Rialto Report: Successfully Operating in Matrix Organisations
|
|
|
- Clinton Douglas
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Rialto Report: Successfully Operating in Matrix Organisations 1
2 Contents Introduction & Historical Context of Matrix Management... 3 Matrix Management... 4 Key Roles... 4 Conditions and Rationale for a Matrix Organisation... 5 Misaligned Goals... 5 Unclear Roles and Responsibilities... 5 Responsibility without Authority... 6 Employee Behaviour... 6 Advantages & Disadvantages of Matrix Management... 7 Advantages:... 7 Disadvantages... 7 Factors for Successful Matrix Operation... 8 Key questions to consider:... 9 Examples of Matrix Organisational structure: Weak Matrix Strong Matrix Balanced Matrix Conclusions Concluding Food For Thought Appendix One: Key articles on Matrix Management, pros, cons and case studies:. 13 Appendix Two: Matrix Management Pyramid:
3 Introduction & Historical Context of Matrix Management Organisational structures can help or hinder performance. In a global economy anything that creates bottlenecks and slows up decision-making is an obstacle. Two critical OD design factors impact success: Hierarchical management Functional silos The solution is to drive and develop teams based around co-ordination, co-operation and flexibility. The matrix model originated from the recognition that companies not only have vertical chains of command but that people also work horizontally, across functions. Encapsulating this principle is to manage people across functions (collaboratively) on key projects in order to achieve strategic objectives. However, it is not just about intrinsic organisational design; it is about managing culture and behaviour. Although all matrix forms have inherent flaws, CEOs adopt the matrix because they: Allow companies to focus on multiple business goals; Facilitate the management of information; Enable companies to establish economies of scale; and Speed up response to demands. Its origins can be traced back to the US space programme of the 1960 s when President Kennedy outlined his vision to put man on the moon. In order to achieve such an objective NASA had to revolutionise its project approach and so the matrix organisation was born to facilitate and manage the multi-disciplinary expertise required to achieve such a complex goal. Other key organisations pioneering this approach included Xerox, Digital Equipment Corporation and Citibank. However, by the 1980 s, it was clear that it wasn t such an easy task due to the cultural and behavioural complexity. By the 1990 s matrix management had found a new form, in the manifestation of empowerment and virtual teams, where the focus was increasingly on customer service and speed of delivery. Nevertheless, the vulnerability of the matrix to pressure from competing managers will always be a problem. Q: How can this be mitigated? 3
4 Matrix Management Matrix Management is a type of organisational management in which people with similar skills are pooled for work assignments. For example, all engineers may be in one engineering department and report to an engineering manager, but these same engineers may be assigned to different projects and report to a project manager while working on that project. Therefore, each engineer may have to work under several managers to get their job done. Typical Matrix Organisational structure: Key Roles There are three key roles in a matrix organisation, each of which have specific responsibilities to make the matrix structure work: Matrix Leader -- The matrix leader is the common point above both matrix bosses. The matrix leader needs to ensure that the power balance is maintained. This is done by delegating decisions and encouraging collaborative problem solving. Matrix Managers -- The matrix managers must collaborate with each other to delineate activities which they are responsible for. Matrixed employees -- The matrixed employee is an integrator. They have more responsibility with less direct authority. They must manage upwards and facilitate resolution of conflicting demands from the two matrix managers. The matrixed employee must be able to maintain relationships with both managers and manage a dual loyalty. However, employees who are able to utilize these skills to operate in a matrixed environment can accomplish much more difficult tasks than non-matrixed employees typically can, because of the increased channels of information and influence. Q: Development needs? 4
5 Conditions and Rationale for a Matrix Organisation The matrix tends to be the best structure when three conditions exist: There are pressures for shared, flexible use of resources across geography or products. This is often due to financial or budgetary constraints. Information processing needs are high because of a highly complex and uncertain environment. There is high complexity because of many different factors which must be considered and / or because there is a high degree of interdependence between many different parts of the organisation. Resources must be responsive to two or more sectors (i.e. focus on two or more critical outputs.) This dual pressure requires a balance of power between the functional perspective and the geographic (or product) perspective. The matrix organisation creates conflicts of interest and forces them to be resolved. When conflicts arise, the individual and both bosses have to resolve the conflict by having discussions about the issues on which they disagree, in order to develop a compromise solution which reflects both viewpoints. Q: Is compromise driving high performance working? Misaligned Goals A primary challenge of operating in matrix organisations is aligning goals among many different dimensions. Points of Intervention Manage competing or conflicting objectives between matrix dimensions. Define adequate processes to align goals and detect possible misalignments. Manage synchronization, coordination, and timing of work plans and objectives. Manage communication and consultation between matrix dimensions. Unclear Roles and Responsibilities Confusion over roles and responsibilities is a problem in almost all matrix organisations. Points of Intervention Clear guidelines and descriptions on roles/areas of responsibility; Assignment of accountability for business objectives; A single point of contact for information or approval for areas of responsibility; A set plan for communication and information sharing (e.g., monthly meetings, newsletters, quarterly company/unit performance). 5
6 Responsibility without Authority In the matrix, leaders can have responsibility without authority as a result of the dual reporting structure. Points of Intervention Manage confusion over who has the final authority. Manage clarity on areas of accountability. Leaders may be unaccustomed to sharing decision rights. Compensate for possible delay in decision-making process. Employee Behaviour Employee behaviour is perhaps the most critical challenge that matrix organisations face. Organisations must enable their employees to behave as one company. Critical Issues to Manage Personal conflicts between leaders hindering collaboration between units. Withholding resources from others. Lack of trust between employees in different business units. Employees lack the requisite skills to function in the matrix. Insufficient communication between different business units. 6
7 Advantages & Disadvantages of Matrix Management Advantages: The basis for the matrix organisation is an endeavour to create synergism through shared responsibility between project and functional management. Other advantages of a pure matrix organisational form, to project management, include: Because key people can be shared, the project cost is minimized Conflicts are minimal, and those requiring hierarchical referrals are more easily resolved There is a better balance between time, cost and performance Authority and responsibility are shared Stress is distributed among the team Achieves coordination necessary to meet dual demands from the operating environment Provides flexible sharing of resources Suited for complex decision making in unstable environments with high information processing requirements Provides opportunities for both function and product knowledge development Allows team members to share information more readily across task boundaries. Allows for specialisation that can increase depth of knowledge and allow professional development and career progression to be managed. Disadvantages The disadvantage of matrix management is that employees can become confused due to conflicting loyalties. The belief is that a properly managed cooperative environment can neutralise these disadvantages. Other disadvantages include: Dual authority can be frustrating and confusing, leading to higher stress for the shared resources employees can become confused due to conflicting loyalties Complex and difficult to implement Shared resources require excellent interpersonal skills and training Frequent meetings and conflict resolution sessions are required Requires a collegial (rather than hierarchical) culture Requires offsetting pressures to maintain the dual focus 7
8 Doubles the number of managers when compared to line managers and as the time to reach a decision increases with the number of managers the result may be an increase in management related overhead expenses. Opponents to matrix management believe that it is an outdated method to organise a company Factors for Successful Matrix Operation The following factors are from: Dale D. McConkey, Across the Hierarchy: A look at the future (Business Quarterly, V 45 (2), Summer 1980, pp ). While they are focused more on matrixed project teams, many of the factors also apply to permanent matrixed positions: Top management understanding of matrix -- and support of its use Commitment by functional departments to matrix organisation and projects Willingness to use a flexible approach to matrix -- no one way exists Willingness to let matrix evolve Selection of competent matrix leaders Clearly defined responsibility and authority of the matrix team Approved objectives, plans and budgets for the team Maximum efforts to foster team effort Skills in conflict resolution Concentrate on the results -- leave considerable flexibility to functional departments to determine the how to Careful and continuous planning to reduce uncertainties Heavy emphasis on lateral communications among functional departments Effective systems for multiple performance evaluations 8
9 Key questions to consider: Why do we have a matrix structure and what's the benefit to me and the organisation? How do I operate effectively with responsibility and accountability without authority? How do I manage the expectations of multiple bosses? What is the best way of dealing with ambiguous and shifting reporting lines? How can I best influence those separated by distance/time/culture? How do I manage communications? How do I manage conflict? How do I develop routine relationships? How do I clarify role specifications / performance objectives? 9
10 Examples of Matrix Organisational structure: There are distinct types of matrix system, designed to balance the ability struggle-struggle between the managers conflicting needs. The principal types are these matrix organisations is listed below. Weak Matrix This type of matrix organisation structure is nightmarish for Project Managers. In the weak matrix organisational structure, project managers are effectively reduced to being project facilitators. They draw plans and supervise the execution, but they have no genuine control over personnel, and are nearly completely reliant upon the functional managers to offer resources. The workers have less allegiance to the project managers (or the plan), because it is the functional managers who determine the progress of the workers. And the workers progress is normally measured solely on the work that is done for their functional manager not on their project work thus it is a fact that working on a project may be seen by the worker as not desirable as they will have less time in doing their functional work, so the project manager may see them as unmotivated. And as the PM has no genuine control over the project members, so they frequently have to report the problem of workers not doing their duties, to the functional managers in anticipation that they will motivate to the workers to perform more on the project. But recall that the functional managers are primarily accountable for the operation of their own areas, so their workers performing plan tasks can really cut the productivity of their region (frequently projects are ignored in the benchmarks. So this leads to a clear-cut dispute of stake between the PM, the functional managers and the respective workers. In this position the PM normally loses and that s the simple to recall it the PM is feeble in a feeble matrix. Strong Matrix All these problems led to the introduction of the strong matrix organisation structure In the strong matrix organisational structure, the tables are reversed from the weak matrix organisation structure. The intent is that project managers that are responsible for the workers, rather than the line managers. But the project managers are not accountable for the human resource management. This gives project managers the power to handle the workers directly, and therefore adequately handling the entire project, but without involving the project managers upward in HR administration. Plan managers manage groups and are accountable for everything with the exception of the HR functions. Plan managers that manage groups would have the Project manager in a role with lone authority and obligation to direct their work, but they also had staff managers who took care of anything that was not project-related, i.e. performance reviews (provision should be made to input to these) training, holiday management, contracts for employments etc. Therefore it would be possible for the Plan managers to focus on project management entirely. So, when a manager for a project starts a new one, they discuss their staffing demand with the functional managers and the functional managers seek to have the resources accessible (and offer education for them, where needed). Normally, the functional managers will sketch out plans and charts (e. g. Gantt charts) of how their folk will be included inside projects, and they might move personnel between projects and project managers as required (after making inquiries with the project managers. 10
11 Effectively the Plan manager and the project managers work jointly, but the whole command of everything project-related is the role of the plan manager then in a powerful matrix, the plan manager is the stronger. Balanced Matrix There is an old saying, power corrupts, and absolute power corrupts absolutely. In each variation of the matrix organisation structure there is a battle for control, hence power. There needs to be some manner to bring each into equilibrium, otherwise one group will rule the other, to the disadvantage of the project, and finally to the detriment of the organisation all together (although private projects or functional areas may bloom for sometime). A really dominant project manager, for instance, might bully functional managers into always giving them the best team members for their projects. One way to reduce these difficulties is to have rules within the organisation that varies who can handle a worker, depending upon certain circumstances. For instance, there could be a regulation that says if a worker is to work on a project for less than one week the functional manager (or project manager) has lone command over the worker, but if the demand is for longer than one week, command changes hand. Or there may be rules that the same worker cannot work for same project manager, on two back-to-back projects. There are many potential rules that could be made, but the goal is to equalize the power between the project managers and the functional managers so as not to have a win/lose position. This is why this matrix organisation structure is referred to as a balanced matrix. So whether the organisational structure is feeble, powerful, or stable, the power is always from the standpoint of the project manager. 11
12 Conclusions - Concluding Food For Thought Mid-level and top-level managers face different challenges in matrix organisations. Specifically, top-level managers, in comparison with mid-level managers cite: Misaligned goals as a challenge. Report that the matrix guardian is a key success factor for optimal matrix performance. In contrast, more mid-level managers cite: Ambiguous roles and responsibilities as a challenge. Ambiguous authority. 12
13 Appendix One: Key articles on Matrix Management, pros, cons and case studies: Advantages of Matrix Organisational Structure: Small PowerPoint presentation of Matrix and e.g. of Martha Stewart!: Advantages/ Disadvantages, Definition and BAYER AG case study: Matrix Management: Not a Structure, a Frame of Mind: Another great article with good description of matrix management, bullet points on key challenges of working in matrix, how to lead and work in matrix and possible effects of Matrix on people and organisations: Lengthy article - Cross-functional structures: a review and integration of matrix organisation and project management (some useful points made): Book on matrix organisation the book description lists companies operating under matrix (IBM, NOKIA and Proctor and Gamble): Actually/dp/ Good article listing drawbacks and how to create a successful matrix: Great article definition, advantage and disadvantages and case study BAYER AG: Great article brief and to the point on pros, cons, examples and comments from people who have worked in Matrix organisations and comments from the author of the article: Interesting article on history of, and problems associated with Matrix org structure: Another great article with good description of matrix management, bullet points on key challenges of working in matrix, how to lead and work in matrix: Article contains a list of companies using structure: Good article on problems and companies using matrix: 13
14 Appendix Two: Matrix Management Pyramid: This report has been produced by Rialto Consultancy Limited. Rialto specialises in unique change management and transformation solutions which deliver exceptional results. We provide a range of services and interventions associated with the entire people agenda which include: Transforming the Performance Culture, Executive Outplacement & Career Realignment, Outplacement & Career Transition, Executive Search, Interim Management, Revitalising Leadership and Talent Management. The Rialto Consultancy Central Court 25 Southampton Buildings Chancery Lane LONDON WC2A 1AL T: +44 (0) E: [email protected] The Rialto Consultancy All rights reserved 14
15 asss The Rialto Consultancy Ltd 25 Southampton Buildings Chancery Lane London WC2A 1AL T: +44 (0) F: +44 (0) E:
Fundamentals of Organization Structure. Organizations and ICT 2014/2015 Fabiano Dalpiaz
 Fundamentals of Organization Structure Organizations and ICT 2014/2015 Fabiano Dalpiaz 1 Acknowledgements Most of these slides are taken from Daft s book Organization Theory and Design, chapter 3 Not part
Fundamentals of Organization Structure Organizations and ICT 2014/2015 Fabiano Dalpiaz 1 Acknowledgements Most of these slides are taken from Daft s book Organization Theory and Design, chapter 3 Not part
Need Information? Go to: www.chr.alberta.ca/apscompetencies. Have Questions? Email: [email protected]
 Need Information? Go to: www.chr.alberta.ca/apscompetencies Have Questions? Email: [email protected] Table of Contents Background... 3 Why Behavioural Competencies?... 3 The APS Competency Model...
Need Information? Go to: www.chr.alberta.ca/apscompetencies Have Questions? Email: [email protected] Table of Contents Background... 3 Why Behavioural Competencies?... 3 The APS Competency Model...
structures stack up Tom McMullen
 Making sure your organization structures stack up October 21, 2009 Tom McMullen Building effective organizations Trends in organization design Optimizing Focusing resources and reducing headcounts Removing
Making sure your organization structures stack up October 21, 2009 Tom McMullen Building effective organizations Trends in organization design Optimizing Focusing resources and reducing headcounts Removing
Making a positive difference for energy consumers. Competency Framework Band C
 Making a positive difference for energy consumers Competency Framework 2 Competency framework Indicators of behaviours Strategic Cluster Setting Direction 1. Seeing the Big Picture Seeing the big picture
Making a positive difference for energy consumers Competency Framework 2 Competency framework Indicators of behaviours Strategic Cluster Setting Direction 1. Seeing the Big Picture Seeing the big picture
Chapter-3 Organization Structure &
 MGMT 4135 Project Management Chapter-3 Organization Structure & Culture 1 Three different project management structures to choose from: 1. Functional organization 2. Projectized or dedicated teams 3. Matrix
MGMT 4135 Project Management Chapter-3 Organization Structure & Culture 1 Three different project management structures to choose from: 1. Functional organization 2. Projectized or dedicated teams 3. Matrix
Optimizing Rewards and Employee Engagement
 Optimizing Rewards and Employee Engagement Improving employee motivation and engagement, and identifying the right total rewards strategy to influence workforce effectiveness. Kevin Aselstine, Towers Perrin
Optimizing Rewards and Employee Engagement Improving employee motivation and engagement, and identifying the right total rewards strategy to influence workforce effectiveness. Kevin Aselstine, Towers Perrin
pm4dev, 2007 management for development series Project Management Organizational Structures PROJECT MANAGEMENT FOR DEVELOPMENT ORGANIZATIONS
 pm4dev, 2007 management for development series Project Management Organizational Structures PROJECT MANAGEMENT FOR DEVELOPMENT ORGANIZATIONS PROJECT MANAGEMENT FOR DEVELOPMENT ORGANIZATIONS A methodology
pm4dev, 2007 management for development series Project Management Organizational Structures PROJECT MANAGEMENT FOR DEVELOPMENT ORGANIZATIONS PROJECT MANAGEMENT FOR DEVELOPMENT ORGANIZATIONS A methodology
Sample interview question list
 Sample interview question list Category A Introductory questions 1. Tell me about yourself. 2. Why would you like to work for this organisation? 3. So what attracts you to this particular opportunity?
Sample interview question list Category A Introductory questions 1. Tell me about yourself. 2. Why would you like to work for this organisation? 3. So what attracts you to this particular opportunity?
HEAD OF TALENT AND RESOURCING JOB DESCRIPTION
 HEAD OF TALENT AND RESOURCING JOB DESCRIPTION Reporting to Location Staff reporting to this post Salary: - Head of SPOD in Organisational Effectiveness team under Deputy CEO - Oxford - 1 HR Executive and
HEAD OF TALENT AND RESOURCING JOB DESCRIPTION Reporting to Location Staff reporting to this post Salary: - Head of SPOD in Organisational Effectiveness team under Deputy CEO - Oxford - 1 HR Executive and
Designing an Effective Organization Structure. January 2009
 Designing an Effective Organization Structure January 2009 Effective organization design considers five, interrelated components Clear vision and priorities Cohesive leadership team 1. Leadership 2. Decision
Designing an Effective Organization Structure January 2009 Effective organization design considers five, interrelated components Clear vision and priorities Cohesive leadership team 1. Leadership 2. Decision
Chapter 3: Managing Conflict with Your Boss
 Chapter 3: Managing Conflict with Your Boss Overview The special case of conflict between a direct report and a boss presents unique challenges. As a manager with responsibilities up and down the organizational
Chapter 3: Managing Conflict with Your Boss Overview The special case of conflict between a direct report and a boss presents unique challenges. As a manager with responsibilities up and down the organizational
Legal Aid Board Training. 2010 Legal Aid Education P, Session 1, Page 1 Session 1. Introduction
 to Legal Aid 2010 Legal Aid Education P, Session 1, Page 1 Session 1 Governance as Leadership What is governance? Governance is the exercise of authority, direction and control of an organization in order
to Legal Aid 2010 Legal Aid Education P, Session 1, Page 1 Session 1 Governance as Leadership What is governance? Governance is the exercise of authority, direction and control of an organization in order
Chapter 8: The Internal Environment
 Chapter 8: The Internal Environment Key Revision Points The Internal Functions of Commercial Organisations In competitive business environments, customers are at the centre of all of an organisation's
Chapter 8: The Internal Environment Key Revision Points The Internal Functions of Commercial Organisations In competitive business environments, customers are at the centre of all of an organisation's
Business Analyst Position Description
 Analyst Position Description September 4, 2015 Analysis Position Description September 4, 2015 Page i Table of Contents General Characteristics... 1 Career Path... 2 Explanation of Proficiency Level Definitions...
Analyst Position Description September 4, 2015 Analysis Position Description September 4, 2015 Page i Table of Contents General Characteristics... 1 Career Path... 2 Explanation of Proficiency Level Definitions...
Perspectives. Employee voice. Releasing voice for sustainable business success
 Perspectives Employee voice Releasing voice for sustainable business success Empower, listen to, and act on employee voice through meaningful surveys to help kick start the UK economy. 2 Releasing voice
Perspectives Employee voice Releasing voice for sustainable business success Empower, listen to, and act on employee voice through meaningful surveys to help kick start the UK economy. 2 Releasing voice
The role of the line in talent management
 The role of the line in talent management A paper from HR in a disordered world: IES Perspectives on HR 2015 Wendy Hirsh, Principal Associate Member Paper 108 The role of the line in talent management
The role of the line in talent management A paper from HR in a disordered world: IES Perspectives on HR 2015 Wendy Hirsh, Principal Associate Member Paper 108 The role of the line in talent management
Barriers To Team Success
 Barriers To Team Success When plans are inadequate Leaders without leadership skills When members have poor attitudes Training that doesn t train Communications breakdowns Team members don t get along
Barriers To Team Success When plans are inadequate Leaders without leadership skills When members have poor attitudes Training that doesn t train Communications breakdowns Team members don t get along
APPLICATIONS GUIDE. TRACOM Sneak Peek. Excerpts from. Improving Personal Effectiveness With Versatility
 APPLICATIONS GUIDE TRACOM Sneak Peek Excerpts from Improving Personal Effectiveness With Versatility TABLE OF CONTENTS PAGE Introduction...1 Prerequisites...1 A Guide for You...1 Why Learn to Become Highly
APPLICATIONS GUIDE TRACOM Sneak Peek Excerpts from Improving Personal Effectiveness With Versatility TABLE OF CONTENTS PAGE Introduction...1 Prerequisites...1 A Guide for You...1 Why Learn to Become Highly
Organizational Design Basics
 15.320 Strategic Organizational Design Organizational Design Basics Elements of organizational patterns What Who Why How Elements of organizational patterns (cont.) Galbraith 15.311 What is being done?
15.320 Strategic Organizational Design Organizational Design Basics Elements of organizational patterns What Who Why How Elements of organizational patterns (cont.) Galbraith 15.311 What is being done?
Competitive Organisational Structures
 Competitive Organisational Structures Organisational structure basics Introduction The way in which a business is organised has a direct effect on its competitiveness. For a business to be able to achieve
Competitive Organisational Structures Organisational structure basics Introduction The way in which a business is organised has a direct effect on its competitiveness. For a business to be able to achieve
Explain how Employee Performance is Measured and Managed
 Explain how Employee Performance is Measured and Managed For this last section of my report I will be discussing how employee performance can be both managed and measured. In addition to this, I will also
Explain how Employee Performance is Measured and Managed For this last section of my report I will be discussing how employee performance can be both managed and measured. In addition to this, I will also
Last updated: July 2009
 Building a High-Performance Culture Last updated: July 2009 Overview A high-performance culture is a key component of effective organizations Culture tends to be an asset for nonprofits, as reflected in
Building a High-Performance Culture Last updated: July 2009 Overview A high-performance culture is a key component of effective organizations Culture tends to be an asset for nonprofits, as reflected in
Talent Management Essential Toolkit
 Talent Management Essential Toolkit Talent Management Essential Toolkit This presentation has been prepared to to provide the reader with an initial overview of five talent management tools that can assist
Talent Management Essential Toolkit Talent Management Essential Toolkit This presentation has been prepared to to provide the reader with an initial overview of five talent management tools that can assist
the Defence Leadership framework
 the Defence Leadership framework Growing Leaders at all Levels Professionalism Loyalty Integrity Courage Innovation Teamwork Foreword One of the founding elements of Building Force 2030, as outlined in
the Defence Leadership framework Growing Leaders at all Levels Professionalism Loyalty Integrity Courage Innovation Teamwork Foreword One of the founding elements of Building Force 2030, as outlined in
Using the Leadership Pipeline transition focused concept as the vehicle in integrating your leadership development approach provides:
 Building your Leadership Pipeline Leadership transition focused development - White Paper The Leadership Pipeline framework Business case reflections: 1. Integrated leadership development 2. Leadership
Building your Leadership Pipeline Leadership transition focused development - White Paper The Leadership Pipeline framework Business case reflections: 1. Integrated leadership development 2. Leadership
Portfolio management tools. Why and when are they used?
 Portfolio management tools Portfolio Management (PM) techniques are systematic ways of looking at a set of projects or activities or even business units, in order to reach an optimum balance between risks
Portfolio management tools Portfolio Management (PM) techniques are systematic ways of looking at a set of projects or activities or even business units, in order to reach an optimum balance between risks
Investors in People Assessment Report. Presented by Alli Gibbons Investors in People Specialist On behalf of Inspiring Business Performance Limited
 Investors in People Assessment Report for Bradstow School Presented by Alli Gibbons Investors in People Specialist On behalf of Inspiring Business Performance Limited 30 August 2013 Project Reference Number
Investors in People Assessment Report for Bradstow School Presented by Alli Gibbons Investors in People Specialist On behalf of Inspiring Business Performance Limited 30 August 2013 Project Reference Number
Maintaining employees focus and motivation is essential if they are to make a full contribution to your business.
 Maintaining employees focus and motivation is essential if they are to make a full contribution to your business. appraisals actively involve employees in understanding what is expected of them. By setting
Maintaining employees focus and motivation is essential if they are to make a full contribution to your business. appraisals actively involve employees in understanding what is expected of them. By setting
The Engineers Canada Leader
 The Engineers Canada Leader Executive Summary Engineers Canada exists to provide national support and leadership on behalf of engineering regulators to promote and maintain the interests, honour, and integrity
The Engineers Canada Leader Executive Summary Engineers Canada exists to provide national support and leadership on behalf of engineering regulators to promote and maintain the interests, honour, and integrity
Policy for delegating authority to foster carers. September 2013
 Policy for delegating authority to foster carers September 2013 Purpose and scope of policy 1.1 Introduction Decision-making around the care of looked after children can be an area of conflict between
Policy for delegating authority to foster carers September 2013 Purpose and scope of policy 1.1 Introduction Decision-making around the care of looked after children can be an area of conflict between
Section 2 - Key Account Management - Core Skills - Critical Success Factors in the Transition to KAM
 Section 2 - Key Account Management - Core Skills - Critical Success Factors in the Transition to KAM 1. This presentation looks at the Core skills required in Key Account Management and the Critical Success
Section 2 - Key Account Management - Core Skills - Critical Success Factors in the Transition to KAM 1. This presentation looks at the Core skills required in Key Account Management and the Critical Success
Motivation Questionnaire
 Motivation Questionnaire > Employee Motivation Report Name: Sample Report Date: 12 August 2009 Employee Motivation Report Introduction This report describes the factors that are likely to have an impact
Motivation Questionnaire > Employee Motivation Report Name: Sample Report Date: 12 August 2009 Employee Motivation Report Introduction This report describes the factors that are likely to have an impact
Global Fund Competency Behaviors by Organisation Level 2016
 Senior Manager (examples: Division Head, Department Head, Regional manager) Core Expertise Scope Applies both professional and management skills effectively and promotes processes and systems to encourage
Senior Manager (examples: Division Head, Department Head, Regional manager) Core Expertise Scope Applies both professional and management skills effectively and promotes processes and systems to encourage
NEGOTIATION: A PERSPECTIVE ON HOW TO IMPROVE THE NEGOTIATION PROCESS AS A TEAM - WHAT S BAD AND HOW TO FIX IT
 NEGOTIATION: A PERSPECTIVE ON HOW TO IMPROVE THE NEGOTIATION PROCESS AS A TEAM - WHAT S BAD AND HOW TO FIX IT by Yolanda Delgadillo Personnel Analyst II City of Lynwood INTRODUCTION Most government agencies
NEGOTIATION: A PERSPECTIVE ON HOW TO IMPROVE THE NEGOTIATION PROCESS AS A TEAM - WHAT S BAD AND HOW TO FIX IT by Yolanda Delgadillo Personnel Analyst II City of Lynwood INTRODUCTION Most government agencies
Using PDPs is not the same as simply putting groups of employees through traditional training programmes.
 development plans (PDPs) provide a powerful, flexible way to link employees professional and personal development with the development of your business. A PDP is a short, unambiguous written document usually
development plans (PDPs) provide a powerful, flexible way to link employees professional and personal development with the development of your business. A PDP is a short, unambiguous written document usually
Why Sales Training Doesn t Work. And What to Do About It!
 Why Sales Training Doesn t Work And What to Do About It! Selling isn t a great sport in which to come second. In the world of winner takes all, anything that gives you a small increase in performance relative
Why Sales Training Doesn t Work And What to Do About It! Selling isn t a great sport in which to come second. In the world of winner takes all, anything that gives you a small increase in performance relative
IT STARTS WITH CHANGE MANAGEMENT
 TRANSFORMING ORGANIZATIONS IT STARTS WITH CHANGE MANAGEMENT THE POWER TO TRANSFORM In today s globalized and inter-connected economy, organizations deal with continually shifting market conditions, customer
TRANSFORMING ORGANIZATIONS IT STARTS WITH CHANGE MANAGEMENT THE POWER TO TRANSFORM In today s globalized and inter-connected economy, organizations deal with continually shifting market conditions, customer
EFFECTIVE STRATEGIC PLANNING IN MODERN INFORMATION AGE ORGANIZATIONS
 EFFECTIVE STRATEGIC PLANNING IN MODERN INFORMATION AGE ORGANIZATIONS Cezar Vasilescu and Aura Codreanu Abstract: The field of strategic management has offered a variety of frameworks and concepts during
EFFECTIVE STRATEGIC PLANNING IN MODERN INFORMATION AGE ORGANIZATIONS Cezar Vasilescu and Aura Codreanu Abstract: The field of strategic management has offered a variety of frameworks and concepts during
Organization architecture and profitability. Organizational architecture. Organizational architecture. Organizational architecture
 13-1 Organization architecture and profitability Organizational architecture 13-2 Totality of a firm s organization, including structure, control systems, incentives, processes, culture and people. Superior
13-1 Organization architecture and profitability Organizational architecture 13-2 Totality of a firm s organization, including structure, control systems, incentives, processes, culture and people. Superior
Organizational Design Toolkit
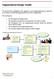 Organizational Design Toolkit We provide below highlights of the approach to developing/confirming the preferred service delivery model and organizational structure for an organization. The key steps are:
Organizational Design Toolkit We provide below highlights of the approach to developing/confirming the preferred service delivery model and organizational structure for an organization. The key steps are:
Leading Self. Leading Others. Leading Performance and Change. Leading the Coast Guard
 Coast Guard Leadership Competencies Leadership competencies are the knowledge, skills, and expertise the Coast Guard expects of its leaders. The 28 leadership competencies are keys to career success. Developing
Coast Guard Leadership Competencies Leadership competencies are the knowledge, skills, and expertise the Coast Guard expects of its leaders. The 28 leadership competencies are keys to career success. Developing
Leadership and Management Competencies
 Leadership and Management Competencies 0 The Saskatchewan Public Service Vision: The Best Public Service in Canada Our Commitment to Excellence Dedicated to service excellence, we demonstrate innovation,
Leadership and Management Competencies 0 The Saskatchewan Public Service Vision: The Best Public Service in Canada Our Commitment to Excellence Dedicated to service excellence, we demonstrate innovation,
HKIHRM HR PROFESSIONAL STANDARDS MODEL
 HKIHRM HR PROFESSIONAL STANDARDS MODEL Creating Values For You and For Organisations Setting Standards Recognising s ABOUT HKIHRM The Hong Kong Institute of Human Resource Management (HKIHRM) is the leading
HKIHRM HR PROFESSIONAL STANDARDS MODEL Creating Values For You and For Organisations Setting Standards Recognising s ABOUT HKIHRM The Hong Kong Institute of Human Resource Management (HKIHRM) is the leading
ABI Position paper. Supplement to ED/2009/12 Financial Instruments: Amortised Cost and Impairment
 ABI Position paper Supplement to ED/2009/12 Financial Instruments: Amortised Cost and Impairment March 2011 Page 1 of 17 Dear Sir/Madam, The Italian Banking Association welcomes the publication of the
ABI Position paper Supplement to ED/2009/12 Financial Instruments: Amortised Cost and Impairment March 2011 Page 1 of 17 Dear Sir/Madam, The Italian Banking Association welcomes the publication of the
Customer Experience Functional Lead - BaseCamp. Business Change Manager
 Position Profile Position: Customer Experience Functional Lead - BaseCamp Position Incumbent: Company: Location: Reporting to: Meridian Energy Christchurch Business Change Manager Date: December 2008 This
Position Profile Position: Customer Experience Functional Lead - BaseCamp Position Incumbent: Company: Location: Reporting to: Meridian Energy Christchurch Business Change Manager Date: December 2008 This
Chris T. Cartwright, Intercultural Communication Institute Mike Greto, Aperian Global Cheryl D. Young, Miami University of Ohio
 Chris T. Cartwright, Intercultural Communication Institute Mike Greto, Aperian Global Cheryl D. Young, Miami University of Ohio Session Objectives Understand - culture impacts interactions Recognize characteristics
Chris T. Cartwright, Intercultural Communication Institute Mike Greto, Aperian Global Cheryl D. Young, Miami University of Ohio Session Objectives Understand - culture impacts interactions Recognize characteristics
pm4dev, 2016 management for development series Project Scope Management PROJECT MANAGEMENT FOR DEVELOPMENT ORGANIZATIONS
 pm4dev, 2016 management for development series Project Scope Management PROJECT MANAGEMENT FOR DEVELOPMENT ORGANIZATIONS PROJECT MANAGEMENT FOR DEVELOPMENT ORGANIZATIONS A methodology to manage development
pm4dev, 2016 management for development series Project Scope Management PROJECT MANAGEMENT FOR DEVELOPMENT ORGANIZATIONS PROJECT MANAGEMENT FOR DEVELOPMENT ORGANIZATIONS A methodology to manage development
Child Selection. Overview. Process steps. Objective: A tool for selection of children in World Vision child sponsorship
 Sponsorship in Programming tool Child Selection Objective: A tool for selection of children in World Vision child sponsorship We ve learned some things about selecting children. It is not a separate sponsorship
Sponsorship in Programming tool Child Selection Objective: A tool for selection of children in World Vision child sponsorship We ve learned some things about selecting children. It is not a separate sponsorship
Survey Results on perceptions between managers and employees
 Survey Results on perceptions between managers and employees Our Aim Retention of talent remains one of the greatest challenges to organizations today. Likewise, one of the most salient variables influencing
Survey Results on perceptions between managers and employees Our Aim Retention of talent remains one of the greatest challenges to organizations today. Likewise, one of the most salient variables influencing
What was the impact for you? For the patient? How did it turn out? How has this helped you in your job? What was the result?
 EXAMPLE VALUE BASED INTERVIEW QUESTIONS VALUE LEADING QUESTION FOLLOW UP QUESTIONS KEY CRITERIA Compassion Give me an example of a time when you were particularly perceptive regarding a Describe what you
EXAMPLE VALUE BASED INTERVIEW QUESTIONS VALUE LEADING QUESTION FOLLOW UP QUESTIONS KEY CRITERIA Compassion Give me an example of a time when you were particularly perceptive regarding a Describe what you
WHO GLOBAL COMPETENCY MODEL
 1. Core Competencies WHO GLOBAL COMPETENCY MODEL 1) COMMUNICATING IN A CREDIBLE AND EFFECTIVE WAY Definition: Expresses oneself clearly in conversations and interactions with others; listens actively.
1. Core Competencies WHO GLOBAL COMPETENCY MODEL 1) COMMUNICATING IN A CREDIBLE AND EFFECTIVE WAY Definition: Expresses oneself clearly in conversations and interactions with others; listens actively.
i2isales Training Solution - Sales Management
 Please note: This document has been created due to requests from some of our customers for an off the shelf solution. It represents a very basic outline of the type of offering(s) we provide - and should
Please note: This document has been created due to requests from some of our customers for an off the shelf solution. It represents a very basic outline of the type of offering(s) we provide - and should
Does Your Business Strategy Prioritize Talent Management?
 ISSUE ANALYSIS Does Your Business Strategy Prioritize Talent Management? Successful talent management strategy starts with leadership By: Lynn Roger, Chief Talent Officer, BMO Financial Group Executive
ISSUE ANALYSIS Does Your Business Strategy Prioritize Talent Management? Successful talent management strategy starts with leadership By: Lynn Roger, Chief Talent Officer, BMO Financial Group Executive
Certificate III in Government PSP30112 Description
 Certificate III in Government PSP30112 Description This generalist qualification covers entry-level competencies for a career in the public sector, with a particular focus on meeting the ethical and legislative
Certificate III in Government PSP30112 Description This generalist qualification covers entry-level competencies for a career in the public sector, with a particular focus on meeting the ethical and legislative
Which is more effective and beneficial to the success of a business, a Democratic or
 Which is more effective and beneficial to the success of a business, a Democratic or Hierarchical organisation? Introduction What is the right and the best way to manage people to maximize their productivity
Which is more effective and beneficial to the success of a business, a Democratic or Hierarchical organisation? Introduction What is the right and the best way to manage people to maximize their productivity
THE FOUR NON NEGOTIABLES
 THE FOUR NON NEGOTIABLES ACADEMIC EXCELLENCE COLLEGE AND CAREER READINESS SAFE AND SUPPORTIVE LEARNING ENVIRONMENT PURPOSEFUL, TIMELY TWO WAY COMMUNICATION ECISD STRATEGIC PLAN 2015 2016 1 Beliefs Definition:
THE FOUR NON NEGOTIABLES ACADEMIC EXCELLENCE COLLEGE AND CAREER READINESS SAFE AND SUPPORTIVE LEARNING ENVIRONMENT PURPOSEFUL, TIMELY TWO WAY COMMUNICATION ECISD STRATEGIC PLAN 2015 2016 1 Beliefs Definition:
TRANSPORT FOR LONDON CORPORATE PANEL
 AGENDA ITEM 4 TRANSPORT FOR LONDON CORPORATE PANEL SUBJECT: EMPLOYEE ENGAGEMENT DATE: 17 NOVEMBER 2009 1 PURPOSE AND DECISION REQUIRED 1.1 The purpose of this report is to advise the Panel on TfL s approach
AGENDA ITEM 4 TRANSPORT FOR LONDON CORPORATE PANEL SUBJECT: EMPLOYEE ENGAGEMENT DATE: 17 NOVEMBER 2009 1 PURPOSE AND DECISION REQUIRED 1.1 The purpose of this report is to advise the Panel on TfL s approach
Team Dynamics in Process Simplification. Introduction to Process Improvement Slide 1
 Team Dynamics in Process Simplification Understanding the Basics of Team Development Slide 1 Teams are all around us Slide 2 Each team should: Define their principles in alignment with organizational vision
Team Dynamics in Process Simplification Understanding the Basics of Team Development Slide 1 Teams are all around us Slide 2 Each team should: Define their principles in alignment with organizational vision
HR Transformation Update. HR Community Town Hall June 18, 2013
 HR Transformation Update HR Community Town Hall June 18, 2013 1 Today s agenda Review HR Transformation initiative Discuss results of HR Online Survey Review guiding principles and HR Vision Share leading
HR Transformation Update HR Community Town Hall June 18, 2013 1 Today s agenda Review HR Transformation initiative Discuss results of HR Online Survey Review guiding principles and HR Vision Share leading
A guide to helping people to succeed at work
 Coaching: Helping you to improve social outcomes A guide to helping people to succeed at work This guide is for anyone wanting to use coaching skills to help colleagues succeed. In particular, it is intended
Coaching: Helping you to improve social outcomes A guide to helping people to succeed at work This guide is for anyone wanting to use coaching skills to help colleagues succeed. In particular, it is intended
Business Benefits of Volunteering
 Business Benefits of Volunteering An introduction to skills based volunteering Mari Frengstad TABLE OF CONTENT: Executive Summary... 3 Introduction... 5 What skills are key to Hammerson s success?... 5
Business Benefits of Volunteering An introduction to skills based volunteering Mari Frengstad TABLE OF CONTENT: Executive Summary... 3 Introduction... 5 What skills are key to Hammerson s success?... 5
50 Tough Interview Questions
 You and Your Accomplishments 1. Tell me a little about yourself. 50 Tough Interview Questions Because this is often the opening question, be careful that you don t run off at the mouth. Keep your answer
You and Your Accomplishments 1. Tell me a little about yourself. 50 Tough Interview Questions Because this is often the opening question, be careful that you don t run off at the mouth. Keep your answer
BC Public Service Competencies
 BC Public Service Competencies Competencies that support LEADING PEOPLE For Executive and Directors: Motivating for Peak Performance Motivating for peak performance involves knowledge and skills in using
BC Public Service Competencies Competencies that support LEADING PEOPLE For Executive and Directors: Motivating for Peak Performance Motivating for peak performance involves knowledge and skills in using
Project Human Resource Management, PMBOK Forth Edition
 Project Human Resource Management, PMBOK Forth Edition PMP Sep, 2009 Administrative Here are some tips for your exam, but of course it is not an exhaustive list. Some project managers will have different
Project Human Resource Management, PMBOK Forth Edition PMP Sep, 2009 Administrative Here are some tips for your exam, but of course it is not an exhaustive list. Some project managers will have different
Appendix B Data Quality Dimensions
 Appendix B Data Quality Dimensions Purpose Dimensions of data quality are fundamental to understanding how to improve data. This appendix summarizes, in chronological order of publication, three foundational
Appendix B Data Quality Dimensions Purpose Dimensions of data quality are fundamental to understanding how to improve data. This appendix summarizes, in chronological order of publication, three foundational
QUALITY TOOLBOX. Understanding Processes with Hierarchical Process Mapping. Robert B. Pojasek. Why Process Mapping?
 QUALITY TOOLBOX Understanding Processes with Hierarchical Process Mapping In my work, I spend a lot of time talking to people about hierarchical process mapping. It strikes me as funny that whenever I
QUALITY TOOLBOX Understanding Processes with Hierarchical Process Mapping In my work, I spend a lot of time talking to people about hierarchical process mapping. It strikes me as funny that whenever I
Process Governance: Definitions and Framework, Part 1
 Process Governance: Definitions and Framework, Part 1 Rafael Paim & Raquel Flexa This Article if the first of a two-part series discussing governance frameworks. In Part `, four existing frameworks are
Process Governance: Definitions and Framework, Part 1 Rafael Paim & Raquel Flexa This Article if the first of a two-part series discussing governance frameworks. In Part `, four existing frameworks are
Software review: A process change model to meet the Enterprise Marketing Automation (EMA) vision Received: 20th July, 2000
 Software review: A process change model to meet the Enterprise Marketing Automation (EMA) vision Received: 20th July, 2000 Shaun Doyle is Chairman of Intrinsic, a campaign management software company.
Software review: A process change model to meet the Enterprise Marketing Automation (EMA) vision Received: 20th July, 2000 Shaun Doyle is Chairman of Intrinsic, a campaign management software company.
Strategic Choices and Key Success Factors for Law Firms June, 2010. Alan Hodgart
 Strategic Choices and Key Success Factors for Law Firms June, 2010 Alan Hodgart The Association of Danish Law Firms 1 Huron Consulting Group Inc. All rights reserved. Huron is a management consulting firm
Strategic Choices and Key Success Factors for Law Firms June, 2010 Alan Hodgart The Association of Danish Law Firms 1 Huron Consulting Group Inc. All rights reserved. Huron is a management consulting firm
Human Resources 101. Human Resources Series. Agenda - HR s Strategic Role. Module 1: HR s Strategic Role
 Human Resources 101 Module 1: HR s Strategic Role University of California San Francisco Human Resources Training Series HR Development & Training Human Resources Series 1. HR s Strategic Role 2. Effective
Human Resources 101 Module 1: HR s Strategic Role University of California San Francisco Human Resources Training Series HR Development & Training Human Resources Series 1. HR s Strategic Role 2. Effective
LEADERSHIP DEVELOPMENT FRAMEWORK
 LEADERSHIP DEVELOPMENT FRAMEWORK February 13, 2008 LEADERSHJP PERSPECTIVE I consider succession planning to be the most important duty I have as the Director of the NOAA Corps. As I look toward the future,
LEADERSHIP DEVELOPMENT FRAMEWORK February 13, 2008 LEADERSHJP PERSPECTIVE I consider succession planning to be the most important duty I have as the Director of the NOAA Corps. As I look toward the future,
2 Organizations and Organizational Structures 2.1 Functional and Project Organizations, Typical Goals and Performance Measures
 2 Organizations and Organizational Structures 2.1 Functional and Project Organizations, Typical Goals and Performance Measures The history of organizations is probably as long as the history of mankind.
2 Organizations and Organizational Structures 2.1 Functional and Project Organizations, Typical Goals and Performance Measures The history of organizations is probably as long as the history of mankind.
Action plan to prevent problem gaming and problem gambling
 Action plan Action plan to prevent problem gaming and problem gambling (2009-2011) Action plan Action plan to prevent problem gaming and problem gambling (2009-2011) Preface The range and the accessibility
Action plan Action plan to prevent problem gaming and problem gambling (2009-2011) Action plan Action plan to prevent problem gaming and problem gambling (2009-2011) Preface The range and the accessibility
SENIOR MANAGEMENT APPRAISAL
 Report Resources Committee 2 April 21 SENIOR MANAGEMENT APPRAISAL 5-1. Reason for Report To appraise Members of developments since the Best Value and Community Planning Audit highlighted a number of issues
Report Resources Committee 2 April 21 SENIOR MANAGEMENT APPRAISAL 5-1. Reason for Report To appraise Members of developments since the Best Value and Community Planning Audit highlighted a number of issues
INTEGRAL 360 LEADERSHIP & MANAGEMENT PROFILE
 INTEGRAL 30 LEADERSHIP & MANAGEMENT PROFILE Sammy Sample INTRODUCTION TO THE INTEGRAL LEADERSHIP & MANAGEMENT 30 PROFILE (ILMP) The Integral Leadership & Management 30 Profile (ILMP) is a 30 feedback process
INTEGRAL 30 LEADERSHIP & MANAGEMENT PROFILE Sammy Sample INTRODUCTION TO THE INTEGRAL LEADERSHIP & MANAGEMENT 30 PROFILE (ILMP) The Integral Leadership & Management 30 Profile (ILMP) is a 30 feedback process
ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOR
 Overview ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOR Lesson 2 In last lecture we tried to understand the term of organizational behavior its need and its impact on the organization. The focus in this discussion is to have
Overview ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOR Lesson 2 In last lecture we tried to understand the term of organizational behavior its need and its impact on the organization. The focus in this discussion is to have
The Audit of Best Value and Community Planning The City of Edinburgh Council. Best Value audit 2016
 The Audit of Best Value and Community Planning The City of Edinburgh Council Best Value audit 2016 Report from the Controller of Audit February 2016 The Accounts Commission The Accounts Commission is the
The Audit of Best Value and Community Planning The City of Edinburgh Council Best Value audit 2016 Report from the Controller of Audit February 2016 The Accounts Commission The Accounts Commission is the
Report on: Strategic and operational planning 2016/17 to 2020/21
 To: The Board For meeting on: 25 February 2016 Agenda item: 7 Report by: Bob Alexander Report on: Strategic and operational planning 2016/17 to 2020/21 Purpose 1. The purpose of this paper is to invite
To: The Board For meeting on: 25 February 2016 Agenda item: 7 Report by: Bob Alexander Report on: Strategic and operational planning 2016/17 to 2020/21 Purpose 1. The purpose of this paper is to invite
INVESTORS IN PEOPLE ASSESSMENT REPORT
 INVESTORS IN PEOPLE ASSESSMENT REPORT Birmingham City University Human Resources Department Page: 1 of 19 Key Information Assessment Type Review Investors in People Specialist Name Bob Morrison Visit Date
INVESTORS IN PEOPLE ASSESSMENT REPORT Birmingham City University Human Resources Department Page: 1 of 19 Key Information Assessment Type Review Investors in People Specialist Name Bob Morrison Visit Date
THE STAR MODEL JAY R. GALBRAITH
 THE STAR MODEL JAY R. GALBRAITH The Star Model framework for organization design is the foundation on which a company bases its design choices. The framework consists of a series of design policies that
THE STAR MODEL JAY R. GALBRAITH The Star Model framework for organization design is the foundation on which a company bases its design choices. The framework consists of a series of design policies that
ARHINFUL LORETTA ABA A (844974) SAM PETRA MENSIMAA (844794) AHMED SK ASHIF (843888)
 GROUP MEMBERS ARHINFUL LORETTA ABA A (844974) SAM PETRA MENSIMAA (844794) AHMED SK ASHIF (843888) P W 1 THE HRM BUSINESS MODEL OF ENTERPRISE LIFE ASSURANCE COMPANY GHANA (ELAC) CONTENT ENTERPRISE LIFE
GROUP MEMBERS ARHINFUL LORETTA ABA A (844974) SAM PETRA MENSIMAA (844794) AHMED SK ASHIF (843888) P W 1 THE HRM BUSINESS MODEL OF ENTERPRISE LIFE ASSURANCE COMPANY GHANA (ELAC) CONTENT ENTERPRISE LIFE
Keystone of Lean Six Sigma: Strong Middle Management
 Keystone of Lean Six Sigma: Strong Middle Management Many companies embarking on Lean efforts find that their organization is too rigid and top-down to support the management principles of Lean and Six
Keystone of Lean Six Sigma: Strong Middle Management Many companies embarking on Lean efforts find that their organization is too rigid and top-down to support the management principles of Lean and Six
Team Building. HR can provide you with support for building effective team work.
 Team Building HR can provide you with support for building effective team work. Developing Effective Teams Model Typically we work with the leader or a smaller working group to determine what they would
Team Building HR can provide you with support for building effective team work. Developing Effective Teams Model Typically we work with the leader or a smaller working group to determine what they would
Skanska Group Diversity and Inclusion Vision 2020 Q&A
 Skanska Group Diversity and Inclusion Vision 2020 Q&A Skanska Group Diversity and Inclusion Vision 2020 Q&A Front cover New Karolinska Solna (NKS) the university hospital of the future is the largest contract
Skanska Group Diversity and Inclusion Vision 2020 Q&A Skanska Group Diversity and Inclusion Vision 2020 Q&A Front cover New Karolinska Solna (NKS) the university hospital of the future is the largest contract
The integrated leadership system. ILS support tools. Leadership pathway: Individual profile EL1
 The integrated leadership system ILS support tools Leadership pathway: Individual profile Executive Level 1 profile Shapes strategic thinking Achieves results Cultivates productive working relationships
The integrated leadership system ILS support tools Leadership pathway: Individual profile Executive Level 1 profile Shapes strategic thinking Achieves results Cultivates productive working relationships
GUIDE TO ERP IMPLEMENTATIONS: WHAT YOU NEED TO CONSIDER
 GUIDE TO ERP IMPLEMENTATIONS: WHAT YOU NEED TO CONSIDER INTRODUCTION You have decided that your business needs a change. It may be to keep up with your competition, to become more efficient and lower operational
GUIDE TO ERP IMPLEMENTATIONS: WHAT YOU NEED TO CONSIDER INTRODUCTION You have decided that your business needs a change. It may be to keep up with your competition, to become more efficient and lower operational
INSTITUTE OF TRANSLATION AND INTERPRETING
 INSTITUTE OF TRANSLATION AND INTERPRETING CODE OF PROFESSIONAL CONDUCT 1 CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION 2. THE PURPOSE OF THE CODE 3. PRINCIPLES OF PRACTICE 4. PROFESSIONAL VALUES 5. AMENDMENTS 6. PRINCIPLE
INSTITUTE OF TRANSLATION AND INTERPRETING CODE OF PROFESSIONAL CONDUCT 1 CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION 2. THE PURPOSE OF THE CODE 3. PRINCIPLES OF PRACTICE 4. PROFESSIONAL VALUES 5. AMENDMENTS 6. PRINCIPLE
Setting SMART mentoring goals ensures a successful learning experience for mentors and mentees.
 Setting SMART mentoring goals ensures a successful learning experience for mentors and mentees. 50 T+D January 2011 Photo by Veer The Goal-Driven Mentoring Relationship By Lois J. Zachary and Lory A. Fischler
Setting SMART mentoring goals ensures a successful learning experience for mentors and mentees. 50 T+D January 2011 Photo by Veer The Goal-Driven Mentoring Relationship By Lois J. Zachary and Lory A. Fischler
ScottishPower Competency Based Recruitment Competency Guidelines External Candidate. pp077682 ScottishPower [Pick the date]
![ScottishPower Competency Based Recruitment Competency Guidelines External Candidate. pp077682 ScottishPower [Pick the date] ScottishPower Competency Based Recruitment Competency Guidelines External Candidate. pp077682 ScottishPower [Pick the date]](/thumbs/40/21430508.jpg) ScottishPower Competency Based Recruitment Competency Guidelines External Candidate pp077682 ScottishPower [Pick the date] Aims and Objectives This document will give you an overview of the selection process
ScottishPower Competency Based Recruitment Competency Guidelines External Candidate pp077682 ScottishPower [Pick the date] Aims and Objectives This document will give you an overview of the selection process
Procurement Programmes & Projects P3M3 v2.1 Self-Assessment Instructions and Questionnaire. P3M3 Project Management Self-Assessment
 Procurement Programmes & Projects P3M3 v2.1 Self-Assessment Instructions and Questionnaire P3M3 Project Management Self-Assessment Contents Introduction 3 User Guidance 4 P3M3 Self-Assessment Questionnaire
Procurement Programmes & Projects P3M3 v2.1 Self-Assessment Instructions and Questionnaire P3M3 Project Management Self-Assessment Contents Introduction 3 User Guidance 4 P3M3 Self-Assessment Questionnaire
RISK MANAGEMENT POLICY
 RISK MANAGEMENT POLICY Approved by Governing Authority February 2016 1. BACKGROUND 1.1 The focus on governance in corporate and public bodies continues to increase. It resulted in an expansion from the
RISK MANAGEMENT POLICY Approved by Governing Authority February 2016 1. BACKGROUND 1.1 The focus on governance in corporate and public bodies continues to increase. It resulted in an expansion from the
THE 7 HABITS OF HIGHLY EFFECTIVE PEOPLE By Stephen R. Covey
 THE 7 HABITS OF HIGHLY EFFECTIVE PEOPLE By Stephen R. Covey PART ONE PARADIGMS AND PRINCIPLES INSIDE-OUT 1. If we want to change a situation, we first have to change. To do this effectively, we must first
THE 7 HABITS OF HIGHLY EFFECTIVE PEOPLE By Stephen R. Covey PART ONE PARADIGMS AND PRINCIPLES INSIDE-OUT 1. If we want to change a situation, we first have to change. To do this effectively, we must first
It will be the line manager s responsibility to structure the programme in such a way that both parties are clear about what to expect.
 A GUIDE TO MANAGING PROBATION PERIODS SUCCESSFULLY During a new employee's probationary period, the line manager should follow a formal structured procedure that is aimed at assessing and reviewing the
A GUIDE TO MANAGING PROBATION PERIODS SUCCESSFULLY During a new employee's probationary period, the line manager should follow a formal structured procedure that is aimed at assessing and reviewing the
