Proprietary Information of Univera Healthcare
|
|
|
- Clementine York
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: BRACHYTHERAPY AFTER BREAST- PAGE: 1 OF: 8 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical policy criteria are not applied. Medical policies apply to commercial and Safety Net products only when a contract benefit for the specific service exists. Medical policies only apply to Medicare products when a contract benefit exists and where there is no national or local Medicare coverage decision for the specific service. POLICY STATEMENT: I. Based upon our criteria and review of the peer-reviewed literature, accelerated partial breast irradiation using either interstitial or balloon brachytherapy of the breast (e.g. the MammoSite TM Radiation Therapy System) or electronic brachytherapy devices (e.g., Axxent electronic brachytherapy (Xoft Inc, Fremont, CA) has been medically proven to be effective, and is therefore a medically appropriate treatment option: A. in BRCA 1 or 2 mutation negative women aged 50 years or older; and B. with Stage T1 or T2, N0 invasive ductal breast cancer with negative or close margins or ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS); and C. tumor size less than or equal to 3 cm. II. Based upon our criteria and review of the peer-reviewed literature, accelerated partial breast irradiation using either interstitial or balloon brachytherapy of the breast (e.g. the MammoSite TM Radiation Therapy System) in women who are treated with breast-conserving surgery and whole-breast external beam radiation therapy, brachytherapy as a boost treatment is considered not medically necessary. III. Based upon our criteria and review of peer-reviewed literature, intra-operative breast radiotherapy, either as a single definitive treatment option or as a boost, is considered investigational. Refer to Corporate Medical Policy # regarding Experimental or Investigational Services POLICY GUIDELINES: I. This policy addresses the use of either interstitial or balloon brachytherapy as alternatives to external beam radiation therapy in three settings: A. Alone, for accelerated partial breast radiation therapy after breast-conserving surgery; or B. In the intra-operative setting; or C. To replace external beam for boost radiation therapy, combined with whole-breast external-beam radiation therapy and breast-conserving surgery. II. Methods other than brachytherapy are also used for partial breast irradiation (PBI), including several types of external beam therapy. They are not addressed in this policy. III. A cavity evaluation device may be placed at the time of surgery as a place holder to simplify insertion of the MammoSite TM balloon catheter at a later date, when final pathology and staging is known and a decision regarding the role of brachytherapy in the patient s treatment plan is established. IV. The Federal Employees Health Benefit Program (FEHBP/FEP) requires that procedures, devices or laboratory tests approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) may not be considered investigational and thus these procedures, devices or laboratory tests may be assessed only on the basis of their medical necessity. DESCRIPTION: Survival after breast-conservation therapy (BCT) is equivalent to survival after mastectomy for patients diagnosed with tumors categorized as stage I or II. BCT is a multi-modality treatment that consists of breast-conserving surgery to excise the tumor with adequate margins, followed by whole-breast external-beam radiation therapy (WB-EBRT) administered as
2 PAGE: 2 OF: 8 5 daily fractions per week over 5 to 6 weeks. For those at higher risk of recurrence, local boost irradiation narrowly directed to the tumor bed often is added to whole breast irradiation, to provide a higher dose of radiation at the site where recurrence most frequently occurs. For some patients BCT also includes axillary lymph node dissection or irradiation of the axilla. Brachytherapy for breast cancer uses radiate sources placed inside the breast. When used after breast-conserving surgery, brachytherapy is one of several methods of accelerated partial breast irradiation (APBI). APBI differs from WB-EBRT in two ways. First, APBI radiation targets only a segment surrounding the tumor rather than the entire breast. Second, since the duration of APBI treatment is 4 to 5 days rather than 5 to 6 weeks, radiation is delivered in fewer fractions at larger doses per fraction. Interstitial breast brachytherapy. Various interstitial brachytherapy techniques have been investigated. They differ in the timing of implantation relative to other components of breast-conserving therapy, the radiation dose rate, the loading technique, the number and volumetric distribution of radioactive sources, and the radioisotopes used. Older forms of local boost irradiation brachytherapy implanted the needles, wires, or seeds for brachytherapy after recovery from surgical tumor excision and WB-EBRT. More recently the hollow needles and catheters that guide placement of the radioactive material are perioperatively implanted. This can be done during the initial lumpectomy if the decision to use brachytherapy has already been made, or at the time of re-excision if pathologic evaluation of margins shows that additional surgery is necessary. Intraoperative implantation avoids the need for a separate surgical procedure with anesthesia for brachytherapy. Both low-dose rate and high-dose rate techniques have been used. In the low-dose rate technique, radioactive seeds are temporarily implanted in hospitalized patients, which deliver radiation continuously over four days and are then removed. In the high-dose rate technique, a computer-controlled device loads highly radioactive isotope sources into catheters that have been placed into the tumor bed. The patient is exposed to the radiation therapy for a brief period (15 minutes) and the radioactive sources are withdrawn. It is typically administered to outpatients as 8 fractions given twice daily over 4 days. Most brachytherapy for stage I or II breast cancer uses high dose-rate iridium-192 in the form or wires or needles. Sometimes seeds containing iodine-125 are used in place of iridium-192. Intracavity breast brachytherapy. Intracavitary brachytherapy is a method for delivering very localized radiation to small tumors, which have not spread, or to deliver an additional dose of radiation to a small volume at high risk for recurrence. It is achieved by placing a small radiation source directly into a naturally occurring body cavity or in a cavity left by a tumor. The brachytherapy can be delivered using the ClearPath HDR Breast Brachytherapy System (NAS Medical, Chatsworth, CA), Contura Multi-Lumen Balloon (SenoRx, Inc., Irvine, CA), Strut-Adjusted Volume Implant (SAVI) (Cianna Medical, Inc., Aliso Viejo, CA). The MammoSite TM radiation therapy system is the most commonly used device and is discussed below. The MammoSite TM radiation therapy system is a brachytherapy device developed to provide a simpler technique for performing breast brachytherapy than interstitial catheter brachytherapy. It reduces the complex procedure and treatment planning of interstitial catheter brachytherapy and does not have the steep learning curve needed for the interstitial technique. It was designed for the purpose of delivering radiation therapy to the lumpectomy bed with breast conserving surgery. MammoSite TM consists of a hollow catheter to which an inflatable balloon is attached. It is implanted into the lumpectomy cavity during or shortly after breast-conserving surgery. The balloon is inflated with sterile solution of contrast media in saline, and its position is confirmed radiographically using computed tomography. A high-dose rate source of iridium-192 is then centrally positioned within the applicator by a remote afterloader. This system is used to deliver 34 Gy in 10 fractions over 5 days. Balloon brachytherapy uses a single radioactive source that delivers radiation to a spherical or elliptical target volume. No radiation remains inside the breast between treatments. The MammoSite TM balloon catheter is usually removed on the last day of treatment. The manufacturer states it may be used to deliver local boost or accelerated partial-breast radiation therapy. The Axxent TM Electronic Radiotherapy device is a balloon brachytherapy system that uses a disposable, microminiature radiation source to deliver radiation rather than radioisotopes. It is designed to deliver doses of x-ray radiation directly to the excised tumor bed to deliver intracavitary or interstitial radiation to surgical margins following lumpectomy for breast
3 PAGE: 3 OF: 8 cancer. It is comprised of three components: the controller (a mobile platform responsible for overall operation of the device), a balloon applicator and an x-ray source. A breast surgeon implants a balloon applicator into the lumpectomy cavity, and the balloon is inflated with sterile saline. Radiation is delivered by a disposable micro-miniature x-ray source located at the end of a flexible cable and is comparable in dosage strength to iridium 192. Use of the Axxent TM device does not utilize a radioactive isotope or require a high dose-rate (HDR) afterloader. Therefore, it does not require the heavily-shielded treatment rooms necessary for the delivery of isotope-based HDR brachytherapy. Treatments are given in 10 fractions, twice a day for five days. RATIONALE: Implanting the guides used to insert radioisotopes for brachytherapy is a surgical procedure and therefore not subject to government regulation. Iodine-125 seeds were marketed prior to enactment of the 1976 Medical Device Amendments. Therefore, they were cleared for marketing on a grandfathered basis. Subsequent radioactive isotope implants, including iridium-192, were approved by the FDA via 510(k) as substantially equivalent to the radioactive iodine seeds. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) cleared the MammoSite TM Radiation Therapy System (Cytyc Surgical Products, formerly Proxima Therapeutics) for marketing via 510(k) in May 2002 as substantially equivalent to other commercially available brachytherapy applicators used with sealed radiation sources. The FDA Office of Device Evaluation judged it reasonably likely that the device will be used in ways outside those specified in the proposed labeling, and that such use could cause harm. Therefore, the FDA required inclusion of the following statement in the Warnings section of the device s labeling: The safety and effectiveness of the MammoSite TM RTS as a replacement for whole breast irradiation in the treatment of breast cancer has not been established. In August 2004 the FDA approved a new version of the MammoSite TM RTS, which offers a thinner catheter shaft and a smaller balloon profile to further minimize intrusion into the lumpectomy cavity during brachytherapy. Additional brachytherapy devices have received FDA 510(k) marketing clearance, such as the SenoRad Multi-lumen Balloon Source Applicator for Brachytherapy (May 2007) and the Contura Multi-Lumen Balloon Source Applicator for Brachytherapy (April 2008), both manufactured by SenoRx, Inc. In December 2005, the FDA cleared the Axxent Electronic Radiotherapy device (Xoft, Inc.) via 510(k) as substantially equivalent to the MammoSite TM and other brachytherapy systems. As with MammoSite TM, the FDA required a warning in a black box stating, The safety and effectiveness of the Axxent Electronic Brachytherapy System as a replacement for whole breast irradiation in the treatment of breast cancer has not been established. MammoSite TM balloon brachytherapy. Initial published results of the MammoSite TM Patient Registry addressed results of 1,403 women with early stage breast cancer regarding cosmetic results and early toxicity. Cosmetic results at 12 months were comparable to those reported with whole-breast radiation therapy. 95% of patients (1,030 of 1,084 patients) who had a cosmetic assessment had good/excellent result at the last follow-up visit. Early toxicity rates (infections, radiation recall) appeared to be acceptable. 8.1% (92 of 1,140 patients) developed an infection in the treated breast. A radiation recall reaction was reported in 3.4% (15 of 442 patients) who had this information recorded. At the time of publication, one local recurrence (.1%) was reported, which was a new primary cancer. Of 158 ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) patients, 2-24 months follow-up of 104 patients showed 94% had an excellent or good cosmetic result and 5% had fair or poor results (Jeruss, 2006). Lowest toxicity was obtained in patients with the greatest device-to-skin distance. Long-term follow-up data regarding patient satisfaction, cosmesis and efficacy are needed. These results are preliminary since the planned follow-up period of the registry is seven years. Data continue to accrue from uncontrolled studies on the use of Mammosite balloon brachytherapy. The longest follow-up fund was 5 years in a study of 36 patients, with no local recurrences reported. Based on development of recurrences beyond five years, longer follow-up is needed, as well as controlled trials. Studies using the Contura multi-lumen balloon show similar results as MammoSite TM. Studies are sparse regarding other devices. Interstitial, multi-catheter brachytherapy. Several single-institution, non-randomized studies using the multicatheter technique have shown low local recurrence rates that are comparable to standard external beam radiation therapy. Data on newer techniques are not yet as mature but show comparable results at shorter follow-up.
4 PAGE: 4 OF: 8 Electronic brachytherapy (EBT). No published clinical studies are available that address the clinical impact of use of the Axxent Electronic Brachytherapy System. Current studies are small and early outcome data was similar to early outcome for iridium-based brachytherapy. The ASTRO emerging technology committee report on electronic brachytherapy states the advantages of electronic brachytherapy over existing technologies are as yet unproven in terms of efficacy or patient outcomes. The impact of clinical use of EBTcould be far-reaching and, if used properly, has potential to benefit patients. EBT is currently an unregulated treatment delivery modality for cancer therapy, with minimal clinical data available from small single institution studies, none with any significant follow-up. The effects of EBT on tumor and normal tissues are not yet well understood, given the paucity of clinical studies. Although the clinical data on this technology is limited, it appears very likely that it will result in results equivalent to those using HDR brachytherapy for APBI. National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) (version ) Breast Cancer guidelines. Preliminary studies of APBI suggest rates of local control in selected patients with early stage breast cancer may be comparable to those treated with standard whole breast RT. Follow-up is limited and studies are on-going. Women with early stage breast cancer are encouraged to participate in clinical trials. If not trial eligible, per the consensus statement from the American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO), patients who may be suitable APBI are women 60 years and older who are not carriers of BRCA 1 or 2 mutation treated with primary surgery for the unifocal T1N0 ER-positive cancer. Histology should be infiltrating ductal or a favorable ductal subtype, not be associated with EIC or LCIS and margins should be negative. The American Society of Breast Surgeons (revised 2011), Consensus Statement of Accelerated Partial Breast Irradiation: 1. Outside of multi-institutional studies and institutional protocols, patients should be carefully selected for APBI and properly informed of the benefits and risks of this type of radiation treatment. The American Society of Breast Surgeons recommends the following selection criteria when considering patients for treatment with APBI, as a sole form of radiation therapy, in lieu of whole breast irradiation: a. Age greater than 45 years old for invasive cancer and age greater than 50 years for DCIS, b. Invasive ductal carcinoma or ductal carcinoma in situ, c. Total tumor size (invasive and DCIS) less than or equal to 3 cm in size, d. Negative microscopic surgical margins of excisions, e. Sentinel lymph node negative. 2. Surgeons, radiation oncologists and physicists who will be utilizing the various APBI techniques should be adequately trained to allow for optimum radiation therapy planning and treatment, including proper 3-D treatment planning. 3. All patients should be monitored regularly to identify adverse events as well as local recurrences. 4. The published dataset for APBI supports the recommendations summarized above. Continuous, long-term, outcomes-based monitoring of APBI is desirable. The American Society of Breast Surgeons maintains an ongoing Mammosite Registry (registration completed in 2004) collecting data on 1440 patients treated via the Mammosite balloon catheter technique. As is the case with all cancer treatments, participation in multi-institutional clinical studies, including NSABP/RTOG B39, or in single-site protocols, or in the context of data-gathering registries, is desirable, if available. 5. Multilumen catheter devices or multicatheter interstitial techniques may provide more flexibility in treatment planning for thin skin-to-lumpectomy cavity distances or devices that abut the pectoralis muscle to avoid high skin and chest wall doses. 6. These recommendations are intended as a guide to treat patients but individual treatment decisions could allow treatment outside of the parameters listed above with appropriate discussion with the patient. The American Society of Radiation Oncology (2009), Consensus Statement of Accelerated Partial Breast Irradiation: The task force proposed three patients groups; 1) a suitable group for whom APBI outside a clinical trial is acceptable, 2) a cautionary group for whom caution and concern should be applied when considering APBI outside of a clinical trial, and 3) an unsuitable group, for whom APBI outside of a clinical trial is not generally considered warranted.
5 PAGE: 5 OF: 8 Patients who choose treatment with APBI should be informed that whole breast irradiation is an established treatment with a much longer track record that has documented long-term effectiveness and safety. While patient selection criteria for APBI has not been established, until there is firmer consensus in the community, it is reasonable to approve APBI when patients are treated within the guidelines of any of the major professional groups. CODES: Number Description Eligibility for reimbursement is based upon the benefits set forth in the member s subscriber contract. CODES MAY NOT BE COVERED UNDER ALL CIRCUMSTANCES. PLEASE READ THE POLICY AND GUIDELINES STATEMENTS CAREFULLY. Codes may not be all inclusive as the AMA and CMS code updates may occur more frequently than policy updates. Code Key: Experimental/Investigational = (E/I), Not medically necessary/ appropriate = (NMN). CPT: Placement of radiotherapy afterloading balloon catheter (single or multichannel) into the breast for interstitial radioelement application following partial mastectomy, includes imaging guidance; on date separate from partial mastectomy concurrent with partial mastectomy (list separately in addition to code for primary procedure) Placement of radiotherapy afterloading brachytherapy catheters (multiple tube and button type) into the breast for interstitial radioelement application following (at the time of or subsequent to) partial mastectomy, includes imaging guidance Brachytherapy isodose plan; simple (calculation[s] made from 1 to 4 sources, or remote afterloading brachytherapy, 1 channel), includes basic dosimetry calculation(s) Brachytherapy isodose plan; intermediate (calculation[s] made from 5 to 10 sources, or remote afterloading brachytherapy, 2-12 channels), includes basic dosimetry calculation(s) Brachytherapy isodose plan; complex (calculation[s] made from over 10 sources, or remote afterloading brachytherapy, over 12 channels, includes basic dosimetry calculation(s) 0182T 0394T 0395T High dose rate electronic brachytherapy, per fraction High dose rate electronic brachytherapy, skin surface application, per fraction, includes basic dosimetry, when performed High dose rate electronic brachytherapy, interstitial or intracavitary treatment, per fraction, includes basic dosimetry, when performed Copyright 2015 American Medical Association, Chicago, IL HCPCS: A9527 Iodine I-125, sodium iodide solution, therapeutic, per millicurie C1717 C2634 C9726 Brachytherapy source, non-stranded, high dose rate iridium-192, per source Brachytherapy source, high activity, iodine 125, greater than 1.01 mci (NIST), per source Placement and removal (if performed) of applicator into breast for radiation therapy ICD9: Malignant neoplasm of female breast (code range)
6 PAGE: 6 OF: Malignant neoplasm of male breast (code range) Secondary malignant neoplasm of the breast Carcinoma in situ of breast V10.3 Personal history of malignant neoplasm breast ICD10: C C Malignant neoplasm of the breast (code range) REFERENCES: C79.81 Secondary malignant neoplasm of breast D05.00-D05.92 Carcinoma in situ of the breast (code range) Z85.3 Personal history of malignant neoplasm of breast Ajkay N, et al. A comparison of complication rates in early-stage breast cancer patients treated with brachytherapy versus whole breast irradiation. Ann Surg Oncol2015 Apr;22(4): *American Society of Breast Surgeons. Consensus statement for accelerated partial breast irradiation. Revised 2011 Aug 15 [ accessed 6/15/15. Bietsch P, et al. Five-year outcome of patients classified in the unsuitable category using the American Society of Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology (ASTRO) Consensus Panel Guidelines for the application of accelerated partial breast irradiation: an analysis of patients treated on the American Society of Breast Surgeons MammoSite Registry Trial. Ann Surg Oncol 2010;17:S Beitsch PD, et al. Accelerated partial breast irradiation. J Surg Oncol 2011 Mar15;103(4): *BlueCross BlueShield Association Technology Evaluation Center (TEC) Assessment. Brachytherapy for accelerated partial breast irradiation after breast-conserving surgery for early stage breast cancer Dec;17(8). *BlueCross BlueShield Association Technology Evaluation Center (TEC) Assessment. Accelerated partial breast irradiation as sole radiotherapy after breast-conserving surgery for early stage breast cancer Aug. Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Technology Evaluation Center (TEC Assessment). Accelerated radiotherapy after breast-conserving surgery for early stage breast cancer. TEC Assessments 2010 Aug. BlueCross BlueShield Association. Breast brachytherapy after breast-conserving surgery, as boost with whole breast irradiation, or alone as accelerated partial breast irradiation (APBI). Medical Policy Reference Manual Policy # Dec 11. Edwards JM, et al. Breast conservation therapy utilizing partial breast brachytherapy for early-stage cancer of the breast: a retrospective review from the Saint Luke s Cancer Institute. Am J Clin Oncol 2013 Apr 19 [Epub ahead of print]. Ferraro DJ, et al. Comparison of accelerated partial breast irradiation via multicatheter interstitial brachytherapy versus whole breast radiation. Radiat Oncol 2012 Mar 29;7(1):53. *Fisher B, et al. Twenty-year follow-up of a randomized trial comparing total mastectomy, lumpectomy, and lumpectomy plus irradiation for the treatment of invasive breast cancer. NEJM 2002 Oct 17;347(16): *Gittleman M, et al. Clinical evaluation of the mammosite breast brachytherapy catheter: an analysis of technical reproducibility, acute toxicity, and patient demographics. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2003 Oct 1;57(2 Suppl):S Goyal S, et al. Ductal carcinoma in situ treated with breast-conserving surgery and accelerated partial breast irradiation: comparison of the Mammosite registry trial with intergroup study E5194. Cancer 2011 Mar 15;117(6):
7 PAGE: 7 OF: 8 Jawad MS, et al. Seven-year outcomes following accelerated partial breast irradiation stratified by ASTRO consensus groupings. Am J Clin Oncol 2015 Apr 1 [Epub ahead of print]. Kahn AJ, et al. Six-year analysis of treatment-related toxicities inpatients treated with accelerated partial breast irradiation on the American Society of Breast Surgeons Mammosite Breast Brachytherapy registry trial. Ann Surg Oncol 2012 May;19(5): Kamrava M, et al. Outcomes of breast cancer patients treated with accelerated partial breast irradiation via multicatheter interstitial brachytherapy: the pooled registry of multicatheter interstitial sties (PROMIS) experience. Ann Surg Oncol 2015 Apr 28 [Epub ahead of print]. *Keisch M, et al. Initial clinical experience with the MammoSite breast brachytherapy applicator in women with earlystage breast cancer treated with breast-conserving therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2003 Feb 1;55(2): *Keisch M, et al. Two-year outcome with the mammosite breast brachytherapy applicator: factors associated with optima cosmetic results when performing partial breast irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2003 Oct 1;572(2 Suppl):S315. Lehman M, et al. Partial breast irradiation for early breast cancer. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2014;6:CD National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology, breast cancer. V [ accessed 6/15/15. Park CC, et al. American Society for Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology (ASTRO) Emerging Technology Committee report on electronic brachytherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2010 Mar 15;76(4): *Poggi MM, et al. Eighteen-year results in the treatment of early breast carcinoma with mastectomy versus breast conservation therapy: the National Cancer Institute randomized trial. Cancer 2003 Aug 15;98(4): Polgár C, et al. Breast-conserving therapy with partial or whole breast irradiation: ten-year results of the Budapest randomized trial. Radiother Oncol 2013 Aug;108(2): *Polgár C, et al. Sole brachytherapy of the tumor bed after conservative surgery for T1 breast cancer: five-year results of a phase I-II study and initial findings of a randomized phase III trial. J Surg Oncol 2002 Jul;80(3): Shah C, et al. The American Brachytherapy Society consensus statement for accelerated partial breast irradiation. Brachytherapy 2013 Jul-Aug;12(4): Smith GL et al. Association between treatment with brachytherapy vs whole-breast irradiation and subsequent mastectomy, complications, and survival among older women with invasive breast cancer. JAMA 2012 May 2;30(7): Valachis A, et al. Partial breast irradiation or whole breast radiotherapy for early breast cancer: a meta analysis of randomized control trials. Breast J 2010;16(3): Vicini F, et al. Limitations of the American Society of Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology Consensus Panel guidelines on the use of accelerated partial breast irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2011 Mar 15:79(4): Vicini F, et al. Five-year analysis of the treatment efficacy and cosmesis by the American Society of Breast Surgeons Mammosite Breast Brachytherapy registry trial in patients treated with accelerated partial breast irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2011 Mar 1;79(3): *Wazer DE, et al. Preliminary results of a phase I/II study of HDR brachytherapy alone for T1/T2 breast cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2002 Jul 15;53(4): Wobb JL, et al. Brachytherapy-based accelerated partial breast irradiation provides equivalent 10-year outcomes to whole breast irradiation: a matched-pair analysis. Am J Clin Oncol 2015 Mar 27 [Epub ahead of print].
8 PAGE: 8 OF: 8 *Zannis VJ, et al. Postoperative ultrasound-guided percutaneous placement of a new breast brachytherapy balloon catheter. Am J Surg 2003 Oct;186(4): Zauls AJ, et al. Outcomes in women treated with MammoSite brachytherapy or whole breast irradiation stratified by ASTRO accelerated partial breast irradiation consensus statement groups. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2012 Jan 1;82(1):21-9. *key article(s) KEY WORDS: Accelerated partial breast irradiation; APBI, Axxent, Electronic brachytherapy, Interstitial brachytherapy, MammoSite. CMS COVERAGE FOR MEDICARE PRODUCT MEMBERS There is currently no National Coverage Determination (NCD) or Local Coverage Determination (LCD) for Brachytherapy.
Accelerated Partial Breast Irradiation (APBI) for Breast Cancer [Preauthorization Required]
![Accelerated Partial Breast Irradiation (APBI) for Breast Cancer [Preauthorization Required] Accelerated Partial Breast Irradiation (APBI) for Breast Cancer [Preauthorization Required]](/thumbs/33/16383903.jpg) Accelerated Partial Breast Irradiation (APBI) for Breast Cancer [Preauthorization Required] Medical Policy: MP-SU-01-11 Original Effective Date: February 24, 2011 Reviewed: Revised: This policy applies
Accelerated Partial Breast Irradiation (APBI) for Breast Cancer [Preauthorization Required] Medical Policy: MP-SU-01-11 Original Effective Date: February 24, 2011 Reviewed: Revised: This policy applies
Accelerated Partial Breast Irradiation (APBI) for Breast Cancer [Pre-authorization Required]
![Accelerated Partial Breast Irradiation (APBI) for Breast Cancer [Pre-authorization Required] Accelerated Partial Breast Irradiation (APBI) for Breast Cancer [Pre-authorization Required]](/thumbs/33/16383859.jpg) Accelerated Partial Breast Irradiation (APBI) for Breast Cancer [Pre-authorization Required] Medical Policy: MP-SU-01-11 Original Effective Date: February 24, 2011 Reviewed: February 24, 2012 Revised:
Accelerated Partial Breast Irradiation (APBI) for Breast Cancer [Pre-authorization Required] Medical Policy: MP-SU-01-11 Original Effective Date: February 24, 2011 Reviewed: February 24, 2012 Revised:
Accelerated Partial Breast Irradiation (APBI) for Breast Cancer
 Accelerated Partial Breast Irradiation (APBI) for Breast Cancer [For the list of services and procedures that need preauthorization, please refer to www.mcs.pr Go to Comunicados a Proveedores, and click
Accelerated Partial Breast Irradiation (APBI) for Breast Cancer [For the list of services and procedures that need preauthorization, please refer to www.mcs.pr Go to Comunicados a Proveedores, and click
BRACHYTHERAPY FOR TREATMENT OF BREAST CANCER
 BRACHYTHERAPY FOR TREATMENT OF BREAST CANCER Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This
BRACHYTHERAPY FOR TREATMENT OF BREAST CANCER Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This
Corporate Medical Policy Brachytherapy Treatment of Breast Cancer
 Corporate Medical Policy Brachytherapy Treatment of Breast Cancer File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: brachytherapy_treatment_of_breast_cancer 7/1996 5/2015 5/2016 5/2015
Corporate Medical Policy Brachytherapy Treatment of Breast Cancer File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: brachytherapy_treatment_of_breast_cancer 7/1996 5/2015 5/2016 5/2015
MEDICAL POLICY POLICY TITLE INTERSTITIAL OR BALLOON BREAST BRACHYTHERAPY AND RADIOTHERAPY POLICY NUMBER MP- 5.006
 Original Issue Date (Created): July 1, 2002 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): Effective Date: October 27, 2009 November 30, 2010- RETIRED I. POLICY Interstitial or balloon brachytherapy may be considered
Original Issue Date (Created): July 1, 2002 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): Effective Date: October 27, 2009 November 30, 2010- RETIRED I. POLICY Interstitial or balloon brachytherapy may be considered
How To Know If You Should Get A Brachytherapy Or Radioactive Seed Implantation
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: BRACHYTHERAPY OR PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical policy
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: BRACHYTHERAPY OR PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical policy
Important Information for Women with Breast Cancer. what lumpectomy
 Important Information for Women with Breast Cancer what lumpectomy begins Your most important decisions MammoSite completes Today, more and more women with early-stage breast cancer are able to treat their
Important Information for Women with Breast Cancer what lumpectomy begins Your most important decisions MammoSite completes Today, more and more women with early-stage breast cancer are able to treat their
DEC 2 2 2005. The three components of the Axxent Electronic Brachytherapy System include the Controller, Balloon Applicators-BR and X-ray Source.
 DEC 2 2 2005 Xoft, Inc. Fremont, California Premarket Notification March 31, 2005 II. 510(k) Summary A. Name of Device Trade name: AxxentTM Electronic Brachytherapy System Common name: X-Ray Radiation
DEC 2 2 2005 Xoft, Inc. Fremont, California Premarket Notification March 31, 2005 II. 510(k) Summary A. Name of Device Trade name: AxxentTM Electronic Brachytherapy System Common name: X-Ray Radiation
Breast Cancer Accelerated Partial Breast Irradiation Bruce G. Haffty, MD Professor and Chairman Dept Radiation Oncology UMDNJ-RWJMS Cancer Institute
 Breast Cancer Accelerated Partial Breast Irradiation Bruce G. Haffty, MD Professor and Chairman Dept Radiation Oncology UMDNJ-RWJMS Cancer Institute of New Jersey Rationale for Partial Breast Radiation
Breast Cancer Accelerated Partial Breast Irradiation Bruce G. Haffty, MD Professor and Chairman Dept Radiation Oncology UMDNJ-RWJMS Cancer Institute of New Jersey Rationale for Partial Breast Radiation
Management of Postmenopausal Women with T1 ER+ Tumors: Options and Tradeoffs. Case Study. Surgery. Lumpectomy and Radiation
 Management of Postmenopausal Women with T1 ER+ Tumors: Options and Tradeoffs Michael Alvarado, MD Associate Professor of Surgery University of California San Francisco Case Study 59 yo woman with new palpable
Management of Postmenopausal Women with T1 ER+ Tumors: Options and Tradeoffs Michael Alvarado, MD Associate Professor of Surgery University of California San Francisco Case Study 59 yo woman with new palpable
Patient Guide. Brachytherapy: The precise answer for tackling breast cancer. Because life is for living
 Patient Guide Brachytherapy: The precise answer for tackling breast cancer Because life is for living This booklet is designed to provide information that helps women who have been diagnosed with early
Patient Guide Brachytherapy: The precise answer for tackling breast cancer Because life is for living This booklet is designed to provide information that helps women who have been diagnosed with early
Non-coronary Brachytherapy
 Non-coronary Brachytherapy I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will reimburse for non-coronary brachytherapy when it is determined to be medically necessary and when it meets the medical criteria
Non-coronary Brachytherapy I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will reimburse for non-coronary brachytherapy when it is determined to be medically necessary and when it meets the medical criteria
Trends in BREAST HEALTH
 Trends in BREAST HEALTH VOL. 1 MAR. 2011 IN THIS ISSUE APBI: The Results Are In 1 Advances in Breast Cancer Detection 3 Meeting Highlights 1 Advocacy Issues 2 Case Study 4 Literature Corner 4 Editor s
Trends in BREAST HEALTH VOL. 1 MAR. 2011 IN THIS ISSUE APBI: The Results Are In 1 Advances in Breast Cancer Detection 3 Meeting Highlights 1 Advocacy Issues 2 Case Study 4 Literature Corner 4 Editor s
Goals and Objectives: Breast Cancer Service Department of Radiation Oncology
 Goals and Objectives: Breast Cancer Service Department of Radiation Oncology The breast cancer service provides training in the diagnosis, management, treatment, and follow-up of breast malignancies, including
Goals and Objectives: Breast Cancer Service Department of Radiation Oncology The breast cancer service provides training in the diagnosis, management, treatment, and follow-up of breast malignancies, including
TITLE: Comparison of the dosimetric planning of partial breast irradiation with and without the aid of 3D virtual reality simulation (VRS) software.
 SAMPLE CLINICAL RESEARCH APPLICATION ABSTRACT: TITLE: Comparison of the dosimetric planning of partial breast irradiation with and without the aid of 3D virtual reality simulation (VRS) software. Hypothesis:
SAMPLE CLINICAL RESEARCH APPLICATION ABSTRACT: TITLE: Comparison of the dosimetric planning of partial breast irradiation with and without the aid of 3D virtual reality simulation (VRS) software. Hypothesis:
Running head: BREAST CANCER TREATMENT OPTIONS: A LITERARURE REVIEW 1
 Running head: BREAST CANCER TREATMENT OPTIONS: A LITERARURE REVIEW 1 Breast Cancer Treatment Options: Surgery and Radiation Therapy: A Literature Review December 2012 2 Abstract There are currently several
Running head: BREAST CANCER TREATMENT OPTIONS: A LITERARURE REVIEW 1 Breast Cancer Treatment Options: Surgery and Radiation Therapy: A Literature Review December 2012 2 Abstract There are currently several
Note: Please see RAD.00056 Intraocular Epiretinal Brachytherapy for additional information.
 Subject: for Oncologic Indications Document #: Current Effective Date: 07/09/2008 Status: Revised (Coding updated 10/01/2008) Last Review Date: 05/15/2008 Description/Scope is a form of radiation treatment
Subject: for Oncologic Indications Document #: Current Effective Date: 07/09/2008 Status: Revised (Coding updated 10/01/2008) Last Review Date: 05/15/2008 Description/Scope is a form of radiation treatment
SUBJECT: MANAGEMENT OF BREAST EFFECTIVE DATE: 12/16/99 IMPLANTS REVISED DATE:
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: MANAGEMENT OF BREAST PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical policy
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: MANAGEMENT OF BREAST PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical policy
Understanding INTRABEAM Intraoperative Radiation Therapy for Breast Cancer A patient guide
 Understanding INTRABEAM Intraoperative Radiation Therapy for Breast Cancer A patient guide A diagnosis of breast cancer is never easy, but today there are more treatment options than ever before. A breast
Understanding INTRABEAM Intraoperative Radiation Therapy for Breast Cancer A patient guide A diagnosis of breast cancer is never easy, but today there are more treatment options than ever before. A breast
Clinical Policy Bulletin: Brachytherapy
 Clinical Policy Bulletin: Brachytherapy I. Heritage Provider Network considers brachytherapy (also known as interstitial radiation, intracavitary radiation, internal radiation therapy) medically necessary
Clinical Policy Bulletin: Brachytherapy I. Heritage Provider Network considers brachytherapy (also known as interstitial radiation, intracavitary radiation, internal radiation therapy) medically necessary
Implementation Date: April 2015 Clinical Operations
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guideline PROSTATE CANCER Original Date: March 2011 Page 1 of 5 Radiation Oncology Last Review Date: March 2015 Guideline Number: NIA_CG_124 Last Revised Date:
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guideline PROSTATE CANCER Original Date: March 2011 Page 1 of 5 Radiation Oncology Last Review Date: March 2015 Guideline Number: NIA_CG_124 Last Revised Date:
Accelerated Radiotherapy after Breast-Conserving Surgery for Early Stage Breast Cancer
 Technology Evaluation Center Accelerated Radiotherapy after Breast-Conserving Surgery for Early Stage Breast Cancer Assessment Program Volume 27, No. 6 February 2013 Executive Summary Background Radiation
Technology Evaluation Center Accelerated Radiotherapy after Breast-Conserving Surgery for Early Stage Breast Cancer Assessment Program Volume 27, No. 6 February 2013 Executive Summary Background Radiation
Understanding ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and deciding about treatment
 Understanding ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and deciding about treatment Developed by National Breast and Ovarian Cancer Centre Funded by the Australian Government Department of Health and Ageing Understanding
Understanding ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and deciding about treatment Developed by National Breast and Ovarian Cancer Centre Funded by the Australian Government Department of Health and Ageing Understanding
Historical. Medical Policy
 Medical Policy Subject: Brachytherapy for Oncologic Indications Policy #: RAD.00014 Current Effective Date: 01/01/2015 Status: Revised Last Review Date: 05/15/2014 Description/Scope Brachytherapy is a
Medical Policy Subject: Brachytherapy for Oncologic Indications Policy #: RAD.00014 Current Effective Date: 01/01/2015 Status: Revised Last Review Date: 05/15/2014 Description/Scope Brachytherapy is a
Medical Policy Brachytherapy for Clinically Localized Prostate Cancer Using Permanently Implanted Seeds
 Medical Policy Brachytherapy for Clinically Localized Prostate Cancer Using Permanently Implanted Seeds Table of Contents Policy: Commercial Coding Information Information Pertaining to All Policies Policy:
Medical Policy Brachytherapy for Clinically Localized Prostate Cancer Using Permanently Implanted Seeds Table of Contents Policy: Commercial Coding Information Information Pertaining to All Policies Policy:
How TARGIT Intra-operative Radiotherapy can help Older Patients with Breast cancer
 How TARGIT Intra-operative Radiotherapy can help Older Patients with Breast cancer Jeffrey S Tobias, Jayant S Vaidya, Frederik Wenz and Michael Baum, University College Hospital, London, UK - on behalf
How TARGIT Intra-operative Radiotherapy can help Older Patients with Breast cancer Jeffrey S Tobias, Jayant S Vaidya, Frederik Wenz and Michael Baum, University College Hospital, London, UK - on behalf
Rotation Specific Goals & Objectives: University Health Network-Princess Margaret Hospital/ Sunnybrook Breast/Melanoma
 Rotation Specific Goals & Objectives: University Health Network-Princess Margaret Hospital/ Sunnybrook Breast/Melanoma Medical Expert: Breast Rotation Specific Competencies/Objectives 1.0 Medical History
Rotation Specific Goals & Objectives: University Health Network-Princess Margaret Hospital/ Sunnybrook Breast/Melanoma Medical Expert: Breast Rotation Specific Competencies/Objectives 1.0 Medical History
Early-stage Breast Cancer Treatment: A Patient and Doctor Dialogue
 page 1 Early-stage Breast Cancer Treatment: A Patient and Doctor Dialogue Q: What is breast cancer, and what type do I have? A: Cancer is a disease in which cells become abnormal and form more cells in
page 1 Early-stage Breast Cancer Treatment: A Patient and Doctor Dialogue Q: What is breast cancer, and what type do I have? A: Cancer is a disease in which cells become abnormal and form more cells in
MVP/Care Core National 2015 Radiation Therapy Prior Authorization List (Effective January 1, 2015)
 MVP/Care Core National 2015 Radiation Therapy Prior Authorization List (Effective January 1, 2015) CODE CODE TYPE Description 0330 REVCODE RADIOLOGY/THERAPEUTIC - GENERAL CLASSIFICATION 0333 REVCODE RADIOLOGY/THERAPEUTIC
MVP/Care Core National 2015 Radiation Therapy Prior Authorization List (Effective January 1, 2015) CODE CODE TYPE Description 0330 REVCODE RADIOLOGY/THERAPEUTIC - GENERAL CLASSIFICATION 0333 REVCODE RADIOLOGY/THERAPEUTIC
ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS)
 Understanding ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and deciding about treatment Understanding ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and deciding about treatment Developed by National Breast and Ovarian Cancer Centre
Understanding ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and deciding about treatment Understanding ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and deciding about treatment Developed by National Breast and Ovarian Cancer Centre
Current Status and Perspectives of Radiation Therapy for Breast Cancer
 Breast Cancer Current Status and Perspectives of Radiation Therapy for Breast Cancer JMAJ 45(10): 434 439, 2002 Masahiro HIRAOKA, Masaki KOKUBO, Chikako YAMAMOTO and Michihide MITSUMORI Department of Therapeutic
Breast Cancer Current Status and Perspectives of Radiation Therapy for Breast Cancer JMAJ 45(10): 434 439, 2002 Masahiro HIRAOKA, Masaki KOKUBO, Chikako YAMAMOTO and Michihide MITSUMORI Department of Therapeutic
Understanding brachytherapy
 Understanding brachytherapy Brachytherapy Cancer Treatment Legacy Cancer Institute Your health care provider has requested that you receive a type of radiation treatment called brachytherapy as part of
Understanding brachytherapy Brachytherapy Cancer Treatment Legacy Cancer Institute Your health care provider has requested that you receive a type of radiation treatment called brachytherapy as part of
Innovative RT - Breast - APBI and Boost
 Innovative RT - Breast - APBI and Boost The variables with REQ in superscript are required. The variables with a are single-select variables; only one answer can be selected. The variables with a are multi-select
Innovative RT - Breast - APBI and Boost The variables with REQ in superscript are required. The variables with a are single-select variables; only one answer can be selected. The variables with a are multi-select
Corporate Medical Policy Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) of the Prostate
 Corporate Medical Policy Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) of the Prostate File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: intensity_modulated_radiation_therapy_imrt_of_the_prostate
Corporate Medical Policy Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) of the Prostate File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: intensity_modulated_radiation_therapy_imrt_of_the_prostate
PROPERTY OF ELSEVIER SAMPLE CONTENT - NOT FINAL
 Oncoplastic breast conservation surgery Melvin J Silverstein C H A P T E R 5 Introduction Oncoplastic breast conservation surgery combines oncologic principles with plastic surgical techniques. But it
Oncoplastic breast conservation surgery Melvin J Silverstein C H A P T E R 5 Introduction Oncoplastic breast conservation surgery combines oncologic principles with plastic surgical techniques. But it
Radiation Oncology Centers Participating in MassHealth. Daniel Tsai, Assistant Secretary and Director of MassHealth
 Executive Office of Health and Human s Office of Medicaid www.mass.gov/masshealth May 2015 TO: FROM: RE: Radiation Oncology Centers Participating in Daniel Tsai, Assistant Secretary and Director of (2015
Executive Office of Health and Human s Office of Medicaid www.mass.gov/masshealth May 2015 TO: FROM: RE: Radiation Oncology Centers Participating in Daniel Tsai, Assistant Secretary and Director of (2015
New Clinical Trials Open for the Treatment of Breast Cancer with Proton Beam Therapy
 ROC Newsletter August 2013 New Clinical Trials Open for the Treatment of Breast Cancer with Proton Beam Therapy There is a large body of evidence suggesting an association between breast radiotherapy and
ROC Newsletter August 2013 New Clinical Trials Open for the Treatment of Breast Cancer with Proton Beam Therapy There is a large body of evidence suggesting an association between breast radiotherapy and
Radiation therapy involves using many terms you may have never heard before. Below is a list of words you could hear during your treatment.
 Dictionary Radiation therapy involves using many terms you may have never heard before. Below is a list of words you could hear during your treatment. Applicator A device used to hold a radioactive source
Dictionary Radiation therapy involves using many terms you may have never heard before. Below is a list of words you could hear during your treatment. Applicator A device used to hold a radioactive source
American College of Radiology ACR Appropriateness Criteria DUCTAL CARCINOMA IN SITU
 American College of Radiology ACR Appropriateness Criteria Date of origin: 1996 Last review date: 2014 DUCTAL CARCINOMA IN SITU Expert Panel on Radiation Oncology Breast: Seth A. Kaufman, MD 1 ; Eleanor
American College of Radiology ACR Appropriateness Criteria Date of origin: 1996 Last review date: 2014 DUCTAL CARCINOMA IN SITU Expert Panel on Radiation Oncology Breast: Seth A. Kaufman, MD 1 ; Eleanor
Radiation Therapy Coverage, Coding, and Reimbursement for New Technologies
 Radiation Therapy Coverage, Coding, and Reimbursement for New Technologies Presented by Susan Granucci, Healthcare Reimbursement Specialist Topics 1. Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) 2. Tomotherapy
Radiation Therapy Coverage, Coding, and Reimbursement for New Technologies Presented by Susan Granucci, Healthcare Reimbursement Specialist Topics 1. Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) 2. Tomotherapy
Understanding Your Surgical Options For Breast Cancer
 RADIATION THERAPY SYMPTOM MANAGEMENT CANCER INFORMATION Understanding Your Surgical Options For Breast Cancer In this booklet you will learn about: Role of surgery in breast cancer diagnosis and treatment
RADIATION THERAPY SYMPTOM MANAGEMENT CANCER INFORMATION Understanding Your Surgical Options For Breast Cancer In this booklet you will learn about: Role of surgery in breast cancer diagnosis and treatment
When it comes to treating breast cancer, doing less does more October is Breast Cancer Awareness Month
 For Immediate Release Oct. 8, 2012 When it comes to treating breast cancer, doing less does more October is Breast Cancer Awareness Month SEATTLE Oncologists and researchers are discovering that when it
For Immediate Release Oct. 8, 2012 When it comes to treating breast cancer, doing less does more October is Breast Cancer Awareness Month SEATTLE Oncologists and researchers are discovering that when it
Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Treated With Breast-Conserving Surgery and Radiotherapy: A Comparison With ECOG Study 5194
 Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Treated With Breast-Conserving Surgery and Radiotherapy: A Comparison With ECOG Study 5194 Sabin B. Motwani, MD 1 ; Sharad Goyal, MD 1 ; Meena S. Moran, MD 2 ; Arpit Chhabra, BS
Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Treated With Breast-Conserving Surgery and Radiotherapy: A Comparison With ECOG Study 5194 Sabin B. Motwani, MD 1 ; Sharad Goyal, MD 1 ; Meena S. Moran, MD 2 ; Arpit Chhabra, BS
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: COGNITIVE REHABILITATION. POLICY NUMBER: 8.01.19 CATEGORY: Therapy/Rehabilitation
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: COGNITIVE REHABILITATION PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: COGNITIVE REHABILITATION PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical
Helen Joseph Breast Care Clinic - Johannesburg, South Africa
 - Johannesburg, South Africa General Information New breast cancer cases treated per year 360 Breast multidisciplinarity team members 12 Radiologists, surgeons, pathologists, medical oncologists, radiotherapists
- Johannesburg, South Africa General Information New breast cancer cases treated per year 360 Breast multidisciplinarity team members 12 Radiologists, surgeons, pathologists, medical oncologists, radiotherapists
NIA RADIATION ONCOLOGY CODING STANDARD. Dosimetry Planning
 NIA RADIATION ONCOLOGY CODING STANDARD Dosimetry Planning CPT Codes: 77295, 77300, 77301, 77306, 77307, 77321, 77316, 77317, 77318, 77331, 77399 Original Date: April, 2011 Last Reviewed Date: November,
NIA RADIATION ONCOLOGY CODING STANDARD Dosimetry Planning CPT Codes: 77295, 77300, 77301, 77306, 77307, 77321, 77316, 77317, 77318, 77331, 77399 Original Date: April, 2011 Last Reviewed Date: November,
Breast Cancer. CSC Cancer Experience Registry Member, breast cancer
 ESSENTIALS Breast Cancer Take things one step at a time. Try not to be overwhelmed by the tidal wave of technical information coming your way. Finally you know your body best; you have to be your own advocate.
ESSENTIALS Breast Cancer Take things one step at a time. Try not to be overwhelmed by the tidal wave of technical information coming your way. Finally you know your body best; you have to be your own advocate.
Breast Cancer. Sometimes cells keep dividing and growing without normal controls, causing an abnormal growth called a tumor.
 Breast Cancer Introduction Cancer of the breast is the most common form of cancer that affects women but is no longer the leading cause of cancer deaths. About 1 out of 8 women are diagnosed with breast
Breast Cancer Introduction Cancer of the breast is the most common form of cancer that affects women but is no longer the leading cause of cancer deaths. About 1 out of 8 women are diagnosed with breast
Azienda Ospedale Annunziata Cosenza - Cosenza, Italy
 - Cosenza, Italy General Information New breast cancer cases treated per year 180 Breast multidisciplinarity team members 9 Radiologists, surgeons, pathologists, medical oncologists, radiotherapists and
- Cosenza, Italy General Information New breast cancer cases treated per year 180 Breast multidisciplinarity team members 9 Radiologists, surgeons, pathologists, medical oncologists, radiotherapists and
Guidelines for the treatment of breast cancer with radiotherapy
 London Cancer Guidelines for the treatment of breast cancer with radiotherapy March 2013 Review March 2014 Version 1.0 Contents 1. Introduction... 3 2. Indications and dosing schedules... 3 2.1. Ductal
London Cancer Guidelines for the treatment of breast cancer with radiotherapy March 2013 Review March 2014 Version 1.0 Contents 1. Introduction... 3 2. Indications and dosing schedules... 3 2.1. Ductal
Cytoreduction and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy for the treatment of pseudomyxoma
 Medical Policy Cytoreduction and Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy for the Treatment of Pseudomyxoma Peritonei and Peritoneal Carcinomatosis of Gastrointestinal Origin, and Peritoneal Mesothelioma
Medical Policy Cytoreduction and Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy for the Treatment of Pseudomyxoma Peritonei and Peritoneal Carcinomatosis of Gastrointestinal Origin, and Peritoneal Mesothelioma
Clinical trial enrollment among older cancer patients
 Clinical trial enrollment among older cancer patients Sharon H. Giordano MD, MPH Professor, Health Services Research Mariana Chavez Mac Gregor MD, MSc Assistant Professor, Breast Medical Oncology Department
Clinical trial enrollment among older cancer patients Sharon H. Giordano MD, MPH Professor, Health Services Research Mariana Chavez Mac Gregor MD, MSc Assistant Professor, Breast Medical Oncology Department
Brachytherapy of the Uterine Corpus: Some Physical Considerations. Bruce Thomadsen. University of Wisconsin -Madison
 Brachytherapy of the Uterine Corpus: Some Physical Considerations Bruce Thomadsen University of Wisconsin -Madison Conflicts of Interest The author has no known conflicts involving this presentation Learning
Brachytherapy of the Uterine Corpus: Some Physical Considerations Bruce Thomadsen University of Wisconsin -Madison Conflicts of Interest The author has no known conflicts involving this presentation Learning
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: MOLECULAR MARKERS IN FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATES OF THE THYROID EFFECTIVE DATE: 11/19/15
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: MOLECULAR MARKERS IN FINE NEEDLE PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases,
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: MOLECULAR MARKERS IN FINE NEEDLE PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases,
Breast Cancer: from bedside and grossing room to diagnoses and beyond. Adriana Corben, M.D.
 Breast Cancer: from bedside and grossing room to diagnoses and beyond Adriana Corben, M.D. About breast anatomy Breasts are special organs that develop in women during puberty when female hormones are
Breast Cancer: from bedside and grossing room to diagnoses and beyond Adriana Corben, M.D. About breast anatomy Breasts are special organs that develop in women during puberty when female hormones are
Basic Radiation Therapy Terms
 Basic Radiation Therapy Terms accelerated radiation: radiation schedule in which the total dose is given over a shorter period of time. (Compare to hyperfractionated radiation.) adjuvant therapy (add-joo-vunt):
Basic Radiation Therapy Terms accelerated radiation: radiation schedule in which the total dose is given over a shorter period of time. (Compare to hyperfractionated radiation.) adjuvant therapy (add-joo-vunt):
Brachytherapy for prostate cancer
 Brachytherapy for prostate cancer Findings by SBU Alert Published Jun 7, 2000 Version 1 Brachytherapy is not widely used in Sweden to treat localized prostate cancer. This treatment method has been available
Brachytherapy for prostate cancer Findings by SBU Alert Published Jun 7, 2000 Version 1 Brachytherapy is not widely used in Sweden to treat localized prostate cancer. This treatment method has been available
HDR Brachytherapy. Patient Information
 HDR Brachytherapy Patient Information 1 About Brachytherapy Cancer is a term used for diseases in which abnormal cells divide without control and then invade other tissues. This disease can affect many
HDR Brachytherapy Patient Information 1 About Brachytherapy Cancer is a term used for diseases in which abnormal cells divide without control and then invade other tissues. This disease can affect many
HAVE YOU BEEN NEWLY DIAGNOSED with DCIS?
 HAVE YOU BEEN NEWLY DIAGNOSED with DCIS? Jen D. Mother and volunteer. Diagnosed with DCIS breast cancer in 2012. An educational guide prepared by Genomic Health This guide is designed to educate women
HAVE YOU BEEN NEWLY DIAGNOSED with DCIS? Jen D. Mother and volunteer. Diagnosed with DCIS breast cancer in 2012. An educational guide prepared by Genomic Health This guide is designed to educate women
Understanding Your Diagnosis of Endometrial Cancer A STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE
 Understanding Your Diagnosis of Endometrial Cancer A STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE Introduction This guide is designed to help you clarify and understand the decisions that need to be made about your care for the
Understanding Your Diagnosis of Endometrial Cancer A STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE Introduction This guide is designed to help you clarify and understand the decisions that need to be made about your care for the
Surgery Choices. National Cancer Institute. For Women with DCIS or Breast Cancer. National Institutes of Health
 National Cancer Institute Surgery Choices For Women with DCIS or Breast Cancer U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health The National Cancer Institute is grateful for our
National Cancer Institute Surgery Choices For Women with DCIS or Breast Cancer U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health The National Cancer Institute is grateful for our
- Pisa, Italy. Azienda Ospedaliero-Universitaria Di Pisa - Ospedale S. Chiara 1/6. General Information
 - Pisa, Italy General Information New breast cancer cases treated per year 500 Breast multidisciplinarity team members 18 Radiologists, surgeons, pathologists, medical oncologists, radiotherapists and
- Pisa, Italy General Information New breast cancer cases treated per year 500 Breast multidisciplinarity team members 18 Radiologists, surgeons, pathologists, medical oncologists, radiotherapists and
Prostate Cancer Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Treatment Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam,
Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Treatment Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam,
Health Policy Advisory Committee on Technology
 Health Policy Advisory Committee on Technology Technology Brief Update Multi-catheter interstitial brachytherapy for early stage breast cancer May 2013 State of Queensland (Queensland Health) 2013 This
Health Policy Advisory Committee on Technology Technology Brief Update Multi-catheter interstitial brachytherapy for early stage breast cancer May 2013 State of Queensland (Queensland Health) 2013 This
Coding Companion for Radiology. A comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement
 Coding Companion for Radiology A comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement 2013 Contents Getting Started with Coding Companion...i Diagnostic Radiology Head/Neck...1 Chest...38 Spine/Pelvis...51
Coding Companion for Radiology A comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement 2013 Contents Getting Started with Coding Companion...i Diagnostic Radiology Head/Neck...1 Chest...38 Spine/Pelvis...51
GYNECOLOGIC CANCERS Facts to Help Patients Make an Informed Decision
 RADIATION THERAPY FOR GYNECOLOGIC CANCERS Facts to Help Patients Make an Informed Decision TARGETING CANCER CARE AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR RADIATION ONCOLOGY FACTS ABOUT GYNECOLOGIC CANCERS Gynecologic cancers
RADIATION THERAPY FOR GYNECOLOGIC CANCERS Facts to Help Patients Make an Informed Decision TARGETING CANCER CARE AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR RADIATION ONCOLOGY FACTS ABOUT GYNECOLOGIC CANCERS Gynecologic cancers
Coalition For The Advancement Of Brachytherapy 660 Pennsylvania Avenue, S.E. Suite 201 Washington, D.C. 20003 (202) 548-2307 Fax: (202) 547-4658
 Coalition For The Advancement Of Brachytherapy 660 Pennsylvania Avenue, S.E. Suite 201 Washington, D.C. 20003 (202) 548-2307 Fax: (202) 547-4658 September 25, 2002 The Honorable Thomas A. Scully Administrator
Coalition For The Advancement Of Brachytherapy 660 Pennsylvania Avenue, S.E. Suite 201 Washington, D.C. 20003 (202) 548-2307 Fax: (202) 547-4658 September 25, 2002 The Honorable Thomas A. Scully Administrator
RADIATION ONCOLOGY GUIDELINES
 MedSolutions, Inc. Clinical Decision Support Tool Diagnostic Strategies This tool addresses common symptoms and symptom complexes. Requests for patients with atypical symptoms or clinical presentations
MedSolutions, Inc. Clinical Decision Support Tool Diagnostic Strategies This tool addresses common symptoms and symptom complexes. Requests for patients with atypical symptoms or clinical presentations
dedicated to curing BREAST CANCER
 dedicated to curing BREAST CANCER When you are diagnosed with breast cancer, you need a team of specialists who will share their knowledge of breast disease and the latest treatments available. At Cancer
dedicated to curing BREAST CANCER When you are diagnosed with breast cancer, you need a team of specialists who will share their knowledge of breast disease and the latest treatments available. At Cancer
Report series: General cancer information
 Fighting cancer with information Report series: General cancer information Eastern Cancer Registration and Information Centre ECRIC report series: General cancer information Cancer is a general term for
Fighting cancer with information Report series: General cancer information Eastern Cancer Registration and Information Centre ECRIC report series: General cancer information Cancer is a general term for
Role of Radiotherapy in Patients with Early Breast Cancer
 Role of Radiotherapy in Patients with Early Breast Cancer a report by M Houman Fekrazad, MD, 1 Anne Marie Wallace, MD, 1 Claire Verschraegen, MD, 1 Vincent Vinh-Hung, MD, PhD, 2 Eva Zavadova 1 and Melanie
Role of Radiotherapy in Patients with Early Breast Cancer a report by M Houman Fekrazad, MD, 1 Anne Marie Wallace, MD, 1 Claire Verschraegen, MD, 1 Vincent Vinh-Hung, MD, PhD, 2 Eva Zavadova 1 and Melanie
Surgical guidelines for the management of breast cancer
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com EJSO xx (2009) S1eS22 www.ejso.com Guidelines Surgical guidelines for the management of breast cancer Contents Association of Breast Surgery at BASO 2009 Introduction...
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com EJSO xx (2009) S1eS22 www.ejso.com Guidelines Surgical guidelines for the management of breast cancer Contents Association of Breast Surgery at BASO 2009 Introduction...
RADIATION THERAPY IN THE MANAGEMENT OF CANCER
 RADIATION THERAPY IN THE MANAGEMENT OF CANCER G K Rath Introduction Radiotherapy or radiation treatment is defined as the treatment of diseases (mostly malignant) with ionizing radiation. The various types
RADIATION THERAPY IN THE MANAGEMENT OF CANCER G K Rath Introduction Radiotherapy or radiation treatment is defined as the treatment of diseases (mostly malignant) with ionizing radiation. The various types
Hereditary Multifocal Breast Cancer. Farin Amersi M.D., F.A.C.S Division of Surgical Oncology Department of Surgery Cedar Sinai Medical Center
 Hereditary Multifocal Breast Cancer Farin Amersi M.D., F.A.C.S Division of Surgical Oncology Department of Surgery Cedar Sinai Medical Center CASE STUDY 30 year old Ashkenazi Jewish woman Nulliparous Felt
Hereditary Multifocal Breast Cancer Farin Amersi M.D., F.A.C.S Division of Surgical Oncology Department of Surgery Cedar Sinai Medical Center CASE STUDY 30 year old Ashkenazi Jewish woman Nulliparous Felt
Radiation Therapy for Cancer Treatment
 Radiation Therapy for Cancer Treatment Guest Expert: Kenneth, MD Associate Professor of Therapeutic Radiology www.wnpr.org www.yalecancercenter.org Welcome to Yale Cancer Center Answers with Dr. Ed and
Radiation Therapy for Cancer Treatment Guest Expert: Kenneth, MD Associate Professor of Therapeutic Radiology www.wnpr.org www.yalecancercenter.org Welcome to Yale Cancer Center Answers with Dr. Ed and
Wisconsin Cancer Data Bulletin Wisconsin Department of Health Services Division of Public Health Office of Health Informatics
 Wisconsin Cancer Data Bulletin Wisconsin Department of Health Services Division of Public Health Office of Health Informatics In Situ Breast Cancer in Wisconsin INTRODUCTION This bulletin provides information
Wisconsin Cancer Data Bulletin Wisconsin Department of Health Services Division of Public Health Office of Health Informatics In Situ Breast Cancer in Wisconsin INTRODUCTION This bulletin provides information
Intraoperative Radiotherapy in Breast Conserving Surgery
 2014;110:68 74 Intraoperative Radiotherapy in Breast Conserving Surgery DENNIS RICKY HOLMES, MD, FACS* Los Angeles Center for Women s Health, California Hospital Medical Center, 1513 South Grand Avenue,
2014;110:68 74 Intraoperative Radiotherapy in Breast Conserving Surgery DENNIS RICKY HOLMES, MD, FACS* Los Angeles Center for Women s Health, California Hospital Medical Center, 1513 South Grand Avenue,
ASTRO Spring Refresher Course 2013: Early Breast Cancer
 ASTRO Spring Refresher Course 2013: Early Breast Cancer Eleanor Harris, MD Professor and Chair Department of Radiation Oncology Brody School of Medicine East Carolina University Objectives: Early Breast
ASTRO Spring Refresher Course 2013: Early Breast Cancer Eleanor Harris, MD Professor and Chair Department of Radiation Oncology Brody School of Medicine East Carolina University Objectives: Early Breast
Table of Contents. Data Supplement 1: Summary of ASTRO Guideline Statements. Data Supplement 2: Definition of Terms
 Definitive and Adjuvant Radiotherapy in Locally Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline Endorsement of the American Society for Radiation
Definitive and Adjuvant Radiotherapy in Locally Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline Endorsement of the American Society for Radiation
Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too.
 Male Breast Cancer Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too. Many people do not know that men can get breast
Male Breast Cancer Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too. Many people do not know that men can get breast
Principles of Radiation Therapy A Bapsi Chakravarthy, MD Associate e P rofessor Professor Radiation Oncology
 Principles of Radiation Therapy A Bapsi Chakravarthy, MD Associate Professor Radiation Oncology Disclosure Information I have no financial relationships to disclose relevant to the conten of this presentation.
Principles of Radiation Therapy A Bapsi Chakravarthy, MD Associate Professor Radiation Oncology Disclosure Information I have no financial relationships to disclose relevant to the conten of this presentation.
Janusz Skowronek MD, PhD
 Janusz Skowronek MD, PhD Greatpoland Cancer Center Pozna, January 2004 1 1. About Brachytherapy Derived from ancient Greek words for short distance (brachios) and treatment (therapy) and refers to the
Janusz Skowronek MD, PhD Greatpoland Cancer Center Pozna, January 2004 1 1. About Brachytherapy Derived from ancient Greek words for short distance (brachios) and treatment (therapy) and refers to the
Prostate Cancer. What is prostate cancer?
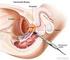 Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam, prostate-specific
Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam, prostate-specific
Horizon Blue Cross Blue Shield of New Jersey 2012 Radiation Therapy Payment Rules
 55875 55876 55876 Description Transperineal placement of needles or catheters into prostate for interstitial radioelement application, with or wout cytosocopy 55920 Placement of interstitial device(s)
55875 55876 55876 Description Transperineal placement of needles or catheters into prostate for interstitial radioelement application, with or wout cytosocopy 55920 Placement of interstitial device(s)
AZ Sint Lucas - Brugge, Belgium
 - Brugge, Belgium General Information New breast cancer cases treated per year 150 Breast multidisciplinarity team members 12 Radiologists, surgeons, pathologists, medical oncologists, radiotherapists
- Brugge, Belgium General Information New breast cancer cases treated per year 150 Breast multidisciplinarity team members 12 Radiologists, surgeons, pathologists, medical oncologists, radiotherapists
Clinical Policy Bulletin: Brachytherapy
 Page 1 of 15 Close Window Aetna.com Home Help Contact Us Search Go Clinical Policy Bulletin: Brachytherapy Number: 0371 Policy History Last Review: 07/17/2012 Effective: 03/08/2000 Next Review: 04/25/2013
Page 1 of 15 Close Window Aetna.com Home Help Contact Us Search Go Clinical Policy Bulletin: Brachytherapy Number: 0371 Policy History Last Review: 07/17/2012 Effective: 03/08/2000 Next Review: 04/25/2013
Cyberknife Information Guide. Prostate Cancer Treatment
 Cyberknife Information Guide Prostate Cancer Treatment CYBERKNIFE INFORMATION GUIDE PROSTATE CANCER TREATMENT As a patient recently diagnosed with localized prostate cancer, it is important that you familiarize
Cyberknife Information Guide Prostate Cancer Treatment CYBERKNIFE INFORMATION GUIDE PROSTATE CANCER TREATMENT As a patient recently diagnosed with localized prostate cancer, it is important that you familiarize
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: hematopoietic_stem-cell_transplantation_for_epithelial_ovarian_cancer 2/2001 11/2015 11/2016 11/2015 Description
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: hematopoietic_stem-cell_transplantation_for_epithelial_ovarian_cancer 2/2001 11/2015 11/2016 11/2015 Description
Breast Reconstruction Surgery
 Breast Reconstruction Surgery I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will reimburse for Breast Reconstruction Surgery when it is determined to be medically necessary and when it meets the medical criteria
Breast Reconstruction Surgery I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will reimburse for Breast Reconstruction Surgery when it is determined to be medically necessary and when it meets the medical criteria
Santa Maria Annunziata Hospital / Azienda Sanitaria di Firenze
 - Firenze, Italy General Information New breast cancer cases treated per year 350 Breast multidisciplinarity team members 12 Radiologists, surgeons, pathologists, medical oncologists, radiotherapists and
- Firenze, Italy General Information New breast cancer cases treated per year 350 Breast multidisciplinarity team members 12 Radiologists, surgeons, pathologists, medical oncologists, radiotherapists and
Loco-regional Recurrence
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer AGO AGO e. e. V. V. Loco-regional Recurrence Loco-regional Recurrence Version 2002: Brunnert / Simon Versions 2003 2012: Audretsch
Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer AGO AGO e. e. V. V. Loco-regional Recurrence Loco-regional Recurrence Version 2002: Brunnert / Simon Versions 2003 2012: Audretsch
CHAPTER 2. Neoplasms (C00-D49) March 2014. 2014 MVP Health Care, Inc.
 Neoplasms (C00-D49) March 2014 2014 MVP Health Care, Inc. CHAPTER SPECIFIC CATEGORY CODE BLOCKS C00-C14 Malignant neoplasms of lip, oral cavity and pharynx C15-C26 Malignant neoplasms of digestive organs
Neoplasms (C00-D49) March 2014 2014 MVP Health Care, Inc. CHAPTER SPECIFIC CATEGORY CODE BLOCKS C00-C14 Malignant neoplasms of lip, oral cavity and pharynx C15-C26 Malignant neoplasms of digestive organs
Audit. Process for managing outliers in breast cancer surgery. March 2005
 Process for managing outliers in breast cancer surgery Audit March 2005 Prepared by: Australian Safety & Efficacy Register of New Interventional Procedures Surgical On behalf of: The Section of Breast
Process for managing outliers in breast cancer surgery Audit March 2005 Prepared by: Australian Safety & Efficacy Register of New Interventional Procedures Surgical On behalf of: The Section of Breast
Smoking and misuse of certain pain medicines can affect the risk of developing renal cell cancer.
 Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
FAQ About Prostate Cancer Treatment and SpaceOAR System
 FAQ About Prostate Cancer Treatment and SpaceOAR System P. 4 Prostate Cancer Background SpaceOAR Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) 1. What is prostate cancer? The vast majority of prostate cancers develop
FAQ About Prostate Cancer Treatment and SpaceOAR System P. 4 Prostate Cancer Background SpaceOAR Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) 1. What is prostate cancer? The vast majority of prostate cancers develop
Breast Cancer & Treatment in ACT and Surrounding Regions QUALITY ASSURANCE PROJECT. Five-year report
 Breast Cancer & Treatment in ACT and Surrounding Regions QUALITY ASSURANCE PROJECT Five-year report Community Health Pathology Southern Area Health Service ACT Health General Practitioners Nurses Social
Breast Cancer & Treatment in ACT and Surrounding Regions QUALITY ASSURANCE PROJECT Five-year report Community Health Pathology Southern Area Health Service ACT Health General Practitioners Nurses Social
Colorectal Cancer Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Colorectal Cancer Treatment Colorectal cancer overview Colorectal cancer, also called large bowel cancer, is the term used to describe malignant tumors found in the colon and rectum.
Scan for mobile link. Colorectal Cancer Treatment Colorectal cancer overview Colorectal cancer, also called large bowel cancer, is the term used to describe malignant tumors found in the colon and rectum.
Breast cancer treatments
 Breast cancer treatments i About us Breast Cancer Network Australia (BCNA) is the peak organisation for all people affected by breast cancer in Australia. We provide a range of free resources, including
Breast cancer treatments i About us Breast Cancer Network Australia (BCNA) is the peak organisation for all people affected by breast cancer in Australia. We provide a range of free resources, including
Subject: Proton Beam Therapy for Prostate Cancer
 Subject: Proton Beam Therapy for Prostate Cancer Guidance Number: MCG-153 Revision Date(s): Original Effective Date: 10/30/13 Medical Coverage Guidance Approval Date: 10/30/13 PREFACE This Medical Guidance
Subject: Proton Beam Therapy for Prostate Cancer Guidance Number: MCG-153 Revision Date(s): Original Effective Date: 10/30/13 Medical Coverage Guidance Approval Date: 10/30/13 PREFACE This Medical Guidance
