A MyPerformance Guide to Performance Conversations
|
|
|
- Edwina Jennings
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A MyPerformance Guide to Performance Conversations brought to you by the BC Public Service Agency
2 contents Elements of a Conversation Preparing for the Conversation Clear on Intent/Topic for Discussion Be Specific: Support your Feedback with Clear Examples Effective Questioning Asking for Feedback/Inquiring into the Other s Perspective Listening Understanding Recognition Making Agreements Conversation Scenarios for Supervisors Planning Conversations (Goal Setting) End-of-Year Rating Conversations Addressing a Performance Issue When There May be a Health Issue
3 Elements of a Conversation A person isn t who they are during the last conversation you had with them they re who they ve been throughout your whole relationship. ~ Rainer Maria Wilke MyPerformance is all about the conversation between a supervisor and an employee. The objective is for all employees to be engaged in meaningful conversations about their performance and development. Research has demonstrated that trusted feedback between supervisors and employees has one of the greatest impacts on employee engagement, motivation and results, and everyone benefits when honest conversations are the norm. This guide is intended for employees and supervisors and will provide you with best practices for having these conversations. There are several common elements to consider when preparing for a performance conversation, keeping in mind that the goal is to engage all employees in meaningful conversations about their performance and development. These conversations are a shared responsibility, with both an employee and a supervisor being active participants and preparing for them. These conversations should be ongoing, and they can be both formal and informal throughout the year. The elements below will go into more detail on where to put your focus as you prepare and have these conversations. Preparing for the Conversation Consider the timing, your own mindset and your clarity of thought. By focusing on what you really want from the conversation for yourself and for the other person you can keep the conversation positive and moving forward. Whether you are an employee or a supervisor, some questions to consider before having a conversation are: What is my intention? How do I want to approach this conversation? What is my focus for this conversation (inquiring, coaching, advising, requesting, directing, dealing with a specific situation or issue, etc.)? What is the impact I want to have? How will my body language mirror my intention? What could be impacting how I view the situation? What have I already said or done relating to the subject of this conversation? Have I contributed to this situation in some way (e.g. being unclear about expectations)? How can we obtain the best possible outcome? Page 3
4 Preparing yourself also includes considering which communication style is appropriate, given the person, the situation, and the intention of the conversation. For example, a supervisor may take a more directive approach with a new employee who is just learning the job and requires specific instructions. A coaching approach may be more appropriate if the conversation is about career goals. Know your audience and be aware of your own default style, possible biases and how they could support or take away from the conversation. When choosing the approach that fits the situation, you may also want to consider demographics. For instance, you will likely need to adjust your communication style for younger employees, who typically like to be well informed but don t like to be in lengthy meetings. Be prepared to resist the temptation to respond quickly to any differing thoughts. It will be more productive to inquire into the other perspective. Instead, be ready to say: Can you tell me more about that? Clear on Intent/Topic for Discussion When you need to have a conversation with someone, it makes a tremendous difference if you briefly explain what you would like to talk about ahead of time, especially if it is a conversation you expect will require more time, effort and involvement. If this is the case, prior to the meeting state your intention: Having the knowledge up front allows everyone the opportunity to better prepare for the topic, understand their role and participate in a conversation. Be Specific: Support your Feedback with Clear Examples Without clear examples, your message and feedback are less likely to be understood and applied. If you are a supervisor, providing facts and reasons behind your observations helps ensure you are evaluating job performance and not the person, and makes feedback easier to understand. Generalizations and unclear feedback, even of a positive nature, will have limited impact. As an example, consider which of the following feedback is more effective: Good job, Aman. ; or Aman, that new procedure you developed for handling priority cases has really improved our customer satisfaction. Thanks for coming up with it. In performance conversations, look at what work was delivered based on quality and quantity relative to job requirements, then how that work was done. Some people have found the STAR method (Situation, Task, Action, Result) of describing a situation a helpful structure for presenting examples. Here s an illustration using the scenario with Aman: I would like to : give/receive feedback... provide advice about give/get instructions make plans for negotiate about explore possibilities make a request ask for support etc. Page 4
5 Situation Priority cases are being missed or incorrectly assigned during the intake process, resulting in delays and customer complaints are on the rise. Task Action Result Find a way to ensure that cases are accurately reviewed and assigned appropriately for timely resolution. Aman reviewed the existing process, identified inefficiencies and trouble spots, and worked collaboratively with intake staff to develop new procedures to correctly review and assign priority cases. Priority cases are assigned and dealt with in a timelier manner, resulting in significantly improved customer satisfaction. Effective Questioning Asking effective questions is integral to having good performance conversations. Consider what it is you want to learn and determine the most appropriate type of questions to gain this information. Remain curious and ask well-formulated questions that encourage employees to look at their own performance and work behaviour. You can encourage your conversation partners to share more of their thoughts and feelings by asking open-ended, rather than yes/no questions. Open-ended questions allow for a wide range of responses. For example, asking How did you find your new work assignment? will evoke a more detailed response than, Did you like it? (which could be answered with a simple yes or no ). Here are a few tips regarding the use of questions: Be open to all possible answers. Sometimes people ask questions but are willing to accept only a specific answer. When you ask a question, you have to be willing to consider whatever responses you get and not overreact. Questions that start with why tend to make people feel defensive. You can replace why questions with phrasing that tends not to cause that reaction. For example, rather than asking, Why are you late so often? try, What kinds of things are preventing you from arriving at work on time? Notice the difference in feel? Don t use questions to say things indirectly. For example, Don t you think you should be more diligent in completing your work? isn t really a legitimate question. It s a rhetorical question or your opinion dressed up as a question. It will be heard as I want you to be more diligent in completing your work. Questions used to mask statements, opinions or requests can create mistrust. Keep your questions simple. For example, a compound question is several questions in one and lacks focus. These questions are confusing and tend to result in low-quality responses. Here s an example: What s causing you to be late on many Fridays and to leave early on Wednesdays? That s two questions and you re not likely to get good answers to both. Separate the issues and make your questions simpler and more specific. Page 5
6 Here are a few sample questions to engage someone in conversation: What do you like best about your job? What s challenging? What do you think are your strengths? Opportunities for development? How can I help you optimize your performance? Who can you collaborate with? What haven t you thought of? How can I support you? Asking for Feedback/Inquiring into the Other s Perspective For conversations to be meaningful and to build a trusting relationship, you want to understand what is happening from the other s perspective. By inquiring into the other person s views you gain an opportunity to really listen for the benefit of your own learning. Supervisors may find it helpful to ask questions to encourage employees to self-evaluate: What s your perspective on this? Or, What are your thoughts? Overall, how do you feel your performance has been? Tell me about some of your successes this year. What areas do you feel you could most improve in? What would help you improve in those areas? What s getting in the way of your success? What do you need from me? Your goal is to encourage the other person to share as much as possible from their point of view. Stay open and curious, listen and let them talk until they are finished. Resist the temptation to interject your opinion about their statements. Listen and learn all you can about the situation. You may be surprised, at times, to learn that how the other person views the subject is different than what you expected. By allowing them to share their thoughts, you will gain a keener insight as to how to approach your points. More sample questions for inviting the other person s perspective: Inviting developmental self-appraisal from the employee How might you improve? What might help increase your effectiveness at? When you consider your performance at, what opportunities do you see for your continued development? When you want someone to talk about why they did something Help me understand. Please tell me more about your reasons for approaching it that way? Listening Listening is not passive, but is a skill to practice and strengthen. It s essential for creating rapport, trust and understanding during performance conversations. Imagine a conversation where the other person was distracted, checking their Blackberry or , maybe missing the point of your message. How did you feel? Maybe those behaviours made you feel that they were too busy for you and that they didn t really care what you were saying. How would you rate the quality of that conversation? Listening well sends the message that this person and their performance are important to you. It also creates an environment where you re more likely to be listened to. Remember the WAIT acronym ~ Why am I talking? Page 6
7 Active listening goes beyond just being in the room. It entails really focusing on what the other person is saying, looking beyond just the words being said and looking for the main ideas being expressed, as well as emotions and body language. Set the environment by avoiding interruptions and managing distractions. Show respectful eye contact, acknowledge what you ve heard, and, rather than making assumptions, paraphrase or ask questions to check your understanding. Don t finish someone s sentences for them or use the time they are speaking to prepare your next comment. By remaining silent while the other person speaks, you will gain insight and understanding. Understanding For many, there is nothing more satisfying in a conversation, and in building relationships, than being seen and understood. Understanding engenders respect, respect encourages openness, and openness lowers one s defenses in a conversation. Acknowledge: Their point of view although you may not agree with it completely. Their experiences and how they feel about them. Do not minimize people s emotions or feelings. What s important to them by showing respect to their ideas and plans, even if you think a plan has missing elements. Acknowledge it first, and then give your suggestions. The art of conversation is the art of hearing as well as of being heard. ~ William Hazlitt, Selected Essays, Recognition People who feel recognized and appreciated are more productive and innovative. Recognition is an effective form of communication that reinforces and rewards the most important outcomes people create. You can refer to the MyPerformance Guide to Employee Recognition to learn more about the practice of meaningful and frequent recognition, and how it benefits individuals, teams and the organization. Making Agreements Before wrapping up your conversation, it s important to ensure mutual understanding and agreement on standards, expectations and timelines. How often have you had a conversation where you walked away not quite sure either of what you re supposed to do, or what the other person is planning to do? Finishing performance conversations clearly, with a quick summary and a common understanding of what s going to happen next, is essential for moving forward. This includes being mutually accountable and honouring whatever commitments have been made. Ideally, you will make mutual agreements; however, there will be situations when a supervisor will find it necessary to give specific directions. In Conclusion Remember, what s really important are the conversations, not just filling out a form at the end of a performance cycle. These conversations are directly impacted by the relationships between employees and supervisors. For conversations to be truly meaningful, people need to know they re supported. Trusted feedback leads to higher engagement, motivation and results and everyone benefits when honest conversations are the norm. Because these conversations are a shared responsibility, the common elements we have considered are relevant for both employees and supervisors. RESOURCE ALERT What does it mean to take a coaching approach to conversations? This is a style of communication that enhances employees engagement and supports improved performance. Communication is more two-way, involving less telling and directing, while increasing listening and drawing out with powerful questions. When using a coaching approach, the leader may still define the goals and tasks, but seeks input and suggestions on how to make those happen. This approach supports the development of staff in their job-related activities and ensures everyone has the skills and knowledge to get their work done. Please read on for specific conversation scenarios for supervisors... Page 7
8 Conversation Scenarios for Supervisors RESOURCE ALERTS A coaching approach can help you support an employee in considering what meaningful and relevant work goals will be, based on the branch s objectives and their strengths. To support supervisors in building this skill, consider the one-day in-person Coaching Approach to Conversations course offered by the Learning Centre. SMART Goals: S pecific M easurable A ttainable R ealistic and Relevant T ime-based HARD Goals: H eartfelt A nimated R equired D ifficult This section of the guide is designed to support supervisors in specific situations they may face. Planning Conversations This type of conversation allows for a common understanding of the way forward and a clarified focus for your employee s day to day work. A planning conversation involves setting goals for the year and agreeing on performance expectations and measures. Clear planning conversations provide a strong foundation for successful performance conversations throughout the year. To go a step further, you can learn how to use MyPerformance to its fullest potential by clarifying the meaning of the vision and strategy with every employee. For more information on this you can refer to A MyPerformance Guide to Maximizing Results. And don t forget to consider the corporate values as well, which describe the qualities we value in our colleagues and in our organization, while providing us with a common language for describing how we do our various jobs. Aspects of a successful planning conversation include the following: Choosing the right time and agreeing ahead on the purpose of the conversation so both of you can come prepared. Taking a coaching approach (see the resource alerts on how to access courses and resources). Agreeing on key work goals and ensuring they are aligned with organizational objectives (consider the principles of SMART and HARD goals). Considering what competencies and behaviours that need to be demonstrated to support those work goals. Discussing learning and development goals for the year. Offering supports as needed. Reviewing the MyPerformance rating scale and discussing how the employee can best contribute during the year and where on the scale they want to be at the end of the cycle. What s really important here is the conversation. MyPerformance Profile is a tool to help you record the highlights of your conversation after you have it. For the process to be meaningful for both of you, you don t want filling out the boxes in the tool to be what drives the conversation. The conversation drives the tool; the tool doesn t drive the conversation. Page 8
9 End-of-Year Rating Conversations In a review and rating conversation, you and your employee will together go back over the employee s results of the past year, linking back to the goals set in your initial planning conversation and all of the ongoing conversations you have had throughout the cycle. Discuss together how you each see the key work goal outcomes, the competencies displayed and any learning accomplishments. Focus on behaviours displayed rather than an assessment of the person. Aim for a shared understanding and discuss the final rating. If you re consistent about addressing issues and giving feedback throughout the year, your overall assessment of the employee s work shouldn t come as a surprise to them. If your planning conversation at the beginning of the year included specific measurables, then you begin with a shared understanding of desired behaviours and the rating conversation will link back to that discussion. However, what if you and your employee don t agree on the rating, despite your best efforts? It s challenging when your rating of your employee s performance doesn t match with how they rate their own work. It s important to provide specific observable behaviours to support your rating. Then, really listen and seek to understand your employee s perspective on their performance and hear their examples. Look behind their self-rating to the reasons for it. What made them select this one? What accomplishments/actions of the last year are they seeing that lead to this rating? Acknowledge their perspective and really consider the information they are sharing. Don t feel pressured to respond right away. Take the time you need to think the matter through and continue the conversation at a later date. This will ensure your final decision is a thoughtful one, based on all the information. It may be that you change your rating. Alternately, you might feel that your original rating is still appropriate. When you come back to have the final rating discussion, be prepared to explain what your employee needs to do to move up to the next level. What are the behaviours they need to display, and how can you support their growth? A Performance Issue Needs Addressing Addressing performance issues are some of the more awkward conversations for many of us. One way supervisors can err is by being so vague that an employee doesn t understand what changes are expected. Conversations can also be abrupt or come from a place of frustration/anger. First, ask yourself if this is a good time to give feedback. Generally, it s best to have discussions about an issue closely following the behaviour. However, you could notice that either you or the other individual isn t in the right frame of mind for a productive conversation. If that s the case, find another moment, but don t postpone the conversation for long. Also consider your responsibilities as a supervisor and whether you may have contributed to the situation (for example, perhaps by giving unclear instructions or not providing necessary training). Be prepared to provide what s necessary if anything has been missed. Addressing issues with an employee in the early stages includes the following: Being able to clearly state the issue. Basing comments on specific situations and being prepared to share an example or two (what was the actual behaviour noticed?). Explaining the impact of the behaviour (why this is important?). Asking the individual for their perspective (and following that by really listening). Involving the individual in determining next steps. If you are working on building your skill in having these kinds of conversations, consider accessing the performance coaching services through MyHR. Repetitive or complex performance issues may require additional steps. Please see the box on this page for resources in those situations. RESOURCE ALERT These principles for addressing issues can be applied in many situations. However, complex or repetitive performance issues or one instance of a serious nature will require more personalized advice from an HR professional. We encourage you to contact an HR Advisor through AskMyHR, selecting the service Supervising and Leading People. Page 9
10 RESOURCE ALERT Information in the form of e-learning modules is also available. The modules cover a range of topics related to supporting employees who may have an illness or injury to stay at work, or return to work, as soon as possible after a period of illness. They include such features as questions you can ask, questions you can t ask and how to communicate regularly with employees who are off work. The purpose of the modules is to provide just- in-time information to help you manage situations on your own, or to direct you to specialists that can support both you and your employee. Two truths: When There May be a Health Issue 1) Employees are responsible for their performance at work, including managing health issues that affect their performance; AND 2) When an employee s performance is deteriorating or their attendance is being affected, supervisors have a responsibility to have a conversation about their observations and/ or concerns so that they are supportive of the employee and able to meet operational requirements. Both these statements are true, yet many managers are aware of potential sensitivities in these areas and don t feel confident in their ability to have a productive performance conversation when health factors may be involved. As supervisors, you re in the best position to observe that an employee may be struggling and you have a responsibility to act. This takes the form of communicating your observations and concerns to the employee and getting their input and perspective. In these conversations, it s best not to assume that there is a health issue, but to provide an opportunity for your employee to let you know about anything that may be affecting his/her performance. Questions like, Is everything alright?, and, Is there anything I should know about factors that might be impacting your performance? are less intrusive and less leading than questions specifically about health. This conversation should be about performance (or attendance) and possibly become about health, if the employee takes it there. It shouldn t begin as a health conversation. In general, building solid respectful relationships with your employees is the foundation that helps these tricky conversations go more smoothly. Maintaining regular contact with employees (including when they are absent on sick leave) is also essential to the success of these situations and the early, sustained return to regular attendance and performance. These scenarios cover general principles for just a few types of conversations. For more information, tools and resources please refer to the MyPerformance page on MyHR. You may also access specialized advice for specific situations through AskMyHR. Wrapping Up This guide was designed in recognition that the most important aspect of performance management is not the forms to be completed or the processes to follow, but the meaningful conversations we can have to promote job success, growth and development. Trusted feedback between supervisors and employees has one of the greatest impacts on employee engagement, motivation and results, and everyone benefits when honest conversations are the norm. By understanding the importance of having regular performance conversations, and practicing the tips provided in this guide, you will be able to approach these conversations with confidence. RESOURCE ALERT Are you looking for support in recording your conversations into your and/or employee s MyPerformance Profile? Click on the Profile Help button Profile Help in your MyPerformance Profile where you will find helpful tools like profile samples, user guide, and FAQ s. To get started, visit MyHR for a direct link to your MyPerformance Profile. Page 10
11
Performance Management
 Performance Management WORKSHOP HANDOUTS Facilitated by: Tara Kemes, Vantage Point Knowledge Philanthropist June 2013 Page 1 of 16 Handout 1 Performance Management System Overview What is performance management?
Performance Management WORKSHOP HANDOUTS Facilitated by: Tara Kemes, Vantage Point Knowledge Philanthropist June 2013 Page 1 of 16 Handout 1 Performance Management System Overview What is performance management?
PERFORMANCE DEVELOPMENT PROGRAM
 PERFORMANCE DEVELOPMENT PROGRAM Document Number SOP2009-056 File No. 08/470-02 (D009/8429) Date issued 16 September 2009 Author Branch Director Workforce Unit Branch contact Strategic Projects Coordinator
PERFORMANCE DEVELOPMENT PROGRAM Document Number SOP2009-056 File No. 08/470-02 (D009/8429) Date issued 16 September 2009 Author Branch Director Workforce Unit Branch contact Strategic Projects Coordinator
Overview of Performance Management. Taking Steps to Enhance Individual & Organizational Effectiveness
 Overview of Performance Management Taking Steps to Enhance Individual & Organizational Effectiveness Performance Management Performance management is the process through which supervisors and those they
Overview of Performance Management Taking Steps to Enhance Individual & Organizational Effectiveness Performance Management Performance management is the process through which supervisors and those they
Guide to Effective Staff Performance Evaluations
 Guide to Effective Staff Performance Evaluations Compiled by Human Resources Siemens Hall, Room 211 The research is clear. The outcome is consistent. We know with certainty that the most powerful leadership
Guide to Effective Staff Performance Evaluations Compiled by Human Resources Siemens Hall, Room 211 The research is clear. The outcome is consistent. We know with certainty that the most powerful leadership
Managing Performance An Introduction/Refresher. March 15, 2000
 Managing Performance An Introduction/Refresher March 15, 2000 Agenda The process is a resource to help measure and improve performance. The Performance Management Process & Form Performance Planning Integrating
Managing Performance An Introduction/Refresher March 15, 2000 Agenda The process is a resource to help measure and improve performance. The Performance Management Process & Form Performance Planning Integrating
DESCRIBING OUR COMPETENCIES. new thinking at work
 DESCRIBING OUR COMPETENCIES new thinking at work OUR COMPETENCIES - AT A GLANCE 2 PERSONAL EFFECTIVENESS Influencing Communicating Self-development Decision-making PROVIDING EXCELLENT CUSTOMER SERVICE
DESCRIBING OUR COMPETENCIES new thinking at work OUR COMPETENCIES - AT A GLANCE 2 PERSONAL EFFECTIVENESS Influencing Communicating Self-development Decision-making PROVIDING EXCELLENT CUSTOMER SERVICE
Tools for Effective Performance Management
 Tools for Effective Performance Management TABLE OF CONTENTS Section Page How to Get the Most from the Formal Review Process 2 Six Key Actions to Prepare for the Review 5 Sample Forms 11 How to Deal with
Tools for Effective Performance Management TABLE OF CONTENTS Section Page How to Get the Most from the Formal Review Process 2 Six Key Actions to Prepare for the Review 5 Sample Forms 11 How to Deal with
EFFECTIVE PERFORMANCE APPRAISALS
 EFFECTIVE PERFORMANCE APPRAISALS When used correctly, the performance appraisal process is a useful technique to hold employees accountable for desired results, and aligning them with business strategy.
EFFECTIVE PERFORMANCE APPRAISALS When used correctly, the performance appraisal process is a useful technique to hold employees accountable for desired results, and aligning them with business strategy.
Table of Contents Page Introduction... 3 Key Feedback Principles... 4 Types of Feedback... 5
 P r o v i d i n g q u a l i t y f e e d b a c k a g o o d p r a c t i c e g u i d e Table of Contents Page Introduction... 3 Key Feedback Principles... 4 Types of Feedback... 5 Positive Feedback... 5 Developmental
P r o v i d i n g q u a l i t y f e e d b a c k a g o o d p r a c t i c e g u i d e Table of Contents Page Introduction... 3 Key Feedback Principles... 4 Types of Feedback... 5 Positive Feedback... 5 Developmental
GUIDE TO EFFECTIVE STAFF PERFORMANCE EVALUATIONS
 GUIDE TO EFFECTIVE STAFF PERFORMANCE EVALUATIONS The research is clear. The outcome is consistent. We know with certainty that the most powerful leadership tool for improving productivity and increasing
GUIDE TO EFFECTIVE STAFF PERFORMANCE EVALUATIONS The research is clear. The outcome is consistent. We know with certainty that the most powerful leadership tool for improving productivity and increasing
Performance Review and Development Plan Guidelines
 Performance Review and Development Plan Guidelines What is a Performance Appraisal?... 1 Benefits of Performance Appraisals... 1 Performance Management vs. Performance Review... 2 NSCAD University s Performance
Performance Review and Development Plan Guidelines What is a Performance Appraisal?... 1 Benefits of Performance Appraisals... 1 Performance Management vs. Performance Review... 2 NSCAD University s Performance
Presented by: Heather J. Donnelly HDI Certified Instructor. Telephone Skills
 Presented by: Heather J. Donnelly HDI Certified Instructor Telephone Skills Objectives Recall the key principles for dealing with an irate caller Apply specific techniques effective in providing excellent
Presented by: Heather J. Donnelly HDI Certified Instructor Telephone Skills Objectives Recall the key principles for dealing with an irate caller Apply specific techniques effective in providing excellent
Preparing for the Performance Review Process
 Preparing for the Performance Review Process 1 HOW AM I DOING? 3 A. WHY CONDUCT PERFORMANCE REVIEWS? 3 A.1 BENEFITS FOR UNIVERSITY 3 A.2 BENEFITS FOR SUPERVISOR/UNIT HEAD 3 A.3 BENEFITS FOR EMPLOYEE 4
Preparing for the Performance Review Process 1 HOW AM I DOING? 3 A. WHY CONDUCT PERFORMANCE REVIEWS? 3 A.1 BENEFITS FOR UNIVERSITY 3 A.2 BENEFITS FOR SUPERVISOR/UNIT HEAD 3 A.3 BENEFITS FOR EMPLOYEE 4
Learning and Development Hiring Manager Guide For Onboarding A New Manager
 Learning and Development Hiring Manager Guide For Onboarding A New Manager www.yorku.ca/hr/hrlearn.html Table of Contents Introduction...1 What is Onboarding?...1 What is the Difference Between Orientation
Learning and Development Hiring Manager Guide For Onboarding A New Manager www.yorku.ca/hr/hrlearn.html Table of Contents Introduction...1 What is Onboarding?...1 What is the Difference Between Orientation
MODULE 10 CHANGE MANAGEMENT AND COMMUNICATION
 MODULE 10 CHANGE MANAGEMENT AND COMMUNICATION PART OF A MODULAR TRAINING RESOURCE Commonwealth of Australia 2015. With the exception of the Commonwealth Coat of Arms and where otherwise noted all material
MODULE 10 CHANGE MANAGEMENT AND COMMUNICATION PART OF A MODULAR TRAINING RESOURCE Commonwealth of Australia 2015. With the exception of the Commonwealth Coat of Arms and where otherwise noted all material
Performance Evaluation Workshop February/March 2015
 February/March 2015 Overview Core Curriculum 2 Preparing Meaningful Performance Evaluations 3 1 February/March 2015 Training Topics: Conducting Performance Evaluations What is the purpose of performance
February/March 2015 Overview Core Curriculum 2 Preparing Meaningful Performance Evaluations 3 1 February/March 2015 Training Topics: Conducting Performance Evaluations What is the purpose of performance
Maximizing the Performance of Your Team
 Maximizing the Performance of Your Team Overview How to work with your employees to ensure they re reaching their potential. Understand the individuals you manage and your team Set goals and make performance
Maximizing the Performance of Your Team Overview How to work with your employees to ensure they re reaching their potential. Understand the individuals you manage and your team Set goals and make performance
Advantages of the Phone Interview. Types of Telephone Interviews. What to Expect
 The Telephone Interview Telephone interviews are used by companies to screen candidates and narrow the pool of applicants who will be invited for in-person interviews. They minimize expenses associated
The Telephone Interview Telephone interviews are used by companies to screen candidates and narrow the pool of applicants who will be invited for in-person interviews. They minimize expenses associated
Performance management the key to ensuring effective staff
 Performance management the key to ensuring effective staff How do you get the best out of your staff? What factors are key in people achieving what they need to achieve -- being effective in their role?
Performance management the key to ensuring effective staff How do you get the best out of your staff? What factors are key in people achieving what they need to achieve -- being effective in their role?
HUMAN RESOURSES COLLEGE OF EDUCATION AND HUMAN ECOLOGY. Manager's Guide to Mid-Year Performance Management
 HUMAN RESOURSES COLLEGE OF EDUCATION AND HUMAN ECOLOGY Manager's Guide to Mid-Year Performance Management Table of Contents Mid-year Performance Reviews... 3 Plan the performance appraisal meeting... 3
HUMAN RESOURSES COLLEGE OF EDUCATION AND HUMAN ECOLOGY Manager's Guide to Mid-Year Performance Management Table of Contents Mid-year Performance Reviews... 3 Plan the performance appraisal meeting... 3
Guide to Effective Staff Performance Evaluations
 Guide to Effective Staff Performance Evaluations HRS Human Resource Services-Operations The research is clear. The outcome is consistent. We know with certainty that the most powerful leadership tool for
Guide to Effective Staff Performance Evaluations HRS Human Resource Services-Operations The research is clear. The outcome is consistent. We know with certainty that the most powerful leadership tool for
PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT
 PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT A practical guide www.totaralms.com 1 Performance management and learning are closely related. Performance management involves constructive feedback so that individuals can learn
PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT A practical guide www.totaralms.com 1 Performance management and learning are closely related. Performance management involves constructive feedback so that individuals can learn
Consultancy Protocol Overview
 Harmony Education Center National School Reform Faculty www.nsrfharmony.org Consultancy Protocol Overview The Consultancy Protocol was developed by Gene Thompson-Grove as part of the Coalition of Essential
Harmony Education Center National School Reform Faculty www.nsrfharmony.org Consultancy Protocol Overview The Consultancy Protocol was developed by Gene Thompson-Grove as part of the Coalition of Essential
Responding to a Disappointing Performance Review
 Responding to a Disappointing Performance Review Overview When your manager reviews your work and finds it wanting. Receiving a disappointing review First steps: Take notes and ask for clarification Gather
Responding to a Disappointing Performance Review Overview When your manager reviews your work and finds it wanting. Receiving a disappointing review First steps: Take notes and ask for clarification Gather
The Four Stages in Building and Sustaining a Service Culture
 The Four Stages in Building and Sustaining a Service Culture A true service culture is a community of leaders at all levels who embrace a service mindset and build lasting relationships with customers
The Four Stages in Building and Sustaining a Service Culture A true service culture is a community of leaders at all levels who embrace a service mindset and build lasting relationships with customers
PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT COACHING AND PERFORMANCE GEORGIA PERIMETER COLLEGE
 PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT COACHING AND PERFORMANCE GEORGIA PERIMETER COLLEGE Module 2 Coaching and Performance with the GPC Strategic Plan Agenda 1. Performance Management Process The Next Plateau 2. Aspects
PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT COACHING AND PERFORMANCE GEORGIA PERIMETER COLLEGE Module 2 Coaching and Performance with the GPC Strategic Plan Agenda 1. Performance Management Process The Next Plateau 2. Aspects
Psychic Guide 101 Written by: Jennifer A. Young www.bestonlinepsychics.net
 Written by: Jennifer A. Young www.bestonlinepsychics.net Page 1 Table of Contents Chapter Title Page 01 Consulting a Psychic 03 02 Why Should You Consult a Psychic? 04 03 What Is a Psychic? 05 04 Choosing
Written by: Jennifer A. Young www.bestonlinepsychics.net Page 1 Table of Contents Chapter Title Page 01 Consulting a Psychic 03 02 Why Should You Consult a Psychic? 04 03 What Is a Psychic? 05 04 Choosing
Performance Management Manual AUBMC
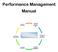 Manual 6. Reward Performance 1. Mutually develop performance plan 5. Communicate the evaluation AUBMC 2. Monitor and document performance 4. Evaluate Performance 3. Provide Coaching and Development 1 SECTION
Manual 6. Reward Performance 1. Mutually develop performance plan 5. Communicate the evaluation AUBMC 2. Monitor and document performance 4. Evaluate Performance 3. Provide Coaching and Development 1 SECTION
your people are our business Performance Management
 Performance Management Introduction As a business owner, it is crucial to ensure that employees are motivated, inspired, productive and working to their fullest potential. As a manager of people, performance
Performance Management Introduction As a business owner, it is crucial to ensure that employees are motivated, inspired, productive and working to their fullest potential. As a manager of people, performance
Leadership Development Catalogue
 The TrainingFolks Approach The importance of superior management, leadership and interpersonal skills are critical to both individual and organizational success. It is also critical to apply these skills
The TrainingFolks Approach The importance of superior management, leadership and interpersonal skills are critical to both individual and organizational success. It is also critical to apply these skills
The Comprehensive Interview
 Uncovering the Real Candidate Behind the Interview Persona Janna Mansker Kelly Land www.berkeassessment.com The Comprehensive Interview When sitting across the table from a candidate during an interview,
Uncovering the Real Candidate Behind the Interview Persona Janna Mansker Kelly Land www.berkeassessment.com The Comprehensive Interview When sitting across the table from a candidate during an interview,
Professional Mentoring Program Information Guide & FAQs
 Professional Mentoring Program Information Guide & FAQs Former PMP protégé Nilesh Bhagat, CHRP Former mentor TJ Schmaltz, LLB, BCL, CHRP Dear HRMA member, So you are interested in participating in our
Professional Mentoring Program Information Guide & FAQs Former PMP protégé Nilesh Bhagat, CHRP Former mentor TJ Schmaltz, LLB, BCL, CHRP Dear HRMA member, So you are interested in participating in our
A Guide to Interpreting StaffPulse Results Prepared for: The National Association of Community Health Centers, Inc. (NACHC) 2014
 A Guide to Interpreting StaffPulse Results Prepared for: The National Association of Community Health Centers, Inc. (NACHC) 2014 Key Analytical Goals Action planning is, by far, the most crucial phase
A Guide to Interpreting StaffPulse Results Prepared for: The National Association of Community Health Centers, Inc. (NACHC) 2014 Key Analytical Goals Action planning is, by far, the most crucial phase
The ABC s of Staying in Touch with Your Child s School. Tips and Techniques for Serving Children through Great Communication
 The ABC s of Staying in Touch with Your Child s School Tips and Techniques for Serving Children through Great Communication from The National School Public Relations Association (NSPRA) and its nearly
The ABC s of Staying in Touch with Your Child s School Tips and Techniques for Serving Children through Great Communication from The National School Public Relations Association (NSPRA) and its nearly
Performance Appraisal Handbook For Supervisors. For the evaluation of Non-Instructional Academic Staff (NIAS) and University Staff
 Performance Appraisal Handbook For Supervisors For the evaluation of Non-Instructional Academic Staff (NIAS) and University Staff Department of Human Resources May 2013 Introduction Performance management
Performance Appraisal Handbook For Supervisors For the evaluation of Non-Instructional Academic Staff (NIAS) and University Staff Department of Human Resources May 2013 Introduction Performance management
Why Accountability Matters
 PREVIEW GUIDE Why Accountability Matters Table of Contents: Sample Pages from Leader s Guide...pgs. 2-8 Program Information and Pricing...pgs. 9-10 Leader s Guide Can We Count on You? CRM Learning s Can
PREVIEW GUIDE Why Accountability Matters Table of Contents: Sample Pages from Leader s Guide...pgs. 2-8 Program Information and Pricing...pgs. 9-10 Leader s Guide Can We Count on You? CRM Learning s Can
Individual Development Planning. Staff Guidelines
 Individual Development Planning Staff Guidelines Guidelines for Creating a Development Plan What is an individual development plan? It s a document created by you, the staff member, then discussed with
Individual Development Planning Staff Guidelines Guidelines for Creating a Development Plan What is an individual development plan? It s a document created by you, the staff member, then discussed with
BUILD YOUR NETWORK. Harvard. Extension School. An Extension School Resource. Build Your Network
 Extension School Build Your Network Harvard OFFICE OF CAREER SERVICES Harvard University Faculty of Arts and Sciences www.ocs.fas.harvard.edu CAREER AND ACADEMIC RESOURCE CENTER Harvard Extension School
Extension School Build Your Network Harvard OFFICE OF CAREER SERVICES Harvard University Faculty of Arts and Sciences www.ocs.fas.harvard.edu CAREER AND ACADEMIC RESOURCE CENTER Harvard Extension School
Why Listening Is So Important
 Why Listening Is So Important There is a saying about listening that eloquently summarizes the nature of the process. The source of the words is unknown, but the message is universal God gave us two ears,
Why Listening Is So Important There is a saying about listening that eloquently summarizes the nature of the process. The source of the words is unknown, but the message is universal God gave us two ears,
06. Create a feedback loop. 01. Create a plan. 02. Improve People skills. 07. Get a tool that supports the workflow. 03. Keep your promises
 01. Create a plan 06. Create a feedback loop Plan how you are going to provide better customer service and take help from both staff and customers. 02. Improve People skills Service is a skill and people
01. Create a plan 06. Create a feedback loop Plan how you are going to provide better customer service and take help from both staff and customers. 02. Improve People skills Service is a skill and people
TRAINING NEEDS ANALYSIS
 TRAINING NEEDS ANALYSIS WHAT IS A NEEDS ANALYSIS? It is a systematic means of determining what training programs are needed. Specifically, when you conduct a needs analysis, you Gather facts about training
TRAINING NEEDS ANALYSIS WHAT IS A NEEDS ANALYSIS? It is a systematic means of determining what training programs are needed. Specifically, when you conduct a needs analysis, you Gather facts about training
PREPARING FOR THE INTERVIEW
 U N I V E R S I T Y C A R E E R S E R V I C E S PREPARING FOR THE INTERVIEW THE INTERVIEW The interview is an opportunity to demonstrate to an employer why you are the best fit for the position. Essentially,
U N I V E R S I T Y C A R E E R S E R V I C E S PREPARING FOR THE INTERVIEW THE INTERVIEW The interview is an opportunity to demonstrate to an employer why you are the best fit for the position. Essentially,
Interpersonal Skills. Leadership, Change Management and Team Building
 Interpersonal Skills Leadership, Change Management and Team Building Capital s Learning and Development team design and deliver tailored skills and competency based programmes to meet your wide range of
Interpersonal Skills Leadership, Change Management and Team Building Capital s Learning and Development team design and deliver tailored skills and competency based programmes to meet your wide range of
15 Most Typically Used Interview Questions and Answers
 15 Most Typically Used Interview Questions and Answers According to the reports of job seekers, made from thousands of job interviews, done at 97 big companies in the United States, we selected the 15
15 Most Typically Used Interview Questions and Answers According to the reports of job seekers, made from thousands of job interviews, done at 97 big companies in the United States, we selected the 15
INTERVIEW QUESTIONS GUIDE
 INTERVIEW QUESTIONS GUIDE Prepared by MBA Career Services USC Marshall School of Business March 2016 1 Table of Contents GENERAL QUESTIONS3 TOP TEN MOST ASKED QUESTIONS... 3 CAREER DIRECTION... 3 CORPORATE
INTERVIEW QUESTIONS GUIDE Prepared by MBA Career Services USC Marshall School of Business March 2016 1 Table of Contents GENERAL QUESTIONS3 TOP TEN MOST ASKED QUESTIONS... 3 CAREER DIRECTION... 3 CORPORATE
Performance Management Handbook. City of American Canyon
 Performance Management Handbook City of American Canyon 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction 1 Background on performance management City Core competencies Performance management model Development of the Core
Performance Management Handbook City of American Canyon 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction 1 Background on performance management City Core competencies Performance management model Development of the Core
Office of the Commissioner for Public Employment COUNSELLING. for better work performance
 Office of the Commissioner for Public Employment COUNSELLING for better work performance Northern Territory Government Contents Introduction Performance Management Page 1 Feedback Page 4 Moving from feedback
Office of the Commissioner for Public Employment COUNSELLING for better work performance Northern Territory Government Contents Introduction Performance Management Page 1 Feedback Page 4 Moving from feedback
North Dakota Human Resource Management Services Performance Evaluation
 North Dakota Human Resource Management Services Performance Evaluation Performance Evaluation is a multi-purpose tool used to: Measure actual performance against expected performance Provide an opportunity
North Dakota Human Resource Management Services Performance Evaluation Performance Evaluation is a multi-purpose tool used to: Measure actual performance against expected performance Provide an opportunity
Human Resources Training. Performance Management Training Module 2: Managing Employee Performance
 Human Resources Training Performance Management Training Module 2: Managing Employee Performance Table of Contents Learning Objectives...1 Expectations Of You As A Leader...3 Setting and Communicating
Human Resources Training Performance Management Training Module 2: Managing Employee Performance Table of Contents Learning Objectives...1 Expectations Of You As A Leader...3 Setting and Communicating
Coaching and Feedback
 Coaching and Feedback Follow the Guidelines for Effective Interpersonal Communication There are fundamental strategies that should always be part of interpersonal communication in the work place. Don t
Coaching and Feedback Follow the Guidelines for Effective Interpersonal Communication There are fundamental strategies that should always be part of interpersonal communication in the work place. Don t
is true for managers, team leaders and team members, individual contributors, professionals and executives.
 HOW TO GET THE MOST (FOR YOURSELF) FROM TRAINING WHY TRAINING? WHY NOW? If training is not important to a particular job today, that job probably will not be important much longer, either. What makes training
HOW TO GET THE MOST (FOR YOURSELF) FROM TRAINING WHY TRAINING? WHY NOW? If training is not important to a particular job today, that job probably will not be important much longer, either. What makes training
How to Design an Employee Engagement Survey
 How to Design an Employee Engagement Survey WITH BEST PRACTICES AND SAMPLE CONTENT by Sarah Marrs, Jordan Menzel Qualtrics Employee Insights SM What will this guide tell me? If you re looking to run an
How to Design an Employee Engagement Survey WITH BEST PRACTICES AND SAMPLE CONTENT by Sarah Marrs, Jordan Menzel Qualtrics Employee Insights SM What will this guide tell me? If you re looking to run an
Insight Guide. E-Learning Compliance. www.kineo.com
 Insight Guide E-Learning Compliance LAST MENU BACK NEXT Insight Guide Overview The challenges of compliance training Questions to ask before you begin your design 20 minutes A new generation of design
Insight Guide E-Learning Compliance LAST MENU BACK NEXT Insight Guide Overview The challenges of compliance training Questions to ask before you begin your design 20 minutes A new generation of design
Performance Management. Office of Human Resources
 Performance Management Office of Human Resources Jean Prather, PHR DEVELOPING EMPLOYEES The conventional definition of management is getting work done through h people, but real management is developing
Performance Management Office of Human Resources Jean Prather, PHR DEVELOPING EMPLOYEES The conventional definition of management is getting work done through h people, but real management is developing
The Global State of Employee Engagement: A 2014 Study
 The Global State of Employee Engagement: A 2014 Study The Global State of Employee Engagement: A 2014 Study In May of 2014, BPI group partnered with research firm BVA to survey the state of employee engagement
The Global State of Employee Engagement: A 2014 Study The Global State of Employee Engagement: A 2014 Study In May of 2014, BPI group partnered with research firm BVA to survey the state of employee engagement
Learning to Delegate
 Learning to Delegate Overview Tips for managers on how to delegate Why is delegation necessary? Why do many managers have a hard time delegating? What to delegate What not to delegate How to delegate Give
Learning to Delegate Overview Tips for managers on how to delegate Why is delegation necessary? Why do many managers have a hard time delegating? What to delegate What not to delegate How to delegate Give
Difficult Conversations: How to Discuss What Matters Most
 Difficult Conversations: How to Discuss What Matters Most A High-Level Summary of the Book by Stone, Patton and Heen Office of Human Resources The Ohio State University 1590 N. High St. Suite 300 Columbus,
Difficult Conversations: How to Discuss What Matters Most A High-Level Summary of the Book by Stone, Patton and Heen Office of Human Resources The Ohio State University 1590 N. High St. Suite 300 Columbus,
Active Listening. Learning Objectives. By the end of this module, the learner will have
 1 Active Listening Learning Objectives By the end of this module, the learner will have An understanding of what is meant by active listening Gained insight into your natural listening strengths and areas
1 Active Listening Learning Objectives By the end of this module, the learner will have An understanding of what is meant by active listening Gained insight into your natural listening strengths and areas
Ten Tips for Coaching Adults
 Ten Tips for Coaching Adults An Emotionally Healthy Approach Rebecca Ruth Curtis, Joy Allen Humbarger, and Terrell Ellene Mann KCPT Kansas City Public Television Sarah (program director, smiling as she
Ten Tips for Coaching Adults An Emotionally Healthy Approach Rebecca Ruth Curtis, Joy Allen Humbarger, and Terrell Ellene Mann KCPT Kansas City Public Television Sarah (program director, smiling as she
Working in a Customer Service Culture
 Working in a Customer Service Culture Customer service skills course designed for participants in the Senior Community Service Employment Program. You can find the student guide to this course located
Working in a Customer Service Culture Customer service skills course designed for participants in the Senior Community Service Employment Program. You can find the student guide to this course located
Onboarding Program. Sponsor s Guide
 Onboarding Program Sponsor s Guide Sponsor s Guide Introduction This guide has been developed to help sponsors in their roles with new employees. We want to help you be effective and successful in this
Onboarding Program Sponsor s Guide Sponsor s Guide Introduction This guide has been developed to help sponsors in their roles with new employees. We want to help you be effective and successful in this
Guide to180 Feedback HUMAN RESOURSES COLLEGE OF EDUCATION AND HUMAN ECOLOGY
 HUMAN RESOURSES COLLEGE OF EDUCATION AND HUMAN ECOLOGY Guide to180 Feedback The goal of an effective 180 feedback implementation should be positive, measurable, long-term leadership growth and development
HUMAN RESOURSES COLLEGE OF EDUCATION AND HUMAN ECOLOGY Guide to180 Feedback The goal of an effective 180 feedback implementation should be positive, measurable, long-term leadership growth and development
Ten Tips for Successfully Coaching Employees by Laurie Maddalena, CEO of Envision Excellence, LLC
 What is Coaching? Ten Tips for Successfully Coaching Employees by Laurie Maddalena, CEO of Envision Excellence, LLC Coaching is a partnership you form with an employee that focuses on helping them learn
What is Coaching? Ten Tips for Successfully Coaching Employees by Laurie Maddalena, CEO of Envision Excellence, LLC Coaching is a partnership you form with an employee that focuses on helping them learn
Critical analysis. Be more critical! More analysis needed! That s what my tutors say about my essays. I m not really sure what they mean.
 Critical analysis Be more critical! More analysis needed! That s what my tutors say about my essays. I m not really sure what they mean. I thought I had written a really good assignment this time. I did
Critical analysis Be more critical! More analysis needed! That s what my tutors say about my essays. I m not really sure what they mean. I thought I had written a really good assignment this time. I did
Onboarding and Engaging New Employees
 Onboarding and Engaging New Employees Onboarding is the process of helping new employees become full contributors to the institution. During onboarding, new employees evolve from institutional outsiders
Onboarding and Engaging New Employees Onboarding is the process of helping new employees become full contributors to the institution. During onboarding, new employees evolve from institutional outsiders
Performance planning:
 Performance planning: A guide for staff development and feedback Version: 2.1 Last Updated: April, 2015 Ryerson University Human Resources 0 Table of contents Performance planning: Staff development and
Performance planning: A guide for staff development and feedback Version: 2.1 Last Updated: April, 2015 Ryerson University Human Resources 0 Table of contents Performance planning: Staff development and
EMPLOYEE JOB IMPROVEMENT PLANS. This Employee Job Improvement Plan designed by Kielley Management Consultants achieves results because:
 EMPLOYEE JOB IMPROVEMENT PLANS This Employee Job Improvement Plan designed by Kielley Management Consultants achieves results because: it is simple and understandable it keeps supervisors and employees
EMPLOYEE JOB IMPROVEMENT PLANS This Employee Job Improvement Plan designed by Kielley Management Consultants achieves results because: it is simple and understandable it keeps supervisors and employees
How to Overcome the Top Ten Objections in Credit Card Processing
 How to Overcome the Top Ten Objections in Credit Card Processing Section #1: Handling the Red Flags Just Fax Your Rates Response: I ll be happy to do that, but until we know if this is truly a fit for
How to Overcome the Top Ten Objections in Credit Card Processing Section #1: Handling the Red Flags Just Fax Your Rates Response: I ll be happy to do that, but until we know if this is truly a fit for
Getting The Most Out of the Performance Management System. Human Resources 2015
 Getting The Most Out of the Performance Management System Human Resources 2015 Purpose of Today s Training Help employees prepare to write and participate in a high quality performance appraisal. Agenda
Getting The Most Out of the Performance Management System Human Resources 2015 Purpose of Today s Training Help employees prepare to write and participate in a high quality performance appraisal. Agenda
Chapter 17 Customer Service
 Chapter 17 Customer Service There is only one boss: the customer. And he can fire everybody from the chairman on down, simply by spending his money elsewhere. -Sam Walton The old adage used to be that
Chapter 17 Customer Service There is only one boss: the customer. And he can fire everybody from the chairman on down, simply by spending his money elsewhere. -Sam Walton The old adage used to be that
Supervisor s Performance Management Guide
 Supervisor s Performance Management Guide 1. Introduction... 2 2. Duties and Job Descriptions... 2 3. Supervisor s Role... 2 4. Goals & Employee Development... 3 5. Annual Performance Evaluation Process...
Supervisor s Performance Management Guide 1. Introduction... 2 2. Duties and Job Descriptions... 2 3. Supervisor s Role... 2 4. Goals & Employee Development... 3 5. Annual Performance Evaluation Process...
Chapter 4 Performance Appraisal Process
 Chapter 4 Performance Appraisal Process Section 1 Performance Appraisal Process A. Purpose: Provide feedback to an employee regarding their job performance, develop performance and career development goals,
Chapter 4 Performance Appraisal Process Section 1 Performance Appraisal Process A. Purpose: Provide feedback to an employee regarding their job performance, develop performance and career development goals,
INDIVIDUAL DEVELOPMENT PLANNING
 INDIVIDUAL DEVELOPMENT PLANNING 1 SMART Development Planning Building a SMART Individual Development Plan Specific: High clarity. Fully understood. Measurable: Expected measurable outcomes. Accepted: Full
INDIVIDUAL DEVELOPMENT PLANNING 1 SMART Development Planning Building a SMART Individual Development Plan Specific: High clarity. Fully understood. Measurable: Expected measurable outcomes. Accepted: Full
Performance Development
 MIT Human Resources Performance Development A Toolkit for Managers Table of Contents The Vision for Performance Development at MIT.. 2 What do we mean by "Baseline" and "Best" Practices?... 3 MIT Performance
MIT Human Resources Performance Development A Toolkit for Managers Table of Contents The Vision for Performance Development at MIT.. 2 What do we mean by "Baseline" and "Best" Practices?... 3 MIT Performance
How To Plan At A Tribe Of People
 ONE Don t Mark My Paper, Help Me Get an A Garry Ridge AS I SHARE with you how we successfully implemented our Don t Mark My Paper, Help Me Get an A philosophy into our performance review system, we ll
ONE Don t Mark My Paper, Help Me Get an A Garry Ridge AS I SHARE with you how we successfully implemented our Don t Mark My Paper, Help Me Get an A philosophy into our performance review system, we ll
BUTLER UNIVERSITY PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT GUIDE
 BUTLER UNIVERSITY PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT GUIDE Performance management is the methodical and organized system for monitoring the results of work activities, collecting information and evaluating performance,
BUTLER UNIVERSITY PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT GUIDE Performance management is the methodical and organized system for monitoring the results of work activities, collecting information and evaluating performance,
Sometimes there is confusion over what mentoring is, and what it is not.
 What is Mentoring? Mentoring is not new. On the contrary, the term mentor originates from Greek Mythology. The practice of mentoring even dates back to earlier times. In recent years there has been a remarkable
What is Mentoring? Mentoring is not new. On the contrary, the term mentor originates from Greek Mythology. The practice of mentoring even dates back to earlier times. In recent years there has been a remarkable
Example Interview Transcript
 Ms Bossy DeBoss Namey Mc Name Thank you for coming to see us for your interview today, Namey. How was your journey, did you have any trouble finding us? My journey was fine thank you, Ms DeBoss. The instructions
Ms Bossy DeBoss Namey Mc Name Thank you for coming to see us for your interview today, Namey. How was your journey, did you have any trouble finding us? My journey was fine thank you, Ms DeBoss. The instructions
Finding Your Gift: Three Paths to Maximizing Impact in Your Career
 Finding Your Gift: Three Paths to Maximizing Impact in Your Career Do you have a job, or a career? Are you working for a paycheck, or are you working on your life s mission? Would you like to discover
Finding Your Gift: Three Paths to Maximizing Impact in Your Career Do you have a job, or a career? Are you working for a paycheck, or are you working on your life s mission? Would you like to discover
Welcome to Part 1 of Performance Appraisal Training. This training is being provided by Human Resource Services.
 Presentation: Performance Appraisal Training Late Updated: 3/27/2012 Slide 1: Welcome to Part 1 of Performance Appraisal Training. This training is being provided by Human Resource Services. Slide 2: Learning
Presentation: Performance Appraisal Training Late Updated: 3/27/2012 Slide 1: Welcome to Part 1 of Performance Appraisal Training. This training is being provided by Human Resource Services. Slide 2: Learning
Introduction to customer journey mapping
 Introduction to customer journey mapping Copyright PeopleMetrics Inc. an ebook by introduction Customer Journey Mapping is growing in popularity in the customer experience space, and it s no surprise.
Introduction to customer journey mapping Copyright PeopleMetrics Inc. an ebook by introduction Customer Journey Mapping is growing in popularity in the customer experience space, and it s no surprise.
THE ROLE OF THE FACILITATOR
 THE ROLE OF THE FACILITATOR What is a Meeting Facilitator? The facilitator is a guide or discussion leader for the group. The process of facilitation is a way of providing leadership without taking the
THE ROLE OF THE FACILITATOR What is a Meeting Facilitator? The facilitator is a guide or discussion leader for the group. The process of facilitation is a way of providing leadership without taking the
Best in Class Customer Retention
 Take your business to the next level Best in Class Customer Retention A 5% Improvement Can Double Your Bottom Line Profits Free Sales and Marketing Audit Call 410-977-7355 Lead Scoring, Prioritization,
Take your business to the next level Best in Class Customer Retention A 5% Improvement Can Double Your Bottom Line Profits Free Sales and Marketing Audit Call 410-977-7355 Lead Scoring, Prioritization,
8 Tips to Engage Your Employees. Brought to you by TNS Employee Insights
 8 Tips to Engage Your Employees Brought to you by TNS Employee Insights Tips 01 Get to Know Your Employees...4 02 Provide Basic Training for Your Employees...6 03 Develop Your People...8 04 Recognize Your
8 Tips to Engage Your Employees Brought to you by TNS Employee Insights Tips 01 Get to Know Your Employees...4 02 Provide Basic Training for Your Employees...6 03 Develop Your People...8 04 Recognize Your
College of Arts & Science Performance Review Cycle March 2009
 College of Arts & Science Performance Review Cycle March 2009 1. Introduction 2. Job Profiles 3. Performance Reviews and Performance Feedback a) Definition of Performance Reviews b) Purpose of Performance
College of Arts & Science Performance Review Cycle March 2009 1. Introduction 2. Job Profiles 3. Performance Reviews and Performance Feedback a) Definition of Performance Reviews b) Purpose of Performance
Difficult Tutoring Situations
 Difficult Tutoring Situations At some time or other, all tutors will find themselves faced with difficult situations in a tutoring session. The following information will provide you with some common categories
Difficult Tutoring Situations At some time or other, all tutors will find themselves faced with difficult situations in a tutoring session. The following information will provide you with some common categories
APPENDIX I. Best Practices: Ten design Principles for Performance Management 1 1) Reflect your company's performance values.
 APPENDIX I Best Practices: Ten design Principles for Performance Management 1 1) Reflect your company's performance values. Identify the underlying priorities that should guide decisions about performance.
APPENDIX I Best Practices: Ten design Principles for Performance Management 1 1) Reflect your company's performance values. Identify the underlying priorities that should guide decisions about performance.
The City of Minneapolis Approach to Performance Management
 The City of Minneapolis Approach to Performance Management Table of Contents Purpose and Introduction... 1 Performance Management Process Overview.. 3 Planning Performance.... 4 Monitoring Performance..
The City of Minneapolis Approach to Performance Management Table of Contents Purpose and Introduction... 1 Performance Management Process Overview.. 3 Planning Performance.... 4 Monitoring Performance..
Results Based Performance Management System (RPMS) FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS (FAQs)
 Results Based Performance Management System (RPMS) FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS (FAQs) 1. What is the Performance Management System? It is an organization-wide process to ensure that employees focus work
Results Based Performance Management System (RPMS) FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS (FAQs) 1. What is the Performance Management System? It is an organization-wide process to ensure that employees focus work
Human Resources Training
 Human Resources Training Performance Management Training Module 2: Managing Employee Performance March 2010 Objectives By the end of this module participants will be able to: Describe the elements of a
Human Resources Training Performance Management Training Module 2: Managing Employee Performance March 2010 Objectives By the end of this module participants will be able to: Describe the elements of a
Complete a Relationships Presentation
 Complete a Relationships Presentation Speech Tips 1. I am so scared of giving my speech. How do I get over my nervousness? Nervousness is natural. Think of it as a friend rather than an enemy. You need
Complete a Relationships Presentation Speech Tips 1. I am so scared of giving my speech. How do I get over my nervousness? Nervousness is natural. Think of it as a friend rather than an enemy. You need
There are some easy steps that you can take that will increase your chances of success at interviews.
 Interview Skills There are some easy steps that you can take that will increase your chances of success at interviews. First, remember that job interviews should be a process of two-way communication.
Interview Skills There are some easy steps that you can take that will increase your chances of success at interviews. First, remember that job interviews should be a process of two-way communication.
Social Security Disability Resources For Self Advocacy
 Social Security Disability Resources For Self Advocacy Introduction This guide is intended to help people with multiple sclerosis (MS) advocate effectively to obtain the Social Security Disability Insurance
Social Security Disability Resources For Self Advocacy Introduction This guide is intended to help people with multiple sclerosis (MS) advocate effectively to obtain the Social Security Disability Insurance
EnglishBusiness CompactMINIs Fast and to the point. Cheap and effective.
 EnglishBusiness CompactMINIs Fast and to the point. Cheap and effective. CLICK ON THE MINI OF YOUR CHOICE TO READ MORE M01: How to present your company in just 5 minutes M02: How to present yourself in
EnglishBusiness CompactMINIs Fast and to the point. Cheap and effective. CLICK ON THE MINI OF YOUR CHOICE TO READ MORE M01: How to present your company in just 5 minutes M02: How to present yourself in
business brief How Mobility Transforms the Art of Customer Interaction jabra.com
 Wireless in the Contact Center? How Mobility Transforms the Art of Customer Interaction Wireless in the Contact Center? 2 The stereotype of the contact center, of row after row of agents tethered physically
Wireless in the Contact Center? How Mobility Transforms the Art of Customer Interaction Wireless in the Contact Center? 2 The stereotype of the contact center, of row after row of agents tethered physically
