case study 7: south east queensland healthy waterways partnership
|
|
|
- Augustine Davis
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
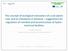
2 2 Australia s National Programme of Action for the Protection of the Marine Environment from Land-Based Activities introduction South-east Queensland s marine systems support large populations of dugongs and turtles, migratory wading birds and major recreational and commercial fisheries. Stretching from the Queensland-New South Wales border, north to Noosa and west to the Great Dividing Range, the region occupies 22,672 square kilometres and includes 15 major river catchments (see Figure 1). More than 2.5 million people live within 50 kilometres of the coast. Figure 1: South East Queensland Region Moreton Bay is a marine park and is listed as a wetland of international significance under the Ramsar Convention. These natural systems have undergone profound modifications since European settlement. The river estuaries are now highly turbid and the lower Brisbane River does not currently meet national standards for primary contact activities such as swimming. The major river flows have been highly regulated through dams and weirs. The agricultural districts contribute significantly to the economy and rely on good quality water supplies and soil protection to maintain viable yields. pollution issues In the early 1990s it became apparent that projected population increases over the next 30 years could seriously impact further on the waterways and catchments in South-east Queensland. Nutrients (particularly nitrogen), fine sediments and toxicants (pesticides and heavy metals) had already been identified as significant environmental problems. Moreton Bay Waterways and Catchments Partnership The projected 1 million population increase will require an estimated 575,000 new dwellings by As population increases, the waste, sediment, nutrients and other pollutants entering waterways increase, natural waterway flows are modified or halted, and natural habitat decreases. Even with the significant improvements in controlling point and diffuse source nutrient inputs over the last five years, the rapidly increasing population will lead to increasing pressures that will degrade many waterways. For example, it is predicted that nutrient loads are likely to increase by up to 46 precent by Initial work has identified a range of social and economic impacts resulting from factors such as increased health risks, loss of income, reduced recreation and tourism opportunities, and increased water treatment costs.
3 3 Australia s National Programme of Action for the Protection of the Marine Environment from Land-Based Activities management context Since the mid-1970s public concerns about declining water quality had been articulated. However, it was only in the 1990s that a coordinated approach to addressing this decline began. The Brisbane River Management Group started in 1993, extended to include all South East Queensland (SEQ) waterways with the development of the 2001 SEQ Regional Water Quality Management Strategy (SEQRWQMS) and resulted in the formation in 2002 of the Moreton Bay Waterways and Catchments Partnership, now called SEQ Healthy Waterways Partnership, to implement SEQRWQMS. seq healthy waterways strategy The SEQ Healthy Waterways Partnership is now preparing the SEQ Healthy Waterways Strategy (SEQ HWS) incorporating the Moreton Bay Water Quality Improvement Plan. The Strategy builds upon SEQRWQMS 2001, which in turn, built on both the Brisbane River Management Plan (1997) and the Stage 2 work of the Brisbane River and Moreton Bay Wastewater Management Study (1998). SEQRWQMS 2001 was based on the National Water Quality Management Strategy (and embedded in the Queensland Environmental Protection (Water) Policy 1997), and provided a means for coordinating the development and implementation of management actions to deal with water quality and ecosystem health impacts on SEQ waterways. SEQRWQMS 2001 detailed 72 management actions ranging from local to regional, with timeframes of up to ten years. At March 2005, 20 actions had been completed, 41 were in progress and 11 had either not commenced or were unable to be reported on. Some actions have been carried forward into the SEQ HWS; others have been modified in the light of new information. The SEQ HWS covers the whole of South East Queensland. It deals with aquatic ecosystem health and water quality issues, and contains measures to avoid or ameliorate the impacts of human activities on aquatic ecosystems. The SEQ HWS recognises the close link between water supply and water quality. It will depend on, and be closely linked with, the statutory water resource plans being developed for the Gold Coast, Logan-Albert and Moreton regions. Through collaboration and reciprocal representation on key bodies the SEQ HWS has been integrated with the SEQ Regional Water Supply Strategy. Overall, the SEQ HWS will complement natural resource management plans and provide a framework within which organisations such as local governments can develop and implement healthy waterways strategies. The Partnership s Vision is: By 2020, our waterways and catchments will be healthy ecosystems supporting the livelihoods and lifestyles of people in South East Queensland, and will be managed through collaboration between community, government and industry. The Partnership uses two decision support tools, a catchment routing model (the Environment Management Support System) and a receiving water quality model to predict future water quality scenarios for Moreton Bay in Based on these predictions management targets have been identified. Achievement of these targets would ensure maintenance of the ecosystem health of Moreton Bay in The setting of targets (or quantifiable objectives) as a goal post for management is critical in the development of water quality improvement plans and natural resource management plans. The approach to develop the SEQ HWS can be summarised in three steps:
4 4 Australia s National Programme of Action for the Protection of the Marine Environment from Land-Based Activities 1. Examine environmental values, water quality issues and water quality objectives for Moreton Bay and the waterways of SEQ. 2. Estimate sustainable pollutant loads (via modelling) that will allow water quality objectives to be achieved and maintained. 3. Determine in consultation with stakeholders the management and support measures and control actions required to ensure agreed pollutant loads are met. Experience from SEQRWQMS 2001 indicated that a more multi-dimensional approach to strategy development and management will be more effective. For example: - An issue-based approach is needed to deal with problems that are common across large parts of the region; - An area-based focus, either across the whole of SEQ or in some special case sub-areas may be needed in some circumstances; and - the success of issues-based and area-based actions needs to be enabled by development and operation of decision-support and monitoring systems, and communications, education and motivation. point source issues In 2001, a core strategy of the SEQRWQMS was to encourage stakeholders to upgrade treatment facilities at government-managed sewage treatment plants (STPs) as well as major industrial treatment plants in South East Queensland. Approximately $300 million has been invested in upgrading treatment plants. By the end of 2006 the amount of nitrogen discharged from STPs will be 44 per cent of pre-2001 discharges. The Point Source Management Action Plan aims to reduce the loads of key pollutants entering waterways from point sources, while taking opportunities where appropriate to reuse treated water. The target for 2020 is 100 per cent reuse of wastewater discharges and minimal levels of key pollutants, while increasing understanding of wastewater management. diffuse source issues There will be significant diffuse source pollution from the increased population. Modelling indicates that diffuse source pollution from roads, stormwater run-off and buildings will increase by 63 per cent for sediment, 55 per cent for nitrogen and 67 per cent for phosphorous over the next 20 years. Currently, in excess of 315,000 tonnes of sediment are discharged to Moreton Bay each year, from gullies and channel erosion, with some from broadacre runoff. Predictive modelling shows the gross sediment load will grow to approximately 370,000 tonnes per year from all sources by 2026, with a five per cent increase in rural sediment projected. Other modelling studies indicate that a significant proportion of rural diffuse pollution originates in a few catchments and these and other studies have pinpointed the likely sources in those catchments. The SEQ HWS includes plans to address diffuse sources of pollution.
5 5 Australia s National Programme of Action for the Protection of the Marine Environment from Land-Based Activities water sensitive urban design (including stormwater management) Water Sensitive Urban Design promotes the integration of stormwater, water supply and sewage management at the development scale to protect ecological processes and water quality, while minimizing sewage discharges and the demand for reticulated water. For future urban and urban infill area development, the target is that by 2008 achieve minimum performance standards or design objectives for WSUD for 100 per cent of all development in SEQ. The target for existing urban areas is that by 2011 achieve minimum WSUD performance standards or design objectives across 100 per cent of existing urban areas. The objective is to reduce loads of Total Suspended Solids by a minimum of 80 per cent; Total Phosphorus by a minimum of 60 per cent; Total Nitrogen by a minimum of 45 per cent compared with untreated stormwater. rural diffuse source pollution management The SEQ HWS incorporates a range of approaches to addressing rural diffuse sources depending on whether the source is hill slope or gully, on-farm or in-stream, private or public land. Protection and conservation of waterways and catchments currently in good condition is a priority. The recommended management outcome for rural lands is a 50 per cent reduction in sediment loads by monitoring, evaluation and reporting Critical to the success of the investment in South East Queensland to date has been the development of a monitoring program, ongoing investment in science and decision support tools, and a commitment to communicate the results of these programs. ecosystem health monitoring program The Ecosystem Health Monitoring Program (EHMP) delivers a cost-effective and integrated regional assessment of ambient ecosystem health of SEQ waterways and Moreton Bay, under a catchment to coast approach. This is achieved by assessing water quality trends, using a suite of biological, physical and chemical indicators of ecosystem health. A total of 375 sites in freshwater and estuarine/marine environments are currently monitored regularly. The EHMP provides an understanding of the cause and effect of management actions, and provides the receiving water quality monitoring required by EPA licensing. EHMP products include the annual EHMP Report Card, annual Technical Report, EHMP newsletters, EHMP website, monthly estuarine/marine data reports and a centralised EHMP database. decision support tools Environmental Management Support Systems (EMSS) have been developed for the region and for the majority of catchments in SEQ. The EMSS model daily runoff and pollutant export loads, flow through the river network, and the effects of major water storages. They are designed to evaluate the relative efficacy of various catchment management actions aimed at improving water quality. Receiving Water Quality Models have been developed for the various river estuaries and Moreton Bay. This combination forms an integrated modelling framework supporting decision making.
6 6 Australia s National Programme of Action for the Protection of the Marine Environment from Land-Based Activities communication, education and motivation Extensive and ongoing communication and education activity are required to ensure the stakeholders embrace the actions needed to reach the Healthy Waterways vision. The Healthy Waterways Campaign is a hallmark of the Partnership s activities. Any change requires communication so stakeholders understand the need, support it and assist with its implementation. Barriers to changes need to be addressed, whilst simultaneously reinforcing the benefits of new procedures and behaviours, effectively cementing new norms. The rapid population growth is continually bringing new stakeholders to the area, requiring repeat communications. Whilst some stakeholders will hear the communication, understand what they can do and be motivated to act, newly arrived stakeholders (whether individuals or businesses) will not have been exposed to the history and significance of waterways issues in the region. Communication, education, consultation are ongoing to reach the constant stream of new stakeholders.
Summary: Introduction
 Summary: Melbourne Water has a range of responsibilities in the Port Phillip and Westernport region, including responsibilities for the protection and restoration of waterways and, in collaboration with
Summary: Melbourne Water has a range of responsibilities in the Port Phillip and Westernport region, including responsibilities for the protection and restoration of waterways and, in collaboration with
DRAINAGE DISCHARGE AGREEMENTS A WAY OF MANAGING RISK Mr. Sam Green Goulburn-Murray Water
 Abstract.: 112 DRAINAGE DISCHARGE AGREEMENTS A WAY OF MANAGING RISK Mr. Sam Green Goulburn-Murray Water ABSTRACT Goulburn-Murray Water (G-MW) owns, operates and maintains an extensive regional drainage
Abstract.: 112 DRAINAGE DISCHARGE AGREEMENTS A WAY OF MANAGING RISK Mr. Sam Green Goulburn-Murray Water ABSTRACT Goulburn-Murray Water (G-MW) owns, operates and maintains an extensive regional drainage
A Business Case for Best Practice Urban Stormwater Management. Version 1.1 September 2010
 A Business Case for Best Practice Urban Stormwater Management Version 1.1 September 2010 Water by Design A Business is a program Case of the for South Best East Practice Queensland Urban Healthy Stormwater
A Business Case for Best Practice Urban Stormwater Management Version 1.1 September 2010 Water by Design A Business is a program Case of the for South Best East Practice Queensland Urban Healthy Stormwater
Integrated water cycle planning processes and systems: A local government case study
 Integrated water cycle planning processes and systems: A local government case study Authors: Alan Barton (Brisbane City Council), Emma Hawkins (MWH, formerly of Lloyd Consulting) Integrated Water Cycle
Integrated water cycle planning processes and systems: A local government case study Authors: Alan Barton (Brisbane City Council), Emma Hawkins (MWH, formerly of Lloyd Consulting) Integrated Water Cycle
INTEGRATED WATER FOR CASEY CLYDE
 INTEGRATED WATER FOR CASEY CLYDE James Westcott 1, Andrew Chapman 1, Jamie Ewert 2, Brigid Adams 3 1. South East Water, Melbourne, Vic, Australia 2. Melbourne Water, Melbourne, Vic, Australia 3. Department
INTEGRATED WATER FOR CASEY CLYDE James Westcott 1, Andrew Chapman 1, Jamie Ewert 2, Brigid Adams 3 1. South East Water, Melbourne, Vic, Australia 2. Melbourne Water, Melbourne, Vic, Australia 3. Department
Clean Water Services. Ecosystems Services Case Study: Tualatin River, Washington
 Viewed broadly, the concept of ecosystem services describes the many resources and services provided by nature. Typically, traditional planning and development practices do not adequately represent the
Viewed broadly, the concept of ecosystem services describes the many resources and services provided by nature. Typically, traditional planning and development practices do not adequately represent the
Improving the physical condition of Scotland s water environment. A supplementary plan for the river basin management plans
 Improving the physical condition of Scotland s water environment A supplementary plan for the river basin management plans Contents Executive summary... 2 1. Introduction... 3 2. Vision... 4 3. Taking
Improving the physical condition of Scotland s water environment A supplementary plan for the river basin management plans Contents Executive summary... 2 1. Introduction... 3 2. Vision... 4 3. Taking
WASTEWATER TREATMENT
 Freshwater WASTEWATER TREATMENT Water Quality 1. INDICATOR (a) Name: Wastewater treatment. (b) Brief Definition: Proportion of wastewater that is treated, in order to reduce pollutants before being discharged
Freshwater WASTEWATER TREATMENT Water Quality 1. INDICATOR (a) Name: Wastewater treatment. (b) Brief Definition: Proportion of wastewater that is treated, in order to reduce pollutants before being discharged
COMPREHENSIVE PLAN SECTION B, ELEMENT 4 WATER RESOURCES. April 20, 2010 EXHIBIT 1
 COMPREHENSIVE PLAN SECTION B, ELEMENT 4 WATER RESOURCES April 20, 2010 EXHIBIT 1 ELEMENT 4 WATER RESOURCES TABLE OF CONTENTS 4.1 INTRODUCTION 4.2 GOALS AND POLICIES 4.2.A General Goals and Policies 1 4.2.B
COMPREHENSIVE PLAN SECTION B, ELEMENT 4 WATER RESOURCES April 20, 2010 EXHIBIT 1 ELEMENT 4 WATER RESOURCES TABLE OF CONTENTS 4.1 INTRODUCTION 4.2 GOALS AND POLICIES 4.2.A General Goals and Policies 1 4.2.B
1 Introduction. 1.1 Key objective. 1.2 Why the South Esk
 1 Introduction 1.1 Key objective The aim of this study is to identify and assess possible options for improving the quality of the river channel and habitats in the River South Esk catchment whilst helping
1 Introduction 1.1 Key objective The aim of this study is to identify and assess possible options for improving the quality of the river channel and habitats in the River South Esk catchment whilst helping
FOUR RIVERS RESTORATION PROJECT
 MLTM Republic of Korea Making Every Drop Count International Workshop on Integrated Urban Water Management WATER & GREEN GROWTH FOUR RIVERS RESTORATION PROJECT Office of National River Restoration, Korea
MLTM Republic of Korea Making Every Drop Count International Workshop on Integrated Urban Water Management WATER & GREEN GROWTH FOUR RIVERS RESTORATION PROJECT Office of National River Restoration, Korea
MASSACHUSETTS COASTAL NONPOINT PROGRAM NOAA/EPA DECISIONS ON CONDITIONS OF APPROVAL
 MASSACHUSETTS COASTAL NONPOINT PROGRAM NOAA/EPA DECISIONS ON CONDITIONS OF APPROVAL FOREWORD This document contains the basis for NOAA and EPA s decision to fully approve Massachusetts Coastal Nonpoint
MASSACHUSETTS COASTAL NONPOINT PROGRAM NOAA/EPA DECISIONS ON CONDITIONS OF APPROVAL FOREWORD This document contains the basis for NOAA and EPA s decision to fully approve Massachusetts Coastal Nonpoint
Section 4 General Strategies and Tools
 Section 4 General Strategies and Tools Key planning issues for WRIA 35 have been identified in Sections 5 and 6 in the areas of water supply, instream flow, water quality, and aquatic habitat. General
Section 4 General Strategies and Tools Key planning issues for WRIA 35 have been identified in Sections 5 and 6 in the areas of water supply, instream flow, water quality, and aquatic habitat. General
Pamela Birak, Jordan Lake State Park, Chatham County, NC
 Pamela Birak, Jordan Lake State Park, Chatham County, NC 3 Lakes, Reservoirs, and Ponds Forty-six states, Puerto Rico, and the District of Columbia (collectively referred to as states in the rest of this
Pamela Birak, Jordan Lake State Park, Chatham County, NC 3 Lakes, Reservoirs, and Ponds Forty-six states, Puerto Rico, and the District of Columbia (collectively referred to as states in the rest of this
Melbourne, Australia. Melbourne: The city as a catchment approach. The importance of holistic urban water management
 SWITCH Training Kit 1 Melbourne: The city as a catchment approach A prolonged period of drought, increasing population and polluted stormwater runoff are adding pressures to Southern Australia s water
SWITCH Training Kit 1 Melbourne: The city as a catchment approach A prolonged period of drought, increasing population and polluted stormwater runoff are adding pressures to Southern Australia s water
WATER: ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE Syllabus
 WATER: ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE Syllabus Course Title Water: Environmental Science Course Description Central to all ecosystems, water is essential to life as we know it. It shapes our planet on every level,
WATER: ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE Syllabus Course Title Water: Environmental Science Course Description Central to all ecosystems, water is essential to life as we know it. It shapes our planet on every level,
A Developer s Guide: Watershed-Wise Development
 A Developer s Guide: Watershed-Wise Development Environmental Protection What is a watershed? It does not matter how far away you build from a creek, lake, or the ocean, you are in a watershed. Another
A Developer s Guide: Watershed-Wise Development Environmental Protection What is a watershed? It does not matter how far away you build from a creek, lake, or the ocean, you are in a watershed. Another
Stormwater management around the world Lessons from Novatech 2010 Dennis Corbett and Marion Urrutiaguer
 Stormwater management around the world Lessons from Novatech 2010 Dennis Corbett and Marion Urrutiaguer Novatech 2010, the 7th international conference on sustainable techniques and strategies in urban
Stormwater management around the world Lessons from Novatech 2010 Dennis Corbett and Marion Urrutiaguer Novatech 2010, the 7th international conference on sustainable techniques and strategies in urban
Foreword. The Hon Andrew Powell MP Queensland Minister for Environment and Heritage Protection
 Table of contents Foreword... 3 Providing comment on this Plan... 4 Executive summary... 5 Introduction... 7 The Great Barrier Reef World Heritage Area... 7 Pressures on the Reef... 9 Current management...
Table of contents Foreword... 3 Providing comment on this Plan... 4 Executive summary... 5 Introduction... 7 The Great Barrier Reef World Heritage Area... 7 Pressures on the Reef... 9 Current management...
Living & Working Managing Natural Resources and Waste
 Living & Working Managing Natural Resources and Waste 5.13 Managing Natural Resources and Waste Background 5.13.1 This chapter focuses on how we manage resources within the AONB. It includes renewable
Living & Working Managing Natural Resources and Waste 5.13 Managing Natural Resources and Waste Background 5.13.1 This chapter focuses on how we manage resources within the AONB. It includes renewable
Redland City Council. 1. Recommendation. 2. Local government metrics. The Commission recommends:
 1. Recommendation The Commission recommends: (i) the existing local government area of Redland Shire Council remains unchanged; (ii) the local government be renamed Redland City Council; (iii) the local
1. Recommendation The Commission recommends: (i) the existing local government area of Redland Shire Council remains unchanged; (ii) the local government be renamed Redland City Council; (iii) the local
Environmental guidelines for preparation of an Environment Management Plan
 Environmental guidelines for preparation of an Environment Management Plan Environment Protection Authority MAY 2013 Australian Capital Territory, Canberra 2013 This work is copyright. Apart from any use
Environmental guidelines for preparation of an Environment Management Plan Environment Protection Authority MAY 2013 Australian Capital Territory, Canberra 2013 This work is copyright. Apart from any use
TURKEY ANATOLIA WATERSHED REHABILITATION PROJECT Sedat Kadioglu Ministry of Environment Abdulmecit Yesil Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs
 TURKEY ANATOLIA WATERSHED REHABILITATION PROJECT Sedat Kadioglu Ministry of Environment Abdulmecit Yesil Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs PROJECT TITLE : Anatolia Watershed Rehabilitation Project
TURKEY ANATOLIA WATERSHED REHABILITATION PROJECT Sedat Kadioglu Ministry of Environment Abdulmecit Yesil Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs PROJECT TITLE : Anatolia Watershed Rehabilitation Project
Ian K. G. Boothroyd, Director, BSc(Hons), MSc, DPhil, MBA, MIBIOL, CBIOL, MRSNZ
 Authors: Co-authors: Presenter: Title: Ian K. G. Boothroyd, Director, BSc(Hons), MSc, DPhil, MBA, MIBIOL, CBIOL, MRSNZ Ms Maree Drury BSc(Hons), MSc Dr Ian Boothroyd Sustainable resource management: A
Authors: Co-authors: Presenter: Title: Ian K. G. Boothroyd, Director, BSc(Hons), MSc, DPhil, MBA, MIBIOL, CBIOL, MRSNZ Ms Maree Drury BSc(Hons), MSc Dr Ian Boothroyd Sustainable resource management: A
Dr. Lidija Globevnik Luka Snoj, Neven Verdnik, Peter Muck. Meta Povž
 The concept of ecological restoration of a sub-alpine river and its tributaries in Slovenia Suggestions for regulation of riverbed and reconstruction of hydrotechnical facilities Dr. Lidija Globevnik Luka
The concept of ecological restoration of a sub-alpine river and its tributaries in Slovenia Suggestions for regulation of riverbed and reconstruction of hydrotechnical facilities Dr. Lidija Globevnik Luka
Action 7 To legislate at the appropriate level to limit the presence of phosphates in detergents
 Action 7 To legislate at the appropriate level to limit the presence of phosphates in detergents 7th Steering Group Meeting of the Priority Area 4 - To restore and maintain the quality of waters - of the
Action 7 To legislate at the appropriate level to limit the presence of phosphates in detergents 7th Steering Group Meeting of the Priority Area 4 - To restore and maintain the quality of waters - of the
Table 2: State Agency Recommendations Agency of Agriculture, Food and Markets
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION ASSOCIATED WITH THE ALLOCATION PRIORITIES FOR CLEAN WATER FUND BOARD Table 2: State Agency Recommendations Agency of Agriculture, Food and Markets 1 Agriculture AAFM On-Farm Implementation
SUPPORTING INFORMATION ASSOCIATED WITH THE ALLOCATION PRIORITIES FOR CLEAN WATER FUND BOARD Table 2: State Agency Recommendations Agency of Agriculture, Food and Markets 1 Agriculture AAFM On-Farm Implementation
Environmental aspects of water fluoridation
 KEY POINTS Fluorides are very common in the environment. Reviews of the literature and environmental impact assessments have found no evidence of any adverse environmental effects resulting from water.
KEY POINTS Fluorides are very common in the environment. Reviews of the literature and environmental impact assessments have found no evidence of any adverse environmental effects resulting from water.
Environmental Guidelines for Preparation of an Environmental Management Plan
 2013 Environmental Guidelines for Preparation of an Environmental Management Plan Environmental Management Division Environmental Protection Agency 3/13/2013 ENVIRONMENTAL GUIDELINES FOR PREPARATION OF
2013 Environmental Guidelines for Preparation of an Environmental Management Plan Environmental Management Division Environmental Protection Agency 3/13/2013 ENVIRONMENTAL GUIDELINES FOR PREPARATION OF
EPA Trends for wastewater Treatment in California - 2011
 EPA S TECHNOLOGY NEEDS FOR THE WATER AND WASTEWATER INDUSTRY Nancy Stoner Acting Assistant Administrator U.S. EPA Office of Water International Emerging Technology Symposium Arlington, VA April 23rd, 2014
EPA S TECHNOLOGY NEEDS FOR THE WATER AND WASTEWATER INDUSTRY Nancy Stoner Acting Assistant Administrator U.S. EPA Office of Water International Emerging Technology Symposium Arlington, VA April 23rd, 2014
Executive Summary Minnesota Nutrient Reduction Strategy
 Executive Summary The (NRS) will guide the state in reducing excess nutrients in waters so that in-state and downstream water quality goals are ultimately met. Nutrient impacts are widespread. Excessive
Executive Summary The (NRS) will guide the state in reducing excess nutrients in waters so that in-state and downstream water quality goals are ultimately met. Nutrient impacts are widespread. Excessive
Toxic Municipal Waste Water Treatment
 FINAL IC/24 February 2000 Recommendation concerning the Treatment of Municipal Waste Water 2 Recommendation concerning the Treatment of Municipal Waste Water The Commission, recalling Paragraph 1 of Article
FINAL IC/24 February 2000 Recommendation concerning the Treatment of Municipal Waste Water 2 Recommendation concerning the Treatment of Municipal Waste Water The Commission, recalling Paragraph 1 of Article
THE NATURAL RESOURCES AND ENVIRONMENT ORDINANCE (CAP. 84 - LAWS OF SARAWAK, 1958 Ed.)
 THE NATURAL RESOURCES AND ENVIRONMENT ORDINANCE (CAP. 84 - LAWS OF SARAWAK, 1958 Ed.) THE NATURAL RESOURCES AND ENVIRONMENT (PRESCRIBED ACTIVITIES) ORDER, 1994 (Made under section 11A(1)) (Incorporating
THE NATURAL RESOURCES AND ENVIRONMENT ORDINANCE (CAP. 84 - LAWS OF SARAWAK, 1958 Ed.) THE NATURAL RESOURCES AND ENVIRONMENT (PRESCRIBED ACTIVITIES) ORDER, 1994 (Made under section 11A(1)) (Incorporating
Watershed Education for Teachers. Cinde Thomas-Jimenez Guadalupe-Blanco River Authority
 Watershed Education for Teachers Cinde Thomas-Jimenez Guadalupe-Blanco River Authority In This Presentation Why Watersheds Matter What Is a Watershed Water Quality Parameters Point Source and NonPoint
Watershed Education for Teachers Cinde Thomas-Jimenez Guadalupe-Blanco River Authority In This Presentation Why Watersheds Matter What Is a Watershed Water Quality Parameters Point Source and NonPoint
SUSTAINABLE URBAN DRAINAGE SYSTEMS
 overflow can lead into a permeable conveyance system to increase further the benefit and reduce the need for pipe systems. Pollutant removal rates have been shown to be high, with some pollutants being
overflow can lead into a permeable conveyance system to increase further the benefit and reduce the need for pipe systems. Pollutant removal rates have been shown to be high, with some pollutants being
Sustainability Brief: Water Quality and Watershed Integrity
 Sustainability Brief: and Watershed Integrity New Jersey depends on water resources for the health of our people, the strength of our economy, and the vitality of our ecosystems. The quality of our water
Sustainability Brief: and Watershed Integrity New Jersey depends on water resources for the health of our people, the strength of our economy, and the vitality of our ecosystems. The quality of our water
Environmental Role of Poplar and Willow Drusilla Riddell-Black Lupus Science United Kingdom
 Environmental Role of Poplar and Willow Drusilla Riddell-Black Lupus Science United Kingdom Environmental roles include Buffer zones Riparian zone protection Slope stabilisation Flooding reduction Carbon
Environmental Role of Poplar and Willow Drusilla Riddell-Black Lupus Science United Kingdom Environmental roles include Buffer zones Riparian zone protection Slope stabilisation Flooding reduction Carbon
Melbourne Water s Submission. Draft Victorian Floodplain Management Strategy
 Melbourne Water s Submission Draft Victorian Floodplain Management Strategy Waterways, drainage and floodplains are essential to life and liveability. The rivers, creeks, estuaries, wetlands and floodplains
Melbourne Water s Submission Draft Victorian Floodplain Management Strategy Waterways, drainage and floodplains are essential to life and liveability. The rivers, creeks, estuaries, wetlands and floodplains
Sewerage Management System for Reduction of River Pollution
 Sewerage Management System for Reduction of River Pollution Peter Hartwig Germany Content page: 1 Introduction 1 2 Total emissions 3 3 Discharge from the wastewater treatment plants 4 4 Discharge from
Sewerage Management System for Reduction of River Pollution Peter Hartwig Germany Content page: 1 Introduction 1 2 Total emissions 3 3 Discharge from the wastewater treatment plants 4 4 Discharge from
Freshwater Resources and Water Pollution
 Visualizing Environmental Science Freshwater Resources and Water Pollution Chapter 10 Copyright The Importance of Water Life on Earth would be impossible without water All living organisms contain water
Visualizing Environmental Science Freshwater Resources and Water Pollution Chapter 10 Copyright The Importance of Water Life on Earth would be impossible without water All living organisms contain water
As amended at General Meeting 04 November 2015 (Item 11.1.2)
 As amended at General Meeting 04 November 2015 (Item 11.1.2) Operational Plan 2015-2016 What is an operational plan? Under the Local Government Act 2009, Council must adopt an operational plan each financial
As amended at General Meeting 04 November 2015 (Item 11.1.2) Operational Plan 2015-2016 What is an operational plan? Under the Local Government Act 2009, Council must adopt an operational plan each financial
Broken Arrow Public Schools AP Environmental Science Objectives Revised 11-19-08
 1 st six weeks 1 Identify questions and problems that can be answered through scientific investigation. 2 Design and conduct scientific investigations to answer questions about the world by creating hypotheses;
1 st six weeks 1 Identify questions and problems that can be answered through scientific investigation. 2 Design and conduct scientific investigations to answer questions about the world by creating hypotheses;
cardno Phu My Bridge Queensland s first light rail system Creative Village Redevelopment Marine Corps environmental reviews
 shaping the future www.cardno.com cardno shapes the future for communities around the world Cardno s vision is to be a world leader in the provision of professional services to improve the physical and
shaping the future www.cardno.com cardno shapes the future for communities around the world Cardno s vision is to be a world leader in the provision of professional services to improve the physical and
Environmental Case Study Decatur, Georgia, DeKalb County A Suburban Creek Resists Channelization
 Introduction A visual examination of Doolittle Creek in a highly developed suburban county in Georgia yielded telltale signs of a creek whose original streambed had been altered. Examination of official
Introduction A visual examination of Doolittle Creek in a highly developed suburban county in Georgia yielded telltale signs of a creek whose original streambed had been altered. Examination of official
Origins and causes of river basin sediment degradation and available remediation and mitigation options. Feedback from the Riskbase workshop
 Origins and causes of river basin sediment degradation and available remediation and mitigation options Feedback from the Riskbase workshop Corinne Merly 1, Olivier Cerdan 1, Laurence Gourcy 1 Emmanuelle
Origins and causes of river basin sediment degradation and available remediation and mitigation options Feedback from the Riskbase workshop Corinne Merly 1, Olivier Cerdan 1, Laurence Gourcy 1 Emmanuelle
ICRI Resolution on Artificial Coral Reef Restoration and Rehabilitation
 ICRI Resolution on Artificial Coral Reef Restoration and Rehabilitation This Resolution was tabled and discussed at the ICRI General Meeting in Seychelles on Wednesday, 27 April 2005. It was approved after
ICRI Resolution on Artificial Coral Reef Restoration and Rehabilitation This Resolution was tabled and discussed at the ICRI General Meeting in Seychelles on Wednesday, 27 April 2005. It was approved after
CBP Efforts to Identify Priority Areas and Enhance Monitoring in the Bay Watershed
 CBP Efforts to Identify Priority Areas and Enhance Monitoring in the Bay Watershed Scott Phillips, USGS Potomac Monitoring Forum U.S. Department of the Interior U.S. Geological Survey Outline Chesapeake
CBP Efforts to Identify Priority Areas and Enhance Monitoring in the Bay Watershed Scott Phillips, USGS Potomac Monitoring Forum U.S. Department of the Interior U.S. Geological Survey Outline Chesapeake
Green Infrastructure Case Study Template
 Green Infrastructure Case Study Template The aim of the exercise is to provide information on how the elements of the Green Infrastructure Strategy are implemented at national level and to provide case
Green Infrastructure Case Study Template The aim of the exercise is to provide information on how the elements of the Green Infrastructure Strategy are implemented at national level and to provide case
Trevor Lloyd Director
 Trevor Lloyd Director Qualifications Environmental Toxicology and Health Risk Assessment Course - Qld Centre for Public Health (1998) Quality Assurance Auditing Training Course - Bywater plc (1994) University
Trevor Lloyd Director Qualifications Environmental Toxicology and Health Risk Assessment Course - Qld Centre for Public Health (1998) Quality Assurance Auditing Training Course - Bywater plc (1994) University
Water Quality Management
 Water Quality Management Sustainable agriculture practices detailed in other sections of this publication are important ways to maintain or improve water quality on the farm and downstream from the farm.
Water Quality Management Sustainable agriculture practices detailed in other sections of this publication are important ways to maintain or improve water quality on the farm and downstream from the farm.
Creating Green Jobs within the Environment and Culture sector.
 Creating Green Jobs within the Environment and Culture sector. Matilda Skosana Environmental Programmes (ILO Definition): 1. DEFINITION OF GREEN JOB. Jobs are green when they help reduce negative environmental
Creating Green Jobs within the Environment and Culture sector. Matilda Skosana Environmental Programmes (ILO Definition): 1. DEFINITION OF GREEN JOB. Jobs are green when they help reduce negative environmental
The River Ribble is one of the longest rivers in the North West of England
 River Ribble The River Ribble is one of the longest rivers in the North West of England Did you know? The tidal limit of the Ribble is 11 miles inland (above Preston); The River Ribble is home to a variety
River Ribble The River Ribble is one of the longest rivers in the North West of England Did you know? The tidal limit of the Ribble is 11 miles inland (above Preston); The River Ribble is home to a variety
A Clean Harbour for Hong Kong. Government s Initial Response To The Report of the International Review Panel On Sewage Treatment for the Harbour Area
 A Clean Harbour for Hong Kong Government s Initial Response To The Report of the International Review Panel On Sewage Treatment for the Harbour Area CONTENTS Page 1 Glossary of Terms... 1 2 Introduction...
A Clean Harbour for Hong Kong Government s Initial Response To The Report of the International Review Panel On Sewage Treatment for the Harbour Area CONTENTS Page 1 Glossary of Terms... 1 2 Introduction...
6 Chemicals from human settlements
 6 Chemicals from human settlements 6.1 Introduction The world is becoming increasingly urban, particularly in developing countries. The transition of people from rural areas to cities represents a major,
6 Chemicals from human settlements 6.1 Introduction The world is becoming increasingly urban, particularly in developing countries. The transition of people from rural areas to cities represents a major,
How To Improve Water Quality In East Pacificon
 WATER STORIES EAST PROVIDENCE, RI We are proud to partner with East Providence on this very important project. Together we developed an innovative, sustainable solution that promotes public, economic
WATER STORIES EAST PROVIDENCE, RI We are proud to partner with East Providence on this very important project. Together we developed an innovative, sustainable solution that promotes public, economic
Source Water Protection Practices Bulletin Managing Sanitary Sewer Overflows and Combined Sewer Overflows to Prevent Contamination of Drinking Water
 United States Office of Water EPA 916-F-01-032 Environmental Protection (4606) July 2001 Agency Source Water Protection Practices Bulletin Managing Sanitary Sewer Overflows and Combined Sewer Overflows
United States Office of Water EPA 916-F-01-032 Environmental Protection (4606) July 2001 Agency Source Water Protection Practices Bulletin Managing Sanitary Sewer Overflows and Combined Sewer Overflows
Restoring Ecosystems. Ecosystem Restoration Services
 Restoring Ecosystems Ecosystem Restoration Services 2 Ecosystem Restoration Services AECOM s integrated approach sciencebased planning, with innovative design and execution delivers sustainable and cost-effective
Restoring Ecosystems Ecosystem Restoration Services 2 Ecosystem Restoration Services AECOM s integrated approach sciencebased planning, with innovative design and execution delivers sustainable and cost-effective
Responding to the Challenges of Water Security: the VIII Phase of the International Hydrological Programme 2014-2021
 3rd UNECWAS Annual Seminar 21st of August, TUT Responding to the Challenges of Water Security: the VIII Phase of the International Hydrological Programme 2014-2021 Blanca Jimenez-Cisneros Director of the
3rd UNECWAS Annual Seminar 21st of August, TUT Responding to the Challenges of Water Security: the VIII Phase of the International Hydrological Programme 2014-2021 Blanca Jimenez-Cisneros Director of the
Restoring Anadromous Fish Habitat in Big Canyon Creek Watershed. Summary Report 2002
 Restoring Anadromous Fish Habitat in Big Canyon Creek Watershed Summary Report 2002 DOE/BP-00005268-5 November 2002 This Document should be cited as follows: "Restoring Anadromous Fish Habitat in Big Canyon
Restoring Anadromous Fish Habitat in Big Canyon Creek Watershed Summary Report 2002 DOE/BP-00005268-5 November 2002 This Document should be cited as follows: "Restoring Anadromous Fish Habitat in Big Canyon
Northern Territory Fisheries Resource Sharing Framework
 Northern Territory Fisheries Resource Sharing Framework Page 1 of 11 Introduction Fishing is important in the Northern Territory (Territory). Coastal Aboriginal people recognise sea country out to the
Northern Territory Fisheries Resource Sharing Framework Page 1 of 11 Introduction Fishing is important in the Northern Territory (Territory). Coastal Aboriginal people recognise sea country out to the
Various options are discussed below.these low cost, low impact interventions can also be applied as general erosion control methods.
 Week 10 River Hydraulics Rehabilitating Urban Waterways (From http://hubpages.com/hub/river-bank-erosion-control-methods) See also the resources placed on Moodle. Water channels should be viewed as a resource
Week 10 River Hydraulics Rehabilitating Urban Waterways (From http://hubpages.com/hub/river-bank-erosion-control-methods) See also the resources placed on Moodle. Water channels should be viewed as a resource
Implementing improvements in water quality and protecting ecosystem services
 Implementing improvements in water quality and protecting ecosystem services Why water quality matters Water is essential for life. The amount of freshwater on Earth is limited, and its quality is under
Implementing improvements in water quality and protecting ecosystem services Why water quality matters Water is essential for life. The amount of freshwater on Earth is limited, and its quality is under
City of Sydney Decentralized Water Master Plan. Developed From Project #4487, Institutional Issues for Integrated One Water Management
 City of Sydney Decentralized Water Master Plan Developed From Project #4487, Institutional Issues for Integrated One Water Management 9.2 City of Sydney Decentralized Water Master Plan The following section
City of Sydney Decentralized Water Master Plan Developed From Project #4487, Institutional Issues for Integrated One Water Management 9.2 City of Sydney Decentralized Water Master Plan The following section
Nipigon Bay. Area of Concern Status of Beneficial Use Impairments September 2010
 Nipigon Bay Area of Concern Status of Beneficial Use Impairments September 2010 Nipigon Bay is in the most northerly area of Lake Superior. The Area of Concern takes in a large portion of Nipigon Bay and
Nipigon Bay Area of Concern Status of Beneficial Use Impairments September 2010 Nipigon Bay is in the most northerly area of Lake Superior. The Area of Concern takes in a large portion of Nipigon Bay and
POLICIES AND PRINCIPLES
 NATIONAL WATER QUALITY MANAGEMENT STRATEGY POLICIES AND PRINCIPLES A Reference Document April 1994 Agriculture and Resource Management Council of Australia and New Zealand Australian and New Zealand Environment
NATIONAL WATER QUALITY MANAGEMENT STRATEGY POLICIES AND PRINCIPLES A Reference Document April 1994 Agriculture and Resource Management Council of Australia and New Zealand Australian and New Zealand Environment
Stormwater harvesting
 Stormwater harvesting How to collect and re-use stormwater from Sydney Water s stormwater system Most of the stormwater pipes and channels in the Sydney metropolitan area are the responsibility of local
Stormwater harvesting How to collect and re-use stormwater from Sydney Water s stormwater system Most of the stormwater pipes and channels in the Sydney metropolitan area are the responsibility of local
Welcome to the Understanding Dissolved Oxygen learning module. This section provides information on the following topics:
 Introduction Welcome to the learning module. This section provides information on the following topics: How dissolved oxygen is defined and measured in numbers Why dissolved oxygen is important Natural
Introduction Welcome to the learning module. This section provides information on the following topics: How dissolved oxygen is defined and measured in numbers Why dissolved oxygen is important Natural
TOUR DE TABLE CANADA
 TOUR DE TABLE CANADA NATO/CCMS Pilot Study Prevention and Remediation In Selected Industrial Sectors: SEDIMENTS Presented by Lisa Keller, P. Eng. Environment Canada June 20, 2007 Outline Contaminated Sites
TOUR DE TABLE CANADA NATO/CCMS Pilot Study Prevention and Remediation In Selected Industrial Sectors: SEDIMENTS Presented by Lisa Keller, P. Eng. Environment Canada June 20, 2007 Outline Contaminated Sites
Community Workshop 5. Overarching Goals for Machado Lake Ecosystem and Wilmington Drain Multi-Use Projects
 City of Los Angeles Department of Public Works Bureau of Engineering Machado Lake Ecosystem Rehabilitation Project & Wilmington Drain Multi-Use Project Community Workshop 5 February 24, 2009 In association
City of Los Angeles Department of Public Works Bureau of Engineering Machado Lake Ecosystem Rehabilitation Project & Wilmington Drain Multi-Use Project Community Workshop 5 February 24, 2009 In association
Aquatic Ecosystems Restoration
 Presenter s name Aquatic Ecosystems Restoration Lessons Learned from Asian Development Bank Operations Qingfeng Zhang, Senior Water Resources Engineer Asian Development Bank This Presentation will discuss
Presenter s name Aquatic Ecosystems Restoration Lessons Learned from Asian Development Bank Operations Qingfeng Zhang, Senior Water Resources Engineer Asian Development Bank This Presentation will discuss
Water Quality in the Fluvial Section
 WATER SHORELINES SEDIMENTS Water Quality in the Fluvial Section Physicochemical and Bacteriological Parameters 3rd Edition Background The St. Lawrence River is the largest river in Quebec. It is crucial
WATER SHORELINES SEDIMENTS Water Quality in the Fluvial Section Physicochemical and Bacteriological Parameters 3rd Edition Background The St. Lawrence River is the largest river in Quebec. It is crucial
1.7.0 Floodplain Modification Criteria
 1.7.0 Floodplain Modification Criteria 1.7.1 Introduction These guidelines set out standards for evaluating and processing proposed modifications of the 100- year floodplain with the following objectives:
1.7.0 Floodplain Modification Criteria 1.7.1 Introduction These guidelines set out standards for evaluating and processing proposed modifications of the 100- year floodplain with the following objectives:
Water Security Agency. Plan for 2015-16. saskatchewan.ca
 Water Security Agency Plan for 2015-16 saskatchewan.ca Statement from the Minister I am pleased to present the Water Security Agency s Plan for 2015-16. The Honourable Scott Moe Minister Responsible for
Water Security Agency Plan for 2015-16 saskatchewan.ca Statement from the Minister I am pleased to present the Water Security Agency s Plan for 2015-16. The Honourable Scott Moe Minister Responsible for
Kristina Veidemane, Baltic Environmental Forum Panevezys, 12.05.2015
 Priority 2 Protection and restoration of biodiversity and soil and promotion of ecosystem services, including through Natura 2000, and green infrastructure Kristina Veidemane, Baltic Environmental Forum
Priority 2 Protection and restoration of biodiversity and soil and promotion of ecosystem services, including through Natura 2000, and green infrastructure Kristina Veidemane, Baltic Environmental Forum
Phosphorus. Phosphorus Lake Whatcom Cooperative Management. www.ecy.wa.gov/programs/wq/nonpoint/phosphorus/phosphorusban.html
 Phosphorus Phosphorus Brochure Lake Whatcom Cooperative Management Reducing Phosphorus Website Washington State Department of Ecology www.ecy.wa.gov/programs/wq/nonpoint/phosphorus/phosphorusban.html Nutrients
Phosphorus Phosphorus Brochure Lake Whatcom Cooperative Management Reducing Phosphorus Website Washington State Department of Ecology www.ecy.wa.gov/programs/wq/nonpoint/phosphorus/phosphorusban.html Nutrients
Ecosystem Services, Wetlands and Houston s Growth. Jim Lester
 Ecosystem Services, Wetlands and Houston s Growth Jim Lester Definitions (MEA 2005) Ecosystem: a dynamic complex of plant, animal, and microorganism communities and the nonliving environment interacting
Ecosystem Services, Wetlands and Houston s Growth Jim Lester Definitions (MEA 2005) Ecosystem: a dynamic complex of plant, animal, and microorganism communities and the nonliving environment interacting
Urban Waters and River Restoration. Pinja Kasvio, Finnish Environment Institute, SYKE RESTORE North Region Closing Seminar 14.8.
 Urban Waters and River Restoration Pinja Kasvio, Finnish Environment Institute, SYKE RESTORE North Region Closing Seminar 14.8.2013 Urban Waters Hålland, Gässlösa (Sweden) Characteristics of urban areas:
Urban Waters and River Restoration Pinja Kasvio, Finnish Environment Institute, SYKE RESTORE North Region Closing Seminar 14.8.2013 Urban Waters Hålland, Gässlösa (Sweden) Characteristics of urban areas:
EPA Grants Supported Restoring the Chesapeake Bay
 OFFICE OF INSPECTOR GENERAL Audit Report Catalyst for Improving the Environment EPA Grants Supported Restoring the Chesapeake Bay Report No. 2006-P-00032 September 6, 2006 Report Contributors: Randy Holthaus
OFFICE OF INSPECTOR GENERAL Audit Report Catalyst for Improving the Environment EPA Grants Supported Restoring the Chesapeake Bay Report No. 2006-P-00032 September 6, 2006 Report Contributors: Randy Holthaus
Preparing a Green Wedge Management Plan
 Preparing a Green Wedge Management Plan Planning Practice Note 31 JUNE 2015 This practice note provides a guide for the preparation of Green Wedge Management Plans and sets out the general requirements
Preparing a Green Wedge Management Plan Planning Practice Note 31 JUNE 2015 This practice note provides a guide for the preparation of Green Wedge Management Plans and sets out the general requirements
Clean Water for a Healthy World
 Clean Water for a Healthy World On World Water Day, we reaf irm that clean water is life, and our lives depend on how we protect the quality of our water. Water Quality: Healthy People, Healthy Ecosystems
Clean Water for a Healthy World On World Water Day, we reaf irm that clean water is life, and our lives depend on how we protect the quality of our water. Water Quality: Healthy People, Healthy Ecosystems
GREAT BARRIER REEF. Climate Change Action Plan
 GREAT BARRIER REEF Climate Change Action Plan 2007 2011 Climate change is now recognised as the greatest long-term threat to the Great Barrier Reef. The Great Barrier Reef is internationally renowned as
GREAT BARRIER REEF Climate Change Action Plan 2007 2011 Climate change is now recognised as the greatest long-term threat to the Great Barrier Reef. The Great Barrier Reef is internationally renowned as
