Roger Williams University Fall Protection Policy
|
|
|
- Gary Bruce
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Roger Williams University Fall Protection Policy Roger Williams University Dept. of Environmental Health and Safety One Old Ferry Road Bristol, RI Adopted: April 26, 2011 (President s Cabinet) Revised August 16, 2011
2 ROGER WILLIAMS UNIVERSITY FALL PROTECTION POLICY I. Introduction II. Fall Protection Guidelines and Program Scope III. Roof Safety IV. Ladder Safety V. Lift Safety VI. Guardrail Requirements VII. Loading Dock Safety VIII. Personal Fall Arrest Systems Requirements IX. Training Requirements X. Contractor Guidelines XI. Exhibit A 1
3 I. Introduction Fall protection is defined as any means used to protect workers from falls when working in areas where fall hazards exist. Fall protection involves the elimination of fall hazards, the prevention of falls, and the control of falls. Fall protection is required whenever there is a change in working level of more than four feet (a drop of four feet or more to the ground or the next level). The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has many standards related to fall protection, including: 29 CFR (Fixed Ladders), 29 CFR (Portable Ladders), 29 CFR (Portable Wood Ladders), ANSI A (Safety Code for Fixed Ladders), 29 CFR (Powered Platforms), 29 CFR (Vehicle-Mounted Elevated and Rotating Work Platforms), 29 CFR (Guarding Floor and Wall Openings and Holes), 29 CFR (Fall Arrest Systems), and the General Duty Clause (Section 5(a)(1), OSH Act). Roger Williams University (RWU) departments are primarily responsible for compliance with, and safe implementation of, all RWU safety programs. RWU EHS is available to assist with compliance and provide policy clarification as necessary. II. Fall Protection Guidelines and Program Scope Fall protection begins with identifying a fall hazard. The following are examples of fall hazards which are covered by this policy: Elevated walking / working surfaces four feet or more above a lower level Skylights and smoke domes that workers could step into or fall through Wall openings such as those for windows or doors that workers could fall through Trenches and other excavations that are not readily seen and workers could fall into Walking / working surfaces from which workers could fall onto dangerous equipment Hoist areas where guardrails have been removed to receive materials Sides and edges of walking / working surfaces such as established floors, mezzanines, balconies, and walkways that are four feet or more above a lower level and not protected by guardrails at least 39 inches high Ramps and runways that are not protected by guardrails at least 39 inches high Leading edges edges of floors, roofs, and decks that change location as additional sections are added The leading edges of loading docks, which are not protected with guardrails Wells, pits, or shafts not protected with guardrails, fences, barricades, or covers Holes in walking/working surfaces that they could step into or fall through When a fall hazard has been identified, the following steps should be followed in deciding the proper fall protection: Step 1: Can the hazard be eliminated by using engineering control? (relocate to ground level, utilize a contractor with expertise in extremely hazardous areas, etc.) Step 2: If the hazard cannot be eliminated, can the possibility of a fall be eliminated be creating a fall prevention system? (guardrails made from steel, wood, or wire rope which comply with OSHA standards, etc.) 2
4 A personal fall arrest system (i.e., a harness and lanyard) must be used only when all possibilities of using Step 1 or 2 options have been exhausted. III. Roof Safety RWU authorizes the following departments to access and perform work on campus roofs: Capital Projects Environmental Health & Safety Facilities Management Public Safety In addition, third-party service/maintenance contractors (e.g. HVAC, electrical, roofing, etc.) may access and perform work on campus roofs if accompanied by an employee from one of the above-referenced departments. In addition, such third-party contractors may access and perform work on campus roofs without an RWU employee present in the discretion of a supervisory employee of one of the abovereferenced departments. In such instances, the authorizing department should properly orient the thirdparty contractor to proper safety and risk issues associated with the roof being accessed. All others (including, but not limited to, employees from other departments, faculty, students, student employees, etc.) may not access campus roofs without prior written authorization. A request for roof access form is attached hereto as Exhibit A. Do not approach within six feet of any: Roof edge, unless protected by guardrails (See Guardrail Requirement section of this plan); o Exception: For intermittent work (less than four times per year), an approved personal fall arrest system may be used in lieu of guardrails (see Personal Fall Arrest System Requirements section of this plan). Access hatch, unless protected by hinged or removable cover, or removable railings; or Skylight, unless protected by skylight screens or covers, guardrails, or if employee is wearing a personal fall arrest system. Protect the area below the elevated work height: When working close to the roof s edge, cordon off the area below to protect pedestrians from falling debris. Prevent materials from falling from exposed edges of fixed heights (roof, floor opening, wall opening, platform, runway or ramp) by erecting toeboards (vertical barriers erected at floor level and extending at least four inches in height). Do not access the roofs of the following buildings without notifying and seeking clearance from the Department of Public Safety (x3333) and the Department of Environmental Health and Safety (x3189): Marine and Natural Science (MNS) o Hazard working near HVAC vents on the roof locations due to fume hoods releasing chemical fumes in exhaust Cedar Hall 3
5 o RF (Radio Frequency) Safety and hearing protection hazards related to working next to Cooper Mass Notification (ESWS; Emergency Siren Warning System) speakers if activated (hearing protection is located at the roof access door) Recreation Center o RF Safety and hearing protection hazards related to working next to Cooper Mass Notification (ESWS; Emergency Siren Warning System) speakers if activated (hearing protection is located at the roof access door) Bayside 200 Building o RF Safety and hearing protection hazards related to working next to Cooper Mass Notification (ESWS; Emergency Siren Warning System) speakers if activated Maple Hall o RF Safety hazard related to working next to WQRI Radio broadcast tower North Campus Dorm o RF Safety hazard related to working next to Cox Communications broadcast tower IV. Ladder Safety Rules for Using all Ladders (Fixed and Portable) Do not use non-ladder objects (buckets, tables, chairs, etc.) in place of a ladder. Follow all manufacturer guidelines and all warnings and instructions on the ladder. Do not load ladders beyond their maximum intended load nor beyond their manufacturer s rated capacity. Use ladders only for their designated purpose. Use ladders only on stable and level surfaces unless secured to prevent accidental movement. Keep areas clear around the top and bottom of ladders. Secure ladders placed in areas such as passageways, doorways, or driveways, or where they can be displaced by workplace activities or traffic to prevent accidental movement. Or use a barricade to keep traffic or activity away from the ladder. Do not move, shift, or extend ladders while in use. Face the ladder when moving up or down. Use at least one hand to grasp the ladder when climbing. Do not carry objects or loads that could cause loss of balance or falling. Ladders must not be tied or fastened together to create longer sections unless they are specifically designed for such use. Defective Ladders (Fixed and Portable) Ladders having defects are to be marked or labeled as defective and taken out of service until repaired by either Facilities Management or the manufacturer. Rules Specific to Portable Ladders (Step, Straight, and Extension Ladders) Location Restrictions All portable ladders (step, straight, and extension) have the following location restrictions: Ladders may not be placed in front of doors opening toward the ladder unless the door is blocked open, locked, or guarded; 4
6 Do not use ladders on slippery surfaces unless secured or provided with slipresistant feet to prevent accidental movement; Ladders may not be placed on boxes, barrels, or other unstable bases to obtain additional height; and No ladder may be used to gain access to a roof unless the top of the ladder extends at least 3 feet above the point of support, at eave, gutter, or roofline. Prohibitions of Use Portable ladders must not be tied or fastened together to provide longer sections. Portable ladders must be equipped with the hardware fittings necessary if the manufacturer endorses extended uses. Do not use portable ladders as a brace, skid, guy, or gin pole, gangway, or for other uses then that for which they were intended, unless specifically recommended for use by the manufacturer. Length Allowances for Portable Ladders Do not use portable ladders that exceed the heights listed in this table: Type of Ladder Max. Length Portable Stepladders Type I Industrial 3-20 feet Type II Commercial 3-12 feet Type III - Household 3-6 feet Portable Rung Ladders Single Ladders Two-Section Ladders Trestle Ladders or extension or base sections Special Purpose Ladders Painter s stepladder Mason s ladder Trolley and side-rolling ladders 30 feet 60 feet 20 feet 12 feet 40 feet 20 feet Stepladder-Specific Requirements The bottoms of the four rails are to be supplied with insulating nonslip material for the safety of the user. A metal spreader or locking device of sufficient size and strength to securely hold the front and back sections in the open position must be a component of each stepladder. The spreader must have all sharp points or edges covered or removed to protect the user. Does not use cross bracing on the rear section of stepladders for climbing unless the ladders are designed and provided with steps for climbing on both front and rear sections. Do not use the top or top step of a step ladder as a step. Straight and Extension Ladder-Specific Requirements The minimum width between side rails of straight ladder or any section of an extension ladder must be 12 inches. 5
7 Extension ladders must be equipped with positive stops which will insure the overlap specified in the table above. Based on the nominal length of the ladder, each section of a multi-section ladder must overlap the adjacent section by at least the number of feet stated in this table: Normal length of ladder (in feet) Up to and including 36. Over 36, up to and including 48 Over 48, up to 60.. Rung Overlap (in feet) V. Lift Safety Fall Protection on Manlifts, Scissor Lifts, and Boom Lifts Fall protection is required on all lifts (manlifts, scissor lifts, and boom lifts). RWU requires a harness and lanyard to be used at all times when using lifts (see Personal Fall Arrest System Requirements section of this plan) Lift Safe Operating Requirements All users must be trained and certified in safe operating procedures and fall protection requirements prior to use. o RSC Equipment Rental provides this training for RWU employees. Inspect and check structural integrity before each use (at the beginning of each shift at a minimum) per manufacturer guidelines. An annual inspection of lifts will be completed by competent person with documentation maintained on file. o RSC Equipment Rental provides the yearly inspection of RWU lifts. Use the lift only for its intended purpose and follow the manufacturer s instructions. Keep the operating manual with the lift. Keep the lift level and stable by using outriggers and intermediate stabilizers. Never move the lift when the boom is up and workers are on the platform, unless allowed by the manufacturer. Stand on the platform floor. Don t sit or climb on the edge of the basket, guardrail, or midrail. Be sure to close the access gate while you re working from the platform. Inspect the lift before using it to make sure that it s working properly and it s in good condition. Know the lift s rated load capacity and don t exceed it. Stay at least ten feet away from electrical power lines. Never use the lift during severe weather. Use warning signs or barricades to keep others out of the work area. Never tie off to other equipment or to a structure next to the platform. Third-parties Use of RWU Lifts Third-parties (vendors, contractors, etc.) may accompany an RWU employee in an RWU lift provided the RWU employee operates the lift and such third-party complies with all safety requirements. 6
8 Third-parties are prohibited from using an RWU lift without an RWU employee accompanying the thirdparty in the lift unless such is approved in advance and in writing by RWU s Office of General Counsel (a fully signed Agreement for Use of Equipment will be required). VI. Guardrail Requirements Before using a guardrail system, check if the hazard be eliminated by using engineering control (relocate to ground level, or utilize a contractor with expertise in extremely hazardous areas, etc.). If guardrails are used, they must meet these requirements: A standard railing shall consist of top rail, intermediate rail, and post, and shall have a vertical height of 42 inches nominal from upper surface of top rail to floor. The complete structure shall be capable of withstanding a load of at least 200 pounds applied in any direction at any point on the top rail. Construction requirements vary by construction type: Wood Posts at least 2 inches x 4 inches, and posts less than 6 feet apart Pipe Railings at least 1 ½ inches in nominal diameter, and posts spaced not more than 8 feet on centers Structural Steel Posts and top and intermediate rails 2 inches x 2 inches by 3/8 inch angles, and posts spaced not more than 8 feet on centers Guardrails are required to be inspected on the following schedule: Temporary systems Daily: A visual inspection will be completed by a competent person. OSHA defines a Competent Person as one who is capable of identifying hazardous and dangerous conditions. Temporary systems Weekly: A complete structural inspection will be completed by a competent person. Permanent Systems Annual: A structural inspection will be completed by a competent person, with future frequency of inspection defined based on conditions/controls present. VII. Loading Dock Safety Loading docks pose potential fall hazards because they are often elevated at a height of 4 feet or greater than the pavement below, and the leading edge of the loading dock has to be open-access (no guardrails) to allow materials to be on- and off-loaded. RWU has one loading dock on campus. It is located at the Dining Commons building on the east side of the building. There are two thirty-yard trash compactors permanently stationed at either end of the dock, and three open bays for receiving materials. The loading dock is concrete and has one hydraulic dock leveler (metal plate used to span the gap between the dock and the truck) located at the center bay. The other bays do not have dock levelers. The dock s non-leading edges have structural steel guardrails which are installed and maintained in accordance with OSHA requirements (see Guardrail Requirements section of this policy). RWU will provide loading dock safety training to all employees that routinely work on the loading dock, specifically: Dining Commons, Public Safety, Facilities Management, and Environmental Health and Safety. Training topics will include: proper use of the dock leveler, 7
9 situational awareness, safe materials handling (including pallet jack and hand truck / dolly usage), and inclement weather safety (ice, snow, rain, etc.). In general, employees working on loading docks should observe these basic safety principles: Use the dock leveler when loading and off-loading materials from / to a truck and the loading dock. Immediately report all unsafe loading dock conditions to supervisor or Facilities Management (cracks or breaks in the concrete, ice or snow on the loading dock surface, insects such as bees at the trash compactors, etc.). When traveling back and forth across the loading dock, stay at least six feet away from the dock s leading edge. Stay in the center of the dock leveler when on- and off-loading materials between a truck and the loading dock. Always enter and exit the back of the truck at a 90-degree angle to the loading dock s leading edge. Follow the safe usage requirements when using pallet jacks and hand trucks / dollies. Do not walk along the leading edge of the loading dock while using this equipment. Push the equipment and load straight off the truck and continue moving straight back until the load is at least six feet back from the leading edge, then move in the desired direction. Do not store items on the loading dock. Keep the loading dock clear so there is plenty of room to safely work away from the leading edge, and to move materials as necessary. Maintain the loading dock in a clean and clutter-free manner to prevent slip/trip/fall hazards. Be aware of other people working and walking on the loading dock. VIII. Personal Fall Arrest Systems Requirements When a fall hazard has been identified, the following steps should be followed in deciding the proper fall protection: Step 1: Can the hazard be eliminated by using engineering control? (i.e., relocate to ground level, or utilize a contractor with expertise in extremely hazardous areas) Step 2: If the hazard cannot be eliminated, can the possibility of a fall be eliminated be creating a fall prevention system? (i.e., guardrails made from steel, wood, or wire rope which comply with OSHA standards) 8
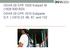
10 A personal fall arrest system (i.e., a harness and lanyard) must be used only when all possibilities of using Step 1 or 2 options have been exhausted. Example of the type of personal fall arrest system employed at RWU Personal fall arrest systems stop a worker s fall from a height, and can include the following components: a full body harness, lanyard, rope grabs, lifelines, anchorage points, and rigging. RWU personal fall arrest systems include a harness and lanyard. Personal fall arrest systems and components are used only for employee fall protection, and are rigged such that an employee can neither free fall more than six feet nor contact any lower level. Inspection Requirements Prior to each use, personal fall arrest systems shall be inspected for mildew, wear, damage and other deterioration, and defective components removed from service if strength or function may be adversely affected. Lifelines are required to be inspected annually by a competent person, and the documentation must be maintained on file. OSHA defines a Competent Person as one who is capable of identifying hazardous and dangerous conditions in the personal fall arrest system or any component thereof, as well as in their application and use with related equipment. RWU will contract RSC Rentals to perform and document the annual inspections. Storage and Maintenance of Personal Fall Arrest System Equipment Never store the personal fall arrest system equipment in the bottom of a tool box, on the ground, or outside exposed to the elements (i.e., sun, rain, snow, etc.). Hang equipment in a cool dry location in a way that retains its shape. Always follow manufacturer recommendations for inspection. Clean according to manufacturer recommendations, typically with a mild, nonabrasive soap, and hang to dry. 9
11 Never dry using heat or sun exposure or use strong detergents in cleaning. Never store equipment near excessive heat, chemicals, moisture, or sunlight. Never store in an area with exposures to fumes or corrosives elements. Avoid dirt and build-up on equipment. Never use this equipment for any purpose other than personal fall arrest. Remove equipment from service immediately once it s been exposed to a fall. Usage Requirements Unless of a locking type designed for the following connections, snap-hooks must not be engaged: o Directly to webbing, rope or rope wire; o To each other; o To a dee-ring to which another snap hook or other connector is attached; o To a horizontal lifeline; or o To any object which is incompatibly shaped or dimensioned in relation to the snap-hook such that unintentional disengagement could occur by the connected object being able to depress the snap-hook keeper and release itself. Devices used to connect to a horizontal lifeline which may become a vertical lifeline must be capable of locking in either direction on the lifeline. Personal fall arrest systems must be rigged such that an employee can neither free fall more than 6 feet, nor contact any lower level or the ground (which may be closer than 6 feet). Personal fall arrest systems must be worn with the attachment point of the body belt located in the center of the wearer s back, and the attachment point of the body harness located in the center of the wearer s back near shoulder level, or above the wearer s back. When vertical lifelines are used, each employee must be provided with a separate lifeline. Inspect all lifelines before each use for structural integrity of line and anchors. Lifelines must be protected against being cut or abraded. The employer must provide for prompt rescue of employees in the event of a fall or must assure that employees are able to rescue themselves. o Employees will work in pairs when performing roof work that requires a personal fall arrest system. In the event of a fall, the second employee will call Facilities Management for assistance, and Facilities employees will assist with a lift. The fallen employee cannot continue to perform work using the personal fall arrest system he or she was wearing when he or she fell. The equipment involved in the fall must be immediately taken out of service because it has been exposed to an impact. Personal Fall Arrest System Performance Criteria Personal fall arrest systems must, when stopping a fall: Limit the maximum arresting force on an employee to 900 pounds when used with a body belt Limit maximum arresting force on an employee to 1,800 pounds when used with a body harness Bring an employee to a complete stop and limit maximum declaration distance an employee travels to 3.5 feet, and have enough strength to withstand twice the potential 10
12 impact of the energy of an employee free fall a distance of 6 feet, or the free fall distance permitted by the system, whichever is less. Connector shall be drop forged, pressed, or formed steel, or made of equivalent material, and have a corrosion-resistant finish. All surfaces and edges shall be smooth. Anchorages for personal fall arrest equipment shall be capable of supporting at least 5,000 pounds per employee attached, or shall be designed, installed and used as part of a complete personal fall arrest system which maintains a safety factor of at least two, under the supervision of a qualified person. OSHA defines a qualified person as one with extensive knowledge and experience in the subject field who is capable of design, analysis, evaluation, and the specifications in the subject work, project, or product. Ropes and straps (webbing) used in lanyards, lifelines, and strength components of body belts and body harnesses shall be made from synthetic fibers or wire rope. IX. Training RWU requires all employees with roof access (Public Safety, Facilities Management, and Environmental Health and Safety Department members) to be knowledgeable in identifying potential fall hazards and how to apply the fall protection procedures in this plan as necessary. RWU EHS will provide required annual fall hazard recognition / fall protection procedures training to employees in these departments. RSC Equipment Rentals will provide training and certification on the various lifts (aerial, scissor, and boom) as necessary. RWU EHS will provide required annual loading dock safety training to the departments which routinely access and perform work on the loading dock (Dining Commons, Public Safety, Facilities Management, and Environmental Health and Safety). As previously noted, RWU departments are primarily responsible for compliance with, and safe implementation of, all RWU safety programs. RWU EHS is available to assist with compliance and provide training as necessary. Fall hazard recognition / fall protection training requirements are not specified in the general industry OSHA standards (29 CFR 1910), so RWU will develop and provide trainings that meet the requirements listed in the construction industry OSHA standards as a matter of best practice. The training requirements in 29 CFR 1926 are as follows: OSHA 29 CFR (a)(1) The employer shall provide a training program for each employee who might be exposed to fall hazards. The program shall enable each employee to recognize the hazards of falling and shall train each employee in the procedures to be followed in order to minimize these hazards. 29 CFR (a)(2) The employer shall assure that each employee has been trained, as necessary, by a competent person qualified in the following areas: (a)(2)(i) The nature of fall hazards in the work area; (a)(2)(ii) 11
13 The correct procedures for erecting, maintaining, disassembling, and inspecting the fall protection systems to be used; and (a)(2)(iii) The use and operation of guardrail systems, personal fall arrest systems, safety net systems, warning line systems, safety monitoring systems, controlled access zones, and other protection to be use X. Contractor Guidelines Contractors working as part of an RWU / contractor team must follow all requirements in the RWU Fall Protection Policy. They must follow all of their own company s requirements as well. They must provide proof of certification and training to RWU EHS before operating any RWU lifts. They must have been trained on the same make and model as the equipment being used. They may use RWU personal fall arrest system components (harness and lanyard) if they choose to and the equipment fits properly. They have the right to inspect the equipment prior to use. Contractors not working with RWU employees must follow RWU s all requirements in the RWU Fall Protection Policy. They must follow all of their own company s requirements as well. They must be provided a copy of the RWU Fall Protection Policy by the RWU contact they are working for. They must provide their own fall protection equipment, including personal fall arrest system components. They must be certified and trained on any equipment they operate, and proof of training and certification must be available for review by RWU EHS upon request. They must notify RWU Public Safety Dispatch at x3333 ( ) prior to beginning any work, and again when they have finished their work. Their RWU contact must make them aware of any special hazards in their work area, such as the RF / noise hazards associated with the Cooper Notification System. 12
14 Request for Roof Access Submit to the Office of Environmental Health & Safety at least 10 days prior to date requested for access Roger Williams University authorizes the following departments to access and perform work on campus roofs: Capital Projects Environmental Health & Safety Facilities Management Public Safety In addition, third- party service/maintenance contractors (e.g. HVAC, electrical, roofing, etc.) may access and perform work on campus roofs if accompanied by an employee from one of the above- referenced departments. In addition, such third- party contractors may access and perform work on campus roofs without an RWU employee present in the discretion of a supervisory employee of one of the above- referenced departments. In such instances, the authorizing department should properly orient the third- party contractor to proper safety and risk issues associated with the roof being accessed. All others (including, but not limited to, employees from other departments, faculty, students, student employees, etc.) may not access campus roofs without prior written authorization. Use the following form to request roof access: Requestor Name: Department: Building for which roof access is sought: Date requested for access: Time: Anticipated length of time on roof: Please provide a brief description for reason for roof access: Individuals who will be accessing roof (list all, use separate sheet if necessary): Name Relationship to RWU (e.g. Faculty, staff, student, contractor, and vendor) Approval For internal use only Y N Environmental Health & Safety: Signature of authorizing EHS Employee Name of EHS / Public Safety / Facilities / Capitol Projects Employee providing escort Conditions/limitations on access:
ELEVATED WORK POLICY
 ELEVATED WORK POLICY 1.0 BACKGROUND The purpose of this program is to prevent accidents and injuries to workers from falls and to provide employees with the information for the safe use of fall protection
ELEVATED WORK POLICY 1.0 BACKGROUND The purpose of this program is to prevent accidents and injuries to workers from falls and to provide employees with the information for the safe use of fall protection
FALL PROTECTION PROGRAM
 FALL PROTECTION PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF RISK MANAGEMENT AND SAFETY CREATED JUNE 2009 Table of Contents Fall Protection Requirements... 1 General Fall Protection... 1 Controlled Access Zones... 1 Guardrail
FALL PROTECTION PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF RISK MANAGEMENT AND SAFETY CREATED JUNE 2009 Table of Contents Fall Protection Requirements... 1 General Fall Protection... 1 Controlled Access Zones... 1 Guardrail
FALL PROTECTION- Part 2 SELF INSPECTION CHECKLIST
 OPTIONAL INFORMATION Name of School: Date of Inspection: Vocational Program/Course/Room: Signature of Inspector: FALL PROTECTION- Part 2 Instructions: This checklist covers fall protection systems criteria
OPTIONAL INFORMATION Name of School: Date of Inspection: Vocational Program/Course/Room: Signature of Inspector: FALL PROTECTION- Part 2 Instructions: This checklist covers fall protection systems criteria
What is Fall protection?
 What is Fall protection? The Occupational Safety and Health Administration s (OSHA s) fall protection standard deals with both human and equipment-related issues. The standard identifies areas or activities
What is Fall protection? The Occupational Safety and Health Administration s (OSHA s) fall protection standard deals with both human and equipment-related issues. The standard identifies areas or activities
FALL PROTECTION PROGRAM
 FALL PROTECTION PROGRAM Page 2 of 15 Table of Contents Applicability... 3 Overview... 3 Definitions... 3 Responsibilities... 5 Risk Assessment... 6 Risk Management... 7 Roof Access Procedure 10 Rescue
FALL PROTECTION PROGRAM Page 2 of 15 Table of Contents Applicability... 3 Overview... 3 Definitions... 3 Responsibilities... 5 Risk Assessment... 6 Risk Management... 7 Roof Access Procedure 10 Rescue
`Fall Protection Guidelines in Construction
 `Fall Protection Guidelines in Construction A Publication Provided by: 1681 Campus Delivery Fort Collins, Colorado 80523 (970) 491-6151 email: [email protected] web: http://www.bernardino.colostate.edu/public/
`Fall Protection Guidelines in Construction A Publication Provided by: 1681 Campus Delivery Fort Collins, Colorado 80523 (970) 491-6151 email: [email protected] web: http://www.bernardino.colostate.edu/public/
Fall Protection Guidelines
 OCT 2015 1 of 6 Fall Protection Guidelines 1.0 PURPOSE To establish the requirements and procedures to protect employees and other persons conducting work from hazards associated with falling from one
OCT 2015 1 of 6 Fall Protection Guidelines 1.0 PURPOSE To establish the requirements and procedures to protect employees and other persons conducting work from hazards associated with falling from one
Fall Protection Program
 Fall Protection Program Policy: It is the policy of our company to provide fall protection for employees exposed to fall hazards greater than 7 ½ feet. Fall hazards include but, are not limited to; work
Fall Protection Program Policy: It is the policy of our company to provide fall protection for employees exposed to fall hazards greater than 7 ½ feet. Fall hazards include but, are not limited to; work
Fall Protection, Title 29 Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) Part 45, Subpart M, Fall Protection, 1926.500, 1926.501, 1926.502, and1926.
 STANDARDS Fall Protection, Title 29 Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) Part 45, Subpart M, Fall Protection, 1926.500, 1926.501, 1926.502, and1926.503 1.0 Purpose This document meets the requirements outlined
STANDARDS Fall Protection, Title 29 Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) Part 45, Subpart M, Fall Protection, 1926.500, 1926.501, 1926.502, and1926.503 1.0 Purpose This document meets the requirements outlined
OSHA 29 CFR 1926 Subpart M (1926.500-503) OSHA 29 CFR 1910 Subparts D,F, I (1910.23, 66, 67, and 132
 OSHA 29 CFR 1926 Subpart M (1926.500-503) OSHA 29 CFR 1910 Subparts D,F, I (1910.23, 66, 67, and 132 Importance of Fall Protection Each year, approximately 14 percent of fatal workplace injuries are caused
OSHA 29 CFR 1926 Subpart M (1926.500-503) OSHA 29 CFR 1910 Subparts D,F, I (1910.23, 66, 67, and 132 Importance of Fall Protection Each year, approximately 14 percent of fatal workplace injuries are caused
Fall protection systems and practices Duty to have fall protection Protection at or above 6' level.
 Duty to have fall protection Protection at or above 6' level. Walking/working surfaces inspected before work begins. Employees can only work on surfaces strong enough to support them. Page 1 Protection
Duty to have fall protection Protection at or above 6' level. Walking/working surfaces inspected before work begins. Employees can only work on surfaces strong enough to support them. Page 1 Protection
Walking Working Surfaces and Fall Protection Program
 DEPAUL UNIVERSITY Walking Working Surfaces and Fall Protection Program Environmental Health & Safety March 2015 TABLE OF CONTENTS SECTION PAGE NO. 1.0 PURPOSE AND SCOPE 3 2.0 BASICS FOR STAFF, FACULTY,
DEPAUL UNIVERSITY Walking Working Surfaces and Fall Protection Program Environmental Health & Safety March 2015 TABLE OF CONTENTS SECTION PAGE NO. 1.0 PURPOSE AND SCOPE 3 2.0 BASICS FOR STAFF, FACULTY,
Walking and Working Surface Checklist:
 Walking and Working Surfaces Purpose: This information is presented to improve the level of safety in our operations, and to inform you that we will comply with the OSHA Standard 29 CFR 1910.23. Responsibility:
Walking and Working Surfaces Purpose: This information is presented to improve the level of safety in our operations, and to inform you that we will comply with the OSHA Standard 29 CFR 1910.23. Responsibility:
Walking/Work Surfaces Fall Protection Program
 Reviewed: 10-2006 Walking/Work Surfaces Fall Protection Program It is the responsibility of all supervisors and/or administrators to implement this safety program. Their responsibility includes yearly,
Reviewed: 10-2006 Walking/Work Surfaces Fall Protection Program It is the responsibility of all supervisors and/or administrators to implement this safety program. Their responsibility includes yearly,
SITE SPECIFIC FALL PROTECTION PLAN
 1 THIS PLAN IS SPECIFIC TO: PROJECT & ADDRESS 1.1 THIS PLAN IS SPECIFIC TO THE FOLLOWING AREA(S) ON SITE: Parkade level: Typical level: Other: Between G/L: 1.2 THIS PLAN IS APPLICABLE TO THE FOLLOWING
1 THIS PLAN IS SPECIFIC TO: PROJECT & ADDRESS 1.1 THIS PLAN IS SPECIFIC TO THE FOLLOWING AREA(S) ON SITE: Parkade level: Typical level: Other: Between G/L: 1.2 THIS PLAN IS APPLICABLE TO THE FOLLOWING
FALL PROTECTION WORK PLAN
 FALL PROTECTION WORK PLAN INSTRUCTIONS A written fall protection work plan must be implemented by each employer on a job site where a fall hazard of 10 feet or greater exists, in accordance with OSHA Standards.
FALL PROTECTION WORK PLAN INSTRUCTIONS A written fall protection work plan must be implemented by each employer on a job site where a fall hazard of 10 feet or greater exists, in accordance with OSHA Standards.
Chapter 3: Fall Protection/ Scaffolding Safety
 Chapter 3: Fall Protection/ Scaffolding Safety Learning Objectives In this chapter you will learn to: recognize the hazards commonly associated with work on or around scaffolds; be aware of common scaffold-related
Chapter 3: Fall Protection/ Scaffolding Safety Learning Objectives In this chapter you will learn to: recognize the hazards commonly associated with work on or around scaffolds; be aware of common scaffold-related
EMPLOYEE FALL PROTECTION
 EMPLOYEE FALL PROTECTION You can fall from any height and be seriously injured or killed. In the construction industry, as well as any other industry, when falls from heights happen, they are usually very
EMPLOYEE FALL PROTECTION You can fall from any height and be seriously injured or killed. In the construction industry, as well as any other industry, when falls from heights happen, they are usually very
Fall Protection and Fall Prevention. San José State University Environmental Health and Safety Facilities Development & Operations
 Fall Protection and Fall Prevention San José State University Environmental Health and Safety Facilities Development & Operations Learning Objectives To understand the hazards of falls To understand when
Fall Protection and Fall Prevention San José State University Environmental Health and Safety Facilities Development & Operations Learning Objectives To understand the hazards of falls To understand when
This material was produced under grant number SH-17792-08-60-F-48 Occupational Safety and Health Administration, U.S. Department of Labor.
 Big Four Construction Hazards: Fall Hazards This material was produced under grant number SH-17792-08-60-F-48 Occupational Safety and Health Administration, U.S. Department of Labor. It does not necessarily
Big Four Construction Hazards: Fall Hazards This material was produced under grant number SH-17792-08-60-F-48 Occupational Safety and Health Administration, U.S. Department of Labor. It does not necessarily
One-third of all fatalities in the U.S. construction
 Guardrail systems: Fall prevention for floor and wall openings and open-sided floors One-third of all fatalities in the U.S. construction industry result from falls from elevations. Falls from elevations
Guardrail systems: Fall prevention for floor and wall openings and open-sided floors One-third of all fatalities in the U.S. construction industry result from falls from elevations. Falls from elevations
WALKING-WORKING SURFACES (SLIPS, TRIPS, AND FALLS)
 WALKING-WORKING SURFACES (SLIPS, TRIPS, AND FALLS) Slips, trips, and falls constitute the majority of general industry accidents. They cause 15% of all accidental deaths, and are second only to motor vehicles
WALKING-WORKING SURFACES (SLIPS, TRIPS, AND FALLS) Slips, trips, and falls constitute the majority of general industry accidents. They cause 15% of all accidental deaths, and are second only to motor vehicles
Fall Protection Basics for Construction Activities
 Fall Protection Basics for Construction Activities Washington State has revised fall protection rules, effective April 1, 2013. This booklet provides an overview of the requirements. www.lni.wa.gov/safety
Fall Protection Basics for Construction Activities Washington State has revised fall protection rules, effective April 1, 2013. This booklet provides an overview of the requirements. www.lni.wa.gov/safety
Drew University Ladder Safety Program Policy and Inspection Procedure Draft 0412
 PURPOSE To establish and define the procedures to ensure that ladders at Drew University are installed, used, inspected and maintained in accordance with applicable standards. REFERENCES OSHA Portable
PURPOSE To establish and define the procedures to ensure that ladders at Drew University are installed, used, inspected and maintained in accordance with applicable standards. REFERENCES OSHA Portable
OSHA Scaffold Standard for Construction. 29 CFR 1926 Subpart L
 OSHA Scaffold Standard for Construction 29 CFR 1926 Subpart L EH&S Jim Walker What is the revised OSHA scaffold standard for construction? Issued on August 30, 1996 and became effective on November 29,
OSHA Scaffold Standard for Construction 29 CFR 1926 Subpart L EH&S Jim Walker What is the revised OSHA scaffold standard for construction? Issued on August 30, 1996 and became effective on November 29,
CHAPTER 10. FALL PROTECTION PROGRAM
 CHAPTER 10. FALL PROTECTION PROGRAM 1000 GENERAL. This chapter establishes policy for developing fall protection programs to protect all Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) personnel working at elevated
CHAPTER 10. FALL PROTECTION PROGRAM 1000 GENERAL. This chapter establishes policy for developing fall protection programs to protect all Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) personnel working at elevated
Guide to Fall Protection Regulations
 Guide to Fall Protection Regulations Produced by: Workers Compensation Board of PEI PO Box 757 Charlottetown PE C1A 7L7 902-368-5697 or 1-800-237-5049 website: www.wcb.pe.ca Revised June 2013 Guide to
Guide to Fall Protection Regulations Produced by: Workers Compensation Board of PEI PO Box 757 Charlottetown PE C1A 7L7 902-368-5697 or 1-800-237-5049 website: www.wcb.pe.ca Revised June 2013 Guide to
Working at Heights and Fall Protection
 Standard Operating Procedures Working at Heights and Fall Protection Last Modified: JAN 2013 1 of 6 Working at Heights and Fall Protection I Purpose Serious accidents can result from falls. All employees
Standard Operating Procedures Working at Heights and Fall Protection Last Modified: JAN 2013 1 of 6 Working at Heights and Fall Protection I Purpose Serious accidents can result from falls. All employees
Ladder Program and Training Materials
 Prepared by Built Insurance Brokerage LLC Ladder Program and Training Materials Table of Contents Ladder Program... 1 Appendix A... 5 Appendix B... 7 Employee Handout... 9 Presentation Instructor Notes...
Prepared by Built Insurance Brokerage LLC Ladder Program and Training Materials Table of Contents Ladder Program... 1 Appendix A... 5 Appendix B... 7 Employee Handout... 9 Presentation Instructor Notes...
WORKING AT HEIGHTS. Introduction. Risk Assessment
 WORKING AT HEIGHTS Introduction This guideline makes reference to the provisions regarding working at heights in the Regulation for Industrial Establishments (Reg. 851) and the Regulation for Construction
WORKING AT HEIGHTS Introduction This guideline makes reference to the provisions regarding working at heights in the Regulation for Industrial Establishments (Reg. 851) and the Regulation for Construction
Environment, Health and Safety Technical Guidance
 Environment, Health and Safety Technical Guidance SOP-06 Working at Height Produced by Environment & Safety Office Campus Facilities Department Table of Contents 1 Overview... 1 1.1 Purpose... 1 1.2 Hazards
Environment, Health and Safety Technical Guidance SOP-06 Working at Height Produced by Environment & Safety Office Campus Facilities Department Table of Contents 1 Overview... 1 1.1 Purpose... 1 1.2 Hazards
Safe Operating Procedure
 Safe Operating Procedure (Revised 5/14) PERSONAL FALL ARREST SYSTEMS Introduction In 2011, falls to a lower level were the second leading cause of occupational fatalities across all industries, claiming
Safe Operating Procedure (Revised 5/14) PERSONAL FALL ARREST SYSTEMS Introduction In 2011, falls to a lower level were the second leading cause of occupational fatalities across all industries, claiming
QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS ON NEW FALL PROTECTION LEGISLATION
 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS ON NEW FALL PROTECTION LEGISLATION 50.4(1) An owner of a place of employment, an employer and a contractor shall each ensure that each component of a fall-protection system is inspected
QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS ON NEW FALL PROTECTION LEGISLATION 50.4(1) An owner of a place of employment, an employer and a contractor shall each ensure that each component of a fall-protection system is inspected
Elkhorn Construction, Inc. Safety Manual Title: Fall Protection Policy Effective Date: 03-01-2000
 1. General Requirements (OSHA References: OSHA 29 CFR 1926.503) 1.1 Elkhorn Construction, Inc. employee-owners and subcontractors are required to use fall protection equipment or systems when an assessment
1. General Requirements (OSHA References: OSHA 29 CFR 1926.503) 1.1 Elkhorn Construction, Inc. employee-owners and subcontractors are required to use fall protection equipment or systems when an assessment
http://www.osha.gov/doc/outreachtraining/htmlfiles/subpartm.html
 Page 1 of 10 www.osha.gov A-Z Index: A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z Search OSHA
Page 1 of 10 www.osha.gov A-Z Index: A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z Search OSHA
Safety and Health Policy and Procedure Manual. FALL PROTECTION Section 0160. Table of Contents
 Safety and Health Policy and Procedure Manual FALL PROTECTION Section 0160 Table of Contents I. INTRODUCTION II. STANDARDS III. PURPOSE IV. SCOPE V. SCAFFOLDING VI. STAIRWAYS AND LADDERS A. Stairways B.
Safety and Health Policy and Procedure Manual FALL PROTECTION Section 0160 Table of Contents I. INTRODUCTION II. STANDARDS III. PURPOSE IV. SCOPE V. SCAFFOLDING VI. STAIRWAYS AND LADDERS A. Stairways B.
CHECKLIST Fall Protection
 Walking/working surfaces can support employees. Employees are protected from falling from elevated surfaces through the use of guardrail systems, safety net systems; personal fall arrest systems, controlled
Walking/working surfaces can support employees. Employees are protected from falling from elevated surfaces through the use of guardrail systems, safety net systems; personal fall arrest systems, controlled
PLEASE NOTE. For more information concerning the history of these regulations, please see the Table of Regulations.
 PLEASE NOTE This document, prepared by the Legislative Counsel Office, is an office consolidation of this regulation, current to June 9, 2012. It is intended for information and reference purposes only.
PLEASE NOTE This document, prepared by the Legislative Counsel Office, is an office consolidation of this regulation, current to June 9, 2012. It is intended for information and reference purposes only.
Fall Hazards 1/3/2014. Introduction
 Fall Hazards Introduction Fall hazards exist at most construction worksites exposing workers to dangerous work environments on a daily basis. A fall hazard is anything that may cause a person to lose his
Fall Hazards Introduction Fall hazards exist at most construction worksites exposing workers to dangerous work environments on a daily basis. A fall hazard is anything that may cause a person to lose his
Fixed and Portable Ladders- A Guide to OSHA Rules
 Fixed and Portable Ladders- A Guide to OSHA Rules Introduction Working on and around stairways and ladders is hazardous. Stairways and ladders are major sources of injuries and fatalities among construction
Fixed and Portable Ladders- A Guide to OSHA Rules Introduction Working on and around stairways and ladders is hazardous. Stairways and ladders are major sources of injuries and fatalities among construction
OSHA Subpart M Fall Protection
 OSHA Subpart M Fall Protection 1926.500 Scope, Application and Definitions (b) Definition "Body harness" means straps which may be secured about the employee in a manner that will distribute the fall arrest
OSHA Subpart M Fall Protection 1926.500 Scope, Application and Definitions (b) Definition "Body harness" means straps which may be secured about the employee in a manner that will distribute the fall arrest
Slip, Trip & Fall Program Table of Contents
 Slip, Trip & Fall Program Table of Contents I. Introduction... 2 II. Scope... 2 III. Definitions... 2 IV. Responsibilities... 4 V. Practices... 5 VI. Slip-Fall Facility Checklist... 7 VII. References...
Slip, Trip & Fall Program Table of Contents I. Introduction... 2 II. Scope... 2 III. Definitions... 2 IV. Responsibilities... 4 V. Practices... 5 VI. Slip-Fall Facility Checklist... 7 VII. References...
SCOPE This guideline applies to all construction projects on Emory University properties, including renovation projects.
 1762 Clifton Road, Suite 1200 Atlanta, Georgia 30322 (404) 727-5922 FAX: (404) 727-9778 FALL PROTECTION DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION GUIDELINES PURPOSE The purpose of this guideline is to provide safe design
1762 Clifton Road, Suite 1200 Atlanta, Georgia 30322 (404) 727-5922 FAX: (404) 727-9778 FALL PROTECTION DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION GUIDELINES PURPOSE The purpose of this guideline is to provide safe design
7. PRINCIPAL STEPS 8. POTENTIAL HAZARDS 9. RECOMMENDED CONTROLS
 ACTIVITY HAZARD ANALYSIS (AHA) 1. Contract Number: 2. Contractor Name: 3. Date prepared: 4. Title/Activity Performed: FIXED SCAFFOLDING 5. Location: 6. Estimated Date of Completion: 7. PRINCIPAL STEPS
ACTIVITY HAZARD ANALYSIS (AHA) 1. Contract Number: 2. Contractor Name: 3. Date prepared: 4. Title/Activity Performed: FIXED SCAFFOLDING 5. Location: 6. Estimated Date of Completion: 7. PRINCIPAL STEPS
Fall Protection Safety Program
 Fall Protection Safety Program ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH & SAFETY pg. 1 Table of Contents A. Introduction... 3 B. Scope... 3 C. Responsibilities... 3 1. Department... 3 2. Environmental Health & Safety (EHS)...
Fall Protection Safety Program ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH & SAFETY pg. 1 Table of Contents A. Introduction... 3 B. Scope... 3 C. Responsibilities... 3 1. Department... 3 2. Environmental Health & Safety (EHS)...
OSHA 1910.66 Remove impacted systems and components. Inspect systems prior to use.
 Q: When do I remove my harness from service? A: ANSI (American National Standards Institute) A10.32-2004 states the service life of fall protection equipment manufactured of synthetic fiber shall be 5
Q: When do I remove my harness from service? A: ANSI (American National Standards Institute) A10.32-2004 states the service life of fall protection equipment manufactured of synthetic fiber shall be 5
Slip, Trip & Fall Program Table of Contents
 Slip, Trip & Fall Program Table of Contents I. Introduction...2 II. Scope...2 III. IV. Definitions...2 Responsibilities...4 V. Practices...5 VI. Slip-Fall Facility Checklist...7 VII. VIII. Training...8
Slip, Trip & Fall Program Table of Contents I. Introduction...2 II. Scope...2 III. IV. Definitions...2 Responsibilities...4 V. Practices...5 VI. Slip-Fall Facility Checklist...7 VII. VIII. Training...8
CONSTRUCTION SAFETY. NOTE: Barriers, guards, and warning signs are required to ensure safety against existing hazards.
 CONSTRUCTION SAFETY Introduction The following sections provide general guidelines and procedures for construction safety. This chapter covers the following topics: TOPIC PAGE General Construction Guidelines
CONSTRUCTION SAFETY Introduction The following sections provide general guidelines and procedures for construction safety. This chapter covers the following topics: TOPIC PAGE General Construction Guidelines
Preventing Slips, Trips, & Falls
 Preventing Slips, Trips, & Falls OSHA s Walking & Working Surfaces, & Fall Protection Standards Contents Introduction and Purpose General Injury Prevention Overview of Slips, Trips and Falls Types of Housekeeping
Preventing Slips, Trips, & Falls OSHA s Walking & Working Surfaces, & Fall Protection Standards Contents Introduction and Purpose General Injury Prevention Overview of Slips, Trips and Falls Types of Housekeeping
ADMINISTRATIVE PROCEDURE
 Page 1 of 12 1. Purpose: The purpose of a Program is to establish procedures to protect all employees engaged in outdoor or indoor work activities that expose them to potential falls from elevations. This
Page 1 of 12 1. Purpose: The purpose of a Program is to establish procedures to protect all employees engaged in outdoor or indoor work activities that expose them to potential falls from elevations. This
Work at Height / Falling Objects
 Introduction This information sheet gives employers and employees practical advice on work at height and falling objects and how to eliminate or reduce the risk of harm or damage occurring. It will assist
Introduction This information sheet gives employers and employees practical advice on work at height and falling objects and how to eliminate or reduce the risk of harm or damage occurring. It will assist
Super Slider ADJUSTABLE FROM 3.5-12 Model #HD26229
 Super Slider ADJUSTABLE FROM 3.5-12 Model #HD26229 IMPORTANT!!! ALL PERSONS USING THIS EQUIPMENT MUST READ AND UNDERSTAND ALL INSTRUCTIONS. FAILURE TO DO SO MAY RESULT IN SERIOUS INJURY OR DEATH. USERS
Super Slider ADJUSTABLE FROM 3.5-12 Model #HD26229 IMPORTANT!!! ALL PERSONS USING THIS EQUIPMENT MUST READ AND UNDERSTAND ALL INSTRUCTIONS. FAILURE TO DO SO MAY RESULT IN SERIOUS INJURY OR DEATH. USERS
Sample Fall Protection Program
 Sample Fall Protection Program Revised August 2000 Table of Contents Page Purpose and Scope...3 Goals...3 Definitions...3 Types of Fall Protection Systems...6 Fall Protection Locations...6 Fall Protection
Sample Fall Protection Program Revised August 2000 Table of Contents Page Purpose and Scope...3 Goals...3 Definitions...3 Types of Fall Protection Systems...6 Fall Protection Locations...6 Fall Protection
The following symbol denotes a generally compliant condition: The following symbol denotes a generally noncompliant condition:
 This guide provides compliance information to help the metal and nonmetal mining industry comply with the requirements of the Mine Safety and Health Administration s (MSHA s) ladder standards. This document
This guide provides compliance information to help the metal and nonmetal mining industry comply with the requirements of the Mine Safety and Health Administration s (MSHA s) ladder standards. This document
Portable Ladder Safety
 Portable Ladder Safety Agenda Importance of Ladder Safety An Approved Ladder Controlling Hazards Inspecting the Ladder Set Up Use Importance of Ladder Safety Any fall can be serious, and a fall from the
Portable Ladder Safety Agenda Importance of Ladder Safety An Approved Ladder Controlling Hazards Inspecting the Ladder Set Up Use Importance of Ladder Safety Any fall can be serious, and a fall from the
VERTICAL / FIXED BEAM CLAMP I-BEAM ANCHOR ADJUSTABLE FROM 4-14 Model # HD26249
 VERTICAL / FIXED BEAM CLAMP I-BEAM ANCHOR ADJUSTABLE FROM 4-14 Model # HD26249 IMPORTANT!!! ALL PERSONS USING THIS EQUIPMENT MUST READ AND UNDERSTAND ALL INSTRUCTIONS. FAILURE TO DO SO MAY RESULT IN SERIOUS
VERTICAL / FIXED BEAM CLAMP I-BEAM ANCHOR ADJUSTABLE FROM 4-14 Model # HD26249 IMPORTANT!!! ALL PERSONS USING THIS EQUIPMENT MUST READ AND UNDERSTAND ALL INSTRUCTIONS. FAILURE TO DO SO MAY RESULT IN SERIOUS
SCAFFOLD, LADDER & FALL PROTECTION PROGRAM
 SCAFFOLD, LADDER & FALL PROTECTION PROGRAM THE UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN PLANT DIVISION Prepared by The Department of Occupational Safety and Environmental Health Ann Arbor, Michigan 48109 Scffall3.doc 5/24/00
SCAFFOLD, LADDER & FALL PROTECTION PROGRAM THE UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN PLANT DIVISION Prepared by The Department of Occupational Safety and Environmental Health Ann Arbor, Michigan 48109 Scffall3.doc 5/24/00
Fixed Access Ladders. Table of Contents. 1. Legislative Requirements
 Fixed Access Ladders Engineering Data Sheet 2-04 Revised: January 1997 Table of Contents 1. Legislative Requirements 2. General 3. Rungs 4. Side Rails 5. Safety Cages 6. Attachment & Anchoring 7. Platforms
Fixed Access Ladders Engineering Data Sheet 2-04 Revised: January 1997 Table of Contents 1. Legislative Requirements 2. General 3. Rungs 4. Side Rails 5. Safety Cages 6. Attachment & Anchoring 7. Platforms
OPTIONAL INFORMATION GUARDING FLOORS, STAIRS, AND OTHER OPENINGS SELF INSPECTION CHECKLIST
 OPTIONAL INFORMATION Name of School: Date of Inspection: Vocational Program/Course/Room: Signature of Inspector: GUARDING FLOORS, STAIRS, AND OTHER OPENINGS Guidelines: This checklist covers some of the
OPTIONAL INFORMATION Name of School: Date of Inspection: Vocational Program/Course/Room: Signature of Inspector: GUARDING FLOORS, STAIRS, AND OTHER OPENINGS Guidelines: This checklist covers some of the
OREGON OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY AND HEALTH STANDARDS. Oregon Administrative Rules, Chapter 437 DIVISION 3 (29 CFR 1926) CONSTRUCTION CONSTRUCTION
 OREGON OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY AND HEALTH STANDARDS Oregon Administrative Rules, Chapter 437 DIVISION 3 (29 CFR 1926) CONSTRUCTION CONSTRUCTION Subdivision M Fall Protection (Oregon OSHA) Department of Consumer
OREGON OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY AND HEALTH STANDARDS Oregon Administrative Rules, Chapter 437 DIVISION 3 (29 CFR 1926) CONSTRUCTION CONSTRUCTION Subdivision M Fall Protection (Oregon OSHA) Department of Consumer
Programme-Based Engagement (ProBE) for Fall From Heights. Statistics
 Programme-Based Engagement (ProBE) for Fall From Heights Statistics For the past ten years, falling from height has been the number one cause of death in workplaces in Singapore. It has accounted for 34%
Programme-Based Engagement (ProBE) for Fall From Heights Statistics For the past ten years, falling from height has been the number one cause of death in workplaces in Singapore. It has accounted for 34%
OSHA GUIDANCE DOCUMENT FALL PROTECTION IN RESIDENTIAL CONSTRUCTION
 OSHA GUIDANCE DOCUMENT FALL PROTECTION IN RESIDENTIAL CONSTRUCTION OSHA GUIDANCE DOCUMENT FALL PROTECTION IN RESIDENTIAL CONSTRUCTION Table of Contents Executive Summary... 1 Introduction... 1 Installing
OSHA GUIDANCE DOCUMENT FALL PROTECTION IN RESIDENTIAL CONSTRUCTION OSHA GUIDANCE DOCUMENT FALL PROTECTION IN RESIDENTIAL CONSTRUCTION Table of Contents Executive Summary... 1 Introduction... 1 Installing
WEEKLY SAFETY MEETING
 Safety Meeting Contents Meeting Notice Leaders Guide Employee Handout Employee Quiz Meeting Sign-In Sheet Employee Puzzle PRIOR TO THE WEEKLY MEETING: - Post the meeting notice by the timeclock - Read
Safety Meeting Contents Meeting Notice Leaders Guide Employee Handout Employee Quiz Meeting Sign-In Sheet Employee Puzzle PRIOR TO THE WEEKLY MEETING: - Post the meeting notice by the timeclock - Read
Slips, Trips, and Falls Plan. Tips and Considerations
 Slips, Trips, and Falls Plan Tips and Considerations Applicability. This Plan covers walking and working surfaces in general industry workplaces. It covers neither the stairway and ladder rules for construction
Slips, Trips, and Falls Plan Tips and Considerations Applicability. This Plan covers walking and working surfaces in general industry workplaces. It covers neither the stairway and ladder rules for construction
Aerial/Scissor Lift Program. Environmental Health & Safety Office
 Aerial/Scissor Lift Program Environmental Health & Safety Office August 2013 Revised 08/2013 - Rev 4.0 Table of Contents INTRODUCTION... 1 PURPOSE... 1 SCOPE... 1 RESPONSIBILITIES... 1 DEFINITIONS:...
Aerial/Scissor Lift Program Environmental Health & Safety Office August 2013 Revised 08/2013 - Rev 4.0 Table of Contents INTRODUCTION... 1 PURPOSE... 1 SCOPE... 1 RESPONSIBILITIES... 1 DEFINITIONS:...
G. D-Ring A connector incorporated into a full body harness as an attachment point for lanyard and energy absorber lifelines.
 D. Buddy System Is intended as an interim measure to provide a safe working environment when removing or opening a manhole, vault or pit covers. Requires a crew of no less than 2 individuals, of which
D. Buddy System Is intended as an interim measure to provide a safe working environment when removing or opening a manhole, vault or pit covers. Requires a crew of no less than 2 individuals, of which
ELECTRICAL SAFETY & ARC FLASH Handbook
 Electricity Forum Handbooks Electrical Safety and Arc Flash Handbook Series ELECTRICAL SAFETY & ARC FLASH Handbook Volume 10 Reprinted by permission of the publisher, Hurst Communications, from the Electrical
Electricity Forum Handbooks Electrical Safety and Arc Flash Handbook Series ELECTRICAL SAFETY & ARC FLASH Handbook Volume 10 Reprinted by permission of the publisher, Hurst Communications, from the Electrical
Sample Fall Protection Program, General Industry
 PLEASE NOTE: This is a sample policy document and is not to be used in its current format. This sample policy should be reviewed and updated to: verify that all of the material included is compliant with
PLEASE NOTE: This is a sample policy document and is not to be used in its current format. This sample policy should be reviewed and updated to: verify that all of the material included is compliant with
Department of Environmental Health & Safety. Fall Protection Program
 Department of Environmental Health & Safety Fall Protection Program Issued by: Jeff Campbell Date Effective: March 2010 University Policy Ohio University is dedicated to the protection of its employees
Department of Environmental Health & Safety Fall Protection Program Issued by: Jeff Campbell Date Effective: March 2010 University Policy Ohio University is dedicated to the protection of its employees
SECTION 5.0 LADDER SAFETY
 SECTION 5.0 LADDER SAFETY The following material is being provided for informational purposes and in order to promote safety awareness. It does not constitute nor should it serve as a substitute for legal
SECTION 5.0 LADDER SAFETY The following material is being provided for informational purposes and in order to promote safety awareness. It does not constitute nor should it serve as a substitute for legal
Introduction to Fall Protection. The University of Tennessee Office of Environmental Health & Safety
 Introduction to Fall Protection The University of Tennessee Office of Environmental Health & Safety What is Fall Protection? Fall protection is the backup system planned for a worker who could loose his
Introduction to Fall Protection The University of Tennessee Office of Environmental Health & Safety What is Fall Protection? Fall protection is the backup system planned for a worker who could loose his
SAFE ACCESS, LADDERS, FLOOR & WALL OPENINGS, STAIRS AND RAILING SYSTEMS
 SECTION 24 SAFE ACCESS, LADDERS, FLOOR & WALL OPENINGS, STAIRS AND RAILING SYSTEMS 24.A SAFE ACCESS - GENERAL 24.A.01 Safe access shall be provided to work areas and where danger exists of workers falling
SECTION 24 SAFE ACCESS, LADDERS, FLOOR & WALL OPENINGS, STAIRS AND RAILING SYSTEMS 24.A SAFE ACCESS - GENERAL 24.A.01 Safe access shall be provided to work areas and where danger exists of workers falling
RZ Guardrail System Installation Manual
 TM RZ Guardrail System Installation Manual RZ Guardrail System Compliance is based on OSHA standards: (Standards - 29 CFR) 1910.23 (e) and (Standards - 29 CFR) 1926.502 (b) Failure to read, understand
TM RZ Guardrail System Installation Manual RZ Guardrail System Compliance is based on OSHA standards: (Standards - 29 CFR) 1910.23 (e) and (Standards - 29 CFR) 1926.502 (b) Failure to read, understand
WorkSafe Guidance Document FALL PROTECTION IN RESIDENTIAL CONSTRUCTION
 WorkSafe Guidance Document FALL PROTECTION IN RESIDENTIAL CONSTRUCTION WorkSafe Guidance Document Fall Protection in Residential Construction Table of Contents Executive Summary... 1 Introduction... 1
WorkSafe Guidance Document FALL PROTECTION IN RESIDENTIAL CONSTRUCTION WorkSafe Guidance Document Fall Protection in Residential Construction Table of Contents Executive Summary... 1 Introduction... 1
Fall Protection System: A system put in place to protect workers from falling. (i.e. installation of guardrails, fall arrest, fall restraint, etc.
 SWP (6) FALL PROTECTION PROGRAM The following information on Fall Protection has been based around the BC OHS Regulations, standards, policies and guidelines. Prior to starting work outside of BC, the
SWP (6) FALL PROTECTION PROGRAM The following information on Fall Protection has been based around the BC OHS Regulations, standards, policies and guidelines. Prior to starting work outside of BC, the
Wire Rope Extender Lanyard
 Reliance Industries, LLC User Instructions for Wire Rope Extender Lanyard Model # 714004 Reliance Industries, LLC PO Box 140008 Denver, CO 80214 Ph. (800) 488-5751 Ph. (303) 424-8650 Fax (303) 424-8670
Reliance Industries, LLC User Instructions for Wire Rope Extender Lanyard Model # 714004 Reliance Industries, LLC PO Box 140008 Denver, CO 80214 Ph. (800) 488-5751 Ph. (303) 424-8650 Fax (303) 424-8670
Ladders. Ladders New Reg
 Ladders Not 3 ft above roof On topcap Not secured Trip hazards Improper slope On top step Not on level surface Ladders New Reg GISO and CSO ladders standards were not consistent or complete safety hazards
Ladders Not 3 ft above roof On topcap Not secured Trip hazards Improper slope On top step Not on level surface Ladders New Reg GISO and CSO ladders standards were not consistent or complete safety hazards
Introduction to Fall Protection
 Introduction to Fall Protection with John Evinger CRSP (204)228-8277 INSERT YOUR LOGO HERE Expected results of the day Today I will provide you with information to make you realize that you don t have
Introduction to Fall Protection with John Evinger CRSP (204)228-8277 INSERT YOUR LOGO HERE Expected results of the day Today I will provide you with information to make you realize that you don t have
D-Ring. Fixed Arm. 1.2 LIMITATIONS: The following application limitations must be recognized and considered before using this product:
 Instructions for the following series products: Parapet Wall Anchor (model number: 8523178) User Instruction Manual for Parapet Wall Anchor This manual is intended to meet the Manufacturer s Instructions
Instructions for the following series products: Parapet Wall Anchor (model number: 8523178) User Instruction Manual for Parapet Wall Anchor This manual is intended to meet the Manufacturer s Instructions
OSHA 3146-05R 2015. Fall Protection in Construction
 OSHA 3146-05R 2015 Fall Protection in Construction Occupational Safety and Health Act of 1970 To assure safe and healthful working conditions for working men and women; by authorizing enforcement of the
OSHA 3146-05R 2015 Fall Protection in Construction Occupational Safety and Health Act of 1970 To assure safe and healthful working conditions for working men and women; by authorizing enforcement of the
User Instruction Manual Vertical Lifelines and Vertical Lifeline Subsystems
 Instructions for the following series products: User Instruction Manual Vertical Lifelines and Vertical Lifeline Subsystems Vertical Lifelines Vertical Lifeline Subsystems (See back pages for specific
Instructions for the following series products: User Instruction Manual Vertical Lifelines and Vertical Lifeline Subsystems Vertical Lifelines Vertical Lifeline Subsystems (See back pages for specific
Sample Fall Rescue Plan for Bridge Work
 This document is intended to provide guidance for developing fall rescue plans for bridge contractors. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration s (OSHA) regulation 29 CFR 1926.502(d)(20) states:
This document is intended to provide guidance for developing fall rescue plans for bridge contractors. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration s (OSHA) regulation 29 CFR 1926.502(d)(20) states:
Fall Protection Equipment
 Fall Protection Equipment Quick Tips #130 Introduction Before you can begin a fall protection program, you must identify the potential fall hazards in your workplace. Any time a worker is at a height of
Fall Protection Equipment Quick Tips #130 Introduction Before you can begin a fall protection program, you must identify the potential fall hazards in your workplace. Any time a worker is at a height of
FALL PROTECTION PROGRAM
 Department of Environmental Safety DIVISION OF ADMINISTRATIVE AFFAIRS FALL PROTECTION PROGRAM Revised December r 2014 UNIVERSITY OF MARYLAND, COLLEGE PARK, MD 20742-3133 (301) 405-3960 FAX (301) 314-9294
Department of Environmental Safety DIVISION OF ADMINISTRATIVE AFFAIRS FALL PROTECTION PROGRAM Revised December r 2014 UNIVERSITY OF MARYLAND, COLLEGE PARK, MD 20742-3133 (301) 405-3960 FAX (301) 314-9294
THE UNIVERSITY OF SHEFFIELD WORK AT HEIGHT POLICY
 THE UNIVERSITY OF SHEFFIELD WORK AT HEIGHT POLICY CONTENTS Page No 1 INTRODUCTION 2 2 LEGISLATION 2 3 HIERARCHY OF CONTROL 2 4 WORK AT HEIGHT POLICY 3 5 ROLES AND RESPONSIBILITIES 3 6 RISK ASSESSMENTS
THE UNIVERSITY OF SHEFFIELD WORK AT HEIGHT POLICY CONTENTS Page No 1 INTRODUCTION 2 2 LEGISLATION 2 3 HIERARCHY OF CONTROL 2 4 WORK AT HEIGHT POLICY 3 5 ROLES AND RESPONSIBILITIES 3 6 RISK ASSESSMENTS
Horizontal Lifeline. SideWalk Rope. User Instructions. 3M Occupational Health and Environmental Safety. Fall Protection Equipment
 3M Occupational Health and Environmental Safety Fall Protection Equipment SideWalk Rope Horizontal Lifeline User Instructions User Instructions for the 3M TM Side Walk 2-Man Rope Horizontal Lifeline System.
3M Occupational Health and Environmental Safety Fall Protection Equipment SideWalk Rope Horizontal Lifeline User Instructions User Instructions for the 3M TM Side Walk 2-Man Rope Horizontal Lifeline System.
Guidance Note GN049. Using portable ladders safely. WorkSafe Tasmania Department of Justice. Introduction and purpose
 Guidance Note GN049 Using portable ladders safely Introduction and purpose The purpose of this guidance note is to answer the most common questions that WorkSafe Tasmania receives about using portable
Guidance Note GN049 Using portable ladders safely Introduction and purpose The purpose of this guidance note is to answer the most common questions that WorkSafe Tasmania receives about using portable
FALL PROTECTION PROGRAM AT SAN DIEGO STATE UNIVERSITY
 FALL PROTECTION PROGRAM AT SAN DIEGO STATE UNIVERSITY Page 1 I. OVERVIEW The information included in this Fall Protection Program is in compliance with applicable California Code of Regulations including
FALL PROTECTION PROGRAM AT SAN DIEGO STATE UNIVERSITY Page 1 I. OVERVIEW The information included in this Fall Protection Program is in compliance with applicable California Code of Regulations including
Ladder, Scaffolding, and Excavation Safety Plan
 Ladder, Scaffolding, and Excavation Safety Plan Environmental Health, Safety, and Risk Management Department Box 6113, SFA Station Nacogdoches, Texas 75962-6113 Revised: January 2011 LADDERS In reducing
Ladder, Scaffolding, and Excavation Safety Plan Environmental Health, Safety, and Risk Management Department Box 6113, SFA Station Nacogdoches, Texas 75962-6113 Revised: January 2011 LADDERS In reducing
ladder Safety Types of Ladders
 Types of Ladders There are many types of ladders and it is important to choose the right ladder for the task. Here are some different types: Extension/straight Fixed access Tripod orchard (orchard use
Types of Ladders There are many types of ladders and it is important to choose the right ladder for the task. Here are some different types: Extension/straight Fixed access Tripod orchard (orchard use
Chapter 10 - Scaffolding Systems
 Chapter 10 - Scaffolding Systems Contents Chapter 10 - Scaffolding Systems... 10-1 Check and Oil the Pump Jacks... 10-4 Set Pump Jack Brackets... Error! Bookmark not defined. Set Pump Jack Poles... 10-5
Chapter 10 - Scaffolding Systems Contents Chapter 10 - Scaffolding Systems... 10-1 Check and Oil the Pump Jacks... 10-4 Set Pump Jack Brackets... Error! Bookmark not defined. Set Pump Jack Poles... 10-5
Operating instructions. 3-in. x 6-ft. Anchor Strap for Skyline Horizontal Lifeline
 Reliance Industrial Products, LLC Operating instructions for 3-in. x 6-ft. Anchor Strap for Skyline Horizontal Lifeline Model # 6095 Reliance Industrial Products PO Box 140008 Denver, CO 80214 Ph. (800)
Reliance Industrial Products, LLC Operating instructions for 3-in. x 6-ft. Anchor Strap for Skyline Horizontal Lifeline Model # 6095 Reliance Industrial Products PO Box 140008 Denver, CO 80214 Ph. (800)
OregonOSHA s. Fall protection. for the construction industry
 OregonOSHA s Fall protection for the construction industry About this guide Fall protection for the construction industry is an Oregon OSHA Standards and Technical Resources publication. Who should read
OregonOSHA s Fall protection for the construction industry About this guide Fall protection for the construction industry is an Oregon OSHA Standards and Technical Resources publication. Who should read
There is no water, surface tension cracks, nor other environmental conditions present that reduce the stability of the excavation.
 Part 1926 Subpart P Introduction The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) issued its first Excavation and Trenching Standard in 1971 to protect workers from excavation hazards. Since then,
Part 1926 Subpart P Introduction The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) issued its first Excavation and Trenching Standard in 1971 to protect workers from excavation hazards. Since then,
Portable Ladder Safety
 Page #: 1 of 6 Last Reviewed/Update Date: 7/27/11 Portable Ladder Safety 1. Purpose / Background The purpose of this Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) is to minimize the risk of injuries due to the incorrect
Page #: 1 of 6 Last Reviewed/Update Date: 7/27/11 Portable Ladder Safety 1. Purpose / Background The purpose of this Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) is to minimize the risk of injuries due to the incorrect
De Beers Canada Inc. OP 050 SLIPS, TRIPS, FALLS AND PEDESTRIAN SAFETY - SURFACE
 1. Purpose And Scope To establish safe procedures for pedestrians travelling on sites, in plants, on roads in offices or the general area of the workplace. 2. Responsibilities Responsible Person All Personnel
1. Purpose And Scope To establish safe procedures for pedestrians travelling on sites, in plants, on roads in offices or the general area of the workplace. 2. Responsibilities Responsible Person All Personnel
