Nutrition Chapter 8 - Infant Nutrition
|
|
|
- Rosemary Young
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Nutrition Chapter 8 - Infant Nutrition - full-term infants: infants born between 37 and 42 weeks gestation - healthy preterm infants: infants born at 34 weeks or later - preterm infant: infants born before 37 weeks of gestation Assessing Newborn Health Birth Weight as an Outcome - the weight of a newborn is a key measure of health status during pregnancy - average full-term baby weighs between lbs and height is inches) Infant Mortality - infant mortality: death that occurs within the first year of life - preterm birth is a key risk factor for infant death since it is continuing to increase - 3 leading causes to of infant mortality in 2006 were congenital malformations, complications related to preterm births, and sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) Combating Infant Mortality -The Early Periodic Screening Detection, and Treatment Program (EPSDT): part of Medicaid and provides routine checkups for low-income families Standard Newborn Growth Assessment - newborn health status is assessed by various indicators of growth and development taken right after birth. Indicators include birth weight, length, and head circumference for gestational age - intrauterine growth retardation (IUGR): fetal under-growth from any cause, resulting in a disproportionality in weight, length, or weight-for-length percentiles for gestational age. Sometimes called intrauterine growth restriction - the designation small for gestational age (SGA); also called small for dates, IUGR, or intrauterine growth restriction - means that newborn s birth weight falls below the 10 th percentile of weight gestational age - infants above the 90 th percentile are considered large for gestational age (LGA) - those in between are appropriate for gestational age (AGA) Infant Development - full-term newborns can hear and move in response to familiar sounds, such as the mother s voice. They demonstrate 4 states of arousal, ranging from sleeping to fully alert, and
2 responsiveness differs in part on their state of arousal - reflex: an automatic (unlearned) response that is triggered by a specific stimulus - rooting reflex: action that occurs if one cheek is touched, resulting in the infant s head turning toward that cheek and the infant opening his mouth - suckle: a reflexive movement of the tongue moving forward and backward; earliest feeding skill Motor Development - motor development reflects an infant s ability to control voluntary muscle movement - the development of muscle control is top-down, meaning head control is the start and last comes lower legs - muscle development is also from central to peripheral, meaning the infant learns to control the shoulder and arm muscles before the muscles in the hands Critical Periods - concept of critical period is based on a fixed time period during which certain behaviours emerge - a critical period for the development of oral feedings may explain some later feeding problems in infancy Cognitive Development - sensorimotor: an early learning system in which the infant s senses and motor skills provide input to the central nervous system Digestive System of Development - during the 3 rd trimester, the fetus swallows amniotic fluid and this stimulates the lining of the intestine to grow and mature - at birth, the healthy newborn s digestive system is sufficiently mature to digest fats, protein and simple sugars and to absorb fats and amino acids - after birth and through the early infancy period, the coordination of peristalsis within the gastrointestinal tract improves. Maturation of peristalsis and rate of passage are associated with some forms of gastrointestinal discomfort in infants - infants often have conditions that reflect the immaturity of the gut, such as colic, gastroesophageal reflux (GER), unexplained diarrhea, and constipation - gastroesophageal reflux (GER): movement of the stomach contents backwards into the esophagus due to stomach muscle contractions. - other factors influence the rate of food passage through the colon and the gastrointestinal discomfort seen in infants. These include: - osmolarity of foods or liquids (which affects how much water is in the intestine)
3 - colon bacteria flora - water and fluid balance in the body - osmolarity: measure of the number of particles in a solution, which predicts the tendency of the particles to move from high to low concentration Energy and Nutrient Needs - recommendations of children aged 2 and older. Recommendations for infants are from the DRI intakes, which are based on research over decades on infant growth and health from professional groups such as the National Academy of Medicine, the American Academy of Pediatrics, and the American Dietetic Association Caloric Needs - the average caloric requirements for individual infants is broad, ranging from 80 to 120 calories per kg (2.2lb) body weight. - average caloric need of infants in the first 6 months of life of 108 cal per kg body weight, based on growth in breastfed infants - from 6-12 months of age, average caloric need is 98 cal/kg - factors that account for the range of caloric needs of infants include the following: - weight - growth rate - sleep/wake cycle - temperature and climate - physical activity - metabolic response to food - health status and recovery from illness Protein Needs - recommended protein intake from birth up to 6 months averages 2.2g of protein per kg of body weight, and from 6-12 months the need is for 1.6g of protein per kg - most young infants who breastfeed or consume the recommended amounts of infant formula meet protein needs without added foods - infants may exceed their protein needs based on the DRI when they consume more formula than recommended for age and when protein sources such as baby cereal are added to infant formula Fats - no specific recommended intake levels of fats for infants - breast milk provides 55% of its calories from fat, and this percentage reflects an adequate intake of fat by infants
4 - percentage of fat in the diet drops after the infant accepts baby foods, since most baby foods are low in fat - short- and medium-chain fats such as those in breast milk are more readily utilized than longchain fats, such as in some infant formulas - infants use fats to supply energy to the liver, brain, and muscles, including the heart Metabolic Rate, Calories, Fats, and Protein - How Do They All Tie Together? - the high metabolic rate is primarily related to infants rapid growth and the high proportion of infant weigh that is made up of muscle - the usual body fuel for metabolism is glucose Other Nutrients and Non-nutrients Fluoride: - DRI for fluoride is 0.1 mg daily for infants less than 6 months of age - DRI for fluoride is 0.5 mg daily for 7-12 month-olds - fluoride is incorporated into the enamel of forming teeth, including those not yet erupted Vitamin D: - vitamin D is recommended for all infants starting shortly after birth at the level of 400 IU/day Sodium: - is a major component of extracellular fluid and an important regulator of fluid balance - estimated minimum requirements for sodium are 120mg for 0-5 months and 200mg for 6-12 month olds Fiber: - there are no dietary recommendations for infants - commercial and homemade baby foods are generally not significant sources of dietary fiber because preparation methods reduce dietary fiber Development of Infant Feeding Skills - several models help assess readiness for a breastfed infant to begin eating from a spoon at around 6 months - developmental model is based on looking for signs of readiness, such as being able to move the tongue from side to side without moving the head - they must be able to keep their head upright and sit with little support - the parents ability to read the infant s cues of hunger, satiation, tiredness, and discomfort influence feeding-skill progression. - cues infants give may include:
5 - watching the food being opened in anticipation of eating - tight fists or reaching for the spoon as a sign of hunger - showing irritation if the feeding pace is too slow or if the feeder temporarily stops - starting to play with the food or spoon as the infant begins to get full - slowing the pace of eating, or turning away from food when they want to end the meal - stopping eating or spitting out food when they have had enough to eat Introduction of Solid Foods - infants begin with food offered on a spoon in a small portion of 1-2 tablespoons for a meal, with one or 2 meals per day - babies respond strongly to new tastes or smells, regardless of the first food. - Introducing a baby to food on a spoon include these recommendations: - time the first spoon-feeding experiences for when the baby is not overly tired or hungry, but active and playful - offer a small spoon with a shallow bowl. The temperature of the spoon may have to be considered if it can conduct hot or cold readily - give the baby time to open his or her mouth to extend the tongue toward the food. If the baby cannot extend the tongue farther out than the lower lip, the baby is not ready for spoon feeding - place the bowl of the spoon on the tongue with slight downward pressure toward the front of the mouth. Touching the back of the tongue may elicit a gag response - the spoon should be almost level. It is not a good practice to scrape the food off the spoon with the baby s gums by tilting the spoon handle up too high. The baby s chin should be slightly down to protect the airway - the pace of eating should be based on watching for the baby to swallow. Rushing will increase the risk of choking and of the infant having an unpleasant experience - first meals may be small in volume - only 5 or 6 baby spoons - and last about 10 minutes Preparing for Drinking from a Cup - weaning: discontinuation of breastfeeding or bottle-feeding and substitution of food for breast milk or infant formula - recommended age for weaning the infant from the breast or from a bottle to drinking from a cup is from months - developmental readiness for a cup begins at 6-8 months. Inappropriate and Unsafe Food Choices - examples of unsafe foods for infants: - popcorn, - peanuts
6 - raisins, whole grapes - uncut stringy meats - gum and gummy-textured candies - hard candy, jelly beans - hot dog pieces - hard raw fruits or vegetables such as apples, green beans - some foods present a choking risk for infants because of their lower chewing skills. Underchewed pieces of food can obstruct the infant s airway because voluntary coughing and clearing the throat are skills not yet learned Common Nutritional Problems and Concerns - common nutritional problems during infancy are failure to thrive, colic, iron-deficiency, anemia, constipation, dental caries, and food allergies Failure to Thrive - failure to thrive (FTT): condition of inadequate weight or height gain thought to result from a caloric deficit, whether or not the cause can be identified as a health problem - organic failure to thrive: inadequate weight or height gain resulting from a health problem, such as iron-deficiency anemia or a cardiac or genetic disease - nonorganic failure to thrive: inadequate weight or height gain without an identifiable biological cause, so that an environmental cause is suspected - developmental disabilities: general term used to group specific diagnoses together that limit daily living and functioning and occur before age 21 Nutrition Intervention for Failure to Thrive - correction of FTT usually is not as simple as just feeding the baby, but increasing caloric and protein intake is the first step - the dietician s role is to assess the growth and nutritional adequacy, establish a care plan, and provide follow-up as part of a team approach - other interventions include: - gaining agreement from the caregivers about how and when intake and weigh monitoring will be done - enrolling the infant in an early intervention program in the local area Colic - colic: a condition marked by a sudden onset of irritability, fussiness, or crying in a young infant between 2 weeks and 3 months of age who is otherwise growing and healthy - recommendations to relieve colic may include rocking, swaddling, bathing, or other ways of
7 calming the infant, positioning the baby well for eating, or burping to relieve gas or change baby formulas if the infant is not breastfeeding Prevention of Baby-Bottle Caries and Ear Infections - found in children older than 1 year - the use of a bottle containing formula, juice, or other high-carb foods to calm a baby enough to sleep may set her up for dental caries - during sleep, the infant swallows less, allowing the contents of the bottle to pool in the mouth - ear infections are also correlated with excessive use of a baby bottle as a bedtime practice, as a result of the feeding position - the shorter and more vertical tubes in the ears of infants are under different pressure during the process of sucking from a bottle. If the infant is feeding by lying down, the liquid does not fully drain from the ear tubes - good feeding practices to limit baby-bottle caries and ear infections related to baby bottles: - limit the use of a bottle as part of a bedtime ritual - offer juices in a cup, not a bottle - put only water in a bottle if offered for sleep - examine and clean emerging baby teeth to prevent caries from developing Lactose Intolerance - is a food intolerance in infancy characterized by cramps, nausea, and pain, and by alternating diarrhea and constipation - lactose: a form of sugar or carbohydrate composed of galactose and glucose - lactose intolerance is less common during infancy than at older ages in groups that are susceptible to it
Suggested Open Ended Questions Suggested Affirming Statements Suggested Nutrition Education Statements
 Suggested Open Ended Questions Suggested Affirming Statements Suggested Nutrition Education Statements Caregiver: How did your baby s last check-up go? Primary Feeding: Tell me about the kind of formula
Suggested Open Ended Questions Suggested Affirming Statements Suggested Nutrition Education Statements Caregiver: How did your baby s last check-up go? Primary Feeding: Tell me about the kind of formula
Super Baby Food Book Sample Chapter: Starting Solids: What Age? Which Food First? How Much? What Consistency?
 Super Baby Food Book Sample Chapter: Starting Solids: What Age? Which Food First? How Much? What Consistency? When Should I Start Feeding My Baby Solid Foods? The answer is: when your pediatrician tells
Super Baby Food Book Sample Chapter: Starting Solids: What Age? Which Food First? How Much? What Consistency? When Should I Start Feeding My Baby Solid Foods? The answer is: when your pediatrician tells
BREASTFEEDING; HOW? January 14 HELEN BORG, INFANT FEEDING MIDWIFE MATER DEI HOSPITAL
 BREASTFEEDING; HOW? January 14 HELEN BORG, INFANT FEEDING MIDWIFE MATER DEI HOSPITAL 1 THE IMMIGRANT MOTHER- BABY DYAD Challenges to Breastfeeding and Bonding Lack of Information How to enhance milk supply
BREASTFEEDING; HOW? January 14 HELEN BORG, INFANT FEEDING MIDWIFE MATER DEI HOSPITAL 1 THE IMMIGRANT MOTHER- BABY DYAD Challenges to Breastfeeding and Bonding Lack of Information How to enhance milk supply
FAILURE TO THRIVE What Is Failure to Thrive?
 FAILURE TO THRIVE The first few years of life are a time when most children gain weight and grow much more rapidly than they will later on. Sometimes, however, babies and children don't meet expected standards
FAILURE TO THRIVE The first few years of life are a time when most children gain weight and grow much more rapidly than they will later on. Sometimes, however, babies and children don't meet expected standards
Infant and young child feeding practices.
 Infant and young child feeding practices. Few things engender more anxiety than symptoms associated with feeding. Early difficulties can influence a mothers relationship with her baby for months or even
Infant and young child feeding practices. Few things engender more anxiety than symptoms associated with feeding. Early difficulties can influence a mothers relationship with her baby for months or even
Caring for your baby in the NICU: feeding
 C1 At birth, all newborns need a great deal of energy and nutrients from food to help their bodies grow, and to adjust to life outside the womb. Babies who are born early (premature) and/or with a very
C1 At birth, all newborns need a great deal of energy and nutrients from food to help their bodies grow, and to adjust to life outside the womb. Babies who are born early (premature) and/or with a very
Gastroschisis and My Baby
 Patient and Family Education Gastroschisis and My Baby Gastroschisis is a condition where a baby is born with the intestine outside the body. Learning about the diagnosis What is gastroschisis? (pronounced
Patient and Family Education Gastroschisis and My Baby Gastroschisis is a condition where a baby is born with the intestine outside the body. Learning about the diagnosis What is gastroschisis? (pronounced
A Parent s Guide to Understanding Congenital Hypothyroidism. Children s of Alabama Department of Pediatric Endocrinology
 A Parent s Guide to Understanding Congenital Hypothyroidism Children s of Alabama Department of Pediatric Endocrinology How did you get here? Every baby born in the state of Alabama is required by law
A Parent s Guide to Understanding Congenital Hypothyroidism Children s of Alabama Department of Pediatric Endocrinology How did you get here? Every baby born in the state of Alabama is required by law
Breastfed Babies in Child Care. Breastfeeding Works! How to Meet the Needs of
 Breastfeeding Works! How to Meet the Needs of Breastfed Babies in Child Care Massachusetts Department of Public Health Bureau of Family and Community Health Nutrition and Physical Activity Unit WIC Nutrition
Breastfeeding Works! How to Meet the Needs of Breastfed Babies in Child Care Massachusetts Department of Public Health Bureau of Family and Community Health Nutrition and Physical Activity Unit WIC Nutrition
High blood sugars caused by steroids
 High blood sugars caused by steroids Your blood sugars are high because you are taking a medication called steroids. Steroids are used to: decrease swelling decrease the natural response of your immune
High blood sugars caused by steroids Your blood sugars are high because you are taking a medication called steroids. Steroids are used to: decrease swelling decrease the natural response of your immune
Frequently Asked Questions: Gastric Bypass Surgery at CMC
 Frequently Asked Questions: Gastric Bypass Surgery at CMC Please feel free to talk with any member of the Obesity Treatment Center team at Catholic Medical Center regarding any questions, concerns or comments
Frequently Asked Questions: Gastric Bypass Surgery at CMC Please feel free to talk with any member of the Obesity Treatment Center team at Catholic Medical Center regarding any questions, concerns or comments
A guide to infant formula for parents who are bottle feeding
 A guide to infant formula for parents who are bottle feeding Introduction This document is designed to help parents who are not breastfeeding decide which infant formula to use to feed their baby. There
A guide to infant formula for parents who are bottle feeding Introduction This document is designed to help parents who are not breastfeeding decide which infant formula to use to feed their baby. There
Premature Infant Care
 Premature Infant Care Introduction A premature baby is born before the 37th week of pregnancy. Premature babies are also called preemies. Premature babies may have health problems because their organs
Premature Infant Care Introduction A premature baby is born before the 37th week of pregnancy. Premature babies are also called preemies. Premature babies may have health problems because their organs
How To Get Healthy
 Dietary Fiber and Alcohol Nana Gletsu Miller, PhD Fall 2-13 Dietary Fiber It is the complex carbohydrate in plants that can not be broken down by human digestive enzymes Sources Grains Fruits and Vegetables
Dietary Fiber and Alcohol Nana Gletsu Miller, PhD Fall 2-13 Dietary Fiber It is the complex carbohydrate in plants that can not be broken down by human digestive enzymes Sources Grains Fruits and Vegetables
Why is prematurity a concern?
 Prematurity What is prematurity? A baby born before 37 weeks of pregnancy is considered premature. Approximately 12% of all babies are born prematurely. Terms that refer to premature babies are preterm
Prematurity What is prematurity? A baby born before 37 weeks of pregnancy is considered premature. Approximately 12% of all babies are born prematurely. Terms that refer to premature babies are preterm
Digestive System Why is digestion important? How is food digested? Physical Digestion and Movement
 Digestive System The digestive system is made up of the digestive tract a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus and other organs that help the body break down
Digestive System The digestive system is made up of the digestive tract a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus and other organs that help the body break down
FAILURE TO THRIVE DR. IBRAHIM AL AYED
 FAILURE TO THRIVE DR. IBRAHIM AL AYED Q1: What factors influence / control growth? Q2: How to know that a child is not growing normally? Q3: What causes failure to thrive? How to classify it? Q4: What
FAILURE TO THRIVE DR. IBRAHIM AL AYED Q1: What factors influence / control growth? Q2: How to know that a child is not growing normally? Q3: What causes failure to thrive? How to classify it? Q4: What
GESTATIONAL DIABETES. Diabete Gestazionale (Lingua Inglese)
 GESTATIONAL DIABETES Diabete Gestazionale (Lingua Inglese) CONTENTS DEFINITION 03 WHAT CAUSES AND HOW TO MANAGE GESTATIONAL DIABETES 04 HOW TO CONTROL DIABETES 06 CORRECT LIFESTYLE 08 DURING AND AFTER
GESTATIONAL DIABETES Diabete Gestazionale (Lingua Inglese) CONTENTS DEFINITION 03 WHAT CAUSES AND HOW TO MANAGE GESTATIONAL DIABETES 04 HOW TO CONTROL DIABETES 06 CORRECT LIFESTYLE 08 DURING AND AFTER
Breastfeeding vs. Formula Feeding
 KidsHealth.org The most-visited site devoted to children's health and development Breastfeeding vs. Formula Feeding A Personal Decision Choosing whether to breastfeed or formula feed your baby is one of
KidsHealth.org The most-visited site devoted to children's health and development Breastfeeding vs. Formula Feeding A Personal Decision Choosing whether to breastfeed or formula feed your baby is one of
Dietary Fiber and Alcohol. Nana Gletsu Miller, PhD Spring 2014
 Dietary Fiber and Alcohol Nana Gletsu Miller, PhD Spring 2014 Dietary Fiber It is the complex carbohydrate in plants that can not be broken down by human digestive enzymes Sources Grains Fruits and Vegetables
Dietary Fiber and Alcohol Nana Gletsu Miller, PhD Spring 2014 Dietary Fiber It is the complex carbohydrate in plants that can not be broken down by human digestive enzymes Sources Grains Fruits and Vegetables
Off to the best start. Important information about feeding your baby
 Off to the best start Important information about feeding your baby mum s milk the best start for your baby What happens in your baby s first years has a big effect on how healthy he or she will be in
Off to the best start Important information about feeding your baby mum s milk the best start for your baby What happens in your baby s first years has a big effect on how healthy he or she will be in
Parents Guide To Primary Congenital Hypothyroidism
 Parents Guide To Primary Congenital Hypothyroidism California Department of Health Services Genetic Disease Branch www.dhs.ca.gov/gdb To Parents: California State Law requires that all babies have the
Parents Guide To Primary Congenital Hypothyroidism California Department of Health Services Genetic Disease Branch www.dhs.ca.gov/gdb To Parents: California State Law requires that all babies have the
Patient Information Once Weekly FOSAMAX (FOSS-ah-max) (alendronate sodium) Tablets and Oral Solution
 Patient Information Once Weekly FOSAMAX (FOSS-ah-max) (alendronate sodium) Tablets and Oral Solution Read this information before you start taking FOSAMAX *. Also, read the leaflet each time you refill
Patient Information Once Weekly FOSAMAX (FOSS-ah-max) (alendronate sodium) Tablets and Oral Solution Read this information before you start taking FOSAMAX *. Also, read the leaflet each time you refill
Gastrointestinal problems in children with Down's syndrome
 Gastrointestinal problems in children with Down's syndrome by Dr Liz Marder This article was written for parents for the Down s Syndrome Association newsletter and is reproduced here with the permission
Gastrointestinal problems in children with Down's syndrome by Dr Liz Marder This article was written for parents for the Down s Syndrome Association newsletter and is reproduced here with the permission
HIGH FIBER DIET. (Article - Web Site) August 20, 2003
 HIGH FIBER DIET (Article - Web Site) August 20, 2003 Dietary fiber, found mainly in fruits, vegetables, whole grains and legumes, is probably best known for its ability to prevent or relieve constipation.
HIGH FIBER DIET (Article - Web Site) August 20, 2003 Dietary fiber, found mainly in fruits, vegetables, whole grains and legumes, is probably best known for its ability to prevent or relieve constipation.
Breastfeeding Your Baby
 Getting the Help You Need If you have questions or problems, don t wait. Another nursing mother or mothers support group can often help. Your hospital, WIC office, baby s doctor, midwife, or obstetrician/gynecologist
Getting the Help You Need If you have questions or problems, don t wait. Another nursing mother or mothers support group can often help. Your hospital, WIC office, baby s doctor, midwife, or obstetrician/gynecologist
Dietary Fiber. Soluble fiber is fiber that partially dissolves in water. Insoluble fiber does not dissolve in water.
 Dietary Fiber Introduction Fiber is a substance in plants. Dietary fiber is the kind of fiber you get from the foods you eat. Fiber is an important part of a healthy diet. Fiber helps get rid of excess
Dietary Fiber Introduction Fiber is a substance in plants. Dietary fiber is the kind of fiber you get from the foods you eat. Fiber is an important part of a healthy diet. Fiber helps get rid of excess
Nutrients: Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Fats. Chapter 5 Lesson 2
 Nutrients: Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Fats Chapter 5 Lesson 2 Carbohydrates Definition- the starches and sugars found in foods. Carbohydrates are the body s preferred source of energy providing four
Nutrients: Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Fats Chapter 5 Lesson 2 Carbohydrates Definition- the starches and sugars found in foods. Carbohydrates are the body s preferred source of energy providing four
Position Statement on Breastfeeding
 ABN 64 005 081 523 RTO 21659 Applies to All ABA staff and volunteers Position statement The Australian Breastfeeding Association (ABA) endorses the following statement from the Joint WHO/ UNICEF Meeting
ABN 64 005 081 523 RTO 21659 Applies to All ABA staff and volunteers Position statement The Australian Breastfeeding Association (ABA) endorses the following statement from the Joint WHO/ UNICEF Meeting
You may continue to use your old manuals by writing in the detailed changes below:
 STANFORD PATIENT EDUCATION RESEARCH CENTER: CHANGES TO THE DSMP LEADER MANUAL (2012 version to the 2015 version) Stanford has corrected the DSMP manuals with the new ADA guidelines. Call- out icons and
STANFORD PATIENT EDUCATION RESEARCH CENTER: CHANGES TO THE DSMP LEADER MANUAL (2012 version to the 2015 version) Stanford has corrected the DSMP manuals with the new ADA guidelines. Call- out icons and
Ear Infections Gastroenteritis gastroenteritis
 Ear Gastroenteritis Infections gastroenteritis Gastroenteritis can be caused by many different germs, and the effects of gastro on babies and children depend on several things including: the age of the
Ear Gastroenteritis Infections gastroenteritis Gastroenteritis can be caused by many different germs, and the effects of gastro on babies and children depend on several things including: the age of the
CHOC CHILDREN SUROLOGY CENTER. Constipation
 Constipation What is constipation? Constipation is a condition in which a person has uncomfortable or infrequent bowel movements. Generally, a person is considered to be constipated when bowel movements
Constipation What is constipation? Constipation is a condition in which a person has uncomfortable or infrequent bowel movements. Generally, a person is considered to be constipated when bowel movements
Water It s Crucial Role in Health. By: James L. Holly, MD
 Water It s Crucial Role in Health By: James L. Holly, MD After a two week hiatus, we return to our series entitled, Aging Well. It is often the case that in health we become so infatuated with the exotic,
Water It s Crucial Role in Health By: James L. Holly, MD After a two week hiatus, we return to our series entitled, Aging Well. It is often the case that in health we become so infatuated with the exotic,
Problems of the Digestive System
 The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists f AQ FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS FAQ120 WOMEN S HEALTH Problems of the Digestive System What are some common digestive problems? What is constipation?
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists f AQ FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS FAQ120 WOMEN S HEALTH Problems of the Digestive System What are some common digestive problems? What is constipation?
Here's how to include more fiber in your diet.
 July 1, 2012 Welcome to our first newsletter which will address the issue of fiber in your diet. If you are not regular or are having difficulty going to the bathroom then you should consider eating more
July 1, 2012 Welcome to our first newsletter which will address the issue of fiber in your diet. If you are not regular or are having difficulty going to the bathroom then you should consider eating more
BREAST FEEDING TEACHING GUIDE
 BREAST FEEDING TEACHING GUIDE This information was developed to address issues related to breast-feeding and identify problems usually encountered in the first six weeks postpartum after discharge from
BREAST FEEDING TEACHING GUIDE This information was developed to address issues related to breast-feeding and identify problems usually encountered in the first six weeks postpartum after discharge from
DIETARY ADVICE FOR CONSTIPATION
 Leicestershire Nutrition and Dietetic Services DIETARY ADVICE FOR CONSTIPATION What is constipation? Constipation is one of the most common digestive complaints. Normal bowel habits vary between people.
Leicestershire Nutrition and Dietetic Services DIETARY ADVICE FOR CONSTIPATION What is constipation? Constipation is one of the most common digestive complaints. Normal bowel habits vary between people.
Getting Energy from Food Your Digestive System
 9 Getting Energy from Food Your Digestive System The Digestive System You know how your body gets the oxygen it needs. But how do your body s cells get the nutrients they need? Nutrients come from the
9 Getting Energy from Food Your Digestive System The Digestive System You know how your body gets the oxygen it needs. But how do your body s cells get the nutrients they need? Nutrients come from the
Medication Guide. Serious loss of body fluid (dehydration) and changes in blood salts (electrolytes) in your blood.
 Medication Guide MoviPrep (moo-vee-prěp) (PEG 3350, sodium sulfate, sodium chloride, potassium chloride, sodium ascorbate, and ascorbic acid for oral solution) Read this Medication Guide before you start
Medication Guide MoviPrep (moo-vee-prěp) (PEG 3350, sodium sulfate, sodium chloride, potassium chloride, sodium ascorbate, and ascorbic acid for oral solution) Read this Medication Guide before you start
Challenges of Foster Parents who Care for Infants with Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome
 Challenges of Foster Parents who Care for Infants with Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome All Health Care Providers are required by law to make a referral to the Department of Children s Services (DCS) Child
Challenges of Foster Parents who Care for Infants with Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome All Health Care Providers are required by law to make a referral to the Department of Children s Services (DCS) Child
Background (cont) World Health Organisation (WHO) and IDF predict that this number will increase to more than 1,3 million in the next 25 years.
 Diabetes Overview Background What is diabetes Non-modifiable risk factors Modifiable risk factors Common symptoms of diabetes Early diagnosis and management of diabetes Non-medical management of diabetes
Diabetes Overview Background What is diabetes Non-modifiable risk factors Modifiable risk factors Common symptoms of diabetes Early diagnosis and management of diabetes Non-medical management of diabetes
Weight-Loss Surgery for Adults With Diabetes or Prediabetes Who Are at the Lower Levels of Obesity
 Weight-Loss Surgery for Adults With Diabetes or Prediabetes Who Are at the Lower Levels of Obesity A Review of the Research for Adults With a BMI Between 30 and 35 Is This Information Right for Me? If
Weight-Loss Surgery for Adults With Diabetes or Prediabetes Who Are at the Lower Levels of Obesity A Review of the Research for Adults With a BMI Between 30 and 35 Is This Information Right for Me? If
How babies' senses develop
 B2 There is much growth and change that must occur in your baby s body. For babies born full-term (37-40 weeks), this growth and change occurred within the warm, dark, watery womb. For the premature baby,
B2 There is much growth and change that must occur in your baby s body. For babies born full-term (37-40 weeks), this growth and change occurred within the warm, dark, watery womb. For the premature baby,
Level 3. Applying the Principles of Nutrition to a Physical Activity Programme Level 3
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number APNU3.0 Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title MOCK PAPER Time allocation 50 minutes Level 3 Applying
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number APNU3.0 Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title MOCK PAPER Time allocation 50 minutes Level 3 Applying
IDAHO EARLY LEARNING EGUJDELINES
 IDAHO EARLY LEARNING EGUJDELINES Sus-DOMAIN: MOTOR DEVELOPMENT Goal 17: Goal 18: Goal19: Children demonstrate strength and coordination of large motor muscles. Children demonstrate strength and coordination
IDAHO EARLY LEARNING EGUJDELINES Sus-DOMAIN: MOTOR DEVELOPMENT Goal 17: Goal 18: Goal19: Children demonstrate strength and coordination of large motor muscles. Children demonstrate strength and coordination
Common Concerns About Breastfeeding
 Patient Education Page 51 Caring for Yourself and Your New Baby Common Concerns About Breastfeeding Breastfeeding is healthy and natural. So are the questions and concerns that come with it. Whether you
Patient Education Page 51 Caring for Yourself and Your New Baby Common Concerns About Breastfeeding Breastfeeding is healthy and natural. So are the questions and concerns that come with it. Whether you
AGES AND STAGES: BREASTFEEDING DURING YOUR BABY S FIRST YEAR
 AGES AND STAGES: BREASTFEEDING DURING YOUR BABY S FIRST YEAR Adapted from Ages and Stages: What to Expect During Breastfeeding by Vicki Schmidt, RN, IBCLC BREASTFEEDING YOUR 1-2 MONTH OLD 2» Turn his head
AGES AND STAGES: BREASTFEEDING DURING YOUR BABY S FIRST YEAR Adapted from Ages and Stages: What to Expect During Breastfeeding by Vicki Schmidt, RN, IBCLC BREASTFEEDING YOUR 1-2 MONTH OLD 2» Turn his head
Digestive System Functions
 Digestive System Functions A. Gastrointestinal Processes 1. Ingestion: placing food in mouth (voluntary) 2. Propulsion: moving food through GI tract a. Peristalsis: alternating waves of contraction and
Digestive System Functions A. Gastrointestinal Processes 1. Ingestion: placing food in mouth (voluntary) 2. Propulsion: moving food through GI tract a. Peristalsis: alternating waves of contraction and
Breastfeeding. Clinical Case Studies. Residency Curriculum
 Teaching Tool Clinical Case Studies These clinical cases highlight common breastfeeding issues and concerns that your residents will encounter. You can use them during grand rounds, noon lecture, journal
Teaching Tool Clinical Case Studies These clinical cases highlight common breastfeeding issues and concerns that your residents will encounter. You can use them during grand rounds, noon lecture, journal
MEDICATION GUIDE. TOPAMAX (TOE-PA-MAX) (topiramate) Tablets and Sprinkle Capsules
 MEDICATION GUIDE TOPAMAX (TOE-PA-MAX) (topiramate) Tablets and Sprinkle Capsules Read this Medication Guide before you start taking TOPAMAX and each time you get a refill. There may be new information.
MEDICATION GUIDE TOPAMAX (TOE-PA-MAX) (topiramate) Tablets and Sprinkle Capsules Read this Medication Guide before you start taking TOPAMAX and each time you get a refill. There may be new information.
Unit 3L.4: Body Parts and Functions
 Unit 3L.4: Organs in the Human body Keeping Healthy The Skeleton Science skills: Classification Observing Making models Data collection By the end of this unit you should: Compare the structure of humans
Unit 3L.4: Organs in the Human body Keeping Healthy The Skeleton Science skills: Classification Observing Making models Data collection By the end of this unit you should: Compare the structure of humans
Maintaining Nutrition as We Age
 SS-207-06 For more information, visit the Ohio Department of Aging web site at: http://www.goldenbuckeye.com and Ohio State University Extension s Aging in Ohio web site at: http://www.hec.ohio-state.edu/famlife/aging
SS-207-06 For more information, visit the Ohio Department of Aging web site at: http://www.goldenbuckeye.com and Ohio State University Extension s Aging in Ohio web site at: http://www.hec.ohio-state.edu/famlife/aging
ARIZONA WIC. Workbook: High Risk Guidebook for Infants
 Workbook: High Risk Guidebook for Infants A Workbook to Accompany the High Risk Guidebook for Infants Last Updated: Wednesday, September 30, 2015 TABLE OF CONTENTS Table of Contents 2 Using this Workbook
Workbook: High Risk Guidebook for Infants A Workbook to Accompany the High Risk Guidebook for Infants Last Updated: Wednesday, September 30, 2015 TABLE OF CONTENTS Table of Contents 2 Using this Workbook
Nutrition and Your Mental Health. Rebecca Sovdi, Registered Dietitian Health Promotion and Disease Prevention Health Canada, FNIHB
 Nutrition and Your Mental Health Rebecca Sovdi, Registered Dietitian Health Promotion and Disease Prevention Health Canada, FNIHB Nutrition and Your Mental Health l Healthy eating practices - influence,
Nutrition and Your Mental Health Rebecca Sovdi, Registered Dietitian Health Promotion and Disease Prevention Health Canada, FNIHB Nutrition and Your Mental Health l Healthy eating practices - influence,
MEDICATION GUIDE JUXTAPID (JUKS-tuh-pid) (lomitapide) capsules
 MEDICATION GUIDE JUXTAPID (JUKS-tuh-pid) (lomitapide) capsules Read this Medication Guide before your treatment. What is the most important information I should know about JUXTAPID? JUXTAPID is available
MEDICATION GUIDE JUXTAPID (JUKS-tuh-pid) (lomitapide) capsules Read this Medication Guide before your treatment. What is the most important information I should know about JUXTAPID? JUXTAPID is available
GROWING HEALTHY. A Guide for Head Start Health Managers and Families about Healthy Active Living for Young Children
 GROWING HEALTHY A Guide for Head Start Health Managers and Families about Healthy Active Living for Young Children STAFF NOTES START TODAY HELP YOUR YOUNG CHILDREN STAY AT A HEALTHY WEIGHT FOR LIFE Why
GROWING HEALTHY A Guide for Head Start Health Managers and Families about Healthy Active Living for Young Children STAFF NOTES START TODAY HELP YOUR YOUNG CHILDREN STAY AT A HEALTHY WEIGHT FOR LIFE Why
The Digestive System
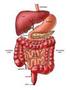 School of Social Work The Digestive System Undergraduate researcher: Nancy D. Bergerson (2010). 1 The Digestive System breaks down and absorbs food. When food is eaten, it is not in a form the body can
School of Social Work The Digestive System Undergraduate researcher: Nancy D. Bergerson (2010). 1 The Digestive System breaks down and absorbs food. When food is eaten, it is not in a form the body can
It s A Gut Feeling: Abdominal Pain in Children. David Deutsch, MD Pediatric Gastroenterology Rockford Health Physicians
 It s A Gut Feeling: Abdominal Pain in Children David Deutsch, MD Pediatric Gastroenterology Rockford Health Physicians Introduction Common Symptom Affects 10-15% of school-aged children Definition (Dr.
It s A Gut Feeling: Abdominal Pain in Children David Deutsch, MD Pediatric Gastroenterology Rockford Health Physicians Introduction Common Symptom Affects 10-15% of school-aged children Definition (Dr.
Nutrition Therapy. ASD Brain Nutrition. HELP My Child Won t Eat! HELP My Child Won t Eat! Nutrients Critical for Brain Function
 HELP My Child Won t Eat! HELP My Child Won t Eat! Elizabeth Strickland, MS, RD, LD PO Box 3297 Glen Rose, TX 76043 Telephone: (830) 237-2886 Fax: (866) 855-8301 Email: [email protected] Website: www.asdpuzzle.com
HELP My Child Won t Eat! HELP My Child Won t Eat! Elizabeth Strickland, MS, RD, LD PO Box 3297 Glen Rose, TX 76043 Telephone: (830) 237-2886 Fax: (866) 855-8301 Email: [email protected] Website: www.asdpuzzle.com
The National Survey of Children s Health 2011-2012 The Child
 The National Survey of Children s 11-12 The Child The National Survey of Children s measures children s health status, their health care, and their activities in and outside of school. Taken together,
The National Survey of Children s 11-12 The Child The National Survey of Children s measures children s health status, their health care, and their activities in and outside of school. Taken together,
Topic 4: Digestion and Nutrition
 Topic 4: Digestion and Nutrition THE CONTENTS OF FOOD Food contains nutrients: Nutrients include: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Nutrients must be small enough to enter our cells. If they are too large they must be digested
Topic 4: Digestion and Nutrition THE CONTENTS OF FOOD Food contains nutrients: Nutrients include: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Nutrients must be small enough to enter our cells. If they are too large they must be digested
Food Allergy Gluten & Diabetes Dr Gary Deed Mediwell 314 Old Cleveland Road Coorparoo 4151 3421 7488
 Food Allergy Gluten & Diabetes Dr Gary Deed Mediwell 314 Old Cleveland Road Coorparoo 4151 3421 7488 SUMMARY Type 1 diabetes Onset common in Children Insulin requiring Immune origins with attack on the
Food Allergy Gluten & Diabetes Dr Gary Deed Mediwell 314 Old Cleveland Road Coorparoo 4151 3421 7488 SUMMARY Type 1 diabetes Onset common in Children Insulin requiring Immune origins with attack on the
Presentation Prepared By: Jessica Rivers, BASc., PTS
 Presentation Prepared By: Jessica Rivers, BASc., PTS Presentation Outline Why should we care about our eating habits? Why is nutrition so important as we age? How do we know if we are eating healthy? What
Presentation Prepared By: Jessica Rivers, BASc., PTS Presentation Outline Why should we care about our eating habits? Why is nutrition so important as we age? How do we know if we are eating healthy? What
Presentation Notes Maintaining a Healthy Digestive System
 Slide 1 Maintaining a Healthy Digestive System 1 Slide 2 Copyright Copyright Texas Education Agency, 2011. These Materials are copyrighted and trademarked as the property of the Texas Education Agency
Slide 1 Maintaining a Healthy Digestive System 1 Slide 2 Copyright Copyright Texas Education Agency, 2011. These Materials are copyrighted and trademarked as the property of the Texas Education Agency
WIC #560 (revised June 2015) WIC #560 (revised June 2015)
 WIC #560 (revised June 2015) WIC #560 (revised June 2015) Table of Contents INFANT NUTRITION MODULE OBJECTIVES... 1 INTRODUCTION... 2 SECTION I: FEEDING THE INFANT FROM BIRTH TO TWELVE MONTHS OF AGE...
WIC #560 (revised June 2015) WIC #560 (revised June 2015) Table of Contents INFANT NUTRITION MODULE OBJECTIVES... 1 INTRODUCTION... 2 SECTION I: FEEDING THE INFANT FROM BIRTH TO TWELVE MONTHS OF AGE...
Constipation in the older child
 Constipation in the older child Definition Constipation in children is a common problem. Constipation in children is often characterized by infrequent bowl movements or hard, dry stools. Various factors
Constipation in the older child Definition Constipation in children is a common problem. Constipation in children is often characterized by infrequent bowl movements or hard, dry stools. Various factors
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM What is digestion? Digestion is the process of breaking down food so that it's small enough to be absorbed and used by the body for energy or in other bodily functions. Digestion involves
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM What is digestion? Digestion is the process of breaking down food so that it's small enough to be absorbed and used by the body for energy or in other bodily functions. Digestion involves
NUTRITION OF THE BODY
 5 Training Objectives:! Knowledge of the most important function of nutrients! Description of both, mechanism and function of gluconeogenesis! Knowledge of the difference between essential and conditionally
5 Training Objectives:! Knowledge of the most important function of nutrients! Description of both, mechanism and function of gluconeogenesis! Knowledge of the difference between essential and conditionally
Breastfeeding. Nursing Education
 Breastfeeding AWHONN supports breastfeeding as the optimal method of infant nutrition. AWHONN believes that women should be encouraged to breastfeed and receive instruction and support from the entire
Breastfeeding AWHONN supports breastfeeding as the optimal method of infant nutrition. AWHONN believes that women should be encouraged to breastfeed and receive instruction and support from the entire
MEDGUIDE SECTION. What is the most important information I should know about SEROQUEL? SEROQUEL may cause serious side effects, including:
 MEDGUIDE SECTION Medication Guide SEROQUEL (SER-oh-kwell) (quetiapine fumarate) Tablets Read this Medication Guide before you start taking SEROQUEL and each time you get a refill. There may be new information.
MEDGUIDE SECTION Medication Guide SEROQUEL (SER-oh-kwell) (quetiapine fumarate) Tablets Read this Medication Guide before you start taking SEROQUEL and each time you get a refill. There may be new information.
Nutritional Challenges After Surgery
 Nutritional Challenges After Surgery L I N D A P A T A K I M S R D C S O L D C N S C M D A N D E R S O N C A N C E R C E N T E R H O U S T O N, T E X A S Objectives Identify the reasons that GIST and its
Nutritional Challenges After Surgery L I N D A P A T A K I M S R D C S O L D C N S C M D A N D E R S O N C A N C E R C E N T E R H O U S T O N, T E X A S Objectives Identify the reasons that GIST and its
Digestive System. About the Digestive System. How Digestion Works
 Digestive System The first step in the digestive process happens before we even taste food. Just by smelling that homemade apple pie or thinking about how delicious that ripe tomato is going to be, you
Digestive System The first step in the digestive process happens before we even taste food. Just by smelling that homemade apple pie or thinking about how delicious that ripe tomato is going to be, you
BENEFITS OF BREASTFEEDING
 BENEFITS OF BREASTFEEDING There are many benefits to breastfeeding. Even if you are able to do it for only a short time, your baby's immune system can benefit from breast milk. Here are many other benefits
BENEFITS OF BREASTFEEDING There are many benefits to breastfeeding. Even if you are able to do it for only a short time, your baby's immune system can benefit from breast milk. Here are many other benefits
MULTIDISCIPLINARY PEDIATRIC FEEDING PROGRAM SCREENING QUESTIONNAIRE QUESTIONNAIRE PAGE OF
 Today s Date: MULTIDISCIPLINARY PEDIATRIC FEEDING PROGRAM BACKGROUND INFORMATION 1. Child s 2. Date of Birth: / / 3. Gender: Male Female 4. Parent/Guardian(s) Name(s): 5. Marital Status: Married Single
Today s Date: MULTIDISCIPLINARY PEDIATRIC FEEDING PROGRAM BACKGROUND INFORMATION 1. Child s 2. Date of Birth: / / 3. Gender: Male Female 4. Parent/Guardian(s) Name(s): 5. Marital Status: Married Single
a guide to understanding pierre robin sequence
 a guide to understanding pierre robin sequence a publication of children s craniofacial association a guide to understanding pierre robin sequence this parent s guide to Pierre Robin Sequence is designed
a guide to understanding pierre robin sequence a publication of children s craniofacial association a guide to understanding pierre robin sequence this parent s guide to Pierre Robin Sequence is designed
BREAST FEEDING AND BOTTLE FEEDING
 BREAST FEEDING AND BOTTLE FEEDING Choosing whether to breastfeed or formula feed your baby is one of the first decisions expectant parents will make. Although there's no right or wrong choice, the American
BREAST FEEDING AND BOTTLE FEEDING Choosing whether to breastfeed or formula feed your baby is one of the first decisions expectant parents will make. Although there's no right or wrong choice, the American
Nutrition: a guide for feeding infants with cystic fibrosis
 Nutrition: a guide for feeding infants with cystic fibrosis Factsheet April 2013 Nutrition: a guide for feeding infants with cystic fibrosis Introduction Feeding a baby with cystic fibrosis (CF) is similar
Nutrition: a guide for feeding infants with cystic fibrosis Factsheet April 2013 Nutrition: a guide for feeding infants with cystic fibrosis Introduction Feeding a baby with cystic fibrosis (CF) is similar
Maintaining Proper Bowel Elimination
 Peak Development Resources, LLC P.O. Box 13267 Richmond, VA 23225 Phone: (804) 233-3707 Fax: (804) 233-3705 After reading the newsletter, the nursing assistant should be able to: 1. Describe the normal
Peak Development Resources, LLC P.O. Box 13267 Richmond, VA 23225 Phone: (804) 233-3707 Fax: (804) 233-3705 After reading the newsletter, the nursing assistant should be able to: 1. Describe the normal
2) Digestion the breakdown of. There are two types of digestion: Mechanical and Chemical. 3) Absorption when the nutrients enter into the blood.
 The Digestive System Video on the digestive system (5 min) The digestive system is responsible for the breakdown of the we eat so that it can be absorbed into the. There are four main stages of the digestive
The Digestive System Video on the digestive system (5 min) The digestive system is responsible for the breakdown of the we eat so that it can be absorbed into the. There are four main stages of the digestive
Gastric Sleeve Surgery
 Gastric Sleeve Surgery Introduction Obesity is associated with many diseases such as diabetes, high blood pressure, heart problems, and degeneration of the joints. These diseases and the obesity itself
Gastric Sleeve Surgery Introduction Obesity is associated with many diseases such as diabetes, high blood pressure, heart problems, and degeneration of the joints. These diseases and the obesity itself
Your child s heart problem and dental care
 Your child s heart problem and dental care Contents p.3 Why is dental health important for my child? p.3 What is tooth decay and what causes it? p.4 How can I prevent this from happening to my child? p.6
Your child s heart problem and dental care Contents p.3 Why is dental health important for my child? p.3 What is tooth decay and what causes it? p.4 How can I prevent this from happening to my child? p.6
Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM)
 Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM) Tena koutou katoa, Kia orana, Talofa lava, Malo e lelei, Fakaalofa lahi atu, Taloha Ni, Ni Sa Bula Vinaka, Greetings and Welcome to National Women's Gestational Diabetes
Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM) Tena koutou katoa, Kia orana, Talofa lava, Malo e lelei, Fakaalofa lahi atu, Taloha Ni, Ni Sa Bula Vinaka, Greetings and Welcome to National Women's Gestational Diabetes
Week 6: Digestive Health
 WEIGHT LOSS BEGINS WITH DIGESTIVE HEALTH Your digestive system is one of the most essential components of your entire body. According to a recent survey, people have a keen interest in digestive health
WEIGHT LOSS BEGINS WITH DIGESTIVE HEALTH Your digestive system is one of the most essential components of your entire body. According to a recent survey, people have a keen interest in digestive health
gestational diabetes my pregnancy, my baby, and me
 gestational diabetes my pregnancy, my baby, and me What is Gestational Diabetes? Gestational diabetes occurs when your body cannot make adequate use of sugar in the blood. It is first found during pregnancy.
gestational diabetes my pregnancy, my baby, and me What is Gestational Diabetes? Gestational diabetes occurs when your body cannot make adequate use of sugar in the blood. It is first found during pregnancy.
MEDICATION GUIDE. (topiramate) Tablets. Sprinkle Capsules
 MEDICATION GUIDE TOPAMAX (TOE-PA-MAX) (topiramate) Tablets TOPAMAX (TOE-PA-MAX) (topiramate) Sprinkle Capsules Read this Medication Guide before you start taking TOPAMAX and each time you get a refill.
MEDICATION GUIDE TOPAMAX (TOE-PA-MAX) (topiramate) Tablets TOPAMAX (TOE-PA-MAX) (topiramate) Sprinkle Capsules Read this Medication Guide before you start taking TOPAMAX and each time you get a refill.
Feeding problems are complicated! And sometimes difficult to treat. Telability: Pediatric Feeding Therapy Using A Medical, Motor, & Behavior Approach
 Telability: Pediatric Feeding Therapy Using A Medical, Motor, & Behavior Approach Krisi Brackett MS SLP/CCC [email protected] What is a Feeding Problem? Developmentally, A feeding problem exists
Telability: Pediatric Feeding Therapy Using A Medical, Motor, & Behavior Approach Krisi Brackett MS SLP/CCC [email protected] What is a Feeding Problem? Developmentally, A feeding problem exists
FORMULA & SPECIALIZED FOOD
 FORMULA & SPECIALIZED FOOD ADMINISTRATIVE POLICY Policy Number: HOME 005.16 T2 Effective Date: December 1, 2014 Table of Contents CONDITIONS OF COVERAGE... COVERAGE RATIONALE BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS...
FORMULA & SPECIALIZED FOOD ADMINISTRATIVE POLICY Policy Number: HOME 005.16 T2 Effective Date: December 1, 2014 Table of Contents CONDITIONS OF COVERAGE... COVERAGE RATIONALE BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS...
Lawrence A. Kotlow D.D.S. P.C. 340 Fuller Road Albany, New York 12203
 Lawrence A. Kotlow D.D.S. P.C. 340 Fuller Road Albany, New York 12203 Practice limited to infants and children from birth to early teens Board Certified Specialist in Pediatric Dentistry 518-489-2571 fax:
Lawrence A. Kotlow D.D.S. P.C. 340 Fuller Road Albany, New York 12203 Practice limited to infants and children from birth to early teens Board Certified Specialist in Pediatric Dentistry 518-489-2571 fax:
MEDICATION GUIDE Trokendi XR (tro-ken-dee eks ahr) (topiramate) Extended-release Capsules
 Page 1 MEDICATION GUIDE Trokendi XR (tro-ken-dee eks ahr) (topiramate) Extended-release Capsules Read this Medication Guide before you start taking Trokendi XR and each time you get a refill. There may
Page 1 MEDICATION GUIDE Trokendi XR (tro-ken-dee eks ahr) (topiramate) Extended-release Capsules Read this Medication Guide before you start taking Trokendi XR and each time you get a refill. There may
MEDICATION GUIDE KOMBIGLYZE XR (kom-be-glyze X-R) (saxagliptin and metformin HCl extended-release) tablets
 MEDICATION GUIDE KOMBIGLYZE XR (kom-be-glyze X-R) (saxagliptin and metformin HCl extended-release) tablets Read this Medication Guide carefully before you start taking KOMBIGLYZE XR and each time you get
MEDICATION GUIDE KOMBIGLYZE XR (kom-be-glyze X-R) (saxagliptin and metformin HCl extended-release) tablets Read this Medication Guide carefully before you start taking KOMBIGLYZE XR and each time you get
B I N G O. Human milk may appear thin and slightly blue in color. There are properties in breastmilk that destroy bacteria.
 BREASTFEEDING BINGO for Childcare Providers Card #1 Produced by Texas Initiative and Texas WIC and putting baby on his back to sleep help prevent SIDS. is good for the environment. Human milk may appear
BREASTFEEDING BINGO for Childcare Providers Card #1 Produced by Texas Initiative and Texas WIC and putting baby on his back to sleep help prevent SIDS. is good for the environment. Human milk may appear
Lesson Title: Nutrient Wise
 Standards This lesson aligns with the OSPI Health and Fitness Standards. This lesson will address GLE 1.5.1 Applies nutrition goals based on dietary guidelines and individual activity needs. GLE 1.5.4
Standards This lesson aligns with the OSPI Health and Fitness Standards. This lesson will address GLE 1.5.1 Applies nutrition goals based on dietary guidelines and individual activity needs. GLE 1.5.4
FIBER IN YOUR DIET WHAT IS FIBER?
 FIBER IN YOUR DIET WHAT IS FIBER? Fiber is the portion of plant foods that our bodies cannot absorb or digest. Fiber is found primarily in fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains. There is no fiber
FIBER IN YOUR DIET WHAT IS FIBER? Fiber is the portion of plant foods that our bodies cannot absorb or digest. Fiber is found primarily in fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains. There is no fiber
BABIES BORN TO ADDICTED MOTHERS
 BABIES BORN TO ADDICTED MOTHERS PATRICA M. MESSERLE LICENSED CLINICAL PSYCHOLOGIST, M.A., ABSNP LICENSED SCHOOL PSYCHOLOGIST DIPLOMATE OF THE AMERICAN BOARD OF SCHOOL- NEUROPSYCHOLOGY 1 Signs and Symptoms
BABIES BORN TO ADDICTED MOTHERS PATRICA M. MESSERLE LICENSED CLINICAL PSYCHOLOGIST, M.A., ABSNP LICENSED SCHOOL PSYCHOLOGIST DIPLOMATE OF THE AMERICAN BOARD OF SCHOOL- NEUROPSYCHOLOGY 1 Signs and Symptoms
What impacts blood glucose levels?
 What you eat and how much you eat has an impact on your blood glucose levels. Your blood glucose level reflects how well your diabetes is controlled. There are many aspects to eating for target BG (Blood
What you eat and how much you eat has an impact on your blood glucose levels. Your blood glucose level reflects how well your diabetes is controlled. There are many aspects to eating for target BG (Blood
