Subject: Proton Beam Therapy for Prostate Cancer
|
|
|
- Buck Waters
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Subject: Proton Beam Therapy for Prostate Cancer Guidance Number: MCG-153 Revision Date(s): Original Effective Date: 10/30/13 Medical Coverage Guidance Approval Date: 10/30/13 PREFACE This Medical Guidance is intended to facilitate the Utilization Management process. It expresses Molina's determination as to whether certain services or supplies are medically necessary, experimental, investigational, or cosmetic for purposes of determining appropriateness of payment. The conclusion that a particular service or supply is medically necessary does not constitute a representation or warranty that this service or supply is covered (i.e., will be paid for by Molina) for a parti cular member. The member's benefit plan determines coverage. Each benefit plan defines which services are covered, which are excluded, and which are subject to dollar caps or other limits. Members and their providers will need to consult the member's benefit plan to determine if there are any exclusions or other benefit limitations applicable to this service or supply. If there is a discrepancy between this policy and a member's plan of benefits, the benefits plan will govern. In addition, coverage may be mandated by applicable legal requirements of a State, the Federal government or CMS for Medicare and Medicaid members. CMS's Coverage Database can be found on the following website: FDA INDICATIONS Proton beam therapy for prostate cancer is a procedure and, therefore, not subject to FDA regulation. Proton beam therapy systems are approved by the FDA as a 510(k) class II medical device designed to produce and deliver a proton beam for the treatment of patients with localized tumors and other conditions susceptible to treatment by radiation. To view a general list of FDA 510(k)-approved proton beam devices use LHN as the Product Code in the form found at the FDA website. 1 CENTERS FOR MEDICARE AND MEDICAID SERVICES (CMS) The coverage directive(s) and criteria from an existing National Coverage Determination (NCD) or Local Coverage Determination (LCD) will supersede the contents of this Molina medical coverage guidance (MCG) document and provide the directive for all Medicare members. The directives from this MCG document may be followed if there are no available NCD or LCD documents available and outlined below. No National Coverage Determination (NCD) for proton beam therapy for prostate cancer was identified on the CMS website. There are several Local Coverage Determinations (LCD) that outline coverage for proton beam therapy. 2 INITIAL COVERAGE CRITERIA Proton beam therapy (PBT) is considered not medically necessary and may not be authorized for the treatment of prostate cancer because clinical outcomes of this treatment have not been shown to be superior to other approaches such as intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) or 3D-conformal radiation therapy. CONTINUATION OF THERAPY N/A Page 1 of 9
2 COVERAGE EXCLUSIONS Proton beam therapy (PBT) is considered not medically necessary and may not be authorized for the treatment of prostate cancer because clinical outcomes of this treatment have not been shown to be superior to other approaches such as intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) or 3D-conformal radiation therapy. DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE/SERVICE/PHARMACEUTICAL Proton Beam radiotherapy is a form of conformal external beam radiation treatment. Protons are positively charged atomic particles and have similar biological effects as conventional x-ray beams, but have very different energy disposition or physics profiles. Proton particles deliver a smaller amount of radiation energy as they enter the body (lower entrance dose) culminating in an intensity dose peak (e.g. Bragg Peak) therefore depositing 100% of the dosage at the targeted tissue. There is no further energy deposition beyond the Bragg peak (no exit dose). Proton beams typically deposit less radiation in normal non-targeted tissues than conventional radiation therapy and have been used to escalate the radiation dose to diseased tissues while minimizing damage to adjacent normal tissues. Proton beam therapy will typically have a significantly lower integral dose (dose to the whole body of the patient) compared to conventional x-ray therapy. In contrast, conventional external beam radiation therapy (EBRT) delivers radiation to all involved tissue, diseased and normal, and targeted tissue receives 60 70% of the intended dose. Proton beam therapy is typically performed on an outpatient basis. For most tumor sites, a standard course of treatment is five to seven weeks, with treatments delivered five days per week. The length of each treatment will vary depending upon the tumor type and stage. The delivery of the proton beam to the patient lasts only a few minutes, although the total time spent in the treatment room will be longer (about 15 to 20 minutes) for positioning and adjustments to the equipment settings. 4 GENERAL INFORMATION Summary of Medical Evidence There are numerous clinical trials underway studying proton beam therapy as a treatment for prostate cancer and to date no clinical trials have demonstrated that proton beam therapy has better outcomes than the conventional methods of radiation therapy. 22 Yu et al (2013) performed a retrospective study of all Medicare beneficiaries aged greater than or equal to 66 years who received PRT or IMRT for prostate cancer during 2008 and/or Multivariable logistic regression was used to identify factors associated with receipt of PRT. To assess toxicity, each PRT patient was matched with two IMRT patients with similar clinical and socio-demographic characteristics. The main outcome measures were receipt of PRT or IMRT, Medicare reimbursement for each treatment, and early genitourinary, gastrointestinal, and other toxicity. All statistical tests were two-sided. 27,647 men; 553 (2%) received PRT and 27,094 (98%) received IMRT. Patients receiving PRT were younger, healthier, and from more affluent areas than patients receiving IMRT. Median Medicare reimbursement was $32,428 for PRT and $18,575 for IMRT. Although PRT was associated with a statistically significant reduction in genitourinary toxicity at 6 months compared with IMRT (5.9% vs 9.5%; odds ratio [OR] = 0.60, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 0.38 to 0.96, P =.03), at 12 months post-treatment there was no difference in genitourinary toxicity (18.8% vs 17.5%; OR = 1.08, Page 2 of 9
3 95% CI = 0.76 to 1.54, P =.66). There was no statistically significant difference in gastrointestinal or other toxicity at 6 months or 12 months post-treatment. The authors concluded that although PRT is substantially more costly than IMRT, there was no difference in toxicity in a comprehensive cohort of Medicare beneficiaries with prostate cancer at 12 months post-treatment. 12 Ohri at al. (2012) performed a review of published series that report late gastrointestinal (GI) and genitourinary (GU) toxicity rates following definitive RT for prostate cancer using the RTOG Late Radiation Morbidity Scoring Schema. Univariate analyses were performed to test RT technique, RT dose, pelvic irradiation, and androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) as predictors of moderate (grade 2) and severe (grade 3) GI and GU toxicity. To isolate the effect of radiotherapy dose on late toxicity a meta-analysis was restricted to randomized trials that tested RT dose escalation. Statistical analyses were repeated using the subset of studies that utilized escalated RT doses. Twenty published reports detailing the treatment techniques and toxicity outcomes of 35 patient series including a total of 11,835 patients were included in this analysis. Median rates of moderate late toxicity were 15% (GI) and 17% (GU). For severe effects, these values were 2% (GI) and 3% (GU). Metaanalysis of five randomized trials revealed that an 8-10 Gy increase in RT dose increases the rate of both moderate (OR = 1.63, 95% CI: [1.44 to 1.82], p < 0.001) and severe (OR = 2.03, 95% CI: [1.64 to 2.42], p < 0.001) late GI toxicity. Among 17 series where doses of at least 74 Gy were utilized, use of intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) or proton beam radiotherapy (PBRT) was associated with a significant decrease in the reported rate of severe GI toxicity compared to 3-D RT. The Meta-analysis of randomized dose escalation trials demonstrates that late toxicity rates increase with RT dose. Series where dose escalated RT is delivered using IMRT or PBRT have relatively short follow up but report lower late GI toxicity rates than those employing 3-D RT. 9 Allen et al. (2012) conducted a systematic review to evaluate the state of the science of proton beam therapy (PBT) and arrive at a recommendation for the use of PBT. The emerging technology committee of the American Society of Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) routinely evaluates new modalities in radiotherapy and assesses the published evidence to determine recommendations for the society as a whole. In 2007, a Proton Task Force was assembled to evaluate the state of the art of PBT. This report reflects evidence collected up to November Data was reviewed for PBT in central nervous system tumors, gastrointestinal malignancies, lung, head and neck, prostate, and pediatric tumors. Current data do not provide sufficient evidence to recommend PBT in lung cancer, head and neck cancer, GI malignancies, and pediatric non-cns malignancies. In hepatocellular carcinoma and prostate cancer and there is evidence for the efficacy of PBT but no suggestion that it is superior to photon based approaches. In pediatric CNS malignancies PBT appears superior to photon approaches but more data is needed. In large ocular melanomas and chordomas, we believe that there is evidence for a benefit of PBT over photon approaches. PBT is an important new technology in radiotherapy. Current evidence provides a limited indication for PBT. More robust prospective clinical trials are needed to determine the appropriate clinical setting for PBT. 10 Page 3 of 9
4 Sheets et al. (2012) conducted a retrospective population-based study using the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER)-Medicare linked database to determine the comparative morbidity and disease control of IMRT, proton therapy, and conformal radiation therapy for primary prostate cancer treatment. A total of 6666 men treated with IMRT, 6310 treated with conformal radiation therapy and 684 treated with PBT met inclusion criteria. Follow-ups occurred at months for IMRT (median 44 months), months for conformal (median 64 months), and months (median 46 months) for PBT. Survival was not examined because death by prostate cancer was expected to occur within five years of diagnosis and not different based on the type of radiation treatment. Using adjusted analysis, men treated with IMRT compared to conformal therapy were significantly less likely to receive a diagnosis of gastrointestinal morbidity (p<0.001), have a hip fracture (p=0.006), and need additional cancer therapy (p<0.001) but more likely to experience erectile dysfunction (p=0.006). There were no significant differences between PBT and IMRT in urinary incontinence, erectile dysfunction, hip fracture, morbidly or additional cancer therapies. PBT patients were more likely to have gastrointestinal side effects and undergo gastrointestinal procedures. The authors concluded that the potential advantage of PBT over IMRT is unclear and these results do not clearly demonstrate a clinical benefit to support the recent increase in PBT for prostate cancer. Additionally, limitations of this study include: the use of the SEER-Medicare data which includes claims files that do not provide detailed clinical information; potential bias in patient and physician reporting of morbidity and additional cancer therapies; and it is unknown if these results are generalizable with respect to choice of treatments, disease severity and rates of outcomes. 5 Coen et al. (2012) conducted a patient survey to assess long-term quality of life (QOL) outcome for men treated with conformal protons. QOL questionnaires were sent at specified intervals to 95 men who received proton radiation. Of these, 87 men reported 3- and/or 12-month outcomes, whereas 73 also reported long-term outcomes (minimum 2 years). Symptom scores were calculated at baseline, 3 months, 12 months, and long-term follow-up. Generalized estimating equation models were constructed to assess longitudinal outcomes while accounting for correlation among repeated measures in an individual patient. Men were stratified into functional groups from their baseline questionnaires (normal, intermediate, or poor function) for each symptom domain. Long-term QOL changes were assessed overall and within functional groups using the Wilcoxon signed-rank test. Statistically significant changes in all four symptom scores were observed in the longitudinal analysis. For the 73 men reporting long-term outcomes, there were significant change scores for incontinence (ID), bowel (BD) and sexual dysfunction (SD), but not obstructive/irritative voiding dysfunction (OID). When stratified by baseline functional category, only men with normal function had increased scores for ID and BD. For SD, there were significant changes in men with both normal and intermediate function, but not poor function. The authors concluded that patient reported outcomes are sensitive indicators of treatment-related morbidity. These results quantitate the long-term consequences of proton monotherapy for prostate cancer. Analysis by baseline functional category provides an individualized prediction of long-term QOL scores. High dose proton radiation was associated with small increases in bowel dysfunction and incontinence, with more pronounced changes in sexual dysfunction. 13 Coen et al. (2011) conducted a case-match analysis (n=282) of two separate clinical trials to compare the outcomes of high-dose radiotherapy (i.e., photon with a proton boost) to brachytherapy. Outcomes of patients Page 4 of 9
5 who were randomized to the high-dose radiotherapy arm in one study were compared to patients who were treated with brachytherapy in a case series. Patients had stage T1c, T2a or T2b cancer. At eight years follow-up, there were no significant differences in overall survival (p=0.45), freedom from distant metastasis (p=0.21) and biochemical failure (p=0.42). The time to PSA nadir was similar in both groups and the number of patients with PSA nadir 0.5 nanograms per milliliter (ng/ml) was significantly higher after brachytherapy (p=0.0003). A well-designed randomized controlled trial comparing these two modalities is needed to validate the results of this retrospective comparison. 6 Jabbari et al. (2010) compared the outcomes of 249 patients treated with permanent prostate implant brachytherapy (PPI) to a matched cohort of 124 patients treated with 3D-CRT and published results of 195 patients, matched cohort treated with high-dose radiotherapy (photon with a proton boost). PPI patients had stages T1-T3a disease, 3D-CRT patients had stages T1-T2a, and radiotherapy patients had stages T1-T2b. Overall, the PPI group had a biochemical no evidence of disease (bned) rate of 92% at five years and 86% at ten years. Patients treated with 3D-CRT had a 5-year bned rate of 78% compared to 94% of a matched PPI subset. There was a significant difference in the five-year median PSA nadir for patients treated with PPI vs. 3D-CRT (p<0001). The five-year bned rate following high-dose radiotherapy was 91% vs. 93% for a matched PPI subgroup. Also at five-years, a 0.5 ng/ml PSA nadir was reported in 91% of the PPI group vs. 59% in the high-dose radiotherapy group. The authors concluded that the results of this retrospective comparative study need to be validated in a well-designed randomized controlled trial comparing these modalities. 7 Mayahara et al. (2007) reported one centers experience with proton therapy to investigate the incidence and influencing factors of acute genitourinary (GU) and gastrointestinal morbidities in patients with prostate cancer. A total of 287 patients with histologically proven Stage ct1-t4n0m0 prostate cancer were treated with proton therapy between 2003 and Of these, 204 (71%) received neoadjuvant androgen suppression therapy. The patients were treated with MeV protons using lateral-opposed techniques to a dose of 74 GyE. Dosevolume histogram analyses were performed. The incidence of acute morbidity was evaluated using the National Cancer Institute Common Toxicity Criteria, version 2.0. Clinical factors, including age, clinical target volume, initial prostate-specific antigen level, T stage, presence of diabetes mellitus, and the use of androgen suppression therapy, were investigated to determine whether those affected the incidence of acute GU morbidity. None developed Grade 2 or higher acute gastrointestinal morbidity. In contrast, 111 (39%) and 4 (1%) patients experienced acute Grade 2 and Grade 3 GU morbidities, respectively. However, 87% of the patients were successfully relieved by the administration of a selective alpha-1 blocker. Multivariate analysis showed that a larger clinical target volume (p = 0.001) and the use of androgen suppression therapy (p = 0.017) were significant factors for the prediction of acute Grade 2-3 GU morbidity. The authors concluded that in our experience with proton therapy, a low incidence of acute gastrointestinal morbidity was observed. In contrast, the incidence of acute GU morbidity was similar to that in other reports of photon radiotherapy. Additional follow-up is warranted to elucidate the long-term safety and efficacy of proton therapy for prostate cancer. 14 Page 5 of 9
6 Hayes, Cochrane, UpToDate Hayes does not have a Directory report on the topic of proton beam therapy for prostate cancer. There is a 2013 Search & Summary report. 3 UpToDate has several reports on prostate cancer treatment and outlines that Proton Beam Therapy spares normal tissues better than IMRT in the low-to-mid dose range, although IMRT may offer a slight benefit in the high-dose range. To date, clinical studies have shown only limited improvement, if any, in toxicity profiles, although comparisons between nonrandomized series are inherently difficult. No randomized trials are currently underway and there are no randomized trials that compare proton beam therapy with photon beam therapy or brachytherapy in men with clinically localized prostate cancer. The most extensive data come from studies in which a combination of proton beam therapy and external beam RT was used. These studies have confirmed the value of high doses of RT. However, retrospective analyses have not established whether proton beam therapy (either alone or in combination with photon therapy) is either more effective or less toxic than photon therapy alone (especially IMRT) or brachytherapy. Professional Organizations American College of Radiology (ACR) appropriateness criteria (2010) for irradiation for T1 and T2 prostate cancer state that there are only limited data comparing proton beam therapy to other methods of irradiation or to radical prostatectomy for treating stage T1 and T2 prostate cancer. Further studies are needed to clearly define PBT s role for such treatment. ACR includes intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) and 3- dimensional computed tomography (3D CT) along with PBT as the recommended forms of external beam radiation therapy. 8 American College of Radiology (ACR) appropriateness criteria (2011) for external beam radiation therapy treatment planning for clinically localized prostate cancer rated proton beam therapy as a level seven therapy for the treatment of prostate cancer with IMRT being rated as a level eight. Regarding IMRT, ACR states that IMRT is most appropriate for patients treated with dose escalation. 15 American Society of Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) 2010 technology evaluation of PBT concluded that outcomes for patients treated with PBT were similar to those treated with intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT). Based on the clinical data, there was no clear benefit from PBT over IMRT including disease control or prevention of late toxicity. In addition, careful attention must be paid to the role of dosimetric issues, including correction for organ motion in this disease. ASTRO stated that further head to head clinical trials may be needed to determine the role of PBT in treating prostate cancer. 16 National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) 2013 guidelines for prostate cancer state that proton beam therapy is not recommended in the routine use for the treatment of prostate cancer. Clinical trials have not reported data that demonstrates superiority or equivalence of proton beam compared to conventional external beam for treatment of prostate cancer. 11 Page 6 of 9
7 American Urological Association (AUA) 2011 Guideline for the Management of Clinically Localized Prostate Cancer does not recommend proton beam therapy over other forms of radiation therapy. 21 CODING INFORMATION CPT Description Proton treatment delivery; simple, without compensation Proton treatment delivery; simple, with compensation Proton treatment delivery; intermediate Proton treatment delivery; complex HCPCS Description N/A ICD-9 Description 185 Malignant neoplasm of prostate Carcinoma in situ of prostate ICD-10 Description C61 Malignant neoplasm of prostate D70.5 Carcinoma in situ of prostate RESOURCE REFERENCES 1. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. 510(k) Premarket Notification Data base. Accessed at: 2. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS). Medicare National Coverage Database. Accessed at: 3. Hayes Search & Summary. Proton Beam Therapy for Prostate Cancer. Winifred Hayes Inc. Lansdale, PA. March 25, American College of Radiology (ACR) website. Proton therapy. May Accessed at: 5. Sheets NC, Goldin GH, Meyer AM, et al. Intensity-modulated radiation therapy, proton therapy, or conformal radiation therapy and morbidity and disease control in localized prostate cancer. JAMA Apr 18;307(15): Coen JJ, Zietman AL, Rossi CJ, Grocela JA, Efstathiou JA, Yan Y, Shipley WU. Comparison of High- Dose Proton Radiotherapy and Brachytherapy in Localized Prostate Cancer: A Case-Matched Analysis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys Apr 4. [Epub ahead of print] Page 7 of 9
8 7. Jabbari S, Weinberg VK, Shinohara K, Speight JL, et al. Equivalent biochemical control and improved prostate-specific antigen nadir after permanent prostate seed implant brachytherapy versus high-dose three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy and high-dose conformal proton beam radiotherapy boost. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys Jan 1;76(1): Moran BJ, DeRose P, Merrick G, Hsu IC, et al. Expert Panel on Radiation Oncology-Prostate. ACR Appropriateness Criteria definitive external beam irradiation in stage T1 and T2 prostate cancer. [online publication]. Reston (VA): American College of Radiology (ACR); p. Accessed at: 9. Ohri N. Dicker AP. Showalter TN. Late toxicity rates following definitive radiotherapy for prostate cancer. Canadian Journal of Urology. 19(4): , 2012 Aug. 10. Allen AM, Pawlicki T, Dong L, Fourkal E, Buyyounouski M, et al. An evidence based review of proton beam therapy: the report of ASTRO's emerging technology committee. Radiother Oncol Apr;103(1):8-11. doi: /j.radonc Epub 2012 Mar National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN ). NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. Prostate cancer. V Accessed at: Yu JB, Soulos PR, Herrin J, et al. Proton versus intensity-modulated radiotherapy for prostate cancer: patterns of care and early toxicity. J Natl Cancer Inst Jan 2;105(1): doi: /jnci/djs463. Epub 2012 Dec Coen JJ, Paly JJ, Niemierko A, et al. Long-term quality of life outcome after proton beam monotherapy for localized prostate cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys Feb 1;82(2):e doi: /j.ijrobp Epub 2011 May Mayahara H, Murakami M, Kagawa K, et al. Acute morbidity of proton therapy for prostate cancer: the Hyogo Ion Beam Medical Center experience. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys Oct 1;69(2): Epub 2007 May Abdel-Wahab M, Mahmoud O, Merrick G, Hsu IC, et al. Expert Panel on Radiation Oncology-Prostate. ACR Appropriateness Criteria external beam radiation therapy treatment planning for clinically localized prostate cancer. [online publication]. Reston (VA): American College of Radiology (ACR); p. Accessed at: American Society of Radiation Oncology (ASTRO). Emerging technology. Proton beam radiation therapy Accessed at: UpToDate: [website]: Ward J, Volgelzang N, Davis B. Initial management of regionally localized intermediate and high-risk prostate cancer. August, UpToDate: [website]: Klein R. Initial approach to low-risk clinically localized prostate cancer. August, UpToDate: [website]: Meyer J, Lee A, DelaneyT. Proton and ion beams in cancer therapy. August UpToDate: [website]: Dibiase S, Roach M. External beam radiation therapy for localized prostate cancer. August, American Urological Association (AUA) Guideline for the Management of Clinically Localized Prostate Cancer reaffirmed Accessed at: Page 8 of 9
9 22. National Institutes of Health. Clinical Trials.gov. Accessed at: Advanced Medical Review (AMR): Policy reviewed by a practicing MD Board certified in Urology. September 22, Page 9 of 9
Implementation Date: April 2015 Clinical Operations
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guideline PROSTATE CANCER Original Date: March 2011 Page 1 of 5 Radiation Oncology Last Review Date: March 2015 Guideline Number: NIA_CG_124 Last Revised Date:
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guideline PROSTATE CANCER Original Date: March 2011 Page 1 of 5 Radiation Oncology Last Review Date: March 2015 Guideline Number: NIA_CG_124 Last Revised Date:
The Science behind Proton Beam Therapy
 The Science behind Proton Beam Therapy Anthony Zietman MD Shipley Professor of Radiation Oncology Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Principles underlying Radiotherapy Radiation related
The Science behind Proton Beam Therapy Anthony Zietman MD Shipley Professor of Radiation Oncology Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Principles underlying Radiotherapy Radiation related
PROTON BEAM THERAPY FOR PROSTATE CANCER. A Technology Assessment
 PROTON BEAM THERAPY FOR PROSTATE CANCER A Technology Assessment INTRODUCTION The California Technology Assessment Forum is requested to review the scientific evidence for the use of proton therapy for
PROTON BEAM THERAPY FOR PROSTATE CANCER A Technology Assessment INTRODUCTION The California Technology Assessment Forum is requested to review the scientific evidence for the use of proton therapy for
Protons vs. CyberKnife. Protons vs. CyberKnife. Page 1 UC SF. What are. Alexander R. Gottschalk, M.D., Ph.D.
 Protons vs. CyberKnife UC SF Protons vs. CyberKnife UC SF Alexander R. Gottschalk, M.D., Ph.D. Associate Professor and Director of the CyberKnife Radiosurgery Program Department of Radiation Oncology University
Protons vs. CyberKnife UC SF Protons vs. CyberKnife UC SF Alexander R. Gottschalk, M.D., Ph.D. Associate Professor and Director of the CyberKnife Radiosurgery Program Department of Radiation Oncology University
IEHP UM Subcommittee Approved Authorization Guidelines Proton Beam Radiation therapy for Prostate Cancer
 Proton Beam Radiation therapy for Prostate Cancer Policy: The use of Proton Beam Therapy (PBT) in Prostate cancer has not been established as more effective than other forms of External Beam Radiation
Proton Beam Radiation therapy for Prostate Cancer Policy: The use of Proton Beam Therapy (PBT) in Prostate cancer has not been established as more effective than other forms of External Beam Radiation
How To Know If You Should Get A Brachytherapy Or Radioactive Seed Implantation
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: BRACHYTHERAPY OR PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical policy
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: BRACHYTHERAPY OR PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical policy
7. Prostate cancer in PSA relapse
 7. Prostate cancer in PSA relapse A patient with prostate cancer in PSA relapse is one who, having received a primary treatment with intent to cure, has a raised PSA (prostate-specific antigen) level defined
7. Prostate cancer in PSA relapse A patient with prostate cancer in PSA relapse is one who, having received a primary treatment with intent to cure, has a raised PSA (prostate-specific antigen) level defined
Corporate Medical Policy Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) of the Prostate
 Corporate Medical Policy Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) of the Prostate File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: intensity_modulated_radiation_therapy_imrt_of_the_prostate
Corporate Medical Policy Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) of the Prostate File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: intensity_modulated_radiation_therapy_imrt_of_the_prostate
PROTON THERAPY FOR PROSTATE CANCER: THE INITIAL LOMA LINDA UNIVERSITY EXPERIENCE
 doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2003.10.011 Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys., Vol. 59, No. 2, pp. 348 352, 2004 Copyright 2004 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0360-3016/04/$ see front
doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2003.10.011 Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys., Vol. 59, No. 2, pp. 348 352, 2004 Copyright 2004 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0360-3016/04/$ see front
CYBERKNIFE RADIOSURGERY FOR EARLY PROSTATE CANCER Rationale and Results. Alan Katz MD JD Flushing, NY USA
 CYBERKNIFE RADIOSURGERY FOR EARLY PROSTATE CANCER Rationale and Results Alan Katz MD JD Flushing, NY USA Prostate Ablative Therapy Over the last 10 years our therapy has improved bned rates for LDR/HDR
CYBERKNIFE RADIOSURGERY FOR EARLY PROSTATE CANCER Rationale and Results Alan Katz MD JD Flushing, NY USA Prostate Ablative Therapy Over the last 10 years our therapy has improved bned rates for LDR/HDR
Medical Policy Brachytherapy for Clinically Localized Prostate Cancer Using Permanently Implanted Seeds
 Medical Policy Brachytherapy for Clinically Localized Prostate Cancer Using Permanently Implanted Seeds Table of Contents Policy: Commercial Coding Information Information Pertaining to All Policies Policy:
Medical Policy Brachytherapy for Clinically Localized Prostate Cancer Using Permanently Implanted Seeds Table of Contents Policy: Commercial Coding Information Information Pertaining to All Policies Policy:
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer: Treatment options and future directions
 Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer: Treatment options and future directions David Weksberg, M.D., Ph.D. PinnacleHealth Cancer Institute September 12, 2015 Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer: Treatment
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer: Treatment options and future directions David Weksberg, M.D., Ph.D. PinnacleHealth Cancer Institute September 12, 2015 Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer: Treatment
Andre Konski, MD, MBA, MA, FACR Professor & Chair Department of Radiation Oncology Wayne State University School of Medicine Barbara Ann Karmanos
 Andre Konski, MD, MBA, MA, FACR Professor & Chair Department of Radiation Oncology Wayne State University School of Medicine Barbara Ann Karmanos Cancer Center Financial None The views that I will be going
Andre Konski, MD, MBA, MA, FACR Professor & Chair Department of Radiation Oncology Wayne State University School of Medicine Barbara Ann Karmanos Cancer Center Financial None The views that I will be going
MEDICARE. Higher Use of Costly Prostate Cancer Treatment by Providers Who Self- Refer Warrants Scrutiny. Report to Congressional Requesters
 United States Government Accountability Office Report to Congressional Requesters July 2013 MEDICARE Higher Use of Costly Prostate Cancer Treatment by Providers Who Self- Refer Warrants Scrutiny GAO-13-525
United States Government Accountability Office Report to Congressional Requesters July 2013 MEDICARE Higher Use of Costly Prostate Cancer Treatment by Providers Who Self- Refer Warrants Scrutiny GAO-13-525
Historical Basis for Concern
 Androgens After : Are We Ready? Mohit Khera, MD, MBA Assistant Professor of Urology Division of Male Reproductive Medicine and Surgery Scott Department of Urology Baylor College of Medicine Historical
Androgens After : Are We Ready? Mohit Khera, MD, MBA Assistant Professor of Urology Division of Male Reproductive Medicine and Surgery Scott Department of Urology Baylor College of Medicine Historical
Proton Therapy for Prostate Cancer
 BRADFORD HOPPE, MD, MPH 1 RANDAL HENDERSON, MD, MBA 1 WILLIAM M. MENDENHALL, MD 1 ROMAINE C. NICHOLS, MD 1 ZUOFENG LI, PhD 1 NANCY P. MENDENHALL, MD 1 Proton Therapy for Prostate Cancer Abstract: Proton
BRADFORD HOPPE, MD, MPH 1 RANDAL HENDERSON, MD, MBA 1 WILLIAM M. MENDENHALL, MD 1 ROMAINE C. NICHOLS, MD 1 ZUOFENG LI, PhD 1 NANCY P. MENDENHALL, MD 1 Proton Therapy for Prostate Cancer Abstract: Proton
Current and Future Trends in Proton Treatment of Prostate Cancer
 Current and Future Trends in Proton Treatment of Prostate Cancer Reinhard W. Schulte Assistant Professor Department of Radiation Medicine Loma Linda University Medical Center Loma Linda, CA, USA Outline
Current and Future Trends in Proton Treatment of Prostate Cancer Reinhard W. Schulte Assistant Professor Department of Radiation Medicine Loma Linda University Medical Center Loma Linda, CA, USA Outline
Prostate Cancer Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Treatment Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam,
Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Treatment Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam,
FAQ About Prostate Cancer Treatment and SpaceOAR System
 FAQ About Prostate Cancer Treatment and SpaceOAR System P. 4 Prostate Cancer Background SpaceOAR Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) 1. What is prostate cancer? The vast majority of prostate cancers develop
FAQ About Prostate Cancer Treatment and SpaceOAR System P. 4 Prostate Cancer Background SpaceOAR Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) 1. What is prostate cancer? The vast majority of prostate cancers develop
Cyberknife Information Guide. Prostate Cancer Treatment
 Cyberknife Information Guide Prostate Cancer Treatment CYBERKNIFE INFORMATION GUIDE PROSTATE CANCER TREATMENT As a patient recently diagnosed with localized prostate cancer, it is important that you familiarize
Cyberknife Information Guide Prostate Cancer Treatment CYBERKNIFE INFORMATION GUIDE PROSTATE CANCER TREATMENT As a patient recently diagnosed with localized prostate cancer, it is important that you familiarize
Proton Therapy for Prostate Cancer
 Proton Therapy for Prostate Cancer Andrew K. Lee, MD, MPH Director, Proton Therapy Center Associate Professor Department of Radiation Oncology M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Randomized studies showing benefit
Proton Therapy for Prostate Cancer Andrew K. Lee, MD, MPH Director, Proton Therapy Center Associate Professor Department of Radiation Oncology M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Randomized studies showing benefit
1 of 6 6/13/11 12:40 PM
 ONCOLOGY. Vol. 25 No. 7 REVIEW ARTICLE Proton Therapy for Prostate Cancer By Bradford Hoppe, MD, MPH 1, Randal Henderson, MD, MBA 1, William M. Mendenhall, MD 1, Romaine C. Nichols, MD 1, Zuofeng Li, PhD
ONCOLOGY. Vol. 25 No. 7 REVIEW ARTICLE Proton Therapy for Prostate Cancer By Bradford Hoppe, MD, MPH 1, Randal Henderson, MD, MBA 1, William M. Mendenhall, MD 1, Romaine C. Nichols, MD 1, Zuofeng Li, PhD
Current Status and Future Direction of Proton Beam Therapy
 Current Status and Future Direction of Proton Beam Therapy National Cancer Center Hospital East Division of Radiation Oncology and Particle Therapy Tetsuo Akimoto Comparison of status of particle therapy
Current Status and Future Direction of Proton Beam Therapy National Cancer Center Hospital East Division of Radiation Oncology and Particle Therapy Tetsuo Akimoto Comparison of status of particle therapy
Local Coverage Determination (LCD): MolDX: Genomic Health Oncotype DX Prostate Cancer Assay (L36153)
 Local Coverage Determination (LCD): MolDX: Genomic Health Oncotype DX Prostate Cancer Assay (L36153) Contractor Information Contractor Name Palmetto GBA LCD Information Document Information LCD ID L36153
Local Coverage Determination (LCD): MolDX: Genomic Health Oncotype DX Prostate Cancer Assay (L36153) Contractor Information Contractor Name Palmetto GBA LCD Information Document Information LCD ID L36153
Jurisdiction Virginia
 PROPOSED/DRAFT Local Coverage Determination (LCD): MolDX: Prolaris Prostate Cancer Genomic Assay (DL35629) Please note: This is a Proposed/Draft policy. Proposed/Draft LCDs are works in progress that are
PROPOSED/DRAFT Local Coverage Determination (LCD): MolDX: Prolaris Prostate Cancer Genomic Assay (DL35629) Please note: This is a Proposed/Draft policy. Proposed/Draft LCDs are works in progress that are
Technology Assessment
 Technology Assessment Technology Assessment Program Comparative evaluation of radiation treatments for clinically localized prostate cancer: an update Prepared for: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality
Technology Assessment Technology Assessment Program Comparative evaluation of radiation treatments for clinically localized prostate cancer: an update Prepared for: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality
Use of Androgen Deprivation Therapy (ADT) in Localized Prostate Cancer
 Use of Androgen Deprivation Therapy (ADT) in Localized Prostate Cancer Adam R. Kuykendal, MD; Laura H. Hendrix, MS; Ramzi G. Salloum, PhD; Paul A. Godley, MD, PhD; Ronald C. Chen, MD, MPH No conflicts
Use of Androgen Deprivation Therapy (ADT) in Localized Prostate Cancer Adam R. Kuykendal, MD; Laura H. Hendrix, MS; Ramzi G. Salloum, PhD; Paul A. Godley, MD, PhD; Ronald C. Chen, MD, MPH No conflicts
These rare variants often act aggressively and may respond differently to therapy than the more common prostate adenocarcinoma.
 Prostate Cancer OVERVIEW Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer diagnosed among American men, accounting for nearly 200,000 new cancer cases in the United States each year. Greater than 65% of
Prostate Cancer OVERVIEW Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer diagnosed among American men, accounting for nearly 200,000 new cancer cases in the United States each year. Greater than 65% of
Prostatectomy, pelvic lymphadenect. Med age 63 years Mean followup 53 months No other cancer related therapy before recurrence. Negative.
 Adjuvante und Salvage Radiotherapie Ludwig Plasswilm Klinik für Radio-Onkologie, KSSG CANCER CONTROL WITH RADICAL PROSTATECTOMY ALONE IN 1,000 CONSECUTIVE PATIENTS 1983 1998 Clinical stage T1 and T2 Mean
Adjuvante und Salvage Radiotherapie Ludwig Plasswilm Klinik für Radio-Onkologie, KSSG CANCER CONTROL WITH RADICAL PROSTATECTOMY ALONE IN 1,000 CONSECUTIVE PATIENTS 1983 1998 Clinical stage T1 and T2 Mean
Prostate Cancer. What is prostate cancer?
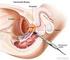 Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam, prostate-specific
Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam, prostate-specific
Clinical Trials and Radiation Treatment. Gerard Morton Odette Cancer Centre Sunnybrook Research Institute University of Toronto
 Clinical Trials and Radiation Treatment Gerard Morton Odette Cancer Centre Sunnybrook Research Institute University of Toronto What I will cover.. A little about radiation treatment The clinical trials
Clinical Trials and Radiation Treatment Gerard Morton Odette Cancer Centre Sunnybrook Research Institute University of Toronto What I will cover.. A little about radiation treatment The clinical trials
LATE MORBIDITY PROFILES IN PROSTATE CANCER PATIENTS TREATED TO 79 84 GY BY A SIMPLE FOUR-FIELD COPLANAR BEAM ARRANGEMENT
 PII S0360-3016(02)03822-1 Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys., Vol. 55, No. 1, pp. 71 77, 2003 Copyright 2003 Elsevier Science Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0360-3016/03/$ see front matter
PII S0360-3016(02)03822-1 Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys., Vol. 55, No. 1, pp. 71 77, 2003 Copyright 2003 Elsevier Science Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0360-3016/03/$ see front matter
TITLE: Comparison of the dosimetric planning of partial breast irradiation with and without the aid of 3D virtual reality simulation (VRS) software.
 SAMPLE CLINICAL RESEARCH APPLICATION ABSTRACT: TITLE: Comparison of the dosimetric planning of partial breast irradiation with and without the aid of 3D virtual reality simulation (VRS) software. Hypothesis:
SAMPLE CLINICAL RESEARCH APPLICATION ABSTRACT: TITLE: Comparison of the dosimetric planning of partial breast irradiation with and without the aid of 3D virtual reality simulation (VRS) software. Hypothesis:
American Urological Association (AUA) Guideline
 1 (AUA) Guideline Approved by the AUA Board of Directors April 2013 Authors disclosure of potential conflicts of interest and author/staff contributions appear at the end of the article. 2013 by the American
1 (AUA) Guideline Approved by the AUA Board of Directors April 2013 Authors disclosure of potential conflicts of interest and author/staff contributions appear at the end of the article. 2013 by the American
Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy Leads to Survival Benefit Only in Patients with High-Risk Prostate Cancer: a Population-Based Study
 Annals of Oncology Advance Access published February 22, 2014 1 Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy Leads to Survival Benefit Only in Patients with High-Risk Prostate Cancer: a Population-Based Study
Annals of Oncology Advance Access published February 22, 2014 1 Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy Leads to Survival Benefit Only in Patients with High-Risk Prostate Cancer: a Population-Based Study
Analysis of Prostate Cancer at Easter Connecticut Health Network Using Cancer Registry Data
 The 2014 Cancer Program Annual Public Reporting of Outcomes/Annual Site Analysis Statistical Data from 2013 More than 70 percent of all newly diagnosed cancer patients are treated in the more than 1,500
The 2014 Cancer Program Annual Public Reporting of Outcomes/Annual Site Analysis Statistical Data from 2013 More than 70 percent of all newly diagnosed cancer patients are treated in the more than 1,500
Michael J. Zelefsky,*, Heather Chan, Margie Hunt, Yoshiya Yamada, Alison M. Shippy and Howard Amols
 Long-Term Outcome of High Dose Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy for Patients With Clinically Localized Prostate Cancer Michael J. Zelefsky,*, Heather Chan, Margie Hunt, Yoshiya Yamada, Alison M. Shippy
Long-Term Outcome of High Dose Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy for Patients With Clinically Localized Prostate Cancer Michael J. Zelefsky,*, Heather Chan, Margie Hunt, Yoshiya Yamada, Alison M. Shippy
Detection and staging of recurrent prostate cancer is still one of the important clinical problems in prostate cancer. A rise in PSA or biochemical
 Summary. 111 Detection and staging of recurrent prostate cancer is still one of the important clinical problems in prostate cancer. A rise in PSA or biochemical recurrence (BCR) is the first sign of recurrent
Summary. 111 Detection and staging of recurrent prostate cancer is still one of the important clinical problems in prostate cancer. A rise in PSA or biochemical recurrence (BCR) is the first sign of recurrent
PRIOR AUTHORIZATION Prior authorization is recommended and obtained via the online tool for participating providers.
 Medical Coverage Policy Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy of the Prostate EFFECTIVE DATE: 02 15 2016 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 03 23 2016 OVERVIEW Radiotherapy (RT) is an integral component in the treatment
Medical Coverage Policy Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy of the Prostate EFFECTIVE DATE: 02 15 2016 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 03 23 2016 OVERVIEW Radiotherapy (RT) is an integral component in the treatment
[Insuree] Page 1 Letter of Appeal
![[Insuree] Page 1 Letter of Appeal [Insuree] Page 1 Letter of Appeal](/thumbs/24/3356957.jpg) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - From: [Insuree]- - - 8/16/09 Board of Trustees - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - From: [Insuree]- - - 8/16/09 Board of Trustees - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Cancer in Primary Care: Prostate Cancer Screening. How and How often? Should we and in which patients?
 Cancer in Primary Care: Prostate Cancer Screening How and How often? Should we and in which patients? PLCO trial (Prostate, Lung, Colorectal and Ovarian) Results In the screening group, rates of compliance
Cancer in Primary Care: Prostate Cancer Screening How and How often? Should we and in which patients? PLCO trial (Prostate, Lung, Colorectal and Ovarian) Results In the screening group, rates of compliance
Proton Therapy: Cutting Edge Treatment for Cancerous Tumors. By: Cherilyn G. Murer, JD, CRA
 Proton Therapy: Cutting Edge Treatment for Cancerous Tumors By: Cherilyn G. Murer, JD, CRA Introduction Put simply, proton therapy is a new cutting edge cancer treatment that promises better outcomes for
Proton Therapy: Cutting Edge Treatment for Cancerous Tumors By: Cherilyn G. Murer, JD, CRA Introduction Put simply, proton therapy is a new cutting edge cancer treatment that promises better outcomes for
PSA Screening for Prostate Cancer Information for Care Providers
 All men should know they are having a PSA test and be informed of the implications prior to testing. This booklet was created to help primary care providers offer men information about the risks and benefits
All men should know they are having a PSA test and be informed of the implications prior to testing. This booklet was created to help primary care providers offer men information about the risks and benefits
PCa Commentary. Volume 73 January-February 2012 PSA AND TREATMENT DECISIONS:
 1101 Madison Street Suite 1101 Seattle, WA 98104 P 206-215-2480 www.seattleprostate.com PCa Commentary Volume 73 January-February 2012 CONTENTS PSA SCREENING & BASIC SCIENCE PSA AND TREATMENT 1 DECISIONS
1101 Madison Street Suite 1101 Seattle, WA 98104 P 206-215-2480 www.seattleprostate.com PCa Commentary Volume 73 January-February 2012 CONTENTS PSA SCREENING & BASIC SCIENCE PSA AND TREATMENT 1 DECISIONS
馬 偕 紀 念 醫 院 新 竹 分 院 前 列 腺 癌 放 射 治 療 指 引
 馬 偕 紀 念 醫 院 新 竹 分 院 前 列 腺 癌 放 射 治 療 指 引 2009.12.02 修 訂 2013.05.13 四 版 前 言 新 竹 馬 偕 醫 院 放 射 腫 瘤 科 藉 由 跨 院 聯 合 會 議 機 制 進 行 討 論, 以 制 定 符 合 現 狀 之 前 列 腺 癌 放 射 治 療 指 引 本 院 前 列 腺 癌 放 射 治 療 指 引 的 建 立, 係 參 考 國 內
馬 偕 紀 念 醫 院 新 竹 分 院 前 列 腺 癌 放 射 治 療 指 引 2009.12.02 修 訂 2013.05.13 四 版 前 言 新 竹 馬 偕 醫 院 放 射 腫 瘤 科 藉 由 跨 院 聯 合 會 議 機 制 進 行 討 論, 以 制 定 符 合 現 狀 之 前 列 腺 癌 放 射 治 療 指 引 本 院 前 列 腺 癌 放 射 治 療 指 引 的 建 立, 係 參 考 國 內
Prostate Cancer Treatment: What s Best for You?
 Prostate Cancer Treatment: What s Best for You? Prostate Cancer: Radiation Therapy Approaches I. Choices There is really a variety of options in prostate cancer management overall and in radiation therapy.
Prostate Cancer Treatment: What s Best for You? Prostate Cancer: Radiation Therapy Approaches I. Choices There is really a variety of options in prostate cancer management overall and in radiation therapy.
Effective for dates of service on or after May 1, 2015 refer to: Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Alabama Radiation Therapy Management RTM Policies
 Effective for dates of service on or after May 1, 2015 refer to: Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Alabama Radiation Therapy Management RTM Policies Name of Policy: Brachytherapy for Clinically Localized Prostate
Effective for dates of service on or after May 1, 2015 refer to: Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Alabama Radiation Therapy Management RTM Policies Name of Policy: Brachytherapy for Clinically Localized Prostate
NATURAL HISTORY OF CLINICALLY STAGED LOW- AND INTERMEDIATE-RISK PROSTATE CANCER TREATED WITH MONOTHERAPEUTIC PERMANENT INTERSTITIAL BRACHYTHERAPY
 doi:1.116/j.ijrobp.9..1 Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys., Vol. 76, No., pp. 349 354, 1 Copyright Ó 1 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 36-316/1/$ see front matter CLINICAL INVESTIGATION
doi:1.116/j.ijrobp.9..1 Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys., Vol. 76, No., pp. 349 354, 1 Copyright Ó 1 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 36-316/1/$ see front matter CLINICAL INVESTIGATION
CMScript. Member of a medical scheme? Know your guaranteed benefits! Issue 7 of 2014
 Background CMScript Member of a medical scheme? Know your guaranteed benefits! Issue 7 of 2014 Prostate cancer is second only to lung cancer as the leading cause of cancer-related deaths in men. It is
Background CMScript Member of a medical scheme? Know your guaranteed benefits! Issue 7 of 2014 Prostate cancer is second only to lung cancer as the leading cause of cancer-related deaths in men. It is
Table of Contents. Data Supplement 1: Summary of ASTRO Guideline Statements. Data Supplement 2: Definition of Terms
 Definitive and Adjuvant Radiotherapy in Locally Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline Endorsement of the American Society for Radiation
Definitive and Adjuvant Radiotherapy in Locally Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline Endorsement of the American Society for Radiation
Gleason Score. Oncotype DX GPS. identified for. about surveillance. time to get sophisticated
 patient: MARK SMITH PSA 6.2 Gleason Score 6 Oncotype DX GPS 8 identified for active surveillance time to get sophisticated about surveillance Accurate prediction of prostate cancer risk is needed at the
patient: MARK SMITH PSA 6.2 Gleason Score 6 Oncotype DX GPS 8 identified for active surveillance time to get sophisticated about surveillance Accurate prediction of prostate cancer risk is needed at the
LONG-TERM URINARY TOXICITY AFTER 3-DIMENSIONAL CONFORMAL RADIOTHERAPY FOR PROSTATE CANCER IN PATIENTS WITH PRIOR HISTORY OF TRANSURETHRAL RESECTION
 PII S0360-3016(00)00714-8 Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys., Vol. 48, No. 3, pp. 643 647, 2000 Copyright 2000 Elsevier Science Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0360-3016/00/$ see front
PII S0360-3016(00)00714-8 Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys., Vol. 48, No. 3, pp. 643 647, 2000 Copyright 2000 Elsevier Science Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0360-3016/00/$ see front
IBA Proton Therapy. Biomed days 2015. Vincent Bossier. System Architect Vincent.bossier@iba-group.com. Protect, Enhance and Save Lives
 Vincent Bossier System Architect Vincent.bossier@iba-group.com IBA Proton Therapy Biomed days 2015 Protect, Enhance and Save Lives 1 Agenda AN INTRODUCTION TO IBA WHY PROTON THERAPY CLINICAL WORKFLOW TREATMENT
Vincent Bossier System Architect Vincent.bossier@iba-group.com IBA Proton Therapy Biomed days 2015 Protect, Enhance and Save Lives 1 Agenda AN INTRODUCTION TO IBA WHY PROTON THERAPY CLINICAL WORKFLOW TREATMENT
Understanding the. Controversies of. testosterone replacement. therapy in hypogonadal men with prostate cancer. controversies surrounding
 Controversies of testosterone replacement therapy in hypogonadal men with prostate cancer Samuel Deem, DO CULTURA CREATIVE (RF) / ALAMY Understanding the controversies surrounding testosterone replacement
Controversies of testosterone replacement therapy in hypogonadal men with prostate cancer Samuel Deem, DO CULTURA CREATIVE (RF) / ALAMY Understanding the controversies surrounding testosterone replacement
A new score predicting the survival of patients with spinal cord compression from myeloma
 A new score predicting the survival of patients with spinal cord compression from myeloma (1) Sarah Douglas, Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Lubeck, Germany; sarah_douglas@gmx.de (2) Steven
A new score predicting the survival of patients with spinal cord compression from myeloma (1) Sarah Douglas, Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Lubeck, Germany; sarah_douglas@gmx.de (2) Steven
Cancer research in the Midland Region the prostate and bowel cancer projects
 Cancer research in the Midland Region the prostate and bowel cancer projects Ross Lawrenson Waikato Clinical School University of Auckland MoH/HRC Cancer Research agenda Lung cancer Palliative care Prostate
Cancer research in the Midland Region the prostate and bowel cancer projects Ross Lawrenson Waikato Clinical School University of Auckland MoH/HRC Cancer Research agenda Lung cancer Palliative care Prostate
Brachytherapy for prostate cancer
 Brachytherapy for prostate cancer Findings by SBU Alert Published Jun 7, 2000 Version 1 Brachytherapy is not widely used in Sweden to treat localized prostate cancer. This treatment method has been available
Brachytherapy for prostate cancer Findings by SBU Alert Published Jun 7, 2000 Version 1 Brachytherapy is not widely used in Sweden to treat localized prostate cancer. This treatment method has been available
Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT)
 Scan for mobile link. Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) Intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) uses linear accelerators to safely and painlessly deliver precise radiation doses to a tumor while
Scan for mobile link. Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) Intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) uses linear accelerators to safely and painlessly deliver precise radiation doses to a tumor while
Proton Therapy for Prostate Cancer: Your Questions, Our Answers.
 Proton Therapy for Prostate Cancer: Your Questions, Our Answers. When you re looking for the right treatment for your prostate cancer, nothing s more important than accurate information. Read on, and learn
Proton Therapy for Prostate Cancer: Your Questions, Our Answers. When you re looking for the right treatment for your prostate cancer, nothing s more important than accurate information. Read on, and learn
4/8/13. Pre-test Audience Response. Prostate Cancer 2012. Screening and Treatment of Prostate Cancer: The 2013 Perspective
 Pre-test Audience Response Screening and Treatment of Prostate Cancer: The 2013 Perspective 1. I do not offer routine PSA screening, and the USPSTF D recommendation will not change my practice. 2. In light
Pre-test Audience Response Screening and Treatment of Prostate Cancer: The 2013 Perspective 1. I do not offer routine PSA screening, and the USPSTF D recommendation will not change my practice. 2. In light
Saturation Biopsy for Diagnosis and Staging of Prostate Cancer. Original Policy Date
 MP 7.01.101 Saturation Biopsy for Diagnosis and Staging of Prostate Cancer Medical Policy Section Surgery Issue 12/2013 Original Policy Date 12/2013 Last Review Status/Date /12/2013 Return to Medical Policy
MP 7.01.101 Saturation Biopsy for Diagnosis and Staging of Prostate Cancer Medical Policy Section Surgery Issue 12/2013 Original Policy Date 12/2013 Last Review Status/Date /12/2013 Return to Medical Policy
Conventional treatment modalities do not provide adequate local tumor control,
 Medical Policy Manual Topic: Charged-Particle (Proton or Helium Ion) Radiation Therapy Date of Origin: April 1998 Section: Medicine Last Reviewed Date: June 2015 Policy No: 49 Effective Date: August 1,
Medical Policy Manual Topic: Charged-Particle (Proton or Helium Ion) Radiation Therapy Date of Origin: April 1998 Section: Medicine Last Reviewed Date: June 2015 Policy No: 49 Effective Date: August 1,
American College of Radiology ACR Appropriateness Criteria DEFINITIVE EXTERNAL-BEAM IRRADIATION IN STAGE T1 AND T2 PROSTATE CANCER
 American College of Radiology ACR Appropriateness Criteria Date of origin: 1996 Last review date: 2013 DEFINITIVE EXTERNAL-BEAM IRRADIATION IN STAGE T1 AND T2 PROSTATE CANCER Expert Panel on Radiation
American College of Radiology ACR Appropriateness Criteria Date of origin: 1996 Last review date: 2013 DEFINITIVE EXTERNAL-BEAM IRRADIATION IN STAGE T1 AND T2 PROSTATE CANCER Expert Panel on Radiation
National And Institutional Outcomes In Prostate Cancer Radiotherapy
 Yale University EliScholar A Digital Platform for Scholarly Publishing at Yale Yale Medicine Thesis Digital Library School of Medicine January 2011 National And Institutional Outcomes In Prostate Cancer
Yale University EliScholar A Digital Platform for Scholarly Publishing at Yale Yale Medicine Thesis Digital Library School of Medicine January 2011 National And Institutional Outcomes In Prostate Cancer
Role of Radiation after Radical Prostatectomy Review of Literature
 Vol. 9, No: 1 Jan - Jun 2013. Page 1-44 Role of Radiation after Radical Prostatectomy Review of Literature S.K. Raghunath, N. Srivatsa Abstract Biochemical relapse after radical prostatectomy occurs in
Vol. 9, No: 1 Jan - Jun 2013. Page 1-44 Role of Radiation after Radical Prostatectomy Review of Literature S.K. Raghunath, N. Srivatsa Abstract Biochemical relapse after radical prostatectomy occurs in
intensity_modulated_radiation_therapy_imrt_of_abdomen_and_pelvis 11/2009 5/2016 5/2017 5/2016
 Corporate Medical Policy Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) of Abdomen File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: intensity_modulated_radiation_therapy_imrt_of_abdomen_and_pelvis
Corporate Medical Policy Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) of Abdomen File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: intensity_modulated_radiation_therapy_imrt_of_abdomen_and_pelvis
FIVE-YEAR BIOCHEMICAL OUTCOME FOLLOWING PERMANENT INTERSTITIAL BRACHYTHERAPY FOR CLINICAL T1 T3 PROSTATE CANCER
 PII S0360-3016(01)01594-2 Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys., Vol. 51, No. 1, pp. 41 48, 2001 Copyright 2001 Elsevier Science Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0360-3016/01/$ see front matter
PII S0360-3016(01)01594-2 Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys., Vol. 51, No. 1, pp. 41 48, 2001 Copyright 2001 Elsevier Science Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0360-3016/01/$ see front matter
Proton Therapy. What is proton therapy and how is it used?
 Scan for mobile link. Proton Therapy Proton therapy delivers radiation to tumor tissue in a much more confined way than conventional photon therapy thus allowing the radiation oncologist to use a greater
Scan for mobile link. Proton Therapy Proton therapy delivers radiation to tumor tissue in a much more confined way than conventional photon therapy thus allowing the radiation oncologist to use a greater
ONLINE CONTINUING EDUCATION ACTIVITY
 ONLINE CONTINUING EDUCATION ACTIVITY Take free quizzes online at acsjournals.com/ce ARTICLE TITLE: Progress and Controversies: Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION ACCREDITATION
ONLINE CONTINUING EDUCATION ACTIVITY Take free quizzes online at acsjournals.com/ce ARTICLE TITLE: Progress and Controversies: Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION ACCREDITATION
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: PROSTATE CANCER SCREENING, DETECTION AND MONITORING
 MEDICAL POLICY PAGE: 1 OF: 8 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical policy criteria are not applied.
MEDICAL POLICY PAGE: 1 OF: 8 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical policy criteria are not applied.
BRACHYTHERAPY OR CONFORMAL EXTERNAL RADIOTHERAPY FOR PROSTATE CANCER: A SINGLE-INSTITUTION MATCHED-PAIR ANALYSIS
 doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.01.081 Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys., Vol. 76, No. 1, pp. 43 49, 2010 Copyright Ó 2010 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0360-3016/10/$ see front
doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.01.081 Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys., Vol. 76, No. 1, pp. 43 49, 2010 Copyright Ó 2010 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0360-3016/10/$ see front
Radiotherapy in Hungary: present status and future needs. Tibor Major, PhD National Institute of Oncology Radiotherapy Department Budapest, Hungary
 Radiotherapy in Hungary: present status and future needs Tibor Major, PhD National Institute of Oncology Radiotherapy Department Budapest, Hungary Academia Europaea Section Workshops, Bergen, 10 September,
Radiotherapy in Hungary: present status and future needs Tibor Major, PhD National Institute of Oncology Radiotherapy Department Budapest, Hungary Academia Europaea Section Workshops, Bergen, 10 September,
Radiation Therapy in Prostate Cancer Current Status and New Advances
 Radiation Therapy in Prostate Cancer Current Status and New Advances Arno J. Mundt MD Professor and Chairman Dept Radiation Oncology Moores Cancer Center UCSD Radiation Therapy Wilhelm Roentgen (1845-1923)
Radiation Therapy in Prostate Cancer Current Status and New Advances Arno J. Mundt MD Professor and Chairman Dept Radiation Oncology Moores Cancer Center UCSD Radiation Therapy Wilhelm Roentgen (1845-1923)
Neoadjuvant hormonal therapy in prostate cancer impact of PSA level before radiotherapy
 JBUON 2013; 18(4): 949-953 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Neoadjuvant hormonal therapy in prostate cancer impact of PSA level
JBUON 2013; 18(4): 949-953 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Neoadjuvant hormonal therapy in prostate cancer impact of PSA level
PSA After Radiation for Prostate Cancer
 Review Article [1] May 01, 2004 By Deborah A. Kuban, MD [2], Howard D. Thames, PhD [3], and Larry B. Levy, MS [4] The introduction of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) as a reliable tumor marker for prostate
Review Article [1] May 01, 2004 By Deborah A. Kuban, MD [2], Howard D. Thames, PhD [3], and Larry B. Levy, MS [4] The introduction of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) as a reliable tumor marker for prostate
Clinical trial enrollment among older cancer patients
 Clinical trial enrollment among older cancer patients Sharon H. Giordano MD, MPH Professor, Health Services Research Mariana Chavez Mac Gregor MD, MSc Assistant Professor, Breast Medical Oncology Department
Clinical trial enrollment among older cancer patients Sharon H. Giordano MD, MPH Professor, Health Services Research Mariana Chavez Mac Gregor MD, MSc Assistant Professor, Breast Medical Oncology Department
A STATISTICAL EVALUATION OF RULES FOR BIOCHEMICAL FAILURE AFTER RADIOTHERAPY IN MEN TREATED FOR PROSTATE CANCER
 doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.01.013 Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys., Vol. 75, No. 5, pp. 1357 1363, 2009 Copyright Ó 2009 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0360-3016/09/$ see front
doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.01.013 Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys., Vol. 75, No. 5, pp. 1357 1363, 2009 Copyright Ó 2009 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0360-3016/09/$ see front
Issues Concerning Development of Products for Treatment of Non-Metastatic Castration- Resistant Prostate Cancer (NM-CRPC)
 Issues Concerning Development of Products for Treatment of Non-Metastatic Castration- Resistant Prostate Cancer (NM-CRPC) FDA Presentation ODAC Meeting September 14, 2011 1 Review Team Paul G. Kluetz,
Issues Concerning Development of Products for Treatment of Non-Metastatic Castration- Resistant Prostate Cancer (NM-CRPC) FDA Presentation ODAC Meeting September 14, 2011 1 Review Team Paul G. Kluetz,
Description of Procedure or Service. gene_based_tests_for_screening_detection_or_management_of_prostate_cancer 4/2009 8/2015 8/2016 8/2015
 Corporate Medical Policy Gene-Based Tests for Screening, Detection, and/or Management File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: gene_based_tests_for_screening_detection_or_management_of_prostate_cancer
Corporate Medical Policy Gene-Based Tests for Screening, Detection, and/or Management File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: gene_based_tests_for_screening_detection_or_management_of_prostate_cancer
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) of Head and Neck File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: intensity_modulated_radiation_therapy_imrt_of_head_and_neck
Corporate Medical Policy Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) of Head and Neck File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: intensity_modulated_radiation_therapy_imrt_of_head_and_neck
Effective for dates of service on or after May 1, 2015, refer to: Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Alabama Radiation Therapy Management RTM Policies
 Effective for dates of service on or after May 1, 2015, refer to: Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Alabama Radiation Therapy Management RTM Policies Name of Policy: Charged-Particle (Proton or Helium Ion)
Effective for dates of service on or after May 1, 2015, refer to: Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Alabama Radiation Therapy Management RTM Policies Name of Policy: Charged-Particle (Proton or Helium Ion)
Forum. Advances in radiation therapy for prostate. cancer. Abstract. Radiation therapy for localised prostate. cancer
 Advances in radiation therapy for prostate cancer Nitya Patanjali 1 and Scott Williams 2 1. Radiation Oncology, Sydney Cancer Centre, Royal Prince Alfred Hospital, Sydney. 2. Radiation Oncology, Peter
Advances in radiation therapy for prostate cancer Nitya Patanjali 1 and Scott Williams 2 1. Radiation Oncology, Sydney Cancer Centre, Royal Prince Alfred Hospital, Sydney. 2. Radiation Oncology, Peter
Analysis of Set-up Errors during CT-scan, Simulation, and Treatment Process in Breast Cancer Patients
 대한방사선종양학회지 2005;23(3):169~175 Analysis of Set-up Errors during CT-scan, Simulation, and Treatment Process in Breast Cancer Patients Department of Radiation Oncology, College of Medicine, Ewha Womans University
대한방사선종양학회지 2005;23(3):169~175 Analysis of Set-up Errors during CT-scan, Simulation, and Treatment Process in Breast Cancer Patients Department of Radiation Oncology, College of Medicine, Ewha Womans University
BRACHYTHERAPY FOR TREATMENT OF BREAST CANCER
 BRACHYTHERAPY FOR TREATMENT OF BREAST CANCER Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This
BRACHYTHERAPY FOR TREATMENT OF BREAST CANCER Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This
In 1946 Harvard physicist Robert Wilson (1914-2000) suggested:
 In 1946 Harvard physicist Robert Wilson (1914-2000) suggested: Protons can be used clinically Accelerators are available Maximum radiation dose can be placed into the tumor Proton therapy provides sparing
In 1946 Harvard physicist Robert Wilson (1914-2000) suggested: Protons can be used clinically Accelerators are available Maximum radiation dose can be placed into the tumor Proton therapy provides sparing
A new score predicting the survival of patients with spinal cord compression from myeloma
 A new score predicting the survival of patients with spinal cord compression from myeloma (1) Sarah Douglas, Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Lubeck, Germany; sarah_douglas@gmx.de (2) Steven
A new score predicting the survival of patients with spinal cord compression from myeloma (1) Sarah Douglas, Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Lubeck, Germany; sarah_douglas@gmx.de (2) Steven
Corporate Medical Policy Brachytherapy Treatment of Breast Cancer
 Corporate Medical Policy Brachytherapy Treatment of Breast Cancer File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: brachytherapy_treatment_of_breast_cancer 7/1996 5/2015 5/2016 5/2015
Corporate Medical Policy Brachytherapy Treatment of Breast Cancer File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: brachytherapy_treatment_of_breast_cancer 7/1996 5/2015 5/2016 5/2015
THE POWER AND PRECISION OF PROTON BEAM THERAPY IS WITHIN REACH
 THE POWER AND PRECISION OF PROTON BEAM THERAPY IS WITHIN REACH PROTON THERAPY OVERVIEW The American Cancer Society estimates 1.6 million new cancer cases in the United States this year. Approximately two
THE POWER AND PRECISION OF PROTON BEAM THERAPY IS WITHIN REACH PROTON THERAPY OVERVIEW The American Cancer Society estimates 1.6 million new cancer cases in the United States this year. Approximately two
NIA RADIATION ONCOLOGY CODING STANDARD. Dosimetry Planning
 NIA RADIATION ONCOLOGY CODING STANDARD Dosimetry Planning CPT Codes: 77295, 77300, 77301, 77306, 77307, 77321, 77316, 77317, 77318, 77331, 77399 Original Date: April, 2011 Last Reviewed Date: November,
NIA RADIATION ONCOLOGY CODING STANDARD Dosimetry Planning CPT Codes: 77295, 77300, 77301, 77306, 77307, 77321, 77316, 77317, 77318, 77331, 77399 Original Date: April, 2011 Last Reviewed Date: November,
Advances In Chemotherapy For Hormone Refractory Prostate Cancer. TAX 327 study results & SWOG 99-16 study results presented at ASCO 2004
 Ronald de Wit Rotterdam Cancer Institute The Netherlands Advances In Chemotherapy For Hormone Refractory Prostate Cancer TAX 327 study results & SWOG 99-16 study results presented at Slide 1 Prostate Cancer
Ronald de Wit Rotterdam Cancer Institute The Netherlands Advances In Chemotherapy For Hormone Refractory Prostate Cancer TAX 327 study results & SWOG 99-16 study results presented at Slide 1 Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is the most common cause of death from cancer in men over age 75. Prostate cancer is rarely found in men younger than 40.
 A.D.A.M. Medical Encyclopedia. Prostate cancer Cancer - prostate; Biopsy - prostate; Prostate biopsy; Gleason score Last reviewed: October 2, 2013. Prostate cancer is cancer that starts in the prostate
A.D.A.M. Medical Encyclopedia. Prostate cancer Cancer - prostate; Biopsy - prostate; Prostate biopsy; Gleason score Last reviewed: October 2, 2013. Prostate cancer is cancer that starts in the prostate
National Medical Policy
 National Medical Policy Subject: Policy Number: Proton Beam Radiotherapy NMP141 Effective Date*: November 2007 Updated: October 2014 This National Medical Policy is subject to the terms in the IMPORTANT
National Medical Policy Subject: Policy Number: Proton Beam Radiotherapy NMP141 Effective Date*: November 2007 Updated: October 2014 This National Medical Policy is subject to the terms in the IMPORTANT
Does my patient need more therapy after prostate cancer surgery?
 Does my patient need more therapy after prostate cancer surgery? Contact the GenomeDx Patient Care Team at: 1.888.792.1601 (toll-free) or e-mail: client.service@genomedx.com Prostate Cancer Classifier
Does my patient need more therapy after prostate cancer surgery? Contact the GenomeDx Patient Care Team at: 1.888.792.1601 (toll-free) or e-mail: client.service@genomedx.com Prostate Cancer Classifier
Radiation Therapy in Prostate Cancer Current Status and New Advances
 Radiation Therapy in Prostate Cancer Current Status and New Advances Arno J. Mundt MD Professor and Chairman Dept Radiation Oncology Moores Cancer Center UCSD Presentation Welcome Overview of UCSD, Moores
Radiation Therapy in Prostate Cancer Current Status and New Advances Arno J. Mundt MD Professor and Chairman Dept Radiation Oncology Moores Cancer Center UCSD Presentation Welcome Overview of UCSD, Moores
PROSTATE CANCER WITH LARGE GLANDS TREATED WITH 3- DIMENSIONAL COMPUTERIZED TOMOGRAPHY GUIDED PARARECTAL BRACHYTHERAPY: UP TO 8 YEARS OF FOLLOWUP
 0022-5347/03/1694-1331/0 Vol. 169, 1331 1336, April 2003 THE JOURNAL OF UROLOGY Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2003 by AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION DOI: 10.1097/01.ju.0000055773.91290.e8 PROSTATE CANCER
0022-5347/03/1694-1331/0 Vol. 169, 1331 1336, April 2003 THE JOURNAL OF UROLOGY Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2003 by AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION DOI: 10.1097/01.ju.0000055773.91290.e8 PROSTATE CANCER
Charged-Particle (Proton or Helium Ion) Radiotherapy
 MEDICAL POLICY POLICY RELATED POLICIES POLICY GUIDELINES DESCRIPTION SCOPE BENEFIT APPLICATION RATIONALE REFERENCES CODING APPENDIX HISTORY Charged-Particle (Proton or Helium Ion) Radiotherapy Number 8.01.534
MEDICAL POLICY POLICY RELATED POLICIES POLICY GUIDELINES DESCRIPTION SCOPE BENEFIT APPLICATION RATIONALE REFERENCES CODING APPENDIX HISTORY Charged-Particle (Proton or Helium Ion) Radiotherapy Number 8.01.534
Questions to Ask My Doctor About Prostate Cancer
 Questions to Ask My Doctor Being told you have prostate cancer can be scary and stressful. You probably have a lot of questions and concerns. Learning about the disease, how it s treated, and how this
Questions to Ask My Doctor Being told you have prostate cancer can be scary and stressful. You probably have a lot of questions and concerns. Learning about the disease, how it s treated, and how this
Proton Beam Radiotherapy Data Points # 10
 Proton beam radiotherapy in the U.S. Medicare population: growth in use between 2006 and 2009 Proton Beam Radiotherapy Data Points # 10 Proton beam radiotherapy is a form of external beam radiation that
Proton beam radiotherapy in the U.S. Medicare population: growth in use between 2006 and 2009 Proton Beam Radiotherapy Data Points # 10 Proton beam radiotherapy is a form of external beam radiation that
The Business of Prostate Cancer Care: A Clinician-Researcher s Perspective
 The Business of Prostate Cancer Care: A Clinician-Researcher s Perspective David F. Penson, MD, MPH Departments of Urology and Preventive Medicine Keck School of Medicine University of Southern California
The Business of Prostate Cancer Care: A Clinician-Researcher s Perspective David F. Penson, MD, MPH Departments of Urology and Preventive Medicine Keck School of Medicine University of Southern California
Prostate Cancer Screening in Taiwan: a must
 Prostate Cancer Screening in Taiwan: a must 吳 俊 德 基 隆 長 庚 醫 院 台 灣 醫 學 會 105 th What is the PSA test? The blood level of PSA is often elevated in men with prostate cancer, and the PSA test was originally
Prostate Cancer Screening in Taiwan: a must 吳 俊 德 基 隆 長 庚 醫 院 台 灣 醫 學 會 105 th What is the PSA test? The blood level of PSA is often elevated in men with prostate cancer, and the PSA test was originally
