Rotator Cuff Tears. Anatomy
|
|
|
- Osborn Denis Shaw
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Rotator Cuff Tears A rotator cuff tear is a common cause of pain and disability among adults. In 2008, close to 2 million people in the United States went to their doctors because of a rotator cuff problem. A torn rotator cuff will weaken your shoulder. This means that many daily activities, like combing your hair or getting dressed, may become painful and difficult to do. Anatomy Your shoulder is made up of three bones: your upper arm bone (humerus), your shoulder blade (scapula), and your collarbone (clavicle). The shoulder is a ball-and-socket joint: The ball, or head, of your upper arm bone fits into a shallow socket in your shoulder blade. Your arm is kept in your shoulder socket by your rotator cuff. The rotator cuff is a network of four muscles that come together as tendons to form a covering around the head of the humerus. The rotator cuff attaches the humerus to the shoulder blade and helps to lift and rotate your arm. There is a lubricating sac called a bursa between the rotator cuff and the bone on top of your shoulder (acromion). The bursa allows the rotator cuff tendons to glide freely when you move your arm. When the rotator cuff tendons are injured or damaged, this bursa can also become inflamed and painful. Normal anatomy of the shoulder.
2 T his illustration more clearly shows the four muscles and their tendons that form the rotator cuff and stabilize the shoulder joint. Reproduced with permission from The Body Almanac. (c) American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, Description When one or more of the rotator cuff tendons is torn, the tendon no longer fully attaches to the head of the humerus. Most tears occur in the supraspinatus muscle and tendon, but other parts of the rotator cuff may also be involved. In many cases, torn tendons begin by fraying. As the damage progresses, the tendon can completely tear, sometimes with lifting a heavy object. There are different types of tears. Partial Tear. This type of tear damages the soft tissue, but does not completely sever it. Full-Thickness Tear. This type of tear is also called a complete tear. It splits the soft tissue into two pieces. In many cases, tendons tear off where they attach to the head of the humerus. With a full-thickness tear, there is basically a hole in the tendon.
3 A rotator cuff tear most often occurs within the tendon. Cause There are two main causes of rotator cuff tears: injury and degeneration. Acute Tear If you fall down on your outstretched arm or lift something too heavy with a jerking motion, you can tear your rotator cuff. This type of tear can occur with other shoulder injuries, such as a broken collarbone or dislocated shoulder. Degenerative Tear Most tears are the result of a wearing down of the tendon that occurs slowly over time. This degeneration naturally occurs as we age. Rotator cuff tears are more common in the dominant arm. If you have a degenerative tear in one shoulder, there is a greater risk for a rotator cuff tear in the opposite shoulder -- even if you have no pain in that shoulder. Several factors contribute to degenerative, or chronic, rotator cuff tears. Repetitive stress. Repeating the same shoulder motions again and again can stress your rotator cuff muscles and tendons. Baseball, tennis, rowing, and weightlifting are examples of sports activities that can put you at risk for overuse tears. Many jobs and routine chores can cause overuse tears, as well. Lack of blood supply. As we get older, the blood supply in our rotator cuff tendons lessens. Without a good blood supply, the body's natural ability to repair tendon damage is impaired. This can ultimately lead to a tendon tear. Bone spurs. As we age, bone spurs (bone overgrowth) often develop on the underside of the acromion bone. When we lift our arms, the spurs rub on the rotator cuff tendon. This condition is called shoulder impingement, and over time will weaken the tendon and make it more likely to tear. Risk Factors Because most rotator cuff tears are largely caused by the normal wear and tear that goes along with aging, people over 40 are at greater risk.
4 People who do repetitive lifting or overhead activities are also at risk for rotator cuff tears. Athletes are especially vulnerable to overuse tears, particularly tennis players and baseball pitchers. Painters, carpenters, and others who do overhead work also have a greater chance for tears. Although overuse tears caused by sports activity or overhead work also occur in younger people, most tears in young adults are caused by a traumatic injury, like a fall. Symptoms The most common symptoms of a rotator cuff tear include: Pain at rest and at night, particularly if lying on the affected shoulder Pain when lifting and lowering your arm or with specific movements Weakness when lifting or rotating your arm Crepitus or crackling sensation when moving your shoulder in certain positions Tears that happen suddenly, such as from a fall, usually cause intense pain. There may be a snapping sensation and immediate weakness in your upper arm. Tears that develop slowly due to overuse also cause pain and arm weakness. You may have pain in the shoulder when you lift your arm to the side, or pain that moves down your arm. At first, the pain may be mild and only present when lifting your arm over your head, such as reaching into a cupboard. Over-the-counter medication, such as aspirin or ibuprofen, may relieve the pain at first. Over time, the pain may become more noticeable at rest, and no longer goes away with medications. You may have pain when you lie on the painful side at night. The pain and weakness in the shoulder may make routine activities such as combing your hair or reaching behind your back more difficult. Doctor Examination A rotator cuff injury can make it painful to lift your arm out to the side. Medical History and Physical Examination After discussing your symptoms and medical history, your doctor will examine your shoulder. He or she will check to see whether it is tender in any area or whether there is a deformity. To measure the range of motion of your shoulder, your doctor will have you move your arm in several different directions. He or she will also test your arm strength. Your doctor will check for other problems with your shoulder joint. He or she may also examine your neck to make sure that the pain is not coming from a "pinched nerve," and to rule out other conditions, such as arthritis. Imaging Tests Other tests which may help your doctor confirm your diagnosis include: X-rays. The first imaging tests performed are usually x-rays. Your doctor will test your range of motion by having you move your arm in different directions. Reproduced with permission from JF Sarwark, ed: Essentials of Musculoskeletal Care, ed 4. Rosemont, IL, American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 2010.
5 Because x-rays do not show the soft tissues of your shoulder like the rotator cuff, plain x-rays of a shoulder with rotator cuff pain are usually normal or may show a small bone spur. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or ultrasound. These studies can better show soft tissues like the rotator cuff tendons. They can show the rotator cuff tear, as well as where the tear is located within the tendon and the size of the tear. An MRI can also give your doctor a better idea of how "old" or "new" a tear is because it can show the quality of the rotator cuff muscles. Treatment If you have a rotator cuff tear and you keep using it despite increasing pain, you may cause further damage. A rotator cuff tear can get larger over time. Chronic shoulder and arm pain are good reasons to see your doctor. Early treatment can prevent your symptoms from getting worse. It will also get you back to your normal routine that much quicker. The goal of any treatment is to reduce pain and restore function. There are several treatment options for a rotator cuff tear, and the best option is different for every person. In planning your treatment, your doctor will consider your age, activity level, general health, and the type of tear you have. There is no evidence of better results from surgery performed near the time of injury versus later on. For this reason, many doctors first recommend nonsurgical management of rotator cuff tears. Nonsurgical Treatment In about 50% of patients, nonsurgical treatment relieves pain and improves function in the shoulder. Shoulder strength, however, does not usually improve without surgery. Nonsurgical treatment options may include: Rest. Your doctor may suggest rest and and limiting overhead activities. He or she may also prescribe a sling to help protect your shoulder and keep it still. Activity modification. Avoid activities that cause shoulder pain. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medication. Drugs like ibuprofen and naproxen reduce pain and swelling. Strengthening exercises and physical therapy. Specific exercises will restore movement and strengthen your shoulder. Your exercise program will include stretches to improve flexibility and range of motion. Strengthening the muscles that support your shoulder can relieve pain and prevent further injury. Steroid injection. If rest, medications, and physical therapy do not relieve your pain, an injection of a local anesthetic and a cortisone preparation may be helpful. Cortisone is a very effective antiinflammatory medicine.
6 A cortisone injection may relieve painful symptoms. Reproduced with permission from JF Sarwark, ed: Essentials of Musculoskeletal Care, ed 4. Rosemont, IL, American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, The chief advantage of nonsurgical treatment is that it avoids the major risks of surgery, such as: Infection Permanent stiffness Anesthesia complications Sometimes lengthy recovery time The disadvantages of nonsurgical treatment are: No improvements in strength Size of tear may increase over time Activities may need to be limited Surgical Treatment Your doctor may recommend surgery if your pain does not improve with nonsurgical methods. Continued pain is the main indication for surgery. If you are very active and use your arms for overhead work or sports, your doctor may also suggest surgery. Other signs that surgery may be a good option for you include: Your symptoms have lasted 6 to 12 months You have a large tear (more than 3 cm) You have significant weakness and loss of function in your shoulder Your tear was caused by a recent, acute injury Surgery to repair a torn rotator cuff most often involves re-attaching the tendon to the head of humerus (upper arm bone). There are a few options for repairing rotator cuff tears. Your orthopaedic surgeon will discuss with you the best procedure to meet your individual health needs. Continue to next page: Rotator Cuff Tears: Surgical Treatment Options (topic.cfm?topic=a00406) Last reviewed: May 2011
7 Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Rotator Cuff Tears: Frequently Asked Questions What is the rotator cuff and what does it do? The rotator cuff is a large tendon comprised of four muscles which combine to form a "cuff" over the upper end of the arm, the head of the humerus. The four muscles supraspinatus, infraspinatus, subscapularis and teres minor originate from the "wing bone," the scapula, and together form a single tendon unit that inserts on the greater tuberosity of the humerus. The rotator cuff helps to lift and rotate the arm and to stabilize the ball of the shoulder within the joint. What causes a rotator cuff tear and how would I know if I have one? A rotator cuff tear may result from an acute injury such as a fall or may be caused by chronic wear and tear with degeneration of the tendon. Impingement of the front of the scapula, the acromion, on the tendon is believed to be a major cause of cuff tears in individuals older than 40 years. Typically, you will feel pain in the front of your shoulder that radiates down the side of your arm. It may be present with overhead activities such as lifting or reaching. You may feel pain when you try to sleep on the affected side. You may note weakness of your arm and difficulty with routine activities such as combing your hair or reaching behind your back. If the tear occurs with injury you may experience acute pain, a snapping sensation, and immediate weakness of the arm. If I have a painful rotator cuff and keep using it, will this cause further damage? A rotator cuff tear can extend or get larger over time. This can occur with repetitive use or a re-injury. It is common for patients with known rotator cuff disease to have acute pain and weakness following a minor injury. This likely represents extension of an existing tear. If you know you have a rotator cuff tear, then worsening pain and decreasing strength may mean the tear is getting larger. When should I see a doctor for a rotator cuff tear? If you have injured your shoulder or have chronic shoulder and arm pain, it is best to see your orthopaedic surgeon. He or she can then make a diagnosis and begin treatment. The doctor may recommend a diagnostic study such as MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) to confirm the diagnosis. Early diagnosis and treatment of a rotator cuff tear may prevent symptoms such as loss of strength and loss of motion from setting in. If your primary physician has already made the diagnosis, an orthopaedic surgeon can review both surgical and nonsurgical options and start treatment.
8 Can a rotator cuff tear be healed or strengthened without surgery? Many rotator cuff tears can be treated nonsurgically. Anti-inflammatory medication, steroid injections, and physical therapy may all be of benefit in treating symptoms of a cuff tear. The goals of treatment are to relieve pain and restore strength to the involved shoulder. Even though most tears cannot heal on their own, satisfactory function can often be achieved without surgery. If, however, you are active and use your arm for overhead work or sports, then surgery is most often recommended because many tears will not heal without surgery. At what point does a rotator cuff tear require surgery to fix it? Surgery is recommended if you have persistent pain or weakness in your shoulder that does not improve with nonsurgical treatment. Frequently, patients who require surgery will report pain at night and difficulty using the arm for lifting and reaching. Many will report ongoing symptoms despite several months of medication and limited use of the arm. Surgery is also indicated in active individuals who use the arm for overhead work or sports. Pitchers, swimmers, and tennis players are common examples. What options are available for surgical repair? The type of repair performed is based on the findings at surgery. A partial tear may require only a trimming or smoothing procedure called a débridement. A full-thickness tear within the substance of the tendon can be repaired side to side. If the tendon is torn from its insertion on the humerus, it is repaired directly to bone. Three techniques are used for rotator cuff repair: traditional open repair, mini-open repair, and arthroscopic repair. Your orthopaedic surgeon can recommend which technique is best for you. How important is rehabilitation in the treatment of a rotator cuff tear? Rehabilitation plays a critical role in both the nonsurgical and surgical treatment of a rotator cuff tear. When a tear occurs, there is frequently atrophy of the muscles around the arm and loss of motion of the shoulder. An exercise or physical therapy program is necessary to regain strength and improve function in the shoulder. Even though surgery repairs the defect in the tendon, the muscles around the arm remain weak, and a strong effort at rehabilitation is necessary for the procedure to succeed. Complete rehabilitation after surgery may take several months. Your orthopaedic surgeon can prescribe an appropriate program based on your needs and the findings at surgery. Last reviewed: May 2011 AAOS does not endorse any treatments, procedures, products, or physicians referenced herein. This information is provided as an educational service and is not intended to serve as medical advice. Anyone seeking specific orthopaedic advice or assistance should consult his or her orthopaedic surgeon, or locate one in your area through the AAOS "Find an Orthopaedist" program on this website. Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
9 Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Rotator Cuff Tears: Surgical Treatment Options The following article provides in-depth information about surgical treatment for rotator cuff injuries, and is a continuation of the article "Rotator Cuff Tears." For a good introduction to the topic of rotator cuff injuries, please refer to Rotator Cuff Tears (topic.cfm?topic=a00064). Surgery to repair a torn rotator cuff most often involves re-attaching the tendon to the head of humerus (upper arm bone). A partial tear, however, may need only a trimming or smoothing procedure called a debridement. A complete tear within the thickest part of the tendon is repaired by stitching the two sides back together. When Rotator Cuff Surgery is Recommended Your doctor may recommend surgery for a torn rotator cuff if your pain does not improve with nonsurgical methods. Continued pain is the main indication for surgery. If you are very active and use your arms for overhead work or sports, your doctor may also suggest surgery. Other signs that surgery may be a good option for you include: Your symptoms have lasted 6 to 12 months You have a large tear (more than 3 cm) You have significant weakness and loss of function in your shoulder Your tear was caused by a recent, acute injury Surgical Repair Options There are a few options for repairing rotator cuff tears. Advancements in surgical techniques for rotator cuff repair include less invasive procedures. While each of the methods available has its own advantages and disadvantages, all have the same goal: getting the tendon to heal. The type of repair performed depends on several factors, including your surgeon's experience and familiarity with a particular procedure, the size of your tear, your anatomy, and the quality of the tendon tissue and bone. Many surgical repairs can be done on an outpatient basis and do not require you to stay overnight in the hospital. Your orthopaedic surgeon will discuss with you the best procedure to meet your individual health needs. You may have other shoulder problems in addition to a rotator cuff tear, such as osteoarthritis, bone spurs, or other soft tissue tears. During the operation, your surgeon may be able to take care of these problems, as well. The three techniques most commonly used for rotator cuff repair include t diti l i th i i d i i i I th d A rotator cuff tear most often occurs where the tendon attaches to the bone
10 traditional open repair, arthroscopic repair, and mini-open repair. In the end, patients rate all three repair methods the same for pain relief, strength improvement, and overall satisfaction. where the tendon attaches to the bone. Open Repair A traditional open surgical incision (several centimeters long) is often required if the tear is large or complex. The surgeon makes the incision over the shoulder and detaches the shoulder muscle (deltoid) to better see and gain access to the torn tendon. During an open repair, the surgeon typically removes bone spurs from the underside of the acromion (this procedure is called an acromioplasty). An open repair may be a good option if the tear is large or complex or if additional reconstruction, such as a tendon transfer, is indicated. Open repair was the first technique used for torn rotator cuffs. Over the years, new technology and improved surgeon experience has led to less invasive procedures. All-Arthroscopic Repair During arthroscopy, your surgeon inserts a small camera, called an arthroscope, into your shoulder joint. The camera displays pictures on a television screen, and your surgeon uses these images to guide miniature surgical instruments. Because the arthroscope and surgical instruments are thin, your surgeon can use very small incisions (cuts), rather than the larger incision needed for standard, open surgery. All-arthroscopic repair is usually an outpatient procedure and is the least invasive method to repair a torn rotator cuff. During arthroscopy, your surgeon inserts the arthroscope and small instruments into your shoulder joint.
11 (Left) An arthroscopic view of a healthy shoulder joint. (Center) In this image of a rotator cuff tear, a large gap can be seen between the edge of the rotator cuff tendon and the humeral head. (Right) The tendon has been re-attached to the humeral head with sutures. Mini-Open Repair The mini-open repair uses newer technology and instruments to perform a repair through a small incision. The incision is typically 3 to 5 cm long. This technique uses arthroscopy to assess and treat damage to other structures within the joint. Bone spurs, for example, are often removed arthroscopically. This avoids the need to detach the deltoid muscle. Once the arthroscopic portion of the procedure is completed, the surgeon repairs the rotator cuff through the mini-open incision. During the tendon repair, the surgeon views the shoulder structures directly, rather than through the video monitor. Rehabilitation Rehabilitation plays a vital role in getting you back to your daily activities. A physical therapy program will help you regain shoulder strength and motion. Immobilization After surgery, therapy progresses in stages. At first, the repair needs to be protected while the tendon heals. To keep your arm from moving, you will most likely use a sling and avoid using your arm for the first 4 to 6 weeks. How long you require a sling depends upon the severity of your injury. Passive Exercise Even though your tear has been repaired, the muscles around your arm remain weak. Once your surgeon decides it is safe for you to move your arm and shoulder, a therapist will help you with passive exercises to improve range of motion in your shoulder. With passive exercise, your therapist supports your arm and moves it in different positions. In most cases, passive exercise is begun within the first 4 to 6 weeks after surgery. Active Exercise After 4 to 6 weeks, you will progress to doing active exercises without the help of your therapist. Moving your muscles on your own will gradually increase your strength and improve your arm control. At 8 to 12 weeks, your therapist will start you on a strengthening exercise program. Expect a complete recovery to take several months. Most patients have a functional range of motion and adequate strength by 4 to 6 months after surgery. Although it is a slow process, your commitment to rehabilitation is key to a successful outcome. Outcome The majority of patients report improved shoulder strength and less pain after surgery for a torn rotator cuff. Each surgical repair technique (open, mini-open, and arthroscopic) has similar results in terms of pain relief, improvement in strength and function, and patient satisfaction. Surgeon expertise is more important in achieving
12 satisfactory results than the choice of technique. Factors that can decrease the likelihood of a satisfactory result include: Poor tendon/tissue quality Large or massive tears Poor patient compliance with rehabilitation and restrictions after surgery Patient age (older than 65 years) Smoking and use of other nicotine products Workers' compensation claims Complications After rotator cuff surgery, a small percentage of patients experience complications. In addition to the risks of surgery in general, such as blood loss or problems related to anesthesia, complications of rotator cuff surgery may include: Nerve injury. This typically involves the nerve that activates your shoulder muscle (deltoid). Infection. Patients are given antibiotics during the procedure to lessen the risk for infection. If an infection develops, an additional surgery or prolonged antibiotic treatment may be needed. Deltoid detachment. During an open repair, this shoulder muscle is detached to provide better access to the rotator cuff. It is stitched back into place at the end of the procedure. It is very important to protect this area after surgery and during rehabilitation to allow it to heal. Stiffness. Early rehabilitation lessens the likelihood of permanent stiffness or loss of motion. Most of the time, stiffness will improve with more aggressive therapy and exercise. Tendon re-tear. There is a chance for re-tear following all types of repairs. The larger the tear, the higher the risk of re-tear. Patients who re-tear their tendons usually do not have greater pain or decreased shoulder function. Repeat surgery is needed only if there is severe pain or loss of function. Future Developments Dissolvable Anchors Many orthopaedic surgeons have begun to use dissolvable anchors. Anchors hold stitches in place in the bone until the repair has healed. Dissolvable anchors are gradually absorbed by the body. Arthroscopic Techniques Future developments in the treatment of rotator cuff disease include newer arthroscopic surgical techniques. These allow more secure repairs that may improve the rate of tendon healing. Orthobiologics One of the most exciting areas of research is orthobiologics. These are tissue grafts and injections that promote growth of new tissue in the body and foster healing. Last reviewed: May 2011 AAOS does not endorse any treatments, procedures, products, or physicians referenced herein. This information is provided as an educational service and is not intended to serve as medical advice. Anyone seeking specific orthopaedic advice or assistance should consult his or her orthopaedic surgeon, or locate one in your area through the AAOS "Find an Orthopaedist" program on this website
.org. Rotator Cuff Tears. Anatomy. Description
 Rotator Cuff Tears Page ( 1 ) A rotator cuff tear is a common cause of pain and disability among adults. In 2008, close to 2 million people in the United States went to their doctors because of a rotator
Rotator Cuff Tears Page ( 1 ) A rotator cuff tear is a common cause of pain and disability among adults. In 2008, close to 2 million people in the United States went to their doctors because of a rotator
.org. Rotator Cuff Tears: Surgical Treatment Options. When Rotator Cuff Surgery is Recommended. Surgical Repair Options
 Rotator Cuff Tears: Surgical Treatment Options Page ( 1 ) The following article provides in-depth information about surgical treatment for rotator cuff injuries, and is a continuation of the article Rotator
Rotator Cuff Tears: Surgical Treatment Options Page ( 1 ) The following article provides in-depth information about surgical treatment for rotator cuff injuries, and is a continuation of the article Rotator
Shoulder Impingement/Rotator Cuff Tendinitis
 Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Shoulder Impingement/Rotator Cuff Tendinitis One of the most common physical complaints is shoulder pain. Your shoulder is made up of several joints
Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Shoulder Impingement/Rotator Cuff Tendinitis One of the most common physical complaints is shoulder pain. Your shoulder is made up of several joints
1 of 6 1/22/2015 10:06 AM
 1 of 6 1/22/2015 10:06 AM 2 of 6 1/22/2015 10:06 AM This cross-section view of the shoulder socket shows a typical SLAP tear. Injuries to the superior labrum can be caused by acute trauma or by repetitive
1 of 6 1/22/2015 10:06 AM 2 of 6 1/22/2015 10:06 AM This cross-section view of the shoulder socket shows a typical SLAP tear. Injuries to the superior labrum can be caused by acute trauma or by repetitive
.org. Shoulder Pain and Common Shoulder Problems. Anatomy. Cause
 Shoulder Pain and Common Shoulder Problems Page ( 1 ) What most people call the shoulder is really several joints that combine with tendons and muscles to allow a wide range of motion in the arm from scratching
Shoulder Pain and Common Shoulder Problems Page ( 1 ) What most people call the shoulder is really several joints that combine with tendons and muscles to allow a wide range of motion in the arm from scratching
Shoulder Arthroscopy
 Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Shoulder Arthroscopy Arthroscopy is a procedure that orthopaedic surgeons use to inspect, diagnose, and repair problems inside a joint. The word
Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Shoulder Arthroscopy Arthroscopy is a procedure that orthopaedic surgeons use to inspect, diagnose, and repair problems inside a joint. The word
Arthritis of the Shoulder
 Arthritis of the Shoulder In 2011, more than 50 million people in the United States reported that they had been diagnosed with some form of arthritis, according to the National Health Interview Survey.
Arthritis of the Shoulder In 2011, more than 50 million people in the United States reported that they had been diagnosed with some form of arthritis, according to the National Health Interview Survey.
.org. Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis) Anatomy. Cause
 Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis) Page ( 1 ) Tennis elbow, or lateral epicondylitis, is a painful condition of the elbow caused by overuse. Not surprisingly, playing tennis or other racquet sports can
Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis) Page ( 1 ) Tennis elbow, or lateral epicondylitis, is a painful condition of the elbow caused by overuse. Not surprisingly, playing tennis or other racquet sports can
J F de Beer, K van Rooyen, D Bhatia. Rotator Cuff Tears
 1 J F de Beer, K van Rooyen, D Bhatia Rotator Cuff Tears Anatomy The shoulder consists of a ball (humeral head) and a socket (glenoid). The muscles around the shoulder act to elevate the arm. The large
1 J F de Beer, K van Rooyen, D Bhatia Rotator Cuff Tears Anatomy The shoulder consists of a ball (humeral head) and a socket (glenoid). The muscles around the shoulder act to elevate the arm. The large
Treatment Options for Rotator Cuff Tears A Guide for Adults
 Treatment Options for Rotator Cuff Tears A Guide for Adults Is This Guide for Me? YES, if your doctor has told you that you have a rotator cuff tear, which is an injury to one or more of the muscles and
Treatment Options for Rotator Cuff Tears A Guide for Adults Is This Guide for Me? YES, if your doctor has told you that you have a rotator cuff tear, which is an injury to one or more of the muscles and
TOWN CENTER ORTHOPAEDIC ASSOCIATES P.C. Labral Tears
 Labral Tears The shoulder is your body s most flexible joint. It is designed to let the arm move in almost any direction. But this flexibility has a price, making the joint prone to injury. The shoulder
Labral Tears The shoulder is your body s most flexible joint. It is designed to let the arm move in almost any direction. But this flexibility has a price, making the joint prone to injury. The shoulder
.org. Achilles Tendinitis. Description. Cause. Achilles tendinitis is a common condition that causes pain along the back of the leg near the heel.
 Achilles Tendinitis Page ( 1 ) Achilles tendinitis is a common condition that causes pain along the back of the leg near the heel. The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. It connects your
Achilles Tendinitis Page ( 1 ) Achilles tendinitis is a common condition that causes pain along the back of the leg near the heel. The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. It connects your
THE SHOULDER. Shoulder Pain. Fractures. Instability and Dislocations of the Shoulder
 THE SHOULDER Shoulder Pain 1. Fractures 2. Sports injuries 3. Instability/Dislocations 4. Rotator Cuff Disease and Tears 5. Arthritis Fractures The shoulder is made up of three primary bones, the clavicle,
THE SHOULDER Shoulder Pain 1. Fractures 2. Sports injuries 3. Instability/Dislocations 4. Rotator Cuff Disease and Tears 5. Arthritis Fractures The shoulder is made up of three primary bones, the clavicle,
.org. Shoulder Joint Replacement. Anatomy
 Shoulder Joint Replacement Page ( 1 ) Although shoulder joint replacement is less common than knee or hip replacement, it is just as successful in relieving joint pain. Shoulder replacement surgery was
Shoulder Joint Replacement Page ( 1 ) Although shoulder joint replacement is less common than knee or hip replacement, it is just as successful in relieving joint pain. Shoulder replacement surgery was
.org. Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction. Anatomy. Cause. Symptoms
 Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
Shoulder Joint Replacement
 Shoulder Joint Replacement Many people know someone with an artificial knee or hip joint. Shoulder replacement is less common, but it is just as successful in relieving joint pain. Shoulder replacement
Shoulder Joint Replacement Many people know someone with an artificial knee or hip joint. Shoulder replacement is less common, but it is just as successful in relieving joint pain. Shoulder replacement
Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck)
 Copyright 2009 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Neck pain is extremely common. It can be caused by many things, and is most often related to getting
Copyright 2009 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Neck pain is extremely common. It can be caused by many things, and is most often related to getting
Ms. Ruth Delaney ROTATOR CUFF DISEASE Orthopaedic Surgeon, Shoulder Specialist
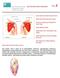 WHAT DOES THE ROTATOR CUFF DO? WHAT DOES THE ROTATOR CUFF DO? WHO GETS ROTATOR CUFF TEARS? HOW DO I CLINICALLY DIAGNOSE A CUFF TEAR? WHO NEEDS AN MRI? DOES EVERY CUFF TEAR NEED TO BE FIXED? WHAT DOES ROTATOR
WHAT DOES THE ROTATOR CUFF DO? WHAT DOES THE ROTATOR CUFF DO? WHO GETS ROTATOR CUFF TEARS? HOW DO I CLINICALLY DIAGNOSE A CUFF TEAR? WHO NEEDS AN MRI? DOES EVERY CUFF TEAR NEED TO BE FIXED? WHAT DOES ROTATOR
Rotator Cuff Pathophysiology. treatment program that will effectively treat it. The tricky part about the shoulder is that it is a ball and
 Rotator Cuff Pathophysiology Shoulder injuries occur to most people at least once in their life. This highly mobile and versatile joint is one of the most common reasons people visit their health care
Rotator Cuff Pathophysiology Shoulder injuries occur to most people at least once in their life. This highly mobile and versatile joint is one of the most common reasons people visit their health care
SHOULDER INSTABILITY. E. Edward Khalfayan, MD
 SHOULDER INSTABILITY E. Edward Khalfayan, MD Instability of the shoulder can occur from a single injury or as the result of repetitive activity such as overhead sports. Dislocations of the shoulder are
SHOULDER INSTABILITY E. Edward Khalfayan, MD Instability of the shoulder can occur from a single injury or as the result of repetitive activity such as overhead sports. Dislocations of the shoulder are
SHOULDER PAIN. Procedures: Subacromial, Glenohumeral and Acromioclavicular Injections Nonprocedural Treatments
 SHOULDER PAIN Anatomy Conditions: Muscular Spasm Pinched Nerve Rotator Cuff Tendonitis Procedures: Subacromial, Glenohumeral and Acromioclavicular Injections Nonprocedural Treatments Surgery: Rotator Cuff
SHOULDER PAIN Anatomy Conditions: Muscular Spasm Pinched Nerve Rotator Cuff Tendonitis Procedures: Subacromial, Glenohumeral and Acromioclavicular Injections Nonprocedural Treatments Surgery: Rotator Cuff
Adult Forearm Fractures
 Adult Forearm Fractures Your forearm is made up of two bones, the radius and ulna. In most cases of adult forearm fractures, both bones are broken. Fractures of the forearm can occur near the wrist at
Adult Forearm Fractures Your forearm is made up of two bones, the radius and ulna. In most cases of adult forearm fractures, both bones are broken. Fractures of the forearm can occur near the wrist at
Shoulder Tendonitis. Brett Sanders, MD Center For Sports Medicine and Orthopaedic 2415 McCallie Ave. Chattanooga, TN (423) 624-2696
 Shoulder Tendonitis Brett Sanders, MD Center For Sports Medicine and Orthopaedic 2415 McCallie Ave. Chattanooga, TN (423) 624-2696 Shoulder tendinitis is a common overuse injury in sports (such as swimming,
Shoulder Tendonitis Brett Sanders, MD Center For Sports Medicine and Orthopaedic 2415 McCallie Ave. Chattanooga, TN (423) 624-2696 Shoulder tendinitis is a common overuse injury in sports (such as swimming,
.org. Clavicle Fracture (Broken Collarbone) Anatomy. Description. Cause. Symptoms
 Clavicle Fracture (Broken Collarbone) Page ( 1 ) A broken collarbone is also known as a clavicle fracture. This is a very common fracture that occurs in people of all ages. Anatomy The collarbone (clavicle)
Clavicle Fracture (Broken Collarbone) Page ( 1 ) A broken collarbone is also known as a clavicle fracture. This is a very common fracture that occurs in people of all ages. Anatomy The collarbone (clavicle)
.org. Herniated Disk in the Lower Back. Anatomy. Description
 Herniated Disk in the Lower Back Page ( 1 ) Sometimes called a slipped or ruptured disk, a herniated disk most often occurs in your lower back. It is one of the most common causes of low back pain, as
Herniated Disk in the Lower Back Page ( 1 ) Sometimes called a slipped or ruptured disk, a herniated disk most often occurs in your lower back. It is one of the most common causes of low back pain, as
.org. Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Anatomy. Cause
 Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Page ( 1 ) Neck pain can be caused by many things but is most often related to getting older. Like the rest of the body, the disks and joints in the neck (cervical
Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck) Page ( 1 ) Neck pain can be caused by many things but is most often related to getting older. Like the rest of the body, the disks and joints in the neck (cervical
Treatment Guide Wave Goodbye to Shoulder Pain
 Treatment Guide Wave Goodbye to Shoulder Pain Shoulder pain and injuries are extremely common whether due to exercise, age, overuse injuries or trauma. In fact, they account for nearly 20 percent of visits
Treatment Guide Wave Goodbye to Shoulder Pain Shoulder pain and injuries are extremely common whether due to exercise, age, overuse injuries or trauma. In fact, they account for nearly 20 percent of visits
.org. Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs. Anatomy. Cause
 Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs Page ( 1 ) Plantar fasciitis (fashee-eye-tiss) is the most common cause of pain on the bottom of the heel. Approximately 2 million patients are treated for this condition
Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs Page ( 1 ) Plantar fasciitis (fashee-eye-tiss) is the most common cause of pain on the bottom of the heel. Approximately 2 million patients are treated for this condition
What Are Bursitis and Tendinitis?
 Bursitis and tendinitis are both common conditions that cause swelling around muscles and bones. They occur most often in the shoulder, elbow, wrist, hip, knee, or ankle. A bursa is a small, fluid-filled
Bursitis and tendinitis are both common conditions that cause swelling around muscles and bones. They occur most often in the shoulder, elbow, wrist, hip, knee, or ankle. A bursa is a small, fluid-filled
When is Hip Arthroscopy recommended?
 HIP ARTHROSCOPY Hip arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that uses a camera inserted through very small incisions to examine and treat problems in the hip joint. The camera displays pictures
HIP ARTHROSCOPY Hip arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that uses a camera inserted through very small incisions to examine and treat problems in the hip joint. The camera displays pictures
.org. Arthritis of the Hand. Description
 Arthritis of the Hand Page ( 1 ) The hand and wrist have multiple small joints that work together to produce motion, including the fine motion needed to thread a needle or tie a shoelace. When the joints
Arthritis of the Hand Page ( 1 ) The hand and wrist have multiple small joints that work together to produce motion, including the fine motion needed to thread a needle or tie a shoelace. When the joints
Temple Physical Therapy
 Temple Physical Therapy A General Overview of Common Neck Injuries For current information on Temple Physical Therapy related news and for a healthy and safe return to work, sport and recreation Like Us
Temple Physical Therapy A General Overview of Common Neck Injuries For current information on Temple Physical Therapy related news and for a healthy and safe return to work, sport and recreation Like Us
.org. Cervical Radiculopathy (Pinched Nerve) Anatomy. Cause
 Cervical Radiculopathy (Pinched Nerve) Page ( 1 ) Cervical radiculopathy, commonly called a pinched nerve occurs when a nerve in the neck is compressed or irritated where it branches away from the spinal
Cervical Radiculopathy (Pinched Nerve) Page ( 1 ) Cervical radiculopathy, commonly called a pinched nerve occurs when a nerve in the neck is compressed or irritated where it branches away from the spinal
Elbow Injuries and Disorders
 Elbow Injuries and Disorders Introduction Your elbow joint is made up of bone, cartilage, ligaments and fluid. Muscles and tendons help the elbow joint move. There are many injuries and disorders that
Elbow Injuries and Disorders Introduction Your elbow joint is made up of bone, cartilage, ligaments and fluid. Muscles and tendons help the elbow joint move. There are many injuries and disorders that
Knee Injuries What are the ligaments of the knee?
 As sporting participants or observers, we often hear a variety of terms used to describe sport-related injuries. Terms such as sprains, strains and tears are used to describe our aches and pains following
As sporting participants or observers, we often hear a variety of terms used to describe sport-related injuries. Terms such as sprains, strains and tears are used to describe our aches and pains following
Basal Joint Arthritis
 Basal Joint Arthritis What Is Basal Joint Arthritis? Arthritis is a disease that causes inflammation and stiffness in the joints. It often affects the joint at the base of the thumb, called the basal joint.
Basal Joint Arthritis What Is Basal Joint Arthritis? Arthritis is a disease that causes inflammation and stiffness in the joints. It often affects the joint at the base of the thumb, called the basal joint.
.org. Distal Radius Fracture (Broken Wrist) Description. Cause
 Distal Radius Fracture (Broken Wrist) Page ( 1 ) The radius is the larger of the two bones of the forearm. The end toward the wrist is called the distal end. A fracture of the distal radius occurs when
Distal Radius Fracture (Broken Wrist) Page ( 1 ) The radius is the larger of the two bones of the forearm. The end toward the wrist is called the distal end. A fracture of the distal radius occurs when
Arthroscopic subacromial decompression and rotator cuff repair
 Further sources of information http://www.patient.co.uk/showdoc/553/ http://www.shoulderdoc.co.uk/article.asp?section=11 http://www.medic8.com/healthguide/articles/painfulshoulder.html http://www.cks.nhs.uk/patientinformationleaflet/shoulderpainarc/st
Further sources of information http://www.patient.co.uk/showdoc/553/ http://www.shoulderdoc.co.uk/article.asp?section=11 http://www.medic8.com/healthguide/articles/painfulshoulder.html http://www.cks.nhs.uk/patientinformationleaflet/shoulderpainarc/st
Dr. Benjamin Hewitt. Subacramial Decompression & Rotator Cuff Repair
 Please contactmethroughthegoldcoasthospitaswityouhaveanyproblemsafteryoursurgery. Dr. Benjamin Hewitt Orthopaedic Surgeon Subacramial Decompression & Rotator Cuff Repair The Rotator Cuff consists of four
Please contactmethroughthegoldcoasthospitaswityouhaveanyproblemsafteryoursurgery. Dr. Benjamin Hewitt Orthopaedic Surgeon Subacramial Decompression & Rotator Cuff Repair The Rotator Cuff consists of four
Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures
 Copyright 2010 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures Fractures of the heel bone, or calcaneus, can be disabling injuries. They most often occur during high-energy collisions
Copyright 2010 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures Fractures of the heel bone, or calcaneus, can be disabling injuries. They most often occur during high-energy collisions
Informed Patient Tutorial Copyright 2012 by the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
 Informed Patient Tutorial Copyright 2012 by the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Informed Patient - Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery Introduction Welcome to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons'
Informed Patient Tutorial Copyright 2012 by the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Informed Patient - Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery Introduction Welcome to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons'
Ankle Fractures - OrthoInfo - AAOS. Copyright 2007 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Ankle Fractures
 Copyright 2007 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Ankle Fractures "I broke my ankle." A broken ankle is also known as an ankle "fracture." This means that one or more of the bones that make up the
Copyright 2007 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Ankle Fractures "I broke my ankle." A broken ankle is also known as an ankle "fracture." This means that one or more of the bones that make up the
InfoSheet Rotator Cuff Problems
 InfoSheet Rotator Cuff Problems David M. Klein, MD Kennedy - White Orthopaedic Center What is Acromioplasty? Description Acromioplasty is a surgical procedure performed to reshape the acromion in your
InfoSheet Rotator Cuff Problems David M. Klein, MD Kennedy - White Orthopaedic Center What is Acromioplasty? Description Acromioplasty is a surgical procedure performed to reshape the acromion in your
SHOULDER ACROMIOPLASTY/ SHOULDER DECOMPRESSION
 ORTHOPAEDIC WARD: 01-293 8687 /01-293 6602 BEACON CENTRE FOR ORTHOPAEDICS: 01-2937575 PHYSIOTHERAPY DEPARTMENT: 01-2936692 GUIDELINES FOR PATIENTS HAVING A SHOULDER ACROMIOPLASTY/ SHOULDER DECOMPRESSION
ORTHOPAEDIC WARD: 01-293 8687 /01-293 6602 BEACON CENTRE FOR ORTHOPAEDICS: 01-2937575 PHYSIOTHERAPY DEPARTMENT: 01-2936692 GUIDELINES FOR PATIENTS HAVING A SHOULDER ACROMIOPLASTY/ SHOULDER DECOMPRESSION
THE REVERSE SHOULDER REPLACEMENT
 THE REVERSE SHOULDER REPLACEMENT The Reverse Shoulder Replacement is a newly approved implant that has been used successfully for over ten years in Europe. It was approved by the FDA for use in the U.S.A.
THE REVERSE SHOULDER REPLACEMENT The Reverse Shoulder Replacement is a newly approved implant that has been used successfully for over ten years in Europe. It was approved by the FDA for use in the U.S.A.
.org. Knee Arthroscopy. Description. Preparing for Surgery. Surgery
 Knee Arthroscopy Page ( 1 ) Arthroscopy is a common surgical procedure in which a joint (arthro-) is viewed (-scopy) using a small camera. Arthroscopy gives doctors a clear view of the inside of the knee.
Knee Arthroscopy Page ( 1 ) Arthroscopy is a common surgical procedure in which a joint (arthro-) is viewed (-scopy) using a small camera. Arthroscopy gives doctors a clear view of the inside of the knee.
ROTATOR CUFF TEARS SMALL
 LOURDES MEDICAL ASSOCIATES Sean Mc Millan, DO Director of Orthopaedic Sports Medicine & Arthroscopy 2103 Burlington-Mount Holly Rd Burlington, NJ 08016 (609) 747-9200 (office) (609) 747-1408 (fax) http://orthodoc.aaos.org/drmcmillan
LOURDES MEDICAL ASSOCIATES Sean Mc Millan, DO Director of Orthopaedic Sports Medicine & Arthroscopy 2103 Burlington-Mount Holly Rd Burlington, NJ 08016 (609) 747-9200 (office) (609) 747-1408 (fax) http://orthodoc.aaos.org/drmcmillan
Herniated Disk in the Lower Back
 Nader M. Hebela, MD Fellow of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons http://orthodoc.aaos.org/hebela Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Neurological Institute Al Maryah Island
Nader M. Hebela, MD Fellow of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons http://orthodoc.aaos.org/hebela Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Neurological Institute Al Maryah Island
Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
 Copyright 2009 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Lumbar Spinal Stenosis Almost everyone will experience low back pain at some point in their lives. A common cause of low back pain is lumbar spinal
Copyright 2009 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Lumbar Spinal Stenosis Almost everyone will experience low back pain at some point in their lives. A common cause of low back pain is lumbar spinal
Rotator Cuff Tears in Football
 Disclosures Rotator Cuff Tears in Football Roger Ostrander, MD Consultant: Mitek Consultant: On-Q Research Support: Arthrex Research Support: Breg Research Support: Arthrosurface 2 Anatomy 4 major muscles:
Disclosures Rotator Cuff Tears in Football Roger Ostrander, MD Consultant: Mitek Consultant: On-Q Research Support: Arthrex Research Support: Breg Research Support: Arthrosurface 2 Anatomy 4 major muscles:
ARTHROSCOPIC (KEY-HOLE) SHOULDER SURGERY
 ARTHROSCOPIC (KEY-HOLE) SHOULDER SURGERY Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 8 What is arthroscopic ( key-hole ) surgery? Key-hole surgery is the technique of performing surgery though
ARTHROSCOPIC (KEY-HOLE) SHOULDER SURGERY Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 8 What is arthroscopic ( key-hole ) surgery? Key-hole surgery is the technique of performing surgery though
Treatment Guide Understanding Elbow Pain. Using this Guide. Choosing Your Care. Table of Contents:
 Treatment Guide Understanding Elbow Pain Elbow pain is extremely common whether due to aging, overuse, trauma or a sports injury. When elbow pain interferes with carrying the groceries, participating in
Treatment Guide Understanding Elbow Pain Elbow pain is extremely common whether due to aging, overuse, trauma or a sports injury. When elbow pain interferes with carrying the groceries, participating in
.org. Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle) Anatomy
 Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle) Page ( 1 ) A broken ankle is also known as an ankle fracture. This means that one or more of the bones that make up the ankle joint are broken. A fractured ankle can range
Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle) Page ( 1 ) A broken ankle is also known as an ankle fracture. This means that one or more of the bones that make up the ankle joint are broken. A fractured ankle can range
Rotator Cuff Repair Protocol
 Rotator Cuff Repair Protocol Anatomy and Biomechanics The shoulder is a wonderfully complex joint that is made up of the ball and socket connection between the humerus (ball) and the glenoid portion of
Rotator Cuff Repair Protocol Anatomy and Biomechanics The shoulder is a wonderfully complex joint that is made up of the ball and socket connection between the humerus (ball) and the glenoid portion of
Frozen shoulder (adhesive capsulitis)
 Patient information Frozen shoulder (adhesive capsulitis) This information has been produced to help you gain the maximum benefit and understanding of your operation. It includes the following information:
Patient information Frozen shoulder (adhesive capsulitis) This information has been produced to help you gain the maximum benefit and understanding of your operation. It includes the following information:
Treatment Guide Knee Pain
 Treatment Guide Knee Pain Choosing Your Care Approximately 18 million patients visit a doctor or a hospital because of knee pain each year. Fortunately, there are many ways to successfully treat knee pain
Treatment Guide Knee Pain Choosing Your Care Approximately 18 million patients visit a doctor or a hospital because of knee pain each year. Fortunately, there are many ways to successfully treat knee pain
Rotator Cuff Injury and Shoulder Tendonitis
 43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) 356 1353. Website: philip-bayliss.com Rotator Cuff Injury and Shoulder Tendonitis The rotator cuff is a group of four muscles that helps to lift
43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) 356 1353. Website: philip-bayliss.com Rotator Cuff Injury and Shoulder Tendonitis The rotator cuff is a group of four muscles that helps to lift
AAOS Guideline on Optimizing the Management of Rotator Cuff Problems
 AAOS Guideline on Optimizing the Management of Rotator Cuff Problems Summary of Recommendations The following is a summary of the recommendations in the AAOS clinical practice guideline, Optimizing the
AAOS Guideline on Optimizing the Management of Rotator Cuff Problems Summary of Recommendations The following is a summary of the recommendations in the AAOS clinical practice guideline, Optimizing the
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Shoulder Arthroscopy
 Rehabilitation Guidelines for Shoulder Arthroscopy Front View Long head of bicep Acromion Figure 1 Shoulder anatomy Supraspinatus Image Copyright 2010 UW Health Sports Medicine Center. Short head of bicep
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Shoulder Arthroscopy Front View Long head of bicep Acromion Figure 1 Shoulder anatomy Supraspinatus Image Copyright 2010 UW Health Sports Medicine Center. Short head of bicep
A Patient s Guide to Shoulder Pain
 A Patient s Guide to Shoulder Pain Part 2 Evaluating the Patient James T. Mazzara, M.D. Shoulder and Elbow Surgery Sports Medicine Occupational Orthopedics Patient Education Disclaimer This presentation
A Patient s Guide to Shoulder Pain Part 2 Evaluating the Patient James T. Mazzara, M.D. Shoulder and Elbow Surgery Sports Medicine Occupational Orthopedics Patient Education Disclaimer This presentation
IMPINGEMENT SYNDROME (Rotator Cuff Tendinitis, Bursitis)
 IMPINGEMENT SYNDROME (Rotator Cuff Tendinitis, Bursitis) Description Impingement syndrome is characterized by pain in the shoulder due to inflammation of the tendons of the rotator cuff or the bursa (subacromial
IMPINGEMENT SYNDROME (Rotator Cuff Tendinitis, Bursitis) Description Impingement syndrome is characterized by pain in the shoulder due to inflammation of the tendons of the rotator cuff or the bursa (subacromial
Arthroscopic rotator cuff repair
 Arthroscopic rotator cuff repair The aim of this leaflet is to help answer some of the questions you may have about having an arthroscopic rotator cuff repair. It explains the benefits, risks and alternatives
Arthroscopic rotator cuff repair The aim of this leaflet is to help answer some of the questions you may have about having an arthroscopic rotator cuff repair. It explains the benefits, risks and alternatives
A Simplified Approach to Common Shoulder Problems
 A Simplified Approach to Common Shoulder Problems Objectives: Understand the basic categories of common shoulder problems. Understand the common patient symptoms. Understand the basic exam findings. Understand
A Simplified Approach to Common Shoulder Problems Objectives: Understand the basic categories of common shoulder problems. Understand the common patient symptoms. Understand the basic exam findings. Understand
Herniated Lumbar Disc
 Herniated Lumbar Disc North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Herniated Disc? The spine is made up of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. The disc is a combination of strong
Herniated Lumbar Disc North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Herniated Disc? The spine is made up of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. The disc is a combination of strong
SLAP repair. An information guide for patients. Delivering the best in care. UHB is a no smoking Trust
 SLAP repair An information guide for patients Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
SLAP repair An information guide for patients Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
A Patient s Guide to Guyon s Canal Syndrome
 A Patient s Guide to DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources. It may not be complete or timely. It does not cover all diseases, physical conditions, ailments or
A Patient s Guide to DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources. It may not be complete or timely. It does not cover all diseases, physical conditions, ailments or
Hand and Upper Extremity Injuries in Outdoor Activities. John A. Schneider, M.D.
 Hand and Upper Extremity Injuries in Outdoor Activities John A. Schneider, M.D. Biographical Sketch Dr. Schneider is an orthopedic surgeon that specializes in the treatment of hand and upper extremity
Hand and Upper Extremity Injuries in Outdoor Activities John A. Schneider, M.D. Biographical Sketch Dr. Schneider is an orthopedic surgeon that specializes in the treatment of hand and upper extremity
Total Shoulder Arthroplasty
 Specialists in Joint Replacement, Spinal Surgery, Orthopaedics and Sport Injuries Total Shoulder Arthroplasty Ms. Ruth Delaney Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon www.sportssurgeryclinic.com Introduction Arthritis
Specialists in Joint Replacement, Spinal Surgery, Orthopaedics and Sport Injuries Total Shoulder Arthroplasty Ms. Ruth Delaney Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon www.sportssurgeryclinic.com Introduction Arthritis
SLAP Repair Protocol
 SLAP Repair Protocol Anatomy and Biomechanics The shoulder is a wonderfully complex joint that is made up of the ball and socket connection between the humerus (ball) and the glenoid portion of the scapula
SLAP Repair Protocol Anatomy and Biomechanics The shoulder is a wonderfully complex joint that is made up of the ball and socket connection between the humerus (ball) and the glenoid portion of the scapula
Wrist and Hand. Patient Information Guide to Bone Fracture, Bone Reconstruction and Bone Fusion: Fractures of the Wrist and Hand: Carpal bones
 Patient Information Guide to Bone Fracture, Bone Reconstruction and Bone Fusion: Wrist and Hand Fractures of the Wrist and Hand: Fractures of the wrist The wrist joint is made up of the two bones in your
Patient Information Guide to Bone Fracture, Bone Reconstruction and Bone Fusion: Wrist and Hand Fractures of the Wrist and Hand: Fractures of the wrist The wrist joint is made up of the two bones in your
Back & Neck Pain Survival Guide
 Back & Neck Pain Survival Guide www.kleinpeterpt.com Zachary - 225-658-7751 Baton Rouge - 225-768-7676 Kleinpeter Physical Therapy - Spine Care Program Finally! A Proven Assessment & Treatment Program
Back & Neck Pain Survival Guide www.kleinpeterpt.com Zachary - 225-658-7751 Baton Rouge - 225-768-7676 Kleinpeter Physical Therapy - Spine Care Program Finally! A Proven Assessment & Treatment Program
Osteoarthritis progresses slowly and the pain and stiffness it causes worsens over time.
 Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Arthritis is the leading cause of disability in the United States. It can occur at any age, and literally means "pain within a joint." As a result, arthritis is a term used
Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Arthritis is the leading cause of disability in the United States. It can occur at any age, and literally means "pain within a joint." As a result, arthritis is a term used
world-class orthopedic care right in your own backyard.
 world-class orthopedic care right in your own backyard. Patient Promise: At Adventist Hinsdale Hospital, our Patient Promise means we strive for continued excellence in everything we do. This means you
world-class orthopedic care right in your own backyard. Patient Promise: At Adventist Hinsdale Hospital, our Patient Promise means we strive for continued excellence in everything we do. This means you
Neck Injuries and Disorders
 Neck Injuries and Disorders Introduction Any part of your neck can be affected by neck problems. These affect the muscles, bones, joints, tendons, ligaments or nerves in the neck. There are many common
Neck Injuries and Disorders Introduction Any part of your neck can be affected by neck problems. These affect the muscles, bones, joints, tendons, ligaments or nerves in the neck. There are many common
Subacromial Decompression Surgery
 Subacromial Decompression Surgery Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered This leaflet aims to help you gain the maximum benefit from your operation. It is not a substitute for professional medical
Subacromial Decompression Surgery Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered This leaflet aims to help you gain the maximum benefit from your operation. It is not a substitute for professional medical
Herniated Cervical Disc
 Herniated Cervical Disc North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Herniated Disc? The backbone, or spine, is composed of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. The vertebrae
Herniated Cervical Disc North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Herniated Disc? The backbone, or spine, is composed of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. The vertebrae
Plantar Fasciitis. Plantar Fascia
 Plantar Fasciitis Introduction Plantar fasciitis is an inflammation of the thick band of tissue that connects your heel bone to your toes. This thick band of tissue is called the plantar fascia. Plantar
Plantar Fasciitis Introduction Plantar fasciitis is an inflammation of the thick band of tissue that connects your heel bone to your toes. This thick band of tissue is called the plantar fascia. Plantar
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME
 ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME Description The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the front of the leg. Where the tendon
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME Description The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the front of the leg. Where the tendon
Scaphoid Fracture of the Wrist
 Page 1 of 6 Scaphoid Fracture of the Wrist Doctors commonly diagnose a sprained wrist after a patient falls on an outstretched hand. However, if pain and swelling don't go away, doctors become suspicious
Page 1 of 6 Scaphoid Fracture of the Wrist Doctors commonly diagnose a sprained wrist after a patient falls on an outstretched hand. However, if pain and swelling don't go away, doctors become suspicious
28% have partial tear of the rotator cuff.
 ROTATOR CUFF TENDON RUPTURE Anatomy: 1. Rotator cuff consists of: Subscapularis anteriorly, Supraspinatus superiorly and Infraspinatus and Teres minor posteriorly. 2 Biceps tendon is present in the rotator
ROTATOR CUFF TENDON RUPTURE Anatomy: 1. Rotator cuff consists of: Subscapularis anteriorly, Supraspinatus superiorly and Infraspinatus and Teres minor posteriorly. 2 Biceps tendon is present in the rotator
Total Hip Joint Replacement. A Patient s Guide
 Total Hip Joint Replacement A Patient s Guide Don t Let Hip Pain Slow You Down What is a Hip Joint? Your joints are involved in almost every activity you do. Simple movements such as walking, bending,
Total Hip Joint Replacement A Patient s Guide Don t Let Hip Pain Slow You Down What is a Hip Joint? Your joints are involved in almost every activity you do. Simple movements such as walking, bending,
Shoulder Instability. Fig 1: Intact labrum and biceps tendon
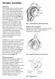 Shoulder Instability What is it? The shoulder joint is a ball and socket joint, with the humeral head (upper arm bone) as the ball and the glenoid as the socket. The glenoid (socket) is a shallow bone
Shoulder Instability What is it? The shoulder joint is a ball and socket joint, with the humeral head (upper arm bone) as the ball and the glenoid as the socket. The glenoid (socket) is a shallow bone
A Patient s Guide to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
 A Patient s Guide to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 [email protected] DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a
A Patient s Guide to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 [email protected] DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a
Dr. Benjamin Hewitt. Shoulder Stabilisation
 Please contactmethroughthegoldcoasthospitaswityouhaveanyproblemsafteryoursurgery. Dr. Benjamin Hewitt Orthopaedic Surgeon Shoulder Stabilisation The shoulder is the most flexible joint in the body, allowing
Please contactmethroughthegoldcoasthospitaswityouhaveanyproblemsafteryoursurgery. Dr. Benjamin Hewitt Orthopaedic Surgeon Shoulder Stabilisation The shoulder is the most flexible joint in the body, allowing
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Knee Arthroscopy
 Rehabilitation Guidelines for Knee Arthroscopy Arthroscopy is a common surgical procedure in which a joint is viewed using a small camera. This technique allows the surgeon to have a clear view of the
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Knee Arthroscopy Arthroscopy is a common surgical procedure in which a joint is viewed using a small camera. This technique allows the surgeon to have a clear view of the
Notice of Independent Review Decision DESCRIPTION OF THE SERVICE OR SERVICES IN DISPUTE:
 Notice of Independent Review Decision DATE OF REVIEW: 12/10/10 IRO CASE #: NAME: DESCRIPTION OF THE SERVICE OR SERVICES IN DISPUTE: Determine the appropriateness of the previously denied request for right
Notice of Independent Review Decision DATE OF REVIEW: 12/10/10 IRO CASE #: NAME: DESCRIPTION OF THE SERVICE OR SERVICES IN DISPUTE: Determine the appropriateness of the previously denied request for right
Arthroscopy of the Hand and Wrist
 Arthroscopy of the Hand and Wrist Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure whereby a small camera is inserted through small incisions of a few millimeters each around a joint to view the joint directly.
Arthroscopy of the Hand and Wrist Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure whereby a small camera is inserted through small incisions of a few millimeters each around a joint to view the joint directly.
PLANTAR FASCITIS (Heel Spur Syndrome)
 PLANTAR FASCITIS (Heel Spur Syndrome) R. Amadeus Mason MD Description Plantar fascitis is characterized by stiffness and inflammation of the main fascia (fibrous connective [ligament-like] tissue) on the
PLANTAR FASCITIS (Heel Spur Syndrome) R. Amadeus Mason MD Description Plantar fascitis is characterized by stiffness and inflammation of the main fascia (fibrous connective [ligament-like] tissue) on the
Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle
 Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic disease that attacks multiple joints throughout the body. It most often
Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic disease that attacks multiple joints throughout the body. It most often
Patient Guide to Neck Surgery
 The following is a sampling of products offered by Zimmer Spine for use in Anterior Cervical Fusion procedures. Patient Guide to Neck Surgery Anterior Cervical Fusion Trinica Select With the Trinica and
The following is a sampling of products offered by Zimmer Spine for use in Anterior Cervical Fusion procedures. Patient Guide to Neck Surgery Anterior Cervical Fusion Trinica Select With the Trinica and
.org. Lisfranc (Midfoot) Injury. Anatomy. Description
 Lisfranc (Midfoot) Injury Page ( 1 ) Lisfranc (midfoot) injuries result if bones in the midfoot are broken or ligaments that support the midfoot are torn. The severity of the injury can vary from simple
Lisfranc (Midfoot) Injury Page ( 1 ) Lisfranc (midfoot) injuries result if bones in the midfoot are broken or ligaments that support the midfoot are torn. The severity of the injury can vary from simple
Rotator Cuff Surgery: Post-Operative Protocol for Mini-Open or Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair
 Rotator Cuff Surgery: Post-Operative Protocol for Mini-Open or Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair Considerations: 1. Mini-Open - shoulder usually assessed arthroscopically and acromioplasty is usually performed.
Rotator Cuff Surgery: Post-Operative Protocol for Mini-Open or Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair Considerations: 1. Mini-Open - shoulder usually assessed arthroscopically and acromioplasty is usually performed.
Herniated Disk. This reference summary explains herniated disks. It discusses symptoms and causes of the condition, as well as treatment options.
 Herniated Disk Introduction Your backbone, or spine, has 24 moveable vertebrae made of bone. Between the bones are soft disks filled with a jelly-like substance. These disks cushion the vertebrae and keep
Herniated Disk Introduction Your backbone, or spine, has 24 moveable vertebrae made of bone. Between the bones are soft disks filled with a jelly-like substance. These disks cushion the vertebrae and keep
Orthopaedic Spine Center. Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) Normal Discs
 Orthopaedic Spine Center Graham Calvert MD James Woodall MD PhD Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) Normal Discs The cervical spine consists of the bony vertebrae, discs, nerves and other structures.
Orthopaedic Spine Center Graham Calvert MD James Woodall MD PhD Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) Normal Discs The cervical spine consists of the bony vertebrae, discs, nerves and other structures.
Orthopaedic Stem Cell Treatment
 Orthopaedic Stem Cell Treatment Stem Cell Injections Surgically Implanted Stem Cells Learn about the treatment option that is best for you. Emory Healthcare patients can benefit from surgical implantation
Orthopaedic Stem Cell Treatment Stem Cell Injections Surgically Implanted Stem Cells Learn about the treatment option that is best for you. Emory Healthcare patients can benefit from surgical implantation
CAPPAGH NATIONAL ORTHOPAEDIC HOSPITAL, FINGLAS, DUBLIN 11. The Sisters of Mercy. Rotator Cuff Repair
 1.0 Policy Statement... 2 2.0 Purpose... 2 3.0 Scope... 2 4.0 Health & Safety... 2 5.0 Responsibilities... 2 6.0 Definitions and Abbreviations... 3 7.0 Guideline... 3 7.1 Pre-Operative... 3 7.2 Post-Operative...
1.0 Policy Statement... 2 2.0 Purpose... 2 3.0 Scope... 2 4.0 Health & Safety... 2 5.0 Responsibilities... 2 6.0 Definitions and Abbreviations... 3 7.0 Guideline... 3 7.1 Pre-Operative... 3 7.2 Post-Operative...
ARTHROSCOPIC HIP SURGERY
 ARTHROSCOPIC HIP SURGERY Hip Arthroscopy is a relatively simple procedure whereby common disorders of the hip can be diagnosed and treated using keyhole surgery. Some conditions, which previously were
ARTHROSCOPIC HIP SURGERY Hip Arthroscopy is a relatively simple procedure whereby common disorders of the hip can be diagnosed and treated using keyhole surgery. Some conditions, which previously were
Page 2 of 6 plantar fascia. This is called the windlass mechanism. Later, we'll discuss how this mechanism is used to treat plantar fasciitis with str
 Page 1 of 6 Plantar Fasciitis (Heel Pain) Plantar fasciitis is a painful condition affecting the bottom of the foot. It is a common cause of heel pain and is sometimes called a heel spur. Plantar fasciitis
Page 1 of 6 Plantar Fasciitis (Heel Pain) Plantar fasciitis is a painful condition affecting the bottom of the foot. It is a common cause of heel pain and is sometimes called a heel spur. Plantar fasciitis
