Preparation of Blood Films
|
|
|
- Stella Franklin
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Preparation of Blood Films Principle: Blood film enables us to evaluate WBC, RBC, and PLT morphology, also, allows us to perform differential WBC count, furthermore estimation of WBC and platelets counts can be done on blood films. Blood films are made on glass microscopic slides. Sample: Finger stick blood or EDTA anticoagulated venous whole blood may be used. Films of peripheral blood must be made immediately. Films may be made from EDTA anticoagulated blood as long as two to three hours after collection. All specimens should be free of clots. Procedure: 1- Use clean standard size glass slides, wiped from dust just immediately before use. 2- Place a small drop of well mixed anticoagulated whole blood, in the center line of the slide, about 1.5 to 2 cm from one end, with the aid of a capillary tube. 3- Immediately, without delay, with the aid of a second clean slide with uniform smooth edges (spreader slide), with a degrees angle, move back so blood drop will spread along the edge of the spreader slide, when this occurs, spread, or smear the film by a quick, forward motion of the spreader.
2 Notes: Before preparing the films, you must check that blood samples are free from clots, and this is done with two wooden applicator sticks. If clots are present the specimen is unsatisfactory. Films can be labeled with patient s name and /or Lab. No. on the thick end of the film itself, after being dried, by using a pencil. DO NOT ATTEMPT TO CENTRIFUGE TO DISCARD PLASMA, THIS MAY DISTORT AND DISINTEGRATE THE CELLS, WHICH ARE OUR INTEREST!
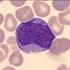
3 Staining Blood Films With Romanovsky Stains Blood films are stained so that morphology of blood cells become more easily viewed, identified, and evaluated. In addition, blood films may be examined for the presence of blood parasites (Malaria, Trypanosoma, Babesia). Furthermore, stained blood films can provide important information about a patients health, they may lead to a diagnosis or verify a diagnosis, or they may rule out a diagnosis. Blood films are stained with one of the Romanovsky stains, which are universally used for staining blood films. There remarkable property is creating distinctions in shades of staining granules differentially and this is dependent on two staining components: Azure B (the basic dye) and Eosin Y ( the acidic dye). Other factors which affects the staining results include : 1) Staining time, 2) Ratio of Azure B to Eosin Y, 3) ph of the staining solution. Azure B will stain the acidic cell Components (e.g. nucleus, because it contains nucleic acids; basophilic granules also take the Azure B staining because they contain heparin, which is acidic in origin), while Eosin Y will stain the alkaline basic components ( e.g. Eosinophilic granules in eosinophils, because these granules contain spermine derivatives, which are basic in origin). Red cells have affinity for acidic Eosin Y dye, because it contain hemoglobin which is basic in origin.
4 Romanovsky stains include: Giemsa Stain Wright s Stain Leishman Stain May-Grünwald Stain Leishman Stain Procedure: 1- Let the films be air dried. 2- Put the films on a staining trough rack. 3- Flood the slides with the stain. 4- After 2 minutes ( or more, if the stain in newly prepared), add double volume of water, and blow to mix the stain with water, until a shiny layer is seen. 5- After 5-7 minutes, wash with a stream of water. 6- Wipe the back of the slides with gauze. 7- Set the films in upright position on a filter paper to dry. 8- Read the blood films microscopically. If delay in staining blood films may occur, fix the films in absolute methanol, for 1-2 minutes, but do not stain the slides until completely dried.
5 Romanovsky Stain Blood Cell Characteristics No. Cell Structure Staining characteristics 1 Red cells Red or pinkish red 2 Nuclei of all cell types Purple/violet 3 Lymphocyte cytoplasm Blue 4 Monocyte cytoplasm Grayish blue 5 Platelets cytoplasm Light blue 6 Neutrophilic granules Violet-pink 7 Eosinophilic granules Orange-red 8 Basophilic granules Purplish black/ Deep blue 9 Platelets granules Purple Sources Of Errors In Staining 1- Stain Precipitate: May obscure cell details, and may cause confusion with inclusion bodies. Filter the stain before use. 2- ph of the buffer or water: Too acidic ph causes too pinkish slides. Too basic ph causes too bluish slides. 3- Improper stain timing may result in faded staining or altered colors: Too long staining time causes too blue slides (overstaining). Too short staining time causes too red slides. 4- Forced drying may alter color intensities and/or distort cell morphology. 5- Non-stain related errors: 1st- EDTA causes crenation of the cells after blood collection.
6 2nd- Severely anemic blood samples causes slower drying (before staining) due to excessive plasma. 3rd- Old blood specimens may cause disintegration in WBC s and decrease in their numbers. 4th- Collection of blood in heparin causes blue staining of RBC s with bluish background, which makes heparin unsatisfactory for routine hematology testing, also heparin induces platelet aggregation and clumping, with subsequent erroneous platelet count with automated counters. Always filter the stain before each use, to eliminate stain precipitates.
STAINING OF PBF AND INTERPRETATION OF NORMAL AND ABNORMAL RED CELL MORPHOLOGY
 9 STAINING OF PBF AND INTERPRETATION OF NORMAL AND ABNORMAL RED CELL MORPHOLOGY 9.1 INTRODUCTION A peripheral blood smear (peripheral blood film) is a glass microscope slide coated on one side with a thin
9 STAINING OF PBF AND INTERPRETATION OF NORMAL AND ABNORMAL RED CELL MORPHOLOGY 9.1 INTRODUCTION A peripheral blood smear (peripheral blood film) is a glass microscope slide coated on one side with a thin
LABORATORY 2 Staining and processing of blood parasites Differential counts of leukocytes (giemsa stains)
 LABORATORY 2 Staining and processing of blood parasites Differential counts of leukocytes (giemsa stains) SPECIMENS TO BE STAINED 1. Thin and thick blood smears from a patient returning from Africa - case
LABORATORY 2 Staining and processing of blood parasites Differential counts of leukocytes (giemsa stains) SPECIMENS TO BE STAINED 1. Thin and thick blood smears from a patient returning from Africa - case
GIEMSA STAIN PREANALYTICAL CONSIDERATIONS
 GIEMSA STAIN PREANALYTICAL CONSIDERATIONS I. Principle Giemsa stain is used to differentiate nuclear and/or cytoplasmic morphology of platelets, RBCs, WBCs, and parasites (1,2). The most dependable stain
GIEMSA STAIN PREANALYTICAL CONSIDERATIONS I. Principle Giemsa stain is used to differentiate nuclear and/or cytoplasmic morphology of platelets, RBCs, WBCs, and parasites (1,2). The most dependable stain
BLOOD FILM STAINING EFFECTS
 An Educational Supplement prepared by ALQEP May 2004 Introduction The stained peripheral blood film is one of the world s most widely and frequently used tests. Since its introduction in the late nineteenth
An Educational Supplement prepared by ALQEP May 2004 Introduction The stained peripheral blood film is one of the world s most widely and frequently used tests. Since its introduction in the late nineteenth
Lab 02: Blood Cytology (20 points)
 Pierce College Putman/Biol 242 Name: Lab 02: Blood Cytology (20 points) Reference: Marieb & Mitchell 9 th Ed: 29A (Activities 1, 2, 3, 4, 7); 10 th Ed: Exercise 29 (Activities 1, 2, 3, 4, 7). Pierce College
Pierce College Putman/Biol 242 Name: Lab 02: Blood Cytology (20 points) Reference: Marieb & Mitchell 9 th Ed: 29A (Activities 1, 2, 3, 4, 7); 10 th Ed: Exercise 29 (Activities 1, 2, 3, 4, 7). Pierce College
SEED Haematology. Sysmex Educational Enhancement and Development February 2013
 SEED Haematology Sysmex Educational Enhancement and Development February 2013 The role of the peripheral blood smear in the modern haematology laboratory Automated haematology cell counting The laboratory
SEED Haematology Sysmex Educational Enhancement and Development February 2013 The role of the peripheral blood smear in the modern haematology laboratory Automated haematology cell counting The laboratory
MICROKROM MICROKROM. Basic Guidelines for Quality Staining with Romanowsky Stains
 MICROKROM M I C R O S C O P Y S TA I N S MICROKROM Basic Guidelines for Quality Staining with Romanowsky Stains Coral Clinical Systems A3, Gitanjali Tulip Block, Dr. A. Do Rego Bagh, Alto Santacruz, Bambolim
MICROKROM M I C R O S C O P Y S TA I N S MICROKROM Basic Guidelines for Quality Staining with Romanowsky Stains Coral Clinical Systems A3, Gitanjali Tulip Block, Dr. A. Do Rego Bagh, Alto Santacruz, Bambolim
serology Agglutination Techniques and Blood Cell Identification
 Serology: Agglutination Techniques and Blood Cell Identification S erology is a branch of immunology dealing with techniques to identify and measure antigens, and to detect serum antibodies. Agglutination
Serology: Agglutination Techniques and Blood Cell Identification S erology is a branch of immunology dealing with techniques to identify and measure antigens, and to detect serum antibodies. Agglutination
ABO-Rh Blood Typing With Synthetic Blood
 70-0101 ABO-Rh Blood Typing With Synthetic Blood Teacher s Manual World-Class Support for Science & Math The ability to type blood is an invaluable tool in the fields of medicine and criminology. Using
70-0101 ABO-Rh Blood Typing With Synthetic Blood Teacher s Manual World-Class Support for Science & Math The ability to type blood is an invaluable tool in the fields of medicine and criminology. Using
Granulocytes vs. Agranulocytes
 Leukocytes are white blood cells (AKA colorless (non-pigmented) blood cells). (Much) smaller in number than RBCs. Unlike RBCs, there are several different types of WBCs. All contain a visible nucleus.
Leukocytes are white blood cells (AKA colorless (non-pigmented) blood cells). (Much) smaller in number than RBCs. Unlike RBCs, there are several different types of WBCs. All contain a visible nucleus.
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. Collection of Blood and Preparation of Blood Smears. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
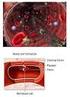 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 3 Collection of Blood and Preparation of Blood Smears. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 3-1 through 3-8. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 3-1. Select
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 3 Collection of Blood and Preparation of Blood Smears. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 3-1 through 3-8. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 3-1. Select
Laboratory 12 Blood Cells
 Laboratory 12 Blood Cells Objectives: Identify microscopically each of the following: erythrocytes (red blood cells or RBCs), the five types of leukocytes (white blood cells or WBCs), and thrombocytes
Laboratory 12 Blood Cells Objectives: Identify microscopically each of the following: erythrocytes (red blood cells or RBCs), the five types of leukocytes (white blood cells or WBCs), and thrombocytes
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg
 Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 2; Session 1 Urine Microscopic Examination The Complete Urinalysis Physical properties already covered Chemical analysis in the next unit Microscopic our current focus
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 2; Session 1 Urine Microscopic Examination The Complete Urinalysis Physical properties already covered Chemical analysis in the next unit Microscopic our current focus
Hematology Sequence. Blood Labs ORIENTATION OBJECTIVES. c. Microscopic Exam of a Peripheral Blood Smear (several parts)
 Hematology Sequence Blood Labs ORIENTATION OBJECTIVES Objectives Procedure 1. Read the three sections that follow: a. Hematocrit b. Preparing a peripheral lood smear c. Microscopic Exam of a Peripheral
Hematology Sequence Blood Labs ORIENTATION OBJECTIVES Objectives Procedure 1. Read the three sections that follow: a. Hematocrit b. Preparing a peripheral lood smear c. Microscopic Exam of a Peripheral
MANUAL PLATELET COUNT
 MANUAL PLATELET COUNT Principle Whole blood is diluted with a 1% ammonium oxalate solution. The isotonic balance of the diluent is such that all erythrocytes are lysed while the leukocytes, platelets,
MANUAL PLATELET COUNT Principle Whole blood is diluted with a 1% ammonium oxalate solution. The isotonic balance of the diluent is such that all erythrocytes are lysed while the leukocytes, platelets,
Hematology Morphology Critique
 Survey Slide: History: 60-year-old female presenting with pneumonia Further Laboratory Data: Hgb : 90 g/l RBC : 2.92 10 12 /L Hct : 0.25 L/L MCV : 87 fl MCH : 30.8 pg MCHC : 355 g/l RDW : 17.7 % WBC :
Survey Slide: History: 60-year-old female presenting with pneumonia Further Laboratory Data: Hgb : 90 g/l RBC : 2.92 10 12 /L Hct : 0.25 L/L MCV : 87 fl MCH : 30.8 pg MCHC : 355 g/l RDW : 17.7 % WBC :
Exercise 9: Blood. Readings: Silverthorn 5 th ed, 547 558, 804 805; 6 th ed, 545 557, 825 826.
 Exercise 9: Blood Readings: Silverthorn 5 th ed, 547 558, 804 805; 6 th ed, 545 557, 825 826. Blood Typing The membranes of human red blood cells (RBCs) contain a variety of cell surface proteins called
Exercise 9: Blood Readings: Silverthorn 5 th ed, 547 558, 804 805; 6 th ed, 545 557, 825 826. Blood Typing The membranes of human red blood cells (RBCs) contain a variety of cell surface proteins called
A simple differential stain of blood smears using black Quink
 A simple differential stain of blood smears using black Quink Chris Thomas, 3 Hall End, Milton, Cambridge CB24 6AQ, [email protected] Published in: Micscape http://www.microscopy-uk.org.uk/mag/artsep15/ct-quink-blood-stain.pdf
A simple differential stain of blood smears using black Quink Chris Thomas, 3 Hall End, Milton, Cambridge CB24 6AQ, [email protected] Published in: Micscape http://www.microscopy-uk.org.uk/mag/artsep15/ct-quink-blood-stain.pdf
Collect and label sample according to standard protocols. Gently invert tube 8-10 times immediately after draw. DO NOT SHAKE. Do not centrifuge.
 Complete Blood Count CPT Code: CBC with Differential: 85025 CBC without Differential: 85027 Order Code: CBC with Differential: C915 Includes: White blood cell, Red blood cell, Hematocrit, Hemoglobin, MCV,
Complete Blood Count CPT Code: CBC with Differential: 85025 CBC without Differential: 85027 Order Code: CBC with Differential: C915 Includes: White blood cell, Red blood cell, Hematocrit, Hemoglobin, MCV,
Cardiovascular System. Blood Components
 Cardiovascular System Blood Components 1 Components of Blood Formed elements: erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets Plasma: water, proteins, other solutes The components of blood can be divided into two
Cardiovascular System Blood Components 1 Components of Blood Formed elements: erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets Plasma: water, proteins, other solutes The components of blood can be divided into two
KEY CHAPTER 14: BLOOD OBJECTIVES. 1. Describe blood according to its tissue type and major functions.
 KEY CHAPTER 14: BLOOD OBJECTIVES 1. Describe blood according to its tissue type and major functions. TISSUE TYPE? MAJOR FUNCTIONS connective Transport Maintenance of body temperature 2. Define the term
KEY CHAPTER 14: BLOOD OBJECTIVES 1. Describe blood according to its tissue type and major functions. TISSUE TYPE? MAJOR FUNCTIONS connective Transport Maintenance of body temperature 2. Define the term
LAB: Blood Exploration
 Name: Period: Date: LAB: Blood Exploration Introduction A liquid called plasma makes up about half (55%) of the content of blood. Plasma contains proteins that help blood to clot, transport substances
Name: Period: Date: LAB: Blood Exploration Introduction A liquid called plasma makes up about half (55%) of the content of blood. Plasma contains proteins that help blood to clot, transport substances
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY RED BLOOD CELLS AND WHITE BLOOD CELLS IN URINALYSIS
 URINALYSIS Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Earn CE Credits under Continuing
URINALYSIS Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Earn CE Credits under Continuing
ABO-Rh Blood Typing Using Neo/BLOOD
 ABO-Rh Blood Typing Using Neo/BLOOD Objectives Determine the ABO and Rh blood type of unknown simulated blood samples. Prepare a simulated blood smear. Examine a prepared blood smear under the microscope
ABO-Rh Blood Typing Using Neo/BLOOD Objectives Determine the ABO and Rh blood type of unknown simulated blood samples. Prepare a simulated blood smear. Examine a prepared blood smear under the microscope
MANUAL PLATELET COUNT
 MANUAL PLATELET COUNT LAB OBJECTIVE The student will be able to perform, within K20% accuracy as compared to the automated result, five manual platelet counts using the Unopette system. and the light microscope.
MANUAL PLATELET COUNT LAB OBJECTIVE The student will be able to perform, within K20% accuracy as compared to the automated result, five manual platelet counts using the Unopette system. and the light microscope.
HISTOLOGY LABORATORY. Microscope Orientation and Blood Smear Lab
 HISTOLOGY LABORATORY Microscope Orientation and Blood Smear Lab For practicing how to use the microscope DO NOT use the blood smear slide (it is too boring for the lower mags). Use a slide from the white
HISTOLOGY LABORATORY Microscope Orientation and Blood Smear Lab For practicing how to use the microscope DO NOT use the blood smear slide (it is too boring for the lower mags). Use a slide from the white
Blood. Functions of Blood. Components of Blood. Transporting. Distributing body heat. A type of connective tissue. Formed elements.
 Blood Functions of Blood Transporting nutrients respiratory gases waste products Distributing body heat Components of Blood A type of connective tissue Formed elements Living blood cells Plasma Nonliving
Blood Functions of Blood Transporting nutrients respiratory gases waste products Distributing body heat Components of Blood A type of connective tissue Formed elements Living blood cells Plasma Nonliving
1. Preparing thin and thick blood films with capillary or venous blood
 Methods in Parasitology 1. Preparing thin and thick blood films with capillary or venous blood Swiss Tropical Institute, Basel April 2005 1.0 Preparing thin and thick blood films Contents 1.1 Preparatory
Methods in Parasitology 1. Preparing thin and thick blood films with capillary or venous blood Swiss Tropical Institute, Basel April 2005 1.0 Preparing thin and thick blood films Contents 1.1 Preparatory
COMPARING PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS
 COMPARING PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS OBJECTIVES: Distinguish between plant and animals cells by their structures Demonstrate the benefit of stains Acquire ability to prepare wet mounts SAFETY: Methylene blue
COMPARING PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS OBJECTIVES: Distinguish between plant and animals cells by their structures Demonstrate the benefit of stains Acquire ability to prepare wet mounts SAFETY: Methylene blue
Haematology what does your blood test mean?
 Haematology what does your blood test mean? This document provides some reading material to be used in preparation for the Haematology what does your blood test mean? workshop at RMIT s Experience Health
Haematology what does your blood test mean? This document provides some reading material to be used in preparation for the Haematology what does your blood test mean? workshop at RMIT s Experience Health
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg. Synovial Fluid. Synovial Fluid. Unit 4. Composition and formation. Functions. Reasons for analysis.
 Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 4 Synovial Fluid Synovial Fluid Composition and formation Secreted by cells of synovial membrane Very viscous, clear ultrafiltrate of plasma Contains Hyaluronic acid
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 4 Synovial Fluid Synovial Fluid Composition and formation Secreted by cells of synovial membrane Very viscous, clear ultrafiltrate of plasma Contains Hyaluronic acid
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY - GRANULOCYTE FORMATION AND CHRONIC MYELOCYTIC LEUKEMIA
 LEUKEMIA Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Earn CE Credits under Continuing Education
LEUKEMIA Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Earn CE Credits under Continuing Education
NEW YORK STATE CYTOHEMATOLOGY PROFICIENCY TESTING PROGRAM Glass Slide Critique ~ November 2010
 NEW YORK STATE CYTOHEMATOLOGY PROFICIENCY TESTING PROGRAM Glass Slide Critique ~ November 2010 Slide 081 Available data: 72 year-old female Diagnosis: MDS to AML WBC 51.0 x 10 9 /L RBC 3.39 x 10 12 /L
NEW YORK STATE CYTOHEMATOLOGY PROFICIENCY TESTING PROGRAM Glass Slide Critique ~ November 2010 Slide 081 Available data: 72 year-old female Diagnosis: MDS to AML WBC 51.0 x 10 9 /L RBC 3.39 x 10 12 /L
White Blood Cells (WBCs) or Leukocytes
 Lec.5 Z.H.Al-Zubaydi Medical Physiology White Blood Cells (WBCs) or Leukocytes Although leukocytes are far less numerous than red blood cells, they are important to body defense against disease. On average,
Lec.5 Z.H.Al-Zubaydi Medical Physiology White Blood Cells (WBCs) or Leukocytes Although leukocytes are far less numerous than red blood cells, they are important to body defense against disease. On average,
Phlebotomy Handbook Blood Collection Essentials Seventh Edition
 Phlebotomy Handbook Blood Collection Essentials Seventh Edition Diana Garza Kathleen Becan-McBride Chapter Four The Cardiovascular System Introduction Circulatory system is a transport system. Contributes
Phlebotomy Handbook Blood Collection Essentials Seventh Edition Diana Garza Kathleen Becan-McBride Chapter Four The Cardiovascular System Introduction Circulatory system is a transport system. Contributes
LABORATORY 3: Microscopic Urinalysis
 LABORATORY 3: Microscopic Urinalysis Note Students are expected to review the corresponding information in the course textbook(s) as well as the classroom notes in preparation for this lab and to aid in
LABORATORY 3: Microscopic Urinalysis Note Students are expected to review the corresponding information in the course textbook(s) as well as the classroom notes in preparation for this lab and to aid in
BioSciences. Peripheral Blood Smear Preparation. Blood Smear Preparation Materials
 PolyFacts Vol. 5 No. 1 BioSciences Use the Wright Stain High Quality StainRITE Ready-to-Use Stains for Hematology Peripheral blood smear (peripheral blood film) is a glass microscope slide coated with
PolyFacts Vol. 5 No. 1 BioSciences Use the Wright Stain High Quality StainRITE Ready-to-Use Stains for Hematology Peripheral blood smear (peripheral blood film) is a glass microscope slide coated with
GLOSSARY of STAINS Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) Periodic acid-schiff s (PAS) Masson s Trichrome Stain Gomori Trichrome Stain Silver Salts
 GLOSSARY of STAINS Your study and comprehension of the slides in your collection will be enhanced if you know something about the staining methods used in their preparation. The following list includes
GLOSSARY of STAINS Your study and comprehension of the slides in your collection will be enhanced if you know something about the staining methods used in their preparation. The following list includes
In order to be useful, a smear must have the following qualities:
 Smear Preparation and Simple Stain Objectives: Make bacterial smear slides (usually called smears) Distinguish cells on these slides using a simple stain procedure Unstained microbial cells are nearly
Smear Preparation and Simple Stain Objectives: Make bacterial smear slides (usually called smears) Distinguish cells on these slides using a simple stain procedure Unstained microbial cells are nearly
EDF Extended Depth of Field
 EDF Extended Depth of Field An upgrade for the ImageStream system Think outside the dot. Break the classic depth of field barrier Improve precision Enhance discrimination Simplify analysis Increase resolution
EDF Extended Depth of Field An upgrade for the ImageStream system Think outside the dot. Break the classic depth of field barrier Improve precision Enhance discrimination Simplify analysis Increase resolution
Exercise 2. The Compound Light Microscope
 6 Exercise 2 The Compound Light Microscope INTRODUCTION: Student Learning Objectives: After completing this exercise students will: a. Demonstrate proficient use of the microscope using low, high dry,
6 Exercise 2 The Compound Light Microscope INTRODUCTION: Student Learning Objectives: After completing this exercise students will: a. Demonstrate proficient use of the microscope using low, high dry,
HAEMATOLOGY LABORATORY
 HAEMATOLOGY LABORATORY Head of Unit : Dr Raudhawati Osman Phone : +603-26155281 Email : [email protected] 1. INTRODUCTION The Haematology Unit, Department of Pathology, HKL provides tertiary diagnostic
HAEMATOLOGY LABORATORY Head of Unit : Dr Raudhawati Osman Phone : +603-26155281 Email : [email protected] 1. INTRODUCTION The Haematology Unit, Department of Pathology, HKL provides tertiary diagnostic
MANUAL WBC LAB OBJECTIVE
 MANUAL WBC LAB OBJECTIVE The student will be able to perform, within K20% accuracy as compared to the automated result, five manual white blood cell counts using the Unopette system. PRINCIPLE Free-flowing
MANUAL WBC LAB OBJECTIVE The student will be able to perform, within K20% accuracy as compared to the automated result, five manual white blood cell counts using the Unopette system. PRINCIPLE Free-flowing
A&P 2 Blood Lab Guide In-Lab Exercises
 A&P 2 Blood Lab Guide In-Lab Exercises Have someone in your group read the following out loud, while the others read along: In this "Lab Guide", we will be looking at the blood and some common blood tests.
A&P 2 Blood Lab Guide In-Lab Exercises Have someone in your group read the following out loud, while the others read along: In this "Lab Guide", we will be looking at the blood and some common blood tests.
Collection Guidelines for Routine & Special Coagulation Testing
 Revised May 2010 Collection Guidelines for Routine & Special Coagulation Testing Best samples come from peripheral stick with evacuated tube system 19 to 22 gauge needle (smaller or bigger could cause
Revised May 2010 Collection Guidelines for Routine & Special Coagulation Testing Best samples come from peripheral stick with evacuated tube system 19 to 22 gauge needle (smaller or bigger could cause
 Blood Sticky, opaque fluid with a metallic taste (Fe 2+ ) Varies from scarlet (P O2 = 100) to dark red (P O2 = 40) ph is between 7.35 and 7.45 Average volume in an adult is 5 L (7% of body weight) 2 L
Blood Sticky, opaque fluid with a metallic taste (Fe 2+ ) Varies from scarlet (P O2 = 100) to dark red (P O2 = 40) ph is between 7.35 and 7.45 Average volume in an adult is 5 L (7% of body weight) 2 L
MALARIA PARASITE COUNTING
 VERSION 1 EFFECTIVE DATE: 01/01/2016 MALARIA PARASITE COUNTING MALARIA MICROSCOPY STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE MM-SOP-09 1. PURPOSE AND SCOPE To describe the procedure for counting malaria parasites on
VERSION 1 EFFECTIVE DATE: 01/01/2016 MALARIA PARASITE COUNTING MALARIA MICROSCOPY STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE MM-SOP-09 1. PURPOSE AND SCOPE To describe the procedure for counting malaria parasites on
Basic Professional Training Program for Associate Medical Technologist
 Basic Professional Training Program for Associate Medical Technologist Basic Cytology Part 2 (Preparartion and normal morphology) Normal Morphology in Liquid based Gynecologic Cytology Speaker: Mr. Fung
Basic Professional Training Program for Associate Medical Technologist Basic Cytology Part 2 (Preparartion and normal morphology) Normal Morphology in Liquid based Gynecologic Cytology Speaker: Mr. Fung
Blood Collection and Processing SOP
 Brisbane Breast Bank Blood Collection and Processing SOP Breast Pathology Laboratory University of Queensland Centre for Clinical Research Blood Collection We collect 30ml of blood from patients who have
Brisbane Breast Bank Blood Collection and Processing SOP Breast Pathology Laboratory University of Queensland Centre for Clinical Research Blood Collection We collect 30ml of blood from patients who have
12.1: The Function of Circulation page 478
 12.1: The Function of Circulation page 478 Key Terms: Circulatory system, heart, blood vessel, blood, open circulatory system, closed circulatory system, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein, aorta, atrioventricular
12.1: The Function of Circulation page 478 Key Terms: Circulatory system, heart, blood vessel, blood, open circulatory system, closed circulatory system, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein, aorta, atrioventricular
Xpert TM Karyotyping Teaching Kit
 Xpert TM Karyotyping Teaching Kit Product Code: CCK012 Contents 1. About the kit 2. Kit contents and storage instructions 3. Materials required but not provided in the kit 4. Aseptic techniques and good
Xpert TM Karyotyping Teaching Kit Product Code: CCK012 Contents 1. About the kit 2. Kit contents and storage instructions 3. Materials required but not provided in the kit 4. Aseptic techniques and good
Cell Biology Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
 Cell Biology Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Observation of cells and organelles In this lab you will be looking at an example of a Prokaryotic cell (Bacillus cereus) and a some examples of Eukaryotic
Cell Biology Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Observation of cells and organelles In this lab you will be looking at an example of a Prokaryotic cell (Bacillus cereus) and a some examples of Eukaryotic
Functions of Blood. Collects O 2 from lungs, nutrients from digestive tract, and waste products from tissues Helps maintain homeostasis
 Blood Objectives Describe the functions of blood Describe blood plasma Explain the functions of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets Summarize the process of blood clotting What is Blood?
Blood Objectives Describe the functions of blood Describe blood plasma Explain the functions of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets Summarize the process of blood clotting What is Blood?
STEP-BY-STEP INSTRUCTIONS FOR INVESTIGATIONAL USE. Rapid HCV Antibody Test FOR ORAQUICK RAPID HCV ANTIBODY TEST
 Before performing testing, all operators MUST read and become familiar with Universal Precautions for Prevention of Transmission of Human Immunodeficiency Virus, Hepatitis B Virus, and other Blood-borne
Before performing testing, all operators MUST read and become familiar with Universal Precautions for Prevention of Transmission of Human Immunodeficiency Virus, Hepatitis B Virus, and other Blood-borne
3. The Circulatory System
 3. The Circulatory System A. Introduction B. Blood 1. Circulatory system transports water, electrolytes, hormones, enzymes, antibodies, cell, gases and nutrients to all cells and carries away metabolic
3. The Circulatory System A. Introduction B. Blood 1. Circulatory system transports water, electrolytes, hormones, enzymes, antibodies, cell, gases and nutrients to all cells and carries away metabolic
BLOOD-Chp. Chp.. 6 What are the functions of blood? What is the composition of blood? 3 major types of plasma proteins
 6.1 Blood: An overview BLOOD-Chp Chp.. 6 What are the functions of blood? Transportation: oxygen, nutrients, wastes, carbon dioxide and hormones Defense: against invasion by pathogens Regulatory functions:
6.1 Blood: An overview BLOOD-Chp Chp.. 6 What are the functions of blood? Transportation: oxygen, nutrients, wastes, carbon dioxide and hormones Defense: against invasion by pathogens Regulatory functions:
1 Blood sampling and blood film preparation and examination
 BCAC01 3/20/06 15:46 Page 1 1 Blood sampling and blood film preparation and examination Obtaining a blood specimen Performing an accurate blood count and correctly interpreting a blood film require that
BCAC01 3/20/06 15:46 Page 1 1 Blood sampling and blood film preparation and examination Obtaining a blood specimen Performing an accurate blood count and correctly interpreting a blood film require that
Circulation Stations
 Circulation Stations This worksheet corresponds with stations around the classrooms. Work in groups of 3 and do the stations in any order. Name: Station 1: Blood smear under a microscope Materials: - Microscope
Circulation Stations This worksheet corresponds with stations around the classrooms. Work in groups of 3 and do the stations in any order. Name: Station 1: Blood smear under a microscope Materials: - Microscope
Hematology Reagents and Controls Our products for your critical process
 Part of a pure process Hematology Reagents and Controls Our products for your critical process 2 Reagents you can count on Mallinckrodt Baker s chemical expertise and 30 years of experience are the foundation
Part of a pure process Hematology Reagents and Controls Our products for your critical process 2 Reagents you can count on Mallinckrodt Baker s chemical expertise and 30 years of experience are the foundation
Subtypes of AML follow branches of myeloid development, making the FAB classificaoon relaovely simple to understand.
 1 2 3 4 The FAB assigns a cut off of 30% blasts to define AML and relies predominantly on morphology and cytochemical stains (MPO, Sudan Black, and NSE which will be discussed later). Subtypes of AML follow
1 2 3 4 The FAB assigns a cut off of 30% blasts to define AML and relies predominantly on morphology and cytochemical stains (MPO, Sudan Black, and NSE which will be discussed later). Subtypes of AML follow
Direct Antiglobulin Test (DAT)
 Exercise 8 Exercise 9 Direct Antiglobulin Test (DAT) Elution Study Task Aim Introduction To perform the DAT and elution procedure with correct interpretation of results. To perform with 100% accuracy the
Exercise 8 Exercise 9 Direct Antiglobulin Test (DAT) Elution Study Task Aim Introduction To perform the DAT and elution procedure with correct interpretation of results. To perform with 100% accuracy the
ABORhCard. ABORhCard Package Insert ABO and Rh Blood Grouping Device
 ABORhCard Package Insert ABO and Rh Blood Grouping Device ABORhCard Intended Use The ABORhCard is a qualitative in vitro test that provides a simultaneous ABO and Rh determination of an individual s ABO
ABORhCard Package Insert ABO and Rh Blood Grouping Device ABORhCard Intended Use The ABORhCard is a qualitative in vitro test that provides a simultaneous ABO and Rh determination of an individual s ABO
Yvette Marie Miller, M.D. Executive Medical Officer American Red Cross October 20, 2012 45 th Annual Great Lakes Cancer Nursing Conference Troy, MI
 Yvette Marie Miller, M.D. Executive Medical Officer American Red Cross October 20, 2012 45 th Annual Great Lakes Cancer Nursing Conference Troy, MI Overview of Hematology, http://www.nu.edu.sa/userfiles/mhmorsy/h
Yvette Marie Miller, M.D. Executive Medical Officer American Red Cross October 20, 2012 45 th Annual Great Lakes Cancer Nursing Conference Troy, MI Overview of Hematology, http://www.nu.edu.sa/userfiles/mhmorsy/h
Pre-Lab Questions. 1. What is cell theory? 2. What do all cells contain? 3. What is a prokaryote? 4. What is a eukaryote? 5. What is an organelle?
 Name: TOC# Background Ever since the first microscope was used, biologists have been interested in studying the cellular organization of all living things. After hundred s of years of observations by many
Name: TOC# Background Ever since the first microscope was used, biologists have been interested in studying the cellular organization of all living things. After hundred s of years of observations by many
Medical Necessity and Advanced Beneficiary Notice (ABN) Policy and Form
 Medical Necessity and Advanced Beneficiary Notice (ABN) Policy and Form Billings Clinic Laboratory believes all health-care providers should order only appropriate tests for the diagnosis and treatment
Medical Necessity and Advanced Beneficiary Notice (ABN) Policy and Form Billings Clinic Laboratory believes all health-care providers should order only appropriate tests for the diagnosis and treatment
Whole Blood Flow Cytometry
 Whole Blood Flow Cytometry y Nailin Li Department t of Medicine, i Clinical i l Pharmacology Unit Karolinska Institute/University Hospital, 171 76 Stockholm Department of Pathology & Pathophysiology Zhejiang
Whole Blood Flow Cytometry y Nailin Li Department t of Medicine, i Clinical i l Pharmacology Unit Karolinska Institute/University Hospital, 171 76 Stockholm Department of Pathology & Pathophysiology Zhejiang
Thibodeau: Anatomy and Physiology, 5/e. Chapter 17: Blood
 Thibodeau: Anatomy and Physiology, 5/e Chapter 17: Blood This chapter begins a new unit. In this unit, the first four chapters deal with transportation one of the body's vital functions. It is important
Thibodeau: Anatomy and Physiology, 5/e Chapter 17: Blood This chapter begins a new unit. In this unit, the first four chapters deal with transportation one of the body's vital functions. It is important
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 10 Blood. Short Answer. Figure 10.1
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 10 Blood Short Answer Figure 10.1 Using Figure 10.1, identify the following: 1) The neutrophil is indicated by letter. Answer: A Diff: 1 Page Ref:
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 10 Blood Short Answer Figure 10.1 Using Figure 10.1, identify the following: 1) The neutrophil is indicated by letter. Answer: A Diff: 1 Page Ref:
Hematology. Diagnostic Value of CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 22 Diagnostic Value of Hematology JAIME SAMOUR, MVZ, P hd, D ipl ECAMS Hematology is the discipline of medical science that studies the blood and blood-forming tissues, and is currently considered
CHAPTER 22 Diagnostic Value of Hematology JAIME SAMOUR, MVZ, P hd, D ipl ECAMS Hematology is the discipline of medical science that studies the blood and blood-forming tissues, and is currently considered
Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
 1 Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins Introduction Amino Acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. In class you learned the structures of the 20 common amino acids that make up proteins. All
1 Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins Introduction Amino Acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. In class you learned the structures of the 20 common amino acids that make up proteins. All
Pentra DX Nexus. Process efficiency in Hematology
 Pentra DX Nexus Process efficiency in Hematology Pentra DX Nexus Be productive and flexible 120 samples per hour 28 parameters Automatic reflex testing Automatic validation of results Integrated cytology
Pentra DX Nexus Process efficiency in Hematology Pentra DX Nexus Be productive and flexible 120 samples per hour 28 parameters Automatic reflex testing Automatic validation of results Integrated cytology
Please list four delivery functions of blood, two regulatory functions, and two protection functions. Delivery (distribution) functions
 Chapter 17 Blood Please list four delivery functions of blood, two regulatory functions, and two protection functions. Delivery (distribution) functions Names Period 1-3 - 2-4 - Regulatory functions 1-2
Chapter 17 Blood Please list four delivery functions of blood, two regulatory functions, and two protection functions. Delivery (distribution) functions Names Period 1-3 - 2-4 - Regulatory functions 1-2
EXERCISE 5: ERYTHROCYTES SEDIMENTATION RATE - ESR, SED RATE
 EXERCISE 5: ERYTHROCYTES SEDIMENTATION RATE - ESR, SED RATE Textbook: Skills: None 10 points Objectives: 1. State the principle of the Erythrocytes Sedimentation Rate - ESR. 2. List two factors which may
EXERCISE 5: ERYTHROCYTES SEDIMENTATION RATE - ESR, SED RATE Textbook: Skills: None 10 points Objectives: 1. State the principle of the Erythrocytes Sedimentation Rate - ESR. 2. List two factors which may
The Golden Rule of Specimen Collection: The Patient Test Result is Only as Good as the Sample We Get
 The Golden Rule of Specimen Collection: The Patient Test Result is Only as Good as the Sample We Get Jan Frerichs, MLS (ASCP) The University of Iowa [email protected] Importance of Phlebotomist
The Golden Rule of Specimen Collection: The Patient Test Result is Only as Good as the Sample We Get Jan Frerichs, MLS (ASCP) The University of Iowa [email protected] Importance of Phlebotomist
Laboratory No. 3 General Stool Examination (GSE) Collection of samples
 Laboratory No. 3 General Stool Examination (GSE) Collection of samples If a faecal sample is not properly collected and taken care of before examination, they will be of little or no value for accurate
Laboratory No. 3 General Stool Examination (GSE) Collection of samples If a faecal sample is not properly collected and taken care of before examination, they will be of little or no value for accurate
06-6542 n/a MYSTERY OF THE BLOOD STAIN (RE)
 DATA SHEET Order code Manufacturer code Description 06-6542 n/a MYSTERY OF THE BLOOD STAIN (RE) The enclosed information is believed to be correct, Information may change without notice due to product
DATA SHEET Order code Manufacturer code Description 06-6542 n/a MYSTERY OF THE BLOOD STAIN (RE) The enclosed information is believed to be correct, Information may change without notice due to product
Chapter 19 Ci C r i cula l t a i t o i n
 Chapter 19 Circulation A closed system Circulatory System Consisting of Heart, Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, Blood & the Lymphatic system Blood Make up The blood is made up of Plasma and three main types
Chapter 19 Circulation A closed system Circulatory System Consisting of Heart, Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, Blood & the Lymphatic system Blood Make up The blood is made up of Plasma and three main types
ABORhCard Applications and Performance Studies White Paper
 ABORhCard Applications and Performance Studies White Paper Contents Background....................................... 2 ABORhCard Simple, Accurate, Fast Blood Typing....... 2 Product Design....................................
ABORhCard Applications and Performance Studies White Paper Contents Background....................................... 2 ABORhCard Simple, Accurate, Fast Blood Typing....... 2 Product Design....................................
Minimal residual disease detection in Acute Myeloid Leukaemia on a Becton Dickinson flow cytometer
 Minimal residual disease detection in Acute Myeloid Leukaemia on a Becton Dickinson flow cytometer Purpose This procedure gives instruction on minimal residual disease (MRD) detection in patients with
Minimal residual disease detection in Acute Myeloid Leukaemia on a Becton Dickinson flow cytometer Purpose This procedure gives instruction on minimal residual disease (MRD) detection in patients with
Blood Tubes and Lancets 1-800-962-9888
 Blood Tubes and Lancets 1-800-962-9888 1-800-962-9888. Table of Contents BLOOD COLLECTION MONOJECT Blood Collection Products Safety Lancet... 4 Lancet... 4 Corvac Integrated Serum Separator Tubes Red/Grey
Blood Tubes and Lancets 1-800-962-9888 1-800-962-9888. Table of Contents BLOOD COLLECTION MONOJECT Blood Collection Products Safety Lancet... 4 Lancet... 4 Corvac Integrated Serum Separator Tubes Red/Grey
Central Line Blood Draw
 Central Line Blood Draw Welcome to the Central Line dressing blood draw refresher. Please use the navigation below to advance to the next page. The Central Line blood draw module is also available as a
Central Line Blood Draw Welcome to the Central Line dressing blood draw refresher. Please use the navigation below to advance to the next page. The Central Line blood draw module is also available as a
And Now, Presenting...
 Presentation and Handling of Clinical Laboratory Data From Test Tube to Table Randall K. Carlson, Wilmington, DE and Nate Freimark, Lakewood, NJ Omnicare Clinical Research. Inc. INTRODUCTION In human clinical
Presentation and Handling of Clinical Laboratory Data From Test Tube to Table Randall K. Carlson, Wilmington, DE and Nate Freimark, Lakewood, NJ Omnicare Clinical Research. Inc. INTRODUCTION In human clinical
Immunophenotyping peripheral blood cells
 IMMUNOPHENOTYPING Attune Accoustic Focusing Cytometer Immunophenotyping peripheral blood cells A no-lyse, no-wash, no cell loss method for immunophenotyping nucleated peripheral blood cells using the Attune
IMMUNOPHENOTYPING Attune Accoustic Focusing Cytometer Immunophenotyping peripheral blood cells A no-lyse, no-wash, no cell loss method for immunophenotyping nucleated peripheral blood cells using the Attune
EXTRACTION OF DNA FROM CALF THYMUS CELLS Revised 2/1/96 Introduction
 Revised 2/1/96 Introduction Cells may be classified into two primary types depending on whether they have a discrete nucleus (eukaryotic) or do not (prokaryotic). Prokaryotes include bacteria, such as
Revised 2/1/96 Introduction Cells may be classified into two primary types depending on whether they have a discrete nucleus (eukaryotic) or do not (prokaryotic). Prokaryotes include bacteria, such as
ArtisanLink Staining System is an automated special stains slide
 Technical Tips Tips on using the ArtisanLink Special Staining System Jamie Nowacek, BS, HT(ASCP) CM, QIHC, PMP Dako North America, Inc. Carpinteria, CA, USA ArtisanLink Staining System is an automated
Technical Tips Tips on using the ArtisanLink Special Staining System Jamie Nowacek, BS, HT(ASCP) CM, QIHC, PMP Dako North America, Inc. Carpinteria, CA, USA ArtisanLink Staining System is an automated
1. BLOOD GROUP SYSTEMS. Page 1. Haematology LECTURE 10. BLOOD GROUPS AND TRANSFUSIONS OVERVIEW. 1. Blood Group Systems
 Undergraduate Course in Veterinary Clinical PathologySocrates Programme Haematology LECTURE 10. BLOOD GROUPS AND TRANSFUSIONS 10-1 OVERVIEW 1. Blood Group Systems 2. Blood group testing and cross-matching
Undergraduate Course in Veterinary Clinical PathologySocrates Programme Haematology LECTURE 10. BLOOD GROUPS AND TRANSFUSIONS 10-1 OVERVIEW 1. Blood Group Systems 2. Blood group testing and cross-matching
What You Will Learn in This Module: Testing for Pullorum-Typhoid Disease
 Module 5-B: Testing Poultry for Pullorum-Typhoid Disease This module applies only to individuals who have attended and successfully completed an Indiana State Poultry Association NPIP Blood Testing School
Module 5-B: Testing Poultry for Pullorum-Typhoid Disease This module applies only to individuals who have attended and successfully completed an Indiana State Poultry Association NPIP Blood Testing School
RECITATION NOTES FOR EXPERIMENT # 5 A&B THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY
 RECITATION NOTES FOR EXPERIMENT # 5 A&B THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY Have your lab textbook available for quick reference to specific pages, indicated in red. BASIC PRINCIPLES OF CHROMATOGRAPHY Chromatography
RECITATION NOTES FOR EXPERIMENT # 5 A&B THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY Have your lab textbook available for quick reference to specific pages, indicated in red. BASIC PRINCIPLES OF CHROMATOGRAPHY Chromatography
37 2 Blood and the Lymphatic System Slide 1 of 34
 1 of 34 Blood is a connective tissue that contains both dissolved substances and specialized cells. 2 of 34 The functions of blood include: collecting oxygen from the lungs, nutrients from the digestive
1 of 34 Blood is a connective tissue that contains both dissolved substances and specialized cells. 2 of 34 The functions of blood include: collecting oxygen from the lungs, nutrients from the digestive
Cells. Introduction WSBCTC 1
 Cells Cells are the fundamental unit of life. All living things are composed of cells. While there are several characteristics that are common to all cells, such as the presence of a cell membrane, cytoplasm,
Cells Cells are the fundamental unit of life. All living things are composed of cells. While there are several characteristics that are common to all cells, such as the presence of a cell membrane, cytoplasm,
Explain the role of blood and bloodstain patterns in forensics science. Analyze and identify bloodstain patterns by performing bloodstain analysis
 Lab 4 Blood Learning Objectives Explain the role of blood and bloodstain patterns in forensics science Analyze and identify bloodstain patterns by performing bloodstain analysis Introduction Blood, a
Lab 4 Blood Learning Objectives Explain the role of blood and bloodstain patterns in forensics science Analyze and identify bloodstain patterns by performing bloodstain analysis Introduction Blood, a
AURAMINE O STAIN. Preanalytical Considerations
 AURAMINE O STAIN Preanalytical Considerations I. PRINCIPLE Acid-fast mycobacteria resist decolorization by acid-alcohol after primary staining owing to the high lipid (mycolic acid) content in their cell
AURAMINE O STAIN Preanalytical Considerations I. PRINCIPLE Acid-fast mycobacteria resist decolorization by acid-alcohol after primary staining owing to the high lipid (mycolic acid) content in their cell
ILLINOIS DEPARTMENT OF CENTRAL MANAGEMENT SERVICES CLASS SPECIFICATION CLINICAL LABORATORY TECHNICIAN SERIES
 ILLINOIS DEPARTMENT OF CENTRAL MANAGEMENT SERVICES CLASS SPECIFICATION CLINICAL LABORATORY TECHNICIAN SERIES CLASS TITLE POSITION CODE CLINICAL LABORATORY TECHNICIAN I 08215 CLINICAL LABORATORY TECHNICIAN
ILLINOIS DEPARTMENT OF CENTRAL MANAGEMENT SERVICES CLASS SPECIFICATION CLINICAL LABORATORY TECHNICIAN SERIES CLASS TITLE POSITION CODE CLINICAL LABORATORY TECHNICIAN I 08215 CLINICAL LABORATORY TECHNICIAN
For in vitro preparation of human mononuclear cells from peripheral blood, bone marrow, and umbilical cord blood. Not for in vitro diagnostic use.
 GE Healthcare Instructions 28-4039-56 AA Cell Preparation Media Ficoll-Paque PREMIUM Intended use For in vitro preparation of human mononuclear cells from peripheral blood, bone marrow, and umbilical cord
GE Healthcare Instructions 28-4039-56 AA Cell Preparation Media Ficoll-Paque PREMIUM Intended use For in vitro preparation of human mononuclear cells from peripheral blood, bone marrow, and umbilical cord
Cytology of Lymph Nodes
 Indications Cytology of Lymph Nodes Lymph node enlargement That was easy Mary Anna Thrall Don Meuten Indications Lymph node enlargement Suspect metastasis Normal sized lymph nodes are Normal Do NOT aspirate
Indications Cytology of Lymph Nodes Lymph node enlargement That was easy Mary Anna Thrall Don Meuten Indications Lymph node enlargement Suspect metastasis Normal sized lymph nodes are Normal Do NOT aspirate
5.0 EXPERIMENT ON DETERMINATION OF TOTAL HARDNESS
 5.0 EXPERIMENT ON DETERMINATION OF TOTAL HARDNESS Sl. No. Contents Preamble 5.1 Aim 5.2 Introduction 5.2.1 Environmental Significance 5.3 Principle 5.4 Materials Required 5.4.1 Apparatus Required 5.4.2
5.0 EXPERIMENT ON DETERMINATION OF TOTAL HARDNESS Sl. No. Contents Preamble 5.1 Aim 5.2 Introduction 5.2.1 Environmental Significance 5.3 Principle 5.4 Materials Required 5.4.1 Apparatus Required 5.4.2
Reference Range: 0.5-1.6 mmol/l (arterial) 0.7-2.1 mmol/l (venous) CPT Code: 83605
 LACTIC ACID Fasting, arterial specimen preferred. Please note whether arterial or venous. 0.5 ml heparinized plasma. Green top or PST must be drawn, placed on ice, and spun within 15 minutes. Immediately
LACTIC ACID Fasting, arterial specimen preferred. Please note whether arterial or venous. 0.5 ml heparinized plasma. Green top or PST must be drawn, placed on ice, and spun within 15 minutes. Immediately
Blood. Blood. Blood Composition. Blood Composition. Fractionation & Hemopoesis
 Blood Blood Chapter 19 Blood is a specialized fluid connective tissue that contains cells suspended in a fluid matrix Functions of blood include: Transport of dissolved gases, nutrients, hormones and metabolic
Blood Blood Chapter 19 Blood is a specialized fluid connective tissue that contains cells suspended in a fluid matrix Functions of blood include: Transport of dissolved gases, nutrients, hormones and metabolic
EVALUATING BLOOD FILMS
 Idea Exchange Mind Over Miller 2004 Annual Index Clinical Solutions for Companion-Animal Practitioners www.vetmedpub.com DECEMBER 2004 EVALUATING BLOOD FILMS Take 3 minutes to bring abnormalities to light
Idea Exchange Mind Over Miller 2004 Annual Index Clinical Solutions for Companion-Animal Practitioners www.vetmedpub.com DECEMBER 2004 EVALUATING BLOOD FILMS Take 3 minutes to bring abnormalities to light
