SPECIMEN COLLECTION 1
|
|
|
- Curtis Weaver
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SPECIMEN COLLECTION 1
2 BLOOD 2
3 BLOOD SPECIMEN COLLECTION, PREPARATION AND HANDLING I. SPECIMEN COLLECTION A. Introduction As members of the health care team, phlebotomist must recognize that their primary responsibility is to the patient's health and well being. It is important for the phlebotomist to maintain a professional attitude and neat appearance. Good interpersonal skills help establish patient trust and alleviate apprehension. Specimen collection by venipuncture or skin puncture involves a series of steps that must receive careful consideration to ensure the best possible specimen for laboratory analysis. It is the responsibility of the phlebotomist to have a thorough understanding of and to abide by these guidelines to avoid the many potential sources of error. B. Preparation Prior to each collection, review the laboratory's specimen requirement. Note the proper specimen to be collected, the amount, the procedure, the collection materials, and the storage and handling requirements. Provide the patient in advance with appropriate collection instructions and information on fasting, diet, and medication restrictions when necessary. Confirm identification in the presence of the patient. Process and store the specimen as required. During specimen collection, preparation, and submission, there is a much greater possibility of critical error than during actual testing or examination of the specimen. Errors in storage and handling compromise the integrity of the specimen and, thus, the test results. Test results are only as good as the specimen collected. C. Patient Instructions and Preparation Procedures with needles induce stress and anxiety in many patients, and emotional stress can affect certain laboratory test values. The phlebotomist therefore should do his or her best to relieve such apprehension. Communicate with the patient in a calm, professional, and reassuring manner. Gain the patient's confidence by soliciting his or her cooperation. Reassure the patient that although the puncture itself maybe slightly painful, it will be over quickly. Never deceive the patient by saying the procedure will not hurt. 3
4 The patient should be comfortable with his or her arm easily accessible and fully extended. Patients in bed should be instructed to lie on their backs, if possible. The phlebotomist should seek assistance if patient movement is anticipated. If additional support is needed, a pillow may be placed under the elbow of the arm from which the specimen is to be drawn. Ambulatory patients should be seated comfortable in a chair, preferably one with an interlocking armrest for firm support. The phlebotomist should position himself or herself in front of the chair to protect the patient from falling forward if fainting occurs. The arm should be extended downward below shoulder level, and the opposite fist should be placed under the elbow for support. Please refer to the test directory section to note any specific dietary requirements or special restrictions for the ordered test. D. Blood Specimen Containers The accuracy of any specimen depends upon the quality of the specimen. Materials for proper specimen collection and transport are supplied by the Altoona Regional Health System Laboratory. Specimen Identification According to the National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards (NCCLS) H3-A4, Vol. ll. No.10, proper identification of specimens is extremely important. "All tubes should be labeled immediately after the blood specimen has been drawn. The completed label must be attached to each tube before leaving the side of the patient, and the identity of the person who drew the blood must be on the label". This procedure eliminates the possibility of mixing up the blood specimens. Unidentified samples will not be tested; therefore, clearly label each specimen with the patient's full name, date and time collected, test name and phlebotomist initials. Information on preprinted computer labels must be verified. Anticoagulants and Preservatives: To ensure accurate test results, all tubes containing an anticoagulant or preservative must be allowed to fill completely. Attempts to force more blood into the tube by exerting pressure will result in damage to the red cells (hemolysis). If the vacuum tube is not filling properly, and you are certain that you have entered the vein properly, substitute another tube. It is important to be certain that a tube is filled in order to avoid spurious results due to an inappropriate anticoagulant to specimen ratio. A partially filled collection tube may be acceptable. If a completely filled tube cannot be obtained, contact the lab to determine specimen acceptability before releasing the patient. 4
5 Vacuum Tubes Containing Anticoagulants: When using vacuum tubes containing anticoagulants and preservatives: 1. Tap the tube gently at a point just below the stopper to release any additive adhering to the tube or stopper 2. Permit the tube to fill completely to ensure the proper ratio of blood additive 3. To ensure adequate mixing of blood with anticoagulant or preservative, use a slow rolling wrist motion to invert the tube gently EIGHT times. Rapid wrist motion or vigorous shaking contributes either to small clot formation or hemolysis and fails to initiate proper mixing action 4. Check to see that all preservative or anticoagulant is dissolved. If any preservative is visible, continue inverting the tube slowly until the powder is dissolved. Vacuum Tubes Without Anticoagulants: When using vacuum tubes containing no anticoagulants or preservative: 1. Permit the tube to fill completely 2. Let the specimen stand for a minimum of 30 minutes and not longer than 45 minutes prior to centrifugation. This allows time for the clot to form. If the specimen is allowed to stand for longer than 45 minutes, chemical activity and degeneration of the cells within the tube will take place, and test results will be altered as a consequence. 3. Centrifuge the specimen at the end of the 30 to 45 minute period in strict accordance with the manufacturer's instructions for speed and duration of centrifugation. Note: Some tubes have clot activators and the clotting time may be less. Please check the package insert. 4. The Gold top tube (Hemogard closure) with clot activator is to be inverted (mixed) FIVE Times. THE ORDER OF DRAW According to the National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards (NCCLS) document H3-A4, "Procedures for the Collection of Diagnostic Blood Specimens by Venipuncture," the order in which tubes should by filled is as follows: 1. Blood culture tube (yellow top or blood culture bottles) 2. Plain tube, non-additive (red top) without clot activator, must check tube 3. Coagulation tube (blue top) 4. Gel separator (speckled or tiger top) without clot activator, must check tube 5. Heparin tube (green top) 6. EDTA tube (lavender top) 7. Plain tube (gold top) gel separator with clot activator Because of the safety risks that accompany glass specimen tubes, infection control and epidemiology experts recommend the use of plastic tubes. 5
6 However, since plastic does not activate clotting, like glass does, red-top tubes must contain a clot activator if they are to be used for serum testing. As a result the order in which tubes are collected must take into consideration that plastic red tops, which contain clot activators, are tubes with an additive and should not occupy the same place in the order of draw as glass red tops without clot activators. The risk of drawing plastic red tops first in the order is that, during the tube exchange, the clot activator can carry over into the next tube. If the next tube is sodium citrate (blue top) for coagulation testing, the clot activator can alter the results. Therefore if using plastic tubes, the red top should be drawn after the blue top. If no blue top is drawn, the plastic red top can precede a heparin (green) or EDTA (lavender) tube without concern for carryover. The current thinking is that any carryover of the clot activator into tubes other than blue tops is irrelevant. It is thought that the minute amount of clot activator will be consumed by the excess heparin or EDTA and will not compromise their ability to anticoagulate the specimen. By contrast, carryover of a clot activator into sodium citrate (blue top) can consume clotting factors and result in prolonged clotting times even though the specimen will still be anticoagulated As a reminder, the NCCLS no longer recommends that a discard tube be drawn prior to a blue top if the blue top is being used for routine coagulation testing, i.e., protime or PTT. However, if factor assays are to be tested, a discard tube is recommended. Therefore, if a physician orders routine chemistries, coagulation studies, and a CBC, the order of draw if using a plastic red top is as follows: 1. Blue top 2. Red top 3. Lavender top If a glass red top is used, the order is: 1. Red top 2. Blue top 3. Lavender top Finally, heparinized tubes (green tops) should never be filled after an EDTA tube (lavender top) if the heparin tube will be tested for potassium. Because EDTA contains potassium salts, any carryover of EDTA into a heparin tube can result in falsely elevated levels of potassium. NCCLS bases the order of draw on well-researched evidence. Yet it remains phlebotomy's best-kept secret. By reinforcing the principles of sound blood collection practices through repetition and education, however, phlebotomists and their supervisors can minimize this frequently committed preanalytical error and maintain the specimen integrity that is essential to accurate results and quality care. 6
7 VACUTAINER INFORMATION Always purchase single use safety devices when performing phlebotomy procedures. YELLOW STOPPER Sterile collection of anticoagulated specimen used for microbiology studies (blood cultures) SPS(sodium polyanetholesulfonate) in 2.5 ml of sodium chloride for difficult venipunctures, pediatric or nursery patients. Use two for one set of blood cultures. Send whole blood in original tube BAC T/ALERT 40 ML STANDARD AEROBIC/F BLUE CAP This is a blood culture bottle. Draw the blue cap aerobic culture 1 st BAC T/ALERT 40 ML STANDARD ANAEROBIC/F PURPLE CAP This is a blood culture bottle. Draw the purple cap anaerobic culture 2 nd (1 SET EQUALS 1 BLUE CAP (AEROBIC) AND 1 PURPLE CAP (ANAEROBIC) RED STOPPER This is a tube that contains no anticoagulant or preservative. The clotted specimen will yield a serum sample. For Blood Bank tests, please submit in original tubes. All other tests, serum must be separated from cells within 45 minutes of venipuncture. Send serum in a plastic transfer tube. GOLD STOPPER TUBE OR MARBLED RED/GRAY Contains clot activator and gel for separating serum from cells, but no anticoagulant. The clotted specimen will yield a serum sample. Maybe used for assays requiring serum unless otherwise stated. Centrifuge tube to separate serum from cells within 45 minutes of venipuncture. Serum can be sent in original tube. BLUE STOPPER (LIGHT) Contains sodium citrate. Sodium citrate yields a plasma sample. Send plasma from a centrifuged sample in a plastic transfer tube labeled "Plasma, Sodium Citrate." If submitted immediately send whole blood in the original blue-stopper tube. GREEN STOPPER (MINT GREEN) Contains lithium heparin and a PST gel separator. Lithium heparin will yield a plasma sample. Plasma must be separated from the cells within 45 minutes of venipuncture. Centrifuge tube to separate the cells from the plasma and send in the original tube. 7
8 LAVENDER STOPPER (PURPLE TOP) Contains liquid K 3 EDTA. This anticoagulant yields plasma or whole blood. Send whole blood in the original lavender stopper tube and plasma in a plastic transfer tube labeled "Plasma, EDTA" GRAY STOPPER Contains Sodium Fluoride and Potassium Oxalate. These anticoagulants yield plasma or whole blood. Send plasma in a plastic transfer tube labeled "Plasma Sodium Fluoride". Send whole blood in the original gray stopper tube. ROYAL BLUE STOPPER TUBE May contain sodium heparin, Na 2 EDTA or no anticoagulant. Used for trace elements, toxicology and nutrient determinations. Send whole blood in the original royal blue stopper tube. BROWN STOPPER TUBES Contains EDTA (Na2). Send whole blood in the original brown stopper tube. 8
9 SELECTING APPROPRIATE COLLECTION TUBES Stopper Color Gold/Marbled Gray Gel Separator (SST) Light Green Gel Separator (PST) Tube Code GLD/ MR LGR Additive No anticoagulant Contains a clot activator and gel for separating serum from cells. Tube is to be gently inverted (mixed) 5 times immediately after collection Lithium heparin anticoagulant and gel for plasma separation. Tube is to be gently inverted (mixed) 8 times immediately after collection. Note: Sodium Heparin should not be used for Electrolyte determination. Red R No Additive No inversions (mixing) necessary. Clot activator Laboratory Use SERUM SST Brand Tube for serum determinations in chemistry. Tube inversions to ensure mixing of clot activator within 45 minutes of collection. Refrigerate Specimens-send in original tube Frozen Specimens-transfer serum to plastic container marked "Serum" NEVER FREEZE A SST TUBE HEPARINZED PLASMA PST Brand Tube for plasma determinations. Tube inversion to prevent clotting. Centrifuge within 45 minutes of collection. Refrigerate specimens - send in the original tube. Frozen Specimens - transfer plasma to a plastic transfer tube marked "Plasma Lithium Heparin". NEVER FREEZE A PST TUBE SERUM OR CLOTTED WHOLE BLOOD All other tests (serology/chemistry) centrifuge within 45 minutes of collection. Transfer serum to a plastic transfer tube marked "Serum". 9
10 SELECTION APROPRIATE BLOOD COLLECTION TUBE (CONTINUED) Stopper Color Tube Code Additive Lavender LV Liquid K 3 EDTA or Freeze-dried NA 2 EDTA Anticoagulant Tube is to be gently inverted (mixed) 8 times immediately after collection Light Blue LBL Sodium Citrate Anticoagulant Tube is to be gently inverted (mixed) 8 times immediately after collection. Yellow SPS SPS Sodium polyanetholesulfonate (STS) Anticoagulant Tube is to be gently inverted (mixed) 8 times immediately after collection Laboratory Use EDTA WHOLE BLOOD OR PLASMA For whole blood hematology determinations. Tube inversion prevents clotting. Send whole blood in original tube. For plasma specimen, centrifuge within 45 minutes of collection. Transfer plasma to a plastic tube marked "Plasma, EDTA" CITRATED PLASMA For coagulation determinations. Tube inversions prevent clotting. Send Whole blood in the original tube. For plasma specimen, centrifuge within 45 minutes of collection. Transfer plasma to plastic tube marked "Plasma, sodium citrate" NOTE: This tube must be completely filled to yield accurate results. Tubes not completely filled will be rejected. SPS WHOLE BLOOD OR BODY FLUID For blood culture specimen collections in microbiology. Tube inversions prevent clotting. Specimen should be submitted in original tube. Refer to microbiology specimen collection section for special collection guidelines. 10
11 SELECTING APPROPRIATE COLLECTION TUBES CONTINUED Stopper Color BAC T/ALERT Blue Cap Tube Additive Code BACT BAC T/ALERT Standard Aerobic 40 ml blood culture bottle. Laboratory Use AEROBIC BLOOD CULTURE BOTTLE WHOLE BLOOD Sterile collection required for Microbiology blood culture. Specimen should be submitted in original bottle. Refer to microbiology specimen collection section for special collection guidelines. 1 BLOOD CULTURE SET EQUALS 1 BLUE CAP (AEROBIC) AND 1 PURPLE CAP (ANAEROBIC ) BOTTLE. BAC T/ALERT Purple Cap BACT BAC T/ALERT Standard Anaerobic 40 ml blood culture bottle. Gray GRA Sodium Fluoride or Potassium Oxalate Tube is to be gently inverted (mixed) 8 times immediately after collection ANAEROBIC BLOOD CULTURE BOTTLE WHOLE BLOOD Sterile anaerobic collection required for Microbiology Blood Culture. Specimen should be submitted in original bottle. Refer to microbiology specimen collection section for special collection guidelines. 1 BLOOD CULTURE SET EQUALS 1 BLUE CAP (AEROBIC) AND 1 PURPLE CAP (ANAEROBIC) BOTTLE SODIUM FLUORIDE WHOLE BLOOD OR PLASMA Tube inversion to prevent clotting. Centrifuge within 45 minutes of collection. Send whole blood in original tube. 11
12 SELECTING APPROPRIATE COLLECTION TUBES CONTINUED Stopper Color Tube Code Additive Dark Green DGR Sodium Heparin, Lithium Heparin or Ammonium Heparin Anticoagulant. Tube is to be gently inverted (mixed) 8 times immediately after collection. Note: Sodium Heparin should not be used for Electrolyte determinations Laboratory Use HEPARINZED PLASMA For plasma determinations in chemistry. Tube inversions prevent clotting. Send whole blood in original tube. For plasma specimen, centrifuge within 45 minutes of collection, transfer plasma to a plastic tube marked "Plasma Sodium Heparin." Royal Blue RBL Red stripe- no additive Lavender stripe- Sodium-EDTA Anticoagulant Tube is to be gently inverted (mixed) 8 times immediately after collection Large yellow HEPARINIZED WHOLE BLOOD For trace element, toxicology and nutrient determinations. Special stopper formulation offers the lowest verified levels of trace elements available. Send in the original tube Tissue Typing - Not to be used for Blood Cultures ACD A or ACD B E. Blood Specimen Collection from a line Please refer to the Altoona Regional Health System s procedures regarding collection of blood culture samples from a line. F. Collection Errors Careful attention to routine procedures can eliminate most of the errors outlined in this section. The complete blood collection system and other collection materials provided by the laboratory can maintain the integrity of the specimen only when they are used in strict accordance with the instructions provided. 12
13 General Specimen Collection Errors: Some of the common errors affecting all types of specimens include: Errors in venipuncture preparation: 1. Failure to label a specimen correctly and to provide pertinent information. All specimens must be properly labeled in the presence of the patient. 2. Failure to check patient adherence to dietary restrictions before drawing. 3. Failure to calm patient prior to blood collection. 4. Use of improper equipment and supplies, i.e. incorrect container for appropriate specimen preservation. Errors in Venipuncture procedure: 1. Failure to dry site completely after cleansing. 2. Inserting needle bevel side down. 3. Use of a needle that has too small of a bore, causing hemolysis. 4. Prolonged tourniquet application. 5. Wrong order of tube draw. 6. Failure to mix blood collected in additive containing tubes immediately. 7. Pulling on a syringe plunger too forcefully. 8. Failure to release tourniquet prior to needle withdrawal. 9. Venipuncture in an unacceptable area: Avoid areas with hematomas, burns, scars, or swelling. Avoid the side on which a mastectomy was performed. If there is an IV infusion, whenever possible, blood should be collected from the opposite arm or from a site below the IV. Please refer to the Altoona Regional Health System s procedures regarding collection of specimens in the presence of an IV. Errors after venipuncture completion: 1. Failure to apply pressure to venipuncture site. 2. Vigorous shaking of anticoagulated specimens 3. Forcing blood through a syringe needle into tube. 4. Mislabeling of tubes. 5. Failure to use the correct container for appropriate specimen preservation. 6. Failure to tighten specimen container lids, resulting in leakage and/or contamination of specimens. 7. Insufficient quantity of specimen to run test or QNS (quantity not sufficient). 13
14 II. SPECIMEN PREPARATION A. Preparing Serum Serum Preparation from Red Stopper Tube: Follow the steps below when Preparing a serum specimen for submission. 1. Draw whole blood in an amount 2 and 1/2 times the required volume of serum so that the expected amount of serum can be obtained. EXAMPLE: A 10 ml red stopper rube will yield approximately 4 ml of serum after clotting and centrifuging. 2. Place the collection tube in the upright position in a test tube rack, and allow the blood to clot at room temperature for no longer than minutes. 3. As soon as possible after a clot has formed, insert the tube in the centrifuge, stopper end up. Operate the centrifuge for minutes at the speed recommended by the manufacturer. Do not allow prolonged centrifugation as this may cause hemolysis. When using a bench top centrifuge, employ a balance tube of the same type containing an equivalent volume of water. The tube stopper should remain. 4. Turn the centrifuge off and allow it to come to a complete stop. Do not stop it by hand or brake. Remove the tube carefully without disturbing the contents. 5. Remove the stopper and carefully aspirate most of the serum from the cells using a separate disposable Pasteur pipette for each tube. Place the tip of the pipette against the side of the tube, approximately 1/4 inch above the cell layer. Do not disturb the cell layer or carry any cells over into the pipette. If cells do enter the pipette, re-centrifuge the entire specimen. 6. Transfer the serum from the pipette into the plastic transfer tube. Inspect the serum for signs of hemolysis and turbidity by holding it up to the light. Be sure to provide the laboratory with the amount of serum specified. 7. Label the tube carefully and clearly with all pertinent information (refer to the specimen identification section). NEVER LEAVE THE PATIENTS BEDSIDE BEFORE PROPERLY LABELING THE SPECIMEN. Unless otherwise indicated, serum samples should be refrigerated until they are sent to the laboratory. When multiple tests requiring frozen serum are ordered, a plastic transfer tube should be prepared for EACH test. 8. When frozen serum is required, place the plastic transfer tube(s) immediately in the freezer. A separate frozen sample must be submitted for each test requiring a frozen specimen. Serum Preparation from Serum-Separator (SST) Tubes: Serum separator (Gold or Marble red/gray stopper) tubes contain clot activator and gel for separating serum From cells but include no anticoagulant. Adhere to the following steps when Using a serum-separator tube. 1. Draw whole blood in an amount 2 and 1/2 times the required volume of serum so that a sufficient amount of serum can be obtained. EXAMPLE: A 10 ml 14
15 Marble top tube will yield approximately 4 ml of serum after clotting and centrifuging. 2. Gently invert the serum-separator tube five times to mix the clot activator and blood. 3. Place the collection tube in the upright position in a test tube rack and allow the blood to clot a room temperature for no longer than minutes. Clots will usually form in minutes. 4. As soon as possible after a clot has formed, insert the tube in the centrifuge, stopper end up. Operate the centrifuge for minutes at the speed recommended by the manufacturer. Do not allow prolonged centrifugation as this may cause hemolysis. When using a bench top centrifuge, employ a balance tube of the same type containing an equivalent volume of water. The tube stopper should remain on the tube. 5. Turn the centrifuge off and allow it to come to a complete stop. Do not stop it by hand or use a brake. Remove the tube carefully without disturbing the contents. Inspect the barrier gel to ensure that it has sealed the serum from the packed cells. Also examine the serum for signs of hemolysis and turbidity by holding it up to the light. Be sure to provide the laboratory with the volume of serum specified. 6. Label the tube carefully and clearly with all pertinent information (refer to the specimen identification section). NEVER LEAVE THE PATIENTS BEDSIDE BEFORE PROPERLY LABELING THE SPECIMEN. 7. If a frozen specimen is not required, it is not necessary to transfer serum to a plastic transport tube. 8. When frozen serum is required, always transfer the serum (using a disposal pipette) into a separate, clearly labeled plastic transfer tube. Place the plastic transfer tube(s) immediately in the freezer. Never freeze a glass serumseparator tube. A separate frozen sample must be submitted for each test requiring a frozen specimen. B. Preparing Plasma Plasma Preparation from a Plasma Separator (PST) Tube: When plasma is Collected in a PST tube the following steps should be followed: 1. Always use the proper tube for tests requiring a special anticoagulant (i.e. EDTA, heparin, sodium citrate, etc.) 2. Tap the tube gently to release additive adhering to the tube or stopper diaphragm. 3. Permit the tube to fill completely. Failure to fill the tube will cause an improper blood-to-anticoagulant ratio and yield questionable tests results. 15
16 4. To avoid clotting, mix the blood with the anticoagulant or preservative immediately after drawing each sample. To ensure adequate mixing, slowly invert the tube five to six times using a gentle wrist rotation motion. 5. Immediately centrifuge the specimen for 5-10 minutes. Do not remove the stopper. 6. Turn the centrifuge off and allow it to come to a complete stop. Do not stop by hand or use a brake. Remove the tube carefully without disturbing the contents. 7. Make sure the tube is clearly labeled with all pertinent information (refer to the specimen identification section) NEVER LEAVE THE PATIENTS BEDSIDE BEFORE PROPERLY LABELING THE SPECIMEN. 8. If a frozen specimen is not required, it is not necessary to transfer plasma to a plastic transport tube. 9. When frozen plasma is required, always transfer the plasma (using a disposable pipette) into a separate properly labeled plastic transfer tube. Be certain to mark the tube as to the contents (Example: "Plasma, lithium heparin"). Place the plastic transfer tube(s) in the freezer. Never freeze a glass or plastic plasma separator tube. A separate frozen sample must be submitted for each test requiring a frozen specimen. Plasma Preparation from Non-SST Tubes: Follow the steps below the prepare plasma from all anticoagulated tubes that do not contain SST gel. 1. Always use the proper tube for tests requiring a special anticoagulant (i.e. EDTA, heparin, sodium citrate, etc.) or preservative. 2. Tap the tube gently to release additive adhering to the tube or stopper diaphragm. 3. Permit the tube to fill completely. Failure to fill the tube will cause an improper blood-to-anticoagulant ratio and yield questionable test results. 4. To avoid clotting, mix the blood with the anticoagulant or preservative immediately after drawing each sample. To ensure adequate mixing, slowly invert the tube five to six times using a gentle wrist rotation motion. 5. Immediately centrifuge the specimen for 5-10 minutes. Do not remove the stopper. 6. Turn the centrifuge off and allow it to come to a complete stop. Do not stop it by hand or brake. Remove the tube carefully without disturbing the contents. 7. Remove the stopper and carefully aspirate plasma using a separate disposable Pasteur pipette for each tube. Place the tip of the pipette against the side of the tube, approximately 1/4 inch above the cell layer. Do not disturb the cell layer or carry any cells over into the pipette. If the cell layer is disturbed, the specimen must be recentrifuged. Do not pour off; use the transfer pipette. 8. Transfer the plasma from the pipette into the transfer tube. Be sure to provide the laboratory with the amount of plasma specified. 16
17 9. Label all transfer tubes clearly and carefully with all required information. All tubes should also be marked as to their content (Example: "Plasma, sodium citrate"). 10. When frozen plasma is required, place plastic transfer tube(s) immediately into the freezer. A separate frozen sample must be submitted for each test requiring a frozen specimen. C. Preparation Errors Serum Preparation Errors: 1. Failure to separate serum from red cells within minutes of collection. 2. Hemolysis: Red blood cells broken down and components spilled into serum (see below). 3. Lipemia: Cloudy or milky serum sometimes due to the patient's diet. 4. Failure to allow complete clotting of the specimen prior to centrifugation. Plasma Preparation Errors: 1. Failure to mix tube immediately - full or partial clotting of specimen may occur. 2. Hemolysis - red blood cells broken down and components spilled into serum (see below). 3. Incomplete filling of the tube, thereby creating a dilution factor excessive for total specimen volume. 4. Failure to separate plasma from cells within minutes of collection. D. Hemolysis Grossly or even moderately hemolyzed blood specimens may not be acceptable for testing. Hemolysis occurs when the red cells rupture and hemoglobin and other intracellular components spill into the serum. Hemolyzed serum is pink or red, rather than the normal clear straw color. Generally, hemolysis is the product of a poor venipuncture. A redraw will often yield an acceptable, non-hemolyzed specimen. III. CRITERIA FOR BLOOD SPECIMEN REJECTION 1. Improperly identified or unidentified specimens. 2. Specimen too old for accurate testing (refer to specific test for such time requirements). 3. Anticoagulated specimen that is partially or completely clotted. 4. Improper tube type used for specimen collection (i.e. wrong anticoagulant, serum rather than plasma, etc.). 17
18 5. Patient did not follow specific instructions associated with certain test procedures. Special instructions may be obtained by calling Altoona Hospital Department of Laboratory Services at (814) Quantity not sufficient for testing. One of the most common and expensive errors in specimen collection is the submission of an insufficient sample for testing. Although Altoona Regional Health System Laboratory will make every effort to complete testing on the specimen submitted, we may have to send out a report marked QNS (quantity not sufficient) and the patient will have to be called back for repeat collection at additional expense and inconvenience to the patient and to the physician. To ensure an adequate quantity of specimen: a. Always check the test section of this manual prior to venipuncture to determine the specimen type and quantity needed. b. Always draw whole blood in an amount 2 1/2 times volume of serum required for a particular test. Example: If 4 ml. of serum is required, draw at least 10 ml. of blood. NOTE: If you are not certain that the quantity of specimen collected is adequate for a particular test, call Altoona Hospital Department of Laboratory Services at (814) before releasing the patient. 18
The Golden Rule of Specimen Collection: The Patient Test Result is Only as Good as the Sample We Get
 The Golden Rule of Specimen Collection: The Patient Test Result is Only as Good as the Sample We Get Jan Frerichs, MLS (ASCP) The University of Iowa [email protected] Importance of Phlebotomist
The Golden Rule of Specimen Collection: The Patient Test Result is Only as Good as the Sample We Get Jan Frerichs, MLS (ASCP) The University of Iowa [email protected] Importance of Phlebotomist
Blood Tubes and Lancets 1-800-962-9888
 Blood Tubes and Lancets 1-800-962-9888 1-800-962-9888. Table of Contents BLOOD COLLECTION MONOJECT Blood Collection Products Safety Lancet... 4 Lancet... 4 Corvac Integrated Serum Separator Tubes Red/Grey
Blood Tubes and Lancets 1-800-962-9888 1-800-962-9888. Table of Contents BLOOD COLLECTION MONOJECT Blood Collection Products Safety Lancet... 4 Lancet... 4 Corvac Integrated Serum Separator Tubes Red/Grey
Collection Guidelines for Routine & Special Coagulation Testing
 Revised May 2010 Collection Guidelines for Routine & Special Coagulation Testing Best samples come from peripheral stick with evacuated tube system 19 to 22 gauge needle (smaller or bigger could cause
Revised May 2010 Collection Guidelines for Routine & Special Coagulation Testing Best samples come from peripheral stick with evacuated tube system 19 to 22 gauge needle (smaller or bigger could cause
VENOUS BLOOD COLLECTION
 Venous Blood Collection p. 1 of 5 Johns Hopkins Medical Laboratories Department of Pathology Core Lab Clinical Services Zd7: Word: JHH Venous Blood Collection Procedure Signature Date Signature Date Written
Venous Blood Collection p. 1 of 5 Johns Hopkins Medical Laboratories Department of Pathology Core Lab Clinical Services Zd7: Word: JHH Venous Blood Collection Procedure Signature Date Signature Date Written
URINE COLLECTION, PREPARATION AND HANDLING
 URINE III-38 URINE COLLECTION, PREPARATION AND HANDLING I. SPECIMEN COLLECTION A. Introduction Laboratory tests requiring urine specimens involve a wide variety of procedures. A basic urinalysis is almost
URINE III-38 URINE COLLECTION, PREPARATION AND HANDLING I. SPECIMEN COLLECTION A. Introduction Laboratory tests requiring urine specimens involve a wide variety of procedures. A basic urinalysis is almost
THE IMPORTANCE OF PRE-ANALYTICAL PHASE IN LABORATORY TESTING AND DIAGNOSIS. Tg Jiu, September, 2010
 THE IMPORTANCE OF PRE-ANALYTICAL PHASE IN LABORATORY TESTING AND DIAGNOSIS Tg Jiu, September, 2010 Cristina Florescu Moraid MD MSc EurClinChem Country Manager Synevo Central Lab Romania-Medicover Holding
THE IMPORTANCE OF PRE-ANALYTICAL PHASE IN LABORATORY TESTING AND DIAGNOSIS Tg Jiu, September, 2010 Cristina Florescu Moraid MD MSc EurClinChem Country Manager Synevo Central Lab Romania-Medicover Holding
Central Line Blood Draw
 Central Line Blood Draw Welcome to the Central Line dressing blood draw refresher. Please use the navigation below to advance to the next page. The Central Line blood draw module is also available as a
Central Line Blood Draw Welcome to the Central Line dressing blood draw refresher. Please use the navigation below to advance to the next page. The Central Line blood draw module is also available as a
Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) Work Package 8. Sample Collection and Storage
 Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) Work Package 8 Sample Collection and Storage May 2008 SOP WP 8 - Sample collection Table of Contents 1 SAMPLE COLLECTION... 3 1.1 Sample collection -summary... 3 1.2
Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) Work Package 8 Sample Collection and Storage May 2008 SOP WP 8 - Sample collection Table of Contents 1 SAMPLE COLLECTION... 3 1.1 Sample collection -summary... 3 1.2
INTERDISCIPLINARY CLINICAL MANUAL Policy and Procedure
 INTERDISCIPLINARY CLINICAL MANUAL Policy and Procedure TITLE: Venipuncture for Blood Specimen NUMBER: Collection Effective Date : October 2013 Page 1 of 10 Applies To: Holders of Interdisciplinary Clinical
INTERDISCIPLINARY CLINICAL MANUAL Policy and Procedure TITLE: Venipuncture for Blood Specimen NUMBER: Collection Effective Date : October 2013 Page 1 of 10 Applies To: Holders of Interdisciplinary Clinical
I-140 Venipuncture for Blood Specimen Collection
 I-140 Venipuncture for Blood Specimen Collection Purpose Obtain a blood specimen by venipuncture for laboratory analysis using aseptic technique. Applies To Registered Nurses Licensed Practical/Vocational
I-140 Venipuncture for Blood Specimen Collection Purpose Obtain a blood specimen by venipuncture for laboratory analysis using aseptic technique. Applies To Registered Nurses Licensed Practical/Vocational
Blood Collection and Processing SOP
 Brisbane Breast Bank Blood Collection and Processing SOP Breast Pathology Laboratory University of Queensland Centre for Clinical Research Blood Collection We collect 30ml of blood from patients who have
Brisbane Breast Bank Blood Collection and Processing SOP Breast Pathology Laboratory University of Queensland Centre for Clinical Research Blood Collection We collect 30ml of blood from patients who have
STEP-BY-STEP INSTRUCTIONS FOR INVESTIGATIONAL USE. Rapid HCV Antibody Test FOR ORAQUICK RAPID HCV ANTIBODY TEST
 Before performing testing, all operators MUST read and become familiar with Universal Precautions for Prevention of Transmission of Human Immunodeficiency Virus, Hepatitis B Virus, and other Blood-borne
Before performing testing, all operators MUST read and become familiar with Universal Precautions for Prevention of Transmission of Human Immunodeficiency Virus, Hepatitis B Virus, and other Blood-borne
MANITOBA PATIENT SERVICE CENTRE STANDARDS
 MANITOBA PATIENT SERVICE CENTRE STANDARDS February 2015 INTRODUCTION These Standards are derived from Z316.7-12 and are approved by the Council of the College of Physicians and Surgeons of Manitoba. These
MANITOBA PATIENT SERVICE CENTRE STANDARDS February 2015 INTRODUCTION These Standards are derived from Z316.7-12 and are approved by the Council of the College of Physicians and Surgeons of Manitoba. These
Abstract... i. Committee Membership... iii. Foreword... vii. 1 Scope... 1. 2 Introduction... 1. 3 Standard Precautions... 1. 4 Definitions...
 Vol. 27 No. 26 Replaces H3-A5 Vol. 23 No. 32 Procedures for the Collection of Diagnostic Blood Specimens by Venipuncture; Approved Standard Sixth Edition This document provides procedures for the collection
Vol. 27 No. 26 Replaces H3-A5 Vol. 23 No. 32 Procedures for the Collection of Diagnostic Blood Specimens by Venipuncture; Approved Standard Sixth Edition This document provides procedures for the collection
Blood Plasma Sample Collection and Handling for Proteomics Analysis - A guide to obtain optimal plasma samples -
 Blood Plasma Sample Collection and Handling for Proteomics Analysis - A guide to obtain optimal plasma samples - 1 Introduction Blood can be regarded as a complex liquid tissue that comprises cells and
Blood Plasma Sample Collection and Handling for Proteomics Analysis - A guide to obtain optimal plasma samples - 1 Introduction Blood can be regarded as a complex liquid tissue that comprises cells and
Preanalytical Variables in the Chemistry Laboratory. Specimen Analysis
 Special Edition LabNotes Volume 15, No.1 2005 A Newsletter from BD Diagnostics Preanalytical Systems At BD, We Understand It s Not Just a Test, It s a Patient... Meeting New Challenges and Setting New
Special Edition LabNotes Volume 15, No.1 2005 A Newsletter from BD Diagnostics Preanalytical Systems At BD, We Understand It s Not Just a Test, It s a Patient... Meeting New Challenges and Setting New
Medical Necessity and Advanced Beneficiary Notice (ABN) Policy and Form
 Medical Necessity and Advanced Beneficiary Notice (ABN) Policy and Form Billings Clinic Laboratory believes all health-care providers should order only appropriate tests for the diagnosis and treatment
Medical Necessity and Advanced Beneficiary Notice (ABN) Policy and Form Billings Clinic Laboratory believes all health-care providers should order only appropriate tests for the diagnosis and treatment
BLOOD BANK SPECIMEN COLLECTION PROCEDURE
 BLOOD BANK SPECIMEN COLLECTION PROCEDURE INTRODUCTION Scientific and technical advances in blood group serology have made the transfusion of blood a relatively safe procedure, but serious adverse effects
BLOOD BANK SPECIMEN COLLECTION PROCEDURE INTRODUCTION Scientific and technical advances in blood group serology have made the transfusion of blood a relatively safe procedure, but serious adverse effects
Ward 29 guide to the safe preparation and administration of intravenous (IV) antibiotics at home
 Ward 29 guide to the safe preparation and administration of intravenous (IV) antibiotics at home Contents Page Important contact numbers 1 General information on preparing and administering IV antibiotics
Ward 29 guide to the safe preparation and administration of intravenous (IV) antibiotics at home Contents Page Important contact numbers 1 General information on preparing and administering IV antibiotics
9.Pediatric Procedures
 9.Pediatric Procedures A. Introduction 1. Pediatric blood collection may be by skin puncture or venipuncture. 2. Skill in pediatric phlebotomy is gained by knowledge of special collection equipment, observation
9.Pediatric Procedures A. Introduction 1. Pediatric blood collection may be by skin puncture or venipuncture. 2. Skill in pediatric phlebotomy is gained by knowledge of special collection equipment, observation
INMA LABORATORY MANUAL
 INMA LABORATORY MANUAL NUTRITION BIOMARKERS Cohorte-VALENCIA This manual describes the collection, separation, storage and transport of blood samples for the INMA study. Careful collection of samples is
INMA LABORATORY MANUAL NUTRITION BIOMARKERS Cohorte-VALENCIA This manual describes the collection, separation, storage and transport of blood samples for the INMA study. Careful collection of samples is
Division of Laboratory Medicine Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania
 Division of Laboratory Medicine Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania General Laboratory Specimen Collection Guidelines The Laboratory will perform
Division of Laboratory Medicine Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania General Laboratory Specimen Collection Guidelines The Laboratory will perform
NIH Clinical Center Patient Education Materials Giving a subcutaneous injection
 NIH Clinical Center Patient Education Materials What is a subcutaenous injection? A subcutaneous injection is given in the fatty layer of tissue just under the skin. A subcutaneous injection into the fatty
NIH Clinical Center Patient Education Materials What is a subcutaenous injection? A subcutaneous injection is given in the fatty layer of tissue just under the skin. A subcutaneous injection into the fatty
Please note: Contact Coppe Laboratories at 262-574-0701 if archival plasma samples need to be tested.
 Collecting a Coppe Laboratories Sample The Coppe Laboratories Sample Kit contains: Test Request Form (TRF) Heparin tube Absorbent sheet Biohazard bag Foil pouch Label for blood tube Box Seal Instructions
Collecting a Coppe Laboratories Sample The Coppe Laboratories Sample Kit contains: Test Request Form (TRF) Heparin tube Absorbent sheet Biohazard bag Foil pouch Label for blood tube Box Seal Instructions
Sheep@Purdue. Blood Sampling in Sheep AS-557-W
 Sheep@Purdue AS-557-W Blood Sampling in Sheep Becky Mitchell, Animal Sciences Student Mike Neary, Extension Sheep Specialist Gerald Kelly, Manager of Sheep Teaching and Research Flock Purdue University
Sheep@Purdue AS-557-W Blood Sampling in Sheep Becky Mitchell, Animal Sciences Student Mike Neary, Extension Sheep Specialist Gerald Kelly, Manager of Sheep Teaching and Research Flock Purdue University
Tests that have had changes to the method/ CPT code, units of measurement, scope of analysis, reference comments, or specimen requirements.
 In our continuing effort to provide you with the highest quality toxicology laboratory services available, we have compiled important changes regarding a number of tests we perform. Listed below are the
In our continuing effort to provide you with the highest quality toxicology laboratory services available, we have compiled important changes regarding a number of tests we perform. Listed below are the
(800) 786-7235 Cryo-Cell.com
 HEALTHCARE PROVIDER Instructions Keep these instructions in the kit [ When handling blood products, use personal protective measures, maintain aseptic techniques and adequate room for collection processes.
HEALTHCARE PROVIDER Instructions Keep these instructions in the kit [ When handling blood products, use personal protective measures, maintain aseptic techniques and adequate room for collection processes.
PRODUCT CATALOGUE RESULTS OF THE SCIENTIFIC PROCESS
 PRODUCT CATALOGUE RESULTS OF THE SCIENTIFIC PROCESS 2 disera RESULTS OF THE SCIENTIFIC PROCESS INDEX About Us 4 Production and Quality Certificates 5 VACUSERA Blood Collection Systems 6 VACUSERA Blood
PRODUCT CATALOGUE RESULTS OF THE SCIENTIFIC PROCESS 2 disera RESULTS OF THE SCIENTIFIC PROCESS INDEX About Us 4 Production and Quality Certificates 5 VACUSERA Blood Collection Systems 6 VACUSERA Blood
BLOOD CULTURE COLLECTION GUIDELINES FOR PHLEBOTOMISTS (WITHIN REGION 6)
 BLOOD CULTURE COLLECTION GUIDELINES FOR PHLEBOTOMISTS (WITHIN REGION 6) The rate of isolation of micro-organisms from blood is directly related to the volume of blood collected. Therefore, it is recommended
BLOOD CULTURE COLLECTION GUIDELINES FOR PHLEBOTOMISTS (WITHIN REGION 6) The rate of isolation of micro-organisms from blood is directly related to the volume of blood collected. Therefore, it is recommended
KABEVETTE. Aspiration and Vacuum in one System! The blood collection by KABE LABORTECHNIK KABEVETTE G KABEVETTE V. Aspiration
 KABEVETTE Aspiration Vacuum Aspiration and Vacuum in one System! The blood collection by KABE LABORTECHNIK KABEVETTE G KABEVETTE V Twice as good: Aspiration- and Vacuum principle can be combined in one
KABEVETTE Aspiration Vacuum Aspiration and Vacuum in one System! The blood collection by KABE LABORTECHNIK KABEVETTE G KABEVETTE V Twice as good: Aspiration- and Vacuum principle can be combined in one
Instructions for Use PROCRIT (PRO KRIT) (epoetin alfa)
 Instructions for Use PROCRIT (PROKRIT) (epoetin alfa) Use these Instructions for Use if you or your caregiver has been trained to give PROCRIT injections at home. Do not give yourself the injection unless
Instructions for Use PROCRIT (PROKRIT) (epoetin alfa) Use these Instructions for Use if you or your caregiver has been trained to give PROCRIT injections at home. Do not give yourself the injection unless
Reference Range: 0.5-1.6 mmol/l (arterial) 0.7-2.1 mmol/l (venous) CPT Code: 83605
 LACTIC ACID Fasting, arterial specimen preferred. Please note whether arterial or venous. 0.5 ml heparinized plasma. Green top or PST must be drawn, placed on ice, and spun within 15 minutes. Immediately
LACTIC ACID Fasting, arterial specimen preferred. Please note whether arterial or venous. 0.5 ml heparinized plasma. Green top or PST must be drawn, placed on ice, and spun within 15 minutes. Immediately
HUMULIN 70/30 KwikPen
 1 Instructions for Use HUMULIN 70/30 KwikPen (70% human insulin isophane suspension 30% human insulin injection [rdna origin]) Read the Instructions for Use before you start taking HUMULIN 70/30 and each
1 Instructions for Use HUMULIN 70/30 KwikPen (70% human insulin isophane suspension 30% human insulin injection [rdna origin]) Read the Instructions for Use before you start taking HUMULIN 70/30 and each
Phlebotomy General Guidelines for Venipuncture Specimen Collection
 Inpatient Policy Phlebotomy General Guidelines for Venipuncture Specimen Collection After documented competence, RNs, LPNs, and ASTs may perform this procedure. In EMTC, paramedics (EMT-P) and EMTs also
Inpatient Policy Phlebotomy General Guidelines for Venipuncture Specimen Collection After documented competence, RNs, LPNs, and ASTs may perform this procedure. In EMTC, paramedics (EMT-P) and EMTs also
Human Free Testosterone(F-TESTO) ELISA Kit
 Human Free Testosterone(F-TESTO) ELISA Kit Catalog Number. MBS700040 For the quantitative determination of human free testosterone(f-testo) concentrations in serum, plasma. This package insert must be
Human Free Testosterone(F-TESTO) ELISA Kit Catalog Number. MBS700040 For the quantitative determination of human free testosterone(f-testo) concentrations in serum, plasma. This package insert must be
Mouse Keyhole Limpet Hemocyanin antibody(igm) ELISA Kit
 Mouse Keyhole Limpet Hemocyanin antibody(igm) ELISA Kit Catalog No. MBS702810 (96 tests) This immunoassay kit allows for the in vitro semi-quantitative determination of mouse KLH(IgM)antibody concentrations
Mouse Keyhole Limpet Hemocyanin antibody(igm) ELISA Kit Catalog No. MBS702810 (96 tests) This immunoassay kit allows for the in vitro semi-quantitative determination of mouse KLH(IgM)antibody concentrations
PEAC CENTRAL LABORATORY SAMPLING MANUAL
 PEAC CENTRAL LABORATORY SAMPLING MANUAL FINAL REVISED VERSION (9.0) PEAC Clinical Study Final 1.0 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS Page No. 1. PEAC CENTRAL LABORATORY - CONTACT NUMBERS... 3 2. IMPORTANT INFORMATION...
PEAC CENTRAL LABORATORY SAMPLING MANUAL FINAL REVISED VERSION (9.0) PEAC Clinical Study Final 1.0 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS Page No. 1. PEAC CENTRAL LABORATORY - CONTACT NUMBERS... 3 2. IMPORTANT INFORMATION...
HUMULIN (HU-mu-lin) N
 Instructions for Use HUMULIN (HU-mu-lin) N (human insulin [rdna origin] isophane suspension) vial (100 Units/mL, U-100) Read the Instructions for Use before you start taking HUMULIN N and each time you
Instructions for Use HUMULIN (HU-mu-lin) N (human insulin [rdna origin] isophane suspension) vial (100 Units/mL, U-100) Read the Instructions for Use before you start taking HUMULIN N and each time you
How To Prepare and Give a Prefilled Syringe Injection
 Diablo Valley Onc&Hem Med Grp, Inc Phone Number: (925)6775041 How To Prepare and Give a Prefilled Syringe Injection Patient Education Quick Reference Guide The following are instructions for use of prefilled
Diablo Valley Onc&Hem Med Grp, Inc Phone Number: (925)6775041 How To Prepare and Give a Prefilled Syringe Injection Patient Education Quick Reference Guide The following are instructions for use of prefilled
Inc. Wuhan. Quantity Pre-coated, ready to use 96-well strip plate 1 Plate sealer for 96 wells 4 Standard (liquid) 2
 Uscn Life Science Inc. Wuhan Website: www.uscnk.com Phone: +86 27 84259552 Fax: +86 27 84259551 E-mail: [email protected] ELISA Kit for Human Prostaglandin E1(PG-E1) Instruction manual Cat. No.: E0904Hu
Uscn Life Science Inc. Wuhan Website: www.uscnk.com Phone: +86 27 84259552 Fax: +86 27 84259551 E-mail: [email protected] ELISA Kit for Human Prostaglandin E1(PG-E1) Instruction manual Cat. No.: E0904Hu
1-800-862-2731 Administration of Meropenem For Child
 1 Drug Name: _Meropenem 1-800-862-2731 Administration of Meropenem For Child Dosage: milligrams every hours over 5 minutes Key Points: FLUSHING: Meropenem Heparin flush 1. Always wash your hands with an
1 Drug Name: _Meropenem 1-800-862-2731 Administration of Meropenem For Child Dosage: milligrams every hours over 5 minutes Key Points: FLUSHING: Meropenem Heparin flush 1. Always wash your hands with an
INTRODUCTION. Viral shedding is crucial for Gene Therapy Products Safety linked with shedding data
 INTRODUCTION Viral shedding is crucial for Gene Therapy Products Safety linked with shedding data For the patient For families and friends For the environment No treatment possible without good safety
INTRODUCTION Viral shedding is crucial for Gene Therapy Products Safety linked with shedding data For the patient For families and friends For the environment No treatment possible without good safety
Blood sampling and transportation Standard Operating Procedure
 Blood sampling and transportation Standard Operating Procedure 1. Rationale for test 2. Requirements 3. Equipment 4. Method for blood taking 5. Instructions for Safe Box and transportation of samples 6.
Blood sampling and transportation Standard Operating Procedure 1. Rationale for test 2. Requirements 3. Equipment 4. Method for blood taking 5. Instructions for Safe Box and transportation of samples 6.
Mouse Creatine Kinase MB isoenzyme (CKMB) ELISA
 KAMIYA BIOMEDICAL COMPANY Mouse Creatine Kinase MB isoenzyme (CKMB) ELISA For the quantitative determination of mouse CKMB in serum, plasma, cell culture fluid and other biological fluids Cat. No. KT-57681
KAMIYA BIOMEDICAL COMPANY Mouse Creatine Kinase MB isoenzyme (CKMB) ELISA For the quantitative determination of mouse CKMB in serum, plasma, cell culture fluid and other biological fluids Cat. No. KT-57681
Collect and label sample according to standard protocols. Gently invert tube 8-10 times immediately after draw. DO NOT SHAKE. Do not centrifuge.
 Complete Blood Count CPT Code: CBC with Differential: 85025 CBC without Differential: 85027 Order Code: CBC with Differential: C915 Includes: White blood cell, Red blood cell, Hematocrit, Hemoglobin, MCV,
Complete Blood Count CPT Code: CBC with Differential: 85025 CBC without Differential: 85027 Order Code: CBC with Differential: C915 Includes: White blood cell, Red blood cell, Hematocrit, Hemoglobin, MCV,
Canine creatine kinase MB isoenzyme (CK-MB)ELISA Kit
 Canine creatine kinase MB isoenzyme (CK-MB)ELISA Kit Catalog No. CSB-E15852c (96T) This immunoassay kit allows for the in vitro quantitative determination of canine CK-MB concentrations in serum and plasma.
Canine creatine kinase MB isoenzyme (CK-MB)ELISA Kit Catalog No. CSB-E15852c (96T) This immunoassay kit allows for the in vitro quantitative determination of canine CK-MB concentrations in serum and plasma.
All About Your Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC)
 All About Your Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) General Information Intravenous (IV) therapy is the delivery of fluid directly into a vein. An intravenous catheter is a hollow tube that is
All About Your Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) General Information Intravenous (IV) therapy is the delivery of fluid directly into a vein. An intravenous catheter is a hollow tube that is
Content Sheet 5-1: Overview of Sample Management
 Content Sheet 5-1: Overview of Management Role in quality management system management is a part of process control, one of the essentials of a quality management system. The quality of the work a laboratory
Content Sheet 5-1: Overview of Management Role in quality management system management is a part of process control, one of the essentials of a quality management system. The quality of the work a laboratory
How to safely collect blood samples from persons suspected to be infected with highly infectious blood-borne pathogens (e.g.
 How to safely collect blood samples from persons suspected to be infected with highly infectious blood-borne pathogens (e.g. Ebola) Step 1: Before entering patient room, assemble all equipment (1 st part)
How to safely collect blood samples from persons suspected to be infected with highly infectious blood-borne pathogens (e.g. Ebola) Step 1: Before entering patient room, assemble all equipment (1 st part)
General Information and Guidelines. Submission of blood tubes
 General Information and Guidelines Submission of blood tubes Note: Do not submit blood samples in syringes (especially with needles attached). Syringes that are submitted to the lab with the needles attached
General Information and Guidelines Submission of blood tubes Note: Do not submit blood samples in syringes (especially with needles attached). Syringes that are submitted to the lab with the needles attached
6 Body Fluid Stains and Standards
 6 Body Fluid Stains and Standards Laboratory examination of body fluids (i.e., blood, semen, saliva, etc.) may produce significant information in certain investigations. This chapter considers the recognition,
6 Body Fluid Stains and Standards Laboratory examination of body fluids (i.e., blood, semen, saliva, etc.) may produce significant information in certain investigations. This chapter considers the recognition,
Promoting safer use of injectable medicines
 Promoting safer use of injectable medicines A template standard operating procedure for: prescribing, preparing and administering injectable medicines in clinical areas Introduction The use of injectable
Promoting safer use of injectable medicines A template standard operating procedure for: prescribing, preparing and administering injectable medicines in clinical areas Introduction The use of injectable
Guidelines for Collection and Transport of Specimen for Laboratory Diagnosis of Pathogenic Leptospira spp.
 Document: Introduction: Guidelines for Collection and Transport of Specimen for Laboratory Diagnosis of Pathogenic Leptospira spp. Leptospirosis is an acute bacterial infection caused by organism belonging
Document: Introduction: Guidelines for Collection and Transport of Specimen for Laboratory Diagnosis of Pathogenic Leptospira spp. Leptospirosis is an acute bacterial infection caused by organism belonging
Understanding quantitative blood alcohol testing in drunk driving cases.
 Understanding quantitative blood alcohol testing in drunk driving cases. 16 By Patrick T. Barone and Jeffery S. Crampton Drunk driving cases involving blood draws are considerably more complicated to litigate
Understanding quantitative blood alcohol testing in drunk driving cases. 16 By Patrick T. Barone and Jeffery S. Crampton Drunk driving cases involving blood draws are considerably more complicated to litigate
Specimen Collection Guide
 Specimen Collection Guide pathology.mater.org.au Specimen Collection Guide This chart indicates the specimen required for most frequently requested tests. If the desired test is not listed here please
Specimen Collection Guide pathology.mater.org.au Specimen Collection Guide This chart indicates the specimen required for most frequently requested tests. If the desired test is not listed here please
VENEPUNCTURE. Eileen Whitehead 2010 East Lancashire HC NHS Trust
 Eileen Whitehead 2010 East Lancashire HC NHS Trust 1 Definition The term venepuncture describes the procedure of inserting a needle into a vein, usually for the purpose of withdrawing blood for haematological,
Eileen Whitehead 2010 East Lancashire HC NHS Trust 1 Definition The term venepuncture describes the procedure of inserting a needle into a vein, usually for the purpose of withdrawing blood for haematological,
EXERCISE 5: ERYTHROCYTES SEDIMENTATION RATE - ESR, SED RATE
 EXERCISE 5: ERYTHROCYTES SEDIMENTATION RATE - ESR, SED RATE Textbook: Skills: None 10 points Objectives: 1. State the principle of the Erythrocytes Sedimentation Rate - ESR. 2. List two factors which may
EXERCISE 5: ERYTHROCYTES SEDIMENTATION RATE - ESR, SED RATE Textbook: Skills: None 10 points Objectives: 1. State the principle of the Erythrocytes Sedimentation Rate - ESR. 2. List two factors which may
Biohazardous, Medical & Biological Waste Guidance Chart
 CSULA Environmental Health and Safety Biohazardous, Medical & Biological Waste Guidance Chart The chart below provides information on how to handle most, if not all, of the items that frequently are collectively
CSULA Environmental Health and Safety Biohazardous, Medical & Biological Waste Guidance Chart The chart below provides information on how to handle most, if not all, of the items that frequently are collectively
HAEMATOLOGY LABORATORY
 HAEMATOLOGY LABORATORY Head of Unit : Dr Raudhawati Osman Phone : +603-26155281 Email : [email protected] 1. INTRODUCTION The Haematology Unit, Department of Pathology, HKL provides tertiary diagnostic
HAEMATOLOGY LABORATORY Head of Unit : Dr Raudhawati Osman Phone : +603-26155281 Email : [email protected] 1. INTRODUCTION The Haematology Unit, Department of Pathology, HKL provides tertiary diagnostic
MANUAL PLATELET COUNT
 MANUAL PLATELET COUNT LAB OBJECTIVE The student will be able to perform, within K20% accuracy as compared to the automated result, five manual platelet counts using the Unopette system. and the light microscope.
MANUAL PLATELET COUNT LAB OBJECTIVE The student will be able to perform, within K20% accuracy as compared to the automated result, five manual platelet counts using the Unopette system. and the light microscope.
14.0 Stem Cell Laboratory Services
 Laboratory Services Contact Information: To inquire about assisting with surgical harvesting of bone marrow, cellular therapy (CT) product processing, cryopreservation, storage, or any other lab services,
Laboratory Services Contact Information: To inquire about assisting with surgical harvesting of bone marrow, cellular therapy (CT) product processing, cryopreservation, storage, or any other lab services,
Parent & Healthcare Professional Instructions for the collection of Maternal & Umbilical Cord Blood
 Parent & Healthcare Professional Instructions for the collection of Maternal & Umbilical Cord Blood 1 2 3 Contents List of Umbilical Cord Blood Collection Kit Thermally insulated transportation box - do
Parent & Healthcare Professional Instructions for the collection of Maternal & Umbilical Cord Blood 1 2 3 Contents List of Umbilical Cord Blood Collection Kit Thermally insulated transportation box - do
Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) for Outpatient
 Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) for Outpatient Introduction A Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter, or PICC line, is a thin, long, soft plastic tube inserted into a vein of the arm. It
Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) for Outpatient Introduction A Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter, or PICC line, is a thin, long, soft plastic tube inserted into a vein of the arm. It
Advanced Phlebotomy: An on-line Course for Working Phlebotomists. MORE QUESTIONS? Send questions to [email protected]
 Advanced Phlebotomy: An on-line Course for Working Phlebotomists MORE QUESTIONS? Send questions to [email protected] This course is designed for whom? This course is specifically designed for experienced
Advanced Phlebotomy: An on-line Course for Working Phlebotomists MORE QUESTIONS? Send questions to [email protected] This course is designed for whom? This course is specifically designed for experienced
PICC & Midline Catheters Patient Information Guide
 PICC & Midline Catheters Patient Information Guide medcompnet.com 1 table of contents Introduction 4 What is a PICC or Midline Catheter? 4 How is the PICC or Midline Catheter Inserted? 6 Catheter Care
PICC & Midline Catheters Patient Information Guide medcompnet.com 1 table of contents Introduction 4 What is a PICC or Midline Catheter? 4 How is the PICC or Midline Catheter Inserted? 6 Catheter Care
Pediatric Blood Draws HELEN MAXWELL
 Pediatric Blood Draws HELEN MAXWELL Special Considerations for Doing Pediatric Blood Draws Communication is a Must Positive Body Language..(Relaxed/Cheerful) Soft Voice Tone Special Considerations for
Pediatric Blood Draws HELEN MAXWELL Special Considerations for Doing Pediatric Blood Draws Communication is a Must Positive Body Language..(Relaxed/Cheerful) Soft Voice Tone Special Considerations for
VACUETTE RNAgard Blood Tubes BioMaxi Blood RNA Purification Kit. For the collection, preservation and purification of RNA from whole blood
 RNAgard Blood System VACUETTE RNAgard Blood Tubes BioMaxi Blood RNA Purification Kit For the collection, preservation and purification of RNA from whole blood Instructions For Use Protocol blood collection,
RNAgard Blood System VACUETTE RNAgard Blood Tubes BioMaxi Blood RNA Purification Kit For the collection, preservation and purification of RNA from whole blood Instructions For Use Protocol blood collection,
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. Collection of Blood and Preparation of Blood Smears. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
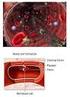 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 3 Collection of Blood and Preparation of Blood Smears. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 3-1 through 3-8. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 3-1. Select
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 3 Collection of Blood and Preparation of Blood Smears. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 3-1 through 3-8. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 3-1. Select
Appendix H IBC Managing Biohazardous Waste SOP
 Biohazardous waste is managed under the State of Rhode Island s Regulated Medical Waste Regulations (Regulation DEM-OWM-MW-1-2009, amended July, 2010). http://www.dem.ri.gov/pubs/regs/regs/waste/medwaste10.pdf
Biohazardous waste is managed under the State of Rhode Island s Regulated Medical Waste Regulations (Regulation DEM-OWM-MW-1-2009, amended July, 2010). http://www.dem.ri.gov/pubs/regs/regs/waste/medwaste10.pdf
EXERCISE 3: SKIN PUNCTURE ON INFANTS
 EXERCISE 3: SKIN PUNCTURE ON INFANTS Textbook: Skills: Chapter 12 Pediatric Procedures Dry Lab Objectives: 1. State the composition of skin puncture blood 2. List five (5) tests that cannot be preformed
EXERCISE 3: SKIN PUNCTURE ON INFANTS Textbook: Skills: Chapter 12 Pediatric Procedures Dry Lab Objectives: 1. State the composition of skin puncture blood 2. List five (5) tests that cannot be preformed
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take, including prescription and nonprescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
 SOMAVERT pegvisomant for injection PATIENT INFORMATION SOMAVERT (SOM-ah-vert) (pegvisomant for injection) Read the patient information that comes with SOMAVERT before you start using it and each time you
SOMAVERT pegvisomant for injection PATIENT INFORMATION SOMAVERT (SOM-ah-vert) (pegvisomant for injection) Read the patient information that comes with SOMAVERT before you start using it and each time you
Experiment 12- Classification of Matter Experiment
 Experiment 12- Classification of Matter Experiment Matter can be classified into two groups: mixtures and pure substances. Mixtures are the most common form of matter and consist of mixtures of pure substances.
Experiment 12- Classification of Matter Experiment Matter can be classified into two groups: mixtures and pure substances. Mixtures are the most common form of matter and consist of mixtures of pure substances.
QuantiFERON TB Gold In Tube Method (QGIT Test) Manufacturer: Cellestis Inc. (USA) a QIAGEN Company
 QuantiFERON TB Gold In Tube Method (QGIT Test) Manufacturer: Cellestis Inc. (USA) a QIAGEN Company P1078 TB APPRISE TB Ante vs. Postpartum Prevention with INH in HIV Seropositive mothers and their Exposed
QuantiFERON TB Gold In Tube Method (QGIT Test) Manufacturer: Cellestis Inc. (USA) a QIAGEN Company P1078 TB APPRISE TB Ante vs. Postpartum Prevention with INH in HIV Seropositive mothers and their Exposed
Objectives At the completion of this module, unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) should be able to:
 Objectives At the completion of this module, unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) should be able to: 1. administer medications by subcutaneous injections. 2. document medication administration in the client
Objectives At the completion of this module, unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) should be able to: 1. administer medications by subcutaneous injections. 2. document medication administration in the client
IgM ELISA. For the quantitative determination of IgM in human serum and plasma. For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
 IgM ELISA For the quantitative determination of IgM in human serum and plasma For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures. Please read carefully due to Critical Changes, e.g., Calibrator
IgM ELISA For the quantitative determination of IgM in human serum and plasma For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures. Please read carefully due to Critical Changes, e.g., Calibrator
A4.7 Management of a totally occluded central catheter and persistent withdrawal occlusion (PWO)
 A4.7 Management of a totally occluded central catheter and persistent withdrawal occlusion (PWO) Types of Catheter Related Thrombotic A catheter-related thrombus may be intraluminal (inside the catheter)
A4.7 Management of a totally occluded central catheter and persistent withdrawal occlusion (PWO) Types of Catheter Related Thrombotic A catheter-related thrombus may be intraluminal (inside the catheter)
Use of Micropipettes
 Use of Micropipettes Prior to lab you should understand: The function of micropipettes in the laboratory Basic parts of micropipette What volumes are measured with P, P and P1 micopipettors How to read
Use of Micropipettes Prior to lab you should understand: The function of micropipettes in the laboratory Basic parts of micropipette What volumes are measured with P, P and P1 micopipettors How to read
Within the Scope of Practice/Role of APRN RN _ X_LPN CNA
 Wyoming State Board of Nursing 130 Hobbs Avenue, Suite B Cheyenne, WY 82002 Phone (307) 777-7601 Fax (307) 777-3519 E-Mail: [email protected] Home Page: https://nursing-online.state.wy.us/ OPINION:
Wyoming State Board of Nursing 130 Hobbs Avenue, Suite B Cheyenne, WY 82002 Phone (307) 777-7601 Fax (307) 777-3519 E-Mail: [email protected] Home Page: https://nursing-online.state.wy.us/ OPINION:
Instructions for Use
 1 Instructions for Use HUMULIN R U-500 KwikPen insulin human injection U-500 (500 units/ml, 3 ml pen) Important: Know your dose of HUMULIN R U-500 insulin. The Pen delivers your dose in insulin units.
1 Instructions for Use HUMULIN R U-500 KwikPen insulin human injection U-500 (500 units/ml, 3 ml pen) Important: Know your dose of HUMULIN R U-500 insulin. The Pen delivers your dose in insulin units.
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE
 TAKING BLOOD FROM INFANTS FOR THE HIV DNA PCR TEST STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE ACRONYMS ARV CCMT DBS Antiretrovirals Comprehensive care, management and treatment Dried blood spots This Standard Operating
TAKING BLOOD FROM INFANTS FOR THE HIV DNA PCR TEST STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE ACRONYMS ARV CCMT DBS Antiretrovirals Comprehensive care, management and treatment Dried blood spots This Standard Operating
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE HUMIRA 40 MG/0.8 ML, 20 MG/0.4 ML AND 10 MG/0.2 ML SINGLE-USE PREFILLED SYRINGE
 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE HUMIRA (Hu-MARE-ah) (adalimumab) 40 MG/0.8 ML, 20 MG/0.4 ML AND 10 MG/0.2 ML SINGLE-USE PREFILLED SYRINGE Do not try to inject HUMIRA yourself until you have been shown the right way
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE HUMIRA (Hu-MARE-ah) (adalimumab) 40 MG/0.8 ML, 20 MG/0.4 ML AND 10 MG/0.2 ML SINGLE-USE PREFILLED SYRINGE Do not try to inject HUMIRA yourself until you have been shown the right way
Rat Creatine Kinase MB isoenzyme,ck-mb ELISA Kit
 Rat Creatine Kinase MB isoenzyme,ck-mb ELISA Kit Catalog No: E0479r 96 Tests Operating instructions www.eiaab.com FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY; NOT FOR THERAPEUTIC OR DIAGNOSTIC APPLICATIONS! PLEASE READ THROUGH
Rat Creatine Kinase MB isoenzyme,ck-mb ELISA Kit Catalog No: E0479r 96 Tests Operating instructions www.eiaab.com FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY; NOT FOR THERAPEUTIC OR DIAGNOSTIC APPLICATIONS! PLEASE READ THROUGH
CHAPTER 17. CHAPTER OUTLINE Introduction to Phlebotomy. Perform a venipuncture using the vacuum tube
 CHR 17 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Venipuncture 1. List and des cribe th e general guidelines that should be followed when performing a venipuncture. 2. Explain how each of the following blood specimens is obtained:
CHR 17 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Venipuncture 1. List and des cribe th e general guidelines that should be followed when performing a venipuncture. 2. Explain how each of the following blood specimens is obtained:
Metabolism: Cellular Respiration, Fermentation and Photosynthesis
 Metabolism: Cellular Respiration, Fermentation and Photosynthesis Introduction: All organisms require a supply of energy and matter to build themselves and to continue to function. To get that supply of
Metabolism: Cellular Respiration, Fermentation and Photosynthesis Introduction: All organisms require a supply of energy and matter to build themselves and to continue to function. To get that supply of
Instructions for Drawing Blood Samples
 Instructions for Drawing Blood Samples For Blood Collection Supplies please contact us. *Whatever means of restraint is used it should cause minimal distress and should be quick and safe for both the animal
Instructions for Drawing Blood Samples For Blood Collection Supplies please contact us. *Whatever means of restraint is used it should cause minimal distress and should be quick and safe for both the animal
Mixtures and Pure Substances
 Unit 2 Mixtures and Pure Substances Matter can be classified into two groups: mixtures and pure substances. Mixtures are the most common form of matter and consist of mixtures of pure substances. They
Unit 2 Mixtures and Pure Substances Matter can be classified into two groups: mixtures and pure substances. Mixtures are the most common form of matter and consist of mixtures of pure substances. They
Policy and Procedure Flushing and / or Blood withdrawal Aspiration Procedure For PICC Line and Midline Catheters
 Policy and Procedure Flushing and / or Blood withdrawal Aspiration Procedure For PICC Line and Midline Catheters Purpose: Blood Withdrawal: To obtain blood samples for laboratory evaluation, eliminating
Policy and Procedure Flushing and / or Blood withdrawal Aspiration Procedure For PICC Line and Midline Catheters Purpose: Blood Withdrawal: To obtain blood samples for laboratory evaluation, eliminating
Malondialdehyde (MDA) ELISA
 Malondialdehyde (MDA) ELISA For the quantitative determination of MDA in serum, plasma and other biological fluids Cat. No. KT-21493 For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Page 1
Malondialdehyde (MDA) ELISA For the quantitative determination of MDA in serum, plasma and other biological fluids Cat. No. KT-21493 For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Page 1
MISSISSIPPI BOARD OF NURSING IV THERAPY COURSE FOR THE EXPANDED ROLE LICENSED PRACTICAL NURSE COURSE OUTLINE
 THEORY MINIMUM 40 HOURS COURSE OUTLINE UNIT TOPIC HOURS* I LEGAL ASPECTS AND PRACTICE OF IV THERAPY 1 II REVIEW OF ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY 6 III FLUID AND ELECTROLYTE BALANCE 10 IV EQUIPMENT AND PROCEDURES
THEORY MINIMUM 40 HOURS COURSE OUTLINE UNIT TOPIC HOURS* I LEGAL ASPECTS AND PRACTICE OF IV THERAPY 1 II REVIEW OF ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY 6 III FLUID AND ELECTROLYTE BALANCE 10 IV EQUIPMENT AND PROCEDURES
Medications or therapeutic solutions may be injected directly into the bloodstream
 Intravenous Therapy Medications or therapeutic solutions may be injected directly into the bloodstream for immediate circulation and use by the body. State practice acts designate which health care professionals
Intravenous Therapy Medications or therapeutic solutions may be injected directly into the bloodstream for immediate circulation and use by the body. State practice acts designate which health care professionals
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE HUMIRA 40 MG/0.8 ML SINGLE-USE PEN
 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE HUMIRA (Hu-MARE-ah) (adalimumab) 40 MG/0.8 ML SINGLE-USE PEN Do not try to inject HUMIRA yourself until you have been shown the right way to give the injections and have read and understand
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE HUMIRA (Hu-MARE-ah) (adalimumab) 40 MG/0.8 ML SINGLE-USE PEN Do not try to inject HUMIRA yourself until you have been shown the right way to give the injections and have read and understand
INJECTION TECHNIQUE. IVF NURSING OFFICE: (301) 400-2151 Darshana (301) 400-2146 Nicole
 IVF NURSING OFFICE: (301) 400-2151 Darshana (301) 400-2146 Nicole PLEASE NOTE: If you do not have medications for the next day s dose, you MUST go to the clinic that morning at 6:30 AM for more medications.
IVF NURSING OFFICE: (301) 400-2151 Darshana (301) 400-2146 Nicole PLEASE NOTE: If you do not have medications for the next day s dose, you MUST go to the clinic that morning at 6:30 AM for more medications.
Hazardous Materials Disposal Handbook Biohazardous Waste
 Created by: Stuart Elle Date: September 10, 2009 Revised by: Hazardous Materials Disposal Handbook Biohazardous Waste n/a Date: n/a 1. Introduction... 2 1.1. Purpose... 2 1.2. The Role of Hazardous Materials
Created by: Stuart Elle Date: September 10, 2009 Revised by: Hazardous Materials Disposal Handbook Biohazardous Waste n/a Date: n/a 1. Introduction... 2 1.1. Purpose... 2 1.2. The Role of Hazardous Materials
Infectious Waste Management Plan
 Infectious Waste Management Plan Infectious Waste Management Plan USC Health & Safety Programs Unit 777-5269 POLICY: A. In keeping with the University of South Carolina's policy of providing protection
Infectious Waste Management Plan Infectious Waste Management Plan USC Health & Safety Programs Unit 777-5269 POLICY: A. In keeping with the University of South Carolina's policy of providing protection
Cold Agglutination Titer detecting Cold Reacting Antibodies
 Objectives: Cold Agglutination Titer detecting Cold Reacting Antibodies 1. Perform a serial dilution to determine the amount of cold reacting antibody present in a patient specimen with the results obtained
Objectives: Cold Agglutination Titer detecting Cold Reacting Antibodies 1. Perform a serial dilution to determine the amount of cold reacting antibody present in a patient specimen with the results obtained
ABORhCard. ABORhCard Package Insert ABO and Rh Blood Grouping Device
 ABORhCard Package Insert ABO and Rh Blood Grouping Device ABORhCard Intended Use The ABORhCard is a qualitative in vitro test that provides a simultaneous ABO and Rh determination of an individual s ABO
ABORhCard Package Insert ABO and Rh Blood Grouping Device ABORhCard Intended Use The ABORhCard is a qualitative in vitro test that provides a simultaneous ABO and Rh determination of an individual s ABO
THE ACTIVITY OF LACTASE
 THE ACTIVITY OF LACTASE Lab VIS-8 From Juniata College Science in Motion Enzymes are protein molecules which act to catalyze the chemical reactions in living things. These chemical reactions make up the
THE ACTIVITY OF LACTASE Lab VIS-8 From Juniata College Science in Motion Enzymes are protein molecules which act to catalyze the chemical reactions in living things. These chemical reactions make up the
Free SO 2. by Aeration-Oxidation. A n o t h e r M o r e M a n u a l!
 Free SO 2 by Aeration-Oxidation A n o t h e r M o r e M a n u a l! Provided by MoreWine! A MoreFlavor!, Inc. Brand www.morewinemaking.com 1-800-600-0033 H570 MT116 MT104 D1702 MT117 R335 D1702 Kit Item
Free SO 2 by Aeration-Oxidation A n o t h e r M o r e M a n u a l! Provided by MoreWine! A MoreFlavor!, Inc. Brand www.morewinemaking.com 1-800-600-0033 H570 MT116 MT104 D1702 MT117 R335 D1702 Kit Item
Good practice for the preparation of injectable medicines in clinical areas
 Further reading Dougherty L and Lister S (Eds). The Royal Marsden Hospital Manual of Clinical Nursing Procedures (th edition), Blackwell Publishing, Oxford, 00. NMC standards for medicines management (008).
Further reading Dougherty L and Lister S (Eds). The Royal Marsden Hospital Manual of Clinical Nursing Procedures (th edition), Blackwell Publishing, Oxford, 00. NMC standards for medicines management (008).
GENOME RUSSIA PROJECT BLOOD SAMPLES COLLECTION, DNA EXTRACTION AND DNA QUALITY CONTROL PROTOCOLS
 ST-PETERSBURG STATE UNIVERSITY THEODOSIUS DOBZHANSKY CENTER FOR GENOME BIOINFORMATICS GENOME RUSSIA PROJECT BLOOD SAMPLES COLLECTION, DNA EXTRACTION AND DNA QUALITY CONTROL PROTOCOLS 2015 The object of
ST-PETERSBURG STATE UNIVERSITY THEODOSIUS DOBZHANSKY CENTER FOR GENOME BIOINFORMATICS GENOME RUSSIA PROJECT BLOOD SAMPLES COLLECTION, DNA EXTRACTION AND DNA QUALITY CONTROL PROTOCOLS 2015 The object of
