ITU-T G.8032 Ethernet Ring Protection Switching
|
|
|
- Marshall Wilson
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The feature implements protection switching mechanisms for Ethernet layer ring topologies. This feature uses the G.8032 Ethernet Ring Protection (ERP) protocol, defined in ITU-T G.8032, to provide protection for Ethernet traffic in a ring topology, while ensuring that no loops are within the ring at the Ethernet layer. The loops are prevented by blocking traffic on either a predetermined link or a failed link. Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for Configuring, page 1 About, page 2 How to Configure, page 8 Configuration Examples for, page 21 Additional References for, page 23 Feature Information For, page 24 Finding Feature Information Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature information, see Bug Search Tool and the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the feature information table. Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to An account on Cisco.com is not required. Prerequisites for Configuring ITU-T G.8032 Ethernet Ring Protection Switching The Ethernet Flow Points (EFPs) and Trunk Ethernet Flow Points (TEFPs) must be configured. 1
2 About About Ring Protection Links An Ethernet ring consists of multiple Ethernet ring nodes. Each Ethernet ring node is connected to adjacent Ethernet ring nodes using two independent ring links. A ring link prohibits formation of loops that affect the network. The Ethernet ring uses a specific link to protect the entire Ethernet ring. This specific link is called the Ring Protection Link (RPL). A ring link is bound by two adjacent Ethernet ring nodes and a port for a ring link (also known as a ring port). There must be at least two Ethernet ring nodes in a Ethernet ring. Functionality The Ethernet ring protection functionality includes the following: Loop avoidance The use of learning, forwarding, and Filtering Database (FDB) mechanisms Loop avoidance in an Ethernet ring is achieved by ensuring that, at any time, traffic flows on all but the Ring Protection Link (RPL). The following is a list of RPL types (or RPL nodes) and their functions: RPL owner Responsible for blocking traffic over the RPL so that no loops are formed in the Ethernet traffic. There can be only one RPL owner in a ring. RPL neighbor node An Ethernet ring node adjacent to the RPL. It is responsible for blocking its end of the RPL under normal conditions. This node type is optional and prevents RPL usage when protected. RPL next-neighbor node Next-neighbor node is an Ethernet ring node adjacent to an RPL owner node or RPL neighbor node. It is mainly used for FDB flush optimization on the ring. This node is also optional. 2
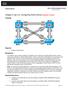
3 R-APS Control Messages The following figure illustrates the G.8032 Ethernet ring topology. Figure 1: G.8032 Ethernet Ring Topology R-APS Control Messages Nodes on the ring use control messages called Ring Automatic Protection Switching (R-APS) messages to coordinate the activities of switching the ring protection link (RPL) on and off. Any failure along the ring triggers a R-APS Signal Failure (R-APS SF) message in both directions of the nodes adjacent to the failed link, after the nodes have blocked the port facing the failed link. On obtaining this message, the RPL owner unblocks the RPL port. Note A single link failure in the ring ensures a loop-free topology. CFM Protocols and Link Failures Connectivity Fault Management (CFM) and line status messages are used to detect ring link and node failure. During the recovery phase, when the failed link is restored, the nodes adjacent to the restored link send Ring Automatic Protection Switching (R-APS) No Request (R-APS NR) messages. On obtaining this message, the ring protection link (RPL) owner blocks the RPL port and sends R-APS NR and R-APS RPL (R-APS NR, RB) messages. These messages cause all other nodes, other than the RPL owner in the ring, to unblock all blocked ports. The Ethernet Ring Protection (ERP) protocol works for both unidirectional failure and multiple link failure scenarios in a ring topology. Note The G.8032 Ethernet Ring Protection (ERP) protocol uses CFM Continuity Check Messages (CCMs) at an interval of 3.3 milliseconds (ms). At this interval (which is supported only on selected platforms), SONET-like switching time performance and loop-free traffic can be achieved. 3
4 G.8032 Ring-Supported Commands and Functionality G.8032 Ring-Supported Commands and Functionality A G.8032 ring supports these basic operator administrative commands: Force switch (FS) Allows the operator to forcefully block a particular ring port. Note the following points about FS commands: Effective even if there is an existing SF condition Multiple FS commands for ring are supported May be used to allow immediate maintenance operations Manual switch (MS) Allows the operator to manually block a particular ring port. Note the following points about MS commands: Ineffective in an existing FS or signal failure (SF) condition Overridden by new FS or SF conditions Multiple MS commands cancel all MS commands Clear Cancels an existing FS or MS command on the ring port. The Clear command is used at the ring protection link (RPL) owner to clear a nonrevertive mode condition. A G.8032 ring can support multiple instances. An instance is a logical ring running over a physical ring. Such instances are used for various reasons, such as load-balancing VLANs over a ring. For example, odd-numbered VLANs may go in one direction of the ring, and even-numbered VLANs may go in the other direction. Specific VLANs can be configured under only one instance. They cannot overlap multiple instances. Otherwise, data traffic or Ring Automatic Protection Switching (R-APS) messages may cross logical rings, which is not desirable. G.8032 ERP Timers The G.8032 Ethernet Ring Protection (ERP) protocol specifies the use of different timers to avoid race conditions and unnecessary switching operations: Delay timers Used by the Ring Protection Link (RPL) owner to verify that the network has stabilized before blocking the RPL. Note the following points about delay timers. After a signal failure (SF) condition, a Wait-to-Restore (WTR) timer is used to verify that the SF is not intermittent. The WTR timer can be configured by the operator. The default time interval is 5 minutes; the time interval ranges from 1 to 12 minutes. After a force switch (FS) or a manual switch (MS) command is issued, a Wait-to-Block (WTB) timer is used to verify that no background condition exists. Note The WTB timer interval may be shorter than the WTR timer interval. 4
5 Protection Switching Functionality in a Single Link Failure and Recovery Guard timer Used by all nodes when changing state; the guard timer blocks latent outdated messages from causing unnecessary state changes. The guard timer can be configured. The default time interval is 500 ms; the time interval ranges from 10 to 2000 ms. Hold-off timers Used by the underlying Ethernet layer to filter out intermittent link faults. The hold-off timer can be configured. The default time interval is 0 seconds; the time interval ranges from 0 to 10 seconds. Faults are reported to the ring protection mechanism only if this timer expires. Protection Switching Functionality in a Single Link Failure and Recovery The following figure illustrates protection switching functionality in a single-link failure. Figure 2: G.8032 Ethernet Ring Protection Switching in a Single-Link Failure The figure represents an Ethernet ring topology consisting of seven Ethernet ring nodes. The ring protection link (RPL) is the ring link between Ethernet ring nodes A and G. In this topology, both ends of the RPL are blocked. Ethernet ring node G is the RPL owner node, and Ethernet ring node A is the RPL neighbor node. The following sequence describes the steps followed in the single-link failure: 1 A link operates in the normal condition. 2 A failure occurs. 5
6 Protection Switching Functionality in a Single Link Failure and Recovery 3 Ethernet ring nodes C and D detect a local signal failure (SF) condition and after the hold-off time interval, block the failed ring port and perform the FDB flush. 4 Ethernet ring nodes C and D start sending Ring Automatic Protection Switching (R-APS) SF messages periodically along with the (node ID and bidirectional path-protected ring (BPR) identifier pair) on both ring ports while the SF condition persists. 5 All Ethernet ring nodes receiving an R-APS SF message perform the FDB flush. When the RPL owner node G and RPL neighbor node A receive an R-APS SF message, the Ethernet ring node unblocks its end of the RPL and performs the FDB flush. 6 All Ethernet ring nodes receiving a second R-APS SF message perform the FDB flush again; the additional FDB flush is because of the node ID and BPR-based configuration. 7 R-APS SF messages are detected on the Ethernet Ring indicating a stable SF condition. Further R-APS SF messages trigger no further action. The following figure illustrates the steps taken in a revertive operation in a single-link failure. Figure 3: Single-Link Failure Recovery (Revertive Operation) The following sequence describes the steps followed in the single-link failure revertive (recovery) operation: 1 A link operates in the stable SF condition. 2 Recovery of link failure occurs. 3 Ethernet ring nodes C and D detect clearing of the SF condition, start the guard timer, and initiate periodic transmission of the R-APS No Request (NR) messages on both ring ports. (The guard timer prevents the reception of R-APS messages.) 6
7 Ethernet Flow Points 4 When the Ethernet ring nodes receive an R-APS NR message, the node ID and BPR identifier pair of a receiving ring port is deleted and the RPL owner node starts the Wait-to-Restore (WTR) timer. 5 When the guard timer expires on Ethernet ring nodes C and D, the nodes may accept the new R-APS messages, if any. Ethernet ring node D receives an R-APS NR message with a higher node ID from Ethernet ring node C, and unblocks its nonfailed ring port. 6 When the WTR timer expires, the RPL owner node blocks its end of the RPL, sends R-APS (NR or route blocked [RB]) message with the (node ID and BPR identifier pair), and performs the FDB flush. 7 When Ethernet ring node C receives an R-APS (NR or RB) message, the node removes the block on its blocked ring ports, and stops sending R-APS NR messages. On the other hand, when the RPL neighbor node A receives an R-APS NR or RB message, the node blocks its end of the RPL. In addition, Ethernet ring nodes A to F perform the FDB flush when receiving an RAPS NR or RB message because of the node ID and BPR-based configuration. Ethernet Flow Points An Ethernet flow point (EFP) is a forwarding decision point in the provider edge (PE) router, which gives network designers flexibility to make many Layer 2 flow decisions within the interface. Many EFPs can be configured on a single physical port. (The number varies from one device to another.) EFPs are the logical demarcation points of an Ethernet virtual connection (EVC) on an interface. An EVC that uses two or more user network interfaces (UNIs) requires an EFP on the associated ingress and egress interfaces of every device that the EVC passes through. EFPs can be configured on any Layer 2 traffic port; however, they are usually configured on UNI ports. The following parameters (matching criteria) can be configured on the EFP: Frames of a specific VLAN, a VLAN range, or a list of VLANs ( or 100,103,110) Frames with no tags (untagged) Frames with identical double-tags (VLAN tags) as specified Frames with identical Class of Service (CoS) values A frame passes each configured match criterion until the correct matching point is found. If a frame does not fit any of the matching criteria, it is dropped. Default criteria can be configured to avoid dropping frames. The following types of commands can be used in an EFP: Rewrite commands In each EFP, VLAN tag management can be specified with the following actions: Pop 1) pops out a tag; 2) pops out two tags Push 1) pushes in a tag; 2) pushes in two tags Translate 1 to 1) changes a tag value; 1 to 2) pops one tag and pushes two tags; 2 to 1) pops two tags and pushes one tag; 2 to 2) changes the value for two tags Forwarding commands Each EFP specifies the forwarding command for the frames that enter the EFP. Only one forwarding command can be configured per EFP. The forwarding options are as follows: Layer 2 point-to-point forwarding to a pseudowire tunnel Multipoint bridge forwarding to a bridge domain entity 7
8 Service Instances and Associated EFPs Local switch-to-switch forwarding between two different interfaces Feature commands In each EFP, the QoS features or parameters can be changed and the ACL can be updated. Service Instances and Associated EFPs Configuring a service instance on a Layer 2 port creates a pseudoport or EFP on which you configure EVC features. Each service instance has a unique number per interface, but you can use the same number on different interfaces because service instances on different ports are not related. An EFP classifies frames from the same physical port to one of the multiple service instances associated with that port, based on user-defined criteria. Each EFP can be associated with different forwarding actions and behavior. When an EFP is created, the initial state is UP. The state changes to DOWN under the following circumstances: The EFP is explicitly shut down by a user. The main interface to which the EFP is associated is down or removed. If the EFP belongs to a bridge domain, the bridge domain is down. The EFP is forced down as an error-prevention measure of certain features. Use the service instance ethernet interface configuration command to create an EFP on a Layer 2 interface and to enter service instance configuration mode. Service instance configuration mode is used to configure all management and control data plane attributes and parameters that apply to the service instance on a per-interface basis. The service instance number is the EFP identifier. After the device enters service instance configuration mode, you can configure these options: default--sets a command to its defaults description--adds a service instance-specific description encapsulation--configures Ethernet frame match criteria exit--exits from service instance configuration mode no--negates a command or sets its defaults shutdown--takes the service instance out of service How to Configure ITU-T G.8032 Ethernet Ring Protection Switching Configuring the Ethernet Ring Profile To configure the Ethernet ring profile, complete the following steps. 8
9 Configuring the Ethernet Ring Profile SUMMARY STEPS 1. enable 2. configure terminal 3. ethernet ring g8032 profile profile-name 4. timer {guard seconds hold-off seconds wtr minutes} 5. non-revertive 6. end DETAILED STEPS Step 1 Step 2 Command or Action enable Device> enable configure terminal Purpose Enables privileged EXEC mode. Enter your password if prompted. Enters global configuration mode. Step 3 Device# configure terminal ethernet ring g8032 profile profile-name Device(config)# ethernet ring g8032 profile profile1 Creates the Ethernet ring profile and enters Ethernet ring profile configuration mode. Step 4 timer {guard seconds hold-off seconds wtr minutes} Specifies the time interval for the guard, hold-off, and Wait-to-Restore (WTR) timers. Step 5 Step 6 Device(config-erp-profile)# timer hold-off 5 non-revertive Device(config-erp-profile)# non-revertive end Specifies a nonrevertive Ethernet ring instance. By default, Ethernet ring instances are revertive. Returns to user EXEC mode. Device(config-erp-profile)# end 9
10 Configuring Ethernet CFM MEPs Configuring Ethernet CFM MEPs Configuring Ethernet Connectivity Fault Management (CFM) maintenance endpoints (MEPs) is optional although recommended for fast failure detection and CFM monitoring. When CFM monitoring is configured, note the following points: Static remote MEP (RMEP) checking should be enabled. The MEPs should be configured to enable Ethernet fault detection. For information about configuring Ethernet Connectivity Fault Management (CFM) maintenance endpoints (MEPs), see the Configuring Ethernet Connectivity Fault Management in a Service Provider Network module of the Carrier Ethernet Configuration Guide. Enabling Ethernet Fault Detection for a Service To enable Ethernet Fault Detection (EFD) for a service to achieve fast convergence, complete the following steps Note Link protection is not supported on the Cisco ASR 900 RSP3 Module. SUMMARY STEPS 1. enable 2. configure terminal 3. ethernet cfm global 4. link-protection enable 5. link-protection group management vlan vlan-id 6. link-protection group group-number pccm vlan vlan-id 7. ethernet cfm domaindomain-name level level-id [direction outward] 8. service {ma-name ma-num vlan-id vlan-id vpn-id vpn-id} [port vlan vlan-id [direction down]] 9. continuity-check [interval time loss-threshold threshold static rmep] 10. efd notify g end DETAILED STEPS Step 1 Command or Action enable Device> enable Purpose Enables privileged EXEC mode. Enter your password if prompted. 10
11 Enabling Ethernet Fault Detection for a Service Step 2 Command or Action configure terminal Purpose Enters global configuration mode. Step 3 Device# configure terminal ethernet cfm global Enables Ethernet CFM globally. Step 4 Device(config)# ethernet cfm global link-protection enable Enables link protection globally on the router. Step 5 Step 6 Device(config)# link-protection enable link-protection group management vlan vlan-id Device(config)# link-protection group management vlan 51 link-protection group group-number pccm vlan vlan-id Device(config)# link-protection group 2 pccm vlan 16 Defines the management VLAN used for link protection. Specifies an ODU-to-ODU continuity check message (P-CCM) VLAN. Step 7 ethernet cfm domaindomain-name level level-id [direction outward] Configures the CFM domain for ODU 1 and enters Ethernet CFM configuration mode. Device(config)# ethernet cfm domain G8032 level 4 Step 8 service {ma-name ma-num vlan-id vlan-id vpn-id vpn-id} [port vlan vlan-id [direction down]] Defines a maintenance association for ODU 1 and enters Ethernet CFM service instance configuration mode. Device(config-ecfm)# service 8032_service evc 8032-evc vlan 1001 direction down 11
12 Configuring the Ethernet Protection Ring Step 9 Command or Action continuity-check [interval time loss-threshold threshold static rmep] Purpose Enables the transmission of continuity check messages (CCMs). Device(config-ecfm-srv)# continuity-check interval 3.3ms Step 10 Step 11 efd notify g8032 Device(config-ecfm-srv)# efd notify g8032 end Enables CFM to notify registered protocols when a defect is detected or cleared, which matches the current fault alarm priority. Returns to user EXEC mode. Device(config-ecfm-srv)# end Configuring the Ethernet Protection Ring To configure the Ethernet Protection Ring (EPR), complete the following steps. 12
13 Configuring the Ethernet Protection Ring SUMMARY STEPS 1. enable 2. configure terminal 3. ethernet ring g8032 ring-name 4. port0 interface type number 5. monitor service instance instance-id 6. exit 7. port1 {interfacetype number none} 8. monitor service instance instance-id 9. exit 10. exclusion-list vlan-ids vlan-id 11. open-ring 12. instance instance-id 13. description descriptive-name 14. profile profile-name 15. rpl {port0 port1} {owner neighbor next-neighbor } 16. inclusion-list vlan-ids vlan-id 17. aps-channel 18. level level-value 19. port0 service instance instance-id 20. port1 service instance {instance-id none } 21. end DETAILED STEPS Step 1 Step 2 Command or Action enable Device> enable configure terminal Purpose Enables privileged EXEC mode. Enter your password if prompted. Enters global configuration mode. Step 3 Device# configure terminal ethernet ring g8032 ring-name Device(config)# ethernet ring g8032 ring1 Specifies the Ethernet ring and enters Ethernet ring port configuration mode. 13
14 Configuring the Ethernet Protection Ring Step 4 Step 5 Step 6 Command or Action port0 interface type number Device(config-erp-ring)# port0 interface fastethernet 0/1/0 Note Fastethernet ports are not supported on the ASR 900 RSP3 Module. monitor service instance instance-id Device(config-erp-ring-port)# monitor service instance 1 exit Purpose Connects port0 of the local node of the interface to the Ethernet ring and enters Ethernet ring protection mode. Assigns the Ethernet service instance to monitor the ring port (port0) and detect ring failures. Exits Ethernet ring port configuration mode. Step 7 Step 8 Step 9 Device(config-erp-ring-port)# exit port1 {interfacetype number none} Device(config-erp-ring)# port1 interface fastethernet 0/1/1 Note Fastethernet ports are not supported on the ASR 900 RSP3 Module. monitor service instance instance-id Device(config-erp-ring-port)# monitor service instance 2 exit Connects port1 of the local node of the interface to the Ethernet ring and enters Ethernet ring protection mode. Assigns the Ethernet service instance to monitor the ring port (port1) and detect ring failures. The interface (to which port1 is attached) must be a subinterface of the main interface. Exits Ethernet ring port configuration mode. Device(config-erp-ring-port)# exit Step 10 exclusion-list vlan-ids vlan-id Device(config-erp-ring)# exclusion-list vlan-ids 2 Specifies VLANs that are unprotected by the Ethernet ring protection mechanism. 14
15 Configuring the Ethernet Protection Ring Step 11 Command or Action open-ring Purpose Specifies the Ethernet ring as an open ring. Step 12 Step 13 Device(config-erp-ring)# open-ring instance instance-id Device(config-erp-ring)# instance 1 description descriptive-name Configures the Ethernet ring instance and enters Ethernet ring instance configuration mode. Specifies a descriptive name for the Ethernet ring instance. Step 14 Device(config-erp-inst)# description cisco_customer_instance profile profile-name Device(config-erp-inst)# profile profile1 Specifies the profile associated with the Ethernet ring instance. Step 15 rpl {port0 port1} {owner neighbor next-neighbor } Specifies the Ethernet ring port on the local node as the RPL owner, neighbor, or next neighbor. Device(config-erp-inst)# rpl port0 neighbor Step 16 inclusion-list vlan-ids vlan-id Device(config-erp-inst)# inclusion-list vlan-ids 11 Specifies VLANs that are protected by the Ethernet ring protection mechanism. Note VLANs should be within or equal to VLAN configured in the interface. Step 17 Step 18 aps-channel Device(config-erp-inst)# aps-channel level level-value Device(config-erp-inst-aps)# level 5 Enters Ethernet ring instance aps-channel configuration mode. Specifies the Automatic Protection Switching (APS) message level for the node on the Ethernet ring. All nodes in the Ethernet ring must be configured with the same level. 15
16 Configuring Topology Change Notification Propagation Step 19 Command or Action port0 service instance instance-id Purpose Associates APS channel information with port0. Step 20 Device(config-erp-inst-aps)# port0 service instance 100 port1 service instance {instance-id none } Associates APS channel information with port1. Step 21 Device(config-erp-inst-aps)# port1 service instance 100 end Returns to user EXEC mode. Device(config-erp-inst-aps)# end Configuring Topology Change Notification Propagation To configure topology change notification (TCN) propagation, complete the following steps. SUMMARY STEPS 1. enable 2. configure terminal 3. ethernet tcn-propagation G8032 to {REP G8032} 4. end DETAILED STEPS Step 1 Step 2 Command or Action enable Device> enable configure terminal Purpose Enables privileged EXEC mode. Enter your password if prompted. Enters global configuration mode. Device# configure terminal 16
17 Configuring a Service Instance Command or Action Purpose Step 3 ethernet tcn-propagation G8032 to {REP G8032} Device(config)# ethernet tcn-propagation G8032 to G8032 Allows topology change notification (TCN) propagation from a source protocol to a destination protocol. Source and destination protocols vary by platform and release. Step 4 end Returns to user EXEC mode. Device(config)# end Configuring a Service Instance To configure a service instance, complete the following steps. SUMMARY STEPS 1. enable 2. configure terminal 3. interface type number 4. service instance instance-id ethernet [evc-id] 5. encapsulation dot1q vlan-id [native] 6. bridge-domain bridge-id [split-horizon [group group-id]] 7. end DETAILED STEPS Step 1 Step 2 Command or Action enable Device> enable configure terminal Purpose Enables privileged EXEC mode. Enter your password if prompted. Enters global configuration mode. Device# configure terminal 17
18 Verifying the Ethernet Ring Protection (ERP) Switching Configuration Step 3 Command or Action interface type number Purpose Specifies the interface type and number. Step 4 Step 5 Step 6 Device(config)# interface fastethernet 4/0/0 service instance instance-id ethernet [evc-id] Device(config-if)# service instance 101 ethernet encapsulation dot1q vlan-id [native] Device(config-if-srv)# encapsulation dot1q 13 bridge-domain bridge-id [split-horizon [group group-id]] Creates a service instance (an instance of an EVC) on an interface and enters service instance configuration mode. Defines the matching criteria to be used in order to map ingress dot1q frames on an interface to the appropriate service instance. Binds the service instance to a bridge domain instance. Step 7 Device(config-if-srv)# bridge-domain 12 end Exits service instance configuration mode. Device(config-if-srv)# end Verifying the Ethernet Ring Protection (ERP) Switching Configuration To verify the ERP switching configuration, use one or more of the following commands in any order. 18
19 Verifying the Ethernet Ring Protection (ERP) Switching Configuration SUMMARY STEPS 1. enable 2. show ethernet ring g8032 status [ring-name] [instance [instance-id]] 3. show ethernet ring g8032 brief [ring-name] [instance [instance-id]] 4. show ethernet ring g8032 summary 5. show ethernet ring g8032 statistics [ring-name] [instance [instance-id]] 6. show ethernet ring g8032 profile [profile-name] 7. show ethernet ring g8032 port status interface [type number] 8. show ethernet ring g8032 configuration [ring-name] instance [instance-id] 9. show ethernet ring g8032 trace {ctrl [ring-name instance instance-id] sm} 10. end DETAILED STEPS Step 1 Step 2 Command or Action enable Device> enable show ethernet ring g8032 status [ring-name] [instance [instance-id]] Purpose Enables privileged EXEC mode. Enter your password if prompted. Displays a status summary for the ERP instance. Step 3 Device# show ethernet ring g8032 status RingA instance 1 show ethernet ring g8032 brief [ring-name] [instance [instance-id]] Displays a brief description of the functional state of the ERP instance. Step 4 Device# show ethernet ring g8032 brief show ethernet ring g8032 summary Device# show ethernet ring g8032 summary Displays a summary of the number of ERP instances in each state of the ERP switching process. 19
20 Verifying the Ethernet Ring Protection (ERP) Switching Configuration Step 5 Step 6 Command or Action show ethernet ring g8032 statistics [ring-name] [instance [instance-id]] Device# show ethernet ring g8032 statistics RingA instance 1 show ethernet ring g8032 profile [profile-name] Purpose Displays the number of events and Ring Automatic Protection Switching (R-APS) messages received for an ERP instance. Displays the settings for one or more ERP profiles. Device# show ethernet ring g8032 profile gold Step 7 show ethernet ring g8032 port status interface [type number] Displays Ethernet ring port status information for the interface. Device# show ethernet ring g8032 port status interface fastethernet 0/0/1 Step 8 show ethernet ring g8032 configuration [ring-name] instance [instance-id] Displays the details of the ERP instance configuration manager. Step 9 Device# show ethernet ring g8032 configuration RingA instance 1 show ethernet ring g8032 trace {ctrl [ring-name instance instance-id] sm} Displays information about ERP traces. Step 10 Device# show ethernet ring g8032 trace sm end Returns to privileged EXEC mode. Device# end 20
21 Configuration Examples for Configuration Examples for ITU-T G.8032 Ethernet Ring Protection Switching Configuring Ethernet Ring Protection Switching The following is an example of an Ethernet Ring Protection (ERP) switching configuration: ethernet ring g8032 profile profile_abc timer wtr 1 timer guard 100 timer hold-off 1 ethernet ring g8032 major_ring_abc exclusion-list vlan-ids 1000 port0 interface FastEthernet 0/0/0 monitor service instance 103 port1 interface FastEthernet 0/1/0 monitor service instance 102 instance 1 profile profile_abc rpl port0 owner inclusion-list vlan-ids 100 aps-channel port0 service instance 100 port1 service instance 100! interface FastEthernet 0/0/0 no ip address service instance 100 ethernet encapsulation dot1q 100 bridge-domain 100 service instance 200 ethernet encapsulation dot1q 200 bridge-domain 200!! interface FastEthernet 0/1/1 no ip address service instance 100 ethernet encapsulation dot1q 100 bridge-domain 100 service instance 200 ethernet encapsulation dot1q 200 bridge-domain 200!! Enabling Ethernet Fault Detection for a Service ethernet cfm domain G8032 level 4 service 8032_service evc 8032-evc vlan 1001 direction down continuity-check continuity-check interval 3.3ms offload sampling 1000 efd notify g8032 ethernet ring g8032 profile TEST timer wtr 1 timer guard
22 Verifying the Ethernet Ring Protection Configuration ethernet ring g8032 open open-ring port0 interface GigabitEthernet0/1/3 monitor service instance 1001 port1 none instance 1 profile TEST inclusion-list vlan-ids 2-500,1001 aps-channel port0 service instance 1001 port1 none!! instance 2 profile TEST rpl port0 owner inclusion-list vlan-ids 1002, aps-channel port0 service instance 1002 port1 none! interface GigabitEthernet0/1/3 no ip address load-interval 30 shutdown negotiation auto storm-control broadcast level storm-control multicast level storm-control unicast level service instance 1 ethernet encapsulation untagged l2protocol peer lldp bridge-domain 1! service instance trunk 10 ethernet encapsulation dot1q 2-500, rewrite ingress tag pop 1 symmetric bridge-domain from-encapsulation! service instance 1001 ethernet 8032-evc encapsulation dot1q 1001 rewrite ingress tag pop 1 symmetric bridge-domain 1001 cfm mep domain G8032 mpid 20! service instance 1002 ethernet 8032-evc-1 encapsulation dot1q 1002 rewrite ingress tag pop 1 symmetric bridge-domain 1002! End Verifying the Ethernet Ring Protection Configuration The following is sample output from the show ethernet ring g8032 configuration command. Use this command to verify if the configuration entered is valid and to check for any missing configuration parameters. Device# show ethernet ring g8032 configuration ethernet ring ring0 Port0: GigabitEthernet0/0/0 (Monitor: GigabitEthernet0/0/0) Port1: GigabitEthernet0/0/4 (Monitor: GigabitEthernet0/0/4) Exclusion-list VLAN IDs: Open-ring: no Instance 1 Description: Profile: opp RPL: 22
23 Additional References for Inclusion-list VLAN IDs: 2, APS channel Level: 7 Port0: Service Instance 1 Port1: Service Instance 1 State: configuration resolved Additional References for ITU-T G.8032 Ethernet Ring Protection Switching Related Documents Related Topic Ethernet Connectivity Fault Management (CFM) G.8032 Ethernet Ring Protection (ERP) administrative procedures Carrier Ethernet commands: complete command syntax, command mode, command history, defaults, usage guidelines, and examples Cisco IOS commands: master list of commands with complete command syntax, command mode, command history, defaults, usage guidelines, and examples Document Title Configuring Ethernet Connectivity Fault Management in a Service Provider Network Ring_Protection_(ERP)_Administrative_Procedures Cisco IOS Carrier Ethernet Command Reference Cisco IOS Master Commands List, All Releases Standards Standard ITU-T Title ITU-T Y.1731 OAM Mechanisms for Ethernet-Based Networks 23
24 Feature Information For Technical Assistance Description The Cisco Support and Documentation website provides online resources to download documentation, software, and tools. Use these resources to install and configure the software and to troubleshoot and resolve technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. Access to most tools on the Cisco Support and Documentation website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password. Link Feature Information For ITU-T G.8032 Ethernet Ring Protection Switching The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature. Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to. An account on Cisco.com is not required. 24
25 Feature Information For Table 1: Feature Information for Feature Name ITU-T G.8032 Ethernet Ring Protection Switching Releases 15.2(4)S 15.3(1)S Feature Information 25
26 Feature Information For Feature Name Releases Feature Information The ITU-T G.8032 Ethernet Ring Protection Switching feature implements protection switching mechanisms for Ethernet layer ring topologies. This feature uses the G.8032 Ethernet Ring Protection (ERP) protocol, defined in ITU-T G.8032, to provide protection for Ethernet traffic in a ring topology, while ensuring that no loops are within the ring at the Ethernet layer. The loops are prevented by blocking traffic on either a predetermined link or a failed link. The following commands were introduced or modified: aps-channel, clear ethernet ring g8032 statistics, debug ethernet ring g8032 errors, debug ethernet ring g8032 events, debug ethernet ring g8032 fsm, debug ethernet ring g8032 packets, description (Ethernet ring), ethernet ring g8032, ethernet ring g8032 profile, ethernet tcn-propagation, exclusion-list, inclusion-list, instance (Ethernet ring), level, monitor service instancenon-revertiveopen-ring, port0, port0 service instance, port1, port1 service instance, profile, rpl, show ethernet cfm domain, show ethernet cfm errors,show ethernet cfm maintenance-points remote, show ethernet cfm maintenance-points remote crosscheck, show ethernet ring g8032 brief, show ethernet ring g8032 configuration, show ethernet ring g8032 port status, show ethernet ring g8032 profile, show ethernet ring g8032 statistics, show ethernet ring g8032 status, show ethernet ring g8032 summary, show ethernet ring g8032 trace,show ethernet service instance and timer (Ethernet ring). 26
27 Feature Information For 27
28 Feature Information For 28
IPSLA Y1731 On-Demand and Concurrent Operations
 IPSLA Y1731 On-Demand and Concurrent Operations This module describes how to configure the IPSLA Y1731 SLM Feature Enhancements feature for enabling real-time Ethernet service troubleshooting for users
IPSLA Y1731 On-Demand and Concurrent Operations This module describes how to configure the IPSLA Y1731 SLM Feature Enhancements feature for enabling real-time Ethernet service troubleshooting for users
G.8032 Ethernet Ring Protection Overview. March, 2008 ITU-T Q9 SG 15
 G.80 Ethernet Ring Protection Overview March, 008 ITU-T Q9 SG 5 genda G.80 Recommendation Introduction G.80 Objectives and Principles G.80 Concepts G.80 Protection Switching G.80 R-PS Messages G.80 Items
G.80 Ethernet Ring Protection Overview March, 008 ITU-T Q9 SG 5 genda G.80 Recommendation Introduction G.80 Objectives and Principles G.80 Concepts G.80 Protection Switching G.80 R-PS Messages G.80 Items
Flow-Based per Port-Channel Load Balancing
 The feature allows different flows of traffic over a Gigabit EtherChannel (GEC) interface to be identified based on the packet header and then mapped to the different member links of the port channel.
The feature allows different flows of traffic over a Gigabit EtherChannel (GEC) interface to be identified based on the packet header and then mapped to the different member links of the port channel.
MPLS VPN over mgre. Finding Feature Information. Prerequisites for MPLS VPN over mgre
 The feature overcomes the requirement that a carrier support multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) by allowing you to provide MPLS connectivity between networks that are connected by IP-only networks. This
The feature overcomes the requirement that a carrier support multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) by allowing you to provide MPLS connectivity between networks that are connected by IP-only networks. This
Configuring IP SLA Service Performance Testing
 9 CHAPTER Configuring IP SLA Service Perfmance Testing First Published: July 2013 Last Updated: November 2013 This chapter describes how to configure the ITU-T Y.1564 Ethernet service perfmance test methodology
9 CHAPTER Configuring IP SLA Service Perfmance Testing First Published: July 2013 Last Updated: November 2013 This chapter describes how to configure the ITU-T Y.1564 Ethernet service perfmance test methodology
Using Link Layer Discovery Protocol in Multivendor Networks
 Using Link Layer Discovery Protocol in Multivendor Networks Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP), standardized by the IEEE as part of 802.1ab, enables standardized discovery of nodes, which in turn facilitates
Using Link Layer Discovery Protocol in Multivendor Networks Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP), standardized by the IEEE as part of 802.1ab, enables standardized discovery of nodes, which in turn facilitates
Configuring Traffic Mirroring on the Cisco ASR 9000 Series Router
 Configuring Traffic Mirring on the Cisco ASR 9000 Series Router This module describes the configuration of traffic mirring on the Cisco ASR 9000 Series Router. Traffic mirring is sometimes called pt mirring,
Configuring Traffic Mirring on the Cisco ASR 9000 Series Router This module describes the configuration of traffic mirring on the Cisco ASR 9000 Series Router. Traffic mirring is sometimes called pt mirring,
VRRPv3: Object Tracking Integration
 Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) enables a group of devices to form a single virtual device to provide redundancy. The LAN clients then can be configured with the virtual device as the default
Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) enables a group of devices to form a single virtual device to provide redundancy. The LAN clients then can be configured with the virtual device as the default
Configuring EtherChannels
 CHAPTER 12 This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on the Cisco 7600 series router Layer 2 or Layer 3 LAN ports. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter,
CHAPTER 12 This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on the Cisco 7600 series router Layer 2 or Layer 3 LAN ports. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter,
Configure IOS Catalyst Switches to Connect Cisco IP Phones Configuration Example
 Configure IOS Catalyst Switches to Connect Cisco IP Phones Configuration Example Document ID: 69632 Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Configure
Configure IOS Catalyst Switches to Connect Cisco IP Phones Configuration Example Document ID: 69632 Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Configure
Configuring a Load-Balancing Scheme
 Configuring a Load-Balancing Scheme Last Updated: October 5, 2011 This module contains information about Cisco Express Forwarding and describes the tasks for configuring a load-balancing scheme for Cisco
Configuring a Load-Balancing Scheme Last Updated: October 5, 2011 This module contains information about Cisco Express Forwarding and describes the tasks for configuring a load-balancing scheme for Cisco
Configuring Port Security
 CHAPTER 62 This chapter describes how to configure the port security feature. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, see the Cisco IOS Master List, at this URL:
CHAPTER 62 This chapter describes how to configure the port security feature. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, see the Cisco IOS Master List, at this URL:
Configuring a Load-Balancing Scheme
 Configuring a Load-Balancing Scheme Finding Feature Information Configuring a Load-Balancing Scheme Last Updated: August 15, 2011 This module contains information about Cisco Express Forwarding and describes
Configuring a Load-Balancing Scheme Finding Feature Information Configuring a Load-Balancing Scheme Last Updated: August 15, 2011 This module contains information about Cisco Express Forwarding and describes
Configuring IKEv2 Load Balancer
 The IKEv2 Load Balancer feature provides support for enabling clusters of FlexVPN gateways and distributes incoming Internet Key Exchange Version 2 (IKEv2) connection requests among FlexVPN gateways. This
The IKEv2 Load Balancer feature provides support for enabling clusters of FlexVPN gateways and distributes incoming Internet Key Exchange Version 2 (IKEv2) connection requests among FlexVPN gateways. This
Configuring Link Bundling on Cisco IOS XR Software
 Configuring Link Bundling on Cisco IOS XR Software This module describes the configuration of link bundle interfaces on the Cisco CRS Router. A link bundle is a group of one or more ports that are aggregated
Configuring Link Bundling on Cisco IOS XR Software This module describes the configuration of link bundle interfaces on the Cisco CRS Router. A link bundle is a group of one or more ports that are aggregated
GLBP - Gateway Load Balancing Protocol
 GLBP - Gateway Load Balancing Protocol Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) protects data traffic from a failed router or circuit, like Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) and Virtual Router Redundancy
GLBP - Gateway Load Balancing Protocol Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) protects data traffic from a failed router or circuit, like Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) and Virtual Router Redundancy
Configuring a Load-Balancing Scheme
 This module contains information about Cisco Express Forwarding and describes the tasks for configuring a load-balancing scheme for Cisco Express Forwarding traffic. Load-balancing allows you to optimize
This module contains information about Cisco Express Forwarding and describes the tasks for configuring a load-balancing scheme for Cisco Express Forwarding traffic. Load-balancing allows you to optimize
Ethernet Overhead Accounting
 The feature enables the router to account for downstream Ethernet frame headers when applying shaping to packets. Finding Feature Information, page 1 Restrictions for, page 1 Information About, page 2
The feature enables the router to account for downstream Ethernet frame headers when applying shaping to packets. Finding Feature Information, page 1 Restrictions for, page 1 Information About, page 2
Configuring DHCP Snooping and IP Source Guard
 CHAPTER 19 This chapter describes how to configure Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) snooping and IP Source Guard on Catalyst 4500 series switches. It provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration
CHAPTER 19 This chapter describes how to configure Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) snooping and IP Source Guard on Catalyst 4500 series switches. It provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration
Configuring Enhanced Object Tracking
 Configuring Enhanced Object Tracking First Published: May 2, 2005 Last Updated: July 1, 2009 Before the introduction of the Enhanced Object Tracking feature, the Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) had
Configuring Enhanced Object Tracking First Published: May 2, 2005 Last Updated: July 1, 2009 Before the introduction of the Enhanced Object Tracking feature, the Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) had
Configuring Auto-QoS
 Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for Auto-QoS, page 1 Restrictions for Auto-QoS, page 2 Information About, page 3 How to Configure Auto-QoS, page 5 Monitoring Auto-QoS, page 9 Configuration
Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for Auto-QoS, page 1 Restrictions for Auto-QoS, page 2 Information About, page 3 How to Configure Auto-QoS, page 5 Monitoring Auto-QoS, page 9 Configuration
Switching in an Enterprise Network
 Switching in an Enterprise Network Introducing Routing and Switching in the Enterprise Chapter 3 Version 4.0 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 Objectives Compare the types of
Switching in an Enterprise Network Introducing Routing and Switching in the Enterprise Chapter 3 Version 4.0 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 Objectives Compare the types of
Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2
 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 Course Number: ICND2 Length: 5 Day(s) Certification Exam This course will help you prepare for the following exam: 640 816: ICND2 Course Overview This course
Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 Course Number: ICND2 Length: 5 Day(s) Certification Exam This course will help you prepare for the following exam: 640 816: ICND2 Course Overview This course
Configuring DHCP Snooping
 CHAPTER 19 This chapter describes how to configure Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) snooping on Catalyst 4500 series switches. It provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples.
CHAPTER 19 This chapter describes how to configure Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) snooping on Catalyst 4500 series switches. It provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples.
Multiprotocol Label Switching Load Balancing
 Multiprotocol Label Switching Load Balancing First Published: July 2013 The Cisco ME 3800 and ME 3600 switches support IPv4 and IPv6 load balancing at the LER and LSR. Effective with Cisco IOS Release
Multiprotocol Label Switching Load Balancing First Published: July 2013 The Cisco ME 3800 and ME 3600 switches support IPv4 and IPv6 load balancing at the LER and LSR. Effective with Cisco IOS Release
CCT vs. CCENT Skill Set Comparison
 Operation of IP Data Networks Recognize the purpose and functions of various network devices such as Routers, Switches, Bridges and Hubs Select the components required to meet a given network specification
Operation of IP Data Networks Recognize the purpose and functions of various network devices such as Routers, Switches, Bridges and Hubs Select the components required to meet a given network specification
Cisco Certified Network Associate Exam. Operation of IP Data Networks. LAN Switching Technologies. IP addressing (IPv4 / IPv6)
 Cisco Certified Network Associate Exam Exam Number 200-120 CCNA Associated Certifications CCNA Routing and Switching Operation of IP Data Networks Operation of IP Data Networks Recognize the purpose and
Cisco Certified Network Associate Exam Exam Number 200-120 CCNA Associated Certifications CCNA Routing and Switching Operation of IP Data Networks Operation of IP Data Networks Recognize the purpose and
NetFlow Subinterface Support
 NetFlow Subinterface Support Feature History Release Modification 12.2(14)S This feature was introduced. 12.2(15)T This feature was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2 T. This document describes the
NetFlow Subinterface Support Feature History Release Modification 12.2(14)S This feature was introduced. 12.2(15)T This feature was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2 T. This document describes the
Configuring EtherChannels
 25 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannel interfaces. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer to the Catalyst 2950 Desktop Switch Command
25 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannel interfaces. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer to the Catalyst 2950 Desktop Switch Command
Ethernet Ring Protection for Carrier Ethernet Networks
 Ethernet Ring Protection for Carrier Ethernet Networks Jeong-dong Ryoo, ETRI Hao Long and Yang Yang, Huawei Technologies Marc Holness, Nortel Networks Zahir Ahmad and J. Kevin Rhee, Information and Communications
Ethernet Ring Protection for Carrier Ethernet Networks Jeong-dong Ryoo, ETRI Hao Long and Yang Yang, Huawei Technologies Marc Holness, Nortel Networks Zahir Ahmad and J. Kevin Rhee, Information and Communications
Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices 1 Course, Class Outline
 www.etidaho.com (208) 327-0768 Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices 1 Course, Class Outline 5 Days Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices, Part 1 (ICND1) v2.0 is a five-day, instructorled training course
www.etidaho.com (208) 327-0768 Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices 1 Course, Class Outline 5 Days Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices, Part 1 (ICND1) v2.0 is a five-day, instructorled training course
AutoQoS. Prerequisites for AutoQoS CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 63 Prerequisites for, page 63-1 Restrictions for, page 63-2 Information About, page 63-2 Default Settings for, page 63-4 How to Configure, page 63-4 For complete syntax and usage information for
CHAPTER 63 Prerequisites for, page 63-1 Restrictions for, page 63-2 Information About, page 63-2 Default Settings for, page 63-4 How to Configure, page 63-4 For complete syntax and usage information for
Note: This case study utilizes Packet Tracer. Please see the Chapter 5 Packet Tracer file located in Supplemental Materials.
 Note: This case study utilizes Packet Tracer. Please see the Chapter 5 Packet Tracer file located in Supplemental Materials. CHAPTER 5 OBJECTIVES Configure a router with an initial configuration. Use the
Note: This case study utilizes Packet Tracer. Please see the Chapter 5 Packet Tracer file located in Supplemental Materials. CHAPTER 5 OBJECTIVES Configure a router with an initial configuration. Use the
You can specify IPv4 and IPv6 addresses while performing various tasks in this feature. The resource
 The feature enables the configuration of a Virtual Private Network (VPN) routing and forwarding instance (VRF) table so that the domain name system (DNS) can forward queries to name servers using the VRF
The feature enables the configuration of a Virtual Private Network (VPN) routing and forwarding instance (VRF) table so that the domain name system (DNS) can forward queries to name servers using the VRF
How To Import Ipv4 From Global To Global On Cisco Vrf.Net (Vf) On A Vf-Net (Virtual Private Network) On Ipv2 (Vfs) On An Ipv3 (Vv
 BGP Support for IP Prefix Import from Global Table into a VRF Table The BGP Support for IP Prefix Import from Global Table into a VRF Table feature introduces the capability to import IPv4 unicast prefixes
BGP Support for IP Prefix Import from Global Table into a VRF Table The BGP Support for IP Prefix Import from Global Table into a VRF Table feature introduces the capability to import IPv4 unicast prefixes
NAT TCP SIP ALG Support
 The feature allows embedded messages of the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) passing through a device that is configured with Network Address Translation (NAT) to be translated and encoded back to the
The feature allows embedded messages of the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) passing through a device that is configured with Network Address Translation (NAT) to be translated and encoded back to the
IxNetwork TM MPLS-TP Emulation
 IxNetwork TM MPLS-TP Emulation Test the Functionality, Performance, and Scalability of an MPLS-TP Ingress, Egress, or Transit Node MPLS has come a long way since its original goal to allow core routers
IxNetwork TM MPLS-TP Emulation Test the Functionality, Performance, and Scalability of an MPLS-TP Ingress, Egress, or Transit Node MPLS has come a long way since its original goal to allow core routers
MPLS VPN Route Target Rewrite
 The feature allows the replacement of route targets on incoming and outgoing Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) updates Typically, Autonomous System Border Routers (ASBRs) perform the replacement of route targets
The feature allows the replacement of route targets on incoming and outgoing Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) updates Typically, Autonomous System Border Routers (ASBRs) perform the replacement of route targets
How To Learn Cisco Cisco Ios And Cisco Vlan
 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices: Accelerated Course CCNAX v2.0; 5 Days, Instructor-led Course Description Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices: Accelerated (CCNAX) v2.0 is a 60-hour instructor-led
Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices: Accelerated Course CCNAX v2.0; 5 Days, Instructor-led Course Description Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices: Accelerated (CCNAX) v2.0 is a 60-hour instructor-led
Configuring IP SLA - Service Performance Testing
 Configuring IP SLA - Service Performance Testing This module describes how to configure the ITU-T Y.1564 Ethernet service performance test methodology to measure the ability of a network device to carry
Configuring IP SLA - Service Performance Testing This module describes how to configure the ITU-T Y.1564 Ethernet service performance test methodology to measure the ability of a network device to carry
Chapter 7 Lab 7-1, Configuring Switches for IP Telephony Support
 Chapter 7 Lab 7-1, Configuring Switches for IP Telephony Support Topology Objectives Background Configure auto QoS to support IP phones. Configure CoS override for data frames. Configure the distribution
Chapter 7 Lab 7-1, Configuring Switches for IP Telephony Support Topology Objectives Background Configure auto QoS to support IP phones. Configure CoS override for data frames. Configure the distribution
VLANs. Application Note
 VLANs Application Note Table of Contents Background... 3 Benefits... 3 Theory of Operation... 4 IEEE 802.1Q Packet... 4 Frame Size... 5 Supported VLAN Modes... 5 Bridged Mode... 5 Static SSID to Static
VLANs Application Note Table of Contents Background... 3 Benefits... 3 Theory of Operation... 4 IEEE 802.1Q Packet... 4 Frame Size... 5 Supported VLAN Modes... 5 Bridged Mode... 5 Static SSID to Static
"Charting the Course...
 Description "Charting the Course... Course Summary Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices: Accelerated (CCNAX), is a course consisting of ICND1 and ICND2 content in its entirety, but with the content
Description "Charting the Course... Course Summary Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices: Accelerated (CCNAX), is a course consisting of ICND1 and ICND2 content in its entirety, but with the content
Objectives. The Role of Redundancy in a Switched Network. Layer 2 Loops. Broadcast Storms. More problems with Layer 2 loops
 ITE I Chapter 6 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 Objectives Implement Spanning Tree Protocols LAN Switching and Wireless Chapter 5 Explain the role of redundancy in a converged
ITE I Chapter 6 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 Objectives Implement Spanning Tree Protocols LAN Switching and Wireless Chapter 5 Explain the role of redundancy in a converged
OAM Operations Administration and Maintenance
 OAM Operations Administration and Maintenance IERU Communications Ltd OAM Rev. A Page 1 of 9 Operations Administration and Maintenance 1. Overview This paper describes the Ethernet and Multi-Protocol Label
OAM Operations Administration and Maintenance IERU Communications Ltd OAM Rev. A Page 1 of 9 Operations Administration and Maintenance 1. Overview This paper describes the Ethernet and Multi-Protocol Label
100-101: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 v2.0 (ICND1)
 100-101: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 v2.0 (ICND1) Course Overview This course provides students with the knowledge and skills to implement and support a small switched and routed network.
100-101: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 v2.0 (ICND1) Course Overview This course provides students with the knowledge and skills to implement and support a small switched and routed network.
Configuring LLDP, LLDP-MED, and Location Service
 27 CHAPTER Configuring LLDP, LLDP-MED, and Location Service This chapter describes how to configure the Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP), LLDP Media Endpoint Discovery (LLDP-MED), and Location Service
27 CHAPTER Configuring LLDP, LLDP-MED, and Location Service This chapter describes how to configure the Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP), LLDP Media Endpoint Discovery (LLDP-MED), and Location Service
Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, Configuring EtherChannel Instructor Version
 Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, Configuring EtherChannel Instructor Version Topology Objective Background Configure EtherChannel. Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer switches are Catalyst
Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, Configuring EtherChannel Instructor Version Topology Objective Background Configure EtherChannel. Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer switches are Catalyst
Configure ISDN Backup and VPN Connection
 Case Study 2 Configure ISDN Backup and VPN Connection Cisco Networking Academy Program CCNP 2: Remote Access v3.1 Objectives In this case study, the following concepts are covered: AAA authentication Multipoint
Case Study 2 Configure ISDN Backup and VPN Connection Cisco Networking Academy Program CCNP 2: Remote Access v3.1 Objectives In this case study, the following concepts are covered: AAA authentication Multipoint
Configuring VoIP Call Setup Monitoring
 The Cisco IOS IP Service Level Agreements (SLAs) VoIP Call Setup (Post-Dial Delay) Monitoring feature provides the ability to measure your network s response time for setting up a Voice over IP (VoIP)
The Cisco IOS IP Service Level Agreements (SLAs) VoIP Call Setup (Post-Dial Delay) Monitoring feature provides the ability to measure your network s response time for setting up a Voice over IP (VoIP)
Implementing MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels on Cisco IOS XR Software
 Implementing MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels on Cisco IOS XR Software The MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels feature lets you deploy Layer 3 Virtual Private Netwk (L3VPN) services, over an IP ce netwk, using L2TPv3 multipoint
Implementing MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels on Cisco IOS XR Software The MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels feature lets you deploy Layer 3 Virtual Private Netwk (L3VPN) services, over an IP ce netwk, using L2TPv3 multipoint
Link Layer Discovery Protocol
 12 Link Layer Discovery Protocol Contents Overview..................................................... 12-2 LLDP..................................................... 12-2 LLDP Messages............................................
12 Link Layer Discovery Protocol Contents Overview..................................................... 12-2 LLDP..................................................... 12-2 LLDP Messages............................................
Juniper Networks EX Series/ Cisco Catalyst Interoperability Test Results. May 1, 2009
 Juniper Networks EX Series/ Cisco Catalyst Interoperability Test Results May 1, 2009 Executive Summary Juniper Networks commissioned Network Test to assess interoperability between its EX4200 and EX8208
Juniper Networks EX Series/ Cisco Catalyst Interoperability Test Results May 1, 2009 Executive Summary Juniper Networks commissioned Network Test to assess interoperability between its EX4200 and EX8208
BFD. (Bidirectional Forwarding Detection) Does it work and is it worth it? Tom Scholl, AT&T Labs NANOG 45
 BFD (Bidirectional Forwarding Detection) Does it work and is it worth it? Tom Scholl, AT&T Labs NANOG 45 What is BFD? BFD provides a method to validate the operation of the forwarding plane between two
BFD (Bidirectional Forwarding Detection) Does it work and is it worth it? Tom Scholl, AT&T Labs NANOG 45 What is BFD? BFD provides a method to validate the operation of the forwarding plane between two
Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway
 Felix Rohrer Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1 S2 VLAN 99 192.168.99.12 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1
Felix Rohrer Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1 S2 VLAN 99 192.168.99.12 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1
Configuring Link Aggregation
 10 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure link aggregation for the ML-Series cards, both EtherChannel and packet-over-sonet/sdh (POS) channel. For additional information about the Cisco IOS commands
10 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure link aggregation for the ML-Series cards, both EtherChannel and packet-over-sonet/sdh (POS) channel. For additional information about the Cisco IOS commands
640-816: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 v1.1
 640-816: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 v1.1 Course Introduction Course Introduction Chapter 01 - Small Network Implementation Introducing the Review Lab Cisco IOS User Interface Functions
640-816: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 v1.1 Course Introduction Course Introduction Chapter 01 - Small Network Implementation Introducing the Review Lab Cisco IOS User Interface Functions
Lab 7-1 Configuring Switches for IP Telephony Support
 Lab 7-1 Configuring Switches for IP Telephony Support Learning Objectives Configure auto QoS to support IP phones Configure CoS override for data frames Configure the distribution layer to trust access
Lab 7-1 Configuring Switches for IP Telephony Support Learning Objectives Configure auto QoS to support IP phones Configure CoS override for data frames Configure the distribution layer to trust access
Service Definition. Internet Service. Introduction. Product Overview. Service Specification
 Service Definition Introduction This Service Definition describes Nexium s from the customer s perspective. In this document the product is described in terms of an overview, service specification, service
Service Definition Introduction This Service Definition describes Nexium s from the customer s perspective. In this document the product is described in terms of an overview, service specification, service
Firewall Support for SIP
 Firewall Support for SIP The Firewall Support for SIP feature integrates Cisco IOS firewalls, Voice over IP (VoIP) protocol, and Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) within a Cisco IOS-based platform, enabling
Firewall Support for SIP The Firewall Support for SIP feature integrates Cisco IOS firewalls, Voice over IP (VoIP) protocol, and Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) within a Cisco IOS-based platform, enabling
AlliedWare Plus OS How To Configure interoperation between PVST+ and RSTP or MSTP
 AlliedWare Plus OS How To Configure interoperation between PVST+ and RSTP or MSTP Introduction Spanning trees that protect networks from loops can provide better traffic load balancing if traffic in different
AlliedWare Plus OS How To Configure interoperation between PVST+ and RSTP or MSTP Introduction Spanning trees that protect networks from loops can provide better traffic load balancing if traffic in different
Virtual Private LAN Service on Cisco Catalyst 6500/6800 Supervisor Engine 2T
 White Paper Virtual Private LAN Service on Cisco Catalyst 6500/6800 Supervisor Engine 2T Introduction to Virtual Private LAN Service The Cisco Catalyst 6500/6800 Series Supervisor Engine 2T supports virtual
White Paper Virtual Private LAN Service on Cisco Catalyst 6500/6800 Supervisor Engine 2T Introduction to Virtual Private LAN Service The Cisco Catalyst 6500/6800 Series Supervisor Engine 2T supports virtual
Troubleshooting an Enterprise Network
 Troubleshooting an Enterprise Network Introducing Routing and Switching in the Enterprise Chapter 9 Released under Creative Commons License 3.0 By-Sa Cisco name, logo and materials are Copyright Cisco
Troubleshooting an Enterprise Network Introducing Routing and Switching in the Enterprise Chapter 9 Released under Creative Commons License 3.0 By-Sa Cisco name, logo and materials are Copyright Cisco
Image Verification. Finding Feature Information. Restrictions for Image Verification
 The feature allows users to automatically verify the integrity of Cisco IOS images. Thus, users can be sure that the image is protected from accidental corruption, which can occur at any time during transit,
The feature allows users to automatically verify the integrity of Cisco IOS images. Thus, users can be sure that the image is protected from accidental corruption, which can occur at any time during transit,
INTRODUCTION TO L2VPNS
 INTRODUCTION TO L2VPNS 4 Introduction to Layer 2 and Layer 3 VPN Services CE Layer 3 VPN Link Comprised of IP Traffic Passed Over IP Backbone LEGEND Layer 3 VPN Layer 2 VPN CE CE PE IP Backbone PE CE Layer
INTRODUCTION TO L2VPNS 4 Introduction to Layer 2 and Layer 3 VPN Services CE Layer 3 VPN Link Comprised of IP Traffic Passed Over IP Backbone LEGEND Layer 3 VPN Layer 2 VPN CE CE PE IP Backbone PE CE Layer
BGP Link Bandwidth. Finding Feature Information. Prerequisites for BGP Link Bandwidth
 The Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Link Bandwidth feature is used to advertise the bandwidth of an autonomous system exit link as an extended community. This feature is configured for links between directly
The Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Link Bandwidth feature is used to advertise the bandwidth of an autonomous system exit link as an extended community. This feature is configured for links between directly
Management Software. Web Browser User s Guide AT-S106. For the AT-GS950/48 Gigabit Ethernet Smart Switch. Version 1.0.0. 613-001339 Rev.
 Management Software AT-S106 Web Browser User s Guide For the AT-GS950/48 Gigabit Ethernet Smart Switch Version 1.0.0 613-001339 Rev. A Copyright 2010 Allied Telesis, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of
Management Software AT-S106 Web Browser User s Guide For the AT-GS950/48 Gigabit Ethernet Smart Switch Version 1.0.0 613-001339 Rev. A Copyright 2010 Allied Telesis, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of
Traffic Mirroring Commands on the Cisco ASR 9000 Series Router
 Traffic Mirroring Commands on the Cisco ASR 9000 Series Router This module describes the commands used to configure and monitor traffic mirroring. acl, page 2 clear monitor-session counters, page 4 destination
Traffic Mirroring Commands on the Cisco ASR 9000 Series Router This module describes the commands used to configure and monitor traffic mirroring. acl, page 2 clear monitor-session counters, page 4 destination
Configuring Switch Ports and VLAN Interfaces for the Cisco ASA 5505 Adaptive Security Appliance
 CHAPTER 4 Configuring Switch Ports and VLAN Interfaces for the Cisco ASA 5505 Adaptive Security Appliance This chapter describes how to configure the switch ports and VLAN interfaces of the ASA 5505 adaptive
CHAPTER 4 Configuring Switch Ports and VLAN Interfaces for the Cisco ASA 5505 Adaptive Security Appliance This chapter describes how to configure the switch ports and VLAN interfaces of the ASA 5505 adaptive
Chapter 7 Configuring Trunk Groups and Dynamic Link Aggregation
 Chapter 7 Configuring Trunk Groups and Dynamic Link Aggregation This chapter describes how to configure trunk groups and 802.3ad link aggregation. Trunk groups are manually-configured aggregate links containing
Chapter 7 Configuring Trunk Groups and Dynamic Link Aggregation This chapter describes how to configure trunk groups and 802.3ad link aggregation. Trunk groups are manually-configured aggregate links containing
DHCP Server Port-Based Address Allocation
 The feature provides port-based address allocation support on the Cisco IOS Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server for the Ethernet platform. The DHCP server provides address assignment support
The feature provides port-based address allocation support on the Cisco IOS Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server for the Ethernet platform. The DHCP server provides address assignment support
Firewall Stateful Inspection of ICMP
 The feature categorizes Internet Control Management Protocol Version 4 (ICMPv4) messages as either malicious or benign. The firewall uses stateful inspection to trust benign ICMPv4 messages that are generated
The feature categorizes Internet Control Management Protocol Version 4 (ICMPv4) messages as either malicious or benign. The firewall uses stateful inspection to trust benign ICMPv4 messages that are generated
Configuring IPS High Bandwidth Using EtherChannel Load Balancing
 Configuring IPS High Bandwidth Using EtherChannel Load Balancing This guide helps you to understand and deploy the high bandwidth features available with IPS v5.1 when used in conjunction with the EtherChannel
Configuring IPS High Bandwidth Using EtherChannel Load Balancing This guide helps you to understand and deploy the high bandwidth features available with IPS v5.1 when used in conjunction with the EtherChannel
Fundamentals of Switching
 1 CCNA 640-801 Exam Notes - Fundamentals of Switching CCNA 640-801 Exam Notes Fundamentals of Switching 1. LAN Segmentation 1.1 In a collision domain, a frame sent by a device can cause collision with
1 CCNA 640-801 Exam Notes - Fundamentals of Switching CCNA 640-801 Exam Notes Fundamentals of Switching 1. LAN Segmentation 1.1 In a collision domain, a frame sent by a device can cause collision with
Configuring Traffic Storm Control
 39 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure the traffic storm control feature on the Catalyst 6500 series switches. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter,
39 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure the traffic storm control feature on the Catalyst 6500 series switches. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter,
BGP Support for Next-Hop Address Tracking
 The feature is enabled by default when a supporting Cisco software image is installed. BGP next-hop address tracking is event driven. BGP prefixes are automatically tracked as peering sessions are established.
The feature is enabled by default when a supporting Cisco software image is installed. BGP next-hop address tracking is event driven. BGP prefixes are automatically tracked as peering sessions are established.
Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and Catalyst Switches Running CatOS
 Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and Catalyst Switches Running CatOS Document ID: 23408 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components
Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and Catalyst Switches Running CatOS Document ID: 23408 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components
QoS Switching. Two Related Areas to Cover (1) Switched IP Forwarding (2) 802.1Q (Virtual LANs) and 802.1p (GARP/Priorities)
 QoS Switching H. T. Kung Division of Engineering and Applied Sciences Harvard University November 4, 1998 1of40 Two Related Areas to Cover (1) Switched IP Forwarding (2) 802.1Q (Virtual LANs) and 802.1p
QoS Switching H. T. Kung Division of Engineering and Applied Sciences Harvard University November 4, 1998 1of40 Two Related Areas to Cover (1) Switched IP Forwarding (2) 802.1Q (Virtual LANs) and 802.1p
TRILL for Data Center Networks
 24.05.13 TRILL for Data Center Networks www.huawei.com enterprise.huawei.com Davis Wu Deputy Director of Switzerland Enterprise Group E-mail: wuhuajun@huawei.com Tel: 0041-798658759 Agenda 1 TRILL Overview
24.05.13 TRILL for Data Center Networks www.huawei.com enterprise.huawei.com Davis Wu Deputy Director of Switzerland Enterprise Group E-mail: wuhuajun@huawei.com Tel: 0041-798658759 Agenda 1 TRILL Overview
Rohde & Schwarz R&S SITLine ETH VLAN Encryption Device Functionality & Performance Tests
 Rohde & Schwarz R&S Encryption Device Functionality & Performance Tests Introduction Following to our test of the Rohde & Schwarz ETH encryption device in April 28 the European Advanced Networking Test
Rohde & Schwarz R&S Encryption Device Functionality & Performance Tests Introduction Following to our test of the Rohde & Schwarz ETH encryption device in April 28 the European Advanced Networking Test
Configuring QoS. Understanding QoS CHAPTER
 24 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure quality of service (QoS) by using standard QoS commands. With QoS, you can give preferential treatment to certain types of traffic at the expense of others.
24 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure quality of service (QoS) by using standard QoS commands. With QoS, you can give preferential treatment to certain types of traffic at the expense of others.
INTERCONNECTING CISCO NETWORK DEVICES PART 1 V2.0 (ICND 1)
 INTERCONNECTING CISCO NETWORK DEVICES PART 1 V2.0 (ICND 1) COURSE OVERVIEW: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices, Part 1 (ICND1) v2.0 is a five-day, instructor-led training course that teaches learners
INTERCONNECTING CISCO NETWORK DEVICES PART 1 V2.0 (ICND 1) COURSE OVERVIEW: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices, Part 1 (ICND1) v2.0 is a five-day, instructor-led training course that teaches learners
Configuring the Device for Access Point Discovery
 Configuring the Device for Access Point Discovery Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for Configuring the Device for Access Point Discovery, page 1 Restrictions for Configuring the Device
Configuring the Device for Access Point Discovery Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for Configuring the Device for Access Point Discovery, page 1 Restrictions for Configuring the Device
Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices, Part 1 (ICND1) v3.0
 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices, Part 1 (ICND1) v3.0 COURSE OVERVIEW: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices, Part 1 (ICND1) v3.0 is a five-day, instructor-led training course that teaches learners
Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices, Part 1 (ICND1) v3.0 COURSE OVERVIEW: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices, Part 1 (ICND1) v3.0 is a five-day, instructor-led training course that teaches learners
Virtual Leased Lines - Martini
 Virtual Lease Lines - Martini Virtual Leased Lines - Martini Martini Drafts draft -martini-l2circuit-encap-mpls -04.txt defines the handling and encapsulation of layer two packets. draft -martini-l2circuit-trans-mpls
Virtual Lease Lines - Martini Virtual Leased Lines - Martini Martini Drafts draft -martini-l2circuit-encap-mpls -04.txt defines the handling and encapsulation of layer two packets. draft -martini-l2circuit-trans-mpls
Catalyst Layer 3 Switch for Wake On LAN Support Across VLANs Configuration Example
 Catalyst Layer 3 Switch for Wake On LAN Support Across VLANs Configuration Example Document ID: 91672 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information
Catalyst Layer 3 Switch for Wake On LAN Support Across VLANs Configuration Example Document ID: 91672 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information
Configuring NetFlow-lite
 CHAPTER 55 Note NetFlow-lite is only supported on Catalyst 4948E Ethernet Switch. This chapter describes how to configure NetFlow-lite on the Catalyst 4948E switch. NetFlow-lite provides traffic monitoring
CHAPTER 55 Note NetFlow-lite is only supported on Catalyst 4948E Ethernet Switch. This chapter describes how to configure NetFlow-lite on the Catalyst 4948E switch. NetFlow-lite provides traffic monitoring
What is VLAN Routing?
 Application Note #38 February 2004 What is VLAN Routing? This Application Notes relates to the following Dell product(s): 6024 and 6024F 33xx Abstract Virtual LANs (VLANs) offer a method of dividing one
Application Note #38 February 2004 What is VLAN Routing? This Application Notes relates to the following Dell product(s): 6024 and 6024F 33xx Abstract Virtual LANs (VLANs) offer a method of dividing one
Getting Started with Configuring Cisco IOS NetFlow and NetFlow Data Export
 Getting Started with Configuring Cisco IOS NetFlow and NetFlow Data Export Last Updated: November 28, 2011 This module contains the minimum amount of information about and instructions necessary for configuring
Getting Started with Configuring Cisco IOS NetFlow and NetFlow Data Export Last Updated: November 28, 2011 This module contains the minimum amount of information about and instructions necessary for configuring
Sampled NetFlow. Feature Overview. Benefits
 Sampled NetFlow This feature module describes the Sampled NetFlow feature. It includes information on the benefits of the new feature, supported platforms, supported standards, and the commands necessary
Sampled NetFlow This feature module describes the Sampled NetFlow feature. It includes information on the benefits of the new feature, supported platforms, supported standards, and the commands necessary
How To Configure Voice Vlan On An Ip Phone
 1 VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) is used to logically divide a physical network into several broadcast domains. VLAN membership can be configured through software instead of physically relocating devices
1 VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) is used to logically divide a physical network into several broadcast domains. VLAN membership can be configured through software instead of physically relocating devices
Abstract. MEP; Reviewed: GAK 10/17/2005. Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes 2005 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
 Configuring Single Instance Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) between an Avaya C360 Converged Switch and HP ProCurve Networking Switches to support Avaya IP Telephony Issue 1.0 Abstract These Application
Configuring Single Instance Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) between an Avaya C360 Converged Switch and HP ProCurve Networking Switches to support Avaya IP Telephony Issue 1.0 Abstract These Application
Configuring Redundancy
 7 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure redundancy and contains these sections: Configuring Fault Tolerance, page 7-1 Configuring HSRP, page 7-5 Configuring Interface and Device Tracking, page
7 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure redundancy and contains these sections: Configuring Fault Tolerance, page 7-1 Configuring HSRP, page 7-5 Configuring Interface and Device Tracking, page
Configuring Static and Dynamic NAT Simultaneously
 Configuring Static and Dynamic NAT Simultaneously Document ID: 13778 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configuring NAT Related Information Introduction In some
Configuring Static and Dynamic NAT Simultaneously Document ID: 13778 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configuring NAT Related Information Introduction In some
Configuring QoS and Per Port Per VLAN QoS
 27 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure quality of service (QoS) by using automatic QoS (auto-qos) commands or by using standard QoS commands on a Catalyst 45 series switch. It also describes
27 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure quality of service (QoS) by using automatic QoS (auto-qos) commands or by using standard QoS commands on a Catalyst 45 series switch. It also describes
MPLS Layer 2 VPNs Functional and Performance Testing Sample Test Plans
 MPLS Layer 2 VPNs Functional and Performance Testing Sample Test Plans Contents Overview 1 1. L2 VPN Padding Verification Test 1 1.1 Objective 1 1.2 Setup 1 1.3 Input Parameters 2 1.4 Methodology 2 1.5
MPLS Layer 2 VPNs Functional and Performance Testing Sample Test Plans Contents Overview 1 1. L2 VPN Padding Verification Test 1 1.1 Objective 1 1.2 Setup 1 1.3 Input Parameters 2 1.4 Methodology 2 1.5
AWS Direct Connect. User Guide API Version 2013-10-22
 AWS Direct Connect User Guide AWS Direct Connect: User Guide AWS Direct Connect User Guide Table of Contents What is AWS Direct Connect?... 1 Requirements... 1 How Do I...?... 2 Getting Started... 3 Getting
AWS Direct Connect User Guide AWS Direct Connect: User Guide AWS Direct Connect User Guide Table of Contents What is AWS Direct Connect?... 1 Requirements... 1 How Do I...?... 2 Getting Started... 3 Getting
QoS: Color-Aware Policer
 QoS: Color-Aware Policer First Published: August 26, 2003 Last Updated: February 28, 2006 The QoS: Color-Aware Policer enables a color-aware method of traffic policing. This feature allows you to police
QoS: Color-Aware Policer First Published: August 26, 2003 Last Updated: February 28, 2006 The QoS: Color-Aware Policer enables a color-aware method of traffic policing. This feature allows you to police
Network Configuration Example
 Network Configuration Example Configuring Multiple Port Mirroring Sessions on EX4200 Switches Published: 2014-04-09 Juniper Networks, Inc. 1194 North Mathilda Avenue Sunnyvale, California 94089 USA 408-745-2000
Network Configuration Example Configuring Multiple Port Mirroring Sessions on EX4200 Switches Published: 2014-04-09 Juniper Networks, Inc. 1194 North Mathilda Avenue Sunnyvale, California 94089 USA 408-745-2000
Lab 3.10.2 Use Network Inspector to Observe STP Behavior
 Lab 3.10.2 Use Network Inspector to Observe STP Behavior Objective The purpose of this lab is to observe STP behavior with the Network Inspector switch trace feature. Scenario A new switched network has
Lab 3.10.2 Use Network Inspector to Observe STP Behavior Objective The purpose of this lab is to observe STP behavior with the Network Inspector switch trace feature. Scenario A new switched network has
