Social Science PRIMARY. Richmond
|
|
|
- Colin Harris
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Richmond Social Science Social Science 6 is a collective work, conceived, designed and created by the Primary Education department at Santillana, under the supervision of Teresa Grence Ruiz. WRITER Belén Garrido PRIMARY MANAGING EDITOR Sheila Tourle PROJECT EDITOR Geona Edwards EDITOR Beatriz Bejarano del Palacio EDITORIAL TEAM Vassilia Katte, Jane Drummond, James Price ILLUSTRATIONS Alademosca il lustració Chema Fernández Román Quino Marín Bartolomé Seguí Agusti Serrano Sanjosé Pablo Velarde Díaz-Padre Carles Salón Do not write in this book. Do all the activities in your notebook.
2 Unit Reading Topics Studying geography 4 1 The landscapes of Spain and Europe The importance of maps The location and relief of Spain The mountains and river basins of the Iberian Peninsula 12 2 Rivers, climates and vegetation of Spain and Europe Environmental health indicators The watersheds of Spain I The watersheds of Spain II 28 3 The economy 42 An invention factory The economy Companies 4 The population and economy of Europe and Spain Airbus, a European aerospace company The population of Europe and Spain The primary sector in Europe and Spain 52 5 Human impact on the environment 66 Reduce, reuse and recycle People and the environment Sustainable development TERM REVISION Studying history 78 6 Contemporary history: Spain in the 19th century 82 Viva la Pepa! The 19th century The Industrial Revolution 7 Contemporary history: Spain in the 20th and 21st centuries A symbol of peace Spain at the beginning of the 20th century The Franco Era 92 8 Spain and the European Union 104 A continent within reach The political organization of Spain The territorial organization of Spain TERM REVISION END-OF-PRIMARY PROJECT 2 two
3 Topics Know how to The relief of the islands The Spanish coasts The location and relief of Europe The European coasts Interpret a physical map The climates and vegetation of Spain Rivers and watersheds in Europe The climates and vegetation of Europe Prepare an oral presentation about improving water quality in rivers Advertising Money Savings and investments Make a personal budget The secondary sector in Europe and Spain The tertiary sector in Europe and Spain I The tertiary sector in Europe and Spain II Role play a negotiation process Environmental problems Climate change Protecting the environment Propose actions to fight climate change Society Architecture and sculpture Painting and literature Discuss a historical text The transition Democracy Painting and sculpture Architecture and literature Analyse a painting The formation of the European Union EU accomplishments and challenges Spain in the European Union Give a presentation about a country in the European Union three 3
4 6 Contemporary history: Spain in the 19th century 6.1 Viva la Pepa! After a long and dangerous journey, I arrive in Cádiz to attend a secret meeting. It is not my first time here; two years ago, in 1812, I was part of a big celebration for the approval of the Constitution of Cádiz, the first Spanish constitution. We call it La Pepa because it was approved on 19th March, Saint Joseph s Day. We believed the Constitution would help modernize Spain. The Constitution recognized Ferdinand VII as king, but it also included new ideas, like making all men equal and protecting freedom of the press. The Constitution only lasted two years, and now they arrest anyone who supported it. A man walks by me in the street and whispers: Viva la Pepa! It is our motto. I follow him, and I promise myself to never stop defending ideas like equality, liberty and justice War of Independence 1812 Constitution of Cádiz 1814 Reign of Ferdinand VII Read and understand KNOW HOW TO Where does this short story take place? In what year? Why was the first Spanish Constitution called La Pepa? What ideas did it include? Why is the character in the story attending a secret meeting? How was the expression Viva la Pepa! used? SPEAKING. In groups, search the Internet for information about the Constitution of Find out about its background, its content, the people involved, etc. Share your findings with your class. Explain political, economic and social changes of the 19th century. Identify the main works of art of the 19th century. FINAL TASK Discuss a historical text. 82 eighty-two
5 Monument to the Constitution of 1812, in Cádiz. C O N T E M P O R A R Y H I S T O R Y 19th Century 1833 Reign of Isabella II 1868 Exile of Isabella II 1873 First Republic 1874 Reign of Alfonso XII; The Restoration WHAT DO YOU REMEMBER? The end of the Modern Age In the 18th century, kings Philip V, Ferdinand VI, Charles III and Charles IV ruled Spain. Which dynasty did these kings belong to? In order to modernize their reigns and improve the quality of life of their subjects, some of these kings put into practice the ideas of the Enlightenment. What is the Enlightenment? Where did this movement originate? Who were its most famous thinkers? eighty-three 83
6 The 19th century 1 The Third of May 1808 by Francisco de Goya represents the beginning of the War of Independence. 6.2 The War of Independence In 1807, Napoleon Bonaparte, the Emperor of France, decided to occupy Portugal. The King of Spain, Charles IV, allowed him to go across Spain. On their way, the French troops invaded some Spanish cities. This caused a popular revolt which forced Charles IV to abdicate. His son, Ferdinand VII, became king. Soon after, Napoleon forced Ferdinand VII to abdicate so he could proclaim his brother, Joseph Bonaparte, the new king. However, the population of Madrid did not accept him and rebelled against the French. This started the War of Independence. 1 This war lasted until 1814, when the French were defeated and Ferdinand VII returned as King of Spain. During the war, the Spanish Parliament moved to Cádiz. In 1812, its members wrote Spain s first constitution, the Constitution of Cádiz. 2 It limited the king s power and established rights for citizens, including the right to vote for men twenty-five years old or older. The reign of Ferdinand VII In 1814, Ferdinand VII returned as King of Spain. 3 He abolished the Constitution of Cádiz and re-established an absolute monarchy. This caused political disorder and, as a result, most of the American colonies became independent. 2 The Constitution of Cádiz, also known as La Pepa, was approved in In 1814, King Ferdinand VII was reinstated as an absolute monarch. 84 eighty-four
7 6 4 Isabella II was crowned queen at age 13 when she was declared legally of age. 5 The monarchy of the Bourbons returned to Spain with Alfonso XII. 6.3 The reign of Isabella II In Spain, according to the law of succession, only men could reign. However, Ferdinand VII changed this law so his daughter could ascend to the throne. Isabella II became queen when Ferdinand VII died in During her reign, there was a constitutional monarchy that limited her power. However, numerous military conflicts and changes of government led to a revolution, and in 1868, Isabella II went into exile. The First Spanish Republic In 1871, Amadeo de Saboya of Italy became king. However, since he was a foreign monarch, he did not have much support, and he abdicated two years later. In 1873, members of Parliament proclaimed a republic, a form of government with no king. This First Spanish Republic also lacked support and failed after about a year. The Spanish Restoration In 1874, the son of Isabella II, Alfonso XII, was crowned King of Spain, and a new historical period, known as the Restoration, began. 5 At the end of the 19th century, Spain lost its last colonies in Cuba, Puerto Rico and the Philippines. 1 WRITING. How did Contemporary history begin? Explain. 2 When and where was the first constitution of Spain approved? Who signed it? 6.4 ACTIVITIES 3 Make a timeline of Spanish monarchs in the 19th century. Include the years they ruled and important events. 4 SPEAKING. Name and explain the different forms of government in the 19th century. eighty-five 85
8 Life in the 19th century In the 19th century, factories were built in cities. The Industrial Revolution The Industrial Revolution originated in the United Kingdom at the end of the 18th century, and then it extended to other countries. In Spain, the Industrial Revolution took place in the 19th century. Factories were built mainly in Catalonia and the Basque Country. Small craftsmen s workshops were replaced by factories with machines operated by workers. The steam engine was invented and a new energy source, coal, was used. Thanks to the steam engine, trains and steamboats were developed, and new machines allowed the textile and metal industries to advance dramatically. 1 As a consequence of the Industrial Revolution, many important economic and social changes took place. A society that was based on agriculture transformed into a society based on industrial activities. WORK WITH THE PICTURE Is the factory located in the city or the countryside? How can you tell it is a factory? What type of industry is shown? What means of transport can you see? Who lived in this part of the city? LEARN MORE The railway In 1814, George Stephenson, an English engineer, built the first steam locomotive. It was used to transport goods. In 1830, the first passenger railway service in England was opened. The first railway line in Spain, between Barcelona and Mataró, opened in eighty-six
9 6 6.6 Society Society in the 19th century was divided into three social classes, based on wealth. 2 The upper class consisted of the wealthiest people: the aristocrats and the bourgeois. The aristocrats were nobles who owned large areas of land. The bourgeois were factory owners, prosperous merchants and bankers. The middle class consisted of small merchants and entrepreneurs, small landowners, and professionals such as doctors, lawyers and engineers. The lower class consisted of poorer people, such as peasants and factory workers. The peasants worked on the land of the large landowners. The factory workers worked in exchange for wages. Their living conditions were very hard. They worked more than twelve hours a day for very low wages. They lived in undeveloped neighbourhoods with no electricity or running water. In addition, many children worked in factories for wages even lower than those paid to adults. In order to protect their interests, workers formed groups known as labour unions. A B C 2 In the 19th century, society was organized into three social classes. A. Upper class. B. Middle class. C. Lower class. ACTIVITIES 1 Make an index card about the Industrial Revolution, including date and place of origin, main inventions and industries developed. 2 WRITING. Compare society in the 19th century with society in the feudal system. How were they alike? How were they different? 3 VALUES EDUCATION. Explain what your life would be like if you had to work. Why do you think it is important for children to go to school? eighty-seven 87
10 Art and culture in the 19th century 1 Gate of Toledo in Madrid. 2 Railway station in Almería. WORK WITH THE PICTURE 6.7 Which of these buildings reminds you of a building in ancient Rome? Why? Which buildings used materials like iron and glass? Which building has many curved elements? 6.8 Architecture At the beginning of the 19th century, neoclassical architecture developed. Buildings were constructed in a style similar to that of Greek and Roman architecture, such as the Gate of Toledo in Madrid. 1 During this century, iron bridges were built and new types of buildings were created, such as railway stations made of iron and glass. 2 At the end of the century, a new architectural style, known as Modernism, was born. Modernist buildings show curved and wavy shapes that simulate forms in nature. In Spain, the best-known modernist architect was Antoni Gaudí, creator of the Casa Milà in Barcelona. 3 3 Casa Milà in Barcelona. Sculpture The transformation of cities influenced sculpture. During this century, squares, gardens and avenues were decorated with beautiful sculptures made mainly of stone. 4 4 The Fallen Angel, by Ricardo Bellver, a famous Spanish sculptor. 88 eighty-eight
11 6 5 The family of Charles IV by Francisco de Goya. 6 Women walking on the beach by Joaquín Sorolla. 6.9 Painting At the beginning of the 19th century, Francisco de Goya was painter at the Spanish Court and painted portraits of Charles IV and Ferdinand VII. However, he also painted popular scenes such as festivals and wine harvests. Goya is considered one of the greatest artists in history. 5 At the end of the 19th century, Impressionism was born. This art movement introduced innovative painting techniques. Impressionist painters put more emphasis on colour than drawing, as well as on the effect of light in landscapes. The most important Spanish impressionist painter was Joaquín Sorolla. 6 Literature During the 19th century, there were great writers in Spain, such as the playwright José Zorrilla; the poets Rosalía de Castro and Gustavo Adolfo Bécquer; and the novelists Benito Pérez Galdós and Leopoldo Alas Clarín. At the end of the century, when Spain lost its last colonies, a group of writers known as the Generation of '98 wrote pessimistically about the social and political situation of Spain. This group included writers such as Pío Baroja, Miguel de Unamuno, Antonio Machado and Ramón María del Valle-Inclán. LEARN MORE Photography and film Photographic cameras were invented in the 19th century. Up until then, images could only be drawn. At the end of the 19th century, the Lumière brothers invented the cinematograph, which allowed them to project moving images. This was the beginning of film. ACTIVITIES 1 Name three artists from the 19th century and write a sentence about their work. 2 ICT. Research a Spanish work of art from the 19th century and make an index card, including name, artist, description and a picture. 3 What was the Generation of '98? Name three writers who belonged to this group. eighty-nine 89
12 KNOW HOW TO Discuss a historical text A historical text is a written source that informs us about past events and allows us to understand other historical periods better. Article 3. Sovereignty resides in the Nation. Only the Nation has the right to establish fundamental laws. Article 14. The government of the Spanish Nation is a moderate hereditary Monarchy. Article 15. The legal authority for making laws resides in the Parliament with the king. Article 16. The legal authority for executing laws resides in the king. Article 371. All Spaniards have the freedom to [...] publish their political ideas. Cádiz, 19th March, 1812 Understand the information. 1 Read the text and answer. When and where was this text written? Did the king have absolute power? From which historical text are these articles? How do you know? Relate the information. 2 Relate the text with its time period. Who was king of Spain in 1812? And in France? Was Spain at war at this time? Which war was it? Who was fighting? How did the war end? After the war, who was proclaimed king of Spain? Show that you can do it. 3 GROUP WORK. Discuss this historical text in groups. Form groups of five. Each member of the group works on one of these articles and presents it in class. Then, discuss why it is important to have a constitution. 90 ninety
13 FINAL ACTIVITIES 6 1 SUMMARY. Copy and complete the text in your notebook, using these words. 2 Copy the timeline and put the following historical events in chronological order Ferdinand VII The Philippines Isabella II Independence colonies Alfonso XII French Cuba rights exile absolute monarchy republic constitution In the War of, the Spaniards rebelled against the invasion. In 1812, the first Spanish was proclaimed in Cádiz. It included the main of the citizens. However, this constitution was abolished by. He reinstated an, and lost most of the American. When Ferdinand VII died, his daughter,, became queen. Constant political changes and conflicts during her reign forced her to go into. After the short reign of a foreign monarch, a new form of government with no king, known as a, was proclaimed. However, it did not last long. In 1874, a new historical period started with the crowning of, the son of Isabella II, as King of Spain. At the end of the 19th century, Spain lost its last colonies:, Puerto Rico and. First Spanish Republic is proclaimed Isabella II is proclaimed queen Spain loses its last colonies Alfonso XII is crowned king of Spain Constitution of Cádiz is signed Ferdinand VII is reinstated as king The 19th century in Spain 3 Copy and complete this table about society in the 19th century. Society in the 19th century social classes members characteristics 4 Look at the photos. Identify the architectural style of each of them and explain their characteristics. A B C Show your skills Choose and carry out one of the following activities. A. ICT. Search the Internet for information about life in your autonomous community during the 19th century. Make a poster, including political, social and economic aspects. B. In groups of three, each student chooses a social class of the 19th century and writes a short story about a day in the life of a child from that social class. Then, share your stories. C. Make a poster with paintings of popular scenes by Francisco de Goya. ninety-one 91
Egyptian History 101 By Vickie Chao
 Egyptian History 101 By Vickie Chao 1 A long time ago, before Egypt was a united country, there were two kingdoms -- Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt. Upper Egypt was in the south. It controlled the areas along
Egyptian History 101 By Vickie Chao 1 A long time ago, before Egypt was a united country, there were two kingdoms -- Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt. Upper Egypt was in the south. It controlled the areas along
Napoleonic France, 1799 1815. Napoleon Bonaparte as a young Officer
 Napoleonic France, 1799 1815 Napoleon Bonaparte as a young Officer 1 2 1796 Napoleon crossed the Alps & drove the Austrians out of Northern Italy. He then turned N. Italy into the Cisalpine Republic and
Napoleonic France, 1799 1815 Napoleon Bonaparte as a young Officer 1 2 1796 Napoleon crossed the Alps & drove the Austrians out of Northern Italy. He then turned N. Italy into the Cisalpine Republic and
Table of Contents. Part One: Social Studies Curriculum
 Table of Contents Part One: Social Studies Curriculum Chapter I: Social Studies Essay Questions and Prewriting Activities 1. Western Political Thought 1 2. The Age of Revolution 6 3. The Age of Napoleon
Table of Contents Part One: Social Studies Curriculum Chapter I: Social Studies Essay Questions and Prewriting Activities 1. Western Political Thought 1 2. The Age of Revolution 6 3. The Age of Napoleon
Material AICLE. 5º de Primaria.: History Through the Ages (Solucionario)
 Material AICLE. 5º de Primaria.: History Through the Ages (Solucionario) 3 SOLUTIONS Activity 2. Read and complete the chart Historical sources Oral Written Graphic Materials - Songs - Books - Theatre
Material AICLE. 5º de Primaria.: History Through the Ages (Solucionario) 3 SOLUTIONS Activity 2. Read and complete the chart Historical sources Oral Written Graphic Materials - Songs - Books - Theatre
Hobbes, Locke, Montesquieu, and Rousseau on Government
 CONSTITUTIONAL RIGHTS FOUNDATION Bill of Rights in Action 20:2 Hobbes, Locke, Montesquieu, and Rousseau on Government Starting in the 1600s, European philosophers began debating the question of who should
CONSTITUTIONAL RIGHTS FOUNDATION Bill of Rights in Action 20:2 Hobbes, Locke, Montesquieu, and Rousseau on Government Starting in the 1600s, European philosophers began debating the question of who should
Late Medieval Period (WHI.12)
 Name Late Medieval Period (WHI.12) Label on Map: England, France, Spain, Russia, Holly Roman Empire, Paris, Rome, Mediterranean Sea, English Channel, Atlantic Ocean Term: Nation-state Describe: Draw: 1
Name Late Medieval Period (WHI.12) Label on Map: England, France, Spain, Russia, Holly Roman Empire, Paris, Rome, Mediterranean Sea, English Channel, Atlantic Ocean Term: Nation-state Describe: Draw: 1
History of the Rule of Law
 History of the Rule of Law CONTEMPORARY FINE ART COLLECTION Since it opened in 1933, the Thomas J. Moyer Ohio Judicial Center has been home to numerous soaring and spectacular murals, and neoclassical,
History of the Rule of Law CONTEMPORARY FINE ART COLLECTION Since it opened in 1933, the Thomas J. Moyer Ohio Judicial Center has been home to numerous soaring and spectacular murals, and neoclassical,
World History Course Summary Department: Social Studies. Semester 1
 World History Course Summary Department: Social Studies All World History courses (Honors or otherwise) utilize the same targets and indicators for student performance. However, students enrolled in Honors
World History Course Summary Department: Social Studies All World History courses (Honors or otherwise) utilize the same targets and indicators for student performance. However, students enrolled in Honors
Name: Class: Global Studies Date: Mr. Wallace. The Enlightenment & The American Revolution Test Review
 Name: Class: Global Studies Date: Mr Wallace The Enlightenment & The American Revolution Test Review 1) The United States "founding fathers" were not influenced by the ideas of Enlightenment thinkers 2)
Name: Class: Global Studies Date: Mr Wallace The Enlightenment & The American Revolution Test Review 1) The United States "founding fathers" were not influenced by the ideas of Enlightenment thinkers 2)
Spain is my country. Spain is where I live.
 Spain is my country Spain is my country. Spain is where I live. Location Spain is located in the south west of Europe. Spain Limits Spain is bordered to the south and east by the Mediterranean Sea, to
Spain is my country Spain is my country. Spain is where I live. Location Spain is located in the south west of Europe. Spain Limits Spain is bordered to the south and east by the Mediterranean Sea, to
Section 1- Geography and the Early Greeks
 Name: Class: Date: 6 th Grade World History Chapter 8 Study Guide: Ancient Greece Section 1- Geography and the Early Greeks 1) Complete the chart below to show how geography shaped the lives of early Greeks.
Name: Class: Date: 6 th Grade World History Chapter 8 Study Guide: Ancient Greece Section 1- Geography and the Early Greeks 1) Complete the chart below to show how geography shaped the lives of early Greeks.
Napoleon Bonaparte Rise & Reform
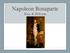 Napoleon Bonaparte Rise & Reform Personal Life Born into a noble family on the French island of Corsica Quickly rose through the military, fighting for the Revolutionary army Supported the Jacobins Self-proclaimed
Napoleon Bonaparte Rise & Reform Personal Life Born into a noble family on the French island of Corsica Quickly rose through the military, fighting for the Revolutionary army Supported the Jacobins Self-proclaimed
YEAR 1: Kings, Queens and Leaders (6 lessons)
 YEAR 1: Kings, Queens and Leaders (6 lessons) Contents Include: The United Kingdom and the Union Jack Kings and Queens The Magna Carta Charles I Parliament The Prime Minister Suggested Teacher Resources:
YEAR 1: Kings, Queens and Leaders (6 lessons) Contents Include: The United Kingdom and the Union Jack Kings and Queens The Magna Carta Charles I Parliament The Prime Minister Suggested Teacher Resources:
AP EUROPEAN HISTORY 2012 SCORING GUIDELINES
 AP EUROPEAN HISTORY 2012 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 4 Analyze various ways in which government policies during the Revolutionary and Napoleonic era contributed to a greater sense of French national identity
AP EUROPEAN HISTORY 2012 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 4 Analyze various ways in which government policies during the Revolutionary and Napoleonic era contributed to a greater sense of French national identity
GEORGIA AMERICAN REVOLUTION
 GEORGIA in the AMERICAN REVOLUTION AMERICA HEADS TOWARD INDEPENDENCE: Until 1763, independence was unthinkable!!! Great Britain was the greatest, most powerful nation on earth, and the American colonists
GEORGIA in the AMERICAN REVOLUTION AMERICA HEADS TOWARD INDEPENDENCE: Until 1763, independence was unthinkable!!! Great Britain was the greatest, most powerful nation on earth, and the American colonists
Degree Type Bachelor of Arts (BA) Degree Title History
 Degree Type Bachelor of Arts (BA) Degree Title History As an integral part of a liberal arts education, history courses introduce students to different historical eras, diverse cultures, famous and ordinary
Degree Type Bachelor of Arts (BA) Degree Title History As an integral part of a liberal arts education, history courses introduce students to different historical eras, diverse cultures, famous and ordinary
PABLO PICASSO PRE-READING QUESTIONS. 1. What kind of art do you like? 2. Do you have a favorite artist?
 Pablo Picasso PABLO PICASSO PRE-READING QUESTIONS 1. What kind of art do you like? 2. Do you have a favorite artist? 3. Have you seen a painting by Picasso? 4. Have you heard of a style of painting called
Pablo Picasso PABLO PICASSO PRE-READING QUESTIONS 1. What kind of art do you like? 2. Do you have a favorite artist? 3. Have you seen a painting by Picasso? 4. Have you heard of a style of painting called
Fourth Grade Social Studies Content Standards and Objectives
 Fourth Grade Social Studies Content Standards and Objectives Standard 1: Citizenship characterize and good citizenship by building social networks of reciprocity and trustworthiness (Civic Dispositions).
Fourth Grade Social Studies Content Standards and Objectives Standard 1: Citizenship characterize and good citizenship by building social networks of reciprocity and trustworthiness (Civic Dispositions).
Rise of the Roman Republic Timeline
 Rise of the Roman Republic Timeline 509 BCE: Tarquin the Proud, the last king of Rome, was overthrown by a group of patricians upset over his abuse of power. The Roman Republic was proclaimed. 494 BCE:
Rise of the Roman Republic Timeline 509 BCE: Tarquin the Proud, the last king of Rome, was overthrown by a group of patricians upset over his abuse of power. The Roman Republic was proclaimed. 494 BCE:
All images Michael Potthast. the
 All images Michael Potthast the Michael Potthast builds on a family legacy BY WILL POLLOCK PORTRAIT OF A BUSINESS arrying on a family tradition can be a heavy lift for one person, especially when it entails
All images Michael Potthast the Michael Potthast builds on a family legacy BY WILL POLLOCK PORTRAIT OF A BUSINESS arrying on a family tradition can be a heavy lift for one person, especially when it entails
The Premier Impressionist
 The Premier Impressionist Claude Monet s paintings were quite different from the art styles that were popular in 1870s France. Traditional artists always did their artwork in a studio and their paintings
The Premier Impressionist Claude Monet s paintings were quite different from the art styles that were popular in 1870s France. Traditional artists always did their artwork in a studio and their paintings
5- Why did the Shogun rule Japan?
 Global History and Geography I The Rise of Feudalism in Japan Name: The emperor was an important political and religious figure in Japan. However, by the 1100s, the emperor s power was so weakened that
Global History and Geography I The Rise of Feudalism in Japan Name: The emperor was an important political and religious figure in Japan. However, by the 1100s, the emperor s power was so weakened that
In this activity, students try to solve a mystery about the Pledge of Allegiance.
 Enrichment Activity 1 The Changing Pledge In this activity, students try to solve a mystery about the Pledge of Allegiance. They are provided with a version of the Pledge from October 1892 and are asked
Enrichment Activity 1 The Changing Pledge In this activity, students try to solve a mystery about the Pledge of Allegiance. They are provided with a version of the Pledge from October 1892 and are asked
Contents. Introduction 4. Joseph-Michel Montgolfier 7. Louis Blériot 19. Charles Lindbergh 31. Amelia Earhart 45. Amy Johnson 59.
 Contents Introduction 4 Joseph-Michel Montgolfier 7 Louis Blériot 19 Charles Lindbergh 31 Amelia Earhart 45 Amy Johnson 59 Glossary 73 Joseph-Michel Montgolfier 1740 1810 the man who helped humans to fly
Contents Introduction 4 Joseph-Michel Montgolfier 7 Louis Blériot 19 Charles Lindbergh 31 Amelia Earhart 45 Amy Johnson 59 Glossary 73 Joseph-Michel Montgolfier 1740 1810 the man who helped humans to fly
The French Revolution Begins Close Read
 The French Revolution Begins Close Read Standards Alignment Text with Close Read instructions for students Intended to be the initial read in which students annotate the text as they read. Students may
The French Revolution Begins Close Read Standards Alignment Text with Close Read instructions for students Intended to be the initial read in which students annotate the text as they read. Students may
Why did the US want to claim small islands in the Pacific Ocean such as Midway Island and Wake Island?
 US History & Government Imperialism Why did the US create an empire in the late 19 th Century? Social: Economic: Political: Religious: Military: China Why did the US want to claim small islands in the
US History & Government Imperialism Why did the US create an empire in the late 19 th Century? Social: Economic: Political: Religious: Military: China Why did the US want to claim small islands in the
Unit 4 Lesson 8 The Qin and Han Dynasties
 Unit 4 Lesson 8 The Qin and Han Dynasties Directions Read the False statements below. Replace each underlined word with one from the word bank that makes each sentence True. Word Bank Ying Zheng army copper
Unit 4 Lesson 8 The Qin and Han Dynasties Directions Read the False statements below. Replace each underlined word with one from the word bank that makes each sentence True. Word Bank Ying Zheng army copper
Words to Know before You Go!
 Words to Know before You Go! American Revolution Neutral Patriot Loyalist Traitor Conspiracy Petticoat Rebel Betray Fun Facts John Jay was the eighth of ten children. Today King s College, the school where
Words to Know before You Go! American Revolution Neutral Patriot Loyalist Traitor Conspiracy Petticoat Rebel Betray Fun Facts John Jay was the eighth of ten children. Today King s College, the school where
1. Which of the following is NOT an argument in support of imperialism or expansionism?
 U.S I Quarterly Assessment Practice Test Circle the best answer to each question. 1. Which of the following is NOT an argument in support of imperialism or expansionism? A. The United States should become
U.S I Quarterly Assessment Practice Test Circle the best answer to each question. 1. Which of the following is NOT an argument in support of imperialism or expansionism? A. The United States should become
The Tudor Myth. and the Place of the Stage
 The Tudor Myth and the Place of the Stage Shakespeare s History Plays Two tetralogies (series of four plays): First Tetralogy (1590-93): Henry VI, parts 1,2 and 3 Richard III Second Tetralogy (1595-1599):
The Tudor Myth and the Place of the Stage Shakespeare s History Plays Two tetralogies (series of four plays): First Tetralogy (1590-93): Henry VI, parts 1,2 and 3 Richard III Second Tetralogy (1595-1599):
History programmes of study: key stage 3
 History programmes of study: key stage 3 National curriculum in England Purpose of study A high-quality history education will help pupils gain a coherent knowledge and understanding of Britain s past
History programmes of study: key stage 3 National curriculum in England Purpose of study A high-quality history education will help pupils gain a coherent knowledge and understanding of Britain s past
History. Bachelor of Arts Major in History. Objectives. Degree Offered. Major Offered. Minor Offered. International Studies.
 History 123 History Thomas W. Taylor, PhD, Chair Objectives Defying classification as either humanity or social science, history functions as both. It focuses on the values, as well as the ideas, personalities,
History 123 History Thomas W. Taylor, PhD, Chair Objectives Defying classification as either humanity or social science, history functions as both. It focuses on the values, as well as the ideas, personalities,
North Carolina Essential Standards Third grade Social Studies
 North Carolina s Third grade Social Studies In third grade, students draw upon knowledge learned in previous grades to develop more sophisticated understandings of how communities may be linked to form
North Carolina s Third grade Social Studies In third grade, students draw upon knowledge learned in previous grades to develop more sophisticated understandings of how communities may be linked to form
My Magna Carta. an international creative writing competition for 11-18 year olds.
 My Magna Carta an international creative writing competition for 11-18 year olds. About the Competition The English-Speaking Union is delighted to present My Magna Carta an international creative writing
My Magna Carta an international creative writing competition for 11-18 year olds. About the Competition The English-Speaking Union is delighted to present My Magna Carta an international creative writing
 Penguin Readers Factsheets Teacher s Notes A History of Britain By Fiona Beddall Summary More than 2,000 years of times past are brought to life in this lively and interesting account of Britain s history.
Penguin Readers Factsheets Teacher s Notes A History of Britain By Fiona Beddall Summary More than 2,000 years of times past are brought to life in this lively and interesting account of Britain s history.
I N V E S T I C E D O R O Z V O J E V Z D Ě L Á V Á N Í ABSOLUTE MONARCHIES
 ABSOLUTE MONARCHIES Absolutism: Louis XIV of France born in 1638, ruled 1643-1715 as a child, he had to face the Frondes Revolt when the French high nobles rebelled against him he managed to take control
ABSOLUTE MONARCHIES Absolutism: Louis XIV of France born in 1638, ruled 1643-1715 as a child, he had to face the Frondes Revolt when the French high nobles rebelled against him he managed to take control
In which part of the world are the Netherlands located?
 1 In which part of the world are the Netherlands located? Europe 2 Which country is south of the Netherlands? Belgium 3 Which country is east of the Netherlands? Germany 4 5 Which country is bigger, the
1 In which part of the world are the Netherlands located? Europe 2 Which country is south of the Netherlands? Belgium 3 Which country is east of the Netherlands? Germany 4 5 Which country is bigger, the
COURSES FOR THE MAJOR AND MINOR IN EUROPEAN STUDIES (ES) (approval pending)
 COURSES FOR THE MAJOR AND MINOR IN EUROPEAN STUDIES (ES) (approval pending) Note: Courses marked *, such as most "topics" courses, vary in content. They count for ES only if predominantly European in content
COURSES FOR THE MAJOR AND MINOR IN EUROPEAN STUDIES (ES) (approval pending) Note: Courses marked *, such as most "topics" courses, vary in content. They count for ES only if predominantly European in content
The Friendship of Washington and His Adopted Son, the Marquis de Lafayette
 The Friendship of Washington and His Adopted Son, the Marquis de Lafayette Diplomatic Reception Rooms U.S. DEPARTMENT of STATE Adolphe Phalipon (active c.1825 1880) Marquis de Lafayette c.1825 oil on canvas
The Friendship of Washington and His Adopted Son, the Marquis de Lafayette Diplomatic Reception Rooms U.S. DEPARTMENT of STATE Adolphe Phalipon (active c.1825 1880) Marquis de Lafayette c.1825 oil on canvas
Chapter 1. The Renaissance and Reformation 1300-1650
 Chapter 1 The Renaissance and Reformation 1300-1650 The Renaissance The Renaissance was a period of history that sought to join the middle ages to the modern times. This age grew into one of the most culturally
Chapter 1 The Renaissance and Reformation 1300-1650 The Renaissance The Renaissance was a period of history that sought to join the middle ages to the modern times. This age grew into one of the most culturally
Note Taking Study Guide PHILOSOPHY IN THE AGE OF REASON
 SECTION 1 Note Taking Study Guide PHILOSOPHY IN THE AGE OF REASON Focus Question: What effects did Enlightenment philosophers have on government and society? As you read this section in your textbook,
SECTION 1 Note Taking Study Guide PHILOSOPHY IN THE AGE OF REASON Focus Question: What effects did Enlightenment philosophers have on government and society? As you read this section in your textbook,
Advanced Placement (AP ) Social Studies Courses
 Advanced Placement (AP ) Social Studies Courses The AP social studies courses are intended to provide a rigorous college level introduction to the social sciences for high school students. While no official
Advanced Placement (AP ) Social Studies Courses The AP social studies courses are intended to provide a rigorous college level introduction to the social sciences for high school students. While no official
History of Law in Society
 History of Law in Society Laws in Canada Our legal system has its origins in many cultures including aspects of Mosaic Law, Greek Law, Roman Law, French Law, and British Laws. In Canada, we are also influenced
History of Law in Society Laws in Canada Our legal system has its origins in many cultures including aspects of Mosaic Law, Greek Law, Roman Law, French Law, and British Laws. In Canada, we are also influenced
Section III: Jefferson, United States Minister to France
 2002 Shaping the World: Conversation on Democracy A Conversation with Thomas Jefferson and Marquis de Lafayette Section III: Jefferson, United States Minister to France "Behold you, then, my dear friend,
2002 Shaping the World: Conversation on Democracy A Conversation with Thomas Jefferson and Marquis de Lafayette Section III: Jefferson, United States Minister to France "Behold you, then, my dear friend,
Name Class Date. Ancient China Section 4
 Name Class Date Ancient China Section 4 MAIN IDEAS 1. Han dynasty government was based on the ideas of Confucius. 2. Family life was supported and strengthened in Han China. 3. The Han made many achievements
Name Class Date Ancient China Section 4 MAIN IDEAS 1. Han dynasty government was based on the ideas of Confucius. 2. Family life was supported and strengthened in Han China. 3. The Han made many achievements
6 th Grade Vocabulary-ALL CAMPUSES
 6 th Grade Vocabulary-ALL CAMPUSES 6.1 History. The student understands that historical events influence contemporary events. (B) analyze the historical background of the United States to evaluate relationships
6 th Grade Vocabulary-ALL CAMPUSES 6.1 History. The student understands that historical events influence contemporary events. (B) analyze the historical background of the United States to evaluate relationships
Witness an online magazine
 Witness an online magazine Cuba: An Island In Transition www.visionproject.org Photos & Text by Richard Falco Cuba: An Island In Transition Photos & Text by Richard Falco Cuba is quickly approaching a
Witness an online magazine Cuba: An Island In Transition www.visionproject.org Photos & Text by Richard Falco Cuba: An Island In Transition Photos & Text by Richard Falco Cuba is quickly approaching a
Ninth Grade History & Social Science World History I
 SEPTEMBER WHI.1 Historical Research and Geographical Analysis *(ongoing throughout year) identify, analyze, and interpret primary and secondary sources use maps, globes, artifacts, pictures identify major
SEPTEMBER WHI.1 Historical Research and Geographical Analysis *(ongoing throughout year) identify, analyze, and interpret primary and secondary sources use maps, globes, artifacts, pictures identify major
Kansas Board of Regents Precollege Curriculum Courses Approved for University Admissions
 Kansas Board of Regents Precollege Curriculum Courses Approved for University Admissions Original Publication April 6, 2011 Revision Dates June 13, 2011 May 23, 2012 Kansas Board of Regents Precollege
Kansas Board of Regents Precollege Curriculum Courses Approved for University Admissions Original Publication April 6, 2011 Revision Dates June 13, 2011 May 23, 2012 Kansas Board of Regents Precollege
Tudor Resource Box. Introduction
 Introduction Tudor Resource Box Welcome to the Tudor box. This resource is for teachers and group leaders working with Special Educational Needs groups. This box contains resources to support your self-directed
Introduction Tudor Resource Box Welcome to the Tudor box. This resource is for teachers and group leaders working with Special Educational Needs groups. This box contains resources to support your self-directed
STANDARD 3.1 Greece & Rome. STANDARD 3.2 - Mali
 2008 Curriculum Framework Grade Three Social Studies Standards Condensed format created by SOLpass. www.solpass.org Key: red text highlights NEW (2008 revision) content; crossout indicates content cut
2008 Curriculum Framework Grade Three Social Studies Standards Condensed format created by SOLpass. www.solpass.org Key: red text highlights NEW (2008 revision) content; crossout indicates content cut
Modern European History courses, fall 2008 B226 Mafia and other Italian mysteries Carl Ipsen T, Th 2:30-3:45
 Modern European History courses, fall 2008 B226 Mafia and other Italian mysteries Carl Ipsen T, Th 2:30-3:45 B323 The Holocaust Mark Roseman M, W 1:25-2:15; plus discussion B357 Modern France Rebecca Spang
Modern European History courses, fall 2008 B226 Mafia and other Italian mysteries Carl Ipsen T, Th 2:30-3:45 B323 The Holocaust Mark Roseman M, W 1:25-2:15; plus discussion B357 Modern France Rebecca Spang
The failure of the Spanish Armada in 1588 permanently crippled the Spanish navy.
 AP European History Mr. Mercado Name Chapter 15B Politics, Religion, and War (Note: only do the sections Politics, Religion, and War ; Changing Attitudes ; and Literature and Art ) A. True or False Where
AP European History Mr. Mercado Name Chapter 15B Politics, Religion, and War (Note: only do the sections Politics, Religion, and War ; Changing Attitudes ; and Literature and Art ) A. True or False Where
World History: Essential Questions
 World History: Essential Questions Content Standard 1.0: Culture encompasses similarities and differences among people including their beliefs, knowledge, changes, values, and traditions. Students will
World History: Essential Questions Content Standard 1.0: Culture encompasses similarities and differences among people including their beliefs, knowledge, changes, values, and traditions. Students will
Created by Paul Hallett
 The Cuban Missile Crisis was a confrontation during the Cold War between the Soviet Union and the United States regarding the deployment of nuclear missiles in Cuba. The missiles had been placed to protect
The Cuban Missile Crisis was a confrontation during the Cold War between the Soviet Union and the United States regarding the deployment of nuclear missiles in Cuba. The missiles had been placed to protect
International Day of Endangered Lawyer 2013 Page 1
 International Day of Endangered Lawyer 2013 Page 1 BASQUE LAWYERS UNDER THREAT GENERAL REPORT 24 JANUARY 2013 International Day of Endangered Lawyer 2013 Page 2 1. INTRODUCTION Lawyers once again have
International Day of Endangered Lawyer 2013 Page 1 BASQUE LAWYERS UNDER THREAT GENERAL REPORT 24 JANUARY 2013 International Day of Endangered Lawyer 2013 Page 2 1. INTRODUCTION Lawyers once again have
French Revolution [10th grade]
![French Revolution [10th grade] French Revolution [10th grade]](/thumbs/40/20826976.jpg) Trinity University Digital Commons @ Trinity Understanding by Design: Complete Collection Understanding by Design 6-15-2006 French Revolution [10th grade] Jenna Smith Trinity University Follow this and
Trinity University Digital Commons @ Trinity Understanding by Design: Complete Collection Understanding by Design 6-15-2006 French Revolution [10th grade] Jenna Smith Trinity University Follow this and
Overview. Mission Gate, ca. late 1700s Courtesy Texas Archeological Research Labs. Photo by Hunt Wellborn
 H C H A P T E R t h r e e H immigration Overview Chapter 3: Immigration covers many groups involved in the early colonization of Texas: farmers, ranchers, soldiers, missionaries, and slaves. Exhibits in
H C H A P T E R t h r e e H immigration Overview Chapter 3: Immigration covers many groups involved in the early colonization of Texas: farmers, ranchers, soldiers, missionaries, and slaves. Exhibits in
No Taxation without Representation
 No Taxation without Representation After the French and Indian War, England was broke. They had spent a lot of money to protect the colonists in America. England thought that America should help to pay
No Taxation without Representation After the French and Indian War, England was broke. They had spent a lot of money to protect the colonists in America. England thought that America should help to pay
Boston University in Madrid CAS SP 300 HISTORY OF SPANISH ART Summer 2014
 Boston University in Madrid CAS SP 300 HISTORY OF SPANISH ART Summer 2014 General overview: This course is intended to give an overview of the periods, styles and artistic movements in Spain, starting
Boston University in Madrid CAS SP 300 HISTORY OF SPANISH ART Summer 2014 General overview: This course is intended to give an overview of the periods, styles and artistic movements in Spain, starting
A Stroll Through Madrid Medieval Madrid
 A Stroll Through Madrid Medieval Madrid Barrio de la Morería (Moorish Quarter), the plaza del Alamillo was the site of the Arab Court. Nearby, on the Calle Segovia, we find the Casa del Pastor (Shepherd's
A Stroll Through Madrid Medieval Madrid Barrio de la Morería (Moorish Quarter), the plaza del Alamillo was the site of the Arab Court. Nearby, on the Calle Segovia, we find the Casa del Pastor (Shepherd's
Remember the Alamo. The Changing Border of the Southwest
 Remember the Alamo The Changing Border of the Southwest Interact: What do you think this picture shows? In the year 1820, the new country of the United States and the newer country of Mexico had a lot
Remember the Alamo The Changing Border of the Southwest Interact: What do you think this picture shows? In the year 1820, the new country of the United States and the newer country of Mexico had a lot
DesignLab: Exploring Skylines
 DesignLab: Exploring Skylines through the V&A+RIBA Architecture collections Teachers Presentation Notes Teachers notes to accompany the Exploring Skylines introductory Presentation as part of At School
DesignLab: Exploring Skylines through the V&A+RIBA Architecture collections Teachers Presentation Notes Teachers notes to accompany the Exploring Skylines introductory Presentation as part of At School
Fundamental Principles of American Democracy
 Fundamental Principles of American Democracy Standard: 12.1 Students explain the fundamental principles and moral values of American democracy as expressed in the U.S. Constitution and other essential
Fundamental Principles of American Democracy Standard: 12.1 Students explain the fundamental principles and moral values of American democracy as expressed in the U.S. Constitution and other essential
Famous Artists Lapbook
 Famous Artists Lapbook 1 Lapbook Planner Sub-Topic Leonardo da Vinci Michelangelo 4 Flap Pocket with 4 cards Activity/ Website Write facts inside each flap about his painting, portrait, inventions and
Famous Artists Lapbook 1 Lapbook Planner Sub-Topic Leonardo da Vinci Michelangelo 4 Flap Pocket with 4 cards Activity/ Website Write facts inside each flap about his painting, portrait, inventions and
SOCIAL STUDIES UNIT OUTLINES - SIXTH GRADE
 SOCIAL STUDIES UNIT OUTLINES - SIXTH GRADE In sixth grade, students are ready to deepen their understanding of the Earth and its peoples through the study of history, geography, politics, culture, and
SOCIAL STUDIES UNIT OUTLINES - SIXTH GRADE In sixth grade, students are ready to deepen their understanding of the Earth and its peoples through the study of history, geography, politics, culture, and
EU Lesson Plan. Name of Teacher: Sharon Goralewski School: Oakland Schools Title of Lesson Plan: The European Union: United in Diversity
 EU Lesson Plan Name of Teacher: School: Oakland Schools Title of Lesson Plan: The European Union: United in Diversity Grades: 6th or 7 th Description: This lesson introduces the students to the countries
EU Lesson Plan Name of Teacher: School: Oakland Schools Title of Lesson Plan: The European Union: United in Diversity Grades: 6th or 7 th Description: This lesson introduces the students to the countries
CH10 Practice Test 2015
 Name Date Mastering the Content Circle the letter next to the best answer. CH10 Practice Test 2015 1. An important way historians learn about ancient Kush is through A. Syrian trade agreements. B. Sumerian
Name Date Mastering the Content Circle the letter next to the best answer. CH10 Practice Test 2015 1. An important way historians learn about ancient Kush is through A. Syrian trade agreements. B. Sumerian
Chapter 8 C E N T R A L A M E R I C A A N D T H E C A R I B B E A N
 Chapter 8 C E N T R A L A M E R I C A A N D T H E C A R I B B E A N Dictator A ruler who has complete power over the government Communist In a communist economy the government owns all large businesses
Chapter 8 C E N T R A L A M E R I C A A N D T H E C A R I B B E A N Dictator A ruler who has complete power over the government Communist In a communist economy the government owns all large businesses
Please note: Each segment in this Webisode has its own Teaching Guide
 Please note: Each segment in this Webisode has its own Teaching Guide The Statue of Liberty, a gift of international friendship from the people of France to the people of the United States, is a universal
Please note: Each segment in this Webisode has its own Teaching Guide The Statue of Liberty, a gift of international friendship from the people of France to the people of the United States, is a universal
PORTRAIT. Pablo Picasso. Self-Portrait, 1907
 PORTRAIT Pablo Picasso Self-Portrait, 1907 Picasso - Background Information Born Spain 1881, died 1973 aged 92. Flamboyant and extrovert character Larger than life with a great need to be creative and
PORTRAIT Pablo Picasso Self-Portrait, 1907 Picasso - Background Information Born Spain 1881, died 1973 aged 92. Flamboyant and extrovert character Larger than life with a great need to be creative and
Visit guide: self-directed visits
 Visit guide: self-directed visits Who are these materials for? These materials are for ESOL, EFL, EAL or IELTS tutors who are planning self-directed visits to the museum. We have provided some background
Visit guide: self-directed visits Who are these materials for? These materials are for ESOL, EFL, EAL or IELTS tutors who are planning self-directed visits to the museum. We have provided some background
The Arts and Architecture
 Lesson 4 The Legacy of Greece MAIN IDEAS Culture Greek art and architecture introduced new styles and concepts that set standards for generations of artists around the world. Culture The Greek love of
Lesson 4 The Legacy of Greece MAIN IDEAS Culture Greek art and architecture introduced new styles and concepts that set standards for generations of artists around the world. Culture The Greek love of
Becoming a World Power. The Imperialist Vision. Imperialism (cont) 1872-1912. Americans wanted to develop overseas markets
 Becoming a World Power 1872-1912 The Imperialist Vision Imperialism economic and political domination of a strong nation over a weaker one Became popular with countries in Europe Imperialism (cont) Protectorates
Becoming a World Power 1872-1912 The Imperialist Vision Imperialism economic and political domination of a strong nation over a weaker one Became popular with countries in Europe Imperialism (cont) Protectorates
Colonial Influences STEP BY STEP. OPTIONAL: A PowerPoint presentation is available to walk students through the activities in this lesson.
 Teacher s Guide Colonial Influences Time Needed: One to two class periods Learning Objectives. Students will be able to: Materials Needed: Student worksheets, overhead or computer projector, scissors,
Teacher s Guide Colonial Influences Time Needed: One to two class periods Learning Objectives. Students will be able to: Materials Needed: Student worksheets, overhead or computer projector, scissors,
Second Grade The War of 1812 Assessment
 Second Grade The War of 1812 Assessment 1a. Who was president during the War of 1812? a. George Washington b. James Madison 1b. Who was president during the War of 1812? a. George Washington b. James Madison
Second Grade The War of 1812 Assessment 1a. Who was president during the War of 1812? a. George Washington b. James Madison 1b. Who was president during the War of 1812? a. George Washington b. James Madison
A-H 106 RENAISSANCE THROUGH MODERN ART. (3) Historical development of Western art and architecture from the fourteenth century through the present.
 101 INTRODUCTION TO VISUAL STUDIES. (3) The course introduces students to the concepts and techniques of visual literacy. It explores a full spectrum of man-made visual forms encountered by contemporary
101 INTRODUCTION TO VISUAL STUDIES. (3) The course introduces students to the concepts and techniques of visual literacy. It explores a full spectrum of man-made visual forms encountered by contemporary
EUROPEAN COURSES OFFERED AT FIU
 EUROPEAN COURSES OFFERED AT FIU Florida International University Core EU Courses CPO 3103 Politics of Western Europe CPO 3104 Politics of the European Union CPO 4461 Politics of Eastern Europe CPO 4930
EUROPEAN COURSES OFFERED AT FIU Florida International University Core EU Courses CPO 3103 Politics of Western Europe CPO 3104 Politics of the European Union CPO 4461 Politics of Eastern Europe CPO 4930
Geneva CUSD 304 Content-Area Curriculum Frameworks Grades 6-12 Social Studies
 Geneva CUSD 304 Content-Area Curriculum Frameworks Grades 6-12 Social Studies Mission Statement It is our belief that Social Studies education is ultimately to prepare students to assume the responsibilities
Geneva CUSD 304 Content-Area Curriculum Frameworks Grades 6-12 Social Studies Mission Statement It is our belief that Social Studies education is ultimately to prepare students to assume the responsibilities
Essential Question: What was the impact of European imperialism in Africa and India?
 Essential Question: What was the impact of European imperialism in Africa and India? Unit X Quiz 2 1. When did the Suez Canal open? 2. Why was it initially difficult for European powers to control their
Essential Question: What was the impact of European imperialism in Africa and India? Unit X Quiz 2 1. When did the Suez Canal open? 2. Why was it initially difficult for European powers to control their
COURSE OFFERINGS at least one FOUR COURSES 12 CREDITS not
 COURSE OFFERINGS UHM Study Abroad Center Lorenzo de Medici (LdM) Semester in Italy: Florence Rome Three Cities www.lorenzodemedici.org ENROLLMENT 1. Not all courses are offered during both semesters. Prospective
COURSE OFFERINGS UHM Study Abroad Center Lorenzo de Medici (LdM) Semester in Italy: Florence Rome Three Cities www.lorenzodemedici.org ENROLLMENT 1. Not all courses are offered during both semesters. Prospective
The French Revolution A Brief Outline
 FOUR STAGES Moderate (1789-1792) Reign of Terror (1793-94) Reaction (1794-98) Napoleonic (1799-1815) The French Revolution A Brief Outline Why? A fed up people revolt against old ways, economic injustice,
FOUR STAGES Moderate (1789-1792) Reign of Terror (1793-94) Reaction (1794-98) Napoleonic (1799-1815) The French Revolution A Brief Outline Why? A fed up people revolt against old ways, economic injustice,
Assignment Discovery Online Curriculum. Lesson Title: U.S.-Cuba Relations. Grade level: 9-12. Subject Area: U.S. History, Geography
 Assignment Discovery Online Curriculum Lesson Title: U.S.-Cuba Relations Grade level: 9-12 Subject Area: U.S. History, Geography Duration: Two class periods Objectives: Students will do the following:
Assignment Discovery Online Curriculum Lesson Title: U.S.-Cuba Relations Grade level: 9-12 Subject Area: U.S. History, Geography Duration: Two class periods Objectives: Students will do the following:
Activity Five: Napoleon
 TEACHER DEBRIEFING SHEET Discussion Questions: 1. What were the goals of the French Revolution? To what extent were those goals met in the decade from 1789 to 1799? To what extent were those goals met
TEACHER DEBRIEFING SHEET Discussion Questions: 1. What were the goals of the French Revolution? To what extent were those goals met in the decade from 1789 to 1799? To what extent were those goals met
Keywords for the study of Junior Cert art
 able abstract acrylic activity aesthetic/aesthetics analyze ancient animation applied arch arches architect architectural architecture art art process artist artistic artists arts artwork artworks assemble
able abstract acrylic activity aesthetic/aesthetics analyze ancient animation applied arch arches architect architectural architecture art art process artist artistic artists arts artwork artworks assemble
Cultural Heritage Management, Master Degree French University in Egypt, Programme Course Contents
 Cultural Management, Master Degree French University in Egypt, Programme Course Contents Semester 1 216 30 Introduction to Cultural heritage Hours Credits Course [Module] Contents 18 2,5 Ses1& 2, Definitions
Cultural Management, Master Degree French University in Egypt, Programme Course Contents Semester 1 216 30 Introduction to Cultural heritage Hours Credits Course [Module] Contents 18 2,5 Ses1& 2, Definitions
Timeline of Egyptian History. Ancient Egypt (Languages: Egyptian written in hieroglyphics and Hieratic script)
 Timeline of Egyptian History 1 Ancient Egypt (Languages: Egyptian written in hieroglyphics and Hieratic script) Timeline of Egyptian History 2 Early Dynastic Period 3100 2686 BCE 1 st & 2 nd Dynasty Narmer
Timeline of Egyptian History 1 Ancient Egypt (Languages: Egyptian written in hieroglyphics and Hieratic script) Timeline of Egyptian History 2 Early Dynastic Period 3100 2686 BCE 1 st & 2 nd Dynasty Narmer
Summer Travel Course Units: 6 Units Dates: Five Weeks from Monday May 27-Friday June 29 (2013)
 Ethnic Studies N180 Summer Session A (Granada, Spain) University of California, Berkeley Muslims in the West: From Islamic Spain (711-1492) and Construction of Otherness (1492-2013) to 911 Professor Hatem
Ethnic Studies N180 Summer Session A (Granada, Spain) University of California, Berkeley Muslims in the West: From Islamic Spain (711-1492) and Construction of Otherness (1492-2013) to 911 Professor Hatem
AP EUROPEAN HISTORY 2014 SCORING GUIDELINES
 AP EUROPEAN HISTORY 2014 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 3 Analyze the similarities in the methods that various absolute monarchs used in the 1600s and 1700s to consolidate and increase their power. 9 8 Points
AP EUROPEAN HISTORY 2014 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 3 Analyze the similarities in the methods that various absolute monarchs used in the 1600s and 1700s to consolidate and increase their power. 9 8 Points
WORLD HISTORY: SCIENTIFIC REVOLUTION AND ENLIGHTENMENT. Jeopardy Version Watch out Alex Trebek
 WORLD HISTORY: SCIENTIFIC REVOLUTION AND ENLIGHTENMENT Jeopardy Version Watch out Alex Trebek Scientists Philosophes Enlightenment Spreads Terms Thnkers 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300
WORLD HISTORY: SCIENTIFIC REVOLUTION AND ENLIGHTENMENT Jeopardy Version Watch out Alex Trebek Scientists Philosophes Enlightenment Spreads Terms Thnkers 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300
A-H 106 RENAISSANCE THROUGH MODERN ART. (3) Historical development of Western art and architecture from the fourteenth century through the present.
 # 101 INTRODUCTION TO VISUAL STUDIES. (3) The course introduces students to the concepts and techniques of visual literacy. It explores a full spectrum of man-made visual forms encountered by contemporary
# 101 INTRODUCTION TO VISUAL STUDIES. (3) The course introduces students to the concepts and techniques of visual literacy. It explores a full spectrum of man-made visual forms encountered by contemporary
ointillism D. a.~. c~~fr2~.ct 1.a14 4A1~ r~ :~ ~ Sq ~Z See the dots that make up the man from Seurat s painting The Circus
 History >> Art History General Overview Art History and Artists ointillism Pointillism is often considered part of the Post-impressionist movement. It was primarily invented by painters George Seurat and
History >> Art History General Overview Art History and Artists ointillism Pointillism is often considered part of the Post-impressionist movement. It was primarily invented by painters George Seurat and
UNIT Y213: THE FRENCH REVOLUTION AND THE RULE OF NAPOLEON
 UNIT Y213: THE FRENCH REVOLUTION AND THE RULE OF NAPOLEON NOTE: BASED ON 2X 50 MINUTE LESSONS PER WEEK TERMS BASED ON 6 TERM YEAR. Key Topic Term Week Number Indicative Content Extended Content Resources
UNIT Y213: THE FRENCH REVOLUTION AND THE RULE OF NAPOLEON NOTE: BASED ON 2X 50 MINUTE LESSONS PER WEEK TERMS BASED ON 6 TERM YEAR. Key Topic Term Week Number Indicative Content Extended Content Resources
THE AGE OF ENLIGHTENMENT
 THE AGE OF ENLIGHTENMENT To view this PDF as a projectable presentation, save the file, click View in the top menu bar of the file, and select Full Screen Mode To request an editable PPT version of this
THE AGE OF ENLIGHTENMENT To view this PDF as a projectable presentation, save the file, click View in the top menu bar of the file, and select Full Screen Mode To request an editable PPT version of this
GRADE 7 SOCIAL STUDIES. History
 GRADE 7 SOCIAL STUDIES History Standard 1 Historical Thinking Skills Students use information and concepts to interpret, analyze, and draw conclusions about United States history from 1763 1877. 7.1.1
GRADE 7 SOCIAL STUDIES History Standard 1 Historical Thinking Skills Students use information and concepts to interpret, analyze, and draw conclusions about United States history from 1763 1877. 7.1.1
