Antarctic Temperature and Sea Ice Trends over the Last Century
|
|
|
- Rudolf Webster
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 Antarctic Temperature and Sea Ice Trends over the Last Century High latitude regions of the Earth (the Arctic and Antarctic) have been considered as bellwethers in the detection of global climate change. According to IPCC (2001), Climate change in polar regions is expected to be among the largest and most rapid of any region on the Earth, and will cause major physical, ecological, sociological, and economic impacts, especially in the Arctic, Antarctic Peninsula, and Southern Ocean. Polar regions contain important drivers of climate change. Once triggered, they may continue for centuries, long after greenhouse gas concentrations are stabilized, and cause irreversible impacts on ice sheets, global ocean circulation, and sea-level rise. Climate models (GCMs) suggest that polar regions should warm more quickly than temperate or tropical regions because the cold temperatures cause the air to be very dry. The low amounts of water vapor, the most important greenhouse gas, causes the relative effects of other gases, notably carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), to be greater. Thus climate change caused by an increase in the latter should be most evident in the polar regions. This paper considers climate trends in Antarctica. In the sections below we examine the results of studies by various researchers who have analyzed Antarctic temperatures and sea ice. We also present temperature data from long-term Antarctic stations. Antarctic Temperature Trends Station Data We begin by examining measured data from surface temperature stations. Below are annual average temperatures from six long-term stations in Antarctica, obtained from the NASA GISS climate page. Amundson-Scott is at the South Pole, McMurdo, Scott Base and Vostok are high-latitude stations, Davis and Casey are in East Antarctica, and Faraday and Rothera Point are in the Antarctic Peninsula.
3
4 Antarctic Temperature Trends Journal Article Summaries Numerous journal articles have reported on studies of temperature trends in Antarctica, with a remarkably consistent conclusion. Doran, et al (2002) conducted a study of temperatures and ecosystem response in Antarctica s dry valleys. They begin by stating that The average air temperature at the Earth s surface has increased by 0.06 C per decade during the 20 th century, according to the IPCC, and by 0.19 C per decade from 1979 to In fact, Climate models generally predict amplified warming in polar regions, which would suggest that Antarctic temperatures should have warmed more than this in response to increases in greenhouse gases. However, Although previous reports suggest slight recent continental warming, they declare that "our spatial analysis of Antarctic meteorological data" demonstrated a net cooling over the entire Antarctic continent between 1966 and 2000, particularly during summer and autumn, when ice melt would be most likely to occur. A study of temperatures and ecosystem response in the McMurdo Dry Valleys indicated a cooling of 0.7 C per decade between 1986 and Antarctic ecosystems show clear evidence of cooling, suggesting that the temperature measurements reported by Doran et al are occurring widely. Among those effects are
5 decreased primary productivity of lakes (6-9% per year) and declining numbers of soil invertebrates (more than 10% per year) The authors conclude by saying, Continental Antarctic cooling, especially the seasonality of cooling, poses challenges to models of climate and ecosystem change. Turner, et al (2005) analyzed 19 long-term stations reporting temperature, sea level pressure, and wind speed over the Antarctic continent. They noticed a warming of the Antarctic Peninsula (as have others), but suggested that since the Peninsula is where the strongest influence of the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) is felt, tropical forcing may be the cause of at least some of the warming. Turner et al also noticed a change in the trend in temperatures between the period and A comparison of the two averaging periods showed that the warming trend was greater (or the cooling trend less) during the period compared to There are relatively few inland stations in Antarctica. The Vostok base shows slight cooling from , while the Amundsen-Scott station shows a cooling in all seasons, with a decrease of 0.17 C per decade. Thompson and Solomon (2002) analyzed recent climate change in the Antarctic and other high southern latitudes. They concluded that Climate variability in the high-latitude Southern Hemisphere (SH) is dominated by the SH annular mode, a large-scale pattern of variability characterized by fluctuations in the strength of the circumpolar vortex. Trends in the SH circulation have been dominated recently by the high-index polarity of this pattern, with stronger westerly flow encircling the polar cap the largest and most significant tropospheric trends can be traced to recent trends in the lower stratospheric polar vortex, which are due largely to photochemical ozone losses. Finally, During the summer-fall season, the trend toward stronger circumpolar flow has contributed substantially to the observed warming over the Antarctic Peninsula and Patagonia and to the cooling over eastern Antarctica and the Antarctic plateau. Comiso (2000) reported predominately positive temperature trends along the Antarctic Peninsula. Other parts of the continent have cooled, however. Furthermore, the trend depends in large part on the length of record analyzed. A 45-year trend from station data showed a warming trend of about.12 C per decade, but over the most recent 20 year period there was cooling in both the station data and from satellite observations. Of the 22 longterm stations on the continent, 13 showed temperature decreases and only 9 showed increases. Comiso was puzzled about the cooling trend because during the same time
6 period a general warming is being observed globally. This corresponds to an increase in the sea ice extent around the continent not a decrease, as would be expected if a general warming were to occur. Bertler, et al (2004) studied isotope records from snow samples in the McMurdo Dry Valleys and concluded that warming in areas such as the Antarctic Peninsula and cooling of the terrestrial Ross Sea region are linked to ENSO changes, not to greenhouse gas effects. Conclusion: Whereas climate models suggest that temperatures in Antarctica should have been warming in recent decades in response to increases in greenhouse gases, measurements show otherwise. Although some regions do show increases, the majority of the continent shows no significant trend or an actual decrease. There is evidence that atmospheric and ocean circulation patterns have much stronger impacts on Antarctic climate than do greenhouse gas increases. Antarctic Sea Ice Trends Cavalieri, et al (2004) extended the analysis of Arctic and Antarctic sea ice variability from two to three decades ( ) by bridging the gap between the Nimbus 7 data and the earlier Nimbus 5 satellite data record. While Arctic sea ice extent decreased by 0.36 ± 0.05 million sq. km. per decade from 1979 through 2002, the Antarctic sea ice extent decreased dramatically over the period , then gradually increased. Over the period , Antarctic sea ice extent has increased by 0.11 ± 0.05 million sq. km. per decade. Yuan and Martinson (2000) stated that the Antarctic Sea Ice Edge (SIE) index responds largely to ENSO and Pacific Ocean precipitation patterns. They reported that there was geographical variation in SIE trends, but that the overall monthly anomalies, averaged around the entire Antarctic continent showed a net increasing trend of ±.043 degrees per year over the period Their figure showing the longitudinal trends in SIE appears below.
7 Antarctic Sea Ice Edge index (SIE) trend, , from Yuan and Morrison (2000). Zwally, et al (2002) used a systematically calibrated and analyzed data set for 20.2 years ( ). They report that the total Antarctic sea ice extent increased by 11,180 ± 4190 sq. km. per year. Regionally, the trends in extent are positive in the Weddell Sea, Pacific Ocean, and Ross sectors, slightly negative in the Indian Ocean, and strongly negative in the Bellingshausen-Amundsen Seas sector. For the entire ice pack, ice increases occur in all seasons, with the largest increase during fall. The authors conclude: The observed increase in Antarctic sea ice cover is counter to the observed decreases in the Arctic. It is also qualitatively consistent with the counterintuitive prediction of a global atmospheric-ocean model of increasing sea ice around Antarctica with climate warming due to the stabilizing effects of increased snowfall on the Southern Ocean. Vyas, et al (2003) used data from several satellite platforms (Nimbus-7, DMSP and OCEANSAT-1) to estimate trends in sea ice around Antarctica. They found decreasing sea ice in the Weddell Sea, increases in the Ross Sea, and insignificant changes elsewhere. For the continent as a whole there has been an increase in sea ice, a weak but consistent increasing trend of approximately 43,000 sq. km. per year. The figure below (Figure 4c from the Vyas, et al article) shows the total sea ice extent trend.
8 Sea Ice for the entire Antarctic (Figure 4c from Vyas, et al, 2003) Vyas et al conclude that their estimates may actually understate the increase in sea ice: the increasing trend in the sea ice extent over the Antarctic region may be slowly accelerating in time, particularly over the last decade. In fact, it is interesting to note that most of the SSM/I derived sea ice extents estimates during the middle of the last decade have been on the higher side of the long-term trend. Antarctic climate and sea ice trends, in fact, are paradoxical in the global warming scenario resulting from increasing greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, which suggest that polar regions should be warming (and melting) in response to greenhouse gas enhancement. Liu, et al (2004) report that total Antarctic sea ice (the area covered by at least 15% ice concentration) has increased significantly since 1979, by about 13,295 sq. km. per year. Regionally, there has been a large increase in the central Pacific sector and a smaller decrease in the Weddell Sea. Although ENSO and the Antarctic Oscillation appear to influence sea ice trends, they cannot explain them. There may be less understood largescale processes at work influencing sea ice. The National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC, 2006) publishes updated values of historical sea ice extent around Antarctica, using data from SMMR and SSM/I satellite platforms. Below is their chart of sea ice extent anomalies since While there has been considerable variation from year to year, the overall linear trend shows an increase of about 400,000 sq. km. in sea ice over the period of record.
9 Antarctic Sea Ice Area Anomalies, , from NSIDC (2006) Conclusion: The data clearly show that Antarctica as a whole is seeing increases in sea ice extent in recent decades, in spite of what climate models suggest should be occurring: steady warming. There are regional differences, with Weddell Sea ice extent decreasing and Ross Sea ice increasing, but overall the pattern is clear: there is more ice, not less, surrounding Antarctica.
10 References Cavalieri, D.J., Parkinson, C.L. and Vinnikov, K.Y Year satellite record reveals contrasting Arctic and Antarctic decadal sea ice variability. Geophysical Research Letters 30: /2003GL Comiso, J.C Variability and trends in Antarctic surface temperatures from in situ and satellite infrared measurements. Journal of Climate 13: Doran, P.T., Priscu, J.C., Lyons, W.B., Walsh, J.E., Fountain, A.G., McKnight, D.M., Moorhead, D.L., Virginia, R.A., Wall, D.H., Clow, G.D., Fritsen, C.H., McKay, C.P. and Parsons, A.N Antarctic climate cooling and terrestrial ecosystem response. Nature 415: IPCC, 2001a. Climate Change 2001: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. McCarthy, J.J., O.F. Canziani, N.A. Leary, D.J. Dokken and K.S.White (eds.). Cambridge University Press, 1032 pp. Liu, J., Curry, J.A. and Martinson, D.G Interpretation of recent Antarctic sea ice variability. Geophysical Research Letters 31: /2003GL National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC), Sea Ice trends and Climatologies from SMMR and SSM/I. Online at ssmi ancillary/regions/total antarctic.html#nsidc Parkinson, C.L Southern Ocean sea ice and its wider linkages: insights revealed from models and observations. Antarctic Science 16: Renwick, James A., Southern Hemisphere Circulation and Relations with Sea Ice and Sea Surface Temperature. Journal of Climate Volume, 15, Turner, J., Colwell, S.R., Marshall, G.J., Lachlan-Cope, T.A., Carleton, A.M., Jones, P.D., Lagun, V., Reid, P.A. and Iagovkina, S Antarctic climate change during the last 50 years. International Journal of Climatology 25: Vyas, N.K., Dash, M.K., Bhandari, S.M., Khare, N., Mitra, A. and Pandey, P.C On the secular trends in sea ice extent over the antarctic region based on OCEANSAT-1 MSMR observations. International Journal of Remote Sensing 24:
11 Yuan, X., ENSO-related impacts on Antarctic sea ice: a synthesis of phenomenon and mechanisms. Antarctic Science 16, Yuan, X. and Martinson, D.G., Antarctic Sea Ice Extent Variability and Its Global Connectivity. Journal of Climate, 13, Zwally, H.J., Comiso, J.C., Parkinson, C.L., Cavalieri, D.J. and Gloersen, P., Variability of Antarctic sea ice Journal of Geophysical Research, VOL. 107, NO. C5, /2000JC000733, 2002 George H. Taylor is the State Climatologist for Oregon. The opinions expressed here are his own.
Temporal variation in snow cover over sea ice in Antarctica using AMSR-E data product
 Temporal variation in snow cover over sea ice in Antarctica using AMSR-E data product Michael J. Lewis Ph.D. Student, Department of Earth and Environmental Science University of Texas at San Antonio ABSTRACT
Temporal variation in snow cover over sea ice in Antarctica using AMSR-E data product Michael J. Lewis Ph.D. Student, Department of Earth and Environmental Science University of Texas at San Antonio ABSTRACT
Temporal and spatial evolution of the Antarctic sea ice prior to the September 2012 record maximum extent
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 40, 5894 5898, doi:10.1002/2013gl058371, 2013 Temporal and spatial evolution of the Antarctic sea ice prior to the September 2012 record maximum extent John Turner, 1
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 40, 5894 5898, doi:10.1002/2013gl058371, 2013 Temporal and spatial evolution of the Antarctic sea ice prior to the September 2012 record maximum extent John Turner, 1
Jessica Blunden, Ph.D., Scientist, ERT Inc., Climate Monitoring Branch, NOAA s National Climatic Data Center
 Kathryn Sullivan, Ph.D, Acting Under Secretary of Commerce for Oceans and Atmosphere and NOAA Administrator Thomas R. Karl, L.H.D., Director,, and Chair of the Subcommittee on Global Change Research Jessica
Kathryn Sullivan, Ph.D, Acting Under Secretary of Commerce for Oceans and Atmosphere and NOAA Administrator Thomas R. Karl, L.H.D., Director,, and Chair of the Subcommittee on Global Change Research Jessica
Mapping of Antarctic sea ice in the depletion phase: an indicator of climatic change?
 Mapping of Antarctic sea ice in the depletion phase: an indicator of climatic change? G. Sreenivasan 1 and T. J. Majumdar 2, * 1 Regional Remote Sensing Service Centre, Nagpur 440 010, India 2 Space Applications
Mapping of Antarctic sea ice in the depletion phase: an indicator of climatic change? G. Sreenivasan 1 and T. J. Majumdar 2, * 1 Regional Remote Sensing Service Centre, Nagpur 440 010, India 2 Space Applications
Data Sets of Climate Science
 The 5 Most Important Data Sets of Climate Science Photo: S. Rahmstorf This presentation was prepared on the occasion of the Arctic Expedition for Climate Action, July 2008. Author: Stefan Rahmstorf, Professor
The 5 Most Important Data Sets of Climate Science Photo: S. Rahmstorf This presentation was prepared on the occasion of the Arctic Expedition for Climate Action, July 2008. Author: Stefan Rahmstorf, Professor
Graphing Sea Ice Extent in the Arctic and Antarctic
 Graphing Sea Ice Extent in the Arctic and Antarctic Summary: Students graph sea ice extent (area) in both polar regions (Arctic and Antarctic) over a three-year period to learn about seasonal variations
Graphing Sea Ice Extent in the Arctic and Antarctic Summary: Students graph sea ice extent (area) in both polar regions (Arctic and Antarctic) over a three-year period to learn about seasonal variations
Radiative effects of clouds, ice sheet and sea ice in the Antarctic
 Snow and fee Covers: Interactions with the Atmosphere and Ecosystems (Proceedings of Yokohama Symposia J2 and J5, July 1993). IAHS Publ. no. 223, 1994. 29 Radiative effects of clouds, ice sheet and sea
Snow and fee Covers: Interactions with the Atmosphere and Ecosystems (Proceedings of Yokohama Symposia J2 and J5, July 1993). IAHS Publ. no. 223, 1994. 29 Radiative effects of clouds, ice sheet and sea
Atmospheric Dynamics of Venus and Earth. Institute of Geophysics and Planetary Physics UCLA 2 Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
 Atmospheric Dynamics of Venus and Earth G. Schubert 1 and C. Covey 2 1 Department of Earth and Space Sciences Institute of Geophysics and Planetary Physics UCLA 2 Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
Atmospheric Dynamics of Venus and Earth G. Schubert 1 and C. Covey 2 1 Department of Earth and Space Sciences Institute of Geophysics and Planetary Physics UCLA 2 Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
SPATIAL DISTRIBUTION OF NORTHERN HEMISPHERE WINTER TEMPERATURES OVER THE SOLAR CYCLE DURING THE LAST 130 YEARS
 SPATIAL DISTRIBUTION OF NORTHERN HEMISPHERE WINTER TEMPERATURES OVER THE SOLAR CYCLE DURING THE LAST 130 YEARS Kalevi Mursula, Ville Maliniemi, Timo Asikainen ReSoLVE Centre of Excellence Department of
SPATIAL DISTRIBUTION OF NORTHERN HEMISPHERE WINTER TEMPERATURES OVER THE SOLAR CYCLE DURING THE LAST 130 YEARS Kalevi Mursula, Ville Maliniemi, Timo Asikainen ReSoLVE Centre of Excellence Department of
Estimating Firn Emissivity, from 1994 to1998, at the Ski Hi Automatic Weather Station on the West Antarctic Ice Sheet Using Passive Microwave Data
 Estimating Firn Emissivity, from 1994 to1998, at the Ski Hi Automatic Weather Station on the West Antarctic Ice Sheet Using Passive Microwave Data Mentor: Dr. Malcolm LeCompte Elizabeth City State University
Estimating Firn Emissivity, from 1994 to1998, at the Ski Hi Automatic Weather Station on the West Antarctic Ice Sheet Using Passive Microwave Data Mentor: Dr. Malcolm LeCompte Elizabeth City State University
Solar Flux and Flux Density. Lecture 3: Global Energy Cycle. Solar Energy Incident On the Earth. Solar Flux Density Reaching Earth
 Lecture 3: Global Energy Cycle Solar Flux and Flux Density Planetary energy balance Greenhouse Effect Vertical energy balance Latitudinal energy balance Seasonal and diurnal cycles Solar Luminosity (L)
Lecture 3: Global Energy Cycle Solar Flux and Flux Density Planetary energy balance Greenhouse Effect Vertical energy balance Latitudinal energy balance Seasonal and diurnal cycles Solar Luminosity (L)
SECTION 3 Making Sense of the New Climate Change Scenarios
 SECTION 3 Making Sense of the New Climate Change Scenarios The speed with which the climate will change and the total amount of change projected depend on the amount of greenhouse gas emissions and the
SECTION 3 Making Sense of the New Climate Change Scenarios The speed with which the climate will change and the total amount of change projected depend on the amount of greenhouse gas emissions and the
climate science A SHORT GUIDE TO This is a short summary of a detailed discussion of climate change science.
 A SHORT GUIDE TO climate science This is a short summary of a detailed discussion of climate change science. For more information and to view the full report, visit royalsociety.org/policy/climate-change
A SHORT GUIDE TO climate science This is a short summary of a detailed discussion of climate change science. For more information and to view the full report, visit royalsociety.org/policy/climate-change
Chapter Overview. Seasons. Earth s Seasons. Distribution of Solar Energy. Solar Energy on Earth. CHAPTER 6 Air-Sea Interaction
 Chapter Overview CHAPTER 6 Air-Sea Interaction The atmosphere and the ocean are one independent system. Earth has seasons because of the tilt on its axis. There are three major wind belts in each hemisphere.
Chapter Overview CHAPTER 6 Air-Sea Interaction The atmosphere and the ocean are one independent system. Earth has seasons because of the tilt on its axis. There are three major wind belts in each hemisphere.
FRENCH ARCTIC INITIATIVE SCIENTIFIC PRIORITIES
 FRENCH ARCTIC INITIATIVE SCIENTIFIC PRIORITIES J.J. Pangrazi / Biosphoto J.J. Pangrazi / Biosphoto Conference audience Edouard Bard introductory lecture Dr. Denis-Didier Rousseau (CNRS Senior Research
FRENCH ARCTIC INITIATIVE SCIENTIFIC PRIORITIES J.J. Pangrazi / Biosphoto J.J. Pangrazi / Biosphoto Conference audience Edouard Bard introductory lecture Dr. Denis-Didier Rousseau (CNRS Senior Research
Fundamentals of Climate Change (PCC 587): Water Vapor
 Fundamentals of Climate Change (PCC 587): Water Vapor DARGAN M. W. FRIERSON UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON, DEPARTMENT OF ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES DAY 2: 9/30/13 Water Water is a remarkable molecule Water vapor
Fundamentals of Climate Change (PCC 587): Water Vapor DARGAN M. W. FRIERSON UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON, DEPARTMENT OF ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES DAY 2: 9/30/13 Water Water is a remarkable molecule Water vapor
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/311/5768/1747/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Paleoclimatic Evidence for Future Ice-Sheet Instability and Rapid Sea- Level Rise Jonathan T. Overpeck,* Bette L. Otto-Bliesner,
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/311/5768/1747/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Paleoclimatic Evidence for Future Ice-Sheet Instability and Rapid Sea- Level Rise Jonathan T. Overpeck,* Bette L. Otto-Bliesner,
Examining the Recent Pause in Global Warming
 Examining the Recent Pause in Global Warming Global surface temperatures have warmed more slowly over the past decade than previously expected. The media has seized this warming pause in recent weeks,
Examining the Recent Pause in Global Warming Global surface temperatures have warmed more slowly over the past decade than previously expected. The media has seized this warming pause in recent weeks,
Future needs of remote sensing science in Antarctica and the Southern Ocean: A report to support the Horizon Scan activity of COMNAP and SCAR
 Future needs of remote sensing science in Antarctica and the Southern Ocean: A report to support the Horizon Scan activity of COMNAP and SCAR Thomas Wagner ([email protected]) Charles Webb NASA Cryospheric
Future needs of remote sensing science in Antarctica and the Southern Ocean: A report to support the Horizon Scan activity of COMNAP and SCAR Thomas Wagner ([email protected]) Charles Webb NASA Cryospheric
Climate Lingo Bingo. Climate Discovery: Climate Future. http://.eo.ucar.edu. Teacher s Guide. National Science Content Standards Addressed:
 Climate Discovery: Climate Future Climate Lingo Bingo Teacher s Guide http://.eo.ucar.edu Subject Focus: Earth Science Environmental Science Political Science and Social Studies Materials & Preparations:
Climate Discovery: Climate Future Climate Lingo Bingo Teacher s Guide http://.eo.ucar.edu Subject Focus: Earth Science Environmental Science Political Science and Social Studies Materials & Preparations:
Geography affects climate.
 KEY CONCEPT Climate is a long-term weather pattern. BEFORE, you learned The Sun s energy heats Earth s surface unevenly The atmosphere s temperature changes with altitude Oceans affect wind flow NOW, you
KEY CONCEPT Climate is a long-term weather pattern. BEFORE, you learned The Sun s energy heats Earth s surface unevenly The atmosphere s temperature changes with altitude Oceans affect wind flow NOW, you
When people think of climate change, they usually think of the atmosphere first. They think of the kind of things they hear about in the weather
 3 Climate change so far When people think of climate change, they usually think of the atmosphere first. They think of the kind of things they hear about in the weather forecast: air temperature, rainfall,
3 Climate change so far When people think of climate change, they usually think of the atmosphere first. They think of the kind of things they hear about in the weather forecast: air temperature, rainfall,
Climate Change on the Prairie:
 Climate Change on the Prairie: A Basic Guide to Climate Change in the High Plains Region - UPDATE Global Climate Change Why does the climate change? The Earth s climate has changed throughout history and
Climate Change on the Prairie: A Basic Guide to Climate Change in the High Plains Region - UPDATE Global Climate Change Why does the climate change? The Earth s climate has changed throughout history and
The Ice Age By: Sue Peterson
 www.k5learning.com Objective sight words (pulses, intermittent, isotopes, chronicle, methane, tectonic plates, volcanism, configurations, land-locked, erratic); concepts (geological evidence and specific
www.k5learning.com Objective sight words (pulses, intermittent, isotopes, chronicle, methane, tectonic plates, volcanism, configurations, land-locked, erratic); concepts (geological evidence and specific
II. Related Activities
 (1) Global Cloud Resolving Model Simulations toward Numerical Weather Forecasting in the Tropics (FY2005-2010) (2) Scale Interaction and Large-Scale Variation of the Ocean Circulation (FY2006-2011) (3)
(1) Global Cloud Resolving Model Simulations toward Numerical Weather Forecasting in the Tropics (FY2005-2010) (2) Scale Interaction and Large-Scale Variation of the Ocean Circulation (FY2006-2011) (3)
How To Predict Climate Change In Tonga
 Niuatoputapu Niuafo'ou Late Island Vava u Group South Pacific Ocean Tofua Island Kotu Group Nomuka Group Ha apai Group NUKU ALOFA Eua Island Tongatapu Group Current and future climate of Tonga > Tonga
Niuatoputapu Niuafo'ou Late Island Vava u Group South Pacific Ocean Tofua Island Kotu Group Nomuka Group Ha apai Group NUKU ALOFA Eua Island Tongatapu Group Current and future climate of Tonga > Tonga
SOUTHERN OCEAN CURRENTS. http://www.polar.org/antsun/oldissues2002-2003/sun121502/current.html
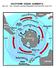 Map from: SOUTHERN OCEAN CURRENTS http://www.polar.org/antsun/oldissues2002-2003/sun121502/current.html FROM: The Antarctic Coastal Current Joanna Gyory, John Cangialosi, Ieng Jo, Arthur J. Mariano, Edward
Map from: SOUTHERN OCEAN CURRENTS http://www.polar.org/antsun/oldissues2002-2003/sun121502/current.html FROM: The Antarctic Coastal Current Joanna Gyory, John Cangialosi, Ieng Jo, Arthur J. Mariano, Edward
What Causes Climate? Use Target Reading Skills
 Climate and Climate Change Name Date Class Climate and Climate Change Guided Reading and Study What Causes Climate? This section describes factors that determine climate, or the average weather conditions
Climate and Climate Change Name Date Class Climate and Climate Change Guided Reading and Study What Causes Climate? This section describes factors that determine climate, or the average weather conditions
Arctic sea ice decline: Faster than forecast
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L09501, doi: 10.1029/2007GL029703, 2007 Arctic sea ice decline: Faster than forecast Julienne Stroeve, 1 Marika M. Holland, 2 Walt Meier,
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L09501, doi: 10.1029/2007GL029703, 2007 Arctic sea ice decline: Faster than forecast Julienne Stroeve, 1 Marika M. Holland, 2 Walt Meier,
Orbital-Scale Climate Change
 Orbital-Scale Climate Change Climate Needed for Ice Age Warm winter and non-frozen oceans so lots of evaporation and snowfall Cool summer so that ice does not melt Ice Age Model When ice growing ocean
Orbital-Scale Climate Change Climate Needed for Ice Age Warm winter and non-frozen oceans so lots of evaporation and snowfall Cool summer so that ice does not melt Ice Age Model When ice growing ocean
Global Warming. Charles F. Keller
 Global Warming Charles F. Keller Smokestacks at an industrial plant. Introduction Global warming is in the news. While scientists agree that temperatures are rising, they disagree as to the causes and
Global Warming Charles F. Keller Smokestacks at an industrial plant. Introduction Global warming is in the news. While scientists agree that temperatures are rising, they disagree as to the causes and
2. The map below shows high-pressure and low-pressure weather systems in the United States.
 1. Which weather instrument has most improved the accuracy of weather forecasts over the past 40 years? 1) thermometer 3) weather satellite 2) sling psychrometer 4) weather balloon 6. Wind velocity is
1. Which weather instrument has most improved the accuracy of weather forecasts over the past 40 years? 1) thermometer 3) weather satellite 2) sling psychrometer 4) weather balloon 6. Wind velocity is
ESCI 107/109 The Atmosphere Lesson 2 Solar and Terrestrial Radiation
 ESCI 107/109 The Atmosphere Lesson 2 Solar and Terrestrial Radiation Reading: Meteorology Today, Chapters 2 and 3 EARTH-SUN GEOMETRY The Earth has an elliptical orbit around the sun The average Earth-Sun
ESCI 107/109 The Atmosphere Lesson 2 Solar and Terrestrial Radiation Reading: Meteorology Today, Chapters 2 and 3 EARTH-SUN GEOMETRY The Earth has an elliptical orbit around the sun The average Earth-Sun
CLIMATE, WATER & LIVING PATTERNS THINGS
 CLIMATE, WATER & LIVING PATTERNS NAME THE SIX MAJOR CLIMATE REGIONS DESCRIBE EACH CLIMATE REGION TELL THE FIVE FACTORS THAT AFFECT CLIMATE EXPLAIN HOW THOSE FACTORS AFFECT CLIMATE DESCRIBE HOW CLIMATES
CLIMATE, WATER & LIVING PATTERNS NAME THE SIX MAJOR CLIMATE REGIONS DESCRIBE EACH CLIMATE REGION TELL THE FIVE FACTORS THAT AFFECT CLIMATE EXPLAIN HOW THOSE FACTORS AFFECT CLIMATE DESCRIBE HOW CLIMATES
Sea level scenarios and extreme weather events
 Extreme weather and nuclear power plants (EXWE) Sea level scenarios and extreme weather events Milla Johansson, Kimmo Kahma, Hilkka Pellikka, Hanna Tietäväinen, Seppo Saku and Kirsti Jylhä Finnish Meteorological
Extreme weather and nuclear power plants (EXWE) Sea level scenarios and extreme weather events Milla Johansson, Kimmo Kahma, Hilkka Pellikka, Hanna Tietäväinen, Seppo Saku and Kirsti Jylhä Finnish Meteorological
Frequently Asked Questions
 From the report accepted by Working Group I of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change but not approved in detail Frequently Asked Questions FAQ Citation: These Frequently Asked Questions have been
From the report accepted by Working Group I of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change but not approved in detail Frequently Asked Questions FAQ Citation: These Frequently Asked Questions have been
Near Real Time Blended Surface Winds
 Near Real Time Blended Surface Winds I. Summary To enhance the spatial and temporal resolutions of surface wind, the remotely sensed retrievals are blended to the operational ECMWF wind analyses over the
Near Real Time Blended Surface Winds I. Summary To enhance the spatial and temporal resolutions of surface wind, the remotely sensed retrievals are blended to the operational ECMWF wind analyses over the
IEAGHG Information Paper 2015-10; The Earth s Getting Hotter and So Does the Scientific Debate
 IEAGHG Information Paper 2015-10; The Earth s Getting Hotter and So Does the Scientific Debate A recent study published in Nature Climate Change 1 suggests that the rate of climate change we're experiencing
IEAGHG Information Paper 2015-10; The Earth s Getting Hotter and So Does the Scientific Debate A recent study published in Nature Climate Change 1 suggests that the rate of climate change we're experiencing
Climate changes. MED-HYCOS CRP IRD BP 5045 AGROPOLIS 34032 - Montpellier [email protected]. by Marc Morell
 MED-HYCOS CRP IRD BP 5045 AGROPOLIS 34032 - Montpellier [email protected] Climate changes by Marc Morell after "A Summary for Deciders" (2000, IGCC) and "Climates of the world" (1992, Bruno Voituriez
MED-HYCOS CRP IRD BP 5045 AGROPOLIS 34032 - Montpellier [email protected] Climate changes by Marc Morell after "A Summary for Deciders" (2000, IGCC) and "Climates of the world" (1992, Bruno Voituriez
ENVIRONMENTAL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: CLIMATE SYSTEM Vol. II - Low-Latitude Climate Zones and Climate Types - E.I. Khlebnikova
 LOW-LATITUDE CLIMATE ZONES AND CLIMATE TYPES E.I. Khlebnikova Main Geophysical Observatory, St. Petersburg, Russia Keywords: equatorial continental climate, ITCZ, subequatorial continental (equatorial
LOW-LATITUDE CLIMATE ZONES AND CLIMATE TYPES E.I. Khlebnikova Main Geophysical Observatory, St. Petersburg, Russia Keywords: equatorial continental climate, ITCZ, subequatorial continental (equatorial
warmıng impacts by degree world
 warmıng impacts world by degree Based on the National Research Council report, Climate Stabilization Targets: Emissions, Concentrations, and Impacts over Decades to Millennia (2011) 2 1 Emissions of carbon
warmıng impacts world by degree Based on the National Research Council report, Climate Stabilization Targets: Emissions, Concentrations, and Impacts over Decades to Millennia (2011) 2 1 Emissions of carbon
Roy W. Spencer 1. Search and Discovery Article #110117 (2009) Posted September 8, 2009. Abstract
 AV Satellite Evidence against Global Warming Being Caused by Increasing CO 2 * Roy W. Spencer 1 Search and Discovery Article #110117 (2009) Posted September 8, 2009 *Adapted from oral presentation at AAPG
AV Satellite Evidence against Global Warming Being Caused by Increasing CO 2 * Roy W. Spencer 1 Search and Discovery Article #110117 (2009) Posted September 8, 2009 *Adapted from oral presentation at AAPG
The Polar Climate Zones
 The Polar Climate Zones How cold is it in the polar climate? Polar areas are the coldest of all the major climate zones The Sun is hardly ever high enough in the sky to cause the plentiful ice to melt,
The Polar Climate Zones How cold is it in the polar climate? Polar areas are the coldest of all the major climate zones The Sun is hardly ever high enough in the sky to cause the plentiful ice to melt,
Report to 8 th session of OOPC. By Dr. Alan R. Thomas, Director, GCOS Secretariat
 Report to 8 th session of OOPC By Dr. Alan R. Thomas, Director, GCOS Secretariat The GCOS is comprised of the climate components of the domain based observing systems including both satellite and in situ
Report to 8 th session of OOPC By Dr. Alan R. Thomas, Director, GCOS Secretariat The GCOS is comprised of the climate components of the domain based observing systems including both satellite and in situ
Seasonal & Daily Temperatures. Seasons & Sun's Distance. Solstice & Equinox. Seasons & Solar Intensity
 Seasonal & Daily Temperatures Seasons & Sun's Distance The role of Earth's tilt, revolution, & rotation in causing spatial, seasonal, & daily temperature variations Please read Chapter 3 in Ahrens Figure
Seasonal & Daily Temperatures Seasons & Sun's Distance The role of Earth's tilt, revolution, & rotation in causing spatial, seasonal, & daily temperature variations Please read Chapter 3 in Ahrens Figure
The Oceans Role in Climate
 The Oceans Role in Climate Martin H. Visbeck A Numerical Portrait of the Oceans The oceans of the world cover nearly seventy percent of its surface. The largest is the Pacific, which contains fifty percent
The Oceans Role in Climate Martin H. Visbeck A Numerical Portrait of the Oceans The oceans of the world cover nearly seventy percent of its surface. The largest is the Pacific, which contains fifty percent
The Science and Ethics of Global warming. Global warming has become one of the central political and scientific issues of
 The Science and Ethics of Global warming Global warming has become one of the central political and scientific issues of our time. It holds a fascination for scientists because of the tremendous complexity
The Science and Ethics of Global warming Global warming has become one of the central political and scientific issues of our time. It holds a fascination for scientists because of the tremendous complexity
IGAD CLIMATE PREDICTION AND APPLICATION CENTRE
 IGAD CLIMATE PREDICTION AND APPLICATION CENTRE CLIMATE WATCH REF: ICPAC/CW/No.32 May 2016 EL NIÑO STATUS OVER EASTERN EQUATORIAL OCEAN REGION AND POTENTIAL IMPACTS OVER THE GREATER HORN OF FRICA DURING
IGAD CLIMATE PREDICTION AND APPLICATION CENTRE CLIMATE WATCH REF: ICPAC/CW/No.32 May 2016 EL NIÑO STATUS OVER EASTERN EQUATORIAL OCEAN REGION AND POTENTIAL IMPACTS OVER THE GREATER HORN OF FRICA DURING
How Do Oceans Affect Weather and Climate?
 How Do Oceans Affect Weather and Climate? In Learning Set 2, you explored how water heats up more slowly than land and also cools off more slowly than land. Weather is caused by events in the atmosphere.
How Do Oceans Affect Weather and Climate? In Learning Set 2, you explored how water heats up more slowly than land and also cools off more slowly than land. Weather is caused by events in the atmosphere.
W.C. Rusty Riese, PhD Adjunct Professor, Rice University
 W.C. Rusty Riese, PhD Adjunct Professor, Rice University What are we being told? What are the data? What are the take-aways? What are your responsibilities? Mann Hockey Stick Curve The Arctic is melting
W.C. Rusty Riese, PhD Adjunct Professor, Rice University What are we being told? What are the data? What are the take-aways? What are your responsibilities? Mann Hockey Stick Curve The Arctic is melting
Stage 4. Geography. Blackline Masters. By Karen Devine
 1 Devine Educational Consultancy Services Stage 4 Geography Blackline Masters By Karen Devine Updated January 2010 2 This book is intended for the exclusive use in NSW Secondary Schools. It is meant to
1 Devine Educational Consultancy Services Stage 4 Geography Blackline Masters By Karen Devine Updated January 2010 2 This book is intended for the exclusive use in NSW Secondary Schools. It is meant to
California Standards Grades 9 12 Boardworks 2009 Science Contents Standards Mapping
 California Standards Grades 912 Boardworks 2009 Science Contents Standards Mapping Earth Sciences Earth s Place in the Universe 1. Astronomy and planetary exploration reveal the solar system s structure,
California Standards Grades 912 Boardworks 2009 Science Contents Standards Mapping Earth Sciences Earth s Place in the Universe 1. Astronomy and planetary exploration reveal the solar system s structure,
Chapter 3 Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems
 Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems Section 1: Community Ecology Section 2: Terrestrial Biomes Section 3: Aquatic Ecosystems Click on a lesson name to select. 3.1 Community Ecology Communities A biological
Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems Section 1: Community Ecology Section 2: Terrestrial Biomes Section 3: Aquatic Ecosystems Click on a lesson name to select. 3.1 Community Ecology Communities A biological
Key Words Forest Ecosystem, Carbon Dynamics, Boreal Forests, Tropical Forests, Plots Network
 1 - i Global Environment Research Account for National Institutes Advancement of East Asia Forest Dynamics Plots Network -Monitoring forest carbon cycling for the development of climate change adaptation-(abstract
1 - i Global Environment Research Account for National Institutes Advancement of East Asia Forest Dynamics Plots Network -Monitoring forest carbon cycling for the development of climate change adaptation-(abstract
The IPCC Special Report on Managing the Risks of Extreme Events and Disasters to Advance Climate Change Adaptation
 The IPCC Special Report on Managing the Risks of Extreme Events and Disasters to Advance Climate Change Adaptation A changing climate leads to changes in extreme weather and climate events 2 How do changes
The IPCC Special Report on Managing the Risks of Extreme Events and Disasters to Advance Climate Change Adaptation A changing climate leads to changes in extreme weather and climate events 2 How do changes
Full name:.. Date:. School: Teacher: Contents:
 Contents: 1.- The atmosphere. 2.- Weather and climate. 3.- The elements of climate 3.1 Temperatures 3.2 Rainfalls 3.3 Atmospheric pressure 3.4 Wind 4.-The Natural Environment. Full name:.. Date:. Class:
Contents: 1.- The atmosphere. 2.- Weather and climate. 3.- The elements of climate 3.1 Temperatures 3.2 Rainfalls 3.3 Atmospheric pressure 3.4 Wind 4.-The Natural Environment. Full name:.. Date:. Class:
Southern AER Atmospheric Education Resource
 Southern AER Atmospheric Education Resource Vol. 9 No. 5 Spring 2003 Editor: Lauren Bell In this issue: g Climate Creations exploring mother nature s remote control for weather and Climate. g Crazy Climate
Southern AER Atmospheric Education Resource Vol. 9 No. 5 Spring 2003 Editor: Lauren Bell In this issue: g Climate Creations exploring mother nature s remote control for weather and Climate. g Crazy Climate
SETTING THE RECORD STRAIGHT
 SETTING THE RECORD STRAIGHT Responses To Common Challenges To Climate Science January 2009 Climate Leadership Initiative Institute for a Sustainable Environment University of Oregon http://climlead.uoregon.edu
SETTING THE RECORD STRAIGHT Responses To Common Challenges To Climate Science January 2009 Climate Leadership Initiative Institute for a Sustainable Environment University of Oregon http://climlead.uoregon.edu
Chapter 6: Cloud Development and Forms
 Chapter 6: Cloud Development and Forms (from The Blue Planet ) Why Clouds Form Static Stability Cloud Types Why Clouds Form? Clouds form when air rises and becomes saturated in response to adiabatic cooling.
Chapter 6: Cloud Development and Forms (from The Blue Planet ) Why Clouds Form Static Stability Cloud Types Why Clouds Form? Clouds form when air rises and becomes saturated in response to adiabatic cooling.
Keeping below 2 degrees
 Keeping below 2 degrees Avoiding dangerous climate change It is widely recognised that if the worst impacts of climate change are to be avoided then the average rise in the surface temperature of the Earth
Keeping below 2 degrees Avoiding dangerous climate change It is widely recognised that if the worst impacts of climate change are to be avoided then the average rise in the surface temperature of the Earth
Climate and Global Dynamics e-mail: [email protected] National Center for Atmospheric Research phone: (303) 497-1761 Boulder, CO 80307
 Sean C. Swenson Climate and Global Dynamics P.O. Box 3000 [email protected] National Center for Atmospheric Research (303) 497-1761 Boulder, CO 80307 Education Ph.D. University of Colorado at Boulder,
Sean C. Swenson Climate and Global Dynamics P.O. Box 3000 [email protected] National Center for Atmospheric Research (303) 497-1761 Boulder, CO 80307 Education Ph.D. University of Colorado at Boulder,
RaysWeather.Com 2015-2016 Winter Fearless Forecast
 Author: Dr. Ray Russell Founder and President of RaysWeather.Com Date: October 10, 2015 RaysWeather.Com 2015-2016 Winter Fearless Forecast Background It's that time of year--leaves change, temperatures
Author: Dr. Ray Russell Founder and President of RaysWeather.Com Date: October 10, 2015 RaysWeather.Com 2015-2016 Winter Fearless Forecast Background It's that time of year--leaves change, temperatures
Queensland rainfall past, present and future
 Queensland rainfall past, present and future Historically, Queensland has had a variable climate, and recent weather has reminded us of that fact. After experiencing the longest drought in recorded history,
Queensland rainfall past, present and future Historically, Queensland has had a variable climate, and recent weather has reminded us of that fact. After experiencing the longest drought in recorded history,
Teacher s Guide For. Glaciers and Ice Caps The Melting
 Teacher s Guide For Glaciers and Ice Caps The Melting For grade 7 - College Program produced by Centre Communications, Inc. for Ambrose Video Publishing, Inc. Executive Producer William V. Ambrose Teacher's
Teacher s Guide For Glaciers and Ice Caps The Melting For grade 7 - College Program produced by Centre Communications, Inc. for Ambrose Video Publishing, Inc. Executive Producer William V. Ambrose Teacher's
GCOS science conference, 2 Mar. 2016, Amsterdam. Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA)
 GCOS science conference, 2 Mar. 2016, Amsterdam Status of Surface Radiation Budget Observation for Climate Nozomu Ohkawara Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) Contents 1. Background 2. Status t of surface
GCOS science conference, 2 Mar. 2016, Amsterdam Status of Surface Radiation Budget Observation for Climate Nozomu Ohkawara Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) Contents 1. Background 2. Status t of surface
Climate Control and Ozone Depletion. Chapter 19
 Climate Control and Ozone Depletion Chapter 19 Global Warming and Global Cooling Are Not New Over the past 4.5 billion years the climate has been altered by Volcanic emissions Changes in solar input Movement
Climate Control and Ozone Depletion Chapter 19 Global Warming and Global Cooling Are Not New Over the past 4.5 billion years the climate has been altered by Volcanic emissions Changes in solar input Movement
Name Period 4 th Six Weeks Notes 2015 Weather
 Name Period 4 th Six Weeks Notes 2015 Weather Radiation Convection Currents Winds Jet Streams Energy from the Sun reaches Earth as electromagnetic waves This energy fuels all life on Earth including the
Name Period 4 th Six Weeks Notes 2015 Weather Radiation Convection Currents Winds Jet Streams Energy from the Sun reaches Earth as electromagnetic waves This energy fuels all life on Earth including the
CHAPTER 3 Heat and energy in the atmosphere
 CHAPTER 3 Heat and energy in the atmosphere In Chapter 2 we examined the nature of energy and its interactions with Earth. Here we concentrate initially on the way in which energy interacts with the atmosphere
CHAPTER 3 Heat and energy in the atmosphere In Chapter 2 we examined the nature of energy and its interactions with Earth. Here we concentrate initially on the way in which energy interacts with the atmosphere
AIR TEMPERATURE IN THE CANADIAN ARCTIC IN THE MID NINETEENTH CENTURY BASED ON DATA FROM EXPEDITIONS
 PRACE GEOGRAFICZNE, zeszyt 107 Instytut Geografii UJ Kraków 2000 Rajmund Przybylak AIR TEMPERATURE IN THE CANADIAN ARCTIC IN THE MID NINETEENTH CENTURY BASED ON DATA FROM EXPEDITIONS Abstract: The paper
PRACE GEOGRAFICZNE, zeszyt 107 Instytut Geografii UJ Kraków 2000 Rajmund Przybylak AIR TEMPERATURE IN THE CANADIAN ARCTIC IN THE MID NINETEENTH CENTURY BASED ON DATA FROM EXPEDITIONS Abstract: The paper
Climate Extremes Research: Recent Findings and New Direc8ons
 Climate Extremes Research: Recent Findings and New Direc8ons Kenneth Kunkel NOAA Cooperative Institute for Climate and Satellites North Carolina State University and National Climatic Data Center h#p://assessment.globalchange.gov
Climate Extremes Research: Recent Findings and New Direc8ons Kenneth Kunkel NOAA Cooperative Institute for Climate and Satellites North Carolina State University and National Climatic Data Center h#p://assessment.globalchange.gov
The Balance of Power in the Earth-Sun System
 NASA Facts National Aeronautics and Space Administration www.nasa.gov The Balance of Power in the Earth-Sun System The Sun is the major source of energy for Earth s oceans, atmosphere, land, and biosphere.
NASA Facts National Aeronautics and Space Administration www.nasa.gov The Balance of Power in the Earth-Sun System The Sun is the major source of energy for Earth s oceans, atmosphere, land, and biosphere.
Climate, water and renewable energy in the Nordic countries
 102 Regional Hydrological Impacts of Climatic Change Hydroclimatic Variability (Proceedings of symposium S6 held during the Seventh IAHS Scientific Assembly at Foz do Iguaçu, Brazil, April 2005). IAHS
102 Regional Hydrological Impacts of Climatic Change Hydroclimatic Variability (Proceedings of symposium S6 held during the Seventh IAHS Scientific Assembly at Foz do Iguaçu, Brazil, April 2005). IAHS
Climate Change Long Term Trends and their Implications for Emergency Management August 2011
 Climate Change Long Term Trends and their Implications for Emergency Management August 2011 Overview A significant amount of existing research indicates that the world s climate is changing. Emergency
Climate Change Long Term Trends and their Implications for Emergency Management August 2011 Overview A significant amount of existing research indicates that the world s climate is changing. Emergency
The atmosphere has a number of gases, often in tiny amounts, which trap the heat given out by the Earth.
 The Earth is wrapped in a blanket of air called the atmosphere, which is made up of several layers of gases. The sun is much hotter than the Earth and it gives off rays of heat (radiation) that travel
The Earth is wrapped in a blanket of air called the atmosphere, which is made up of several layers of gases. The sun is much hotter than the Earth and it gives off rays of heat (radiation) that travel
Anyone Else Notice That Its Been Windy Lately?
 National Weather Service Aberdeen, South Dakota January 2014 Inside this issue: Has it Been Windy Lately or What? 2013 Year in Review 2013 Year in Review (cont.) 1 2 3 Has it Been Windy Lately or What?
National Weather Service Aberdeen, South Dakota January 2014 Inside this issue: Has it Been Windy Lately or What? 2013 Year in Review 2013 Year in Review (cont.) 1 2 3 Has it Been Windy Lately or What?
CHAPTER 5 Lectures 10 & 11 Air Temperature and Air Temperature Cycles
 CHAPTER 5 Lectures 10 & 11 Air Temperature and Air Temperature Cycles I. Air Temperature: Five important factors influence air temperature: A. Insolation B. Latitude C. Surface types D. Coastal vs. interior
CHAPTER 5 Lectures 10 & 11 Air Temperature and Air Temperature Cycles I. Air Temperature: Five important factors influence air temperature: A. Insolation B. Latitude C. Surface types D. Coastal vs. interior
of Climate Change in Mesoamerica
 Technical Series Technical Report No. 383 ABC of Climate Change in Mesoamerica Miguel Cifuentes Jara Tropical Agriculture Research and higher Education Center (CATIE) Climate Change Program Turrialba,
Technical Series Technical Report No. 383 ABC of Climate Change in Mesoamerica Miguel Cifuentes Jara Tropical Agriculture Research and higher Education Center (CATIE) Climate Change Program Turrialba,
2008 Global Surface Temperature in GISS Analysis
 2008 Global Surface Temperature in GISS Analysis James Hansen, Makiko Sato, Reto Ruedy, Ken Lo Calendar year 2008 was the coolest year since 2000, according to the Goddard Institute for Space Studies analysis
2008 Global Surface Temperature in GISS Analysis James Hansen, Makiko Sato, Reto Ruedy, Ken Lo Calendar year 2008 was the coolest year since 2000, according to the Goddard Institute for Space Studies analysis
