Configuring DHCP Snooping and IP Source Guard
|
|
|
- Marcia Mason
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CHAPTER 19 This chapter describes how to configure Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) snooping and IP Source Guard on Catalyst 4500 series switches. It provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter consists of the following major sections: Overview of DHCP Snooping, page 19-1 Configuring DHCP Snooping on the Switch, page 19-3 Displaying DHCP Snooping Information, page Overview of IP Source Guard, page Configuring IP Source Guard on the Switch, page Displaying IP Source Guard Information, page For complete syntax and usage information for the switch commands used in this chapter, refer to the Catalyst 4500 Series Switch Cisco IOS Command Reference and related publications at Overview of DHCP Snooping DHCP snooping is a DHCP security feature that provides security by filtering untrusted DHCP messages and by building and maintaining a DHCP snooping binding table. An untrusted message is a message that is received from outside the network or firewall and that can cause traffic attacks within your network. The DHCP snooping binding table contains the MAC address, IP address, lease time, binding type, VLAN number, and interface information that corresponds to the local untrusted interfaces of a switch; it does not contain information regarding hosts interconnected with a trusted interface. An untrusted interface is an interface that is configured to receive messages from outside the network or firewall. A trusted interface is an interface that is configured to receive only messages from within the network. DHCP snooping acts like a firewall between untrusted hosts and DHCP servers. It also gives you a way to differentiate between untrusted interfaces connected to the end-user and trusted interfaces connected to the DHCP server or another switch. In order to enable DHCP snooping on a VLAN, you must enable DHCP snooping on the switch. 19-1
2 Overview of DHCP Snooping Chapter 19 You can configure DHCP snooping for switches and VLANs. When you enable DHCP snooping on a switch, the interface acts as a Layer 2 bridge, intercepting and safeguarding DHCP messages going to a Layer 2 VLAN. When you enable DHCP snooping on a VLAN, the switch acts as a Layer 2 bridge within a VLAN domain. Overview of the DHCP Snooping Database Agent To retain the bindings across switch reloads, you must use the DHCP snooping database agent. Without this agent, the bindings established by DHCP snooping are lost upon switch reload. Connectivity is lost as well. The mechanism for the database agent stores the bindings in a file at a configured location. Upon reload, the switch reads the file to build the database for the bindings. The switch keeps the file current by writing to the file as the database changes. The format of the file that contains the bindings is as follows: <initial-checksum> TYPE DHCP-SNOOPING VERSION 1 BEGIN <entry-1> <checksum-1> <entry-2> <checksum-1-2> <entry-n> <checksum n> END Each entry in the file is tagged with a checksum that is used to validate the entries whenever the file is read. The <initial-checksum> entry on the first line helps distinguish entries associated with the latest write from entries that are associated with a previous write. This is a sample bindings file: 3ebe1518 TYPE DHCP-SNOOPING VERSION 1 BEGIN EBE2881 Gi1/1 e5e1e EBE2881 Gi1/1 4b3486ec EBE2881 Gi1/1 f0e EBE2881 Gi1/1 ac41adf EBE2881 Gi1/1 34b3273e END Each entry holds an IP address, VLAN, MAC address, lease time (in hex), and the interface associated with a binding. At the end of each entry is a checksum that accounts for all the bytes from the start of the file through all the bytes associated with the entry. Each entry consists of 72 bytes of data, followed by a space, followed by a checksum. Upon bootup, when the calculated checksum equals the stored checksum, a switch reads entries from the file and adds the bindings to the DHCP snooping database. When the calculated checksum does not equal the stored checksum, the entry read from the file is ignored and so are all the entries following the failed entry. The switch also ignores all those entries from the file whose lease time has expired. (This is possible because the lease time might indicate an expired time.) An entry from the file is also ignored if the interface referred to in the entry, no longer exists on the system or if it is a router port or a DHCP snooping-trusted interface. 19-2
3 Chapter 19 Configuring DHCP Snooping on the Switch When a switch learns of new bindings or when it loses some bindings, the switch writes the modified set of entries from the snooping database to the file. The writes are performed with a configurable delay to batch as many changes as possible before the actual write happens. Associated with each transfer is a timeout after which a transfer is aborted if it is not completed. These timers are referred to as the write delay and abort timeout. Configuring DHCP Snooping on the Switch When you configure DHCP snooping on your switch, you are enabling the switch to differentiate untrusted interfaces from trusted interfaces. You must enable DHCP snooping globally before you can use DHCP snooping on a VLAN. You can enable DHCP snooping independently from other DHCP features. Once you have enabled DHCP snooping, all the DHCP relay information option configuration commands are disabled; this includes the following commands: ip dhcp relay information check ip dhcp relay information policy ip dhcp relay information trusted ip dhcp relay information trust-all These sections describe how to configure DHCP snooping: Default Configuration for DHCP Snooping, page 19-3 Enabling DHCP Snooping, page 19-4 Enabling DHCP Snooping on Private VLAN, page 19-5 Enabling the DHCP Snooping Database Agent, page 19-6 Configuration Examples for the Database Agent, page 19-6 For DHCP server configuration information, refer to Configuring DHCP in the Cisco IOS IP and IP Routing Configuration Guide at: Default Configuration for DHCP Snooping DHCP snooping is disabled by default. Table 19-1 shows all the default configuration values for each DHCP snooping option. Table 19-1 Default Configuration Values for DHCP Snooping Option DHCP snooping DHCP snooping information option DHCP snooping limit rate DHCP snooping trust DHCP snooping vlan Default Value/State Disabled Enabled Infinite (functions as if rate limiting were disabled) Untrusted Disabled 19-3
4 Configuring DHCP Snooping on the Switch Chapter 19 If you want to change the default configuration values, see the Enabling DHCP Snooping section. Enabling DHCP Snooping When DHCP snooping is enabled globally, DHCP requests are dropped until the ports are configured. Consequently, you should probably this feature during a maintenance window and not during production. To enable DHCP snooping, perform this task: Command Purpose Step 1 Switch(config)# ip dhcp snooping Enables DHCP snooping globally. You can use the no keyword to disable DHCP snooping. Step 2 Switch(config)# ip dhcp snooping vlan number [number] vlan {vlan range}] Enables DHCP snooping on your VLAN or VLAN range Step 3 Switch(config-if)# ip dhcp snooping trust Configures the interface as trusted or untrusted. You can use the no keyword to configure an interface to receive messages from an untrusted client. Step 4 Switch(config-if)# ip dhcp snooping limit rate rate Configures the number of DHCP packets per second (pps) that an interface can receive. 1 Step 5 Switch(config)# end Exits configuration mode. Step 6 show ip dhcp snooping Verifies the configuration. 1. Cisco recommends not configuring the untrusted interface rate limit to more than 100 packets per second. The recommended rate limit for each untrusted client is 15 packets per second. Normally, the rate limit applies to untrusted interfaces. If you want to set up rate limiting for trusted interfaces, keep in mind that trusted interfaces aggregate all DHCP traffic in the switch, and you will need to adjust the rate limit to a higher value. You should fine tune this threshold depending on the network configuration. The CPU should not receive DHCP packets at a sustained rate of more than 1,000 packets per second You can configure DHCP snooping for a single VLAN or a range of VLANs. To configure a single VLAN, enter a single VLAN number. To configure a range of VLANs, enter a beginning and an ending VLAN number or a dash and range of VLANs. This example shows how to enable DHCP snooping on VLANs 10 through 100: configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Switch(config)# ip dhcp snooping Switch(config)# ip dhcp snooping vlan Switch(config)# interface GigabitEthernet 5/1 Switch(config-if)# ip dhcp snooping trust Switch(config-if)# interface FastEthernet 2/1 Switch(config-if)# ip dhcp snooping limit rate 100 Switch(config)# end show ip dhcp snooping Switch DHCP snooping is enabled. 19-4
5 Chapter 19 Configuring DHCP Snooping on the Switch DHCP Snooping is configured on the following VLANs: Insertion of option 82 information is enabled. Interface Trusted Rate limit (pps) FastEthernet2/1 yes 100 FastEthernet2/2 yes none FastEthernet3/1 no 20 GigabitEthernet5/1 yes none The following configuration describes the DHCP snooping configuration steps if routing is defined on another Catalyst switch (for example, Catalyst 6500): // Trust the uplink gigabit Ethernet trunk port interface range GigabitEthernet 1/1 2 switchport mode trunk switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q ip dhcp snooping trust! interface VLAN 14 ip address ip helper-address If you are enabling trunking on uplink gigabit interfaces and have the above routing defined on Catalyst 6500, you must configure the trust" relationship with downstream DHCP Snooping (4500) which adds Option 82. On Catalyst 6500, this is accomplished with ip dhcp relay information trusted VLAN configuration command. Enabling DHCP Snooping on Private VLAN DHCP snooping can be enabled on private VLANs, which provide isolation between Layer 2 ports within the same VLAN. If DHCP snooping is enabled (or disabled), the configuration is propagated to both the primary VLAN and its associated secondary VLANs. You cannot enable (or disable) DHCP snooping on a primary VLAN without reflecting this configuration change on the secondary VLANs. Configuring DHCP snooping on a secondary VLAN is still allowed, but it will not take effect if the associated primary VLAN is already configured. If the associated primary VLAN is configured, the effective DHCP snooping mode on the secondary VLAN is derived from the corresponding primary VLAN. Manually configuring DHCP snooping on a secondary VLAN will cause the switch to issue this warning message: DHCP Snooping configuration may not take effect on secondary vlan XXX The show ip dhcp snooping command will display all VLANs (both primary and secondary) that have DHCP snooping enabled. 19-5
6 Configuring DHCP Snooping on the Switch Chapter 19 Enabling the DHCP Snooping Database Agent To configure the database agent, perform one or more of the following tasks: Command Switch(config)# ip dhcp snooping database { url write-delay seconds timeout seconds } Switch(config)# no ip dhcp snooping database [write-delay timeout] show ip dhcp snooping database [detail] clear ip dhcp snooping database statistics renew ip dhcp snooping database [validation none] [url] ip dhcp snooping binding mac-addr vlan vlan ipaddr interface ifname expiry lease-in-seconds Purpose (Required) Configures a URL for the database agent (or file) and the related timeout values. (Optional) Displays the current operating state of the database agent and statistics associated with the transfers. (Optional) Clears the statistics associated with the database agent. (Optional) Requests the read entries from a file at the given URL. (Optional) Adds/deletes bindings to the snooping database. no ip dhcp snooping binding mac-addr vlan vlan ipaddr interface ifname Because both NVRAM and bootflash have limited storage capacity, storing a file on an TFTP server is preferred. Moreover, when a file is stored in a remote location accessible through TFTP, an RPR standby supervisor engine can take over the binding list when a switchover occurs. Network-based URLs (such as TFTP and FTP) require that you create an empty file at the configured URL before the switch can write the set of bindings for the first time. Configuration Examples for the Database Agent The following examples show how to use the above commands. Example 1: Enabling the Database Agent The following example shows how to configure the DHCP snooping database agent to store the bindings at a given location and to view the configuration and operating state: configure terminal Switch(config)# ip dhcp snooping database tftp:// /directory/file Switch(config)# end show ip dhcp snooping database detail Agent URL : tftp:// /directory/file Write delay Timer : 300 seconds Abort Timer : 300 seconds 19-6
7 Chapter 19 Configuring DHCP Snooping on the Switch Agent Running : No Delay Timer Expiry : 7 (00:00:07) Abort Timer Expiry : Not Running Last Succeded Time : None Last Failed Time : 17:14:25 UTC Sat Jul Last Failed Reason : Unable to access URL. Total Attempts : 21 Startup Failures : 0 Successful Transfers : 0 Failed Transfers : 21 Successful Reads : 0 Failed Reads : 0 Successful Writes : 0 Failed Writes : 21 Media Failures : 0 First successful access: Read Last ignored bindings counters : Binding Collisions : 0 Expired leases : 0 Invalid interfaces : 0 Unsupported vlans : 0 Parse failures : 0 Last Ignored Time : None Total ignored bindings counters: Binding Collisions : 0 Expired leases : 0 Invalid interfaces : 0 Unsupported vlans : 0 Parse failures : 0 The first three lines of output show the configured URL and related timer configuration values. The next three lines show the operating state and the amount of time left for expiry of write delay and abort timers. Among the statistics shown in the output, startup failures indicate the number of attempts the read or create of the file has failed upon bootup. Because the location is based off in the network, you must create a temporary file on the TFTP server. You can create a temporary file on a typical UNIX workstation by creating a 0 byte file file in the directory directory that can be referenced by the TFTP server daemon. With some server implementations on UNIX workstations, the file should be provided with full (777) permissions for write access to the file. DHCP snooping bindings are keyed on the MAC address and VLAN combination. Therefore, if an entry in the remote file has an entry for a given MAC address and VLAN set, for which the switch already has a binding, the entry from the remote file is ignored when the file is read. This condition is referred to as the binding collision. An entry in a file may no longer be valid because the lease indicated by the entry may have expired by the time it is read. The expired leases counter indicates the number of bindings ignored because of this condition. The Invalid interfaces counter refers to the number of bindings that have been ignored when the interface referred by the entry either does not exist on the system or is a router or DHCP snooping trusted interface if it exists, when the read happened. Unsupported VLANs refers to the number of entries that have been ignored because the indicated VLAN is not supported on the system. The Parse failures counter provides the number of entries that have been ignored when the switch is unable to interpret the meaning of the entries from the file. 19-7
8 Configuring DHCP Snooping on the Switch Chapter 19 The switch maintains two sets of counters for these ignored bindings. One provides the counters for a read that has at least one binding ignored by at least one of these conditions. These counters are shown as the Last ignored bindings counters. The total ignored bindings counters provides a sum of the number of bindings that have been ignored because of all the reads since the switch bootup. These two set of counters are cleared by the clear command. Therefore, the total counter set may indicate the number of bindings that have been ignored since the last clear. Example 2: Reading Binding Entries from a TFTP File To manually read the entries from a tftp file, perform this task: Command Purpose Step 1 sh ip dhcp snooping database Displays the DHCP snooping database agent statistics. Step 2 renew ip dhcp snoop data url Directs the switch to read the file from given URL. Step 3 sh ip dhcp snoop data Displays the read status. Step 4 sh ip dhcp snoop bind Verifies whether the bindings were read successfully. This is an example of how to manually read entries from the tftp:// /directory/file: sh ip dhcp snooping database Agent URL : Write delay Timer : 300 seconds Abort Timer : 300 seconds Agent Running : No Delay Timer Expiry : Not Running Abort Timer Expiry : Not Running Last Succeded Time : None Last Failed Time : None Last Failed Reason : No failure recorded. Total Attempts : 0 Startup Failures : 0 Successful Transfers : 0 Failed Transfers : 0 Successful Reads : 0 Failed Reads : 0 Successful Writes : 0 Failed Writes : 0 Media Failures : 0 renew ip dhcp snoop data tftp:// /directory/file Loading directory/file from (via GigabitEthernet1/1):! [OK bytes] Database downloaded successfully. 00:01:29: %DHCP_SNOOPING-6-AGENT_OPERATION_SUCCEEDED: DHCP snooping database Read succeeded. sh ip dhcp snoop data Agent URL : Write delay Timer : 300 seconds Abort Timer : 300 seconds Agent Running : No Delay Timer Expiry : Not Running Abort Timer Expiry : Not Running 19-8
9 Chapter 19 Configuring DHCP Snooping on the Switch Last Succeded Time : 15:24:34 UTC Sun Jul Last Failed Time : None Last Failed Reason : No failure recorded. Total Attempts : 1 Startup Failures : 0 Successful Transfers : 1 Failed Transfers : 0 Successful Reads : 1 Failed Reads : 0 Successful Writes : 0 Failed Writes : 0 Media Failures : 0 sh ip dhcp snoop bind MacAddress IpAddress Lease(sec) Type VLAN Interface :01:00:01:00: dhcp-snooping 512 GigabitEthernet1/1 00:01:00:01:00: dhcp-snooping 512 GigabitEthernet1/1 00:01:00:01:00: dhcp-snooping 1536 GigabitEthernet1/1 00:01:00:01:00: dhcp-snooping 1024 GigabitEthernet1/1 00:01:00:01:00: dhcp-snooping 1 GigabitEthernet1/1 clear ip dhcp snoop bind sh ip dhcp snoop bind MacAddress IpAddress Lease(sec) Type VLAN Interface Example 3: Adding Information to the DHCP Snooping Database To manually add a binding to the DHCP snooping database, perform the following task: Command Purpose Step 1 show ip dhcp snooping binding Views the DHCP snooping database Step 2 ip dhcp snooping binding binding-id vlan vlan-id interface interface expiry lease-time Adds the binding using the 'ip dhcp snooping' exec command Step 3 show ip dhcp snooping binding Checks the DHCP snooping database This example shows how to manually add a binding to the DHCP snooping database: show ip dhcp snooping binding MacAddress IpAddress Lease(sec) Type VLAN Interface ip dhcp snooping binding vlan interface gi1/1 expiry 1000 show ip dhcp snooping binding MacAddress IpAddress Lease(sec) Type VLAN Interface :01:00:01:00: dhcp-snooping 1 GigabitEthernet1/1 19-9
10 Displaying DHCP Snooping Information Chapter 19 Displaying DHCP Snooping Information You can display a DHCP snooping binding table and configuration information for all interfaces on a switch. Displaying a Binding Table The DHCP snooping binding table for each switch contains binding entries that correspond to untrusted ports. The table does not contain information about hosts interconnected with a trusted port because each interconnected switch will have its own DHCP snooping binding table. This example shows how to display the DHCP snooping binding information for a switch: sh ip dhcp snooping binding MacAddress IpAddress Lease(sec) Type VLAN Interface :02:B3:3F:3B: dhcp-snooping 10 FastEthernet6/10 Table 19-2 describes the fields in the show ip dhcp snooping binding command output. Table 19-2 show ip dhcp snooping binding Command Output Field MAC Address IP Address Lease (seconds) Type VLAN Interface Description Client hardware MAC address Client IP address assigned from the DHCP server IP address lease time Binding type; dynamic binding learned by dhcp-snooping or statically-configured binding. VLAN number of the client interface Interface that connects to the DHCP client host Displaying the DHCP Snooping Configuration This example shows how to display the DHCP snooping configuration for a switch. show ip dhcp snooping Switch DHCP snooping is enabled. DHCP Snooping is configured on the following VLANs: Insertion of option 82 information is enabled. Interface Trusted Rate limit (pps) FastEthernet2/1 yes 10 FastEthernet3/1 yes none GigabitEthernet1/1 no
11 Chapter 19 Overview of IP Source Guard Overview of IP Source Guard Similar to DHCP snooping, this feature is enabled on a DHCP snooping untrusted Layer 2 port. Initially, all IP traffic on the port is blocked except for DHCP packets that are captured by the DHCP snooping process. When a client receives a valid IP address from the DHCP server, or when a static IP source binding is configured by the user, a per-port and VLAN Access Control List (PVACL) is installed on the port. This process restricts the client IP traffic to those source IP addresses configured in the binding; any IP traffic with a source IP address other than that in the IP source binding will be filtered out. This filtering limits a host s ability to attack the network by claiming a neighbor host's IP address. If IP Source Guard is enabled on a trunk port with a large number of VLANs that have DHCP snooping enabled, you might run out of ACL hardware resources and some packets might be switched in software. IP Source Guard supports only the Layer 2 port, including both access and trunk. For each untrusted Layer 2 port, there are two levels of IP traffic security filtering: Source IP address filter IP traffic is filtered based on its source IP address. Only IP traffic with a source IP address that matches the IP source binding entry is permitted. An IP source address filter is changed when a new IP source entry binding is created or deleted on the port. The port PVACL will be recalculated and reapplied in the hardware to reflect the IP source binding change. By default, if the IP filter is enabled without any IP source binding on the port, a default PVACL that denies all IP traffic is installed on the port. Similarly, when the IP filter is disabled, any IP source filter PVACL will be removed from the interface. Source IP and MAC address filter IP traffic is filtered based on its source IP address as well as its MAC address; only IP traffic with source IP and MAC addresses matching the IP source binding entry are permitted. When IP source guard is enabled in IP and MAC filtering mode, the DHCP snooping option 82 must be enabled to ensure that the DHCP protocol works properly. Without option 82 data, the switch cannot locate the client host port to forward the DHCP server reply. Instead, the DHCP server reply is dropped and the client cannot obtain an IP address. Configuring IP Source Guard on the Switch To enable IP Source Guard, perform this task: Command Purpose Step 1 Switch(config)# ip dhcp snooping Enables DHCP snooping globally. You can use the no keyword to disable DHCP snooping. Step 2 Switch(config)# ip dhcp snooping vlan number [number] Enables DHCP snooping on your VLANs. Step 3 Switch(config-if)# no ip dhcp snooping trust Configures the interface as trusted or untrusted. You can use the no keyword of to configure an interface to receive only messages from within the network
12 Configuring IP Source Guard on the Switch Chapter 19 Step 4 Step 5 Step 6 Command Switch(config-if)# ip verify source vlan dhcp-snooping port-security Switch(config-if)# switchport port-security limit rate invalid-source-mac N Switch(config)# ip source binding mac-address vlan vlan-id ip-address interface interface-name Purpose Enables IP source guard, source IP, and source MAC address filtering on the port. Enables security rate limiting for learned source MAC addresses on the port. This limit only applies to the port where IP Source Guard is enabled as filtering both IP and MAC addresses. Configures a static IP binding on the port. Step 7 Switch(config)# end Exits configuration mode. Step 8 show ip verify source interface Verifies the configuration. interface-name The static IP source binding can only be configured on switch port. If you issue the ip source binding vlan interface command on a Layer 3 port, you will receive this error message: Static IP source binding can only be configured on switch port. This example shows how to enable per-layer 2-port IP source guard on VLANs 10 through 20: configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Switch(config)# ip dhcp snooping Switch(config)# ip dhcp snooping vlan Switch(config)# interface fa6/1 Switch(config-if)# switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q Switch(config-if)# switchport mode trunk Switch(config-if)# switchport trunk native vlan 10 Switch(config-if)# switchport trunk allowed vlan Switch(config-if)# no ip dhcp snooping trust Switch(config-if)# ip verify source vlan dhcp-snooping Switch(config)# end sh ip verify source interface f6/1 Interface Filter-type Filter-mode IP-address Mac-address Vlan Fa6/1 ip-mac active Fa6/1 ip-mac active deny-all The output shows that there is one valid DHCP binding to VLAN
13 Chapter 19 Displaying IP Source Guard Information Configuring IP Source Guard on Private VLANs For private VLAN ports, you must enable DHCP snooping on primary VLANs in order for IP source guard to be effective. IP source guard on a primary VLAN will automatically propagate to a secondary VLAN. Configuring a static IP source binding on a secondary VLAN is allowed, but it will not take effect. When manually configuring a static IP source binding on a secondary VLAN, you will receive the following warning: Warning IP source filter may not take effect on secondary vlan where IP source binding is configured. If private vlan feature is enabled, IP source filter on primary vlan will automatically propagate to all secondary vlans. Displaying IP Source Guard Information You can display IP Source Guard PVACL information for all interfaces on a switch using the show ip verify source command. This example shows displayed PVACLs if DHCP snooping is enabled on VLAN 10 through 20, if interface fa6/1 is configured for IP filtering, and if there is an existing IP address binding on VLAN 10: Interface Filter-type Filter-mode IP-address Mac-address Vlan fa6/1 ip active fa6/1 ip active deny-all The second entry shows that a default PVACL (deny all IP traffic) is installed on the port for those snooping-enabled VLANs that do not have a valid IP source binding. This example shows displayed PVACL for a trusted port: Interface Filter-type Filter-mode IP-address Mac-address Vlan fa6/2 ip inactive-trust-port This example shows displayed PVACL for a port in a VLAN not configured for DHCP snooping: Interface Filter-type Filter-mode IP-address Mac-address Vlan fa6/3 ip inactive-no-snooping-vlan This example shows displayed PVACLs for a port with multiple bindings configured for an IP/MAC filtering: Interface Filter-type Filter-mode IP-address Mac-address Vlan fa6/4 ip-mac active aaaa.bbbb.cccc 10 fa6/4 ip-mac active aaaa.bbbb.cccd 11 fa6/4 ip-mac active deny-all deny-all
14 Displaying IP Source Binding Information Chapter 19 This example shows displayed PVACLs for a port configured for IP/MAC filtering but not for port security: Interface Filter-type Filter-mode IP-address Mac-address Vlan fa6/5 ip-mac active permit-all 10 fa6/5 ip-mac active deny-all permit-all The MAC filter shows permit-all because port security is not enabled, so the MAC filter cannot apply to the port/vlan and is effectively disabled. Always enable port security first. This example shows displayed error message when issuing the show ip verify source command on a port that does not have an IP source filter mode configured: IP Source Guard is not configured on the interface fa6/6. You can also use the show ip verify source command to display all interfaces on the switch that have IP source guard enabled: Interface Filter-type Filter-mode IP-address Mac-address Vlan fa6/1 ip active fa6/1 ip active deny-all fa6/2 ip inactive-trust-port fa6/3 ip inactive-no-snooping-vlan fa6/4 ip-mac active aaaa.bbbb.cccc 10 fa6/4 ip-mac active aaaa.bbbb.cccd 11 fa6/4 ip-mac active deny-all deny-all fa6/5 ip-mac active permit-all 10 fa6/5 ip-mac active deny-all permit-all Displaying IP Source Binding Information You can display all IP source bindings configured on all interfaces on a switch using the show ip source binding command. sh ip source binding MacAddress IpAddress Lease(sec) Type VLAN Interface :02:B3:3F:3B: dhcp-snooping 10 FastEthernet6/10 00:00:00:0A:00:0B infinite static 10 FastEthernet6/10 Table 19-3 describes the fields in the show ip source binding command output. Table 19-3 show ip source binding Command Output Field MAC Address IP Address Lease (seconds) Type Description Client hardware MAC address Client IP address assigned from the DHCP server IP address lease time Binding type; static bindings configured from CLI to dynamic binding learned from DHCP Snooping 19-14
15 Chapter 19 Displaying IP Source Binding Information Table 19-3 Field VLAN Interface show ip source binding Command Output (continued) Description VLAN number of the client interface Interface that connects to the DHCP client host 19-15
16 Displaying IP Source Binding Information Chapter
Configuring DHCP Snooping
 CHAPTER 19 This chapter describes how to configure Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) snooping on Catalyst 4500 series switches. It provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples.
CHAPTER 19 This chapter describes how to configure Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) snooping on Catalyst 4500 series switches. It provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples.
Security Considerations in IP Telephony Network Configuration
 Security Considerations in IP Telephony Network Configuration Abstract This Technical Report deals with fundamental security settings in networks to provide secure VoIP services. Example configurations
Security Considerations in IP Telephony Network Configuration Abstract This Technical Report deals with fundamental security settings in networks to provide secure VoIP services. Example configurations
Configuring Port Security
 32 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure port security on Catalyst 4500 series switches. It provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. Note For complete syntax and usage information
32 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure port security on Catalyst 4500 series switches. It provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. Note For complete syntax and usage information
Note: This case study utilizes Packet Tracer. Please see the Chapter 5 Packet Tracer file located in Supplemental Materials.
 Note: This case study utilizes Packet Tracer. Please see the Chapter 5 Packet Tracer file located in Supplemental Materials. CHAPTER 5 OBJECTIVES Configure a router with an initial configuration. Use the
Note: This case study utilizes Packet Tracer. Please see the Chapter 5 Packet Tracer file located in Supplemental Materials. CHAPTER 5 OBJECTIVES Configure a router with an initial configuration. Use the
Configuring NetFlow-lite
 CHAPTER 55 Note NetFlow-lite is only supported on Catalyst 4948E Ethernet Switch. This chapter describes how to configure NetFlow-lite on the Catalyst 4948E switch. NetFlow-lite provides traffic monitoring
CHAPTER 55 Note NetFlow-lite is only supported on Catalyst 4948E Ethernet Switch. This chapter describes how to configure NetFlow-lite on the Catalyst 4948E switch. NetFlow-lite provides traffic monitoring
Configuring Port Security
 CHAPTER 62 This chapter describes how to configure the port security feature. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, see the Cisco IOS Master List, at this URL:
CHAPTER 62 This chapter describes how to configure the port security feature. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, see the Cisco IOS Master List, at this URL:
Chapter 25 DHCP Snooping
 Chapter 25 DHCP Snooping Introduction...25-2 The Binding Database... 25-2 DHCP Filtering... 25-4 DHCP Option 82... 25-4 DHCP Snooping ARP Security... 25-5 Configuration Examples...25-5 Command Reference...25-6
Chapter 25 DHCP Snooping Introduction...25-2 The Binding Database... 25-2 DHCP Filtering... 25-4 DHCP Option 82... 25-4 DHCP Snooping ARP Security... 25-5 Configuration Examples...25-5 Command Reference...25-6
Configuring Redundancy
 7 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure redundancy and contains these sections: Configuring Fault Tolerance, page 7-1 Configuring HSRP, page 7-5 Configuring Interface and Device Tracking, page
7 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure redundancy and contains these sections: Configuring Fault Tolerance, page 7-1 Configuring HSRP, page 7-5 Configuring Interface and Device Tracking, page
Configure IOS Catalyst Switches to Connect Cisco IP Phones Configuration Example
 Configure IOS Catalyst Switches to Connect Cisco IP Phones Configuration Example Document ID: 69632 Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Configure
Configure IOS Catalyst Switches to Connect Cisco IP Phones Configuration Example Document ID: 69632 Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Configure
Configuring Network Security with ACLs
 CHAPTER 46 This chapter describes how to use access control lists (ACLs) to configure network security on the Catalyst 4500 series switches. The Catalyst 4500 series switch supports time-based ACLs. For
CHAPTER 46 This chapter describes how to use access control lists (ACLs) to configure network security on the Catalyst 4500 series switches. The Catalyst 4500 series switch supports time-based ACLs. For
Configuring the Transparent or Routed Firewall
 5 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to set the firewall mode to routed or transparent, as well as how the firewall works in each firewall mode. This chapter also includes information about customizing
5 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to set the firewall mode to routed or transparent, as well as how the firewall works in each firewall mode. This chapter also includes information about customizing
Configuring LLDP, LLDP-MED, and Location Service
 27 CHAPTER Configuring LLDP, LLDP-MED, and Location Service This chapter describes how to configure the Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP), LLDP Media Endpoint Discovery (LLDP-MED), and Location Service
27 CHAPTER Configuring LLDP, LLDP-MED, and Location Service This chapter describes how to configure the Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP), LLDP Media Endpoint Discovery (LLDP-MED), and Location Service
Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, Configuring EtherChannel Instructor Version
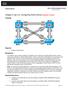 Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, Configuring EtherChannel Instructor Version Topology Objective Background Configure EtherChannel. Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer switches are Catalyst
Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, Configuring EtherChannel Instructor Version Topology Objective Background Configure EtherChannel. Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer switches are Catalyst
Catalyst Layer 3 Switch for Wake On LAN Support Across VLANs Configuration Example
 Catalyst Layer 3 Switch for Wake On LAN Support Across VLANs Configuration Example Document ID: 91672 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information
Catalyst Layer 3 Switch for Wake On LAN Support Across VLANs Configuration Example Document ID: 91672 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information
Configuring EtherChannels
 25 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannel interfaces. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer to the Catalyst 2950 Desktop Switch Command
25 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannel interfaces. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer to the Catalyst 2950 Desktop Switch Command
LAYER 2 ATTACKS & MITIGATION TECHNIQUES
 LAYER 2 ATTACKS & MITIGATION TECHNIQUES Yusuf Bhaiji Cisco Systems 1 Agenda Layer 2 Attack Landscape Attacks and Countermeasures VLAN Hopping MAC Attacks DHCP Attacks ARP Attack Spoofing Attacks Summary
LAYER 2 ATTACKS & MITIGATION TECHNIQUES Yusuf Bhaiji Cisco Systems 1 Agenda Layer 2 Attack Landscape Attacks and Countermeasures VLAN Hopping MAC Attacks DHCP Attacks ARP Attack Spoofing Attacks Summary
Configuring Static and Dynamic NAT Translation
 This chapter contains the following sections: Network Address Translation Overview, page 1 Information About Static NAT, page 2 Dynamic NAT Overview, page 3 Timeout Mechanisms, page 4 NAT Inside and Outside
This chapter contains the following sections: Network Address Translation Overview, page 1 Information About Static NAT, page 2 Dynamic NAT Overview, page 3 Timeout Mechanisms, page 4 NAT Inside and Outside
DHCP Server Port-Based Address Allocation
 The feature provides port-based address allocation support on the Cisco IOS Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server for the Ethernet platform. The DHCP server provides address assignment support
The feature provides port-based address allocation support on the Cisco IOS Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server for the Ethernet platform. The DHCP server provides address assignment support
- Virtual LANs (VLANs) and VTP -
 1 - Virtual LANs (VLANs) and VTP - Collision vs. Broadcast Domains A collision domain is simply defined as any physical segment where a collision can occur. Hubs can only operate at half-duplex, and thus
1 - Virtual LANs (VLANs) and VTP - Collision vs. Broadcast Domains A collision domain is simply defined as any physical segment where a collision can occur. Hubs can only operate at half-duplex, and thus
Network security includes the detection and prevention of unauthorized access to both the network elements and those devices attached to the network.
 By: Ziad Zubidah CCNP Security IT Security Officer National Information Technology Center Network security includes the detection and prevention of unauthorized access to both the network elements and
By: Ziad Zubidah CCNP Security IT Security Officer National Information Technology Center Network security includes the detection and prevention of unauthorized access to both the network elements and
CCT vs. CCENT Skill Set Comparison
 Operation of IP Data Networks Recognize the purpose and functions of various network devices such as Routers, Switches, Bridges and Hubs Select the components required to meet a given network specification
Operation of IP Data Networks Recognize the purpose and functions of various network devices such as Routers, Switches, Bridges and Hubs Select the components required to meet a given network specification
How To Configure InterVLAN Routing on Layer 3 Switches
 How To Configure InterVLAN Routing on Layer 3 Switches Document ID: 41860 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure InterVLAN Routing Task Step by Step Instructions
How To Configure InterVLAN Routing on Layer 3 Switches Document ID: 41860 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure InterVLAN Routing Task Step by Step Instructions
Configuring EtherChannels
 CHAPTER 12 This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on the Cisco 7600 series router Layer 2 or Layer 3 LAN ports. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter,
CHAPTER 12 This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on the Cisco 7600 series router Layer 2 or Layer 3 LAN ports. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter,
Lab 3.5.1: Basic VLAN Configuration (Instructor Version)
 (Instructor Version) Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0
(Instructor Version) Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0
Configuring Switch Ports and VLAN Interfaces for the Cisco ASA 5505 Adaptive Security Appliance
 CHAPTER 4 Configuring Switch Ports and VLAN Interfaces for the Cisco ASA 5505 Adaptive Security Appliance This chapter describes how to configure the switch ports and VLAN interfaces of the ASA 5505 adaptive
CHAPTER 4 Configuring Switch Ports and VLAN Interfaces for the Cisco ASA 5505 Adaptive Security Appliance This chapter describes how to configure the switch ports and VLAN interfaces of the ASA 5505 adaptive
Configuring the Cisco IOS In-Service Software Upgrade Process
 CHAPTER 6 Configuring the Cisco IOS In-Service Software Upgrade Process Starting with Cisco IOS 12.2(31)SGA, ISSU is supported on the Catalyst 4500. All line cards are supported. Operating on redundant
CHAPTER 6 Configuring the Cisco IOS In-Service Software Upgrade Process Starting with Cisco IOS 12.2(31)SGA, ISSU is supported on the Catalyst 4500. All line cards are supported. Operating on redundant
Catalyst 6500/6000 Switches NetFlow Configuration and Troubleshooting
 Catalyst 6500/6000 Switches NetFlow Configuration and Troubleshooting Document ID: 70974 Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Configure Network Diagram
Catalyst 6500/6000 Switches NetFlow Configuration and Troubleshooting Document ID: 70974 Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Configure Network Diagram
Configuring Flexible NetFlow
 CHAPTER 62 Note Flexible NetFlow is only supported on Supervisor Engine 7-E, Supervisor Engine 7L-E, and Catalyst 4500X. Flow is defined as a unique set of key fields attributes, which might include fields
CHAPTER 62 Note Flexible NetFlow is only supported on Supervisor Engine 7-E, Supervisor Engine 7L-E, and Catalyst 4500X. Flow is defined as a unique set of key fields attributes, which might include fields
Configuring Network Load Balancing for vethernet
 Configuring Network Load Balancing for vethernet This chapter contains the following sections: Information About Microsoft Network Load Balancing, page 1 Guidelines and Limitations, page 1 Configuring
Configuring Network Load Balancing for vethernet This chapter contains the following sections: Information About Microsoft Network Load Balancing, page 1 Guidelines and Limitations, page 1 Configuring
GLBP - Gateway Load Balancing Protocol
 GLBP - Gateway Load Balancing Protocol Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) protects data traffic from a failed router or circuit, like Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) and Virtual Router Redundancy
GLBP - Gateway Load Balancing Protocol Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) protects data traffic from a failed router or circuit, like Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) and Virtual Router Redundancy
Command Manual - Network Protocol Quidway S3000 Series Ethernet Switches. Table of Contents
 Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 ARP Configuration Commands... 1-1 1.1 ARP Configuration Commands... 1-1 1.1.1 arp static... 1-1 1.1.2 arp timer aging... 1-2 1.1.3 debugging arp packet...
Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 ARP Configuration Commands... 1-1 1.1 ARP Configuration Commands... 1-1 1.1.1 arp static... 1-1 1.1.2 arp timer aging... 1-2 1.1.3 debugging arp packet...
Apache CloudStack 4.x (incubating) Network Setup: excerpt from Installation Guide. Revised February 28, 2013 2:32 pm Pacific
 Apache CloudStack 4.x (incubating) Network Setup: excerpt from Installation Guide Revised February 28, 2013 2:32 pm Pacific Apache CloudStack 4.x (incubating) Network Setup: excerpt from Installation Guide
Apache CloudStack 4.x (incubating) Network Setup: excerpt from Installation Guide Revised February 28, 2013 2:32 pm Pacific Apache CloudStack 4.x (incubating) Network Setup: excerpt from Installation Guide
Configuring MAC ACLs
 Send document comments to [email protected] 12 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure MAC access lists (ACLs) on NX-OS devices. This chapter includes the following sections: Information
Send document comments to [email protected] 12 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure MAC access lists (ACLs) on NX-OS devices. This chapter includes the following sections: Information
LiveAction Application Note
 LiveAction Application Note Layer 2 Monitoring and Host Location Using LiveAction to monitor and identify inter-/intra-switch VLAN configurations, and locating workstations within the network infrastructure.
LiveAction Application Note Layer 2 Monitoring and Host Location Using LiveAction to monitor and identify inter-/intra-switch VLAN configurations, and locating workstations within the network infrastructure.
Enabling NetFlow and NetFlow Data Export (NDE) on Cisco Catalyst Switches
 Enabling NetFlow and NetFlow Data Export (NDE) on Cisco Catalyst Switches Revised 2/1/2007 Introduction...2 Requirements...2 Catalyst 4500 Series...2 Enabling NetFlow...2 Configuring a NetFlow Destination...3
Enabling NetFlow and NetFlow Data Export (NDE) on Cisco Catalyst Switches Revised 2/1/2007 Introduction...2 Requirements...2 Catalyst 4500 Series...2 Enabling NetFlow...2 Configuring a NetFlow Destination...3
Configuring NetFlow. Information About NetFlow. NetFlow Overview. Send document comments to [email protected]. CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 16 This chapter describes how to configure the NetFlow feature on Cisco NX-OS devices. This chapter includes the following sections: Information About NetFlow, page 16-1 Licensing Requirements
CHAPTER 16 This chapter describes how to configure the NetFlow feature on Cisco NX-OS devices. This chapter includes the following sections: Information About NetFlow, page 16-1 Licensing Requirements
NetFlow Aggregation. Feature Overview. Aggregation Cache Schemes
 NetFlow Aggregation This document describes the Cisco IOS NetFlow Aggregation feature, which allows Cisco NetFlow users to summarize NetFlow export data on an IOS router before the data is exported to
NetFlow Aggregation This document describes the Cisco IOS NetFlow Aggregation feature, which allows Cisco NetFlow users to summarize NetFlow export data on an IOS router before the data is exported to
Configuring IPS High Bandwidth Using EtherChannel Load Balancing
 Configuring IPS High Bandwidth Using EtherChannel Load Balancing This guide helps you to understand and deploy the high bandwidth features available with IPS v5.1 when used in conjunction with the EtherChannel
Configuring IPS High Bandwidth Using EtherChannel Load Balancing This guide helps you to understand and deploy the high bandwidth features available with IPS v5.1 when used in conjunction with the EtherChannel
Configuring QoS and Per Port Per VLAN QoS
 27 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure quality of service (QoS) by using automatic QoS (auto-qos) commands or by using standard QoS commands on a Catalyst 45 series switch. It also describes
27 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure quality of service (QoS) by using automatic QoS (auto-qos) commands or by using standard QoS commands on a Catalyst 45 series switch. It also describes
Configuring Link Aggregation
 10 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure link aggregation for the ML-Series cards, both EtherChannel and packet-over-sonet/sdh (POS) channel. For additional information about the Cisco IOS commands
10 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure link aggregation for the ML-Series cards, both EtherChannel and packet-over-sonet/sdh (POS) channel. For additional information about the Cisco IOS commands
Monitoring and Analyzing Switch Operation
 B Monitoring and Analyzing Switch Operation Contents Overview..................................................... B-3....................................... B-4 Menu Access To Status and Counters.........................
B Monitoring and Analyzing Switch Operation Contents Overview..................................................... B-3....................................... B-4 Menu Access To Status and Counters.........................
Configuring NetFlow. Information About NetFlow. NetFlow Overview. Send document comments to [email protected]. CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 19 This chapter describes how to configure the NetFlow feature on Cisco NX-OS devices. This chapter includes the following sections: Information About NetFlow, page 19-1 Licensing Requirements
CHAPTER 19 This chapter describes how to configure the NetFlow feature on Cisco NX-OS devices. This chapter includes the following sections: Information About NetFlow, page 19-1 Licensing Requirements
LAYER 2 ATTACKS & MITIGATION TECHNIQUES
 LAYER 2 ATTACKS & MITIGATION TECHNIQUES SANOG8 Karachi 1 st August 2006 Yusuf Bhaiji Cisco Systems 1 Agenda Layer 2 Attack Landscape Attacks and Countermeasures Spanning Tree Attack VLAN Hopping MAC Attacks
LAYER 2 ATTACKS & MITIGATION TECHNIQUES SANOG8 Karachi 1 st August 2006 Yusuf Bhaiji Cisco Systems 1 Agenda Layer 2 Attack Landscape Attacks and Countermeasures Spanning Tree Attack VLAN Hopping MAC Attacks
Chapter 7 Lab 7-1, Configuring Switches for IP Telephony Support
 Chapter 7 Lab 7-1, Configuring Switches for IP Telephony Support Topology Objectives Background Configure auto QoS to support IP phones. Configure CoS override for data frames. Configure the distribution
Chapter 7 Lab 7-1, Configuring Switches for IP Telephony Support Topology Objectives Background Configure auto QoS to support IP phones. Configure CoS override for data frames. Configure the distribution
Cisco IOS Flexible NetFlow Command Reference
 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman Drive San Jose, CA 95134-1706 USA http://www.cisco.com Tel: 408 526-4000 800 553-NETS (6387) Fax: 408 527-0883 THE SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION
Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman Drive San Jose, CA 95134-1706 USA http://www.cisco.com Tel: 408 526-4000 800 553-NETS (6387) Fax: 408 527-0883 THE SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION
Configuring Switch Ports and VLAN Interfaces for the Cisco ASA 5505 Adaptive Security Appliance
 CHAPTER 5 Configuring Switch Ports and VLAN Interfaces for the Cisco ASA 5505 Adaptive Security Appliance This chapter describes how to configure the switch ports and VLAN interfaces of the ASA 5505 adaptive
CHAPTER 5 Configuring Switch Ports and VLAN Interfaces for the Cisco ASA 5505 Adaptive Security Appliance This chapter describes how to configure the switch ports and VLAN interfaces of the ASA 5505 adaptive
Cisco Certified Network Associate Exam. Operation of IP Data Networks. LAN Switching Technologies. IP addressing (IPv4 / IPv6)
 Cisco Certified Network Associate Exam Exam Number 200-120 CCNA Associated Certifications CCNA Routing and Switching Operation of IP Data Networks Operation of IP Data Networks Recognize the purpose and
Cisco Certified Network Associate Exam Exam Number 200-120 CCNA Associated Certifications CCNA Routing and Switching Operation of IP Data Networks Operation of IP Data Networks Recognize the purpose and
Monitoring Traffic Interception
 CHAPTER 2 This chapter describes how to use traffic interception to monitor your WAAS devices and contains the following sections: Verifying WCCPv2 Interception, page 2-1 Verifying Inline Interception,
CHAPTER 2 This chapter describes how to use traffic interception to monitor your WAAS devices and contains the following sections: Verifying WCCPv2 Interception, page 2-1 Verifying Inline Interception,
Use MAC-Forced Forwarding with DHCP Snooping to Create Enhanced Private VLANs
 How To Use MAC-Forced Forwarding with DHCP Snooping to Create Enhanced Private VLANs Introduction In a large network where internal users cannot be trusted, it is nearly impossible to stop a host from
How To Use MAC-Forced Forwarding with DHCP Snooping to Create Enhanced Private VLANs Introduction In a large network where internal users cannot be trusted, it is nearly impossible to stop a host from
Lab 3.10.2 Use Network Inspector to Observe STP Behavior
 Lab 3.10.2 Use Network Inspector to Observe STP Behavior Objective The purpose of this lab is to observe STP behavior with the Network Inspector switch trace feature. Scenario A new switched network has
Lab 3.10.2 Use Network Inspector to Observe STP Behavior Objective The purpose of this lab is to observe STP behavior with the Network Inspector switch trace feature. Scenario A new switched network has
CT5760 Controller and Catalyst 3850 Switch Configuration Example
 CT5760 Controller and Catalyst 3850 Switch Configuration Example Document ID: 116342 Contributed by Antoine KMEID and Serge Yasmine, Cisco TAC Engineers. Aug 13, 2013 Contents Introduction Prerequisites
CT5760 Controller and Catalyst 3850 Switch Configuration Example Document ID: 116342 Contributed by Antoine KMEID and Serge Yasmine, Cisco TAC Engineers. Aug 13, 2013 Contents Introduction Prerequisites
Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and Catalyst Switches Running CatOS
 Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and Catalyst Switches Running CatOS Document ID: 23408 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components
Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and Catalyst Switches Running CatOS Document ID: 23408 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components
Configuring iscsi Multipath
 CHAPTER 13 Revised: April 27, 2011, OL-20458-01 This chapter describes how to configure iscsi multipath for multiple routes between a server and its storage devices. This chapter includes the following
CHAPTER 13 Revised: April 27, 2011, OL-20458-01 This chapter describes how to configure iscsi multipath for multiple routes between a server and its storage devices. This chapter includes the following
Network Detector Setup and Configuration
 339 N. Bernardo Avenue, Suite 200 Mountain View, CA 94043 www.airtightnetworks.net MODE SYST RPS MASTR STAT SPEDUPLX STACK 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 91 0 11 12 1X 2X 11X 12X 13 14 15 16 1718 19 20 2122 23 24 13X
339 N. Bernardo Avenue, Suite 200 Mountain View, CA 94043 www.airtightnetworks.net MODE SYST RPS MASTR STAT SPEDUPLX STACK 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 91 0 11 12 1X 2X 11X 12X 13 14 15 16 1718 19 20 2122 23 24 13X
What is VLAN Routing?
 Application Note #38 February 2004 What is VLAN Routing? This Application Notes relates to the following Dell product(s): 6024 and 6024F 33xx Abstract Virtual LANs (VLANs) offer a method of dividing one
Application Note #38 February 2004 What is VLAN Routing? This Application Notes relates to the following Dell product(s): 6024 and 6024F 33xx Abstract Virtual LANs (VLANs) offer a method of dividing one
Virtual PortChannel Quick Configuration Guide
 Virtual PortChannel Quick Configuration Guide Overview A virtual PortChannel (vpc) allows links that are physically connected to two different Cisco Nexus 5000 Series devices to appear as a single PortChannel
Virtual PortChannel Quick Configuration Guide Overview A virtual PortChannel (vpc) allows links that are physically connected to two different Cisco Nexus 5000 Series devices to appear as a single PortChannel
Lab 8.3.13 Configure Cisco IOS Firewall CBAC
 Lab 8.3.13 Configure Cisco IOS Firewall CBAC Objective Scenario Topology In this lab, the students will complete the following tasks: Configure a simple firewall including CBAC using the Security Device
Lab 8.3.13 Configure Cisco IOS Firewall CBAC Objective Scenario Topology In this lab, the students will complete the following tasks: Configure a simple firewall including CBAC using the Security Device
642 523 Securing Networks with PIX and ASA
 642 523 Securing Networks with PIX and ASA Course Number: 642 523 Length: 1 Day(s) Course Overview This course is part of the training for the Cisco Certified Security Professional and the Cisco Firewall
642 523 Securing Networks with PIX and ASA Course Number: 642 523 Length: 1 Day(s) Course Overview This course is part of the training for the Cisco Certified Security Professional and the Cisco Firewall
- EtherChannel - Port Aggregation
 1 Port Aggregation - EtherChannel - A network will often span across multiple switches. Trunk ports are usually used to connect switches together. There are two issues with using only a single physical
1 Port Aggregation - EtherChannel - A network will often span across multiple switches. Trunk ports are usually used to connect switches together. There are two issues with using only a single physical
NetFlow Subinterface Support
 NetFlow Subinterface Support Feature History Release Modification 12.2(14)S This feature was introduced. 12.2(15)T This feature was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2 T. This document describes the
NetFlow Subinterface Support Feature History Release Modification 12.2(14)S This feature was introduced. 12.2(15)T This feature was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2 T. This document describes the
Lab 8.1.10.2 Introduction to the Modular QoS Command-Line Interface
 Lab 8.1.10.2 Introduction to the Modular QoS Command-Line Interface Objective Configuring Quality of Service (QoS) involves classifying, marking, and policing traffic flows. It is often necessary to apply
Lab 8.1.10.2 Introduction to the Modular QoS Command-Line Interface Objective Configuring Quality of Service (QoS) involves classifying, marking, and policing traffic flows. It is often necessary to apply
Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices 1 Course, Class Outline
 www.etidaho.com (208) 327-0768 Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices 1 Course, Class Outline 5 Days Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices, Part 1 (ICND1) v2.0 is a five-day, instructorled training course
www.etidaho.com (208) 327-0768 Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices 1 Course, Class Outline 5 Days Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices, Part 1 (ICND1) v2.0 is a five-day, instructorled training course
Cisco - Catalyst 2950 Series Switches Quality of Service (QoS) FAQ
 Page 1 of 8 Catalyst 2950 Series Switches Quality of Service (QoS) FAQ Document ID: 46523 TAC Notice: What's C han g i n g o n T A C We b H el p u s h el p y ou. Questions Introduction What is the software
Page 1 of 8 Catalyst 2950 Series Switches Quality of Service (QoS) FAQ Document ID: 46523 TAC Notice: What's C han g i n g o n T A C We b H el p u s h el p y ou. Questions Introduction What is the software
ProCurve Networking. Hardening ProCurve Switches. Technical White Paper
 ProCurve Networking Hardening ProCurve Switches Technical White Paper Executive Summary and Purpose... 3 Insecure Protocols and Secure Alternatives... 3 Telnet vs. Secure Shell... 3 HTTP vs. HTTPS... 3
ProCurve Networking Hardening ProCurve Switches Technical White Paper Executive Summary and Purpose... 3 Insecure Protocols and Secure Alternatives... 3 Telnet vs. Secure Shell... 3 HTTP vs. HTTPS... 3
Configuring the Switch IP Address and Default Gateway
 CHAPTER 3 Configuring the Switch IP Address and Default Gateway This chapter describes how to configure the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway on the Catalyst enterprise LAN switches. Note For
CHAPTER 3 Configuring the Switch IP Address and Default Gateway This chapter describes how to configure the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway on the Catalyst enterprise LAN switches. Note For
- Advanced IOS Functions -
 1 The Configuration Register - Advanced IOS Functions - The configuration register (config-register) is a hexadecimal value that controls various aspects of how a router boots, including: Baud Rate Boot
1 The Configuration Register - Advanced IOS Functions - The configuration register (config-register) is a hexadecimal value that controls various aspects of how a router boots, including: Baud Rate Boot
AutoQoS. Prerequisites for AutoQoS CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 63 Prerequisites for, page 63-1 Restrictions for, page 63-2 Information About, page 63-2 Default Settings for, page 63-4 How to Configure, page 63-4 For complete syntax and usage information for
CHAPTER 63 Prerequisites for, page 63-1 Restrictions for, page 63-2 Information About, page 63-2 Default Settings for, page 63-4 How to Configure, page 63-4 For complete syntax and usage information for
VLANs. Application Note
 VLANs Application Note Table of Contents Background... 3 Benefits... 3 Theory of Operation... 4 IEEE 802.1Q Packet... 4 Frame Size... 5 Supported VLAN Modes... 5 Bridged Mode... 5 Static SSID to Static
VLANs Application Note Table of Contents Background... 3 Benefits... 3 Theory of Operation... 4 IEEE 802.1Q Packet... 4 Frame Size... 5 Supported VLAN Modes... 5 Bridged Mode... 5 Static SSID to Static
CCNA Exploration: Accessing the WAN Chapter 7 Case Study
 Objectives: Mitigate attacks based on DHCP rogue servers. Intro: ChurchBells Inc. is having connectivity issues and needs your help. The Scenario: According to the reports, some user PCs within the company
Objectives: Mitigate attacks based on DHCP rogue servers. Intro: ChurchBells Inc. is having connectivity issues and needs your help. The Scenario: According to the reports, some user PCs within the company
Fundamentals of Switching
 1 CCNA 640-801 Exam Notes - Fundamentals of Switching CCNA 640-801 Exam Notes Fundamentals of Switching 1. LAN Segmentation 1.1 In a collision domain, a frame sent by a device can cause collision with
1 CCNA 640-801 Exam Notes - Fundamentals of Switching CCNA 640-801 Exam Notes Fundamentals of Switching 1. LAN Segmentation 1.1 In a collision domain, a frame sent by a device can cause collision with
Lab 5-5 Configuring the Cisco IOS DHCP Server
 Lab 5-5 Configuring the Cisco IOS DHCP Server Learning Objectives Configure and verify the operation of the Cisco IOS DHCP server Configure an IP Helper address Review the EIGRP configuration Topology
Lab 5-5 Configuring the Cisco IOS DHCP Server Learning Objectives Configure and verify the operation of the Cisco IOS DHCP server Configure an IP Helper address Review the EIGRP configuration Topology
AT-S41 Version 1.1.4 Management Software for the AT-8326 and AT-8350 Series Fast Ethernet Switches. Software Release Notes
 AT-S41 Version 1.1.4 Management Software for the AT-8326 and AT-8350 Series Fast Ethernet Switches Software Release Notes Please read this document before you begin to use the AT-S41 management software.
AT-S41 Version 1.1.4 Management Software for the AT-8326 and AT-8350 Series Fast Ethernet Switches Software Release Notes Please read this document before you begin to use the AT-S41 management software.
Lab 5.5.3 Developing ACLs to Implement Firewall Rule Sets
 Lab 5.5.3 Developing ACLs to Implement Firewall Rule Sets All contents are Copyright 1992 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 1 of 8 Device Interface
Lab 5.5.3 Developing ACLs to Implement Firewall Rule Sets All contents are Copyright 1992 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 1 of 8 Device Interface
Cisco Networking Academy CCNP Multilayer Switching
 CCNP 3 v5 - Chapter 4 Cisco Networking Academy CCNP Multilayer Switching Implementing Inter-VLAN Routing VLANs VLANs are associated with individual networks or subnetworks Network devices in different
CCNP 3 v5 - Chapter 4 Cisco Networking Academy CCNP Multilayer Switching Implementing Inter-VLAN Routing VLANs VLANs are associated with individual networks or subnetworks Network devices in different
Configuring Auto-QoS
 Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for Auto-QoS, page 1 Restrictions for Auto-QoS, page 2 Information About, page 3 How to Configure Auto-QoS, page 5 Monitoring Auto-QoS, page 9 Configuration
Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for Auto-QoS, page 1 Restrictions for Auto-QoS, page 2 Information About, page 3 How to Configure Auto-QoS, page 5 Monitoring Auto-QoS, page 9 Configuration
Lab 2 - Basic Router Configuration
 CS326 Fall 2001 Room: PAI 5.48 Name: Lab 2 - Basic Router Configuration In this lab you will learn: the various configuration modes of Cisco 2621 routers how to set up IP addresses for such routers how
CS326 Fall 2001 Room: PAI 5.48 Name: Lab 2 - Basic Router Configuration In this lab you will learn: the various configuration modes of Cisco 2621 routers how to set up IP addresses for such routers how
ICND1-100-101 IOS CLI Study Guide (CCENT)
 ICND1-100-101 IOS CLI Study Guide (CCENT) Hostname: 2. hostname SW1 SWITCH CONFIGURATION Mgmt IP: 2. interface vlan 1 3. ip address 10.0.0.2 4. no shut Gateway: 2. ip default-gateway 10.0.0.1 Local User/Pwd:
ICND1-100-101 IOS CLI Study Guide (CCENT) Hostname: 2. hostname SW1 SWITCH CONFIGURATION Mgmt IP: 2. interface vlan 1 3. ip address 10.0.0.2 4. no shut Gateway: 2. ip default-gateway 10.0.0.1 Local User/Pwd:
Basic Router and Switch Instructions (Cisco Devices)
 Basic Router and Switch Instructions (Cisco Devices) Basic Device Connection 1. Connect to the device via the console cable (light blue cable) and the use of a terminal program (Windows Hyperterminal,
Basic Router and Switch Instructions (Cisco Devices) Basic Device Connection 1. Connect to the device via the console cable (light blue cable) and the use of a terminal program (Windows Hyperterminal,
Configuring Denial of Service Protection
 24 CHAPTER This chapter contains information on how to protect your system against Denial of Service (DoS) attacks. The information covered in this chapter is unique to the Catalyst 6500 series switches,
24 CHAPTER This chapter contains information on how to protect your system against Denial of Service (DoS) attacks. The information covered in this chapter is unique to the Catalyst 6500 series switches,
Managing vlan.dat in Cisco Catalyst Switches Running Cisco IOS Software
 Managing vlan.dat in Cisco Catalyst Switches Running Cisco IOS Software Document ID: 109304 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions Background Information
Managing vlan.dat in Cisco Catalyst Switches Running Cisco IOS Software Document ID: 109304 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions Background Information
Lab 7-1 Configuring Switches for IP Telephony Support
 Lab 7-1 Configuring Switches for IP Telephony Support Learning Objectives Configure auto QoS to support IP phones Configure CoS override for data frames Configure the distribution layer to trust access
Lab 7-1 Configuring Switches for IP Telephony Support Learning Objectives Configure auto QoS to support IP phones Configure CoS override for data frames Configure the distribution layer to trust access
100-101: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 v2.0 (ICND1)
 100-101: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 v2.0 (ICND1) Course Overview This course provides students with the knowledge and skills to implement and support a small switched and routed network.
100-101: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 v2.0 (ICND1) Course Overview This course provides students with the knowledge and skills to implement and support a small switched and routed network.
Example: Configuring VoIP on an EX Series Switch Without Including 802.1X Authentication
 Example: Configuring VoIP on an EX Series Switch Without Including 802.1X Authentication Requirements You can configure voice over IP (VoIP) on an EX Series switch to support IP telephones. To configure
Example: Configuring VoIP on an EX Series Switch Without Including 802.1X Authentication Requirements You can configure voice over IP (VoIP) on an EX Series switch to support IP telephones. To configure
AT-S60 Version 1.1.4 Management Software for the AT-8400 Series Switch. Software Release Notes
 AT-S60 Version 1.1.4 Management Software for the AT-8400 Series Switch Supported Platforms Software Release Notes Please read this document before you begin to use the AT-S60 management software. The AT-S60
AT-S60 Version 1.1.4 Management Software for the AT-8400 Series Switch Supported Platforms Software Release Notes Please read this document before you begin to use the AT-S60 management software. The AT-S60
MAC Address Table Attribute Configuration
 Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 Configuring MAC Address Attribute... 1 1.1 MAC Address Configuration Task List... 1 1.2 MAC Address Configuration Task... 1 1.2.1 Configuring Static Mac Address...
Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 Configuring MAC Address Attribute... 1 1.1 MAC Address Configuration Task List... 1 1.2 MAC Address Configuration Task... 1 1.2.1 Configuring Static Mac Address...
Basic Configuration of the Cisco 12000 Series Internet Router
 CHAPTER 2 Basic Configuration of the Cisco 12000 Series Internet Router This chapter describes how to boot and configure the Cisco 12000 Series Internet Router. It discusses the following subjects: Cisco
CHAPTER 2 Basic Configuration of the Cisco 12000 Series Internet Router This chapter describes how to boot and configure the Cisco 12000 Series Internet Router. It discusses the following subjects: Cisco
Configuring Static and Dynamic NAT Simultaneously
 Configuring Static and Dynamic NAT Simultaneously Document ID: 13778 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configuring NAT Related Information Introduction In some
Configuring Static and Dynamic NAT Simultaneously Document ID: 13778 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configuring NAT Related Information Introduction In some
Firewall Load Balancing
 CHAPTER 6 This chapter describes the (FWLB) feature. It includes the following sections: FWLB Overview, page 6-1 FWLB Features, page 6-2 FWLB Configuration Tasks, page 6-3 Monitoring and Maintaining FWLB,
CHAPTER 6 This chapter describes the (FWLB) feature. It includes the following sections: FWLB Overview, page 6-1 FWLB Features, page 6-2 FWLB Configuration Tasks, page 6-3 Monitoring and Maintaining FWLB,
IOS Server Load Balancing
 IOS Server Load Balancing This feature module describes the Cisco IOS Server Load Balancing (SLB) feature. It includes the following sections: Feature Overview, page 1 Supported Platforms, page 5 Supported
IOS Server Load Balancing This feature module describes the Cisco IOS Server Load Balancing (SLB) feature. It includes the following sections: Feature Overview, page 1 Supported Platforms, page 5 Supported
Configuring Traffic Mirroring on the Cisco ASR 9000 Series Router
 Configuring Traffic Mirring on the Cisco ASR 9000 Series Router This module describes the configuration of traffic mirring on the Cisco ASR 9000 Series Router. Traffic mirring is sometimes called pt mirring,
Configuring Traffic Mirring on the Cisco ASR 9000 Series Router This module describes the configuration of traffic mirring on the Cisco ASR 9000 Series Router. Traffic mirring is sometimes called pt mirring,
ClearPass Policy manager Cisco Switch Setup with CPPM. Technical Note
 ClearPass Policy manager Cisco Switch Setup with CPPM Technical Note Copyright 2012 Aruba Networks, Inc. Aruba Networks trademarks include, Aruba Networks, Aruba Wireless Networks, the registered Aruba
ClearPass Policy manager Cisco Switch Setup with CPPM Technical Note Copyright 2012 Aruba Networks, Inc. Aruba Networks trademarks include, Aruba Networks, Aruba Wireless Networks, the registered Aruba
Configuring Network Address Translation (NAT)
 8 Configuring Network Address Translation (NAT) Contents Overview...................................................... 8-3 Translating Between an Inside and an Outside Network........... 8-3 Local and
8 Configuring Network Address Translation (NAT) Contents Overview...................................................... 8-3 Translating Between an Inside and an Outside Network........... 8-3 Local and
NetStream (Integrated) Technology White Paper HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Issue 01. Date 2012-9-6
 (Integrated) Technology White Paper Issue 01 Date 2012-9-6 HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. 2012. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means
(Integrated) Technology White Paper Issue 01 Date 2012-9-6 HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. 2012. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means
16-PORT POWER OVER ETHERNET WEB SMART SWITCH
 16-PORT POWER OVER ETHERNET WEB SMART SWITCH User s Manual (DN-95312) - 0 - Content Web Smart Switch Configure login ---------------------------------- 2 Administrator Authentication Configuration ---------------------------------------------
16-PORT POWER OVER ETHERNET WEB SMART SWITCH User s Manual (DN-95312) - 0 - Content Web Smart Switch Configure login ---------------------------------- 2 Administrator Authentication Configuration ---------------------------------------------
Configuring PA Firewalls for a Layer 3 Deployment
 Configuring PA Firewalls for a Layer 3 Deployment Configuring PAN Firewalls for a Layer 3 Deployment Configuration Guide January 2009 Introduction The following document provides detailed step-by-step
Configuring PA Firewalls for a Layer 3 Deployment Configuring PAN Firewalls for a Layer 3 Deployment Configuration Guide January 2009 Introduction The following document provides detailed step-by-step
Topic 7 DHCP and NAT. Networking BAsics.
 Topic 7 DHCP and NAT Networking BAsics. 1 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) IP address assignment Default Gateway assignment Network services discovery I just booted. What network is this? What
Topic 7 DHCP and NAT Networking BAsics. 1 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) IP address assignment Default Gateway assignment Network services discovery I just booted. What network is this? What
Session Title: Exploring Packet Tracer v5.3 IP Telephony & CME. Scenario
 Session Title: Exploring Packet Tracer v5.3 IP Telephony & CME Scenario With the scheduled release of Packet Tracer v5.3 in the near future, this case study is designed to provide you with an insight into
Session Title: Exploring Packet Tracer v5.3 IP Telephony & CME Scenario With the scheduled release of Packet Tracer v5.3 in the near future, this case study is designed to provide you with an insight into
Configuring the Firewall Management Interface
 Configuring the Firewall Management Interface The firewall management interface can be configured under each firewall context to provide a virtualized management interface (see Figure 7). The management
Configuring the Firewall Management Interface The firewall management interface can be configured under each firewall context to provide a virtualized management interface (see Figure 7). The management
Configuring System Message Logging
 CHAPTER 25 This chapter describes how to configure system message logging on the Catalyst 2960 switch. Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, see the Cisco
CHAPTER 25 This chapter describes how to configure system message logging on the Catalyst 2960 switch. Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, see the Cisco
