How to build, configure and maintain a FreeBSD firewall with PF, BIND (DNS) and Squid (Proxy Server).
|
|
|
- Claire Smith
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 How to build, configure and maintain a FreeBSD firewall with PF, BIND (DNS) and Squid (Proxy Server). Twelve years ago, I couldn t afford the types of firewalls that were available at the time. They were big and expensive. Today, the cost has dropped dramatically and they are integrated into pretty much every cable modem and wireless access point. So the question comes, why would a person want to spend any of their time building a firewall when they could procure one for less than $100? The simple answer to this question is the search for knowledge. If you are of the mindset that you like understanding how the underlying technology works and enjoy periodically analyzing network traffic to further your knowledge base, then this article is for you. With a functional firewall, you can easily run tcpdump captures of network traffic and run saved captures through WireShark. The platform of choice for this article will be FreeBSD 8.1 which you can obtain from I chose this platform because I really enjoying the thoroughness of the documentation: Their documentation covers every aspect of what you need to achieve and is updated religiously. FreeBSD also comes with the binaries for BIND (link) and PF (link), so you will spend less time getting software and more time performing what s important to you (whether that is doing something else or performing network analysis on this system). These two applications will do
2 the bulk of the heavy lifting for the system associating common names (URLs) with IP addresses and deciding what packets are allowed and which are to be blocked. The hardware is an old Dell Precision with two physical cores. It is not 64 bit and has 2 GB of RAM. I ve put two old IDE hard drives into the system, one is an IBM Deskstar (Primary Master) that is 9 GB and the other is a no name brand (Secondary Master) that has 30 GB of space. You don t have to have two disks, but I chose to follow this pattern because I want to split the IO load going to the disks. The larger hard drive will host the data for Squid, while the smaller one will serve the OS and swap space. I would recommend at least a 1GHz processor with at least 512MB of memory and at least a 30 GB hard drive. This system will work with much less, but it will run very slow. You will be much happier with these minimum requirements. Lastly before we begin, the site that I have deployed at has three interfaces on the firewall. One attaches to a cable modem that routes traffic outbound. This cable modem has a software firewall installed and configured with the default settings from my ISP. The second interface attaches to a wireless access point to allow employee laptops to connect. This is secured with WPA2, MAC address control and has a non-broadcasting SSID. The third interface connects to servers and workstations. For the normal home/small office setup, you really only need two network interfaces. One for the outside interface that connects to your ISP cable modem and one that connects to a small switch that will connect all of your computer/networking equipment. OS Install Before installing the OS, thoroughly read the following section of the FreeBSD handbook: Partition the hard drive as needed for your site. I ve set up the following partitions:
3 Partition Recommended Size / 1 GB swap 2 GB /usr 3 GB /tmp 512 MB /var remaining space hard drive 1 /opt all space on hard drive 2 When you get to the point of choosing Distributions, select Minimal and then proceed. I chose this because I want the least amount of software and services running to maximize the limited amount of memory on this system for the components I ve selected (PF, BIND and Squid). OS Install Post Configuration One of the most critical files on the system is /etc/rc.conf. This file is used to store all Multi- User mode configuration settings (this sounds like a Dr. Suess tongue twister, but means that this one file contains information about all installed applications and their startup settings, plus the network interface settings). Change this file to match your site requirements. Refer to the Appendix and the /etc/rc.conf sample. I recommend running a dmesg or scan through /var/log/messages to determine the device names for the NICs (run dmges less to see the device names). Change the file rc.conf to match your sites needs. Restart the network with the command, /etc/rc.d/netif restart after changing the references to the NICs inside of /etc/rc.conf. Again, refer to the Appendix and the sample code, this is very straight forward. BIND DNS server install FreeBSD currently comes with BIND9 DNS server software by default.
4 Squid proxy server install On FreeBSD there are many ways to download and install software. Probably the easiest if you are connected to the internet is by using the pkg_add command with the flags -vr. Issue the following command as root, pkg_add vr squid. You can also use the portsnap collection and compile quickly the Squid software. Read the handbook to understand this capability. PF firewall install FreeBSD currently comes with the OpenBSD packet filtering software by default. Configure BIND Activating the software was performed in the file /etc/rc.conf. The configuration file is /var/named/etc/namedb/named.conf. Refer to the Appendix for samples. Modify your configuration files to match your site requirements. Refer back to the FreeBSD handbook as needed for understanding how the files work together. Again, the documentation is excellent and doesn t need to be duplicated here. Test BIND from remote client From the command line, use nslookup to test the remote DNS server. $ nslookup > server tell nslookup to use for DNS queries > darthvader.fortress.lan checking the name of my new firewall Server: darthvader.fortress.lan Address: Name: darthvader.fortress.lan Address: this is the response I want to see, his own IP. > test external address Server: darthvader.fortress.lan Address: Non-authoritative answer: Name: Addresses: this is the response I want to see.
5 Configure Squid Activating the software was performed in the file /etc/rc.conf. I used this link to install and startup WebMin: I used the WebMin admin page to then configure Squid. You will need to read the documentation on: to understand what s going on for squid. Basically, I have setup client authentication that forces the user to supply a username/password for web connections. Review my sample configuration file to understand what s going on and then compare against the documentation from squid-cache.org. Squid by default is not very complicated to configure and get running. However, if you deviate from the default configuration, it can become very complicated quickly and potentially stop working. When debugging, review the log files for the OS and for Squid, /var/log/messages and /opt/squid/logs/debug.log respectively. Test Squid from remote client Configure your browser to use proxy port 3128 on the internal NIC (either TCB or DMZ). i.e. I used Go to a sample URL, i.e. If your browser doesn t connect, make sure the service is running. Execute /usr/local/etc/rc.d/squid restart. If this still doesn t work, it is because the firewall hasn t been configured and told to perform NAT ing. Configure the firewall and then retest this component. Configure PF Activating the software was performed in the file /etc/rc.conf. Refer to the sample file /usr/local/etc/pf.conf. Modify your site as needed to match the requirements.
6 Test PF from remote client Restart the PF binary with the command, /etc/rc.d/pf restart. Open a command prompt or terminal and ping the firewall s IP address. Open a web browser (configured to use the proxy port) and connect to an external site. Positive and negative test cases Positive: Ping an external site. SSH to ip address of firewall. Configure the proxy port in your web browser and try to connect to an external site. Perform a DNS query to the firewall s DNS server. Negative: Unconfigure the proxy port in your web browser and try to connect to an external site. SSH to an external site. Perform a DNS query to an external DNS server. Maintenance of packages and Operating System Review the sample root crontab in the Appendix. I strongly recommend that you follow a similar pattern using the command freebsd-update. This will ensure your software packages are always up-to-date. Conclusion At the end of this journey you should have a solid working firewall that blocks all traffic coming inbound and only allows outbound traffic through the proxy server. I ve put all of my relevant configuration files and scripts into the Appendix. Along this journey, you should have read the documentation in the FreeBSD handbook (at least read through the installation procedures), learned BIND and Squid. The last step after the system is working is to gain an understanding of tcpdump. Read this site first, Then start analyzing small dumps of traffic from the system through a tool like Wireshark. I like to start off broad and then narrow my searches. I will SSH into the firewall and run something like:
7 tcpdump i sk2 c w /tmp/quick.dmp s 1524 ip and not tcp port After tcpdump has written 10,000 packets, I will secure copy the file over to a workstation with Wireshark installed and analyze the contents. You should learn all sorts of useful information from this exercise. From network broadcasts to mis-configured devices/services, you will learn what is happening on the network segment and hopefully be able to make better business decisions that shape your sites policies and guidelines. By analyzing the DNS queries performed, you can gain an understanding of where people and systems are trying to connect to. From this, you can choose to perform DNS blackholing to prevent unwanted traffic from being able to resolve the destination IP. Finally, with the logs from the squid proxy server, you can analyze these and make the decision to block sites if you choose. You can setup an access control list (ACL) in Squid that reads from a file and blocks those destinations. Don t forget if you do this that every connection that goes through Squid will perform this lookup. So if you have many addresses in this file, your server s performance will suffer. Contact and disclaimer information Securityhardening.com provides ideas, concepts and patterns regarding computer security. This site and its content are intended as a way to share these thoughts with the security community. Any questions, comments, or complaints can be directed to the contact address on the support page. Anyone considering implementing any recommendation published on Securityhardening.com (in any form) should read the Disclaimer page. -- Secure the system... live life! Copyright 2010 securityhardening.com. All rights reserved.
8 Appendix /etc/rc.conf sample: hostname= darthvader.fortress.lan ifconfig_sk0= inet netmask ifconfig_sk1= inet netmask ifconfig_sk2= inet netmask defaultrouter= gateway_enable= YES inetd_enable= NO sshd_enable= YES pf_enable= YES pf_rules= /usr/local/etc/pf.conf pf_flags= pflog_enable= YES pflog_logfile= /var/log/pflog pflog_flags= ntpd_enable= YES ntpd_sync_on_start= NO update_motd= NO dhcpd_enable= YES named_enable= YES squid_enable= YES apache22_enable= YES webmin_enable= YES /var/named/etc/namedb/named.conf sample: // Fortress.lan DNS config. // acl "friendlies" { / /24 } acl "dmz" { /24 } options { directory pid-file dump-file "/etc/namedb" "/var/run/named/pid" "/var/dump/named_dump.db"
9 statistics-file "/var/stats/named.stats" // datasize 32768k version "Nunya Business Sucka" transfer-format many-answers recursion yes allow-query { "friendlies" "dmz" } allow-transfer { "none" } allow-update { "none" } stacksize 32768k // listen-on { } // disable-empty-zone " IN-ADDR.ARPA" disable-empty-zone " IP6.ARPA" disable-empty-zone " IP6.ARPA" } logging { channel my_debug { file "/var/log/named_debug.log" versions 9 size 5m severity debug 5 print-time yes print-severity yes print-category yes } channel security_info { file "/var/log/named_auth.log" versions 9 size 5m severity notice print-time yes print-severity yes print-category yes } channel info { file "/var/log/named_info.log" versions 9 size 5m severity info print-time yes print-severity yes print-category yes } category update { my_debug } category security { security_info } category queries { info } } // RFC 1912 zone "localhost" { type master file "master/localhost-forward.db" } zone "127.in-addr.arpa" { type master file "master/localhost-reverse.db" } zone "255.in-addr.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } // RFC 1912-style zone for IPv6 localhost address zone "0.ip6.arpa" { type master file "master/localhost-reverse.db" } // "This" Network (RFCs 1912 and 3330) zone "0.in-addr.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } // Private Use Networks (RFC 1918) //zone "10.in-addr.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } //zone " in-addr.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" }
10 zone " in-addr.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone " in-addr.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone " in-addr.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone " in-addr.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone " in-addr.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone " in-addr.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone " in-addr.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone " in-addr.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone " in-addr.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone " in-addr.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone " in-addr.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone " in-addr.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone " in-addr.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone " in-addr.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone " in-addr.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } //zone " in-addr.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } // Link-local/APIPA (RFCs 3330 and 3927) zone " in-addr.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } // TEST-NET for Documentation (RFC 3330) zone " in-addr.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } // Router Benchmark Testing (RFC 3330) zone " in-addr.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone " in-addr.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } // IANA Reserved - Old Class E Space zone "240.in-addr.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone "241.in-addr.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone "242.in-addr.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone "243.in-addr.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone "244.in-addr.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone "245.in-addr.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone "246.in-addr.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone "247.in-addr.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone "248.in-addr.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone "249.in-addr.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone "250.in-addr.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone "251.in-addr.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone "252.in-addr.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone "253.in-addr.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone "254.in-addr.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } // IPv6 Unassigned Addresses (RFC 4291) zone "1.ip6.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone "3.ip6.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone "4.ip6.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone "5.ip6.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone "6.ip6.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone "7.ip6.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone "8.ip6.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone "9.ip6.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone "a.ip6.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone "b.ip6.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone "c.ip6.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone "d.ip6.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone "e.ip6.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone "0.f.ip6.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone "1.f.ip6.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone "2.f.ip6.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone "3.f.ip6.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone "4.f.ip6.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" }
11 zone "5.f.ip6.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone "6.f.ip6.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone "7.f.ip6.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone "8.f.ip6.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone "9.f.ip6.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone "a.f.ip6.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone "b.f.ip6.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone "0.e.f.ip6.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone "1.e.f.ip6.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone "2.e.f.ip6.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone "3.e.f.ip6.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone "4.e.f.ip6.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone "5.e.f.ip6.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone "6.e.f.ip6.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone "7.e.f.ip6.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } // IPv6 ULA (RFC 4193) zone "c.f.ip6.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone "d.f.ip6.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } // IPv6 Link Local (RFC 4291) zone "8.e.f.ip6.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone "9.e.f.ip6.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone "a.e.f.ip6.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone "b.e.f.ip6.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } // IPv6 Deprecated Site-Local Addresses (RFC 3879) zone "c.e.f.ip6.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone "d.e.f.ip6.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone "e.e.f.ip6.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } zone "f.e.f.ip6.arpa" { type master file "master/empty.db" } // IP6.INT is Deprecated (RFC 4159) zone "ip6.int" { type master file "master/empty.db" } // Master zones zone "fortress.lan" { type master file "master/fortress.lan" allow-query { "friendlies" } } zone " in-addr.arpa" { type master file "master/ in-addr.arpa" allow-query { "friendlies" } } zone " in-addr.arpa" { type master file "master/ in-addr.arpa" allow-query { "friendlies" } } zone " in-addr.arpa" { type master file "master/ in-addr.arpa" allow-query { "friendlies" } } zone " in-addr.arpa" { type master file "master/ in-addr.arpa"
12 } allow-query { "friendlies" } zone "." { type hint file "named.root" } /var/named/etc/namedb/named.root sample: $FreeBSD: src/etc/namedb/named.root,v /04/15 03:14:26 kensmith Exp $ This file holds the information on root name servers needed to initialize cache of Internet domain name servers (e.g. reference this file in the "cache. <file>" configuration file of BIND domain name servers). This file is made available by InterNIC under anonymous FTP as file /domain/named.root on server FTP.INTERNIC.NET -OR- RS.INTERNIC.NET last update: Feb 04, 2008 related version of root zone: formerly NS.INTERNIC.NET IN NS A.ROOT-SERVERS.NET. A.ROOT-SERVERS.NET A A.ROOT-SERVERS.NET AAAA 2001:503:BA3E::2:30 formerly NS1.ISI.EDU NS B.ROOT-SERVERS.NET. B.ROOT-SERVERS.NET A formerly C.PSI.NET NS C.ROOT-SERVERS.NET. C.ROOT-SERVERS.NET A formerly TERP.UMD.EDU NS D.ROOT-SERVERS.NET. D.ROOT-SERVERS.NET A formerly NS.NASA.GOV NS E.ROOT-SERVERS.NET. E.ROOT-SERVERS.NET A formerly NS.ISC.ORG NS F.ROOT-SERVERS.NET. F.ROOT-SERVERS.NET A F.ROOT-SERVERS.NET AAAA 2001:500:2f::f
13 formerly NS.NIC.DDN.MIL NS G.ROOT-SERVERS.NET. G.ROOT-SERVERS.NET A formerly AOS.ARL.ARMY.MIL NS H.ROOT-SERVERS.NET. H.ROOT-SERVERS.NET A H.ROOT-SERVERS.NET AAAA 2001:500:1::803f:235 formerly NIC.NORDU.NET NS I.ROOT-SERVERS.NET. I.ROOT-SERVERS.NET A operated by VeriSign, Inc NS J.ROOT-SERVERS.NET. J.ROOT-SERVERS.NET A J.ROOT-SERVERS.NET AAAA 2001:503:C27::2:30 operated by RIPE NCC NS K.ROOT-SERVERS.NET. K.ROOT-SERVERS.NET A K.ROOT-SERVERS.NET AAAA 2001:7fd::1 operated by ICANN NS L.ROOT-SERVERS.NET. L.ROOT-SERVERS.NET A operated by WIDE NS M.ROOT-SERVERS.NET. M.ROOT-SERVERS.NET A M.ROOT-SERVERS.NET AAAA 2001:dc3::35 End of File /var/named/etc/namedb/master/ in-addr.arpa sample: $TTL IN SOA fortress.lan. darthvader.fortress.lan. ( Serial Refresh (3 hours) 3600 Retry (1 hour) Expire (1 week) ) Minimum (1 day) IN NS darthvader.fortress.lan. 1 IN PTR shumai.fortress.lan. 2 IN PTR pooja.fortress.lan. /var/named/etc/namedb/master/ in-addr.arpa sample: $TTL 86400
14 @ IN SOA fortress.lan. darthvader.fortress.lan. ( Serial Refresh (3 hours) 3600 Retry (1 hour) Expire (1 week) ) Minimum (1 day) IN NS darthvader.fortress.lan. 1 IN PTR seitaria.fortress.lan. 2 IN PTR darthmaul.fortress.lan. /var/named/etc/namedb/master/ in-addr.arpa sample: $TTL IN SOA fortress.lan. darthvader.fortress.lan. ( Serial Refresh (3 hours) 3600 Retry (1 hour) Expire (1 week) ) Minimum (1 day) IN NS darthvader.fortress.lan. 1 IN PTR darthvader.fortress.lan. 2 IN PTR palpatine.fortress.lan. 3 IN PTR landocalrissian.fortress.lan. 4 IN PTR countdooku.fortress.lan. 5 IN PTR bobafett.fortress.lan. /var/named/etc/namedb/master/fortress.lan sample: $TTL IN SOA fortress.lan. darthvader.fortress.lan. ( Serial Refresh (3 hours) 3600 Retry (1 hour) Expire (1 week) ) Minimum (1 day) IN NS darthvader.fortress.lan. localhost IN A DMZ & Firewall shumai IN A pooja IN A DMZ seitaria IN A darthmaul IN A Internal Fortress darthvader IN A palpatine IN A landocalrissian IN A countdooku IN A bobafett IN A
15 /usr/local/etc/squid/squid.conf sample: auth_param basic program /usr/local/libexec/squid/ncsa_auth \ /usr/local/etc/squid/squid.passwd auth_param basic children 5 auth_param basic realm Squid proxy-caching web server auth_param basic credentialsttl 2 hours auth_param basic casesensitive off acl windowsupdate dstdomain windowsupdate.microsoft.com acl windowsupdate dstdomain.update.microsoft.com acl windowsupdate dstdomain download.windowsupdate.com acl windowsupdate dstdomain redir.metaservices.microsoft.com acl windowsupdate dstdomain images.metaservices.microsoft.com acl windowsupdate dstdomain c.microsoft.com acl windowsupdate dstdomain acl windowsupdate dstdomain wustat.windows.com acl windowsupdate dstdomain crl.microsoft.com acl windowsupdate dstdomain sls.microsoft.com acl windowsupdate dstdomain productactivation.one.microsoft.com acl windowsupdate dstdomain ntservicepack.microsoft.com acl CONNECT method CONNECT acl wuconnect dstdomain acl wuconnect dstdomain sls.microsoft.com acl employees ident employee_username1 employee_username2 employee_username3 acl managers ident manager_username1 manager_username2 acl pam proxy_auth REQUIRED acl all src all acl manager proto cache_object acl localhost src /32 acl to_localhost dst / /32 acl localnet src /24 RFC1918 possible internal network acl localnet src /24 RFC1918 possible internal network acl SSL_ports port 443 RFC1918 possible internal network acl Safe_ports port 80 acl Safe_ports port 21 http acl Safe_ports port 443 ftp acl Safe_ports port 70 https acl Safe_ports port 210 gopher acl Safe_ports port wais acl Safe_ports port 280 unregistered ports acl Safe_ports port 488 http-mgmt acl Safe_ports port 591 gss-http acl Safe_ports port 777 filemaker acl CONNECT method CONNECT multiling http acl shoutcast rep_header X-HTTP09-First-Line ^ICY.[0-9] acl ncsa_users proxy_auth REQUIRED acl business_hours_week time M T W H F 16:00-19:00 acl business_hours_weekend time A S 8:00-19:00 acl Employees.Good.Sites dstdomain "/usr/local/etc/squid/employee.allowed-sites.squid" http_access allow CONNECT wuconnect localnet http_access allow windowsupdate localnet http_access allow ncsa_users http_access allow manager localhost http_access deny manager http_access deny!safe_ports http_access deny CONNECT!SSL_ports
16 http_access deny to_localhost http_access allow localnet http_access deny all icp_access allow localnet icp_access deny all ident_lookup_access allow all http_port :3128 http_port :3128 hierarchy_stoplist cgi-bin? cache_mem 256 MB memory_replacement_policy heap LFUDA cache_replacement_policy heap LFUDA cache_dir ufs /opt/squid/cache maximum_object_size 8192 KB access_log /opt/squid/logs/access.log cache_log /opt/squid/logs/debug.log cache_store_log /opt/squid/logs/storage.log refresh_pattern ^ftp: % refresh_pattern ^gopher: % 1440 refresh_pattern -i (/cgi-bin/ \?) 0 0% 0 refresh_pattern. 0 20% 4320 quick_abort_min -1 range_offset_limit -1 half_closed_clients off store_avg_object_size 14 KB cache_swap_high 100% cache_swap_low 80% acl apache rep_header Server ^Apache upgrade_http0.9 deny shoutcast broken_vary_encoding allow apache cache_effective_user squid cache_mgr [email protected] icp_port 0 dns_testnames dns_nameservers fqdncache_size 8192 coredump_dir /var/tmp cache_swap_log /opt/squid/logs/cache.log cache_effective_group squid visible_hostname darthvader unique_hostname darthvader.fortress.lan /usr/local/etc/pf.conf sample: MACROS Definition tcb_if="sk0" Trusted Computing Base dmz_if="sk1" DMZ - Wireless network ext_if="sk2" External Network - to Screening Router Loop="lo0" Loopback address. TCP_Flags = "S/SAFR modulate state" TCP_OutBound = "{ 3128 }"
17 UDP_OutBound = "{ }" TCB_Networks = "{ /24 }" DMZ_Networks = "{ /24 }" OPTIONS set limit { states 10000, frags 5000 } set timeout { interval 30, frag 10 } set timeout { tcp.first 120, tcp.opening 30, tcp.established } set timeout { tcp.closing 900, tcp.finwait 45, tcp.closed 90 } set timeout { udp.first 60, udp.single 30, udp.multiple 60 } set timeout { icmp.first 20, icmp.error 10 } set timeout { other.first 60, other.single 30, other.multiple 60 } set fingerprints "/usr/local/etc/pf.os" set ruleset-optimization basic set optimization conservative set block-policy return set require-order yes set state-policy if-bound set loginterface $tcb_if set skip on $Loop set debug urgent NORMALIZATION scrub in on $ext_if all fragment reassemble scrub out on $ext_if all fragment reassemble random-id no-df TRANSLATION nat on $ext_if from /24 to any -> ($ext_if) nat on $ext_if from /24 to any -> ($ext_if) PACKET FILTERING Defaults block in log all pass out all Loopback specific rules: pass in quick on lo0 all pass out quick on lo0 all antispoof log for lo0 Allow Restrictive UDP From TCB to firewall DNS pass in quick on { $tcb_if } proto udp from \ $TCB_Networks to { $tcb_if } \ port 53 keep state Allow Restrictive UDP From DMZ to firewall DNS pass in quick on { $dmz_if } proto udp from \ $DMZ_Networks to { $dmz_if } \ port 53 keep state
18 Allow Less Restrictive TCP From TCB to External pass in quick on { $tcb_if } proto tcp from \ $TCB_Networks to { $tcb_if } \ port $TCP_OutBound flags $TCP_Flags Allow Less Restrictive TCP From DMZ to External pass in quick on { $dmz_if } proto tcp from \ $DMZ_Networks to { $dmz_if } \ port $TCP_OutBound flags $TCP_Flags Management stuff SSH on pass in quick on { $tcb_if } proto tcp from \ $TCB_Networks to { $tcb_if } \ port { 10000, 11000, } flags $TCP_Flags Allow Less Restrictive ICMP From Int to External pass in quick on { $tcb_if } proto icmp from \ $TCB_Networks to any \ icmp-type 8 keep state Note: my /usr/local/etc/pf.os is empty. /etc/ntp.conf sample: restrict default nomodify notrap noquery server restrict server restrict mask nomodify notrap noquery server restrict mask nomodify notrap noquery fudge stratum 10 driftfile /var/lib/ntp/drift broadcastdelay keys /etc/ntp/keys broadcastclient /etc/sysctl.conf sample: kern.ps_showallprocs=0 net.inet.tcp.blackhole=1 net.inet.udp.blackhole=1 net.inet.tcp.log_in_vain=1 net.inet.udp.log_in_vain=1 net.inet.ip.forwarding=1 net.inet.ip.ttl=32 net.inet.icmp.icmplim=200 net.inet.icmp.bmcastecho=0
19 net.inet.icmp.maskrepl=0 net.inet.tcp.sendspace=32768 net.inet.tcp.recvspace=65536 net.inet.tcp.recvbuf_auto=1 net.inet.tcp.recvbuf_inc=16384 net.inet.tcp.recvbuf_max= net.inet.tcp.sendbuf_auto=1 net.inet.tcp.sendbuf_inc=8192 net.inet.tcp.sendbuf_max= net.inet.tcp.syncookies=0 net.inet.tcp.slowstart_flightsize=2 net.inet.tcp.local_slowstart_flightsize=5 net.inet.tcp.newreno=1 net.inet.tcp.tso=1 net.inet.tcp.sack.enable=1 net.inet.tcp.always_keepalive=1 net.link.log_link_state_change=1 /etc/ssh/sshd_config sample: Port Protocol 2 PermitRootLogin no X11Forwarding no PrintMotd yes PrintLastLog yes KeepAlive yes PermitEmptyPasswords no PasswordAuthentication yes ReverseMappingCheck no GatewayPorts no AllowTcpForwarding yes AllowGroups ssh Banner /etc/issue MaxStartups 4 /root/bin/backup.sh sample:!/usr/bin/env bash backup critical system files PATH="/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/root/bin" BACKUP_DIR="/var/backups" [! -d $BACKUP_DIR ] && mkdir -p $BACKUP_DIR DATE=`date +%Y%m%d` BACKUP_DAILY="$BACKUP_DIR/$DATE" [! -d $BACKUP_DAILY ] && mkdir -p $BACKUP_DAILY cd $BACKUP_DAILY [ -f $DATE.tgz ] && rm -f $DATE.tgz find /etc -depth -type f pax -w -x tar gzip -9 > etc.tgz find /var/named/etc -depth -type f pax -w -x tar gzip -9 > var.named.etc.tgz
20 find /usr/local/etc -depth -type f pax -w -x tar gzip -9 > usr.local.etc.tgz cd $BACKUP_DIR tar cf - $DATE gzip -9 > $DATE.tgz rm -rf $BACKUP_DAILY exit 0 Root crontab sample (crontab l u root): PATH="/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/root/bin" Critical System Files * * * /root/bin/backup.sh 2>/dev/null System Updates * * * /usr/sbin/freebsd-update cron Ports Tree update * * * /usr/sbin/portsnap cron update
DNS Domain Name System
 DNS Domain Name System Domain names and IP addresses People prefer to use easy-to-remember names instead of IP addresses Domain names are alphanumeric names for IP addresses e.g., neon.cs.virginia.edu,
DNS Domain Name System Domain names and IP addresses People prefer to use easy-to-remember names instead of IP addresses Domain names are alphanumeric names for IP addresses e.g., neon.cs.virginia.edu,
DNS : Domain Name System
 1/30 DNS : Domain Name System Surasak Sanguanpong [email protected] http://www...ac.th/~nguan Last updated: May 24, 1999 Outline 2/30 DNS basic name space name resolution process protocol configurations Why
1/30 DNS : Domain Name System Surasak Sanguanpong [email protected] http://www...ac.th/~nguan Last updated: May 24, 1999 Outline 2/30 DNS basic name space name resolution process protocol configurations Why
Configuring the BIND name server (named) Configuring the BIND resolver Constructing the name server database files
 Configuring DNS BIND: UNIX Name Service Configuring the BIND name server (named) Configuring the BIND resolver Constructing the name server database files Zone: a collection of domain information contained
Configuring DNS BIND: UNIX Name Service Configuring the BIND name server (named) Configuring the BIND resolver Constructing the name server database files Zone: a collection of domain information contained
CS244A Review Session Routing and DNS
 CS244A Review Session Routing and DNS January 18, 2008 Peter Pawlowski Slides derived from: Justin Pettit (2007) Matt Falkenhagen (2006) Yashar Ganjali (2005) Guido Appenzeller (2002) Announcements PA
CS244A Review Session Routing and DNS January 18, 2008 Peter Pawlowski Slides derived from: Justin Pettit (2007) Matt Falkenhagen (2006) Yashar Ganjali (2005) Guido Appenzeller (2002) Announcements PA
DHCP & Firewall & NAT
 DHCP & Firewall & NAT DHCP Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol DHCP introduction DHCP Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol A system can connect to a network and obtain the necessary information dynamically
DHCP & Firewall & NAT DHCP Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol DHCP introduction DHCP Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol A system can connect to a network and obtain the necessary information dynamically
The role of JANET CSIRT
 The role of JANET CSIRT Bradley Freeman JANET(UK) CSIRT Member UKNOF 15 21 st January 2010 [email protected] Copyright JNT Association 2009 1 What to expect Overview of how we detect and deal with
The role of JANET CSIRT Bradley Freeman JANET(UK) CSIRT Member UKNOF 15 21 st January 2010 [email protected] Copyright JNT Association 2009 1 What to expect Overview of how we detect and deal with
Proxy. Proxy. Computer Center, CS, NCTU. Proxy. A proxy server is a server which services the requests of its clients by: Goals: Server.
 Web A proxy server is a server which services the requests of its clients by: Making requests to other servers Caching some results for further same requests Goals: Performance Stability Central Control
Web A proxy server is a server which services the requests of its clients by: Making requests to other servers Caching some results for further same requests Goals: Performance Stability Central Control
DNS Service on Linux. Supawit Wannapila CCNA, RHCE [email protected]
 DNS Service on Linux Supawit Wannapila CCNA, RHCE [email protected] Host Name Resolution Common Host Name Service Files (/etc/hosts and /etc/networks) DNS (/etc/resolv.conf) Multiple client-side resolvers:
DNS Service on Linux Supawit Wannapila CCNA, RHCE [email protected] Host Name Resolution Common Host Name Service Files (/etc/hosts and /etc/networks) DNS (/etc/resolv.conf) Multiple client-side resolvers:
1. What is this? Why would I want it?
 HOWTO - Jeanne, redirector for Squid Reverse Proxy Vincent Berk (c)2001 [email protected] GNU/GPL Marion Bates (c) 2001 [email protected] Installation Guide with Examples (ALPHA distribution)
HOWTO - Jeanne, redirector for Squid Reverse Proxy Vincent Berk (c)2001 [email protected] GNU/GPL Marion Bates (c) 2001 [email protected] Installation Guide with Examples (ALPHA distribution)
Networking Domain Name System
 System i Networking Domain Name System Version 6 Release 1 System i Networking Domain Name System Version 6 Release 1 Note Before using this information and the product it supports, read the information
System i Networking Domain Name System Version 6 Release 1 System i Networking Domain Name System Version 6 Release 1 Note Before using this information and the product it supports, read the information
Copyright International Business Machines Corporation 2001. All rights reserved. US Government Users Restricted Rights Use, duplication or disclosure
 iseries DNS iseries DNS Copyright International Business Machines Corporation 2001. All rights reserved. US Government Users Restricted Rights Use, duplication or disclosure restricted by GSA ADP Schedule
iseries DNS iseries DNS Copyright International Business Machines Corporation 2001. All rights reserved. US Government Users Restricted Rights Use, duplication or disclosure restricted by GSA ADP Schedule
NetSpective Global Proxy Configuration Guide
 NetSpective Global Proxy Configuration Guide Table of Contents NetSpective Global Proxy Deployment... 3 Configuring NetSpective for Global Proxy... 5 Restrict Admin Access... 5 Networking... 6 Apply a
NetSpective Global Proxy Configuration Guide Table of Contents NetSpective Global Proxy Deployment... 3 Configuring NetSpective for Global Proxy... 5 Restrict Admin Access... 5 Networking... 6 Apply a
Tunnel Client FAQ. Table of Contents. Version 0v5, November 2014 Revised: Kate Lance Author: Karl Auer
 Tunnel Client FAQ Version 0v5, November 2014 Revised: Kate Lance Author: Karl Auer Table of Contents A. Tunnelling 1 How does tunnelling work? 2 What operating systems are supported? 3 Where can I get
Tunnel Client FAQ Version 0v5, November 2014 Revised: Kate Lance Author: Karl Auer Table of Contents A. Tunnelling 1 How does tunnelling work? 2 What operating systems are supported? 3 Where can I get
K-Root Name Server Operations
 K-Root Name Server Operations Andrei Robachevsky [email protected] 1 Outline Root Server System brief update Architecture Current locations Anycast deployment K.root-servers.net Server Major milestones Current
K-Root Name Server Operations Andrei Robachevsky [email protected] 1 Outline Root Server System brief update Architecture Current locations Anycast deployment K.root-servers.net Server Major milestones Current
HOWTO. Bandwidth Management for ADSL with OpenBSD
 Bandwidth Management for ADSL with OpenBSD OpenBSD 4.2 based Router with Bandwidth Management for PPPOE-based Internet Connections like ADSL 1. Introduction...1 2. Install your OpenBSD System...2 3. Configure
Bandwidth Management for ADSL with OpenBSD OpenBSD 4.2 based Router with Bandwidth Management for PPPOE-based Internet Connections like ADSL 1. Introduction...1 2. Install your OpenBSD System...2 3. Configure
How to Configure Split DNS
 How to Configure Split DNS Split DNS is a concept that allows a hostname to resolve to one IP address on the internal network, and another on the external network. An example is the G/On Server if it is
How to Configure Split DNS Split DNS is a concept that allows a hostname to resolve to one IP address on the internal network, and another on the external network. An example is the G/On Server if it is
Networking Domain Name System
 System i Networking Domain Name System Version 5 Release 4 System i Networking Domain Name System Version 5 Release 4 Note Before using this information and the product it supports, read the information
System i Networking Domain Name System Version 5 Release 4 System i Networking Domain Name System Version 5 Release 4 Note Before using this information and the product it supports, read the information
Setting up pfsense as a Stateful Bridging Firewall.
 Setting up pfsense as a Stateful Bridging Firewall. Contents Contents Setting up pfsense as a Stateful Bridging Firewall.... 1 What king of system these directions will try and help you create.... 1 Selecting
Setting up pfsense as a Stateful Bridging Firewall. Contents Contents Setting up pfsense as a Stateful Bridging Firewall.... 1 What king of system these directions will try and help you create.... 1 Selecting
FreeBSD Firewalls SS- E 2014. Kevin Chege ISOC
 FreeBSD Firewalls SS- E 2014 Kevin Chege ISOC What s a Firewall? Computer network security device to protect devices, or restrict access to or from a network Analyzes traffic coming in or going out (or
FreeBSD Firewalls SS- E 2014 Kevin Chege ISOC What s a Firewall? Computer network security device to protect devices, or restrict access to or from a network Analyzes traffic coming in or going out (or
Creating a master/slave DNS server combination for your Grid Infrastructure
 Creating a master/slave DNS server combination for your Grid Infrastructure When doing a Grid Infrastructure installation, a DNS server is needed to resolve addresses for the cluster- scan addresses. In
Creating a master/slave DNS server combination for your Grid Infrastructure When doing a Grid Infrastructure installation, a DNS server is needed to resolve addresses for the cluster- scan addresses. In
NEFSIS DEDICATED SERVER
 NEFSIS TRAINING SERIES Nefsis Dedicated Server version 5.2.0.XXX (DRAFT Document) Requirements and Implementation Guide (Rev5-113009) REQUIREMENTS AND INSTALLATION OF THE NEFSIS DEDICATED SERVER Nefsis
NEFSIS TRAINING SERIES Nefsis Dedicated Server version 5.2.0.XXX (DRAFT Document) Requirements and Implementation Guide (Rev5-113009) REQUIREMENTS AND INSTALLATION OF THE NEFSIS DEDICATED SERVER Nefsis
F-Secure Messaging Security Gateway. Deployment Guide
 F-Secure Messaging Security Gateway Deployment Guide TOC F-Secure Messaging Security Gateway Contents Chapter 1: Deploying F-Secure Messaging Security Gateway...3 1.1 The typical product deployment model...4
F-Secure Messaging Security Gateway Deployment Guide TOC F-Secure Messaging Security Gateway Contents Chapter 1: Deploying F-Secure Messaging Security Gateway...3 1.1 The typical product deployment model...4
1 Basic Configuration of Cisco 2600 Router. Basic Configuration Cisco 2600 Router
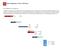 1 Basic Configuration of Cisco 2600 Router Basic Configuration Cisco 2600 Router I decided to incorporate the Cisco 2600 into my previously designed network. This would give me two seperate broadcast domains
1 Basic Configuration of Cisco 2600 Router Basic Configuration Cisco 2600 Router I decided to incorporate the Cisco 2600 into my previously designed network. This would give me two seperate broadcast domains
Protecting the Home Network (Firewall)
 Protecting the Home Network (Firewall) Basic Tab Setup Tab DHCP Tab Advanced Tab Options Tab Port Forwarding Tab Port Triggers Tab DMZ Host Tab Firewall Tab Event Log Tab Status Tab Software Tab Connection
Protecting the Home Network (Firewall) Basic Tab Setup Tab DHCP Tab Advanced Tab Options Tab Port Forwarding Tab Port Triggers Tab DMZ Host Tab Firewall Tab Event Log Tab Status Tab Software Tab Connection
Setting up a Squid-Proxy Server
 LinuxFocus article number 235 http://linuxfocus.org Setting up a Squid-Proxy Server by D.S. Oberoi About the author: D.S. Oberoi lives in Jammu, India and has currently problems
LinuxFocus article number 235 http://linuxfocus.org Setting up a Squid-Proxy Server by D.S. Oberoi About the author: D.S. Oberoi lives in Jammu, India and has currently problems
User Manual. Onsight Management Suite Version 5.1. Another Innovation by Librestream
 User Manual Onsight Management Suite Version 5.1 Another Innovation by Librestream Doc #: 400075-06 May 2012 Information in this document is subject to change without notice. Reproduction in any manner
User Manual Onsight Management Suite Version 5.1 Another Innovation by Librestream Doc #: 400075-06 May 2012 Information in this document is subject to change without notice. Reproduction in any manner
Use Domain Name System and IP Version 6
 Use Domain Name System and IP Version 6 What You Will Learn The introduction of IP Version 6 (IPv6) into an enterprise environment requires some changes both in the provisioned Domain Name System (DNS)
Use Domain Name System and IP Version 6 What You Will Learn The introduction of IP Version 6 (IPv6) into an enterprise environment requires some changes both in the provisioned Domain Name System (DNS)
BorderWare Firewall Server 7.1. Release Notes
 BorderWare Firewall Server 7.1 Release Notes BorderWare Technologies is pleased to announce the release of version 7.1 of the BorderWare Firewall Server. This release includes following new features and
BorderWare Firewall Server 7.1 Release Notes BorderWare Technologies is pleased to announce the release of version 7.1 of the BorderWare Firewall Server. This release includes following new features and
Innominate mguard Version 6
 Innominate mguard Version 6 Configuration Examples mguard smart mguard PCI mguard blade mguard industrial RS EAGLE mguard mguard delta Innominate Security Technologies AG Albert-Einstein-Str. 14 12489
Innominate mguard Version 6 Configuration Examples mguard smart mguard PCI mguard blade mguard industrial RS EAGLE mguard mguard delta Innominate Security Technologies AG Albert-Einstein-Str. 14 12489
Solaris Networking Guide. Stewart Watkiss. Volume. New User To Technical Expert Solaris Bookshelf. This document is currently under construction
 Volume 3 New User To Technical Expert Solaris Bookshelf Stewart Watkiss This document is currently under construction This version is to be considered a preview only Solaris Networking Guide Copyright
Volume 3 New User To Technical Expert Solaris Bookshelf Stewart Watkiss This document is currently under construction This version is to be considered a preview only Solaris Networking Guide Copyright
642 523 Securing Networks with PIX and ASA
 642 523 Securing Networks with PIX and ASA Course Number: 642 523 Length: 1 Day(s) Course Overview This course is part of the training for the Cisco Certified Security Professional and the Cisco Firewall
642 523 Securing Networks with PIX and ASA Course Number: 642 523 Length: 1 Day(s) Course Overview This course is part of the training for the Cisco Certified Security Professional and the Cisco Firewall
Step-by-Step Configuration
 Step-by-Step Configuration Kerio Technologies Kerio Technologies. All Rights Reserved. Printing Date: August 15, 2007 This guide provides detailed description on configuration of the local network which
Step-by-Step Configuration Kerio Technologies Kerio Technologies. All Rights Reserved. Printing Date: August 15, 2007 This guide provides detailed description on configuration of the local network which
The Domain Name System
 DNS " This is the means by which we can convert names like news.bbc.co.uk into IP addresses like 212.59.226.30 " Purely for the benefit of human users: we can remember numbers (e.g., telephone numbers),
DNS " This is the means by which we can convert names like news.bbc.co.uk into IP addresses like 212.59.226.30 " Purely for the benefit of human users: we can remember numbers (e.g., telephone numbers),
FWSM introduction Intro 5/1
 Intro 5/0 Content: FWSM introduction Requirements for FWSM 3.2 How the Firewall Services Module Works with the Switch Using the MSFC Firewall Mode Overview Stateful Inspection Overview Security Context
Intro 5/0 Content: FWSM introduction Requirements for FWSM 3.2 How the Firewall Services Module Works with the Switch Using the MSFC Firewall Mode Overview Stateful Inspection Overview Security Context
Firewall Firewall August, 2003
 Firewall August, 2003 1 Firewall and Access Control This product also serves as an Internet firewall, not only does it provide a natural firewall function (Network Address Translation, NAT), but it also
Firewall August, 2003 1 Firewall and Access Control This product also serves as an Internet firewall, not only does it provide a natural firewall function (Network Address Translation, NAT), but it also
Firewall Defaults, Public Server Rule, and Secondary WAN IP Address
 Firewall Defaults, Public Server Rule, and Secondary WAN IP Address This quick start guide provides the firewall defaults and explains how to configure some basic firewall rules for the ProSafe Wireless-N
Firewall Defaults, Public Server Rule, and Secondary WAN IP Address This quick start guide provides the firewall defaults and explains how to configure some basic firewall rules for the ProSafe Wireless-N
Linux Squid Proxy Server
 Linux Squid Proxy Server Descriptions and Purpose of Lab Exercise Squid is caching proxy server, which improves the bandwidth and the reponse time by caching the recently requested web pages. Now a days
Linux Squid Proxy Server Descriptions and Purpose of Lab Exercise Squid is caching proxy server, which improves the bandwidth and the reponse time by caching the recently requested web pages. Now a days
Building a Linux IPv6 DNS Server
 Building a Linux IPv6 DS Server By David Gordon and Ibrahim Haddad Open Systems Lab Ericsson Research Corporate Unit This article presents a tutorial on building an IPv6 DS Linux server that provides IPv6
Building a Linux IPv6 DS Server By David Gordon and Ibrahim Haddad Open Systems Lab Ericsson Research Corporate Unit This article presents a tutorial on building an IPv6 DS Linux server that provides IPv6
Broadband Phone Gateway BPG510 Technical Users Guide
 Broadband Phone Gateway BPG510 Technical Users Guide (Firmware version 0.14.1 and later) Revision 1.0 2006, 8x8 Inc. Table of Contents About your Broadband Phone Gateway (BPG510)... 4 Opening the BPG510's
Broadband Phone Gateway BPG510 Technical Users Guide (Firmware version 0.14.1 and later) Revision 1.0 2006, 8x8 Inc. Table of Contents About your Broadband Phone Gateway (BPG510)... 4 Opening the BPG510's
Securing an Internet Name Server
 Securing an Internet Name Server Cricket Liu [email protected] Securing an Internet Name Server Name servers exposed to the Internet are subject to a wide variety of attacks: Attacks against the name
Securing an Internet Name Server Cricket Liu [email protected] Securing an Internet Name Server Name servers exposed to the Internet are subject to a wide variety of attacks: Attacks against the name
Virtual Web Appliance Setup Guide
 Virtual Web Appliance Setup Guide 2 Sophos Installing a Virtual Appliance Installing a Virtual Appliance This guide describes the procedures for installing a Virtual Web Appliance. If you are installing
Virtual Web Appliance Setup Guide 2 Sophos Installing a Virtual Appliance Installing a Virtual Appliance This guide describes the procedures for installing a Virtual Web Appliance. If you are installing
NSi Mobile Installation Guide. Version 6.2
 NSi Mobile Installation Guide Version 6.2 Revision History Version Date 1.0 October 2, 2012 2.0 September 18, 2013 2 CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS PREFACE... 5 Purpose of this Document... 5 Version Compatibility...
NSi Mobile Installation Guide Version 6.2 Revision History Version Date 1.0 October 2, 2012 2.0 September 18, 2013 2 CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS PREFACE... 5 Purpose of this Document... 5 Version Compatibility...
HOWTO: Set up a Vyatta device with ThreatSTOP in router mode
 HOWTO: Set up a Vyatta device with ThreatSTOP in router mode Overview This document explains how to set up a minimal Vyatta device in a routed configuration and then how to apply ThreatSTOP to it. It is
HOWTO: Set up a Vyatta device with ThreatSTOP in router mode Overview This document explains how to set up a minimal Vyatta device in a routed configuration and then how to apply ThreatSTOP to it. It is
DNS Resolving using nslookup
 DNS Resolving using nslookup Oliver Hohlfeld & Andre Schröder January 8, 2007 Abstract This report belongs to a talk given at the networking course (Institue Eurecom, France) in January 2007. It is based
DNS Resolving using nslookup Oliver Hohlfeld & Andre Schröder January 8, 2007 Abstract This report belongs to a talk given at the networking course (Institue Eurecom, France) in January 2007. It is based
AutoDownload: SQL Server and Network Trouble Shooting
 AutoDownload: SQL Server and Network Trouble Shooting AutoDownload uses Microsoft s SQL Server database software. Since 2005 when AutoDownload was first released Microsoft have also released new versions
AutoDownload: SQL Server and Network Trouble Shooting AutoDownload uses Microsoft s SQL Server database software. Since 2005 when AutoDownload was first released Microsoft have also released new versions
H3C Firewall and UTM Devices DNS and NAT Configuration Examples (Comware V5)
 H3C Firewall and UTM Devices DNS and NAT Configuration Examples (Comware V5) Copyright 2015 Hangzhou H3C Technologies Co., Ltd. All rights reserved. No part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted
H3C Firewall and UTM Devices DNS and NAT Configuration Examples (Comware V5) Copyright 2015 Hangzhou H3C Technologies Co., Ltd. All rights reserved. No part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted
Configuring PA Firewalls for a Layer 3 Deployment
 Configuring PA Firewalls for a Layer 3 Deployment Configuring PAN Firewalls for a Layer 3 Deployment Configuration Guide January 2009 Introduction The following document provides detailed step-by-step
Configuring PA Firewalls for a Layer 3 Deployment Configuring PAN Firewalls for a Layer 3 Deployment Configuration Guide January 2009 Introduction The following document provides detailed step-by-step
Websense Content Gateway v7.x: Troubleshooting
 Websense Content Gateway v7.x: Troubleshooting Topic 60042 Content Gateway Troubleshooting Updated: 28-October-2013 Dropped HTTPS connections Websites that have difficulty transiting Content Gateway Low
Websense Content Gateway v7.x: Troubleshooting Topic 60042 Content Gateway Troubleshooting Updated: 28-October-2013 Dropped HTTPS connections Websites that have difficulty transiting Content Gateway Low
SI455 Advanced Computer Networking. Lab2: Adding DNS and Email Servers (v1.0) Due 6 Feb by start of class
 SI455 Advanced Computer Networking Lab2: Adding DNS and Email Servers (v1.0) Due 6 Feb by start of class WHAT TO HAND IN: 1. Completed checklist from the last page of this document 2. 2-4 page write-up
SI455 Advanced Computer Networking Lab2: Adding DNS and Email Servers (v1.0) Due 6 Feb by start of class WHAT TO HAND IN: 1. Completed checklist from the last page of this document 2. 2-4 page write-up
Smart Tips. Enabling WAN Load Balancing. Key Features. Network Diagram. Overview. Featured Products. WAN Failover. Enabling WAN Load Balancing Page 1
 Smart Tips Enabling WAN Load Balancing Overview Many small businesses today use broadband links such as DSL or Cable, favoring them over the traditional link such as T1/E1 or leased lines because of the
Smart Tips Enabling WAN Load Balancing Overview Many small businesses today use broadband links such as DSL or Cable, favoring them over the traditional link such as T1/E1 or leased lines because of the
GlobalSCAPE DMZ Gateway, v1. User Guide
 GlobalSCAPE DMZ Gateway, v1 User Guide GlobalSCAPE, Inc. (GSB) Address: 4500 Lockhill-Selma Road, Suite 150 San Antonio, TX (USA) 78249 Sales: (210) 308-8267 Sales (Toll Free): (800) 290-5054 Technical
GlobalSCAPE DMZ Gateway, v1 User Guide GlobalSCAPE, Inc. (GSB) Address: 4500 Lockhill-Selma Road, Suite 150 San Antonio, TX (USA) 78249 Sales: (210) 308-8267 Sales (Toll Free): (800) 290-5054 Technical
Lab - Observing DNS Resolution
 Objectives Part 1: Observe the DNS Conversion of a URL to an IP Address Part 2: Observe DNS Lookup Using the nslookup Command on a Web Site Part 3: Observe DNS Lookup Using the nslookup Command on Mail
Objectives Part 1: Observe the DNS Conversion of a URL to an IP Address Part 2: Observe DNS Lookup Using the nslookup Command on a Web Site Part 3: Observe DNS Lookup Using the nslookup Command on Mail
THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY Department of Electronic and Information Engineering
 THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY Department of Electronic and Information Engineering ENG 224 Information Technology Laboratory 6: Internet Connection Sharing Objectives: Build a private network that
THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY Department of Electronic and Information Engineering ENG 224 Information Technology Laboratory 6: Internet Connection Sharing Objectives: Build a private network that
INTRODUCTION TO FIREWALL SECURITY
 INTRODUCTION TO FIREWALL SECURITY SESSION 1 Agenda Introduction to Firewalls Types of Firewalls Modes and Deployments Key Features in a Firewall Emerging Trends 2 Printed in USA. What Is a Firewall DMZ
INTRODUCTION TO FIREWALL SECURITY SESSION 1 Agenda Introduction to Firewalls Types of Firewalls Modes and Deployments Key Features in a Firewall Emerging Trends 2 Printed in USA. What Is a Firewall DMZ
Using Webmin and Bind9 to Setup DNS Sever on Linux
 Global Open Versity Systems Integration Hands-on Labs Training Manual Using Webmin and Bind9 to Setup DNS Sever on Linux By Kefa Rabah, [email protected] March 2008 Installing and Configuring
Global Open Versity Systems Integration Hands-on Labs Training Manual Using Webmin and Bind9 to Setup DNS Sever on Linux By Kefa Rabah, [email protected] March 2008 Installing and Configuring
Firewalling with OpenBSD and PF
 Firewalling with OpenBSD and PF Written by Kevin Korb September 5, 2007 1 What is a firewall? A firewall is a router that has rules defining what kinds of packets are routed and what kinds aren t. It is
Firewalling with OpenBSD and PF Written by Kevin Korb September 5, 2007 1 What is a firewall? A firewall is a router that has rules defining what kinds of packets are routed and what kinds aren t. It is
Network Security. Chapter 3. Cornelius Diekmann. Version: October 21, 2015. Lehrstuhl für Netzarchitekturen und Netzdienste Institut für Informatik
 Network Security Chapter 3 Cornelius Diekmann Lehrstuhl für Netzarchitekturen und Netzdienste Institut für Informatik Version: October 21, 2015 IN2101, WS 15/16, Network Security 1 Security Policies and
Network Security Chapter 3 Cornelius Diekmann Lehrstuhl für Netzarchitekturen und Netzdienste Institut für Informatik Version: October 21, 2015 IN2101, WS 15/16, Network Security 1 Security Policies and
REQUIREMENTS AND INSTALLATION OF THE NEFSIS DEDICATED SERVER
 NEFSIS TRAINING SERIES Nefsis Dedicated Server version 5.1.0.XXX Requirements and Implementation Guide (Rev 4-10209) REQUIREMENTS AND INSTALLATION OF THE NEFSIS DEDICATED SERVER Nefsis Training Series
NEFSIS TRAINING SERIES Nefsis Dedicated Server version 5.1.0.XXX Requirements and Implementation Guide (Rev 4-10209) REQUIREMENTS AND INSTALLATION OF THE NEFSIS DEDICATED SERVER Nefsis Training Series
Installing and Configuring Websense Content Gateway
 Installing and Configuring Websense Content Gateway Websense Support Webinar - September 2009 web security data security email security Support Webinars 2009 Websense, Inc. All rights reserved. Webinar
Installing and Configuring Websense Content Gateway Websense Support Webinar - September 2009 web security data security email security Support Webinars 2009 Websense, Inc. All rights reserved. Webinar
Firewall Defaults and Some Basic Rules
 Firewall Defaults and Some Basic Rules ProSecure UTM Quick Start Guide This quick start guide provides the firewall defaults and explains how to configure some basic firewall rules for the ProSecure Unified
Firewall Defaults and Some Basic Rules ProSecure UTM Quick Start Guide This quick start guide provides the firewall defaults and explains how to configure some basic firewall rules for the ProSecure Unified
Local DNS Attack Lab. 1 Lab Overview. 2 Lab Environment. SEED Labs Local DNS Attack Lab 1
 SEED Labs Local DNS Attack Lab 1 Local DNS Attack Lab Copyright c 2006 Wenliang Du, Syracuse University. The development of this document was partially funded by the National Science Foundation s Course,
SEED Labs Local DNS Attack Lab 1 Local DNS Attack Lab Copyright c 2006 Wenliang Du, Syracuse University. The development of this document was partially funded by the National Science Foundation s Course,
Network setup and troubleshooting
 ACTi Knowledge Base Category: Troubleshooting Note Sub-category: Network Model: All Firmware: All Software: NVR Author: Jane.Chen Published: 2009/12/21 Reviewed: 2010/10/11 Network setup and troubleshooting
ACTi Knowledge Base Category: Troubleshooting Note Sub-category: Network Model: All Firmware: All Software: NVR Author: Jane.Chen Published: 2009/12/21 Reviewed: 2010/10/11 Network setup and troubleshooting
Troubleshooting the Firewall Services Module
 25 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to troubleshoot the FWSM, and includes the following sections: Testing Your Configuration, page 25-1 Reloading the FWSM, page 25-6 Performing Password Recovery, page
25 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to troubleshoot the FWSM, and includes the following sections: Testing Your Configuration, page 25-1 Reloading the FWSM, page 25-6 Performing Password Recovery, page
Firewall VPN Router. Quick Installation Guide M73-APO09-380
 Firewall VPN Router Quick Installation Guide M73-APO09-380 Firewall VPN Router Overview The Firewall VPN Router provides three 10/100Mbit Ethernet network interface ports which are the Internal/LAN, External/WAN,
Firewall VPN Router Quick Installation Guide M73-APO09-380 Firewall VPN Router Overview The Firewall VPN Router provides three 10/100Mbit Ethernet network interface ports which are the Internal/LAN, External/WAN,
Network Traffic Analysis
 2013 Network Traffic Analysis Gerben Kleijn and Terence Nicholls 6/21/2013 Contents Introduction... 3 Lab 1 - Installing the Operating System (OS)... 3 Lab 2 Working with TCPDump... 4 Lab 3 - Installing
2013 Network Traffic Analysis Gerben Kleijn and Terence Nicholls 6/21/2013 Contents Introduction... 3 Lab 1 - Installing the Operating System (OS)... 3 Lab 2 Working with TCPDump... 4 Lab 3 - Installing
Quick Note 052. Connecting to Digi Remote Manager SM Through Web Proxy
 Quick Note 052 Connecting to Digi Remote Manager SM Through Web Proxy Digi Product Management August 2015 Contents 1 Document Version...2 2 Abstract...3 3 Introduction...3 4 Web Proxy Configuration...4
Quick Note 052 Connecting to Digi Remote Manager SM Through Web Proxy Digi Product Management August 2015 Contents 1 Document Version...2 2 Abstract...3 3 Introduction...3 4 Web Proxy Configuration...4
Virtual Managment Appliance Setup Guide
 Virtual Managment Appliance Setup Guide 2 Sophos Installing a Virtual Appliance Installing a Virtual Appliance As an alternative to the hardware-based version of the Sophos Web Appliance, you can deploy
Virtual Managment Appliance Setup Guide 2 Sophos Installing a Virtual Appliance Installing a Virtual Appliance As an alternative to the hardware-based version of the Sophos Web Appliance, you can deploy
Quick Start for Network Agent. 5-Step Quick Start. What is Network Agent?
 What is Network Agent? The Websense Network Agent software component uses sniffer technology to monitor all of the internet traffic on the network machines that you assign to it. Network Agent filters
What is Network Agent? The Websense Network Agent software component uses sniffer technology to monitor all of the internet traffic on the network machines that you assign to it. Network Agent filters
Understanding and Configuring NAT Tech Note PAN-OS 4.1
 Understanding and Configuring NAT Tech Note PAN-OS 4.1 Revision C 2012, Palo Alto Networks, Inc. www.paloaltonetworks.com Contents Overview... 3 Scope... 3 Design Consideration... 3 Software requirement...
Understanding and Configuring NAT Tech Note PAN-OS 4.1 Revision C 2012, Palo Alto Networks, Inc. www.paloaltonetworks.com Contents Overview... 3 Scope... 3 Design Consideration... 3 Software requirement...
Step-by-Step Configuration
 Step-by-Step Configuration Kerio Technologies C 2001-2003 Kerio Technologies. All Rights Reserved. Printing Date: December 17, 2003 This guide provides detailed description on configuration of the local
Step-by-Step Configuration Kerio Technologies C 2001-2003 Kerio Technologies. All Rights Reserved. Printing Date: December 17, 2003 This guide provides detailed description on configuration of the local
Lab - Observing DNS Resolution
 Objectives Part 1: Observe the DNS Conversion of a URL to an IP Address Part 2: Observe DNS Lookup Using the Nslookup Command on a Web Site Part 3: Observe DNS Lookup Using the Nslookup Command on Mail
Objectives Part 1: Observe the DNS Conversion of a URL to an IP Address Part 2: Observe DNS Lookup Using the Nslookup Command on a Web Site Part 3: Observe DNS Lookup Using the Nslookup Command on Mail
How to Create, Setup, and Configure an Ubuntu Router with a Transparent Proxy.
 In this tutorial I am going to explain how to setup a home router with transparent proxy using Linux Ubuntu and Virtualbox. Before we begin to delve into the heart of installing software and typing in
In this tutorial I am going to explain how to setup a home router with transparent proxy using Linux Ubuntu and Virtualbox. Before we begin to delve into the heart of installing software and typing in
Firewall implementation and testing
 Firewall implementation and testing Patrik Ragnarsson, Niclas Gustafsson E-mail: [email protected], [email protected] Supervisor: David Byers, [email protected] Project Report for Information
Firewall implementation and testing Patrik Ragnarsson, Niclas Gustafsson E-mail: [email protected], [email protected] Supervisor: David Byers, [email protected] Project Report for Information
How to Secure RHEL 6.2 Part 2
 How to Secure RHEL 6.2 Part 2 Motivation This paper is part of a multi-part series on securing Redhat Enterprise Linux 6.2. This paper focuses on implementing IPtables as a host based firewall. If you
How to Secure RHEL 6.2 Part 2 Motivation This paper is part of a multi-part series on securing Redhat Enterprise Linux 6.2. This paper focuses on implementing IPtables as a host based firewall. If you
ISERink Installation Guide
 ISERink Installation Guide Version 1.1 January 27, 2015 First developed to support cyber defense competitions (CDCs), ISERink is a virtual laboratory environment that allows students an opportunity to
ISERink Installation Guide Version 1.1 January 27, 2015 First developed to support cyber defense competitions (CDCs), ISERink is a virtual laboratory environment that allows students an opportunity to
Password Reset PRO. Quick Setup Guide for Single Server or Two-Tier Installation
 Password Reset PRO Quick Setup Guide for Single Server or Two-Tier Installation This guide covers the features and settings available in Password Reset PRO version 3.x.x. Please read this guide completely
Password Reset PRO Quick Setup Guide for Single Server or Two-Tier Installation This guide covers the features and settings available in Password Reset PRO version 3.x.x. Please read this guide completely
Firewalls. Firewalls. Idea: separate local network from the Internet 2/24/15. Intranet DMZ. Trusted hosts and networks. Firewall.
 Firewalls 1 Firewalls Idea: separate local network from the Internet Trusted hosts and networks Firewall Intranet Router DMZ Demilitarized Zone: publicly accessible servers and networks 2 1 Castle and
Firewalls 1 Firewalls Idea: separate local network from the Internet Trusted hosts and networks Firewall Intranet Router DMZ Demilitarized Zone: publicly accessible servers and networks 2 1 Castle and
Lesson Plans Managing a Windows 2003 Network Infrastructure
 Lesson Plans Managing a Windows 2003 Network Infrastructure (Exam 70-291) Table of Contents Course Overview... 2 Section 0.1: Introduction... 3 Section 1.1: Client Configuration... 4 Section 1.2: IP Addressing...
Lesson Plans Managing a Windows 2003 Network Infrastructure (Exam 70-291) Table of Contents Course Overview... 2 Section 0.1: Introduction... 3 Section 1.1: Client Configuration... 4 Section 1.2: IP Addressing...
Lab 8.4.2 Configuring Access Policies and DMZ Settings
 Lab 8.4.2 Configuring Access Policies and DMZ Settings Objectives Log in to a multi-function device and view security settings. Set up Internet access policies based on IP address and application. Set
Lab 8.4.2 Configuring Access Policies and DMZ Settings Objectives Log in to a multi-function device and view security settings. Set up Internet access policies based on IP address and application. Set
1 Data information is sent onto the network cable using which of the following? A Communication protocol B Data packet
 Review questions 1 Data information is sent onto the network cable using which of the following? A Communication protocol B Data packet C Media access method D Packages 2 To which TCP/IP architecture layer
Review questions 1 Data information is sent onto the network cable using which of the following? A Communication protocol B Data packet C Media access method D Packages 2 To which TCP/IP architecture layer
Hosting more than one FortiOS instance on. VLANs. 1. Network topology
 Hosting more than one FortiOS instance on a single FortiGate unit using VDOMs and VLANs 1. Network topology Use Virtual domains (VDOMs) to divide the FortiGate unit into two or more virtual instances of
Hosting more than one FortiOS instance on a single FortiGate unit using VDOMs and VLANs 1. Network topology Use Virtual domains (VDOMs) to divide the FortiGate unit into two or more virtual instances of
Syncplicity On-Premise Storage Connector
 Syncplicity On-Premise Storage Connector Implementation Guide Abstract This document explains how to install and configure the Syncplicity On-Premise Storage Connector. In addition, it also describes how
Syncplicity On-Premise Storage Connector Implementation Guide Abstract This document explains how to install and configure the Syncplicity On-Premise Storage Connector. In addition, it also describes how
Firewalls. Pehr Söderman KTH-CSC [email protected]
 Firewalls Pehr Söderman KTH-CSC [email protected] 1 Definition A firewall is a network device that separates two parts of a network, enforcing a policy for all traversing traffic. 2 Fundamental requirements
Firewalls Pehr Söderman KTH-CSC [email protected] 1 Definition A firewall is a network device that separates two parts of a network, enforcing a policy for all traversing traffic. 2 Fundamental requirements
Load Balancing for esafe Gateway 3.0 when using Alteon s AD2 or AD3
 Load Balancing for esafe Gateway 3.0 when using Alteon s AD2 or AD3 page 3 Load Balancing for esafe Gateway 3.0 when using Alteon s AD2 or AD3 This document describes how to setup and configure Alteon
Load Balancing for esafe Gateway 3.0 when using Alteon s AD2 or AD3 page 3 Load Balancing for esafe Gateway 3.0 when using Alteon s AD2 or AD3 This document describes how to setup and configure Alteon
Implementing Network Address Translation and Port Redirection in epipe
 Implementing Network Address Translation and Port Redirection in epipe Contents 1 Introduction... 2 2 Network Address Translation... 2 2.1 What is NAT?... 2 2.2 NAT Redirection... 3 2.3 Bimap... 4 2.4
Implementing Network Address Translation and Port Redirection in epipe Contents 1 Introduction... 2 2 Network Address Translation... 2 2.1 What is NAT?... 2 2.2 NAT Redirection... 3 2.3 Bimap... 4 2.4
Firewalls 1 / 43. Firewalls
 What s a Firewall Why Use? Tradttional by Analogy Should We Fix the Network Protocols Instead? Firewall Advantages Schematic of a Firewall Conceptual Pieces The DMZ Positioning Why Administrative Domains?
What s a Firewall Why Use? Tradttional by Analogy Should We Fix the Network Protocols Instead? Firewall Advantages Schematic of a Firewall Conceptual Pieces The DMZ Positioning Why Administrative Domains?
Appendix D: Configuring Firewalls and Network Address Translation
 Appendix D: Configuring Firewalls and Network Address Translation The configuration information in this appendix will help the network administrator plan and configure the network architecture for Everserve.
Appendix D: Configuring Firewalls and Network Address Translation The configuration information in this appendix will help the network administrator plan and configure the network architecture for Everserve.
Password Reset PRO INSTALLATION GUIDE
 Password Reset PRO INSTALLATION GUIDE This guide covers the new features and settings available in Password Reset PRO. Please read this guide completely to ensure a trouble-free installation. March 2009
Password Reset PRO INSTALLATION GUIDE This guide covers the new features and settings available in Password Reset PRO. Please read this guide completely to ensure a trouble-free installation. March 2009
F-SECURE MESSAGING SECURITY GATEWAY
 F-SECURE MESSAGING SECURITY GATEWAY DEFAULT SETUP GUIDE This guide describes how to set up and configure the F-Secure Messaging Security Gateway appliance in a basic e-mail server environment. AN EXAMPLE
F-SECURE MESSAGING SECURITY GATEWAY DEFAULT SETUP GUIDE This guide describes how to set up and configure the F-Secure Messaging Security Gateway appliance in a basic e-mail server environment. AN EXAMPLE
Deployment Guide AX Series with Active Directory Federation Services 2.0 and Office 365
 Deployment Guide AX Series with Active Directory Federation Services 2.0 and Office 365 DG_ADFS20_120907.1 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Overview... 4 2 Deployment Guide Overview... 4 3 Deployment Guide Prerequisites...
Deployment Guide AX Series with Active Directory Federation Services 2.0 and Office 365 DG_ADFS20_120907.1 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Overview... 4 2 Deployment Guide Overview... 4 3 Deployment Guide Prerequisites...
Technical Support Information Belkin internal use only
 The fundamentals of TCP/IP networking TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocols) is a set of networking protocols that is used for communication on the Internet and on many other networks.
The fundamentals of TCP/IP networking TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocols) is a set of networking protocols that is used for communication on the Internet and on many other networks.
Proxy Server, Network Address Translator, Firewall. Proxy Server
 Proxy Server, Network Address Translator, Firewall 1 Proxy Server 2 1 Introduction What is a proxy server? Acts on behalf of other clients, and presents requests from other clients to a server. Acts as
Proxy Server, Network Address Translator, Firewall 1 Proxy Server 2 1 Introduction What is a proxy server? Acts on behalf of other clients, and presents requests from other clients to a server. Acts as
Configuring DNS. Finding Feature Information
 The Domain Name System (DNS) is a distributed database in which you can map hostnames to IP addresses through the DNS protocol from a DNS server. Each unique IP address can have an associated hostname.
The Domain Name System (DNS) is a distributed database in which you can map hostnames to IP addresses through the DNS protocol from a DNS server. Each unique IP address can have an associated hostname.
MN-700 Base Station Configuration Guide
 MN-700 Base Station Configuration Guide Contents pen the Base Station Management Tool...3 Log ff the Base Station Management Tool...3 Navigate the Base Station Management Tool...4 Current Base Station
MN-700 Base Station Configuration Guide Contents pen the Base Station Management Tool...3 Log ff the Base Station Management Tool...3 Navigate the Base Station Management Tool...4 Current Base Station
Troubleshooting the Firewall Services Module
 CHAPTER 25 This chapter describes how to troubleshoot the FWSM, and includes the following sections: Testing Your Configuration, page 25-1 Reloading the FWSM, page 25-6 Performing Password Recovery, page
CHAPTER 25 This chapter describes how to troubleshoot the FWSM, and includes the following sections: Testing Your Configuration, page 25-1 Reloading the FWSM, page 25-6 Performing Password Recovery, page
Installation and Deployment
 Installation and Deployment Help Documentation This document was auto-created from web content and is subject to change at any time. Copyright (c) 2016 SmarterTools Inc. Installation and Deployment SmarterStats
Installation and Deployment Help Documentation This document was auto-created from web content and is subject to change at any time. Copyright (c) 2016 SmarterTools Inc. Installation and Deployment SmarterStats
