS}" ]; then echo " Filesystem exists, exiting..." echo " Please delete this lesystem" zonecfg -z ${Z3HN} -f ${ZPATH3TMP} zoneadm -z ${Z3HN} clone ${SZHN} cat > ${ZPATH3SYSIDCFG} << terminal=vt100 system_locale=c timezone=us/pacic nfs4_domain=dynamic security_policy=none root_password=${rpw} network_interface=${mvnic3} {primary hostname=${z3hn} ip_address=${vnic3ip} netmask=${nm} protocol_ipv6=${ipv6} default_route=${dr3}} security_policy=none timeserver=localhost name_service=none zoneadm -z ${Z3HN} boot ========================================================================= create the zone ${Z4HN} ========================================================================= DZ4FS=`zfs list grep ${Z4HN} awk -F"/" '{print $NF}'` if [ -n "${DZ4FS}" ]; then echo " Filesystem exists, exiting..." 28
32 echo " Please delete this lesystem" zonecfg -z ${Z4HN} -f ${ZPATH4TMP} zoneadm -z ${Z4HN} clone ${SZHN} cat > ${ZPATH4SYSIDCFG} << terminal=vt100 system_locale=c timezone=us/pacic nfs4_domain=dynamic security_policy=none root_password=${rpw} network_interface=${mvnic4} {primary hostname=${z4hn} ip_address=${vnic4ip} netmask=${nm} protocol_ipv6=${ipv6} default_route=${dr4}} security_policy=none timeserver=localhost name_service=none zoneadm -z ${Z4HN} boot } The exec_os_mk_crossbow.sh Script To execute and control a function of interest, use this script. If, for example, you want to create zones but not etherstubs, you just comment out the appropriate function. This is a script for Oracle Solaris 11 Express based systems. For Solaris Express Community Edition based systems, use exec_nv_mk_crossbow.sh instead.!/bin/sh -x DIR="`/bin/dirname $0`" export DIR. ${DIR}/var.init../os_mk_crossbow.sh verify_user mketherstub mkvnics 29
33 prepare_templatezone prepare_gzone mk_template_les mkzones The nv_mk_crossbow.sh Script This script is a collection of function modules to perform a creation of etherstubs, vnics, zones, and so on. This is a script for Solaris Express Community Edition based systems. For Oracle Solaris 11 Express based systems, use os_mk_crossbow.sh instead.!/bin/sh x DIR="`/bin/dirname $0`" export DIR. ${DIR}/var.init ========================================================================= Verify you can only run this script as a root ========================================================================= verify_user() { Verify we can only run as root RUSER=0 EUSER=`id -u` if [ ${RUSER} -ne ${EUSER} ]; then echo "you must be a root user; Exiting..." } ========================================================================= Function to check the existence of pool or lesystem for the zones, then create the template zone to clone the production zones ========================================================================= mketherstub() { ========================================================================= Create etherstub for the virtual network 30
34 ========================================================================= for i in do eval DEST=`dladm show-etherstub grep -v LINK grep -i etherstub$i` eval MESTS=`echo $MEST$i` if [ -n "$MESTS" ]; then eval EST=`echo $MESTS` eval EST=`echo $DEST` if [ -z "$DEST" ]; then echo "Etherstub does not exists" dladm create-etherstub $EST echo "please make sure the same etherstub does not exist" echo " " dladm show-etherstub echo " " done } mkvnics() { ========================================================================= Create VNIC for the rst subnetwork vswitch0 ========================================================================= DEST=`dladm show-etherstub grep -v LINK grep -i $MEST0` if [ -n "$DEST" ]; then for i in do eval DVNIC=`dladm show-vnic grep -v LINK grep -i vnic$i awk '{print $1}'` eval MVNICS=`echo $MVNIC$i` if [ -n "$MVNICS" ]; then eval VNIC=`echo $MVNICS` 31
35 eval VNIC=`echo $DVNIC` if [ -z "$DVNIC" ]; then echo "VNIC does not exists" dladm create-vnic -l $DEST $VNIC echo "please make sure the same VNIC does not exist" echo " " dladm show-vnic echo " " done ========================================================================= Create VNIC for the second subnetwork vswitch1 ========================================================================= DEST=`dladm show-etherstub grep -v LINK grep -i $MEST1` if [ -n "$DEST" ]; then for i in do eval DVNIC=`dladm show-vnic grep -v LINK grep -i vnic$i awk '{print $1}'` eval MVNICS=`echo $MVNIC$i` if [ -n "$MVNICS" ]; then eval VNIC=`echo $MVNICS` eval VNIC=`echo $DVNIC` if [ -z "$DVNIC" ]; then echo "VNIC does not exists" dladm create-vnic -l $DEST $VNIC echo "please make sure the same VNIC does not exist" 32
36 echo " " dladm show-vnic echo " " done ========================================================================= Create VNIC for the third subnetwork vswitch2 ========================================================================= DEST=`dladm show-etherstub grep -v LINK grep -i $MEST2` if [ -n "$DEST" ]; then for i in 7 8 do eval DVNIC=`dladm show-vnic grep -v LINK grep -i vnic$i awk '{print $1}'` eval MVNICS=`echo $MVNIC$i` if [ -n "$MVNICS" ]; then eval VNIC=`echo $MVNICS` eval VNIC=`echo $DVNIC` if [ -z "$DVNIC" ]; then echo "VNIC does not exists" dladm create-vnic -l $DEST $VNIC echo "please make sure the same VNIC does not exist" echo " " dladm show-vnic echo " " done } prepare_gzone() { DVNIC=`dladm show-vnic grep -v LINK grep -i vnic8 awk '{print $1}'` echo " " echo " conguring the Global Zone..." 33
37 echo " " if [ -n "$DVNIC" ]; then echo "Conguring gzone..." ifcong ${MVNIC8} plumb ifcong ${MVNIC8} ${VNIC8IP} netmask ${NM} up routeadm -e ipv4-forwarding routeadm -e ipv4-routing routeadm -u echo "VNIC does not exists" echo "please make sure the VNIC exists" echo " " routeadm echo " " } prepare_templatezone() { ========================================================================= Create a template zone to clone the other zones from Check the template zone is not used ========================================================================= DZNFS=`zfs list grep -v "${ZZFS}" grep ${MZNFS} awk -F"/" '{print $NF}'` DZNPL=`zfs list grep -v "${ZZFS}" grep ${MZNFS} awk -F"/" '{print $1}'` ZZ=`zoneadm list -c grep -c ${SZHN}` if [ ${ZZ} -gt 0 ]; then echo "${SZHN} exists" if [ -n "${MZNFS}" ] && [ -n "${MZNPL}" ]; then ZNFS="${MZNFS}" ZNPL="${MZNPL}" ZNFS="${DZNFS}" ZNPL="${DZNPL}" 34
38 if [ -z "${DZNFS}" ]; then echo " " echo " Filesystem does not exist... " echo " Creating ZFS Filesystem... " echo " " zfs create -o compression=on -o mountpoint=/${znfs} ${ZNPL}/${ZNFS} cat > ${CFG}/${SZHN} << create -b set zonepath=${pathsz} set ip-type=exclusive commit zonecfg -z ${SZHN} -f ${PATHSZCFG} zoneadm -z ${SZHN} install echo "Please delete this lesystem" } mk_template_les() { ========================================================================= Create template le to create the zones cloned out of the template zone ========================================================================= for i in do DVNIC=`dladm show-vnic grep -v LINK grep -i vnic$i awk '{print $1}'` eval MVNICS=`echo $MVNIC$i` if [ -z "$DVNIC" ]; then echo " prior creating template les VNIC must exist, exiting..." echo " Please please make sure VNIC is properly congured" cat > ${CFG}/${ZGWHN} << create -b set zonepath=${zpathgwhost} set autoboot=true set ip-type=exclusive 35
39 set dir=/lib set dir=/platform set dir=/sbin set dir=/usr set dir=/opt add net set physical=${mvnic5} add net set physical=${mvnic6} add net set physical=${mvnic7} commit cat > ${CFG}/${Z1HN} << create -b set zonepath=${zpathzone1} set autoboot=true set ip-type=exclusive set dir=/lib set dir=/platform set dir=/sbin 36
40 set dir=/usr set dir=/opt add net set physical=${mvnic1} commit cat > ${CFG}/${Z2HN} << create -b set zonepath=${zpathzone2} set autoboot=true set ip-type=exclusive set dir=/lib set dir=/platform set dir=/sbin set dir=/usr set dir=/opt add net set physical=${mvnic2} commit cat > ${CFG}/${Z3HN} << 37
41 create -b set zonepath=${zpathzone3} set autoboot=true set ip-type=exclusive set dir=/lib set dir=/platform set dir=/sbin set dir=/usr set dir=/opt add net set physical=${mvnic3} commit cat > ${CFG}/${Z4HN} << create -b set zonepath=${zpathzone4} set autoboot=true set ip-type=exclusive set dir=/lib set dir=/platform set dir=/sbin set dir=/usr 38
42 set dir=/opt add net set physical=${mvnic4} commit done } mkzones() { ========================================================================= create the zone ${ZGWHN} which acts as a router ========================================================================= DZGWFS=`zfs list grep ${ZGWHN} awk -F"/" '{print $NF}'` if [ -n "${DZGWFS}" ]; then echo " Filesystem exists, exiting..." echo " Please delete this lesystem" zonecfg -z ${ZGWHN} -f ${ZPATHGWTMP} zoneadm -z ${ZGWHN} clone ${SZHN} cat > ${ZPATHGWSYSIDCFG} << terminal=vt100 system_locale=c timezone=us/pacic nfs4_domain=dynamic security_policy=none root_password=${rpw} network_interface=${mvnic7} {primary hostname=${zgwhn} ip_address=${vnic7ip} netmask=${nm} protocol_ipv6=${ipv6} default_route=${drgw}} network_interface=${mvnic5} {hostname=${zgwhn1} ip_address=${vnic5ip} netmask=${nm} protocol_ipv6=${ipv6} default_route=${dr}} 39
43 network_interface=${mvnic6} {hostname=${zgwhn2} ip_address=${vnic6ip} netmask=${nm} protocol_ipv6=${ipv6} default_route=${dr}} security_policy=none timeserver=localhost name_service=none cat > ${MZNGWFS}/root/etc/ipf/ipf_set.conf << map vnic /24 -> /32 portmap tcp/udp auto map vnic /24 -> /32 map vnic /24 -> /32 portmap tcp/udp auto map vnic /24 -> /32 cp -p ${LSITE} ${RSITE} zoneadm -z ${ZGWHN} boot ========================================================================= create the zone ${Z1HN} ========================================================================= DZ1FS=`zfs list grep ${Z1HN} awk -F"/" '{print $NF}'` if [ -n "${DZ1FS}" ]; then echo " Filesystem exists, exiting..." echo " Please delete this lesystem" zonecfg -z ${Z1HN} -f ${ZPATH1TMP} zoneadm -z ${Z1HN} clone ${SZHN} cat > ${ZPATH1SYSIDCFG} << terminal=vt100 system_locale=c timezone=us/pacic nfs4_domain=dynamic security_policy=none root_password=${rpw} network_interface=${mvnic1} {primary hostname=${z1hn} ip_address=${vnic1ip} netmask=${nm} protocol_ipv6=${ipv6} default_route=${dr1}} security_policy=none 40
44 timeserver=localhost name_service=none zoneadm -z ${Z1HN} boot ========================================================================= create the zone ${Z2HN} ========================================================================= DZ2FS=`zfs list grep ${Z2HN} awk -F"/" '{print $NF}'` if [ -n "${DZ2FS}" ]; then echo " Filesystem exists, exiting..." echo " Please delete this lesystem" zonecfg -z ${Z2HN} -f ${ZPATH2TMP} zoneadm -z ${Z2HN} clone ${SZHN} cat > ${ZPATH2SYSIDCFG} << terminal=vt100 system_locale=c timezone=us/pacic nfs4_domain=dynamic security_policy=none root_password=${rpw} network_interface=${mvnic2} {primary hostname=${z2hn} ip_address=${vnic2ip} netmask=${nm} protocol_ipv6=${ipv6} default_route=${dr2}} security_policy=none timeserver=localhost name_service=none zoneadm -z ${Z2HN} boot ========================================================================= create the zone ${Z3HN} ========================================================================= DZ3FS=`zfs list grep ${Z3HN} awk -F"/" '{print $NF}'` if [ -n "${DZ3FS}" ]; then 41
45 echo " Filesystem exists, exiting..." echo " Please delete this lesystem" zonecfg -z ${Z3HN} -f ${ZPATH3TMP} zoneadm -z ${Z3HN} clone ${SZHN} cat > ${ZPATH3SYSIDCFG} << terminal=vt100 system_locale=c timezone=us/pacic nfs4_domain=dynamic security_policy=none root_password=${rpw} network_interface=${mvnic3} {primary hostname=${z3hn} ip_address=${vnic3ip} netmask=${nm} protocol_ipv6=${ipv6} default_route=${dr3}} security_policy=none timeserver=localhost name_service=none zoneadm -z ${Z3HN} boot ========================================================================= create the zone ${Z4HN} ========================================================================= DZ4FS=`zfs list grep ${Z4HN} awk -F"/" '{print $NF}'` if [ -n "${DZ4FS}" ]; then echo " Filesystem exists, exiting..." echo " Please delete this lesystem" zonecfg -z ${Z4HN} -f ${ZPATH4TMP} zoneadm -z ${Z4HN} clone ${SZHN} cat > ${ZPATH4SYSIDCFG} << terminal=vt100 system_locale=c timezone=us/pacic nfs4_domain=dynamic 42
46 security_policy=none root_password=${rpw} network_interface=${mvnic4} {primary hostname=${z4hn} ip_address=${vnic4ip} netmask=${nm} protocol_ipv6=${ipv6} default_route=${dr4}} security_policy=none timeserver=localhost name_service=none zoneadm -z ${Z4HN} boot } The exec_nv_mk_crossbow.sh Script To execute and control a function of interest, use this script. If, for example, you want to create zones but not etherstubs, you just comment out the appropriate function. This is a script for Solaris Express Community Edition based systems. For Oracle Solaris 11 Express based systems, use exec_os_mk_crossbow.sh instead.!/bin/sh -x DIR="`/bin/dirname $0`" export DIR. ${DIR}/var.init../nv_mk_crossbow.sh verify_user mketherstub mkvnics prepare_templatezone prepare_gzone mk_template_les mkzones 43
47 The cl_crossbow.sh Script This script is a collection of function modules to remove the entire virtual network or just part of its conguration.!/bin/sh -x DIR="`/bin/dirname $0`" export DIR. ${DIR}/var.init ========================================================================= Verify you can only run this script as a root ========================================================================= verify_user() { Verify we can only run as root RUSER=0 EUSER=`id -u` if [ ${RUSER} -ne ${EUSER} ]; then echo "you must be a root user; Exiting..." } cleanup_zones() { ========================================================================= remove the zones 1-4 ========================================================================= for i in ${Z1HN} ${Z2HN} ${Z3HN} ${Z4HN} ${ZGWHN} ${SZHN} for i in ${Z1HN} ${Z2HN} ${Z3HN} ${Z4HN} ${ZGWHN} do DZNFS=`zfs list grep "${i}" awk -F"/" '{print $NF}'` DZNPL=`zfs list grep "${i}" awk -F"/" '{print $1}'` ZZ=`zoneadm list -i grep ${i} awk '{print $1}'` RV=$? if [ ${RV} -eq 0 ]; then echo "zone ${i} will be removed..." zoneadm -z ${i} halt zoneadm -z ${i} uninstall -F 44
48 zonecfg -z ${i} delete -F zfs destroy -rf ${MZNPL}/${MZNFS}/${i} echo "${i} does not exist" done zfs destroy -f ${MZNPL}/${MZNFS} rm -rf /${MZNFS} } cleanup_vinterfaces() { ========================================================================= If NIC name is not set manually obtain the name automatically from the dladam command. ========================================================================= ifcong ${MVNIC8} unplumb EST0=`dladm show-etherstub grep -v LINK grep -i ${MEST0} awk '{print $1}'` EST1=`dladm show-etherstub grep -v LINK grep -i ${MEST1} awk '{print $1}'` EST2=`dladm show-etherstub grep -v LINK grep -i ${MEST2} awk '{print $1}'` if [ -z "${EST0}" ] && [ -z "${EST1}" ] && [ -z "${EST2}" ]; then if [ "${EST0}"!= "${MEST0}" ] && [ "{EST1}!= "${MEST1}" ] && [ "{EST2}!= "${MEST2}" ]; then echo "Etherstub does not exist" exit for i in do dladm delete-vnic vnic$i done for i in do 45
49 } done dladm delete-etherstub etherstub${i} The exec_cl_crossbow.sh Script Use this script to execute the cl_crossbow.sh script.!/bin/sh -x DIR="`/bin/dirname $0`" export DIR. ${DIR}/var.init../cl_crossbow.sh verify_user cleanup_zones cleanup_vinterfaces The var.init File All user-denable variables are initialized within this le.!/bin/sh -x Note: The following line is commented out in the var.init le: RPW=`cat /etc/shadow grep root awk -F":" '{print $2}'` Then, the next line contains a hard-coded, encrypted password. The password used to generate the encrypted password was newroot. If you prefer to extract the password from your system, uncomment the commented-out line and then comment out the next line. ========================================================================= umask 022 CFG=/repository/crossbow-build TIME=$(date +"%F-%H:%M") LOGFILE=${CFG}/log.${TIME} MZNPL=rpool MZNFS=zones PROF=root/var/svc/prole 46
50 SYSIDCFG=root/etc/sysidcfg ZNFS=${MZNPL}/${MZNFS} ZZFS=${MZNPL}/${MZNFS}/ MZN1FS=/${MZNFS}/zone1 MZN2FS=/${MZNFS}/zone2 MZN3FS=/${MZNFS}/zone3 MZN4FS=/${MZNFS}/zone4 MZNGWFS=/${MZNFS}/zgwhost ========================================================================= Dene general variables ========================================================================= ========================================================================= Manually dene the VNICS specic variables. ========================================================================= MVNIC=vnic MVNIC1=vnic1 MVNIC2=vnic2 MVNIC3=vnic3 MVNIC4=vnic4 MVNIC5=vnic5 MVNIC6=vnic6 MVNIC7=vnic7 MVNIC8=vnic8 ========================================================================= Manually dene the Phy. Interface specic variables. ========================================================================= VNIC8IP= MIFC=rge0 NM= DR1= DR2= DR3= DR4= DR=NONE DRGW= IPV6=no ========================================================================= Manually dene the Etherstubs. Interface specic variables. ========================================================================= MEST=etherstub MEST0=etherstub0 47
51 MEST1=etherstub1 MEST2=etherstub2 ========================================================================= Extract root password from shadow specic variables. ========================================================================= RPW=`cat /etc/shadow grep root awk -F":" '{print $2}'` RPW="i.93FnIMC3xc." ========================================================================= Dene the template zone specic variables. ========================================================================= SZHN=szone PATHSZ=/${MZNFS}/${SZHN} PATHSZCFG=${CFG}/${SZHN} ========================================================================= Dene the gateway zone specic variables. ========================================================================= LSITE=${CFG}/site.xml RSITE=${MZNGWFS}/${PROF}/site.xml ZGWHN=zgwhost ZGWHN1=zgwhost1 ZGWHN2=zgwhost2 VNIC5IP= VNIC6IP= VNIC7IP= ZPATHGWHOST=/${MZNFS}/${ZGWHN} ZPATHGWTMP=${CFG}/${ZGWHN} ZPATHGWSYSIDCFG=/${MZNFS}/${ZGWHN}/${SYSIDCFG} ZONEGWBASEPATH=/${MZNFS}/${ZGWHN} ========================================================================= Dene the zone1 zone specic variables. ========================================================================= Z1HN=zone1 VNIC1IP= ZPATHZONE1=/${MZNFS}/${Z1HN} ZPATH1TMP=${CFG}/${Z1HN} ZPATH1SYSIDCFG=/${MZNFS}/${Z1HN}/${SYSIDCFG} 48
52 ZONE1BASEPATH=/${MZNFS}/${Z1HN} ========================================================================= Dene the zone2 zone specic variables. ========================================================================= Z2HN=zone2 VNIC2IP= ZPATHZONE2=/${MZNFS}/${Z2HN} ZPATH2TMP=${CFG}/${Z2HN} ZPATH2SYSIDCFG=/${MZNFS}/${Z2HN}/${SYSIDCFG} ZONE2BASEPATH=/${MZNFS}/${Z2HN} ========================================================================= Dene the zone3 zone specic variables. ========================================================================= Z3HN=zone3 VNIC3IP= ZPATHZONE3=/${MZNFS}/${Z3HN} ZPATH3TMP=${CFG}/${Z3HN} ZPATH3SYSIDCFG=/${MZNFS}/${Z3HN}/${SYSIDCFG} ZONE3BASEPATH=/${MZNFS}/${Z3HN} ========================================================================= Dene the zone4 zone specic variables. ========================================================================= Z4HN=zone4 VNIC4IP= ZPATHZONE4=/${MZNFS}/${Z4HN} ZPATH4TMP=${CFG}/${Z4HN} ZPATH4SYSIDCFG=/${MZNFS}/${Z4HN}/${SYSIDCFG} ZONE4BASEPATH=/${MZNFS}/${Z4HN} 49
53 For More Information Here are some Project Crossbow resources: Project Crossbow web site: Networking in Solaris 10 on opensolaris.org: Upcoming Solaris Features: Crossbow - Part 1: Virtualisation on c0t0d0s0.org: Virtualisation.html Here are additional resources. Sun download site: Oracle University web site: Discussions, such as Sun forums ( and the BigAdmin Discussions collection ( Sun product documentation at and the Sun Documentation Center ( Sun wikis, such as the Sun BluePrints wiki ( the BigAdmin wiki ( Support: Sun resources: o o o Register your gear: Sun Services: SunSolve Online: Community system administration experts: 50
54 Setting Up a Virtual Network Automatically Using Oracle Solaris 11 Express Project Crossbow December 2010 Author: Aklilu Hadish Oracle Corporation World Headquarters 500 Oracle Parkway Redwood Shores, CA U.S.A. Worldwide Inquiries: Phone: Fax: oracle.com Copyright 2010, Oracle and/or its afliates. All rights reserved. This document is provided for information purposes only and the contents hereof are subject to change without notice. This document is not warranted to be error-free, nor subject to any other warranties or conditions, whether expressed orally or implied in law, including implied warranties and conditions of merchantability or tness for a particular purpose. We specically disclaim any liability with respect to this document and no contractual obligations are formed either directly or indirectly by this document. This document may not be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, for any purpose, without our prior written permission. Oracle and Java are registered trademarks of Oracle Corporation and/or its afliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective owners. AMD, Opteron, the AMD logo, and the AMD Opteron logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Advanced Micro Devices. Intel and Intel Xeon are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation. All SPARC trademarks are used under license and are trademarks or registered trademarks of SPARC International, Inc. UNIX is a registered trademark licensed through X/Open Company, Ltd. 0109
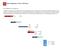
stub (Private Switch) Solaris 11 Operating Environment In the Solaris 11 Operating Environment, four zones are created namely:
 Building MySQL Cluster in a Box Using Solaris 11 Zones datanode1 datanode2 mgmnode stub (Private Switch) sqlnode Solaris 11 Operating Environment In the Solaris 11 Operating Environment, four zones are
Building MySQL Cluster in a Box Using Solaris 11 Zones datanode1 datanode2 mgmnode stub (Private Switch) sqlnode Solaris 11 Operating Environment In the Solaris 11 Operating Environment, four zones are
Развертывание сервера приложений Oracle GlassFish Server на OpenSolaris: мониторинг, подготовка к работе и резервное копирование
 Развертывание сервера приложений Oracle GlassFish Server на OpenSolaris: мониторинг, подготовка к работе и резервное копирование Филипп Торчинский Sun Microsystems 1 Agenda Introduction What is OpenSolaris,
Развертывание сервера приложений Oracle GlassFish Server на OpenSolaris: мониторинг, подготовка к работе и резервное копирование Филипп Торчинский Sun Microsystems 1 Agenda Introduction What is OpenSolaris,
How to build secure Apache Tomcat deployments with RPM.
 How to build secure Apache Tomcat deployments with RPM. My security experiences really tie into everyday work. A colleague called me from my last gig and asked how to build a RedHat Package Manager (RPM)
How to build secure Apache Tomcat deployments with RPM. My security experiences really tie into everyday work. A colleague called me from my last gig and asked how to build a RedHat Package Manager (RPM)
Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source list C
 Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source list C Table of Contents Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source list Command...1 Introduction...1 Before You Begin...1 Conventions...1
Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source list C Table of Contents Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source list Command...1 Introduction...1 Before You Begin...1 Conventions...1
HIGH AVAILABILITY SETUP USING VERITAS CLUSTER SERVER AND NETAPP SYNCHRONOUS SNAPMIRROR. Jorge Costa, NetApp June 2008
 HIGH AVAILABILITY SETUP USING VERITAS CLUSTER SERVER AND NETAPP SYNCHRONOUS SNAPMIRROR Jorge Costa, NetApp June 2008 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 PROBLEM DESCRIPTION 4 2 SOLUTION OVERVIEW 5 21 STORAGE 5 22 VCS
HIGH AVAILABILITY SETUP USING VERITAS CLUSTER SERVER AND NETAPP SYNCHRONOUS SNAPMIRROR Jorge Costa, NetApp June 2008 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 PROBLEM DESCRIPTION 4 2 SOLUTION OVERVIEW 5 21 STORAGE 5 22 VCS
VDCF - Virtual Datacenter Control Framework for the Solaris TM Operating System
 VDCF - Virtual Datacenter Control Framework for the Solaris TM Operating System VDCF Blueprint Software Deployment Version 1.1 August 2014 Copyright 2005-2014 JomaSoft GmbH All rights reserved. [email protected]
VDCF - Virtual Datacenter Control Framework for the Solaris TM Operating System VDCF Blueprint Software Deployment Version 1.1 August 2014 Copyright 2005-2014 JomaSoft GmbH All rights reserved. [email protected]
Using SmartOS as a Hypervisor
 Using SmartOS as a Hypervisor SCALE 10x Robert Mustacchi [email protected] (@rmustacc) Software Engineer What is SmartOS? Solaris heritage Zones - OS level virtualization Crossbow - virtual NICs ZFS - pooled
Using SmartOS as a Hypervisor SCALE 10x Robert Mustacchi [email protected] (@rmustacc) Software Engineer What is SmartOS? Solaris heritage Zones - OS level virtualization Crossbow - virtual NICs ZFS - pooled
Configuring an OpenNMS Stand-by Server
 WHITE PAPER Conguring an OpenNMS Stand-by Server Version 1.2 The OpenNMS Group, Inc. 220 Chatham Business Drive Pittsboro, NC 27312 T +1 (919) 533-0160 F +1 (503) 961-7746 [email protected] URL: http://blogs.opennms.org/david
WHITE PAPER Conguring an OpenNMS Stand-by Server Version 1.2 The OpenNMS Group, Inc. 220 Chatham Business Drive Pittsboro, NC 27312 T +1 (919) 533-0160 F +1 (503) 961-7746 [email protected] URL: http://blogs.opennms.org/david
TransNav Management System Documentation. Management Server Guide
 Force10 Networks Inc. TransNav Management System Documentation Management Server Guide Release TN4.2.2 Publication Date: April 2009 Document Number: 800-0006-TN422 Rev. A Copyright 2009 Force10 Networks,
Force10 Networks Inc. TransNav Management System Documentation Management Server Guide Release TN4.2.2 Publication Date: April 2009 Document Number: 800-0006-TN422 Rev. A Copyright 2009 Force10 Networks,
Private Server and Physical Server Backup and Restoration:
 Technical Document Series Number 014 Private Server and Physical Server Backup and Restoration: A Technical Guide for ISP/HSP Administrator Covers Ensim ServerXchange 2.5 and Earlier Date: September 25,
Technical Document Series Number 014 Private Server and Physical Server Backup and Restoration: A Technical Guide for ISP/HSP Administrator Covers Ensim ServerXchange 2.5 and Earlier Date: September 25,
Basic Installation of the Cisco Collection Manager
 CHAPTER 3 Basic Installation of the Cisco Collection Manager Introduction This chapter gives the information required for a basic installation of the Cisco Collection Manager and the bundled Sybase database.
CHAPTER 3 Basic Installation of the Cisco Collection Manager Introduction This chapter gives the information required for a basic installation of the Cisco Collection Manager and the bundled Sybase database.
SUSE Manager in the Public Cloud. SUSE Manager Server in the Public Cloud
 SUSE Manager in the Public Cloud SUSE Manager Server in the Public Cloud Contents 1 Instance Requirements... 2 2 Setup... 3 3 Registration of Cloned Systems... 6 SUSE Manager delivers best-in-class Linux
SUSE Manager in the Public Cloud SUSE Manager Server in the Public Cloud Contents 1 Instance Requirements... 2 2 Setup... 3 3 Registration of Cloned Systems... 6 SUSE Manager delivers best-in-class Linux
NexentaConnect for VMware Virtual SAN
 NexentaConnect for VMware Virtual SAN User Guide 1.0.2 FP3 Date: April, 2016 Subject: NexentaConnect for VMware Virtual SAN User Guide Software: NexentaConnect for VMware Virtual SAN Software Version:
NexentaConnect for VMware Virtual SAN User Guide 1.0.2 FP3 Date: April, 2016 Subject: NexentaConnect for VMware Virtual SAN User Guide Software: NexentaConnect for VMware Virtual SAN Software Version:
CO 246 - Web Server Administration and Security. By: Szymon Machajewski
 CO 246 - Web Server Administration and Security By: Szymon Machajewski CO 246 - Web Server Administration and Security By: Szymon Machajewski Online: < http://cnx.org/content/col11452/1.1/ > C O N N E
CO 246 - Web Server Administration and Security By: Szymon Machajewski CO 246 - Web Server Administration and Security By: Szymon Machajewski Online: < http://cnx.org/content/col11452/1.1/ > C O N N E
New Lab Intro to KDE Terminal Konsole
 New Lab Intro to KDE Terminal Konsole After completing this lab activity the student will be able to; Access the KDE Terminal Konsole and enter basic commands. Enter commands using a typical command line
New Lab Intro to KDE Terminal Konsole After completing this lab activity the student will be able to; Access the KDE Terminal Konsole and enter basic commands. Enter commands using a typical command line
FreeFlow Accxes Print Server V15.0 August 2010 701P50924. Xerox FreeFlow Accxes Print Server Drivers and Client Tools Software Installation Guide
 FreeFlow Accxes Print Server V15.0 August 2010 701P50924 Xerox FreeFlow Accxes Print Server Drivers and Client Tools Software 2010 Xerox Corporation. All rights reserved. XEROX and Xerox and Design, 6204,
FreeFlow Accxes Print Server V15.0 August 2010 701P50924 Xerox FreeFlow Accxes Print Server Drivers and Client Tools Software 2010 Xerox Corporation. All rights reserved. XEROX and Xerox and Design, 6204,
RSA Authentication Manager 7.1 to 8.1 Migration Guide: Upgrading RSA SecurID Appliance 3.0 On Existing Hardware
 RSA Authentication Manager 7.1 to 8.1 Migration Guide: Upgrading RSA SecurID Appliance 3.0 On Existing Hardware Contact Information Go to the RSA corporate website for regional Customer Support telephone
RSA Authentication Manager 7.1 to 8.1 Migration Guide: Upgrading RSA SecurID Appliance 3.0 On Existing Hardware Contact Information Go to the RSA corporate website for regional Customer Support telephone
1 Basic Configuration of Cisco 2600 Router. Basic Configuration Cisco 2600 Router
 1 Basic Configuration of Cisco 2600 Router Basic Configuration Cisco 2600 Router I decided to incorporate the Cisco 2600 into my previously designed network. This would give me two seperate broadcast domains
1 Basic Configuration of Cisco 2600 Router Basic Configuration Cisco 2600 Router I decided to incorporate the Cisco 2600 into my previously designed network. This would give me two seperate broadcast domains
Volume AGKSOFT. Gilbarco Passport Back Office Software. Gilbarco Passport Guide
 Volume P AGKSOFT Gilbarco Passport Back Office Software Gilbarco Passport Guide Introduction T he Gilbarco Passport can be connected to your Windows PC using a straight CAT5/RJ45 cable connected to the
Volume P AGKSOFT Gilbarco Passport Back Office Software Gilbarco Passport Guide Introduction T he Gilbarco Passport can be connected to your Windows PC using a straight CAT5/RJ45 cable connected to the
Configuring MailArchiva with Insight Server
 Copyright 2009 Bynari Inc., All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopy, recording, or any
Copyright 2009 Bynari Inc., All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopy, recording, or any
Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source static
 Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source static Table of Contents Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source static Command...1 Introduction...1 Before You Begin...1 Conventions...1
Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source static Table of Contents Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source static Command...1 Introduction...1 Before You Begin...1 Conventions...1
McAfee SMC Installation Guide 5.7. Security Management Center
 McAfee SMC Installation Guide 5.7 Security Management Center Legal Information The use of the products described in these materials is subject to the then current end-user license agreement, which can
McAfee SMC Installation Guide 5.7 Security Management Center Legal Information The use of the products described in these materials is subject to the then current end-user license agreement, which can
Mass Deploying Bomgar Software to Macs
 Mass Deploying Bomgar Software to Macs Starting with Bomgar 14.2, the installer les for representative consoles and Jump Clients have been tweaked to help you mass deploy Bomgar software to your Macs.
Mass Deploying Bomgar Software to Macs Starting with Bomgar 14.2, the installer les for representative consoles and Jump Clients have been tweaked to help you mass deploy Bomgar software to your Macs.
LOCKSS on LINUX. Network Data Transition 02/17/2011
 LOCKSS on LINUX Network Data Transition 02/17/2011 1 Table of Contents Overview... 3 Prerequisites... 4 Network Transition Checklist... 5 Network Setup... 7 Test the Network Setup... 9 Create Transfer
LOCKSS on LINUX Network Data Transition 02/17/2011 1 Table of Contents Overview... 3 Prerequisites... 4 Network Transition Checklist... 5 Network Setup... 7 Test the Network Setup... 9 Create Transfer
How to Enable Internet for Guest Virtual Machine using Wi-Fi wireless Internet Connection.
 How to Enable Internet for Guest Virtual Machine using Wi-Fi wireless Internet Connection. Table of Contents 1) Host, Guest and VBox version.... 2 2) Check your current Host and Guest Details... 3 3) Now
How to Enable Internet for Guest Virtual Machine using Wi-Fi wireless Internet Connection. Table of Contents 1) Host, Guest and VBox version.... 2 2) Check your current Host and Guest Details... 3 3) Now
Cloud.com CloudStack 2.1.3 Release Notes
 Cloud.com CloudStack 2.1.3 Release Notes September, 2010 1 Specifications are subject to change without notice. The Cloud.com logo, Cloud.com, Hypervisor Attached Storage, HAS, Hypervisor Aware Network,
Cloud.com CloudStack 2.1.3 Release Notes September, 2010 1 Specifications are subject to change without notice. The Cloud.com logo, Cloud.com, Hypervisor Attached Storage, HAS, Hypervisor Aware Network,
Installing a Symantec Backup Exec Agent on a SnapScale Cluster X2 Node or SnapServer DX1 or DX2. Summary
 Technical Bulletin Application Note April 2013 Installing a Symantec Backup Exec Agent on a SnapScale Cluster X2 Node or SnapServer DX1 or DX2 Summary This application note describes how to install the
Technical Bulletin Application Note April 2013 Installing a Symantec Backup Exec Agent on a SnapScale Cluster X2 Node or SnapServer DX1 or DX2 Summary This application note describes how to install the
Security Gateway for OpenStack
 Security Gateway for OpenStack R77.20 Administration Guide 17 August 2014 Protected 2014 Check Point Software Technologies Ltd. All rights reserved. This product and related documentation are protected
Security Gateway for OpenStack R77.20 Administration Guide 17 August 2014 Protected 2014 Check Point Software Technologies Ltd. All rights reserved. This product and related documentation are protected
Enterprise Reporting Server v3.5
 Enterprise Reporting Server v3.5 Administrator s Guide January 2001 Edition 2001 WebTrends Corporation Disclaimer WebTrends Corporation makes no representations or warranties with respect to the contents
Enterprise Reporting Server v3.5 Administrator s Guide January 2001 Edition 2001 WebTrends Corporation Disclaimer WebTrends Corporation makes no representations or warranties with respect to the contents
WES 9.2 DRIVE CONFIGURATION WORKSHEET
 WES 9.2 DRIVE CONFIGURATION WORKSHEET This packet will provide you with a paper medium external to your WES box to write down the device names, partitions, and mount points within your machine. You may
WES 9.2 DRIVE CONFIGURATION WORKSHEET This packet will provide you with a paper medium external to your WES box to write down the device names, partitions, and mount points within your machine. You may
TransNav Management System Documentation. Management Server Guide
 Turin Networks Inc. TransNav Management System Documentation Management Server Guide Release TN3.1.x Publication Date: March 2007 Document Number: 800-0006-TN31 Rev. A FCC Compliance This equipment has
Turin Networks Inc. TransNav Management System Documentation Management Server Guide Release TN3.1.x Publication Date: March 2007 Document Number: 800-0006-TN31 Rev. A FCC Compliance This equipment has
Attix5 Pro Server Edition
 Attix5 Pro Server Edition V7.0.3 User Manual for Linux and Unix operating systems Your guide to protecting data with Attix5 Pro Server Edition. Copyright notice and proprietary information All rights reserved.
Attix5 Pro Server Edition V7.0.3 User Manual for Linux and Unix operating systems Your guide to protecting data with Attix5 Pro Server Edition. Copyright notice and proprietary information All rights reserved.
Table of Contents. Module 1: Overview of SolarisTM 10 Patching...3
 is a supplement to the web-based training course: WS-2700-S10: SolarisTM 10 Patching Best Practices. The guide presents the key concepts of the course but it does not contain all the content presented
is a supplement to the web-based training course: WS-2700-S10: SolarisTM 10 Patching Best Practices. The guide presents the key concepts of the course but it does not contain all the content presented
SFTP SHELL SCRIPT USER GUIDE
 SFTP SHELL SCRIPT USER GUIDE FCA US INFORMATION & COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY MANAGEMENT Overview The EBMX SFTP shell scripts provide a parameter driven workflow to place les on the EBMX servers and queue
SFTP SHELL SCRIPT USER GUIDE FCA US INFORMATION & COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY MANAGEMENT Overview The EBMX SFTP shell scripts provide a parameter driven workflow to place les on the EBMX servers and queue
Dialogic IP Media Server
 Dialogic IP Media Server Upgrading from Release 2.5.0 to 2.6.0 on Red Hat Enterprise Linux Platforms September 2009 64-0523-01 www.dialogic.com Copyright and Legal Disclaimer Copyright and Legal Disclaimer
Dialogic IP Media Server Upgrading from Release 2.5.0 to 2.6.0 on Red Hat Enterprise Linux Platforms September 2009 64-0523-01 www.dialogic.com Copyright and Legal Disclaimer Copyright and Legal Disclaimer
Acano solution. Virtualized Deployment R1.1 Installation Guide. Acano. February 2014 76-1025-03-B
 Acano solution Virtualized Deployment R1.1 Installation Guide Acano February 2014 76-1025-03-B Contents Contents 1 Introduction... 3 1.1 Before You Start... 3 1.1.1 About the Acano virtualized solution...
Acano solution Virtualized Deployment R1.1 Installation Guide Acano February 2014 76-1025-03-B Contents Contents 1 Introduction... 3 1.1 Before You Start... 3 1.1.1 About the Acano virtualized solution...
DocuShare Installation Guide
 DocuShare Installation Guide Publication date: February 2011 This document supports DocuShare Release 6.6.1 Prepared by: Xerox Corporation DocuShare Business Unit 3400 Hillview Avenue Palo Alto, California
DocuShare Installation Guide Publication date: February 2011 This document supports DocuShare Release 6.6.1 Prepared by: Xerox Corporation DocuShare Business Unit 3400 Hillview Avenue Palo Alto, California
An Oracle White Paper April 2010. Best Practices for Running Oracle Databases in Oracle Solaris Containers
 An Oracle White Paper April 2010 Best Practices for Running Oracle Databases in Oracle Solaris Containers Introduction... 1 Oracle Solaris Containers... 2 Oracle Solaris Zones Partitioning Technology...
An Oracle White Paper April 2010 Best Practices for Running Oracle Databases in Oracle Solaris Containers Introduction... 1 Oracle Solaris Containers... 2 Oracle Solaris Zones Partitioning Technology...
The VRRP Project. (Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol) Design Document
 The VRRP Project (Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol) Design Document [email protected] Solaris Networking Sun Microsystems, Inc. Revision 1.0 July 7, 2009 Contents 1 Introduction...1 2 Requirements...1
The VRRP Project (Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol) Design Document [email protected] Solaris Networking Sun Microsystems, Inc. Revision 1.0 July 7, 2009 Contents 1 Introduction...1 2 Requirements...1
How To Install An Org Vm Server On A Virtual Box On An Ubuntu 7.1.3 (Orchestra) On A Windows Box On A Microsoft Zephyrus (Orroster) 2.5 (Orner)
 Oracle Virtualization Installing Oracle VM Server 3.0.3, Oracle VM Manager 3.0.3 and Deploying Oracle RAC 11gR2 (11.2.0.3) Oracle VM templates Linux x86 64 bit for test configuration In two posts I will
Oracle Virtualization Installing Oracle VM Server 3.0.3, Oracle VM Manager 3.0.3 and Deploying Oracle RAC 11gR2 (11.2.0.3) Oracle VM templates Linux x86 64 bit for test configuration In two posts I will
Using VirtualBox ACHOTL1 Virtual Machines
 Using VirtualBox ACHOTL1 Virtual Machines The steps in the Apache Cassandra Hands-On Training Level One courseware book were written using VMware as the virtualization technology. Therefore, it is recommended
Using VirtualBox ACHOTL1 Virtual Machines The steps in the Apache Cassandra Hands-On Training Level One courseware book were written using VMware as the virtualization technology. Therefore, it is recommended
ISERink Installation Guide
 ISERink Installation Guide Version 1.1 January 27, 2015 First developed to support cyber defense competitions (CDCs), ISERink is a virtual laboratory environment that allows students an opportunity to
ISERink Installation Guide Version 1.1 January 27, 2015 First developed to support cyber defense competitions (CDCs), ISERink is a virtual laboratory environment that allows students an opportunity to
Backup of ESXi Virtual Machines using Affa
 Backup of ESXi Virtual Machines using Affa From SME Server Skill level: Advanced The instructions on this page may require deviations from procedure, a good understanding of linux and SME is recommended.
Backup of ESXi Virtual Machines using Affa From SME Server Skill level: Advanced The instructions on this page may require deviations from procedure, a good understanding of linux and SME is recommended.
ANSYS Remote Solve Manager User's Guide
 ANSYS Remote Solve Manager User's Guide ANSYS, Inc. Southpointe 275 Technology Drive Canonsburg, PA 15317 [email protected] http://www.ansys.com (T) 724-746-3304 (F) 724-514-9494 ANSYS Release 15.0 November
ANSYS Remote Solve Manager User's Guide ANSYS, Inc. Southpointe 275 Technology Drive Canonsburg, PA 15317 [email protected] http://www.ansys.com (T) 724-746-3304 (F) 724-514-9494 ANSYS Release 15.0 November
Configuring Static and Dynamic NAT Simultaneously
 Configuring Static and Dynamic NAT Simultaneously Document ID: 13778 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configuring NAT Related Information Introduction In some
Configuring Static and Dynamic NAT Simultaneously Document ID: 13778 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configuring NAT Related Information Introduction In some
STONEGATE IPSEC VPN 5.1 VPN CONSORTIUM INTEROPERABILITY PROFILE
 STONEGATE IPSEC VPN 5.1 VPN CONSORTIUM INTEROPERABILITY PROFILE V IRTUAL PRIVATE NETWORKS C ONTENTS Introduction to the Scenarios... 3 Scenario 1: Gateway-to-Gateway With Pre-Shared Secrets... 3 Configuring
STONEGATE IPSEC VPN 5.1 VPN CONSORTIUM INTEROPERABILITY PROFILE V IRTUAL PRIVATE NETWORKS C ONTENTS Introduction to the Scenarios... 3 Scenario 1: Gateway-to-Gateway With Pre-Shared Secrets... 3 Configuring
RSA Security Analytics Virtual Appliance Setup Guide
 RSA Security Analytics Virtual Appliance Setup Guide Copyright 2010-2015 RSA, the Security Division of EMC. All rights reserved. Trademarks RSA, the RSA Logo and EMC are either registered trademarks or
RSA Security Analytics Virtual Appliance Setup Guide Copyright 2010-2015 RSA, the Security Division of EMC. All rights reserved. Trademarks RSA, the RSA Logo and EMC are either registered trademarks or
Private Cloud Devotional
 Private Cloud Devotional Sacristan Gordon is the consultant's answer to The Swiss Army knife versatile and always at hand. Gordon's core competency is to undertake projects that no one else dare, will,
Private Cloud Devotional Sacristan Gordon is the consultant's answer to The Swiss Army knife versatile and always at hand. Gordon's core competency is to undertake projects that no one else dare, will,
OpenOffice.org 3 Installation Guide
 OpenOffice.org 3 Installation Guide Table of Contents Copyright and trademarks...4 Feedback...4 Versions of this document...5 Preface...6 Related documentation...6 Accessing documentation on the web...6
OpenOffice.org 3 Installation Guide Table of Contents Copyright and trademarks...4 Feedback...4 Versions of this document...5 Preface...6 Related documentation...6 Accessing documentation on the web...6
Perceptive Intelligent Capture. Product Migration Guide. with Supervised Learning. Version 5.5 SP3
 Perceptive Intelligent Capture with Supervised Learning Product Migration Guide Version 5.5 SP3 Written by: Product Documentation, QA Date: March 2014 2014 Perceptive Software, Inc.. All rights reserved
Perceptive Intelligent Capture with Supervised Learning Product Migration Guide Version 5.5 SP3 Written by: Product Documentation, QA Date: March 2014 2014 Perceptive Software, Inc.. All rights reserved
Create a virtual machine at your assigned virtual server. Use the following specs
 CIS Networking Installing Ubuntu Server on Windows hyper-v Much of this information was stolen from http://www.isummation.com/blog/installing-ubuntu-server-1104-64bit-on-hyper-v/ Create a virtual machine
CIS Networking Installing Ubuntu Server on Windows hyper-v Much of this information was stolen from http://www.isummation.com/blog/installing-ubuntu-server-1104-64bit-on-hyper-v/ Create a virtual machine
Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway
 Felix Rohrer Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1 S2 VLAN 99 192.168.99.12 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1
Felix Rohrer Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1 S2 VLAN 99 192.168.99.12 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1
HOWTO: Set up a Vyatta device with ThreatSTOP in router mode
 HOWTO: Set up a Vyatta device with ThreatSTOP in router mode Overview This document explains how to set up a minimal Vyatta device in a routed configuration and then how to apply ThreatSTOP to it. It is
HOWTO: Set up a Vyatta device with ThreatSTOP in router mode Overview This document explains how to set up a minimal Vyatta device in a routed configuration and then how to apply ThreatSTOP to it. It is
Host Configuration (Linux)
 : Location Date Host Configuration (Linux) Trainer Name Laboratory Exercise: Host Configuration (Linux) Objectives In this laboratory exercise you will complete the following tasks: Check for IPv6 support
: Location Date Host Configuration (Linux) Trainer Name Laboratory Exercise: Host Configuration (Linux) Objectives In this laboratory exercise you will complete the following tasks: Check for IPv6 support
How to Configure an Initial Installation of the VMware ESXi Hypervisor
 How to Configure an Initial Installation of the VMware ESXi Hypervisor I am not responsible for your actions or their outcomes, in any way, while reading and/or implementing this tutorial. I will not provide
How to Configure an Initial Installation of the VMware ESXi Hypervisor I am not responsible for your actions or their outcomes, in any way, while reading and/or implementing this tutorial. I will not provide
4013779 Rev C. DBDS Backup and Restore Procedures For System Release 2.2 Through 4.3
 4013779 Rev C DBDS Backup and Restore Procedures For System Release 2.2 Through 4.3 Please Read Important Please read this entire guide. If this guide provides installation or operation instructions,
4013779 Rev C DBDS Backup and Restore Procedures For System Release 2.2 Through 4.3 Please Read Important Please read this entire guide. If this guide provides installation or operation instructions,
Preparing for the Installation
 CHAPTER 3 This section describes how to set up the environment for installation. To ensure a successful installation, use the checklist provided in Installation Scenarios and Checklists, page 1-3 for the
CHAPTER 3 This section describes how to set up the environment for installation. To ensure a successful installation, use the checklist provided in Installation Scenarios and Checklists, page 1-3 for the
LOCKSS on LINUX. CentOS6 Installation Manual 08/22/2013
 LOCKSS on LINUX CentOS6 Installation Manual 08/22/2013 1 Table of Contents Overview... 3 LOCKSS Hardware... 5 Installation Checklist... 6 BIOS Settings... 9 Installation... 10 Firewall Configuration...
LOCKSS on LINUX CentOS6 Installation Manual 08/22/2013 1 Table of Contents Overview... 3 LOCKSS Hardware... 5 Installation Checklist... 6 BIOS Settings... 9 Installation... 10 Firewall Configuration...
Introduction to Operating Systems
 Introduction to Operating Systems It is important that you familiarize yourself with Windows and Linux in preparation for this course. The exercises in this book assume a basic knowledge of both of these
Introduction to Operating Systems It is important that you familiarize yourself with Windows and Linux in preparation for this course. The exercises in this book assume a basic knowledge of both of these
Sun ZFS Storage Appliance Rule-Based Identity Mapping Between Active Directory and Network Information Services Implementation Guide
 An Oracle White Paper February 2011 Sun ZFS Storage Appliance Rule-Based Identity Mapping Between Active Directory and Network Information Services Implementation Guide Introduction... 4 Overview and Prerequisites...
An Oracle White Paper February 2011 Sun ZFS Storage Appliance Rule-Based Identity Mapping Between Active Directory and Network Information Services Implementation Guide Introduction... 4 Overview and Prerequisites...
Site to Site VPN s between two networks with the same IP Address scheme.
 Site to Site VPN s between two networks with the same IP Address scheme. Authored By: Elie Bitton Creation Date: June 21, 2001 Revision Date: December 3 rd, 2001 Purpose: Describe a configuration allowing
Site to Site VPN s between two networks with the same IP Address scheme. Authored By: Elie Bitton Creation Date: June 21, 2001 Revision Date: December 3 rd, 2001 Purpose: Describe a configuration allowing
GeBro-BACKUP. Die Online-Datensicherung. Manual Pro Backup Client on a NAS
 GeBro-BACKUP Die Online-Datensicherung. Manual Pro Backup Client on a NAS Created and tested on a QNAP TS-559 Pro Firmware 4.0.2 Intel x86 Architecture Default hardware configuration OBM v6.15.0.0 Last
GeBro-BACKUP Die Online-Datensicherung. Manual Pro Backup Client on a NAS Created and tested on a QNAP TS-559 Pro Firmware 4.0.2 Intel x86 Architecture Default hardware configuration OBM v6.15.0.0 Last
vsphere Host Profiles
 ESXi 5.1 vcenter Server 5.1 This document supports the version of each product listed and supports all subsequent versions until the document is replaced by a new edition. To check for more recent editions
ESXi 5.1 vcenter Server 5.1 This document supports the version of each product listed and supports all subsequent versions until the document is replaced by a new edition. To check for more recent editions
Solaris For The Modern Data Center. Taking Advantage of Solaris 11 Features
 Solaris For The Modern Data Center Taking Advantage of Solaris 11 Features JANUARY 2013 Contents Introduction... 2 Patching and Maintenance... 2 IPS Packages... 2 Boot Environments... 2 Fast Reboot...
Solaris For The Modern Data Center Taking Advantage of Solaris 11 Features JANUARY 2013 Contents Introduction... 2 Patching and Maintenance... 2 IPS Packages... 2 Boot Environments... 2 Fast Reboot...
Tue Apr 19 11:03:19 PDT 2005 by Andrew Gristina thanks to Luca Deri and the ntop team
 Tue Apr 19 11:03:19 PDT 2005 by Andrew Gristina thanks to Luca Deri and the ntop team This document specifically addresses a subset of interesting netflow export situations to an ntop netflow collector
Tue Apr 19 11:03:19 PDT 2005 by Andrew Gristina thanks to Luca Deri and the ntop team This document specifically addresses a subset of interesting netflow export situations to an ntop netflow collector
DocuShare Installation Guide
 DocuShare Installation Guide Publication date: May 2009 This document supports DocuShare Release 6.5/DocuShare CPX Release 6.5 Prepared by: Xerox Corporation DocuShare Business Unit 3400 Hillview Avenue
DocuShare Installation Guide Publication date: May 2009 This document supports DocuShare Release 6.5/DocuShare CPX Release 6.5 Prepared by: Xerox Corporation DocuShare Business Unit 3400 Hillview Avenue
Planning for an Amanda Disaster Recovery System
 Planning for an Amanda Disaster Recovery System Bernd Harmsen [email protected] www.datasysteme.de 22nd April 2003 Contents 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Why we need a specialized Amanda Disaster Recovery System?..............
Planning for an Amanda Disaster Recovery System Bernd Harmsen [email protected] www.datasysteme.de 22nd April 2003 Contents 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Why we need a specialized Amanda Disaster Recovery System?..............
Data Center Automation with the VM-Series
 Data Center Automation with the VM-Series Tech Note PAN-OS 5.0 Revision A 2012, Palo Alto Networks, Inc. www.paloaltonetworks.com Contents Overview... 3 Process... 3 Creating the Gold Standard... 3 Initial
Data Center Automation with the VM-Series Tech Note PAN-OS 5.0 Revision A 2012, Palo Alto Networks, Inc. www.paloaltonetworks.com Contents Overview... 3 Process... 3 Creating the Gold Standard... 3 Initial
SSL VPN. Virtual Appliance Installation Guide. Virtual Private Networks
 SSL VPN Virtual Appliance Installation Guide Virtual Private Networks C ONTENTS Introduction... 2 Installing the Virtual Appliance... 2 Configuring Appliance Operating System Settings... 3 Setting up the
SSL VPN Virtual Appliance Installation Guide Virtual Private Networks C ONTENTS Introduction... 2 Installing the Virtual Appliance... 2 Configuring Appliance Operating System Settings... 3 Setting up the
An Oracle White Paper July 2012. Oracle VM 3: Building a Demo Environment using Oracle VM VirtualBox
 An Oracle White Paper July 2012 Oracle VM 3: Building a Demo Environment using Oracle VM VirtualBox Introduction... 1 Overview... 2 The Concept... 2 The Process Flow... 3 What You Need to Get Started...
An Oracle White Paper July 2012 Oracle VM 3: Building a Demo Environment using Oracle VM VirtualBox Introduction... 1 Overview... 2 The Concept... 2 The Process Flow... 3 What You Need to Get Started...
Backing Up and Restoring Data
 Backing Up and Restoring Data Cisco Unity Express backup and restore functions use an FTP server to store and retrieve data. The backup function copies the files from the Cisco Unity Express application
Backing Up and Restoring Data Cisco Unity Express backup and restore functions use an FTP server to store and retrieve data. The backup function copies the files from the Cisco Unity Express application
How to configure Microsoft System Center Operations Manager (SCOM) 2012 R2 as SNMP trap receiver for VMware vcenter on MS Windows?
 How to congure Microsoft System Center Operations Manager (SCOM) 2012 R2 as SNMP trap receiver for VMware vcenter on MS Windows? One of the most interesting and very often asked things is how do I congure
How to congure Microsoft System Center Operations Manager (SCOM) 2012 R2 as SNMP trap receiver for VMware vcenter on MS Windows? One of the most interesting and very often asked things is how do I congure
How To Backup In Cisco Uk Central And Cisco Cusd (Cisco) Cusm (Custodian) (Cusd) (Uk) (Usd).Com) (Ucs) (Cyse
 This chapter includes the following sections: Backup and Import in Cisco UCS Central, page 1 Backing up and Restoring Cisco UCS Central, page 4 Backing up and Restoring Cisco UCS Domains, page 8 Import
This chapter includes the following sections: Backup and Import in Cisco UCS Central, page 1 Backing up and Restoring Cisco UCS Central, page 4 Backing up and Restoring Cisco UCS Domains, page 8 Import
Installation Guide for WebSphere Application Server (WAS) and its Fix Packs on AIX V5.3L
 Installation Guide for WebSphere Application Server (WAS) and its Fix Packs on AIX V5.3L Introduction: This guide is written to help any person with little knowledge in AIX V5.3L to prepare the P Server
Installation Guide for WebSphere Application Server (WAS) and its Fix Packs on AIX V5.3L Introduction: This guide is written to help any person with little knowledge in AIX V5.3L to prepare the P Server
Lab 1: Introduction to the network lab
 CSCI 312 - DATA COMMUNICATIONS AND NETWORKS FALL, 2014 Lab 1: Introduction to the network lab NOTE: Be sure to bring a flash drive to the lab; you will need it to save your data. For this and future labs,
CSCI 312 - DATA COMMUNICATIONS AND NETWORKS FALL, 2014 Lab 1: Introduction to the network lab NOTE: Be sure to bring a flash drive to the lab; you will need it to save your data. For this and future labs,
VMware Tools Configuration Utility User's Guide
 VMware Tools Configuration Utility User's Guide VMware Fusion 3.0 vsphere 4.1 VMware Workstation 7.0 VMware Player 3.0 This document supports the version of each product listed and supports all subsequent
VMware Tools Configuration Utility User's Guide VMware Fusion 3.0 vsphere 4.1 VMware Workstation 7.0 VMware Player 3.0 This document supports the version of each product listed and supports all subsequent
How to Create, Setup, and Configure an Ubuntu Router with a Transparent Proxy.
 In this tutorial I am going to explain how to setup a home router with transparent proxy using Linux Ubuntu and Virtualbox. Before we begin to delve into the heart of installing software and typing in
In this tutorial I am going to explain how to setup a home router with transparent proxy using Linux Ubuntu and Virtualbox. Before we begin to delve into the heart of installing software and typing in
DocuSign for SharePoint 2010 1.5.1
 Quick Start Guide DocuSign for SharePoint 2010 1.5.1 Published December 22, 2014 Overview DocuSign for SharePoint 2010 allows users to sign or send documents out for signature from a SharePoint library.
Quick Start Guide DocuSign for SharePoint 2010 1.5.1 Published December 22, 2014 Overview DocuSign for SharePoint 2010 allows users to sign or send documents out for signature from a SharePoint library.
Abstract. Avaya Solution & Interoperability Test Lab
 Avaya Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes for configuring NICE IEX Workforce Management R4.6 with Avaya Call Management System R16.3 with the IEX-RTA and Historical Interfaces Issue
Avaya Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes for configuring NICE IEX Workforce Management R4.6 with Avaya Call Management System R16.3 with the IEX-RTA and Historical Interfaces Issue
User Guide Terminal Service Plus
 User Guide Terminal Service Plus Terminal Service Plus product range is the greatest offering of the world market today! It is a powerful and the easiest way to publish any of your Windows application
User Guide Terminal Service Plus Terminal Service Plus product range is the greatest offering of the world market today! It is a powerful and the easiest way to publish any of your Windows application
Instructor Notes for Lab 3
 Instructor Notes for Lab 3 Do not distribute instructor notes to students! Lab Preparation: Make sure that enough Ethernet hubs and cables are available in the lab. The following tools will be used in
Instructor Notes for Lab 3 Do not distribute instructor notes to students! Lab Preparation: Make sure that enough Ethernet hubs and cables are available in the lab. The following tools will be used in
Monitoring Clearswift Gateways with SCOM
 Technical Guide Version 01 28/11/2014 Documentation Information File Name Document Author Document Filename Monitoring the gateways with _v1.docx Iván Blesa Monitoring the gateways with _v1.docx Issue
Technical Guide Version 01 28/11/2014 Documentation Information File Name Document Author Document Filename Monitoring the gateways with _v1.docx Iván Blesa Monitoring the gateways with _v1.docx Issue
SuperLumin Nemesis. Administration Guide. February 2011
 SuperLumin Nemesis Administration Guide February 2011 SuperLumin Nemesis Legal Notices Information contained in this document is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, SuperLumin assumes no responsibility
SuperLumin Nemesis Administration Guide February 2011 SuperLumin Nemesis Legal Notices Information contained in this document is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, SuperLumin assumes no responsibility
Best Practices. AIX Operating System Level Backup and Recovery for an IBM Smart Analytics System
 IBM Smart Analytics System Best Practices AIX Operating System Level Backup and Recovery for an IBM Smart Analytics System Garrett Fitzsimons IBM Smart Analytics Systems Best Practices Richard Lubell IBM
IBM Smart Analytics System Best Practices AIX Operating System Level Backup and Recovery for an IBM Smart Analytics System Garrett Fitzsimons IBM Smart Analytics Systems Best Practices Richard Lubell IBM
Exam 70-411: Administrating Windows Server 2012 R2. Course Overview
 Exam 70-411: Administrating Windows Server 2012 R2 Course Overview This course teaches students server deployment and image management, managing servers and updates, file and print services, configuring
Exam 70-411: Administrating Windows Server 2012 R2 Course Overview This course teaches students server deployment and image management, managing servers and updates, file and print services, configuring
50.XXX is based on your station number
 Lab 6: Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol The purpose of this lab is to configure a DHCP server for multiple subnets. You will configure additional options along with an IP address and netmask, and you
Lab 6: Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol The purpose of this lab is to configure a DHCP server for multiple subnets. You will configure additional options along with an IP address and netmask, and you
Using Parallel Computing to Run Multiple Jobs
 Beowulf Training Using Parallel Computing to Run Multiple Jobs Jeff Linderoth August 5, 2003 August 5, 2003 Beowulf Training Running Multiple Jobs Slide 1 Outline Introduction to Scheduling Software The
Beowulf Training Using Parallel Computing to Run Multiple Jobs Jeff Linderoth August 5, 2003 August 5, 2003 Beowulf Training Running Multiple Jobs Slide 1 Outline Introduction to Scheduling Software The
MAX_RMAN_08137_IGNORE=5 DISK_RETENTION_POLICY='RECOVERY WINDOW OF 7 DAYS'
 !/bin/sh Example shell script to perform a nightly full backup of the database and scan for errors Copyright (c) 2008, 2014 Caleb.com All Rights Reserved This script is provided as an EXAMPLE ONLY and
!/bin/sh Example shell script to perform a nightly full backup of the database and scan for errors Copyright (c) 2008, 2014 Caleb.com All Rights Reserved This script is provided as an EXAMPLE ONLY and
Introduction. Created by Richard Bell 10/29/2014
 Introduction GNU Radio is open source software that provides built in modules for standard tasks of a wireless communications system. Within the GNU Radio framework is gnuradio-companion, which is a GUI
Introduction GNU Radio is open source software that provides built in modules for standard tasks of a wireless communications system. Within the GNU Radio framework is gnuradio-companion, which is a GUI
Install Guide for JunosV Wireless LAN Controller
 The next-generation Juniper Networks JunosV Wireless LAN Controller is a virtual controller using a cloud-based architecture with physical access points. The current functionality of a physical controller
The next-generation Juniper Networks JunosV Wireless LAN Controller is a virtual controller using a cloud-based architecture with physical access points. The current functionality of a physical controller
Using a login script for deployment of Kaspersky Network Agent to Mac OS X clients
 Using a login script for deployment of Kaspersky Network Agent to Mac OS X clients EXECUTIVE SUMMARY This document describes how an administrator can configure a login script to deploy Kaspersky Lab Network
Using a login script for deployment of Kaspersky Network Agent to Mac OS X clients EXECUTIVE SUMMARY This document describes how an administrator can configure a login script to deploy Kaspersky Lab Network
Load Balancing - Single Multipath Route HOWTO
 Load Balancing - Single Multipath Route HOWTO Shakthi Kannan, shaks_wants_no_spam_at_shakthimaan_dot_com January 5, 2007 Revision: 1.2 Abstract This documentation provides the steps to setup load-balancing
Load Balancing - Single Multipath Route HOWTO Shakthi Kannan, shaks_wants_no_spam_at_shakthimaan_dot_com January 5, 2007 Revision: 1.2 Abstract This documentation provides the steps to setup load-balancing
Administration Manual for UrBackup Server 1.3.x
 Administration Manual for UrBackup Server 1.3.x Martin Raiber February 1, 2014 Contents 1 Introduction 2 2 Architecture 3 2.1 Server architecture.................................... 3 2.2 Client architecture....................................
Administration Manual for UrBackup Server 1.3.x Martin Raiber February 1, 2014 Contents 1 Introduction 2 2 Architecture 3 2.1 Server architecture.................................... 3 2.2 Client architecture....................................
