Course Principles of LPSCS. Unit IV Corrections
|
|
|
- Eileen Brown
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Course Principles of LPSCS Unit IV Corrections Essential Question What is the role and function of the correctional system in society? TEKS (c) (10)(A)(B)(C) (D)(E)(F) Prior Student Learning none Estimated Time 3 hours Roles and Functions of the Correctional System Rationale The correctional system in the United States plays a key role in society. It is important to understand what careers are available, their required duties, and the differences between the types of correctional systems. It is also imperative that we address the rights of those confined within the correctional system. Objectives The student will be able to: 1. Explain what career opportunities are available in the correctional system, including probation and parole. 2. Explain the duties and responsibilities of correctional officers. 3. Outline the history of prisons in the U.S. 4. Explain the differences between jails and prisons. 5. Identify the levels of security in prisons and jails. 6. Explain the constitutional rights of inmates in prisons and jails. Engage Career Exploration. Allow the students to research careers in corrections within their geographical area, including information about hiring guidelines, job duties, and salaries. The students should report their findings to the class. They can then compare and contrast correctional careers, and discuss the differences between jails and prisons. The Discussion and/or Presentation Rubrics may be used for assessment. Key Points I. Correctional Careers and Duties there are many career options available to individuals seeking careers within the correctional system. Job duties, hiring requirements, and salaries vary by employer. A. Probation or Parole Officer counsel, monitor, and evaluate the progress of offenders to determine whether they are abiding by the court s expectations of them, and whether they will be eventually released from supervision 1. Probation an alternative to incarceration 2. Parole a supervised release from incarceration before the expiration of the sentence a. District Parole Officers supervise offenders who have been released on parole, or mandatory supervision, to complete their sentences while living in Texas communities b. Institutional Parole Officers physically assigned to Texas Department of Criminal Justice (TDCJ) units. They interview incarcerated offenders in TDCJ Units, federal correctional institutions, contracted facilities, and county 1
2 jails statewide to prepare Parole Case Summaries. B. Correctional Officers primarily responsible for the safety and security of the unit and the offenders within the unit C. Jailers/Detention Officers similar to correctional officers, usually work in pretrial detention facilities D. Juvenile Detention Officers similar to correctional officers with a specialization in juvenile offenders E. Federal Correctional Officers similar to correctional officers with a specialization in the federal correctional system F. Warden the chief administrator of a prison II. Four Early Prison Systems A. Early Jail conditions were primitive and inhumane 1. Sixteen people in a 12-foot by 12-foot cell 2. Prisoners provided their own food and medical needs 3. Could buy alcohol, food, privileges, and cell space 4. Indigents had to work for their keep 5. Men, women, and children all housed together 6. Sick and healthy housed together 7. No heat, no plumbing, and no adequate sleeping or living space 8. Many deaths from sickness and starvation B. Walnut Street Jail law passed by Pennsylvania legislature a. Humane physical facilities b. Adequate food and water at public expense c. Separation of men, women, and children d. Prohibition on buying better treatment e. Debtors and mentally ill separated from criminal population f. Orphans were moved to separate buildings 2. Prison Life a. Prisoners worked but were paid for labor b. Earn early release for good behavior c. Attempted to rehabilitate prisoners d. Became overcrowded e. Conditions deteriorated and costs skyrocketed f. Prison failed at rehabilitation C. Eastern State Penitentiary 1. Built in Cost $500,000 to house 250 prisoners 3. The most expensive building in the new world 4. First in the country to have flush toilets and heat 5. Designed as a penitentiary, not jail or prison a. Penitentiary a correctional institution based on the concept that inmates could change their criminality through reflection and penitence b. It had individual cells, and the prisoners had to become proficient with a skill for use after release 6. Expected to read the Bible when not working or exercising 7. Use of the silent system 2
3 8. Maximum security, walled, self-contained 9. Cells 12 x 7.5 with had a window 10. Working, exercising, eating, and sleeping all performed in the prisoner s cell D. The Auburn System 1. Built in 1816, walled, maximum security 2. Cells 7 x 4, 7 high, back to back, 5 tiers located in the center of the building inside cell blocks 3. Cells poorly lit, no fresh air 4. Inmates moved to other locations in the unit for work, exercise, and eating 5. Silent system used but hard to enforce 6. Corporal punishment used for violations 7. Marched from place to place 8. Short haircuts 9. Distinctive uniforms 10. First use of solitary confinement 11. Prison industries (the prison was self-sufficient) 12. Prototype American prison E. Southern Penal System 1. Convict lease system was implemented after the end of slavery 2. Construction work, factory work, agricultural work 3. Very poor work and living conditions 4. Worked hours a day 5. Often lived in cages, and discipline was brutal 6. Origin of chain gangs 7. The 1930 Prison Farm System replaced the lease system 8. Inmate labor used to sustain prisons and other profit industries 9. Used prisoners as guards and supervisors to cut costs 10. Arkansas and Texas brought about U.S. Supreme Court decisions on the 8th amendment III. Jails short-term, multipurpose holding facilities that serve as the gateway for the criminal justice system A. Jails house different types of offenders 1. Defendants awaiting trial 2. Defendants convicted of misdemeanors 3. The mentally ill, pending movement to a health facility 4. Local, state, and federal prisoners 5. Adults 6. Juveniles 7. Absconders 8. Witnesses 9. Awaiting trial or transport 10. Convicted prisoners 11. Adults of both genders B. Punishment ranges for jail 1. Class A Misdemeanor up to 2 years and $4,000 fine 2. Class B Misdemeanor up to 180 days and $2,000 fine 3
4 3. Class C Misdemeanor up to $500 fine C. County Jails 1. Over 3,300 local/county jails 2. Vary in size from less than 50 to more than 7,000 inmates 3. The population has more than doubled since Very few municipal jails IV. Prisons correctional institutions for prisoners convicted of felonies A. Extended sentences B. Inmates separated by sex C. Architecture reflective of gender bias D. Punishment ranges for prison 1. State Jail Felony 180 days to 2 years, $10,000 fine 2. 3rd degree Felony 2 to 10 years, $10,000 fine 3. 2nd degree Felony 2 to 20 years, $10,000 fine 4. 1st degree Felony 2 to 99 years, $10,000 fine 5. Capital Felony life without parole, or death E. Security levels 1. Minimum few physical barriers to escape and lots of programs for offenders 2. Medium self-contained, walled fortresses that offer vocational, education, and rehabilitation for offenders 3. Maximum dangerous or violent offenders are housed in a selfcontained, fortress-like facility 4. Administrative segregation (solitary confinement) offenders are kept in single cells 23 hours a day F. Private jails and prisons 1. For-profit facilities run by private security companies 2. Contracted by counties at lower cost 3. Fewer programs or opportunities for offenders 4. Less training and lower pay the conditions are often below state standards 5. Escapes and assaults carry smaller penalties V. Constitutional rights A. Retain all the rights of free citizens B. Three government interests, however, justify curtailing offenders rights: 1. Maintaining internal order and discipline 2. Securing the institution against unauthorized access or escape 3. Rehabilitating offenders C. Types of cases filed 1. Habeus Corpus a single offender files suit for unlawful imprisonment based on a violation of constitutional rights 2. Section 1983 a class action suit based on unfavorable prison conditions and seeking monetary damages. The judgment affects all offenders. D. Bill of Rights 1. First Amendment 4
5 a. Freedom of speech b. Freedom of religion c. Freedom of press d. Freedom of assembly e. Freedom to petition government for redress of grievances 2. Fourth Amendment protects against unreasonable search and seizure 3. Fifth Amendment a. Right to jury b. Protects against double jeopardy c. Protects against self-incrimination d. Prohibits the taking of life, liberty, or property without due process e. Prevents the taking of private property without just compensation 4. Sixth Amendment a. Public and speedy trial b. Impartial jury c. Informed of nature and causation against you d. Confront witnesses e. Compulsory process for obtaining witnesses f. Right to an attorney 5. Eighth Amendment a. Protects against unreasonable bail b. Prohibits cruel and unusual punishment 6. Fourteenth Amendment a. Privileges and immunities b. Right to due process c. Right to equal protection under law VI. Case Law A. Turner v. Safely the most important prison law case ever decided on by the Supreme Court. This case established that penal institutions could limit offender correspondence for the overall safety of the institution, but could not limit the scope under which the marriage of an offender could occur. Activities 1. Case Law Activity. The students will read Turner v. Safely and answer the fundamental questions addressed to better understand the ruling of the court. Discuss the answers as a group. Have the students argue the facts of the case, for and against. Use the Case Law Activity Handout for the activity and the Case Law Activity Handout Key for assessment. 2. Who Wants to Be a Zillionaire? Divide the students into teams. Each team will take turns answering questions, either as individuals or as a team. Assign a student to keep score. Read each question and its possible answers. Give the answering student or team a designated amount of time to answer the question. You may allow the opposite team to answer if the 5
6 first team answers incorrectly. 3. Outline the History of U.S. Prisons. Have the students work individually or in groups to research and create a general outline of the History of U.S. Prisons. Use the Individual Work Rubric and the Research Rubric for assessment. Assessments Roles and Functions of the Correctional System Exam and Key Discussion Rubric Individual Work Rubric Presentation Rubric Research Rubric Materials Roles and Functions of the Correctional System computer-based presentation Who Wants to be a Zillionaire computer-based presentation Case Law Activity Handout and Key Computers with Internet access Projector and screen Resources X, Fagin, James. Criminal Justice: Prentice Hall, , del Carmen, Rolando v. Susan E. Ritter, Betsy A. Witt. Briefs of Leading Cases in Corrections: Anderson, , O Brien, Edward; Fisher, Margaret; Austern, David T. Practical Law for Jail and Prison Personnel: West Group, Civil Liabilities and Other Legal Issues: Do an Internet search for the following: Findlaw Turner Safely Supreme justia Turner Safely Accommodations for Learning Differences For reinforcement, the students can interview a correctional employee about their job duties and requirements. Students can be creative in the type of correctional employee they interview. Some examples would be jailers, correctional officers (TDCJ), parole officers, probation officers, or juvenile probation/parole officers. Use the Individual Work Rubric for assessment. For enrichment, have the students create their own prison in groups using the information contained in this lesson. The unit should include which style prison it is being modeled after, the offense levels housed, the staff s qualifications, the staff s salary, the style of the housing unit, how the prison is funded, and the unit s level of security (including the security system). Have the students present their prison to the class. Use the Presentation Rubric for assessment. State Education Standards 6
7 Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Career and Technical Education Principles of Law, Public Safety, Corrections, and Security (One- Half to One Credit). (10) The student identifies the roles and functions of the correctional system. The student is expected to: (A) Explain career opportunities available in the correctional system, including probation and parole; (B) Explain the duties and responsibilities of correctional officers; (C) Outline the history of prisons in the U.S.; (D) Explain the difference between jails and prisons; (E) Identify the levels of security in prisons and jails; (F) Explain the constitutional rights of inmates in prisons and jails. College and Career Readiness Standards II. Foundational Skills E. Technology 1. Use technology to gather information. 2. Use technology to organize, manage, and analyze information. 3. Use technology to communicate and display findings in a clear and coherent manner. 4. Use technology appropriately. 7
8 Name: Date: Case Law Activity Instructions: read the court decision Turner v. Safely and answer the following questions. Which two regulations were challenged by this case? What are the two main issues? What was the court s decision? What factors can be considered in making the reasonableness determination? 8
9 Case Law Activity Key Have students read the court decision Turner v. Safely and answer the following questions. Which two regulations were challenged by this case? 1. Regulations were in place regarding correspondence between family members who are offenders at different institutions, and between offenders concerning legal matters, but allowed correspondence based on each offender s classification or treatment. Offenderto-offender correspondence was prohibited. 2. A policy prohibiting the marriage of offenders, except under compelling circumstances; generally a pregnancy or the birth of an illegitimate child. What are the two main issues? 1. Does a policy that regulates correspondence between family members housed at different institutions and between offenders concerning legal matters, but allows other correspondence between offenders violate the constitutional rights of the offenders? No 2. Does a policy permitting an offender to marry only under compelling reasons violate an offender s constitutional rights? Yes What was the court s decision? The Federal District Court found both regulations unconstitutional, and the Court of Appeals affirmed. What factors can be considered in making the reasonableness determination? A policy impinging on offender s constitutional rights is valid if it reasonably relates to the interest of the penal facility. The factors of reasonableness include 1. Is there a valid connection between the policy and the government interest justifying it? 2. Does the offender have alternate methods of exercising their rights? 3. How will the constitutional right impact correctional officers, prison resources, and offenders? 4. Are there any alternatives to granting the right? 9
10 Name: Date: Roles and Functions of the Correctional System Exam 1. Jails house what type(s) of offenders? a. Misdemeanor b. Felony c. Both d. Neither 2. Prisons house what type(s) of offenders? a. Misdemeanors b. Both c. Felonies d. Neither 3. Johnny commits Possession of Prohibited Weapon, which is a Class A offense. He can be sentenced with what penalty? a. 2 years/$4,000 fine b. 180 days/$500 fine c. 2 years/$2,000 fine d. 180 days/$2,000 fine 4. Rachel receives a ticket for speeding. Can Rachel be arrested? a. Yes b. No 5. Jason is serving a State Jail sentence for theft of livestock ($1,500-$5,000). What is the punishment range that Jason can be sentenced to? a years b. 1 year c. 180 days-2 years d. None, Jason can receive probation 6. What is the punishment for a Class C ticket? a. $500 fine/30 days in jail b. $500 fine only c. $2,000 fine/180 days jail d. None of the above 7. Gerard has a baggie of less than 2 oz of marijuana in his pocket. He is charged with a Class B offense for possession. What might his punishment be? a. 2 years/$4,000 fine b. 2 years/$2,000 fine c. 180 days/$4,000 fine d. 180 days/$2,000 fine 8. What is the punishment for a 1 st degree felony? a years/$10k fine b years/#10k fine c years/$10k fine d. Death 10
11 9. What is the punishment for a 2 nd degree Felony? a years/$10k fine b years/$10k fine c years/$10k fine d. Death 10. What is the punishment for a 3 rd degree felony? a years/$10k fine b years/$10k fine c years/$10k fine d. Death 11. Death is the only punishment available for a capital crime in Texas. a. True b. False 12. Prisons house what type of offenders? a. High level property offenders b. High level drug offenders c. Violent offenders d. All of the above 13. Probation and parole officers may have to supervise offenders with different types of needs, such as mentally retarded, elderly, sick, or homeless people. a. True b. False 14. Early jail conditions included all but which of the following? a. Men, women, and children all housed together b. Purchase of alcohol, food, privileges, and cell space c. Prisoners provided their own food and medical care d. 2 people housed in 12 x 12 cell 15. The Walnut Street Jail reforms included which of the following? a. Separation of men, women, and children b. Humane physical facilities c. Orphans moved to separate building d. All of the above 16. Which facility was built in 1892 and was deemed the world s most expensive building? a. Walnut Street Jail b. Eastern State Penitentiary c. Auburn Prison d. Southern Penal System 17. A correctional institution based on the concept that inmates could change their criminality through reflection and penitence. a. Jail b. Prison c. Penitentiary d. None of the above 11
12 18. Which system used the silent system? a. Walnut Street Jail b. Southern penal system c. Eastern Penitentiary d. Auburn system and Eastern Penitentiary 19. The Auburn system was the first to move offenders to different locations for work, exercise, and eating. a. True b. False 20. The Auburn system included which of the following? a. Solitary confinement b. Prison industries c. Short haircuts d. All of the above 21. Which system utilized convict labor for construction, factory, and agricultural work? a. Eastern penitentiary b. Walnut Street jail c. Auburn system d. Southern Penal System 22. The Southern Penal System is characterized by which of the following? a. Chain gangs b. Prison reforms c. Use of prisoners as guards d. All of the above 23. In the 1980 s, the U.S. Supreme court ruled that inmates could sue for all but which of the following violations? a. Living conditions b. Medical treatment c. Prison policies d. Sexual relations policies 24. A short-term, multipurpose holding facility that serves as a gateway for the criminal justice system. a. Prison b. Jail c. Penitentiary d. SAFP 25. Jails may hold which of the following types of individuals? a. Defendants convicted of misdemeanors b. Parole Absconders c. Witnesses d. All of the above 12
13 26. A correctional institution for prisoners convicted of felonies. a. Prison b. Jail c. Penitentiary d. SAFP 27. Which security level institution is described as a fortress-like, walled, selfcontained institution that offers inmates education, vocations, and rehabilitation? a. Administrative segregation b. Maximum security c. Minimum security d. Medium security 28. Offenders are kept in single cells for 23 hours a day. They are allowed to shower and recreate for 1 hour a day. a. Minimum security b. Administrative segregation c. Maximum security d. Medium security 29. Contains few physical barriers to escape, and many work and rehabilitative programs for offenders. a. Minimum security b. Medium security c. Maximum security d. Administrative segregation 30. Houses violent, high-risk offenders that may be at risk for escape. a. Minimum security b. Medium security c. Maximum security d. Administrative segregation 31. Common problems of private prison and jails include all but which of the following? a. Less programs for offenders b. Less training and pay, and sub-standard conditions c. Escapes and assaults carry lesser penalties d. Substantially lower operating costs 32. All but which of the following are career options in the correctional field? a. Jailer/Detention officer b. Parole officer c. Police officer d. Correctional officer 33. Correctional officer duties include which of the following? a. Conduct searches of offenders and their property b. Supervise offenders released from prison into the community c. Report to the courts about offender behavior d. Conduct home, office, and work visits 13
14 34. Which is not one of the government interests that justify curtailing offender s rights? a. Rehabilitating offenders b. Maintaining internal order and discipline c. The image of the warden d. Securing the institution against unauthorized access or escape 35. Which type of case can an offender file if he or she is seeking release based on unlawful confinement? a. Section 1983 b. Constitutional rights violation c. Habeas Corpus d. None of the above 36. Section 1983 cases affect all offenders and may seek monetary damages. a. True b. False 37. Which amendment allows for freedom of religion? a. 1 b. 4 c. 5 d Which amendment gives offenders the right to confront witnesses? a. 4 b. 5 c. 6 d What Supreme Court case determined that offenders rights can be restricted based on the needs of the penal institution? a. Ruiz v. Estelle b. Lamar v. Coffield c. Turner v. Safely d. Terry v. Ohio 40. Which amendment protects against the taking of life, liberty, and property without due process? a. 1 b. 5 c. 6 d. 8 14
15 Roles and Functions of the Correctional System Exam Key 1. A 2. C 3. A 4. B 5. C 6. B 7. D 8. C 9. B 10. A 11. B 12. D 13. A 14. D 15. D 16. B 17. C 18. D 19. A 20. D 21. D 22. D 23. D 24. B 25. D 26. A 27. D 28. B 29. A 30. C 31. D 32. C 33. A 34. C 35. C 36. A 37. A 38. C 39. C 40. B 15
16 Name Date Objectives 4 pts. Excellent Discussion Rubric 3 pts. Good 2 pts. Needs Some Improvement 1 pt. Needs Much Improvement N/A Pts. Participates in group discussion Encourages others to join the conversation Keeps the discussion progressing to achieve goals Shares thoughts actively while offering helpful recommendations to others Gives credit to others for their ideas Respects the opinions of others Involves others by asking questions or requesting input Expresses thoughts and ideas clearly and effectively Total Points (32 pts.) Comments: 16
17 Name Date Objectives Follows directions Student completed the work as directed, following the directions given, in order and to the level of quality indicated Individual Work Rubric 4 pts. Excellent 3 pts. Good 2 pts. Needs Some Improvement 1 pt. Needs Much Improvement N/A Pts. Time management Student used time wisely and remained on task 100% of the time Organization Student kept notes and materials in a neat, legible, and organized manner. Information was readily retrieved Evidence of learning Student documented information in his or her own words and can accurately answer questions related to the information retrieved *Research/Gathering information (if relevant) Student used a variety of methods and sources to gather information. Student took notes while gathering information Total Points (20 pts.) Comments: 17
18 Name: Date: Presentation Rubric Objectives Topic/Content Topic discussed completely and in-depth Includes properly cited sources (if used) Creativity/Neatness Integrates a variety of multimedia effects to create a professional presentation (transition and graphics) or appropriate visual aid used Title slide, table of contents, bibliography are included, using acceptable format Mechanics Grammar, spelling, punctuation, and capitalization are correct Image and font size are legible to the entire audience Oral Presentation Communicates with enthusiasm and eye contact Voice delivery and projection are dynamic and audible Audience Interaction Presentation holds audience s attention and relates a clear message Clearly and effectively communicates the content throughout the presentation 4 pts. Excellent 3 pts. Good 2 pts. Needs Some Improvement 1 pt. Needs Much Improvement N/A Pts. Total Points (20 pts.) Comments: 18
19 Name Date Objectives Question/goal Student identified and communicated a question or goal of the research 4 pts. Excellent Research Rubric 3 pts. Good 2 pts. Needs Some Improvement 1 pt. Needs Much Improvement N/A Pts. Research/Gathering information (if relevant) Student used a variety of methods and sources to gather information. Student took notes while gathering information Conclusion/Summary Student drew insightful conclusions and observations from the information gathered. Information is organized in a logical manner Communication Student communicated the information gathered and summary or conclusions persuasively. Student demonstrated skill in the use of media used to communicate the results of research Reflection Student reflected on the importance of the research and its potential application Total Points (20 pts.) Comments: 19
Course Court Systems and Practices
 Course Court Systems and Practices Unit I Criminal Justice System Essential Question What are the history, structure, and function of the state and federal courts and criminal procedure? TEKS 130.296(c)
Course Court Systems and Practices Unit I Criminal Justice System Essential Question What are the history, structure, and function of the state and federal courts and criminal procedure? TEKS 130.296(c)
Course Law Enforcement I. Unit III United States Legal Systems
 Course Law Enforcement I Unit III United States Legal Systems Essential Question What is the difference between civil and criminal law? TEKS 130.293(c) (5)(E) Prior Student Learning State and Federal Court
Course Law Enforcement I Unit III United States Legal Systems Essential Question What is the difference between civil and criminal law? TEKS 130.293(c) (5)(E) Prior Student Learning State and Federal Court
SUN PRAIRIE AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT COURSE SYLLABUS. Curriculum Area: Social Studies Course Length: Semester
 SUN PRAIRIE AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT COURSE SYLLABUS Course Title: Legal Studies Curriculum Area: Social Studies Course Length: Semester Credit Status: Elective Date submitted: 2/07 District Adopted Texts/Materials/Resources:
SUN PRAIRIE AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT COURSE SYLLABUS Course Title: Legal Studies Curriculum Area: Social Studies Course Length: Semester Credit Status: Elective Date submitted: 2/07 District Adopted Texts/Materials/Resources:
Course Forensic Science. Unit II History
 Course Forensic Science Unit II History Essential Question What is legally and ethically expected of forensic scientists and Crime Scene Investigators? TEKS 130.295(c) (4)(C) Prior Student Learning History
Course Forensic Science Unit II History Essential Question What is legally and ethically expected of forensic scientists and Crime Scene Investigators? TEKS 130.295(c) (4)(C) Prior Student Learning History
CONSTITUTIONAL RIGHTS
 RIGHTS OF THE CRIMINALLY ACCUSED GENERAL LEGAL RIGHTS CHAPTER 10 INTRODUCTION Constitutional rights relating to American criminal law are the same for all adult persons, whether they have a disability
RIGHTS OF THE CRIMINALLY ACCUSED GENERAL LEGAL RIGHTS CHAPTER 10 INTRODUCTION Constitutional rights relating to American criminal law are the same for all adult persons, whether they have a disability
Course Court Systems and Practices. Unit X Pre-trial
 Course Court Systems and Practices Unit X Pre-trial Essential Question What happens to a case between the time a person is arrested and the time they have their trial? TEKS 130.296(c) (1)(G) (4)(B)(E)
Course Court Systems and Practices Unit X Pre-trial Essential Question What happens to a case between the time a person is arrested and the time they have their trial? TEKS 130.296(c) (1)(G) (4)(B)(E)
KENTUCKY VICTIMS RIGHTS LAWS1
 CONSTITUTION STATUTES KENTUCKY VICTIMS RIGHTS LAWS1 Kentucky does not have a victims' rights amendment to its constitution. Title XXXVIII, Witnesses, Evidence, Notaries, Commissioners of Foreign Deeds,
CONSTITUTION STATUTES KENTUCKY VICTIMS RIGHTS LAWS1 Kentucky does not have a victims' rights amendment to its constitution. Title XXXVIII, Witnesses, Evidence, Notaries, Commissioners of Foreign Deeds,
Myths about Criminal Justice 17 Summary 18 Key Terms 19 Review Questions 19 In the Field 20 On the Net 20 Critical Thinking Exercises 20
 CONTENTS PART ONE The Foundations of Criminal Justice 1 CHAPTER ONE Criminal Justice in the United States: An Overview 3 Criminal Justice: An Institution of Social Control 4 Crime and Criminal Law 4 Criminal
CONTENTS PART ONE The Foundations of Criminal Justice 1 CHAPTER ONE Criminal Justice in the United States: An Overview 3 Criminal Justice: An Institution of Social Control 4 Crime and Criminal Law 4 Criminal
Use the Discussion Rubric for assessment.
 Course Court Systems and Practices Unit VI Crime Classifications Essential Question What are legal reasons for an accused person to either avoid criminal liability or receive a lesser sentence? TEKS 130.296(c)
Course Court Systems and Practices Unit VI Crime Classifications Essential Question What are legal reasons for an accused person to either avoid criminal liability or receive a lesser sentence? TEKS 130.296(c)
APPLICATION QUESTIONNAIRE FOR THE VAWA PILOT PROJECT ON TRIBAL CRIMINAL JURISDICTION
 APPENDIX APPLICATION QUESTIONNAIRE FOR THE VAWA PILOT PROJECT ON TRIBAL CRIMINAL JURISDICTION Instructions Completing this Application Questionnaire is a necessary step for any Indian tribe that wishes
APPENDIX APPLICATION QUESTIONNAIRE FOR THE VAWA PILOT PROJECT ON TRIBAL CRIMINAL JURISDICTION Instructions Completing this Application Questionnaire is a necessary step for any Indian tribe that wishes
6 The Development of the Criminal Justice System. 7 Organization and Operation of Law Enforcement Systems
 Introduction to Criminal Justice Week # Subject Matter 1 Orientation Current Events 2/3 Overview of the System Bulletin Board Project 4 Evolution of the Present System 5 Explanation of Contemporary Crime
Introduction to Criminal Justice Week # Subject Matter 1 Orientation Current Events 2/3 Overview of the System Bulletin Board Project 4 Evolution of the Present System 5 Explanation of Contemporary Crime
Tarrant County College Police Department
 Tarrant County College Police Department VICTIM ASSISTANCE An Assistance Program for Victims and Family Survivors of Violent Crimes Tarrant County College The Tarrant County College District Police Department
Tarrant County College Police Department VICTIM ASSISTANCE An Assistance Program for Victims and Family Survivors of Violent Crimes Tarrant County College The Tarrant County College District Police Department
Introduction. 1 P age
 Introduction The New York City criminal justice system is made up of many different agencies and organizations. These include the independent judiciary, the five elected District Attorneys and the Special
Introduction The New York City criminal justice system is made up of many different agencies and organizations. These include the independent judiciary, the five elected District Attorneys and the Special
Proposition 5. Nonviolent Offenders. Sentencing, Parole and Rehabilitation. Statute.
 Proposition 5 Nonviolent Offenders. Sentencing, Parole and Rehabilitation. Statute. SUMMARY This measure (1) expands drug treatment diversion programs for criminal offenders, (2) modifies parole supervision
Proposition 5 Nonviolent Offenders. Sentencing, Parole and Rehabilitation. Statute. SUMMARY This measure (1) expands drug treatment diversion programs for criminal offenders, (2) modifies parole supervision
Criminal Justice Study Consensus Questions
 1 Criminal Justice Study Consensus Questions Questions correspond to the sections of the study materials. Each question should be answered on the Likert scale of 1 = strongly disagree, 2 = disagree, 3
1 Criminal Justice Study Consensus Questions Questions correspond to the sections of the study materials. Each question should be answered on the Likert scale of 1 = strongly disagree, 2 = disagree, 3
Glossary of Court-related Terms
 Glossary of Court-related Terms Acquittal Adjudication Appeal Arraignment Arrest Bail Bailiff Beyond a reasonable doubt Burden of proof Capital offense Certification Charge Circumstantial evidence Citation
Glossary of Court-related Terms Acquittal Adjudication Appeal Arraignment Arrest Bail Bailiff Beyond a reasonable doubt Burden of proof Capital offense Certification Charge Circumstantial evidence Citation
BASIC CRIMINAL LAW. Joe Bodiford. Overview of a criminal case Presented by: Board Certified Criminal Trial Lawyer
 BASIC CRIMINAL LAW Overview of a criminal case Presented by: Joe Bodiford Board Certified Criminal Trial Lawyer www.floridacriminaldefense.com www.blawgger.com THE FLORIDA CRIMINAL PROCESS Source: http://www.fsu.edu/~crimdo/cj-flowchart.html
BASIC CRIMINAL LAW Overview of a criminal case Presented by: Joe Bodiford Board Certified Criminal Trial Lawyer www.floridacriminaldefense.com www.blawgger.com THE FLORIDA CRIMINAL PROCESS Source: http://www.fsu.edu/~crimdo/cj-flowchart.html
Criminal Justice 101. The Criminal Justice System in Colorado and the Impact on Individuals with Mental Illness. April 2009
 Criminal Justice 101 The Criminal Justice System in Colorado and the Impact on Individuals with Mental Illness April 2009 Acronyms DOC = Department of Corrections DYC = Division of Youth Corrections DCJ
Criminal Justice 101 The Criminal Justice System in Colorado and the Impact on Individuals with Mental Illness April 2009 Acronyms DOC = Department of Corrections DYC = Division of Youth Corrections DCJ
Title 34-A: CORRECTIONS
 Title 34-A: CORRECTIONS Chapter 5: PROBATION AND PAROLE Table of Contents Subchapter 1. GENERAL PROVISIONS... 3 Section 5001. DEFINITIONS... 3 Section 5002. PARDONS BY THE GOVERNOR... 4 Section 5003. PROHIBITED
Title 34-A: CORRECTIONS Chapter 5: PROBATION AND PAROLE Table of Contents Subchapter 1. GENERAL PROVISIONS... 3 Section 5001. DEFINITIONS... 3 Section 5002. PARDONS BY THE GOVERNOR... 4 Section 5003. PROHIBITED
Orange County, Texas Adult Criminal Justice Data Sheet
 Orange County, Texas Adult Criminal Justice Data Sheet For more information, contact Dr. Ana Yáñez- Correa at [email protected], or (512) 587-7010. The Texas Criminal Justice Coalition seeks the implementation
Orange County, Texas Adult Criminal Justice Data Sheet For more information, contact Dr. Ana Yáñez- Correa at [email protected], or (512) 587-7010. The Texas Criminal Justice Coalition seeks the implementation
Criminal Law. Month Content Skills August. Define the term jurisprudence. Introduction to law. What is law? Explain several reasons for having laws.
 Criminal Law Month Content Skills August Introduction to law Define the term jurisprudence. What is law? Explain several reasons for having laws. Discuss the relationship between laws and values. Give
Criminal Law Month Content Skills August Introduction to law Define the term jurisprudence. What is law? Explain several reasons for having laws. Discuss the relationship between laws and values. Give
CRIMINAL LAW UPDATE 2014 LEGISLATURE. André de Gruy Capital Defender
 CRIMINAL LAW UPDATE 2014 LEGISLATURE André de Gruy Capital Defender Corrections and Criminal Justice Task Force Created - HB 1231 2013 Leg. Judge and Prosecutor concerns about lack of certainty in sentencing/time-served
CRIMINAL LAW UPDATE 2014 LEGISLATURE André de Gruy Capital Defender Corrections and Criminal Justice Task Force Created - HB 1231 2013 Leg. Judge and Prosecutor concerns about lack of certainty in sentencing/time-served
Youth and the Law. Presented by The Crime Prevention Unit
 Youth and the Law Presented by The Crime Prevention Unit Objectives Explaining the juvenile justice system and the differences between it and the adult system. Discussing juveniles rights and responsibilities
Youth and the Law Presented by The Crime Prevention Unit Objectives Explaining the juvenile justice system and the differences between it and the adult system. Discussing juveniles rights and responsibilities
The Legal System in the United States
 The Legal System in the United States At the conclusion of this chapter, students will be able to: 1. Understand how the legal system works; 2. Explain why laws are necessary; 3. Discuss how cases proceed
The Legal System in the United States At the conclusion of this chapter, students will be able to: 1. Understand how the legal system works; 2. Explain why laws are necessary; 3. Discuss how cases proceed
Copyright Texas Education Agency, 2011. All rights reserved.
 Course Security Services Unit V Legal Issues Essential Question What is the difference between civil law, criminal law, and juvenile law? What are the steps in the juvenile law process? How is security
Course Security Services Unit V Legal Issues Essential Question What is the difference between civil law, criminal law, and juvenile law? What are the steps in the juvenile law process? How is security
Maryland Courts, Criminal Justice, and Civil Matters
 Maryland Courts, Criminal Justice, and Civil Matters Presentation to the New Members of the Maryland General Assembly Department of Legislative Services Office of Policy Analysis Annapolis, Maryland December
Maryland Courts, Criminal Justice, and Civil Matters Presentation to the New Members of the Maryland General Assembly Department of Legislative Services Office of Policy Analysis Annapolis, Maryland December
The Texas Judicial System. Criminal Appeals, in Courts of Appeals, in District Courts, in County Courts, in
 The Texas Judicial System The judicial power of the State of Texas is derived from Article 5, Section 1 of the Texas Constitution, which provides: The judicial power of this State shall be vested in one
The Texas Judicial System The judicial power of the State of Texas is derived from Article 5, Section 1 of the Texas Constitution, which provides: The judicial power of this State shall be vested in one
1.1 1.1 8/11/14 1.1 CHAPTER OBJECTIVES CHAPTER OBJECTIVES CHAPTER OBJECTIVES
 CHAPTER OBJECTIVES CHAPTER OBJECTIVES Summarize the definition, mission, and role of corrections. Outline the development of the prison. Identify how corrections can affect the crime rate by understanding
CHAPTER OBJECTIVES CHAPTER OBJECTIVES Summarize the definition, mission, and role of corrections. Outline the development of the prison. Identify how corrections can affect the crime rate by understanding
How to Apply for a Pardon. State of California. Office of the Governor
 How to Apply for a Pardon State of California Office of the Governor Statement of Philosophy A California Governor's pardon is an honor traditionally granted only to individuals who have demonstrated exemplary
How to Apply for a Pardon State of California Office of the Governor Statement of Philosophy A California Governor's pardon is an honor traditionally granted only to individuals who have demonstrated exemplary
It s time to shift gears on criminal justice VOTER
 It s time to shift gears on criminal justice VOTER TOOLKIT 2014 Who are the most powerful elected officials most voters have never voted for? ANSWER: Your District Attorney & Sheriff THE POWER OF THE DISTRICT
It s time to shift gears on criminal justice VOTER TOOLKIT 2014 Who are the most powerful elected officials most voters have never voted for? ANSWER: Your District Attorney & Sheriff THE POWER OF THE DISTRICT
Criminal Justice System Commonly Used Terms & Definitions
 Criminal Justice System Commonly Used Terms & Definitions A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z Accused: Acquittal: Adjudication: Admissible Evidence: Affidavit: Alford Doctrine: Appeal:
Criminal Justice System Commonly Used Terms & Definitions A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z Accused: Acquittal: Adjudication: Admissible Evidence: Affidavit: Alford Doctrine: Appeal:
GETTING TO KNOW THE CRIMINAL JUSTICE SYSTEM
 Patricia A. DeAngelis District Attorney GETTING TO KNOW THE CRIMINAL JUSTICE SYSTEM AN OFFENSE IS COMMITTED There are three types of offenses that can be committed in New York State: VIOLATION MISDEMEANOR
Patricia A. DeAngelis District Attorney GETTING TO KNOW THE CRIMINAL JUSTICE SYSTEM AN OFFENSE IS COMMITTED There are three types of offenses that can be committed in New York State: VIOLATION MISDEMEANOR
Adult Plea Negotiation Guidelines
 From the office of the Rice County Attorney: Adult Plea Negotiation Guidelines Revision June, 2004 1. These guidelines apply to any adult felony defendant case prosecuted by this office, which is not disposed
From the office of the Rice County Attorney: Adult Plea Negotiation Guidelines Revision June, 2004 1. These guidelines apply to any adult felony defendant case prosecuted by this office, which is not disposed
The Juvenile and Domestic Relations District Court
 The Juvenile and Domestic Relations District Court I. General Information The juvenile and domestic relations district court handles cases involving: Juveniles accused of delinquent acts, traffic infractions
The Juvenile and Domestic Relations District Court I. General Information The juvenile and domestic relations district court handles cases involving: Juveniles accused of delinquent acts, traffic infractions
UNITED STATES DISTRICT COURT DISTRICT OF MINNESOTA CRIMINAL JUSTICE ACT PLAN
 UNITED STATES DISTRICT COURT DISTRICT OF MINNESOTA CRIMINAL JUSTICE ACT PLAN I. AUTHORITY Under the Criminal Justice Act of 1964, as amended, (CJA), 18 U.S.C. 3006A and the Guidelines for Administering
UNITED STATES DISTRICT COURT DISTRICT OF MINNESOTA CRIMINAL JUSTICE ACT PLAN I. AUTHORITY Under the Criminal Justice Act of 1964, as amended, (CJA), 18 U.S.C. 3006A and the Guidelines for Administering
GETTING THROUGH THE CRIMINAL JUSTICE SYSTEM
 GETTING THROUGH THE CRIMINAL JUSTICE SYSTEM ARREST An ARREST starts the criminal justice process. It is called an arrest whether the police officer hands you a summons or puts handcuffs on you and takes
GETTING THROUGH THE CRIMINAL JUSTICE SYSTEM ARREST An ARREST starts the criminal justice process. It is called an arrest whether the police officer hands you a summons or puts handcuffs on you and takes
AB 109 is DANGEROUS. Governor Brown signed AB 109 the Criminal Justice Realignment Bill into law on April 5, 2011.
 AB 109 is DANGEROUS Governor Brown signed AB 109 the Criminal Justice Realignment Bill into law on April 5, 2011. Governor Brown stated in his signing message on AB 109 - "For too long, the state s prison
AB 109 is DANGEROUS Governor Brown signed AB 109 the Criminal Justice Realignment Bill into law on April 5, 2011. Governor Brown stated in his signing message on AB 109 - "For too long, the state s prison
Facts for. Federal Criminal Defendants
 Facts for Federal Criminal Defendants FACTS FOR FEDERAL CRIMINAL DEFENDANTS I. INTRODUCTION The following is a short summary of what will happen to you if you are charged in a federal criminal case. This
Facts for Federal Criminal Defendants FACTS FOR FEDERAL CRIMINAL DEFENDANTS I. INTRODUCTION The following is a short summary of what will happen to you if you are charged in a federal criminal case. This
Senate Bill No. 86 Committee on Transportation and Homeland Security
 Senate Bill No. 86 Committee on Transportation and Homeland Security CHAPTER... AN ACT relating to offenses; providing that counseling and evaluations required for certain offenses may be conducted in
Senate Bill No. 86 Committee on Transportation and Homeland Security CHAPTER... AN ACT relating to offenses; providing that counseling and evaluations required for certain offenses may be conducted in
Juvenile Law. Course Law Enforcement I
 Course Law Enforcement I Unit IX Juvenile Law Essential Question How are juveniles handled differently than adults when they are in custody? TEKS 130.293(c) (6)(B) (9)(A)(B) Prior Student Learning Discussion
Course Law Enforcement I Unit IX Juvenile Law Essential Question How are juveniles handled differently than adults when they are in custody? TEKS 130.293(c) (6)(B) (9)(A)(B) Prior Student Learning Discussion
The Circuit Court. Judges and Clerks. Jurisdiction
 The Circuit Court The circuit court is the trial court of general jurisdiction in Virginia, and the court has authority to try a full range of both civil and criminal cases. Civil cases involve disputes
The Circuit Court The circuit court is the trial court of general jurisdiction in Virginia, and the court has authority to try a full range of both civil and criminal cases. Civil cases involve disputes
Commonwealth of Kentucky Court of Appeals
 RENDERED: MARCH 14, 2008; 2:00 P.M. NOT TO BE PUBLISHED Commonwealth of Kentucky Court of Appeals NO. 2007-CA-001304-MR DONALD T. CHRISTY APPELLANT v. APPEAL FROM MASON CIRCUIT COURT HONORABLE STOCKTON
RENDERED: MARCH 14, 2008; 2:00 P.M. NOT TO BE PUBLISHED Commonwealth of Kentucky Court of Appeals NO. 2007-CA-001304-MR DONALD T. CHRISTY APPELLANT v. APPEAL FROM MASON CIRCUIT COURT HONORABLE STOCKTON
RULES OF SUPREME COURT OF VIRGINIA PART THREE A CRIMINAL PRACTICE AND PROCEDURE APPENDIX
 RULES OF SUPREME COURT OF VIRGINIA PART THREE A CRIMINAL PRACTICE AND PROCEDURE APPENDIX Form 6. Suggested Questions to Be Put by the Court to an Accused Who Has Pleaded Guilty (Rule 3A:8). Before accepting
RULES OF SUPREME COURT OF VIRGINIA PART THREE A CRIMINAL PRACTICE AND PROCEDURE APPENDIX Form 6. Suggested Questions to Be Put by the Court to an Accused Who Has Pleaded Guilty (Rule 3A:8). Before accepting
How To Understand The Law Of The United States
 Course Principles of LPSCS Unit I History and Development of Criminal Law Essential Question Where do our laws come from and how do they apply? TEKS 130.292(c) (7)(A)(B)(C) (D)(E)(F) Prior Student Learning
Course Principles of LPSCS Unit I History and Development of Criminal Law Essential Question Where do our laws come from and how do they apply? TEKS 130.292(c) (7)(A)(B)(C) (D)(E)(F) Prior Student Learning
CRIMINAL LAW AND VICTIMS RIGHTS
 Chapter Five CRIMINAL LAW AND VICTIMS RIGHTS In a criminal case, a prosecuting attorney (working for the city, state, or federal government) decides if charges should be brought against the perpetrator.
Chapter Five CRIMINAL LAW AND VICTIMS RIGHTS In a criminal case, a prosecuting attorney (working for the city, state, or federal government) decides if charges should be brought against the perpetrator.
2010 CRIMINAL CODE SENTENCING PROVISIONS. Effective July 29, 2010
 010 CRIMINAL CODE SENTENCING PROVISIONS Effective July 9, 010-0- GENERAL CRIMES SENTENCING RANGES Class NON-DANGEROUS OFFENSES ( 13-70) First Offense ( 13-70(D)) MIT* MIN P MAX AGG* 3 4 5 10 1.5 3.5 3.5
010 CRIMINAL CODE SENTENCING PROVISIONS Effective July 9, 010-0- GENERAL CRIMES SENTENCING RANGES Class NON-DANGEROUS OFFENSES ( 13-70) First Offense ( 13-70(D)) MIT* MIN P MAX AGG* 3 4 5 10 1.5 3.5 3.5
2011 REGULAR SESSION HB 463 PENAL CODE AND CONTROLLED SUBSTANCES LEGISLATION Full text of the bill: http://www.lrc.ky.gov/record/11rs/hb463.
 2011 REGULAR SESSION HB 463 PENAL CODE AND CONTROLLED SUBSTANCES LEGISLATION Full text of the bill: http://www.lrc.ky.gov/record/11rs/hb463.htm SECTION 1. -description of reasoning behind legislation SECTION
2011 REGULAR SESSION HB 463 PENAL CODE AND CONTROLLED SUBSTANCES LEGISLATION Full text of the bill: http://www.lrc.ky.gov/record/11rs/hb463.htm SECTION 1. -description of reasoning behind legislation SECTION
The Texas Judicial System
 The Texas Judicial System The Texas Judicial System OFFICE OF COURT ADMINISTRATION Prepared by the Office of Court Administration P.O. BOX 12066 AUSTIN, TEXAS 78711-2066 512.463.1625 www.txcourts.gov September
The Texas Judicial System The Texas Judicial System OFFICE OF COURT ADMINISTRATION Prepared by the Office of Court Administration P.O. BOX 12066 AUSTIN, TEXAS 78711-2066 512.463.1625 www.txcourts.gov September
PROPOSAL. Expansion of Drug Treatment Diversion Programs. December 18, 2007
 December 18, 2007 Hon. Edmund G. Brown Jr. Attorney General 1300 I Street, 17 th Floor Sacramento, California 95814 Attention: Ms. Krystal Paris Initiative Coordinator Dear Attorney General Brown: Pursuant
December 18, 2007 Hon. Edmund G. Brown Jr. Attorney General 1300 I Street, 17 th Floor Sacramento, California 95814 Attention: Ms. Krystal Paris Initiative Coordinator Dear Attorney General Brown: Pursuant
INFORMATION FOR FEDERAL CRIMINAL DEFENDANTS
 INFORMATION FOR FEDERAL CRIMINAL DEFENDANTS TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION............................................................................ 1 SILENCE...................................................................................
INFORMATION FOR FEDERAL CRIMINAL DEFENDANTS TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION............................................................................ 1 SILENCE...................................................................................
ACCELERATED REHABILITATIVE DISPOSITION APPLICATION
 OFFICE OF THE WARREN COUNTY DISTRICT ATTORNEY WARREN COUNTY COURT HOUSE 204 Fourth Avenue WARREN, PENNSYLVANIA 16365 Phone 814-728-3460 FAX 814-728-3483 ACCELERATED REHABILITATIVE DISPOSITION APPLICATION
OFFICE OF THE WARREN COUNTY DISTRICT ATTORNEY WARREN COUNTY COURT HOUSE 204 Fourth Avenue WARREN, PENNSYLVANIA 16365 Phone 814-728-3460 FAX 814-728-3483 ACCELERATED REHABILITATIVE DISPOSITION APPLICATION
MINNESOTA S EXPERIENCE IN REVISING ITS JUVENILE CODE AND PROSECUTOR INPUT IN THE PROCESS September 1997
 MINNESOTA S EXPERIENCE IN REVISING ITS JUVENILE CODE AND PROSECUTOR INPUT IN THE PROCESS September 1997 In 1991, Minnesota began a major effort to substantially revise the laws governing our juvenile justice
MINNESOTA S EXPERIENCE IN REVISING ITS JUVENILE CODE AND PROSECUTOR INPUT IN THE PROCESS September 1997 In 1991, Minnesota began a major effort to substantially revise the laws governing our juvenile justice
Criminal Justice System Glossary of Terms
 Criminal Justice System Glossary of Terms Terms included in this glossary of terms are adapted from the Victims Rights Education Toolkit. The justice system uses specific terms to represent processes,
Criminal Justice System Glossary of Terms Terms included in this glossary of terms are adapted from the Victims Rights Education Toolkit. The justice system uses specific terms to represent processes,
Mercyhurst College Civic Institute. An Overview of the Erie County Criminal Justice System
 Mercyhurst College Civic Institute An Overview of the Criminal Justice System January 2005 Erika Brown, Research Analyst Art Amann, Director Table of Contents Table of Contents...1 Introduction...2 Methodology...2
Mercyhurst College Civic Institute An Overview of the Criminal Justice System January 2005 Erika Brown, Research Analyst Art Amann, Director Table of Contents Table of Contents...1 Introduction...2 Methodology...2
DEPUTY PROBATION OFFICER I / II
 DEFINITION To investigate cases of juvenile delinquency or dependency and adult applicants for probation; to supervise and counsel juveniles and adults on probation; to prepare reports and recommendations
DEFINITION To investigate cases of juvenile delinquency or dependency and adult applicants for probation; to supervise and counsel juveniles and adults on probation; to prepare reports and recommendations
PROBATION PEACE OFFICERS & OFF-DUTY WEAPONS
 PROBATION PEACE OFFICERS & OFF-DUTY WEAPONS By Christopher W. Miller, General Counsel State Coalition of Probation Organizations This article provides an overview of current legal authority governing the
PROBATION PEACE OFFICERS & OFF-DUTY WEAPONS By Christopher W. Miller, General Counsel State Coalition of Probation Organizations This article provides an overview of current legal authority governing the
Information about the Criminal Justice System**
 1 Victim s Guide to the Nebraska Criminal Justice System Information about the Criminal Justice System** ** Please note that the information contained in this booklet is only in relationship to felony
1 Victim s Guide to the Nebraska Criminal Justice System Information about the Criminal Justice System** ** Please note that the information contained in this booklet is only in relationship to felony
OFFICE OF THE STATE PUBLIC DEFENDER ATTORNEY S EDUCATION AND EXPERIENCE QUESTIONNAIRE
 OFFICE OF THE STATE PUBLIC DEFENDER ATTORNEY S EDUCATION AND EXPERIENCE QUESTIONNAIRE Name: First Middle Last Address: _ Business _ Home Business Phone: _ Other phone _ E-mail: Are you currently collecting
OFFICE OF THE STATE PUBLIC DEFENDER ATTORNEY S EDUCATION AND EXPERIENCE QUESTIONNAIRE Name: First Middle Last Address: _ Business _ Home Business Phone: _ Other phone _ E-mail: Are you currently collecting
Mental Illness and the Criminal Justice System. Ashley Rogers, M.A. LPC
 Mental Illness and the Criminal Justice System Ashley Rogers, M.A. LPC 1. Dallas County Diversion Program options, components, and interventions 2. Outline of the Dallas County Court System and required
Mental Illness and the Criminal Justice System Ashley Rogers, M.A. LPC 1. Dallas County Diversion Program options, components, and interventions 2. Outline of the Dallas County Court System and required
httpjlceo.lacounty.gov
 WILLIAM T FUJIOKA Chief Executive Offcer County of Los Angeles CHIEF EXECUTIVE OFFICE Kenneth Hahn Hall of Administration 500 West Temple Street, Room 713, Los Angeles, California 90012 (213) 974-1101
WILLIAM T FUJIOKA Chief Executive Offcer County of Los Angeles CHIEF EXECUTIVE OFFICE Kenneth Hahn Hall of Administration 500 West Temple Street, Room 713, Los Angeles, California 90012 (213) 974-1101
(1) Sex offenders who have been convicted of: * * * an attempt to commit any offense listed in this subdivision. (a)(1). * * *
 House Proposal of Amendment S. 292 An act relating to term probation, the right to bail, medical care of inmates, and a reduction in the number of nonviolent prisoners, probationers, and detainees. The
House Proposal of Amendment S. 292 An act relating to term probation, the right to bail, medical care of inmates, and a reduction in the number of nonviolent prisoners, probationers, and detainees. The
COLLATERAL CONSEQUENCES OF JUVENILE ADJUDICATIONS OF DELINQUENCY
 COLLATERAL CONSEQUENCES OF JUVENILE ADJUDICATIONS OF DELINQUENCY This document is meant to provide general information about the collateral consequences of juvenile adjudications. This document is not
COLLATERAL CONSEQUENCES OF JUVENILE ADJUDICATIONS OF DELINQUENCY This document is meant to provide general information about the collateral consequences of juvenile adjudications. This document is not
C RIMINAL LAW O V E RVIEW OF T H E T E XAS C RIMINAL J USTICE P ROCESS
 T E X A S Y O U N G L A W Y E R S A S S O C I A T I O N A N D S T A T E B A R O F T E X A S C RIMINAL LAW 1 0 1 : O V E RVIEW OF T H E T E XAS C RIMINAL J USTICE P ROCESS A C RIMINAL LAW 1 0 1 Prepared
T E X A S Y O U N G L A W Y E R S A S S O C I A T I O N A N D S T A T E B A R O F T E X A S C RIMINAL LAW 1 0 1 : O V E RVIEW OF T H E T E XAS C RIMINAL J USTICE P ROCESS A C RIMINAL LAW 1 0 1 Prepared
Cuyahoga County Common Pleas Court Local Rules 33.0 ASSIGNMENT AND COMPENSATION OF COUNSEL TO DEFEND
 33.0 ASSIGNMENT AND OF COUNSEL TO DEFEND PART I. (A) No attorney will be assigned to defend any indigent person in a criminal case unless his or her name appears on one of the approved trial counsel lists
33.0 ASSIGNMENT AND OF COUNSEL TO DEFEND PART I. (A) No attorney will be assigned to defend any indigent person in a criminal case unless his or her name appears on one of the approved trial counsel lists
2012 Party Platforms On Criminal Justice Policy
 2012 Party Platforms On Criminal Justice Policy September 2012 1 2012 PARTY PLATFORMS ON CRIMINAL JUSTICE POLICY THE SENTENCING PROJECT The Washington Post recently reported that the gulf between Republicans
2012 Party Platforms On Criminal Justice Policy September 2012 1 2012 PARTY PLATFORMS ON CRIMINAL JUSTICE POLICY THE SENTENCING PROJECT The Washington Post recently reported that the gulf between Republicans
Removal of Youth in the Adult Criminal Justice System: A State Trends Update. Rebecca Gasca on behalf of Campaign for Youth Justice
 Removal of Youth in the Adult Criminal Justice System: A State Trends Update Rebecca Gasca on behalf of Campaign for Youth Justice Juvenile Court founded in 1899 to create a separate justice system for
Removal of Youth in the Adult Criminal Justice System: A State Trends Update Rebecca Gasca on behalf of Campaign for Youth Justice Juvenile Court founded in 1899 to create a separate justice system for
YOSEMITE REGIONAL OCCUPATIONAL PROGRAM CRIMINAL JUSTICE
 CBEDS Code: 5847 YOSEMITE REGIONAL OUPATIONAL PROGRAM IMINAL JUSTICE JOB TITLES DOT NO. Correction Officer 372.667-018 Criminalist 029.261-026 Guard, Security 372.667-034 Police Officer 375.263-014 Probation/Parole
CBEDS Code: 5847 YOSEMITE REGIONAL OUPATIONAL PROGRAM IMINAL JUSTICE JOB TITLES DOT NO. Correction Officer 372.667-018 Criminalist 029.261-026 Guard, Security 372.667-034 Police Officer 375.263-014 Probation/Parole
Title 17-A: MAINE CRIMINAL CODE
 Title 17-A: MAINE CRIMINAL CODE Chapter 51: SENTENCES OF IMPRISONMENT Table of Contents Part 3.... Section 1251. IMPRISONMENT FOR MURDER... 3 Section 1252. IMPRISONMENT FOR CRIMES OTHER THAN MURDER...
Title 17-A: MAINE CRIMINAL CODE Chapter 51: SENTENCES OF IMPRISONMENT Table of Contents Part 3.... Section 1251. IMPRISONMENT FOR MURDER... 3 Section 1252. IMPRISONMENT FOR CRIMES OTHER THAN MURDER...
CHAPTER 15. AN ACT concerning rehabilitation of drug and alcohol dependent offenders and amending N.J.S.2C:35-14 and N.J.S.2C:35-15.
 CHAPTER 15 AN ACT concerning rehabilitation of drug and alcohol dependent offenders and amending N.J.S.2C:35-14 and N.J.S.2C:35-15. BE IT ENACTED by the Senate and General Assembly of the State of New
CHAPTER 15 AN ACT concerning rehabilitation of drug and alcohol dependent offenders and amending N.J.S.2C:35-14 and N.J.S.2C:35-15. BE IT ENACTED by the Senate and General Assembly of the State of New
CJ-310 ADMINISTRATION OF JUSTICE
 INTRODUCTION ADMINISTRATION OF JUSTICE Welcome to,. This course is designed to provide a range of information about the criminal justice system and to teach criminal justice students fundamental concepts
INTRODUCTION ADMINISTRATION OF JUSTICE Welcome to,. This course is designed to provide a range of information about the criminal justice system and to teach criminal justice students fundamental concepts
Crime. What is the sequence of events in the criminal justice system? Prosecution and pretrial services Refusal to indict.
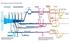 What is the sequence of events in the criminal justice system? Entry into the system Prosecution and pretrial services Refusal to indict Grand jury Charge dismissed Acquitted Sentencing and sanctions Appeal
What is the sequence of events in the criminal justice system? Entry into the system Prosecution and pretrial services Refusal to indict Grand jury Charge dismissed Acquitted Sentencing and sanctions Appeal
The Family Court Process for Children Charged with Criminal and Status Offenses in South Carolina
 The Family Court Process for Children Charged with Criminal and Status Offenses in South Carolina The Children s Law Offi ce is a training, project, and resource center in child protection and juvenile
The Family Court Process for Children Charged with Criminal and Status Offenses in South Carolina The Children s Law Offi ce is a training, project, and resource center in child protection and juvenile
What you don t know can hurt you.
 What you don t know can hurt you. Why you need a defense lawyer if you are charged with a misdemeanor. A misdemeanor conviction is SERIOUS A misdemeanor is not a minor crime. If you are convicted of a
What you don t know can hurt you. Why you need a defense lawyer if you are charged with a misdemeanor. A misdemeanor conviction is SERIOUS A misdemeanor is not a minor crime. If you are convicted of a
Queensland DRUG REHABILITATION (COURT DIVERSION) ACT 2000
 Queensland DRUG REHABILITATION (COURT DIVERSION) ACT 2000 Act No. 3 of 2000 Queensland DRUG REHABILITATION (COURT DIVERSION) ACT 2000 Section TABLE OF PROVISIONS PART 1 PRELIMINARY Page 1 Short title.....................................................
Queensland DRUG REHABILITATION (COURT DIVERSION) ACT 2000 Act No. 3 of 2000 Queensland DRUG REHABILITATION (COURT DIVERSION) ACT 2000 Section TABLE OF PROVISIONS PART 1 PRELIMINARY Page 1 Short title.....................................................
Criminal Justice 101 (Part II) Grand Jury, Trial, & Sentencing. The Charging Decision. Grand Jury 5/22/2014. Misdemeanors v.
 Criminal Justice 101 (Part II) Grand Jury, Trial, & Sentencing Presented at: Office of the Attorney General 2014 Texas Crime Victim s Services Conference Transformations: Building Community Networks Grand
Criminal Justice 101 (Part II) Grand Jury, Trial, & Sentencing Presented at: Office of the Attorney General 2014 Texas Crime Victim s Services Conference Transformations: Building Community Networks Grand
NJ JUVENILE DEFENSE A. OVERVIEW OF THE JUVENILE JUSTICE SYSTEM. 1. What does the New Jersey s juvenile justice system entail?
 NJ JUVENILE DEFENSE A. OVERVIEW OF THE JUVENILE JUSTICE SYSTEM 1. What does the New Jersey s juvenile justice system entail? Juvenile law deals with the crimes that are committed by your beloved teenagers.
NJ JUVENILE DEFENSE A. OVERVIEW OF THE JUVENILE JUSTICE SYSTEM 1. What does the New Jersey s juvenile justice system entail? Juvenile law deals with the crimes that are committed by your beloved teenagers.
A Federal Criminal Case Timeline
 A Federal Criminal Case Timeline The following timeline is a very broad overview of the progress of a federal felony case. Many variables can change the speed or course of the case, including settlement
A Federal Criminal Case Timeline The following timeline is a very broad overview of the progress of a federal felony case. Many variables can change the speed or course of the case, including settlement
UNDERSTANDING THE CRIMINAL JUSTICE SYSTEM Anne Benson
 UNDERSTANDING THE CRIMINAL JUSTICE SYSTEM Anne Benson What is the Criminal Justice System? The criminal justice system is the system we have in the United States for addressing situations where it is believed
UNDERSTANDING THE CRIMINAL JUSTICE SYSTEM Anne Benson What is the Criminal Justice System? The criminal justice system is the system we have in the United States for addressing situations where it is believed
HANDOUT 1: Purpose and Principles of Sentencing in Canada
 HANDOUT 1: Purpose and Principles of Sentencing in Canada Principles of Sentencing The Criminal Code of Canada outlines the principles and purpose of sentencing in s. 718. These principles are placed in
HANDOUT 1: Purpose and Principles of Sentencing in Canada Principles of Sentencing The Criminal Code of Canada outlines the principles and purpose of sentencing in s. 718. These principles are placed in
Adult Probation: Terms, Conditions and Revocation
 Adult Probation: Terms, Conditions and Revocation Mandatory Conditions of Community Supervision Restitution Mandatory that it be pronounced at sentencing Sauceda v. State, 309 S.W. 3 rd 767 (Amarillo Ct
Adult Probation: Terms, Conditions and Revocation Mandatory Conditions of Community Supervision Restitution Mandatory that it be pronounced at sentencing Sauceda v. State, 309 S.W. 3 rd 767 (Amarillo Ct
CRIMINAL JUSTICE GLOSSARY
 CRIMINAL JUSTICE GLOSSARY ACQUITTAL: a judgment of a court, based either on the verdict of a jury or a judicial officer, that the defendant is not guilty of the offense(s) for which he or she was tried.
CRIMINAL JUSTICE GLOSSARY ACQUITTAL: a judgment of a court, based either on the verdict of a jury or a judicial officer, that the defendant is not guilty of the offense(s) for which he or she was tried.
Juvenile Justice. CJ 3650 Professor James J. Drylie Chapter 2
 Juvenile Justice CJ 3650 Professor James J. Drylie Chapter 2 The juvenile court system came into existence in 1899. Unlike the criminal justice system, a separate juvenile justice system is not constitutionally
Juvenile Justice CJ 3650 Professor James J. Drylie Chapter 2 The juvenile court system came into existence in 1899. Unlike the criminal justice system, a separate juvenile justice system is not constitutionally
UNITED STATES DISTRICT COURT EASTERN DISTRICT OF ARKANSAS INSTRUCTIONS FOR FILING COMPLAINT BY PRISONERS UNDER THE CIVIL RIGHTS ACT, 42 U.S.C.
 UNITED STATES DISTRICT COURT EASTERN DISTRICT OF ARKANSAS INSTRUCTIONS FOR FILIN COMPLAINT BY PRISONERS UNDER THE CIVIL RIHTS ACT, 42 U.S.C. 1983 This packet contains two copies of a complaint form and
UNITED STATES DISTRICT COURT EASTERN DISTRICT OF ARKANSAS INSTRUCTIONS FOR FILIN COMPLAINT BY PRISONERS UNDER THE CIVIL RIHTS ACT, 42 U.S.C. 1983 This packet contains two copies of a complaint form and
I. Introduction. Objectives. Definitions
 United States District Court Southern District of Illinois David R. Herndon, Chief United States District Judge Nancy J. Rosenstengel, Clerk of Court CRIMINAL JUSTICE ACT PLAN I. Introduction Pursuant
United States District Court Southern District of Illinois David R. Herndon, Chief United States District Judge Nancy J. Rosenstengel, Clerk of Court CRIMINAL JUSTICE ACT PLAN I. Introduction Pursuant
Course Forensic Science. Unit II History
 Course Forensic Science Unit II History Essential Question What are some examples of careers in Forensic Science? TEKS 130.295(c) (4)(A)(B) Prior Student Learning History of Forensic Science Estimated
Course Forensic Science Unit II History Essential Question What are some examples of careers in Forensic Science? TEKS 130.295(c) (4)(A)(B) Prior Student Learning History of Forensic Science Estimated
2014 ANNUAL REPORT DISTRICT ATTORNEY WASHINGTON COUNTY
 2014 ANNUAL REPORT DISTRICT ATTORNEY WASHINGTON COUNTY 2014 Annual Report presented in April 2015 FUNCTIONS AND RESPONSIBILITIES The primary function of the Office of the District Attorney is to prosecute
2014 ANNUAL REPORT DISTRICT ATTORNEY WASHINGTON COUNTY 2014 Annual Report presented in April 2015 FUNCTIONS AND RESPONSIBILITIES The primary function of the Office of the District Attorney is to prosecute
Restoration of Civil Rights
 Restoration of Civil Rights Application for More Serious Offenses PLEASE READ CAREFULLY: Persons who have been convicted of a violent offense, an offense against a minor, or an election law offense must
Restoration of Civil Rights Application for More Serious Offenses PLEASE READ CAREFULLY: Persons who have been convicted of a violent offense, an offense against a minor, or an election law offense must
DRUG COURT DEFERRED JUDGMENT INFORMATION SHEET
 DRUG COURT DEFERRED JUDGMENT INFORMATION SHEET If you have been charged with a crime involving possession of a controlled substance and/or possession of drug paraphernalia, you may be eligible to participate
DRUG COURT DEFERRED JUDGMENT INFORMATION SHEET If you have been charged with a crime involving possession of a controlled substance and/or possession of drug paraphernalia, you may be eligible to participate
Glossary of Terms Acquittal Affidavit Allegation Appeal Arraignment Arrest Warrant Assistant District Attorney General Attachment Bail Bailiff Bench
 Glossary of Terms The Glossary of Terms defines some of the most common legal terms in easy-tounderstand language. Terms are listed in alphabetical order. A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W
Glossary of Terms The Glossary of Terms defines some of the most common legal terms in easy-tounderstand language. Terms are listed in alphabetical order. A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W
IN THE COURT OF CRIMINAL APPEALS OF TENNESSEE AT JACKSON Assigned on Briefs November 3, 2015
 IN THE COURT OF CRIMINAL APPEALS OF TENNESSEE AT JACKSON Assigned on Briefs November 3, 2015 STATE OF TENNESSEE v. JUNE CURTIS LOUDERMILK Appeal from the Criminal Court for Shelby County No. 12-00078 W.
IN THE COURT OF CRIMINAL APPEALS OF TENNESSEE AT JACKSON Assigned on Briefs November 3, 2015 STATE OF TENNESSEE v. JUNE CURTIS LOUDERMILK Appeal from the Criminal Court for Shelby County No. 12-00078 W.
MODEL CRIMINAL DEFENSE MENTORING PROGRAM Utah State Bar New Lawyer Training Program
 MODEL CRIMINAL DEFENSE MENTORING PROGRAM Utah State Bar New Lawyer Training Program The following is submitted as a Model Mentoring Plan for the criminal defense practice field. It was prepared by an experienced
MODEL CRIMINAL DEFENSE MENTORING PROGRAM Utah State Bar New Lawyer Training Program The following is submitted as a Model Mentoring Plan for the criminal defense practice field. It was prepared by an experienced
Virginia Courts In Brief
 Virginia's Judicial System Virginia Courts In Brief The mission of Virginia's judicial system is to assure that disputes are resolved justly, promptly, and economically. The components necessary to discharge
Virginia's Judicial System Virginia Courts In Brief The mission of Virginia's judicial system is to assure that disputes are resolved justly, promptly, and economically. The components necessary to discharge
IAC 7/2/08 Parole Board[205] Ch 11, p.1. CHAPTER 11 PAROLE REVOCATION [Prior to 2/22/89, Parole, Board of[615] Ch 7]
![IAC 7/2/08 Parole Board[205] Ch 11, p.1. CHAPTER 11 PAROLE REVOCATION [Prior to 2/22/89, Parole, Board of[615] Ch 7] IAC 7/2/08 Parole Board[205] Ch 11, p.1. CHAPTER 11 PAROLE REVOCATION [Prior to 2/22/89, Parole, Board of[615] Ch 7]](/thumbs/30/14732577.jpg) IAC 7/2/08 Parole Board[205] Ch 11, p.1 CHAPTER 11 PAROLE REVOCATION [Prior to 2/22/89, Parole, Board of[615] Ch 7] 205 11.1(906) Voluntary termination of parole. Any voluntary termination of parole should
IAC 7/2/08 Parole Board[205] Ch 11, p.1 CHAPTER 11 PAROLE REVOCATION [Prior to 2/22/89, Parole, Board of[615] Ch 7] 205 11.1(906) Voluntary termination of parole. Any voluntary termination of parole should
STORAGE NAME: h0151.wfm DATE: October 1, 1999 HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES COMMITTEE ON CRIME AND PUNISHMENT ANALYSIS BILL #: HB 151
 HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES COMMITTEE ON CRIME AND PUNISHMENT ANALYSIS BILL #: HB 151 RELATING TO: SPONSOR(S): TIED BILL(S): Driving Under the Influence Rep. Dockery None ORIGINATING COMMITTEE(S)/COMMITTEE(S)
HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES COMMITTEE ON CRIME AND PUNISHMENT ANALYSIS BILL #: HB 151 RELATING TO: SPONSOR(S): TIED BILL(S): Driving Under the Influence Rep. Dockery None ORIGINATING COMMITTEE(S)/COMMITTEE(S)
