Losing Weight in Singapore - Public Perception of Obesity
|
|
|
- Anastasia Mathews
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Singapore Med J 2012; 53(2) : 104 Public perceptions of obesity and bariatric surgery in Singapore: a pilot study Teo EY 1, MBBS, MRCP, Lew PS 2, MBBS, Foo CS 2, FRCS, FAMS Introduction Obesity is a real and dangerous problem with rising incidence. This study aimed to examine public perceptions of obesity as a disease, as well as the community s impression of the various modalities in the management of obesity, particularly bariatric surgery, in Singapore. Methods Volunteers from the public were approached in 2010 to complete a questionnaire that collected both their demographic data and perceptions on obesity, management of obesity and bariatric surgery. The perceptions of the respondents were analysed based on various demographic factors. Results The incidence of obesity was 16.8%. Consistent with previous studies in developed countries, the highest mean body mass index was noted in the age range of years. 95.6% of the population surveyed were aware that obesity was related to significant medical conditions. 60% of the population surveyed had attempted weight loss in the past, with 41.7% expressing lack of success, and 58.4% expressed that they had not heard of surgery as a modality. Conclusion This study shows that the majority of the population understands the significance of obesity as a medical problem and would take steps to combat it. However, there is suboptimal knowledge of the various modalities of managing obesity as a disease, especially with regard to surgical options. More education on the modalities available and access to them would help in the combat of this obesity epidemic. Keywords: bariatric surgery, obesity, public perceptions Singapore Med J 2012; 53(2): INTRODUCTION The prevalence of obesity is high in many parts of the world, with several studies showing a rising incidence, along with an increase in obesity-related significant disabilities and premature deaths. According to the World Health Organization (WHO) projection in 2008, approximately 1.5 billion adults (age 20+ years) were overweight, and of these, more than 200 million men and nearly 300 million women were obese. WHO further projects that by 2015, approximately 2.3 billion adults would be overweight and more than 700 million obese. (1) This increasing trend is also shown in a recent review of the epidemic of obesity by Low et al in (2) The same worrying trend is reflected in the Singapore National Health Survey in 2004, which showed an increase in the prevalence of obesity from 5.1% in 1992 to 6.0% in 1998 and 6.9% in (3) Even more concerning is the fact that the 2004 figures were based on the WHO international cut-off for obesity as a body mass index (BMI) of 30 kg/m 2 ; should the figures be recalculated based on the revised Asian cut-off for obesity of 27 kg/m 2 (due to the higher percentage body fat at lower BMI found in studies), (4,5) the prevalence of obesity may be as high as 16%. (6) Several demographic factors have been shown to affect the incidence of obesity in various studies, especially socioeconomic status, age and gender. (2,7-10) Obesity is identified as a cause of serious health consequences, with the risk of these consequences increasing with BMI. WHO has identified raised BMI as a major risk factor for chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disease (the world number one cause of death), diabetes mellitus (a rising global epidemic), musculoskeletal disorders and certain cancers. (1) This burden of co-morbidities and premature death has prompted the World Health Assembly in 2004 to formulate the WHO Global Strategy on Diet, Physical Activity and Health in an attempt to stave off this epidemic. As evidenced by the above, obesity is a real and dangerous problem requiring strategies to prevent its onset and also methods to manage it in view of the rising prevalence, These include conservative methods such as dietary modifications and exercise, medical options of pharmacological interventions and surgery. Conservative and medical options have been shown to give inconsistent and unsustained results; (6) however, surgical intervention for the management of obesity is currently not a well-recognised modality in Singapore. (6,11-13) Public perception of obesity and bariatric surgery has not been well described in previous studies, as these were mainly epidemiological studies. Therefore, this prospective cohort pilot study aimed to examine public perceptions of obesity as a disease and the demographic factors influencing the prevalence of obesity. We also explored public knowledge and perception of the options for management of obesity (including bariatric surgery). METHODS A questionnaire was designed to collect demographic data and public perceptions of the above (Appendix). The questionnaire 1 Department of Dermatology, 2 Department of General Surgery, Changi General Hospital, Singapore Correspondence: Dr Eng Yee Teo, Registrar, Department of Dermatology, Changi General Hospital, 2 Simei Street 3, Singapore [email protected]
2 Table I. Demographics of the sample population (n = 137). Demographic No. (%) Mean age; range (yrs) 32.5; Mean BMI; range (kg/m 2 ) 23.3; Gender Male Female Race Chinese Malay Indian Monthly income (SGD) < 1,000 1,000 1,999 2,000 2,999 3,000 3,999 4,000 4,999 5,000 5,999 6,000 Education level Primary Secondary Polytechnic Junior college University Graduate Post-graduate BMI: body mass index 60 (43.8) 77 (56.2) 97 (70.8) 19 (13.9) 6 (4.4) 15 (10.9) 15 (10.9) 31 (22.6) 45 (32.8) 17 (12.4) 9 (6.6) 11 (8.0) 9 (6.6) 2 (1.5) 30 (21.9) 30 (21.9) 8 (5.8) 49 (35.8) 10 (7.3) 8 (5.8) was pre-tested by 50 volunteers before being administered to the study population. It was administered in English and Mandarin (where possible) over a two-month period (between August and September 2010). The questionnaire comprised two sections: the first consisted of demographic data including age, gender, race, educational level, occupation, monthly income and BMI (participants provided their most recent height and weight and the BMI was calculated); and the second consisted of questions on perceptions of ideal weight and medical problems associated with obesity, participants personal exposure to various methods of weight loss, methods that they would consider, as well as factors that would influence their decision on a particular modality. The population consisted of individuals (both patients and visitors) at General Surgery Clinic F of Changi General Hospital, Bedok Polyclinic and a general practitioner clinic in the western part of Singapore, as well as a small number of staff members of Changi General Hospital. The population was approached by administers of the questionnaire and asked to volunteer, after which they were handed the questionnaire to complete. The demographics and number of non-responders were not recorded in this pilot study. To ensure accuracy of responses, only the questionnaires completed by adults (subjects aged 21 years) were included for final analysis. The Statistical Package for the Social Sciences version (SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA) was used for univariate, bivariate and multivariate analyses. The perceptions of the participants were further analysed against the demographic factors with exploratory factor analysis. Table II. Body mass index of the different demographic groups. Demographic Body mass index (kg/m 2 ) p-value Gender Male Female Race Chinese Malay Indian Age group (yrs) Monthly income (SGD) < 1,000 1,000 1,999 2,000 2,999 3,000 3,999 4,000 4,999 5,000 5,999 6,000 SD: standard deviation Mean ± SD Min Max 24.3 ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± RESULTS A total of 161 fully completed questionnaires were returned, and 137 were included for final analysis (a total of 202 questionnaires were returned with 41 excluded as incomplete and a further 24 were excluded as the subjects were < 21 years of age). Overweight was defined as BMI 23 kg/m 2 and obesity BMI 27 kg/m 2, based on the recommended Asian cut-offs, (5) The demographics of the surveyed population (n = 137) was analysed (Table I). 40.1% (n = 5) were found to be overweight by the above criteria and 16.8% (n = 23) were obese. 43.8% were male, and 70.8% were Chinese, 13.9% Malay, 4.4% Indian and 10.9% of other races. From the 2009 population census of Singapore residents, (14) Chinese constitute 74.2%, Malays 13.4%, Indians 9.2% and other races 3.2%; however, the census did not include the 25.3% of non-residents and as such, it was not possible to correlate the racial distribution of the participants with the general population of Singapore (residents and nonresidents). The mean age of the participants was 32.5 (range 21 67) years. The majority were between the ages of years. The majority (66.5%) of the participants declared their monthly income to be < SGD 3,000 (Table I). From Singapore population studies, (14) the median household income stood at SGD 5,000 in As the participants of this study were mainly visitors or patients of government-subsidised specialist clinic or polyclinic, this would explain the income distribution of the participants matching or falling below the median household income of the general population. The vast majority of the surveyed population (98.5%) had at least a secondary education. From the Singapore Census 2000, (14) 68.8% of residents in Singapore had at least a secondary education; this percentage would have increased over the years since that census. A further analysis of the education Singapore Med J 2012; 53(2) : 105
3 distribution of the surveyed population showed that 49.6% comprised those with secondary, polytechnic and junior college education, and 43.1% were at least university graduates. The BMI distribution of the surveyed population showed a mean BMI of 23.3 (range ) kg/m 2. The BMI distribution was further analysed against gender, race, age group and income level (Table II). Males have a higher mean BMI of 24.3 (range 20.1 ) kg/m 2 as compared with females at 22.6 (range ) kg/m 2. This was statistically significant (p = 0.009). Although the majority of the population surveyed were aged years, the highest mean BMI was recorded for the group aged years. This corresponds to previous studies, which found that BMI peaks at ages years among individuals in developed countries. There was no difference between the BMI among the various races. This was in contrast to studies conducted previously. (7 10) There was also no statistical difference in the BMI among the income groups. With the monthly income of 66% of the surveyed population being < SGD 3,000, the BMI of this group was further analysed against that of the population with income SGD 3,000; there was again no statistical significance. 95.6% of the surveyed population were aware that obesity was related to some medical conditions. Generally, hypertension, hyperlipidaemia, depression and diabetes mellitus were correctly identified as being related to obesity. On being asked if they thought that they were overweight, 39% of the surveyed population indicated they were not and 31% were affirmative. Although 9% of the population had a BMI > 23 kg/m 2, they did not think that they were overweight, whereas another 12% with a BMI < 23 kg/m 2 still felt that they were overweight. Among the 56 (41%) participants who felt that they were overweight, the mean BMI was 26.2 kg/m 2, with 75% (n = 42) having a BMI > 23 kg/m 2 and 25% (n = 14) having a BMI < 23 kg/m 2. Those who felt that they were overweight were asked to indicate their perceived ideal weight, and this was calculated into their perceived ideal BMI and analysed. The mean perceived ideal BMI was 22.1 kg/m 2, which was within the normal BMI range. 60% (n = 82) of the surveyed population had attempted weight loss in the past. The most common methods employed were exercise and diet (89% and 71%, respectively), while 11% had tried pharmacological means of weight loss, 4% slimming centres and only one participant had tried surgery. Of those who had attempted weight loss in the past, 58.3% (n = 49) felt that they had some degree of success. However, the mean weight loss was only about 4 kg, with five (10.2%) having a significant weight loss of 10 kg. For the 41.7% who attempted weight loss but did not succeed, the most common reason was failure to keep to dietary restrictions (69.7%), followed by having no time or energy to exercise (60.6%). 40% of the surveyed population had made no previous attempts at weight loss. Of these, 75% (n = 45) felt they did not need to lose weight. On analysing these 45 individuals, 28.9% had a BMI > 23 kg/m 2. The most common reasons for not attempting weight loss were no time or energy (36.6%), no 100% 90% 80% 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% Safety Risk of op Side effects Cost Fig. 1. Factors affecting choice of surgery. Persistence of effect Ease of procedure Degree of weight loss Reversibility money to explore weight loss options (20.0%) and ignorant of or no access to the options available (18.3%). Consistent with the most commonly attempted means of weight loss as mentioned above, the preferred method of weight loss (should this be needed) was exercise (58.4%), followed by diet (32.8%). Only 7.3% chose pharmacological means, and a small minority (2.2%) would consider surgery. 58.4% of the surveyed population expressed that they had not heard of surgery as a modality for management of obesity. It is hence unsurprising that only 41.6% of the surveyed population knew that bariatric surgery was a medical procedure, while 28.5% felt that it was a cosmetic procedure and 29.9% were unsure. Of the group that had not heard of surgery as an option, 25% had secondary education, 25% polytechnic level, and 28.8% were university graduates. The mean BMI of the group that had not heard of surgery as an option was 23.7 (range ) kg/m 2. With regard to the factors influencing the choice of surgery, the safety profile of the procedure and risks of operation were the two main considerations (Fig. 1). DISCUSSION This pilot study aimed to examine public perceptions of obesity as a disease, as well as the community s impression of the various modalities in the management of obesity, particularly bariatric surgery, in Singapore. Areas for improvement of the study materials and methodology were identified. In terms of materials, in the background of a multiracial community such as Singapore, the questionnaire would be better administered in the four main languages (English, Chinese, Malay and Tamil), with administers of the questionnaire being able to translate accurately the questions asked in the various languages and dialects. This could potentially improve the data collected to include the less literate in the community. It is also anticipated that the translations would enable the older population in Singapore to be included in the study, thereby increasing the mean age to be more representative. As previously mentioned, the surveyed population consisted of a large proportion of those whose monthly income was < SGD 3,000. This was attributed to a large number of the questionnaires being administered at government-subsidised clinics. For improvement of the study and removal of such a confounding factor, a larger and more representative population should be Singapore Med J 2012; 53(2) : 106
4 targeted. Despite the shortcomings of this pilot study, the captured data does show results that were consistent with previous studies as well as population census information. Although not one of the aims of this study, the study suggests an increased incidence of obesity in the population, especially if calculated based on the recommended Asian cut-off of BMI 27 kg/m % was found to be overweight and 16.8% obese; this was significantly higher than that reflected in the 2004 Census but consistent with the expected rise in the problem of obesity in Singapore. Also of concern is the BMI distribution of the surveyed population, which showed a mean BMI in the overweight range of 23.3 ( ) kg/m 2. However, due to the small and perhaps not truly representative population studied, it is not possible to comment on the above findings. Future population census or epidemiological studies would be needed to make any conclusion as to the rising incidence of obesity in Singapore. Similar to other developed countries, this study showed that the peak BMI occurs at ages years, suggesting that methods to combat obesity should be targeted at the younger age groups in an effort to prevent the onset of obesity and its associated comorbidities. The vast majority of the surveyed population knew that obesity is related to significant medical conditions. Of those who felt they were overweight, there was a good perception of the ideal body weight (as evidenced by the mean perceived ideal BMI of kg/m 2 ). This study showed minimal weight loss experienced by those who had attempted weight loss with conservative and medical options; however, again, the small sample size makes it impossible to comment on the significance of this finding. The main barriers to successful weight loss with conservative measures appeared to be failure to keep to dietary restrictions and a lack of time or energy for exercise, both of which would be expected problems in a developed westernised country. Almost 60% of the surveyed population, despite the majority having at least secondary education, had not heard of bariatric surgery as an option, and it is hence not surprising that only 2.2% of the population would consider surgery as a choice for managing obesity. The vast majority expressed concerns in the safety and risks involved in surgical procedures. This shows that there is a real need to improve public education in the available modalities for the management of obesity, especially that of bariatric surgery in those who would fit the criteria for such an intervention. The availability of patient-specific, structured weight loss programmes would help those who have trouble achieving and sustaining weight loss via conservative and pharmacological means. With studies consistently showing a rising trend in obesity, all efforts must be made to combat this epidemic. As evidence points to a peak BMI in the years age group, these efforts should target the younger population so as to provide them with the knowledge of obesity as a disease and the available options for the management of the condition. In conclusion, Singapore faces a significant, growing incidence of obesity that will bring with it multiple associated co-morbidities and premature mortality, similar to other developed countries. This incidence may be greater than anticipated by previous population studies in view of the lower recommended cut-off for obesity in the Asian population. Future studies using the lower recommended cut-off for obesity would be beneficial to monitor this worrying trend. Greater efforts to increase public education are required in order to combat this epidemic of obesity, with these efforts targeted at the younger population to achieve a preventive effect. Our study found a lack of knowledge of bariatric surgery among the general population, and thus, there is concern that individuals who require these interventions would be excluded due to a lack of access to these specialist services. As such, education on the various modalities for weight loss should include increasing public awareness of bariatric surgery. Incidentally, it is of concern that the surveyed population demonstrated an increased incidence of overweight and obese subjects. Although this may not reflect the incidence of obesity in the general population, future epidemiological studies would be beneficial for monitoring this trend. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We thank clinical assistants Ms Ann Chua and Ms Karen Chew for their assistance in administering the questionnaires. REFERENCES 1. WHO Obesity and overweight Fact Sheet No.311; updated Mar Available at: 2. Low S, Chin MC, Deurenberg-Yap M. Review on epidemic of obesity. Ann Acad Med Singapore 2009; 38: National Health Survey Statistics Singapore Newsletter 2005; Deurenberg-Yap M, Schmidt G, van Staveren WA, Deurenberg P. The paradox of low body mass index and high body fat percentage among Chinese, Malays and Indians in Singapore. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2000; 24: Deurenberg-Yap M, Deurenberg P. Is a re-evaluation of WHO body mass index cut-off values needed? The case of Asians in Singapore. Nutr Rev 2003; 61(5 pt 2):S Foo CS, Tay KH, Ravintharan T. Treatment of obesity with laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding in Singapore: an initial experience. Singapore Med J 2005; 46: Sabanayagam C, Shankar A, Wong TY, Saw SM, Foster PJ. Socioeconomic status and overweight/obesity in an adult Chinese population in Singapore. J Epidemiol 2007; 17: Erratum in: J Epidemiol 2008; 18: Sabanayagam C, Shankar A, Saw SM, Tai ES, Wong TY. The association between socioeconomic status and overweight/obesity in a Malay population in Singapore. Asia Pac J Public Health 2009; 21: Cheah JS. Obesity in Singapore. Ann Acad Med Singapore 2001; 30: Ong SK, Fong CW, Ma S, et al. Longitudinal study of the socio-demographic determinants of changes in body weight and waist circumference in a multiethnic Asian population. Int J Obes (Lond) 2009; 33: Sum CF. Pharmacotherapy and surgery in the treatment of obesity: evaluating risks and benefits. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 2002; 11 Suppl 8:S Ti TK. Singapore experience in obesity surgery. Obes Surg 2004; 14: Shabbir A, Loi TH, Lomanto D, Ti TK, So JB. Surgical management of obesity National University Hospital experience. Ann Acad Med Singapore 2009; 38: Department of Statistics, Singapore. Available at: Singapore Med J 2012; 53(2) : 107
5 Appendix Questionnaire on perceptions of obesity and bariatric surgery Name (optional): NRIC (optional): Age: Sex: Race: Height: m Weight: kg BMI: Highest Education level: [Please circle choice] Primary School / Secondary School / Polytechnic/ Junior College / University Graduate / Post-graduate Occupation: Monthly Income (average): [Please circle choice] < $1,000 / $1,000 1,999 / $2,000 2,999 / $3,000 3,999 / $4,000 4,999 / $5,000 5,999 / $6,000 6,999 / $7,000 7,999 / $8,000 8,999 / $9,000 9,999 / > $10, Do you think that being overweight or obese can cause significant medical problems? 2. Which of these do you think is related to obesity? [Please circle choice(s), can select more than one] A. High blood pressure G. Depression B. Diabetes H. Weak bones C. High cholesterol I. Teeth/ Dental problems D. Heart Disease J. Skin problems (eg. sensitive skin, acne) E. Stroke L. Asthma F. Cancer M. Kidney disease 3. Have you come across the following methods for the management of weight problems? A. Diet B. Exercise C. Traditional Medicine D. Slimming Centres E. Western Medicine F. Surgery 4. Do you think you are overweight? A. If Yes, what do you feel is your ideal weight? kg 5. Have you done anything to reduce your weight? A. If Yes, what have you tried? i. Diet ii. Exercise iii. Traditional Medicine (Includes massage therapy/acupuncture) iv. Slimming Centres v. Western Medicine vi. Surgery B. If No, why not? i. Do not feel the need to do anything. ii. No time or energy. iii. No money. iv. Do not know where to go/ options. 6. If you have answered Yes to Qn 5, were you successful in losing weight? A. If Yes, how much weight did you lose? B. If No, why not? i. Could not keep to dietary restraints ii. No time or energy to exercise iii. No money to continue with slimming program iv. Side effects of medications 7. If you had a choice of options for management of weight problems, which of the options in Question 5A would you choose, and why? 8. Do you think that surgery for obesity is a medical procedure or a cosmetic procedure? Medical/Cosmetic/Not Sure 9. Which of the following options would you choose for reduction of weight/management of obesity? [Rank in order of preference (1 to 6)] A. Diet E. Traditional Methods (Spa, B. Exercise Massage, Traditional Medicine, C. Medicine (Western) Acupuncture) D. Surgery F. Slimming Centres 10. What would influence your choices of surgery? [Rank in order of importance (1 to 8)] A. Safety E. Cost B. Degree of weight loss F. Ease of procedure C. Reversibility of procedure G. Persistence of effect D. Risks of operation H. Side effects of procedure Singapore Med J 2012; 53(2) : 108
Trends in Bariatric Surgery for Morbid Obesity in Wisconsin
 Trends in Bariatric Surgery for Morbid Obesity in Wisconsin Jennifer L. Erickson, BA; Patrick L. Remington, MD, MPH; Paul E. Peppard, PhD ABSTRACT Background: Obesity is a national epidemic with rates
Trends in Bariatric Surgery for Morbid Obesity in Wisconsin Jennifer L. Erickson, BA; Patrick L. Remington, MD, MPH; Paul E. Peppard, PhD ABSTRACT Background: Obesity is a national epidemic with rates
Trends in Bariatric Surgery for Morbid Obesity. in Wisconsin
 Trends in Bariatric Surgery for Morbid Obesity in Wisconsin Jennifer L. Erickson, B.A. Patrick L. Remington, M.D., M.P.H. Paul E. Peppard, PhD A Working Paper of the Wisconsin Public Health and Health
Trends in Bariatric Surgery for Morbid Obesity in Wisconsin Jennifer L. Erickson, B.A. Patrick L. Remington, M.D., M.P.H. Paul E. Peppard, PhD A Working Paper of the Wisconsin Public Health and Health
Weight Loss Surgery DA participants- 18 months later. By: Caitlyn Patrick and Evan Morgan
 Weight Loss Surgery DA participants- 18 months later By: Caitlyn Patrick and Evan Morgan Outline Background Obesity Comorbidities Treatments Barriers to care Kylee Miller s work PDSA Plan: Systematic follow
Weight Loss Surgery DA participants- 18 months later By: Caitlyn Patrick and Evan Morgan Outline Background Obesity Comorbidities Treatments Barriers to care Kylee Miller s work PDSA Plan: Systematic follow
The weight of the world.
 The weight of the world. SONY ANTHONY Obesity Derived from the Latin word obesus to devour Definition: having a very high amount of body fat in relation to lean body mass Classifications using Body Mass
The weight of the world. SONY ANTHONY Obesity Derived from the Latin word obesus to devour Definition: having a very high amount of body fat in relation to lean body mass Classifications using Body Mass
THE CORRELATION BETWEEN PHYSICAL HEALTH AND MENTAL HEALTH
 HENK SWINKELS (STATISTICS NETHERLANDS) BRUCE JONAS (US NATIONAL CENTER FOR HEALTH STATISTICS) JAAP VAN DEN BERG (STATISTICS NETHERLANDS) THE CORRELATION BETWEEN PHYSICAL HEALTH AND MENTAL HEALTH IN THE
HENK SWINKELS (STATISTICS NETHERLANDS) BRUCE JONAS (US NATIONAL CENTER FOR HEALTH STATISTICS) JAAP VAN DEN BERG (STATISTICS NETHERLANDS) THE CORRELATION BETWEEN PHYSICAL HEALTH AND MENTAL HEALTH IN THE
Clinical Research on Lifestyle Interventions to Treat Obesity and Asthma in Primary Care Jun Ma, M.D., Ph.D.
 Clinical Research on Lifestyle Interventions to Treat Obesity and Asthma in Primary Care Jun Ma, M.D., Ph.D. Associate Investigator Palo Alto Medical Foundation Research Institute Consulting Assistant
Clinical Research on Lifestyle Interventions to Treat Obesity and Asthma in Primary Care Jun Ma, M.D., Ph.D. Associate Investigator Palo Alto Medical Foundation Research Institute Consulting Assistant
Mortality Assessment Technology: A New Tool for Life Insurance Underwriting
 Mortality Assessment Technology: A New Tool for Life Insurance Underwriting Guizhou Hu, MD, PhD BioSignia, Inc, Durham, North Carolina Abstract The ability to more accurately predict chronic disease morbidity
Mortality Assessment Technology: A New Tool for Life Insurance Underwriting Guizhou Hu, MD, PhD BioSignia, Inc, Durham, North Carolina Abstract The ability to more accurately predict chronic disease morbidity
Obesity Affects Quality of Life
 Obesity Obesity is a serious health epidemic. Obesity is a condition characterized by excessive body fat, genetic and environmental factors. Obesity increases the likelihood of certain diseases and other
Obesity Obesity is a serious health epidemic. Obesity is a condition characterized by excessive body fat, genetic and environmental factors. Obesity increases the likelihood of certain diseases and other
Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass
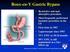 Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Restrictive and malabsorptive procedure Most frequently performed bariatric procedure in the US First done in 1967 Laparoscopic since 1993 75% EWL in 18-24 months 50% EWL is still
Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Restrictive and malabsorptive procedure Most frequently performed bariatric procedure in the US First done in 1967 Laparoscopic since 1993 75% EWL in 18-24 months 50% EWL is still
Karen Kovach M.S, R.D Chief Scientific Officer Weight Watchers International Inc.
 Waking up to real solutions to Chronic Disease: Tackling obesity can reduce the burden of chronic disease and deliver substantial cost savings to struggling European healthcare systems Karen Kovach M.S,
Waking up to real solutions to Chronic Disease: Tackling obesity can reduce the burden of chronic disease and deliver substantial cost savings to struggling European healthcare systems Karen Kovach M.S,
The National Survey of Children s Health 2011-2012 The Child
 The National Survey of Children s 11-12 The Child The National Survey of Children s measures children s health status, their health care, and their activities in and outside of school. Taken together,
The National Survey of Children s 11-12 The Child The National Survey of Children s measures children s health status, their health care, and their activities in and outside of school. Taken together,
Preservation and Incorporation of Valuable Endoscopic Innovations (PIVI)
 Preservation and Incorporation of Valuable Endoscopic Innovations (PIVI) The American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy PIVI on Endoscopic Bariatric Procedures (short form) Please see related White
Preservation and Incorporation of Valuable Endoscopic Innovations (PIVI) The American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy PIVI on Endoscopic Bariatric Procedures (short form) Please see related White
Pricing the Critical Illness Risk: The Continuous Challenge.
 Pricing the Critical Illness Risk: The Continuous Challenge. To be presented at the 6 th Global Conference of Actuaries, New Delhi 18 19 February 2004 Andres Webersinke, ACTUARY (DAV), FASSA, FASI 9 RAFFLES
Pricing the Critical Illness Risk: The Continuous Challenge. To be presented at the 6 th Global Conference of Actuaries, New Delhi 18 19 February 2004 Andres Webersinke, ACTUARY (DAV), FASSA, FASI 9 RAFFLES
The Link Between Obesity and Diabetes The Rapid Evolution and Positive Results of Bariatric Surgery
 The Link Between Obesity and Diabetes The Rapid Evolution and Positive Results of Bariatric Surgery Michael E. Farkouh, MD, MSc Peter Munk Chair in Multinational Clinical Trials Director, Heart and Stroke
The Link Between Obesity and Diabetes The Rapid Evolution and Positive Results of Bariatric Surgery Michael E. Farkouh, MD, MSc Peter Munk Chair in Multinational Clinical Trials Director, Heart and Stroke
Section 2. Overview of Obesity, Weight Loss, and Bariatric Surgery
 Section 2 Overview of Obesity, Weight Loss, and Bariatric Surgery What is Weight Loss? How does surgery help with weight loss? Short term versus long term weight loss? Conditions Improved with Weight Loss
Section 2 Overview of Obesity, Weight Loss, and Bariatric Surgery What is Weight Loss? How does surgery help with weight loss? Short term versus long term weight loss? Conditions Improved with Weight Loss
Jill Malcolm, Karen Moir
 Evaluation of Fife- DICE: Type 2 diabetes insulin conversion Article points 1. Fife-DICE is an insulin conversion group education programme. 2. People with greater than 7.5% on maximum oral therapy are
Evaluation of Fife- DICE: Type 2 diabetes insulin conversion Article points 1. Fife-DICE is an insulin conversion group education programme. 2. People with greater than 7.5% on maximum oral therapy are
Diabetes Prevention in Latinos
 Diabetes Prevention in Latinos Matthew O Brien, MD, MSc Assistant Professor of Medicine and Public Health Northwestern Feinberg School of Medicine Institute for Public Health and Medicine October 17, 2013
Diabetes Prevention in Latinos Matthew O Brien, MD, MSc Assistant Professor of Medicine and Public Health Northwestern Feinberg School of Medicine Institute for Public Health and Medicine October 17, 2013
DISCLOSURES RISK ASSESSMENT. Stroke and Heart Disease -Is there a Link Beyond Risk Factors? Daniel Lackland, MD
 STROKE AND HEART DISEASE IS THERE A LINK BEYOND RISK FACTORS? D AN IE L T. L AC K L AN D DISCLOSURES Member of NHLBI Risk Assessment Workgroup RISK ASSESSMENT Count major risk factors For patients with
STROKE AND HEART DISEASE IS THERE A LINK BEYOND RISK FACTORS? D AN IE L T. L AC K L AN D DISCLOSURES Member of NHLBI Risk Assessment Workgroup RISK ASSESSMENT Count major risk factors For patients with
HEALTH RISK ASSESSMENT (HRS) QUESTIONNAIRE
 HEALTH RISK ASSESSMENT (HRS) QUESTIONNAIRE The Health Risk Assessment (HRA) questionnaire provides participants with an evaluation of their current health and quality of life. The assessment promotes health
HEALTH RISK ASSESSMENT (HRS) QUESTIONNAIRE The Health Risk Assessment (HRA) questionnaire provides participants with an evaluation of their current health and quality of life. The assessment promotes health
MATERNAL AND CHILD HEALTH BRIEF #2:
 MATERNAL AND CHILD HEALTH BRIEF #2: OBESITY AMONG CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENTS SEPTEMBER 2012 OBESITY DEFINED Obesity and overweight are typically measured OVERVIEW in terms of Body Mass Index or BMI. BMI
MATERNAL AND CHILD HEALTH BRIEF #2: OBESITY AMONG CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENTS SEPTEMBER 2012 OBESITY DEFINED Obesity and overweight are typically measured OVERVIEW in terms of Body Mass Index or BMI. BMI
CHAPTER V DISCUSSION. normal life provided they keep their diabetes under control. Life style modifications
 CHAPTER V DISCUSSION Background Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition but people with diabetes can lead a normal life provided they keep their diabetes under control. Life style modifications (LSM)
CHAPTER V DISCUSSION Background Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition but people with diabetes can lead a normal life provided they keep their diabetes under control. Life style modifications (LSM)
Treating Patients with PRE-DIABETES David Doriguzzi, PA-C First Valley Medical Group. Learning Objectives. Background. CAPA 2015 Annual Conference
 Treating Patients with PRE-DIABETES David Doriguzzi, PA-C First Valley Medical Group Learning Objectives To accurately make the diagnosis of pre-diabetes/metabolic syndrome To understand the prevalence
Treating Patients with PRE-DIABETES David Doriguzzi, PA-C First Valley Medical Group Learning Objectives To accurately make the diagnosis of pre-diabetes/metabolic syndrome To understand the prevalence
inflammation of the pancreas and damage to the an increased risk of hypertension, stroke and Table 7.1: Classification of alcohol consumption
 H E A LT H SURVEY Alcohol Consumption 7 Alcohol Consumption N AT I O N A L Introduction Excessive alcohol consumption is associated with inflammation of the pancreas and damage to the an increased risk
H E A LT H SURVEY Alcohol Consumption 7 Alcohol Consumption N AT I O N A L Introduction Excessive alcohol consumption is associated with inflammation of the pancreas and damage to the an increased risk
2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: CLAIMS, REGISTRY
 Measure #128 (NQF 0421): Preventive Care and Screening: Body Mass Index (BMI) Screening and Follow-Up Plan National Quality Strategy Domain: Community/Population Health 2016 PQRS OPTIONS F INDIVIDUAL MEASURES:
Measure #128 (NQF 0421): Preventive Care and Screening: Body Mass Index (BMI) Screening and Follow-Up Plan National Quality Strategy Domain: Community/Population Health 2016 PQRS OPTIONS F INDIVIDUAL MEASURES:
Surgical Weight Loss Program for Teens
 Surgical Weight Loss Program for Teens Surgical Weight Loss Program for Teens The Surgical Weight Loss Program team understands the impact that being severely overweight can have on your life. Our guiding
Surgical Weight Loss Program for Teens Surgical Weight Loss Program for Teens The Surgical Weight Loss Program team understands the impact that being severely overweight can have on your life. Our guiding
Comorbidity of mental disorders and physical conditions 2007
 Comorbidity of mental disorders and physical conditions 2007 Comorbidity of mental disorders and physical conditions, 2007 Australian Institute of Health and Welfare Canberra Cat. no. PHE 155 The Australian
Comorbidity of mental disorders and physical conditions 2007 Comorbidity of mental disorders and physical conditions, 2007 Australian Institute of Health and Welfare Canberra Cat. no. PHE 155 The Australian
Adult Weight Management Training Summary
 Adult Weight Management Training Summary The Commission on Dietetic Registration, the credentialing agency for the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics Marilyn Holmes, MS, RDN, LDN About This Presentation
Adult Weight Management Training Summary The Commission on Dietetic Registration, the credentialing agency for the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics Marilyn Holmes, MS, RDN, LDN About This Presentation
Mortality Associated with Diabetes
 Mortality Associated with Diabetes A review paper prepared for the 7th Global Conference of Actuaries, New Delhi, 15-16 February, 2005 Dr. David Muiry, MB;BS, FIA, FASI [email protected] Introduction
Mortality Associated with Diabetes A review paper prepared for the 7th Global Conference of Actuaries, New Delhi, 15-16 February, 2005 Dr. David Muiry, MB;BS, FIA, FASI [email protected] Introduction
WHAT DOES DYSMETABOLIC SYNDROME MEAN?
 ! WHAT DOES DYSMETABOLIC SYNDROME MEAN? Dysmetabolic syndrome (also referred to as syndrome X, insulin resistance syndrome, and metabolic syndrome ) is a condition in which a group of risk factors for
! WHAT DOES DYSMETABOLIC SYNDROME MEAN? Dysmetabolic syndrome (also referred to as syndrome X, insulin resistance syndrome, and metabolic syndrome ) is a condition in which a group of risk factors for
Recommendations for Prescribing Exercise to Overweight and Obese Patients
 10 Recommendations for Prescribing Exercise to Overweight and Obese Patients 10 10 Recommendations for Prescribing Exercise to Overweight and Obese Patients Effects of Exercise The increasing prevalence
10 Recommendations for Prescribing Exercise to Overweight and Obese Patients 10 10 Recommendations for Prescribing Exercise to Overweight and Obese Patients Effects of Exercise The increasing prevalence
ADMISSION TO THE PSYCHIATRIC EMERGENCY SERVICES OF PATIENTS WITH ALCOHOL-RELATED MENTAL DISORDER
 Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Series VI: Medical Sciences Vol. 4 (53) No. 2-2011 ADMISSION TO THE PSYCHIATRIC EMERGENCY SERVICES OF PATIENTS WITH ALCOHOL-RELATED MENTAL DISORDER P.
Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Series VI: Medical Sciences Vol. 4 (53) No. 2-2011 ADMISSION TO THE PSYCHIATRIC EMERGENCY SERVICES OF PATIENTS WITH ALCOHOL-RELATED MENTAL DISORDER P.
Kansas Behavioral Health Risk Bulletin
 Kansas Behavioral Health Risk Bulletin Kansas Department of Health and Environment November 7, 1995 Bureau of Chronic Disease and Health Promotion Vol. 1 No. 12 Diabetes Mellitus in Kansas Diabetes mellitus
Kansas Behavioral Health Risk Bulletin Kansas Department of Health and Environment November 7, 1995 Bureau of Chronic Disease and Health Promotion Vol. 1 No. 12 Diabetes Mellitus in Kansas Diabetes mellitus
Understanding Obesity
 Your Guide to Understanding Obesity As your partner in health for your life s journey, we want you to be as informed and confident as possible regarding the disease or medical issue you may be facing.
Your Guide to Understanding Obesity As your partner in health for your life s journey, we want you to be as informed and confident as possible regarding the disease or medical issue you may be facing.
DIET AND EXERCISE STRATEGIES FOR WEIGHT LOSS AND WEIGHT MAINTENANCE
 DIET AND EXERCISE STRATEGIES FOR WEIGHT LOSS AND WEIGHT MAINTENANCE 40 yo woman, BMI 36. Motivated to begin diet therapy. Which of the following is contraindicated: Robert B. Baron MD MS Professor and
DIET AND EXERCISE STRATEGIES FOR WEIGHT LOSS AND WEIGHT MAINTENANCE 40 yo woman, BMI 36. Motivated to begin diet therapy. Which of the following is contraindicated: Robert B. Baron MD MS Professor and
Against the Growing Burden of Disease. Kimberly Elmslie Director General, Centre for Chronic Disease Prevention
 Kimberly Elmslie Director General, Centre for Chronic Disease Prevention Chronic diseases are an increasing global challenge Most significant cause of death (63%) worldwide 1 Chronic diseases cause premature
Kimberly Elmslie Director General, Centre for Chronic Disease Prevention Chronic diseases are an increasing global challenge Most significant cause of death (63%) worldwide 1 Chronic diseases cause premature
General and Abdominal Adiposity and Risk of Death in Europe
 Deutsches Institut für Ernährungsforschung Potsdam-Rehbrücke General and Abdominal Adiposity and Risk of Death in Europe Tobias Pischon Department of Epidemiology German Institute of Human Nutrition Potsdam-Rehbruecke
Deutsches Institut für Ernährungsforschung Potsdam-Rehbrücke General and Abdominal Adiposity and Risk of Death in Europe Tobias Pischon Department of Epidemiology German Institute of Human Nutrition Potsdam-Rehbruecke
Catholic Medical Center & Androscoggin Valley Hospital. Surgical Weight Loss Options For a Healthier Tomorrow
 Catholic Medical Center & Androscoggin Valley Hospital Surgical Weight Loss Options For a Healthier Tomorrow Presentation Overview Obesity Health Related Risks Who Qualifies for Weight Loss Surgery? Gastric-bypass
Catholic Medical Center & Androscoggin Valley Hospital Surgical Weight Loss Options For a Healthier Tomorrow Presentation Overview Obesity Health Related Risks Who Qualifies for Weight Loss Surgery? Gastric-bypass
Aspects of Underwriting for Actuaries
 Aspects of Underwriting for Actuaries Cathal Rabbitte Presented to: Global Conference of Actuaries February 2009, Mumbai Introduction This presentation does not set out to be comprehensive on the broad
Aspects of Underwriting for Actuaries Cathal Rabbitte Presented to: Global Conference of Actuaries February 2009, Mumbai Introduction This presentation does not set out to be comprehensive on the broad
Sedentarity and Exercise in the Canadian Population. Angelo Tremblay Division of kinesiology
 Sedentarity and Exercise in the Canadian Population Angelo Tremblay Division of kinesiology Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest Évolution de la pratique d activité physique des adultes canadiens
Sedentarity and Exercise in the Canadian Population Angelo Tremblay Division of kinesiology Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest Évolution de la pratique d activité physique des adultes canadiens
Treatment for Severely Obese Patients
 Treatment for Severely Obese Patients Associate Professor Jimmy So Senior Consultant Surgeon Director, Centre for Obesity Management and Surgery (COMS) National University Hospital Obesity Shortens Lives
Treatment for Severely Obese Patients Associate Professor Jimmy So Senior Consultant Surgeon Director, Centre for Obesity Management and Surgery (COMS) National University Hospital Obesity Shortens Lives
Psoriasis Co-morbidities: Changing Clinical Practice. Theresa Schroeder Devere, MD Assistant Professor, OHSU Dermatology. Psoriatic Arthritis
 Psoriasis Co-morbidities: Changing Clinical Practice Theresa Schroeder Devere, MD Assistant Professor, OHSU Dermatology Psoriatic Arthritis Psoriatic Arthritis! 11-31% of patients with psoriasis have psoriatic
Psoriasis Co-morbidities: Changing Clinical Practice Theresa Schroeder Devere, MD Assistant Professor, OHSU Dermatology Psoriatic Arthritis Psoriatic Arthritis! 11-31% of patients with psoriasis have psoriatic
Position Statement Weight Loss Surgery (Bariatric Surgery) and its Use in Treating Obesity or Treating and Preventing Diabetes
 Position Statement Weight Loss Surgery (Bariatric Surgery) and its Use in Treating Obesity or Treating and Preventing Diabetes People with diabetes Losing excess weight will assist in the management of
Position Statement Weight Loss Surgery (Bariatric Surgery) and its Use in Treating Obesity or Treating and Preventing Diabetes People with diabetes Losing excess weight will assist in the management of
NHS Diabetes Prevention Programme (NHS DPP) Non-diabetic hyperglycaemia. Produced by: National Cardiovascular Intelligence Network (NCVIN)
 NHS Diabetes Prevention Programme (NHS DPP) Non-diabetic hyperglycaemia Produced by: National Cardiovascular Intelligence Network (NCVIN) Date: August 2015 About Public Health England Public Health England
NHS Diabetes Prevention Programme (NHS DPP) Non-diabetic hyperglycaemia Produced by: National Cardiovascular Intelligence Network (NCVIN) Date: August 2015 About Public Health England Public Health England
Preventing Pediatric Diabetes: Are Racial Disparities A Factor? A Children s Health Fund Issue Brief February 2004
 Preventing Pediatric Diabetes: Are Racial Disparities A Factor? A Children s Health Fund Issue Brief February 2004 The Children s Health Fund The Children s Health Fund (CHF), working with hospitals and
Preventing Pediatric Diabetes: Are Racial Disparities A Factor? A Children s Health Fund Issue Brief February 2004 The Children s Health Fund The Children s Health Fund (CHF), working with hospitals and
New York State s Racial, Ethnic, and Underserved Populations. Demographic Indicators
 New York State s Racial, Ethnic, and Underserved Populations While much progress has been made to improve the health of racial and ethnic populations, and increase access to care, many still experience
New York State s Racial, Ethnic, and Underserved Populations While much progress has been made to improve the health of racial and ethnic populations, and increase access to care, many still experience
A Passage to India: Establishing a Cardiac Rehabilitation program in India s south-east
 A Passage to India: Establishing a Cardiac Rehabilitation program in India s south-east Kathryn Kelly Clinical Nurse Consultant, Cardiac Rehabilitation Coordinator The Royal Melbourne Hospital India 1,025,000,000
A Passage to India: Establishing a Cardiac Rehabilitation program in India s south-east Kathryn Kelly Clinical Nurse Consultant, Cardiac Rehabilitation Coordinator The Royal Melbourne Hospital India 1,025,000,000
THE IMPACT OF USING BLOOD SUGAR HOME MONITORING DEVICE TO CONTROL BLOOD SUGAR LEVEL IN DIABETIC PATIENTS
 THE IMPACT OF USING BLOOD SUGAR HOME MONITORING DEVICE TO CONTROL BLOOD SUGAR LEVEL IN DIABETIC PATIENTS Alshammari S., *Al-Jameel N., Al-Johani H, Al-Qahtani A., Al-Hakbani A., Khan A. and Alfaraj S.
THE IMPACT OF USING BLOOD SUGAR HOME MONITORING DEVICE TO CONTROL BLOOD SUGAR LEVEL IN DIABETIC PATIENTS Alshammari S., *Al-Jameel N., Al-Johani H, Al-Qahtani A., Al-Hakbani A., Khan A. and Alfaraj S.
PREOPERATIVE MANAGEMENT FOR BARIATRIC PATIENTS. Adrienne R. Gomez, MD Bariatric Physician St. Vincent Bariatric Center of Excellence
 PREOPERATIVE MANAGEMENT FOR BARIATRIC PATIENTS Adrienne R. Gomez, MD Bariatric Physician St. Vincent Bariatric Center of Excellence BARIATRIC SURGERY Over 200,000 bariatric surgical procedures are performed
PREOPERATIVE MANAGEMENT FOR BARIATRIC PATIENTS Adrienne R. Gomez, MD Bariatric Physician St. Vincent Bariatric Center of Excellence BARIATRIC SURGERY Over 200,000 bariatric surgical procedures are performed
Sue Flocke, PhD Eileen L. Seeholzer, MD MS Heidi Gullett, MD MPH
 Sue Flocke, PhD Eileen L. Seeholzer, MD MS Heidi Gullett, MD MPH Brigid Jackson, MA Samantha Smith, MA Elizabeth Antognoli, PhD Sue Krejci, MBA Peter J. Lawson, MA MPH MBA Practice-based Research Network
Sue Flocke, PhD Eileen L. Seeholzer, MD MS Heidi Gullett, MD MPH Brigid Jackson, MA Samantha Smith, MA Elizabeth Antognoli, PhD Sue Krejci, MBA Peter J. Lawson, MA MPH MBA Practice-based Research Network
Weight-Loss Surgery for Adults With Diabetes or Prediabetes Who Are at the Lower Levels of Obesity
 Weight-Loss Surgery for Adults With Diabetes or Prediabetes Who Are at the Lower Levels of Obesity A Review of the Research for Adults With a BMI Between 30 and 35 Is This Information Right for Me? If
Weight-Loss Surgery for Adults With Diabetes or Prediabetes Who Are at the Lower Levels of Obesity A Review of the Research for Adults With a BMI Between 30 and 35 Is This Information Right for Me? If
Family History and Diabetes. Practical Genomics for the Public Health Professional
 Family History and Diabetes Practical Genomics for the Public Health Professional Outline Overview of Type 2 Diabetes/Gestational Diabetes Familial/Genetic Nature of Diabetes Interaction of Genes and Environment
Family History and Diabetes Practical Genomics for the Public Health Professional Outline Overview of Type 2 Diabetes/Gestational Diabetes Familial/Genetic Nature of Diabetes Interaction of Genes and Environment
SUMMA HEALTH SYSTEM BARIATRIC CARE CENTER. Laura Ilg RD, LD Adrian Dan MD, FACS
 SUMMA HEALTH SYSTEM BARIATRIC CARE CENTER Laura Ilg RD, LD Adrian Dan MD, FACS GOALS The Many Benefits of Bariatric surgery and Weight Reduction Bariatric Care Center Surgical Weight Loss Program Medical
SUMMA HEALTH SYSTEM BARIATRIC CARE CENTER Laura Ilg RD, LD Adrian Dan MD, FACS GOALS The Many Benefits of Bariatric surgery and Weight Reduction Bariatric Care Center Surgical Weight Loss Program Medical
The relationship between socioeconomic status and healthy behaviors: A mediational analysis. Jenn Risch Ashley Papoy.
 Running head: SOCIOECONOMIC STATUS AND HEALTHY BEHAVIORS The relationship between socioeconomic status and healthy behaviors: A mediational analysis Jenn Risch Ashley Papoy Hanover College Prior research
Running head: SOCIOECONOMIC STATUS AND HEALTHY BEHAVIORS The relationship between socioeconomic status and healthy behaviors: A mediational analysis Jenn Risch Ashley Papoy Hanover College Prior research
Appendix: Description of the DIETRON model
 Appendix: Description of the DIETRON model Much of the description of the DIETRON model that appears in this appendix is taken from an earlier publication outlining the development of the model (Scarborough
Appendix: Description of the DIETRON model Much of the description of the DIETRON model that appears in this appendix is taken from an earlier publication outlining the development of the model (Scarborough
Statistics on Obesity, Physical Activity and Diet. England 2015
 Statistics on Obesity, Physical Activity and Diet England 2015 Published 3 March 2015 We are the trusted national provider of high-quality information, data and IT systems for health and social care. www.hscic.gov.uk
Statistics on Obesity, Physical Activity and Diet England 2015 Published 3 March 2015 We are the trusted national provider of high-quality information, data and IT systems for health and social care. www.hscic.gov.uk
The cost of physical inactivity
 The cost of physical inactivity October 2008 The cost of physical inactivity to the Australian economy is estimated to be $13.8 billion. It is estimated that 16,178 Australians die prematurely each year
The cost of physical inactivity October 2008 The cost of physical inactivity to the Australian economy is estimated to be $13.8 billion. It is estimated that 16,178 Australians die prematurely each year
Administration of Emergency Medicine
 doi:10.1016/j.jemermed.2005.07.008 The Journal of Emergency Medicine, Vol. 30, No. 4, pp. 455 460, 2006 Copyright 2006 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0736-4679/06 $ see front matter
doi:10.1016/j.jemermed.2005.07.008 The Journal of Emergency Medicine, Vol. 30, No. 4, pp. 455 460, 2006 Copyright 2006 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0736-4679/06 $ see front matter
Bariatric Surgery. OHTAC Recommendation. Bariatric Surgery
 OHTAC Recommendation Bariatric Surgery January 21, 2005 1 The Ontario Health Technology Advisory Committee (OHTAC) met on January 21, 2005 and reviewed bariatric surgery for morbid obesity. Obesity is
OHTAC Recommendation Bariatric Surgery January 21, 2005 1 The Ontario Health Technology Advisory Committee (OHTAC) met on January 21, 2005 and reviewed bariatric surgery for morbid obesity. Obesity is
GASTRIC SLEEVE SURGERY FOR WEIGHT LOSS. www.malleysurgical.com GASTRIC SLEEVE SURGERY FOR WEIGHT LOSS
 GASTRIC SLEEVE SURGERY FOR WEIGHT LOSS www.malleysurgical.com GASTRIC SLEEVE SURGERY FOR WEIGHT LOSS 1 CONTENTS What is sleeve gastrectomy? Why choose sleeve gastrectomy? Health risks associated with excess
GASTRIC SLEEVE SURGERY FOR WEIGHT LOSS www.malleysurgical.com GASTRIC SLEEVE SURGERY FOR WEIGHT LOSS 1 CONTENTS What is sleeve gastrectomy? Why choose sleeve gastrectomy? Health risks associated with excess
GASTRIC SLEEVE SURGERY FOR WEIGHT LOSS. www.carepointhealth.org GASTRIC SLEEVE SURGERY FOR WEIGHT LOSS. 201-795-8175 CarePointHealth.
 www.carepointhealth.org GASTRIC SLEEVE SURGERY FOR WEIGHT LOSS 201-795-8175 CarePointHealth.org 1 CONTENTS What is sleeve gastrectomy? Why choose sleeve gastrectomy? Health risks associated with excess
www.carepointhealth.org GASTRIC SLEEVE SURGERY FOR WEIGHT LOSS 201-795-8175 CarePointHealth.org 1 CONTENTS What is sleeve gastrectomy? Why choose sleeve gastrectomy? Health risks associated with excess
FACILITATOR/MENTOR GUIDE
 FACILITATOR/MENTOR GUIDE Descriptive analysis variables table shells hypotheses Measures of association methods design justify analytic assess calculate analysis problem stratify confounding statistical
FACILITATOR/MENTOR GUIDE Descriptive analysis variables table shells hypotheses Measures of association methods design justify analytic assess calculate analysis problem stratify confounding statistical
The Effects of Participation in Marching Band on Physical Activity and Physical Fitness in College Aged Men and Women
 University of Rhode Island DigitalCommons@URI Senior Honors Projects Honors Program at the University of Rhode Island 2013 The Effects of Participation in Marching Band on Physical Activity and Physical
University of Rhode Island DigitalCommons@URI Senior Honors Projects Honors Program at the University of Rhode Island 2013 The Effects of Participation in Marching Band on Physical Activity and Physical
Upstate New York adults with diagnosed type 1 and type 2 diabetes and estimated treatment costs
 T H E F A C T S A B O U T Upstate New York adults with diagnosed type 1 and type 2 diabetes and estimated treatment costs Upstate New York Adults with diagnosed diabetes: 2003: 295,399 2008: 377,280 diagnosed
T H E F A C T S A B O U T Upstate New York adults with diagnosed type 1 and type 2 diabetes and estimated treatment costs Upstate New York Adults with diagnosed diabetes: 2003: 295,399 2008: 377,280 diagnosed
THE NHS HEALTH CHECK AND INSURANCE FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
 THE NHS HEALTH CHECK AND INSURANCE FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS Introduction The following document has been produced by the Department of Health in partnership with the Association of British Insurers,
THE NHS HEALTH CHECK AND INSURANCE FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS Introduction The following document has been produced by the Department of Health in partnership with the Association of British Insurers,
Type 1 Diabetes ( Juvenile Diabetes)
 Type 1 Diabetes W ( Juvenile Diabetes) hat is Type 1 Diabetes? Type 1 diabetes, also known as juvenile-onset diabetes, is one of the three main forms of diabetes affecting millions of people worldwide.
Type 1 Diabetes W ( Juvenile Diabetes) hat is Type 1 Diabetes? Type 1 diabetes, also known as juvenile-onset diabetes, is one of the three main forms of diabetes affecting millions of people worldwide.
16. ARTHRITIS, OSTEOPOROSIS, AND CHRONIC BACK CONDITIONS
 16. ARTHRITIS, OSTEOPOROSIS, AND CHRONIC BACK CONDITIONS Goal Reduce the impact of several major musculoskeletal conditions by reducing the occurrence, impairment, functional limitations, and limitation
16. ARTHRITIS, OSTEOPOROSIS, AND CHRONIC BACK CONDITIONS Goal Reduce the impact of several major musculoskeletal conditions by reducing the occurrence, impairment, functional limitations, and limitation
Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) Brief
 Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) Brief What is Coronary Heart Disease? Coronary Heart Disease (CHD), also called coronary artery disease 1, is the most common heart condition in the United States. It occurs
Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) Brief What is Coronary Heart Disease? Coronary Heart Disease (CHD), also called coronary artery disease 1, is the most common heart condition in the United States. It occurs
King County City Health Profile Vashon Island
 King County City Health Profile Vashon Island West Seattle North Highline Burien SeaTac/Tukwila Vashon Island Des Moines/Normandy Park Kent-West East Federal Way Fed Way-Dash Point/Woodmont December, 212
King County City Health Profile Vashon Island West Seattle North Highline Burien SeaTac/Tukwila Vashon Island Des Moines/Normandy Park Kent-West East Federal Way Fed Way-Dash Point/Woodmont December, 212
Diabetes: The Numbers
 Diabetes: The Numbers Changing the Way Diabetes is Treated. What is Diabetes? Diabetes is a group of diseases characterized by high levels of blood glucose (blood sugar) Diabetes can lead to serious health
Diabetes: The Numbers Changing the Way Diabetes is Treated. What is Diabetes? Diabetes is a group of diseases characterized by high levels of blood glucose (blood sugar) Diabetes can lead to serious health
Connecticut Diabetes Statistics
 Connecticut Diabetes Statistics What is Diabetes? State Public Health Actions (1305, SHAPE) Grant March 2015 Page 1 of 16 Diabetes is a disease in which blood glucose levels are above normal. Blood glucose
Connecticut Diabetes Statistics What is Diabetes? State Public Health Actions (1305, SHAPE) Grant March 2015 Page 1 of 16 Diabetes is a disease in which blood glucose levels are above normal. Blood glucose
really help your physical, social and emotional wellbeing helping you do more of the things you want and feel more confident and relaxed.
 Weight loss surgery If you are seriously overweight, losing excess weight can transform your life. Find out how you can make that change with the help of Spire Healthcare. If you One are off seriously
Weight loss surgery If you are seriously overweight, losing excess weight can transform your life. Find out how you can make that change with the help of Spire Healthcare. If you One are off seriously
abcdefghijklmnopqrstu
 The Quality Unit Planning and Quality Division E: [email protected] [email protected] T: 0131-244 2287 abcdefghijklmnopqrstu NHSScotland Board Chief Executives NHSScotland Board Medical
The Quality Unit Planning and Quality Division E: [email protected] [email protected] T: 0131-244 2287 abcdefghijklmnopqrstu NHSScotland Board Chief Executives NHSScotland Board Medical
The American Cancer Society Cancer Prevention Study I: 12-Year Followup
 Chapter 3 The American Cancer Society Cancer Prevention Study I: 12-Year Followup of 1 Million Men and Women David M. Burns, Thomas G. Shanks, Won Choi, Michael J. Thun, Clark W. Heath, Jr., and Lawrence
Chapter 3 The American Cancer Society Cancer Prevention Study I: 12-Year Followup of 1 Million Men and Women David M. Burns, Thomas G. Shanks, Won Choi, Michael J. Thun, Clark W. Heath, Jr., and Lawrence
Selected Health Status Indicators DALLAS COUNTY. Jointly produced to assist those seeking to improve health care in rural Alabama
 Selected Health Status Indicators DALLAS COUNTY Jointly produced to assist those seeking to improve health care in rural Alabama By The Office of Primary Care and Rural Health, Alabama Department of Public
Selected Health Status Indicators DALLAS COUNTY Jointly produced to assist those seeking to improve health care in rural Alabama By The Office of Primary Care and Rural Health, Alabama Department of Public
Comorbidities associated with psoriasis in the Newfoundland and Labrador founder population
 Comorbidities associated with psoriasis in the Newfoundland and Labrador founder population Don MacDonald, PhD(c), Wayne Gulliver, MD, FRCPC, Neil Gladney, BTech, MSc (c), Kayla D. Collins, PhD(c), Jeff
Comorbidities associated with psoriasis in the Newfoundland and Labrador founder population Don MacDonald, PhD(c), Wayne Gulliver, MD, FRCPC, Neil Gladney, BTech, MSc (c), Kayla D. Collins, PhD(c), Jeff
Listen to your heart: Good Cardiovascular Health for Life
 Listen to your heart: Good Cardiovascular Health for Life Luis R. Castellanos MD, MPH Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine University of California San Diego School of Medicine Sulpizio Family Cardiovascular
Listen to your heart: Good Cardiovascular Health for Life Luis R. Castellanos MD, MPH Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine University of California San Diego School of Medicine Sulpizio Family Cardiovascular
Diabetes. African Americans were disproportionately impacted by diabetes. Table 1 Diabetes deaths by race/ethnicity CHRONIC DISEASES
 Diabetes African Americans were disproportionately impacted by diabetes. African Americans were most likely to die of diabetes. People living in San Pablo, Pittsburg, Antioch and Richmond were more likely
Diabetes African Americans were disproportionately impacted by diabetes. African Americans were most likely to die of diabetes. People living in San Pablo, Pittsburg, Antioch and Richmond were more likely
Understanding Diseases and Treatments with Canadian Real-world Evidence
 Understanding Diseases and Treatments with Canadian Real-world Evidence Real-World Evidence for Successful Market Access WHITEPAPER REAL-WORLD EVIDENCE Generating real-world evidence requires the right
Understanding Diseases and Treatments with Canadian Real-world Evidence Real-World Evidence for Successful Market Access WHITEPAPER REAL-WORLD EVIDENCE Generating real-world evidence requires the right
Diabetes Brief. Pre diabetes occurs when glucose levels are elevated in the blood, but are not as high as someone who has diabetes.
 Diabetes Brief What is Diabetes? Diabetes mellitus is a disease of abnormal carbohydrate metabolism in which the level of blood glucose, or blood sugar, is above normal. The disease occurs when the body
Diabetes Brief What is Diabetes? Diabetes mellitus is a disease of abnormal carbohydrate metabolism in which the level of blood glucose, or blood sugar, is above normal. The disease occurs when the body
The Influence of Infant Health on Adult Chronic Disease
 The Influence of Infant Health on Adult Chronic Disease Womb to Tomb Dr Clare MacVicar Introduction Many diseases in adulthood are related to growth patterns during early life Maternal nutrition important
The Influence of Infant Health on Adult Chronic Disease Womb to Tomb Dr Clare MacVicar Introduction Many diseases in adulthood are related to growth patterns during early life Maternal nutrition important
Future Market Insights
 Global Bariatric Surgery Devices Market Share, Global Trends, Analysis, Research, Report, Opportunities, Segmentation and Forecast, 2015 Future Market Insights www.futuremarketinsights.com [email protected]
Global Bariatric Surgery Devices Market Share, Global Trends, Analysis, Research, Report, Opportunities, Segmentation and Forecast, 2015 Future Market Insights www.futuremarketinsights.com [email protected]
EXPANDING THE EVIDENCE BASE IN OUTCOMES RESEARCH: USING LINKED ELECTRONIC MEDICAL RECORDS (EMR) AND CLAIMS DATA
 EXPANDING THE EVIDENCE BASE IN OUTCOMES RESEARCH: USING LINKED ELECTRONIC MEDICAL RECORDS (EMR) AND CLAIMS DATA A CASE STUDY EXAMINING RISK FACTORS AND COSTS OF UNCONTROLLED HYPERTENSION ISPOR 2013 WORKSHOP
EXPANDING THE EVIDENCE BASE IN OUTCOMES RESEARCH: USING LINKED ELECTRONIC MEDICAL RECORDS (EMR) AND CLAIMS DATA A CASE STUDY EXAMINING RISK FACTORS AND COSTS OF UNCONTROLLED HYPERTENSION ISPOR 2013 WORKSHOP
Bariatric Surgery in 2015
 Bariatric Surgery in 2015 Peter Nau, MD, MS Assistant Professor The University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics 1 Objectives Define the obesity epidemic The cost of obesity Discuss the complications associated
Bariatric Surgery in 2015 Peter Nau, MD, MS Assistant Professor The University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics 1 Objectives Define the obesity epidemic The cost of obesity Discuss the complications associated
Surgical Weight Loss. Mission Bariatrics
 Surgical Weight Loss Mission Bariatrics Obesity is a major health problem in the United States, with more than one in every three people suffering from this chronic condition. Obese adults are at an increased
Surgical Weight Loss Mission Bariatrics Obesity is a major health problem in the United States, with more than one in every three people suffering from this chronic condition. Obese adults are at an increased
