Novel Rheumatoid Arthritis Susceptibility Locus at 22q12 Identified in an Extended UK Genome-Wide Association Study
|
|
|
- Winifred Allison
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY Vol. 66, No. 1, January 2014, pp DOI /art The Authors. Arthritis & Rheumatology is published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of the American College of Rheumatology. This is an open access article under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs License, which permits use and distribution in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited, the use is non-commercial and no modifications or adaptations are made. Novel Rheumatoid Arthritis Susceptibility Locus at 22q12 Identified in an Extended UK Genome-Wide Association Study Gisela Orozco, 1 Sebastien Viatte, 1 John Bowes, 1 Paul Martin, 1 Anthony G. Wilson, 2 Ann W. Morgan, 3 Sophia Steer, 4 Paul Wordsworth, 5 Lynne J. Hocking, 6 UK Rheumatoid Arthritis Genetics Consortium, Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium, Biologics in Rheumatoid Arthritis Genetics and Genomics Study Syndicate Consortium, Anne Barton, 1 Jane Worthington, 1 and Stephen Eyre 1 Objective. The number of confirmed rheumatoid arthritis (RA) loci currently stands at 32, but many lines of evidence indicate that expansion of existing genomewide association studies (GWAS) enhances the power to detect additional loci. This study was undertaken to Funding to generate the genome-wide association study data was provided by Arthritis Research UK (grant 17552), Sanofi-Aventis, and the European Union Seventh Framework Programme (project POCEMON; FP7-ICT ). Genotyping was performed at the University of Milan. Dr. Orozco s work was supported by the Wellcome Trust (Research Career Development Fellowship / Z/11/A). Dr. Viatte s work was supported by the Swiss Foundation for Medical-Biological Scholarships, which is managed by the Swiss National Science Foundation (SSMBS grant PASMP3_134380, funded by a donation from Novartis to the Foundation). 1 Gisela Orozco, PhD, Sebastien Viatte, MD, PhD, John Bowes, PhD, Paul Martin, MPhil, Anne Barton, PhD, FRCP, Jane Worthington, PhD, Stephen Eyre, PhD: Arthritis Research UK Epidemiology Unit, Centre for Musculoskeletal Research, Institute of Inflammation and Repair, University of Manchester, and NIHR Manchester Musculoskeletal Biomedical Research Unit, Manchester Academic Health Science Centre, Manchester, UK; 2 Anthony G. Wilson, MB, PhD, FRCP: University of Sheffield, Sheffield, UK; 3 Ann W. Morgan, PhD, FRCP: University of Leeds, Leeds, UK; 4 Sophia Steer, PhD, MRCP: Kings College Hospital National Health Service Foundation Trust, London, UK; 5 Paul Wordsworth, MA, MB, BS, FRCP: NIHR Oxford Musculoskeletal Research Unit and Botnar Research Centre, Nuffield Orthopaedic Centre, Oxford, UK; 6 Lynne J. Hocking, PhD: University of Aberdeen, Aberdeen, UK. Dr. Martin has received consulting fees, speaking fees, and/or honoraria from Eli Lilly, Pfizer, AbbVie, and Merck (less than $10,000 each). Address correspondence to Stephen Eyre, PhD, University of Manchester, Arthritis Research UK Epidemiology Unit, Centre for Musculoskeletal Research, Institute of Inflammation and Repair, Manchester Academic Health Science Centre, Stopford Building, Oxford Road, Manchester M13 9PT, UK. stephen.eyre@ manchester.ac.uk. Submitted for publication August 22, 2012; accepted in revised form September 10, extend our previous RA GWAS in a UK cohort, adding more independent RA cases and healthy controls, with the aim of detecting novel association signals for susceptibility to RA in a homogeneous UK cohort. Methods. A total of 3,223 UK RA cases and 5,272 UK controls were available for association analyses, with the extension adding 1,361 cases and 2,334 controls to the original GWAS data set. The genotype data for all RA cases were imputed using the Impute program version 2. After stringent quality control thresholds were applied, 3,034 cases and 5,271 controls (1,831,729 single-nucleotide polymorphisms [SNPs]) were available for analysis. Association testing was performed using Plink software. Results. The analyses indicated a suggestive association with susceptibility to RA (P < ) for 6 novel RA loci that have been previously found to be associated with other autoimmune diseases; these 6 SNPs were genotyped in independent samples. Two of the associated loci were validated, one of which was associated with RA at genome-wide levels of significance in the combined analysis, identifying a novel RA locus at 22q12 (P ). In addition, most of the previously known RA susceptibility loci were confirmed to be associated with RA, and for 16 of the loci, the strength of the association was increased. Conclusion. This study identified a new RA locus mapping to 22q12. These results support the notion that increasing the power of GWAS enhances novel gene discovery. Understanding the genetic component of susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis (RA) will increase our 24
2 NEW RA RISK LOCUS AT 22q12 25 Table 1. Previously confirmed rheumatoid arthritis (RA) loci association results in the original WTCCC association analysis and the expanded UK RA GWAS* WTCCC study Expanded UK RA GWAS Chr. SNP Gene Proxy P OR (95% CI) Proxy P OR (95% CI) 1 rs TNFRSF ( ) ( ) 1 rs PTPN22 rs ( ) ( ) 1 rs CD2, CD ( ) rs ( ) 1 rs FCGR2A ( ) ( ) 1 rs PTPRC ( ) ( ) 2 rs REL None rs ( ) 2 rs SPRED ( ) ( ) 2 rs AFF3 rs ( ) rs ( ) 2 rs STAT4 rs ( ) rs ( ) 2 rs CD ( ) ( ) 2 rs CTLA ( ) ( ) 3 rs PXK ( ) None 4 rs RBPJ None rs ( ) 4 rs IL2, IL21 None rs ( ) 5 rs ANKRD55, ( ) None IL6ST 5 rs26232 C5orf30 rs ( ) rs ( ) 6 rs HLA DRB1 rs ( ) rs ( ) 6 rs PRDM ( ) ( ) 6 rs TNFAIP ( ) ( ) 6 rs TAGAP ( ) None 6 rs CCR6 rs (1 1.18) rs ( ) 7 rs IRF5 rs ( ) ( ) 8 rs BLK ( ) (1 1.15) 9 rs CCL ( ) None 9 rs TRAF1, C ( ) ( ) 10 rs IL2RA ( ) ( ) 10 rs PRKCQ ( ) ( ) 11 rs TRAF ( ) rs ( ) 12 rs KIF5A ( ) ( ) 20 rs CD ( ) rs ( ) 22 rs IL2RB ( ) ( ) * WTCCC Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium; GWAS genome-wide association study; Chr. chromosome; SNP single-nucleotide polymorphism; OR odds ratio; 95% CI 95% confidence interval. knowledge of the disease process and has the potential to inform new approaches to disease management. For example, the identification of disease-associated genetic variations, which are presumed to cause modified immune responses and precede the onset of disease symptoms, could inform stratification of patients into more phenotypically homogeneous subgroups and provide testable hypotheses regarding response to treatment. The use of genome-wide association studies (GWAS) has been remarkably successful in locating novel genetic loci associated with RA, and there are now more than 30 gene regions that have been confirmed as RA susceptibility loci, but, in total, they account for fewer than 50% of the total genetic heritability (1,2). It is likely that there are more common variants of small effect size that could be identified by increasing the power of the GWAS through the use of larger sample sizes. Indeed, this approach has been used successfully in a number of autoimmune diseases, such as type 1 diabetes (3) and inflammatory bowel disease (4,5), resulting in a more complete picture of the genetic background. In the present study, we used the data set from an RA GWAS in the UK (6) and increased the sample sizes of the RA cases and healthy controls by 75% and 80%, respectively. With this extended data set, together with the data obtained in a validation study of the UK cohort, we were able to discover potential novel RA risk loci in the UK population. This study constitutes the largest UK-only GWAS to date, and the results will enhance the power to investigate whether population heterogeneity exists, i.e., whether different genes are associated with RA in different populations. PATIENTS AND METHODS Genotype data were available for 1,862 RA cases and 2,938 controls from the original Wellcome Trust Case Control
3 26 OROZCO ET AL Consortium (WTCCC) study (6); these genotypes were obtained using the Affymetrix 500K array. Together with this data set, we added GWAS genotype data for a further 2,334 UK controls and 1,361 UK RA cases (sample call rate 95%). The additional samples were from 5 different studies, with genotypes obtained using a range of GWAS arrays. Members of the WTCCC, UK Rheumatoid Arthritis Genetics Group, and Biologics in Rheumatoid Arthritis Genetics and Genomics Study Syndicate Consortiums and details on the platforms used are given in the Supplementary Materials and Supplementary Table 1, available on the Arthritis & Rheumatology web site at Since each GWAS array contains different singlenucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), the first stage of the current study was to impute genotypes to generate data for a common set of SNPs, thus allowing combined analysis of the data from the 5 different studies. The genotypes of the patients in each RA case cohort were imputed using the Impute program (version 2) (7), based on 2 reference panels, the 1000 Genomes Project pilot data and HapMap3. The genotypes of control subjects were imputed using the same 1000 Genomes Project reference panel, with imputation performed using MaCH software (8). Stringent quality control (QC) thresholds were applied to individual cohorts and then to the merged data set (see Supplementary Figure 1, available on the Arthritis & Rheumatology web site at /art.38196/abstract). Self-reported information on each subject s ethnicity was used to exclude non-caucasians from the analyses. Identity-by-descent analysis was performed in Plink statistical software. Pairs of samples with genome identity (pi-hat values) greater than 0.9 were reported to be duplicate samples, and those with pi-hat values greater than 0.2 were considered to be closely related. Case and control genotype data were compared using logistic regression, performed in Plink (9). Novel SNPs not previously found to be associated with RA in the UK population were selected for validation if the association P value was less than , and if the region had been previously found to be associated with another autoimmune disease. The SNPs satisfying these criteria were genotyped in independent UK samples (4,726 cases and 2,625 controls), using Sequenom technology. Additional control data were available using non autoimmune disease cases (n 7,670) from the WTCCC study (6). A regional association plot for the 22q12 locus was created using LocusZoom ( locuszoom/). Bioinformatics analysis was performed using publicly available functional annotation files ( ucsc.edu/) and our own custom query SQL-code (Assimilator; available at assimilator.pl) (10). RESULTS Forty-two duplicate samples were removed after identity-by-descent analysis. There were 14 pairs of individual samples with pi-hat values greater than 0.2, and thus 1 sample from each pair was removed due to possible relatedness. A total of 1,831,729 SNPs passed Figure 1. Manhattan plots showing P values for genetic association with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in the original Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium genome-wide association study (GWAS) (a) and the expanded UK GWAS (b). Panels are truncated at a log 10 P value of 35. Single-nucleotide polymorphisms having an association with RA at genome-wide levels of significance are shown above the horizontal red line. QC and were included in the association analysis. In the expanded GWAS, 3,034 RA cases and 5,271 controls passed QC. The genetic inflation factor lambda ( GC ) was 1.06, implying that there was a low possibility of falsepositive associations attributable to population stratification, genotyping errors, or other artifacts. For most of the previously known RA susceptibility loci (2), we confirmed their association with RA in the present study (Table 1). Interestingly, when compared to the original WTCCC study (6), the extended RA GWAS showed that the strength of the association with RA susceptibility was increased for 16 of the loci in the UK population (TNFAIP3, STAT4, PTPN22, HLA DRB1, PTPRC, IL2/ IL21, C5orf30, CD247, CTLA4, RBPJ, PRDM1, CCR6, IRF5, TRAF6, KIF5A, and CD28). For example, the association of TNFAIP3 with RA risk reached genomewide levels of significance in this expansion of the WTCCC analysis, and the robustly validated locus STAT4, for which no significant association had been found in the original WTCCC study, was found to be associated with RA in the present study (Figure 1). Similar to the findings in the original WTCCC study, some of the known RA loci (CD40, REL, SPRED2, BLK, and TRAF1/C5) were not found to have an association with RA in the present study. Finally, no proxies were available for 4 of the known RA loci. Six of the SNPs with suggestive evidence of association with RA in the present study and with additional evidence of association in other studies were selected for validation analysis (Table 2). Evidence of an association with susceptibility to RA was found for rs (on chromosome 22q12) in this validation study (P ), and the association exceeded
4 NEW RA RISK LOCUS AT 22q12 27 Table 2. Candidate rheumatoid arthritis (RA) susceptibility loci previously associated with other autoimmune diseases and showing suggestive evidence of association with RA in the expanded UK RA GWAS* Expanded UK RA GWAS Validation study Chr. SNP Locus MAF MAF Combined analysis Assoicated autoimmune disease RA Controls P OR (95% CI) Proxy/ comment RA Controls P OR (95% CI) P OR (95% CI) 7 rs SNX10 T1D, IBD ( ) Failed QC 11 rs CXCR5 PBC ( ) ( ) ( ) 12 rs YAF2 MS ( ) rs ( ) ( ) 16 rs CNTAP4 T1D ( ) rs ( ) 19 rs CDC37 IBD ( ) rs ( ) ( ) 22 rs GATSL3 CD, T1D ( ) ( ) ( ) * Associations were identified at the significance level of P Chr. chromosome; MAF minor allele frequency; T1D type 1 diabetes; IBD inflammatory bowel disease; QC quality control; PBC primary biliary cirrhosis; MS multiple sclerosis; CD celiac disease. Corrected P values (corrected for genetic inflation factor lambda) were as follows: for rs , P ; for rs , P ; for rs , P ; for rs , P ; for rs , P ; for rs , P Association results in the original Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium study were as follows: for rs , P , odds ratio (OR) 0.74 (95% confidence interval [95% CI] ); for rs , P 0.02, OR 0.88 (95% CI ); for rs , P , OR 0.83 (95% CI ); for rs , P , OR 0.80 (95% CI ); for rs , P , OR 0.87 (95% CI ); for rs , P , OR 0.81 (95% CI ). Single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) rs was not present in the expanded UK RA genome-wide association study (GWAS) data set, and therefore combined analysis of this SNP could not be performed.
5 28 OROZCO ET AL Figure 2. Regional plot of association with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) at chromosome 22q12. The P values for association ( log 10 values) of each single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) are plotted against their physical position on chromosome 22 (top panel). Estimated recombination rates from the 1000 Genomes Project population show the local linkage disequilibrium (LD) structure (middle panel). Different colors indicate the LD of each SNP with rs , based on pairwise r 2 values from the 1000 Genomes Project. Gene annotations are shown in the lower panel. genome-wide significance thresholds in the combined analysis (P ) (Figure 2). A SNP on chromosome 11, near CXCR5 and in strong linkage disequilibrium (LD) (r 2 0.9) with a SNP previously associated with RA at genome-wide significance levels (11), was also associated with RA in the validation cohort (P 0.02), and there was suggestive evidence of association in the combined analysis (P ). In further analyses, we interrogated publicly available functional annotation data (10,12) and found evidence to indicate that rs and its correlated SNPs (r 2 0.8) may have regulatory activity in RA. First, the SNP alleles were found to be associated with expression levels of the SF3A1 gene (which encodes subunit 1 of the splicing factor 3a protein complex) ( (Mangravite LM, et al: unpublished observations). Second, several of the SNPs map to sites of transcription factor binding, histone modification, and open chromatin (Table 3), suggesting that these SNPs could influence gene transcription. We then stratified the expanded UK GWAS and validation data sets according to the presence or absence of anti cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-ccp) antibodies in RA patients. The proportion of anti-ccp positive RA patients in the original WTCCC study, expanded UK GWAS, and validation study was 79%, 73.5%, and 67%, respectively. SNP rs was significantly associated with both anti-ccp positive RA and anti-ccp negative RA. In contrast, SNP rs was associated with anti-ccp positive RA only (see Supplementary Table 2, available on the Arthritis & Rheumatology web site at art.38196/abstract). Similar results were obtained when patients were stratified by the presence of rheumatoid Table 3. SNP Potential regulatory role of the rheumatoid arthritis associated single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) rs and its proxies* Relative location Gene Transcribed region Histone modifications TFBS DNase I HS FAIRE CTCF binding rs GATSL3 Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes rs Exonic, 3 -UTR GATSL3 Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes rs GATSL3 Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes rs Intronic TBC1D10A Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes rs Intronic TBC1D10A Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes rs Intronic TBC1D10A Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes rs SF3A1 Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes rs10376 Exonic, 3 -UTR SF3A1 Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes rs Intronic SF3A1 Yes Yes Yes Yes rs Intronic SF3A1 Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes rs Intronic SF3A1 Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes rs Intronic SF3A1 Yes Yes Yes rs Intronic SF3A1 Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes rs Intronic SF3A1 Yes Yes Yes rs Intronic CCDC157 Yes Yes Yes rs Intronic CCDC157 Yes Yes Yes Yes rs CCDC157 Yes Yes Yes Yes * Proxies of rs were correlated at r Results are the summary output from the Assimilator bioinformatics analysis. TFBS transcription factor binding site; HS hypersensitive sites; FAIRE open chromatin by formaldehyde-assisted isolation of regulatory elements; CTCF CCCTC binding factor; eqtl expression quantitative trait loci; 3 -UTR 3 -untranslated region. eqtl
6 NEW RA RISK LOCUS AT 22q12 29 factor (see Supplementary Table 3, available on the Arthritis & Rheumatology web site at onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/ /art.38196/abstract). DISCUSSION In this study, we discovered a new RA risk locus on chromosome 22q12, rs , for which the association with susceptibility to RA reached genome-wide levels of significance (combined P ). This locus has previously been associated with other autoimmune diseases, including type 1 diabetes (3) and inflammatory bowel disease (5,13). The SNP lies within a gene of unknown function, GATSL3. It will be interesting to better fine-map this region in RA, as well as in other autoimmune diseases, to help determine which gene is causal. Using bioinformatics analysis, we showed that rs and its correlated SNPs have potential regulatory activity. Interestingly, evidence suggests that these SNPs act as expression quantitative trait loci for the SF3A1 gene. SFA1 is involved in messenger RNA splicing, but the particular role that this gene might have in the pathogenesis of RA has not yet been explored. Further functional studies will be required to determine which of the SNPs is causal and to elucidate the mechanisms of action of each SNP. Of the remaining SNPs tested in the validation samples, evidence of increased strength of the association with susceptibility to RA was found only for rs on chromosome 11q23 (combined P ). This SNP maps 5 to the CXCR5 gene, which is a chemokine involved in B cell migration and localization, and has previously been associated with primary biliary cirrhosis (14). Different SNPs in the same region have been found to be associated with multiple sclerosis (15) and RA (11). The SNP identified as being significantly associated with RA and celiac disease in a combined analysis, rs , is adjacent to the gene DDX6, and although it is 130 kb from rs , the 2 SNPs are strongly correlated (r 2 0.9). Therefore, which of these 2 strong candidate genes will ultimately be found to be causal requires further fine-mapping and functional studies. The added power provided by this study strengthens the evidence for an association with RA for 16 loci that were already confirmed to be associated with RA in the UK population (2). The most striking findings supporting an association with RA within the UK population, as evidenced by an increase in the significance of the association from the original WTCCC study to the expanded GWAS, were seen for the loci at PTPRC (increasing from P to P ), TNFAIP3 (increasing from P to P ), and KIF5A (increasing from P to P ). RBPJ, not available for analysis in the original WTCCC study, showed evidence of a strong association with RA in this expanded GWAS (P ). There was little evidence of an association with other previously confirmed RA loci in this expanded UK data set, including FCGR2A, REL, SPRED2, CTLA4, BLK, TRAF1, and CD40. This could be attributed to a number of factors, but the most likely explanation is that the current study was underpowered to detect such associations. Although we performed a relatively large discovery study, the power to detect all of the associations was limited (average power across SNPs with a minor allele frequency 5% was 47% for an odds ratio [OR] of 1.1, and 90% for an OR of 1.2), and therefore failure to detect a signal could simply be the result of stochastic variations leading to a false-negative result. Indeed, it is well established that even the most strongly associated signals across multiple diseases are not found to be consistently associated in all cohorts, and often an accumulation of evidence is required in many thousands of samples. In this regard, a recent meta-analysis failed to detect the association between the 22q12 locus and RA that we identified in the current study (for rs929454, P 0.63, r for LD with rs ) (2). Interestingly, most of the confirmed RA loci for which we did not find any association with RA in the expanded UK data set (FCGR2A, REL, SPRED2, CTLA4, BLK, TRAF1, and CD40) were found to have an association with anti-ccp positive RA, but not anti- CCP negative RA, in a recent study, which was the largest anti-ccp stratified RA sample size studied to date (16). We found very modest evidence of association with anti-ccp positive RA for only 2 of the abovementioned variants (P 0.03 for FCGR2A, and P 0.03 for BLK), and therefore it is likely that the present study was underpowered to detect serotype-specific effects at these RA loci. This study has added to the argument that increasing the size, and consequently the power, of RA GWAS can prove fruitful in the discovery of novel genes. Increasing the number of known disease loci will facilitate the estimation of disease risk, potentially allowing early intervention in high-risk groups, possibly informing prognosis, and, ultimately, aiding in the discovery of novel targets for pharmacologic therapy. Future work will involve adding this new extended UK data to existing meta-analyses of RA case data with the aim of
7 30 OROZCO ET AL expanding our knowledge of the common genetic variants predisposing to RA. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS We would like to thank Edward Flynn for preparing and genotyping the UK Rheumatoid Arthritis Group samples. We thank Eleftheria Zeggini for providing the imputed data for healthy controls. AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS All authors were involved in drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content, and all authors approved the final version to be published. Dr. Eyre had full access to all of the data in the study and takes responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis. Study conception and design. Orozco, Wilson, Barton, Worthington, Eyre. Acquisition of data. Orozco, Steer, Wordsworth, Hocking. Analysis and interpretation of data. Orozco, Viatte, Bowes, Martin, Morgan, Barton, Eyre. REFERENCES 1. Orozco G, Barton A. Update on the genetic risk factors for rheumatoid arthritis. Expert Rev Clin Immunol 2010;6: Stahl EA, Raychaudhuri S, Remmers EF, Xie G, Eyre S, Thomson BP, et al. Genome-wide association study meta-analysis identifies seven new rheumatoid arthritis risk loci. Nat Genet 2010;42: Barrett JC, Clayton DG, Concannon P, Akolkar B, Cooper JD, Erlich HA, et al. Genome-wide association study and meta-analysis find that over 40 loci affect risk of type 1 diabetes. Nat Genet 2009;41: Anderson CA, Boucher G, Lees CW, Franke A, D Amato M, Taylor KD, et al. Meta-analysis identifies 29 additional ulcerative colitis risk loci, increasing the number of confirmed associations to 47. Nat Genet 2011;43: Franke A, McGovern DP, Barrett JC, Wang K, Radford-Smith GL, Ahmad T, et al. Genome-wide meta-analysis increases to 71 the number of confirmed Crohn s disease susceptibility loci. Nat Genet 2010;42: Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium. Genome-wide association study of 14,000 cases of seven common diseases and 3,000 shared controls. Nature 2007;447: Howie BN, Donnelly P, Marchini J. A flexible and accurate genotype imputation method for the next generation of genomewide association studies. PLoS Genet 2009;5:e Li Y, Willer CJ, Ding J, Scheet P, Abecasis GR. MaCH: using sequence and genotype data to estimate haplotypes and unobserved genotypes. Genet Epidemiol 2010;34: Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K, Thomas L, Ferreira MA, Bender D, et al. PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet 2007; 81: Martin P, Barton A, Eyre S. ASSIMILATOR: a new tool to inform selection of associated genetic variants for functional studies. Bioinformatics 2011;27: Zhernakova A, Stahl EA, Trynka G, Raychaudhuri S, Festen EA, Franke L, et al. Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies in celiac disease and rheumatoid arthritis identifies fourteen non-hla shared loci. PLoS Genet 2011;7:e ENCODE Project Consortium. The ENCODE (ENCyclopedia Of DNA Elements) Project. Science 2004;306: Imielinski M, Baldassano RN, Griffiths A, Russell RK, Annese V, Dubinsky M, et al. Common variants at five new loci associated with early-onset inflammatory bowel disease. Nat Genet 2009;41: Mells GF, Floyd JA, Morley KI, Cordell HJ, Franklin CS, Shin SY, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies 12 new susceptibility loci for primary biliary cirrhosis. Nat Genet 2011;43: Sawcer S, Hellenthal G, Pirinen M, Spencer CC, Patsopoulos NA, Moutsianas L, et al. Genetic risk and a primary role for cellmediated immune mechanisms in multiple sclerosis. Nature 2011; 476: Viatte S, Plant D, Bowes J, Lunt M, Eyre S, Barton A, et al. Genetic markers of rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility in anticitrullinated peptide antibody negative patients. Ann Rheum Dis 2012;71:
Identification of BACH2 and RAD51B as Rheumatoid Arthritis Susceptibility Loci in a Meta-Analysis of Genome-Wide Data
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 65, No. 12, December 2013, pp 3058 3062 DOI 10.1002/art.38183 2013 The Authors. Arthritis & Rheumatism is published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of the American College
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 65, No. 12, December 2013, pp 3058 3062 DOI 10.1002/art.38183 2013 The Authors. Arthritis & Rheumatism is published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of the American College
ARC Epidemiology Unit, The University of Manchester, Manchester 2. Norfolk Arthritis Register, Norfolk 3. Norwich University Hospital, Norwich, UK
 LUCRĂRI ORIGINALE THE ROLE OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS GENETIC SUSCEPTIBILITY MARKERS IN THE PREDICTION OF EROSIVE DISEASE IN PATIENTS WITH EARLY INFLAMMATORY POLYARTHRITIS: RESULTS FROM THE NORFOLK ARTHRITIS
LUCRĂRI ORIGINALE THE ROLE OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS GENETIC SUSCEPTIBILITY MARKERS IN THE PREDICTION OF EROSIVE DISEASE IN PATIENTS WITH EARLY INFLAMMATORY POLYARTHRITIS: RESULTS FROM THE NORFOLK ARTHRITIS
Women s Hospital and The Broad Institute, Boston, Massachusetts; 3 Doyt L. Conn, MD: Emory University, Atlanta, Georgia; 4 Beth L.
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 62, No. 12, December 2010, pp 3547 3553 DOI 10.1002/art.27732 2010, American College of Rheumatology Most Common Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms Associated With Rheumatoid Arthritis
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 62, No. 12, December 2010, pp 3547 3553 DOI 10.1002/art.27732 2010, American College of Rheumatology Most Common Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms Associated With Rheumatoid Arthritis
Genetics of Rheumatoid Arthritis Markey Lecture Series
 Genetics of Rheumatoid Arthritis Markey Lecture Series Al Kim akim@dom.wustl.edu 2012.09.06 Overview of Rheumatoid Arthritis Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) Autoimmune disease primarily targeting the synovium
Genetics of Rheumatoid Arthritis Markey Lecture Series Al Kim akim@dom.wustl.edu 2012.09.06 Overview of Rheumatoid Arthritis Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) Autoimmune disease primarily targeting the synovium
Recent advances in the genetics of rheumatoid arthritis Soumya Raychaudhuri
 Recent advances in the genetics of rheumatoid arthritis Soumya Raychaudhuri Division of Rheumatology, Immunology, and Allergy, Brigham and Women s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts, USA Correspondence to
Recent advances in the genetics of rheumatoid arthritis Soumya Raychaudhuri Division of Rheumatology, Immunology, and Allergy, Brigham and Women s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts, USA Correspondence to
GENETIC STUDIES OF AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES. Benedicte Alexandre Lie Institute of Immunology Rikshospitalet University Hospital
 GENETIC STUDIES OF AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES Benedicte Alexandre Lie Institute of Immunology Rikshospitalet University Hospital Autoimmune diseases Affects approximately 5 % of the population Results from an
GENETIC STUDIES OF AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES Benedicte Alexandre Lie Institute of Immunology Rikshospitalet University Hospital Autoimmune diseases Affects approximately 5 % of the population Results from an
The Functional but not Nonfunctional LILRA3 Contributes to Sex Bias in Susceptibility and Severity of ACPA-Positive Rheumatoid Arthritis
 The Functional but not Nonfunctional LILRA3 Contributes to Sex Bias in Susceptibility and Severity of ACPA-Positive Rheumatoid Arthritis Yan Du Peking University People s Hospital 100044 Beijing CHINA
The Functional but not Nonfunctional LILRA3 Contributes to Sex Bias in Susceptibility and Severity of ACPA-Positive Rheumatoid Arthritis Yan Du Peking University People s Hospital 100044 Beijing CHINA
Globally, about 9.7% of cancers in men are prostate cancers, and the risk of developing the
 Chapter 5 Analysis of Prostate Cancer Association Study Data 5.1 Risk factors for Prostate Cancer Globally, about 9.7% of cancers in men are prostate cancers, and the risk of developing the disease has
Chapter 5 Analysis of Prostate Cancer Association Study Data 5.1 Risk factors for Prostate Cancer Globally, about 9.7% of cancers in men are prostate cancers, and the risk of developing the disease has
Association of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) with chronic plaque type psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis
 Arch Dermatol Res (2016) 308:201 205 DOI 10.1007/s00403-016-1620-4 CONCISE COMMUNICATION Association of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) with chronic plaque type psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis Rh. Ll. Smith
Arch Dermatol Res (2016) 308:201 205 DOI 10.1007/s00403-016-1620-4 CONCISE COMMUNICATION Association of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) with chronic plaque type psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis Rh. Ll. Smith
Genetic Risk Factors for Rheumatoid Arthritis Differ in Caucasian and Korean Populations
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 60, No. 2, February 2009, pp 364 371 DOI 10.1002/art.24245 2009, American College of Rheumatology Genetic Risk Factors for Rheumatoid Arthritis Differ in Caucasian and Korean
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 60, No. 2, February 2009, pp 364 371 DOI 10.1002/art.24245 2009, American College of Rheumatology Genetic Risk Factors for Rheumatoid Arthritis Differ in Caucasian and Korean
Heritability: Twin Studies. Twin studies are often used to assess genetic effects on variation in a trait
 TWINS AND GENETICS TWINS Heritability: Twin Studies Twin studies are often used to assess genetic effects on variation in a trait Comparing MZ/DZ twins can give evidence for genetic and/or environmental
TWINS AND GENETICS TWINS Heritability: Twin Studies Twin studies are often used to assess genetic effects on variation in a trait Comparing MZ/DZ twins can give evidence for genetic and/or environmental
Autoimmunity and immunemediated. FOCiS. Lecture outline
 1 Autoimmunity and immunemediated inflammatory diseases Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails Genetics of autoimmune diseases Therapeutic
1 Autoimmunity and immunemediated inflammatory diseases Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails Genetics of autoimmune diseases Therapeutic
Collaborative Association Study of Psoriasis. Gonçalo Abecasis, Anne Bowcock, James Elder, Jerry Krueger
 Collaborative Association Study of Psoriasis Gonçalo Abecasis, Anne Bowcock, James Elder, Jerry Krueger Psoriasis Chronic, inflammatory skin condition Characteristic lesions, can affect substantial proportion
Collaborative Association Study of Psoriasis Gonçalo Abecasis, Anne Bowcock, James Elder, Jerry Krueger Psoriasis Chronic, inflammatory skin condition Characteristic lesions, can affect substantial proportion
Predicting The Risk Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Predicting The Risk Of Rheumatoid Arthritis Modelling Genetic And Environmental Risk Factors Ian Scott Arthritis Research UK Clinical Research Fellow Declaration Of Interests: No Competing Interests Describe
Predicting The Risk Of Rheumatoid Arthritis Modelling Genetic And Environmental Risk Factors Ian Scott Arthritis Research UK Clinical Research Fellow Declaration Of Interests: No Competing Interests Describe
Combining Data from Different Genotyping Platforms. Gonçalo Abecasis Center for Statistical Genetics University of Michigan
 Combining Data from Different Genotyping Platforms Gonçalo Abecasis Center for Statistical Genetics University of Michigan The Challenge Detecting small effects requires very large sample sizes Combined
Combining Data from Different Genotyping Platforms Gonçalo Abecasis Center for Statistical Genetics University of Michigan The Challenge Detecting small effects requires very large sample sizes Combined
A Genetic Analysis of Rheumatoid Arthritis
 A Genetic Analysis of Rheumatoid Arthritis Introduction to Rheumatoid Arthritis: Classification and Diagnosis Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disorder that affects mainly synovial joints.
A Genetic Analysis of Rheumatoid Arthritis Introduction to Rheumatoid Arthritis: Classification and Diagnosis Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disorder that affects mainly synovial joints.
ESF-Sponsored International Myositis Genetics Conference. Conference Report
 ESF-Sponsored International Myositis Genetics Conference 1. Summary: Conference Report As Myositis is so rare, undertaking Myositis genetic research had proved extremely difficult prior to 2000, because
ESF-Sponsored International Myositis Genetics Conference 1. Summary: Conference Report As Myositis is so rare, undertaking Myositis genetic research had proved extremely difficult prior to 2000, because
Genetics of Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Impressionist Perspective
 Genetics of Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Impressionist Perspective Noam Jacob, MD, Chaim O. Jacob, MD, PhD* KEYWORDS Rheumatoid arthritis Anti-citrullinated protein antibodies HLA Risk allele Key Points More
Genetics of Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Impressionist Perspective Noam Jacob, MD, Chaim O. Jacob, MD, PhD* KEYWORDS Rheumatoid arthritis Anti-citrullinated protein antibodies HLA Risk allele Key Points More
Factors for success in big data science
 Factors for success in big data science Damjan Vukcevic Data Science Murdoch Childrens Research Institute 16 October 2014 Big Data Reading Group (Department of Mathematics & Statistics, University of Melbourne)
Factors for success in big data science Damjan Vukcevic Data Science Murdoch Childrens Research Institute 16 October 2014 Big Data Reading Group (Department of Mathematics & Statistics, University of Melbourne)
Linking biobanks to registries: Why and how? Anne Barton
 Linking biobanks to registries: Why and how? Anne Barton Biobanks why should we collect samples? Anti-TNF treatment in RA Cost approx. 8,000/person/year 30-40% RA patients do not respond Rare, serious
Linking biobanks to registries: Why and how? Anne Barton Biobanks why should we collect samples? Anti-TNF treatment in RA Cost approx. 8,000/person/year 30-40% RA patients do not respond Rare, serious
Outline. Personal profile & research interests. Rheumatology research in Ireland. Current standing. Future plans
 Outline Personal profile & research interests Rheumatology research in Ireland Current standing Future plans Personal profile 1983 MB Queens University 1990-3 ARUK Clinical Research Fellowship 1990-93
Outline Personal profile & research interests Rheumatology research in Ireland Current standing Future plans Personal profile 1983 MB Queens University 1990-3 ARUK Clinical Research Fellowship 1990-93
NGS and complex genetics
 NGS and complex genetics Robert Kraaij Genetic Laboratory Department of Internal Medicine r.kraaij@erasmusmc.nl Gene Hunting Rotterdam Study and GWAS Next Generation Sequencing Gene Hunting Mendelian gene
NGS and complex genetics Robert Kraaij Genetic Laboratory Department of Internal Medicine r.kraaij@erasmusmc.nl Gene Hunting Rotterdam Study and GWAS Next Generation Sequencing Gene Hunting Mendelian gene
School of Nursing. Presented by Yvette Conley, PhD
 Presented by Yvette Conley, PhD What we will cover during this webcast: Briefly discuss the approaches introduced in the paper: Genome Sequencing Genome Wide Association Studies Epigenomics Gene Expression
Presented by Yvette Conley, PhD What we will cover during this webcast: Briefly discuss the approaches introduced in the paper: Genome Sequencing Genome Wide Association Studies Epigenomics Gene Expression
Big Data for Population Health
 Big Data for Population Health Prof Martin Landray Nuffield Department of Population Health Deputy Director, Big Data Institute, Li Ka Shing Centre for Health Information and Discovery University of Oxford
Big Data for Population Health Prof Martin Landray Nuffield Department of Population Health Deputy Director, Big Data Institute, Li Ka Shing Centre for Health Information and Discovery University of Oxford
GAW 15 Problem 3: Simulated Rheumatoid Arthritis Data Full Model and Simulation Parameters
 GAW 15 Problem 3: Simulated Rheumatoid Arthritis Data Full Model and Simulation Parameters Michael B Miller , Michael Li , Gregg Lind , Soon-Young
GAW 15 Problem 3: Simulated Rheumatoid Arthritis Data Full Model and Simulation Parameters Michael B Miller , Michael Li , Gregg Lind , Soon-Young
HLA-Cw*0602 associates with a twofold higher prevalence. of positive streptococcal throat swab at the onset of
 1 HLA-Cw*0602 associates with a twofold higher prevalence of positive streptococcal throat swab at the onset of psoriasis: a case control study Lotus Mallbris, MD, PhD, Katarina Wolk, MD, Fabio Sánchez
1 HLA-Cw*0602 associates with a twofold higher prevalence of positive streptococcal throat swab at the onset of psoriasis: a case control study Lotus Mallbris, MD, PhD, Katarina Wolk, MD, Fabio Sánchez
GENETIC PREDISPOSITIONS TO RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS IN MALAYSIAN POPULATION
 From the Rheumatology Unit, Department of Medicine, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden GENETIC PREDISPOSITIONS TO RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS IN MALAYSIAN POPULATION Chun Lai Too 杜 翠 麗 Stockholm 2012 On
From the Rheumatology Unit, Department of Medicine, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden GENETIC PREDISPOSITIONS TO RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS IN MALAYSIAN POPULATION Chun Lai Too 杜 翠 麗 Stockholm 2012 On
SNPbrowser Software v3.5
 Product Bulletin SNP Genotyping SNPbrowser Software v3.5 A Free Software Tool for the Knowledge-Driven Selection of SNP Genotyping Assays Easily visualize SNPs integrated with a physical map, linkage disequilibrium
Product Bulletin SNP Genotyping SNPbrowser Software v3.5 A Free Software Tool for the Knowledge-Driven Selection of SNP Genotyping Assays Easily visualize SNPs integrated with a physical map, linkage disequilibrium
SeattleSNPs Interactive Tutorial: Web Tools for Site Selection, Linkage Disequilibrium and Haplotype Analysis
 SeattleSNPs Interactive Tutorial: Web Tools for Site Selection, Linkage Disequilibrium and Haplotype Analysis Goal: This tutorial introduces several websites and tools useful for determining linkage disequilibrium
SeattleSNPs Interactive Tutorial: Web Tools for Site Selection, Linkage Disequilibrium and Haplotype Analysis Goal: This tutorial introduces several websites and tools useful for determining linkage disequilibrium
A Multi-locus Genetic Risk Score for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
 A Multi-locus Genetic Risk Score for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Zi Ye, 1 MD, Erin Austin, 1,2 PhD, Daniel J Schaid, 2 PhD, Iftikhar J. Kullo, 1 MD Affiliations: 1 Division of Cardiovascular Diseases and
A Multi-locus Genetic Risk Score for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Zi Ye, 1 MD, Erin Austin, 1,2 PhD, Daniel J Schaid, 2 PhD, Iftikhar J. Kullo, 1 MD Affiliations: 1 Division of Cardiovascular Diseases and
Core Facility Genomics
 Core Facility Genomics versatile genome or transcriptome analyses based on quantifiable highthroughput data ascertainment 1 Topics Collaboration with Harald Binder and Clemens Kreutz Project: Microarray
Core Facility Genomics versatile genome or transcriptome analyses based on quantifiable highthroughput data ascertainment 1 Topics Collaboration with Harald Binder and Clemens Kreutz Project: Microarray
Clinically Actionable Biomarkers in Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Clinically Actionable Biomarkers in Rheumatoid Arthritis PepTalk January 6, 2009 William Robinson, MD, PhD Stanford University School of Medicine VA Palo Alto Health Care System T cell mediated Autoimmune
Clinically Actionable Biomarkers in Rheumatoid Arthritis PepTalk January 6, 2009 William Robinson, MD, PhD Stanford University School of Medicine VA Palo Alto Health Care System T cell mediated Autoimmune
Genetic Risk Score Predicting Risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis Phenotypes and Age of Symptom Onset
 Genetic Risk Score Predicting Risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis Phenotypes and Age of Symptom Onset Lori B. Chibnik 1 *, Brendan T. Keenan 1, Jing Cui 2, Katherine P. Liao 2, Karen H. Costenbader 2, Robert
Genetic Risk Score Predicting Risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis Phenotypes and Age of Symptom Onset Lori B. Chibnik 1 *, Brendan T. Keenan 1, Jing Cui 2, Katherine P. Liao 2, Karen H. Costenbader 2, Robert
Human Genome Organization: An Update. Genome Organization: An Update
 Human Genome Organization: An Update Genome Organization: An Update Highlights of Human Genome Project Timetable Proposed in 1990 as 3 billion dollar joint venture between DOE and NIH with 15 year completion
Human Genome Organization: An Update Genome Organization: An Update Highlights of Human Genome Project Timetable Proposed in 1990 as 3 billion dollar joint venture between DOE and NIH with 15 year completion
IL2RA Genetic Heterogeneity in Multiple Sclerosis and Type 1 Diabetes Susceptibility and Soluble Interleukin-2 Receptor Production
 IL2RA Genetic Heterogeneity in Multiple Sclerosis and Type 1 Diabetes Susceptibility and Soluble Interleukin-2 Receptor Production Lisa M. Maier 1,2., Christopher E. Lowe 3., Jason Cooper 3, Kate Downes
IL2RA Genetic Heterogeneity in Multiple Sclerosis and Type 1 Diabetes Susceptibility and Soluble Interleukin-2 Receptor Production Lisa M. Maier 1,2., Christopher E. Lowe 3., Jason Cooper 3, Kate Downes
Unlocking the genetics of coeliac disease. Małgorzata Barbara Trynka
 Unlocking the genetics of coeliac disease Małgorzata Barbara Trynka Małgorzata, Barbara (Gosia) Trynka Unlocking the genetics of coeliac disease Thesis, University of Groningen, with summary in Dutch and
Unlocking the genetics of coeliac disease Małgorzata Barbara Trynka Małgorzata, Barbara (Gosia) Trynka Unlocking the genetics of coeliac disease Thesis, University of Groningen, with summary in Dutch and
Online Supplement to Polygenic Influence on Educational Attainment. Genotyping was conducted with the Illumina HumanOmni1-Quad v1 platform using
 Online Supplement to Polygenic Influence on Educational Attainment Construction of Polygenic Score for Educational Attainment Genotyping was conducted with the Illumina HumanOmni1-Quad v1 platform using
Online Supplement to Polygenic Influence on Educational Attainment Construction of Polygenic Score for Educational Attainment Genotyping was conducted with the Illumina HumanOmni1-Quad v1 platform using
How To Find Rare Variants In The Human Genome
 UNIVERSITÀ DEGLI STUDI DI SASSARI Scuola di Dottorato in Scienze Biomediche XXV CICLO DOTTORATO DI RICERCA IN SCIENZE BIOMEDICHE INDIRIZZO DI GENETICA MEDICA, MALATTIE METABOLICHE E NUTRIGENOMICA Direttore:
UNIVERSITÀ DEGLI STUDI DI SASSARI Scuola di Dottorato in Scienze Biomediche XXV CICLO DOTTORATO DI RICERCA IN SCIENZE BIOMEDICHE INDIRIZZO DI GENETICA MEDICA, MALATTIE METABOLICHE E NUTRIGENOMICA Direttore:
VISUAL INTEGRATION OF RESULTS FROM A LARGE DNA BIOBANK (BIOVU) USING SYNTHESIS-VIEW *
 VISUAL INTEGRATION OF RESULTS FROM A LARGE DNA BIOBANK (BIOVU) USING SYNTHESIS-VIEW * SARAH PENDERGRASS Center for Human Genetics Research, Department of Molecular Physiology and Biophysics, Vanderbilt
VISUAL INTEGRATION OF RESULTS FROM A LARGE DNA BIOBANK (BIOVU) USING SYNTHESIS-VIEW * SARAH PENDERGRASS Center for Human Genetics Research, Department of Molecular Physiology and Biophysics, Vanderbilt
Analysis of Neuropeptide S Receptor Gene (NPSR1) Polymorphism in Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Analysis of Neuropeptide S Receptor Gene (NPSR1) Polymorphism in Rheumatoid Arthritis Mauro D Amato 1, Marco Zucchelli 1, Maria Seddighzadeh 2, Francesca Anedda 1,3, Staffan Lindblad 2, Juha Kere 1, Lars
Analysis of Neuropeptide S Receptor Gene (NPSR1) Polymorphism in Rheumatoid Arthritis Mauro D Amato 1, Marco Zucchelli 1, Maria Seddighzadeh 2, Francesca Anedda 1,3, Staffan Lindblad 2, Juha Kere 1, Lars
Genomes and SNPs in Malaria and Sickle Cell Anemia
 Genomes and SNPs in Malaria and Sickle Cell Anemia Introduction to Genome Browsing with Ensembl Ensembl The vast amount of information in biological databases today demands a way of organising and accessing
Genomes and SNPs in Malaria and Sickle Cell Anemia Introduction to Genome Browsing with Ensembl Ensembl The vast amount of information in biological databases today demands a way of organising and accessing
Proposta di studio multicentrico A.I.S.F. Genetica della PBC e PSC
 Proposta di studio multicentrico A.I.S.F. Genetica della PBC e PSC Coordinatore Pietro Invernizzi A.I.S.F., Rome, 25 February 2011 STUDY 1 Primary biliary cirrhosis Identification of common and uncommon
Proposta di studio multicentrico A.I.S.F. Genetica della PBC e PSC Coordinatore Pietro Invernizzi A.I.S.F., Rome, 25 February 2011 STUDY 1 Primary biliary cirrhosis Identification of common and uncommon
Validation and Replication
 Validation and Replication Overview Definitions of validation and replication Difficulties and limitations Working examples from our group and others Why? False positive results still occur. even after
Validation and Replication Overview Definitions of validation and replication Difficulties and limitations Working examples from our group and others Why? False positive results still occur. even after
High-Order Interactions in Rheumatoid Arthritis Detected by Bayesian Method using Genome-Wide Association Studies Data
 American Medical Journal 3 (1): 56-66, 2012 ISSN 1949-0070 2012 Science Publications High-Order Interactions in Rheumatoid Arthritis Detected by Bayesian Method using Genome-Wide Association Studies Data
American Medical Journal 3 (1): 56-66, 2012 ISSN 1949-0070 2012 Science Publications High-Order Interactions in Rheumatoid Arthritis Detected by Bayesian Method using Genome-Wide Association Studies Data
Progress and promise in understanding the genetic basis of common diseases
 rspb.royalsocietypublishing.org Progress and promise in understanding the genetic basis of common diseases Alkes L. Price 1,2, Chris C. A. Spencer 3 and Peter Donnelly 3,4 Review Cite this article: Price
rspb.royalsocietypublishing.org Progress and promise in understanding the genetic basis of common diseases Alkes L. Price 1,2, Chris C. A. Spencer 3 and Peter Donnelly 3,4 Review Cite this article: Price
DISCOVERY TOOL FOR GENOME-WIDE ASSOCIATION STUDIES
 IPINBPA: AN INTEGRATIVE NETWORK-BASED FUNCTIONAL MODULE DISCOVERY TOOL FOR GENOME-WIDE ASSOCIATION STUDIES LILI WANG School of Computing, Queen s University 25 Union Street, Goodwin Hall, Kingston, Ontario,
IPINBPA: AN INTEGRATIVE NETWORK-BASED FUNCTIONAL MODULE DISCOVERY TOOL FOR GENOME-WIDE ASSOCIATION STUDIES LILI WANG School of Computing, Queen s University 25 Union Street, Goodwin Hall, Kingston, Ontario,
Just the Facts: A Basic Introduction to the Science Underlying NCBI Resources
 1 of 8 11/7/2004 11:00 AM National Center for Biotechnology Information About NCBI NCBI at a Glance A Science Primer Human Genome Resources Model Organisms Guide Outreach and Education Databases and Tools
1 of 8 11/7/2004 11:00 AM National Center for Biotechnology Information About NCBI NCBI at a Glance A Science Primer Human Genome Resources Model Organisms Guide Outreach and Education Databases and Tools
Genetic Studies of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Progress and Challenges
 Journal of Rheumatic Diseases Vol. 22, No. 5, October, 2015 http://dx.doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2015.22.5.274 Review Article Genetic Studies of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Progress and Challenges Changsoo Kang Department
Journal of Rheumatic Diseases Vol. 22, No. 5, October, 2015 http://dx.doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2015.22.5.274 Review Article Genetic Studies of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Progress and Challenges Changsoo Kang Department
EHRs and large scale comparative effectiveness research
 EHRs and large scale comparative effectiveness research September 16, 2014 Dana C. Crawford, PhD Associate Professor Epidemiology and Biostatistics Institute for Computational Biology Single Nucleotide
EHRs and large scale comparative effectiveness research September 16, 2014 Dana C. Crawford, PhD Associate Professor Epidemiology and Biostatistics Institute for Computational Biology Single Nucleotide
Meta-analysis demonstrates association between TLR polymorphisms and rheumatoid arthritis
 Meta-analysis demonstrates association between TLR polymorphisms and rheumatoid arthritis Y.H. Lee 1, S.-C. Bae 2 and G.G. Song 1 1 Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, College of
Meta-analysis demonstrates association between TLR polymorphisms and rheumatoid arthritis Y.H. Lee 1, S.-C. Bae 2 and G.G. Song 1 1 Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, College of
C-Reactive Protein and Diabetes: proving a negative, for a change?
 C-Reactive Protein and Diabetes: proving a negative, for a change? Eric Brunner PhD FFPH Reader in Epidemiology and Public Health MRC Centre for Causal Analyses in Translational Epidemiology 2 March 2009
C-Reactive Protein and Diabetes: proving a negative, for a change? Eric Brunner PhD FFPH Reader in Epidemiology and Public Health MRC Centre for Causal Analyses in Translational Epidemiology 2 March 2009
CASSI: Genome-Wide Interaction Analysis Software
 CASSI: Genome-Wide Interaction Analysis Software 1 Contents 1 Introduction 3 2 Installation 3 3 Using CASSI 3 3.1 Input Files................................... 4 3.2 Options....................................
CASSI: Genome-Wide Interaction Analysis Software 1 Contents 1 Introduction 3 2 Installation 3 3 Using CASSI 3 3.1 Input Files................................... 4 3.2 Options....................................
Genetic Basis of Autoantibody Positive and Negative Rheumatoid Arthritis Risk in a Multi-ethnic Cohort Derived from Electronic Health Records
 Genetic Basis of Autoantibody Positive and Negative Rheumatoid Arthritis Risk in a Multi-ethnic Cohort Derived from Electronic Health Records ARTICLE Fina Kurreeman, 1,2,3 Katherine Liao, 1 Lori Chibnik,
Genetic Basis of Autoantibody Positive and Negative Rheumatoid Arthritis Risk in a Multi-ethnic Cohort Derived from Electronic Health Records ARTICLE Fina Kurreeman, 1,2,3 Katherine Liao, 1 Lori Chibnik,
Pharmacogenetics of Topiramate Treatment for Heavy Drinking
 Pharmacogenetics of Topiramate Treatment for Heavy Drinking Henry R. Kranzler, M.D. Perelman School of Medicine of the University of Pennsylvania and VISN 4 MIRECC, Philadelphia VAMC kranzler@mail.med.upenn.edu
Pharmacogenetics of Topiramate Treatment for Heavy Drinking Henry R. Kranzler, M.D. Perelman School of Medicine of the University of Pennsylvania and VISN 4 MIRECC, Philadelphia VAMC kranzler@mail.med.upenn.edu
SOP 3 v2: web-based selection of oligonucleotide primer trios for genotyping of human and mouse polymorphisms
 W548 W552 Nucleic Acids Research, 2005, Vol. 33, Web Server issue doi:10.1093/nar/gki483 SOP 3 v2: web-based selection of oligonucleotide primer trios for genotyping of human and mouse polymorphisms Steven
W548 W552 Nucleic Acids Research, 2005, Vol. 33, Web Server issue doi:10.1093/nar/gki483 SOP 3 v2: web-based selection of oligonucleotide primer trios for genotyping of human and mouse polymorphisms Steven
A map of human genome variation from population-scale sequencing
 doi:1.138/nature9534 A map of human genome variation from population-scale sequencing The 1 Genomes Project Consortium* The 1 Genomes Project aims to provide a deep characterization of human genome sequence
doi:1.138/nature9534 A map of human genome variation from population-scale sequencing The 1 Genomes Project Consortium* The 1 Genomes Project aims to provide a deep characterization of human genome sequence
GENETIC DATA ANALYSIS
 GENETIC DATA ANALYSIS 1 Genetic Data: Future of Personalized Healthcare To achieve personalization in Healthcare, there is a need for more advancements in the field of Genomics. The human genome is made
GENETIC DATA ANALYSIS 1 Genetic Data: Future of Personalized Healthcare To achieve personalization in Healthcare, there is a need for more advancements in the field of Genomics. The human genome is made
Focusing on results not data comprehensive data analysis for targeted next generation sequencing
 Focusing on results not data comprehensive data analysis for targeted next generation sequencing Daniel Swan, Jolyon Holdstock, Angela Matchan, Richard Stark, John Shovelton, Duarte Mohla and Simon Hughes
Focusing on results not data comprehensive data analysis for targeted next generation sequencing Daniel Swan, Jolyon Holdstock, Angela Matchan, Richard Stark, John Shovelton, Duarte Mohla and Simon Hughes
Logistic Regression (1/24/13)
 STA63/CBB540: Statistical methods in computational biology Logistic Regression (/24/3) Lecturer: Barbara Engelhardt Scribe: Dinesh Manandhar Introduction Logistic regression is model for regression used
STA63/CBB540: Statistical methods in computational biology Logistic Regression (/24/3) Lecturer: Barbara Engelhardt Scribe: Dinesh Manandhar Introduction Logistic regression is model for regression used
Workshop on Establishing a Central Resource of Data from Genome Sequencing Projects
 Report on the Workshop on Establishing a Central Resource of Data from Genome Sequencing Projects Background and Goals of the Workshop June 5 6, 2012 The use of genome sequencing in human research is growing
Report on the Workshop on Establishing a Central Resource of Data from Genome Sequencing Projects Background and Goals of the Workshop June 5 6, 2012 The use of genome sequencing in human research is growing
A Primer of Genome Science THIRD
 A Primer of Genome Science THIRD EDITION GREG GIBSON-SPENCER V. MUSE North Carolina State University Sinauer Associates, Inc. Publishers Sunderland, Massachusetts USA Contents Preface xi 1 Genome Projects:
A Primer of Genome Science THIRD EDITION GREG GIBSON-SPENCER V. MUSE North Carolina State University Sinauer Associates, Inc. Publishers Sunderland, Massachusetts USA Contents Preface xi 1 Genome Projects:
Genotyping and quality control of UK Biobank, a large- scale, extensively phenotyped prospective resource
 Genotyping and quality control of UK Biobank, a large- scale, extensively phenotyped prospective resource Information for researchers Interim Data Release, 2015 1 Introduction... 3 1.1 UK Biobank... 3
Genotyping and quality control of UK Biobank, a large- scale, extensively phenotyped prospective resource Information for researchers Interim Data Release, 2015 1 Introduction... 3 1.1 UK Biobank... 3
Phenotypes and Classification of Psoriasis
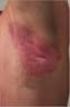 Rheumatology 2010 Birmingham 21 April 2010 Phenotypes and Classification of Psoriasis Christopher E.M. Griffiths Abbott Centocor Incyte Galderma Janssen-Cilag Leo Pharma Lynxx Novartis Pfizer Schering-Plough
Rheumatology 2010 Birmingham 21 April 2010 Phenotypes and Classification of Psoriasis Christopher E.M. Griffiths Abbott Centocor Incyte Galderma Janssen-Cilag Leo Pharma Lynxx Novartis Pfizer Schering-Plough
Current understanding of the genetic aetiology of rheumatoid arthritis and likely future developments
 Rheumatology 5;(Suppl. ):iv9 iv Current understanding of the genetic aetiology of rheumatoid arthritis and likely future developments L. A. Criswell and P. K. Gregersen doi:.9/rheumatology/kei5 Most of
Rheumatology 5;(Suppl. ):iv9 iv Current understanding of the genetic aetiology of rheumatoid arthritis and likely future developments L. A. Criswell and P. K. Gregersen doi:.9/rheumatology/kei5 Most of
Discovery and Quantification of RNA with RNASeq Roderic Guigó Serra Centre de Regulació Genòmica (CRG) roderic.guigo@crg.cat
 Bioinformatique et Séquençage Haut Débit, Discovery and Quantification of RNA with RNASeq Roderic Guigó Serra Centre de Regulació Genòmica (CRG) roderic.guigo@crg.cat 1 RNA Transcription to RNA and subsequent
Bioinformatique et Séquençage Haut Débit, Discovery and Quantification of RNA with RNASeq Roderic Guigó Serra Centre de Regulació Genòmica (CRG) roderic.guigo@crg.cat 1 RNA Transcription to RNA and subsequent
Technical Issues in Aggregating and Analyzing Data from Heterogeneous EHR Systems
 Technical Issues in Aggregating and Analyzing Data from Heterogeneous EHR Systems Josh Denny, MD, MS josh.denny@vanderbilt.edu Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tennessee, USA 2/12/2015 EHR data are dense
Technical Issues in Aggregating and Analyzing Data from Heterogeneous EHR Systems Josh Denny, MD, MS josh.denny@vanderbilt.edu Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tennessee, USA 2/12/2015 EHR data are dense
RegulomeDB scores and functional assignments of 153 SCARB1
 Table S13. RegulomeDB scores and functional assignments of 153 SCARB1 variants. SNP Chr12 Name a SNP ID b Position c p972 rs181338950 125348548 p1048 insc (1048_ 1049) 125348472 Location Amino Acid Change
Table S13. RegulomeDB scores and functional assignments of 153 SCARB1 variants. SNP Chr12 Name a SNP ID b Position c p972 rs181338950 125348548 p1048 insc (1048_ 1049) 125348472 Location Amino Acid Change
A Functional Haplotype of the PADI4 Gene Associated With Increased Rheumatoid Arthritis Susceptibility in Koreans
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 54, No. 1, January 2006, pp 90 96 DOI 10.1002/art.21536 2006, American College of Rheumatology A Functional Haplotype of the PADI4 Gene Associated With Increased Rheumatoid
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 54, No. 1, January 2006, pp 90 96 DOI 10.1002/art.21536 2006, American College of Rheumatology A Functional Haplotype of the PADI4 Gene Associated With Increased Rheumatoid
SAP HANA Enabling Genome Analysis
 SAP HANA Enabling Genome Analysis Joanna L. Kelley, PhD Postdoctoral Scholar, Stanford University Enakshi Singh, MSc HANA Product Management, SAP Labs LLC Outline Use cases Genomics review Challenges in
SAP HANA Enabling Genome Analysis Joanna L. Kelley, PhD Postdoctoral Scholar, Stanford University Enakshi Singh, MSc HANA Product Management, SAP Labs LLC Outline Use cases Genomics review Challenges in
Building risk prediction models - with a focus on Genome-Wide Association Studies. Charles Kooperberg
 Building risk prediction models - with a focus on Genome-Wide Association Studies Risk prediction models Based on data: (D i, X i1,..., X ip ) i = 1,..., n we like to fit a model P(D = 1 X 1,..., X p )
Building risk prediction models - with a focus on Genome-Wide Association Studies Risk prediction models Based on data: (D i, X i1,..., X ip ) i = 1,..., n we like to fit a model P(D = 1 X 1,..., X p )
Biological Sciences Initiative. Human Genome
 Biological Sciences Initiative HHMI Human Genome Introduction In 2000, researchers from around the world published a draft sequence of the entire genome. 20 labs from 6 countries worked on the sequence.
Biological Sciences Initiative HHMI Human Genome Introduction In 2000, researchers from around the world published a draft sequence of the entire genome. 20 labs from 6 countries worked on the sequence.
Genome-Wide and Species-Wide Dissection of the Genetics of Arthritis Severity in Heterogeneous Stock Mice
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 63, No. 9, September 2011, pp 2630 2640 DOI 10.1002/art.30425 2011, American College of Rheumatology Genome-Wide and Species-Wide Dissection of the Genetics of Arthritis Severity
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 63, No. 9, September 2011, pp 2630 2640 DOI 10.1002/art.30425 2011, American College of Rheumatology Genome-Wide and Species-Wide Dissection of the Genetics of Arthritis Severity
Sample Reproducibility of Genetic Association Using Different Multimarker TDTs in Genome-Wide Association Studies: Characterization and a New Approach
 Sample Reproducibility of Genetic Association Using Different Multimarker TDTs in Genome-Wide Association Studies: Characterization and a New Approach Mara M. Abad-Grau 1 *, Nuria Medina-Medina 1, Rosana
Sample Reproducibility of Genetic Association Using Different Multimarker TDTs in Genome-Wide Association Studies: Characterization and a New Approach Mara M. Abad-Grau 1 *, Nuria Medina-Medina 1, Rosana
Genome-Wide Meta-Analysis of Psoriatic Arthritis Identifies Susceptibility Locus at REL
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Genome-Wide -Analysis of Psoriatic Arthritis Identifies Susceptibility Locus at REL Eva Ellinghaus 1, Philip E. Stuart 2, David Ellinghaus 1, Rajan P. Nair 2, Sophie Debrus 3, John V.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Genome-Wide -Analysis of Psoriatic Arthritis Identifies Susceptibility Locus at REL Eva Ellinghaus 1, Philip E. Stuart 2, David Ellinghaus 1, Rajan P. Nair 2, Sophie Debrus 3, John V.
Electronic Medical Records and Genomics: Possibilities, Realities, Ethical Issues to Consider
 Electronic Medical Records and Genomics: Possibilities, Realities, Ethical Issues to Consider Daniel Masys, M.D. Affiliate Professor Biomedical and Health Informatics University of Washington, Seattle
Electronic Medical Records and Genomics: Possibilities, Realities, Ethical Issues to Consider Daniel Masys, M.D. Affiliate Professor Biomedical and Health Informatics University of Washington, Seattle
An example of bioinformatics application on plant breeding projects in Rijk Zwaan
 An example of bioinformatics application on plant breeding projects in Rijk Zwaan Xiangyu Rao 17-08-2012 Introduction of RZ Rijk Zwaan is active worldwide as a vegetable breeding company that focuses on
An example of bioinformatics application on plant breeding projects in Rijk Zwaan Xiangyu Rao 17-08-2012 Introduction of RZ Rijk Zwaan is active worldwide as a vegetable breeding company that focuses on
B I O I N F O R M A T I C S
 B I O I N F O R M A T I C S Kristel Van Steen, PhD 2 Montefiore Institute - Systems and Modeling GIGA - Bioinformatics ULg kristel.vansteen@ulg.ac.be CHAPTER 4: GENOME-WIDE ASSOCIATION STUDIES 1 Setting
B I O I N F O R M A T I C S Kristel Van Steen, PhD 2 Montefiore Institute - Systems and Modeling GIGA - Bioinformatics ULg kristel.vansteen@ulg.ac.be CHAPTER 4: GENOME-WIDE ASSOCIATION STUDIES 1 Setting
THE UNIVERSITY OF OXFORD MEDICAL SCIENCES DIVISION. Final Report to Cure Crohn s Colitis
 THE UNIVERSITY OF OXFORD MEDICAL SCIENCES DIVISION Final Report to Cure Crohn s Colitis MARCH 2008 CONTENTS Introduction 2 Project background 3 Crohn s and Colitis research at Oxford 4 Project progress
THE UNIVERSITY OF OXFORD MEDICAL SCIENCES DIVISION Final Report to Cure Crohn s Colitis MARCH 2008 CONTENTS Introduction 2 Project background 3 Crohn s and Colitis research at Oxford 4 Project progress
Epigenetic variation and complex disease risk
 Epigenetic variation and complex disease risk Caroline Relton Institute of Human Genetics Newcastle University ALSPAC Research Symposium 2 & 3 March 2009 Missing heritability Even when dozens of genes
Epigenetic variation and complex disease risk Caroline Relton Institute of Human Genetics Newcastle University ALSPAC Research Symposium 2 & 3 March 2009 Missing heritability Even when dozens of genes
Big Data for Population Health and Personalised Medicine through EMR Linkages
 Big Data for Population Health and Personalised Medicine through EMR Linkages Zheng-Ming CHEN Professor of Epidemiology Nuffield Dept. of Population Health, University of Oxford Big Data for Health Policy
Big Data for Population Health and Personalised Medicine through EMR Linkages Zheng-Ming CHEN Professor of Epidemiology Nuffield Dept. of Population Health, University of Oxford Big Data for Health Policy
From Disease Association to Risk Assessment: An Optimistic View from Genome-Wide Association Studies on Type 1 Diabetes
 From Disease Association to Risk Assessment: An Optimistic View from Genome-Wide Association Studies on Type 1 Diabetes Zhi Wei 1., Kai Wang 2., Hui-Qi Qu 3, Haitao Zhang 2, Jonathan Bradfield 2, Cecilia
From Disease Association to Risk Assessment: An Optimistic View from Genome-Wide Association Studies on Type 1 Diabetes Zhi Wei 1., Kai Wang 2., Hui-Qi Qu 3, Haitao Zhang 2, Jonathan Bradfield 2, Cecilia
Statistical analysis of genome-wide association (GWAS) data
 Statistical analysis of genome-wide association (GWAS) data Jim Stankovich Menzies Research Institute University of Tasmania J.Stankovich@utas.edu.au Outline Introduction Confounding variables and linkage
Statistical analysis of genome-wide association (GWAS) data Jim Stankovich Menzies Research Institute University of Tasmania J.Stankovich@utas.edu.au Outline Introduction Confounding variables and linkage
GOBII. Genomic & Open-source Breeding Informatics Initiative
 GOBII Genomic & Open-source Breeding Informatics Initiative My Background BS Animal Science, University of Tennessee MS Animal Breeding, University of Georgia Random regression models for longitudinal
GOBII Genomic & Open-source Breeding Informatics Initiative My Background BS Animal Science, University of Tennessee MS Animal Breeding, University of Georgia Random regression models for longitudinal
NIH/NIGMS Trainee Forum: Computational Biology and Medical Informatics at Georgia Tech
 ACM-BCB 2015 (Sept. 10 th, 10:00am-12:30pm) NIH/NIGMS Trainee Forum: Computational Biology and Medical Informatics at Georgia Tech Chair: Professor Greg Gibson Georgia Institute of Technology Co-Chair:
ACM-BCB 2015 (Sept. 10 th, 10:00am-12:30pm) NIH/NIGMS Trainee Forum: Computational Biology and Medical Informatics at Georgia Tech Chair: Professor Greg Gibson Georgia Institute of Technology Co-Chair:
Biologics in Rheumatoid Arthritis Genetics and Genomics Study Syndicate (BRAGGSS): DATA AND SAMPLE ACCESS AND OWNERSHIP POLICY February 2007
 Biologics in Rheumatoid Arthritis Genetics and Genomics Study Syndicate (BRAGGSS): DATA AND SAMPLE ACCESS AND OWNERSHIP POLICY February 2007 1. Summary This paper covers the procedures that should be followed
Biologics in Rheumatoid Arthritis Genetics and Genomics Study Syndicate (BRAGGSS): DATA AND SAMPLE ACCESS AND OWNERSHIP POLICY February 2007 1. Summary This paper covers the procedures that should be followed
IL1A and IL1B: A Search For Network Marketing Agreements
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 58, No. 7, July 2008, pp 1947 1957 DOI 10.1002/art.23592 2008, American College of Rheumatology A Broad Analysis of IL1 Polymorphism and Rheumatoid Arthritis Alyssa K. Johnsen,
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 58, No. 7, July 2008, pp 1947 1957 DOI 10.1002/art.23592 2008, American College of Rheumatology A Broad Analysis of IL1 Polymorphism and Rheumatoid Arthritis Alyssa K. Johnsen,
Lecture 6: Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms (RFLPs)
 Lecture 6: Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms (RFLPs) Single nucleotide polymorphisms or SNPs (pronounced "snips") are DNA sequence variations that occur
Lecture 6: Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms (RFLPs) Single nucleotide polymorphisms or SNPs (pronounced "snips") are DNA sequence variations that occur
Characterizing Genetic Risk at Known Prostate Cancer Susceptibility Loci in African Americans
 Characterizing Genetic Risk at Known Prostate Cancer Susceptibility Loci in African Americans Christopher A. Haiman 1 *, Gary K. Chen 1, William J. Blot 2,3,4, Sara S. Strom 5, Sonja I. Berndt 6,RickA.
Characterizing Genetic Risk at Known Prostate Cancer Susceptibility Loci in African Americans Christopher A. Haiman 1 *, Gary K. Chen 1, William J. Blot 2,3,4, Sara S. Strom 5, Sonja I. Berndt 6,RickA.
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON HARMONISATION OF TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR REGISTRATION OF PHARMACEUTICALS FOR HUMAN USE Q5B
 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON HARMONISATION OF TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR REGISTRATION OF PHARMACEUTICALS FOR HUMAN USE ICH HARMONISED TRIPARTITE GUIDELINE QUALITY OF BIOTECHNOLOGICAL PRODUCTS: ANALYSIS
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON HARMONISATION OF TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR REGISTRATION OF PHARMACEUTICALS FOR HUMAN USE ICH HARMONISED TRIPARTITE GUIDELINE QUALITY OF BIOTECHNOLOGICAL PRODUCTS: ANALYSIS
Sequencing and microarrays for genome analysis: complementary rather than competing?
 Sequencing and microarrays for genome analysis: complementary rather than competing? Simon Hughes, Richard Capper, Sandra Lam and Nicole Sparkes Introduction The human genome is comprised of more than
Sequencing and microarrays for genome analysis: complementary rather than competing? Simon Hughes, Richard Capper, Sandra Lam and Nicole Sparkes Introduction The human genome is comprised of more than
Marker-Assisted Backcrossing. Marker-Assisted Selection. 1. Select donor alleles at markers flanking target gene. Losing the target allele
 Marker-Assisted Backcrossing Marker-Assisted Selection CS74 009 Jim Holland Target gene = Recurrent parent allele = Donor parent allele. Select donor allele at markers linked to target gene.. Select recurrent
Marker-Assisted Backcrossing Marker-Assisted Selection CS74 009 Jim Holland Target gene = Recurrent parent allele = Donor parent allele. Select donor allele at markers linked to target gene.. Select recurrent
ITT Advanced Medical Technologies - A Programmer's Overview
 ITT Advanced Medical Technologies (Ileri Tip Teknolojileri) ITT Advanced Medical Technologies (Ileri Tip Teknolojileri) is a biotechnology company (SME) established in Turkey. Its activity area is research,
ITT Advanced Medical Technologies (Ileri Tip Teknolojileri) ITT Advanced Medical Technologies (Ileri Tip Teknolojileri) is a biotechnology company (SME) established in Turkey. Its activity area is research,
Next Generation Sequencing: Technology, Mapping, and Analysis
 Next Generation Sequencing: Technology, Mapping, and Analysis Gary Benson Computer Science, Biology, Bioinformatics Boston University gbenson@bu.edu http://tandem.bu.edu/ The Human Genome Project took
Next Generation Sequencing: Technology, Mapping, and Analysis Gary Benson Computer Science, Biology, Bioinformatics Boston University gbenson@bu.edu http://tandem.bu.edu/ The Human Genome Project took
GENOMIC SELECTION: THE FUTURE OF MARKER ASSISTED SELECTION AND ANIMAL BREEDING
 GENOMIC SELECTION: THE FUTURE OF MARKER ASSISTED SELECTION AND ANIMAL BREEDING Theo Meuwissen Institute for Animal Science and Aquaculture, Box 5025, 1432 Ås, Norway, theo.meuwissen@ihf.nlh.no Summary
GENOMIC SELECTION: THE FUTURE OF MARKER ASSISTED SELECTION AND ANIMAL BREEDING Theo Meuwissen Institute for Animal Science and Aquaculture, Box 5025, 1432 Ås, Norway, theo.meuwissen@ihf.nlh.no Summary
The experiment will be conducted in two phases; find the optimal statistical detection method and apply to collected data.
 SPECIFIC AIMS Plasmodium falciparum is the most lethal causative agent of malaria, affecting over 500 million annually with 1 to 3 million of those cases resulting in death 1. Widespread drug use has been
SPECIFIC AIMS Plasmodium falciparum is the most lethal causative agent of malaria, affecting over 500 million annually with 1 to 3 million of those cases resulting in death 1. Widespread drug use has been
Simplifying Data Interpretation with Nexus Copy Number
 Simplifying Data Interpretation with Nexus Copy Number A WHITE PAPER FROM BIODISCOVERY, INC. Rapid technological advancements, such as high-density acgh and SNP arrays as well as next-generation sequencing
Simplifying Data Interpretation with Nexus Copy Number A WHITE PAPER FROM BIODISCOVERY, INC. Rapid technological advancements, such as high-density acgh and SNP arrays as well as next-generation sequencing
Association of HLA-DRB1 Haplotypes With Rheumatoid Arthritis Severity, Mortality, and Treatment Response
 Research Original Investigation Association of HLA-DRB1 Haplotypes With Rheumatoid Arthritis Severity, Mortality, and Treatment Response SebastienViatte, MD, PhD; Darren Plant, PhD; Buhm Han, PhD; Bo Fu,
Research Original Investigation Association of HLA-DRB1 Haplotypes With Rheumatoid Arthritis Severity, Mortality, and Treatment Response SebastienViatte, MD, PhD; Darren Plant, PhD; Buhm Han, PhD; Bo Fu,
GWASrap User Manual v1.1
 GWASrap User Manual v1.1 1 / 28 Table of contents Introduction... 3 System Requirements... 3 Welcome... 3 Features... 4 Create New Run... 5 GWAS Representation... 7 GWAS Annotation... 13 GWAS Prioritization...
GWASrap User Manual v1.1 1 / 28 Table of contents Introduction... 3 System Requirements... 3 Welcome... 3 Features... 4 Create New Run... 5 GWAS Representation... 7 GWAS Annotation... 13 GWAS Prioritization...
Replacing TaqMan SNP Genotyping Assays that Fail Applied Biosystems Manufacturing Quality Control. Begin
 User Bulletin TaqMan SNP Genotyping Assays May 2008 SUBJECT: Replacing TaqMan SNP Genotyping Assays that Fail Applied Biosystems Manufacturing Quality Control In This Bulletin Overview This user bulletin
User Bulletin TaqMan SNP Genotyping Assays May 2008 SUBJECT: Replacing TaqMan SNP Genotyping Assays that Fail Applied Biosystems Manufacturing Quality Control In This Bulletin Overview This user bulletin
Journal of Statistical Software
 JSS Journal of Statistical Software October 2006, Volume 16, Code Snippet 3. http://www.jstatsoft.org/ LDheatmap: An R Function for Graphical Display of Pairwise Linkage Disequilibria between Single Nucleotide
JSS Journal of Statistical Software October 2006, Volume 16, Code Snippet 3. http://www.jstatsoft.org/ LDheatmap: An R Function for Graphical Display of Pairwise Linkage Disequilibria between Single Nucleotide
