Awareness and Knowledge of Diabetes in Chennai - The Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study [CURES - 9]
|
|
|
- Joan Flynn
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Article Awareness and Knowledge of Diabetes in Chennai - The Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study [CURES - 9] Deepa Mohan*, Deepa Raj*, CS Shanthirani*, Manjula Datta**, NC Unwin***, A Kapur +, V Mohan* Abstract Background and Aim : There are virtually no epidemiological studies from India assessing the level of awareness of diabetes in a whole population. The aim of the present study was to assess the awareness of diabetes in an urban south Indian population in Chennai. Methods : The Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study (CURES) is an ongoing population based study conducted using a systematic sampling method on a representative population (aged 20 years individuals) of Chennai [formerly Madras], the largest city in Southern India. A structured questionnaire was used to obtain information related to demography, education and medical history. The questionnaire included five questions on diabetes awareness. Results : Of the total 26,001 individuals, only 75.5% (19642/26001) of the whole population reported that they knew about a condition called diabetes or conversely nearly 25% of the Chennai population was unaware of a condition called diabetes. 60.2% (15656/26001) of all participants and 76.7% (1173/1529) of the self reported diabetic subjects knew that the prevalence of diabetes was increasing in India. Only 22.2% (5764/ 26001) of the whole population and 41.0% (627/1529) of the known diabetic subjects were aware that diabetes could be prevented. Knowledge of the role of obesity and physical inactivity in producing diabetes was very low, with only 11.9% (3083/26001) of study subjects reporting these as risk factors for diabetes. Only 19.0% (4951/26001) of whole population knew that diabetes could cause complications. Even among the self reported diabetic subjects, only 40.6% (621/1529) were aware that diabetes could produce some complications. Conclusion : Awareness and knowledge regarding diabetes is still grossly inadequate in India. Massive diabetes education programmes are urgently needed both in urban and rural India. INTRODUCTION Demographic transition combined with urbanization and industrialization has resulted in drastic changes in lifestyles globally but the impact is felt more in developing countries because of their more rapid pace of growth. One of the consequences of this transition is a change in disease patterns with communicable diseases being replaced by non-communicable or life style related diseases like diabetes, obesity, cardiovascular disease and cancer. 1 Until a decade ago, diabetes was not considered a major public health problem in developing *Dr. Mohans M.V. Diabetes Specialities Centre and Madras Diabetes Research Foundation, Gopalapuram, Chennai, India; **Department of Epidemiology, The Tamil Nadu Dr. M.G.R. Medical University, Chennai; ***Division of non-communicable diseases (NCD), World Health Organization, Geneva; + World Diabetes Federation, Bangalore. Received : ; Revised : ; Accepted : countries like India but the situation has now dramatically changed. According to the recent World Health Organization report (WHO), India today leads the world with over 32 million diabetic patients and this number is projected to increase to 79.4 million by the year Recent surveys indicate that diabetes now affects a staggering 10-16% of the urban population in India. 3-5 Diabetes has thus become a great economic challenge as it drains between 5 25 % of the family income of an average Indian, 6 which translates to 2.2 billion US dollars per annum. 7,8 The quality of life is also greatly affected particularly in young adults, the group which is predicted to see the greatest increase in diabetes prevalence in developing countries. 2 There is very little data on the level of awareness about diabetes in developing countries like India. Such data is extremely important to plan the public health polices with specific reference to implementation of national JAPI VOL. 53 APRIL
2 diabetes control programs. A literature search on knowledge about diabetes in developing countries yielded very few studies actually dealing with the awareness of diabetes among people with the disease 9,10 and virtually no data on a whole population. Even in other developing countries, such studies have mainly focused on diabetic patients and are mostly clinic based which introduces referral bias Knowledge about the level of awareness about diabetes in a population is the first step in formulating a prevention programme for diabetes. This study is a step in this direction where the awareness and knowledge of diabetes in urban Chennai in southern India was assessed in a population-based study. METHODS AND MATERIAL The study subjects were recruited from the Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study (CURES), an ongoing epidemiological study conducted on a representative population (aged 20 years) of Chennai (formerly Madras) the fourth largest city in India. The methodology of the study has been published elsewhere. 13 Briefly, in Phase 1 of the urban component of CURES, 26,001 individuals were recruited based on a systematic sampling technique covering the whole population of Chennai. Self reported diabetes (n=1529) was diagnosed if the subjects stated that they had diabetes and or if they were on treatment with anti-diabetic drugs. 14 A detailed questionnaire was used to obtain basic data regarding awareness, knowledge, traditional beliefs, treatment practices and other issues. Educational status was graded as illiterates, middle school, high school, graduates, postgraduates and professionals. Table 1 shows a partial set of questions used for the survey which was administered both in English as well as local language (Tamil). Table 1 : Questions used for obtaining data regarding knowledge of diabetes Questions 1. Do you know what diabetes is? Yes No 2. Do you think, in general, more and more people are getting affected with with diabetes nowadays? 3. What are the factors you think that contribute to diabetes? a. Obesity b. Decreased physical activity c. Family history of diabetes d. Mental stress e. Consuming more sweets f. Others (name) 4. Do you know that diabetes can cause complications in other organs? a) If yes, what are they? Can diabetes be prevented? Composite score for knowledge of diabetes The answers to the questions were analyzed and a scoring system was used as follows: a) For closed questions, 1,2,4,5 correct answers were graded as 1 and incorrect answers (inclusive of don t know ) as 0. b) For question No. 3 which was on causative factors for diabetes, highest score of 4 was awarded for subjects who ticked obesity, decreased physical activity or family history of diabetes, 3 was given for consuming sweets and other high calorie or junk foods, 2 for mental stress and 1 for any other answer which made sense or was close to the above answers, while all other answers were scored 0. c) Thus the least possible score was 0 if all answers were incorrect and the maximum score was 8, if all answers were correct. d) A composite score in percentage was then derived by dividing each individual s score by the maximum score possible e.g. if an individual had obtained 2 correct answers, for the closed question 1,2,4,5 and ticked mental stress (score = 2) for question no. 3, then the composite score would be 4 / 8 X100 = 50% RESULTS Knowledge about diabetes and its prevalence Only 75.5% (19642/26001) of the whole population reported that they knew about a condition called diabetes or conversely nearly 25% of the Chennai population was unaware of a condition called diabetes. 77.6% (9956/12838) of males knew about diabetes compared to 73.6% (9684/13163) of females. 60.2% (15656/26001) of participants felt that the prevalence of diabetes was increasing (62.6% of males (8032/12838) and 57.9% (7624/13163) of females). Even among selfreported diabetic subjects, only 76.7% (1173/1529) knew that the prevalence of diabetes was increasing in India [Fig. 1]. Knowledge of prevention of diabetes Only 22.2% (5764/26001) of the whole population Fig. 1 : Knowledge about diabetes in subjects with and without self reported diabetes JAPI VOL. 53 APRIL 2005
3 Table 2 : Various causes of diabetes as stated by the participants Causes Individuals with self Non-diabetic Total population reported diabetes population (n = 26,001) (n = 1,529) (n = 24,472) Family history of diabetes n(%) 584 (38.2) 7627 (31.2) 8211 (31.6) Consuming more sweets n(%) 341 (22.3) 5194 (21.2) 5535 (21.3) Lack of physical activity n(%) 143 (9.4) 1851(7.6) 1994 (7.7) Obesity n(%) 98 (6.4) 1107 (4.5) 1205 (4.6) Mental stress n(%) 80 (5.2 ) 954 (3.9) 1034 (4.0) The numbers will not add up to 100% as some of the participants ticked multiple risk factors. Table 3 : Knowledge of diabetic complications Complications Individuals Non- Total with self diabetic population reported population (n = 4951) diabetes (n =4330 ) (n = 621) Fig. 2 : Response to the question on diabetes prevention in related to education levels. and 41.0% (627/1529) of the known diabetic subjects were aware that diabetes could be prevented. As expected, knowledge about prevention of diabetes increased with the level of education. However, even among postgraduates and professionals which included lawyers and doctors, only 42.6% (102/185) felt diabetes was preventable [Fig. 2]. Knowledge about risk factors for diabetes The list of causes of diabetes as stated by the participants is shown in Table 2. Only 31.2% (7627/ 26001) of the participants felt that family history of diabetes was one of the causes of diabetes and 21.2% (5197/26001) listed consuming sweets and high calorie foods as the main reason for diabetes. Even among self reported diabetic subjects, only 38.2% (584/1529) felt that family history of diabetes was a cause of diabetes. Knowledge of the role of obesity and physical inactivity in producing diabetes was very low, with only 11.9% (3083/26001) of study subjects reporting these as risk factors for diabetes. The other causes of diabetes stated by the participants were overeating 0.08% (22/26001), alcohol consumption 0.01% (3/26001), smoking 0.01% (3/26001) and vitamin deficiency 0.004% (1/26001). Thirty seven percent of study subjects (9612/26001) did not provide any answer for this question. Awareness of complications of diabetes Only 19.0% (4951/26001) of whole population knew that diabetes could cause complications. Even among those who knew that diabetes could cause complications, 55.7% (2756/4951) were not able to specify a single organ which could get affected. Among those who knew about diabetic complications, the most common complications reported by the non-diabetic Foot problems n(%) 143 (23.0) 942 (21.8) 1085 (21.9) Kidney disease n(%) 108 (17.4) 688 (15.9) 796 (16.1) Eye disease n(%) 91 (14.7) 704 (16.3) 795 (16.1) Hypertension n(%) 43 (6.9) 412 (9.5) 455 (9.2) Heart attack n(%) 36 (5.8) 253 (5.8) 289 (5.8) Stroke n(%) 12 (1.9) 96 (2.2) 108 (2.2) Note : Only 4951 (19.0%) of the whole population and 621 (40.6%) of the self reported diabetic subjects answered Yes to the question Do you know that diabetes can cause complications in other organs? Table 4 : Composite knowledge score of diabetes Composite Individuals with Non-diabetic Total score self reported population population diabetes (n =24472 ) (n = 26001) (n =1529) 0 n(%) 3523 (14.4) 3523 (13.5) 1-24 n(%) 107 (7.0) 2200 (9.0) 2307 (8.9) n(%) 339 (22.2) 4845 (19.8) 5184 (19.9) n(%) 385 (25.2) 6628 (27.1) 7013 (27.0) n(%) 543 (35.5) 6577 (26.9) 7120 (27.4) 100 n(%) 155 (10.1) 699 (2.9) 854 (3.3) population were foot problems (21.8%), kidney disease (15.9%) and eye disease (16.3%). Other complications like heart attacks, hypertension and stroke were occasionally mentioned. Even among the self reported diabetic subjects, only 40.6% (621/1529) were aware that diabetes could produce some complications. Foot problems (23.0%) and kidney disease (17.4%) were the most commonly reported complications (Table 3). Composite score for knowledge about diabetes The mean percent score of the total population regarding knowledge of diabetes was 47.5%. Among the non diabetic population, 14.4% (3523/24472) obtained the least score (0%) and only 2.9% (699/24472) obtained the maximum score of 8 (100%) [Table 4]. Even among the self reported diabetic subjects, only 10.1% (155/1529) could get the maximum score. Table 5 shows the mean value of composite scores (percent) in relation to levels JAPI VOL. 53 APRIL
4 Table 5 : Mean composite score (percent) values according to education in the total population Composite Individuals with Non-diabetic Total score self reported population population diabetes (n =24472 ) (n = 26001) (n =1529) Illiterates 54.7 ± ± ± 29.9 Middle school 59.2 ± ± ± 30.0 High school 65.1 ± ± ± 29.6 Graduates 66.3 ± ± ± 28.8 Post graduates 67.1 ± ± ± 28.2 and professionals of education. The mean percent score increased with level of education, with professionals scoring the highest. DISCUSSION The major finding in the study is the lack of awareness of diabetes among the Chennai residents. This is worrying in the context of the fact that India currently leads the world with over 32 million diabetic subjects and these numbers are expected to increase to 79.4 by the year Moreover, the WHO report predicts that while the main increase in diabetes would be in the >65 years age group in developed countries, in India and other developing countries, the highest increase would occur in the age group of years which includes people in the peak of their lives. This can have a huge negative impact on the economy of developing countries. This underscores the urgent need to improve the knowledge and awareness about diabetes particularly in developing countries like India. In this context, it is noteworthy that nearly 25% of Chennai residents were not even aware of a condition called diabetes. Not surprisingly, knowledge about complications of diabetes was even worse. Table 4 shows that the knowledge scores by self reported diabetic subjects were not very much higher than non diabetic subjects. The fact that even among self reported diabetic subjects, knowledge about diabetes including awareness of complications of diabetes was poor indicates that the majority of patients have not been taught about diabetes by their physicians. This may be due to several factors such as inappropriate ways of providing information and most importantly lack of time due to the huge patient loads and lack of appropriately trained support staff like educators 15. This emphasizes the need for more continuing medical education programmes on diabetes for doctors and also for developing a cadre of diabetes educators in developing countries in order that better diabetes education is imparted to patients. Recent studies like the Diabetes Prevention Programme, 16 the Finnish Diabetes Prevention Study 17 and the Da Qing study 18 have clearly demonstrated that diabetes is preventable. Yet even among highly qualified professionals, less than 60% knew that diabetes could be prevented, and even among known diabetic subjects less than 50% knew that the disease is preventable. This shows that the results of path breaking clinical trials percolates down to the community very slowly and extra efforts must be made to transmit important public health messages through the popular press and media. It is also clear that unless individuals with diabetes know that the disease can be transmitted to the offspring, steps cannot be taken to prevent diabetes in the next generation, which would be the target high risk group. The questions related to risk factors for diabetes revealed that many misconceptions were present and more worrisome was the fact that only 12% were aware that obesity and physical inactivity could predispose to diabetes. Traditionally in poor and developing economies being overweight is considered as a sign of health, wealth and power. This perception drives food habits, eating and exercise behavior. As prevention of diabetes is primarily dependent on altering lifestyle and increasing levels of physical activity, changing societal perceptions of health and improving knowledge about the risk factors of diabetes and steps to promote physical activity must receive urgent attention of policy makers and health care planners. It is likely that the results of the study represent only the tip of the iceberg and indeed probably perhaps reflects the best scenario in India as Chennai is traditionally considered to be the one of the best cities in India in terms of diabetes education activities for several reasons. One of the first diabetic clinics in India was established at the Government Stanley Hospital, Chennai in the year Two of the senior most diabetologists of India worked tirelessly for nearly 50 years promoting the cause of diabetes and trained several diabetologists who practice in Chennai. Currently there are atleast five major private diabetes care centres in addition to several government run diabetic clinics in Chennai, one of the highest in any city in the country. In addition, three major diabetes exhibitions have been organized in Chennai during the last 6 years which have been attended by several thousand people. 19 With all these well organized diabetes activities, Chennai is considered the model city for diabetes related activities in India. One can therefore safely assume that the situation in other cities in India is probably much worse, not to speak of rural areas where knowledge regarding diabetes could be expected to be abysmally poor. This emphasizes the need for carrying the right messages regarding diabetes right down to the masses and also extending diabetes education activities to rural areas as well where the prevalence rates of diabetes have already begun to rise. 20 There are several limitations in using a questionnaire such as this for assessing knowledge of a disease in the community: open-ended questions often depend on the verbal ability and recall memory while some closed JAPI VOL. 53 APRIL 2005
5 questions can be guessed by the respondent. However, for large population based studies such as this, use of a questionnaire is perhaps the only feasible method to obtain such data. Moreover, the fact that it was conducted on a large representative sample of Chennai and the absence of such data from any developing country, make the results significant. In conclusion, this study done on a large representative sample of Chennai city in southern India reflects the poor knowledge and awareness about diabetes in urban India. This emphasizes the need for increasing diabetes awareness activities in the form of mass media campaigns, public lectures and door to door campaigns on a massive scale in both urban and rural India. Acknowledgement We are grateful to the Chennai Willingdon Corporate Foundation, Chennai for the financial support provided for the study. This is the 9 th publication from Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study (CURES) REFERENCES 1. Omran AR. The epidemiologic transition. A theory of the epidemiology of population change. Milbank Mem Fund Q 1971;49: Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, Sicree R, King H. Global prevalence of diabetes: estimates for the year 2000 and projections for Diabetes Care 2004;27: Ramachandran A, Snehalatha C, Kapur A, et al. For the Diabetes Epidemiology Study Group in India (DESI). High prevalence of diabetes and impaired glucose tolerance in India: National Urban Diabetes Survey. Diabetologia 2001;44: Mohan V, Shanthirani CS, Deepa R. Glucose intolerance (diabetes and IGT) in a selected south Indian population with special reference to family history, obesity and life style factors The Chennai Urban Population Study (CUPS 14). J Assoc Physicians India 2003;51: Pradeepa R, Mohan V. The changing scenario of the diabetes epidemic: implications for India. Indian J Med Res 2002;116: Shobhana R, Rama Rao P, Lavanya A, Williams R, Vijay V, Ramachandran A. Expenditure on health care incurred by diabetic subjects in a developing country a study from southern India. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2000;48: Bjork S, Kapur A, King H, Nair J, Ramachandran A. Global policy: aspects of diabetes in India. Health Policy 2003;66: Raheja BS, Kapur A, Bhoraskar A, et al. DiabCare Asia India Study: diabetes care in India current status. J Assoc Physicians India 2001;49: Wee HL, Ho HK, Li SC. Public awareness of diabetes mellitus in Singapore. Singapore Med J 2002;43: Badruddin N, Basit A, Hydrie MZI, Hakeem R. Knowledge, attitude and practices of patients visiting a diabetes care unit. Pak J Nutrition 2002;1: Ambigapathy R, Ambigapathy S, Ling HM. A Knowledge, Attitude and practice (KAP) study of diabetes mellitus among patients attending Klinik Kesihatan Seri Manjung. NCD Malaysia : Habib SS, Aslam M. Risk factors, knowledge and health status in diabetic patients. Saudi Med J 2003;24: Deepa M, Pradeepa R, Rema M, Mohan A, Deepa R, Shanthirani S, Mohan V. The Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study (CURES) study design and methodology (urban component) (CURES-I). J Assoc Physicians India 2003;51: Report of the Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of diabetes mellitus. The Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Care 1997;20: Kapur A, Influence of socio-economic factors on diabetes care. Int J Diab Dev Countries 2001;21: Knowler WC, Barrett-Connor E, Fowler SE, et al. Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group. Reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes with lifestyle intervention or metformin. N Engl J Med 2002;346: Tuomilehto J, Lindstrom J, Eriksson JG, et al. Finnish Diabetes Prevention Study Group. Prevention of Type 2 diabetes mellitus by changes in lifestyle among subjects with impaired glucose tolerance. N Engl J Med 2001;344: Li G, Hu Y, Yang W, et al. Effects of insulin resistance and insulin secretion on the efficacy of interventions to retard development of type 2 diabetes mellitus: the DA Qing IGT and Diabetes Study. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2002;58: Mohan V. Thinking big to raise awareness in India: the mega diabetes show. Diabetes Voice. Bulletin of the International Diabetes Federation. 2003;48: Ramachandran A, Snehalatha C, Baskar AD, et al. Temporal changes in prevalence of diabetes and impaired glucose tolerance associated with lifestyle transition occurring in the rural population in India. Diabetologia 2004;47: Announcement Regional Asian Stroke Congress Regional Asian Stroke Congress will be held in Chennai on January 5-8, Eminent International and National Faculty will discuss the National and Regional Stroke themes by way of invited/special lectures, plenary sessions, interactive group discussions on various aspects of stroke. A consensus document for Asian Region on public awareness/education and optimal low-cost diagnostic and therapeutic approaches for urban and rural areas will be discussed. Control of Risk Factors and Stroke Prevention Strategies will be major themes. This International Regional meeting is endorsed by International Stroke Society. For details on registration/participation please contact: Dr. G Arjundas, President: Indian Stroke Association, 36, Pantheon Road, Egmore, Chennai, India Tel: ; arjundas@satyam.net.in JAPI VOL. 53 APRIL
Management of Diabetes Mellitus among Elderly Men and Women Impact of Intervention Programme
 International Research Journal of Biological Sciences ISSN 2278-3202 Management of Diabetes Mellitus among Elderly Men and Women Impact of Intervention Programme Roopa K.S. and Rama Devi G. Dept. of Human
International Research Journal of Biological Sciences ISSN 2278-3202 Management of Diabetes Mellitus among Elderly Men and Women Impact of Intervention Programme Roopa K.S. and Rama Devi G. Dept. of Human
Prevalence of Undiagnosed Type 2 Diabetes and its Associated Risk Factors in Rural Population of Tamil Nadu
 World Journal of Medical Sciences 11 (2): 222-227, 2014 ISSN 1817-3055 IDOSI Publications, 2014 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.wjms.2014.11.2.84252 Prevalence of Undiagnosed Type 2 Diabetes and its Associated Risk
World Journal of Medical Sciences 11 (2): 222-227, 2014 ISSN 1817-3055 IDOSI Publications, 2014 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.wjms.2014.11.2.84252 Prevalence of Undiagnosed Type 2 Diabetes and its Associated Risk
Life Style and Nutritional Profile of Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus (NIDDM) Patients
 Life Style and Nutritional Profile of Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus (NIDDM) Patients Kaur, I. P. and Kalra, R. Govt. College for Girls, Patiala-147001, Punjab, India Abstract The present investigation
Life Style and Nutritional Profile of Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus (NIDDM) Patients Kaur, I. P. and Kalra, R. Govt. College for Girls, Patiala-147001, Punjab, India Abstract The present investigation
The Burden of the Complicated Type 2 Diabetes Patient in China. White Paper
 White Paper Catalysts driving successful decisions in life sciences. The Burden of the Complicated Type 2 Diabetes Patient in China by Marco DiBonaventura, Ph.D. Director, Health Economics and Outcomes
White Paper Catalysts driving successful decisions in life sciences. The Burden of the Complicated Type 2 Diabetes Patient in China by Marco DiBonaventura, Ph.D. Director, Health Economics and Outcomes
ECONOMIC COSTS OF PHYSICAL INACTIVITY
 ECONOMIC COSTS OF PHYSICAL INACTIVITY This fact sheet highlights the prevalence and health-consequences of physical inactivity and summarises some of the key facts and figures on the economic costs of
ECONOMIC COSTS OF PHYSICAL INACTIVITY This fact sheet highlights the prevalence and health-consequences of physical inactivity and summarises some of the key facts and figures on the economic costs of
Diagnosis, classification and prevention of diabetes
 Diagnosis, classification and prevention of diabetes Section 1 1 of 4 Curriculum Module II 1 Diagnosis, classification and presentation of diabetes Slide 2 of 48 Polyurea Definition of diabetes Slide 3
Diagnosis, classification and prevention of diabetes Section 1 1 of 4 Curriculum Module II 1 Diagnosis, classification and presentation of diabetes Slide 2 of 48 Polyurea Definition of diabetes Slide 3
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition that occurs as a result of problems with the production and/or action of insulin in the body.
 International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Background Information Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition that occurs as a result of problems with the production and/or action of insulin in the body.
International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Background Information Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition that occurs as a result of problems with the production and/or action of insulin in the body.
Knowledge of diabetes mellitus amongst nursing students Effect of an intervention
 Knowledge of diabetes mellitus amongst nursing students Effect of an intervention Sukhpal Kaur, Indarjit Walia Abstract : Nurses are the key providers of diabetes care. However the information provided
Knowledge of diabetes mellitus amongst nursing students Effect of an intervention Sukhpal Kaur, Indarjit Walia Abstract : Nurses are the key providers of diabetes care. However the information provided
CHAPTER V DISCUSSION. normal life provided they keep their diabetes under control. Life style modifications
 CHAPTER V DISCUSSION Background Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition but people with diabetes can lead a normal life provided they keep their diabetes under control. Life style modifications (LSM)
CHAPTER V DISCUSSION Background Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition but people with diabetes can lead a normal life provided they keep their diabetes under control. Life style modifications (LSM)
6.4 Diabetes. 6 Priority diseases and reasons for inclusion. Background. Developments since 2004. See Background Paper 6.4 (BP6_4DM.
 6 Priority diseases and reasons for inclusion 6.4 Diabetes See Background Paper 6.4 (BP6_4DM.pdf) Background Diabetes and diabetes-related illnesses place an enormous burden on the health care systems
6 Priority diseases and reasons for inclusion 6.4 Diabetes See Background Paper 6.4 (BP6_4DM.pdf) Background Diabetes and diabetes-related illnesses place an enormous burden on the health care systems
Mortality Associated with Diabetes
 Mortality Associated with Diabetes A review paper prepared for the 7th Global Conference of Actuaries, New Delhi, 15-16 February, 2005 Dr. David Muiry, MB;BS, FIA, FASI David_Muiry@swissre.com Introduction
Mortality Associated with Diabetes A review paper prepared for the 7th Global Conference of Actuaries, New Delhi, 15-16 February, 2005 Dr. David Muiry, MB;BS, FIA, FASI David_Muiry@swissre.com Introduction
Type 2 Diabetes in India: Challenges and Possible Solutions
 Chapter 40 Type 2 Diabetes in India: Challenges and Possible Solutions Ambady Ramachandran, Ananth Samith Shetty, Arun Nanditha, Chamukuttan Snehalatha INTRODUCTION ABSTRACT India has huge health care
Chapter 40 Type 2 Diabetes in India: Challenges and Possible Solutions Ambady Ramachandran, Ananth Samith Shetty, Arun Nanditha, Chamukuttan Snehalatha INTRODUCTION ABSTRACT India has huge health care
NCDs POLICY BRIEF - INDIA
 Age group Age group NCDs POLICY BRIEF - INDIA February 2011 The World Bank, South Asia Human Development, Health Nutrition, and Population NON-COMMUNICABLE DISEASES (NCDS) 1 INDIA S NEXT MAJOR HEALTH CHALLENGE
Age group Age group NCDs POLICY BRIEF - INDIA February 2011 The World Bank, South Asia Human Development, Health Nutrition, and Population NON-COMMUNICABLE DISEASES (NCDS) 1 INDIA S NEXT MAJOR HEALTH CHALLENGE
How To Prevent Type 2 Diabetes
 Introduction The Primary Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes AADE Practice Synopsis Issued December 1, 2014 The prevalence of type 2 diabetes is reaching epidemic proportions with more than 9.3% of adults in
Introduction The Primary Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes AADE Practice Synopsis Issued December 1, 2014 The prevalence of type 2 diabetes is reaching epidemic proportions with more than 9.3% of adults in
Epidemiology of hypertension and its risk factors in a village of west Bengal
 Original Research Paper IJRRMS 03;3(3) Epidemiology of hypertension and its risk factors in a village of west Bengal Basu G, Biswas S ABSTRACT Background: Hypertension is a leading public health problem
Original Research Paper IJRRMS 03;3(3) Epidemiology of hypertension and its risk factors in a village of west Bengal Basu G, Biswas S ABSTRACT Background: Hypertension is a leading public health problem
Diabetes. Gojka Roglic. Department of Chronic Diseases and Health Promotion. World Health Organization
 Diabetes Gojka Roglic What is diabetes? Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disorder of multiple aetiology, characterized by chronic hyperglycaemia with disturbances of carbohydrate, fat and protein metabolism
Diabetes Gojka Roglic What is diabetes? Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disorder of multiple aetiology, characterized by chronic hyperglycaemia with disturbances of carbohydrate, fat and protein metabolism
Treating Patients with PRE-DIABETES David Doriguzzi, PA-C First Valley Medical Group. Learning Objectives. Background. CAPA 2015 Annual Conference
 Treating Patients with PRE-DIABETES David Doriguzzi, PA-C First Valley Medical Group Learning Objectives To accurately make the diagnosis of pre-diabetes/metabolic syndrome To understand the prevalence
Treating Patients with PRE-DIABETES David Doriguzzi, PA-C First Valley Medical Group Learning Objectives To accurately make the diagnosis of pre-diabetes/metabolic syndrome To understand the prevalence
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is defined
 Prevalence of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in a Medical College in South India: A Pilot Study K Sreekanthan*, A Belicita, K Rajendran, Anil Vijayakumar Abstract Background: The prevalence of diabetes
Prevalence of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in a Medical College in South India: A Pilot Study K Sreekanthan*, A Belicita, K Rajendran, Anil Vijayakumar Abstract Background: The prevalence of diabetes
THE NHS HEALTH CHECK AND INSURANCE FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
 THE NHS HEALTH CHECK AND INSURANCE FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS Introduction The following document has been produced by the Department of Health in partnership with the Association of British Insurers,
THE NHS HEALTH CHECK AND INSURANCE FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS Introduction The following document has been produced by the Department of Health in partnership with the Association of British Insurers,
Connecticut Diabetes Statistics
 Connecticut Diabetes Statistics What is Diabetes? State Public Health Actions (1305, SHAPE) Grant March 2015 Page 1 of 16 Diabetes is a disease in which blood glucose levels are above normal. Blood glucose
Connecticut Diabetes Statistics What is Diabetes? State Public Health Actions (1305, SHAPE) Grant March 2015 Page 1 of 16 Diabetes is a disease in which blood glucose levels are above normal. Blood glucose
Shutterstock TACstock
 Shutterstock TACstock 10 Introduction Since 2000, the IDF Diabetes Atlas has detailed the extent of diabetes and this seventh edition shows how it is impacting every country, every age group and every
Shutterstock TACstock 10 Introduction Since 2000, the IDF Diabetes Atlas has detailed the extent of diabetes and this seventh edition shows how it is impacting every country, every age group and every
Type 2 Diabetes: Making Prevention a Priority The IGT Care Call Project
 Type 2 Diabetes: Making Prevention a Priority The IGT Care Call Project Katherine Grady, Care Call Development Manager, SRFT. Linda Savas, Knowledge Transfer Associate, NIHR CLAHRC Greater Manchester.
Type 2 Diabetes: Making Prevention a Priority The IGT Care Call Project Katherine Grady, Care Call Development Manager, SRFT. Linda Savas, Knowledge Transfer Associate, NIHR CLAHRC Greater Manchester.
Diabetes. C:\Documents and Settings\wiscs\Local Settings\Temp\Diabetes May02revised.doc Page 1 of 12
 Diabetes Introduction The attached paper is adapted from the initial background paper on Diabetes presented to the Capital and Coast District Health Board Community and Public Health Advisory Committee
Diabetes Introduction The attached paper is adapted from the initial background paper on Diabetes presented to the Capital and Coast District Health Board Community and Public Health Advisory Committee
THE STUDY OF NEWLY DISCOVERED CASES OF DIABETES MELLITUS IN BIHOR COUNTY
 Analele UniversităŃii din Oradea Fascicula:Ecotoxicologie, Zootehnie şi Tehnologii de Industrie Alimentară, 2012 THE STUDY OF NEWLY DISCOVERED CASES OF DIABETES MELLITUS IN BIHOR COUNTY *University of
Analele UniversităŃii din Oradea Fascicula:Ecotoxicologie, Zootehnie şi Tehnologii de Industrie Alimentară, 2012 THE STUDY OF NEWLY DISCOVERED CASES OF DIABETES MELLITUS IN BIHOR COUNTY *University of
Upstate New York adults with diagnosed type 1 and type 2 diabetes and estimated treatment costs
 T H E F A C T S A B O U T Upstate New York adults with diagnosed type 1 and type 2 diabetes and estimated treatment costs Upstate New York Adults with diagnosed diabetes: 2003: 295,399 2008: 377,280 diagnosed
T H E F A C T S A B O U T Upstate New York adults with diagnosed type 1 and type 2 diabetes and estimated treatment costs Upstate New York Adults with diagnosed diabetes: 2003: 295,399 2008: 377,280 diagnosed
4. Does your PCT provide structured education programmes for people with type 2 diabetes?
 PCT Prescribing Report Drugs used in Type 2 Diabetes Discussion Points 1. Does your PCT have a strategy for prevention of type 2 diabetes? Does your PCT provide the sort of intensive multifactorial lifestyle
PCT Prescribing Report Drugs used in Type 2 Diabetes Discussion Points 1. Does your PCT have a strategy for prevention of type 2 diabetes? Does your PCT provide the sort of intensive multifactorial lifestyle
WHAT DOES DYSMETABOLIC SYNDROME MEAN?
 ! WHAT DOES DYSMETABOLIC SYNDROME MEAN? Dysmetabolic syndrome (also referred to as syndrome X, insulin resistance syndrome, and metabolic syndrome ) is a condition in which a group of risk factors for
! WHAT DOES DYSMETABOLIC SYNDROME MEAN? Dysmetabolic syndrome (also referred to as syndrome X, insulin resistance syndrome, and metabolic syndrome ) is a condition in which a group of risk factors for
Diabetes: The Numbers
 Diabetes: The Numbers Changing the Way Diabetes is Treated. What is Diabetes? Diabetes is a group of diseases characterized by high levels of blood glucose (blood sugar) Diabetes can lead to serious health
Diabetes: The Numbers Changing the Way Diabetes is Treated. What is Diabetes? Diabetes is a group of diseases characterized by high levels of blood glucose (blood sugar) Diabetes can lead to serious health
How To Determine The Prevalence Of Microalbuminuria
 Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences Prevalence of Microalbuminuria in relation to HbA1c among known Type2 Diabetic Patients in Puducherry population Muraliswaran P 1 *,
Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences Prevalence of Microalbuminuria in relation to HbA1c among known Type2 Diabetic Patients in Puducherry population Muraliswaran P 1 *,
Pricing the Critical Illness Risk: The Continuous Challenge.
 Pricing the Critical Illness Risk: The Continuous Challenge. To be presented at the 6 th Global Conference of Actuaries, New Delhi 18 19 February 2004 Andres Webersinke, ACTUARY (DAV), FASSA, FASI 9 RAFFLES
Pricing the Critical Illness Risk: The Continuous Challenge. To be presented at the 6 th Global Conference of Actuaries, New Delhi 18 19 February 2004 Andres Webersinke, ACTUARY (DAV), FASSA, FASI 9 RAFFLES
A Fuzzy Logic Based Model for Life Insurance Underwriting When Insurer Is Diabetic
 European Journal of Applied Sciences 4 (5): 196-202, 2012 ISSN 2079-2077 IDOSI Publications, 2012 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.ejas.2012.4.5.2027 A Fuzzy Logic Based Model for Life Insurance Underwriting When Insurer
European Journal of Applied Sciences 4 (5): 196-202, 2012 ISSN 2079-2077 IDOSI Publications, 2012 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.ejas.2012.4.5.2027 A Fuzzy Logic Based Model for Life Insurance Underwriting When Insurer
Sanjeev Kumar 1 and Hemlata Jain 2
 IJFSRS: 5(1), June 2012, pp. 51-58, Life Insurance Serials Publications, Underwriting ISSN: when 0974-858 Insurer is Diabetic: A Fuzzy Approach 51 Sanjeev Kumar 1 and Hemlata Jain 2 1,2 Department of Mathematics,
IJFSRS: 5(1), June 2012, pp. 51-58, Life Insurance Serials Publications, Underwriting ISSN: when 0974-858 Insurer is Diabetic: A Fuzzy Approach 51 Sanjeev Kumar 1 and Hemlata Jain 2 1,2 Department of Mathematics,
Diabetes Brief. Pre diabetes occurs when glucose levels are elevated in the blood, but are not as high as someone who has diabetes.
 Diabetes Brief What is Diabetes? Diabetes mellitus is a disease of abnormal carbohydrate metabolism in which the level of blood glucose, or blood sugar, is above normal. The disease occurs when the body
Diabetes Brief What is Diabetes? Diabetes mellitus is a disease of abnormal carbohydrate metabolism in which the level of blood glucose, or blood sugar, is above normal. The disease occurs when the body
Physical Activity, Obesity, and the Incidence of Type 2 Diabetes in a High-Risk Population
 American Journal of Epidemiology Copyright 2003 by the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health All rights reserved Vol. 158, No. 7 Printed in U.S.A. DOI: 10.1093/aje/kwg191 Physical Activity, Obesity,
American Journal of Epidemiology Copyright 2003 by the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health All rights reserved Vol. 158, No. 7 Printed in U.S.A. DOI: 10.1093/aje/kwg191 Physical Activity, Obesity,
Diabetes 101. Francisco J. Prieto, M.D. American Diabetes Association National Advocacy Committee Latino Diabetes Action Council
 Diabetes 101 Francisco J. Prieto, M.D. American Diabetes Association National Advocacy Committee Latino Diabetes Action Council www.diabetes.org 1-800-DIABETES www.diabetes.org 1-800-DIABETES Age-Adjusted
Diabetes 101 Francisco J. Prieto, M.D. American Diabetes Association National Advocacy Committee Latino Diabetes Action Council www.diabetes.org 1-800-DIABETES www.diabetes.org 1-800-DIABETES Age-Adjusted
Metabolic Syndrome with Prediabetic Factors Clinical Study Summary Concerning the Efficacy of the GC Control Natural Blood Sugar Support Supplement
 CLINICALLY T E S T E D Natural Blood Sugar Metabolic Syndrome with Prediabetic Factors Clinical Study Summary Concerning the Efficacy of the GC Control Natural Blood Sugar Metabolic Syndrome with Prediabetic
CLINICALLY T E S T E D Natural Blood Sugar Metabolic Syndrome with Prediabetic Factors Clinical Study Summary Concerning the Efficacy of the GC Control Natural Blood Sugar Metabolic Syndrome with Prediabetic
Position Statement Weight Loss Surgery (Bariatric Surgery) and its Use in Treating Obesity or Treating and Preventing Diabetes
 Position Statement Weight Loss Surgery (Bariatric Surgery) and its Use in Treating Obesity or Treating and Preventing Diabetes People with diabetes Losing excess weight will assist in the management of
Position Statement Weight Loss Surgery (Bariatric Surgery) and its Use in Treating Obesity or Treating and Preventing Diabetes People with diabetes Losing excess weight will assist in the management of
Diabetes Prevention in Latinos
 Diabetes Prevention in Latinos Matthew O Brien, MD, MSc Assistant Professor of Medicine and Public Health Northwestern Feinberg School of Medicine Institute for Public Health and Medicine October 17, 2013
Diabetes Prevention in Latinos Matthew O Brien, MD, MSc Assistant Professor of Medicine and Public Health Northwestern Feinberg School of Medicine Institute for Public Health and Medicine October 17, 2013
Quality of life of Elderly Diabetic and Hypertensive People Impact of Intervention Programme
 IOSR Journal Of Humanities And Social Science (IOSR-JHSS) Volume 19, Issue 3, Ver. IV (Mar. 2014), PP 67-73 e-issn: 2279-0837, p-issn: 2279-0845. Quality of life of Elderly Diabetic and Hypertensive People
IOSR Journal Of Humanities And Social Science (IOSR-JHSS) Volume 19, Issue 3, Ver. IV (Mar. 2014), PP 67-73 e-issn: 2279-0837, p-issn: 2279-0845. Quality of life of Elderly Diabetic and Hypertensive People
Preventing and managing diabetes: an exemplar for NCDs
 Preventing and managing diabetes: an exemplar for NCDs A C3 briefing paper, December 2012 Summary Tackling the growing epidemic of diabetes demonstrates what is required to stem the rise in and rising
Preventing and managing diabetes: an exemplar for NCDs A C3 briefing paper, December 2012 Summary Tackling the growing epidemic of diabetes demonstrates what is required to stem the rise in and rising
Family History and Diabetes. Practical Genomics for the Public Health Professional
 Family History and Diabetes Practical Genomics for the Public Health Professional Outline Overview of Type 2 Diabetes/Gestational Diabetes Familial/Genetic Nature of Diabetes Interaction of Genes and Environment
Family History and Diabetes Practical Genomics for the Public Health Professional Outline Overview of Type 2 Diabetes/Gestational Diabetes Familial/Genetic Nature of Diabetes Interaction of Genes and Environment
COST ANALYSIS OF ANTIDIABETIC DRUGS FOR DIABETES MELLITUS OUTPATIENT IN KODYA YOGYAKARTA HOSPITAL
 Malaysian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Vol. 5, No. 1, 19 23 (2007) COST ANALYSIS OF ANTIDIABETIC DRUGS FOR DIABETES MELLITUS OUTPATIENT IN KODYA YOGYAKARTA HOSPITAL TRI MURTI ANDAYANI* AND IKE IMANINGSIH
Malaysian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Vol. 5, No. 1, 19 23 (2007) COST ANALYSIS OF ANTIDIABETIC DRUGS FOR DIABETES MELLITUS OUTPATIENT IN KODYA YOGYAKARTA HOSPITAL TRI MURTI ANDAYANI* AND IKE IMANINGSIH
Overview of Diabetes Management. By Cindy Daversa, M.S.,R.D.,C.D.E. UCI Health
 Overview of Diabetes Management By Cindy Daversa, M.S.,R.D.,C.D.E. UCI Health Objectives: Describe the pathophysiology of diabetes. From a multiorgan systems viewpoint. Identify the types of diabetes.
Overview of Diabetes Management By Cindy Daversa, M.S.,R.D.,C.D.E. UCI Health Objectives: Describe the pathophysiology of diabetes. From a multiorgan systems viewpoint. Identify the types of diabetes.
DIABETES A chronic, debilitating and often deadly disease A global epidemic Diabetes in Africa
 DIABETES A chronic, debilitating and often deadly disease Diabetes is a chronic condition that arises when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin, or when the body cannot effectively use the insulin
DIABETES A chronic, debilitating and often deadly disease Diabetes is a chronic condition that arises when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin, or when the body cannot effectively use the insulin
Alcoholism and Drug Abuse in China By David J. Powell, Ph.D. President, International Center for Health Concerns, Inc.
 Alcoholism and Drug Abuse in China By David J. Powell, Ph.D. President, International Center for Health Concerns, Inc. Introduction Alcohol and drug abuse and dependence are worldwide concerns. In China,
Alcoholism and Drug Abuse in China By David J. Powell, Ph.D. President, International Center for Health Concerns, Inc. Introduction Alcohol and drug abuse and dependence are worldwide concerns. In China,
Statistics of Type 2 Diabetes
 Statistics of Type 2 Diabetes Of the 17 million Americans with diabetes, 90 percent to 95 percent have type 2 diabetes. Of these, half are unaware they have the disease. People with type 2 diabetes often
Statistics of Type 2 Diabetes Of the 17 million Americans with diabetes, 90 percent to 95 percent have type 2 diabetes. Of these, half are unaware they have the disease. People with type 2 diabetes often
How To Lose Weight With Diabetes
 1 of 5 1/9/2014 9:22 AM Published: Summer 2013 Margaret Stevens was diagnosed with Type 2 diabetes nearly three decades ago. A Type 2 diabetic, Margaret Stevens has lost over 100 pounds and has her glucose
1 of 5 1/9/2014 9:22 AM Published: Summer 2013 Margaret Stevens was diagnosed with Type 2 diabetes nearly three decades ago. A Type 2 diabetic, Margaret Stevens has lost over 100 pounds and has her glucose
Shaping our future: a call to action to tackle the diabetes epidemic and reduce its economic impact
 Shaping our future: a call to action to tackle the diabetes epidemic and reduce its economic impact Task Force for the National Conference on Diabetes: The Task Force is comprised of Taking Control of
Shaping our future: a call to action to tackle the diabetes epidemic and reduce its economic impact Task Force for the National Conference on Diabetes: The Task Force is comprised of Taking Control of
published online 8-25-10, http://healthpolicyandreform.nejm.org/?p=12171&query=home.
 Comments to Interim Final Rules for group health plans and health insurance issuers relating to coverage of preventive services under the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (PPACA) File Code: OCIIO-9992-IFC
Comments to Interim Final Rules for group health plans and health insurance issuers relating to coverage of preventive services under the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (PPACA) File Code: OCIIO-9992-IFC
Proof of Concept Project for a Diabetes Prevention Service in Greater Manchester, United Kingdom
 18 Hitachi Review Vol. 64 (2015), No. 1 Featured Articles Proof of Concept Project for a Diabetes Prevention Service in Greater Manchester, United Kingdom Steven Zhang Shuntaro Yui, Dr. Eng. Takuya Akashi
18 Hitachi Review Vol. 64 (2015), No. 1 Featured Articles Proof of Concept Project for a Diabetes Prevention Service in Greater Manchester, United Kingdom Steven Zhang Shuntaro Yui, Dr. Eng. Takuya Akashi
How To Know If You Have Microalbuminuria
 3 PREVALENCE AND PREDICTORS OF MICROALBUMINURIA IN PATIENTS WITH TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS: A CROSS-SECTIONAL OBSERVATIONAL STUDY Dr Ashok S Goswami *, Dr Janardan V Bhatt**; Dr Hitesh Patel *** *Associate
3 PREVALENCE AND PREDICTORS OF MICROALBUMINURIA IN PATIENTS WITH TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS: A CROSS-SECTIONAL OBSERVATIONAL STUDY Dr Ashok S Goswami *, Dr Janardan V Bhatt**; Dr Hitesh Patel *** *Associate
1990 Life Insurance and Diabetes
 ADS Position Statements 1990 Life Insurance and Diabetes John Carter, John Greenway, Royal Prince Alfred Hospital, Concord Hospital and Hornsby Hospital, NSW Page 1 LIFE INSURANCE AND DIABETES MELLITUS
ADS Position Statements 1990 Life Insurance and Diabetes John Carter, John Greenway, Royal Prince Alfred Hospital, Concord Hospital and Hornsby Hospital, NSW Page 1 LIFE INSURANCE AND DIABETES MELLITUS
A study on new products. available in India for. diabetics. Note: Source:
 A study on new products available in India for diabetics Novo Nordisk In one generation, the prevalence of diabetes has increased SIX fold Incidence of Diabetes Europe 2000: 33.3 Million 2030: 48.0 Million
A study on new products available in India for diabetics Novo Nordisk In one generation, the prevalence of diabetes has increased SIX fold Incidence of Diabetes Europe 2000: 33.3 Million 2030: 48.0 Million
Diabetes and Heart Disease
 Diabetes and Heart Disease Diabetes and Heart Disease According to the American Heart Association, diabetes is one of the six major risk factors of cardiovascular disease. Affecting more than 7% of the
Diabetes and Heart Disease Diabetes and Heart Disease According to the American Heart Association, diabetes is one of the six major risk factors of cardiovascular disease. Affecting more than 7% of the
Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) Brief
 Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) Brief What is Coronary Heart Disease? Coronary Heart Disease (CHD), also called coronary artery disease 1, is the most common heart condition in the United States. It occurs
Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) Brief What is Coronary Heart Disease? Coronary Heart Disease (CHD), also called coronary artery disease 1, is the most common heart condition in the United States. It occurs
HEALTH CARE COSTS 11
 2 Health Care Costs Chronic health problems account for a substantial part of health care costs. Annually, three diseases, cardiovascular disease (including stroke), cancer, and diabetes, make up about
2 Health Care Costs Chronic health problems account for a substantial part of health care costs. Annually, three diseases, cardiovascular disease (including stroke), cancer, and diabetes, make up about
Nutrition for Family Living
 Susan Nitzke, Nutrition Specialist; susan.nitzke@ces.uwex.edu Sherry Tanumihardjo, Nutrition Specialist; sherry.tan@ces.uwex.edu Amy Rettammel, Outreach Specialist; arettamm@facstaff.wisc.edu Betsy Kelley,
Susan Nitzke, Nutrition Specialist; susan.nitzke@ces.uwex.edu Sherry Tanumihardjo, Nutrition Specialist; sherry.tan@ces.uwex.edu Amy Rettammel, Outreach Specialist; arettamm@facstaff.wisc.edu Betsy Kelley,
Losing Weight in Singapore - Public Perception of Obesity
 Singapore Med J 2012; 53(2) : 104 Public perceptions of obesity and bariatric surgery in Singapore: a pilot study Teo EY 1, MBBS, MRCP, Lew PS 2, MBBS, Foo CS 2, FRCS, FAMS Introduction Obesity is a real
Singapore Med J 2012; 53(2) : 104 Public perceptions of obesity and bariatric surgery in Singapore: a pilot study Teo EY 1, MBBS, MRCP, Lew PS 2, MBBS, Foo CS 2, FRCS, FAMS Introduction Obesity is a real
TABLE OF CONTENTS. The Cost of Diabesity... 3. Employer Solutions... 4 Provide a Worksite Weight Loss Program Tailored for Diabetes...
 TH E TABLE OF CONTENTS The Cost of Diabesity... 3 Employer Solutions... 4 Provide a Worksite Weight Loss Program Tailored for Diabetes... 4 Provide Healthy Food Options at the Workplace... 4 Make it Easy
TH E TABLE OF CONTENTS The Cost of Diabesity... 3 Employer Solutions... 4 Provide a Worksite Weight Loss Program Tailored for Diabetes... 4 Provide Healthy Food Options at the Workplace... 4 Make it Easy
British Columbia Pharmacy Association (BCPhA) Clinical Service Proposal Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose in Type 2 Diabetes
 British Columbia Pharmacy Association (BCPhA) Clinical Service Proposal Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose in Type 2 Diabetes Introduction Self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) is in widespread use among
British Columbia Pharmacy Association (BCPhA) Clinical Service Proposal Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose in Type 2 Diabetes Introduction Self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) is in widespread use among
TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS: NEW HOPE FOR PREVENTION. Robert Dobbins, M.D. Ph.D.
 TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS: NEW HOPE FOR PREVENTION Robert Dobbins, M.D. Ph.D. Learning Objectives Recognize current trends in the prevalence of type 2 diabetes. Learn differences between type 1 and type
TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS: NEW HOPE FOR PREVENTION Robert Dobbins, M.D. Ph.D. Learning Objectives Recognize current trends in the prevalence of type 2 diabetes. Learn differences between type 1 and type
Burden of Obesity, Diabetes and Heart Disease in New Hampshire, 2013 Update
 Burden of Obesity, Diabetes and Heart Disease in New Hampshire, 2013 Update Background Overweight and obesity have greatly increased among all age groups and regardless of income and education. Contributing
Burden of Obesity, Diabetes and Heart Disease in New Hampshire, 2013 Update Background Overweight and obesity have greatly increased among all age groups and regardless of income and education. Contributing
Adherence to insulin therapy at a tertiary care diabetes center in South India
 Original Article: Adherence to insulin therapy at a tertiary care diabetes center in South India M.S. Raut, J. Balasubramanian, R.M. Anjana, R Unnikrishnan, *V. Mohan Abstract To assess patient adherence
Original Article: Adherence to insulin therapy at a tertiary care diabetes center in South India M.S. Raut, J. Balasubramanian, R.M. Anjana, R Unnikrishnan, *V. Mohan Abstract To assess patient adherence
ESC/EASD Pocket Guidelines Diabetes, pre-diabetes and cardiovascular disease
 Diabetes, prediabetes and cardiovascular disease Classes of recommendations Levels of evidence Recommended treatment targets for patients with diabetes and CAD Definition, classification and screening
Diabetes, prediabetes and cardiovascular disease Classes of recommendations Levels of evidence Recommended treatment targets for patients with diabetes and CAD Definition, classification and screening
Like John Fogerty said in one of his hit songs, I see a bad moon arising, How to Decrease Your Health Care Costs for Employees with Diabetes
 How to Decrease Your Health Care Costs for Employees with Diabetes Written by Tom Milam Like John Fogerty said in one of his hit songs, I see a bad moon arising, I see trouble on the way, the self-insured
How to Decrease Your Health Care Costs for Employees with Diabetes Written by Tom Milam Like John Fogerty said in one of his hit songs, I see a bad moon arising, I see trouble on the way, the self-insured
Office ID Location: City State Date / / PRIMARY CARE SURVEY
 A. Organizational Characteristics PRIMARY CARE SURVEY We want to learn more about the general features of your office. A1. What health-related services does your office provide (check all that apply)?
A. Organizational Characteristics PRIMARY CARE SURVEY We want to learn more about the general features of your office. A1. What health-related services does your office provide (check all that apply)?
Nutrition. Type 2 Diabetes: A Growing Challenge in the Healthcare Setting NAME OF STUDENT
 1 Nutrition Type 2 Diabetes: A Growing Challenge in the Healthcare Setting NAME OF STUDENT 2 Type 2 Diabetes: A Growing Challenge in the Healthcare Setting Introduction and background of type 2 diabetes:
1 Nutrition Type 2 Diabetes: A Growing Challenge in the Healthcare Setting NAME OF STUDENT 2 Type 2 Diabetes: A Growing Challenge in the Healthcare Setting Introduction and background of type 2 diabetes:
echat: Screening & intervening for mental health & lifestyle issues
 echat: Screening & intervening for mental health & lifestyle issues Felicity Goodyear-Smith Professor & Academic Head Dept of General Practice & Primary Health Care Faculty of Medicine & Health Science
echat: Screening & intervening for mental health & lifestyle issues Felicity Goodyear-Smith Professor & Academic Head Dept of General Practice & Primary Health Care Faculty of Medicine & Health Science
Poorly controlled diabetes mellitus the way forward
 Poorly controlled diabetes mellitus the way forward Presentation at HA Convention 2008 6 May, 2008 Dr. M K Cheung Associate Consultant Department of Family Medicine Community Care Division New Territories
Poorly controlled diabetes mellitus the way forward Presentation at HA Convention 2008 6 May, 2008 Dr. M K Cheung Associate Consultant Department of Family Medicine Community Care Division New Territories
Am I at Risk for type 2 Diabetes? Taking Steps to Lower the Risk of Getting Diabetes NATIONAL DIABETES INFORMATION CLEARINGHOUSE
 NATIONAL DIABETES INFORMATION CLEARINGHOUSE Am I at Risk for type 2 Diabetes? Taking Steps to Lower the Risk of Getting Diabetes U.S. Department of Health and Human Services National Institutes of Health
NATIONAL DIABETES INFORMATION CLEARINGHOUSE Am I at Risk for type 2 Diabetes? Taking Steps to Lower the Risk of Getting Diabetes U.S. Department of Health and Human Services National Institutes of Health
Diabetes Complications
 Managing Diabetes: It s s Not Easy But It s s Worth It Presenter Disclosures W. Lee Ball, Jr., OD, FAAO (1) The following personal financial relationships with commercial interests relevant to this presentation
Managing Diabetes: It s s Not Easy But It s s Worth It Presenter Disclosures W. Lee Ball, Jr., OD, FAAO (1) The following personal financial relationships with commercial interests relevant to this presentation
DIABETES MELLITUS. By Tracey Steenkamp Biokineticist at the Institute for Sport Research, University of Pretoria
 DIABETES MELLITUS By Tracey Steenkamp Biokineticist at the Institute for Sport Research, University of Pretoria What is Diabetes Diabetes Mellitus (commonly referred to as diabetes ) is a chronic medical
DIABETES MELLITUS By Tracey Steenkamp Biokineticist at the Institute for Sport Research, University of Pretoria What is Diabetes Diabetes Mellitus (commonly referred to as diabetes ) is a chronic medical
Post-Transplant Diabetes: What Every Patient Needs to Know
 Post-Transplant Diabetes: What Every Patient Needs to Know International Transplant Nurses Society What is Diabetes? Diabetes is an illness that effects how your body makes and uses a hormone called insulin.
Post-Transplant Diabetes: What Every Patient Needs to Know International Transplant Nurses Society What is Diabetes? Diabetes is an illness that effects how your body makes and uses a hormone called insulin.
Baskets of Care Diabetes Subcommittee
 Baskets of Care Diabetes Subcommittee Disclaimer: This background information is not intended to be a comprehensive scientific discussion of the topic, but rather an attempt to provide a baseline level
Baskets of Care Diabetes Subcommittee Disclaimer: This background information is not intended to be a comprehensive scientific discussion of the topic, but rather an attempt to provide a baseline level
REPORT ON DIABETES i
 AFRICAN UNION UNION AFRICAINE UNIÃO AFRICANA AU CONFERENCE OF MINISTERS OF HEALTH (CAMH6) Sixth Ordinary Session, 22-26 April 2013, Addis Ababa, ETHIOPIA CAMH/Exp/6(VI) iv THEME: The Impact of Non-Communicable
AFRICAN UNION UNION AFRICAINE UNIÃO AFRICANA AU CONFERENCE OF MINISTERS OF HEALTH (CAMH6) Sixth Ordinary Session, 22-26 April 2013, Addis Ababa, ETHIOPIA CAMH/Exp/6(VI) iv THEME: The Impact of Non-Communicable
Awareness among Family Members of Children with Intellectual Disability on Relevant Legislations in India
 92 BRIEF REPORTS Awareness among Family Members of Children with Intellectual Disability on Relevant Legislations in India Bala Baskar Kuppusamy 1*, Jayanthi Narayan N. 2, Deepa Nair N. 3 1. Lecturer and
92 BRIEF REPORTS Awareness among Family Members of Children with Intellectual Disability on Relevant Legislations in India Bala Baskar Kuppusamy 1*, Jayanthi Narayan N. 2, Deepa Nair N. 3 1. Lecturer and
The Influence of Infant Health on Adult Chronic Disease
 The Influence of Infant Health on Adult Chronic Disease Womb to Tomb Dr Clare MacVicar Introduction Many diseases in adulthood are related to growth patterns during early life Maternal nutrition important
The Influence of Infant Health on Adult Chronic Disease Womb to Tomb Dr Clare MacVicar Introduction Many diseases in adulthood are related to growth patterns during early life Maternal nutrition important
Facts about Diabetes in Massachusetts
 Facts about Diabetes in Massachusetts Diabetes is a disease in which the body does not produce or properly use insulin (a hormone used to convert sugar, starches, and other food into the energy needed
Facts about Diabetes in Massachusetts Diabetes is a disease in which the body does not produce or properly use insulin (a hormone used to convert sugar, starches, and other food into the energy needed
Preventing Pediatric Diabetes: Are Racial Disparities A Factor? A Children s Health Fund Issue Brief February 2004
 Preventing Pediatric Diabetes: Are Racial Disparities A Factor? A Children s Health Fund Issue Brief February 2004 The Children s Health Fund The Children s Health Fund (CHF), working with hospitals and
Preventing Pediatric Diabetes: Are Racial Disparities A Factor? A Children s Health Fund Issue Brief February 2004 The Children s Health Fund The Children s Health Fund (CHF), working with hospitals and
PATHWAYS TO TYPE 2 DIABETES. Vera Tsenkova, PhD Assistant Scientist Institute on Aging University of Wisconsin-Madison
 PATHWAYS TO TYPE 2 DIABETES Vera Tsenkova, PhD Assistant Scientist Institute on Aging University of Wisconsin-Madison Overview Diabetes 101 How does diabetes work Types of diabetes Diabetes in numbers
PATHWAYS TO TYPE 2 DIABETES Vera Tsenkova, PhD Assistant Scientist Institute on Aging University of Wisconsin-Madison Overview Diabetes 101 How does diabetes work Types of diabetes Diabetes in numbers
Prescription Pattern of Anti Hypertensive Drugs used in Hypertensive Patients with Associated Type2 Diabetes Mellitus in A Tertiary Care Hospital
 Research Article Prescription Pattern of Anti Hypertensive Drugs used in Hypertensive Patients with Associated Type2 Diabetes Mellitus in A Tertiary Care Hospital *T. JANAGAN 1, R. KAVITHA 1, S. A. SRIDEVI
Research Article Prescription Pattern of Anti Hypertensive Drugs used in Hypertensive Patients with Associated Type2 Diabetes Mellitus in A Tertiary Care Hospital *T. JANAGAN 1, R. KAVITHA 1, S. A. SRIDEVI
Effect of Nutrition Education Program on Dietary Eating Patterns of Adolescent Girls (16-19 Years)
 Available online at www.ijpab.com INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE & APPLIED BIOSCIENCE ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 3 (2): 427-431 (2015) Research Article Effect of Nutrition Education Program
Available online at www.ijpab.com INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE & APPLIED BIOSCIENCE ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 3 (2): 427-431 (2015) Research Article Effect of Nutrition Education Program
The National Diabetes Prevention Program: An Update on Efforts in Michigan
 The National Diabetes Prevention Program: An Update on Efforts in Michigan Gretchen A. Piatt, PhD, MPH Assistant Professor Department of Medical Education University of Michigan 10/11/12 WHY PREVENT DIABETES?
The National Diabetes Prevention Program: An Update on Efforts in Michigan Gretchen A. Piatt, PhD, MPH Assistant Professor Department of Medical Education University of Michigan 10/11/12 WHY PREVENT DIABETES?
RISK FACTORS OF TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS IN THE RURAL POPULATION OF NORTH KERALA, INDIA: A CASE CONTROL STUDY
 1 Department of Internal Medicine, Academy of Medical Sciences, Pariayaram, Kannur, Kerala, India; 2 Research Division, Gulf Medical University, Ajman, United Arab Emirates Original Research Article RISK
1 Department of Internal Medicine, Academy of Medical Sciences, Pariayaram, Kannur, Kerala, India; 2 Research Division, Gulf Medical University, Ajman, United Arab Emirates Original Research Article RISK
Kansas Behavioral Health Risk Bulletin
 Kansas Behavioral Health Risk Bulletin Kansas Department of Health and Environment November 7, 1995 Bureau of Chronic Disease and Health Promotion Vol. 1 No. 12 Diabetes Mellitus in Kansas Diabetes mellitus
Kansas Behavioral Health Risk Bulletin Kansas Department of Health and Environment November 7, 1995 Bureau of Chronic Disease and Health Promotion Vol. 1 No. 12 Diabetes Mellitus in Kansas Diabetes mellitus
Review of diabetes care in London Health and Environment Committee
 The London Assembly s Health and Environment Committee intends to review diabetes care in London. Aim of review The purpose of this review is for the Committee to understand the extent of diabetes prevalence
The London Assembly s Health and Environment Committee intends to review diabetes care in London. Aim of review The purpose of this review is for the Committee to understand the extent of diabetes prevalence
THE IMPACT OF SOCIO-ECONOMIC FACTORS ON DIABETES CARE
 THE IMPACT OF SOCIO-ECONOMIC FACTORS ON DIABETES CARE PH Rayappa*, KNM Raju*, Anil Kapur, Stefan Bjork**, Camilla Sylvest, ** KM Dilip Kumar INTRODUCTION Diabetes is rapidly emerging as a major health
THE IMPACT OF SOCIO-ECONOMIC FACTORS ON DIABETES CARE PH Rayappa*, KNM Raju*, Anil Kapur, Stefan Bjork**, Camilla Sylvest, ** KM Dilip Kumar INTRODUCTION Diabetes is rapidly emerging as a major health
Against the Growing Burden of Disease. Kimberly Elmslie Director General, Centre for Chronic Disease Prevention
 Kimberly Elmslie Director General, Centre for Chronic Disease Prevention Chronic diseases are an increasing global challenge Most significant cause of death (63%) worldwide 1 Chronic diseases cause premature
Kimberly Elmslie Director General, Centre for Chronic Disease Prevention Chronic diseases are an increasing global challenge Most significant cause of death (63%) worldwide 1 Chronic diseases cause premature
what is diabetes? What actually goes wrong? Talking diabetes No.42
 Talking diabetes No.42 what is diabetes? Diabetes is the name given to a group of different conditions in which there is too much glucose in the blood. The pancreas either cannot make insulin or the insulin
Talking diabetes No.42 what is diabetes? Diabetes is the name given to a group of different conditions in which there is too much glucose in the blood. The pancreas either cannot make insulin or the insulin
Karen Kovach M.S, R.D Chief Scientific Officer Weight Watchers International Inc.
 Waking up to real solutions to Chronic Disease: Tackling obesity can reduce the burden of chronic disease and deliver substantial cost savings to struggling European healthcare systems Karen Kovach M.S,
Waking up to real solutions to Chronic Disease: Tackling obesity can reduce the burden of chronic disease and deliver substantial cost savings to struggling European healthcare systems Karen Kovach M.S,
Epidemiology of type 2 diabetes: Indian scenario
 Indian J Med Res 125, March 2007, pp 217-230 Epidemiology of type 2 diabetes: Indian scenario V. Mohan, S. Sandeep, R. Deepa, B. Shah* & C. Varghese** Madras Diabetes Research Foundation & Dr Mohan s Diabetes
Indian J Med Res 125, March 2007, pp 217-230 Epidemiology of type 2 diabetes: Indian scenario V. Mohan, S. Sandeep, R. Deepa, B. Shah* & C. Varghese** Madras Diabetes Research Foundation & Dr Mohan s Diabetes
How To Find Out What The Hmong Believe About Type 2 Diabetes
 Perspectives from the Hmong Population on Type 2 Diabetes Phoua Xiong, Pharm.D. and Sarah M. Westberg, PharmD, BCPS College of Pharmacy, University of Minnesota Abstract The primary goal of the study was
Perspectives from the Hmong Population on Type 2 Diabetes Phoua Xiong, Pharm.D. and Sarah M. Westberg, PharmD, BCPS College of Pharmacy, University of Minnesota Abstract The primary goal of the study was
HealthCare Partners of Nevada. Heart Failure
 HealthCare Partners of Nevada Heart Failure Disease Management Program 2010 HF DISEASE MANAGEMENT PROGRAM The HealthCare Partners of Nevada (HCPNV) offers a Disease Management program for members with
HealthCare Partners of Nevada Heart Failure Disease Management Program 2010 HF DISEASE MANAGEMENT PROGRAM The HealthCare Partners of Nevada (HCPNV) offers a Disease Management program for members with
HEALTH EVIDENCE REVIEW COMMISSION (HERC) COVERAGE GUIDANCE: DIAGNOSIS OF SLEEP APNEA IN ADULTS DATE: 5/9/2013 HERC COVERAGE GUIDANCE
 HEALTH EVIDENCE REVIEW COMMISSION (HERC) COVERAGE GUIDANCE: DIAGNOSIS OF SLEEP APNEA IN ADULTS DATE: 5/9/2013 HERC COVERAGE GUIDANCE The following diagnostic tests for Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) should
HEALTH EVIDENCE REVIEW COMMISSION (HERC) COVERAGE GUIDANCE: DIAGNOSIS OF SLEEP APNEA IN ADULTS DATE: 5/9/2013 HERC COVERAGE GUIDANCE The following diagnostic tests for Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) should
Take a moment Confer with your neighbour And try to solve the following word picture puzzle slides.
 Take a moment Confer with your neighbour And try to solve the following word picture puzzle slides. Example: = Head Over Heels Take a moment Confer with your neighbour And try to solve the following word
Take a moment Confer with your neighbour And try to solve the following word picture puzzle slides. Example: = Head Over Heels Take a moment Confer with your neighbour And try to solve the following word
Successful prevention of non-communicable diseases: 25 year experiences with North Karelia Project in Finland
 Public Health Medicine 2002; 4(1):5-7 Successful prevention of non-communicable diseases: 25 year experiences with North Karelia Project in Finland Pekka Puska Abstracts The paper describes the experiences
Public Health Medicine 2002; 4(1):5-7 Successful prevention of non-communicable diseases: 25 year experiences with North Karelia Project in Finland Pekka Puska Abstracts The paper describes the experiences
Understanding diabetes Do the recent trials help?
 Understanding diabetes Do the recent trials help? Dr Geoffrey Robb Consultant Physician and Diabetologist CMO RGA UK Services and Partnership Assurance AMUS 25 th March 2010 The security of experience.
Understanding diabetes Do the recent trials help? Dr Geoffrey Robb Consultant Physician and Diabetologist CMO RGA UK Services and Partnership Assurance AMUS 25 th March 2010 The security of experience.
CME Test for AMDA Clinical Practice Guideline. Diabetes Mellitus
 CME Test for AMDA Clinical Practice Guideline Diabetes Mellitus Part I: 1. Which one of the following statements about type 2 diabetes is not accurate? a. Diabetics are at increased risk of experiencing
CME Test for AMDA Clinical Practice Guideline Diabetes Mellitus Part I: 1. Which one of the following statements about type 2 diabetes is not accurate? a. Diabetics are at increased risk of experiencing
Chronic Disease and Nursing:
 Chronic Disease and Nursing: A Summary of the Issues What s the issue? Chronic diseases are now the major global disease problem facing the world and a key barrier to development, to alleviating poverty,
Chronic Disease and Nursing: A Summary of the Issues What s the issue? Chronic diseases are now the major global disease problem facing the world and a key barrier to development, to alleviating poverty,
Original Article. Risk factors for diabetic retinopathy in selfreported rural population with diabetes
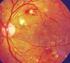 Original Article www.jpgmonline.com Risk factors for diabetic retinopathy in selfreported rural population with diabetes Rani PK, Raman R, Chandrakantan A, Pal SS, Perumal GM, Sharma T Vision Research
Original Article www.jpgmonline.com Risk factors for diabetic retinopathy in selfreported rural population with diabetes Rani PK, Raman R, Chandrakantan A, Pal SS, Perumal GM, Sharma T Vision Research
