Title Diagnosing Heel Pain in Adults
|
|
|
- Peregrine Marsh
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Title Diagnosing Heel Pain in Adults AUTHOR TRACY ALDRIDGE, NAME, Location M.D., Southern Illinois University School of Medicine, Springfield, Illinois Heel pain is a common condition in adults that may cause significant discomfort and disability. A variety of soft tissue, osseous, and systemic disorders can cause heel pain. Narrowing the differential diagnosis begins with a history and physical examination of the lower extremity to pinpoint the anatomic origin of the heel pain. The most common cause of heel pain in adults is plantar fasciitis. Patients with plantar fasciitis report increased heel pain with their first steps in the morning or when they stand up after prolonged sitting. Tenderness at the calcaneal tuberosity usually is apparent on examination and is increased with passive dorsiflexion of the toes. Tendonitis also may cause heel pain. Achilles tendonitis is associated with posterior heel pain. Bursae adjacent to the Achilles tendon insertion may become inflamed and cause pain. Calcaneal stress fractures are more likely to occur in athletes who participate in sports that require running and jumping. Patients with plantar heel pain accompanied by tingling, burning, or numbness may have tarsal tunnel syndrome. Heel pad atrophy may present with diffuse plantar heel pain, especially in patients who are older and obese. Less common causes of heel pain, which should be considered when symptoms are prolonged or unexplained, include osteomyelitis, bony abnormalities (such as calcaneal stress fracture), or tumor. Heel pain rarely is a presenting symptom in patients with systemic illnesses, but the latter may be a factor in persons with bilateral heel pain, pain in other joints, or known inflammatory arthritis conditions. (Am Fam Physician 2004;70: Copyright 2004 American Academy of Family Physicians.) See page 231 for definitions of strength-ofrecommendation labels. Heel pain in adults can be caused by various soft tissue, osseous, and systemic disorders. A thorough history and a physical examination of the lower extremity should be conducted to locate the pain, define its attributes, and narrow the differential diagnosis (Tables 1 1 and 2). Imaging studies may be indicated when there is suspicion of infection, stress fracture, or trauma. The history should provide a description of the pain and related conditions and circumstances. The location and onset of heel pain, its variation in character and severity throughout the day, and the relieving and aggravating factors all provide important diagnostic clues. Increased levels of activity or exercise may indicate a musculoskeletal injury caused by overuse. 2 If the patient describes the sensation as burning, tingling, or numbness, the cause may be peripheral nerve entrapment. 3 Systemic disorders are uncommon causes of heel pain; however, a history of diabetes, rheumatologic disorders, or malignancy should prompt consideration of a systemic cause for heel pain, especially when there is no obvious local etiology. The physical examination should include inspection of the patient s foot at rest and in a weight-bearing position. A visual survey of the foot may reveal swelling, bony deformities, bruising, or skin breaks. The physician should palpate bony prominences and tendinous insertions near the heel and midfoot, noting any tenderness or palpable defects. Passive range of motion of the foot and ankle joints should be assessed for indications of restricted movement. Foot posture and arch formation should be visually examined while the patient is bearing weight; the physician is looking for abnormal pronation or other biomechanical irregularities. Observation of the foot while the patient is walking may allow the physician to identify gait abnormalities that provide further diagnostic clues. This article details specific maneuvers that may reproduce pain symptoms and help physicians identify particular causes of heel pain. 332 American Family Physician Volume 70, Number 2 July 15, 2004
2 Plantar Fascia Lesions The plantar fascia is a multilayered, fibrous aponeurosis with three portions medial, central, and lateral. This fascia attaches to the three main weight-bearing points of the foot (i.e., calcaneus, first and fifth metatarsal heads) to form the longitudinal arch, which is integral to proper foot biomechanics during heel strike, foot plant, and push off. Conditions that increase tension on the plantar fascia and may cause pain include pes planus, pes cavus, decreased subtalar joint mobility, and a tight Achilles tendon. Plantar fasciitis, the most common cause of heel pain in adults, typically results from repetitive use or excessive load on the fascia. 4 Although the word fasciitis implies inflammation, recent research indicates that it is more likely to be a noninflammatory, degenerative process that might be more appropriately termed plantar fasciosis. 5 The typical presentation is a gradual onset of plantar heel pain that is worse on taking the first steps in the morning or when standing up after prolonged sitting. Tenderness over the medial aspect of the calcaneal tuberosity usually is demonstrated, and the pain increases when the plantar fascia is stretched by passive dorsiflexion of the toes. Acute onset of severe plantar heel pain after trauma or vigorous athletics may indi- TABLE 1 Cause of Heel Pain by Anatomic Location Pain in the midfoot Lateral Tendonitis of peroneus brevis Tendonitis of peroneus longus Medial Tendonitis of the flexor digitorum longus Tendonitis of the flexor hallucis longus Tendonitis of the tibialis posterior Pain in the posterior heel Achilles tendonitis Retroachilles bursitis Retrocalcaneal bursitis Pain in the plantar aspect of heel Plantar fasciitis Plantar fascia rupture Heel pad atrophy Tarsal tunnel syndrome Neuroma Bone cyst Osteomyelitis Fracture Tumor Information from Brown C. A review of subcalcaneal heel pain and plantar fasciitis. Aust Fam Physician 1996;25:881. TABLE 2 Common Causes of Heel Pain: History, Physical Examination Findings, and Treatment Options Clinical entity* History Physical examination Conservative treatment Plantar fasciitis Achilles tendonitis Morning pain or pain on standing after prolonged sitting Pain with running, jumping, or making quick turns Tenderness over calcaneus Increased pain with passive dorsiflexion of toes Pain and tenderness over insertion of Achilles tendon on calcaneus Pain may increase with dorsiflexion Retrocalcaneal bursitis Stiff posterior shoe edge Pain and tenderness at posterior calcaneus Tarsal tunnel syndrome Pain or numbness in heel radiating to the sole and toes Reproduction of symptoms with percussion of tarsal tunnel or dorsiflexion and eversion of foot Analgesics, stretching, exercise, orthotics, night splint Rest, analgesics, stretching, and strengthening exercises Analgesics, proper shoes with Achilles notch and padding over posterior heel Analgesics, correcting foot posture with orthotics * Listed in order of frequency of presentation. July 15, 2004 Volume 70, Number 2 American Family Physician 333
3 Flexor digitorum longus tendon Achilles tendon Posterior tibialis tendon Posterior tibial nerve Flexor hallucis longus tendon Flexor retinaculum Retroachilles bursa Retrocalcaneal bursa ILLUSTRATIONS BY STEVEN OH Figure 1. Medial view of the ankle illustrating the tendons, bursa, and nerves, which can be sources of heel pain. cate rupture of the plantar fascia. Findings suggestive of rupture include a palpable defect at the calcaneal tuberosity accompanied by localized swelling and ecchymosis. 6 If conservative treatment of plantar fasciitis fails to alleviate symptoms, radiographs are advisable to check for other causes of heel pain such as stress fractures, arthritis, or skeletal abnormalities. Radiographs may reveal a calcification of the proximal plantar fascia, which is known as a heel spur. However, these spurs often are present in asymptomatic persons, are nonspecific, and should not be construed as an explanation for heel pain. 1 Tendinous Lesions Patients who have tendonitis generally present with pain and swelling at the tendon insertion site. Passive dorsiflexion of the foot and palpation at the insertion Tendonitis involving the site may increase the tenderness. 2 peroneal tendons is a The history may reveal difficulty less common cause of in performing strenuous activities such as running, jumping, or heel pain but may be important when a patient making quick turns. 2 localizes a medial or lateral location of heel pain. The Achilles tendon is formed by the union of the gastrocnemius and soleus muscle tendons and inserts on the posterior aspect of the calcaneus. Achilles tendonitis is another common cause of posterior heel pain. Typically, it results from overuse of the calf muscles (e.g., running, jumping) or abnormal biomechanical stress on the foot and ankle. The tendons of the posterior tibialis, the flexor digitorum longus, and the flexor hallucis longus pass through the medial flexor retinaculum and insert on the medial side of the midfoot (Figure 1). The peroneal tendons insert on the lateral side of the midfoot. Tendonitis involving these structures is a less common cause of heel pain but may be important when a patient localizes a medial or lateral location of heel pain. Bursal Lesions The posterior heel includes the retrocalcaneal bursa, which is located between the calcaneus and the Achilles tendon insertion site, and the retroachilles bursa, which is located between the Achilles tendon and the skin. Each bursa is a potential site of inflammation. The most common cause of posterior heel bursitis is ill-fitting footwear with a stiff posterior edge that abrades the area of the Achilles tendon insertion. Retrocalcaneal inflammation also may be associated with Achilles tendonitis and Haglund s disease (a bony spur on the superior aspect of the posterior calcaneus) 7 and, occasionally, may be caused by a systemic inflammatory arthritis such as rheumatoid arthritis. Patients with posterior heel bursitis have redness and swelling of 334 American Family Physician Volume 70, Number 2 July 15, 2004
4 Posterior tibial nerve Flexor retinaculum Medial plantar nerve Calcaneal branches Lateral plantar nerve Nerve to abductor digiti minimi Figure 2. Medial view of the ankle illustrating the course of the posterior tibial nerve through the tarsal tunnel. the affected bursa, which is tender on direct palpation. Osseous Lesions After the metatarsals, the calcaneus is the most common location in the foot for a stress fracture. 8 Calcaneal stress fractures are more likely to occur in athletes involved in sports that require running and jumping or in persons with osteopenia of the calcaneus. Patients present with diffuse heel pain and tenderness on medial and lateral compression of the calcaneus. Refractory heel pain that persists despite conservative treatment may require further diagnostic procedures to exclude bony pathology. Radionuclide bone scans and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are more effective than plain-film radiographs in confirming a calcaneal stress fracture. Both methods detect stress fractures several weeks earlier than plain-film radiographs, and MRI permits visualization of abnormal soft tissue structures that may indicate other causes of heel pain. 9,10 Calcaneal stress fractures are treated by cutting back on the quantity and intensity of walking and athletic activities. Non weight-bearing status with crutches or cast immobilization may be necessary in some refractory cases. 9 Simple bone cysts within the calcaneus generally are not associated with pain, although they may weaken the calcaneal structure. A pathologic fracture that extends to the wall of a bone cyst may induce heel pain. Although rare, Ewing s sarcoma is the most common primary bony tumor of the heel. 11 Reported metastatic tumors to the calcaneus include endometrial adenocarcinoma, bronchogenic carcinoma, transitional cell bladder carcinoma, and gastric cancer Patients who have heel pain of unclear etiology and a history of known malignancy should undergo radiographic evaluation or radionuclide bone scanning. Peripheral Nerve Disorders The tarsal tunnel, which is located on the medial aspect of the posterior heel, is bounded by the flexor retinaculum and the medial surfaces of the talus and calcaneus. The posterior tibial nerve courses through this tunnel and divides into its terminal branches, the medial and lateral plantar nerves (Figure 2). Heel pain accompanied by July 15, 2004 Volume 70, Number 2 American Family Physician 335
5 Tarsal tunnel area Figure 3. The dorsiflexion-eversion test used in the physical examination to reproduce the symptoms of tarsal tunnel syndrome. The Author TRACY ALDRIDGE, M.D., is assistant professor in the Department of Family and Community Medicine at Southern Illinois University School of Medicine, Springfield, where she earned her medical degree. Dr. Aldridge completed a family practice residency and fellowship at the Southern Illinois University School of Medicine Springfield Family Practice Residency Program, Springfield. Address correspondence to Tracy Aldridge, M.D., Southern Illinois University School of Medicine, Department of Family and Community Medicine, P.O. Box 19671, Springfield, IL Reprints are not available from the author. neuropathic features such as tingling, burning, or numbness may indicate tarsal tunnel syndrome, a compression neuropathy caused by entrapment of the posterior tibial nerve branches within the tunnel. Pain and numbness often radiate to the plantar heel and, in some cases, extend even to the distal sole and toes. The clinical examination includes percussion of the nerve within the tarsal tunnel. Simultaneous dorsiflexion and eversion of the foot may reproduce symptoms as the posterior tibial nerve is stretched and compressed (Figure 3). Pes planus causes increased abduction of the forefoot and valgus deviation of the hindfoot (Figure 4), thereby increasing tension on the tibial nerve. 2,15,16 Pes planus is a common cause of tarsal tunnel syndrome. In some cases, nerve conduction velocities and electromyography may be used to confirm the diagnosis if treatment for presumptive neuropathic heel pain fails to improve symptoms. Heel pain caused by a neuroma of the medial calcaneal nerve is uncommon and may present with symptoms quite similar to those of plantar fasciitis. Palpation of the sole over the heel and proximal midfoot may 336 American Family Physician Volume 70, Number 2 July 15, 2004
6 pinpoint a painful lump (known as the lamp cord sign because the lump feels like a lamp cord under a rug) 17 that easily can be misdiagnosed as inflamed plantar fascia. If conservative treatment of plantar fasciitis fails to alleviate symptoms, the physician should evaluate for a neuroma. Heel Pad Disorders The heel pad is composed of columns of adipose tissue separated by fibrous septae. It is located directly beneath the calcaneus and acts as a hydraulic shock-absorbing layer. Elderly and obese patients who present with plantar heel pain may have symptoms caused by heel pad damage or atrophy. Inflammation of the heel pad also may be present in younger adults with sports-related injuries. Although the symptoms of heel pad disorders overlap considerably with those of plantar fasciitis, heel pad pain is typically more diffuse. Heel pad pain involves most of the weight-bearing portion of the calcaneus, whereas plantar fasciitis pain is centered for the most part near the calcaneal tuberosity. In contrast to pain caused by plantar fasciitis, heel pad pain tends not to radiate anteriorly, and dorsiflexion of the toes does not increase the pain. Infectious Etiologies Although rarely a cause of heel pain, osteomyelitis of the calcaneus generally results from contiguous infection of surrounding soft tissue. 18 During a visual examination of the foot, clues that should increase suspicion of a possible infectious cause for heel pain include puncture wounds, open skin lesions, Medial Outward drift of heel localized warmth, erythema, or apparent cellulitis. Serious foot infections are more likely to occur in patients who have diabetes mellitus or vascular insufficiency. Radionuclide bone scanning and MRI are more sensitive and specific than plain-film radiographs in diagnosing osteomyelitis (Table 3). 20,21 Systemic Disease Patients with known systemic arthritis conditions, bilateral heel pain, or symptoms Outward drift of toes Lateral Figure 4. Posterior view of foot posture in patients with pes planus. TABLE 3 Comparison of Imaging Modalities in Diagnosis of Osteomyelitis Imaging modality Sensitivity (%) Specificity (%) Magnetic resonance* Bone scan Plain radiographs * With gadolinium contrast enhancement. Information from references 20 and 21. July 15, 2004 Volume 70, Number 2 American Family Physician 337
7 Strength of Recommendations Key clinical recommendation Labels References Radionuclide bone scanning and magnetic resonance imaging are more sensitive and specific than plain-film radiographs in diagnosing osteomyelitis. B 20, 21 involving joints beyond the heel should undergo a thorough review of symptoms to assess for systemic illness as a possible cause of heel pain. The seronegative spondyloarthropathies (i.e., ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis, reactive arthritis, and inflammatory bowel disease associated arthritis) may produce heel pain. Rheumatoid arthritis can affect the calcaneus and other adjacent structures; however, isolated heel pain as a presenting complaint would be uncommon, because hindfoot involvement typically occurs with advanced disease. 22 Members of various family practice departments develop articles for Problem-Oriented Diagnosis. This is one in a series from the Department of Family and Community Medicine at Southern Illinois University School of Medicine, Springfield. Guest editor of the series is Robert M. Wesley, M.A. The author indicates that she does not have any conflicts of interest. Sources of funding: none reported. References 1. Brown C. A review of subcalcaneal heel pain and plantar fasciitis. Aust Fam Physician 1996;25:875-81, Schepsis AA, Jones H, Haas AL. Achilles tendon disorders in athletes. Am J Sports Med 2002;30: Kinoshita M, Okuda R, Morikawa J, Jotoku T, Abe M. The dorsiflexion-eversion test for diagnosis of tarsal tunnel syndrome. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 2001;83-A: Martin JE, Hosch JC, Goforth WP, Murff RT, Lynch DM, Odom RD. Mechanical treatment of plantar fasciitis. A prospective study. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc 2001;91: Lemont H, Ammirati KM, Usen N. Plantar fasciitis: a degenerative process (fasciosis) without inflammation. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc 2003;93: Ahstrom JP Jr. Spontaneous rupture of the plantar fascia. Am J Sports Med 1988;16: Stephens MM. Haglund s deformity and retrocalcaneal bursitis. Orthop Clin North Am 1994;25: Narvaez JA, Narvaez J, Ortega R, Aguilera C, Sanchez A, Andia E. Painful heel: MR imaging findings. Radiographics 2000;20: Norfray JF, Schlachter L, Kernahan WT Jr, Arenson DJ, Smith SD, Roth IE, et al. Early confirmation of stress fractures in joggers. JAMA 1980;243: Spitz DJ, Newberg AH. Imaging of stress fractures in the athlete. Radiol Clin North Am 2002;40: Berlin SJ, Mirkin GS, Tubridy SP. Tumors of the heel. Clin Podiatr Med Surg 1990;7: Cooper JK, Wong FL, Swenerton KD. Endometrial adenocarcinoma presenting as an isolated calcaneal metastasis. A rare entity with good prognosis. Cancer 1994;73: Bergqvist D, Mattsson J. Solitary calcaneal metastasis as the first sign of gastric cancer. A case report. Ups J Med Sci 1978;83: Kaufmann J, Schulze E, Hein G. Monarthritis of the ankle as manifestation of a calcaneal metastasis of bronchogenic carcinoma. Scand J Rheumatol 2001;30: Trepman E, Kadel NJ, Chisholm K, Razzano L. Effect of foot and ankle position on tarsal tunnel compartment pressure. Foot Ankle Int 1999;20: Daniels TR, Lau JT, Hearn TC. The effects of foot position and load on tibial nerve tension. Foot Ankle Int 1998;19: Davidson MR, Copoloff JA. Neuromas of the heel. Clin Podiatr Med Surg 1990;7: Kosinski M, Lilja E. Infectious causes of heel pain. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc 1999;89: Brown ML, Kamida CB, Bequest TH, Fitzgerald RH. An imaging approach to musculoskeletal infections. In: Berquist TH, ed. Imaging of orthopedic trauma and surgery. Philadelphia: Saunders, 1986: Morrison WB, Schweitzer ME, Wapner KL, Hecht PJ, Gannon FH, Behm WR. Osteomyelitis in feet of diabetics: clinical accuracy, surgical utility, and cost effectiveness of MR imaging. Radiology 1995;196: Israel O, Gips S, Jerushalmi J, Frenkel A, Front D. Osteomyelitis and soft-tissue infection: differential diagnosis with 24 hour/4 hour ratio of Tc-99m MDP uptake. Radiology 1987;163: Geppert MJ, Mizel MS. Management of heel pain in the inflammatory arthritides. Clin Orthop 1998;349: American Family Physician Volume 70, Number 2 July 15, 2004
Common Foot & Ankle Sports Injuries
 Common Foot & Ankle Sports Injuries Symptoms Related to Abnormal Foot Biomechanics & their Differential Diagnosis Daniel Pang BSc (Hon) P&O, Cped Certified Pedorthist (USA) Only 10% of foot having structure
Common Foot & Ankle Sports Injuries Symptoms Related to Abnormal Foot Biomechanics & their Differential Diagnosis Daniel Pang BSc (Hon) P&O, Cped Certified Pedorthist (USA) Only 10% of foot having structure
Plantar fascia. Plantar Fasciitis (pain in the heel of the foot)
 ! Plantar fascia Plantar Fasciitis (pain in the heel of the foot) Plantar Fasciitis is the most common foot problem seen in runners and is often associated with an increase in running mileage. Typically
! Plantar fascia Plantar Fasciitis (pain in the heel of the foot) Plantar Fasciitis is the most common foot problem seen in runners and is often associated with an increase in running mileage. Typically
Objectives Learn the anatomy of the foot. Identify key terms associated with plantar fasciitis. Determine the causes of plantar fasciitis and understa
 Plantar Fasciitis Objectives Learn the anatomy of the foot. Identify key terms associated with plantar fasciitis. Determine the causes of plantar fasciitis and understand why it occurs. Recognize the injury
Plantar Fasciitis Objectives Learn the anatomy of the foot. Identify key terms associated with plantar fasciitis. Determine the causes of plantar fasciitis and understand why it occurs. Recognize the injury
Heel Pain: Heal! Amie C. Scantlin, DPM, MS, FACFAS Glencoe Regional Health Services (320) 864-3121 ext. 1933
 Heel Pain: Heal! Amie C. Scantlin, DPM, MS, FACFAS Glencoe Regional Health Services (320) 864-3121 ext. 1933 www.grhsonline.org Important Notice The information contained in this document is for informational
Heel Pain: Heal! Amie C. Scantlin, DPM, MS, FACFAS Glencoe Regional Health Services (320) 864-3121 ext. 1933 www.grhsonline.org Important Notice The information contained in this document is for informational
Heel pain and Plantar fasciitis
 A patient s guide Heel pain and Plantar fasciitis Fred Robinson BSc FRCS FRCS(orth) Consultant Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgeon Alex Wee BSc FRCS(orth) Consultant Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgeon. What causes
A patient s guide Heel pain and Plantar fasciitis Fred Robinson BSc FRCS FRCS(orth) Consultant Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgeon Alex Wee BSc FRCS(orth) Consultant Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgeon. What causes
Clinical Analysis of Foot Problems
 Clinical Analysis of Foot Problems by Karen S. Seale, M.D. Introduction Orthotists are vital members of the foot care team. Their expertise and special interests in materials and biomechanics add a unique
Clinical Analysis of Foot Problems by Karen S. Seale, M.D. Introduction Orthotists are vital members of the foot care team. Their expertise and special interests in materials and biomechanics add a unique
Plantar fasciitis is a common foot problem that occurs in 10%
 Review Article Plantar Fasciitis Heel Pain: Part 1 a Practical Management Plantar fasciitis is a common foot problem that occurs in 10% of the population. 1,2 The most involved age group is 40-50 3,4 Actually,
Review Article Plantar Fasciitis Heel Pain: Part 1 a Practical Management Plantar fasciitis is a common foot problem that occurs in 10% of the population. 1,2 The most involved age group is 40-50 3,4 Actually,
Chapter 140 Heel Pain
 Chapter 140 Heel Pain David R. Richardson, MD E. Greer Richardson, MD I. Overview and Epidemiology A. General characteristics Heel pain (subcalcaneal pain syndrome) is the most common foot-related symptom
Chapter 140 Heel Pain David R. Richardson, MD E. Greer Richardson, MD I. Overview and Epidemiology A. General characteristics Heel pain (subcalcaneal pain syndrome) is the most common foot-related symptom
.org. Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction. Anatomy. Cause. Symptoms
 Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
PRISCILLA TU, DO, and JEFFREY R. BYTOMSKI, DO, Duke University, Durham, North Carolina
 Diagnosis of Heel Pain PRISCILLA TU, DO, and JEFFREY R. BYTOMSKI, DO, Duke University, Durham, North Carolina Heel pain is a common presenting symptom in ambulatory clinics. There are many causes, but
Diagnosis of Heel Pain PRISCILLA TU, DO, and JEFFREY R. BYTOMSKI, DO, Duke University, Durham, North Carolina Heel pain is a common presenting symptom in ambulatory clinics. There are many causes, but
Outline. The Agony of the Foot: Disclosure. Plantar Fasciitis. Top 5 Foot and Ankle Problems in Primary Care. Daniel Thuillier, M.D.
 The Agony of the Foot: Top 5 Foot and Ankle Problems in Primary Care Daniel Thuillier, M.D. Assistant Professor of Clinical Orthopaedics University of California San Francisco Plantar Fasciitis Achilles
The Agony of the Foot: Top 5 Foot and Ankle Problems in Primary Care Daniel Thuillier, M.D. Assistant Professor of Clinical Orthopaedics University of California San Francisco Plantar Fasciitis Achilles
Page 2 of 6 plantar fascia. This is called the windlass mechanism. Later, we'll discuss how this mechanism is used to treat plantar fasciitis with str
 Page 1 of 6 Plantar Fasciitis (Heel Pain) Plantar fasciitis is a painful condition affecting the bottom of the foot. It is a common cause of heel pain and is sometimes called a heel spur. Plantar fasciitis
Page 1 of 6 Plantar Fasciitis (Heel Pain) Plantar fasciitis is a painful condition affecting the bottom of the foot. It is a common cause of heel pain and is sometimes called a heel spur. Plantar fasciitis
Podo Pediatrics Identifying Biomechanical Pathologies
 Podo Pediatrics Identifying Biomechanical Pathologies David Lee, D.P.M., D. A.B.P.S. Purpose Identification of mechanical foot and ankle conditions Base treatments Knowing when to refer to a podiatrist
Podo Pediatrics Identifying Biomechanical Pathologies David Lee, D.P.M., D. A.B.P.S. Purpose Identification of mechanical foot and ankle conditions Base treatments Knowing when to refer to a podiatrist
.org. Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs. Anatomy. Cause
 Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs Page ( 1 ) Plantar fasciitis (fashee-eye-tiss) is the most common cause of pain on the bottom of the heel. Approximately 2 million patients are treated for this condition
Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs Page ( 1 ) Plantar fasciitis (fashee-eye-tiss) is the most common cause of pain on the bottom of the heel. Approximately 2 million patients are treated for this condition
A Guide to Heel Pain
 The Society of Chiropodists and Podiatrists A Guide to Heel Pain The Society of Chiropodists and Podiatrists Heel pain may be caused by a number of different problems; for effective treatment you need
The Society of Chiropodists and Podiatrists A Guide to Heel Pain The Society of Chiropodists and Podiatrists Heel pain may be caused by a number of different problems; for effective treatment you need
Lower Back Spinal Fusion & Exercise
 & Exercise with Rick Kaselj, MS More FREE Information on Exercise & Injuries $299 Fitness Education Returning the Shoulder Back to Optimal Function Seminar Exercise Modification for the Sensitive Shoulder
& Exercise with Rick Kaselj, MS More FREE Information on Exercise & Injuries $299 Fitness Education Returning the Shoulder Back to Optimal Function Seminar Exercise Modification for the Sensitive Shoulder
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE
 PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE Presenter Dr. Richard Coughlin AOFAS Lecture Series OBJECTIVES 1. ASSESS 2. DIAGNOSE 3. TREAT HISTORY TAKING Take a HISTORY What is the patient s chief complaint?
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE Presenter Dr. Richard Coughlin AOFAS Lecture Series OBJECTIVES 1. ASSESS 2. DIAGNOSE 3. TREAT HISTORY TAKING Take a HISTORY What is the patient s chief complaint?
PLANTAR FASCITIS (Heel Spur Syndrome)
 PLANTAR FASCITIS (Heel Spur Syndrome) R. Amadeus Mason MD Description Plantar fascitis is characterized by stiffness and inflammation of the main fascia (fibrous connective [ligament-like] tissue) on the
PLANTAR FASCITIS (Heel Spur Syndrome) R. Amadeus Mason MD Description Plantar fascitis is characterized by stiffness and inflammation of the main fascia (fibrous connective [ligament-like] tissue) on the
HEEL PAIN. Differential diagnosis. 1. Insertional Plantar fascitis. 2. Enthesis. 3. Heel pad atrophy. 4. Tarsal tunnel syndrome
 HEEL PAIN Differential diagnosis 1. Insertional Plantar fascitis 2. Enthesis 3. Heel pad atrophy 4. Tarsal tunnel syndrome 5. Calcaneal stress fracture 6. Haglund s syndrome 7. Posterior ankle impingement
HEEL PAIN Differential diagnosis 1. Insertional Plantar fascitis 2. Enthesis 3. Heel pad atrophy 4. Tarsal tunnel syndrome 5. Calcaneal stress fracture 6. Haglund s syndrome 7. Posterior ankle impingement
Plantar Fasciitis. Plantar Fascia
 Plantar Fasciitis Introduction Plantar fasciitis is an inflammation of the thick band of tissue that connects your heel bone to your toes. This thick band of tissue is called the plantar fascia. Plantar
Plantar Fasciitis Introduction Plantar fasciitis is an inflammation of the thick band of tissue that connects your heel bone to your toes. This thick band of tissue is called the plantar fascia. Plantar
Plantar Heel Pain. By: Kevin Kleiner, M.B.S. New York College of Podiatric Medicine
 Plantar Heel Pain By: Kevin Kleiner, M.B.S. New York College of Podiatric Medicine Plantar Heel Pain: - Many Etiologies but few solutions Plantar heel pain more specifically: Heel pain felt in ones rear-foot
Plantar Heel Pain By: Kevin Kleiner, M.B.S. New York College of Podiatric Medicine Plantar Heel Pain: - Many Etiologies but few solutions Plantar heel pain more specifically: Heel pain felt in ones rear-foot
.org. Achilles Tendinitis. Description. Cause. Achilles tendinitis is a common condition that causes pain along the back of the leg near the heel.
 Achilles Tendinitis Page ( 1 ) Achilles tendinitis is a common condition that causes pain along the back of the leg near the heel. The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. It connects your
Achilles Tendinitis Page ( 1 ) Achilles tendinitis is a common condition that causes pain along the back of the leg near the heel. The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. It connects your
A Patient s Guide to Plantar Fasciitis. Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, P.C.
 A Patient s Guide to Plantar Fasciitis Welcome to Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, where we believe in accelerating your learning curve with educational materials that are clearly written and professionally
A Patient s Guide to Plantar Fasciitis Welcome to Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, where we believe in accelerating your learning curve with educational materials that are clearly written and professionally
Structure & Function of the Ankle and Foot. A complicated model of simplicity that you really think little about until you have a problem with one.
 Structure & Function of the Ankle and Foot A complicated model of simplicity that you really think little about until you have a problem with one. The Foot and Ankle Terminology Plantar flexion Dorsi flexion
Structure & Function of the Ankle and Foot A complicated model of simplicity that you really think little about until you have a problem with one. The Foot and Ankle Terminology Plantar flexion Dorsi flexion
PODIATRIC SURGERY INFORMATION GUIDE: MANAGEMENT OF PLANTAR FASCIITIS/HEEL PAIN
 PODIATRIC SURGERY INFORMATION GUIDE: MANAGEMENT OF PLANTAR FASCIITIS/HEEL PAIN What is Plantar Fasciitis? Plantar fasciitis is pain in the heel and arch area of the foot. The plantar fascia is a strong
PODIATRIC SURGERY INFORMATION GUIDE: MANAGEMENT OF PLANTAR FASCIITIS/HEEL PAIN What is Plantar Fasciitis? Plantar fasciitis is pain in the heel and arch area of the foot. The plantar fascia is a strong
RUNNING INJURIES: PREVENTION AND REHABILITATION
 RUNNING INJURIES: PREVENTION AND REHABILITATION Topics of Tonight s s Lecture Common Injuries and Treatments Causes of Common Injuries Measures to Avoid Injury Most Common Running Injuries Plantar Fascitis
RUNNING INJURIES: PREVENTION AND REHABILITATION Topics of Tonight s s Lecture Common Injuries and Treatments Causes of Common Injuries Measures to Avoid Injury Most Common Running Injuries Plantar Fascitis
.org. Lisfranc (Midfoot) Injury. Anatomy. Description
 Lisfranc (Midfoot) Injury Page ( 1 ) Lisfranc (midfoot) injuries result if bones in the midfoot are broken or ligaments that support the midfoot are torn. The severity of the injury can vary from simple
Lisfranc (Midfoot) Injury Page ( 1 ) Lisfranc (midfoot) injuries result if bones in the midfoot are broken or ligaments that support the midfoot are torn. The severity of the injury can vary from simple
Predislocation syndrome
 Predislocation syndrome Sky Ridge Medical Center, Aspen Building Pre-dislocation syndrome, capsulitis, and metatarsalgia are all similar problems usually at the ball of the foot near the second and third
Predislocation syndrome Sky Ridge Medical Center, Aspen Building Pre-dislocation syndrome, capsulitis, and metatarsalgia are all similar problems usually at the ball of the foot near the second and third
Foot and Ankle Complaints
 Foot and Ankle Complaints INTRODUCTION Anatomy and Function Foot Ankle Common complaints Common diagnoses FOOT AND ANKLE ANATOMY 26 bones and 2 sesamoids Forefoot Metatarsals phalanges Midfoot 5 tarsals
Foot and Ankle Complaints INTRODUCTION Anatomy and Function Foot Ankle Common complaints Common diagnoses FOOT AND ANKLE ANATOMY 26 bones and 2 sesamoids Forefoot Metatarsals phalanges Midfoot 5 tarsals
Heel Pain Syndromes DELLON INSTITUTES FOR PERIPHERAL NERVE SURGERY
 Heel Pain s 5 3333 N CALVERT ST, SUITE 370, BALTIMORE, MD 21218 T410 467 5400 F410 366 9826 delloninstitutes.com your complaints are Pain, numbness or burning in your heel. The timing of this pain and
Heel Pain s 5 3333 N CALVERT ST, SUITE 370, BALTIMORE, MD 21218 T410 467 5400 F410 366 9826 delloninstitutes.com your complaints are Pain, numbness or burning in your heel. The timing of this pain and
Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures
 Copyright 2010 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures Fractures of the heel bone, or calcaneus, can be disabling injuries. They most often occur during high-energy collisions
Copyright 2010 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures Fractures of the heel bone, or calcaneus, can be disabling injuries. They most often occur during high-energy collisions
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. EXCISION OF RETROCALCANEAL SPUR BY A LATERAL APPROACH FOR RELIEF OF HEEL PAIN. Nandivada V.S. Kiran Kumar
 EXCISION OF RETROCALCANEAL SPUR BY A LATERAL APPROACH FOR RELIEF OF HEEL PAIN. Nandivada V.S. Kiran Kumar 1. Assistant Professor. Department of Orthopaedics, King George Hospital. Visakhapatnam. CORRESPONDING
EXCISION OF RETROCALCANEAL SPUR BY A LATERAL APPROACH FOR RELIEF OF HEEL PAIN. Nandivada V.S. Kiran Kumar 1. Assistant Professor. Department of Orthopaedics, King George Hospital. Visakhapatnam. CORRESPONDING
Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle. Dr. Travis Kieckbusch August 7, 2014
 Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle Dr. Travis Kieckbusch August 7, 2014 Foot and Ankle Injuries in Athletes Lateral ankle sprains Syndesmosis sprains high ankle sprain Achilles tendon injuries Lisfranc
Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle Dr. Travis Kieckbusch August 7, 2014 Foot and Ankle Injuries in Athletes Lateral ankle sprains Syndesmosis sprains high ankle sprain Achilles tendon injuries Lisfranc
GET A HANDLE ON YOUR HEEL PAIN GUIDE
 GET A HANDLE ON YOUR HEEL PAIN GUIDE American Podiatric Medical Association www.apma.org/heelpain Take a Moment to Focus in on Your Feet. Does one (or even both) of your heels hurt? If so, you aren t alone.
GET A HANDLE ON YOUR HEEL PAIN GUIDE American Podiatric Medical Association www.apma.org/heelpain Take a Moment to Focus in on Your Feet. Does one (or even both) of your heels hurt? If so, you aren t alone.
Plantar Fascia Release
 Plantar Fascia Release Introduction Plantar fasciitis is a common condition that causes pain around the heel. It may be severe enough to affect regular activities. If other treatments are unsuccessful,
Plantar Fascia Release Introduction Plantar fasciitis is a common condition that causes pain around the heel. It may be severe enough to affect regular activities. If other treatments are unsuccessful,
Osteoarthritis progresses slowly and the pain and stiffness it causes worsens over time.
 Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Arthritis is the leading cause of disability in the United States. It can occur at any age, and literally means "pain within a joint." As a result, arthritis is a term used
Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Arthritis is the leading cause of disability in the United States. It can occur at any age, and literally means "pain within a joint." As a result, arthritis is a term used
Chapter 5. Objectives. Normal Ankle Range of Motion. Lateral Ankle Sprains. Lateral Ankle Sprains. Assessment of Lateral Ankle Sprains
 Objectives Chapter 5 Assessment of Ankle & Lower Leg Injuries Review the following components of injury assessment related to the ankle and lower leg Stress tests Special tests Normal Ankle Range of Motion
Objectives Chapter 5 Assessment of Ankle & Lower Leg Injuries Review the following components of injury assessment related to the ankle and lower leg Stress tests Special tests Normal Ankle Range of Motion
The Diagnosis and Management of Heel Pain in Active People
 The Diagnosis and Management of Heel Pain in Active People Perry Julien, D.P.M. Past President, American Academy of Podiatric Sports Medicine Podiatry Coordinator, 1996 Summer Olympic Games Atlanta Georgia
The Diagnosis and Management of Heel Pain in Active People Perry Julien, D.P.M. Past President, American Academy of Podiatric Sports Medicine Podiatry Coordinator, 1996 Summer Olympic Games Atlanta Georgia
The Ankle Sprain That Won t Get Better. By: George E. Quill, Jr., M.D. With springtime in Louisville upon us, the primary care physician and the
 The Ankle Sprain That Won t Get Better By: George E. Quill, Jr., M.D. With springtime in Louisville upon us, the primary care physician and the orthopaedist alike can expect to see more than his or her
The Ankle Sprain That Won t Get Better By: George E. Quill, Jr., M.D. With springtime in Louisville upon us, the primary care physician and the orthopaedist alike can expect to see more than his or her
Temple Physical Therapy
 Temple Physical Therapy A General Overview of Common Neck Injuries For current information on Temple Physical Therapy related news and for a healthy and safe return to work, sport and recreation Like Us
Temple Physical Therapy A General Overview of Common Neck Injuries For current information on Temple Physical Therapy related news and for a healthy and safe return to work, sport and recreation Like Us
This is caused by muscle strain to the Achilles tendon in the heel of the foot.
 Foot Facts Our feet were designed to move across uneven earthy surfaces. The hard, inflexible surfaces that we regularly walk on today, such as concrete, tile or wood, leave our feet wanting in terms of
Foot Facts Our feet were designed to move across uneven earthy surfaces. The hard, inflexible surfaces that we regularly walk on today, such as concrete, tile or wood, leave our feet wanting in terms of
November 2012 Case Study. Authors: Kyle Nagle, MD, MPH; Karl Fry, PT, DPT, OCS; David Bernhardt, MD
 CC: Right foot pain November 2012 Case Study Authors: Kyle Nagle, MD, MPH; Karl Fry, PT, DPT, OCS; David Bernhardt, MD HPI: A 17 year old female cross country runner presents with right foot pain. At a
CC: Right foot pain November 2012 Case Study Authors: Kyle Nagle, MD, MPH; Karl Fry, PT, DPT, OCS; David Bernhardt, MD HPI: A 17 year old female cross country runner presents with right foot pain. At a
What Are Bursitis and Tendinitis?
 Bursitis and tendinitis are both common conditions that cause swelling around muscles and bones. They occur most often in the shoulder, elbow, wrist, hip, knee, or ankle. A bursa is a small, fluid-filled
Bursitis and tendinitis are both common conditions that cause swelling around muscles and bones. They occur most often in the shoulder, elbow, wrist, hip, knee, or ankle. A bursa is a small, fluid-filled
.org. Shoulder Pain and Common Shoulder Problems. Anatomy. Cause
 Shoulder Pain and Common Shoulder Problems Page ( 1 ) What most people call the shoulder is really several joints that combine with tendons and muscles to allow a wide range of motion in the arm from scratching
Shoulder Pain and Common Shoulder Problems Page ( 1 ) What most people call the shoulder is really several joints that combine with tendons and muscles to allow a wide range of motion in the arm from scratching
Treatment of Recalcitrant Intermetatarsal Neuroma With 4% Sclerosing Alcohol Injection: A Pilot Study
 Treatment of Recalcitrant Intermetatarsal Neuroma With 4% Sclerosing Alcohol Injection: A Pilot Study Christopher F. Hyer, DPM,' Lynette R. Mehl, DPM,2 Alan J. Block, DPM, MS, FACFAS,3 and Robert B. Vancourt,
Treatment of Recalcitrant Intermetatarsal Neuroma With 4% Sclerosing Alcohol Injection: A Pilot Study Christopher F. Hyer, DPM,' Lynette R. Mehl, DPM,2 Alan J. Block, DPM, MS, FACFAS,3 and Robert B. Vancourt,
How To Treat Heel Pain
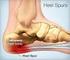 Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, Heel Pain The Plantar Fasciitis Organization is dedicated to the understanding of Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, and all other forms of Heel Pain. Welcome to the Plantar
Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, Heel Pain The Plantar Fasciitis Organization is dedicated to the understanding of Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, and all other forms of Heel Pain. Welcome to the Plantar
Endoscopic Plantar Fasciotomy
 Endoscopic Plantar Fasciotomy Introduction Plantar fasciitis is a common condition that causes pain centralized around the heel. It may be severe enough to affect regular activities. Health care providers
Endoscopic Plantar Fasciotomy Introduction Plantar fasciitis is a common condition that causes pain centralized around the heel. It may be severe enough to affect regular activities. Health care providers
Shoulder Impingement/Rotator Cuff Tendinitis
 Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Shoulder Impingement/Rotator Cuff Tendinitis One of the most common physical complaints is shoulder pain. Your shoulder is made up of several joints
Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Shoulder Impingement/Rotator Cuff Tendinitis One of the most common physical complaints is shoulder pain. Your shoulder is made up of several joints
The Land of Os: Accessory Ossicles of the Foot
 The Land of Os: Accessory Ossicles of the Foot Susan Cross, Anshul Rastogi, Rosy Jalan; Dept of Radiology, Barts Health NHS Trust, London, UK Contact: [email protected] Pictorial review Abstract
The Land of Os: Accessory Ossicles of the Foot Susan Cross, Anshul Rastogi, Rosy Jalan; Dept of Radiology, Barts Health NHS Trust, London, UK Contact: [email protected] Pictorial review Abstract
The Five Most Common Pathomechanical Foot Types (Rearfoot varus, forefoot varus, equinus, plantarflexed first ray, forefoot valgus)
 The Five Most Common Pathomechanical Foot Types (Rearfoot varus, forefoot varus, equinus, plantarflexed first ray, forefoot valgus) Pathomechanical foot types usually refer to structural deformities that
The Five Most Common Pathomechanical Foot Types (Rearfoot varus, forefoot varus, equinus, plantarflexed first ray, forefoot valgus) Pathomechanical foot types usually refer to structural deformities that
Arches. Foot Injuries. Medial Longitudinal Arch. Lateral Longitudinal Arch. Transverse Arch. Arch Strains
 Arches Foot Injuries Three arches in the foot: 1) Lateral longitudinal arch 2) Medial longitudinal arch 3) Transverse arch These arches are maintained and supported by the wedging of the interlocking tarsal
Arches Foot Injuries Three arches in the foot: 1) Lateral longitudinal arch 2) Medial longitudinal arch 3) Transverse arch These arches are maintained and supported by the wedging of the interlocking tarsal
Hamstring Apophyseal Injuries in Adolescent Athletes
 Hamstring Apophyseal Injuries in Adolescent Athletes Kyle Nagle, MD MPH University of Colorado Department of Orthopedics Children s Hospital Colorado Orthopedics Institute June 14, 2014 Disclosures I have
Hamstring Apophyseal Injuries in Adolescent Athletes Kyle Nagle, MD MPH University of Colorado Department of Orthopedics Children s Hospital Colorado Orthopedics Institute June 14, 2014 Disclosures I have
Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle
 Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic disease that attacks multiple joints throughout the body. It most often
Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic disease that attacks multiple joints throughout the body. It most often
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME
 ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME Description The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the front of the leg. Where the tendon
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME Description The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the front of the leg. Where the tendon
Synopsis of Causation. Pes Planus
 Ministry of Defence Synopsis of Causation Pes Planus Author: Mr Matthew J Wilson, Ninewells Hospital and Medical School, Dundee Validator: Mr William Body, The Hillingdon Hospital, Uxbridge September 2008
Ministry of Defence Synopsis of Causation Pes Planus Author: Mr Matthew J Wilson, Ninewells Hospital and Medical School, Dundee Validator: Mr William Body, The Hillingdon Hospital, Uxbridge September 2008
LATERAL PAIN SYNDROMES OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE
 C H A P T E R 3 LATERAL PAIN SYNDROMES OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE William D. Fishco, DPM The majority of patient encounters with the podiatrist are secondary to pain in the foot and/or ankle. If we draw an
C H A P T E R 3 LATERAL PAIN SYNDROMES OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE William D. Fishco, DPM The majority of patient encounters with the podiatrist are secondary to pain in the foot and/or ankle. If we draw an
Posttraumatic medial ankle instability
 Posttraumatic medial ankle instability Alexej Barg, Markus Knupp, Beat Hintermann Orthopaedic Department University Hospital of Basel, Switzerland Clinic of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kantonsspital Baselland
Posttraumatic medial ankle instability Alexej Barg, Markus Knupp, Beat Hintermann Orthopaedic Department University Hospital of Basel, Switzerland Clinic of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kantonsspital Baselland
Acute Ankle Injuries, Part 1: Office Evaluation and Management
 t June 08, 2009 Each acute ankle injury commonly seen in the office has associated with it a mechanism by which it can be injured, trademark symptoms that the patient experiences during the injury, and
t June 08, 2009 Each acute ankle injury commonly seen in the office has associated with it a mechanism by which it can be injured, trademark symptoms that the patient experiences during the injury, and
Hand Injuries and Disorders
 Hand Injuries and Disorders Introduction Each of your hands has 27 bones, 15 joints and approximately 20 muscles. There are many common problems that can affect your hands. Hand problems can be caused
Hand Injuries and Disorders Introduction Each of your hands has 27 bones, 15 joints and approximately 20 muscles. There are many common problems that can affect your hands. Hand problems can be caused
Ankle Block. Indications The ankle block is suitable for the following: Orthopedic and podiatry surgical procedures of the distal foot.
 Ankle Block The ankle block is a common peripheral nerve block. It is useful for procedures of the foot and toes, as long as a tourniquet is not required above the ankle. It is a safe and effective technique.
Ankle Block The ankle block is a common peripheral nerve block. It is useful for procedures of the foot and toes, as long as a tourniquet is not required above the ankle. It is a safe and effective technique.
George E. Quill, Jr., M.D. Louisville Orthopaedic Clinic Louisville, KY
 George E. Quill, Jr., M.D. Louisville Orthopaedic Clinic Louisville, KY The Ankle Sprain That Won t Get Better With springtime in Louisville upon us, the primary care physician and the orthopaedist alike
George E. Quill, Jr., M.D. Louisville Orthopaedic Clinic Louisville, KY The Ankle Sprain That Won t Get Better With springtime in Louisville upon us, the primary care physician and the orthopaedist alike
Common Foot Pathologies
 Common Foot Pathologies Chondromalacia Patella (patellofemoral pain syndrome) Chondromalacia Patella (patellofemoral pain syndrome) What is it? Chondromalacia (of Greek origin meaning softening of the
Common Foot Pathologies Chondromalacia Patella (patellofemoral pain syndrome) Chondromalacia Patella (patellofemoral pain syndrome) What is it? Chondromalacia (of Greek origin meaning softening of the
Elbow Injuries and Disorders
 Elbow Injuries and Disorders Introduction Your elbow joint is made up of bone, cartilage, ligaments and fluid. Muscles and tendons help the elbow joint move. There are many injuries and disorders that
Elbow Injuries and Disorders Introduction Your elbow joint is made up of bone, cartilage, ligaments and fluid. Muscles and tendons help the elbow joint move. There are many injuries and disorders that
INJURIES OF THE HAND AND WRIST By Derya Dincer, M.D.
 05/05/2007 INJURIES OF THE HAND AND WRIST By Derya Dincer, M.D. Hand injuries, especially the fractures of metacarpals and phalanges, are the most common fractures in the skeletal system. Hand injuries
05/05/2007 INJURIES OF THE HAND AND WRIST By Derya Dincer, M.D. Hand injuries, especially the fractures of metacarpals and phalanges, are the most common fractures in the skeletal system. Hand injuries
Rotator Cuff Pathophysiology. treatment program that will effectively treat it. The tricky part about the shoulder is that it is a ball and
 Rotator Cuff Pathophysiology Shoulder injuries occur to most people at least once in their life. This highly mobile and versatile joint is one of the most common reasons people visit their health care
Rotator Cuff Pathophysiology Shoulder injuries occur to most people at least once in their life. This highly mobile and versatile joint is one of the most common reasons people visit their health care
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Lateral Ankle Reconstruction
 UW HEALTH SPORTS REHABILITATION Rehabilitation Guidelines for Lateral Ankle Reconstruction The ankle is a very complex joint. There are actually three joints that make up the ankle complex: the tibiotalar
UW HEALTH SPORTS REHABILITATION Rehabilitation Guidelines for Lateral Ankle Reconstruction The ankle is a very complex joint. There are actually three joints that make up the ankle complex: the tibiotalar
Imaging of Lisfranc Injury
 November 2011 Imaging of Lisfranc Injury Greg Cvetanovich, Harvard Medical School Year IV Agenda Case Presentation Introduction Anatomy Lisfranc Injury Classification Imaging Treatment 2 Case Presentation
November 2011 Imaging of Lisfranc Injury Greg Cvetanovich, Harvard Medical School Year IV Agenda Case Presentation Introduction Anatomy Lisfranc Injury Classification Imaging Treatment 2 Case Presentation
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF LOW BACK PAIN
 CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF LOW BACK PAIN Low back pain is very common, up to 90+% of people are affected by back pain at some time in their lives. Most often back pain is benign and
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF LOW BACK PAIN Low back pain is very common, up to 90+% of people are affected by back pain at some time in their lives. Most often back pain is benign and
Toe fractures are one of the most
 Evaluation and Management of Toe Fractures ROBERT L. HATCH, M.D., M.P.H., and SCOTT HACKING, M.D., University of Florida College of Medicine, Gainesville, Florida Fractures of the toe are one of the most
Evaluation and Management of Toe Fractures ROBERT L. HATCH, M.D., M.P.H., and SCOTT HACKING, M.D., University of Florida College of Medicine, Gainesville, Florida Fractures of the toe are one of the most
Plantar Fasciitis Information Leaflet. Maneesh Bhatia. Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon
 Plantar Fasciitis Information Leaflet Maneesh Bhatia Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon What is plantar fasciitis? The plantar fascia is a strong band of tissue that stretches from the heel to the toes. It
Plantar Fasciitis Information Leaflet Maneesh Bhatia Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon What is plantar fasciitis? The plantar fascia is a strong band of tissue that stretches from the heel to the toes. It
OS TRIGONUM SYNDROME. Incidence: 10% unilateral and 2% bilateral in general population 1. Bilateral occurs in 50% of os trigonum population 4.
 OS TRIGONUM SYNDROME Incidence: 10% unilateral and 2% bilateral in general population 1. Bilateral occurs in 50% of os trigonum population 4. Mechanism of Injury: Os trigonum syndrome occurs due to repetitive,
OS TRIGONUM SYNDROME Incidence: 10% unilateral and 2% bilateral in general population 1. Bilateral occurs in 50% of os trigonum population 4. Mechanism of Injury: Os trigonum syndrome occurs due to repetitive,
Glossary of Foot & Ankle Terminology
 Glossary of Foot & Ankle Terminology Achilles Tendon One of the longer tendons in the body, stretching from the bones of the heel to the calf muscles. Abrasion An injury in which superficial layers of
Glossary of Foot & Ankle Terminology Achilles Tendon One of the longer tendons in the body, stretching from the bones of the heel to the calf muscles. Abrasion An injury in which superficial layers of
Adult Forearm Fractures
 Adult Forearm Fractures Your forearm is made up of two bones, the radius and ulna. In most cases of adult forearm fractures, both bones are broken. Fractures of the forearm can occur near the wrist at
Adult Forearm Fractures Your forearm is made up of two bones, the radius and ulna. In most cases of adult forearm fractures, both bones are broken. Fractures of the forearm can occur near the wrist at
Understanding. Heel Pain
 Understanding Heel Pain What Causes Heel Pain? Heel pain is a common problem that occurs when the heel is placed under too much stress. Heel pain is most often caused by walking in ways that irritate tissues
Understanding Heel Pain What Causes Heel Pain? Heel pain is a common problem that occurs when the heel is placed under too much stress. Heel pain is most often caused by walking in ways that irritate tissues
Trigger Point Master Course. Chapter 12. Muscles of the Leg and Foot
 Trigger Point Master Course Chapter 12 Muscles of the Leg and Foot 12 Muscles of the Leg and Foot Regional Trigger Points for Lower Leg, Ankle, and Foot Pain MUSCLE PAGE REFERENCE Abductor digiti minimi...
Trigger Point Master Course Chapter 12 Muscles of the Leg and Foot 12 Muscles of the Leg and Foot Regional Trigger Points for Lower Leg, Ankle, and Foot Pain MUSCLE PAGE REFERENCE Abductor digiti minimi...
Plantar Heel Pain. Papers. Shazia Ali, FY2 Davinder Paul Singh Baghla
 Shazia Ali, FY2 Davinder Paul Singh Baghla Abstract Plantar Heel pain is one of the most commonly encountered problems of foot pain in active adults over the age of 40. One in ten people will experience
Shazia Ali, FY2 Davinder Paul Singh Baghla Abstract Plantar Heel pain is one of the most commonly encountered problems of foot pain in active adults over the age of 40. One in ten people will experience
Get Rid of Elbow Pain
 Get Rid of Elbow Pain Self Regional Healthcare Optimum Life Center 115 Academy Avenue Greenwood, SC 29646 Office: (864) 725-7088 Self Regional Healthcare Physical Therapy Savannah Lakes 207 Holiday Road
Get Rid of Elbow Pain Self Regional Healthcare Optimum Life Center 115 Academy Avenue Greenwood, SC 29646 Office: (864) 725-7088 Self Regional Healthcare Physical Therapy Savannah Lakes 207 Holiday Road
Screening Examination of the Lower Extremities BUY THIS BOOK! Lower Extremity Screening Exam
 Screening Examination of the Lower Extremities Melvyn Harrington, MD Department of Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation Loyola University Medical Center BUY THIS BOOK! Essentials of Musculoskeletal Care
Screening Examination of the Lower Extremities Melvyn Harrington, MD Department of Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation Loyola University Medical Center BUY THIS BOOK! Essentials of Musculoskeletal Care
Taking Care of Flat Feet in Children
 1 Contact: Customer Service Foot Levelers, Inc. P.O. Box 12611 Roanoke, VA 24027-2611 (800) 553-4860 Ext. 3189 [email protected] Taking Care of Flat Feet in Children by Mark N. Charrette, DC Flatfoot
1 Contact: Customer Service Foot Levelers, Inc. P.O. Box 12611 Roanoke, VA 24027-2611 (800) 553-4860 Ext. 3189 [email protected] Taking Care of Flat Feet in Children by Mark N. Charrette, DC Flatfoot
.org. Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle) Anatomy
 Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle) Page ( 1 ) A broken ankle is also known as an ankle fracture. This means that one or more of the bones that make up the ankle joint are broken. A fractured ankle can range
Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle) Page ( 1 ) A broken ankle is also known as an ankle fracture. This means that one or more of the bones that make up the ankle joint are broken. A fractured ankle can range
Treatment Guide Understanding Elbow Pain. Using this Guide. Choosing Your Care. Table of Contents:
 Treatment Guide Understanding Elbow Pain Elbow pain is extremely common whether due to aging, overuse, trauma or a sports injury. When elbow pain interferes with carrying the groceries, participating in
Treatment Guide Understanding Elbow Pain Elbow pain is extremely common whether due to aging, overuse, trauma or a sports injury. When elbow pain interferes with carrying the groceries, participating in
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH)
 A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Achilles Tendon Repair
 UW HEALTH SPORTS REHABILITATION Rehabilitation Guidelines for Achilles Tendon Repair The Achilles tendon is the strongest and thickest tendon in the body. It attaches the calf muscles (soleus and gastrocnemius)
UW HEALTH SPORTS REHABILITATION Rehabilitation Guidelines for Achilles Tendon Repair The Achilles tendon is the strongest and thickest tendon in the body. It attaches the calf muscles (soleus and gastrocnemius)
CHRONIC HEEL PAIN AN ESSAY. Submitted For Fulfillment Of Master Degree in Orthopedic Surgery. Ahmed Ali Mohammed El Sayed M.B.B.ch
 CHRONIC HEEL PAIN AN ESSAY Submitted For Fulfillment Of Master Degree in Orthopedic Surgery BY Ahmed Ali Mohammed El Sayed M.B.B.ch Under Supervision Of Prof. Dr. AHMED AMIN GALAL Professor of Orthopedic
CHRONIC HEEL PAIN AN ESSAY Submitted For Fulfillment Of Master Degree in Orthopedic Surgery BY Ahmed Ali Mohammed El Sayed M.B.B.ch Under Supervision Of Prof. Dr. AHMED AMIN GALAL Professor of Orthopedic
Refer to Specialist. The Diagnosis and Management of Shoulder Pain 1. SLAP lesions, types 1 through 4
 The Diagnosis Management of Shoulder Pain 1 Significant Hisry -Age -Extremity Dominance -Hisry of trauma, dislocation, subluxation -Weakness, numbness, paresthesias -Sports participation -Past medical
The Diagnosis Management of Shoulder Pain 1 Significant Hisry -Age -Extremity Dominance -Hisry of trauma, dislocation, subluxation -Weakness, numbness, paresthesias -Sports participation -Past medical
Ankle-Foot Injury Injuries
 Ankle-Foot Injury Injuries Ed Mulligan, PT, DPT, OCS, SCS, ATC Clinical Orthopedic Rehabilitation Education What are the possible imposters to orthopedic foot/ankle injuries? 1. Lumbar Radiculopathy 2.
Ankle-Foot Injury Injuries Ed Mulligan, PT, DPT, OCS, SCS, ATC Clinical Orthopedic Rehabilitation Education What are the possible imposters to orthopedic foot/ankle injuries? 1. Lumbar Radiculopathy 2.
