1.a Number of broadband Internet retail lines, by type of access technology and by class of service (defined in terms of downstream speed)
|
|
|
- Berniece Horn
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 QUARTERLY QUESTIONNAIRE ON ELECTRONIC COMMUNICATION SERVICES AS A FIXED LOCATION AND NOMADIC VOIP SERVICES Fixed Telephone Service (FTS) Nomadic VoIP service Internet Access Services (IAS) Pay-TV Service 1. lines 1.1 Number of lines to the fixed telephone service 1.2 Number of lines to broadband Internet access service 1.3 Number of hotspots (Wi-FI) 1.a Number of broadband Internet retail lines, by type of access technology and by class of service (defined in terms of downstream speed) 2. Customers 2.1 Number of customers of the fixed telephone service 2.2 Number of Calling Cards, prepaid cards, etc. 2.3 Active Nomadic VoIP Service customers 2.4 Number of Internet access service customers 2.5 Number of pay-tv service subscibers 3. Customers of services provided in bundles 4. Traffic 4.1 Traffic volume of the telephone service at a fixed location 4.2 Traffic volume of the telephone service at a fixed location 4.3 Traffic volume of the broadband internet access service (in GB). 4.4 Traffic volume of pay-tv services (in GB). 5. Revenues 5.1 Revenues from telephone service at a fixed location (excludes Revenues from FTS offered as part of a bundle of services), (in euros, net of discounts) 5.2 Revenues from nomadic VoIP services (in euros, net of discounts) 5.3 Revenues from Internet access service ( excludes revenues from Internet access service offered as part of a bundle of services) 5.4 Revenues from pay-tv services (excludes revenues from pay-tv offered as part of a bundle of services) 5.5 Revenues from services offered in bundles Definitions
2 No. Indicators 1. Number of Lines 1.1. Number of Lines to the fixed telephone service (FTS) Number of lines of FTS, by support Number of lines installed at customer request Own infrastructure Copper Coaxial cable HFC (Hybrid Fibre Coaxial) PLC FTTx (of which) FTTN+VDSL (of which) FTTH/B Radio resources GSM/ GPRS/ UMTS/ CDMA FWA BWA Other radio resources (specify. Add as many rows as necessary) Others (specify. Add as many rows as necessary) Leased infrastructure Unbundled local loop WLR Leased Lines Resale Unbundled access to the fibre loop Optical fibre access on the terminal segment Other (specify. Add as many rows as necessary) Lines installed for use by the provider itself Own infrastructure Third party infrastructure No. of Public Payphones Own infrastructure Third party infrastructure Number of lines to the fixed telephone service, by type of access Analogue lines Digital lines ISDN lines Basic ISDN lines Direct equivalent basic ISDN lines Primary ISDN lines Direct equivalent primary ISDN lines Fractioned ISDN lines Direct equivalent fractioned ISDN lines Other digital lines (specify) Other equivalent digital lines Lines to Voice over Internet Service (VoIP)/VoB Other types of lines (specify. Add as many rows as necessary) 1.2. Number of broadband Internet retail lines, by type of access technology Number of ADSL lines, by type of access Own Network Unbundled Local Loop - Full Access Unbundled Local Loop - Shared Access Bitstream (aggregated ATM/IP/others) Resale Naked ADSL Other types of access (specify. Add as many rows as necessary) Number of lines via Cable Modem Number of FWA lines Number of lines over Optical Fibre (FTTH/B) Own Network Unbundled access to the fibre loop Optical fibre access on the terminal segment Wholesale broadband access Others (specify. Add as many rows as necessary) Number of lines via Leased Lines Number of lines via Satellite Number of lines using PLC Number of lines using other technologies (specify. Add as many rows as necessary) 1.3 Number of hotspots (Wi-FI)
3 INFORMATION TO BE REPORTED ON A SIX-MONTHLY BASIS: IN 2ND AND 4TH QUARTERS No. Indicators Quarter X 1a Number of broadband Internet retail lines, by type of access technology and by class of service (defined in terms of downstream speed) 0 1a.1 Number of xdsl lines, by class of service 0 1a Kbps < Speed < 2 Mbps 1a Mbps 1a Mbps < Speed < 10 Mbps 1a Mbps 1a Mbps < Speed < 20 Mbps 1a Mbps <= Speed < 30 Mbps 1a.1.7 1a.1.8 1a.1.9 Speed => 100 Mbps 1a.2 Number of lines via Cable Modem 0 1a Kbps < Speed < 2 Mbps 1a Mbps 1a Mbps < Speed < 10 Mbps 1a Mbps 1a Mbps < Speed < 20 Mbps 1a Mbps <= Speed < 30 Mbps 1a.2.7 1a.2.8 1a.2.9 Speed => 100 Mbps 1a.3 Number of FWA lines 0 1a Kbps < Speed < 2 Mbps 1a Mbps 1a Mbps < Speed < 10 Mbps 1a Mbps 1a Mbps < Speed < 20 Mbps 1a Mbps <= Speed < 30 Mbps 1a.3.7 1a.3.8 1a.3.9 Speed => 100 Mbps 1a.4 Number of lines over Optical Fibre (FTTH/B) 0 1a Kbps < Speed < 2 Mbps 1a Mbps 1a Mbps < Speed < 10 Mbps 1a Mbps 1a Mbps < Speed < 20 Mbps 1a Mbps <= Speed < 30 Mbps 1a.4.7 1a.4.8 1a.4.9 Speed => 100 Mbps 1a.5 Number of lines via Leased Lines 0 1a Kbps < Speed < 2 Mbps 1a Mbps 1a Mbps < Speed < 10 Mbps 1a Mbps 1a Mbps < Speed < 20 Mbps 1a Mbps <= Speed < 30 Mbps 1a.5.7 1a.5.8 1a.5.9 Speed => 100 Mbps 1a.6 Number of lines via Satellite 0 1a Kbps < Speed < 2 Mbps 1a Mbps 1a Mbps < Speed < 10 Mbps 1a Mbps 1a Mbps < Speed < 20 Mbps 1a Mbps <= Speed < 30 Mbps 1a.6.7 1a.6.8 1a.6.9 Speed => 100 Mbps 1a.7 Number of lines using PLC 0 1a Kbps < Speed < 2 Mbps 1a Mbps 1a Mbps < Speed < 10 Mbps 1a Mbps 1a Mbps < Speed < 20 Mbps 1a Mbps <= Speed < 30 Mbps 1a.7.7 1a.7.8 1a.7.9 Speed => 100 Mbps 1a.8 Number of lines using other technologies (specify. Add as many rows as necessary) 0 1a Kbps < Speed < 2 Mbps 1a Mbps 1a Mbps < Speed < 10 Mbps 1a Mbps 1a Mbps < Speed < 20 Mbps 1a Mbps <= Speed < 30 Mbps 1a.8.7 1a.8.8 1a.8.9 Speed => 100 Mbps
4 No. Indicators 2. Customers 2.1. Number of customers of the fixed telephone service (FTS) FTS direct access customers Residential FTS direct access customers Non-residential FTS direct access customers FTS Indirect Access customers Call by call selection customers Pre-selection customers Number of customers with services of calls which are free to the caller (800 prefix) No. of customers with shared cost calls (808 and 809 prefixes) No. of customers with personal number services (884 prefix) No. of customers with "universal access" services (707 and 708 prefixes) No. of customers with flat-rate call services (760, 761 and 762 prefix) 2.2 Number of Calling Cards, prepaid cards, etc Active Nomadic VoIP Service customers 2.4. Number of Internet access service customers Number of broadband Internet access service customers Number of Internet access service customers, by segment Residential offers Non-residential offers Total broadband Internet access service customers who were active during the period being reported Number of narrowband Internet access service customers (dial-up) of which non-residential narrowband Internet access service customers (dial-up) 2.5. Number of Pay-TV service subscribers Number of cable television service subscribers (of which) subscribers of service in digital format Number of satellite television (DTH) subscribers Number of pay-tv service subscribers over the public telephone network (xdsl/ip) Number of pay-tv service subscribers over FWA Number of subscribers of digital terrestrial television broadcasting service (DTT) Number of pay-tv service subscribers using other technologies (Specify. Add as many rows as necessary)
5 No. Indicators Quarter X 3. Number of subscribers to services provided in bundles 3.1 FTS + FBB 3.2 FTS + STV 3.3 FTS + MTS 3.4 FBB + STV 3.5 FBB + MTS 3.6 MTS + STV 3.7 FBB+MBB 3.8 MBB+FTS 3.9 STV+MBB 3.10 FTS + FBB + STV 3.11 FTS + MTS + FBB 3.12 FTS + MTS + STV 3.13 MTS + STV + FBB 3.14 MTS+MBB+STV 3.15 FTS+MBB+STV 3.16 FTS+MBB+FBB 3.17 FTS+MBB+MTS 3.18 FBB+MBB+MTS 3.19 FBB+MBB+STV 3.20 FTS+FBB+MBB+STV 3.21 FBB+FTS+MBB+MTS 3.22 FBB+FTS+STV+MTS 3.23 FBB+FTS+STV+MBB 3.24 Other bundles (specify, add as many rows as necessary)
6 No. Indicators Quarter X 4. TRAFFIC 4.1. Traffic volume of the telephone service at a fixed location Number of Calls National Traffic Direct Access (excluding payphones and excluding calling cards etc...) Intra-network voice calls Fixed inter-network voice calls Voice calls to Mobile networks Indirect Access (excluding payphones and calling cards excluding etc...) Intra-network voice calls Fixed inter-network voice calls Voice calls to Mobile networks National Calls access via calling cards, prepaid cards, etc National calls to numbers with prefixes: 800, 802, 808, 809, 884, 707, 708, 760, 761 and National calls to short numbers Other national calls originating on fixed telephone network Internet Access Calls of which through calling cards, prepaid cards, etc Outgoing international traffic Direct Access (excluding payphones and excluding calling cards etc...) Calls to fixed networks Calls to mobile networks Indirect Access (excluding payphones and calling cards excluding etc...) Calls to fixed networks Calls to mobile networks International outgoing traffic access via calling cards, prepaid cards, etc Traffic originating on public payphones National calls originated on payphones Outgoing international calls originating on payphones Calls from other traffic using calling cards, prepaid cards, etc Calls from other traffic (specify. Add as many rows as necessary) Number of Minutes National Traffic Direct Access (excluding payphones and excluding calling cards etc...) Minutes of intra-net Voice traffic Minutes of inter-network fixed Voice traffic Minutes of Voice traffic to mobile networks Indirect Access (excluding payphones and excluding calling cards etc...) Minutes of intra-net Voice traffic Minutes of fixed inter-network Voice traffic Minutes of Voice traffic to mobile networks Minutes of national traffic with access via calling cards, prepaid cards, etc Minutes of national traffic destined for numbers with prefixes: 800, 802, 808, 809, 884, 707, 708, 760, 761 and Minutes of national traffic to short numbers Minutes from other national traffic originating on fixed telephone network Number of Minutes of Internet Access of which through calling cards, prepaid cards, etc Outgoing international traffic Direct Access (excluding payphones and excluding calling cards etc...) Minutes of traffic to fixed networks Minutes of traffic to mobile networks Indirect Access (excluding payphones and excluding calling cards etc...) Minutes of traffic to fixed networks Minutes of traffic to mobile networks Minutes of outgoing international traffic access through calling cards, prepaid cards, etc Traffic originating on payphones Minutes of national traffic originated on payphones Minutes of outgoing international traffic originated on payphones Minutes from other traffic using calling cards, prepaid cards, etc Minutes of other traffic types. (Specify. Add as many rows as necessary) Data traffic generated by customers of the Fixed Telephone Service in GB 4.2 Volume of nomadic VoIP Service Traffic Number of Calls National nomadic VoIP Traffic Intra-net Nomadic VoIP calls Calls to other nomadic VoIP services Calls to FTS Calls to the MTS Calls to other non-geographic numbers and short numbers International outgoing nomadic VoIP traffic Number of Minutes National nomadic VoIP traffic Minutes of intra-network traffic Minutes of traffic to other nomadic VoIP services Minutes of traffic to FTS Minutes of traffic to MTS Minutes of Traffic to other non-geographic numbers and short numbers International outgoing nomadic VoIP traffic 4.3. Traffic volume of the broadband internet access service (in GB).
7 No. Indicators Quarter X 5. Revenues 5.1. Revenues from telephone service at a fixed location (excludes Revenues from FTS offered as part of a bundle of services), (in euros, net of discounts) Revenue from subscriptions, installation fees and supplementary services Traffic revenues Revenues from local, regional and national traffic originated on the fixed network Revenues from outgoing international traffic originated on the fixed network Revenues from fixed-mobile traffic on the fixed network Revenues from traffic originating on calling cards, prepaid cards, etc Revenues from traffic to services of calls which are free to the caller (800 prefix) Revenues from traffic to services of shared cost calls (808, 809 prefix) Revenues from traffic to personal number services (884 prefix) Revenues from traffic to services of "universal access" numbers (707 and 708 prefixes) Revenues from traffic to flat-rate call services (760, 761 and 762 prefix) Revenues from traffic to short numbers Revenues from traffic originating on public payphones Revenue associated with text messages Other revenues (specify. Add as many rows as necessary) 5.2 Revenues from nomadic VoIP services (in euros, net of discounts) Revenues from subscriptions and activation charges Revenues from originated traffic 5.3 Revenues from Internet access service ( excludes Internet access service offered as part of a bundle of services) 5.4 Revenues from subscription TV services (excludes STV offered as part of a bundle of services) 5.5 Revenues from services offered in bundles FTS + FBB FTS + STV FTS + MTS FBB + STV FBB + MTS MTS + STV FBB+MBB MBB+FTS STV+MBB FTS + FBB + STV FTS + MTS + FBB FTS + MTS + STV MTS + STV + FBB MTS+MBB+STV FTS+MBB+STV FTS+MBB+FBB FTS+MBB+MTS FBB+MBB+MTS FBB+MBB+STV FTS+FBB+MBB+STV FBB+FTS+MBB+MTS FBB+FTS+STV+MTS FBB+FTS+STV+MBB Other bundles (specify, add as many rows as necessary)
8 DEFINITIONS 1. Number of lines Access indicators must include the number of lines indicated below at the end of the respective period Number of lines to the fixed telephone service lines to Telephone service at a fixed location (FTS), provided by entities with a general authorisation to provide this service as well as by the universal service provider. lines allocated to the resale of telephone services at a fixed location, resale of voice telephone traffic, virtual private networks service (VPN) and GFU voice transport service. In the case of resale of lines, the provider entering into contract with the end-user shall be responsible for completion. (E.g. if the customer has a contract with the reseller, the reseller will be responsible for reporting the information). The field for this indicator does not require completion Number of lines to the FTS, by support This indicator is segmented according to supports which can be used to provide FTS. Non-equivalent access should be considered Number of lines installed at customer request Customer lines should be reported which are covered by a contractual relationship which is current at the end of the period being reported. That is, where a contractual relationship is terminated during the quarter, the lines associated with this contract should not be reported Own infrastructure Local access infrastructure access belonging to the operator Copper Traditional support technology used mostly by PT Comunicações, the incumbent operator Coaxial cable Transmission technology which uses a cable made up of a central copper wire,surrounded by a shield of braided copper wire,which is separated from the central wire by an insulating material separated by a material isolator. This type of cable is suitable for carrying electrical signals with higher frequencies than those supported by a simple metallic wire pair HFC (Hybrid Fibre Coaxial) Transmission technology which uses a broadband network which combines optical fibre with coaxial cable PLC Powerline Communications. Access technology which uses low voltage electricity cables for broadband voice and data transmission. The technology allows the use of a local domestic network,with which any energy socket can be used to provide high-speed Internet access, voice and fax services FTTx Broadband network architectures which use optical fibre over the whole or part of the local loop. There are different configurations with FTTN (Fiber to the node), FTTC (Fiber to the cabinet), FTTB (Fiber to the building) and FTTH (Fiber to the home) most widely used (of which) FTTN+VDSL Of the lines reported in the previous item,specify which are covered by FTTN+VDSL configuration, where broadband access is based on FTTN (Fiber to the node) technology and where VDSL (Very-high-bit-rate DSL) technology is used in the section up to the customer's house (of which) FTTH/B Fiber to the Building (FTTB): physical means of transmission based on optical fibre cables where the optical signal reaches as far as the building where the customer is located. However, the optical fibre terminates before reaching the customer's actual premises. Fiber to the Home (FTTH): physical means of transmission based on optical fibre cables, where the optical signal reaches as far as the customer's actual premises (residence of company) Radio resources GSM/ GPRS/ UMTS/ CDMA Access supported using frequencies allocated for the provision of the Mobile Telephone Service (MTS). ICP-ANACOM allows the use of frequencies assigned to GSM and UMTS networks for the provision of FTS, with imposition of limits on the mobility of the equipment to provide the service FWA Fixed Wireless Access. Access technology which allows operators to supply customers with a direct connection to their telecommunications network through a fixed wireless connection (FWA) between their premises and the operator's local exchange BWA Access technology which allows operators to supply customers with a direct connection to their telecommunications network through a wireless broadband connection (BWA) between their premises and the operator's local exchange Others (specify. Add as many rows as necessary) Identify other radio resources offered. In cases where more than one alternative radio resource is offered, the values for each one should be given separately. Add as many rows as necessary to provide this information Others (specify. Add as many rows as necessary) Identify other technologies used. Where more than one alternative technology is offered, the values for each one should be given separately. Add as many rows as necessary to provide this information Third party infrastructure Unbundled local loop Whole or partial use of the local loops of another operator between the customer premises and the local exchange for the provision of services to the end-user WLRO Wholesale Line Rental Offer in accordance with ICP-ANACOM determination of 14 December Leased Lines Telecommunications resource of a public network which provides transmission capacity between terminal points not involving user controlled switching functions. It is a permanent point to point circuit for exclusive use by its customer(s) and may be used for voice communication or for data or image transmission Resale Resale occurs when an operator receives and sells to end customers - without the possibility of adding value added features to the service - a commercial product which is identical to the one offered by the wholesale operator to its retail customers Unbundled access to the fibre loop Use of optical fibre local loops of another operator between the customer premises and the metropolitan Point of Presence (MPoP) to provide services to the end-user, in accordance with EC Recommendation of on regulated access to next generation access networks (NGA) Optical fibre access on the terminal segment Use of the terminal segment of the access network of another operator, including the cabling inside the building, to provide services to the end-user, in accordance with EC Recommendation of on regulated access to next generation access networks (NGA) Other (specify. Add as many rows as necessary) Identify other third party infrastructure used. Where more than one third party infrastructure is used, the values for each one should be given separately. Add as many rows as necessary to provide this information Lines installed for use by the provider itself Lines installed for use by the provider itself. It should be noted that lines associated with companies with which the provider has a controlling or group relationship should not be included in its own stock, and should be counted as "lines installed at customer request" Own infrastructure Third party infrastructure No. of Public Payphones Public payphone means terminal equipment to access the FTS, installed in public places, including restricted access, available to the general public, in the regime of a commercial offer Own infrastructure Public payphones whose access infrastructure is owned by the operator Third party infrastructure Public payphones whose access infrastructure is owned by third parties Number of lines to the fixed telephone service, by type of access Analogue lines lines which provide a single 64 kbit s channel, in principle to carry voice and data up to 56 kbit/s Digital lines ISDN lines Integrated Services Digital Network corresponds to a set of telecommunications infrastructure that enable the provision of connections between terminal points, supporting a wide range of telecommunications services, such as telephone and video conferencing. Access to this network can be achieved through basic or primary access, which corresponds to speeds of 128 Kbit/s and 2 Mbit/s respectively, excluding signalisation Basic ISDN lines ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network) lines with two channels of 64 kbit/s, to transport voice and data, and a 16 kbit/s, channel for signalisation Direct equivalent basic ISDN lines Total direct equivalent lines: this indicator (which should not exclude the provider's own stock) is the sum of the number of lines associated with the FTS supported in each installed access, and therefore should include the lines on which, even if at a residual level, FTS traffic is routed. In the case of basic ISDN lines, the total number of equivalent lines is two for each basic ISDN access Primary ISDN lines ISDN (Integrated Services Digital) lines with thirty channels of 64 kbit/s, to transport voice and data, one 16 kbit/s channel for signalisation and another channel for synchronization, with a global bit rate of 2 Mbit/s Direct equivalent primary ISDN lines Total direct equivalent lines: this indicator (which should not exclude the provider's own stock) is the sum of the number of lines associated with the FTS supported in each installed access, and therefore should include the lines on which, even if at a residual level, FTS traffic is routed. In the case of primary ISDN lines, the total number of equivalent lines is 30 for each primary ISDN access Fractioned ISDN lines Fractioned lines are parts of primary ISDN lines corresponding to the use of a fraction of n/30 channels of 64Kbit/s, where n is an integer that can vary between 1 and 29. Where n = 15, the fractioned access takes the designation of primary (access) resource Direct equivalent fractioned ISDN lines Total direct equivalent lines: this indicator (which should not exclude the provider's own stock) is the sum of the number of lines associated with the FTS supported in each installed access, and therefore should include the lines on which, even if at a residual level, FTS traffic is routed. In the case of fractioned ISDN lines the total number of equivalent lines is variable for each fractioned ISDN Other digital lines (specify) Identify other digital lines used. Where more than one alternative digital access is offered, the values for each one should be given separately. Add as many rows as necessary to provide this information Other equivalent digital lines Note the number of lines associated with FTS which are supported by other installed digital lines lines to Voice over Internet Service (VoIP)/VoB VoIP / VoB (voice over broadband) services allow the user to establish telephone calls over a data network such as the Internet, converting an analogue voice signal into a set of digital signals in the form of packets with IP addressing, which can be sent, for example, through an Internet connection (preferably broadband - VoB). See ICP-ANACOM position on VoIP services available at Other types of lines (specify. Add as many rows as necessary) lines should be reported here where associated with voice services via the internet provided at a fixed location and in conditions perceived as being equivalent to those of the traditional FTS. Includes VoIP/VoB services over FWA, DSL, cable or other fixed Internet access platforms that enable the offer of fixed telephony over IP protocol, but excludes software-based VoIP applications (e.g. VoIP via Skype, hotmail or Yahoo) and Nomadic VoIP. Identify other types of access used. Where more than one type of alternative access is used, the values for each one should be given separately. Add as many rows as necessary to provide this information Number of broadband Internet retail lines, by type of access technology Physical lines should be considered. For example, if 1 customer has more than 1 physical access, the reported value should correspond to the number of the customer's physical lines. and by class of service (defined in terms of downstream speed) For the present purpose, broadband means services which are characterized by the provision to end-users of asymmetric and speeds which, in the downstream direction (i.e. originating on the network and destined to the customer) exceed 144 Kbps Number of ADSL lines, by type of access Number of Internet access via ADSL, disaggregated by type of access Own Network ADSL broadband lines using own infrastructure Unbundled Local Loop - Full Access Broadband lines based on full access unbundled local loops, as defined in the respective wholesale offer (e.g.: PTC's RUO). Full access local loop bundling consists of full use of local loops of other operators between the customer premises and the local exchange to provide services to the end-user Unbundled Local Loop - Shared Access Broadband lines based on shared access unbundled local loops, as defined in the respective wholesale offer (e.g.: PTC's RUO). Shared access local loop bundling consists of partial use of local loops of other operators between the customer premises and the local exchange to provide services to the end-user Bitstream (aggregated ATM/IP/others) Broadband lines based on a bitstream offer, with ATM and/or IP aggregation or others, as referenced in the respective wholesale offer (e.g. PTC's "Rede ADSL PT" offer) Resale In contrast to bitstream access, resale occurs when an operator receives and sells to end customers - without the possibility of adding value added features to the DSL service - a commercial product which is identical to the DSL offered by the wholesale operator to its retail customers Naked ADSL "Naked DSL" (NDSL) is a form of wholesale offer that enables the provision of an ADSL service to the end-user, who is not required by the operator holding the local loop to engage (or maintain) a fixed telephone service Other types of access (specify. Add as many rows as necessary) Identify other types of access used. Where more than one type of access is used, the values for each one should be given separately. Add as many rows as necessary to provide this information Number of lines via Cable Modem Number of Internet lines via cable modem Number of FWA lines Number of Internet lines using FWA. Only one connection should be considered per access point, regardless of the estimated number of end-users Number of lines over Optical Fibre (FTTH/B) Number of Internet lines via Optical Fibre (FTTH / B). See definition in item Own Network Broadband access over Optical Fibre (FTTH / B) using own infrastructure Unbundled access to the fibre loop Broadband lines based on the unbundling of optical fibre local loops of another operator between the customer premises and the metropolitan Point of Presence (MPoP) to provide services to the end-user, in accordance with EC Recommendation of on regulated access to next generation access networks (NGA) Optical fibre access on the terminal segment Use of the terminal segment of the access network of another operator, including the cabling inside the building, to provide broadband services to the end-user, in accordance with EC Recommendation of on regulated access to next generation access networks (NGA) Wholesale broadband access Broadband lines based on wholesale offers using optical fibre networks (e.g. Bitstream offer or equivalent) in accordance with EC Recommendation of on regulated access to next generation access networks (NGA) Others (specify. Add as many rows as necessary) Other Optical Fibre Broadband lines (FTTH/B) Number of lines via Leased Lines Number of Internet lines using Leased Lines Number of lines via Satellite Number of Internet lines via satellite Number of lines using PLC Broadband Internet connections using Powerline Communications (PLC) - the use of low voltage electricity distribution networks for voice and data transmission. The number of Internet lines via PLC should be reported Number of lines using other technologies (specify. Add as many rows as necessary) Number of broadband internet lines using other technologies. Where more than one alternative technology is offered, the values of each one should be given separately. Add as many rows as necessary to provide this information. Only one connection should be considered per access point, regardless of the estimated number of end-users. Wi-Fi hotspots should not be considered for the purposes of this indicator. Number of Number of Wi-Fi hotspots with public access. 1.3 hotspots (Wi-FI)
9 1a Number of broadband Internet retail lines, broken down by technology type and class of service. Number of broadband Internet retail lines, by type of access technology and by class of service (defined in terms of downstream speed) Information to be sent every six months: 2nd Quarter and 4th Quarter. 1a.1 Number of xdsl lines, by class of service Number of xdsl Internet lines, broken down by class of service (in terms of downstream speed), in accordance with the contracted theoretical maximum speed. 1a Kbps < Speed < 2 Mbps 1a Mbps 1a Mbps < Speed < 10 Mbps 1a Mbps 1a Mbps < Speed < 20 Mbps 1a Mbps <= Speed < 30 Mbps 1a.1.7 1a.1.8 1a.1.9 Speed => 100 Mbps 1a.2 Number of lines via Cable Modem Number of Internet lines via cable modem, broken down by class of service (in terms of downstream speed), in accordance with the contracted theoretical maximum speed. 1a Kbps < Speed < 2 Mbps 1a Mbps 1a Mbps < Speed < 10 Mbps 1a Mbps 1a Mbps < Speed < 20 Mbps 1a Mbps <= Speed < 30 Mbps 1a.2.7 1a.2.8 1a.2.9 Speed => 100 Mbps 1a.3 Number of FWA lines Number of Internet lines using FWA, broken down by class of service (in terms of downstream speed), in accordance with the contracted theoretical maximum speed. Only one connection should be considered per access point, regardless of the estimated number of end-users. 1a Kbps < Speed < 2 Mbps 1a Mbps 1a Mbps < Speed < 10 Mbps 1a Mbps 1a Mbps < Speed < 20 Mbps 1a Mbps <= Speed < 30 Mbps 1a.3.7 1a.3.8 1a.3.9 Speed => 100 Mbps 1a.4 Number of lines over Optical Fibre (FTTH/B) Number of Internet lines using optical fibre, broken down by class of service (in terms of downstream speed), in accordance with the contracted theoretical maximum speed. 1a Kbps < Speed < 2 Mbps 1a Mbps 1a Mbps < Speed < 10 Mbps 1a Mbps 1a Mbps < Speed < 20 Mbps 1a Mbps <= Speed < 30 Mbps 1a.4.7 1a.4.8 1a.4.9 Speed => 100 Mbps 1a.5 Number of lines via Leased Lines Number of Internet lines using leased lines, broken down by class of service (in terms of downstream speed), in accordance with the contracted theoretical maximum speed. 1a Kbps < Speed < 2 Mbps 1a Mbps 1a Mbps < Speed < 10 Mbps 1a Mbps 1a Mbps < Speed < 20 Mbps 1a Mbps <= Speed < 30 Mbps 1a.5.7 1a.5.8 1a.5.9 Speed => 100 Mbps 1a.6 Number of lines via Satellite Number of Internet lines via satellite, broken down by class of service (in terms of downstream speed),in accordance with the contracted theoretical maximum speed. 1a Kbps < Speed < 2 Mbps 1a Mbps 1a Mbps < Speed < 10 Mbps 1a Mbps 1a Mbps < Speed < 20 Mbps 1a Mbps <= Speed < 30 Mbps 1a.6.7 1a.6.8 1a.6.9 Speed => 100 Mbps 1a.7 Number of lines using PLC Broadband Internet connections using Powerline Communications (PLC) - the use of low voltage electricity distribution networks for voice and data transmission. The number of Internet lines using PLC should be reported, broken down by class of service (in terms of downstream speed), in accordance with the contracted theoretical maximum speed. 1a Kbps < Speed < 2 Mbps 1a Mbps 1a Mbps < Speed < 10 Mbps 1a Mbps 1a Mbps < Speed < 20 Mbps 1a Mbps <= Speed < 30 Mbps 1a.7.7 1a.7.8 1a.7.9 Speed => 100 Mbps 1a.8 Number of lines using other technologies (specify. Add as many rows as Number of broadband internet lines using other technologies, broken down by class of service (in terms of downstream speed), in accordance with the contracted theoretical maximum speed. Where more than one alternative technology necessary) is offered, the values of each one should be given separately. Add as many rows as necessary to provide this information. Only one connection should be considered per access point, regardless of the estimated number of end-users. Wi-Fi hotspots should not be considered for the purposes of this indicator. 1a Kbps < Speed < 2 Mbps 1a Mbps 1a Mbps < Speed < 10 Mbps 1a Mbps 1a Mbps < Speed < 20 Mbps 1a Mbps <= Speed < 30 Mbps 1a.8.7 1a.8.8 1a.8.9 Speed => 100 Mbps 2. Customers Customer indicators should be reported considering the number of customers indicated below at the end of the respective period Number of customers of the fixed telephone service (FTS) Number of users covered by at least one contractual relationship in force at the end of the reporting period in respect of the considered services. The calculation of "total number of customers" of the fixed telephone service (FTS) is not performed, since a direct access customer of a given provider may simultaneously be an indirect access customer of other providers. As such, the indicators "total number of direct access customer" and "total number of indirect access customers" will be analyzed separately.on the other hand, the total number of indirect access customers is not obtained from the sum of the number of pre-selection customers and the number of call-by-call selection customer, since the same entity may have some pre-selected phone numbers and use others for call-to-call selection. Although a single entity with a contractual relationship established with the provider may correspond to more than one bill, the entity will actually be counted as a "customer" and not according to the number of invoices issued in its name. This item should also be used to report the customers of the resale of telephone services at a fixed location,resale of telephone voice traffic, virtual private networks (VPN) service and voice transport service on GFU.In the case of resale of telephone services at a fixed location or resale of voice telephone traffic, the provider that holds the contract with the end-user shall be responsible for completing the item. (E.g.: if the customer has a contract with the reseller, the reseller will be responsible for reporting this information). The fields for this indicator do not require completion FTS direct access customers All users covered by a contractual relationship in force should be counted as customers of the fixed telephone service (FTS), including FTS subscribers or subscribers to a package of services which includes FTS (e.g. double play, triple play and multiple play). Only direct access customers should be considered for this item. Direct access means that there is a line installed from the place where the client is domiciled and,if necessary, from the respective terminal equipment, to an entry point of a public switched telecommunications network. Access to the client will be guaranteed with own infrastructure in the final section of the network through the installation of cables or fixed wireless access equipment Residential FTS direct access customers Residential customers should be considered as users who mostly do not use the service in question as intermediate consumption of their economic activity. As a proxy, the classification resulting from the "NIF - Número de informação fiscal" (Tax Information Number) should be used (customers without NIF or with NIFs starting with 1 and 2 are non-business customers). Other equivalent criteria may be used, which should, in these cases, be explained Non-residential FTS direct access customers Non-residential customers should be considered as users who mostly use the service in question as intermediate consumption of their economic activity. As a proxy, the classification resulting from the "NIF - Número de informação fiscal" (Tax Information Number) should be used (customers with NIF not starting with 1 and 2 are business customers). Other equivalent criteria may be used, which should, in these cases, be explained FTS indirect access customers All users covered by a contractual relationship in force should be counted as customers of the fixed telephone service (FTS), including FTS subscribers or subscribers to a package of services which includes FTS (e.g. double play, triple play and multiple play), as at the end of the quarter being reported. Only indirect access customers should be considered for this item. Access which guarantees accessibility to all customers of a given supplier of the fixed telephone service to the services of other suppliers, known as carriers, or traffic transporters Call by call selection customers Call-by-call selection means the spot choice of the supplier of a fixed telephone service through which a determined telephone call is to be made. It implies the dialling of an initial code which gives access to the desired provider. This code is "10xy" where "xy" identifies the provider. In the case of call-by-call selection contractual obligations do not have to be established in writing and in each month of the quarter being reported only customers who have made calls during that same month must be counted Pre-selection customers Pre-selection corresponds to an indirect access modality that requires pre-designation of a provider, which means that all comprised calls will be automatically forwarded through this company without the company's identification code having to be dialled Number of customers with services of calls which are free to the caller (800 prefix) Customers of the operator should be counted who made calls to numbers with 800 prefixes, in the quarter being reported No. of customers with shared cost calls (808 and 809 prefixes) Customers of the operator should be counted who made calls to numbers with 808 and 809 prefixes, in the quarter being reported No. of customers with personal number services (884 prefix) No. of customers with "universal access" services (707 and 708 prefixes) No. of customers with flat-rate call services (760, 761 and 762 prefix) Customers of the operator should be counted who made calls to numbers with 884 prefixes, during the quarter being reported Customers of the operator should be counted who made calls to numbers with 707 and 708 prefixes, during the quarter being reported Customers of the operator should be counted who made calls to numbers with 760, 761 and 762 prefixes, during the quarter being reported 2.2. Number of Calling Cards, prepaid cards, etc. This item is used to report users of the virtual calling card service, which is a service that allows the user to make telephone calls by dialling a specific access code of the National Numbering Plan (''882xy''), with two relevant features: billing/collection and mobility. So that the user is able to make calls, the account associated with the card needs to be identified and authenticated (e.g. number and PIN) based on a set of dialled characters, whereas the account associated with the dialled identification is billed for the cost of the call. Cards meant for use in public payphones to access the FTS which do not have characteristics of virtual calling cards should not be reported under this item. If the provider does not directly provide calling cards, prepaid cards, etc. to the end user, using third parties who are not operators/providers authorized for their resale,the cards sold by such entities/agents should be reported under this indicator.
10 2.3. Active Nomadic VoIP Service customers Users with a contractual relationship with the nomadic VoIP provider should be reported under this item where they have been allocated a numbering resource and have actually used the service during the quarter being reported, in terms of access for the origination or reception of calls. See ICP-ANACOM position on VoIP services available at Number of Internet access service customers Number of broadband Internet access service customers Number of Internet access service customers, by segment No. of customers covered, at least, by one contractual relationship in force, including as subscribers to an Internet access service or a package of services which includes the broadband Internet access service. For the present purpose, broadband means services which are characterized by the provision to end-users of asymmetric and speeds which, in the downstream direction (i.e. originating on the network and destined to the customer) exceed 144 Kbps Residential offers Residential customers should be considered as users who mostly do not use the service in question as intermediate consumption of their economic activity. As a proxy, the classification resulting from the "NIF - Número de informação fiscal" (Tax Information Number) should be used (customers without NIF or with NIFs starting with 1 and 2 are non-business customers). Other equivalent criteria may be used, which should, in these cases, be explained Non-residential offers Non-residential customers should be considered as users who mostly use the service in question as intermediate consumption of their economic activity. As a proxy, the classification resulting from the "NIF - Número de informação fiscal" (Tax Information Number) should be used (customers with NIF not starting with 1 and 2 are business customers). Other equivalent criteria may be used, which should, in these cases, be explained. Number of customers who accessed the internet access service at least once in the quarter in question. All customers in these conditions should be considered, even those who may have ceased to be customers of the service in this Total broadband Internet access service customers who were active during the period being reported quarter Number of narrowband Internet access service customers (dial-up) For the present purpose, narrowband means services which are characterized by the provision to end-users of asymmetric speeds which, in the downstream direction (i.e. originating on the network and destined for the customer) are less than or equal to 144 Kbps (maximum contracted speed) of which non-residential narrowband Internet access service customers (dialup) Number of non-residential customers with narrowband Internet access (Maximum contracted speed less than or equal to 144 Kbps) Number of pay-tv service subscribers Subscribers of all television signal broadcast or distribution services other than free-to-air services, including services included in bundles whose subscription/use involves payment Number of cable television service subscribers No. of customers covered by at least one contractual relationship in force, including as subscribers to the cable television service or to a bundle of services that includes the cable television service (e.g. double play, triple play or multiple play) as at the end of the quarter in question. Report "1 subscriber" per address, regardless of the number of services or bundles of services subscribed to (of which) subscribers of service in digital format Indicate the number of subscribers reported in who receive the signal in digital format (by using a set-top box or equivalent equipment) Number of satellite television (DTH) subscribers No.of customers covered by at least one contractual relationship in force,including as subscribers to the satellite television service (DTH) or to a bundle of services that includes the satellite television service (DTH) (e.g.double play, triple play or multiple play) as at the end of the quarter in question. Report "1 subscriber" per address, regardless of the number of services or bundles of services subscribed to Number of subscribers to television service over the public telephone network (xdsl/ip) No.of customers covered by at least one contractual relationship in force, including as subscribers to the television service over the public telephone network (xdsl/ip) or to a bundle of services that includes the television service over the public telephone network (xdsl/ip) (e.g. double play, triple play or multiple play) as at the end of the quarter in question. Report "1 subscriber" per address, regardless of the number of services or bundles of services subscribed to Number of pay TV services subscribers over FWA No. of customers covered by at least one contractual relationship in force, including as subscribers to the television service over FWA or to a bundle of services that includes the television service over FWA (e.g. double play, triple play or multiple play) as at the end of the quarter in question. Report "1 subscriber" per address, regardless of the number of services or bundles of services subscribed to Number of subscribers of digital terrestrial television broadcasting service (DTT) No. of customers covered by at least one contractual relationship in force, including as subscribers to the digital terrestrial television broadcasting services or to a bundle of services that includes the digital terrestrial television broadcasting services (e.g. double play, triple play or multiple play) as at the end of the quarter in question. Report "1 subscriber" per address, regardless of the number of services or bundles of services subscribed to Number of pay-tv service subscribers using other technologies (Specify. Add as many rows as necessary) No. of customers covered by at least one contractual relationship in force, including as subscribers to the television service using other technologies or a bundle of services that includes the television service using other technologies (e.g. double play, triple play or multiple play) as at the end of the quarter in question. Report "1 subscriber" per address, regardless of the number of services or bundles of services subscribed to. Identify other technology types. Where more than one type of technology is offered, the values of each one should be given separately. Add as many rows as necessary to provide this information. 3. Number of subscribers to services provided in bundles "Bundle of Services" means a commercial offer of a single operator which includes two or more services (fixed telephone service, broadband internet access service, subscription television service, mobile telephone service, mobile broadband internet access service, etc..) and which is sold as a single offer with a single bill. 'Number of subscribers' means the number of contracts with the supplier of publicly available electronic communication services for the provision of an offer comprising a bundle of services. For indicators on bundles, the number of subscribers of the offers indicated below should be reported as at the end of the respective period. 3.1 FTS + FBB Number of subscribers of double-play offers incorporating the fixed telephone service and fixed broadband Internet access service. 3.2 FTS + STV Number of subscribers of double-play offers incorporating the fixed telephone service and pay-tv service. 3.3 FTS + MTS Number of subscribers of double-play offers incorporating the fixed telephone service and mobile telephone service. 3.4 FBB + STV Number of subscribers of double-play offers incorporating the fixed broadband Internet access service and pay-tv service. 3.5 FBB + MTS Number of subscribers of double-play offers incorporating the fixed broadband Internet access service and mobile telephone service. 3.6 MTS + STV Number of subscribers of double-play offers incorporating the fixed broadband Internet access service and pay-tv service. 3.7 FBB+MBB Number of subscribers of double-play offers incorporating the fixed broadband Internet access service and mobile broadband Internet access service. 3.8 MBB+FTS Number of subscribers of double-play offers incorporating the mobile broadband Internet access service and fixed telephone service. 3.9 STV+MBB Number of subscribers of double-play offers incorporating the pay-tv service and mobile broadband Internet access service FTS + FBB + STV Number of subscribers of triple-play offers incorporating the fixed telephone service, fixed broadband Internet access service and pay-tv service FTS + MTS + FBB Number of subscribers of triple-play offers incorporating the fixed telephone service, mobile telephone service and fixed broadband Internet access service FTS + MTS + STV Number of subscribers of triple-play offers incorporating the fixed telephone service, mobile telephone service and pay-tv service MTS + STV + FBB Number of subscribers of triple-play offers incorporating the mobile telephone service, pay-tv service and fixed broadband Internet access service MTS+MBB+STV Number of subscribers of triple-play offers incorporating the mobile telephone service, mobile broadband Internet access service and pay-tv service FTS+MBB+STV Number of subscribers of triple-play offers incorporating the Fixed Telephone Service, mobile broadband Internet access service and pay-tv service FTS+MBB+FBB Number of subscribers of triple-play offers incorporating the Fixed Telephone Service, mobile broadband Internet access service and fixed broadband Internet access service FTS+MBB+MTS Number of subscribers of triple-play offers incorporating the fixed telephone service, mobile broadband internet access service and mobile telephone service FBB+MBB+MTS Number of subscribers of triple-play offers incorporating the fixed broadband Internet access service, mobile broadband internet access service and mobile telephone service FBB+MBB+STV Number of subscribers of triple-play offers incorporating the fixed broadband Internet access service, mobile broadband internet access service and pay-tv service FTS+FBB+MBB+STV Number of subscribers of quadruple-play offers incorporating the fixed telephone service, fixed broadband Internet access service, mobile broadband Internet access service and pay-tv service FBB+FTS+MBB+MTS Number of subscribers of quadruple-play offers incorporating the fixed broadband Internet access service, fixed telephone service, mobile broadband Internet access service and mobile telephone service FBB+FTS+STV+MTS Number of subscribers of quadruple-play offers incorporating the fixed broadband Internet access service, fixed telephone service, pay-tv service and mobile telephone service FBB+FTS+STV+MBB Number of subscribers of quadruple-play offers incorporating the fixed broadband Internet access service, fixed telephone service, pay-tv service and mobile broadband Internet access service Other bundles (specify, add as many rows as necessary) Number of subscribers to other offers sold in bundles. Identify other packages that include more than one service, as defined in point 3. Separate values should be given for each bundle of services. Add as many rows as necessary to provide this information. 4. TRAFFIC 4.1. Traffic volume of the telephone service at a fixed location Volume of traffic generated by FTS customers, reported in Number of Calls Traffic originating from the provider, measured in terms of number of calls National Traffic National voice traffic, originating from the provider, measured in terms of number of calls per type of access. Only report local, regional and national traffic (or equivalent type of calls established by the providers) and Internet access traffic (only direct access traffic to this service should be reported where originating on the provider's network). In particular, this item does not include traffic related to "fixed-mobile" and "fixed-data" calls, calls to audio text services, calls which are free to the caller (800 and 802 prefixes ), shared cost calls (808 and 809 prefixes), flat-rate calls (760 prefix) and calls to short numbers, personal numbers (884 prefix), universal access numbers (707 and 708 prefixes) and traffic originating from public pay phones. Traffic corresponding to each provider's own stock should not be considered in this indicator. Carrier transit traffic should not be reported Direct Access (excluding payphones and excluding calling cards etc...) National voice traffic, measured in terms of number of calls, with regard to residential and non-residential direct access customers. Direct access means that there is a line installed from the place where the client is domiciled and, if necessary, from the respective terminal equipment, to an entry point of a public switched telecommunications network. Access to the client will be guaranteed with own infrastructure in the final section of the network through the installation of cables or fixed wireless access equipment. Traffic originating on the provider's own lines should not be excluded from the calculation of indicators. Carrier transit traffic should not be reported. Traffic should not be reported where associated with public payphones, calling cards, short numbers and numbers with the following prefixes: 800, 802, 808, 809, 884, 707, 708 and 760. This should be considered in the respective indicators Intra-network voice calls National voice traffic associated with direct access customers, measured in terms of number of calls originating from the provider and destined for the provider's own customers Fixed inter-network voice calls National voice traffic associated with direct access customers, measured in terms of number of calls originating from the provider and destined for customers of other FTS providers Voice calls to mobile networks National voice traffic associated with direct access customers, measured in terms of number of calls originating from the provider and destined for customers of national MTS providers Indirect Access (excluding payphones and calling cards excluding etc...) National voice traffic, measured in terms of number of calls, related to residential and non-residential indirect access customers. Indirect access means access which guarantees accessibility to all customers of a given supplier of the fixed telephone service to the services of other suppliers, known as carriers, or traffic transporters. In an indirect access call (establishment of an end-to-end communication), where various providers may be involved, reporting should be performed only by the provider selected by the user. Traffic should not be reported where associated with public payphones, calling cards, short numbers and numbers with the following prefixes: 800, 802, 808, 809, 884, 707, 708, 760, 761 and 762. This should be considered in the respective indicators Intra-network voice calls National voice traffic, associated with indirect access customers, measured in terms of number of calls, originating from the provider and destined for the provider's own customers Fixed inter-network voice calls National voice traffic, associated with indirect access customers, measured in terms of number of calls, originating from the provider and destined for customers of other national FTS providers Voice calls to mobile networks National voice traffic, associated with indirect access customers, measured in terms of number of calls, originating from the provider and destined for customers of national MTS providers National Calls access via calling cards, prepaid cards, etc. National traffic, measured in terms of number of calls, associated with the virtual calling card service, which is a service that allows the user to make telephone calls by dialling a specific access code of the National Numbering Plan (''882xy''), with two relevant features: billing/collection and mobility. So that the user is able to make calls, the account associated with the card needs to be identified and authenticated (e.g. number and PIN) based on a set of dialled characters, whereas the account associated with the dialled identification is billed for the cost of the call. Cards meant for use in public payphones to access the FTS which do not have characteristics of virtual calling cards should not be reported under this item. The Operator that is the holder of the numbering should report the number of calls originated on its network and routed through the "882" numbering range. Excludes Internet access traffic National calls to numbers with prefixes: 800, 802, 808, 809, 884, 707, 708, National voice traffic, measured in terms of number of calls, originating from the provider and destined for numbers with the following prefixes: 800, 802, 808, 809, 884, 707, 708, 760, 761 and , 761 and 762 Traffic generated by both direct access and indirect access customers should be reported.
11 National calls to short numbers National voice traffic, measured in terms of number of calls, originating from the provider and destined for short numbers. Short numbers means numbers whose length is less than the other numbers of the NNP (9 digits), with a length ranging from three to six digits. Examples of short numbers include: 112, 1414, The codes that enable the selection of indirect access providers (call selection and pre-selection) are sometimes designated generally as "Short Numbers", even while they are prefixes which allow selection of different number formats, networks or services, but which are not part of the number. View short numbers defined in the Plano Nacional de Numeração (National Numbering Plan), with the exception of 10xy numbers. Traffic generated by both direct access and indirect access customers should be reported Other national calls originating on fixed telephone network Other fixed traffic originated by provider, measured in terms of number of calls. May include fixed-paging traffic, fixed-data traffic and fixed-audiotext services traffic Internet Access Calls National traffic associated with Internet access, originating on the provider's network, measured in terms of number of calls. Traffic originated by Direct Access and Indirect Access customers should be reported of which through calling cards, prepaid cards, etc. National traffic associated with Internet access, originating on the provider's network, calling cards, prepaid cards, etc., measured in terms of number of calls Outgoing International traffic Direct Access (excluding payphones and excluding calling cards etc...) Calls to fixed networks Calls to mobile networks Voice traffic, measured in terms of number of calls, originated by national FTS provider and destined to customers of international providers, associated with residential and non-residential direct access customers. Direct access means that there is a line installed from the place where the client is domiciled and, if necessary, from the respective terminal equipment, to an entry point of a public switched telecommunications network. Access to the client will be guaranteed with own infrastructure in the final section of the network through the installation of cables or fixed wireless access equipment. Traffic originating on the provider's own lines should not be excluded from the calculation of indicators. Carrier transit traffic should not be reported. Traffic should not be reported where associated with public payphones, calling cards, short numbers and numbers with the following prefixes: 800, 802, 808, 809, 884, 707, 708, 760, 761 and 762. This should be considered in the respective indicators. Voice traffic, measured in terms of number of calls, originated by national FTS provider and destined to customers of international providers of fixed networks, associated with residential and non-residential direct access customers. Voice traffic, measured in terms of number of calls, originated by national FTS provider and destined to customers of international providers of mobile networks, associated with residential and non-residential direct access customers Indirect Access (excluding payphones and calling cards excluding etc...) Voice traffic, measured in terms of number of calls, originated by national FTS provider and destined to customers of international providers, associated with residential and non-residential indirect access customers. Indirect access means access which guarantees accessibility to all customers of a given supplier of the fixed telephone service to the services of other suppliers, known as carriers, or traffic transporters. In an indirect access call (establishment of an end-to-end communication), where various providers may be involved, reporting should be performed only by the provider selected by the user. Traffic should not be reported where associated with public payphones, calling cards, short numbers and numbers with the following prefixes: 800, 802, 808, 809, 884, 707, 708, 760, 761 and 762. This should be considered in the respective indicators Calls to fixed networks Voice traffic, measured in terms of number of calls, originated by national FTS provider and destined to customers of international providers of fixed networks, associated with residential and non-residential indirect access customers Calls to mobile networks Voice traffic, measured in terms of number of calls, originated by national FTS provider and destined to customers of international providers of mobile networks, associated with residential and non-residential indirect access customers International outgoing traffic access via calling cards, prepaid cards, etc. Voice traffic, measured in terms of number of calls, originated by national provider of calling cards and pre-paid cards and destined to customers of international providers. The Operator that is the holder of the numbering should report the number of calls originated in its network and routed through the "882" numbering range Traffic originating on public payphones National calls originated on payphones Outgoing international calls originating on payphones Calls from other traffic using calling cards, prepaid cards, etc Calls from other traffic (specify. Add as many rows as necessary) National voice traffic originated on payphones, measured in terms of number of calls. Entities authorized to install and operate public pay phones to access the FTS are required to send FTS providers a systematically updated list of the Public payphones in their possession, in addition to the necessary information to be sent to ANACOM on indicators on traffic originating from these payphones. Voice traffic originating from national public pay phones and destined to customers of international providers, measured in terms of number of calls. Entities authorized to install and operate public pay phones to access the FTS are required to send FTS providers a systematically updated list of the Public payphones in their possession, in addition to the necessary information to be sent to ANACOM on indicators on traffic originating from these payphones. Other processable voice traffic, originating from the provider of calling cards, prep-aid cards, measured in terms of number of calls. Other fixed traffic originating on the provider's network, measured in terms of number of calls. Separate values should be given for each type of call. Add as many rows as necessary to provide this information Number of Minutes Corresponds to the traffic, originating from the provider, measured in terms of number of minutes. The fields for this indicator do not require completion National Traffic National voice traffic, originating from the provider, measured in terms of number of minutes per type of access. Only report local, regional and national traffic (or equivalent type of calls established by the providers) and Internet access traffic (where only direct access traffic to this service should be reported where originating on the provider's network). In particular, this item does not include traffic related to "fixed-mobile" and "fixed-data" calls, calls to audio text services, calls which are free to the caller (800 and 802 prefixes ), shared cost calls (808 and 809 prefixes), flat-rate calls (760 prefix) and calls to short numbers, personal numbers (884 prefix), universal access numbers (707 and 708 prefixes) and traffic originating from public pay phones. Traffic corresponding to each provider's own stock should not be considered in this indicator. Carrier transit traffic should not be reported Direct Access (excluding payphones and excluding calling cards etc...) Minutes of intra-net Voice traffic Minutes of inter-network fixed Voice traffic Minutes of Voice traffic to MTS National voice traffic, measured in terms of number of minutes, associated with residential and non-residential direct access customers. Direct access means that there is a line installed from the place where the client is domiciled and, if necessary, from the respective terminal equipment, to an entry point of a public switched telecommunications network. Access to the client will be guaranteed with own infrastructure in the final section of the network through the installation of cables or fixed wireless access equipment. Traffic originating on the provider's own lines should not be excluded from the calculation of indicators. Carrier transit traffic should not be reported. Traffic should not be reported where associated with public payphones, calling cards, short numbers and numbers with the following prefixes: 800, 802, 808, 809, 884, 707, 708 and 760. This should be considered in the respective indicators. National voice traffic, measured in terms of number of minutes, associated with residential and non-residential direct access customers, originating from the provider and destined for the provider's own customers. National voice traffic, measured in terms of number of minutes, associated with residential and non-residential direct access customers, originating from the provider and destined for customers of other FTS providers. National voice traffic, measured in terms of number of minutes, associated with residential and non-residential direct access customers, originating from the provider and destined for customers of national MTS providers Indirect Access (excluding payphones and excluding calling cards etc...) National voice traffic, measured in terms of number of minutes, associated with residential and non-residential indirect access customers. Indirect access means access which guarantees accessibility to all customers of a given supplier of the fixed telephone service to the services of other suppliers, known as carriers, or traffic transporters. In an indirect access call (establishment of an end-to-end communication), where various providers may be involved, reporting should be performed only by the provider selected by the user. Traffic should not be reported where associated with public payphones, calling cards, short numbers and numbers with the following prefixes: 800, 802, 808, 809, 884, 707, 708 and 760. This should be considered in the respective indicators Minutes of intra-net Voice traffic National voice traffic, associated with residential and non-residential indirect access customers, measured in terms of number of minutes, originating from the provider and destined for the provider's own customers Minutes of fixed inter-network Voice traffic National voice traffic, associated with residential and non-residential indirect access customers, measured in terms of number of minutes, originating from the provider and destined for customers of other national FTS providers Minutes of Voice traffic to MTS National voice traffic, associated with residential and non-residential indirect access customers, measured in terms of number of minutes, originating from the provider and destined for customers of national MTS providers Minutes of national traffic with access via calling cards, prepaid cards, etc. National traffic, measured in terms of number of minutes, associated with the virtual calling card service, which is a service that allows the user to make telephone calls by dialling a specific access code of the National Numbering Plan (''882xy''), with two relevant features: billing/collection and mobility. So that the user is able to make calls, the account associated with the card needs to be identified and authenticated (e.g. number and PIN) based on a set of dialled characters, whereas the account associated with the dialled identification is billed for the cost of the call. Cards meant for use in public payphones to access the FTS which do not have characteristics of virtual calling cards should not be reported under this item. The Operator that is the holder of the numbering should report the number of calls originated in its network and routed through the "882" numbering range. Excludes Internet access traffic Minutes of national traffic destined for numbers with prefixes: 800, 802, 808, 809, 884, 707, 708, 760, 761 and 762 National voice traffic, measured in terms of number of minutes, originating from the provider and destined the numbers with the following prefixes: 800, 802, 808, 809, 884, 707, 708, 760, 761 and 762. Traffic generated by both direct access and indirect access customers should be reported Minutes of national traffic to short numbers National voice traffic, originating from the provider and destined for short numbers, measured in terms of number of minutes.short numbers means numbers whose length is less than the other numbers of the NNP (9 digits), with a length ranging from three to six digits. Examples of short numbers include: 112, 1414, The codes that enable the selection of indirect access providers (call selection and pre-selection) are sometimes designated generally as "Short Numbers", even while they are prefixes which allow selection of different number formats, networks or services, but which are not part of the number. View short numbers defined in the Plano Nacional de Numeração (National Numbering Plan), with the exception of 10xy numbers. Traffic generated by both direct access and indirect access customers should be reported Minutes from other national traffic originating on fixed telephone network Other fixed national traffic originated from provider, measured in terms of number of minutes. May include fixed-paging traffic, fixed-data traffic and fixed-audiotext services traffic Number of Minutes of Internet Access National traffic associated with Internet access, originating on the provider's network, measured in terms of number of minutes. Traffic originated by Direct Access and Indirect Access customers should be reported of which through calling cards, prepaid cards, etc. National traffic associated with Internet access, originating on the provider' network, calling cards, prepaid cards, etc., measured in terms of number of minutes Outgoing International traffic Voice traffic originating from national providers and destined to customers of international providers, measured in terms of number of minutes, by type of access. Carrier transit traffic should not be reported. communications established through indirect access, the accounting of calls and their durations should be performed only by the provider selected by the user. In the case of Direct Access (excluding payphones and excluding calling cards etc...) Minutes of traffic to fixed networks Minutes of traffic to mobile networks Voice traffic, measured in terms of number of minutes, originated by national FTS provider and destined to customers of international providers, associated with residential and non-residential direct access customers. Direct access means that there is a line installed from the place where the client is domiciled and, if necessary, from the respective terminal equipment, to an entry point of a public switched telecommunications network. Access to the client will be guaranteed with own infrastructure in the final section of the network through the installation of cables or fixed wireless access equipment. Traffic originating on the provider's own lines should not be excluded from the calculation of indicators. Carrier transit traffic should not be reported. Traffic should not be reported where associated with public payphones, calling cards, short numbers and numbers with the following prefixes: 800, 802,808, 809, 884, 707,708, 760, 761 and 762. This should be considered in the respective indicators. Voice traffic, measured in terms of number of minutes, originated by national FTS provider and destined to customers of international providers of fixed networks, associated with residential and non-residential direct access customers. Voice traffic, measured in terms of number of minutes, originated by national FTS provider and destined to customers of international providers of mobile networks, associated with residential and non-residential direct access customers Indirect Access (excluding payphones and excluding calling cards etc...) Minutes of traffic to fixed networks Voice traffic, measured in terms of number of minutes, originated by national FTS provider and destined to customers of international providers, associated with residential and non-residential indirect access customers. Indirect access means access which guarantees accessibility to all customers of a given supplier of the fixed telephone service to the services of other suppliers, known as carriers, or traffic transporters. In an indirect access call (establishment of an endto-end communication), where various providers may be involved, reporting should be performed only by the provider selected by the user. numbers and numbers with the following prefixes: 800, 802, 808, 809, 884, 707, 708 and 760. This should be considered in the respective indicators. Traffic should not be reported where associated with public payphones, calling cards, short Voice traffic, measured in terms of number of minutes, originated by national FTS provider and destined to customers of international providers of fixed networks, associated with residential and non-residential indirect access customers Minutes of traffic to mobile networks Voice traffic, measured in terms of number of minutes, originated by national FTS provider and destined to customers of international providers of mobile networks, associated with residential and non-residential indirect access customers Minutes of outgoing International traffic access through calling cards, prepaid cards, etc. Voice traffic, measured in terms of number of minutes, originated by national provider of calling cards and pre-paid cards and destined to customers of international providers. The Operator that is the holder of the numbering should report the number of calls originated in its network and routed through the "882" numbering range Traffic originating on payphones
12 Minutes of national traffic originated on payphones Minutes of outgoing international traffic originated on payphones National voice traffic originated on payphones, measured in terms of number of minutes. Entities authorized to install and operate public pay phones to access the FTS are required to send FTS providers a systematically updated list of the Public payphones in their possession, in addition to the necessary information to be sent to ANACOM on indicators on traffic originating from these payphones. Voice traffic originating from national public pay phones and destined to customers of international providers, measured in terms of number of minutes. Entities authorized to install and operate public pay phones to access the FTS are required to send FTS providers a systematically updated list of the Public payphones in their possession, in addition to the necessary information to be sent to ANACOM on indicators on traffic originating from these payphones Minutes of other traffic using calling cards, prepaid cards, etc. Other processable voice traffic, originating from the provider of calling cards, pre-paid cards, measured in terms of number of minutes Minutes of other traffic types. (Specify. Add as many rows as necessary) Other fixed traffic originating on the provider's network, measured in terms of number of minutes. Separate values should be given for each type of traffic. Add as many rows as necessary to provide this information Data traffic generated by customers of the Fixed Telephone Service in GB Volume of data traffic generated by customers of the fixed telephone service and of the narrowband (dial-up) Internet access service, measured in GB. 4.2 Volume of nomadic VoIP Service Traffic Number of Calls National nomadic VoIP Traffic Intra-net Nomadic VoIP calls Calls to other nomadic VoIP services Calls to FTS Calls to the MTS National traffic, measured in terms of number of calls, associated with residential and non-residential customers and associated with nomadic VoIP services which inherently uses the non-geographic "30" numbering range. National traffic, measured in terms of number of calls, associated with residential and non-residential customers of nomadic VoIP services, originating from the provider and destined for the provider's own customers. National traffic, measured in terms of number of calls, associated with customers of nomadic VoIP services, originating from the provider and destined for customers of other providers of VoIP services. National traffic, measured in terms of number of calls, associated with customers of nomadic VoIP services, originating from the provider and destined for customers of national FTS providers. National traffic, measured in terms of number of calls, associated with customers of nomadic VoIP services, originating from the provider and destined for customers of national MTS providers Calls to other non-geographic numbers and short numbers National voice traffic, measured in terms of number of calls, originating from the provider and destined for numbers with the following prefixes: 800, 802, 808, 809, 884, 707, 708, 760, 761 and 762 and national voice traffic, originating from the provider and destined to short numbers, measured in terms of number of minutes. Short numbers means numbers whose length is less than the other numbers of the NNP (9 digits), with a length ranging from three to six digits. Examples of short numbers include: 112, 1414, The codes that enable the selection of indirect access providers (call selection and pre-selection) are sometimes designated generally as "Short Numbers", even while they are prefixes which allow selection of different number formats, networks or services, but which are not part of the number. View short numbers defined in the Plano Nacional de Numeração (National Numbering Plan), with the exception of 10xy numbers International outgoing nomadic VoIP traffic Voice traffic, measured in terms of number of calls, originated by national provider of VoIP services and destined to customers of international providers, associated with residential and non-residential customers Number of Minutes National nomadic VoIP traffic National traffic, measured in terms of number of minutes, associated with residential and non-residential customers and associated with nomadic VoIP services which inherently uses the non-geographic "30" numbering range Minutes of intra-network traffic National traffic, associated with residential and non-residential customers, of nomadic VoIP services, measured in terms of number of minutes, originating from the provider and destined for the provider's own customers Minutes of traffic to other nomadic VoIP services National traffic, measured in terms of number of minutes, associated with residential and non-residential customers of nomadic VoIP services, originating from the provider and destined for customers of other providers of VoIP services Minutes of traffic to FTS National traffic, measured in terms of number of minutes, associated with residential and non-residential customers of nomadic VoIP services, originating from the provider and destined for customers of national FTS providers Minutes of traffic to MTS National traffic, measured in terms of number of minutes, associated with residential and non-residential customers of nomadic VoIP services, originating from the provider and destined for customers of national MTS providers Minutes of Traffic to other non-geographic numbers and short numbers National voice traffic, measured in terms of number of minutes, originating from the provider and destined for numbers with the following prefixes: 800, 802, 808, 809, 884, 707, 708, 760, 761 and 762 and national voice traffic, originating from the provider and destined to short numbers,measured in terms of number of minutes. Short numbers means numbers whose length is less than the other numbers of the NNP (9 digits), with a length ranging from three to six digits. Examples of short numbers include: 112, 1414, The codes that enable the selection of indirect access providers (call selection and pre-selection) are sometimes designated generally as "Short Numbers", even while they are prefixes which allow selection of different number formats, networks or services, but which are not part of the number. View short numbers defined in the Plano Nacional de Numeração (National Numbering Plan), with the exception of 10xy numbers International outgoing nomadic VoIP traffic Voice traffic, measured in terms of minutes, originated by national provider of VoIP services and destined to customers of international providers, associated with residential and non-residential customers Traffic volume of the broadband internet access service (in GB). Traffic volume of the broadband internet access service (upload and download), measured in GB. 5. Revenues 5.1. Revenues from telephone service at a fixed location (excludes Revenues from FTS offered as part of a bundle of services), (in euros, net of discounts) Revenue from fixed telephone services which are not offered as part of a bundle of services, generated by the customers reported in item 2.1. Revenues should be reported in euros, net of discounts and accumulated over the quarters (from the beginning of the year) Revenue from subscriptions, installation fees and supplementary services Revenue not from traffic associated with the provision of the service (excluding equipment rental, supplementary services (as defined in Recommendation I. 250 of the International Telecommunication Union "Definition of Supplementary Services") and service transfer or termination prices, associated with residential and non-residential customers. Revenues should be reported in euros, net of discounts and accumulated over the quarters (from the beginning of the year) Traffic revenues Retail revenue from any call originating on the fixed network should be reported, for residential and non-residential customers, other than Internet access traffic and other traffic components whose retail price definition does not fall to the FTS provider (e.g.: traffic for special services, etc.). As such, interconnection revenues are excluded. Revenues should be reported in euros, net of discounts and accumulated over the quarters (from the beginning of the year). Retail revenues should be reported for local, regional and national calls originated on the fixed network by residential and non-residential customers. As such, interconnection revenues are excluded. Revenues should be reported in euros, Revenues from local, regional and national traffic originated on the fixed network net of discounts and accumulated over the quarters (from the beginning of the year) Revenues from outgoing international traffic originated on the fixed network Revenues from outgoing international traffic should be reported where originated on the fixed network by residential and non-residential customers. Revenues should be reported in euros, net of discounts and accumulated over the quarters (from the beginning of the year) Revenues from fixed-mobile traffic on the fixed network Retail revenues should be reported derived from calls originated on fixed networks by residential customers and non-residential customers and destined to customers of national MTS operators. As such, interconnection revenues are excluded. Revenues should be reported in euros, net of discounts and accumulated over the quarters (from the beginning of the year) Revenues from traffic originating on calling cards, prepaid cards, etc. Revenue of the support operator, holder of "882" numbering. Revenues should be reported from calls made using calling cards, prepaid cards, etc... Revenues should be reported in euros, net of discounts and accumulated over the quarters (from the beginning of the year) Revenues from traffic to services of calls which are free to the caller (800 prefix) Retail revenues should be reported derived from calls originated on the fixed network by residential and non-residential customers and destined to numbers with 800 prefixes. Should include all retail revenues associated with calls to the number of the operator, both made by the operator's customers and made by the customer's of other operators, as well as revenues derived from entities using the operator's own non-geographic numbering. Revenues should be reported in euros, net of discounts and accumulated over the quarters (from the beginning of the year) Revenues from traffic to services of shared cost calls (808, 809 prefix) Retail revenues should be reported derived from calls originated on fixed network by residential and non-residential customers and destined to numbers with 808 and 809 prefixes. Should include all retail revenues associated with calls to the numbers of the operator, both made by the operator's customers and made by the customer's of other operators, as well as revenues derived from entities using the operator's own non-geographic numbering. Revenues should be reported in euros, net of discounts and accumulated over the quarters (from the beginning of the year) Revenues from traffic to services of shared cost calls (884 prefix) Retail revenues should be reported derived from calls originated on the fixed network by residential and non-residential customers and destined to numbers with 884 prefixes. Should include all retail revenues associated with calls to the numbers of the operator, both made by the operator's customers and made by the customer's of other operators, as well as revenues derived from entities using the operator's own non-geographic numbering. Revenues should be reported in euros, net of discounts and accumulated over the quarters (since the beginning of the year) Revenues from traffic to services of "universal access" numbers (707 and 708 prefixes) Retail revenues should be reported derived from calls originated on the fixed network by residential and non-residential customers and destined to numbers with 707 and 708 prefixes. Should include all retail revenues associated with calls to the numbers of the operator, both made by the operator's customers and made by the customer's of other operators, as well as revenues derived from entities using the operator's own non-geographic numbering. Revenues should be reported in euros, net of discounts and accumulated over the quarters (since the beginning of the year) Revenues from traffic to flat-rate call services (760, 761 and 762 prefix) Retail revenues should be reported derived from calls originated on the fixed network by residential and non-residential customers and destined to numbers with 760, 761 and 762 prefixes. Should include all retail revenues associated with calls to the numbers of the operator, both made by the operator's customers and made by the customer's of other operators, as well as revenues derived from entities using the operator's own non-geographic numbering. Revenues should be reported in euros, net of discounts and accumulated over the quarters (from the beginning of the year) Revenues from traffic to short numbers Retail revenues should be reported derived from calls originated on the fixed network by residential and non-residential customers and destined to short numbers. Should include all retail revenues associated with calls to the numbers of the operator, both made by the operator's customers and made by the customer's of other operators, as well as revenues derived from entities using the operator's own non-geographic numbering. Revenues should be reported in euros, net of discounts and accumulated over the quarters (from the beginning of the year) Revenues from traffic originating on public payphones Revenues should be reported originating on public payphones. Revenues should be reported in euros, net of discounts and accumulated over the quarters (since the beginning of the year) Revenue associated with text messages Retail revenues related to text messages originating on the fixed network. Revenues should be reported in euros, net of discounts and accumulated over the quarters (from the beginning of the year) Other revenues (specify. Add as many rows as necessary) Other retail revenues should be reported from calls originated on the fixed networks by residential and non-residential customers and not reported in the previous categories. Separate values should be given for each type of revenue. Add as many rows as necessary to provide this information. Interconnection revenues should be excluded. Revenues should be reported in euros, net of discounts and accumulated over the quarters (from the beginning of the year). 5.2 Revenues from nomadic VoIP services (in euros, net of discounts) Revenues from nomadic VoIP services which are not offered as part of a bundle of services. Revenues should be reported in euros, net of discounts and accumulated over the quarters (from the beginning of the year) Revenues from subscriptions and activation charges Revenue not from traffic associated with the provision of the service (excluding equipment rental, supplementary services (as defined in Recommendation I. 250 of the International Telecommunication Union "Definition of Supplementary Services") and service transfer or termination prices, associated with residential and non-residential customers. Revenues should be reported in euros, net of discounts and accumulated over the quarters. This indicator only applies to offers where the tariff model includes a monthly fee and/or activation charge Revenues from originated traffic Retail revenues should be reported where derived from any call originated in the context of nomadic VoIP services by residential and non-residential customers, other than Internet access traffic and other traffic components whose retail price definition does not fall to the nomadic VoIP provider (e.g.: traffic for special services, etc.). As such, interconnection revenues are excluded. Revenues should be reported in euros, net of discounts and accumulated over the quarters. 5.3 Revenues from Internet access service not offered as part of a bundle of services Revenues from the Internet access service not offered as part of a bundle of services. Revenues should be reported in euros, net of discounts and accumulated over the quarters (since the beginning of the year). 5.4 Revenues from subscription TV services not offered as part of a bundle of services Revenues from television subscription service not offered as part of a bundle of services. Revenues should be reported in euros, net of discounts and accumulated over the quarters (since the beginning of the year). 5.5 Revenues from services offered in bundles Revenue from services offered as bundles. "Bundle of Services" means a commercial offer of a single operator which includes two or more services (fixed telephone service, broadband internet access service, pay-tv service, mobile telephone service, mobile broadband internet access service, etc..) and which is sold as a single offer with a single bill. Revenues should be reported in euros,net of discounts and accumulated over the quarters (from the beginning of the year) FTS + FBB Revenues from double-play bundles of services that include the fixed telephone service and fixed broadband Internet access service. Revenues should be reported in euros, net of discounts and accumulated over the quarters (from the beginning of the year) FTS + STV Revenues from double-play bundles of services that include the fixed telephone service and pay-tv service. Revenues should be reported in euros, net of discounts and accumulated over the quarters (from the beginning of the year) FTS + MTS Revenues from double-play bundles of services that include the fixed telephone service and mobile telephone service. Revenues should be reported in euros,net of discounts and accumulated over the quarters (from the beginning of the year) FBB + STV Revenues from double-play bundles of services that include the fixed broadband Internet access service and pay-tv service. Revenues should be reported in euros, net of discounts and accumulated over the quarters (from the beginning of the year) FBB + MTS Revenues from double-play bundles of services that include the fixed broadband Internet access service and mobile telephone service. Revenues should be reported in euros, net of discounts and accumulated over the quarters (from the beginning of the year) MTS + STV Revenues from double-play bundles of services that include the mobile telephone service and the pay-tv service. Revenues should be reported in euros, net of discounts and accumulated over the quarters (from the beginning of the year) FBB+MBB Revenues from double-play bundles of services that include the fixed broadband Internet access service and the mobile broadband Internet access service. Revenues should be reported in euros,net of discounts and accumulated over the quarters (from the beginning of the year).
13 5.5.8 MBB+FTS Revenues from double-play bundles of services that include the mobile broadband Internet access service and the fixed telephone service. Revenues should be reported in euros, net of discounts and accumulated over the quarters (from the beginning of the year) STV+MBB Revenues from double-play bundles of services that include the pay-tv service and the mobile broadband Internet access service. Revenues should be reported in euros, net of discounts and accumulated over the quarters (from the beginning of the year) FTS + FBB + STV Revenues from triple-play bundles of services that include the Fixed Telephone Service, the fixed broadband Internet service and the pay-tv service. Revenues should be reported in euros, net of discounts and accumulated over the quarters (from the beginning of the year) FTS + MTS + FBB Revenues from triple-play bundles of services that include the fixed telephone service, the mobile telephone service and the fixed broadband Internet service. Revenues should be reported in euros, net of discounts and accumulated over the quarters (from the beginning of the year) FTS + MTS + STV Revenues from triple-play bundles of services that include the fixed telephone service, the mobile telephone service and the pay-tv service.revenues should be reported in euros,net of discounts and accumulated over the quarters (from the beginning of the year) MTS + STV + FBB Revenues from triple-play bundles of services that include the fixed broadband Internet service, the subscription television service and the mobile telephone service. Revenues should be reported in euros, net of discounts and accumulated over the quarters (from the beginning of the year) MTS+MBB+STV Revenues from triple-play bundles of services that include the mobile telephone service, the mobile broadband Internet access service and subscription television service. Revenues should be reported in euros, net of discounts and accumulated over the quarters (from the beginning of the year) FTS+MBB+STV Revenues from triple-play bundles of services that include the fixed telephone service, the mobile broadband Internet access service and the subscription television service. Revenues should be reported in euros, net of discounts and accumulated over the quarters (from the beginning of the year) FTS+MBB+FBB Revenues from triple-play bundles of services that include the fixed telephone service, mobile broadband Internet access service and fixed broadband Internet access service. Revenues should be reported in euros, net of discounts and accumulated over the quarters (from the beginning of the year) FTS+MBB+MTS Revenues from triple-play bundles of services that include the Fixed Telephone Service, mobile broadband Internet access service and the mobile telephone service. Revenues should be reported in euros,net of discounts and accumulated over the quarters (from the beginning of the year) FBB+MBB+MTS Revenues from triple-play bundles of services that include the fixed broadband Internet access service, mobile broadband Internet access service and mobile telephone service. Revenues should be reported in euros, net of discounts and accumulated over the quarters (from the beginning of the year) FBB+MBB+STV Revenues from triple-play bundles of services that include the fixed broadband Internet access service, the mobile broadband Internet access service and subscription television service. Revenues should be reported in euros, net of discounts and accumulated over the quarters (from the beginning of the year) FTS+FBB+MBB+STV Revenues from quadruple-play bundles of services that include the fixed telephone service, fixed broadband Internet access service, pay-tv service and mobile broadband Internet access service. Revenues should be reported in euros, net of discounts and accumulated over the quarters (from the beginning of the year) FBB+FTS+MBB+MTS Revenues from quadruple-play bundles of services that include the fixed broadband Internet access service, fixed telephone service, mobile broadband Internet access service and the mobile telephone service. Revenues should be reported in euros, net of discounts and accumulated over the quarters (from the beginning of the year) FBB+FTS+STV+MTS Revenues from quadruple-play bundles of services that include the fixed broadband Internet access service, fixed telephone service, pay-tv service and mobile telephone service. Revenues should be reported in euros, net of discounts and accumulated over the quarters (from the beginning of the year) FBB+FTS+STV+MBB Revenues from quadruple-play bundles of services that include the fixed broadband Internet access service, fixed telephone service, pay-tv service and mobile broadband Internet access service. Revenues should be reported in euros, net of discounts and accumulated over the quarters (from the beginning of the year) Other bundles (specify, add as many rows as necessary) Revenues from other offers sold in bundles. Identify other bundles that include more than one service, as defined in point 3. Separate values should be given for each bundle of services. Add as many rows as necessary to provide this information. Revenues should be reported in euros, net of discounts and accumulated over the quarters (from the beginning of the year).
STATISTICAL INFORMATION TO BE SUBMITTED BY THE FIXED TELEPHONE SERVICE (FTS) PROVIDERS
 http://www.anacom.pt/template31.jsp?categoryid=214702 STATISTICAL INFORMATION TO BE SUBMITTED BY THE FIXED TELEPHONE SERVICE (FTS) PROVIDERS Explanatory notes (1 to 26) on the last pages of this document
http://www.anacom.pt/template31.jsp?categoryid=214702 STATISTICAL INFORMATION TO BE SUBMITTED BY THE FIXED TELEPHONE SERVICE (FTS) PROVIDERS Explanatory notes (1 to 26) on the last pages of this document
Appendix A: Basic network architecture
 Appendix A: Basic network architecture TELECOMMUNICATIONS LOCAL ACCESS NETWORKS Traditionally, telecommunications networks are classified as either fixed or mobile, based on the degree of mobility afforded
Appendix A: Basic network architecture TELECOMMUNICATIONS LOCAL ACCESS NETWORKS Traditionally, telecommunications networks are classified as either fixed or mobile, based on the degree of mobility afforded
Definitions of the Telecommunication indicators used in the EUROSTAT telecommunications inquiry
 Definitions of the Telecommunication indicators used in the EUROSTAT telecommunications inquiry Table 1 Operators (Unit: number (NBR)) Number of active operators (only active) offering publicly available
Definitions of the Telecommunication indicators used in the EUROSTAT telecommunications inquiry Table 1 Operators (Unit: number (NBR)) Number of active operators (only active) offering publicly available
Internet access services Leased line and data transmission services
 Internet access services Leased line and data transmission services - statistical data report - (updated based upon the statistical data corresponding to 1 July 31 December 2011 reporting period) ANCOM/Regulation
Internet access services Leased line and data transmission services - statistical data report - (updated based upon the statistical data corresponding to 1 July 31 December 2011 reporting period) ANCOM/Regulation
Internet access services Leased line and data transmission services
 Internet access services Leased line and data transmission services - statistical data report - (updated based upon the statistical data corresponding to 1 January 30 June 2011 reporting period) ANCOM/Regulation
Internet access services Leased line and data transmission services - statistical data report - (updated based upon the statistical data corresponding to 1 January 30 June 2011 reporting period) ANCOM/Regulation
STATISTICAL INFORMATION FIXED TELEPHONE SERVICE 2ND QUARTER 2015
 STATISTICAL INFORMATION FIXED TELEPHONE SERVICE 2ND QUARTER 2015 Fixed Telephone Service 2nd quarter 2015 Index HIGHLIGHTS... 4 1. Providers of the Fixed Telephone, Voice over Internet, nomadic VoIP and
STATISTICAL INFORMATION FIXED TELEPHONE SERVICE 2ND QUARTER 2015 Fixed Telephone Service 2nd quarter 2015 Index HIGHLIGHTS... 4 1. Providers of the Fixed Telephone, Voice over Internet, nomadic VoIP and
Appendix 1: Satellite broadband service providers
 Appendixes Appendix 1: Satellite broadband service providers In 2005 06, satellite broadband services were provided by the following companies: Australian Private Networks (ACTIV8me) Be Communications
Appendixes Appendix 1: Satellite broadband service providers In 2005 06, satellite broadband services were provided by the following companies: Australian Private Networks (ACTIV8me) Be Communications
How To Compare Landline To Cell Phone Service In Honduras
 Flash report on landline service October 214 thousand Flash report on landline services for October 214 Data suppliers: Magyar Telekom Nyrt., Invitel Zrt., GTS Hungary Kft., UPC Magyarország Kft., DIGI
Flash report on landline service October 214 thousand Flash report on landline services for October 214 Data suppliers: Magyar Telekom Nyrt., Invitel Zrt., GTS Hungary Kft., UPC Magyarország Kft., DIGI
Flash report on wireline service. May 2012
 Flash report on wireline service May 212 Flash report on landline services for May 212 Data suppliers: Magyar Telekom Nyrt., Invitel Zrt., GTS Hungary Kft., UPC Magyarország Kft., DIGI Kft., PR- TELEKOM
Flash report on wireline service May 212 Flash report on landline services for May 212 Data suppliers: Magyar Telekom Nyrt., Invitel Zrt., GTS Hungary Kft., UPC Magyarország Kft., DIGI Kft., PR- TELEKOM
Flash report on landline services for April 2013
 Flash report on landline services for April 213 Data suppliers: Magyar Telekom Nyrt., Invitel Zrt., GTS Hungary Kft., UPC Magyarország Kft., DIGI Kft., PR- TELEKOM Zrt., Tarr Kft., ViDaNet Zrt., PARISAT
Flash report on landline services for April 213 Data suppliers: Magyar Telekom Nyrt., Invitel Zrt., GTS Hungary Kft., UPC Magyarország Kft., DIGI Kft., PR- TELEKOM Zrt., Tarr Kft., ViDaNet Zrt., PARISAT
Flash report on landline services for February 2016
 thousand 1 312 1 283 1 221 1 175 1 118 1 82 1 45 1 26 97 937 937 924 94 Flash report on landline services for February 216 Data suppliers: Magyar Telekom Nyrt., Invitel Zrt., UPC Magyarország Kft., DIGI
thousand 1 312 1 283 1 221 1 175 1 118 1 82 1 45 1 26 97 937 937 924 94 Flash report on landline services for February 216 Data suppliers: Magyar Telekom Nyrt., Invitel Zrt., UPC Magyarország Kft., DIGI
Quarterly Key Data Report
 Irish Communications Market Quarterly Key Data Report Data as of Q4 2013 Document No: 14/19 Date: 14 March 2014 Table of Contents SUMMARY... 6 Notes to data:... 8 1. OVERALL MARKET DATA... 10 1.1 Number
Irish Communications Market Quarterly Key Data Report Data as of Q4 2013 Document No: 14/19 Date: 14 March 2014 Table of Contents SUMMARY... 6 Notes to data:... 8 1. OVERALL MARKET DATA... 10 1.1 Number
Quarterly Key Data Report
 Irish Communications Market Quarterly Key Data Report Data as of Q1 2014 Document No: 14/61 Date: 20 June 2014 Table of Contents SUMMARY... 6 Notes to data:... 8 1. OVERALL MARKET DATA... 10 1.1 Number
Irish Communications Market Quarterly Key Data Report Data as of Q1 2014 Document No: 14/61 Date: 20 June 2014 Table of Contents SUMMARY... 6 Notes to data:... 8 1. OVERALL MARKET DATA... 10 1.1 Number
The part of the network that connects customers to the exchange, sometimes called the local loop or the last mile.
 Glossary of broadband terms 3G: Refers to the third generation of mobile phone technology following on from 2G. 3G allows for faster access to the internet and allows services including video calls and
Glossary of broadband terms 3G: Refers to the third generation of mobile phone technology following on from 2G. 3G allows for faster access to the internet and allows services including video calls and
Getting Broadband. FCC Consumer Facts. What Is Broadband?
 Getting Broadband FCC Consumer Facts What Is Broadband? Broadband or high-speed Internet access allows users to access the Internet and Internetrelated services at significantly higher speeds than those
Getting Broadband FCC Consumer Facts What Is Broadband? Broadband or high-speed Internet access allows users to access the Internet and Internetrelated services at significantly higher speeds than those
ADSL or Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line. Backbone. Bandwidth. Bit. Bits Per Second or bps
 ADSL or Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line Backbone Bandwidth Bit Commonly called DSL. Technology and equipment that allow high-speed communication across standard copper telephone wires. This can include
ADSL or Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line Backbone Bandwidth Bit Commonly called DSL. Technology and equipment that allow high-speed communication across standard copper telephone wires. This can include
Observatory of the Electronic communications market in France
 4 april 213 Observatory of the Electronic communications market in France 4 th quarter 212 final results ISSN : 2258-316 2 Contents 1 the electronic market in its entirety... 3 1.1 The end customer market...
4 april 213 Observatory of the Electronic communications market in France 4 th quarter 212 final results ISSN : 2258-316 2 Contents 1 the electronic market in its entirety... 3 1.1 The end customer market...
Irish Communications Market
 Irish Communications Market Quarterly Key Data Report Data as of Q3 2015 Reference: ComReg 15/130 Version: Final Date: 10/12/2015 An Coimisiún um Rialáil Cumarsáide Commission for Communications Regulation
Irish Communications Market Quarterly Key Data Report Data as of Q3 2015 Reference: ComReg 15/130 Version: Final Date: 10/12/2015 An Coimisiún um Rialáil Cumarsáide Commission for Communications Regulation
ITU World Telecommunication/ICT Indicators Long Questionnaire 2015
 ITU World Telecommunication/ICT Indicators Long Questionnaire 2015 SAMPLE QUESTIONNAIRE Please complete the Answer and Notes columns in the table below. Black cells must NOT be completed. Please do NOT
ITU World Telecommunication/ICT Indicators Long Questionnaire 2015 SAMPLE QUESTIONNAIRE Please complete the Answer and Notes columns in the table below. Black cells must NOT be completed. Please do NOT
4G: Fourth generation mobile phone standards and technology. Provides faster mobile data speeds than the 3G standards that it succeeds.
 Department for Culture, Media & Sport 1 Annex B: Glossary 2G: Second generation of mobile telephony systems. Uses digital transmission to support voice, low-speed data communications, and short messaging
Department for Culture, Media & Sport 1 Annex B: Glossary 2G: Second generation of mobile telephony systems. Uses digital transmission to support voice, low-speed data communications, and short messaging
Avancerede Datanet. Ole Brun Madsen Professor Department of Control Engineering University of Aalborg. Infrastruktur
 Department of Control Engineering Distributed Real-time Systems Avancerede Datanet Infrastruktur Ole Brun Madsen Professor Department of Control Engineering University of Aalborg Avancerede Datanet Infrastructure
Department of Control Engineering Distributed Real-time Systems Avancerede Datanet Infrastruktur Ole Brun Madsen Professor Department of Control Engineering University of Aalborg Avancerede Datanet Infrastructure
DEFINITIONS OF WORLD TELECOMMUNICATION/ICT INDICATORS
 DEFINITIONS OF WORLD TELECOMMUNICATION/ICT INDICATORS MARCH 2010 Fixed telephone network 112 Fixed telephone lines 117 Total capacity of local public switching exchanges 1142 Percent of fixed telephone
DEFINITIONS OF WORLD TELECOMMUNICATION/ICT INDICATORS MARCH 2010 Fixed telephone network 112 Fixed telephone lines 117 Total capacity of local public switching exchanges 1142 Percent of fixed telephone
Services for Telecommunication Service Providers
 Services for Telecommunication Service Providers www.otewholesale.gr Wholesale A. Broadband Services 1. Wholesale ADSL Bitstream Access ARYS Service 2. Wholesale ADSL Bitstream Backhaul OKSYA Service B.
Services for Telecommunication Service Providers www.otewholesale.gr Wholesale A. Broadband Services 1. Wholesale ADSL Bitstream Access ARYS Service 2. Wholesale ADSL Bitstream Backhaul OKSYA Service B.
Irish Communications Market
 Irish Communications Market Quarterly Key Data Report Data as of Q4 2014 Document No: 15/27 Date: 12 March 2015 Table of Contents SUMMARY... 6 Notes to data:... 8 1. OVERALL MARKET DATA... 10 1.1 Number
Irish Communications Market Quarterly Key Data Report Data as of Q4 2014 Document No: 15/27 Date: 12 March 2015 Table of Contents SUMMARY... 6 Notes to data:... 8 1. OVERALL MARKET DATA... 10 1.1 Number
3.1 TELECOMMUNICATIONS, NETWORKS AND THE INTERNET
 3.1 TELECOMMUNICATIONS, NETWORKS AND THE INTERNET The Business Value of Telecommunications and Networking Business value impacts of the telecommunications and Networking are: Declining transaction costs
3.1 TELECOMMUNICATIONS, NETWORKS AND THE INTERNET The Business Value of Telecommunications and Networking Business value impacts of the telecommunications and Networking are: Declining transaction costs
BERMUDA REGULATORY AUTHORITY (MARKET DEFINITION AND SIGNIFICANT MARKET POWER) GENERAL DETERMINATION 2013 BR 47 / 2013
 QUO FA T A F U E R N T BERMUDA REGULATORY AUTHORITY (MARKET DEFINITION AND SIGNIFICANT BR 47 / 2013 The Regulatory Authority, in exercise of the power conferred by section 62 of the Regulatory Authority
QUO FA T A F U E R N T BERMUDA REGULATORY AUTHORITY (MARKET DEFINITION AND SIGNIFICANT BR 47 / 2013 The Regulatory Authority, in exercise of the power conferred by section 62 of the Regulatory Authority
Broadband Access Technologies
 Broadband Access Technologies Chris Wong Communications Engineering Sector Analysis & Reporting Branch International Training Program 23 October 2007 Presentation Outline What is broadband? What are the
Broadband Access Technologies Chris Wong Communications Engineering Sector Analysis & Reporting Branch International Training Program 23 October 2007 Presentation Outline What is broadband? What are the
Wholesale IP Bitstream on a Cable HFC infrastructure
 Wholesale IP Bitstream on a Cable HFC infrastructure In order to understand the issues related to an ISP reselling Cable Based Internet access it is necessary to look at similarities and dissimilarities
Wholesale IP Bitstream on a Cable HFC infrastructure In order to understand the issues related to an ISP reselling Cable Based Internet access it is necessary to look at similarities and dissimilarities
OVERVIEW OF THE TELECOMMUNICATIONS INDUSTRY
 Certain facts, statistics and data presented in this section and elsewhere in this document have been derived, in part, from various government or official sources. Whilst the Directors have taken all
Certain facts, statistics and data presented in this section and elsewhere in this document have been derived, in part, from various government or official sources. Whilst the Directors have taken all
Telecommunications, Networks, and Wireless Computing
 Objectives Telecommunications, Networks, and Wireless Computing 1. What are the features of a contemporary corporate telecommunications system? On what major technology developments are they based? 2.
Objectives Telecommunications, Networks, and Wireless Computing 1. What are the features of a contemporary corporate telecommunications system? On what major technology developments are they based? 2.
Quarterly Key Data Report
 Irish Communications Market Quarterly Key Data Report Data as of Q4 2008 Document No: 09/17 Date: 19 March 2009 Table of Contents SUMMARY... 6 Notes to data:... 7 1 OVERALL MARKET DATA... 8 1.1 Number
Irish Communications Market Quarterly Key Data Report Data as of Q4 2008 Document No: 09/17 Date: 19 March 2009 Table of Contents SUMMARY... 6 Notes to data:... 7 1 OVERALL MARKET DATA... 8 1.1 Number
Broadband 101: Installation and Testing
 Broadband 101: Installation and Testing Fanny Mlinarsky Introduction Today the Internet is an information superhighway with bottlenecks at every exit. These congested exits call for the deployment of broadband
Broadband 101: Installation and Testing Fanny Mlinarsky Introduction Today the Internet is an information superhighway with bottlenecks at every exit. These congested exits call for the deployment of broadband
GLOSSARY. access channel. ACD (automatic call distribution) ADSL (Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line) ARPL (average revenue per line)
 GLOSSARY 3G access channel ACD (automatic call distribution) ADSL (Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line) ARPL (average revenue per line) ARPU (average revenue per user) ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode) Base
GLOSSARY 3G access channel ACD (automatic call distribution) ADSL (Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line) ARPL (average revenue per line) ARPU (average revenue per user) ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode) Base
INTERNET CONNECTIVITY
 INTERNET CONNECTIVITY http://www.tutorialspoint.com/internet_technologies/internet_connectivity.htm Copyright tutorialspoint.com Here in this tutorial, we will discuss how to connect to internet i.e. internet
INTERNET CONNECTIVITY http://www.tutorialspoint.com/internet_technologies/internet_connectivity.htm Copyright tutorialspoint.com Here in this tutorial, we will discuss how to connect to internet i.e. internet
NAPCS Product List for NAICS 517: Telecom Products
 NAPCS List for NAICS 517: Telecom s 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 National 1.1 X Carrier services and Internet backbone services Providing wired or wireless facilities to originate, terminate or transit voice or data
NAPCS List for NAICS 517: Telecom s 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 National 1.1 X Carrier services and Internet backbone services Providing wired or wireless facilities to originate, terminate or transit voice or data
E1-E2 (EB) Chapter 8A. Broadband Services
 E1-E2 (EB) Chapter 8A Broadband Services 8A. Broadband and Broadband Services 8A.1 Introduction In toady s globally networked society through internet, there is always increasing demand for higher capacity
E1-E2 (EB) Chapter 8A Broadband Services 8A. Broadband and Broadband Services 8A.1 Introduction In toady s globally networked society through internet, there is always increasing demand for higher capacity
ADSL BROADBAND BASICS FOR THE DOMESTIC USER. The Main Limitations of ADSL Broadband are as follows.
 ADSL BROADBAND BASICS FOR THE DOMESTIC USER AS NOTHING MAN MADE IS PERFECT, ADSL IS NOT AN EXCEPTION. The Main Limitations of ADSL Broadband are as follows. 1. ADSL is not a Guaranteed Bandwidth Service.
ADSL BROADBAND BASICS FOR THE DOMESTIC USER AS NOTHING MAN MADE IS PERFECT, ADSL IS NOT AN EXCEPTION. The Main Limitations of ADSL Broadband are as follows. 1. ADSL is not a Guaranteed Bandwidth Service.
VDSL (VERY HIGH DATA BIT RATE DIGITAL SUBSCRIBER LINE)
 1 VDSL (VERY HIGH DATA BIT RATE DIGITAL SUBSCRIBER LINE) INTRODUCTION 1. Recent events in the telecommunications environment are giving rise to a new class of service providers, setting the stage for how
1 VDSL (VERY HIGH DATA BIT RATE DIGITAL SUBSCRIBER LINE) INTRODUCTION 1. Recent events in the telecommunications environment are giving rise to a new class of service providers, setting the stage for how
Quarterly Key Data Report
 Irish Communications Market Quarterly Key Data Report Data as of Q4 2009 Document No: 10/19 Date: 18 th March 2010 Table of Contents SUMMARY... 6 Notes to data:... 7 1. OVERALL MARKET DATA... 9 1.1 Number
Irish Communications Market Quarterly Key Data Report Data as of Q4 2009 Document No: 10/19 Date: 18 th March 2010 Table of Contents SUMMARY... 6 Notes to data:... 7 1. OVERALL MARKET DATA... 9 1.1 Number
Growing Optical Fiber Deployment Drives Demand for Semiconductors in Copper-Based Telephony
 Growing Optical Fiber Deployment Drives Demand for Semiconductors in Copper-Based Telephony Wireline telephony may seem like old technology, having been around for more than 100 years, but it is still
Growing Optical Fiber Deployment Drives Demand for Semiconductors in Copper-Based Telephony Wireline telephony may seem like old technology, having been around for more than 100 years, but it is still
Next Generation Access Glossary. 21CN: BT s upgrade of their core network (the backbone of the network).
 Next Generation Access Glossary 21CN: BT s upgrade of their core network (the backbone of the network). Access network: The part of the network that connects directly to customers from the local telephone
Next Generation Access Glossary 21CN: BT s upgrade of their core network (the backbone of the network). Access network: The part of the network that connects directly to customers from the local telephone
HIGH CAPACITY DSL-SYSTEMS
 Electronic Communications Committee (ECC) within the European Conference of Postal and Telecommunications Administrations (CEPT) HIGH CAPACITY DSL-SYSTEMS Oulu, March 2006 Page 2 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY In this
Electronic Communications Committee (ECC) within the European Conference of Postal and Telecommunications Administrations (CEPT) HIGH CAPACITY DSL-SYSTEMS Oulu, March 2006 Page 2 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY In this
Mobility and cellular networks
 Mobility and cellular s Wireless WANs Cellular radio and PCS s Wireless data s Satellite links and s Mobility, etc.- 2 Cellular s First generation: initially debuted in Japan in 1979, analog transmission
Mobility and cellular s Wireless WANs Cellular radio and PCS s Wireless data s Satellite links and s Mobility, etc.- 2 Cellular s First generation: initially debuted in Japan in 1979, analog transmission
Definitions. "All Ireland Landline Numbers" means fixed telephone exchange line numbers in the State (including Northern Ireland).
 the Acts mean the Communications Regulation (Amendment) Act 2007, the Communications Regulation Act, 2002, the Postal and Telecommunications Services Act, 1983 as amended, and any applicable secondary
the Acts mean the Communications Regulation (Amendment) Act 2007, the Communications Regulation Act, 2002, the Postal and Telecommunications Services Act, 1983 as amended, and any applicable secondary
Session 4.1. Network Planning Strategy for evolving Network Architectures Session 4.1-1. Service matrix forecasting. Broadband
 ITU Seminar Warsaw, Poland, 6-10 October 2003 Session 4.1 Service and applications matrix forecasting Network Planning Strategy for evolving Network Architectures Session 4.1-1 Service matrix forecasting
ITU Seminar Warsaw, Poland, 6-10 October 2003 Session 4.1 Service and applications matrix forecasting Network Planning Strategy for evolving Network Architectures Session 4.1-1 Service matrix forecasting
COMPUTERS ARE YOUR FUTURE CHAPTER 8 WIRED & WIRELESS COMMUNICATION
 COMPUTERS ARE YOUR FUTURE CHAPTER 8 WIRED & WIRELESS COMMUNICATION Answers to End-of-Chapter Questions Matching g 1. whiteboard i 2. sending device o 3. streaming j 4. WiFi m 5. Webcam d 6. data transfer
COMPUTERS ARE YOUR FUTURE CHAPTER 8 WIRED & WIRELESS COMMUNICATION Answers to End-of-Chapter Questions Matching g 1. whiteboard i 2. sending device o 3. streaming j 4. WiFi m 5. Webcam d 6. data transfer
2 box model (in the SOP)
 Term 2 box model (in the SOP) Definition Refers to the arrangement under which Telecom structurally separates into Chorus2 (network and some wholesale) and Telecom2 (retail and some wholesale), but is
Term 2 box model (in the SOP) Definition Refers to the arrangement under which Telecom structurally separates into Chorus2 (network and some wholesale) and Telecom2 (retail and some wholesale), but is
Chapter 9A. Network Definition. The Uses of a Network. Network Basics
 Chapter 9A Network Basics 1 Network Definition Set of technologies that connects computers Allows communication and collaboration between users 2 The Uses of a Network Simultaneous access to data Data
Chapter 9A Network Basics 1 Network Definition Set of technologies that connects computers Allows communication and collaboration between users 2 The Uses of a Network Simultaneous access to data Data
Network+ Guide to Networks 6 th Edition. Chapter 7 Wide Area Networks
 Network+ Guide to Networks 6 th Edition Chapter 7 Wide Area Networks Objectives Identify a variety of uses for WANs Explain different WAN topologies, including their advantages and disadvantages Compare
Network+ Guide to Networks 6 th Edition Chapter 7 Wide Area Networks Objectives Identify a variety of uses for WANs Explain different WAN topologies, including their advantages and disadvantages Compare
Objectives. Remote Connection Options. Teleworking. Connecting Teleworkers to the Corporate WAN. Providing Teleworker Services
 ITE I Chapter 6 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 Objectives Providing Teleworker Services Describe the enterprise requirements for providing teleworker services Explain how
ITE I Chapter 6 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 Objectives Providing Teleworker Services Describe the enterprise requirements for providing teleworker services Explain how
Analysis of xdsl Technologies
 International Journal of Electronics and Computer Science Engineering 897 Available Online at www.ijecse.org ISSN- 2277-1956 Analysis of xdsl Technologies Dimple Saproo 1, Megha Goyal 2, Asha Bhagashra
International Journal of Electronics and Computer Science Engineering 897 Available Online at www.ijecse.org ISSN- 2277-1956 Analysis of xdsl Technologies Dimple Saproo 1, Megha Goyal 2, Asha Bhagashra
Appendix C. Glossary of Broadband Terms
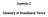 Appendix C Glossary of Broadband Terms Glossary 3G Third Generation: Intended to be the nest great wireless technology, wideband mobile services and applications offering users faster access to the web.
Appendix C Glossary of Broadband Terms Glossary 3G Third Generation: Intended to be the nest great wireless technology, wideband mobile services and applications offering users faster access to the web.
Long Distance Connection and WAN
 Lecture 6 Long Distance Connection and WAN Digital Telephone, PCM and Nyquist Sampling Theorem DSU/CSU, T Line Series and OC line Series Local Loop DSL Technologies - ADSL, HDSL, SDSL, VDSL Cable Modem
Lecture 6 Long Distance Connection and WAN Digital Telephone, PCM and Nyquist Sampling Theorem DSU/CSU, T Line Series and OC line Series Local Loop DSL Technologies - ADSL, HDSL, SDSL, VDSL Cable Modem
Voluntary Business Broadband Speeds Code of Practice
 Voluntary Business Broadband Speeds Code of Practice Publication date: 26 January 2016 1 About this document The Voluntary Business Broadband Speeds Code of Practice aims to provide business customers
Voluntary Business Broadband Speeds Code of Practice Publication date: 26 January 2016 1 About this document The Voluntary Business Broadband Speeds Code of Practice aims to provide business customers
ANNUAL ELECTRONIC COMMUNICATIONS QUESTIONNAIRE (2011)
 ANNUAL ELECTRONIC COMMUNICATIONS QUESTIONNAIRE (2011) PART I - IDENTIFICATION INFORMATION AND ACTIVITY CHARACTERIZATION OF ELECTRONIC COMMUNICATIONS SERVICE OPERATORS 1. COMPANY IDENTIFICATION INFORMATION
ANNUAL ELECTRONIC COMMUNICATIONS QUESTIONNAIRE (2011) PART I - IDENTIFICATION INFORMATION AND ACTIVITY CHARACTERIZATION OF ELECTRONIC COMMUNICATIONS SERVICE OPERATORS 1. COMPANY IDENTIFICATION INFORMATION
Connection Services. Hakim S. ADICHE, MSc
 Connection Services Hakim S. ADICHE, MSc adiche@ccse.kfupm.edu.sa Department of Computer Engineering King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals Dhahran, Saudi Arabia Connection Services Different connectivity
Connection Services Hakim S. ADICHE, MSc adiche@ccse.kfupm.edu.sa Department of Computer Engineering King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals Dhahran, Saudi Arabia Connection Services Different connectivity
Broadband Access in the BT Fixed Network extract of BCS Essex presentation, 20 March 2007. Dr Elspeth MacFadyen, Programme Director BT Group CTO
 Broadband Access in the BT Fixed Network extract of BCS Essex presentation, 20 March 2007 Dr Elspeth MacFadyen, Programme Director BT Group CTO What I ll be talking about General context Access network
Broadband Access in the BT Fixed Network extract of BCS Essex presentation, 20 March 2007 Dr Elspeth MacFadyen, Programme Director BT Group CTO What I ll be talking about General context Access network
Networks 2. Gabriela Ochoa. 2014 University of Stirling CSCU9B1 Essential Skills for the Information Age. Content
 Networks 2 Gabriela Ochoa Lecture Networks 2/Slide 1 Content How is Internet connected? Internet backbone Internet service providers (ISP) How to connect a home computer to the Internet? How do networks
Networks 2 Gabriela Ochoa Lecture Networks 2/Slide 1 Content How is Internet connected? Internet backbone Internet service providers (ISP) How to connect a home computer to the Internet? How do networks
ANNEX 2. Active SIM Cards refers to the number of SIM cards with one or more billing events in the past three months.
 ANNEX 2 The following definitions apply: Active SIM Cards refers to the number of SIM cards with one or more billing events in the past three months. Fixed Customers Active refers to the number of customers
ANNEX 2 The following definitions apply: Active SIM Cards refers to the number of SIM cards with one or more billing events in the past three months. Fixed Customers Active refers to the number of customers
Residential Broadband: Technologies for High-Speed Access To Homes
 Residential Broadband: Technologies for High-Speed Access To Homes The Ohio State University Columbus, OH 43210-1277 1277 http://www.cse.ohio-state.edu/~jain/ 1 Overview 56 kbps Modems, ISDN ADSL, VDSL
Residential Broadband: Technologies for High-Speed Access To Homes The Ohio State University Columbus, OH 43210-1277 1277 http://www.cse.ohio-state.edu/~jain/ 1 Overview 56 kbps Modems, ISDN ADSL, VDSL
Public Network. 1. Relatively long physical distance 2. Requiring a service provider (carrier) Branch Office. Home. Private Network.
 Introduction to LAN TDC 363 Week 4 Connecting LAN to WAN Book: Chapter 7 1 Outline Wide Area Network (WAN): definition WAN Topologies Choices of WAN technologies Dial-up ISDN T1 Frame Relay DSL Remote
Introduction to LAN TDC 363 Week 4 Connecting LAN to WAN Book: Chapter 7 1 Outline Wide Area Network (WAN): definition WAN Topologies Choices of WAN technologies Dial-up ISDN T1 Frame Relay DSL Remote
BROADBAND VALUE CHAIN. Request for Information (RFI)
 BROADBAND VALUE CHAIN Request for Information (RFI) The Independent Communications Authority of South Africa (The Authority) hereby requests information in terms of a section 4B inquiry process on the
BROADBAND VALUE CHAIN Request for Information (RFI) The Independent Communications Authority of South Africa (The Authority) hereby requests information in terms of a section 4B inquiry process on the
How To Get High Speed Internet In Australia
 ADSL vs Cable Cable subscribers are connected directly to high speed lines while ADSL subscribers are connected directly to medium speed lines Cable subscribers share the line connecting them to neighbourhood
ADSL vs Cable Cable subscribers are connected directly to high speed lines while ADSL subscribers are connected directly to medium speed lines Cable subscribers share the line connecting them to neighbourhood
Network Neutrality Statement
 Network Neutrality Statement CTC continues to comply with all applicable FCC requirements while providing the best possible customer experience for its Internet users. As such, CTC commits to the open
Network Neutrality Statement CTC continues to comply with all applicable FCC requirements while providing the best possible customer experience for its Internet users. As such, CTC commits to the open
ECE 510 -- Chapter 1
 ECE 510 -- Chapter 1 Definition: Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) Public network technology that delivers high bandwidth over conventional copper wiring at limited distances. There are four major types of
ECE 510 -- Chapter 1 Definition: Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) Public network technology that delivers high bandwidth over conventional copper wiring at limited distances. There are four major types of
FACT SHEET INTERCONNECT AND ACCESS ISDN2, ISDN2 ENHANCED AND ISDN 10/20/30 SERVICES
 END TO END SWITCHED DATA NETWORK Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) is an end-to-end digital switched network that is capable of delivering voice and data calls to national and international destinations.
END TO END SWITCHED DATA NETWORK Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) is an end-to-end digital switched network that is capable of delivering voice and data calls to national and international destinations.
Glossary of Telco Terms
 Glossary of Telco Terms Access Generally refers to the connection between your business and the public phone network, or between your business and another dedicated location. A large portion of your business
Glossary of Telco Terms Access Generally refers to the connection between your business and the public phone network, or between your business and another dedicated location. A large portion of your business
Narrowband and Broadband Access Technologies
 Computer Networks and Internets, 5e Chapters 12 and 16 Access and Interconnection Technologies (slidesets abridged/combined) By Douglas Comer Modified from the lecture slides of Lami Kaya (LKaya@ieee.org)
Computer Networks and Internets, 5e Chapters 12 and 16 Access and Interconnection Technologies (slidesets abridged/combined) By Douglas Comer Modified from the lecture slides of Lami Kaya (LKaya@ieee.org)
By: Mohsen Aminifar Fall 2014
 By: Mohsen Aminifar Fall 2014 Contact Information: E-Mail: m.aminifar@modares.ac.ir admin@parsenet.ir Phone : 021-22919726 09128442885 Website : http://parsenet.ir http://aminifar.ir SMS Center : 5000262175
By: Mohsen Aminifar Fall 2014 Contact Information: E-Mail: m.aminifar@modares.ac.ir admin@parsenet.ir Phone : 021-22919726 09128442885 Website : http://parsenet.ir http://aminifar.ir SMS Center : 5000262175
Notification of the National Telecommunications Commission Re: Nature and Categories of Telecommunications Business Translation
 Notification of the National Telecommunications Commission Re: Nature and Categories of Telecommunications Business Translation Whereas Section 5 () of the Act on Organization to Assign Radio Frequency
Notification of the National Telecommunications Commission Re: Nature and Categories of Telecommunications Business Translation Whereas Section 5 () of the Act on Organization to Assign Radio Frequency
TELECOMMUNICATIONS STANDARDS ADVISORY COMMITTEE TSAC WORKING GROUP ON NEW STANDARDS AND POLICY (NSP)
 TELECOMMUNICATIONS STANDARDS ADVISORY COMMITTEE TSAC WORKING GROUP ON NEW STANDARDS AND POLICY (NSP) Introduction Development of Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) Technology This paper introduces the development
TELECOMMUNICATIONS STANDARDS ADVISORY COMMITTEE TSAC WORKING GROUP ON NEW STANDARDS AND POLICY (NSP) Introduction Development of Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) Technology This paper introduces the development
Broadband Definitions and Acronyms
 The New Mexico Broadband Program Broadband Definitions and Acronyms Version 1, April 2013 Prepared for: The New Mexico Broadband Program NM Department of Information Technology http://www.doit.state.nm.us/broadband/
The New Mexico Broadband Program Broadband Definitions and Acronyms Version 1, April 2013 Prepared for: The New Mexico Broadband Program NM Department of Information Technology http://www.doit.state.nm.us/broadband/
Hong Kong - Telecoms, Mobile, Broadband and Forecasts
 Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/1226790/ Hong Kong - Telecoms, Mobile, Broadband and Forecasts Description: This report covers the sophisticated Hong Kong telecommunications
Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/1226790/ Hong Kong - Telecoms, Mobile, Broadband and Forecasts Description: This report covers the sophisticated Hong Kong telecommunications
Fiber to the Home. Definition. Overview. Topics
 Fiber to the Home Definition Fiber to the home (FTTH) is the ideal fiber-optics architecture. In this architecture, fiber deployment is carried all the way to the customer s home (premises). Overview Today
Fiber to the Home Definition Fiber to the home (FTTH) is the ideal fiber-optics architecture. In this architecture, fiber deployment is carried all the way to the customer s home (premises). Overview Today
Communication Networks. MAP-TELE 2011/12 José Ruela
 Communication Networks MAP-TELE 2011/12 José Ruela Network basic mechanisms Introduction to Communications Networks Communications networks Communications networks are used to transport information (data)
Communication Networks MAP-TELE 2011/12 José Ruela Network basic mechanisms Introduction to Communications Networks Communications networks Communications networks are used to transport information (data)
CTS2134 Introduction to Networking. Module 07: Wide Area Networks
 CTS2134 Introduction to Networking Module 07: Wide Area Networks WAN cloud Central Office (CO) Local loop WAN components Demarcation point (demarc) Consumer Premises Equipment (CPE) Channel Service Unit/Data
CTS2134 Introduction to Networking Module 07: Wide Area Networks WAN cloud Central Office (CO) Local loop WAN components Demarcation point (demarc) Consumer Premises Equipment (CPE) Channel Service Unit/Data
1 Which network type is a specifically designed configuration of computers and other devices located within a confined area? A Peer-to-peer network
 Review questions 1 Which network type is a specifically designed configuration of computers and other devices located within a confined area? A Peer-to-peer network B Local area network C Client/server
Review questions 1 Which network type is a specifically designed configuration of computers and other devices located within a confined area? A Peer-to-peer network B Local area network C Client/server
Traffic Forecasting Models for the Incumbent Based on New Drivers in the Market
 Traffic Forecasting Models for the Incumbent Based on New Drivers in the Market KJELL STORDAHL Kjell Stordahl (58) received his M.S. in statistics from Oslo University in 1972. He worked with Telenor R&D
Traffic Forecasting Models for the Incumbent Based on New Drivers in the Market KJELL STORDAHL Kjell Stordahl (58) received his M.S. in statistics from Oslo University in 1972. He worked with Telenor R&D
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) - An Introduction
 PITCOM Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) - An Introduction Peter Ingram Chief Technology Officer Ofcom 18th January 2005 Ofcom What is Voice over IP? Carrying Voice Traffic on Networks Designed for Data
PITCOM Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) - An Introduction Peter Ingram Chief Technology Officer Ofcom 18th January 2005 Ofcom What is Voice over IP? Carrying Voice Traffic on Networks Designed for Data
Internet Public Network
 Internet Public Network Bandwidth Data rate measured in bits (not bytes) per seconds Kbps (Kilobits per seconds) 125 chars/sec Mbps (Megabits per seconds) 1,250 chars/sec Gbps (Gigabits per seconds) 12,500
Internet Public Network Bandwidth Data rate measured in bits (not bytes) per seconds Kbps (Kilobits per seconds) 125 chars/sec Mbps (Megabits per seconds) 1,250 chars/sec Gbps (Gigabits per seconds) 12,500
Division 12 Report Record-Keeping and Reporting Rules. Issued under section 151BU of the Trade Practices Act 1974
 Division 12 Report Record-Keeping and Reporting Rules Issued under section 151BU of the Trade Practices Act 1974 December 2004 1. TITLE (1) These Rules, made by the Australian Competition and Consumer
Division 12 Report Record-Keeping and Reporting Rules Issued under section 151BU of the Trade Practices Act 1974 December 2004 1. TITLE (1) These Rules, made by the Australian Competition and Consumer
why fixed.plan? We only connect to Tier 1 partners, including Openreach, BT and Talk Talk Business, ensuring a robust and reliable service.
 fixed.plan Operating directly with tier 1 suppliers including Openreach, BT and TalkTalk Business plan com provides you with access to the biggest and most reliable telecommunications networks in the UK.
fixed.plan Operating directly with tier 1 suppliers including Openreach, BT and TalkTalk Business plan com provides you with access to the biggest and most reliable telecommunications networks in the UK.
Traffic load and cost analysis for different IPTV architectures
 Traffic load and cost analysis for different IPTV architectures SKENDER RUGOVA, ARIANIT MARAJ Post and Telecommunication of Kosova-PTK Dardania, p.nr., Prishtina, Republic of Kosova Skender.rugova@ptkonline.com,
Traffic load and cost analysis for different IPTV architectures SKENDER RUGOVA, ARIANIT MARAJ Post and Telecommunication of Kosova-PTK Dardania, p.nr., Prishtina, Republic of Kosova Skender.rugova@ptkonline.com,
RTR Telekom Monitor. Annual Review 2013
 RTR Telekom Monitor Annual Review RTR Telekom Monitor Annual Review Preface 5 1 Fixed network 7 Fixed lines 8 Fixed-line penetration 9 Development of fixed lines 1 Carrier pre-selection and call-by-call
RTR Telekom Monitor Annual Review RTR Telekom Monitor Annual Review Preface 5 1 Fixed network 7 Fixed lines 8 Fixed-line penetration 9 Development of fixed lines 1 Carrier pre-selection and call-by-call
Copyright. Transport networks. Physical layer Transport and access networks. Pag. 1
 Physical layer Transport and access networks Gruppo Reti TLC nome.cognome@polito.it http://www.telematica.polito.it/ COMPUTER NETWORK DESIGN Physical layer review - 1 Copyright Quest opera è protetta dalla
Physical layer Transport and access networks Gruppo Reti TLC nome.cognome@polito.it http://www.telematica.polito.it/ COMPUTER NETWORK DESIGN Physical layer review - 1 Copyright Quest opera è protetta dalla
Residential Broadband: Technologies for High-Speed Access To Homes
 Residential Broadband: Technologies for High-Speed Access To Homes Columbus, OH 43210 Jain@CIS.Ohio-State.Edu http://www.cis.ohio-state.edu/~jain/cis788-97/ Email questions to mbone@netlab.ohio-state.edu
Residential Broadband: Technologies for High-Speed Access To Homes Columbus, OH 43210 Jain@CIS.Ohio-State.Edu http://www.cis.ohio-state.edu/~jain/cis788-97/ Email questions to mbone@netlab.ohio-state.edu
R2. The word protocol is often used to describe diplomatic relations. How does Wikipedia describe diplomatic protocol?
 Chapter 1 Review Questions R1. What is the difference between a host and an end system? List several different types of end systems. Is a Web server an end system? 1. There is no difference. Throughout
Chapter 1 Review Questions R1. What is the difference between a host and an end system? List several different types of end systems. Is a Web server an end system? 1. There is no difference. Throughout
Broadband Primer. A Guide to High Speed Internet Technologies. Indiana Office of Utility Consumer Counselor
 Broadband Primer A Guide to High Speed Internet Technologies Indiana Office of Utility Consumer Counselor 100 N. Senate Av., Room N501 Indianapolis, IN 46204-2215 www.openlines.in.gov toll-free: 1-888-441-2494
Broadband Primer A Guide to High Speed Internet Technologies Indiana Office of Utility Consumer Counselor 100 N. Senate Av., Room N501 Indianapolis, IN 46204-2215 www.openlines.in.gov toll-free: 1-888-441-2494
Broadband Symmetric Q&A
 Broadband Symmetric Q&A 1. What is SHDSL technology? SHDSL is the acronym for Symmetric High bit rate Digital Subscriber Line. SHDSL is one of a number of services that utilise digital subscriber line
Broadband Symmetric Q&A 1. What is SHDSL technology? SHDSL is the acronym for Symmetric High bit rate Digital Subscriber Line. SHDSL is one of a number of services that utilise digital subscriber line
Chapter 9. Communications and Networks. McGraw-Hill/Irwin. Copyright 2008 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 9 Communications and Networks McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2008 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Competencies (Page 1 of 2) Discuss connectivity, the wireless revolution,
Chapter 9 Communications and Networks McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2008 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Competencies (Page 1 of 2) Discuss connectivity, the wireless revolution,
Chapter 11: WAN. Abdullah Konak School of Information Sciences and Technology Penn State Berks. Wide Area Networks (WAN)
 Chapter 11: WAN Abdullah Konak School of Information Sciences and Technology Penn State Berks Wide Area Networks (WAN) The scope of a WAN covers large geographic areas including national and international
Chapter 11: WAN Abdullah Konak School of Information Sciences and Technology Penn State Berks Wide Area Networks (WAN) The scope of a WAN covers large geographic areas including national and international
TAXONOMY OF TELECOM TERMS
 TAXONOMY OF TELECOM TERMS Prepared by TUFF Ltd This short taxonomy is designed to describe the various terms used in today s telecommunications industry. It is not intended to be all embracing but to describe
TAXONOMY OF TELECOM TERMS Prepared by TUFF Ltd This short taxonomy is designed to describe the various terms used in today s telecommunications industry. It is not intended to be all embracing but to describe
why fixed.plan? We only connect to Tier 1 partners, including Openreach, BT and Talk Talk Business, ensuring a robust and reliable service.
 fixed.plan Operating directly with tier 1 suppliers including Openreach, BT and TalkTalk Business plan.com provides you with access to the biggest and most reliable telecommunications networks in the UK.
fixed.plan Operating directly with tier 1 suppliers including Openreach, BT and TalkTalk Business plan.com provides you with access to the biggest and most reliable telecommunications networks in the UK.
BROADBAND CONNECTION VOUCHER SCHEME
 BROADBAND CONNECTION VOUCHER SCHEME Glossary What are the services available? These are some of the descriptions you will see when you start to look for a broadband connection. Contended/Shared Service
BROADBAND CONNECTION VOUCHER SCHEME Glossary What are the services available? These are some of the descriptions you will see when you start to look for a broadband connection. Contended/Shared Service
PUBLIC NOTICE WIRELINE COMPETITION BUREAU RELEASES DATA SPECIFICATION FOR FORM 477 DATA COLLECTION. WC Docket No. 11-10
 PUBLIC NOTICE Federal Communications Commission 445 12 th St., S.W. Washington, D.C. 20554 News Media Information 202 / 418-0500 Internet: http://www.fcc.gov TTY: 1-888-835-5322 DA 13-1805 Released: August
PUBLIC NOTICE Federal Communications Commission 445 12 th St., S.W. Washington, D.C. 20554 News Media Information 202 / 418-0500 Internet: http://www.fcc.gov TTY: 1-888-835-5322 DA 13-1805 Released: August
XDSL and DSLAM Access Technologies
 XDSL and DSLAM Access Technologies Abstract What are the differences between the different forms of xdsl technology, such as ADSL and HDSL? How are they implemented. What are the limitations? What are
XDSL and DSLAM Access Technologies Abstract What are the differences between the different forms of xdsl technology, such as ADSL and HDSL? How are they implemented. What are the limitations? What are
What is telecommunication? electronic communications. service?
 What is telecommunication? Telecommunication: Any transmission, emission or reception of signs, signals, writing, images and sounds or intelligence of any nature by wire, radio, optical or other electromagnetic
What is telecommunication? Telecommunication: Any transmission, emission or reception of signs, signals, writing, images and sounds or intelligence of any nature by wire, radio, optical or other electromagnetic
Introduction Page 2. Understanding Bandwidth Units Page 3. Internet Bandwidth V/s Download Speed Page 4. Optimum Utilization of Bandwidth Page 8
 INDEX Introduction Page 2 Understanding Bandwidth Units Page 3 Internet Bandwidth V/s Download Speed Page 4 Factors Affecting Download Speed Page 5-7 Optimum Utilization of Bandwidth Page 8 Conclusion
INDEX Introduction Page 2 Understanding Bandwidth Units Page 3 Internet Bandwidth V/s Download Speed Page 4 Factors Affecting Download Speed Page 5-7 Optimum Utilization of Bandwidth Page 8 Conclusion
GERMANY INTRODUCTION REGULATORY ENVIRONMENT. Main regulatory developments
 GERMANY INTRODUCTION Fixed broadband and mobile broadband penetration rates continued to increase during 2008. The number of cable broadband connections has grown considerably, mainly driven by a high
GERMANY INTRODUCTION Fixed broadband and mobile broadband penetration rates continued to increase during 2008. The number of cable broadband connections has grown considerably, mainly driven by a high
Appendix A. Analysis of wholesale market for terminating segments of leased lines. (Market 6)
 Appendix A Analysis of wholesale market for terminating segments of leased lines (Market 6) 6 May 2014 1 Table of Contents 1.0 Introduction... 5 1.1 General... 5 1.2 Electronic communications legislation...
Appendix A Analysis of wholesale market for terminating segments of leased lines (Market 6) 6 May 2014 1 Table of Contents 1.0 Introduction... 5 1.1 General... 5 1.2 Electronic communications legislation...
