Nasogastric Tube Feedings at Home
|
|
|
- Lindsey McCormick
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Nasogastric Tube Feedings at Home What is a nasogastric (feeding) tube? A nasogastric tube is a thin, flexible, soft tube that is passed through your child s nose (nostril), down the back of the throat, through the swallowing tube (esophagus), and into the stomach. It is taped under the nose to stay in place. A nasogastric tube is sometimes called an NG or feeding tube. How is the NG used? If the tube is needed for giving medicine, this is done using a syringe. For scheduled feedings, a syringe or pump may be used. For continuous feeding, formula is given using a pump. The pump controls the rate of fluid flow. What is the feeding schedule? Feeding method: Formula name: Total amount of formula per day: _ Total amount of water per day: Why does my child need a NG (feeding) tube? A nasogastric feeding tube is used to give fluids, food, and medicine when a child cannot take them by mouth. Reasons a child may need an NG include: Problems with sucking, chewing, or swallowing. Unable to get enough nutrition with a normal diet. Unable to swallow needed medicines. To remove fluids and gas from the stomach. To prevent nausea and vomiting. To prevent pressure on stitches after surgery. Amount of each feeding: Feeding Schedule: Flush the tube with ml of water before and after each feeding Other Instructions:
2 Do not make changes in the type or amount of formula without talking to your child s provider first. Provider to call: Provider: Phone: After Hours Instructions: How do I give formula with a feeding bag? 1. Wash your hands with soap and water for 30 seconds. 2. Position your child sitting up if possible, or on the right side with the head of bed raised degrees. 3. Be sure the NG tube is in the stomach by looking at the placement of the tape, and measuring the distance from the nose to the tip of the tube. The tape should be in the same place as the last feeding. The measurement should be the same as the last feeding. 4. Clamp the feeding bag tubing. 5. Fill the feeding bag with formula. 6. Close the cover tightly. Hang the bag at least 2 feet above your child s head. 7. Open the clamp. Let the tubing fill until you see no air. Air in the tubing will not hurt your child, but will make your child s stomach feel full. 8. Clamp the tubing. 9. Connect the bag to the feeding tube. 10. Open the clamp. 11. Watch your child for any signs of nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, stomach swelling, or increased fussiness. Any one of these signs may mean that your child is not able to digest the formula at the rate it is running. 2 If these symptoms occur, stop the feeding and contact your provider for instructions. 12. When the feeding is done, fill the bag with the prescribed amount of water. If it isn t time to take extra water, be sure to flush the tube after each feeding with at least 10 ml of tap water so that it doesn t clog. 13. Clamp or cap the tube. Disconnect the tube from your child. 14. Clean the supplies by rinsing the bag and tubing with cold water. Then, swish them in warm water and a drop of liquid dishwashing soap. Rinse thoroughly so that all of the soap is removed. Hang to dry. How do I give formula with a syringe? 1. Wash your hands with soap and water for 30 seconds. 2. Position your child in a sitting position, or on the right side with the head raised Check placement of the NG tube using the method described in step 3 above. 4. Remove the plunger from a 60 ml syringe. Connect the syringe to the feeding tube. 5. Hold the syringe upright and pour the formula into it. 6. Hold the syringe inches above your child s head. Allow formula to be delivered by gravity over minutes. 7. Keep filling the syringe as it empties until the entire amount of formula is given. 8. If the feeding should stop, you may use the plunger of the syringe to give a gentle push to get the feeding going again. 9. Give the prescribed amount of water to flush the tube. 10. Clean supplies as above (#14).
3 Can I give medicines through the NG tube? Medicine can be given with a syringe through the feeding tube. It is best to use medicine in a liquid form. If you must give pills, be sure to thoroughly crush and dissolve pills in warm water so they do not clog the tube. Give each medicine separately. Do not mix medicines together or mix with formula. Never crush enteric-coated or timerelease capsules. If you have questions about which medicines can be crushed, please talk to your pharmacist or health care provider. Flush the feeding tube with 5 ml of water after each medicine is given, and ml of water after all medicines are given to be sure they get into the stomach. Do not add any medicines to formula in the feeding container. How do I check the placement of the feeding tube? The most important part of caring for an NG at home is checking that it is in the correct position (i.e. sitting in the stomach) before you put anything down it. The feeding tube should be marked where it exits the nose after the first placement. This mark should not change over time. Use a tape measure to measure the distance from where your child s tube exits the nostril to the end cap of the tube. Record this measurement every time you use the tube, or every 4-6 hours during a continuous feeding. If the mark moves, and the tube has slipped, call your provider before using the tube. Another way to tell if the NG tube is in the stomach is to attach a syringe to the end of the feeding tube and gently pull back. There may be fluid in the syringe and/or tubing that looks like formula, or clear green to yellow fluid. Return this fluid to the stomach. If you do not obtain fluid, it may be a sign that the tube is not in the stomach. Contact your provider before using the tube. The securing tape should be changed every other day, or when it is loose, so that the NG tube stays secure. Babies and children who need the tube for a long time at home will need to have the tube replaced at times. This normally means your child will need to return to a provider to have the tube replaced. Do not try to reinsert an NG tube if you have not been trained to do so. If you are going home with an NG tube, you need to have a clear plan in place before leaving the hospital. This plan should include who to contact and what to do if the tube moves or comes out. Any adult caring for your child will need education on how to care for the tube and how to feed your child. Please ask your nurse for more information. If your child s nose is sore, move the tape to a different place on the nose. The tape may also need to be changed if it is coming loose. This is a good time to clean the skin under the tape. Be careful not to let the tube slip out. 1. Wrap or swaddle your child in a blanket, or have another person hold your child s arms so the tube cannot be pulled while you are caring for the site. 2. Wash your hands with soap and water. Dry well. 3. Prepare your supplies tape, cottontipped swabs, water, soap, and lotion. 4. While carefully holding the tube, remove the old tape. 5. Use a cotton-tipped swab moistened with water and soap to clean the edges of both nostrils. Rinse thoroughly. Pat dry. 6. Look inside the nostril where the tube is to check for any redness, pain, or sores. You may put a small amount of lotion or Vaseline in the nostril to prevent irritation. 3
4 7. Secure the tube to the nose by wrapping a narrow piece of tape around the tube in each direction. Secure the other end of the tube to the cheek on the same side of the face where the tube exits. 8. If you feel your child is having pain, you note a sore area, or the tube has come out, tape the tube down. Do not use the tube. Contact the provider who is ordering the feedings to get further instruction. What is a residual, and how do I check for it The residual is the amount of contents remaining in your child s stomach from the previous feeding. The residual is checked before a feeding to make sure your child is not too full before another feeding is given. To check for a residual: 1. Place an empty syringe on the end of the feeding tube. 2. Pull the plunger back to withdraw stomach contents. 3. Measure the amount of residual on the syringe. Your provider will discuss with you how much residual is appropriate for your child. 4. Return the stomach contents to your child. 5. Flush the tube with 5-10 ml of warm water to prevent clogging. 6. If the residual is more than recommended for your child, delay the feeding for 30 minutes, and then check the residual again. What can I do while my child is being fed? Feeding time is a special time for babies. Babies enjoy being held closely, cuddled, rocked, or talked to during tube feedings just as if they were being fed by mouth. Hold your baby, and encourage the baby to use a pacifier during feeding to practice sucking and swallowing. 4 Toddlers will need to stay in one place, so playing a game or doing a quiet activity may be useful. Older children can sit at the table with the family and receive a tube feeding while the family eats a meal. More information about feeding tubes 1. What should I do if the tube is blocked? If the tube won t flush, try using warm water. Gently flush ml of fluid through the tube. Do not use carbonated beverages, juice, or vigorous pressure to unclog the tube. If the tube still will not flush, call your nurse or doctor. Flushing the tube before and after giving medicines, after intermittent feedings, and every 4-6 hours during continuous feedings will prevent this problem. 2. What should I do if the tube is leaking? If the tube is cracked or leaking, the tube will need to be replaced. 3. What should I do if my child is vomiting? Call your doctor if vomiting persists after 1 day. Vomiting causes a loss of body fluids, salts and nutrients. Do not give a feeding if your child is vomiting. Check the residual. It the residual is higher than recommended, delay the feeding. Recheck the residual every minutes until the residual is low enough to start the feeding. Give feedings in an upright position to decrease the chances of vomiting. Try smaller, more frequent feedings, being sure that the total amount of feeding for the day is the same as what is ordered. Try to slow the rate of the feeding.
5 Have your child rest after each feeding. But, do not let him or her lie down flat during the feeding and for 1 hour after a feeding. If your child develops difficulty breathing during or immediately after a feeding, stop the feeding and call your provider. It is possible your child may have inhaled formula or stomach contents into the lungs. Infection may cause vomiting. Clean and rinse equipment well between feedings. Do not let formula in the feeding bag hang longer than 8 hours. After the formula can is opened, the can should be stored in the refrigerator until used. If your child has nausea and vomiting, your provider may recommend changing the feedings temporarily. Follow your provider s instructions about feeding during illness. 4. What should I do if my child has diarrhea? Diarrhea is frequent loose, watery stools. Diarrhea can be caused by giving too much feeding at once, running the feeding too quickly, unable to tolerate the type of formula, spoiled formula, or infection. Some medicines can cause diarrhea. Some children have loose stools with changes in formula, medicines, or feeding routines. Avoid hanging formula for longer than 8 hours. Keep opened formula in the refrigerator for no more than 24 hours. Slow the feeding rate or give smaller amounts of formula more often. Give more water after each feeding to replace water lost in diarrhea. Call your provider if the diarrhea does not stop after 1 day. 5. What should I do if my child becomes dehydrated? Dehydration is a loss of water and fluids from the body. Dehydration may occur for a variety of reasons diarrhea, vomiting, fever, or sweating for example. Signs of dehydration include decreased or dark urine, crying with no tears, dry skin, fatigue, irritability, dizziness, dry mouth, weight loss, and/or headache. Extra water may be given after each feeding to replace water lost. Call your provider if you notice signs of dehydration. 6. What should I do if my child becomes constipated? Constipation may be caused by certain types of formula, changes in formula, medicines, or feeding patterns, or not enough water. Give more water flushes throughout the day, especially during hot weather. If constipation becomes chronic, contact your provider. 7. How do I bathe my child with a NG in place? Bathe your child as is normal for the age and developmental level, as long as the NG tube is not submerged under water. 8. What should I do if my child has gas, bloating or cramping? Be sure there is no air in the tubing before attaching the feeding tube. 5
6 9. Why is oral care still important? Good mouth care is essential for overall health. Your child should have their teeth, gums and mouth brushed at least twice a day using a soft toothbrush or sponge brush even if he/she is not eating by mouth. 10. What to do if the tube is out of place If the tube is longer in the stomach, call your provider or Home Health Nurse. Do not use the tube. You will need to have a new tube placed. If the tube is pulled out during a feeding, stop the feeding right away, and contact your Provider to have the tube replaced. 11. When should I call my child s provider? Your child has trouble breathing. Your child turns blue. You see blood around the tube, in your child s stool, or in stomach contents. Your child coughs, chokes, or vomits while feeding (stop the feeding if this occurs during feeding). Your child has a bloated or rigid belly (belly feels hard when it is gently pressed). Your child has diarrhea or constipation. Your child has a fever of F or higher. The Spanish version of this Health Facts for You is # 7232 Your health care team may have given you this information as part of your care. If so, please use it and call if you have any questions. If this information was not given to you as part of your care, please check with your doctor. This is not medical advice. This is not to be used for diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. Because each person s health needs are different, you should talk with your doctor or others on your health care team when using this information. If you have an emergency, please call 911. Copyright 11/2016. University of Wisconsin Hospitals and Clinics Authority. All rights reserved. Produced by the Department of Nursing. HF#7223 6
Caring for Your Gastrostomy
 Caring for Your Gastrostomy Table of Contents What Is a Gastrostomy Tube (G-tube)?... 2 Types of Gastrostomy Tubes... 3 Cleaning the Gastrostomy Site... 4 Gastrostomy Feedings... 5 Giving Medicines...
Caring for Your Gastrostomy Table of Contents What Is a Gastrostomy Tube (G-tube)?... 2 Types of Gastrostomy Tubes... 3 Cleaning the Gastrostomy Site... 4 Gastrostomy Feedings... 5 Giving Medicines...
Caring for Your Child s Gastrostomy Tube
 Caring for Your Child s Gastrostomy Tube Table of Contents What Is a Gastrostomy Tube (G-tube)?... 2 Types of Feeding Tubes... 3 Cleaning the Gastrostomy Site... 5 Gastrostomy Feedings... 7 Giving Medicines...
Caring for Your Child s Gastrostomy Tube Table of Contents What Is a Gastrostomy Tube (G-tube)?... 2 Types of Feeding Tubes... 3 Cleaning the Gastrostomy Site... 5 Gastrostomy Feedings... 7 Giving Medicines...
GJ TUBE (GASTROJEJUNOSTOMY TUBE) Daily Care
 GJ TUBE (GASTROJEJUNOSTOMY TUBE) Daily Care Your child has a Picture 1 The GJ Tube inside the body. gastrojejunostomy (GJ) tube Disc (Picture 1). This set of tubes lets food or medicine go into either
GJ TUBE (GASTROJEJUNOSTOMY TUBE) Daily Care Your child has a Picture 1 The GJ Tube inside the body. gastrojejunostomy (GJ) tube Disc (Picture 1). This set of tubes lets food or medicine go into either
Patients First. Tube Feeding Guidelines. Careful handwashing and a clean work surface help prevent infection. Patient Education CARE AND TREATMENT
 Patient Education CARE AND TREATMENT Careful handwashing and a clean work surface help prevent infection. Tube Feeding Guidelines This information will guide you in learning about the procedure for tube
Patient Education CARE AND TREATMENT Careful handwashing and a clean work surface help prevent infection. Tube Feeding Guidelines This information will guide you in learning about the procedure for tube
Information for people being discharged with a naso-gastric (NG) feeding tube
 Information for people being discharged with a naso-gastric (NG) feeding tube The aim of this leaflet is to provide patients with the relevant information for the use of a nasogastric tube. It will include:
Information for people being discharged with a naso-gastric (NG) feeding tube The aim of this leaflet is to provide patients with the relevant information for the use of a nasogastric tube. It will include:
FOLFOX Chemotherapy. This handout provides information about FOLFOX chemotherapy. It is sometimes called as FLOX chemotherapy.
 FOLFOX Chemotherapy This handout provides information about FOLFOX chemotherapy. It is sometimes called as FLOX chemotherapy. What is chemotherapy? Chemotherapy is a method of treating cancer by using
FOLFOX Chemotherapy This handout provides information about FOLFOX chemotherapy. It is sometimes called as FLOX chemotherapy. What is chemotherapy? Chemotherapy is a method of treating cancer by using
Gastrostomy Feeding CARE GUIDELINES FOR PATIENTS & CARERS. Accessory items. Freka UK Funnel Adapter. Fixation Plate CH9. Male Luer Lock Adapter
 Accessory items Freka UK Funnel Adapter Fixation Plate CH9 Code: 7755681 Code: 7903002 Male Luer Lock Adapter CH9 Fixation Plate CH15 Code: 7981311 Code: 7904002 Male Luer Lock Adapter CH15 Code: 798137Y
Accessory items Freka UK Funnel Adapter Fixation Plate CH9 Code: 7755681 Code: 7903002 Male Luer Lock Adapter CH9 Fixation Plate CH15 Code: 7981311 Code: 7904002 Male Luer Lock Adapter CH15 Code: 798137Y
Gastrostomy Tubes Home Care Manual (Corpak, Foley catheter, Genie, Malecot, Mic-G)
 Physician who placed the gastrostomy: Date placed: Type of gastrostomy tube: Size of the gastrostomy: Gastrostomy tubes are measured in French (Fr.) sizes. A size 16 Fr. gastrostomy is larger than a 14
Physician who placed the gastrostomy: Date placed: Type of gastrostomy tube: Size of the gastrostomy: Gastrostomy tubes are measured in French (Fr.) sizes. A size 16 Fr. gastrostomy is larger than a 14
TUBE FEEDING AT HOME
 TUBE FEEDING AT HOME Adapted from the former Taming the Feeding Tube, Royal North Shore Hospital. Revised 2005, 2007, Jan 2009 1 Where do I find information in this booklet? Only the pages that you need
TUBE FEEDING AT HOME Adapted from the former Taming the Feeding Tube, Royal North Shore Hospital. Revised 2005, 2007, Jan 2009 1 Where do I find information in this booklet? Only the pages that you need
Tube Feeding at Home Gravity or Syringe Feeding
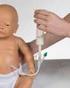 Tube Feeding at Home Gravity or Syringe Feeding Adapted from the former Taming the Feeding Tube, North Shore Hospital. 1 Where do I find information in this booklet? Subject Page How do I contact my health
Tube Feeding at Home Gravity or Syringe Feeding Adapted from the former Taming the Feeding Tube, North Shore Hospital. 1 Where do I find information in this booklet? Subject Page How do I contact my health
Biliary Drain. What is a biliary drain?
 Biliary Drain What is a biliary drain? A biliary drain is a tube to drain bile from your liver. It is put in by a doctor called an Interventional Radiologist. The tube or catheter is placed through your
Biliary Drain What is a biliary drain? A biliary drain is a tube to drain bile from your liver. It is put in by a doctor called an Interventional Radiologist. The tube or catheter is placed through your
PATIENT GUIDE. Care and Maintenance Drainage Frequency: Max. Drainage Volume: Dressing Option: Clinician s Signature: Every drainage Weekly
 PATIENT GUIDE Care and Maintenance Drainage Frequency: Max. Drainage Volume: Dressing Option: Every drainage Weekly Clinician s Signature: ACCESS SYSTEMS Pleural Space Insertion Site Cuff Exit Site Catheter
PATIENT GUIDE Care and Maintenance Drainage Frequency: Max. Drainage Volume: Dressing Option: Every drainage Weekly Clinician s Signature: ACCESS SYSTEMS Pleural Space Insertion Site Cuff Exit Site Catheter
Care of Gastrostomy Tubes for Adults with IDD in Community Settings: The Nurse s Role. Lillian Khalil, BSN, RN Volunteers of America, Chesapeake
 Care of Gastrostomy Tubes for Adults with IDD in Community Settings: The Nurse s Role Lillian Khalil, BSN, RN Volunteers of America, Chesapeake Objectives The participants will be able to identify the
Care of Gastrostomy Tubes for Adults with IDD in Community Settings: The Nurse s Role Lillian Khalil, BSN, RN Volunteers of America, Chesapeake Objectives The participants will be able to identify the
TUBE-FEEDING INSTRUCTIONS FOR HOME
 Name Clinic Number Room: TUBE-FEEDING INSTRUCTIONS FOR HOME CENTER FOR HUMAN NUTRITION, M17/ DIGESTIVE DISEASE INSTITUTE 9500 Euclid Avenue Cleveland, OH 44195 1.800.CCF.CARE 1.216.444.3046 YOUR TUBE-FEEDING
Name Clinic Number Room: TUBE-FEEDING INSTRUCTIONS FOR HOME CENTER FOR HUMAN NUTRITION, M17/ DIGESTIVE DISEASE INSTITUTE 9500 Euclid Avenue Cleveland, OH 44195 1.800.CCF.CARE 1.216.444.3046 YOUR TUBE-FEEDING
Are any artificial parts used in the ACE Malone surgery?
 ACE Malone (Antegrade Continence Enema) What is the ACE Malone? The Antegrade Continence Enema (ACE) is a type of surgery designed for the child who has chronic bowel problems with bouts of constipation,
ACE Malone (Antegrade Continence Enema) What is the ACE Malone? The Antegrade Continence Enema (ACE) is a type of surgery designed for the child who has chronic bowel problems with bouts of constipation,
All About Your Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC)
 All About Your Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) General Information Intravenous (IV) therapy is the delivery of fluid directly into a vein. An intravenous catheter is a hollow tube that is
All About Your Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) General Information Intravenous (IV) therapy is the delivery of fluid directly into a vein. An intravenous catheter is a hollow tube that is
Care for your child s Central Venous Catheter (CVC)
 Care for your child s Central Venous Catheter (CVC) This booklet is intended for general informational purposes only. You should consult your doctor for medical advice. Please call the clinic or your home
Care for your child s Central Venous Catheter (CVC) This booklet is intended for general informational purposes only. You should consult your doctor for medical advice. Please call the clinic or your home
Gallbladder Surgery with an Incision (Cholecystectomy)
 Gallbladder Surgery with an Incision (Cholecystectomy) It is normal to have questions about your surgery. This handout gives you information about what will happen to you before, during and after your
Gallbladder Surgery with an Incision (Cholecystectomy) It is normal to have questions about your surgery. This handout gives you information about what will happen to you before, during and after your
For the Patient: Paclitaxel injection Other names: TAXOL
 For the Patient: Paclitaxel injection Other names: TAXOL Paclitaxel (pak'' li tax' el) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a clear liquid that is injected into a vein. Tell your
For the Patient: Paclitaxel injection Other names: TAXOL Paclitaxel (pak'' li tax' el) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a clear liquid that is injected into a vein. Tell your
You will be having surgery to remove a tumour(s) from your liver.
 Liver surgery You will be having surgery to remove a tumour(s) from your liver. This handout will help you learn about the surgery, how to prepare for surgery and your care after surgery. Surgery can be
Liver surgery You will be having surgery to remove a tumour(s) from your liver. This handout will help you learn about the surgery, how to prepare for surgery and your care after surgery. Surgery can be
Parent Information for USING A NASOGASTRIC TUBE
 Parent Information for USING A NASOGASTRIC TUBE The information sheet has been written for parents whose baby / child requires a nasogastric tube for short or long term feeding. WHAT IS A NASOGRASTRIC
Parent Information for USING A NASOGASTRIC TUBE The information sheet has been written for parents whose baby / child requires a nasogastric tube for short or long term feeding. WHAT IS A NASOGRASTRIC
After Your Gastrectomy
 After Your Gastrectomy UHN Information for patients and families Read this information to learn: what a gastrectomy is how to care for yourself what problems to look out for who to call if you have any
After Your Gastrectomy UHN Information for patients and families Read this information to learn: what a gastrectomy is how to care for yourself what problems to look out for who to call if you have any
Getting Ready for Your Colonoscopy (PEG) - APC
 Getting Ready for Your Colonoscopy (PEG) - APC To help you get ready for your procedure; we, the staff of the Ambulatory Procedure Center at UW Hospital have made this handout for you that has information
Getting Ready for Your Colonoscopy (PEG) - APC To help you get ready for your procedure; we, the staff of the Ambulatory Procedure Center at UW Hospital have made this handout for you that has information
For the Patient: GDP Other names: LYGDP
 1 For the Patient: GDP Other names: LYGDP G D P Gemcitabine Dexamethasone (taken by mouth) CISPlatin Uses: GDP is a drug treatment given for Non-Hodgkins and Hodgkin Lymphoma with the expectation of destroying
1 For the Patient: GDP Other names: LYGDP G D P Gemcitabine Dexamethasone (taken by mouth) CISPlatin Uses: GDP is a drug treatment given for Non-Hodgkins and Hodgkin Lymphoma with the expectation of destroying
Delivering nutrition, fluids & medication via a PEG. By Julia Pointer & Caroline Ross, Staff Nurses, Hospice Day Service
 Delivering nutrition, fluids & medication via a PEG By Julia Pointer & Caroline Ross, Staff Nurses, Hospice Day Service Aims of this session? To give an explanation of the theory and practice of a Percutaneous
Delivering nutrition, fluids & medication via a PEG By Julia Pointer & Caroline Ross, Staff Nurses, Hospice Day Service Aims of this session? To give an explanation of the theory and practice of a Percutaneous
Gastroschisis and My Baby
 Patient and Family Education Gastroschisis and My Baby Gastroschisis is a condition where a baby is born with the intestine outside the body. Learning about the diagnosis What is gastroschisis? (pronounced
Patient and Family Education Gastroschisis and My Baby Gastroschisis is a condition where a baby is born with the intestine outside the body. Learning about the diagnosis What is gastroschisis? (pronounced
Gemcitabine and Cisplatin
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu What is Gemcitabine (jem-site-a been)? Gemcitabine is a chemotherapy medicine known as an anti-metabolite. Another name for this drug is Gemzar. This drug is
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu What is Gemcitabine (jem-site-a been)? Gemcitabine is a chemotherapy medicine known as an anti-metabolite. Another name for this drug is Gemzar. This drug is
Home Care for Your Nephrostomy Catheter
 Home Care for Your Nephrostomy Catheter This handout covers information about caring for your nephrostomy catheter right after placement and caring for it long term. If you have any questions, please call
Home Care for Your Nephrostomy Catheter This handout covers information about caring for your nephrostomy catheter right after placement and caring for it long term. If you have any questions, please call
PATIENT GUIDE. Care and Maintenance Drainage Frequency: Max. Drainage Volume: Dressing Option: Clinician s Signature: Every drainage Weekly
 PATIENT GUIDE Care and Maintenance Drainage Frequency: Max. Drainage Volume: Dressing Option: Every drainage Weekly Clinician s Signature: ACCESS SYSTEMS Pleural Space Insertion Site Cuff Exit Site Catheter
PATIENT GUIDE Care and Maintenance Drainage Frequency: Max. Drainage Volume: Dressing Option: Every drainage Weekly Clinician s Signature: ACCESS SYSTEMS Pleural Space Insertion Site Cuff Exit Site Catheter
CATHETER for Hemodialysis
 CATHETER for Hemodialysis What You Need to Know to Stay Healthy with a Catheter One treatment choice for kidney failure is hemodialysis (HD). HD removes wastes and excess fluid from your blood. Your lifeline
CATHETER for Hemodialysis What You Need to Know to Stay Healthy with a Catheter One treatment choice for kidney failure is hemodialysis (HD). HD removes wastes and excess fluid from your blood. Your lifeline
Name of Child: Date: About Blood Cells
 The Emily Center About Blood Cells Procedure/Treatment/Home Care Si usted desea esta información en español, por favor pídasela a su enfermero o doctor. #736 Name of Child: Date: About Blood Cells Blood
The Emily Center About Blood Cells Procedure/Treatment/Home Care Si usted desea esta información en español, por favor pídasela a su enfermero o doctor. #736 Name of Child: Date: About Blood Cells Blood
TCH: Docetaxel, Carboplatin and Trastuzumab
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu TCH: Docetaxel, Carboplatin and Trastuzumab What is TCH? It is the short name for the drugs used for this chemotherapy treatment. The three drugs you will receive
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu TCH: Docetaxel, Carboplatin and Trastuzumab What is TCH? It is the short name for the drugs used for this chemotherapy treatment. The three drugs you will receive
Caring for Your PleurX Pleural Catheter
 Caring for Your PleurX Pleural Catheter A PleurX Pleural Catheter has been placed in your chest through a small incision in your skin into the pleural space (see picture below). This allows you to drain
Caring for Your PleurX Pleural Catheter A PleurX Pleural Catheter has been placed in your chest through a small incision in your skin into the pleural space (see picture below). This allows you to drain
Going home after an AV Fistula or AV Graft
 Going home after an AV Fistula or AV Graft TGH Information for patients and families During your hospital stay, your surgeon created an: AV Fistula AV Graft Read this booklet to learn: how to care for
Going home after an AV Fistula or AV Graft TGH Information for patients and families During your hospital stay, your surgeon created an: AV Fistula AV Graft Read this booklet to learn: how to care for
Long Term Tube Feeding. Sunnybrook. A Guide for Patients and Substitute Decision Makers VETERANS & COMMUNITY
 Long Term Tube Feeding A Guide for Patients and Substitute Decision Makers Sunnybrook VETERANS & COMMUNITY Sunnybrook VETERANS & COMMUNITY This brochure has been produced by: Sunnybrook Health Sciences
Long Term Tube Feeding A Guide for Patients and Substitute Decision Makers Sunnybrook VETERANS & COMMUNITY Sunnybrook VETERANS & COMMUNITY This brochure has been produced by: Sunnybrook Health Sciences
Total Abdominal Hysterectomy
 What is a total abdominal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through an abdominal incision (either an up and down or bikini cut). Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient.
What is a total abdominal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through an abdominal incision (either an up and down or bikini cut). Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient.
Problems of the Digestive System
 The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists f AQ FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS FAQ120 WOMEN S HEALTH Problems of the Digestive System What are some common digestive problems? What is constipation?
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists f AQ FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS FAQ120 WOMEN S HEALTH Problems of the Digestive System What are some common digestive problems? What is constipation?
Medications to help you quit smoking
 Medications to help you quit smoking How can medication help me quit smoking? Using medications can increase your chances of quitting smoking 2 to 3 times more than quitting without using medications.
Medications to help you quit smoking How can medication help me quit smoking? Using medications can increase your chances of quitting smoking 2 to 3 times more than quitting without using medications.
CMF: Cyclophosphamide, Methotrexate and Fluorouracil
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu CMF: Cyclophosphamide, Methotrexate and Fluorouracil What is CMF? This is the short name for the drugs used for this chemotherapy treatment. The three drugs
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu CMF: Cyclophosphamide, Methotrexate and Fluorouracil What is CMF? This is the short name for the drugs used for this chemotherapy treatment. The three drugs
Emergency Care for Patients of The James
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Emergency Care for Patients of The James Emergency Care During and After Treatment Here are guidelines about when and how to report problems that you may have
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Emergency Care for Patients of The James Emergency Care During and After Treatment Here are guidelines about when and how to report problems that you may have
Chemotherapy Side Effects Worksheet
 Page 1 of 6 Chemotherapy Side Effects Worksheet Medicines or drugs that destroy cancer cells are called cancer chemotherapy. It is sometimes the first choice for treating many cancers. Chemotherapy differs
Page 1 of 6 Chemotherapy Side Effects Worksheet Medicines or drugs that destroy cancer cells are called cancer chemotherapy. It is sometimes the first choice for treating many cancers. Chemotherapy differs
TC: Docetaxel and Cyclophosphamide
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu What is TC? It is the short name for the drugs used for this chemotherapy treatment. The two drugs you will receive during this treatment are Docetaxel (Taxotere
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu What is TC? It is the short name for the drugs used for this chemotherapy treatment. The two drugs you will receive during this treatment are Docetaxel (Taxotere
PATIENT GUIDE. Understand and care for your peripherally inserted central venous catheter (PICC). MEDICAL
 PATIENT GUIDE Understand and care for your peripherally inserted central venous catheter (PICC). MEDICAL Introduction The following information is presented as a guideline for your reference. The best
PATIENT GUIDE Understand and care for your peripherally inserted central venous catheter (PICC). MEDICAL Introduction The following information is presented as a guideline for your reference. The best
After Your Abdominal Surgery
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION After Your Abdominal Surgery Self-care and follow-up You recently had abdominal surgery. This handout explains what to expect during your recovery. Please read these instructions
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION After Your Abdominal Surgery Self-care and follow-up You recently had abdominal surgery. This handout explains what to expect during your recovery. Please read these instructions
For the Patient: Dasatinib Other names: SPRYCEL
 For the Patient: Dasatinib Other names: SPRYCEL Dasatinib (da sa' ti nib) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. Tell your doctor if you have ever
For the Patient: Dasatinib Other names: SPRYCEL Dasatinib (da sa' ti nib) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. Tell your doctor if you have ever
AC: Doxorubicin and Cyclophosphamide
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu What is AC? It is the short name for the drugs used for this chemotherapy treatment. The two drugs you will receive during this treatment are Doxorubicin (Adriamycin
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu What is AC? It is the short name for the drugs used for this chemotherapy treatment. The two drugs you will receive during this treatment are Doxorubicin (Adriamycin
After Your Gastric Bypass Surgery
 After Your Gastric Bypass Surgery UHN Information for patients and families Read this information to learn: what problems to look out for how to care for yourself at home about your follow-up appointment
After Your Gastric Bypass Surgery UHN Information for patients and families Read this information to learn: what problems to look out for how to care for yourself at home about your follow-up appointment
Your Recovery After a Cesarean Delivery
 Your Recovery After a Cesarean Delivery It is normal to have many questions about your care after delivery. Cesarean delivery is surgery and your body needs time to heal and recover for the next 6 weeks,
Your Recovery After a Cesarean Delivery It is normal to have many questions about your care after delivery. Cesarean delivery is surgery and your body needs time to heal and recover for the next 6 weeks,
AC Chemotherapy Regimen (Doxorubicin + Cyclophosphamide)
 AC Chemotherapy Regimen (Doxorubicin + Cyclophosphamide) AC is a regimen or treatment plan that includes a combination of chemotherapy drugs that your doctor prescribed for the treatment of your cancer.
AC Chemotherapy Regimen (Doxorubicin + Cyclophosphamide) AC is a regimen or treatment plan that includes a combination of chemotherapy drugs that your doctor prescribed for the treatment of your cancer.
Recto-vaginal Fistula Repair
 What is a recto-vaginal fistula repair? Rectovaginal fistula repair is a procedure in which the healthy tissue between the rectum and vagina is closed in multiple tissue layers. An incision is made either
What is a recto-vaginal fistula repair? Rectovaginal fistula repair is a procedure in which the healthy tissue between the rectum and vagina is closed in multiple tissue layers. An incision is made either
Dental Care and Chronic Conditions. Respiratory Disease Cardiovascular Disease Diabetes
 Dental Care and Chronic Conditions Respiratory Disease Cardiovascular Disease Diabetes Shape Up Your Smile and Avoid Some Complications of Chronic Diseases When you take good care of your oral health,
Dental Care and Chronic Conditions Respiratory Disease Cardiovascular Disease Diabetes Shape Up Your Smile and Avoid Some Complications of Chronic Diseases When you take good care of your oral health,
USE AND CARE INSTRUCTIONS for your Invisalign aligners
 USE AND CARE INSTRUCTIONS for your Invisalign aligners WEARING AND USING YOURINVISALIGN ALIGNERS - ENGLISH Here are some tips to help ensure proper use and avoid damaging your aligners. Always Remember
USE AND CARE INSTRUCTIONS for your Invisalign aligners WEARING AND USING YOURINVISALIGN ALIGNERS - ENGLISH Here are some tips to help ensure proper use and avoid damaging your aligners. Always Remember
WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW ABOUT. low blood counts.
 WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW ABOUT low blood counts. 1 INTRODUCTION Overview It is important for you to be aware that cancer, and some treatments for cancer, may affect your blood counts. Radiation therapy and
WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW ABOUT low blood counts. 1 INTRODUCTION Overview It is important for you to be aware that cancer, and some treatments for cancer, may affect your blood counts. Radiation therapy and
PICCs and Midline Catheters
 Patient Education PICCs and Midline Catheters Patient s guide to PICC (peripherally inserted central catheter) and midline catheters What are PICCs and midline catheters used for? Any medicine given over
Patient Education PICCs and Midline Catheters Patient s guide to PICC (peripherally inserted central catheter) and midline catheters What are PICCs and midline catheters used for? Any medicine given over
Paclitaxel and Carboplatin
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu What is Paclitaxel (pak-li-tax-el) and how does it work? Paclitaxel is a chemotherapy drug known as an anti-microtubule inhibitor. Another name for this drug
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu What is Paclitaxel (pak-li-tax-el) and how does it work? Paclitaxel is a chemotherapy drug known as an anti-microtubule inhibitor. Another name for this drug
For the Patient: Protocol LUAJNP Other names: Adjuvant Treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Cisplatin and Vinorelbine
 For the Patient: Protocol LUAJNP Other names: Adjuvant Treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Cisplatin and Vinorelbine LU = LUng AJ = AdJuvant NP = Navelbine (vinorelbine), cisplatin ABOUT THIS
For the Patient: Protocol LUAJNP Other names: Adjuvant Treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Cisplatin and Vinorelbine LU = LUng AJ = AdJuvant NP = Navelbine (vinorelbine), cisplatin ABOUT THIS
Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) Patient Instructions
 Patient Care Services 300 Pasteur Drive Stanford, CA 94305 Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) Patient Instructions A Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) is a soft flexible tube inserted
Patient Care Services 300 Pasteur Drive Stanford, CA 94305 Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) Patient Instructions A Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) is a soft flexible tube inserted
Better Breathing with COPD
 Better Breathing with COPD People with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) often benefit from learning different breathing techniques. Pursed Lip Breathing Pursed Lip Breathing (PLB) can be very
Better Breathing with COPD People with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) often benefit from learning different breathing techniques. Pursed Lip Breathing Pursed Lip Breathing (PLB) can be very
Patient Information Once Weekly FOSAMAX (FOSS-ah-max) (alendronate sodium) Tablets and Oral Solution
 Patient Information Once Weekly FOSAMAX (FOSS-ah-max) (alendronate sodium) Tablets and Oral Solution Read this information before you start taking FOSAMAX *. Also, read the leaflet each time you refill
Patient Information Once Weekly FOSAMAX (FOSS-ah-max) (alendronate sodium) Tablets and Oral Solution Read this information before you start taking FOSAMAX *. Also, read the leaflet each time you refill
Maintaining Proper Bowel Elimination
 Peak Development Resources, LLC P.O. Box 13267 Richmond, VA 23225 Phone: (804) 233-3707 Fax: (804) 233-3705 After reading the newsletter, the nursing assistant should be able to: 1. Describe the normal
Peak Development Resources, LLC P.O. Box 13267 Richmond, VA 23225 Phone: (804) 233-3707 Fax: (804) 233-3705 After reading the newsletter, the nursing assistant should be able to: 1. Describe the normal
Excision of Vaginal Mesh
 What is excision of vaginal mesh? This procedure is done to remove mesh from the vagina. When is this surgery used? If mesh has eroded into the vagina, bladder, urethra, or bowel If there is pain associated
What is excision of vaginal mesh? This procedure is done to remove mesh from the vagina. When is this surgery used? If mesh has eroded into the vagina, bladder, urethra, or bowel If there is pain associated
Ear Infections Gastroenteritis gastroenteritis
 Ear Gastroenteritis Infections gastroenteritis Gastroenteritis can be caused by many different germs, and the effects of gastro on babies and children depend on several things including: the age of the
Ear Gastroenteritis Infections gastroenteritis Gastroenteritis can be caused by many different germs, and the effects of gastro on babies and children depend on several things including: the age of the
Mouth care during chemotherapy
 Some people having chemotherapy treatment find that their mouth gets sore. This information gives some tips about how you can look after your mouth before and during your chemotherapy treatment. In this
Some people having chemotherapy treatment find that their mouth gets sore. This information gives some tips about how you can look after your mouth before and during your chemotherapy treatment. In this
How to Care for Your Premature Baby s Skin
 The Emily Center How to Care for Your Premature Baby s Skin Child Care/Health Promotion Si usted desea esta información en español, por favor pídasela a su enfermero o doctor. Name of Child: Date: How
The Emily Center How to Care for Your Premature Baby s Skin Child Care/Health Promotion Si usted desea esta información en español, por favor pídasela a su enfermero o doctor. Name of Child: Date: How
How To Care For A Sick Person
 39 How to Take Care of a Sick Person Sickness weakens the body. To gain strength and get well quickly, special care is needed. Medicines are often not necessary. But good care is always important. The
39 How to Take Care of a Sick Person Sickness weakens the body. To gain strength and get well quickly, special care is needed. Medicines are often not necessary. But good care is always important. The
How to care for a Midline Catheter
 How to care for a Midline Catheter Developed by the health care professionals of the IV Program with assistance from the Department of Learning and Development. All rights reserved. No part of this book
How to care for a Midline Catheter Developed by the health care professionals of the IV Program with assistance from the Department of Learning and Development. All rights reserved. No part of this book
X-Plain Foley Catheter Male Reference Summary
 X-Plain Foley Catheter Male Reference Summary Introduction A Foley catheter is a tube that is put through the urinary opening and into your bladder to drain urine. Your doctor may have placed or may ask
X-Plain Foley Catheter Male Reference Summary Introduction A Foley catheter is a tube that is put through the urinary opening and into your bladder to drain urine. Your doctor may have placed or may ask
The Take-Apart Human Body
 The Take-Apart Human Body As any teacher knows, children are naturally curious about their bodies. Their questions are endless, and present a tremendous educational opportunity: How do my ears work? Where
The Take-Apart Human Body As any teacher knows, children are naturally curious about their bodies. Their questions are endless, and present a tremendous educational opportunity: How do my ears work? Where
Heat Illnesses. Common Heat Rash Sites
 Heat Illnesses Introduction Heat illnesses happen when the body becomes too hot and cannot cool itself. There are several different types of heat-related illnesses. This includes heat cramps, heat exhaustion,
Heat Illnesses Introduction Heat illnesses happen when the body becomes too hot and cannot cool itself. There are several different types of heat-related illnesses. This includes heat cramps, heat exhaustion,
Common Concerns About Breastfeeding
 Patient Education Page 51 Caring for Yourself and Your New Baby Common Concerns About Breastfeeding Breastfeeding is healthy and natural. So are the questions and concerns that come with it. Whether you
Patient Education Page 51 Caring for Yourself and Your New Baby Common Concerns About Breastfeeding Breastfeeding is healthy and natural. So are the questions and concerns that come with it. Whether you
Safety FIRST: Infection Prevention Tips
 Reading Hospital Safety FIRST: Infection Prevention Tips Reading Hospital is committed to providing high quality care to our patients. Your healthcare team does many things to help prevent infections.
Reading Hospital Safety FIRST: Infection Prevention Tips Reading Hospital is committed to providing high quality care to our patients. Your healthcare team does many things to help prevent infections.
Your Own Teeth and Gums
 Your Own Teeth and Gums CHAPTER1 Next time you look in a mirror, look at your teeth and the skin (gums) around them. Look in your children s mouths, too. Look at both gums and teeth, because the health
Your Own Teeth and Gums CHAPTER1 Next time you look in a mirror, look at your teeth and the skin (gums) around them. Look in your children s mouths, too. Look at both gums and teeth, because the health
Managing Side Effects of Palliative Radiation Therapy
 RADIATION THERAPY SYMPTOM MANAGEMENT Managing Side Effects of Palliative Radiation Therapy In this booklet you will learn about: Common side effects when you receive palliative radiation therapy Tips on
RADIATION THERAPY SYMPTOM MANAGEMENT Managing Side Effects of Palliative Radiation Therapy In this booklet you will learn about: Common side effects when you receive palliative radiation therapy Tips on
Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy
 Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy What is Intraperitoneal (IP) Chemotherapy? Intraperitoneal (IP) chemotherapy is a way to put some of your chemotherapy into your abdomen (also called the peritoneal cavity)
Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy What is Intraperitoneal (IP) Chemotherapy? Intraperitoneal (IP) chemotherapy is a way to put some of your chemotherapy into your abdomen (also called the peritoneal cavity)
In-Patient Radioactive Iodine ( 131 I) Treatment
 In-Patient Radioactive Iodine ( 131 I) Treatment Information for patients and families Princess Margaret Read this booklet to learn: what radioactive iodine treatment is what to expect instructions to
In-Patient Radioactive Iodine ( 131 I) Treatment Information for patients and families Princess Margaret Read this booklet to learn: what radioactive iodine treatment is what to expect instructions to
Total Vaginal Hysterectomy
 What is a total vaginal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through the vagina. Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient. Why is this surgery used? To treat disease of
What is a total vaginal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through the vagina. Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient. Why is this surgery used? To treat disease of
TC Chemotherapy Regimen (Docetaxel + Cyclophosphamide)
 TC Chemotherapy Regimen (Docetaxel + Cyclophosphamide) TC is a regimen or treatment plan that includes a combination of chemotherapy drugs that your doctor prescribed for the treatment of your cancer.
TC Chemotherapy Regimen (Docetaxel + Cyclophosphamide) TC is a regimen or treatment plan that includes a combination of chemotherapy drugs that your doctor prescribed for the treatment of your cancer.
Urinary Indwelling Catheter. The Urinary System
 Patient Education CARE AND TREATMENT Urinary Indwelling Catheter This information will help you care for a urinary indwelling catheter at home. It will answer many of your questions. Please ask your doctor
Patient Education CARE AND TREATMENT Urinary Indwelling Catheter This information will help you care for a urinary indwelling catheter at home. It will answer many of your questions. Please ask your doctor
However, each person may be managed in a different way as bowel pattern is different in each person.
 Department of colorectal surgery Reversal of ileostomy A guide for patients Introduction This booklet is designed to tell you about your reversal of ileostomy operation and how your bowels might work after
Department of colorectal surgery Reversal of ileostomy A guide for patients Introduction This booklet is designed to tell you about your reversal of ileostomy operation and how your bowels might work after
Guy s, King s and St Thomas Cancer Centre The Cancer Outpatient Clinic Central venous catheter: Peripherally inserted central catheter
 Guy s, King s and St Thomas Cancer Centre The Cancer Outpatient Clinic Central venous catheter: Peripherally inserted central catheter This information leaflet aims to help answer some of the questions
Guy s, King s and St Thomas Cancer Centre The Cancer Outpatient Clinic Central venous catheter: Peripherally inserted central catheter This information leaflet aims to help answer some of the questions
HICKMAN Catheter Care with a Needleless Connector
 HICKMAN Catheter Care with a Needleless Connector Table of Contents Part 1 Learning about the HICKMAN Catheter... 2 Part 2 Caring for Your Hickman Catheter... 3 A. Preventing Infection... 3 B. Bathing...
HICKMAN Catheter Care with a Needleless Connector Table of Contents Part 1 Learning about the HICKMAN Catheter... 2 Part 2 Caring for Your Hickman Catheter... 3 A. Preventing Infection... 3 B. Bathing...
Total Vaginal Hysterectomy with an Anterior and Posterior Repair
 Total Vaginal Hysterectomy with an Anterior and Posterior Repair What is a total vaginal hysterectomy with an anterior and posterior repair? Total vaginal hysterectomy is the removal of the uterus and
Total Vaginal Hysterectomy with an Anterior and Posterior Repair What is a total vaginal hysterectomy with an anterior and posterior repair? Total vaginal hysterectomy is the removal of the uterus and
Laparoscopic Colectomy. What do I need to know about my laparoscopic colorectal surgery?
 Laparoscopic Colectomy What do I need to know about my laparoscopic colorectal surgery? Traditionally, colon & rectal surgery requires a large, abdominal and/or pelvic incision, which often requires a
Laparoscopic Colectomy What do I need to know about my laparoscopic colorectal surgery? Traditionally, colon & rectal surgery requires a large, abdominal and/or pelvic incision, which often requires a
STRATTERA (Stra-TAIR-a)
 1 PV 5859 AMP MEDICATION GUIDE STRATTERA (Stra-TAIR-a) (atomoxetine) Capsules Read the Medication Guide that comes with STRATTERA before you or your child starts taking it and each time you get a refill.
1 PV 5859 AMP MEDICATION GUIDE STRATTERA (Stra-TAIR-a) (atomoxetine) Capsules Read the Medication Guide that comes with STRATTERA before you or your child starts taking it and each time you get a refill.
WHEN COPD* SYMPTOMS GET WORSE
 WHEN COPD* SYMPTOMS GET WORSE *Includes chronic bronchitis, emphysema, or both. Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. has no ownership interest in any other organization that advertises or markets
WHEN COPD* SYMPTOMS GET WORSE *Includes chronic bronchitis, emphysema, or both. Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. has no ownership interest in any other organization that advertises or markets
A guide for parents of babies at risk of Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome Planning care for you and your baby
 A guide for parents of babies at risk of Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome Planning care for you and your baby Reading this booklet can help you: learn how certain drugs can affect your baby during pregnancy
A guide for parents of babies at risk of Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome Planning care for you and your baby Reading this booklet can help you: learn how certain drugs can affect your baby during pregnancy
Instructions for Care after Esophageal Surgery
 Instructions for Care after Esophageal Surgery As you recover from your esophageal surgery, it is important to follow these guidelines which have been developed for you. Nutrition Your surgeon will decide
Instructions for Care after Esophageal Surgery As you recover from your esophageal surgery, it is important to follow these guidelines which have been developed for you. Nutrition Your surgeon will decide
Pneumonia. Pneumonia is an infection that makes the tiny air sacs in your lungs inflamed (swollen and sore). They then fill with liquid.
 Pneumonia Pneumonia is an infection that makes the tiny air sacs in your lungs inflamed (swollen and sore). They then fill with liquid. People with mild (not so bad) pneumonia can usually be treated at
Pneumonia Pneumonia is an infection that makes the tiny air sacs in your lungs inflamed (swollen and sore). They then fill with liquid. People with mild (not so bad) pneumonia can usually be treated at
Surgical removal of fibroids through an abdominal incision-either up and down or bikini cut. The uterus and cervix are left in place.
 What is an abdominal myomectomy? Surgical removal of fibroids through an abdominal incision-either up and down or bikini cut. The uterus and cervix are left in place. When is this surgery used? Treatment
What is an abdominal myomectomy? Surgical removal of fibroids through an abdominal incision-either up and down or bikini cut. The uterus and cervix are left in place. When is this surgery used? Treatment
INFLUENZA (FLU) Flu and You
 Influenza (Flu) What is the flu? The flu is an illness caused by flu viruses. The flu may make people cough and have a sore throat and fever. They may also have a runny or stuffy nose, feel tired, have
Influenza (Flu) What is the flu? The flu is an illness caused by flu viruses. The flu may make people cough and have a sore throat and fever. They may also have a runny or stuffy nose, feel tired, have
VAD Chemotherapy Regimen for Multiple Myeloma Information for Patients
 VAD Chemotherapy Regimen for Multiple Myeloma Information for Patients The Regimen contains: V = vincristine (Oncovin ) A = Adriamycin (doxorubicin) D = Decadron (dexamethasone) How Is This Regimen Given?
VAD Chemotherapy Regimen for Multiple Myeloma Information for Patients The Regimen contains: V = vincristine (Oncovin ) A = Adriamycin (doxorubicin) D = Decadron (dexamethasone) How Is This Regimen Given?
Going Home with a Urinary Catheter
 Going Home with a Urinary Catheter Doctor: Phone Number: About Your Catheter A urinary catheter is a small tube that goes through your urethra and into your bladder. This tube then drains the urine made
Going Home with a Urinary Catheter Doctor: Phone Number: About Your Catheter A urinary catheter is a small tube that goes through your urethra and into your bladder. This tube then drains the urine made
Thyroid Cancer Finding It and Treating It Using Radioiodine
 Thyroid Cancer Finding It and Treating It Using Radioiodine Your doctor has referred you to Nuclear Medicine to learn more about the extent of your thyroid cancer, and perhaps even for treatment of the
Thyroid Cancer Finding It and Treating It Using Radioiodine Your doctor has referred you to Nuclear Medicine to learn more about the extent of your thyroid cancer, and perhaps even for treatment of the
My patient has a feeding tube
 My patient has a feeding tube What does that mean? Martha Kliebenstein, MSN, RN Clinical Educator (December, 2014) Types of tubes Gastrostomy (G-tube) Gastrostomy jejunostomy (G-J tube) Naso gastric (NG
My patient has a feeding tube What does that mean? Martha Kliebenstein, MSN, RN Clinical Educator (December, 2014) Types of tubes Gastrostomy (G-tube) Gastrostomy jejunostomy (G-J tube) Naso gastric (NG
Catheter Care How to Care for a Urinary Catheter
 Catheter Care How to Care for a Urinary Catheter Ensure patient/client is provided with any available product specific instructions along with this booklet. About Your Catheter Your urinary catheter allows
Catheter Care How to Care for a Urinary Catheter Ensure patient/client is provided with any available product specific instructions along with this booklet. About Your Catheter Your urinary catheter allows
Name of Child: Date: Fever
 The Emily Center Fever First Aid and Home Care Si usted desea esta información en español, por favor pídasela a su enfermero o doctor. Name of Child: Date: #666 What is it? Fever When body temperature
The Emily Center Fever First Aid and Home Care Si usted desea esta información en español, por favor pídasela a su enfermero o doctor. Name of Child: Date: #666 What is it? Fever When body temperature
Challenges of Foster Parents who Care for Infants with Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome
 Challenges of Foster Parents who Care for Infants with Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome All Health Care Providers are required by law to make a referral to the Department of Children s Services (DCS) Child
Challenges of Foster Parents who Care for Infants with Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome All Health Care Providers are required by law to make a referral to the Department of Children s Services (DCS) Child
X-Plain Sinus Surgery Reference Summary
 X-Plain Sinus Surgery Reference Summary Introduction Sinus surgery is a very common and safe operation. Your doctor may recommend that you have sinus surgery. The decision whether or not to have sinus
X-Plain Sinus Surgery Reference Summary Introduction Sinus surgery is a very common and safe operation. Your doctor may recommend that you have sinus surgery. The decision whether or not to have sinus
Home Care for Your Wound Drain
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu When you go home after surgery, you may have one or more drains in place to help your wounds heal. Hemovac, Jackson Pratt (JP) and Blake are common drains used
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu When you go home after surgery, you may have one or more drains in place to help your wounds heal. Hemovac, Jackson Pratt (JP) and Blake are common drains used
Tunneled Central Venous Catheter (CVC) Placement
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Tunneled Central Venous Catheter (CVC) Placement A tunneled Central Venous Catheter (CVC) is a special type of intravenous (IV) line that is placed into a large
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Tunneled Central Venous Catheter (CVC) Placement A tunneled Central Venous Catheter (CVC) is a special type of intravenous (IV) line that is placed into a large
