A BNORMALITES OF T EETH
|
|
|
- Dora Williamson
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A BNORMALITES OF T EETH CONTENTS Supernumerary teeth Hyperdontia and Cleidocranial Dysplasia Hypodontia, Oligodontia and Ectodermal Dysplasia... 2 Taurodontism Fusion, Gemination, Dilaceration and Concrescence... 3 Hypercementosis, Screwdriver incisors and Mulberry molars Macrodontia, Dens in dente, & Enamelomas Attrition, Erosion and Abrasion Internal and External Resorption Dentinogenesis Imperfecta, types I, II, & III Dentin Dysplasia, types I & II Regional Odontodysplasia Segmental Odontomaxillary Dysplasia Amelogenesis Imperfecta Self-Exam Cases There are many acquired and inherited developmental abnormalities that alter the size, shape and number of teeth. Individually, they are rare but collectively they form a body of knowledge with which all dentists should be familiar. The discussion of each condition is short and to the point. Comprehensive reviews of each may be found in any reasonably new textbook of oral pathology. For those conditions that are inherited (eg: ectodermal dysplasia, dentinogenesis imperfecta and others) go to: www3.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/,it will bookmark as OMIM (Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man). Supernumerary Teeth Slide #1 is an example of an extra incisor. When located in the midline between the two permanent central incisors, they are referred to as mesiodens. Slide #2 depicts an extra molar tooth (a paramolar) and Slide #3 is an example of a supernumerary bicuspid tooth. These are the most common supernumerary teeth in the order shown. Slide 1: mesiodens Slide 2: fourth molar Slide 3: supernumerary bicuspid Hyperdontia and Cleidocranial dysplasia Count the teeth in Slide #4 there are more than 50. This patient has cleidocranial dysplasia (CCD). This is inherited as an autosomal dominant trait, the gene maps to chromosome #6. The gene encodes a protein called Core Binding Factor Alpha 1 (CBFA1). This protein is essential for the formation of a normal skeleton but its role in tooth formation is not yet known. The heterozygous state produces the CCD phenotype, the homozygous state is lethal. Main features of the phenotype include hyperdontia, small or missing clavicles, delayed closure of the cranial fontanelles (soft spots) and short stature. Slide #5 shows multiple supernumerary teeth removed from a patient with CCD. Gardner syndrome (intestinal polyposis and skeletal osteomas) also features supernumerary teeth but not to the extent seen in CCD. ( J. Med. Genetics 1999;36 p and Cell 89; May 1997) Slide #6 is a little tricky. The coin shape radiolucent lesion between the mandibular bicuspid teeth was thought to be a cyst. It was removed and found to be a tooth germ of a developing supernumerary tooth. It was discovered early in development before mineralization commenced. Radiographically, it resembles a lateral periodontal cyst. Slide 4: cleidocranial dysplasia Slide 5: cleidocranial dysplasia Slide 6: supernumerary tooth germ "Abnormalities of Teeth" 1 Charles Dunlap, DDS
2 Hypodontia and Oligodontia Glossary: Anodontia: failure of teeth to develop (same as agenesis of teeth) Hypodontia: having less than 6 congenitally missing teeth. (partial anodontia) Oligodontia: having 6 or more congenitally missing teeth. Hyperdontia: extra teeth, same as supernumerary teeth, may be single or multiple as in CCD. (*To see how the web site OMIM works, log on and enter hypodontia.) Congenitally missing teeth (hypodontia and oligodontia) are not rare. Generations of dental students have learned about ectodermal dysplasia, the best know of the missing teeth syndromes. With the discovery of the Pax 9 gene, some light has been shed on the molecular genetics of congenitally missing teeth. Pax 9 maps to chromosome #14, it encodes a transcription factor that functions in the development of derivatives of the pharyngeal pouches. Mice with Pax 9 mutations have craniofacial and limb anomalies and teeth fail to form beyond the bud stage. A family with a framshift mutation in Pax 9 had normal deciduous teeth but lacked permanent molars in both the maxilla and mandible. It is transmitted as a dominant trait. (Nature Genetics 24; Jan, also European Journal of Oral Sciences 106; ) The best known of the missing teeth syndromes is X-linked hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia. Ectodermal derivatives such as hair, sweat glands, nails and teeth are involved. Head hair, eye lashes and brows are sparse, nails are dystrophic and there is marked oligodontia, rarely total anodontia. Diminished sweat glands leads to the inability to regulate body temperature, a major disability in warm months in a hot climate. According to your text ( Neville s Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology 2nd ed), there are 150 variants of this syndrome. Dominant, recessive and X-linked inheritance have been reported. Slide #7 shows the mildest form of hypodontia, a single congenitally missing tooth, in this case a bicuspid. Notice the deciduous molar has been retained. Slide #8 illustrates the other extreme, a 10 year old child missing virtually all permanent teeth except 1st molars. Slides #9 and #10 are of a child with ectodermal dysplasia. There is profound oligodontia and teeth that are present are cone shaped. Note the sparse scalp hair, brows and lashes. (Remember X-linked disease are milder in females because they enjoy partial protection thanks to lyonization.) We will exit the subject of hypodontia/oligodontia by looking at Slide #11, an example of a cone-shaped lateral incisor, a peg lateral, a form of microdontia. This may be inherited as a dominant trait. If both parents have peg laterals, the homozygous child will have total anodontia of succedaneous teeth. (Am. J. or Med. Genetics 26: ) Slide 7: congenitally missing bicuspid Slide 8: oligodontia Slide 9: ectodermal dysplasia Slide 10: ectodermal dysplasia Slide 11: microdontia or "peg lateral" "Abnormalities of Teeth" 2 Charles Dunlap, DDS
3 Taurodontism A morphologic abnormality of teeth called taurodontism (bull teeth) is seen in slide #12. Slide #13 is a normal cynodont for comparison. Slide #14 is also a taurodont. This condition is most conspicuous in the molar teeth. The distance from the roof of the pulp chamber to the root bifurcation is greatly increased. Variants include hypotaurodontism, mesotaurodontism and hypertaurodontism. Cases illustrated here are hypertaurodonts. This conditions may exist as an isolated trait (autosomal dominant) or as part of several syndromes including the trichodentoosseous syndrome (TDO), otodental dysplasia, ectodermal dysplasia, tooth and nail syndrome, amelogenesis imperfecta and others. (Am. J. Med. Genetics 11; April). Visit OMIM for more. Slide 12: taurodont Slide 13: cynodont (normal) Slide 14: taurodont Fusion, Gemination, Dilacertion & Concrescence These conditions are illustrated in Slides #15 through #27 and require little comment. Fusion, the joining of two adjacent tooth germs to form a single large tooth is seen in Slide #15. Notice the lateral incisor is missing, it fused with the central incison. Gemination, an attempt by a single tooth germ to form two teeth twinning, seen in Slides #16 and #17.* It is not always readily apparent if a large tooth is an example of Slide 15: fusion fusion or germination. If you have a problem, just count the teeth. If one is missing it is fusion, if one is not missing, it is gemination. Slide #18, dilaceration, an abnormal deviation (bend) in the root of a tooth, presumably caused by traumatic displacement during root development. of both central incisors Slide 17: germination Slide # 19 is an example of concrescence, the fusion of cementum of adjacent teeth, a good reason to have radiographs before extraction of a tooth. Slide 16: gemination Slide 18: dilaceration Slide 19: concrescence "Abnormalities of Teeth" 3 Charles Dunlap, DDS
4 Hypercementosis, screwdriver incisors and mulberry molars: Hypercementosis is seen in Slides #20 and #21. Note the thick mantle of cementum that makes the root look fat. (a national board pearl: If the jaws are involved in Paget disease of the skeleton (osteitis deformans), the teeth may show hypercementosis. But in practice, Paget disease seldom involves the jaws. Somewhere long ago in a faraway place, a case of osteitis deformans of the jaws with hypercementosis was reported and has endured in dental literature.) Slides #22 and #23 also show dental defects that have endured in dental literature but have virtually disappeared in practice. They illustrate Screwdriver incisors and Mulberry molars, dental defects seen in congenital syphilis and caused by direct invasion of tooth germs by Treponema organisms (yes, Treponema pallidum can pass through the placenta).*** Slides #22 and #23 are not UMKC slides and are not to be copied or published. Slide 20: hypercementosis Slide 21: hypercementosis Slide 22: "screwdriver teeth" Slide 23: "mulberry molars" Macrodontia, Dens in Dente, and Enamelomas Slide #24 is an example of macrodontia, note the unerupted lower 2nd bicuspid teeth are as large or larger than the molar teeth, molarization of the bicuspids. Slides #25 and #26 show a developmental defect called dens in dente, dens invaginatus or tooth within a tooth. Invagination of the cingulum has resulted in enamel being reflected into the tooth. This is of no clinical significance except that caries may develop in the invagination and escape detection. The ectopic formation of enamel is depicted in Slide #27. Small droplets of enamel form on the root surface, so-called enamelomas or enamel pearls. Slide 24: Macrodontia Slide 24: Slide 26: Slide 27: enamel pearls dens in dente dens invaginatus or enamelomas (also dens invaginatus) "Abnormalities of Teeth" 4 Charles Dunlap, DDS
5 Attrition, Erosion and Abrasion of teeth. ATTRITION: Loss of tooth surface due to normal wear. Some wearing is normal (physiologic) but accelerated wear beyond normal is pathologic. EROSION: The chemical dissolution of tooth structure often attributed to regurgitation of gastric acid, excessive intake of acidic food or drink, (eg, two liters of cola/day for years) Sometimes a cause cannot be identified, it is idiopathic. ABRASION: Wear beyond normal caused by mechanical forces. This sounds like pathologic attrition but the difference is the pattern of wear. Attrition is ordinarily confined to the occlusal and incisal surfaces. Abrasion is ordinarily used when the loss is on a non-occluding surface. ABFRACTION: I have avoided this because I am not sure it exists but it is in the literature and you should be familiar with the term. It is proposed that with each bite, occlusal forces causes the teeth to flex ever so little. Constant flexing causes enamel to break from the crown, usually on the buccal surface. Does this really happen? If it does, why don t we all have it? ("Abfraction lesions: myth or reality." Journal of Esthetic & Restorative Dentistry 15(5):263-71, 2003) As the following slides will show, it is not always easy to distinguish between attrition, erosion and abrasion, they may coexist. Slides #28 and #29 are of a 21-yearold man who had occlusal wear that had flattened the occlusal surfaces and loss of enamel on the buccal surfaces that cannot be explained by occlusion. Is the occlusal wear just an example of advanced attrition and the buccal lesions caused by erosion or abfraction? We could not identify a reason for erosion and he denied nocturnal bruxing or coarse diet that could account for the wear. Slide #30 shows advanced wear on the occlusal and incisal surfaces presumably due to end to end occlusion coupled with erosion. We could not identify an erosive agent but there is an almost identical picture in your text that identifies it as erosion. (Neville s 2nd ed. Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology) Slides #31 and #32 are two different people with what appears to be erosion but I was not able to identify a chemical or dietary habit that could account for it. Slide #33 is a little less mysterious. Notice the loss of enamel on the lingual surfaces caused by long term, daily exposure to gastric acid reflux in a patient with bulimia. And finally Slide #34 is abrasion caused by tooth brushing. Toothbrush abrasion is common but usually not to the extent seen here. Slide 28: pathologic attrition on occlusal surface (21y.o. male) Slide 29: erosion or abfractions? Slide 30: pathologic attrition or erosion or both? Slide 31: erosion of unknown cause Slide 32: erosion of unknown cause Slide 33: bulimic erosion Slide 34: abrasion "Abnormalities of Teeth" 5 Charles Dunlap, DDS
6 Internal and External Resorption Slide 35: internal resorption Slide 36: internal resorption Slides #35 39 illustrate resorption from within, internal resorption. One or many teeth may be involved and the cause is a total mystery. (*Skeletal bone has a counterpart in which a bone or adjacent bones mysteriously disappear, so-called vanishing bone disease or Gorham s syndrome.) Internal resorption may mimic dental caries as seen in Slide #36 (although you can t see it, there was a thin shell of tooth structure covering the lesions). Osteoclasts (dentinoclasts?) arising in the dental pulp inexorably resorb dentin and enamel that can be stopped only by complete removal of all pulp tissue following early recognition and prompt endodontic treatment. Slide #40 shows dentin on the left lined with a row of multinucleated osteoclasts occupying Howship s lacunae. Inflamed pulp is seen on the right. External resorption starts on the root surface and progresses inward. Although the cause may be idiopathic, in some cases the cause is apparent. Slide #41 exhibits short roots on lower incisor teeth in a person who had orthodontic treatment, a well known cause of minor external root resorption. Slide #42 exhibits resorption of the roots of a molar tooth caused by a keratocyst (the black hole) and Slide #43 shows resorption of the roots of teeth # 30 & 31 by a tumor, an ossifying fibroma. Slides # are examples of idiopathic external resorption. This is mysterious and frustating to patient and dentist alike. ("Multiple Idiopathic Root Resorption." Oral Surg. Oral Med & Oral Path. 67: ) ("Extensive Idiopathic Apical Root Resorption" Oral Surg. Oral Med. & Oral Path. 78: ) *Caution: when you see short teeth, it is not always external resorption. Sometimes teeth never form completely. Slide # 47 shows short roots, almost no roots in the maxillary teeth. This patient had radiation treatment for a brain tumor at age 3. The maxillary teeth were in the field of radiation and the formative tissue of the roots were irrepairably damaged so root development was terminated. And sometimes roots never form and a cause cannot be found as seen in Slide #48. Slide 37: internal resorption Slide 38: internal Slide 39: internal resorp- Slide 40: internal Slide 41: external resorption (arrows) tion, unknown cause resorption resorption, secondary to orthodontic treatment 42: external resorption Slide 43: external resorption Slide 44: idiopathic Slide 45: idiopathic secondary to cyst resorption secondary to tumor external resorption external resorption 46: idiopathic Slide 47: failure to form secondary Slide 48: failure to form, external resorption to radiation injury no known cause "Abnormalities of Teeth" 6 Charles Dunlap, DDS
7 Dentinogenesis Imperfecta (DI), also known as opalescent dentin) This is an autosomal dominant condition affecting both deciduous and permanent teeth. Affected teeth are gray to yellowbrown and have broad crowns with constriction of the cervical area resulting in a tulip shape. Radiographically, the teeth appear solid, lacking pulp chambers and root canals. Enamel is easily broken leading to exposure of dentin that undergoes accelerated attrition. Slides #49 52 are examples of DI. The gene maps to chromosome #4. It encodes a protein called dentin sialophosphoprotein (DSPP). This protein constitutes about 50% of the noncollagenous component of dentin matrix. It is not known how the mutant protein causes near obliteration of the pulp. A clinically and radiographically indistinguishable dental condition is seen sometimes in patients with osteogenesis imperfecta. The following classification has been proposed. A. Dentinogenesis imperfecta type I, with osteogenesis imperfecta B. Dentinogenesis imperfecta type II, without osteogenesis imperfecta C. Dentinogenesis imperfecta type III (see below) DI type III is even more rare and paradoxically characterized by too little rather than too much dentin resulting in shell teeth, Slide #53. Type III DI may be and allelic variant of type II DI, ( a different mutation in the same gene) both genes map to the same region on chromosome #4. (Slide #53 was loaned to us by another pathologist and is not to be copied or published. It is exclusively for the use of students at UMKC.) Slide 49: dentinogenesis imperfecta Slide 50: dentinogenesis imperfecta Slide 51: dentinogenesis imperfecta Slide 52: dentinogenesis imperfecta Slide 53: DI type III "Abnormalities of Teeth" 7 Charles Dunlap, DDS
8 Dentin Dysplasia type I & type II (DD I & DD II) Dentin dysplasia type I is a rare dominantly inherited dental developmental abnormality that maps to the same site on chromosome #4 as does dentinogenesis imperfecta type II & type III. It too may be an allelic variant. The phenotype varies considerably from solid teeth with no roots and periapical radiolucent lesions (Slide #54) to teeth with nearly normal root length but with partial obliteration of the pulp and large pulp stones (Slide #55). The periapical abscesses are due to extension of the pulp horns nearly to the surface. Minimal occlusal wear exposes the pulp to oral bacteria. Dentin dysplasia type II (coronal DD) is characterized by teeth of nearly normal length but as the pulp ascends to the crown, it flares into a flame shape or thistle tube shape as seen in Slides #56 and #57. ( See: "Dentin Dysplasia type I, five cases in one family." Oral Surg Oral Med. Oral Path. 86: ) Slide 54: dentin dysplasia type I Slide 55: dentin Slide 56: dentin dysplasia type II Slide 57: dentin dysplasia type II dysplasia type I Regional Odontodysplasia (ROD, ghost teeth) This is a sporadic (not inherited) developmental defect involving only a few teeth in a small REGION of the jaw. Slide # 58 illustrates ROD involving a lower incisor, cuspid and 1st bicuspid teeth.the dentin and enamel are thin and the pulp huge producing a ghost like appearance. Slide #59 is an example of ROD in the mandible of a 7-year-old boy. It involves five teeth: two incisors, the cuspid and both bicuspids. Slide #60 is histology of ROD, notice the huge pulp and thin rim of tooth structure, mostly dentin. Slide 58: regional odontodysplasia Slide 59: regional odontodysplasia Slide 60: regional odontodisplasia "Abnormalities of Teeth" 8 Charles Dunlap, DDS
9 Segmental Odontomaxillary Dysplasia (SOD or SOMD) SOD is illustrated in Slides # 61 and #62, the patients are age 13 and 4 respectively. The right maxilla is involved in both cases. Unlike regional odontodysplasia which involves only teeth, segmental odontomaxillary dysplasia involves teeth and bone. The segment of the jaw that is involved is expanded due to enlargement of the bone and hyperplasia of Slide 61: segmental odontomaxillary dysplasia overlying gingiva. Teeth in the involved are malformed and some may be congenitally missing. The condition is not progressive, i.e. it has a limited growth potential. Radiographs show increased density of the affect bone with a granular pattern, the maxillary sinus may be smaller than normal. Those who are not familiar with this condition may interpret the enlarged bone to be evidence of a tumor or fibrous dysplasia of bone, both of which are progressive diseases. Amelogenesis Imperfecta (AI) There is a large group of inherited developmental defects in enamel collectively referred to as amelogenesis imperfecta. At least 14 phenotypes have been identified and autosomal dominant, recessive and X linked inheritance have been reported. The conditions is rare, only about 1 in 14,000 have it. Establishing a pattern of inheritance requires constructing a pedigree (family tree) of several generations, identifying those with and without the condition. This is no minor task. Futhermore there is subtle overlaps in the phenotypes so that you may not be able to identify a specific type of AI when only a single or few patients are available for study. Much of what is known about AI comes from northern Sweden where the condition is more common. Three general categories of AI are recognized: 1. Hypoplastic type: Inadequate formation of enamel matrix, both pitting and smooth types exist. Enamel may be reduced in quantity but is of normal hardness. 2. Hypomaturation type: A defect in the crystal structure of enamel leads to a mottled enamel with white to brown to yellow colors. 3. Hypocalcified type: A defect not in the quantity but in the quality of enamel. It is poorly mineralized, soft and chips and wears easily. Slides # 63 and #64 are examples of the hypocalcified type of AI. Slide # 65 is the smooth hypoplastic type. Slide # 66 shows the mottled appearance of the hypomaturation type. Slide 65: hypoplastic amelogenesis imperfecta Slide 66: amelogenesis imperfecta hypomaturation type Slide 62: segmental odontomaxillary dysplasia Slide 63: hypocalcified amelogenesis imperfecta Slide 64: hypocalcified amelogenesis imperfecta *** Acquired (not inherited) defects in enamel may cause color and pitting defects, see your text for more information. The matrix of enamel is comprised mainly of a protein called amelogenin. The gene for this protein is on the short (petit) arm of the X chromosome (Xp22.1). A number of mutations have been described including deletions, missense and nonsense mutations. Autosomal dominant AI has been traced to a gene on chromosome #4 near the site as the gene for dentinogenesis imperfecta and dental dysplasia. (It appears that a region on #4 chromosome is a hot spot for dental developmental abnormalities). The AI gene at this site codes for another enamel protein, enamelin. Enamelin is thought to serve as a nucleation site for hydroxyapatite crystals See: (1) "Detection of a novel mutation in X-linked amelogenesis imperfecta" Journal of Dental Research 79 (12): (2.) "An amelogenin gene defect associated with human x-linked AI" Archives of Oral Biology 42: (3) "Localization of a gene for autosomal dominant AI to chromosome 4q." Human Molecular Genetics 3: "Abnormalities of Teeth" 9 Charles Dunlap, DDS
10 SELF-EXAM CASES #1 What is your diagnosis of the condition in Slide #67? #3 Slide #70 Several children in the family had mottled teeth, the parents did not. Is this an example of recessively inherited hypomaturation amelogenesis imperfecta? Note the marked similarity to HAI in Slide # 66. Slide 67 #2 Slides # 68 and #69. Does this child have dentinogenesis imperfecta? Neither parent had discolored teeth. Slide 70 Slide 68 Slide 69 Answers #1 The answer is taurodontism and hypoplastic (smooth) amelogenesis imperfecta. Note the large, tall pulp chamber and the thin enamel cap on the teeth. #2 The answer is no. This child has mottled teeth caused by taking tetracycline during the years the teeth were forming. This antibiotic is deposited in teeth and bone and darkens both. Slide # 69 is an undemineralized, thin section of a tooth viewed with fluorescent light. Each yellow band of fluorescence in the dentin marks an episode of treatment with tetracycline. #3 Slide #70 is an example of dental fluorosis. The family moved to a farm in the Texas panhandle and drank water from a well with a fluoride content of greater than four ppm. Charles Dunlap, DDS September 2004 "Abnormalities of Teeth" 10 Charles Dunlap, DDS
Anatomic Anomalies. Anomalies. Anomalies. Anomalies. Supernumerary Teeth. Supernumerary Teeth. Steven R. Singer, DDS 212.305.5674 srs2@columbia.
 Anatomic Anomalies Steven R. Singer, DDS 212.305.5674 [email protected] Anomalies! Anomalies are variations in the:! Size! Morphology! Number! Eruption of the teeth Anomalies Anomalies There are two categories:!
Anatomic Anomalies Steven R. Singer, DDS 212.305.5674 [email protected] Anomalies! Anomalies are variations in the:! Size! Morphology! Number! Eruption of the teeth Anomalies Anomalies There are two categories:!
Abnormalities of the Teeth. Abnomalities of teeth. Local factors associated with enamel defects. Environmental alterations
 Abnormalities of the Teeth Abnomalities of teeth Environmental alterations Developmental alterations Steven Chussid D.D.S. Director, Division of Pediatric Dentistry Environmental alterations Effects on
Abnormalities of the Teeth Abnomalities of teeth Environmental alterations Developmental alterations Steven Chussid D.D.S. Director, Division of Pediatric Dentistry Environmental alterations Effects on
Development of Teeth
 Development of Teeth Dr. Khaldoun Darwich Specialist in Oral and Maxillo-Facial Surgery Hamburg University PhD Hamburg University Academic Teacher - Department of OMF Surgery in Damascus University Instructor
Development of Teeth Dr. Khaldoun Darwich Specialist in Oral and Maxillo-Facial Surgery Hamburg University PhD Hamburg University Academic Teacher - Department of OMF Surgery in Damascus University Instructor
A. DEVELOPMENT OF THE DENTAL ORGAN (ENAMEL ORGAN):
 A. DEVELOPMENT OF THE DENTAL ORGAN (ENAMEL ORGAN): AS EARLY AS THE SECOND MONTH OF FETAL LIFE, THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE DECIDUOUS TEETH MAY FIRST BECOME EVIDENT. 1. Dental lamina and Bud stage At about six
A. DEVELOPMENT OF THE DENTAL ORGAN (ENAMEL ORGAN): AS EARLY AS THE SECOND MONTH OF FETAL LIFE, THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE DECIDUOUS TEETH MAY FIRST BECOME EVIDENT. 1. Dental lamina and Bud stage At about six
Dental Radiography collimator Ionising radiation image radiolucent area radiopaque area controlled zone scatter radiation intraoral
 Dental Radiography X-rays for dental radiography are produced by high voltages of electricity within an x-ray head and come out through a metal tube called a collimator. This ensures the x-rays only come
Dental Radiography X-rays for dental radiography are produced by high voltages of electricity within an x-ray head and come out through a metal tube called a collimator. This ensures the x-rays only come
Congenital absence of 1 or more teeth without any
 Trichodental Dysplasia: A Rare Syndrome With Distinct Dental Findings Ericka Montalvan, DMD 1 Christina Mazzone, DMD 2 Nanci Tofsky, DDS 3 Muralidhar Mupparapu, DMD 4 Abstract The association of fine,
Trichodental Dysplasia: A Rare Syndrome With Distinct Dental Findings Ericka Montalvan, DMD 1 Christina Mazzone, DMD 2 Nanci Tofsky, DDS 3 Muralidhar Mupparapu, DMD 4 Abstract The association of fine,
Non-carious dental conditions
 Non-carious dental conditions Children s Dental Health in the United Kingdom, 2003 Barbara Chadwick, Liz Pendry October 2004 Crown copyright 2004 Office for National Statistics 1 Drummond Gate London SW1V
Non-carious dental conditions Children s Dental Health in the United Kingdom, 2003 Barbara Chadwick, Liz Pendry October 2004 Crown copyright 2004 Office for National Statistics 1 Drummond Gate London SW1V
Secondary dentition permanent teeth - 32. Primary dentition deciduous teeth - 20
 Department of Histology and Embryology, P. J. Šafárik University, Medical Faculty, Košice DEVELOPMENT OF TEETH: Sylabus for foreign students Dental medicine Author: doc. MVDr. Iveta Domoráková, PhD. Primary
Department of Histology and Embryology, P. J. Šafárik University, Medical Faculty, Košice DEVELOPMENT OF TEETH: Sylabus for foreign students Dental medicine Author: doc. MVDr. Iveta Domoráková, PhD. Primary
CLASSIFICATION OF CARIOUS LESIONS AND TOOTH PREPARATION.
 CLASSIFICATION OF CARIOUS LESIONS AND TOOTH PREPARATION. ١ G.V. BLACK who is known as the father of operative dentistry,he classified carious lesions into groups according to their locations in permanent
CLASSIFICATION OF CARIOUS LESIONS AND TOOTH PREPARATION. ١ G.V. BLACK who is known as the father of operative dentistry,he classified carious lesions into groups according to their locations in permanent
MEDICAID DENTAL PROGRAMS CODING, POLICY AND RELATED FEE REVISION INFORMATION
 MEDICAID DENTAL PROGRAMS CODING, POLICY AND RELATED FEE REVISION INFORMATION Effective for dates of service on and after November 1, 2005, the following dental coding, policy and related fee revisions
MEDICAID DENTAL PROGRAMS CODING, POLICY AND RELATED FEE REVISION INFORMATION Effective for dates of service on and after November 1, 2005, the following dental coding, policy and related fee revisions
Cysts of the Jaws. Cyst. Types. Effects on adjacent structures. Non-Odontogenic cysts. Odontogenic Cysts
 Cyst A Cyst is a benign pathologic cavity filled with fluid, lined by epithelium, and surrounded by a connective tissue wall A = connective tissue wall Cysts of the Jaws B = epithelium Effects on adjacent
Cyst A Cyst is a benign pathologic cavity filled with fluid, lined by epithelium, and surrounded by a connective tissue wall A = connective tissue wall Cysts of the Jaws B = epithelium Effects on adjacent
DENTAL FOR EVERYONE SUMMARY OF BENEFITS, LIMITATIONS AND EXCLUSIONS
 DENTAL FOR EVERYONE SUMMARY OF BENEFITS, LIMITATIONS AND EXCLUSIONS DEDUCTIBLE The dental plan features a deductible. This is an amount the Enrollee must pay out-of-pocket before Benefits are paid. The
DENTAL FOR EVERYONE SUMMARY OF BENEFITS, LIMITATIONS AND EXCLUSIONS DEDUCTIBLE The dental plan features a deductible. This is an amount the Enrollee must pay out-of-pocket before Benefits are paid. The
Guideline on Dental Management of Heritable Dental Developmental Anomalies
 REFERENCE MANUAL V 37 / NO 6 15 / 16 Guideline on Dental Management of Heritable Dental Developmental Anomalies Originating Council Council on Clinical Affairs Adopted 2008 Revised 2013 Purpose The American
REFERENCE MANUAL V 37 / NO 6 15 / 16 Guideline on Dental Management of Heritable Dental Developmental Anomalies Originating Council Council on Clinical Affairs Adopted 2008 Revised 2013 Purpose The American
1. day. New horizons in prevention and treatment of tooth impaction and tooth retention. Friday March 7 th, 2014
 1. day Friday March 7 th, 2014 New horizons in prevention and treatment of tooth impaction and tooth retention. 8.00 9.00 registration and coffee/bread 9.00 9.30 1 Classification of tooth eruption in disturbances
1. day Friday March 7 th, 2014 New horizons in prevention and treatment of tooth impaction and tooth retention. 8.00 9.00 registration and coffee/bread 9.00 9.30 1 Classification of tooth eruption in disturbances
Classification of Malocclusion
 Classification of Malocclusion What s going on here? How would you describe this? Dr. Robert Gallois REFERENCE: Where Do We Begin? ESSENTIALS FOR ORTHODONTIC PRACTICE By Riolo and Avery Chapter 6 pages
Classification of Malocclusion What s going on here? How would you describe this? Dr. Robert Gallois REFERENCE: Where Do We Begin? ESSENTIALS FOR ORTHODONTIC PRACTICE By Riolo and Avery Chapter 6 pages
4-1-2005. Dental Clinical Criteria and Documentation Requirements
 4-1-2005 Dental Clinical Criteria and Documentation Requirements Table of Contents Dental Clinical Criteria Cast Restorations and Veneer Procedures... Pages 1-3 Crown Repair... Page 3 Endodontic Procedures...
4-1-2005 Dental Clinical Criteria and Documentation Requirements Table of Contents Dental Clinical Criteria Cast Restorations and Veneer Procedures... Pages 1-3 Crown Repair... Page 3 Endodontic Procedures...
Case Report(s): Uncomplicated Crown Fractures
 Case Report(s): Uncomplicated Crown Fractures Tooth fractures can be classified as follows: Uncomplicated crown fracture = fracture limited to the crown of the tooth with dentin exposure but no pulp exposure.
Case Report(s): Uncomplicated Crown Fractures Tooth fractures can be classified as follows: Uncomplicated crown fracture = fracture limited to the crown of the tooth with dentin exposure but no pulp exposure.
Introduction to Dental Anatomy
 Introduction to Dental Anatomy Vickie P. Overman, RDH, MEd Continuing Education Units: N/A This continuing education course is intended for dental students and dental hygiene students. Maintaining the
Introduction to Dental Anatomy Vickie P. Overman, RDH, MEd Continuing Education Units: N/A This continuing education course is intended for dental students and dental hygiene students. Maintaining the
Bonitas Dental Benefit Table 2015
 Bonitas Dental Benefit Table 2015 Dental benefits are paid at the Bonitas Dental tariff (BDT). Hospitalisation and certain specialised dentistry and treatment must be pre-authorised*. Procedures and treatment
Bonitas Dental Benefit Table 2015 Dental benefits are paid at the Bonitas Dental tariff (BDT). Hospitalisation and certain specialised dentistry and treatment must be pre-authorised*. Procedures and treatment
Retrospective analysis of factors influencing the eruption of delayed permanent incisors after supernumerary tooth removal
 Retrospective analysis of factors influencing the eruption of delayed permanent incisors after supernumerary tooth removal R.A.E. BRYAN*, B.O.I. COLE**, R.R. WELBURY* ABSTRACT. Aim This was to assess the
Retrospective analysis of factors influencing the eruption of delayed permanent incisors after supernumerary tooth removal R.A.E. BRYAN*, B.O.I. COLE**, R.R. WELBURY* ABSTRACT. Aim This was to assess the
Tooth Formation. Chapter 1
 Chapter Tooth Formation Teeth develop from epithelial cells from the mucosal lining of the oral cavity and cranial neural crest-derived ectomesenchymal cells. These latter cells originate at the ectodermal/neuroectodermal
Chapter Tooth Formation Teeth develop from epithelial cells from the mucosal lining of the oral cavity and cranial neural crest-derived ectomesenchymal cells. These latter cells originate at the ectodermal/neuroectodermal
Guidelines for Referrals for Orthodontic Treatment
 Advice for General Dental Practitioners, PCTs and LHBs Guidelines for Referrals for Orthodontic Treatment This document has been produced by the British Orthodontic Society Guidelines for Referrals for
Advice for General Dental Practitioners, PCTs and LHBs Guidelines for Referrals for Orthodontic Treatment This document has been produced by the British Orthodontic Society Guidelines for Referrals for
05 - DENTAL SURGERY. (02) MS (Oral Surgery) Part II Examination
 05 - DENTAL SURGERY (02) MS (Oral Surgery) Part II Examination 01. October 1990 02. October 1991 03. October 1992 04. October 1993 05. October 1994 06. November 1995 07. October 1996 08. November 1997
05 - DENTAL SURGERY (02) MS (Oral Surgery) Part II Examination 01. October 1990 02. October 1991 03. October 1992 04. October 1993 05. October 1994 06. November 1995 07. October 1996 08. November 1997
The etiology of orthodontic problems Fifth session
 بنام خداوند جان و خرد The etiology of orthodontic problems Fifth session دکتر مھتاب نوری دانشيار گروه ارتدنسی Course Outline( 5 sessions) Specific causes of malocclusion Genetic Influences Environmental
بنام خداوند جان و خرد The etiology of orthodontic problems Fifth session دکتر مھتاب نوری دانشيار گروه ارتدنسی Course Outline( 5 sessions) Specific causes of malocclusion Genetic Influences Environmental
A Dental Benefit Summary for Rice University
 Aetna Dental presents A Dental Benefit Summary for Rice University CODE CODE Office Visit Copay $5 DIAGNOSTIC CROWNS/BRIDGES D0120 Exam-Periodic No Charge D2510 Inlay, Metallic, One surface $225 D0150
Aetna Dental presents A Dental Benefit Summary for Rice University CODE CODE Office Visit Copay $5 DIAGNOSTIC CROWNS/BRIDGES D0120 Exam-Periodic No Charge D2510 Inlay, Metallic, One surface $225 D0150
Clinical Practice Guideline For Orthodontics
 Clinical Practice Guideline For Orthodontics MOH- Oral Health CSN -Orthodontics -2010 Page 1 of 15 Orthodontic Management Guidelines 1. Definitions: Orthodontics is the branch of dentistry concerned with
Clinical Practice Guideline For Orthodontics MOH- Oral Health CSN -Orthodontics -2010 Page 1 of 15 Orthodontic Management Guidelines 1. Definitions: Orthodontics is the branch of dentistry concerned with
Dentalworkers JOB DESCRIPTIONS Great Team Members make your Office function!
 Dentalworkers JOB DESCRIPTIONS Great Team Members make your Office function! Dental Assistant Registered Dental Assistant with Expanded Function: RDAEF Sterilization Assistant Dental Hygienist General
Dentalworkers JOB DESCRIPTIONS Great Team Members make your Office function! Dental Assistant Registered Dental Assistant with Expanded Function: RDAEF Sterilization Assistant Dental Hygienist General
Bonitas Medical Scheme Dental Benefit Table
 Bonitas Medical Dental Benefit Table 2015 PRIMARY DENTAL BENEFIT TABLE 2015 BONSAVE DENTAL BENEFIT TABLE 2015 STANDARD DENTAL BENEFIT TABLE 2015 BONCOM DENTAL BENEFIT TABLE 2015 Dental benefits are paid
Bonitas Medical Dental Benefit Table 2015 PRIMARY DENTAL BENEFIT TABLE 2015 BONSAVE DENTAL BENEFIT TABLE 2015 STANDARD DENTAL BENEFIT TABLE 2015 BONCOM DENTAL BENEFIT TABLE 2015 Dental benefits are paid
Dental Care for People with Osteogenesis Imperfecta
 Dental Care for People with Osteogenesis Imperfecta 804 W. Diamond Ave., Ste. 210 Gaithersburg, MD 20878 (800) 981-2663 (301) 947-0083 Fax: (301) 947-0456 Internet: www.oif.org Email: [email protected]
Dental Care for People with Osteogenesis Imperfecta 804 W. Diamond Ave., Ste. 210 Gaithersburg, MD 20878 (800) 981-2663 (301) 947-0083 Fax: (301) 947-0456 Internet: www.oif.org Email: [email protected]
TABLE OF DENTAL PROCEDURES PLEASE READ THE FOLLOWING INFORMATION CAREFULLY FOR YOUR PROCEDURE FREQUENCIES AND PROVISIONS.
 TABLE OF DENTAL PROCEDURES PLEASE READ THE FOLLOWING INFORMATION CAREFULLY FOR YOUR PROCEDURE FREQUENCIES AND PROVISIONS. The attached is a list of dental procedures for which benefits are payable under
TABLE OF DENTAL PROCEDURES PLEASE READ THE FOLLOWING INFORMATION CAREFULLY FOR YOUR PROCEDURE FREQUENCIES AND PROVISIONS. The attached is a list of dental procedures for which benefits are payable under
CCR Biology - Chapter 7 Practice Test - Summer 2012
 Name: Class: Date: CCR Biology - Chapter 7 Practice Test - Summer 2012 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A person who has a disorder caused
Name: Class: Date: CCR Biology - Chapter 7 Practice Test - Summer 2012 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A person who has a disorder caused
Using The Canary System to Develop a Caries Management Program for Children. we design therapies to treat or remineralize early carious lesions?
 Using The Canary System to Develop a Caries Management Program for Children Dr. Stephen H. Abrams Dental caries is the most common oral disease we treat in paediatric dentistry. We place restorations to
Using The Canary System to Develop a Caries Management Program for Children Dr. Stephen H. Abrams Dental caries is the most common oral disease we treat in paediatric dentistry. We place restorations to
Child Abuse or Osteogenesis Imperfecta?
 Child Abuse or Osteogenesis Imperfecta? 804 W. Diamond Ave., Ste. 210 Gaithersburg, MD 20878 (800) 981-2663 (301) 947-0083 Fax: (301) 947-0456 Internet: www.oif.org Email: [email protected] The Osteogenesis
Child Abuse or Osteogenesis Imperfecta? 804 W. Diamond Ave., Ste. 210 Gaithersburg, MD 20878 (800) 981-2663 (301) 947-0083 Fax: (301) 947-0456 Internet: www.oif.org Email: [email protected] The Osteogenesis
An Overview of Your Dental Benefits
 An Overview of Your Dental Benefits Educators Health Alliance ii \ DENTAL BENEFITS PPO Dental Plan Options OPTION 1 Maintenance Dentistry OPTION 2 (STANDARD PLAN) IN-NETWORK OUT-OF-NETWORK Maintenance
An Overview of Your Dental Benefits Educators Health Alliance ii \ DENTAL BENEFITS PPO Dental Plan Options OPTION 1 Maintenance Dentistry OPTION 2 (STANDARD PLAN) IN-NETWORK OUT-OF-NETWORK Maintenance
Resorptive Changes of Maxillary and Mandibular Bone Structures in Removable Denture Wearers
 Resorptive Changes of Maxillary and Mandibular Bone Structures in Removable Denture Wearers Dubravka KnezoviÊ-ZlatariÊ Asja»elebiÊ Biserka LaziÊ Department of Prosthodontics School of Dental Medicine University
Resorptive Changes of Maxillary and Mandibular Bone Structures in Removable Denture Wearers Dubravka KnezoviÊ-ZlatariÊ Asja»elebiÊ Biserka LaziÊ Department of Prosthodontics School of Dental Medicine University
Managing worn teeth with composites
 6 Managing worn teeth with composites Clinical details A 50-year-old man presents to you complaining about his worn teeth and would like the appearance improved (Fig. 6.1). He complains of regurgitation
6 Managing worn teeth with composites Clinical details A 50-year-old man presents to you complaining about his worn teeth and would like the appearance improved (Fig. 6.1). He complains of regurgitation
portion of the tooth such as 3/4 Crown, 7/8Crown.
 Lecture.1 Dr.Adel F.Ibraheem Crown and Bridge: It s a branch of dental science that deals with restoration of damaged teeth with artificial crown replacing the missing natural teeth by a cast prosthesis
Lecture.1 Dr.Adel F.Ibraheem Crown and Bridge: It s a branch of dental science that deals with restoration of damaged teeth with artificial crown replacing the missing natural teeth by a cast prosthesis
2007 Insurance Benefits Guide. Dental and Dental Plus. Dental and. Dental Plus. www.eip.sc.gov Employee Insurance Program 91
 Dental and www.eip.sc.gov Employee Insurance Program 91 Table of Contents Introduction...93 Your Dental Benefits at a Glance...94 Claim Examples (using Class III procedure claims)...95 How to File a Dental
Dental and www.eip.sc.gov Employee Insurance Program 91 Table of Contents Introduction...93 Your Dental Benefits at a Glance...94 Claim Examples (using Class III procedure claims)...95 How to File a Dental
Activity: Can You Identify the Age?
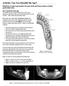 Activity: Can You Identify the Age? Skeletons are good age markers because teeth and bones mature at fairly predictable rates. How Teeth Reveal Age For toddler to age 21, teeth are the most accurate age
Activity: Can You Identify the Age? Skeletons are good age markers because teeth and bones mature at fairly predictable rates. How Teeth Reveal Age For toddler to age 21, teeth are the most accurate age
Attachment S: Benefits Covered - ADULTS - AGE 21 AND OVER
 Diagnostic services include the oral examinations and selected radiographs needed to assess the oral health, diagnose oral pathology and develop an adequate treatment plan for the Participant s oral health.
Diagnostic services include the oral examinations and selected radiographs needed to assess the oral health, diagnose oral pathology and develop an adequate treatment plan for the Participant s oral health.
IMPLANT DENTISTRY EXAM BANK
 IMPLANT DENTISTRY EXAM BANK 1. Define osseointegration. (4 points, 1/4 2. What are the critical components of an acceptable clinical trial? (10 points) 3. Compare the masticatory performance of individuals
IMPLANT DENTISTRY EXAM BANK 1. Define osseointegration. (4 points, 1/4 2. What are the critical components of an acceptable clinical trial? (10 points) 3. Compare the masticatory performance of individuals
ORTHODONTIC PROBLEMS IN PATIENTS WITH HYPODONTIA AND TAURODONTISM OF PERMANENT MOLARS
 Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers) 2011, vol. 17, book 2 ORTHODONTIC PROBLEMS IN PATIENTS WITH HYPODONTIA AND TAURODONTISM OF PERMANENT MOLARS Miroslava Yordanova 1, Svetlana Yordanova
Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers) 2011, vol. 17, book 2 ORTHODONTIC PROBLEMS IN PATIENTS WITH HYPODONTIA AND TAURODONTISM OF PERMANENT MOLARS Miroslava Yordanova 1, Svetlana Yordanova
General Dentist Fees
 General Dentist Fees January 1, 2015 Not all codes are covered benefits. Please check the member s plan for verification and limitations. There are no fee increases for 2015, but new CDT codes have been
General Dentist Fees January 1, 2015 Not all codes are covered benefits. Please check the member s plan for verification and limitations. There are no fee increases for 2015, but new CDT codes have been
DENTAL TRAUMATIC INJURIES
 DENTAL TRAUMATIC INJURIES Nitrous Oxide Not Contraindicated Predisposing Factors > 90% of All Injuries Protrusion of Anterior Teeth Poor Lip Coverage Mouthguards Girls as Well as Boys Off - the - Shelf
DENTAL TRAUMATIC INJURIES Nitrous Oxide Not Contraindicated Predisposing Factors > 90% of All Injuries Protrusion of Anterior Teeth Poor Lip Coverage Mouthguards Girls as Well as Boys Off - the - Shelf
Dental care and treatment for patients with head and neck cancer. Department of Restorative Dentistry Information for patients
 Dental care and treatment for patients with head and neck cancer Department of Restorative Dentistry Information for patients i Why have I been referred to the Restorative Dentistry Team? Treatment of
Dental care and treatment for patients with head and neck cancer Department of Restorative Dentistry Information for patients i Why have I been referred to the Restorative Dentistry Team? Treatment of
Dr. Cindi Sherwood, DDS, Independence House Committee on Health and Human Services (HB 2079)
 Dr. Cindi Sherwood, DDS, Independence House Committee on Health and Human Services (HB 2079) My name is Cindi Sherwood and I am speaking in opposition to House Bill 2079. My background is that I was trained
Dr. Cindi Sherwood, DDS, Independence House Committee on Health and Human Services (HB 2079) My name is Cindi Sherwood and I am speaking in opposition to House Bill 2079. My background is that I was trained
Course Curriculum for the Master Degree in Dentistry/Orthodontics
 Jordan University of Science and Technology Faculty of Graduate Studies Course Curriculum for the Master Degree in Dentistry/Orthodontics The Master Degree in Dentistry/ Orthodontics is awarded by the
Jordan University of Science and Technology Faculty of Graduate Studies Course Curriculum for the Master Degree in Dentistry/Orthodontics The Master Degree in Dentistry/ Orthodontics is awarded by the
Humana Health Plans of Florida. Important:
 Humana Health Plans of Florida Important: Dental discount membership in Florida is determined by viewing the member s ID card and verifying that the Humana Logo and Medicare name is listed with an effective
Humana Health Plans of Florida Important: Dental discount membership in Florida is determined by viewing the member s ID card and verifying that the Humana Logo and Medicare name is listed with an effective
Dental. Covered services and limitations module
 Dental Covered services and limitations module Dental Covered Services and Limitations Module Covered Dental Services for Patients Under the Age of 21...2 Examinations...2 Radiographs and Diagnostic Imaging...2
Dental Covered services and limitations module Dental Covered Services and Limitations Module Covered Dental Services for Patients Under the Age of 21...2 Examinations...2 Radiographs and Diagnostic Imaging...2
Dental Billing and Coding. Janet Bozzone, DMD, FAGD Open Door Family Medical Centers Ossining, Sleepy Hollow, Port Chester & Mount Kisco, NY
 Dental Billing and Coding Janet Bozzone, DMD, FAGD Open Door Family Medical Centers Ossining, Sleepy Hollow, Port Chester & Mount Kisco, NY What makes me an expert? I have over 20 years experience working
Dental Billing and Coding Janet Bozzone, DMD, FAGD Open Door Family Medical Centers Ossining, Sleepy Hollow, Port Chester & Mount Kisco, NY What makes me an expert? I have over 20 years experience working
CHAPTER 10 RESTS AND PREPARATIONS. 4. Serve as a reference point for evaluating the fit of the framework to the teeth.
 CHAPTER 10 RESTS AND DEFINITIONS A REST is any rigid part of an RPD framework which contacts a properly prepared surface of a tooth. A REST PREPARATION or REST SEAT is any portion of a tooth or restoration
CHAPTER 10 RESTS AND DEFINITIONS A REST is any rigid part of an RPD framework which contacts a properly prepared surface of a tooth. A REST PREPARATION or REST SEAT is any portion of a tooth or restoration
Appendix 1 Orthodontic Referral Guidelines for referring practitioners
 Appendix 1 Orthodontic Referral Guidelines for referring practitioners These guidelines are intended to assist General Dental Practitioners (GDPs), Community Dental Service (CDS) Dentists and Primary Care
Appendix 1 Orthodontic Referral Guidelines for referring practitioners These guidelines are intended to assist General Dental Practitioners (GDPs), Community Dental Service (CDS) Dentists and Primary Care
Put Your Panoramic Imaging on Steroids While Reducing the Patient s Dose!
 Put Your Panoramic Imaging on Steroids While Reducing the Patient s Dose! Dale A. Miles BA, DDS, MS, FRCD(C) Diplomate, American Board of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology It used to be that panoramic images
Put Your Panoramic Imaging on Steroids While Reducing the Patient s Dose! Dale A. Miles BA, DDS, MS, FRCD(C) Diplomate, American Board of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology It used to be that panoramic images
Classification of dental trauma & management of dental avulsions
 Dr Tony Skapetis The University of Sydney Clinical Director Education WCOH Clinical Senior Lecturer University of Sydney [email protected] Classification of dental trauma & management of dental
Dr Tony Skapetis The University of Sydney Clinical Director Education WCOH Clinical Senior Lecturer University of Sydney [email protected] Classification of dental trauma & management of dental
Classification of severe tooth discolorations and treatment options
 Master thesis Classification of severe tooth discolorations and treatment options Lotte Jenssen and Huy Quoc Tran Supervisor: Catarina Wallman Universitetet i Tromsø Det helsevitenskapelige fakultet Institutt
Master thesis Classification of severe tooth discolorations and treatment options Lotte Jenssen and Huy Quoc Tran Supervisor: Catarina Wallman Universitetet i Tromsø Det helsevitenskapelige fakultet Institutt
Dental-based Injuries
 Dental-based Injuries LUXATIONS CROWN FRACTURE CROWN/ROOT FRACTURE ROOT FRACTURE ALVEOLAR BONE FRACTURE AVULSIONS LUXATIONS The tooth is loose, now what? 1. Concussive-not loose or displaced, but tender
Dental-based Injuries LUXATIONS CROWN FRACTURE CROWN/ROOT FRACTURE ROOT FRACTURE ALVEOLAR BONE FRACTURE AVULSIONS LUXATIONS The tooth is loose, now what? 1. Concussive-not loose or displaced, but tender
Introduction to Charting. Tooth Surfaces: M = mesial D = distal O = Occlusal B = buccal F = facial I = incisal L = lingual
 Tooth Surfaces: M = mesial D = distal O = Occlusal B = buccal F = facial I = incisal L = lingual When combining tooth surfaces, as in defining cavity preparations or restorations, there are some spelling
Tooth Surfaces: M = mesial D = distal O = Occlusal B = buccal F = facial I = incisal L = lingual When combining tooth surfaces, as in defining cavity preparations or restorations, there are some spelling
Role of dentistry in the health scciences, the dental team. Dr. Dézsi Anna Júlia
 Role of dentistry in the health scciences, the dental team Dr. Dézsi Anna Júlia The art of medicine Herodatus, a historian, described the medical art in Egypt: "The art of medicineis distributed thus:
Role of dentistry in the health scciences, the dental team Dr. Dézsi Anna Júlia The art of medicine Herodatus, a historian, described the medical art in Egypt: "The art of medicineis distributed thus:
Acute Dental Problems in the School Setting
 Acute Dental Problems in the School Setting Keri Discepolo, D.D.S., M.P.H. Clinical Faculty, Yale Pediatric Dentistry Residency Program Associate, Yale School of Medicine Objectives Brief Description of
Acute Dental Problems in the School Setting Keri Discepolo, D.D.S., M.P.H. Clinical Faculty, Yale Pediatric Dentistry Residency Program Associate, Yale School of Medicine Objectives Brief Description of
The Treatment of Traumatic Dental Injuries
 The Recommended Guidelines of the American Association of Endodontists for The Treatment of Traumatic Dental Injuries 2013 American Association of Endodontists Revised 9/13 The Recommended Guidelines of
The Recommended Guidelines of the American Association of Endodontists for The Treatment of Traumatic Dental Injuries 2013 American Association of Endodontists Revised 9/13 The Recommended Guidelines of
Porcelain Veneers for Children and Teens. By Fred S. Margolis, D.D.S., F.I.C.D., F.A.C.D., F.A.D.I. Abstract
 Porcelain Veneers for Children and Teens By Fred S. Margolis, D.D.S., F.I.C.D., F.A.C.D., F.A.D.I. Abstract This article will discuss the advantages of providing our young patients and their parents an
Porcelain Veneers for Children and Teens By Fred S. Margolis, D.D.S., F.I.C.D., F.A.C.D., F.A.D.I. Abstract This article will discuss the advantages of providing our young patients and their parents an
CLINICAL GOALS OF PATIENT CARE AND CLINIC MANAGEMENT. Philosophical Basis of the Patient Care System. Patient Care Goals
 University of Washington School of Dentistry CLINICAL GOALS OF PATIENT CARE AND CLINIC MANAGEMENT Philosophical Basis of the Patient Care System The overall mission of the patient care system in the School
University of Washington School of Dentistry CLINICAL GOALS OF PATIENT CARE AND CLINIC MANAGEMENT Philosophical Basis of the Patient Care System The overall mission of the patient care system in the School
Develop a specialist who is capable of correlation of basic sciences and clinical sciences, and challenge the requirements for certification.
 Course Specification Faculty : Dentistry Department : Endodontics Program Specification: Diploma Degree A-Basic Information 1-Programme Title: Diploma in Endodontics 2-Departments (s): Endodontics 4-Coordinator:
Course Specification Faculty : Dentistry Department : Endodontics Program Specification: Diploma Degree A-Basic Information 1-Programme Title: Diploma in Endodontics 2-Departments (s): Endodontics 4-Coordinator:
Schedule B Indemnity plan People First Plan Code #4084
 : Calendar year deductible Waived for Type I preventive dental services Calendar year maximum Type I, II, III Waiting period Type I, II, III $50 individual $150 family (3 per family) $1,000 per covered
: Calendar year deductible Waived for Type I preventive dental services Calendar year maximum Type I, II, III Waiting period Type I, II, III $50 individual $150 family (3 per family) $1,000 per covered
The traumatic injuries of permanent teeth and complex therapy
 The traumatic injuries of permanent teeth and complex therapy Dr. Katalin Déri Semmelweis Egyetem Department of Pedodontics and Orthodontics Risk Angle II/1 Predisposing factor: overjet insufficient lip
The traumatic injuries of permanent teeth and complex therapy Dr. Katalin Déri Semmelweis Egyetem Department of Pedodontics and Orthodontics Risk Angle II/1 Predisposing factor: overjet insufficient lip
ICD-10: What Dental Programs Need to Know Safety Net Solutions Technical Assistance Webinar July 30, 2015
 ICD-10: What Dental Programs Need to Know Safety Net Solutions Technical Assistance Webinar July 30, 2015 Dr. Carolyn Brown, SNS Expert Advisor Learning Objectives 1. To highlight the essentials of ICD-
ICD-10: What Dental Programs Need to Know Safety Net Solutions Technical Assistance Webinar July 30, 2015 Dr. Carolyn Brown, SNS Expert Advisor Learning Objectives 1. To highlight the essentials of ICD-
Replacing Hopeless Retained Deciduous Teeth in Adults Utilizing Dental Implants: Concepts and Case Presentation
 Replacing Hopeless Retained Deciduous Teeth in Adults Utilizing Dental Implants: Concepts and Case Presentation by Michael Tischler, DDS Published: Dentistry Today November 2005 Photos at end of article
Replacing Hopeless Retained Deciduous Teeth in Adults Utilizing Dental Implants: Concepts and Case Presentation by Michael Tischler, DDS Published: Dentistry Today November 2005 Photos at end of article
Dental Radiology Related With Pedodontics
 Dental Radiology Related With Pedodontics Presented by: Dr. Rajeev Kumar Singh Radiology The branch of medicine that deals with the use of X- rays and radioactive substances in the diagnosis and treatment
Dental Radiology Related With Pedodontics Presented by: Dr. Rajeev Kumar Singh Radiology The branch of medicine that deals with the use of X- rays and radioactive substances in the diagnosis and treatment
Delta Dental Individual and Family Dental Plans. EHB Certified DELTA DENTAL OF NORTH CAROLINA
 Delta Dental Individual and Family Dental Plans EHB Certified DELTA DENTAL OF NORTH CAROLINA You ll benefit from: Freedom Enjoy access to two Delta Dental networks Delta Dental PPO and Delta Dental Premier.
Delta Dental Individual and Family Dental Plans EHB Certified DELTA DENTAL OF NORTH CAROLINA You ll benefit from: Freedom Enjoy access to two Delta Dental networks Delta Dental PPO and Delta Dental Premier.
Objectives Role of Medical Genetics in Hearing Loss Evaluation. 5 y.o. boy with severe SNHL
 Objectives Role of Medical Genetics in Hearing Loss Evaluation Millan Patel, MD UBC Dept. of Medical Genetics October 22, 2010 Case presentation to illustrate importance of defining syndromic hearing loss
Objectives Role of Medical Genetics in Hearing Loss Evaluation Millan Patel, MD UBC Dept. of Medical Genetics October 22, 2010 Case presentation to illustrate importance of defining syndromic hearing loss
DENTAL PLAN ADMINISTERED BY MEDBEN
 DENTAL PLAN ADMINISTERED BY MEDBEN 2.9 SCHEDULE OF DENTAL BENEFITS This Schedule of Dental Benefits is intended to provide only a general description of a Covered Person s dental benefits under this Plan.
DENTAL PLAN ADMINISTERED BY MEDBEN 2.9 SCHEDULE OF DENTAL BENEFITS This Schedule of Dental Benefits is intended to provide only a general description of a Covered Person s dental benefits under this Plan.
Aetna Life Insurance Company Hartford, Connecticut 06156
 Aetna Life Insurance Company Hartford, Connecticut 06156 Extraterritorial Certificate Rider (GR-9N-CR1) Policyholder: Choctaw Enterprises Group Policy No.: GP-819977 Rider: Florida ET Dental (PPO) Issue
Aetna Life Insurance Company Hartford, Connecticut 06156 Extraterritorial Certificate Rider (GR-9N-CR1) Policyholder: Choctaw Enterprises Group Policy No.: GP-819977 Rider: Florida ET Dental (PPO) Issue
How To Get A Ppo Plan In Texas
 Aetna Dental Plan Dental Benefits Summary With PPOII Network Participating Non-participating Annual Deductible* Individual $100 $125 Family $300 $375 Preventive Services 100% 80% Basic Services 80% 70%
Aetna Dental Plan Dental Benefits Summary With PPOII Network Participating Non-participating Annual Deductible* Individual $100 $125 Family $300 $375 Preventive Services 100% 80% Basic Services 80% 70%
Children s Dental Health in the United Kingdom, 2003
 Children s Dental Health in the United Kingdom, 2003 Summary Report Deborah Lader Barbara Chadwick Ivor Chestnutt Rachael Harker John Morris Nigel Nuttall Nigel Pitts Jimmy Steele Deborah White Crown copyright
Children s Dental Health in the United Kingdom, 2003 Summary Report Deborah Lader Barbara Chadwick Ivor Chestnutt Rachael Harker John Morris Nigel Nuttall Nigel Pitts Jimmy Steele Deborah White Crown copyright
Hypohidrotic Ectodermal Dysplasia. A Peer-Reviewed Publication Written by Sherri Lukes RDH, MS and Jennifer S. Sherry RDH, MSEd
 Earn 1 CE credit This course was written for dentists, dental hygienists, and assistants. Hypohidrotic Ectodermal Dysplasia A Peer-Reviewed Publication Written by Sherri Lukes RDH, MS and Jennifer S. Sherry
Earn 1 CE credit This course was written for dentists, dental hygienists, and assistants. Hypohidrotic Ectodermal Dysplasia A Peer-Reviewed Publication Written by Sherri Lukes RDH, MS and Jennifer S. Sherry
Kathleen A. Russell, BSc, DDS, MSc Magdalena A. Folwarczna, BSc, DDS
 C L I N I C A L P R A C T I C E Mesiodens Diagnosis and Management of a Common Supernumerary Tooth Kathleen A. Russell, BSc, DDS, MSc Magdalena A. Folwarczna, BSc, DDS A b s t r a c t Mesiodentes are the
C L I N I C A L P R A C T I C E Mesiodens Diagnosis and Management of a Common Supernumerary Tooth Kathleen A. Russell, BSc, DDS, MSc Magdalena A. Folwarczna, BSc, DDS A b s t r a c t Mesiodentes are the
Pseudohypoparathyroidism: A Variation on the Theme of Hypoparathyroidism
 Pseudohypoparathyroidism: A Variation on the Theme of Hypoparathyroidism Amanda Tencza MS IV 1 and Michael A. Levine, MD 2 1 Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine of Case Western Reserve University
Pseudohypoparathyroidism: A Variation on the Theme of Hypoparathyroidism Amanda Tencza MS IV 1 and Michael A. Levine, MD 2 1 Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine of Case Western Reserve University
Characteristics of regional odontodysplasia: A case report
 Acta Scientiarum http://www.uem.br/acta ISSN printed: 1679-9291 ISSN on-line: 1807-8648 Doi: 10.4025/actascihealthsci.v34i2.13380 Characteristics of regional odontodysplasia: A case report Saulo André
Acta Scientiarum http://www.uem.br/acta ISSN printed: 1679-9291 ISSN on-line: 1807-8648 Doi: 10.4025/actascihealthsci.v34i2.13380 Characteristics of regional odontodysplasia: A case report Saulo André
ADA Dental Claim Form (2012 American Dental Association) Completion Instructions Page 1 of 17
 Page 1 of 17 Introduction The ADA Dental Claim Form has been revised to incorporate key changes to the HIPAA standard electronic dental claim transaction. This version of the form, front and reverse sides,
Page 1 of 17 Introduction The ADA Dental Claim Form has been revised to incorporate key changes to the HIPAA standard electronic dental claim transaction. This version of the form, front and reverse sides,
INITIAL MANAGEMENT OF DENTAL TRAUMA BY DR. LUKE MOLONEY
 INITIAL MANAGEMENT OF DENTAL TRAUMA BY DR. LUKE MOLONEY CONSULTANT ENDODONTIST ROYAL CHILDREN S HOSPITAL MELBOURNE This article has been prepared on the basis that it may provide a useful aid for Dentists
INITIAL MANAGEMENT OF DENTAL TRAUMA BY DR. LUKE MOLONEY CONSULTANT ENDODONTIST ROYAL CHILDREN S HOSPITAL MELBOURNE This article has been prepared on the basis that it may provide a useful aid for Dentists
Powertome Assisted Atraumatic Tooth Extraction
 Powertome Assisted Atraumatic Tooth Extraction White et al Jason White, DDS 1 2 3 Abstract Background: While traditional dental extraction techniques encourage minimal trauma, luxated elevation and forceps
Powertome Assisted Atraumatic Tooth Extraction White et al Jason White, DDS 1 2 3 Abstract Background: While traditional dental extraction techniques encourage minimal trauma, luxated elevation and forceps
Position Classification Standard for Dental Officer Series, GS-0680
 Position Classification Standard for Dental Officer Series, GS-0680 Table of Contents SERIES DEFINITION... 2 BACKGROUND... 2 TITLES... 3 GRADE-LEVEL EVALUATION CRITERIA... 3 NOTES ON THE USE OF THE STANDARDS...
Position Classification Standard for Dental Officer Series, GS-0680 Table of Contents SERIES DEFINITION... 2 BACKGROUND... 2 TITLES... 3 GRADE-LEVEL EVALUATION CRITERIA... 3 NOTES ON THE USE OF THE STANDARDS...
GRADE 6 DENTAL HEALTH
 GRADE 6 DENTAL HEALTH DENTAL HEALTH GRADE: 6 LESSON: 1 THEME: STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION CONCEPT: THE STRUCTURE OF A TOOTH IS RELATED TO ITS FUNCTION PREPARATION: 1. Prepare an overhead transparency of Parts
GRADE 6 DENTAL HEALTH DENTAL HEALTH GRADE: 6 LESSON: 1 THEME: STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION CONCEPT: THE STRUCTURE OF A TOOTH IS RELATED TO ITS FUNCTION PREPARATION: 1. Prepare an overhead transparency of Parts
Best Practices for Oral Health Assessments for School Nurses. Jill Fernandez RDH, MPH. National Association of School Nurses June 22, 2012
 Best Practices for Oral Health Assessments for School Nurses Jill Fernandez RDH, MPH National Association of School Nurses June 22, 2012 Jill Fernandez RDH, MPH Clinical Associate Professor Department
Best Practices for Oral Health Assessments for School Nurses Jill Fernandez RDH, MPH National Association of School Nurses June 22, 2012 Jill Fernandez RDH, MPH Clinical Associate Professor Department
FLORIDA COMBINED LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY, INC.
 FLORIDA COMBINED LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY, INC. PEDIATRIC POLICY SCHEDULE This Pediatric Policy Schedule applies only to Covered Persons who are age 19 and under. Pediatric Dental Benefits end on the last
FLORIDA COMBINED LIFE INSURANCE COMPANY, INC. PEDIATRIC POLICY SCHEDULE This Pediatric Policy Schedule applies only to Covered Persons who are age 19 and under. Pediatric Dental Benefits end on the last
Tooth Decay. What Is Tooth Decay? Tooth decay happens when you have an infection of your teeth.
 Tooth Decay What Is Tooth Decay? Tooth decay happens when you have an infection of your teeth. When you eat food and drink, it is broken down into acid. This acid helps to make plaque (a sticky substance).
Tooth Decay What Is Tooth Decay? Tooth decay happens when you have an infection of your teeth. When you eat food and drink, it is broken down into acid. This acid helps to make plaque (a sticky substance).
Lecture 3: Mutations
 Lecture 3: Mutations Recall that the flow of information within a cell involves the transcription of DNA to mrna and the translation of mrna to protein. Recall also, that the flow of information between
Lecture 3: Mutations Recall that the flow of information within a cell involves the transcription of DNA to mrna and the translation of mrna to protein. Recall also, that the flow of information between
Dr. Park's Publications
 Dr. Park's Publications Jae Hyun Park, D.M.D., M.S.D., M.S., Ph.D. Diplomate, American Board of Orthodontics Editor-in-Chief, Pacific Coast Society of Orthodontists Chief Editor, Computed Tomography: New
Dr. Park's Publications Jae Hyun Park, D.M.D., M.S.D., M.S., Ph.D. Diplomate, American Board of Orthodontics Editor-in-Chief, Pacific Coast Society of Orthodontists Chief Editor, Computed Tomography: New
USA provided by Delta Dental of California
 DeltaCare USA provided by Delta Dental of California Weʼll do whatever it takes and then some. Find a DeltaCare USA dentist Select from among the many conveniently located DeltaCare USA contracted general
DeltaCare USA provided by Delta Dental of California Weʼll do whatever it takes and then some. Find a DeltaCare USA dentist Select from among the many conveniently located DeltaCare USA contracted general
Influence of Sex on Genetics. Chapter Six
 Influence of Sex on Genetics Chapter Six Humans 23 Autosomes Chromosomal abnormalities very severe Often fatal All have at least one X Deletion of X chromosome is fatal Males = heterogametic sex XY Females
Influence of Sex on Genetics Chapter Six Humans 23 Autosomes Chromosomal abnormalities very severe Often fatal All have at least one X Deletion of X chromosome is fatal Males = heterogametic sex XY Females
OVERVIEW The MetLife Dental Plan for Retirees
 OVERVIEW The MetLife Dental Plan for Retirees IN NETWORK: Staying in network saves you money. 1 Participating dentists have agreed to MetLife s negotiated fees which are typically 15% to 45% below the
OVERVIEW The MetLife Dental Plan for Retirees IN NETWORK: Staying in network saves you money. 1 Participating dentists have agreed to MetLife s negotiated fees which are typically 15% to 45% below the
The Obvious and the Obscure:Diagnostic Steps for Crack Confirmation
 Cracking the Cracked Tooth Code In response to your requests... At the end of each issue of ENDODONTICS: Colleagues for Excellence, the American Association of Endodontists (AAE) asks readers to send in
Cracking the Cracked Tooth Code In response to your requests... At the end of each issue of ENDODONTICS: Colleagues for Excellence, the American Association of Endodontists (AAE) asks readers to send in
Chromosomes, Mapping, and the Meiosis Inheritance Connection
 Chromosomes, Mapping, and the Meiosis Inheritance Connection Carl Correns 1900 Chapter 13 First suggests central role for chromosomes Rediscovery of Mendel s work Walter Sutton 1902 Chromosomal theory
Chromosomes, Mapping, and the Meiosis Inheritance Connection Carl Correns 1900 Chapter 13 First suggests central role for chromosomes Rediscovery of Mendel s work Walter Sutton 1902 Chromosomal theory
deltadentalins.com/usc
 Plan Benefit Highlights for: UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA STUDENT PLAN Group No: 05008 The Delta Dental PPO table plan provides you great dental benefits at a reasonable cost. With a table of allowance
Plan Benefit Highlights for: UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA STUDENT PLAN Group No: 05008 The Delta Dental PPO table plan provides you great dental benefits at a reasonable cost. With a table of allowance
