Competitive Organisational Structures
|
|
|
- Oswald Johnston
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Competitive Organisational Structures Organisational structure basics Introduction The way in which a business is organised has a direct effect on its competitiveness. For a business to be able to achieve its aims and objectives, it needs to organise its people in a suitable way that is known as the organisational structure. The organisational structure of a business is important because it determines: Authority and responsibility who is responsible for whom and who is in charge? Individual job roles and titles The people to whom others are accountable The formal routes through which communication flows in the business One way to think of the organisation structure is of an explanation of the command and control system in a business. The organisation structure of a business will depend on several factors, including: Factor Size of the business Type of business Management and leadership style The competitive environment Explanation Small businesses will tend to have informal or flat hierarchical structures. Larger and more complex businesses will develop more complicated and detailed structures involving more layers of hierarchy, departments and functions Does the business operate from just one or several locations? Is the business in the service or manufacturing sector? Does it have overseas operations or outsource any significant business activities? Is the workforce mainly unskilled, semi-skilled, highly skilled? Often over-looked, but very important. An autocratic leadership style will often result in a very different structure compared with one designed by a leader who prefers to delegate responsibility Organisation structures are often influenced and changed by developments in the market for example changes in the use of distribution channels, suppliers, competitor actions Functional structures The traditional organisation structure of a business has focused on the functions, departments and main activities of a business. The traditional functional structure is based around certain principles of organisation which have historically been seen as important, including the principles of:
2 Principle Specialisation Authority Responsibility Definition Span of control Chain of command What is involved Employees should be a member of one specialisation or function In every organisation, authority for taking a decision must rest somewhere + the line of authority should be clear A superior is responsible for the actions of his/her subordinates Each position in the structure has a clearly defined role and responsibility No person should supervise too many subordinates There is a clear, unbroken line of authority and responsibility from the top of the organisation down to the bottom The result of these principles is the common functional structure an example of which is shown below: The main advantages and disadvantages of using a functional structure can be summarised as follows: Advantages Simple to understand Control is from the top down gives business a strong sense of direction Clear lines of communication and command Disadvantages Decision-making can soon become bureaucratic and too slow Structure is prone to inter-departmental conflicts (e.g. marketing arguing with finance) Not always easy to get co-ordinated action
3 Allows specialists to manage in their relevant functional areas Encourages employees to seek promotion across departments or functions Employees not encouraged to develop an overview of the whole business they can be stuck in silos Little reward for functions working together Matrix structures This type of structure combines the traditional departments seen in functional structures with project teams. In a matrix structure, individuals work across teams and projects as well as within their own department or function. For example, a project or task team established to develop a new product might include engineers and design specialists as well as those with marketing, financial, personnel and production skills. These teams can be temporary or permanent depending on the tasks they are asked to complete. Each team member can find himself/herself with two managers - their normal functional manager as well as the team leader of the project. An example of a matrix structure is illustrated below: Matrix structures have advantages and disadvantages. Advantages Can help to break down traditional department barriers, improving communication across the entire organisation Can allow individuals to use particular skills within a variety of contexts Avoid the need for several departments to meet regularly, so reducing costs and improving coordination Likely to result in greater motivation amongst the team members
4 Encourages cross-fertilisation of ideas across departments e.g. helping to share good practice and ideas A good way of sharing resources across departments which can make a project more cost-effective Disadvantages Members of project teams may have divided loyalties as they report to two line managers. Equally, this scenario can put project team members under a heavy pressure of work. There may not be a clear line of accountability for project teams given the complex nature of matrix structures. Difficult to co-ordinate It takes time for matrix team members to get used to working in this kind of structure Team members may neglect their functional responsibilities It is important to remember that a matrix structure often sites alongside a traditional functional structure it is not necessarily a replacement. Informal structures Nicely drawn, clearly labelled organisational structures look good in business studies textbooks. However, it is relatively rare to actually find them in use in real businesses. You would be very unlikely to find a functional organisational structure in a small or mediumsized business, and even in complex businesses, the organisation structure is probably outof-date and gathering dust in the HR Director s drawer. The reality is that organisation charts and structures usually do not describe what really happens in business. Many businesses rely on informal structures to make decisions rather than the command and control approach of functional structures. Centralised versus decentralised structures One of the organisational issues that a business needs to address is where decision-making power resides in the structure. Decision-making is about authority. A key question is whether authority should rest with senior management at the centre of a business (centralised), or whether it should be delegated further down the hierarchy, away from the centre (decentralised) The choice between centralised or decentralised is not an either/or choice. Most large businesses necessarily involve a degree of decentralisation when it starts to operate from several locations or it adds new business units and markets. The issue is really how much independence do business units or groups within a business have when it comes to the key decisions? Centralised structures
5 Businesses that have a centralised structure keep decision-making firmly at the top of the hierarchy (amongst the most senior management). Fast-food businesses like Burger King, Pizza Hut and McDonalds use a predominantly centralised structure to ensure that control is maintained over their many thousands of outlets. The need to ensure consistency of customer experience and quality at every location, together with a desire to exploit economies of scale, are the main reasons for this choice. The main advantages and disadvantages of this approach can be summarised as follows: Advantages Easier to implement common policies and practices for the business as a whole Prevents other parts of the business from becoming too independent Easier to co-ordinate and control from the centre e.g. with budgets Economies of scale and overhead savings easier to achieve Greater use of specialisation Quicker decision-making (usually) easier to show strong leadership Disadvantages More bureaucratic often extra layers in the hierarchy Local or junior managers are likely to much closer to customer needs Lack of authority down the hierarchy may reduce manager motivation Customer service does not benefit from flexibility and speed in local decision-making Decentralised structures In a decentralised structure, decision-making is spread out to include more junior managers in the hierarchy, as well as individual business units or trading locations. Good examples of businesses which use a decentralised structure include the major supermarket chains like WM Morrison and Tesco. Each supermarket has a store manager who can make certain decisions concerning areas like staffing, sales promotions. The store manager is responsible to a regional or area manager. Hotel chains are particularly keen on using decentralised structures so that local hotel managers are empowered to make on-thespot decisions to handle customer problems or complaints. The main advantages and disadvantages of this approach can be summarised as follows: Advantages Decisions are made closer to the customer Better able to respond to local circumstances Improved level of customer service Consistent with aiming for a flatter hierarchy Disadvantages Decision-making is not necessarily strategic More difficult to ensure consistent practices and policies (customers might prefer consistency from location to location) May be some diseconomies of scale e.g. duplication of roles Who provides strong leadership when needed
6 Good way of training and developing junior management Should improve staff motivation (e.g. in a crisis)? Harder to achieve tight financial control risk of cost-overruns Delayering The traditional way to achieve a flatter organisational structure is through delayering. Delayering involves removing one or more levels of hierarchy from the organisational structure. Frequently, the layers removed are those containing middle managers. For example, many high-street banks no longer have a manager in each of their branches, preferring to appoint a manager to oversee a number of branches. Some schools adopt this policy too with a director of studies looking after several schools in a local area. Delayering does not necessarily involve cutting jobs and overheads. But it does usually mean increasing the average span of control of senior managers within the business. This can, in effect, chop the number of layers without removing a single name from the payroll, as the people affected are moved elsewhere in the business. However, it is fair to say that, increasingly delayering is seen as a way of reducing operating costs, particularly as a response to the economic downturn. Delayering can offer a number of advantages to business: It offers opportunities for better delegation, empowerment and motivation as the number of managers is reduced and more authority passed down the hierarchy It can improve communication within the business as messages have to pass through fewer levels of hierarchy It can remove departmental rivalry if department heads are removed and the workforce is organised more in teams It can reduce costs as fewer (expensive) managers are required It can encourage innovation It brings managers into closer contact with the business customers which should (in theory) result in better customer service But disadvantages exist too, making a decision to delayer less clear cut: Not all organisations are suited to flatter organisational structures - mass production industries with low-skilled employees may not adapt easily Delayering can have a negative impact on motivation due to job losses, especially if it is really just an excuse for redundancies A period of disruption may occur as people take on new responsibilities and fulfil new roles
7 Those managers remaining will have a wider span of control which, if it is too wide, can damage communication within the business. There is also a danger of increasing the workload of the remaining managers beyond that which is reasonable. Delayering may create skills shortages within the business a danger is that delayering means that the business loses managers and staff with valuable experience Any programme of delayering needs to be carefully thought-through. Get it wrong, and the damage to a business can be significant. Flexible working What is flexible working? The term describes a range of employment options designed to help employees balance work and home life. Why use the term flexible? It is because flexible working relates to working arrangements where there are a variety of options offered to employees in terms of working time, working location and the pattern of working. Amongst the most popular flexible working practices are the following: Part-time working Term-time working Working from home Flexitime Career breaks Job sharing Annual hours contracts Mobile working Shift swapping Of the options listed above, by far the most popular in the UK currently is part-time working. 86% of businesses surveyed by the CPID in 2007 offered part-time working options. Job sharing, flexitime and working from home are also increasingly popular. There are good business reasons why businesses are increasingly likely to offer employees one or more flexible working options. For example: Most importantly, savings on costs. A business can make substantial savings on overheads if it does not have to provide office and other accommodation for so many employees or if staff can work from home rather than commute into work every day As a way of helping with recruitment and staff retention. There is lots of evidence that flexible working results in better job satisfaction and higher staff morale To reflect the changing profile of the UK workforce. There are more women in the labour market and an ageing population as a result, it is increasingly common for staff to have caring responsibilities outside work To take advantage of developments in technology it is now simple and costeffective for employees to be able to access their employers online and other networked systems, and to communicate digitally with colleagues An increasing need for businesses to be able to deliver services to customers on a 24/7 basis. Flexible working makes it easier for businesses to offer extended opening hours, for example
8 The credit crunch - some organisations, for example firms of lawyers and accountants, have offered part-time working or career breaks as a method of avoiding or minimising redundancies To meet employment legislation increasingly the law allows certain groups of employees the legal right to request flexible working Whilst there any many advantages to flexible working, it is not always simple or appropriate to introduce it. Amongst the concerns that employers often raise about flexible working are: Additional administrative work and red-tape involved in setting up and running flexible working The potential loss of customers if key employees reduce their working hours Lower employee productivity Inability to substitute for certain skills if certain employees are absent (a common concern of smaller businesses_ Managers finding it difficult to manage or administer the flexibility A recent study by the Joseph Rowntree Foundation found that flexible working practices were most likely to be found in the following situations: In large organisations and businesses In public sector organisations Where the business does not operate in a highly competitive industry Where there are recognised unions Where there is a well established HR function Where there is high employee involvement in decision-making In workforces with larger proportions of women Where there is a highly educated workforce who has a large amount of discretion in organising work (e.g. professions, creative industries) Outsourcing A business does not have to do everything that is required to produce its products and services. A retailer does not design and make the fixtures and fittings that create the shop interior A large consumer products business will not do all its own primary market research A local baker will not grow wheat or even mill it into flour Why don t these businesses do these things? Because there are other businesses that are specialised in the tasks required and can do it better and cheaper. This process is called outsourcing. Outsourcing can be defined as follows:
9 the delegation of one or more business processes to an external provider, who then owns, manages and administers the selected processes to an agreed standard [CIPD] It is important to note that outsourcing is NOT the same thing as offshoring (the two terms are commonly, but wrongly taken as meaning the same thing. Offshoring involves either outsourcing business activities or services to a third party overseas and/or moving business activities or services to another country as a direct or indirect employer. In other words, offshoring does not always involve the services of an external provider. Outsourcing always involves getting another business or organisation to provide the service for you. Most businesses have always outsourced some of their activities. However in recent decades a larger proportion of business activities and processes are now bought-in from suppliers. The main reason for increased outsourcing is normally as a way of reducing costs. However, there can also be some significant gains in the quality and flexibility of the service or product offered. The choice of whether to outsource or not is really part of a debate that a business has about what the scope of its business should be. In other words: What should a business do itself? What should a business buy in from others? There are several factors that a business needs to take into account in deciding whether to do something in-house or whether to outsource. These relate to the corporate and functional objectives of a business and can be summarised as follows: Objective Do it in-house Outsource Quality Cost Speed Flexibility Easier to ensure quality and trace problems if done in-house In-house departments don t have to make a profit so might be cheaper Maybe too small to obtain economies of scale Easier communication Easier to schedule work or production to fit in with business needs Closest to the real needs of the business Ability to respond may be limited by Supplier may be a specialist, with greater experience and better equipment The main reason to outsource. Supplier likely to achieve economies of scale Motivated to keep costs low in order to make a profit Extra costs of communication Speed of response can be set as a requirement of the outsourcing contract Commercial pressure should encourage good performance Suppliers likely to have greater capacity and flexibility than in-house May have to balance conflicting
10 capacity demands from other customers
The three most important things in retailing are location, location and location.
 Location Introduction Most business studies textbooks can t resist starting a section on business location with the following phrase: The three most important things in retailing are location, location
Location Introduction Most business studies textbooks can t resist starting a section on business location with the following phrase: The three most important things in retailing are location, location
Organisational Structure - Basics
 Name: Class: Date Taken: Total Possible Marks: Organisational Structure - Basics Complete the following questions in the time allowed by your teacher. Define the term "organisational structure". List three
Name: Class: Date Taken: Total Possible Marks: Organisational Structure - Basics Complete the following questions in the time allowed by your teacher. Define the term "organisational structure". List three
pm4dev, 2007 management for development series Project Management Organizational Structures PROJECT MANAGEMENT FOR DEVELOPMENT ORGANIZATIONS
 pm4dev, 2007 management for development series Project Management Organizational Structures PROJECT MANAGEMENT FOR DEVELOPMENT ORGANIZATIONS PROJECT MANAGEMENT FOR DEVELOPMENT ORGANIZATIONS A methodology
pm4dev, 2007 management for development series Project Management Organizational Structures PROJECT MANAGEMENT FOR DEVELOPMENT ORGANIZATIONS PROJECT MANAGEMENT FOR DEVELOPMENT ORGANIZATIONS A methodology
Chapter 8: The Internal Environment
 Chapter 8: The Internal Environment Key Revision Points The Internal Functions of Commercial Organisations In competitive business environments, customers are at the centre of all of an organisation's
Chapter 8: The Internal Environment Key Revision Points The Internal Functions of Commercial Organisations In competitive business environments, customers are at the centre of all of an organisation's
Introduction. Page 2 of 11
 Page 1 of 11 Introduction It has been a year since The Walton Centre brought its recruitment function in-house and it was critical that the organisation took this step. This is a specialist organisation
Page 1 of 11 Introduction It has been a year since The Walton Centre brought its recruitment function in-house and it was critical that the organisation took this step. This is a specialist organisation
WE HELP COMPANIES IDENTIFY, SELECT & DEVELOP EXCEPTIONAL LEADERS, MANAGERS & TEAMS
 WE HELP COMPANIES IDENTIFY, SELECT & DEVELOP EXCEPTIONAL LEADERS, MANAGERS & TEAMS HR Solutions & Services www.ajyal-hr.com RECRUITMENT Talent is the single most important item on the minds of CEO s today.
WE HELP COMPANIES IDENTIFY, SELECT & DEVELOP EXCEPTIONAL LEADERS, MANAGERS & TEAMS HR Solutions & Services www.ajyal-hr.com RECRUITMENT Talent is the single most important item on the minds of CEO s today.
Restructure, Redeployment and Redundancy
 Restructure, Redeployment and Redundancy Purpose and Scope From time to time the Lake District National Park Authority will need to reorganise its services and staffing to meet changes that arise in future
Restructure, Redeployment and Redundancy Purpose and Scope From time to time the Lake District National Park Authority will need to reorganise its services and staffing to meet changes that arise in future
THE PROFESSIONAL S FIRST CHOICE. Bridging the Gap How technology can help HR reach out to line management A Croner white paper
 THE PROFESSIONAL S FIRST CHOICE Bridging the Gap How technology can help HR reach out to line management A Croner white paper Executive summary The practice of human resources, or HR, has reached a transitional
THE PROFESSIONAL S FIRST CHOICE Bridging the Gap How technology can help HR reach out to line management A Croner white paper Executive summary The practice of human resources, or HR, has reached a transitional
Redeployment of staff within the Public Service
 ISBN 0-478-24479-7 December 2004 Redeployment of staff within the Public Service Context This paper has been prepared under the Human Resources Framework by a project team comprising representatives from
ISBN 0-478-24479-7 December 2004 Redeployment of staff within the Public Service Context This paper has been prepared under the Human Resources Framework by a project team comprising representatives from
EMPLOYEE OUTLOOK. April 2016 EMPLOYEE VIEWS ON WORKING LIFE FOCUS. Commuting and flexible working
 EMPLOYEE OUTLOOK EMPLOYEE VIEWS ON WORKING LIFE April 2016 FOCUS Commuting and flexible working The CIPD is the professional body for HR and people development. The not-for-profit organisation champions
EMPLOYEE OUTLOOK EMPLOYEE VIEWS ON WORKING LIFE April 2016 FOCUS Commuting and flexible working The CIPD is the professional body for HR and people development. The not-for-profit organisation champions
Handling Redundancies and Layoffs
 Handling Redundancies and Layoffs What is redundancy? For the purposes of these guidelines the terms redundancy 1, layoff 2 and retrenchment are used interchangeably and describe the situation where the
Handling Redundancies and Layoffs What is redundancy? For the purposes of these guidelines the terms redundancy 1, layoff 2 and retrenchment are used interchangeably and describe the situation where the
Outsourcing. Definitions. Outsourcing Strategy. Potential Advantages of an Outsourced Service. Procurement Process
 CIPS takes the view that the outsourcing of services to specialist providers can often lead to better quality of services and increased value for money. Purchasing and supply management professionals should
CIPS takes the view that the outsourcing of services to specialist providers can often lead to better quality of services and increased value for money. Purchasing and supply management professionals should
Human Resources Trainee
 Human Resources Trainee SUMMARY INFORMATION HR TRAINEE (Vacancy Number 351) Duration 3 years Salary 16,131 to 18,588 per annum Entry qualifications English and Maths Highers What is HR? Human Resources
Human Resources Trainee SUMMARY INFORMATION HR TRAINEE (Vacancy Number 351) Duration 3 years Salary 16,131 to 18,588 per annum Entry qualifications English and Maths Highers What is HR? Human Resources
D 1. Working with people Develop productive working relationships with colleagues. Unit Summary. effective performance.
 1 Develop productive working relationships with colleagues Unit Summary What is the unit about? This unit is about developing working relationships with colleagues, within your own organisation and within
1 Develop productive working relationships with colleagues Unit Summary What is the unit about? This unit is about developing working relationships with colleagues, within your own organisation and within
3 Why Flexibility? Employers and Trades Unions
 3 Why Flexibility? Employers and Trades Unions Employer perspectives There are a variety of reasons why employers adopt new, more flexible patterns of working time. In part, they may be responding to changes
3 Why Flexibility? Employers and Trades Unions Employer perspectives There are a variety of reasons why employers adopt new, more flexible patterns of working time. In part, they may be responding to changes
THE HEALTH & SOCIAL CARE
 THE HEALTH & SOCIAL CARE SECTOR in greater manchester overview of skills ISSUES 1. INTRODUCTION This briefing summarises the findings of primary and secondary research in respect of the skills and training
THE HEALTH & SOCIAL CARE SECTOR in greater manchester overview of skills ISSUES 1. INTRODUCTION This briefing summarises the findings of primary and secondary research in respect of the skills and training
JSE Accredited to Audit JSE Listed Companies
 Internal Audit: JSE Accredited to Audit JSE Listed Companies Background Since the introduction of King III, the need for a risk based internal audit has been emphasised through the following five principles;
Internal Audit: JSE Accredited to Audit JSE Listed Companies Background Since the introduction of King III, the need for a risk based internal audit has been emphasised through the following five principles;
How To Manage An In House Legal Team
 December 2014 A Guide for General Counsel Structuring your legal team contents: THE TEAM 03 THE STRUCTURE 04 RISK AND COMPLIANCE 07 LEVEL AND NATURE OF OUTSOURCING 08 FUNCTIONS 09 SUPPORT SERVICES 10 CONCLUSION
December 2014 A Guide for General Counsel Structuring your legal team contents: THE TEAM 03 THE STRUCTURE 04 RISK AND COMPLIANCE 07 LEVEL AND NATURE OF OUTSOURCING 08 FUNCTIONS 09 SUPPORT SERVICES 10 CONCLUSION
Test your talent How does your approach to talent strategy measure up?
 1 Test your talent How does your approach to talent strategy measure up? Talent strategy or struggle? Each year at Head Heart + Brain we carry out research projects to help understand best practice in
1 Test your talent How does your approach to talent strategy measure up? Talent strategy or struggle? Each year at Head Heart + Brain we carry out research projects to help understand best practice in
BMJcareers. Informing Choices
 : The Need for Career Advice in Medical Training How should the support provided to doctors and medical students to help them make career decisions during their training be improved? Experience elsewhere
: The Need for Career Advice in Medical Training How should the support provided to doctors and medical students to help them make career decisions during their training be improved? Experience elsewhere
Types of Business Organisation
 Types of Business Organisation Revision Presentations 2004 Introduction A business is always owned by someone. This can just be one person, or thousands. So a business can have a number of different types
Types of Business Organisation Revision Presentations 2004 Introduction A business is always owned by someone. This can just be one person, or thousands. So a business can have a number of different types
THE CUSTOMER COMES SECOND!
 THE CUSTOMER COMES SECOND! THE CUSTOMER COMES SECOND! To most of us, this statement seems so alien when, for the duration of our careers, we have had it drummed into us (as we have drummed it into others),
THE CUSTOMER COMES SECOND! THE CUSTOMER COMES SECOND! To most of us, this statement seems so alien when, for the duration of our careers, we have had it drummed into us (as we have drummed it into others),
Organizational Design Toolkit
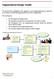 Organizational Design Toolkit We provide below highlights of the approach to developing/confirming the preferred service delivery model and organizational structure for an organization. The key steps are:
Organizational Design Toolkit We provide below highlights of the approach to developing/confirming the preferred service delivery model and organizational structure for an organization. The key steps are:
CHAPTER 3 - CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT (CRM)
 CHAPTER 3 - CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT (CRM) 3.1 INTRODUCTION The most important purpose of any service orientated organisation is to retain customers. It is critical for any organization to keep
CHAPTER 3 - CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT (CRM) 3.1 INTRODUCTION The most important purpose of any service orientated organisation is to retain customers. It is critical for any organization to keep
The automotive manufacturing sector is
 BUILDING A SUSTAINABLE WORKFORCE: APPRENTICESHIP IN THE CANADIAN AUTOMOTIVE INDUSTRY The Canadian Automotive Manufacturing Industry at a Glance The automotive manufacturing sector is struggling in the
BUILDING A SUSTAINABLE WORKFORCE: APPRENTICESHIP IN THE CANADIAN AUTOMOTIVE INDUSTRY The Canadian Automotive Manufacturing Industry at a Glance The automotive manufacturing sector is struggling in the
Managing Innovation. A guide to help you adopt a more structured approach to managing innovation in your business
 Managing Innovation A guide to help you adopt a more structured approach to managing innovation in your business There are many definitions of innovation but, in its simplest form, it can be said to be
Managing Innovation A guide to help you adopt a more structured approach to managing innovation in your business There are many definitions of innovation but, in its simplest form, it can be said to be
JOB DESCRIPTION. Executive Assistant to Director of Operations
 JOB DESCRIPTION JOB TITLE: JOB HOLDER: DEPARTMENT: Executive Assistant to Director of vacant DIRECTORATE/NATIONAL OFFICE MSNC LOCATION: MANAGER S NAME: MANAGER S JOB TITLE: NW London Naudette Harvey Administration
JOB DESCRIPTION JOB TITLE: JOB HOLDER: DEPARTMENT: Executive Assistant to Director of vacant DIRECTORATE/NATIONAL OFFICE MSNC LOCATION: MANAGER S NAME: MANAGER S JOB TITLE: NW London Naudette Harvey Administration
Performance Management Rating Scales
 Performance Management Rating Scales When looking at Performance Management, a 5 point rating scale is the most common. A CIPD report suggests that: 47% of companies use 5 point scale 28% of companies
Performance Management Rating Scales When looking at Performance Management, a 5 point rating scale is the most common. A CIPD report suggests that: 47% of companies use 5 point scale 28% of companies
Controlled Assessment
 7 th Jun 18 th Jun 7 th Jun 18 th Jun 7 th Jun 18 th Jun GCSE Business Studies Year 11 AQA Unit 2: Growing as a Business Controlled Assessment The Unit may be introduced by inviting in outside business
7 th Jun 18 th Jun 7 th Jun 18 th Jun 7 th Jun 18 th Jun GCSE Business Studies Year 11 AQA Unit 2: Growing as a Business Controlled Assessment The Unit may be introduced by inviting in outside business
Buying and Setting up a Business with a Post Office A Guide
 Buying and Setting up a Business with a Post Office A Guide NOTE: The information in this document is not intended as an exhaustive list of all the information you require in order to set up a business
Buying and Setting up a Business with a Post Office A Guide NOTE: The information in this document is not intended as an exhaustive list of all the information you require in order to set up a business
BASES OF COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE: THE `STRATEGY
 DO YOU HAVE A COMPETITIVE STRATEGY? Many managers talk about the importance of developing an effective competitive strategy. Indeed since Michael Porter wrote about this in 1980 it has become a central
DO YOU HAVE A COMPETITIVE STRATEGY? Many managers talk about the importance of developing an effective competitive strategy. Indeed since Michael Porter wrote about this in 1980 it has become a central
Health and Safety Policy and Procedures
 Health and Safety Policy and Procedures Health & Safety Policy & Procedures Contents s REVISION AND AMENDMENT RECORD : Summary of Change Whole Policy 4.0 05 Nov 08 Complete re-issue Whole Policy 4.1 10
Health and Safety Policy and Procedures Health & Safety Policy & Procedures Contents s REVISION AND AMENDMENT RECORD : Summary of Change Whole Policy 4.0 05 Nov 08 Complete re-issue Whole Policy 4.1 10
Domain 2 -Values and Ethics: Apply social work ethical principles and values to guide professional practice.
 Case study 'Joanne', evidence 5: Action plan Domain 1, Professionalism Social workers are members of an internationally recognised profession, a title protected in UK law. Social workers demonstrate professional
Case study 'Joanne', evidence 5: Action plan Domain 1, Professionalism Social workers are members of an internationally recognised profession, a title protected in UK law. Social workers demonstrate professional
UCISA CASE STUDY. Middlesex University succeeds in offshoring core operations to India. www.ucisa.ac.uk. Outcomes. Drivers
 Middlesex University succeeds in offshoring core operations to India Drivers Make significant savings on UK staffing Streamline business processes Improve data quality Improvements to the student experience,
Middlesex University succeeds in offshoring core operations to India Drivers Make significant savings on UK staffing Streamline business processes Improve data quality Improvements to the student experience,
Point of View. Planning for success after a merger or acquisition. Danny A Davis, Programme Director, Mergers & Acquisitions
 Point of View Planning for success after a merger or acquisition Danny A Davis, Programme Director, Mergers & Acquisitions Without understanding the motive behind the deal, a clear link to postdeal activity
Point of View Planning for success after a merger or acquisition Danny A Davis, Programme Director, Mergers & Acquisitions Without understanding the motive behind the deal, a clear link to postdeal activity
Redundancy Guide For Employers
 Redundancy Guide For Employers 1. Introduction Handling redundancy becomes more complex every day. There is, of course, the need to keep up to date with redundancy legislation. But there are also: i. the
Redundancy Guide For Employers 1. Introduction Handling redundancy becomes more complex every day. There is, of course, the need to keep up to date with redundancy legislation. But there are also: i. the
2070 Work Life Balance Survey - Employees
 2070 Work Life Balance Survey - Employees Record no: Introduction We would be grateful if you could spare the time to take part in our survey it should only take around 15 minutes to complete. The survey
2070 Work Life Balance Survey - Employees Record no: Introduction We would be grateful if you could spare the time to take part in our survey it should only take around 15 minutes to complete. The survey
Extract of article published in International HR Adviser magazine 2013. The role of HR in global mobility
 Extract of article published in International HR Adviser magazine 2013 The role of HR in global mobility Increasingly the regional HR director for Asia Pacific for many large multinationals will be based
Extract of article published in International HR Adviser magazine 2013 The role of HR in global mobility Increasingly the regional HR director for Asia Pacific for many large multinationals will be based
The Five Key Elements of Student Engagement
 Background Info The key agencies in Scotland have developed and agreed this framework for student engagement in Scotland. The framework does not present one definition or recommend any particular approach,
Background Info The key agencies in Scotland have developed and agreed this framework for student engagement in Scotland. The framework does not present one definition or recommend any particular approach,
A Guide to Efficient MRO Procurement & Management White Paper
 A Guide to Efficient MRO Procurement & Management White Paper Brammer 117554 WhitePaper_V5_SP.indd 1 19/04/2010 15:19 Executive summary The purchasing of spares for the daily maintenance, repair and overhaul
A Guide to Efficient MRO Procurement & Management White Paper Brammer 117554 WhitePaper_V5_SP.indd 1 19/04/2010 15:19 Executive summary The purchasing of spares for the daily maintenance, repair and overhaul
CONSUMER ENGAGEMENT IN THE CURRENT ACCOUNT MARKET
 CONSUMER ENGAGEMENT IN THE CURRENT ACCOUNT MARKET Why people don t switch current accounts March 2016 A Bacs Research Paper 1 FOREWORD Since 2013 Bacs has operated the Current Account Switch Service (CASS)
CONSUMER ENGAGEMENT IN THE CURRENT ACCOUNT MARKET Why people don t switch current accounts March 2016 A Bacs Research Paper 1 FOREWORD Since 2013 Bacs has operated the Current Account Switch Service (CASS)
A9. What is the total number of employees worldwide including Denmark by headcount?
 SURVEY OF EMPLOYMENT PRACTICES OF MULTINATIONAL COMPANIES OPERATING IN DENMARK Home-based English version Please select a language: SECTION A: INTRODUCTION English... 1 Danish... 2 First page: EMPLOYMENT
SURVEY OF EMPLOYMENT PRACTICES OF MULTINATIONAL COMPANIES OPERATING IN DENMARK Home-based English version Please select a language: SECTION A: INTRODUCTION English... 1 Danish... 2 First page: EMPLOYMENT
Loyalty program assessment: flybuys
 Loyalty program assessment: flybuys Coles Supermarkets Australia Pty Ltd Summary report Australian Privacy Principles assessment Section 33C(1)(a) Privacy Act 1988 Assessment undertaken: November 2015
Loyalty program assessment: flybuys Coles Supermarkets Australia Pty Ltd Summary report Australian Privacy Principles assessment Section 33C(1)(a) Privacy Act 1988 Assessment undertaken: November 2015
Managing Customer. Relationships
 Managing Customer Relationships A guide to help you identify a range of areas to address in order to get the most from your relationships with your customers Managing customer relationships should be seen
Managing Customer Relationships A guide to help you identify a range of areas to address in order to get the most from your relationships with your customers Managing customer relationships should be seen
Introduction to Team-based Organizations
 INTRODUCTION TO TEAM-BASED ORGANIZATIONS 1 1 Introduction to Team-based Organizations He makes tools (and does so within more than one technical tradition), builds shelters, takes over natural refuges
INTRODUCTION TO TEAM-BASED ORGANIZATIONS 1 1 Introduction to Team-based Organizations He makes tools (and does so within more than one technical tradition), builds shelters, takes over natural refuges
Investors in People Assessment Report. Presented by Alli Gibbons Investors in People Specialist On behalf of Inspiring Business Performance Limited
 Investors in People Assessment Report for Bradstow School Presented by Alli Gibbons Investors in People Specialist On behalf of Inspiring Business Performance Limited 30 August 2013 Project Reference Number
Investors in People Assessment Report for Bradstow School Presented by Alli Gibbons Investors in People Specialist On behalf of Inspiring Business Performance Limited 30 August 2013 Project Reference Number
FOCUS ON. Business success through training & recruitment. invest in your workforce and gain the competitive edge
 FOCUS ON Business success through training & recruitment invest in your workforce and gain the competitive edge Everything we do at Lincoln College is with your success in mind. We live in a fast-paced,
FOCUS ON Business success through training & recruitment invest in your workforce and gain the competitive edge Everything we do at Lincoln College is with your success in mind. We live in a fast-paced,
Specimen 2016 Morning Time allowed: 1 hour 45 minutes
 DRAFT SPECIMEN MATERIAL Please write clearly, in block capitals. Centre number Candidate number Surname Forename(s) Candidate signature GCSE BUSINESS Paper 1 Specimen 2016 Morning Time allowed: 1 hour
DRAFT SPECIMEN MATERIAL Please write clearly, in block capitals. Centre number Candidate number Surname Forename(s) Candidate signature GCSE BUSINESS Paper 1 Specimen 2016 Morning Time allowed: 1 hour
CORPORATE PLAN 2012-13 2013-14 2014-15
 CORPORATE PLAN 2012-13 2013-14 2014-15 V0.3 170412 1 1. Introduction This Corporate Plan identifies the main strategic challenges facing the Agency over the next three years, and sets out its key performance
CORPORATE PLAN 2012-13 2013-14 2014-15 V0.3 170412 1 1. Introduction This Corporate Plan identifies the main strategic challenges facing the Agency over the next three years, and sets out its key performance
HUMAN RESOURCES FOR HEALTH A KEY PRIORITY FOR THE MINISTRY OF HEALTH
 HUMAN RESOURCES FOR HEALTH A KEY PRIORITY FOR THE MINISTRY OF HEALTH BACKGROUND In line with a global awakening of the imminent crisis in human resources for health, the WHO country office has reflected
HUMAN RESOURCES FOR HEALTH A KEY PRIORITY FOR THE MINISTRY OF HEALTH BACKGROUND In line with a global awakening of the imminent crisis in human resources for health, the WHO country office has reflected
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education MAXIMUM MARK: 80
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education BUSINESS STUDIES 0450/01 Paper 1 For Examination from 2015 SPECIMEN MARK SCHEME MAXIMUM MARK: 80
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education BUSINESS STUDIES 0450/01 Paper 1 For Examination from 2015 SPECIMEN MARK SCHEME MAXIMUM MARK: 80
360 feedback. Manager. Development Report. Sample Example. name: email: date: [email protected]
 60 feedback Manager Development Report name: email: date: Sample Example [email protected] 9 January 200 Introduction 60 feedback enables you to get a clear view of how others perceive the way you work.
60 feedback Manager Development Report name: email: date: Sample Example [email protected] 9 January 200 Introduction 60 feedback enables you to get a clear view of how others perceive the way you work.
The value of apprenticeships: Beyond wages
 The value of apprenticeships: Beyond wages NIDA BROUGHTON June 2016 There is strong political commitment to the apprenticeships programme as a part of the strategy to achieve a high quality workforce that
The value of apprenticeships: Beyond wages NIDA BROUGHTON June 2016 There is strong political commitment to the apprenticeships programme as a part of the strategy to achieve a high quality workforce that
5 steps to rid your small business of payroll stress
 5 steps to rid your small business of payroll stress Introduction The demands of payroll are only getting worse, with mounting risks and costs Human resources are crucial to any business success. As a
5 steps to rid your small business of payroll stress Introduction The demands of payroll are only getting worse, with mounting risks and costs Human resources are crucial to any business success. As a
The policy also aims to make clear the actions required when faced with evidence of work related stress.
 STRESS MANAGEMENT POLICY 1.0 Introduction Stress related illness accounts for a significant proportion of sickness absence in workplaces in the UK. Stress can also be a contributing factor to a variety
STRESS MANAGEMENT POLICY 1.0 Introduction Stress related illness accounts for a significant proportion of sickness absence in workplaces in the UK. Stress can also be a contributing factor to a variety
National Deaf Children s Society (NDCS) submission to Work and Pensions Select Committee inquiry
 National Deaf Children s Society (NDCS) submission to Work and Pensions Select Committee inquiry Employment support for disabled people: Access to Work Summary Access to Work (AtW) plays a vital role in
National Deaf Children s Society (NDCS) submission to Work and Pensions Select Committee inquiry Employment support for disabled people: Access to Work Summary Access to Work (AtW) plays a vital role in
Chesterfield Borough Council. Internal Communications Strategy. April 2014 - April 2017.
 Appendix 1 Chesterfield Borough Council Internal Communications Strategy April 2014 - April 2017. Section 1: Introduction 1.1 Chesterfield Borough Council s single biggest asset is its employees. 1.2 It
Appendix 1 Chesterfield Borough Council Internal Communications Strategy April 2014 - April 2017. Section 1: Introduction 1.1 Chesterfield Borough Council s single biggest asset is its employees. 1.2 It
CIPD Employee engagement
 CIPD Employee engagement See www.cipd.co.uk for further details January 2007 This factsheet gives introductory guidance. It: considers what is meant by employee engagement and why organisations are interested
CIPD Employee engagement See www.cipd.co.uk for further details January 2007 This factsheet gives introductory guidance. It: considers what is meant by employee engagement and why organisations are interested
Investors in People First Assessment Report
 Investors in People First Assessment Report K.H.Construction Cambridge Assessor: Lesley E Ling On-site Date/s: 3 rd September 2008. Recognition Date: Contents 1. Introduction Page 2 2. Assessment and Client
Investors in People First Assessment Report K.H.Construction Cambridge Assessor: Lesley E Ling On-site Date/s: 3 rd September 2008. Recognition Date: Contents 1. Introduction Page 2 2. Assessment and Client
Sands, the stillbirth and neonatal charity, is a well established and widely respected national charity that:
 POST TITLE HR Manager DIVISION/DEPARTMENT Executive Team REPORTS TO Deputy Chief Executive DATE April 2013 BACKGROUND Sands, the stillbirth and neonatal charity, is a well established and widely respected
POST TITLE HR Manager DIVISION/DEPARTMENT Executive Team REPORTS TO Deputy Chief Executive DATE April 2013 BACKGROUND Sands, the stillbirth and neonatal charity, is a well established and widely respected
"/0,&(00$"-0,10$-&+$2,&-&1(!"#$%&'()*(+,-'($!.-)+$
 INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS SKILLS COURSEWARE "/0,&(00$"-0,10$-&+$2,&-&1(!"#$%&'()*(+,-'($!.-)+$!""#$%&'$%()*!++,"&-'&,.(,/(01+&.$++( 2#-"'&'&,.$#+ INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS SKILLS COURSEWARE PUBLISHED BY: British
INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS SKILLS COURSEWARE "/0,&(00$"-0,10$-&+$2,&-&1(!"#$%&'()*(+,-'($!.-)+$!""#$%&'$%()*!++,"&-'&,.(,/(01+&.$++( 2#-"'&'&,.$#+ INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS SKILLS COURSEWARE PUBLISHED BY: British
Child Selection. Overview. Process steps. Objective: A tool for selection of children in World Vision child sponsorship
 Sponsorship in Programming tool Child Selection Objective: A tool for selection of children in World Vision child sponsorship We ve learned some things about selecting children. It is not a separate sponsorship
Sponsorship in Programming tool Child Selection Objective: A tool for selection of children in World Vision child sponsorship We ve learned some things about selecting children. It is not a separate sponsorship
Some examples of how I have worked with firms to identify and develop the scope of the secretarial role are:-
 Clodagh Beaty Secretarial Role Development Experience The Legal Secretarial Role I am a recognised expert in the legal secretarial role and am regularly invited to speak at conferences and forums and contribute
Clodagh Beaty Secretarial Role Development Experience The Legal Secretarial Role I am a recognised expert in the legal secretarial role and am regularly invited to speak at conferences and forums and contribute
MANAGING THE RISKS OF CHANGE
 MANAGING THE RISKS OF CHANGE Dr Andrew Brazier, Consultant www.andybrazier.co.uk [email protected] þ 44 7984 284642 The process industry has always had to deal with changes to plant and equipment,
MANAGING THE RISKS OF CHANGE Dr Andrew Brazier, Consultant www.andybrazier.co.uk [email protected] þ 44 7984 284642 The process industry has always had to deal with changes to plant and equipment,
Employee Performance Management Policy and Procedure
 Employee Performance Management Policy and Procedure Document Control Document Ref: HREPM001 Date Created: Sept 2007 Version: 1.4 Date Modified: April 2015 Revision due Author: Jane Milone Sign & Date:
Employee Performance Management Policy and Procedure Document Control Document Ref: HREPM001 Date Created: Sept 2007 Version: 1.4 Date Modified: April 2015 Revision due Author: Jane Milone Sign & Date:
The Basics of a Compensation Program
 The Basics of a Compensation Program Learning Objectives By the end of this chapter, you should be able to: List three ways in which compensation plays a role in the management of the enterprise. Describe
The Basics of a Compensation Program Learning Objectives By the end of this chapter, you should be able to: List three ways in which compensation plays a role in the management of the enterprise. Describe
Perspectives. Employee voice. Releasing voice for sustainable business success
 Perspectives Employee voice Releasing voice for sustainable business success Empower, listen to, and act on employee voice through meaningful surveys to help kick start the UK economy. 2 Releasing voice
Perspectives Employee voice Releasing voice for sustainable business success Empower, listen to, and act on employee voice through meaningful surveys to help kick start the UK economy. 2 Releasing voice
1. What types of organisation do you fund? 2. Do you give grants for individual children and young people?
 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) Who can apply for a grant? 1. What types of organisation do you fund? 2. Do you give grants for individual children and young people? 3. Some of the young people our organisation
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) Who can apply for a grant? 1. What types of organisation do you fund? 2. Do you give grants for individual children and young people? 3. Some of the young people our organisation
A Review of the Integration of Brokerage Services in the South West
 A Review of the Integration of Brokerage Services in the South West EXECUTIVE SUMMARY This report presents the findings of the research study, A Review of the Integration of Brokerage Services in the South
A Review of the Integration of Brokerage Services in the South West EXECUTIVE SUMMARY This report presents the findings of the research study, A Review of the Integration of Brokerage Services in the South
Strategic Human Resource Management Catherine Truss, David Mankin & Clare Kelliher
 Catherine Truss, David Mankin & Clare Kelliher Oxford University Press (2012) ISBN: 978-0199583065 Theme of the Book What makes a good HR strategy and how does one develop it? These are just two of the
Catherine Truss, David Mankin & Clare Kelliher Oxford University Press (2012) ISBN: 978-0199583065 Theme of the Book What makes a good HR strategy and how does one develop it? These are just two of the
Scheme of Work Units 1 and 2: Setting up a Business and Growing as a Business an Integrated Approach
 GCSE Business Studies Scheme of Work Units 1 and 2: Setting up a Business and Growing as a Business an Integrated Approach Copyright 2012 AQA and its licensors. All rights reserved. The Assessment and
GCSE Business Studies Scheme of Work Units 1 and 2: Setting up a Business and Growing as a Business an Integrated Approach Copyright 2012 AQA and its licensors. All rights reserved. The Assessment and
How to Become a Data Driven Business
 January 2012 Executive summary Becoming a Data Driven Business, particularly from a Marketing perspective, presents significant benefits in helping your business to grow, develop and succeed, by working
January 2012 Executive summary Becoming a Data Driven Business, particularly from a Marketing perspective, presents significant benefits in helping your business to grow, develop and succeed, by working
HCPC 2015 Employee Exit Interview Report
 HCPC 2015 Employee Exit Interview Report Section Page 1. Introduction 3 2. Scope 3 3. Employee turnover rates 3 4. Summary of findings 3 5. Analysis of data 4 6. Conclusions and actions 11 2 1. Introduction
HCPC 2015 Employee Exit Interview Report Section Page 1. Introduction 3 2. Scope 3 3. Employee turnover rates 3 4. Summary of findings 3 5. Analysis of data 4 6. Conclusions and actions 11 2 1. Introduction
Chapter 1. Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction What is productivity, how is it measured and why is it important? These questions are a useful starting point from which we can define and explain the range of productivity measures
Chapter 1 Introduction What is productivity, how is it measured and why is it important? These questions are a useful starting point from which we can define and explain the range of productivity measures
It s not just about the environment
 Supply Chain Consultancy It s not just about the environment Sustainable Supply Chains Paul Goose discusses the need to take a wider, more integrated view of operations to ensure long term growth. A great
Supply Chain Consultancy It s not just about the environment Sustainable Supply Chains Paul Goose discusses the need to take a wider, more integrated view of operations to ensure long term growth. A great
1 INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT
 1 INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT Objectives This chapter will help you to: define human resource management (HRM) become familiar with the concept of HRM and its place in an organisation trace
1 INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT Objectives This chapter will help you to: define human resource management (HRM) become familiar with the concept of HRM and its place in an organisation trace
Talent Management. Terry Meyer. November 2005 ALL RIGHTS RESERVED COPYRIGHT
 Talent Management Terry Meyer November 2005 ALL RIGHTS RESERVED COPYRIGHT Disclaimer Publication or other use of this document by any unauthorised person is strictly prohibited. The views expressed in
Talent Management Terry Meyer November 2005 ALL RIGHTS RESERVED COPYRIGHT Disclaimer Publication or other use of this document by any unauthorised person is strictly prohibited. The views expressed in
GCSE Business Studies
 GCSE Business Studies Unit 2: Investigating small business Controlled Assessment 25% of final grade Name Teacher Page 1 of 15 GCSE BUSINESS STUDIES UNIT 2: Investigating small business CONTROLLED ASSESSMENT
GCSE Business Studies Unit 2: Investigating small business Controlled Assessment 25% of final grade Name Teacher Page 1 of 15 GCSE BUSINESS STUDIES UNIT 2: Investigating small business CONTROLLED ASSESSMENT
OCR Business Studies for AS
 Size and structure of a business 5 Revision questions (38 marks; 40 minutes) 1 Analyse why both small and large businesses can operate successfully within the same environment. (8) Reasons why small and
Size and structure of a business 5 Revision questions (38 marks; 40 minutes) 1 Analyse why both small and large businesses can operate successfully within the same environment. (8) Reasons why small and
Sources of finance (Or where can we get money from?)
 Sources of finance (Or where can we get money from?) Why do we need finance? 1. Setting up a business 2. Need to finance our day-to-day activities 3. Expansion 4. Research into new products 5. Special
Sources of finance (Or where can we get money from?) Why do we need finance? 1. Setting up a business 2. Need to finance our day-to-day activities 3. Expansion 4. Research into new products 5. Special
The changing role of the IT department in a cloud-based world. Vodafone Power to you
 The changing role of the IT department in a cloud-based world Vodafone Power to you 02 Introduction With competitive pressures intensifying and the pace of innovation accelerating, recognising key trends,
The changing role of the IT department in a cloud-based world Vodafone Power to you 02 Introduction With competitive pressures intensifying and the pace of innovation accelerating, recognising key trends,
Six top tips for travel managers to create savings in 2015
 Six top tips for travel managers to create savings in 2015 E-Guide 2 Introduction Savings remain a key focal point for Travel Managers in 2015 and through regular reviews and analysis, using management
Six top tips for travel managers to create savings in 2015 E-Guide 2 Introduction Savings remain a key focal point for Travel Managers in 2015 and through regular reviews and analysis, using management
Understanding the links between employer branding and total reward
 8 September 2010 Understanding the links between employer branding and total reward An overview of our research findings and the implications for reward Limited is authorised and regulated by the Financial
8 September 2010 Understanding the links between employer branding and total reward An overview of our research findings and the implications for reward Limited is authorised and regulated by the Financial
GCSE Applied Business Studies. Scheme of Work. Unit 4 People in Business
 GCSE Applied Business Studies Scheme of Work Unit People in Business Teacher Resource Bank / GCSE Applied Business / Scheme of Work Unit People in Business / Version 1.1 GCSE APPLIED BUSINESS UNIT SCHEME
GCSE Applied Business Studies Scheme of Work Unit People in Business Teacher Resource Bank / GCSE Applied Business / Scheme of Work Unit People in Business / Version 1.1 GCSE APPLIED BUSINESS UNIT SCHEME
A target cost is arrived at by identifying the market price of a product and then subtracting a desired profit margin from it.
 Answers Fundamentals Level Skills Module, Paper F5 Performance Management June 2015 Answers Section A 1 C Divisional profit before depreciation = $2 7m x 15% = $405,000 per annum. Less depreciation = $2
Answers Fundamentals Level Skills Module, Paper F5 Performance Management June 2015 Answers Section A 1 C Divisional profit before depreciation = $2 7m x 15% = $405,000 per annum. Less depreciation = $2
TAXREP 01/16 (ICAEW REP 02/16)
 TAXREP 01/16 (ICAEW REP 02/16) January 2016 ICAEW research survey: HMRC Customer Service Standards 2015 Results of the ICAEW 2015 research survey among ICAEW smaller agents about HMRC service standards.
TAXREP 01/16 (ICAEW REP 02/16) January 2016 ICAEW research survey: HMRC Customer Service Standards 2015 Results of the ICAEW 2015 research survey among ICAEW smaller agents about HMRC service standards.
WFBSC Policy Position: Employment, outsourcing and the cleaning sector
 Introduction WFBSC Policy Position: Employment, outsourcing and the cleaning sector Until recently cleaning employers have been under represented in the global institutions that legislate and/or set the
Introduction WFBSC Policy Position: Employment, outsourcing and the cleaning sector Until recently cleaning employers have been under represented in the global institutions that legislate and/or set the
TAUHEEDUL EDUCATION TRUST
 TAUHEEDUL EDUCATION TRUST JOB DESCRIPTION Job Title: Base: Head of Human Resources Tauheedul Education Trust Central Office Reports to: Chief Executive Grade: TSM4 Sc 54-59 Staff Responsibility for: As
TAUHEEDUL EDUCATION TRUST JOB DESCRIPTION Job Title: Base: Head of Human Resources Tauheedul Education Trust Central Office Reports to: Chief Executive Grade: TSM4 Sc 54-59 Staff Responsibility for: As
JOB AND PERSON SPECIFICATION. It has an annual budget of approximately 50 million and currently a staff of approximately 300.
 JOB AND PERSON SPECIFICATION Job Title: Division Grade: HR Adviser - HR Operations Section G Reports To: Head of HR Operations General Information The Commonwealth Secretariat is the principal intergovernmental
JOB AND PERSON SPECIFICATION Job Title: Division Grade: HR Adviser - HR Operations Section G Reports To: Head of HR Operations General Information The Commonwealth Secretariat is the principal intergovernmental
Resource document for school governors and schools. Summary of Special Educational Needs (SEN) Code of Practice for Wales
 Resource document for school governors and schools Summary of Special Educational Needs (SEN) Code of Practice for Wales Teifion Rees SEN Governor Cwrt Sart Comprehensive School April 2004 1 Acknowledgements
Resource document for school governors and schools Summary of Special Educational Needs (SEN) Code of Practice for Wales Teifion Rees SEN Governor Cwrt Sart Comprehensive School April 2004 1 Acknowledgements
Standards of proficiency. Dietitians
 Standards of proficiency Dietitians Contents Foreword 1 Introduction 3 Standards of proficiency 7 Foreword We are pleased to present the Health and Care Professions Council s standards of proficiency for
Standards of proficiency Dietitians Contents Foreword 1 Introduction 3 Standards of proficiency 7 Foreword We are pleased to present the Health and Care Professions Council s standards of proficiency for
SFJ EFSM14 Manage the performance of teams and individuals to achieve objectives
 Manage the performance of teams and individuals to achieve objectives Overview This standard is about making the best use of your team and its members so that they can achieve your organisation's objectives.
Manage the performance of teams and individuals to achieve objectives Overview This standard is about making the best use of your team and its members so that they can achieve your organisation's objectives.
Promote equality of opportunity, diversity and inclusion in your organisation
 M&LB12 Overview Promote equality of opportunity, diversity and inclusion in your organisation What this Unit is about This Unit is about taking a lead in actively promoting equality of opportunity, diversity
M&LB12 Overview Promote equality of opportunity, diversity and inclusion in your organisation What this Unit is about This Unit is about taking a lead in actively promoting equality of opportunity, diversity
Show your value, grow your business:
 Show your value, grow your business: A SUPPLIER GUIDE TO MOVE FROM A TRANSACTIONAL PROVIDER TO A STRATEGIC PARTNER KAREN A. CALINSKI INTRODUCTION /02 At KellyOCG we take a holistic approach to talent sourcing
Show your value, grow your business: A SUPPLIER GUIDE TO MOVE FROM A TRANSACTIONAL PROVIDER TO A STRATEGIC PARTNER KAREN A. CALINSKI INTRODUCTION /02 At KellyOCG we take a holistic approach to talent sourcing
Introduction. Employment and occupational characteristics of retail commerce and working conditions in the sector INTERNATIONAL LABOUR ORGANIZATION
 INTERNATIONAL LABOUR ORGANIZATION Global Dialogue Forum on the Needs of Workers in relation to Changing Work Processes and the Working Environment in Retail Commerce GDFRC/2011/9 Geneva 21 22 September
INTERNATIONAL LABOUR ORGANIZATION Global Dialogue Forum on the Needs of Workers in relation to Changing Work Processes and the Working Environment in Retail Commerce GDFRC/2011/9 Geneva 21 22 September
