FLEXOR MUSCLE SLIDE IN THE SPASTIC HAND. The Max Page Operation
|
|
|
- Sheryl Holt
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 FLEXOR MUSCLE SLIDE IN THE SPASTIC HAND The Max Page Operation W. F. WHITE, UDDINGSTON, SCOTLAND Froni the Orthopaedic Department, Law Hospital, ( arh,,ke In cerebral palsy the scope for operation on the hand is much less than that for operation on the lower limb. This is determined by the intricacies of hand function (Zuck 1964). Operation is only of value in the spastic type. When done early, in carefully chosen cases, it may assist physical re-education and rehabilitation by improving muscle balance and thus correcting or partly correcting deformity. SELECTION There are many contra-indications to operation and selection is crucial. The most important single attribute called for in the patient is drive-a compelling urge or will to succeed. Usually it is associated with reasonable intelligence, but there are some children and adults of low intelligence, yet with good drive and cooperation, who become adept at using their hands. Nevertheless, on the whole, the more intelligent patients do better. Unfortunately, poor intelligence is often linked with an extensive motor disability and this combination virtually rules out operation. About three-quarters of these patients have some alteration of sensibility. Tactile cognition is poor, perhaps because of lack of experience, but more often from lack of the required manipulative facility. However, if there is marked impairment of sensibility, operation is not justified. Severe athetoid movements with poor voluntary muscle control are contra-indications. The patient must be able to put his hand to an object reasonably well. Inadequacy of training facilities prohibits operation. Age is important. The extraordinary adaptability of the young child leads to successful rehabilitation even though there are the obvious disadvantages of bone growth and recurring imbalance. Nevertheless, it is probably advisable to wait until the child is six or seven before operating. The criteria for selection are therefore stringent and the proportion of cases suitable for operation is small. After clinical assessment patients may be divided broadly into three groups. The first and largest consists of those who are too severely affected for operation. At least half fall into this category. They are so afflicted mentally and physically that they are ineducable and untrainable. In about a quarter, function is so good that it is unwise to interfere. This leaves about a fifth who are eligible for consideration. BASIC FAULTS Loss of function is due, in the main, to three basic faults. First, flexion of the wrist and fingers associated with pronation of the forearm. Secondly, flexion and adduction of the thumb causing the grip reflex. Thirdly and most important of all, inability to release the grip. This to some extent resembles the position of the hand in the normal new-born child-the first flexor stage. Use of the hand is thwarted by the powerful flexor contractions initiated by the stretch reflex (Kenney and Heaberlin 1962). The extensors are weak perhaps from pyramidal involvement. More often, long stretched and overwhelmed, they cease to function through disuse (Zuck 1964). VOL. 54 B, NO. 3, AUGUST
2 454 V. F. WHITE RATIONALE The crux of the problem is the stretch reflex. The main object is to try to control or diminish this, to relieve the spasm and thus to correct or at any rate to improve the deformity. It seems rational therefore to alter the length and tone of the flexors by releasing their origin and allowing them to slide distally, as suggested by Page nearly half a century ago (Page 1923). / Exposuriof FIG. I flexororigin. FIG. 2 Branch of median nerve preventing further descent. This might promote better muscle balance around the wrist and hand, thus enhancing extensor ability. The first muscle slide in the series was done in 1959 and preliminary reports were made in 1961 and at the meeting of the Soci#{233}t#{233} Internationale de Chirurgie Orthop#{233}dique et de Traumatologie in Paris in 1966 (White 1961). Since then selection has become even more strict. THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY
3 FLEXOR MUSCLE SLIDE IN THE SPASTIC HAND 455 OPERATION The operation is shown in Figures 1 to 3. It is carried out through an antero-medial incision and the displacement of the flexor orign is about three and a half centimetres (Inglis and Cooper 1966). Further descent is prevented by branches of the median and to a lesser extent the ulnar nerves. These nerve branches are stripped proximally; on a few occasions they have been divided. The ulnar nerve has been transposed on three occasions. Through FIG. 3 Extent of displacement of origin. a separate incision the insertion of pronator teres is severed and the radial origins of flexor pollicis longus and flexor superficialis are stripped. In two cases early in the series the origin of adductor pollicis was released from the third metacarpal and carpal bones. After operation a plaster slab is applied to maintain the elbow in extension, the wrist in neutral position and the fingers just short of full extension. This is kept on for three weeks. Thereafter the wrist alone is immobilised for one month. This splint is used during the night only for a further three months. TABLE I TABLE II TYPE OF OPERATION ASSESSMENT Operation Numerof Function Marks Muscle slide Muscle slide with arthrodesis 12 Arthrodesis Grip 3 Pinch 3 Release 6 Good 9 or more Total Fair 7or8 In the first year or so a compression arthrodesis of the wrist was done after the muscle slide. Position was chosen after a trial in plaster. It was usually in slight palmar flexion, and always in ulnar deviation to correct to some extent the thumb in palm attitude (Cooper 1952). The carpo-metacarpal joints were not fused. This left a little movement which might assist grip and release (Goldner 1955). Over the last nine years arthrodesis has been done much less often. VOL. 54B, NO. 3, AUGUST 1972
4 456 W. F. WHITE MATERIAL There were thirty-two patients-less than 20 per cent of those examined. The total number of procedures was seventy-one, but it is intended here to concentrate only on three groups (Table I): those who had a muscle slide-fifteen: those who had a muscle slide followed Fi;. 4 FIG. 5 FIG. 6 Figure 4-Grip. Figure 5-Pinch. Figure 6-Release. by arthrodesis-twelve: those who had arthrodesis-five. The average age of the patients was eighteen and the average follow-up was seven and a half years. It would be foolish to expect anything approaching normal function after operation in the spastic hand. The aim is to make the hand more useful. Assessment of results is difficult. ASSESSMENT (TABLE II) Function was divided into three basic elements-grip, pinch and release (Figs. 4 to 6). Grip and pinch were given three marks each. It was accepted that in the spastic hand pinch is often between the pulp of the thumb and the side of the index finger rather than its pulp- THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY
5 FLEXOR MUSCLE SLIDE IN THE SPASTIC HAND 457 the key pinch. Since inability to open the hand is perhaps the major disability, release was given six marks. Full marks does not imply normal function. For one thing movements are almost always at slow speed. Nine or more was considered to represent good function. Seven or eight represented fair function and anything less than seven was a failure. Before operation all patients were in the failure group. TABLE III TABLE IV RESULTS GOOD AND FAIR RESULTS RELATED TO TYPE OF OPERATION Results Number:f Operation Number:f Good 10 Muscle slide..... Ii 21 Fair Muscle slide with arthrodesis.. 6 Failure 11 Arthrodesis Total 32 Total TABLE FAILURES RELATED TO TYPE OF OPERATION V 0 pe ration Number patients of Muscle slide... 4 Muscle slide with arthrodesis 6 Arthrodesis... 1 Total RESULTS (TABLE III) The results in ten patients were classed as good, in eleven as fair and in eleven as failures. The good and fair groups were considered satisfactory and were taken together to simplify the figures. These results were analysed according to operation and the means of selection were critically reviewed. ANALYSIS BY OPERATION (TABLES IV AND V) Of the twenty-one patients with satisfactory results eleven had only a muscle slide ; six had a muscle slide followed by an arthrodesis ; and four had only an arthrodesis. This conflicts with the modern view which is against arthrodesis-for sound reasons. Nevertheless, in some patients arthrodesis is still of value. In the numerous failures six patients had a muscle slide followed by an arthrodesis: four had only a muscle slide and one had only an arthrodesis. The outstanding lesson was in the last failure which was total: an arthrodesis done on demand for the sake of appearance. Any operation must have as its primary object improvement in function. A review of the factors governing selection is more significant. Emphasis was placed on the twin attributes of drive and intelligence, and on the extent of motor disability. VOL. 54B, NO. 3, AUGUST 1972
6 458 W. F. WHITE SELECTION AND RESULTS (TABLES VI, VII AND VIII) Of the twenty-one patients with satisfactory results, nineteen had drive and seventeen were of reasonable intelligence. There were fifteen hemiplegics and five tetraplegics but it is doubtful ifthese figures really substantiate the view that hemiplegics do better than tetraplegics. In the best results-those classed as good, there were eight hemiplegics and two tetraplegics. It must be stressed that any gain in the tetraplegic is much more vital. It has to be put to use and is in no danger of being dissociated as sometimes happens in the hemiplegic (Samilson 1966). The eleven failures demonstrated the faults in selection. Only one of the eleven patients had good drive and reasonable intelligence. TABLE VI GOOD AND FAIR RESULTS RELATED TO SELECTION OF PATIENTS (TWENTY-ONE PATIENTS) Characteristics Number:f Hemiplegic Tetraplegic Triplegic Drive Good intelligence.. 17 TABLE VII TABLE VIII GOOD RESULTS RELATED TO SELECTION FAILURES RELATED TO SELECTION OF PATIENTS (TEN PATIENTS) OF PATIENTS (ELEVEN PATIENTS) Characteristics Number:f Characteristics Number:f Hemiplegic.. 8 Hemiplegic. 8 Tetraplegic.. Tetraplegic. 3 Drive Drive.. 1 Good intelligence. 9 Good intelligence 1 COMMENT It is unrealistic to expect uniform success in this field. Nevertheless there were many failures. The fault almost certainly lay in selection and it has been emphasised that the criteria for operation are strict. The most important single attribute is drive. Any operation must be simple and designed for a specific and limited purpose. Burman (1938) wrote: There is a certain sympathy in spastic hands by which an operative procedure directed at one point diminishes spasticity in another. Long before that, in 1919, Sir Arthur Keith wrote of Hugh Owen Thomas: He treated muscles as he treated his patients. He relieved the weak and oppressed, he restrained the strong. That, in effect, sums up the rationale of the muscle slide. THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY
7 FLEXOR MUSCLE SLIDE IN THE SPASTIC HAND 459 SUMMARY 1. A study has been made of thirty-two patients who had had operations for their spastic hands. 2. In twenty-seven a flexor muscle slide was done, either by itself or in association with an arthrodesis of the wrist. The rationale of the operation is discussed. 3. The first muscle slide was done in 1959 and the average follow-up was seven and a half years. 4. Selection is crucial : drive, usually coupled with intelligence, is essential for success. 5. Operation is not a replacement for physical therapy. The object is to make rehabilitation easier. The flexor muscle slide, in carefully chosen cases, may play a significant part in achieving this. I wish to thank Mr James Garden for his help and Mr Athol Parkes for his encouragement and for referring a number of patients to me. I am also grateful to Mr John Hunter, photographer at Law Hospital, and to Miss Catherine Loudon, who did the drawings. REFERENCES BURMAN, M. S. (1938): The Spastic Hand. Journal ofbone and Joint Surgery, 20, 133. COOPER, W. (1952): Surgery of the Upper Extremity in Spastic Paralysis. Quarterly Review ofpaediatrics, 7, 139. GOLDNER, J. L. (1955): Reconstructive Surgery of the Hand in Cerebral Palsy and Spastic Paralysis Resulting from Injury to the Spinal Cord. Journal ofbone and Joint Surgery, 37-A, INGLIS, A. E., and COOPER, W. (1966) : Release of the Flexor-pronator Origin for Flexion Deformities of the Hand and Wrist in Spastic Paralysis. Journal ofbone and Joint Surgery, 48-A, 847. KEITH, Sir Arthur (1919): Menders of the Maimed, p. 60. London : Oxford University Press. KENNEY, W. E., and HEABERLIN, P. C., Jun. (1962): An Electromyographic Study of the Locomotor Pattern of Spastic Children. Clinical Orthopaedics, 24, 139. PAGE, C. M. (1923): An Operation for the Relief of Flexion-contracture in the Forearm. Journal ofbone and Joint Surgery, 5, 233. SAMILSON, R. L. (1966): Principles of Assessment of the Upper Limb in Cerebral Palsy. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research, 47, 105. WHrrE, W. F. (1961): Surgery of the Spastic Hand. Proceedings of the Second Hand Club and the Scandinavian Club for Surgery of the Hand, Copenhagen, May 15-19, 1961, p. 57. ZUCK, F. N. (1964): Cerebral Palsy. In Orthopaedic Surgery by Sir Walter Mercer and Robert B. Duthie. Sixth edition, p London: Edward Arnold (Publishers) Ltd. VOL. 54 B, NO. 3, AUGUST 1972
Surgery of the Upper Extremity in Children with Hemiplegic Cerebral Palsy
 Article submitted, at the request of CHASA, by Robert Bunata, M.D., Board Certified Orthopedic Surgeon. Dr. Bunata has a special interest in upper extremity surgery in children who have hemiplegia. He
Article submitted, at the request of CHASA, by Robert Bunata, M.D., Board Certified Orthopedic Surgeon. Dr. Bunata has a special interest in upper extremity surgery in children who have hemiplegia. He
Hemiplegic shoulder pain/shoulder subluxation
 UPPER LIMB NEUROMUSCULAR ELECTRICAL STIMULATION: Electrode positions Please note that the polarity (red and black leads) can be altered according to your clinical reasoning. The area in which you want
UPPER LIMB NEUROMUSCULAR ELECTRICAL STIMULATION: Electrode positions Please note that the polarity (red and black leads) can be altered according to your clinical reasoning. The area in which you want
EQUINUS DEFORMITY IN CEREBRAL PALSY. A Comparison between Elongation of the Tendo Calcaneus and Gastrocnemius Recession
 EQUINUS DEFORMITY IN CEREBRAL PALSY A Comparison between Elongation of the Tendo Calcaneus and Gastrocnemius Recession W. J. W. SHARRARD and S. BERNSTEIN,* SHEFFIELD, ENGLAND From the Children s Hospital,
EQUINUS DEFORMITY IN CEREBRAL PALSY A Comparison between Elongation of the Tendo Calcaneus and Gastrocnemius Recession W. J. W. SHARRARD and S. BERNSTEIN,* SHEFFIELD, ENGLAND From the Children s Hospital,
Chapter 7 The Wrist and Hand Joints
 Chapter 7 The Wrist and Hand Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS Many Archery, Relate wrist require sports require precise functioning of flexion, & hand & hand functional combined
Chapter 7 The Wrist and Hand Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS Many Archery, Relate wrist require sports require precise functioning of flexion, & hand & hand functional combined
Hand and Upper Extremity Injuries in Outdoor Activities. John A. Schneider, M.D.
 Hand and Upper Extremity Injuries in Outdoor Activities John A. Schneider, M.D. Biographical Sketch Dr. Schneider is an orthopedic surgeon that specializes in the treatment of hand and upper extremity
Hand and Upper Extremity Injuries in Outdoor Activities John A. Schneider, M.D. Biographical Sketch Dr. Schneider is an orthopedic surgeon that specializes in the treatment of hand and upper extremity
EXTENSOR POLLICIS TENDONITIS SYNDROME
 EXTENSOR POLLICIS TENDONITIS SYNDROME The extensor pollicis longus muscle has its origin on the lateral part of the middle third of the ulnar shaft on the dorsal border below the abductor pollicis longus
EXTENSOR POLLICIS TENDONITIS SYNDROME The extensor pollicis longus muscle has its origin on the lateral part of the middle third of the ulnar shaft on the dorsal border below the abductor pollicis longus
Wrist and Hand. Patient Information Guide to Bone Fracture, Bone Reconstruction and Bone Fusion: Fractures of the Wrist and Hand: Carpal bones
 Patient Information Guide to Bone Fracture, Bone Reconstruction and Bone Fusion: Wrist and Hand Fractures of the Wrist and Hand: Fractures of the wrist The wrist joint is made up of the two bones in your
Patient Information Guide to Bone Fracture, Bone Reconstruction and Bone Fusion: Wrist and Hand Fractures of the Wrist and Hand: Fractures of the wrist The wrist joint is made up of the two bones in your
Medical Report Checklist: Upper Extremities Peripheral Nerve Disorders Impairments (PND)
 http://www.pdratings.com/ Craig Andrew Lange craig@pdratings.com California Workers Compensation Certified AMA Guides Impairment & Disability Rating Specialists Voice: (415) 861-4040 / Fax: (415) 276-3741
http://www.pdratings.com/ Craig Andrew Lange craig@pdratings.com California Workers Compensation Certified AMA Guides Impairment & Disability Rating Specialists Voice: (415) 861-4040 / Fax: (415) 276-3741
Repetitive Strain Injury (RSI)
 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and Other Musculoskeletal Problems in the Workplace: What s the Solution? by Richard N. Hinrichs, Ph.D. Dept. of Kinesiology Arizona State University Repetitive Strain Injury (RSI)
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and Other Musculoskeletal Problems in the Workplace: What s the Solution? by Richard N. Hinrichs, Ph.D. Dept. of Kinesiology Arizona State University Repetitive Strain Injury (RSI)
Effects of Upper Extremity Mobilization Techniques on Fine-Motor Performance in Children with Neuromotor Disorders
 This program has been approved for CEUs by the American Occupational Therapy Association (AOTA), the Board of Certification (BOC), and is accepted for PDUs by the National Board of Certification of Occupational
This program has been approved for CEUs by the American Occupational Therapy Association (AOTA), the Board of Certification (BOC), and is accepted for PDUs by the National Board of Certification of Occupational
www.ghadialisurgery.com
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
LSU Health Sciences Center Occupational Therapy Flexor Tendon Injury Treatment Protocol
 . LSU Health Sciences Center Occupational Therapy Flexor Tendon Injury Treatment Protocol DIP PIP MCP Zone 1 Zone 2 T 1 T 2 Zone 3 T 3 Zone 4 Zone 5 Zone 5 cs Carla M. Saulsbery LOTR, CHT Dr. A. Hollister,
. LSU Health Sciences Center Occupational Therapy Flexor Tendon Injury Treatment Protocol DIP PIP MCP Zone 1 Zone 2 T 1 T 2 Zone 3 T 3 Zone 4 Zone 5 Zone 5 cs Carla M. Saulsbery LOTR, CHT Dr. A. Hollister,
Ergonomics Monitor Training Manual
 Table of contents I. Introduction Ergonomics Monitor Training Manual II. Definition of Common Injuries Common Hand & Wrist Injuries Common Neck & Back Injuries Common Shoulder & Elbow Injuries III. Ergonomics
Table of contents I. Introduction Ergonomics Monitor Training Manual II. Definition of Common Injuries Common Hand & Wrist Injuries Common Neck & Back Injuries Common Shoulder & Elbow Injuries III. Ergonomics
Carpal Tunnel Release. Relieving Pressure in Your Wrist
 Carpal Tunnel Release Relieving Pressure in Your Wrist Understanding Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a problem that affects the wrist and hand. If you have CTS, tingling and numbness
Carpal Tunnel Release Relieving Pressure in Your Wrist Understanding Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a problem that affects the wrist and hand. If you have CTS, tingling and numbness
International Standards for the Classification of Spinal Cord Injury Motor Exam Guide
 C5 Elbow Flexors Biceps Brachii, Brachialis Patient Position: The shoulder is in neutral rotation, neutral flexion/extension, and adducted. The elbow is fully extended, with the forearm in full supination.
C5 Elbow Flexors Biceps Brachii, Brachialis Patient Position: The shoulder is in neutral rotation, neutral flexion/extension, and adducted. The elbow is fully extended, with the forearm in full supination.
Self-Range of Motion Exercises for Shoulders, Arms, Wrists, Fingers
 Self-Range of Motion Exercises for Shoulders, Arms, Wrists, Fingers These exercises will help keep your muscles strong and mobile, and your joints flexible. Other benefits of these exercises include: C
Self-Range of Motion Exercises for Shoulders, Arms, Wrists, Fingers These exercises will help keep your muscles strong and mobile, and your joints flexible. Other benefits of these exercises include: C
Scaphoid Fracture of the Wrist
 Page 1 of 6 Scaphoid Fracture of the Wrist Doctors commonly diagnose a sprained wrist after a patient falls on an outstretched hand. However, if pain and swelling don't go away, doctors become suspicious
Page 1 of 6 Scaphoid Fracture of the Wrist Doctors commonly diagnose a sprained wrist after a patient falls on an outstretched hand. However, if pain and swelling don't go away, doctors become suspicious
Upper limb electrical stimulation exercises. P Taylor, G Mann, C Johnson, L Malone
 Upper limb electrical stimulation exercises. P Taylor, G Mann, C Johnson, L Malone In this article we wish to document some of the electrical stimulation techniques we use for the upper limb, primarily
Upper limb electrical stimulation exercises. P Taylor, G Mann, C Johnson, L Malone In this article we wish to document some of the electrical stimulation techniques we use for the upper limb, primarily
Systemic condition affecting synovial tissue Hypertrohied synovium destroys. Synovectomy. Tenosynovectomy Tendon Surgery Arthroplasty Arthrodesis
 Surgical Options for Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Wrist Raj Bhatia Consultant Hand & Orthopaedic Surgeon Bristol Royal Infirmary & Avon Orthopaedic Centre Rheumatoid Arthritis Systemic condition affecting
Surgical Options for Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Wrist Raj Bhatia Consultant Hand & Orthopaedic Surgeon Bristol Royal Infirmary & Avon Orthopaedic Centre Rheumatoid Arthritis Systemic condition affecting
Most active and intricate part of the upper extremity Especially vulnerable to injury Do not respond well to serious trauma. Magee, 2008. pg.
 PTA 216 Most active and intricate part of the upper extremity Especially vulnerable to injury Do not respond well to serious trauma Magee, 2008. pg. 396 28 bones Numerous articulations 19 intrinsic muscles
PTA 216 Most active and intricate part of the upper extremity Especially vulnerable to injury Do not respond well to serious trauma Magee, 2008. pg. 396 28 bones Numerous articulations 19 intrinsic muscles
Fractures around wrist
 Fractures around wrist Colles Fracture Smiths fracture Barton s fracture Chauffer s fracture Scaphoid fracture Lunate dislocation Vivek Pandey Colles fracture Definition: Fracture of the distal end radius
Fractures around wrist Colles Fracture Smiths fracture Barton s fracture Chauffer s fracture Scaphoid fracture Lunate dislocation Vivek Pandey Colles fracture Definition: Fracture of the distal end radius
Hand & Plastics Physiotherapy Department Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Hand & Plastics Physiotherapy Department Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients page 2 What is the Carpal Tunnel? The carpal tunnel is made up of the bones
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Hand & Plastics Physiotherapy Department Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients page 2 What is the Carpal Tunnel? The carpal tunnel is made up of the bones
Examination of the Elbow. Elbow Examination. Structures to Examine. Active Range of Motion. Active Range of Motion 8/22/2012
 Examination of the Elbow The elbow is a complex modified hinge joint The humero-ulnar joint is a hinge joint allowing flexion and extension The radio-ulnar joint allows for pronation and supination of
Examination of the Elbow The elbow is a complex modified hinge joint The humero-ulnar joint is a hinge joint allowing flexion and extension The radio-ulnar joint allows for pronation and supination of
A Patient's Guide to Arthritis of the Finger Joints
 Introduction A Patient's Guide to Arthritis of the Finger Joints When you stop to think about how much you use your hands, it's easy to see why the joints of the fingers are so important. Arthritis of
Introduction A Patient's Guide to Arthritis of the Finger Joints When you stop to think about how much you use your hands, it's easy to see why the joints of the fingers are so important. Arthritis of
10/15/2012. The Hand. Clarification of Terms. Osteology of the Hand (Bones) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=idxuwerttj A&feature=related
 The Hand http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=idxuwerttj A&feature=related Clarification of Terms The hand is made up of the thumb, metacarpals, and phalanges The digits are numbered (with the thumb being #1
The Hand http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=idxuwerttj A&feature=related Clarification of Terms The hand is made up of the thumb, metacarpals, and phalanges The digits are numbered (with the thumb being #1
Integra. MCP Joint Replacement PATIENT INFORMATION
 Integra MCP Joint Replacement PATIENT INFORMATION Integra MCP Patient Information This brochure summarizes information about the use, risks, and benefits of the Integra MCP finger implant. Be sure to discuss
Integra MCP Joint Replacement PATIENT INFORMATION Integra MCP Patient Information This brochure summarizes information about the use, risks, and benefits of the Integra MCP finger implant. Be sure to discuss
THE WRIST. At a glance. 1. Introduction
 THE WRIST At a glance The wrist is possibly the most important of all joints in everyday and professional life. It is under strain not only in many blue collar trades, but also in sports and is therefore
THE WRIST At a glance The wrist is possibly the most important of all joints in everyday and professional life. It is under strain not only in many blue collar trades, but also in sports and is therefore
Radial Head Fracture Repair and Rehabilitation
 1 Radial Head Fracture Repair and Rehabilitation Surgical Indications and Considerations Anatomical Considerations: The elbow is a complex joint due to its intricate functional anatomy. The ulna, radius
1 Radial Head Fracture Repair and Rehabilitation Surgical Indications and Considerations Anatomical Considerations: The elbow is a complex joint due to its intricate functional anatomy. The ulna, radius
Brachial Plexus Palsy
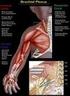 Patient and Family Education Brachial Plexus Palsy A Therapy Guide for Your Baby Brachial Plexus Palsy is caused by trauma to the nerves of the arm. This trauma may have caused muscle weakness, lack of
Patient and Family Education Brachial Plexus Palsy A Therapy Guide for Your Baby Brachial Plexus Palsy is caused by trauma to the nerves of the arm. This trauma may have caused muscle weakness, lack of
The surgical management of cerebral palsy
 The surgical management of cerebral palsy T. DUCKWORTH University Department of Orthopaedics, Sheffield Cerebral palsy more than any other paralytic condition presents some of the most difficult and challenging
The surgical management of cerebral palsy T. DUCKWORTH University Department of Orthopaedics, Sheffield Cerebral palsy more than any other paralytic condition presents some of the most difficult and challenging
by joe muscolino body mechanics
 by joe muscolino body mechanics carpal tunnel syndrome The word carpal means wrist. Therefore, the carpal tunnel is a tunnel that is formed by the structural configuration of the wrist (carpal) bones.
by joe muscolino body mechanics carpal tunnel syndrome The word carpal means wrist. Therefore, the carpal tunnel is a tunnel that is formed by the structural configuration of the wrist (carpal) bones.
POLICY 2: DEATH AND PERMANENT DISABILITY
 POLICY 2: DEATH AND PERMANENT DISABILITY Article 1 - Death (as a result from any cause) 1.1. - Amount of indemnity The capital sum payable on the death of an Insured Person, shall be: 1. 25.000 USD in
POLICY 2: DEATH AND PERMANENT DISABILITY Article 1 - Death (as a result from any cause) 1.1. - Amount of indemnity The capital sum payable on the death of an Insured Person, shall be: 1. 25.000 USD in
A Patient s Guide to Guyon s Canal Syndrome
 A Patient s Guide to DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources. It may not be complete or timely. It does not cover all diseases, physical conditions, ailments or
A Patient s Guide to DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources. It may not be complete or timely. It does not cover all diseases, physical conditions, ailments or
Injuries to Upper Limb
 Injuries to Upper Limb 1 The following is a list of common sporting conditions and injuries. The severity of each condition may lead to different treatment protocols and certainly varying levels of intervention.
Injuries to Upper Limb 1 The following is a list of common sporting conditions and injuries. The severity of each condition may lead to different treatment protocols and certainly varying levels of intervention.
Hand & Plastics Physiotherapy Department Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Hand & Plastics Physiotherapy Department Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients This leaflet has been developed to answer any questions you may have regarding
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Hand & Plastics Physiotherapy Department Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients This leaflet has been developed to answer any questions you may have regarding
Proximal border = palmar wrist crease Distal border = Kaplan + ring finger axis
 FPL FCR Proximal border = palmar wrist crease Distal border = Kaplan + ring finger axis Thenar motor branch Kaplan s cardinal line: distal TCL thenar branch Superficial palmar arch superficial arch Originates
FPL FCR Proximal border = palmar wrist crease Distal border = Kaplan + ring finger axis Thenar motor branch Kaplan s cardinal line: distal TCL thenar branch Superficial palmar arch superficial arch Originates
Adult Forearm Fractures
 Adult Forearm Fractures Your forearm is made up of two bones, the radius and ulna. In most cases of adult forearm fractures, both bones are broken. Fractures of the forearm can occur near the wrist at
Adult Forearm Fractures Your forearm is made up of two bones, the radius and ulna. In most cases of adult forearm fractures, both bones are broken. Fractures of the forearm can occur near the wrist at
Median Nerve Injuries in, Fractures in the Region of the Wrist
 252 Median Nerve Injuries in, Fractures in the Region of the Wrist N. MEADOFF, M.D., Bakersfield SUMMARY Injuries of the median nerve in fractures in the region of the wrist are not uncommon. Median nerve
252 Median Nerve Injuries in, Fractures in the Region of the Wrist N. MEADOFF, M.D., Bakersfield SUMMARY Injuries of the median nerve in fractures in the region of the wrist are not uncommon. Median nerve
Triceps Pronation-Supination Orthosis
 Triceps Pronation-Supination Orthosis Daniel P. Cole, C.O. Paula J. Clarkson, COTA/L INTRODUCTION The Triceps-Supination Orthosis* was designed for a patient with flexion contractures of the right elbow
Triceps Pronation-Supination Orthosis Daniel P. Cole, C.O. Paula J. Clarkson, COTA/L INTRODUCTION The Triceps-Supination Orthosis* was designed for a patient with flexion contractures of the right elbow
Splinting in Neurology. Jo Tuckey MSc MCSP
 Splinting in Neurology Jo Tuckey MSc MCSP Splinting in Neurology When should splinting be considered? How to choose the most appropriate splint or position for splinting. Practicalities of providing a
Splinting in Neurology Jo Tuckey MSc MCSP Splinting in Neurology When should splinting be considered? How to choose the most appropriate splint or position for splinting. Practicalities of providing a
Westmount UCC 751 Victoria Street South, Kitchener, ON N2M 5N4 519-745-2273 Fairway UCC 385 Fairway Road South, Kitchener, ON N2C 2N9 519-748-2327
 K-W URGENT CARE CLINICS INC. Westmount UCC 751 Victoria Street South, Kitchener, ON N2M 5N4 519-745-2273 Fairway UCC 385 Fairway Road South, Kitchener, ON N2C 2N9 519-748-2327 OPEN Mon-Fri 8am-5pm, Sa
K-W URGENT CARE CLINICS INC. Westmount UCC 751 Victoria Street South, Kitchener, ON N2M 5N4 519-745-2273 Fairway UCC 385 Fairway Road South, Kitchener, ON N2C 2N9 519-748-2327 OPEN Mon-Fri 8am-5pm, Sa
WRIST EXAMINATION. Look. Feel. Move. Special Tests
 WRIST EXAMINATION Look o Dorsum, side, palmar- palmar flex wrist to exacerbate dorsal swellings o Deformity e.g. radial deviation after colles, prominent ulna o Swellings e.g. ganglion o Scars, muscle
WRIST EXAMINATION Look o Dorsum, side, palmar- palmar flex wrist to exacerbate dorsal swellings o Deformity e.g. radial deviation after colles, prominent ulna o Swellings e.g. ganglion o Scars, muscle
The results of surgical treatment for pronation deformities of the forearm in cerebral palsy after a mean follow-up of 17.5 years
 Čobeljić et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2015) 10:106 DOI 10.1186/s13018-015-0251-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The results of surgical treatment for pronation deformities of the forearm
Čobeljić et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2015) 10:106 DOI 10.1186/s13018-015-0251-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The results of surgical treatment for pronation deformities of the forearm
Hand Injuries and Disorders
 Hand Injuries and Disorders Introduction Each of your hands has 27 bones, 15 joints and approximately 20 muscles. There are many common problems that can affect your hands. Hand problems can be caused
Hand Injuries and Disorders Introduction Each of your hands has 27 bones, 15 joints and approximately 20 muscles. There are many common problems that can affect your hands. Hand problems can be caused
Elbow, Forearm, Wrist, & Hand. Bony Anatomy. Objectives. Bones. Bones. Bones
 Objectives Elbow, Forearm, Wrist, & Hand Chapter 19 Identify and discuss the functional anatomy of the elbow and forearm Discuss the common injuries associated with these anatomical structures Bones Humerus
Objectives Elbow, Forearm, Wrist, & Hand Chapter 19 Identify and discuss the functional anatomy of the elbow and forearm Discuss the common injuries associated with these anatomical structures Bones Humerus
Abdominal Pedicle Flaps To The Hand And Forearm John C. Kelleher M.D., F.A.C.S.
 Abdominal Pedicle Flaps To The Hand And Forearm John C. Kelleher M.D., F.A.C.S. Global-HELP Publications Chapter Eight: TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR FORMATION OF A TUBED PEDICLE FLAP Creating a tube pedicle
Abdominal Pedicle Flaps To The Hand And Forearm John C. Kelleher M.D., F.A.C.S. Global-HELP Publications Chapter Eight: TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR FORMATION OF A TUBED PEDICLE FLAP Creating a tube pedicle
Active Range of Motion: A. Flexion: Gently try to bend your wrist forward. Hold for 5 seconds. Repeat for 3 sets of 10.
 Rehabilitation Exercises for Wrist and Hand Injuries If instructed by your medical doctor, you may begin these exercises when the pain has started to decrease. Active Range of Motion: A. Flexion: Gently
Rehabilitation Exercises for Wrist and Hand Injuries If instructed by your medical doctor, you may begin these exercises when the pain has started to decrease. Active Range of Motion: A. Flexion: Gently
Wrist Fracture. Please stick addressograph here
 ORTHOPAEDIC UNIT: 01-293 8687 /01-293 6602 UPMC BEACON CENTRE FOR ORTHOPAEDICS: 01-2937575 PHYSIOTHERAPY DEPARTMENT: 01-2936692 GUIDELINES FOR PATIENTS FOLLOWING WRIST FRACTURE Please stick addressograph
ORTHOPAEDIC UNIT: 01-293 8687 /01-293 6602 UPMC BEACON CENTRE FOR ORTHOPAEDICS: 01-2937575 PHYSIOTHERAPY DEPARTMENT: 01-2936692 GUIDELINES FOR PATIENTS FOLLOWING WRIST FRACTURE Please stick addressograph
THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME
 THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME The Problem The term thoracic outlet syndrome is used to describe a condition of compression of the nerves and/or blood vessels in the region around the neck and collarbone, called
THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME The Problem The term thoracic outlet syndrome is used to describe a condition of compression of the nerves and/or blood vessels in the region around the neck and collarbone, called
COMPUTER-RELATED MUSCLE, TENDON, AND JOINT INJURIES
 CHAPTER ELEVEN COMPUTER-RELATED MUSCLE, TENDON, AND JOINT INJURIES To reduce the risk of pain in your neck and shoulders, stay within these recommended ranges of movement: Neck Flexion: 0 o -15 o (bending
CHAPTER ELEVEN COMPUTER-RELATED MUSCLE, TENDON, AND JOINT INJURIES To reduce the risk of pain in your neck and shoulders, stay within these recommended ranges of movement: Neck Flexion: 0 o -15 o (bending
TENDON INJURIES OF THE HAND KEY FIGURES:
 Chapter 32 TENDON INJURIES OF THE HAND KEY FIGURES: Extensor surface of hand Mallet finger Mallet splints Injured finger in stack splint Repair of open mallet Most hand specialists believe that the earlier
Chapter 32 TENDON INJURIES OF THE HAND KEY FIGURES: Extensor surface of hand Mallet finger Mallet splints Injured finger in stack splint Repair of open mallet Most hand specialists believe that the earlier
Exercise and FES cycle fact sheet
 Exercise and FES cycle fact sheet FES = Functional Electrical Stimulation. An electrical current is passed through paralysed muscle causing it to contract. The electrical current uses the peripheral nerves
Exercise and FES cycle fact sheet FES = Functional Electrical Stimulation. An electrical current is passed through paralysed muscle causing it to contract. The electrical current uses the peripheral nerves
Surgery for Disc Prolapse
 Contact Details Spinal Team Nuffield Orthopaedic Centre Windmill Road Headington Oxford OX3 7LD Surgery for Disc Prolapse Phone: 01865 738051 Fax: 01865 738027 Web Site www.noc.nhs.uk Surgery for disc
Contact Details Spinal Team Nuffield Orthopaedic Centre Windmill Road Headington Oxford OX3 7LD Surgery for Disc Prolapse Phone: 01865 738051 Fax: 01865 738027 Web Site www.noc.nhs.uk Surgery for disc
Ulnar Neuropathy Differential Diagnosis and Prognosis. Disclosures: None
 Ulnar Neuropathy Differential Diagnosis and Prognosis Disclosures: None Goals of Lecture Describe anatomy: sites of entrapment Ulnar nerve Discuss differential diagnosis of ulnar nerve pathology Identify
Ulnar Neuropathy Differential Diagnosis and Prognosis Disclosures: None Goals of Lecture Describe anatomy: sites of entrapment Ulnar nerve Discuss differential diagnosis of ulnar nerve pathology Identify
Dr. Enas Elsayed. Brunnstrom Approach
 Brunnstrom Approach Learning Objectives: By the end of this lab, the student will be able to: 1. Demonstrate different reflexes including stimulus and muscle tone response. 2. Demonstrate how to evoke
Brunnstrom Approach Learning Objectives: By the end of this lab, the student will be able to: 1. Demonstrate different reflexes including stimulus and muscle tone response. 2. Demonstrate how to evoke
Differentiating Cervical Radiculopathy and Peripheral Neuropathy. Adam P. Smith, MD
 Differentiating Cervical Radiculopathy and Peripheral Neuropathy Adam P. Smith, MD I have no financial, personal, or professional conflicts of interest to report Radiculopathy versus Neuropathy Radiculopathy
Differentiating Cervical Radiculopathy and Peripheral Neuropathy Adam P. Smith, MD I have no financial, personal, or professional conflicts of interest to report Radiculopathy versus Neuropathy Radiculopathy
Workplace Health, Safety & Compensation Review Division
 Workplace Health, Safety & Compensation Review Division WHSCRD Case No: 14152-06 WHSCC Claim No: 606499 and 791748 Decision Number: 14147 Lloyd Piercey Review Commissioner The Review Proceedings 1. The
Workplace Health, Safety & Compensation Review Division WHSCRD Case No: 14152-06 WHSCC Claim No: 606499 and 791748 Decision Number: 14147 Lloyd Piercey Review Commissioner The Review Proceedings 1. The
Informed Patient Tutorial Copyright 2012 by the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
 Informed Patient Tutorial Copyright 2012 by the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Informed Patient - Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery Introduction Welcome to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons'
Informed Patient Tutorial Copyright 2012 by the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Informed Patient - Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery Introduction Welcome to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons'
Splinting for individuals with Spinal Cord Injury
 Splinting for individuals with Spinal Cord Injury A Resource for Health Service Providers WA State Spinal Injury Unit Version 1 October 2013 Review Date October 2016 This information is developed to direct
Splinting for individuals with Spinal Cord Injury A Resource for Health Service Providers WA State Spinal Injury Unit Version 1 October 2013 Review Date October 2016 This information is developed to direct
ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR BO POVLSEN Emeritus Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Guy s & St Thomas Hospitals NHS Trust GMC no. 3579329
 ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR BO POVLSEN Emeritus Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Guy s & St Thomas Hospitals NHS Trust GMC no. 3579329 Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon London Bridge Hospital Medico-Legal Secretary:
ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR BO POVLSEN Emeritus Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Guy s & St Thomas Hospitals NHS Trust GMC no. 3579329 Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon London Bridge Hospital Medico-Legal Secretary:
Muscles of the Forearm and Hand
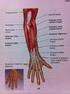 8 Muscles of the Forearm and Hand 132 PRONATOR TERES Strengthening exercises Pronation with strength bar Self stretches Weight of stick increases supination via gravity PRONATOR TERES 133 Latin, pronate,
8 Muscles of the Forearm and Hand 132 PRONATOR TERES Strengthening exercises Pronation with strength bar Self stretches Weight of stick increases supination via gravity PRONATOR TERES 133 Latin, pronate,
A TECHNIQUE FOR MAKING HAND SPLINTS FROM STYROFOAM AND PLYWOOD
 A TECHNIQUE FOR MAKING HAND SPLINTS FROM STYROFOAM AND PLYWOOD David Woodruff Thomforde* ABSTRACT A technique has been developed in Paraguay, for making hand splints from styrofoam, plywood and paper.
A TECHNIQUE FOR MAKING HAND SPLINTS FROM STYROFOAM AND PLYWOOD David Woodruff Thomforde* ABSTRACT A technique has been developed in Paraguay, for making hand splints from styrofoam, plywood and paper.
Rehabilitation Program for Children With Brachial Plexus and Peripheral Nerve Injury
 Rehabilitation Program for Children With Brachial Plexus and Peripheral Nerve Injury Lorna E. Ramos and Joan P. Zell An aggressive and integrated physical and occupational therapy program is essential
Rehabilitation Program for Children With Brachial Plexus and Peripheral Nerve Injury Lorna E. Ramos and Joan P. Zell An aggressive and integrated physical and occupational therapy program is essential
CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME A PATIENT GUIDE TO THE NURSE-LED CARPAL TUNNEL SERVICE
 CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME A PATIENT GUIDE TO THE NURSE-LED CARPAL TUNNEL SERVICE Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What is carpal tunnel syndrome? It is entrapment of a nerve at the
CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME A PATIENT GUIDE TO THE NURSE-LED CARPAL TUNNEL SERVICE Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What is carpal tunnel syndrome? It is entrapment of a nerve at the
NERVE COMPRESSION DISORDERS
 Common Disorders of the Hand and Wrist Ryan Klinefelter, MD Associate Professor of Orthopaedics Department of Orthopaedics The Ohio State University Medical Center NERVE COMPRESSION DISORDERS 1 Carpal
Common Disorders of the Hand and Wrist Ryan Klinefelter, MD Associate Professor of Orthopaedics Department of Orthopaedics The Ohio State University Medical Center NERVE COMPRESSION DISORDERS 1 Carpal
NDT Treatment Planning Worksheet
 Child s Name: Kalab DOB: 01/01/02 Diagnosis: CP-Right-sided Heimplegia DOE: May 29, 2009 Therapist s Name: Mary Rose Franjoine Discipline: PT Current Participation: Attends his neighborhood school with
Child s Name: Kalab DOB: 01/01/02 Diagnosis: CP-Right-sided Heimplegia DOE: May 29, 2009 Therapist s Name: Mary Rose Franjoine Discipline: PT Current Participation: Attends his neighborhood school with
Hand and Wrist Injuries and Conditions
 Hand and Wrist Injuries and Conditions Julia Wild Hand Therapist www.southernhandtherapy.com.au 02 9553 8597 POSI Position of Safe Immobilisation So everything is balanced Wrist 30⁰ ext MCP 70⁰ flex for
Hand and Wrist Injuries and Conditions Julia Wild Hand Therapist www.southernhandtherapy.com.au 02 9553 8597 POSI Position of Safe Immobilisation So everything is balanced Wrist 30⁰ ext MCP 70⁰ flex for
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients Therapy Services Phone no: 01625 661481 www.eastcheshire.nhs.uk @eastcheshirenhs Ref: 11437 Review: 06/2015 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Ref: 11437 Page 1 Review:
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients Therapy Services Phone no: 01625 661481 www.eastcheshire.nhs.uk @eastcheshirenhs Ref: 11437 Review: 06/2015 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Ref: 11437 Page 1 Review:
Elbow arthroscopy. Key points
 Patient information Elbow arthroscopy This information has been produced to help you gain the maximum benefit and understanding of your operation. It includes the following information: Key points About
Patient information Elbow arthroscopy This information has been produced to help you gain the maximum benefit and understanding of your operation. It includes the following information: Key points About
CERVICAL DISC HERNIATION
 CERVICAL DISC HERNIATION Most frequent at C 5/6 level but also occur at C 6 7 & to a lesser extent at C4 5 & other levels In relatively younger persons soft disk protrusion is more common than hard disk
CERVICAL DISC HERNIATION Most frequent at C 5/6 level but also occur at C 6 7 & to a lesser extent at C4 5 & other levels In relatively younger persons soft disk protrusion is more common than hard disk
Cerebral Palsy. 1995-2014, The Patient Education Institute, Inc. www.x-plain.com nr200105 Last reviewed: 06/17/2014 1
 Cerebral Palsy Introduction Cerebral palsy, or CP, can cause serious neurological symptoms in children. Thousands of children are diagnosed with cerebral palsy every year. This reference summary explains
Cerebral Palsy Introduction Cerebral palsy, or CP, can cause serious neurological symptoms in children. Thousands of children are diagnosed with cerebral palsy every year. This reference summary explains
Mini TightRope CMC Surgical Technique
 Mini TightRope CMC Surgical Technique Mini TightRope CMC Mini TightRope CMC Fixation The Mini TightRope provides a unique means to suspend the thumb metacarpal after partial or complete trapezial resection
Mini TightRope CMC Surgical Technique Mini TightRope CMC Mini TightRope CMC Fixation The Mini TightRope provides a unique means to suspend the thumb metacarpal after partial or complete trapezial resection
Wrist Fractures. Wrist Defined: Carpal Bones Distal Radius Distal Ulna
 Wrist Fractures Wrist Fractures Wrist Defined: Carpal Bones Distal Radius Distal Ulna Wrist Fractures Wrist Joints: CMC Intercarpal Radiocarpal DRUJ drudge Wrist Fractures Wrist Fractures: (that we are
Wrist Fractures Wrist Fractures Wrist Defined: Carpal Bones Distal Radius Distal Ulna Wrist Fractures Wrist Joints: CMC Intercarpal Radiocarpal DRUJ drudge Wrist Fractures Wrist Fractures: (that we are
Switch Assessment and Planning Framework for Individuals with Physical Disabilities
 Guidance Notes Pre- assessment: It is important to gather together appropriate information before the assessment to inform on possible starting points for the assessment. The Pre-Assessment Form should
Guidance Notes Pre- assessment: It is important to gather together appropriate information before the assessment to inform on possible starting points for the assessment. The Pre-Assessment Form should
Musculoskeletal System
 CHAPTER 3 Impact of SCI on the Musculoskeletal System Voluntary movement of the body is dependent on a number of systems. These include: The brain initiates the movement and receives feedback to assess
CHAPTER 3 Impact of SCI on the Musculoskeletal System Voluntary movement of the body is dependent on a number of systems. These include: The brain initiates the movement and receives feedback to assess
Cerebral Palsy. In order to function, the brain needs a continuous supply of oxygen.
 Cerebral Palsy Introduction Cerebral palsy, or CP, can cause serious neurological symptoms in children. Up to 5000 children in the United States are diagnosed with cerebral palsy every year. This reference
Cerebral Palsy Introduction Cerebral palsy, or CP, can cause serious neurological symptoms in children. Up to 5000 children in the United States are diagnosed with cerebral palsy every year. This reference
SPLINTING THE HAND WITH A PERIPHERAL-NERVE INJURY
 Chapter 34 SPLINTING THE HAND WITH A PERIPHERAL-NERVE INJURY Judy C. Colditz Splinting the hand with a peripheral-nerve injury is both easy and difficult. The ease of splinting results from the readily
Chapter 34 SPLINTING THE HAND WITH A PERIPHERAL-NERVE INJURY Judy C. Colditz Splinting the hand with a peripheral-nerve injury is both easy and difficult. The ease of splinting results from the readily
NOT DESIGNATED FOR PUBLICATION
 NOT DESIGNATED FOR PUBLICATION BEFORE THE ARKANSAS WORKERS' COMPENSATION COMMISSION CLAIM NO. F503749 EVLYNENE KIRKENDOLPH, EMPLOYEE C L A I M ANT DF&A REVENUE SERVICES DIVISION/ OFFICE OF CHILD SUPPORT
NOT DESIGNATED FOR PUBLICATION BEFORE THE ARKANSAS WORKERS' COMPENSATION COMMISSION CLAIM NO. F503749 EVLYNENE KIRKENDOLPH, EMPLOYEE C L A I M ANT DF&A REVENUE SERVICES DIVISION/ OFFICE OF CHILD SUPPORT
The Elbow, Forearm, Wrist, and Hand
 Elbow - Bones The Elbow, Forearm, Wrist, and Hand Chapters 23 & 24 Humerus Distal end forms the medial & lateral condyles Lateral: capitulum Medial: trochlea Radius Ulna Sports Medicine II Elbow - Bones
Elbow - Bones The Elbow, Forearm, Wrist, and Hand Chapters 23 & 24 Humerus Distal end forms the medial & lateral condyles Lateral: capitulum Medial: trochlea Radius Ulna Sports Medicine II Elbow - Bones
Chiropractic Coding. Michael D. Miscoe JD, CPC, CASCC, CUC, CCPC, CPCO, CHCC. Disclaimer
 Chiropractic Coding Michael D. Miscoe JD, CPC, CASCC, CUC, CCPC, CPCO, CHCC 1 Disclaimer DISCLAIMER This presentation is for general education purposes only. The information contained in these materials,
Chiropractic Coding Michael D. Miscoe JD, CPC, CASCC, CUC, CCPC, CPCO, CHCC 1 Disclaimer DISCLAIMER This presentation is for general education purposes only. The information contained in these materials,
The wrist and hand are constructed of a series of complex, delicately balanced joints whose function is essential to almost every act of daily living.
 TOPIC OUTLINE 9- THE WRIST AND HAND. Introduction. The wrist and hand are constructed of a series of complex, delicately balanced joints whose function is essential to almost every act of daily living.
TOPIC OUTLINE 9- THE WRIST AND HAND. Introduction. The wrist and hand are constructed of a series of complex, delicately balanced joints whose function is essential to almost every act of daily living.
Range of Motion. A guide for you after spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord Injury Rehabilitation Program
 Range of Motion A guide for you after spinal cord injury Spinal Cord Injury Rehabilitation Program This booklet has been written by the health care providers who provide care to people who have a spinal
Range of Motion A guide for you after spinal cord injury Spinal Cord Injury Rehabilitation Program This booklet has been written by the health care providers who provide care to people who have a spinal
CP Factsheet An introduction to ageing and cerebral palsy
 An introduction to ageing and cerebral palsy The concept of ageing and cerebral palsy is now becoming more recognised and more research is being undertaken. However many people, including some professionals,
An introduction to ageing and cerebral palsy The concept of ageing and cerebral palsy is now becoming more recognised and more research is being undertaken. However many people, including some professionals,
Cerebral Palsy. www.teachinngei.org p. 1
 Cerebral Palsy What is cerebral palsy? Cerebral palsy (CP) is a motor disability caused by a static, non-progressive lesion (encephalopathy) in the brain that occurs in early childhood, usually before
Cerebral Palsy What is cerebral palsy? Cerebral palsy (CP) is a motor disability caused by a static, non-progressive lesion (encephalopathy) in the brain that occurs in early childhood, usually before
Muscle Movements, Types, and Names
 Muscle Movements, Types, and Names A. Gross Skeletal Muscle Activity 1. With a few exceptions, all muscles cross at least one joint 2. Typically, the bulk of the muscle lies proximal to the joint it crossed
Muscle Movements, Types, and Names A. Gross Skeletal Muscle Activity 1. With a few exceptions, all muscles cross at least one joint 2. Typically, the bulk of the muscle lies proximal to the joint it crossed
THE TREATMENT OF FLEXION CONTRACTURES OF THE KNEE
 THE TREATMENT OF FLEXION CONTRACTURES OF THE KNEE IN POLIOMYELITIS ALAN N. CONNER, GLASGOW, SCOTLAND In some parts of the world poliomyelitis is still endemic and there are thousands of young people with
THE TREATMENT OF FLEXION CONTRACTURES OF THE KNEE IN POLIOMYELITIS ALAN N. CONNER, GLASGOW, SCOTLAND In some parts of the world poliomyelitis is still endemic and there are thousands of young people with
Non-Surgical Treatments for Spasticity in Cerebral Palsy and Similar Conditions by Susan Agrawal
 www.complexchild.com Non-Surgical Treatments for Spasticity in Cerebral Palsy and Similar Conditions by Susan Agrawal Children with cerebral palsy and other conditions that affect muscle tone often present
www.complexchild.com Non-Surgical Treatments for Spasticity in Cerebral Palsy and Similar Conditions by Susan Agrawal Children with cerebral palsy and other conditions that affect muscle tone often present
Chapter 3 Impairment of Spine and Limbs
 Chapter 3 of Spine and Limbs This chapter contains six parts: Part 3.1 Upper Limbs Part 3.2 Lower Limbs Part 3.3 Spine Part 3.4 Resting Joint Pain Part 3.5 Ranges of Joint Movement Part 3.6 Spine and Limbs
Chapter 3 of Spine and Limbs This chapter contains six parts: Part 3.1 Upper Limbs Part 3.2 Lower Limbs Part 3.3 Spine Part 3.4 Resting Joint Pain Part 3.5 Ranges of Joint Movement Part 3.6 Spine and Limbs
Mini Medical School: Focus on Orthopaedics
 from The Cleveland Clinic Mini Medical School: Focus on Orthopaedics Common Disorders of the Hand and Wrist Jeffrey Lawton, MD Associate Staff, Department of Orthopaedic The Cleveland Clinic Appointments:
from The Cleveland Clinic Mini Medical School: Focus on Orthopaedics Common Disorders of the Hand and Wrist Jeffrey Lawton, MD Associate Staff, Department of Orthopaedic The Cleveland Clinic Appointments:
Webinar title: Know Your Options for Treating Severe Spasticity
 Webinar title: Know Your Options for Treating Severe Spasticity Presented by: Dr. Gerald Bilsky, Physiatrist Medical Director of Outpatient Services and Associate Medical Director of Acquired Brain Injury
Webinar title: Know Your Options for Treating Severe Spasticity Presented by: Dr. Gerald Bilsky, Physiatrist Medical Director of Outpatient Services and Associate Medical Director of Acquired Brain Injury
.org. Distal Radius Fracture (Broken Wrist) Description. Cause
 Distal Radius Fracture (Broken Wrist) Page ( 1 ) The radius is the larger of the two bones of the forearm. The end toward the wrist is called the distal end. A fracture of the distal radius occurs when
Distal Radius Fracture (Broken Wrist) Page ( 1 ) The radius is the larger of the two bones of the forearm. The end toward the wrist is called the distal end. A fracture of the distal radius occurs when
Fact Sheet: Occupational Overuse Syndrome (OOS)
 Fact Sheet: Occupational Overuse Syndrome (OOS) What is OOS? Occupational Overuse Syndrome (OOS) is the term given to a range of conditions characterised by discomfort or persistent pain in muscles, tendons
Fact Sheet: Occupational Overuse Syndrome (OOS) What is OOS? Occupational Overuse Syndrome (OOS) is the term given to a range of conditions characterised by discomfort or persistent pain in muscles, tendons
3. Be able to perform a detailed clinical examination of the forearm and wrist.
 Patient Care: 1. Demonstrate appropriate evaluation and treatment of patients with hand/wrist surgery problems in the emergency room and as part of the inpatient consultation service, including application
Patient Care: 1. Demonstrate appropriate evaluation and treatment of patients with hand/wrist surgery problems in the emergency room and as part of the inpatient consultation service, including application
.org. Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis) Anatomy. Cause
 Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis) Page ( 1 ) Tennis elbow, or lateral epicondylitis, is a painful condition of the elbow caused by overuse. Not surprisingly, playing tennis or other racquet sports can
Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis) Page ( 1 ) Tennis elbow, or lateral epicondylitis, is a painful condition of the elbow caused by overuse. Not surprisingly, playing tennis or other racquet sports can
Treatment Guide Understanding Hand and Wrist Pain. Using this Guide. Choosing Your Care
 Treatment Guide Understanding Hand and Wrist Pain With how much we rely on our hands, there s no wonder hand and wrist pain can be so disabling and frustrating. When this pain interferes with typing on
Treatment Guide Understanding Hand and Wrist Pain With how much we rely on our hands, there s no wonder hand and wrist pain can be so disabling and frustrating. When this pain interferes with typing on
Lean-Ergonomic methods to reduce workers compensation costs (Part 2 of 2) Cumulative trauma disorders can be classified as: What is CTD?
 #425 Lean-ergonomic methods to reduce workers compensation costs, Part 2 of 2 Lean-Ergonomic methods to reduce workers compensation costs (Part 2 of 2) Govid Bharwani, Ph.D, Biomedical Engineering Thursday,
#425 Lean-ergonomic methods to reduce workers compensation costs, Part 2 of 2 Lean-Ergonomic methods to reduce workers compensation costs (Part 2 of 2) Govid Bharwani, Ph.D, Biomedical Engineering Thursday,
GALLAND/KIRBY UCL RECONSTRUCTION (TOMMY JOHN) POST-SURGICAL REHABILITATION PROTOCOL
 GALLAND/KIRBY UCL RECONSTRUCTION (TOMMY JOHN) POST-SURGICAL REHABILITATION PROTOCOL INTRODUCTION The ulnar collateral ligament reconstruction is a tendon transfer procedure. No muscles are transected during
GALLAND/KIRBY UCL RECONSTRUCTION (TOMMY JOHN) POST-SURGICAL REHABILITATION PROTOCOL INTRODUCTION The ulnar collateral ligament reconstruction is a tendon transfer procedure. No muscles are transected during
ASOP Exams PO Box 7440 Seminole, FL 33775. The Manual of Fracture Casting & Bracing Exam 80% Passing ID # Name Title. Address. City State Zip.
 The Manual of Fracture Casting & Bracing Exam 80% Passing ID # Name Title Address City State Zip Tel# Email Certification Organization Cert# Mail a copy of your completed exam to: ASOP Exams PO Box 7440
The Manual of Fracture Casting & Bracing Exam 80% Passing ID # Name Title Address City State Zip Tel# Email Certification Organization Cert# Mail a copy of your completed exam to: ASOP Exams PO Box 7440

 Full version is >>> HERE
Full version is >>> HERE