NEUROSURGERY REVISION KEY TOPICS
|
|
|
- Arthur Hicks
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1. Neurological examination 2. Special investigations 3. General care 4. Head Injury 5. Cerebrovascular disease 6. Brain tumour 7. Neurosurgical infections 8. Spinal disease 9. Congenital abnormalities 10. Functional neurosurgery 1. Neurological examination : NEUROSURGERY REVISION KEY TOPICS Refer to a standard textbook on clinical neurological examination. 2. Special investigations : Plain X-ray : skull, C-spine, thoraco-lumbar spine Myelogram : indications, contra-indications CT Scan principles : iso-, hypo- and hyperdense lesions, contrast enhancement, good for bone and trauma, poor for posterior fossa and intramedullary spinal cord lesions, CT angiography MRI principles : iso-, hypo- and hyperintense lesions, flow void, T1, T2, contrast enhancement, poor for bone and trauma but good for all soft tissue pathology. MR angiography. 3. General care : Fluid and electrolyte disturbances ie. hyponatraemia, SIADHS and diabetes insipidus, diagnosis and management Anticonvulsants and treatment of status epilepticus. Steroid use, indications and complications Raised intracranial pressure : Concept of the pressure/volume curve, cerebral perfusion pressure, methods of measuring ICP, hyperemia vs edema, herniation syndromes, RICP treatment, general principles eg patient position, control of pain, empty bladder, no restriction of chest movement; specific treatment eg removal of mass lesions, steroids for edema, mannitol, hyperventilation, drugs eg barbiturates.
2 4. Head injury : General : coma, Glasgow Coma Score, approach to a comatose patient ie ABC, blood investigations esp. glucose!, look for lateralising signs then consider CT scan, teat seizures, consider medical causes eg, metabolic coma, diabetes, drug overdose, C2H5OH, infections, organ failure, hypertensive encephalopathy. Always remember the collateral history. Brain death : criteria and consideration for organ donation. Blunt head injury vs penetrating head injury ( stab and gunshot ) Diffuse head injury vs focal injury. Skull fractures : Open vs closed, linear #, depressed #, base of skull #, growing skull # Haematomas ; Traumatic SAH, extradural, subdural (acute vs chronic), intracerebral and intraventricular haemorrhage. Diffuse head injury : concussion, diffuse axonal injury Subdural hygroma Child abuse 5. Cerebrovascular disease : SAH and aneurysms, arteriovenous malformations, spontaneous intracerebral haemorrhage and stroke. Aneurysmal SAH : clinical features, grading SAH, investigations (ie. CT scan, CSF, MRA, CTA, DSA), general management ie. bed rest, analgesia, neuro-observations, BP control, electrolyte management, calcium channel blocks, stool softeners. specific problems : rebleeding, hydrocephalus and vasospasm. : diagnosis and management. aneurysm management : conservative vs clipping vs coiling. Arteriovenous malformations : presentation : haemorrhage (ICH, SAH), seizures, mass effect, ischemia, headache, bruit (eg dural avm), increased ICP (eg hydrocephalus in pediatric malformations). Treatment options : observation vs surgery vs radiosurgery. carotid-cavernous fistula : clinical features, diagnosis and treatment. Spontaneous ICH : primary (hypertensive) vs secondary, position of haemorrhage ( ie lobar / putamen / thalamic / brainstem / cerebellar ) management of hypertensive ICH, medical vs surgical. Investigation of secondary (non-hypertensive haemorrhage) Ischemic stroke : embolic vs thrombotic. Regarding embolic stroke, role of carotid stenosis, diagnosis and medical vs surgical treatment thereof.
3 6. Brain tumour : General principles : presentation ie raised intracranial pressure, seizures progressive neurological deficit, changes in mental state, endocrine disturbances (pituitary pathology) Classification ; Primary vs secondary Secondary tumours : metastases are the most common brain tumour. metastatic work up to look for primary disease, management : medical, steroids, anticonvulsants. radiotherapy, surgery ( indications, diagnosis unknown, symptomatic or life threatening, primary disease controlled or life expectancy reasonable, solitary lesion). Primary tumours : Gliomas : most common primary tumour. types : astrocytoma, oligodendroglioma, ependymoma. Grading of astrocytomas, broad principles of treatment ie medical, surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, Meningiomas : usually benign and slow growing, common, treatment : observation, surgery plus or minus radiotherapy. Vestibular schwannoma (acoustic neuroma) : symptoms and signs, investigations, treatment, conservative vs surgery (radiosurgery), link this tumour up with the disease neurofibromatosis Pituitary tumours : NB appreciate the anatomy and physiology of the hypothalamicpituitary axis!! Secretory vs non-secretory tumours. general clinical symptoms and signs, specific syndromes ie acromegali, Cushing s disease, prolactinoma. Medical and surgical treatment of pituitary disease (general principles) Posterior fossa tumours in children : Four common types 1. Medulloblastoma 2. Ependymoma 3. Cerebellar pilocytic astrocytoma 4. Brainstem glioma. General principles of clinical presentation and treatment. Hydrocephalus, surgery, radiotherapy, craniospinal metastatic disease. Spinal tumours : Clinical features, radiological investigations, treatment : surgery/radiotherapy. Pathology : 1. Extradural disease : metastases 2. Intradural disease : Extramedullary - meningioma, neurofibroma Intramedullary - astrocytoma, ependymoma
4 7. Infections : Brain abscess, subdural and extradural empyema, parasitic infections, tuberculosis. AIDS. Abscess, SDE, EDE : Etiology: ENT infections ie sinusitis and mastoiditis, hematogenous spread ie congenital heart disease, endocarditis, lung infections, penetrating trauma, post surgical infection. Principles in treatment: drainage of the abscess, treatment of the primary disease and prolonged antibiotic therapy. Neurocysticercosis : infection by the larval stage of Taenia Solium. Multiple lesions, may be calcified or cystic. often ring enhancing, may cause hydrocephalus. Treatment: Medical : Praziquantel or Albendazole Surgical : Hydrocephalus, mass lesions, diagnosis unsure. Tuberculosis : neurosurgical involvement is mainly to confirm the diagnosis or treat hydrocephalus AIDS : Aids is a disease that will come more on the forefront in the future. Neurosurgical involvement is common. Mass lesions found : toxoplasmosis, cryptococcus, fungi, tuberculosis, other lymphoma, PML (progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy) 8. Spinal disease : Degenerative spinal disease, spinal trauma, spinal infections : Degenerative spinal disease : most common sites are cervical and lumbar. Cervical disease: Clinical features : myelopathy vs radiculopathy, special investigations: plain X-rays and MRI, treatment : indications are pain not responsive to consvervative management and neurological deficit especially if progressive. Surgery involves either an anterior or posterior surgical procedure depending on the pathology and involved anatomical level/levels. Lumbar disease: Lumbar spinal stenosis. Clinical features ie neurogenic claudication. Treatment ie decompression most commonly a laminectomy Lumbar disc prolaps : Radiculopathy, clinical features treatment ie conservative eg bed rest, analgesia, physiotherapy, surgery ie discectomy. Cauda equina syndrome is a neurosurgical emergency. Clinical features (pain, paraparesis/plegia, bladder and/or fecal incontinence) Requires urgent neurosurgical referral.
5 Spinal trauma : Principles of the management of a spinal injury ie. ABC, immobilization, maintain BP, maintain oxygenation, methylprednisolone, clinical examination, radiological identification of pathology (X-ray C-spine C1/T1, open mouth view, thoracic and lumbar AP and lateral views if fracture suspected ) Urgent MRI required if : incomplete lesion, neurological deterioration noted, no bony pathology noted in presence of neurological deficit (? disc prolaps or epidural haematoma). Surgical treatment is specialized and taken care of by the orthopedic/neurosurgical specialities. Spinal infection : Spinal epidural abscess is a neurosurgical emergency. Clinical features : Back pain, fever, spinal tenderness, neurological deficit. Risk factors : DM, IV drug abuse, immunocompromised state. Treatment : urgent drainage. 9. Congenital abnormalities : Common abnormalities include arachnoid cysts, craniofacial abnormalities eg synostosis, encephalocele, Chiari malformations, Dandy-Walker malformation, aquaduct stenosis, spina bifida (dysraphism), tethered cord syndrome. Hydrocephalus : communicating vs non-communicating. Clinical features in children vs adults. Treatment options : conservative vs surgical, shunt/ ventriculostomy. Spina bifida : spina bifida occulta vs aperta(open). Tethered cord syndrome, clinical features, radiological investigations and treatment. Myelomeningocele, clinical features, treatment and comprehension of the long term multidisciplinary involvement in the care of these patients ( neurosurgery, urology, orthopedics, pediatric surgery, physiotherapy and occupational therapy, psychological support) 10. Functional neurosurgery : Neurosurgery also involves the treatment of pain (eg trigeminal neuralgia and other chronic pain syndromes), movement disorders (eg parkinsonism), the surgical treatment of epilepsy, the treatment of spasticity etc. Understand the concept of functional neurosurgery and appreciate some of the common conditions ie trigeminal neuralgia, parkinsonism, temporal lobe epilepsy. Mr R. Boet (1999)
The Clinical Evaluation of the Comatose Patient in the Emergency Department
 The Clinical Evaluation of the Comatose Patient in the Emergency Department patients with altered mental status (AMS) and coma. treat patients who present to the Emergency Department with altered mental
The Clinical Evaluation of the Comatose Patient in the Emergency Department patients with altered mental status (AMS) and coma. treat patients who present to the Emergency Department with altered mental
REFERRAL GUIDELINES: NEUROSURGERY
 Outpatient Referral Guidelines Page 1 1 REFERRAL GUIDELINES: NEUROSURGERY Essential Referral Content Date of birth Demographic Contact details (including mobile phone) Referring GP details Interpreter
Outpatient Referral Guidelines Page 1 1 REFERRAL GUIDELINES: NEUROSURGERY Essential Referral Content Date of birth Demographic Contact details (including mobile phone) Referring GP details Interpreter
2015 Recertification Handbook
 THE AMERICAN BOARD OF NEUROSCIENCE NURSING Certified Neuroscience Registered Nurse (CNRN ) 2015 Recertification Handbook For CNRNs initially certified in 2010 or recertified effective January 1, 2011 Application
THE AMERICAN BOARD OF NEUROSCIENCE NURSING Certified Neuroscience Registered Nurse (CNRN ) 2015 Recertification Handbook For CNRNs initially certified in 2010 or recertified effective January 1, 2011 Application
6.0 Management of Head Injuries for Maxillofacial SHOs
 6.0 Management of Head Injuries for Maxillofacial SHOs As a Maxillofacial SHO you are not required to manage established head injury, however an awareness of the process is essential when dealing with
6.0 Management of Head Injuries for Maxillofacial SHOs As a Maxillofacial SHO you are not required to manage established head injury, however an awareness of the process is essential when dealing with
Musculoskeletal: Acute Lower Back Pain
 Musculoskeletal: Acute Lower Back Pain Acute Lower Back Pain Back Pain only Sciatica / Radiculopathy Possible Cord or Cauda Equina Compression Possible Spinal Canal Stenosis Red Flags Initial conservative
Musculoskeletal: Acute Lower Back Pain Acute Lower Back Pain Back Pain only Sciatica / Radiculopathy Possible Cord or Cauda Equina Compression Possible Spinal Canal Stenosis Red Flags Initial conservative
Head Injury. Dr Sally McCarthy Medical Director ECI
 Head Injury Dr Sally McCarthy Medical Director ECI Head injury in the emergency department A common presentation 80% Mild Head Injury = GCS 14 15 10% Moderate Head Injury = GCS 9 13 10% Severe Head Injury
Head Injury Dr Sally McCarthy Medical Director ECI Head injury in the emergency department A common presentation 80% Mild Head Injury = GCS 14 15 10% Moderate Head Injury = GCS 9 13 10% Severe Head Injury
Management of spinal cord compression
 Management of spinal cord compression (SUMMARY) Main points a) On diagnosis, all patients should receive dexamethasone 10mg IV one dose, then 4mg every 6h. then switched to oral dose and tapered as tolerated
Management of spinal cord compression (SUMMARY) Main points a) On diagnosis, all patients should receive dexamethasone 10mg IV one dose, then 4mg every 6h. then switched to oral dose and tapered as tolerated
Clinical guidance for MRI referral
 MRI for cervical radiculopathy Referral by a medical practitioner (excluding a specialist or consultant physician) for a scan of spine for a patient 16 years or older for suspected: cervical radiculopathy
MRI for cervical radiculopathy Referral by a medical practitioner (excluding a specialist or consultant physician) for a scan of spine for a patient 16 years or older for suspected: cervical radiculopathy
Hitting a Nerve: The Triggers of Sciatica. Bruce Tranmer MD FRCS FACS
 Hitting a Nerve: The Triggers of Sciatica Bruce Tranmer MD FRCS FACS Disclosures I have no financial disclosures Objectives - Sciatica Historical Perspective What is Sciatica What can cause Sciatica Clinical
Hitting a Nerve: The Triggers of Sciatica Bruce Tranmer MD FRCS FACS Disclosures I have no financial disclosures Objectives - Sciatica Historical Perspective What is Sciatica What can cause Sciatica Clinical
Physicians at-a-glance
 Ohio Physicians Neurosurgery Office UC Physicians Office - Clifton Expertise traumatic brain injury, intracerebral hemorrhage, stroke, carotid artery disease, moyamoya disease, brain tumors; spine surgery,
Ohio Physicians Neurosurgery Office UC Physicians Office - Clifton Expertise traumatic brain injury, intracerebral hemorrhage, stroke, carotid artery disease, moyamoya disease, brain tumors; spine surgery,
NEURO MRI PROTOCOLS TABLE OF CONTENTS
 TABLE OF CONTENTS NEURO MRI PROTOCOLS BRAIN...2 Brain 1 Screen... 2 Brain 2 Brain Tumor... 2 Brain 3 Brain Infection / Meningitis... 2 Brain 4 Trauma... 3 Brain 5 Hemorrhage... 3 Brain 6 Demyelinating
TABLE OF CONTENTS NEURO MRI PROTOCOLS BRAIN...2 Brain 1 Screen... 2 Brain 2 Brain Tumor... 2 Brain 3 Brain Infection / Meningitis... 2 Brain 4 Trauma... 3 Brain 5 Hemorrhage... 3 Brain 6 Demyelinating
PE finding: Left side extremities mild weakness No traumatic wound No bloody otorrhea, nor rhinorrhea
 Case report A 82-year-old man was suffered from sudden onset spasm of extremities then he fell down to the ground with loss of consciousness. He recovered his consciousness 7-8 mins later but his conscious
Case report A 82-year-old man was suffered from sudden onset spasm of extremities then he fell down to the ground with loss of consciousness. He recovered his consciousness 7-8 mins later but his conscious
Emergency Neurological Life Support. Spinal Cord Compression. Version: 1.0 Last Updated: 8/3/2014. Checklist & Communication
 Emergency Neurological Life Support 18 Spinal Cord Compression Version: 1.0 Last Updated: 8/3/2014 17 5 10 12 9 7 13 6 15 4 Checklist & Communication Spinal Cord Compression Page 2 Checklist Quadriplegia?
Emergency Neurological Life Support 18 Spinal Cord Compression Version: 1.0 Last Updated: 8/3/2014 17 5 10 12 9 7 13 6 15 4 Checklist & Communication Spinal Cord Compression Page 2 Checklist Quadriplegia?
6/3/2011. High Prevalence and Incidence. Low back pain is 5 th most common reason for all physician office visits in the U.S.
 High Prevalence and Incidence Prevalence 85% of Americans will experience low back pain at some time in their life. Incidence 5% annual Timothy C. Shen, M.D. Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Sub-specialty
High Prevalence and Incidence Prevalence 85% of Americans will experience low back pain at some time in their life. Incidence 5% annual Timothy C. Shen, M.D. Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Sub-specialty
DUBAI DRIVER'S MEDICAL STANDARD
 DUBAI DRIVER'S MEDICAL STANDARD This document is provided by the Dubai Roads and Transport Authority and the Dubai Health Authority for the guidance of Medical Professionals in the medical assessment of
DUBAI DRIVER'S MEDICAL STANDARD This document is provided by the Dubai Roads and Transport Authority and the Dubai Health Authority for the guidance of Medical Professionals in the medical assessment of
Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery For Your Patients
 Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery For Your Patients Lukas P. Zebala, M.D. Assistant Professor Orthopaedic and Neurological Spine Surgery Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Washington University School of
Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery For Your Patients Lukas P. Zebala, M.D. Assistant Professor Orthopaedic and Neurological Spine Surgery Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Washington University School of
Measure Title X RAY PRIOR TO MRI OR CAT SCAN IN THE EVAULATION OF LOWER BACK PAIN Disease State Back pain Indicator Classification Utilization
 Client HMSA: PQSR 2009 Measure Title X RAY PRIOR TO MRI OR CAT SCAN IN THE EVAULATION OF LOWER BACK PAIN Disease State Back pain Indicator Classification Utilization Strength of Recommendation Organizations
Client HMSA: PQSR 2009 Measure Title X RAY PRIOR TO MRI OR CAT SCAN IN THE EVAULATION OF LOWER BACK PAIN Disease State Back pain Indicator Classification Utilization Strength of Recommendation Organizations
Spinal Surgery 2. Teaching Aims. Common Spinal Pathologies. Disc Degeneration. Disc Degeneration. Causes of LBP 8/2/13. Common Spinal Conditions
 Teaching Aims Spinal Surgery 2 Mr Mushtaque A. Ishaque BSc(Hons) BChir(Cantab) DM FRCS FRCS(Ed) FRCS(Orth) Hunterian Professor at The Royal College of Surgeons of England Consultant Orthopaedic Spinal
Teaching Aims Spinal Surgery 2 Mr Mushtaque A. Ishaque BSc(Hons) BChir(Cantab) DM FRCS FRCS(Ed) FRCS(Orth) Hunterian Professor at The Royal College of Surgeons of England Consultant Orthopaedic Spinal
If you or a loved one have suffered because of a negligent error during spinal surgery, you will be going through a difficult time.
 If you or a loved one have suffered because of a negligent error during spinal surgery, you will be going through a difficult time. You may be worried about your future, both in respect of finances and
If you or a loved one have suffered because of a negligent error during spinal surgery, you will be going through a difficult time. You may be worried about your future, both in respect of finances and
Chiari Malformation: An Overview
 Chiari Malformation: An Overview SYMPTOMS DIAGNOSIS LIVING WITH CHIARI TREATMENT Rick Labuda, Executive Director [email protected] 724-940-0116 Disclaimer: This presentation is intended for informational
Chiari Malformation: An Overview SYMPTOMS DIAGNOSIS LIVING WITH CHIARI TREATMENT Rick Labuda, Executive Director [email protected] 724-940-0116 Disclaimer: This presentation is intended for informational
SERVICE: Neurosurgery - Sinai, PGY 1
 SERVICE: Neurosurgery - Sinai, PGY 1 General description: The Sinai surgical residents will rotate in the Department of Neurosurgery at Sinai Hospital during their intern year. The duration of this rotation
SERVICE: Neurosurgery - Sinai, PGY 1 General description: The Sinai surgical residents will rotate in the Department of Neurosurgery at Sinai Hospital during their intern year. The duration of this rotation
What Is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)?
 What Is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D., Chair 1 What
What Is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D., Chair 1 What
Sample Treatment Protocol
 Sample Treatment Protocol 1 Adults with acute episode of LBP Definition: Acute episode Back pain lasting
Sample Treatment Protocol 1 Adults with acute episode of LBP Definition: Acute episode Back pain lasting
Chiari malformations
 A fact sheet for patients and carers Chiari malformations This fact sheet provides information on Chiari malformations. It focuses on Chiari malformations in adults. Our fact sheets are designed as general
A fact sheet for patients and carers Chiari malformations This fact sheet provides information on Chiari malformations. It focuses on Chiari malformations in adults. Our fact sheets are designed as general
Advanced Practice Provider Academy
 (+)Dean T. Harrison, MPAS,PA C,DFAAPA Director of Mid Level Practitioners; Assistant Medical Director Clinical Evaluation Unit, Division of Emergency Medicine, Department of Surgery, Duke University Medical
(+)Dean T. Harrison, MPAS,PA C,DFAAPA Director of Mid Level Practitioners; Assistant Medical Director Clinical Evaluation Unit, Division of Emergency Medicine, Department of Surgery, Duke University Medical
Spinal Cord Diseases in Bernese Mountain Dogs
 Spinal Cord Diseases in Bernese Mountain Dogs 0 A N O V E R V I E W F O R BERNER O W N E R S O R G A N I Z E D B Y N A N C Y M E L O N E, P H. D. Based on materials obtained from the Berner Garde Foundation
Spinal Cord Diseases in Bernese Mountain Dogs 0 A N O V E R V I E W F O R BERNER O W N E R S O R G A N I Z E D B Y N A N C Y M E L O N E, P H. D. Based on materials obtained from the Berner Garde Foundation
Brain Spots on Imaging Tests
 Brain Spots on Imaging Tests To Be or Not to Be Concerned Metropolitan Underwriting Discussion Group 1/29/13 Charles Levy, MD Aviva USA CT and MRI 2 most common forms of brain imaging today As with any
Brain Spots on Imaging Tests To Be or Not to Be Concerned Metropolitan Underwriting Discussion Group 1/29/13 Charles Levy, MD Aviva USA CT and MRI 2 most common forms of brain imaging today As with any
Adult Spine Rotation Specific Evaluation Orthopaedic Surgery Training Program School of Medicine, Queen s University
 Adult Spine Rotation Specific Evaluation Orthopaedic Surgery Training Program School of Medicine, Queen s University CanMEDS Roles / Competencies Name: PGY Rotation Dates: s s Exceeds N/A Attending Staff:
Adult Spine Rotation Specific Evaluation Orthopaedic Surgery Training Program School of Medicine, Queen s University CanMEDS Roles / Competencies Name: PGY Rotation Dates: s s Exceeds N/A Attending Staff:
The Lewin Group undertook the following steps to identify the guidelines relevant to the 11 targeted procedures:
 Guidelines The following is a list of proposed medical specialty guidelines that have been found for the 11 targeted procedures to be included in the Medicare Imaging Demonstration. The list includes only
Guidelines The following is a list of proposed medical specialty guidelines that have been found for the 11 targeted procedures to be included in the Medicare Imaging Demonstration. The list includes only
SPINE SERVICE ROTATION ROTATION SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES (RSO) DEPT. OF ORTHOPEDICS AND PHYSICAL REHABILITATION UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS
 SPINE SERVICE ROTATION ROTATION SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES (RSO) DEPT. OF ORTHOPEDICS AND PHYSICAL REHABILITATION UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS The purpose of this RSO is to outline and clarify the objectives of
SPINE SERVICE ROTATION ROTATION SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES (RSO) DEPT. OF ORTHOPEDICS AND PHYSICAL REHABILITATION UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS The purpose of this RSO is to outline and clarify the objectives of
Ischaemic stroke 85% (85 in every 100 strokes)
 UNDERSTANDING STROKE DUE TO INTRACEREBRAL HAEMORRHAGE This factsheet provides information for people who have had a stroke due to an intracerebral (bleed in the brain) and for their families and carers.
UNDERSTANDING STROKE DUE TO INTRACEREBRAL HAEMORRHAGE This factsheet provides information for people who have had a stroke due to an intracerebral (bleed in the brain) and for their families and carers.
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF LOW BACK PAIN
 CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF LOW BACK PAIN Low back pain is very common, up to 90+% of people are affected by back pain at some time in their lives. Most often back pain is benign and
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF LOW BACK PAIN Low back pain is very common, up to 90+% of people are affected by back pain at some time in their lives. Most often back pain is benign and
DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA OF STROKE
 DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA OF STROKE Diagnostic criteria are used to validate clinical diagnoses. Here below MONICA diagnostic criteria are reported. MONICA - MONItoring trends and determinants of CArdiovascular
DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA OF STROKE Diagnostic criteria are used to validate clinical diagnoses. Here below MONICA diagnostic criteria are reported. MONICA - MONItoring trends and determinants of CArdiovascular
Disorders of the Spine & Peripheral Nerves
 Disorders of the Spine & Peripheral Nerves An Introduction The LSU-Shreveport Department of Neurosurgery Presenting Authors: Neurosurgery Residents & Faculty Spine Disorders & Neurosurgery Neurosurgery
Disorders of the Spine & Peripheral Nerves An Introduction The LSU-Shreveport Department of Neurosurgery Presenting Authors: Neurosurgery Residents & Faculty Spine Disorders & Neurosurgery Neurosurgery
Contents. Introduction 1. Anatomy of the Spine 1. 2. Spinal Imaging 7. 3. Spinal Biomechanics 23. 4. History and Physical Examination of the Spine 33
 Contents Introduction 1. Anatomy of the Spine 1 Vertebrae 1 Ligaments 3 Intervertebral Disk 4 Intervertebral Foramen 5 2. Spinal Imaging 7 Imaging Modalities 7 Conventional Radiographs 7 Myelography 9
Contents Introduction 1. Anatomy of the Spine 1 Vertebrae 1 Ligaments 3 Intervertebral Disk 4 Intervertebral Foramen 5 2. Spinal Imaging 7 Imaging Modalities 7 Conventional Radiographs 7 Myelography 9
ICD-9-CM coding for patients with Spinal Cord Injury*
 ICD-9-CM coding for patients with Spinal Cord Injury* indicates intervening codes have been left out of this list. OTHER DISORDERS OF THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM (340-349) 344 Other paralytic syndromes
ICD-9-CM coding for patients with Spinal Cord Injury* indicates intervening codes have been left out of this list. OTHER DISORDERS OF THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM (340-349) 344 Other paralytic syndromes
Basic Stroke for the New Recruit
 Basic Stroke for the New Recruit Authors Erin Conahan MSN, RN, ACNS-BC, CNRN, SCRN Julie FussnerBSN, RN, CPHQ, SCRN The authors have nothing to disclose. 1 Objectives List causes of small vessel stroke
Basic Stroke for the New Recruit Authors Erin Conahan MSN, RN, ACNS-BC, CNRN, SCRN Julie FussnerBSN, RN, CPHQ, SCRN The authors have nothing to disclose. 1 Objectives List causes of small vessel stroke
What You Should Know About Cerebral Aneurysms
 What You Should Know About Cerebral Aneurysms From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Interventions Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Radiology Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D.,
What You Should Know About Cerebral Aneurysms From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Interventions Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Radiology Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D.,
AMERICAN BRAIN TUMOR ASSOCIATION. Ependymoma
 AMERICAN BRAIN TUMOR ASSOCIATION Ependymoma ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ABOUT THE AMERICAN BRAIN TUMOR ASSOCIATION Founded in 1973, the American Brain Tumor Association (ABTA) was the first national nonprofit organization
AMERICAN BRAIN TUMOR ASSOCIATION Ependymoma ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ABOUT THE AMERICAN BRAIN TUMOR ASSOCIATION Founded in 1973, the American Brain Tumor Association (ABTA) was the first national nonprofit organization
GUIDELINES FOR ASSESSMENT OF SPINAL STABILITY THE CHRISTIE, GREATER MANCHESTER & CHESHIRE. CP57 Version: V3
 GUIDELINES FOR ASSESSMENT OF SPINAL STABILITY THE CHRISTIE, GREATER MANCHESTER & CHESHIRE Procedure Reference: Document Owner: CP57 Version: V3 Dr V. Misra Accountable Committee: Acute Oncology Group Network
GUIDELINES FOR ASSESSMENT OF SPINAL STABILITY THE CHRISTIE, GREATER MANCHESTER & CHESHIRE Procedure Reference: Document Owner: CP57 Version: V3 Dr V. Misra Accountable Committee: Acute Oncology Group Network
Spine Trauma: When to Transfer. Alexander Ching, MD Director, Orthopaedic Spine Trauma OHSU
 Spine Trauma: When to Transfer Alexander Ching, MD Director, Orthopaedic Spine Trauma OHSU Disclosures Depuy Spine Consultant (teaching and courses) Department education and research funds Atlas Spine
Spine Trauma: When to Transfer Alexander Ching, MD Director, Orthopaedic Spine Trauma OHSU Disclosures Depuy Spine Consultant (teaching and courses) Department education and research funds Atlas Spine
James A. Sanfilippo, M.D. CONSENT FOR SPINAL SURGERY PATIENT: DATE:
 James A. Sanfilippo, M.D. CONSENT FOR SPINAL SURGERY PATIENT: DATE: 1. I have been strongly advised to carefully read and consider this operative permit. I realize that it is important that I understand
James A. Sanfilippo, M.D. CONSENT FOR SPINAL SURGERY PATIENT: DATE: 1. I have been strongly advised to carefully read and consider this operative permit. I realize that it is important that I understand
X Stop Spinal Stenosis Decompression
 X Stop Spinal Stenosis Decompression Am I a candidate for X Stop spinal surgery? You may be a candidate for the X Stop spinal surgery if you have primarily leg pain rather than mostly back pain and your
X Stop Spinal Stenosis Decompression Am I a candidate for X Stop spinal surgery? You may be a candidate for the X Stop spinal surgery if you have primarily leg pain rather than mostly back pain and your
Spina Bifida Occulta. Lo-Call 1890 20 22 60. Occulta Means Hidden
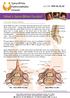 Occulta Means Hidden Spina Bifida Occulta is not easily detected because skin covers the area, such as the spinal cord, spinal bone or nerve roots, which may be affected. Spina Bifida Occulta can affect
Occulta Means Hidden Spina Bifida Occulta is not easily detected because skin covers the area, such as the spinal cord, spinal bone or nerve roots, which may be affected. Spina Bifida Occulta can affect
STEREOTACTIC RADIOSURGERY COMMISSIONING POLICY
 STEREOTACTIC RADIOSURGERY COMMISSIONING POLICY Release Version 3.1 Date: 21 st September 2006 Author: Owner: Client: Ian Langfield, Service Group Commissioner, HCW Ian Langfield, Service Group Commissioner,
STEREOTACTIC RADIOSURGERY COMMISSIONING POLICY Release Version 3.1 Date: 21 st September 2006 Author: Owner: Client: Ian Langfield, Service Group Commissioner, HCW Ian Langfield, Service Group Commissioner,
APPENDIX B SAMPLE PEDIATRIC CRITICAL CARE NURSE PRACTITIONER GOALS AND OBJECTIVES
 APPENDIX B SAMPLE PEDIATRIC CRITICAL CARE NURSE PRACTITIONER GOALS AND OBJECTIVES The critical care nurse practitioner orientation is an individualized process based on one s previous experiences and should
APPENDIX B SAMPLE PEDIATRIC CRITICAL CARE NURSE PRACTITIONER GOALS AND OBJECTIVES The critical care nurse practitioner orientation is an individualized process based on one s previous experiences and should
Baylor Radiosurgery Center
 Radiosurgery Center Baylor Radiosurgery Center Sophisticated Radiosurgery for both Brain and Body University Medical Center at Dallas Radiosurgery Center 3500 Gaston Avenue Hoblitzelle Hospital, First
Radiosurgery Center Baylor Radiosurgery Center Sophisticated Radiosurgery for both Brain and Body University Medical Center at Dallas Radiosurgery Center 3500 Gaston Avenue Hoblitzelle Hospital, First
Types of Brain Injury
 Types of Brain Injury The bones of your skull are hard and they protect your brain. Your brain is soft, like firm Jell-O. When your head moves, your brain moves inside your skull. When your head is hit
Types of Brain Injury The bones of your skull are hard and they protect your brain. Your brain is soft, like firm Jell-O. When your head moves, your brain moves inside your skull. When your head is hit
Diagnosis and Treatment of Lumbar Spinal Canal Stenosis
 Low Back Pains Diagnosis and Treatment of Lumbar Spinal Canal Stenosis JMAJ 46(10): 439 444, 2003 Katsuro TOMITA Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Kanazawa University Abstract: Lumbar spinal canal stenosis
Low Back Pains Diagnosis and Treatment of Lumbar Spinal Canal Stenosis JMAJ 46(10): 439 444, 2003 Katsuro TOMITA Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Kanazawa University Abstract: Lumbar spinal canal stenosis
Neurological System Best Practice Documentation
 Neurological System Best Practice Documentation Click on the desired Diagnoses link or press Enter to view all information. Diagnoses: Dementia Delirium/Encephalopathy Parkinson s Epilepsy /Seizure Migraines
Neurological System Best Practice Documentation Click on the desired Diagnoses link or press Enter to view all information. Diagnoses: Dementia Delirium/Encephalopathy Parkinson s Epilepsy /Seizure Migraines
Chiari Malformation: Treatment
 Chiari Malformation: Treatment SYMPTOMS DIAGNOSIS LIVING WITH CHIARI TREATMENT Rick Labuda, Executive Director [email protected] 724-940-0116 Disclaimer: This presentation is intended for informational
Chiari Malformation: Treatment SYMPTOMS DIAGNOSIS LIVING WITH CHIARI TREATMENT Rick Labuda, Executive Director [email protected] 724-940-0116 Disclaimer: This presentation is intended for informational
Spine University s Guide to Cauda Equina Syndrome
 Spine University s Guide to Cauda Equina Syndrome 2 Introduction Your spine is a very complicated part of your body. It s made up of the bones (vertebrae) that keep it aligned, nerves that channel down
Spine University s Guide to Cauda Equina Syndrome 2 Introduction Your spine is a very complicated part of your body. It s made up of the bones (vertebrae) that keep it aligned, nerves that channel down
Brain Cancer. This reference summary will help you understand how brain tumors are diagnosed and what options are available to treat them.
 Brain Cancer Introduction Brain tumors are not rare. Thousands of people are diagnosed every year with tumors of the brain and the rest of the nervous system. The diagnosis and treatment of brain tumors
Brain Cancer Introduction Brain tumors are not rare. Thousands of people are diagnosed every year with tumors of the brain and the rest of the nervous system. The diagnosis and treatment of brain tumors
Low Back Pain Protocols
 Low Back Pain Protocols Introduction: Diagnostic Triage And 1. Patient Group Adults aged 18 years and over with routine low back problems. Patients who have had recent surgery should be referred directly
Low Back Pain Protocols Introduction: Diagnostic Triage And 1. Patient Group Adults aged 18 years and over with routine low back problems. Patients who have had recent surgery should be referred directly
SPINE ANATOMY AND PROCEDURES. Tulsa Spine & Specialty Hospital 6901 S. Olympia Avenue Tulsa, Oklahoma 74132
 SPINE ANATOMY AND PROCEDURES Tulsa Spine & Specialty Hospital 6901 S. Olympia Avenue Tulsa, Oklahoma 74132 SPINE ANATOMY The spine consists of 33 bones called vertebrae. The top 7 are cervical, or neck
SPINE ANATOMY AND PROCEDURES Tulsa Spine & Specialty Hospital 6901 S. Olympia Avenue Tulsa, Oklahoma 74132 SPINE ANATOMY The spine consists of 33 bones called vertebrae. The top 7 are cervical, or neck
MALIGNANT SPINAL CORD COMPRESSION. Kate Hamilton Head of Medical Oncology Ballarat Health Services
 MALIGNANT SPINAL CORD COMPRESSION Kate Hamilton Head of Medical Oncology Ballarat Health Services OVERVIEW Background Epidemiology Pathophysiology Diagnosis Investigation Differential Diagnosis Management
MALIGNANT SPINAL CORD COMPRESSION Kate Hamilton Head of Medical Oncology Ballarat Health Services OVERVIEW Background Epidemiology Pathophysiology Diagnosis Investigation Differential Diagnosis Management
Clinical Guideline. Low Back Pain Orthopaedics. Princess Alexandra Hospital Emergency Department. 1 Purpose. 2 Background
 Princess Alexandra Hospital Emergency Department Clinical Guideline Orthopaedics Review Officer: Katherine Isoardi Version no: 1 Approval date: 18/03/2015 Review date: 18/03/2017 Approving Officer Dr James
Princess Alexandra Hospital Emergency Department Clinical Guideline Orthopaedics Review Officer: Katherine Isoardi Version no: 1 Approval date: 18/03/2015 Review date: 18/03/2017 Approving Officer Dr James
CHILDREN S NEUROSCIENCE CENTER
 CHILDREN S NEUROSCIENCE CENTER W hen families come to Children s Memorial Hermann Hospital, they expect to find the technological advances and healing expertise of a university-affiliated, academic hospital.
CHILDREN S NEUROSCIENCE CENTER W hen families come to Children s Memorial Hermann Hospital, they expect to find the technological advances and healing expertise of a university-affiliated, academic hospital.
Pathophysiology of Acute and Chronic Low Back Pain
 Pathophysiology of Acute and Chronic Low Back Pain Mary Beth Partyka MSN APN Adult Nurse Practitioner Adult Pain Service Advocate Christ Medical Center Presentation Objectives Review the incidence of acute
Pathophysiology of Acute and Chronic Low Back Pain Mary Beth Partyka MSN APN Adult Nurse Practitioner Adult Pain Service Advocate Christ Medical Center Presentation Objectives Review the incidence of acute
Low Back Injury in the Industrial Athlete: An Anatomic Approach
 Low Back Injury in the Industrial Athlete: An Anatomic Approach Earl J. Craig, M.D. Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Epidemiology
Low Back Injury in the Industrial Athlete: An Anatomic Approach Earl J. Craig, M.D. Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Epidemiology
Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy (ETV)
 Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy (ETV) Information for Patients, Parents and Carers Joanne Kehoe Neurosurgical Nurse Co-ordinator 01 892 1753 Monday to Thursday 8am and 4pm Friday 8am -12pm Main Hospital
Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy (ETV) Information for Patients, Parents and Carers Joanne Kehoe Neurosurgical Nurse Co-ordinator 01 892 1753 Monday to Thursday 8am and 4pm Friday 8am -12pm Main Hospital
* 3D VIDEO SESSIONS * INTERACTIVE SESSIONS * WORKSHOPS
 * 3D VIDEO SESSIONS * INTERACTIVE SESSIONS * WORKSHOPS March 14, 2014 Friday 13:00 Registration 14:00 AOC Meeting 19:00 Opening Cocktail Exhibition Area SESSION I Duration HALL A HALL B hsan Solaroğlu
* 3D VIDEO SESSIONS * INTERACTIVE SESSIONS * WORKSHOPS March 14, 2014 Friday 13:00 Registration 14:00 AOC Meeting 19:00 Opening Cocktail Exhibition Area SESSION I Duration HALL A HALL B hsan Solaroğlu
First Year. PT7040- Clinical Skills and Examination II
 First Year Summer PT7010 Anatomical Dissection for Physical Therapists This is a dissection-based, radiographic anatomical study of the spine, lower extremity, and upper extremity as related to physical
First Year Summer PT7010 Anatomical Dissection for Physical Therapists This is a dissection-based, radiographic anatomical study of the spine, lower extremity, and upper extremity as related to physical
1 REVISOR 5223.0070. (4) Pain associated with rigidity (loss of motion or postural abnormality) or
 1 REVISOR 5223.0070 5223.0070 MUSCULOSKELETAL SCHEDULE; BACK. Subpart 1. Lumbar spine. The spine rating is inclusive of leg symptoms except for gross motor weakness, bladder or bowel dysfunction, or sexual
1 REVISOR 5223.0070 5223.0070 MUSCULOSKELETAL SCHEDULE; BACK. Subpart 1. Lumbar spine. The spine rating is inclusive of leg symptoms except for gross motor weakness, bladder or bowel dysfunction, or sexual
Traumatic Head Injuries
 Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Traumatic Head Injuries Major contributing cause of trauma deaths Many survivors have permanent disability Commonly occurs in young adults (mostly males) Spokane County EMS
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Traumatic Head Injuries Major contributing cause of trauma deaths Many survivors have permanent disability Commonly occurs in young adults (mostly males) Spokane County EMS
Laminectomy for Tethered Cord
 Laminectomy for Tethered Cord A tethered spinal cord is characterized by an abnormal attachment of the spinal cord to the surrounding tissues. The lower end of a normal spinal cord is found in the upper
Laminectomy for Tethered Cord A tethered spinal cord is characterized by an abnormal attachment of the spinal cord to the surrounding tissues. The lower end of a normal spinal cord is found in the upper
.org. Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine. Cause. Description
 Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Page ( 1 ) Spinal fractures can vary widely in severity. While some fractures are very serious injuries that require emergency treatment, other fractures can
Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Page ( 1 ) Spinal fractures can vary widely in severity. While some fractures are very serious injuries that require emergency treatment, other fractures can
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF LOW BACK PAIN. Arnold J. Weil, M.D., M.B.A. Non-Surgical Orthopaedics, P.C. Atlanta, GA
 DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF LOW BACK PAIN Arnold J. Weil, M.D., M.B.A. Non-Surgical Orthopaedics, P.C. Atlanta, GA MEDICAL ALGORITHM OF REALITY LOWER BACK PAIN Yes Patient will never get better until case
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF LOW BACK PAIN Arnold J. Weil, M.D., M.B.A. Non-Surgical Orthopaedics, P.C. Atlanta, GA MEDICAL ALGORITHM OF REALITY LOWER BACK PAIN Yes Patient will never get better until case
The Spine Center at Beth Israel Deaconess
 Spinal Pain The Spine Center at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center developed the following detailed eplanation of our care pathways for primary care providers to help support your interactions with patients
Spinal Pain The Spine Center at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center developed the following detailed eplanation of our care pathways for primary care providers to help support your interactions with patients
Anatomy: The sella is a depression in the sphenoid bone that makes up part of the skull base located behind the eye sockets.
 Pituitary Tumor Your doctor thinks you may have a pituitary tumor. Pituitary tumors are benign (non-cancerous) overgrowth of cells that make up the pituitary gland (the master gland that regulates other
Pituitary Tumor Your doctor thinks you may have a pituitary tumor. Pituitary tumors are benign (non-cancerous) overgrowth of cells that make up the pituitary gland (the master gland that regulates other
White Paper: Reducing Utilization Concerns Regarding Spinal Fusion and Artificial Disc Implants
 White Paper: Reducing Utilization Concerns Regarding Spinal Fusion and Artificial Disc Implants For Health Plans, Medical Management Organizations and TPAs Executive Summary Back pain is one of the most
White Paper: Reducing Utilization Concerns Regarding Spinal Fusion and Artificial Disc Implants For Health Plans, Medical Management Organizations and TPAs Executive Summary Back pain is one of the most
The Abbreviated Injury Scale (AIS) A brief introduction
 The Abbreviated Injury Scale (AIS) A brief introduction Abbreviated Injury Scale 1990 Revision Update 98 The Abbreviated Injury Scale produced by: Association for the Advancement of Automotive Medicine
The Abbreviated Injury Scale (AIS) A brief introduction Abbreviated Injury Scale 1990 Revision Update 98 The Abbreviated Injury Scale produced by: Association for the Advancement of Automotive Medicine
FERNE / EMRA 2009 Mid-Atlantic Emergency Medicine Medical Student Symposium: ABCs of Head CT Interpretation; Heather M. Prendergast MD, MPH.
 ABCs of Head CT Interpretation in the Emergency Department: CT Interpretation Workshop Guide Heather M. Prendergast, MD, MPH, FACEP Associate Professor Department of Emergency Medicine University of Illinois
ABCs of Head CT Interpretation in the Emergency Department: CT Interpretation Workshop Guide Heather M. Prendergast, MD, MPH, FACEP Associate Professor Department of Emergency Medicine University of Illinois
Discovery of an Aneurysm Following a Motorcycle Accident. Maya Babu, MSIII Gillian Lieberman, M.D.
 Discovery of an Aneurysm Following a Motorcycle Accident Maya Babu, MSIII Gillian Lieberman, M.D. Patient CC: July 2004 65 yo male transferred to the BI from an OSH s/p motorcycle crash w/o a helmet CC
Discovery of an Aneurysm Following a Motorcycle Accident Maya Babu, MSIII Gillian Lieberman, M.D. Patient CC: July 2004 65 yo male transferred to the BI from an OSH s/p motorcycle crash w/o a helmet CC
Neuroimaging of Headache. Kenneth D. Williams, MD
 Neuroimaging of Headache Kenneth D. Williams, MD Disclosures Financial: None Off Label Usage: None Key Points Headache is an extremely common symptom. Structural abnormalities (Primary HA) are rare. Clinical
Neuroimaging of Headache Kenneth D. Williams, MD Disclosures Financial: None Off Label Usage: None Key Points Headache is an extremely common symptom. Structural abnormalities (Primary HA) are rare. Clinical
Bleeding in the brain haemorrhagic stroke
 Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Bleeding in the brain haemorrhagic stroke Most strokes are caused by a blockage in an artery leading to the brain an ischaemic stroke. However, about
Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Bleeding in the brain haemorrhagic stroke Most strokes are caused by a blockage in an artery leading to the brain an ischaemic stroke. However, about
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
 Chapter 7: The Nervous System I. Organization of the Nervous System Objectives: List the general functions of the nervous system Explain the structural and functional classifications of the nervous system
Chapter 7: The Nervous System I. Organization of the Nervous System Objectives: List the general functions of the nervous system Explain the structural and functional classifications of the nervous system
UBC Pain Medicine Residency Program: CanMEDS Goals and Objectives of the Neurology Rotation
 UBC Pain Medicine Residency Program: CanMEDS Goals and Objectives of the Neurology Rotation Goals of the Program To acquire the knowledge and skills necessary to assess and provide a management plan for
UBC Pain Medicine Residency Program: CanMEDS Goals and Objectives of the Neurology Rotation Goals of the Program To acquire the knowledge and skills necessary to assess and provide a management plan for
Differential Diagnosis of Craniofacial Pain
 1. Differential Diagnosis of Craniofacial Pain 2. Headache Page - 1 3. International Headache Society International Classification... 4. The Primary Headaches (1-4) Page - 2 5. The Secondary Headaches
1. Differential Diagnosis of Craniofacial Pain 2. Headache Page - 1 3. International Headache Society International Classification... 4. The Primary Headaches (1-4) Page - 2 5. The Secondary Headaches
Cavernous Angioma. Cerebral Cavernous Malformation ...
 Cavernous Angioma... Cerebral Cavernous Malformation Information For Patients And Loved Ones 107 Quaker Meeting House Road Williamsburg, Virginia 23188 USA 1-866-HEAL-CCM 1-757-258-3355 www.angiomaalliance.org
Cavernous Angioma... Cerebral Cavernous Malformation Information For Patients And Loved Ones 107 Quaker Meeting House Road Williamsburg, Virginia 23188 USA 1-866-HEAL-CCM 1-757-258-3355 www.angiomaalliance.org
Spinal Surgery Functional Status and Quality of Life Outcome Specifications 2015 (01/01/2013 to 12/31/2013 Dates of Procedure) September 2014
 Description Methodology For patients ages 18 years and older who undergo a lumbar discectomy/laminotomy or lumbar spinal fusion procedure during the measurement year, the following measures will be calculated:
Description Methodology For patients ages 18 years and older who undergo a lumbar discectomy/laminotomy or lumbar spinal fusion procedure during the measurement year, the following measures will be calculated:
Day Rehab ICD-10 documentation
 Day Rehab documentation Seven key impacts to documentation 1. Disease or disorder site 2. Acuity and/or encounter status of treatment 3. Etiology, causative agent, or disease type and injury/ poisoning
Day Rehab documentation Seven key impacts to documentation 1. Disease or disorder site 2. Acuity and/or encounter status of treatment 3. Etiology, causative agent, or disease type and injury/ poisoning
Nuno Morais 1 José António Moreira da Costa 2
 Nuno Morais 1 José António Moreira da Costa 2 1 Neurosurgery Department, Hospital de Braga, Braga, Portugal 2 Private Practice, Clínica Neurológica e da Coluna Vertebral, Braga, Portugal Disclosure Funding
Nuno Morais 1 José António Moreira da Costa 2 1 Neurosurgery Department, Hospital de Braga, Braga, Portugal 2 Private Practice, Clínica Neurológica e da Coluna Vertebral, Braga, Portugal Disclosure Funding
Neurology Clerkship Learning Objectives
 Neurology Clerkship Learning Objectives Clinical skills Perform a neurological screening examination of the cranial nerves, motor system, reflexes, and sensory system under the observation and guidance
Neurology Clerkship Learning Objectives Clinical skills Perform a neurological screening examination of the cranial nerves, motor system, reflexes, and sensory system under the observation and guidance
III./8.4.2: Spinal trauma. III./8.4.2.1 Injury of the spinal cord
 III./8.4.2: Spinal trauma Introduction Causes: motor vehicle accidents, falls, sport injuries, industrial accidents The prevalence of spinal column trauma is 64/100,000, associated with neurological dysfunction
III./8.4.2: Spinal trauma Introduction Causes: motor vehicle accidents, falls, sport injuries, industrial accidents The prevalence of spinal column trauma is 64/100,000, associated with neurological dysfunction
Guideline for Emergency CT scanning Tony Bleetman Aidan Macnamara October 2008. June annually Emergency Department guidelines
 Meta Data Guideline Title: Guideline Author: Guideline Sponsor: Date of Ratification (CSC): Review Date: Related Policies/Topic/Driver Stored Centrally: Guideline for Emergency CT scanning Tony Bleetman
Meta Data Guideline Title: Guideline Author: Guideline Sponsor: Date of Ratification (CSC): Review Date: Related Policies/Topic/Driver Stored Centrally: Guideline for Emergency CT scanning Tony Bleetman
Imaging degenerative disk disease in the lumbar spine. Elaine Besancon MS III Dr. Gillian Lieberman
 Imaging degenerative disk disease in the lumbar spine Elaine Besancon MS III Dr. Gillian Lieberman Learning Objectives Anatomy review Pathophysiology of degenerative disc disease Common sequelae of disk
Imaging degenerative disk disease in the lumbar spine Elaine Besancon MS III Dr. Gillian Lieberman Learning Objectives Anatomy review Pathophysiology of degenerative disc disease Common sequelae of disk
.org. Herniated Disk in the Lower Back. Anatomy. Description
 Herniated Disk in the Lower Back Page ( 1 ) Sometimes called a slipped or ruptured disk, a herniated disk most often occurs in your lower back. It is one of the most common causes of low back pain, as
Herniated Disk in the Lower Back Page ( 1 ) Sometimes called a slipped or ruptured disk, a herniated disk most often occurs in your lower back. It is one of the most common causes of low back pain, as
Surgery for cervical disc prolapse or cervical osteophyte
 Mr Paul S. D Urso MBBS(Hons), PhD, FRACS Neurosurgeon Provider Nº: 081161DY Epworth Centre Suite 6.1 32 Erin Street Richmond 3121 Tel: 03 9421 5844 Fax: 03 9421 4186 AH: 03 9483 4040 email: [email protected]
Mr Paul S. D Urso MBBS(Hons), PhD, FRACS Neurosurgeon Provider Nº: 081161DY Epworth Centre Suite 6.1 32 Erin Street Richmond 3121 Tel: 03 9421 5844 Fax: 03 9421 4186 AH: 03 9483 4040 email: [email protected]
How To Get An Mri Of The Lumbar Spine W/O Contrast
 Date notice sent to all parties: May 27, 2014 IRO CASE #: ReviewTex, Inc. 1818 Mountjoy Drive San Antonio, TX 78232 (phone) 210-598-9381 (fax) 210-598-9382 [email protected] Notice of Independent Review
Date notice sent to all parties: May 27, 2014 IRO CASE #: ReviewTex, Inc. 1818 Mountjoy Drive San Antonio, TX 78232 (phone) 210-598-9381 (fax) 210-598-9382 [email protected] Notice of Independent Review
CMS Limitations Guide Mammograms and Bone Density Radiology Services
 CMS Limitations Guide Mammograms and Bone Density Radiology Services Starting July 1, 2008, CMS has placed numerous medical necessity limits on tests and procedures. This reference guide provides you with
CMS Limitations Guide Mammograms and Bone Density Radiology Services Starting July 1, 2008, CMS has placed numerous medical necessity limits on tests and procedures. This reference guide provides you with
For customers Friends Life Individual Protection Critical Illness Cover. Critical Illness Cover. It s critical illness. And more.
 For customers Friends Life Individual Protection Critical Illness Cover Critical Illness Cover It s critical illness. And more. It s critical illness. And 2 it s designed with your needs in mind. it covers
For customers Friends Life Individual Protection Critical Illness Cover Critical Illness Cover It s critical illness. And more. It s critical illness. And 2 it s designed with your needs in mind. it covers
Diagnosis and Management for Chronic Back Pain: Critical for your Recovery
 Diagnosis and Management for Chronic Back Pain: Critical for your Recovery Dr. Connie D Astolfo, DC, PhD (candidate) In past articles I have stressed that the causes of back pain can be very complex. This
Diagnosis and Management for Chronic Back Pain: Critical for your Recovery Dr. Connie D Astolfo, DC, PhD (candidate) In past articles I have stressed that the causes of back pain can be very complex. This
Advances In Spine Care. James D. Bruffey M.D. Scripps Clinic Division of Orthopaedic Surgery Section of Spinal Surgery
 Advances In Spine Care James D. Bruffey M.D. Scripps Clinic Division of Orthopaedic Surgery Section of Spinal Surgery Introduction The Spine - A common source of problems Back pain is the #2 presenting
Advances In Spine Care James D. Bruffey M.D. Scripps Clinic Division of Orthopaedic Surgery Section of Spinal Surgery Introduction The Spine - A common source of problems Back pain is the #2 presenting
