Multiple Sclerosis CALL DASCO TODAY FOR MORE INFORMATION
|
|
|
- Ruth Hill
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Multiple Sclerosis Multiple sclerosis (abbreviated MS, also known as disseminated sclerosis orencephalomyelitis disseminata) is an autoimmune condition in which the immune system attacks the central nervous system (CNS), leading to demyelination. It may cause numerous physical and mental symptoms, and often progresses to physical and cognitive disability. Disease onset usually occurs in young adults, is more common in women, and has a prevalence that ranges between 2 and 150 per 100,000 depending on the country or specific population. MS was first described in 1868 by Jean-Martin Charcot. MS affects the areas of the brain and spinal cord known as the white matter. White matter cells carry signals between the grey matter areas, where the processing is done, and the rest of the body. More specifically, MS destroys oligodendrocytes which are the cells responsible for creating and maintaining a fatty layer, known as the myelin sheath, which helps the neurons carry electrical signals. MS results in a thinning or complete loss of myelin and, less frequently, the cutting (transection) of the neuron's extensions or axons. When the myelin is lost, the neurons can no longer effectively conduct their electrical signals. The name multiple sclerosis refers to the scars (scleroses - better known as plaques or lesions) in the white matter. Loss of myelin in these lesions causes some of the symptoms, which vary widely depending upon which signals are interrupted. However, more advanced forms of imaging are now showing that much of the damage happens outside these regions. Almost any neurological symptom can accompany the disease. MS takes several forms, with new symptoms occurring either in discrete attacks (relapsing forms) or slowly accumulating over time (progressive forms). Most people are first diagnosed with relapsingremitting MS but develop secondary-progressive MS (SPMS) after a number of years. Between attacks, symptoms may go away completely,
2 but permanent neurological problems often persist, especially as the disease advances. Although much is known about the mechanisms involved in the disease process, the cause remains elusive: the most widely-held theory being that the condition results from attacks to the nervous system by the body's own immune system. Some believe it is a metabolically dependent disease while others think that it might be caused by a virus such as Epstein-Barr. Still others believe that its virtual absence from tropical areas points to a deficiency of vitamin D during childhood. This disease does not have a cure, but several therapies have proven helpful. Treatments attempt to return function after an attack, prevent new attacks, and prevent disability. MS medications can have adverse effects or be poorly tolerated, and many patients pursue alternative treatments, despite the paucity of supporting scientific study. Many candidate therapies are still under investigation. The prognosis, or expected course of the disease, depends on the subtype of the disease, the individual patient's disease characteristics, the initial symptoms, and the degree of disability the person experiences as time advances. Life expectancy of patients, however, is nearly the same as that of the unaffected population, and in some cases a near-normal life is possible. Signs and symptoms MS presents with a variety of symptoms, including changes in sensation (hypoesthesia), muscle weakness, abnormal muscle spasms, or difficulty in moving; difficulties with coordination and balance (ataxia); problems in speech (dysarthria) or swallowing (dysphagia), visual problems (nystagmus, optic neuritis, or diplopia), fatigue and acute or chronic pain syndromes, and bladder and bowel difficulties. Cognitive impairment of varying degrees, or emotional
3 symptomatology in the form of depression or pseudobulbar affect are also common. Neuropathic pain is usual, and this can be in the form of Lhermitte's sign. Neuropathic pain is the most common, distressing and intractable of the pain syndromes in MS. This pain is described as constant, boring, burning or tingling intensely. It usually occurs in the legs. Paraesthesias include pins and needles; tingling; shivering; burning pains; feelings of pressure; and areas of skin with heightened sensitivity to touch. The pains associated with these can be aching, throbbing, stabbing, shooting, gnawing, tingling, tightness and numbness. The main clinical measure of disability progression and severity of the symptoms is the Expanded Disability Status Scale or EDSS. The initial attacks (also known as exacerbations or relapses) are often transient, mild (or asymptomatic), and self-limited. They often do not prompt a health care visit and sometimes are only identified in retrospect once the diagnosis has been made based on further attacks. The most common initial symptoms reported are: changes in sensation in the arms, legs or face (33%), complete or partial vision loss (optic neuritis) (16%), weakness (13%), double vision (7%), unsteadiness when walking (5%), and balance problems (3%); but many rare initial symptoms have been reported such as aphasia or psychosis. Fifteen percent of individuals have multiple symptoms when they first seek medical attention. Optic neuritis or focal leg weakness may lead to falls and other serious accidents. For some people the initial MS attack is preceded by infection, trauma, or strenuous physical effort. Diagnosis Multiple sclerosis is difficult to diagnose in its early stages. In fact, a definite diagnosis cannot be made until other disease processes (differential diagnoses) have been ruled out and, in the case of relapsing-remitting MS, there is evidence of at least two anatomically separate demyelinating events separated by at least thirty days. In the
4 case of primary progressive, a slow progression of signs and symptoms over at least 6 months is required. Historically, different criteria were used and the Schumacher and Poser criteria were both popular. Currently, the McDonald criteria represent international efforts to standardize the diagnosis of MS using clinical, laboratory and radiologic data. Clinical data alone may be sufficient for a diagnosis of MS. If an individual has suffered two separate episodes of neurologic symptoms characteristic of MS, and the individual also has consistent abnormalities on physical examination, a diagnosis of MS can be made with no further testing. Since some people with MS seek medical attention after only one attack, other testing may hasten the diagnosis and allow earlier initiation of therapy. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) of the brain and spine is often used during the diagnostic process. MRI shows areas of demyelination (lesions) as bright spots on the image. Gadolinium can be administered intravenously to highlight active plaques and, by elimination, demonstrate the existence of historical lesions not associated with clinical symptoms. This can provide the evidence of chronic disease needed for a definitive diagnosis of MS. Testing of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) can provide evidence of chronic inflammation of the central nervous system. The CSF is tested for oligoclonal bands, which are immunoglobulins found in 75% to 85% of people with definite MS (but also found in people with other diseases). Combined with MRI and clinical data, the presence of oligoclonal bands can help make a definite diagnosis of MS. Lumbar puncture is the procedure used to collect a sample of CSF. The brain of a person with MS often responds less actively to stimulation of the optic nerve and sensory nerves. These brain responses can be examined using visual evoked potentials (VEPs) and somatosensory evoked potentials (SEPs). Decreased activity on either test can reveal demyelination which may be otherwise asymptomatic. Along with other data, these exams can help find the
5 widespread nerve involvement required for a definite diagnosis of MS. Another test, which may become important in the future, is measurement of antibodies against myelin proteins such as myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG) and myelin basic protein (MBP). As of 2007, however, there is no established role for these tests in diagnosing MS. Optical coherence tomography of the eye's retina is also under study, mainly as a tool to measure response to medication and axonal degeneration. The signs and symptoms of MS can be similar to other medical problems, such as neuromyelitis optica, stroke, brain inflammation, infections such as Lyme disease (which can produce identical MRI lesions and CSF abnormalities), tumors, and other autoimmune problems, such as lupus. Additional testing may be needed to help distinguish MS from these other problems. Disease course and clinical subtypes The course of MS is difficult to predict, and the disease may at times either lie dormant or progress steadily. Several subtypes, or patterns of progression, have been described. Subtypes use the past course of the disease in an attempt to predict the future course. Subtypes are important not only for prognosis but also for therapeutic decisions. In 1996 the United States National Multiple Sclerosis Society standardized the following four subtype definitions: Relapsing-remitting
6 Relapsing-remitting describes the initial course of 85% to 90% of individuals with MS. This subtype is characterized by unpredictable attacks (relapses) followed by periods of months to years of relative quiet (remision) with no new signs of disease activity. Deficits suffered during the attacks may either resolve or may be permanent. When deficits always resolve between attacks, this is referred to as "benign" MS. Secondary progressive Secondary progressive describes around 80% of those with initial relapsing-remitting MS, who then begin to have neurologic decline between their acute attacks without any definite periods of remission. This decline may include new neurologic symptoms, worsening cognitive function, or other deficits. Secondary progressive is the most common type of MS and causes the greatest amount of disability. Primary progressive Primary progressive describes the approximately 10% of individuals who never have remission after their initial MS symptoms. Decline occurs continuously without clear attacks. The primary progressive subtype tends to affect people who are older at disease onset.
7 Progressive relapsing Progressive relapsing describes those individuals who, from the onset of their MS, have a steady neurologic decline but also suffer superimposed attacks; and is the least common of all subtypes Nevertheless the earliest clinical presentation of relapsing-remitting MS (RRMS) is the clinically isolated syndrome (CIS). In CIS, there is a subacute attack suggestive of demyelination but the person does not fulfill the criteria for multiple sclerosis. Several studies have shown that starting treatment with interferons during the initial attack can decrease the chance that a patient will develop clinical MS. Cases of MS before the CIS are sometimes found during other neurological inspections and are referred to as subclinical MS. Preclinical MS refers to cases after the CIS but before the confirming second attack. During the standard clinical course, relapses rate decreases with disease time. Special cases of the disease with non-standard behavior have also been described although many researchers believe they are different diseases. These cases are sometimes referred to as borderline forms of multiple sclerosis and are Neuromyelitis optica (NMO), Balo concentric sclerosis, Schilder's diffuse sclerosis and Marburg multiple sclerosis. Factors triggering a relapse
8 Multiple sclerosis relapses are often unpredictable and can occur without warning with no obvious inciting factors. Some attacks, however, are preceded by common triggers. In general, relapses occur more frequently during spring and summer than during autumn and winter. Infections, such as the common cold, influenza, and gastroenteritis, increase the risk for a relapse. Emotional and physical stress may also trigger an attack, as can severe illness of any kind. Statistically, there is no good evidence that either trauma or surgery trigger relapses. People with MS can participate in sports, but they should probably avoid extremely strenuous exertion, such as marathon running. Heat can transiently increase symptoms, which is known as Uhthoff's phenomenon. This is why some people with MS avoid saunas or even hot showers. However, heat is not an established trigger of relapses. Pregnancy can directly affect the susceptibility for relapse. The last three months of pregnancy offer a natural protection against relapses. However, during the first few months after delivery, the risk for a relapse is increased 20% 40%. Pregnancy does not seem to influence long-term disability. Children born to mothers with MS are not at increased risk for birth defects or other problems. Many potential triggers have been examined and found not to influence relapse rates in MS. Influenza vaccination is safe, does not trigger relapses, and can therefore be recommended for people with MS. There is also no evidence that vaccines for hepatitis B, varicella, tetanus, or Bacille Calmette-Guerin (BCG immunization for tuberculosis) increases the risk for relapse. Pathophysiology Although much is known about how multiple sclerosis causes damage, the reasons why multiple sclerosis occurs are not known. Multiple sclerosis is a disease in which the myelin (a fatty substance
9 which covers the axons of nerve cells) degenerates. According to the view of most researchers, a special subset of lymphocytes, called T cells, plays a key role in the development of MS. According to a strictly immunological explanation of MS, the inflammatory process is triggered by the T cells. T cells gain entry into the brain via the blood-brain barrier (a capillary system that should prevent entrance of T-cells into the nervous system). The blood brain barrier is normally not permeable to these types of cells, unless triggered by either infection or a virus, where the integrity of the tight junctions forming the blood-brain barrier is decreased. When the blood brain barrier regains its integrity (usually after infection or virus has cleared) the T cells are trapped inside the brain. These lymphocytes recognize myelin as foreign and attack it as if it were an invading virus. That triggers inflammatory processes, stimulating other immune cells and soluble factors like cytokines and antibodies. Leaks form in the blood-brain barrier. These leaks, in turn, cause a number of other damaging effects such as swelling, activation of macrophages, and more activation of cytokines and other destructive proteins such as matrix metalloproteinases. A deficiency of uric acid has been implicated in this process. It is known that a repair process, called remyelination, takes place in early phases of the disease, but the oligodendrocytes that originally formed a myelin sheath cannot completely rebuild a destroyed myelin sheath. The newly-formed myelin sheaths are thinner and often not as effective as the original ones. Repeated attacks lead to successively fewer effective remyelinations, until a scar-like plaque is built up around the damaged axons, according to four different damage patterns. The central nervous system should be able to recruit oligodendrocyte stem cells capable of turning into mature myelinating oligodendrocytes, but it is suspected that something inhibits stem cells in affected areas. The axons themselves can also be damaged by the attacks. Often, the brain is able to compensate for some of this damage, due to an ability called neuroplasticity. MS symptoms develop as the cumulative result of multiple lesions in the brain and spinal cord. This is why symptoms can vary greatly between different individuals, depending on where their lesions occur.
10 Causes Although many risk factors for multiple sclerosis have been identified, no definitive cause has been found. MS likely occurs as a result of some combination of both environmental and genetic factors. Various theories try to combine the known data into plausible explanations. Although most accept an autoimmune explanation, several theories suggest that MS is an appropriate immune response to one or several underlying conditions (the etiology could be heterogeneous). The need for alternative theories is supported by the poor results of present therapies, since autoimmune theory predicted greater success. Environmental The most popular hypothesis is that a viral infection or retroviral reactivation primes a susceptible immune system for an abnormal reaction later in life. On a molecular level, this might occur if there is a structural similarity between the infectious virus and some component of the central nervous system, leading to eventual confusion in the immune system. A correlation between clinical MS and presence of an endogenous retrovirus called HERV has been found. The strong correlation of MS to HERV infection, suggests that MS patients might benefit from use of HERV targeted antivirals or a gene therapy strategy to neutralize the HERV infection directly. Since MS seems to be more common in people who live farther from
11 the equator, another theory proposes that decreased sunlight exposure and possibly decreased vitamin D production may help cause MS. This theory is bolstered by recent research into the biochemistry of vitamin D, which has shown that it is an important immune system regulator. A large, 2006 study by the Harvard School of Public Health, reported evidence of a link between vitamin D deficiency and the onset of multiple sclerosis. Other data comes from a 2007 study which concluded that sun exposure during childhood reduces the risk of suffering MS, while controlling for genetic factors. Other theories, noting that MS is less common in children with siblings, suggest that less exposure to illness in childhood leads to an immune system which is not primed to fight infection and is thus more likely to attack the body. One explanation for this would be an imbalance between the Th1 type of helper T-cells, which fight infection, and the Th2 type, which are more active in allergy and more likely to attack the body. Other theories describe MS as an immune response to a chronic infection. The association of MS with the Epstein-Barr virus suggests a potential viral contribution in at least some individuals. Human endogenous retroviruses could also be involved, specially one called MSRV (MS associated retrovirus). Still others believe that MS may sometimes result from a chronic infection with spirochetal bacteria, a hypothesis supported by research in which cystic forms were isolated from the cerebrospinal fluid of all MS patients in a small study. When the cysts were cultured, propagating spirochetes emerged. Another bacterium that has been implicated in MS is Chlamydophila pneumoniae; it or its DNA has been found in the cerebrospinal fluid of MS patients by several research laboratories, with one study finding that the oligoclonal bands of 14 of the 17 MS patients studied consisted largely of antibodies to Chlamydophila antigens. Varicella zoster virus is also suspected to be involved. Severe stress may also be a factor a large study in Denmark found that parents who had lost a child unexpectedly were 50% more likely to develop MS than parents who had not. Smoking has also been shown to be an independent risk factor for developing MS.
12 Genetic MS is not considered a hereditary disease. However, increasing scientific evidence suggests that genetics may play a role in determining a person's susceptibility to MS: Some populations, such as the Roma, Inuit, and Bantus, rarely if ever develop MS. The indigenous peoples of the Americas and Asians have very low incidence rates. In the population at large, the chance of developing MS is less than a tenth of one percent. However, if one person in a family has MS, that person's first-degree relatives parents, children, and siblings have a one to three percent chance of getting the disease. For identical twins, the likelihood that the second twin may develop MS if the first twin does is about 30%. For fraternal twins (who do not inherit an identical set of genes), the likelihood is closer to that for non-twin siblings, at about 4%. This pattern suggests that, while genetic factors clearly help determine the risk of MS, other factors such as environmental effects or random chance are also involved. The actual correlation may be somewhat higher than reported by these numbers as people with MS lesions remain essentially asymptomatic throughout their lives. Further indications that more than one gene is involved in MS susceptibility comes from studies of families in which more than one member has MS. Several research teams found that people with MS inherit certain regions on individual genes more frequently than people without MS. Of particular interest is the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) or major histocompatibility complex region on chromosome 6. HLAs are genetically determined proteins that influence the immune system. However, there are other genes in this region which are not related to the immune system.
13 The HLA patterns of MS patients tend to be different from those of people without the disease. Investigations in northern Europe and America have detected three HLAs that are more prevalent in people with MS than in the general population. Studies of American MS patients have shown that people with MS also tend to exhibit these HLAs in combination that is, they have more than one of the three HLAs more frequently than the rest of the population. Furthermore, there is evidence that different combinations of the HLAs may correspond to variations in disease severity and progression. A large study examining 334,923 single nucleotide polymorphisms (small variations in genes) in 931 families showed that apart from HLA- DRA there were two genes in which polymorphisms strongly predicted MS; these were the IL2RA (a subunit of the receptor for interleukin 2) and the IL7RA (idem for interleukin 7) genes. Mutations in these genes were already known to be associated with diabetes mellitus type 1 and other autoimmune conditions; the findings circumstantially support the notion that MS is an autoimmune disease. Studies of families with multiple cases of MS and research comparing proteins expressed in humans with MS to those of mice with EAE suggest that another area related to MS susceptibility may be located on chromosome 5. Other regions on chromosomes 2, 3, 7, 11, 17, 19, and X have also been identified as possibly containing genes involved in the development of MS. These studies strengthen the theory that MS is the result of a number of factors rather than a single gene or other agent. Development of MS is likely to be influenced by the interactions of a number of genes, each of which (individually) has only a modest effect. Additional studies are needed to specifically pinpoint which genes are involved, determine their function, and learn how each gene's interactions with other genes and with the environment make an individual susceptible to MS. Treatment
14 Although there is no known cure for multiple sclerosis, several therapies have proven helpful. The primary aims of therapy are returning function after an attack, preventing new attacks, and preventing disability. As with any medical treatment, medications used in the management of MS have several adverse effects, and many possible therapies are still under investigation. At the same time different alternative treatments are pursued by many patients, despite the paucity of supporting, comparable, replicated scientific study. Management of acute attacks During symptomatic attacks administration of high doses of intravenous corticosteroids, such as methylprednisolone, is the routine therapy for acute relapses. The aim of this kind of treatment is to end the attack sooner and leave fewer lasting deficits in the patient. Although generally effective in the short term for relieving symptoms, corticosteroid treatments do not appear to have a significant impact on long-term recovery. Potential side effects include osteoporosis and impaired memory, the latter being reversible. Disease modifying treatments Disease-modifying treatments are expensive and most of these require frequent (up-to-daily) injections. Others require IV infusions at 1-3
15 month intervals. The earliest clinical presentation of relapsing-remitting MS (RRMS) is the clinically isolated syndrome (CIS). Several studies have shown that treatment with interferons during an initial attack can decrease the chance that a patient will develop MS. As of 2007, six disease-modifying treatments have been approved by regulatory agencies of different countries for relapsing-remitting MS. Three are interferons: two formulations of interferon beta-1a (trade names Avonex and Rebif) and one of interferon beta-1b (U.S. trade namebetaseron, in Europe and Japan Betaferon). A fourth medication is glatiramer acetate (Copaxone). The fifth medication, mitoxantrone, is an immunosuppressant also used in cancer chemotherapy, is approved only in the USA and largely for SPMS. Finally, the sixth is natalizumab (marketed as Tysabri). All six medications are modestly effective at decreasing the number of attacks and slowing progression to disability, although they differ in their efficacy rate and studies of their long-term effects are still lacking. Comparisons between immunomodulators (all but mitoxantrone) show that the most effective is natalizumab, both in terms of relapse rate reduction and halting disability progression; it has also been shown to reduce the severity of MS. Mitoxantrone may be the most effective of them all; however, it is generally considered not as a long-term therapy as its use is limited by severe cardiotoxicity. The interferons and glatiramer acetate are delivered by frequent injections, varying from once-per-day for glatiramer acetate to onceper-week (but intra-muscular) for Avonex. Natalizumab and mitoxantrone are given by IV infusion at monthly intervals. Treatment of progressive MS is more difficult than relapsing-remitting MS. Mitoxantrone has shown positive effects in patients with a secondary progressive and progressive relapsing courses. It is moderately effective in reducing the progression of the disease and the frequency of relapses in patients in short-term follow-up. On the other hand no treatment has been proven to modify the course of primary progressive MS. As with any medical treatment, these treatments have several adverse
16 effects. One of the most common is irritation at the injection site for glatiramer acetate and the Interferon treatments. Over time, a visible dent at the injection site due to the local destruction of fat tissue, known as lipoatrophy, may develop. Interferons also produce symptoms similar to influenza; while some patients taking glatiramer experience a post-injection reaction manifested by flushing, chest tightness, heart palpitations, breathlessness, and anxiety, which usually lasts less than thirty minutes. More dangerous are liver damage of interferons and mitoxantrone, the immunosuppressive effects and cardiac toxicity of the latter; or the putative link between natalizumab and some cases of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in patients who had taken it in combination with interferons. Management of the effects of MS Disease-modifying treatments only reduce the progression rate of the disease but do not stop it. As multiple sclerosis progresses, the symptomatology tends to increase. The disease is associated with a variety of symptoms and functional deficits that result in a range of progressive impairments and handicap. Management of these deficits is therefore very important. Both drug therapy and neurorehabilitation have shown to ease the burden of some symptoms, even though neither influence disease progression. As for any patient with neurologic deficits, a multidisciplinary approach is key to limiting and overcoming disability; however there are particular difficulties in specifying a core team because people with MS may need help from almost any health profession or service at some point. Similarly for each symptom there are different treatment options. Treatments should therefore be individualized depending both on the patient and the physician
17 Therapies under investigation Scientists continue their extensive efforts to create new and better therapies for MS. There are a number of treatments under investigation that may improve function, curtail attacks, or limit the progression of the underlying disease. Many treatments already in clinical trials involve drugs that are used in other diseases or medications that have not been designed specifically for MS. There are also trials involving the combination of drugs that are already in use for multiple sclerosis. Finally, there are also many basic investigations that try to understand better the disease and in the future may help to find new treatments. Alternative treatments Different alternative treatments are pursued by many patients, despite the paucity of supporting, comparable, replicated scientific study. Examples are dietary regimens, herbal medicine, including the use of medical cannabis to help alleviate symptoms, or hyperbaric oxygenation. On the other hand the therapeutic practice of martial arts such as tai chi, relaxation disciplines such as yoga, or general exercise, seem to mitigate fatigue and improve quality of life. Prognosis
18 The prognosis (the expected future course of the disease) for a person with multiple sclerosis depends on the subtype of the disease; the individual's sex, race, age, and initial symptoms; and the degree of disability the person experiences. The life expectancy of people with MS, at least for earlier years, is now nearly the same as that of unaffected people. This is due mainly to improved methods of limiting disability, such as physical therapy, occupational therapy and speech therapy, along with more successful treatment of common complications of disability, such as pneumonia and urinary tract infections. Nevertheless, half of the deaths in people with MS are directly related to the consequences of the disease, while 15% more are due to suicide. Individuals with progressive subtypes of MS, particularly the primary progressive subtype, have a more rapid decline in function. In the primary progressive subtype, supportive equipment (such as a wheelchair or standing frame) is often needed after six to seven years. However, when the initial disease course is the relapsingremitting subtype, the average time until such equipment is needed is twenty years. This means that many individuals with MS will never need a wheelchair. There is also more cognitive impairment in the progressive forms than in the relapsing-remitting course. The earlier in life MS occurs, the slower disability progresses. Individuals who are older than fifty when diagnosed are more likely to experience a chronic progressive course, with more rapid progression of disability. Those diagnosed before age 35 have the best prognosis. Females generally have a better prognosis than males. Although individuals of African descent tend to develop MS less frequently, they are often older at the time of onset and may have a worse prognosis. Initial MS symptoms of visual loss or sensory problems, such as numbness or tingling, are markers for a relatively good prognosis, whereas difficulty walking and weakness are markers for a relatively poor prognosis. Better outcomes are also associated with the presence of only a single symptom at onset, the rapid
19 development of initial symptoms, and the rapid regression of initial symptoms. The degree of disability varies among individuals with MS. In general, one of three individuals will still be able to work after years. Fifteen percent of people diagnosed with MS never have a second relapse, and these people have minimal or no disability after ten years. The degree of disability after five years correlates well with the degree of disability after fifteen years. This means that two-thirds of people with MS with low disability after five years will not get much worse during the next ten years. It should be noted that most of these outcomes were observed before the use of medications such as interferon, which can delay disease progression for several years. Apart from physical disability, cognitive impairment in MS occurs in approximately half of all patients. In its earlier stages, this impairment can include loss of short-term memory, depression and the pseudobulbar affect. As the disease progresess, the impairment can become more profound, ranging from loss of deductive reasoning to dementia. Currently there are no clinically established laboratory investigations available that can predict prognosis or response to treatment. However, several promising approaches have been proposed. These include measurement of the two antibodies anti-myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein and anti-myelin basic protein, and measurement of TRAIL (TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand).
Disease Modifying Therapies for MS
 Disease Modifying Therapies for MS The term disease-modifying therapy (DMT) means a drug that can modify or change the course of a disease. In other words a DMT should be able to reduce the number of attacks
Disease Modifying Therapies for MS The term disease-modifying therapy (DMT) means a drug that can modify or change the course of a disease. In other words a DMT should be able to reduce the number of attacks
Disease Modifying Therapies for MS
 Disease Modifying Therapies for MS The term disease-modifying therapy means a drug that can modify or change the course of a disease. In other words a DMT should be able to reduce the number of attacks
Disease Modifying Therapies for MS The term disease-modifying therapy means a drug that can modify or change the course of a disease. In other words a DMT should be able to reduce the number of attacks
CNS DEMYLINATING DISORDERS
 CNS DEMYLINATING DISORDERS Multiple sclerosis A Dutch saint named Lidwina, who died in 1433, may have been one of the first known MS patients. After she fell while ice skating, she developed symptoms such
CNS DEMYLINATING DISORDERS Multiple sclerosis A Dutch saint named Lidwina, who died in 1433, may have been one of the first known MS patients. After she fell while ice skating, she developed symptoms such
A Definition of Multiple Sclerosis
 English 182 READING PRACTICE by Alyx Meltzer, Spring 2009 Vocabulary Preview (see bolded, underlined words) gait: (n) a particular way of walking transient: (adj) temporary; synonym = transitory remission:
English 182 READING PRACTICE by Alyx Meltzer, Spring 2009 Vocabulary Preview (see bolded, underlined words) gait: (n) a particular way of walking transient: (adj) temporary; synonym = transitory remission:
Multiple Sclerosis: What You Need To Know. For Professionals
 Multiple Sclerosis: What You Need To Know For Professionals What will I learn today? The Basics: What is MS? Living with MS: A Family Affair We Can Help: The National MS Society What MS Is: MS is thought
Multiple Sclerosis: What You Need To Know For Professionals What will I learn today? The Basics: What is MS? Living with MS: A Family Affair We Can Help: The National MS Society What MS Is: MS is thought
FastTest. You ve read the book... ... now test yourself
 FastTest You ve read the book...... now test yourself To ensure you have learned the key points that will improve your patient care, read the authors questions below. The answers will refer you back to
FastTest You ve read the book...... now test yourself To ensure you have learned the key points that will improve your patient care, read the authors questions below. The answers will refer you back to
Understanding How Existing and Emerging MS Therapies Work
 Understanding How Existing and Emerging MS Therapies Work This is a promising and hopeful time in the field of multiple sclerosis (MS). Many new and different therapies are nearing the final stages of
Understanding How Existing and Emerging MS Therapies Work This is a promising and hopeful time in the field of multiple sclerosis (MS). Many new and different therapies are nearing the final stages of
The Nuts and Bolts of Multiple Sclerosis. Rebecca Milholland, M.D., Ph.D. Center for Neurosciences
 The Nuts and Bolts of Multiple Sclerosis Rebecca Milholland, M.D., Ph.D. Center for Neurosciences Objectives Discuss which patients are at risk for Multiple Sclerosis Discuss the diagnostic criteria for
The Nuts and Bolts of Multiple Sclerosis Rebecca Milholland, M.D., Ph.D. Center for Neurosciences Objectives Discuss which patients are at risk for Multiple Sclerosis Discuss the diagnostic criteria for
What is Multiple Sclerosis? Gener al information
 What is Multiple Sclerosis? Gener al information Kim, diagnosed in 1986 What is MS? Multiple sclerosis (or MS) is a chronic, often disabling disease that attacks the central nervous system (brain and spinal
What is Multiple Sclerosis? Gener al information Kim, diagnosed in 1986 What is MS? Multiple sclerosis (or MS) is a chronic, often disabling disease that attacks the central nervous system (brain and spinal
Understanding. Multiple Sclerosis. Tim, diagnosed in 2004.
 Understanding Multiple Sclerosis Tim, diagnosed in 2004. What Is Multiple Sclerosis? Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a neurologic disorder that affects the central nervous system (CNS). The CNS includes the
Understanding Multiple Sclerosis Tim, diagnosed in 2004. What Is Multiple Sclerosis? Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a neurologic disorder that affects the central nervous system (CNS). The CNS includes the
Multiple Sclerosis. Matt Hulvey BL A - 615
 Multiple Sclerosis Matt Hulvey BL A - 615 Multiple Sclerosis Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is an idiopathic inflammatory disease of the central nervous system (CNS) MS is characterized by demyelination (lesions)
Multiple Sclerosis Matt Hulvey BL A - 615 Multiple Sclerosis Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is an idiopathic inflammatory disease of the central nervous system (CNS) MS is characterized by demyelination (lesions)
Relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis Ambulatory with or without aid
 AVONEX/BETASERON/COPAXONE/EXTAVIA/GILENYA/REBIF/TYSABRI Applicant must be covered on an Alberta Government sponsored drug program. Page 1 of 5 PATIENT INFMATION Surname First Name Middle Initial Sex Date
AVONEX/BETASERON/COPAXONE/EXTAVIA/GILENYA/REBIF/TYSABRI Applicant must be covered on an Alberta Government sponsored drug program. Page 1 of 5 PATIENT INFMATION Surname First Name Middle Initial Sex Date
Progress in MS: Current and Emerging Therapies
 Progress in MS: Current and Emerging Therapies Presented by: Dr. Kathryn Giles, MD MSc FRCPC The MS Society gratefully acknowledges the grant received from Biogen Idec Canada, which makes possible the
Progress in MS: Current and Emerging Therapies Presented by: Dr. Kathryn Giles, MD MSc FRCPC The MS Society gratefully acknowledges the grant received from Biogen Idec Canada, which makes possible the
CBT IN THE CITY. adjusted to the news of being with MS? April 2013. Experts at your fingertips call now. Check out our new services in you local area
 April 2013 Experts at your fingertips call now CBT IN THE CITY Check out our new services in you local area contents. A message from Susie, Information Multiple Sclerosis CBT can make a difference on the
April 2013 Experts at your fingertips call now CBT IN THE CITY Check out our new services in you local area contents. A message from Susie, Information Multiple Sclerosis CBT can make a difference on the
About MS. An introduction to. An introduction to multiple sclerosis for people who have recently been diagnosed. What is MS? Is it common?
 An introduction to multiple sclerosis for people who have recently been diagnosed When you have just been diagnosed with multiple sclerosis, you will probably have many questions about the condition and
An introduction to multiple sclerosis for people who have recently been diagnosed When you have just been diagnosed with multiple sclerosis, you will probably have many questions about the condition and
Trauma Insurance Claims Seminar Invitation
 Trauma Insurance Claims Seminar Invitation Introduction Since the development of Trauma Insurance in Australia in the 1980s, the product has evolved at a great pace. Some of the challenges faced by claims
Trauma Insurance Claims Seminar Invitation Introduction Since the development of Trauma Insurance in Australia in the 1980s, the product has evolved at a great pace. Some of the challenges faced by claims
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is a disease of the central nervous system (including the brain and spinal cord) in which the nerves degenerate.
 What is Multiple Sclerosis? Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is a disease of the central nervous system (including the brain and spinal cord) in which the nerves degenerate. A disease of the central nervous system
What is Multiple Sclerosis? Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is a disease of the central nervous system (including the brain and spinal cord) in which the nerves degenerate. A disease of the central nervous system
Life with MS: Striving for Maximal Independence & Fulfillment
 Life with MS: Striving for Maximal Independence & Fulfillment St. Louis, May 7, 2005 Florian P. Thomas, MA, MD, PhD MS Center, Department of Neurology Associate Professor, Saint Louis University Brain
Life with MS: Striving for Maximal Independence & Fulfillment St. Louis, May 7, 2005 Florian P. Thomas, MA, MD, PhD MS Center, Department of Neurology Associate Professor, Saint Louis University Brain
Optic Neuritis. The optic nerve fibers are coated with myelin to help them conduct the electrical signals back to your brain.
 Optic Neuritis Your doctor thinks that you have had an episode of optic neuritis. This is the most common cause of sudden visual loss in a young patient. It is often associated with discomfort in or around
Optic Neuritis Your doctor thinks that you have had an episode of optic neuritis. This is the most common cause of sudden visual loss in a young patient. It is often associated with discomfort in or around
Understanding your Tecfidera treatment
 Understanding your Tecfidera treatment Information for patients who have been prescribed treatment with Tecfidera. (dimethyl fumarate) Contents About Multiple Sclerosis (MS) What is MS? Symptoms of MS
Understanding your Tecfidera treatment Information for patients who have been prescribed treatment with Tecfidera. (dimethyl fumarate) Contents About Multiple Sclerosis (MS) What is MS? Symptoms of MS
Understanding your Tecfidera treatment
 Understanding your Tecfidera treatment Information for patients who have been prescribed treatment with Tecfidera. (dimethyl fumarate) Contents About Multiple Sclerosis (MS) What is MS? Symptoms of MS
Understanding your Tecfidera treatment Information for patients who have been prescribed treatment with Tecfidera. (dimethyl fumarate) Contents About Multiple Sclerosis (MS) What is MS? Symptoms of MS
Muscular Dystrophy and Multiple Sclerosis. ultimately lead to the crippling of the muscular system, there are many differences between these
 Battles 1 Becky Battles Instructor s Name English 1013 21 November 2006 Muscular Dystrophy and Multiple Sclerosis Although muscular dystrophy and multiple sclerosis are both progressive diseases that ultimately
Battles 1 Becky Battles Instructor s Name English 1013 21 November 2006 Muscular Dystrophy and Multiple Sclerosis Although muscular dystrophy and multiple sclerosis are both progressive diseases that ultimately
IF YOU ARE RECEIVING TREATMENT WITH TYSABRI FOR RELAPSING-REMITTING MS (NATALIZUMAB)
 IF YOU ARE RECEIVING (NATALIZUMAB) TREATMENT WITH TYSABRI FOR RELAPSING-REMITTING MS Read the patient information leaflet that accompanies the medicine carefully. 1 This brochure is a supplement to the
IF YOU ARE RECEIVING (NATALIZUMAB) TREATMENT WITH TYSABRI FOR RELAPSING-REMITTING MS Read the patient information leaflet that accompanies the medicine carefully. 1 This brochure is a supplement to the
Clinical Trials of Disease Modifying Treatments
 MS CENTER CLINICAL RESEARCH The UCSF MS Center is an internationally recognized leader in multiple sclerosis clinical research. We conduct clinical trials involving the use of experimental treatments,
MS CENTER CLINICAL RESEARCH The UCSF MS Center is an internationally recognized leader in multiple sclerosis clinical research. We conduct clinical trials involving the use of experimental treatments,
National MS Society Information Sourcebook www.nationalmssociety.org/sourcebook
 National MS Society Information Sourcebook www.nationalmssociety.org/sourcebook Chemotherapy The literal meaning of the term chemotherapy is to treat with a chemical agent, but the term generally refers
National MS Society Information Sourcebook www.nationalmssociety.org/sourcebook Chemotherapy The literal meaning of the term chemotherapy is to treat with a chemical agent, but the term generally refers
Original Policy Date
 MP 5.01.20 Tysabri (natalizumab) Medical Policy Section Prescription Drug Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date Local Policy/12:2013 Return to Medical Policy Index Disclaimer
MP 5.01.20 Tysabri (natalizumab) Medical Policy Section Prescription Drug Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date Local Policy/12:2013 Return to Medical Policy Index Disclaimer
There's no cure for multiple sclerosis. However treatments can help treat attacks, modify the course of the disease and treat symptoms.
 MayoClinic.com reprints This single copy is for your personal, noncommercial use only. For permission to reprint multiple copies or to order presentation-ready copies for distribution, use the reprints
MayoClinic.com reprints This single copy is for your personal, noncommercial use only. For permission to reprint multiple copies or to order presentation-ready copies for distribution, use the reprints
Clinically isolated syndrome (CIS)
 Clinically isolated syndrome (CIS) Spirella Building, Letchworth, SG6 4ET 01462 476700 www.mstrust.org.uk reg charity no. 1088353 We hope you find the information in this factsheet helpful. If you would
Clinically isolated syndrome (CIS) Spirella Building, Letchworth, SG6 4ET 01462 476700 www.mstrust.org.uk reg charity no. 1088353 We hope you find the information in this factsheet helpful. If you would
III./5.3.: Multiple sclerosis. Epidemiology. Etiology. Pathology
 III./5.3.: Multiple sclerosis Epidemiology Multiple sclerosis (MS) is the most common neuroimmunological disorder of the central nervous system. This chronic illness begins in early adulthood, mostly at
III./5.3.: Multiple sclerosis Epidemiology Multiple sclerosis (MS) is the most common neuroimmunological disorder of the central nervous system. This chronic illness begins in early adulthood, mostly at
A Genetic Analysis of Rheumatoid Arthritis
 A Genetic Analysis of Rheumatoid Arthritis Introduction to Rheumatoid Arthritis: Classification and Diagnosis Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disorder that affects mainly synovial joints.
A Genetic Analysis of Rheumatoid Arthritis Introduction to Rheumatoid Arthritis: Classification and Diagnosis Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disorder that affects mainly synovial joints.
Which injectable medication should I take for relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis?
 Which injectable medication should I take for relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis? A decision aid to discuss options with your doctor This decision aid is for you if you: Have multiple sclerosis Have
Which injectable medication should I take for relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis? A decision aid to discuss options with your doctor This decision aid is for you if you: Have multiple sclerosis Have
A blood sample will be collected annually for up to 2 years for JCV antibody testing.
 Mellen Center Currently Enrolling Non-Treatment Trials STRATIFY-2 JCV Antibody Program in Patients with Relapsing Multiple Sclerosis Receiving or Considering Treatment with Tysabri Primary Investigator:
Mellen Center Currently Enrolling Non-Treatment Trials STRATIFY-2 JCV Antibody Program in Patients with Relapsing Multiple Sclerosis Receiving or Considering Treatment with Tysabri Primary Investigator:
Novel therapeutic approaches in multiple sclerosis Neuroprotective and remyelinating agents, the future of clinical trials in MS?
 Novel therapeutic approaches in multiple sclerosis Neuroprotective and remyelinating agents, the future of clinical trials in MS? Marie Trad, M.D., Lynne Hughes, Cathy VanBelle, Amy Del Medico 3rd International
Novel therapeutic approaches in multiple sclerosis Neuroprotective and remyelinating agents, the future of clinical trials in MS? Marie Trad, M.D., Lynne Hughes, Cathy VanBelle, Amy Del Medico 3rd International
AUBMC Multiple Sclerosis Center
 AUBMC Multiple Sclerosis Center 1 AUBMC Multiple Sclerosis Center The vision of the American University of Beirut Medical Center (AUBMC) is to be the leading academic medical center in Lebanon and the
AUBMC Multiple Sclerosis Center 1 AUBMC Multiple Sclerosis Center The vision of the American University of Beirut Medical Center (AUBMC) is to be the leading academic medical center in Lebanon and the
Eastern Health MS Service. Tysabri Therapy. Information for People with MS and their Families
 Eastern Health MS Service Tysabri Therapy Information for People with MS and their Families The Eastern Health MS Service has developed this information for you as a guide through what will happen to you
Eastern Health MS Service Tysabri Therapy Information for People with MS and their Families The Eastern Health MS Service has developed this information for you as a guide through what will happen to you
 CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY CENTRE FOR BRAIN REPAIR A layman's account of our scientific objectives What is Brain Damage? Many forms of trauma and disease affect the nervous system to produce permanent neurological
CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY CENTRE FOR BRAIN REPAIR A layman's account of our scientific objectives What is Brain Damage? Many forms of trauma and disease affect the nervous system to produce permanent neurological
MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS. Mary Beth Rensberger, RN, BSN, MPH Author
 MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS Mary Beth Rensberger, RN, BSN, MPH Author All rights reserved. Purchasers of this module are permitted to reproduce the forms contained herein for their individual internal use only.
MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS Mary Beth Rensberger, RN, BSN, MPH Author All rights reserved. Purchasers of this module are permitted to reproduce the forms contained herein for their individual internal use only.
Summary HTA. Interferons and Natalizumab for Multiple Sclerosis Clar C, Velasco-Garrido M, Gericke C. HTA-Report Summary
 Summary HTA HTA-Report Summary Interferons and Natalizumab for Multiple Sclerosis Clar C, Velasco-Garrido M, Gericke C Health policy background Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic inflammatory disease
Summary HTA HTA-Report Summary Interferons and Natalizumab for Multiple Sclerosis Clar C, Velasco-Garrido M, Gericke C Health policy background Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic inflammatory disease
RELAPSE MANAGEMENT. Pauline Shaw MS Nurse Specialist 25 th June 2010
 RELAPSE MANAGEMENT Pauline Shaw MS Nurse Specialist 25 th June 2010 AIMS OF SESSION Relapsing/Remitting MS Definition of relapse/relapse rate Relapse Management NICE Guidelines Regional Clinical Guidelines
RELAPSE MANAGEMENT Pauline Shaw MS Nurse Specialist 25 th June 2010 AIMS OF SESSION Relapsing/Remitting MS Definition of relapse/relapse rate Relapse Management NICE Guidelines Regional Clinical Guidelines
New Treatment Options for MS Patients: Understanding risks versus benefits
 New Treatment Options for MS Patients: Understanding risks versus benefits By Michael A. Meyer, MD Department of Neurology, Sisters Hospital, Buffalo, NY Objectives: 1. to understand fundamentals of MS
New Treatment Options for MS Patients: Understanding risks versus benefits By Michael A. Meyer, MD Department of Neurology, Sisters Hospital, Buffalo, NY Objectives: 1. to understand fundamentals of MS
Committee Approval Date: December 12, 2014 Next Review Date: December 2015
 Medication Policy Manual Policy No: dru299 Topic: Tecfidera, dimethyl fumarate Date of Origin: May 16, 2013 Committee Approval Date: December 12, 2014 Next Review Date: December 2015 Effective Date: January
Medication Policy Manual Policy No: dru299 Topic: Tecfidera, dimethyl fumarate Date of Origin: May 16, 2013 Committee Approval Date: December 12, 2014 Next Review Date: December 2015 Effective Date: January
Many people with MS use some form of conventional medical treatment, and many people also use complementary and alternative medicine (CAM).
 Complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) CAM therapies can generally be divided into the following categories: Biologically based therapies (eg, dietary supplements, diets, bee venom therapy, hyperbaric
Complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) CAM therapies can generally be divided into the following categories: Biologically based therapies (eg, dietary supplements, diets, bee venom therapy, hyperbaric
Summary chapter 2 chapter 2
 Summary Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is a chronic disease of the brain and the spinal cord. The cause of MS is unknown. MS usually starts in young adulthood. In the course of the disease progression of neurological
Summary Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is a chronic disease of the brain and the spinal cord. The cause of MS is unknown. MS usually starts in young adulthood. In the course of the disease progression of neurological
Brain Cancer. This reference summary will help you understand how brain tumors are diagnosed and what options are available to treat them.
 Brain Cancer Introduction Brain tumors are not rare. Thousands of people are diagnosed every year with tumors of the brain and the rest of the nervous system. The diagnosis and treatment of brain tumors
Brain Cancer Introduction Brain tumors are not rare. Thousands of people are diagnosed every year with tumors of the brain and the rest of the nervous system. The diagnosis and treatment of brain tumors
Multiple sclerosis disease-modifying drugs second line treatments
 Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families Multiple sclerosis disease-modifying drugs second line treatments The following information should be read in conjunction
Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families Multiple sclerosis disease-modifying drugs second line treatments The following information should be read in conjunction
acquired chronic immune-mediated inflammatory condition of CNS. MS in children: 10% +secondary progressive MS: rare +primary progressive MS: rare
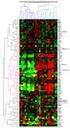 Immunomodulatory Therapies in Pediatric MS Vuong Chinh Quyen Neurology Department Medscape Mar 8, 2013 Multiple Sclerosis in Children. Iran J Child Neurol. 2013 Spring Introduction acquired chronic immune-mediated
Immunomodulatory Therapies in Pediatric MS Vuong Chinh Quyen Neurology Department Medscape Mar 8, 2013 Multiple Sclerosis in Children. Iran J Child Neurol. 2013 Spring Introduction acquired chronic immune-mediated
We move our mission forward through Client Education & Services, Research, Advocacy and Professional Education.
 1 It is the National MS Society s mission to mobilize people and resources to drive research for a cure and to address the challenges of everyone affected by MS. The National MS Society, Greater Northwest
1 It is the National MS Society s mission to mobilize people and resources to drive research for a cure and to address the challenges of everyone affected by MS. The National MS Society, Greater Northwest
Stepping toward a different treatment option LEARN WHAT ACTHAR CAN DO FOR YOU
 FOR MS RELAPSES Stepping toward a different treatment option LEARN WHAT ACTHAR CAN DO FOR YOU As a person with multiple sclerosis (MS), you know firsthand the profound impact MS relapses can have on your
FOR MS RELAPSES Stepping toward a different treatment option LEARN WHAT ACTHAR CAN DO FOR YOU As a person with multiple sclerosis (MS), you know firsthand the profound impact MS relapses can have on your
Disease Modifying Therapies (DMTs) in Multiple Sclerosis
 Disease Modifying Therapies (DMTs) in Multiple Sclerosis Gary Stobbe, MD Medical Director, MS Project ECHO Clinical Assistant Professor, UW Neurology Conflict of Interest Dr. Stobbe has no conflicts of
Disease Modifying Therapies (DMTs) in Multiple Sclerosis Gary Stobbe, MD Medical Director, MS Project ECHO Clinical Assistant Professor, UW Neurology Conflict of Interest Dr. Stobbe has no conflicts of
Multiple sclerosis (MS)
 Multiple sclerosis (MS) Summary Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an incurable disease of the central nervous system that can affect the brain, spinal cord and optic nerves. The effects of MS are varied and unpredictable,
Multiple sclerosis (MS) Summary Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an incurable disease of the central nervous system that can affect the brain, spinal cord and optic nerves. The effects of MS are varied and unpredictable,
Multiple Sclerosis Update. Bridget A. Bagert, MD, MPH Director, Ochsner Multiple Sclerosis Center
 Multiple Sclerosis Update Bridget A. Bagert, MD, MPH Director, Ochsner Multiple Sclerosis Center None Disclosures First of All. Why is my talk in the Neurodegenerative hour? I respectfully object! Case
Multiple Sclerosis Update Bridget A. Bagert, MD, MPH Director, Ochsner Multiple Sclerosis Center None Disclosures First of All. Why is my talk in the Neurodegenerative hour? I respectfully object! Case
Multiple Sclerosis & MS Ireland Media Fact Sheet
 Multiple Sclerosis & MS Ireland Media Fact Sheet This fact sheets gives a summary of the main facts and issues relating to Multiple Sclerosis and gives an overview of the services offered by MS Ireland.
Multiple Sclerosis & MS Ireland Media Fact Sheet This fact sheets gives a summary of the main facts and issues relating to Multiple Sclerosis and gives an overview of the services offered by MS Ireland.
Information About Medicines for Multiple Sclerosis
 Information About Medicines for Multiple Sclerosis Information About Medicines for Multiple Sclerosis What is multiple sclerosis? 1 Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a lifelong disease that affects your brain
Information About Medicines for Multiple Sclerosis Information About Medicines for Multiple Sclerosis What is multiple sclerosis? 1 Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a lifelong disease that affects your brain
http://images.tutorvista.com/content/control5coordination/human5brain.jpeg!! 387
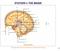 http://images.tutorvista.com/content/control5coordination/human5brain.jpeg!! 387! 388! http://my.fresnounified.org/personal/lygonza/gonzalez/neuron/neuron5synapse%20communication.png!! http://www.urbanchildinstitute.org/sites/all/files/databooks/2011/ch15fg25communication5between5neurons.jpg!!
http://images.tutorvista.com/content/control5coordination/human5brain.jpeg!! 387! 388! http://my.fresnounified.org/personal/lygonza/gonzalez/neuron/neuron5synapse%20communication.png!! http://www.urbanchildinstitute.org/sites/all/files/databooks/2011/ch15fg25communication5between5neurons.jpg!!
Multiple Sclerosis: An imaging review and update on new treatments.
 Multiple Sclerosis: An imaging review and update on new treatments. Dr Marcus Likeman Consultant Neuroradiologist North Bristol NHS Trust Bristol Royal Hospital for Children MRI appearances - White Matter
Multiple Sclerosis: An imaging review and update on new treatments. Dr Marcus Likeman Consultant Neuroradiologist North Bristol NHS Trust Bristol Royal Hospital for Children MRI appearances - White Matter
AUBAGIO (teriflunomide) oral tablet
 AUBAGIO (teriflunomide) oral tablet Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Pharmacy
AUBAGIO (teriflunomide) oral tablet Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Pharmacy
Transverse Myelitis ISBN 978-1-901893-57-1. A guide for patients and carers
 Transverse Myelitis ISBN 978-1-901893-57-1 A guide for patients and carers The Brain and Spine Foundation provides support and information on all aspects of neurological conditions. Our publications are
Transverse Myelitis ISBN 978-1-901893-57-1 A guide for patients and carers The Brain and Spine Foundation provides support and information on all aspects of neurological conditions. Our publications are
Disclosures. Consultant and Speaker for Biogen Idec, TEVA Neuroscience, EMD Serrono, Mallinckrodt, Novartis, Genzyme, Accorda Therapeutics
 Mitzi Joi Williams, MD Neurologist MS Center of Atlanta, Atlanta, GA Disclosures Consultant and Speaker for Biogen Idec, TEVA Neuroscience, EMD Serrono, Mallinckrodt, Novartis, Genzyme, Accorda Therapeutics
Mitzi Joi Williams, MD Neurologist MS Center of Atlanta, Atlanta, GA Disclosures Consultant and Speaker for Biogen Idec, TEVA Neuroscience, EMD Serrono, Mallinckrodt, Novartis, Genzyme, Accorda Therapeutics
F r e q u e n t l y A s k e d Q u e s t i o n s
 Myasthenia Gravis Q: What is myasthenia gravis (MG)? A: Myasthenia gravis (meye-uhss- THEEN-ee-uh GRAV uhss) (MG) is an autoimmune disease that weakens the muscles. The name comes from Greek and Latin
Myasthenia Gravis Q: What is myasthenia gravis (MG)? A: Myasthenia gravis (meye-uhss- THEEN-ee-uh GRAV uhss) (MG) is an autoimmune disease that weakens the muscles. The name comes from Greek and Latin
MS Treatments Gilenya
 1 MSology Essentials Series Gilenya (fingolimod) Developed by MSology with the invaluable assistance of multiple sclerosis nurse advisors: Trudy Campbell Dalhousie MS Research Unit, Capital Health, Halifax,
1 MSology Essentials Series Gilenya (fingolimod) Developed by MSology with the invaluable assistance of multiple sclerosis nurse advisors: Trudy Campbell Dalhousie MS Research Unit, Capital Health, Halifax,
A neurologist would assess your eligibility and suitability for the DMTs.
 Choices Disease Modifying Treatments Disease modifying treatments (DMTs) are medications which modify the disease course. They target inflammation and are designed to reduce the damage caused by relapses.
Choices Disease Modifying Treatments Disease modifying treatments (DMTs) are medications which modify the disease course. They target inflammation and are designed to reduce the damage caused by relapses.
2.1 Who first described NMO?
 History & Discovery 54 2 History & Discovery 2.1 Who first described NMO? 2.2 What is the difference between NMO and Multiple Sclerosis? 2.3 How common is NMO? 2.4 Who is affected by NMO? 2.1 Who first
History & Discovery 54 2 History & Discovery 2.1 Who first described NMO? 2.2 What is the difference between NMO and Multiple Sclerosis? 2.3 How common is NMO? 2.4 Who is affected by NMO? 2.1 Who first
A Letter From the MS Coalition
 0 A Letter From the MS Coalition The treatment of multiple sclerosis (MS) requires a comprehensive management strategy. One important component of that strategy is modifying the disease course. When deciding
0 A Letter From the MS Coalition The treatment of multiple sclerosis (MS) requires a comprehensive management strategy. One important component of that strategy is modifying the disease course. When deciding
Facts About Chickenpox and Shingles for Adults
 Facts About Chickenpox and Shingles for Adults What is chickenpox? Chickenpox, also known as varicella, is a very contagious disease caused by the varicella-zoster virus. It is spread easily through the
Facts About Chickenpox and Shingles for Adults What is chickenpox? Chickenpox, also known as varicella, is a very contagious disease caused by the varicella-zoster virus. It is spread easily through the
Managing the Symptoms of Multiple Sclerosis. Yolanda Harris, MSN, CRNP-AC CPODD Nurse Practitioner
 Managing the Symptoms of Multiple Sclerosis Yolanda Harris, MSN, CRNP-AC CPODD Nurse Practitioner What is Multiple Sclerosis An autoimmune disease that affects the central nervous system (CNS) The immune
Managing the Symptoms of Multiple Sclerosis Yolanda Harris, MSN, CRNP-AC CPODD Nurse Practitioner What is Multiple Sclerosis An autoimmune disease that affects the central nervous system (CNS) The immune
OHTAC Recommendation
 OHTAC Recommendation Multiple Sclerosis and Chronic Cerebrospinal Venous Insufficiency Presented to the Ontario Health Technology Advisory Committee in May 2010 May 2010 Issue Background A review on the
OHTAC Recommendation Multiple Sclerosis and Chronic Cerebrospinal Venous Insufficiency Presented to the Ontario Health Technology Advisory Committee in May 2010 May 2010 Issue Background A review on the
The MS Disease- Modifying Drugs. Gener al information
 The MS Disease- Modifying Drugs Gener al information Current as of October 30, 2009. This online version is updated as breaking news requires. If you have downloaded and printed a copy from the web, please
The MS Disease- Modifying Drugs Gener al information Current as of October 30, 2009. This online version is updated as breaking news requires. If you have downloaded and printed a copy from the web, please
06/06/2012. The Impact of Multiple Sclerosis in the Pacific Northwest. James Bowen, MD. Swedish Neuroscience Institute
 The Impact of Multiple Sclerosis in the Pacific Northwest James Bowen, MD Multiple Sclerosis Center Multiple Sclerosis Center Swedish Neuroscience Institute 1 2 Motor Symptoms of MS Weakness Spasticity
The Impact of Multiple Sclerosis in the Pacific Northwest James Bowen, MD Multiple Sclerosis Center Multiple Sclerosis Center Swedish Neuroscience Institute 1 2 Motor Symptoms of MS Weakness Spasticity
Thymus Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand what thymus cancer is and what treatment options are available.
 Thymus Cancer Introduction Thymus cancer is a rare cancer. It starts in the small organ that lies in the upper chest under the breastbone. The thymus makes white blood cells that protect the body against
Thymus Cancer Introduction Thymus cancer is a rare cancer. It starts in the small organ that lies in the upper chest under the breastbone. The thymus makes white blood cells that protect the body against
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Aprile Royal, Novartis Pharma Canada Inc. September 21, 2011 Toronto, ON
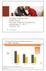 Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Aprile Royal, Novartis Pharma Canada Inc. September 21, 2011 Toronto, ON First-line DMTs Reduce Relapse Frequency by ~30% vs. Placebo Frequency of relapse with various DMTs, based
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Aprile Royal, Novartis Pharma Canada Inc. September 21, 2011 Toronto, ON First-line DMTs Reduce Relapse Frequency by ~30% vs. Placebo Frequency of relapse with various DMTs, based
Voting for your top research questions Survey
 MS Priority Setting Partnership Voting for your top research questions Survey Prioritising important research questions for multiple sclerosis a partnership between people affected by MS and healthcare
MS Priority Setting Partnership Voting for your top research questions Survey Prioritising important research questions for multiple sclerosis a partnership between people affected by MS and healthcare
An introduction to modern MS treatments
 BETAFERON is a Prescription Medicine. Use strictly as directed. Consult your pharmacist or other health professional in case of side effects. BETAFERON is reimbursed for some patients. See your neurologist
BETAFERON is a Prescription Medicine. Use strictly as directed. Consult your pharmacist or other health professional in case of side effects. BETAFERON is reimbursed for some patients. See your neurologist
SECTION 2. Section 2 Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Drug Coverage
 SECTION 2 Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Drug Coverage Section 2 Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Drug Coverage ALBERTA HEALTH AND WELLNESS DRUG BENEFIT LIST Selected Drug Products used in the treatment of patients with
SECTION 2 Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Drug Coverage Section 2 Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Drug Coverage ALBERTA HEALTH AND WELLNESS DRUG BENEFIT LIST Selected Drug Products used in the treatment of patients with
Coping with Symptoms of Multiple Sclerosis
 Coping with Symptoms of Multiple Sclerosis Josée Poirier B. Sc. Nursing, MSCN Outline What Is a Pseudo exacerbation? Awareness Advancement of Treatments Treatment of Symptoms Uhthoff s Phenomenon What
Coping with Symptoms of Multiple Sclerosis Josée Poirier B. Sc. Nursing, MSCN Outline What Is a Pseudo exacerbation? Awareness Advancement of Treatments Treatment of Symptoms Uhthoff s Phenomenon What
New treatments in MS What s here and what s nearly here
 5 th MS Research Day, June 14 th 2014 New treatments in MS What s here and what s nearly here David Miller Queen Square MS Centre at UCL and UCLH Course of MS and its treatment Relapsing remitting Disability
5 th MS Research Day, June 14 th 2014 New treatments in MS What s here and what s nearly here David Miller Queen Square MS Centre at UCL and UCLH Course of MS and its treatment Relapsing remitting Disability
Cerebral Palsy. In order to function, the brain needs a continuous supply of oxygen.
 Cerebral Palsy Introduction Cerebral palsy, or CP, can cause serious neurological symptoms in children. Up to 5000 children in the United States are diagnosed with cerebral palsy every year. This reference
Cerebral Palsy Introduction Cerebral palsy, or CP, can cause serious neurological symptoms in children. Up to 5000 children in the United States are diagnosed with cerebral palsy every year. This reference
Multiple Sclerosis Disease Report
 April 2009 Published by: The FasterCures Philanthropy Advisory Service FasterCures / The Center for Accelerating Medical Solutions 1101 New York Ave. St., NW, #620 Washington, D.C. 20005 (202) 336-8900
April 2009 Published by: The FasterCures Philanthropy Advisory Service FasterCures / The Center for Accelerating Medical Solutions 1101 New York Ave. St., NW, #620 Washington, D.C. 20005 (202) 336-8900
Taylor Slotte Pathology Disease Report Spring 2014 Multiple Sclerosis
 Taylor Slotte Pathology Disease Report Spring 2014 Multiple Sclerosis Abstract Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic autoimmune disorder that attacks the body s central nervous system. It affects the brain,
Taylor Slotte Pathology Disease Report Spring 2014 Multiple Sclerosis Abstract Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic autoimmune disorder that attacks the body s central nervous system. It affects the brain,
Information about medicines for multiple sclerosis
 Information about medicines for multiple sclerosis Information about medicines for multiple sclerosis What is multiple sclerosis? 1 Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a lifelong disease that affects your brain
Information about medicines for multiple sclerosis Information about medicines for multiple sclerosis What is multiple sclerosis? 1 Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a lifelong disease that affects your brain
Disease modifying drug therapy
 Disease modifying drug therapy what you need to know Third Edition Karen Alldus Simon Webster SECTION 2 We hope you find the information in this book helpful. If you would like to speak with someone about
Disease modifying drug therapy what you need to know Third Edition Karen Alldus Simon Webster SECTION 2 We hope you find the information in this book helpful. If you would like to speak with someone about
PCORI Workshop on Treatment for Multiple Sclerosis. Breakout Group Topics and Questions Draft 3-27-15
 PCORI Workshop on Treatment for Multiple Sclerosis Breakout Group Topics and Questions Draft 3-27-15 Group 1 - Comparison across DMTs, including differential effects in subgroups Consolidated straw man
PCORI Workshop on Treatment for Multiple Sclerosis Breakout Group Topics and Questions Draft 3-27-15 Group 1 - Comparison across DMTs, including differential effects in subgroups Consolidated straw man
Acute Low Back Pain. North American Spine Society Public Education Series
 Acute Low Back Pain North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Acute Low Back Pain? Acute low back pain (LBP) is defined as low back pain present for up to six weeks. It may be experienced
Acute Low Back Pain North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Acute Low Back Pain? Acute low back pain (LBP) is defined as low back pain present for up to six weeks. It may be experienced
Multiple sclerosis. Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for young people. What is Multiple Sclerosis?
 Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for young people Multiple sclerosis When young people are told that they have a diagnosis of Multiple Sclerosis (MS) they usually
Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for young people Multiple sclerosis When young people are told that they have a diagnosis of Multiple Sclerosis (MS) they usually
CHPN Review Course Pain Management Part 1 Hospice and Palliative Nurses Association
 CHPN Review Course Pain Management Part 1 Disclosures Bonnie Morgan has no real or perceived conflicts of interest that relate to this presentation. Copyright 2015 by the. HPNA has the exclusive rights
CHPN Review Course Pain Management Part 1 Disclosures Bonnie Morgan has no real or perceived conflicts of interest that relate to this presentation. Copyright 2015 by the. HPNA has the exclusive rights
Choices Primary Progressive MS (PPMS)
 Choices Primary Progressive MS (PPMS) What is primary progressive MS? Approximately 10% of people with MS worldwide are told they have primary progressive MS a form of MS where from the very first symptoms,
Choices Primary Progressive MS (PPMS) What is primary progressive MS? Approximately 10% of people with MS worldwide are told they have primary progressive MS a form of MS where from the very first symptoms,
Managing Relapsing Remitting MS Risks & benefits of emerging therapies. Dr Mike Boggild The Walton Centre
 Managing Relapsing Remitting MS Risks & benefits of emerging therapies Dr Mike Boggild The Walton Centre MS: Facts and figures Affects 1 in 800 in the UK Commonest cause of acquired neurological disability
Managing Relapsing Remitting MS Risks & benefits of emerging therapies Dr Mike Boggild The Walton Centre MS: Facts and figures Affects 1 in 800 in the UK Commonest cause of acquired neurological disability
Multifocal Motor Neuropathy. Jonathan Katz, MD Richard Lewis, MD
 Multifocal Motor Neuropathy Jonathan Katz, MD Richard Lewis, MD What is Multifocal Motor Neuropathy? Multifocal Motor Neuropathy (MMN) is a rare condition in which multiple motor nerves are attacked by
Multifocal Motor Neuropathy Jonathan Katz, MD Richard Lewis, MD What is Multifocal Motor Neuropathy? Multifocal Motor Neuropathy (MMN) is a rare condition in which multiple motor nerves are attacked by
Accuracy in Space and Time: Diagnosing Multiple Sclerosis. 2012 Genzyme Corporation, a Sanofi company.
 Accuracy in Space and Time: Diagnosing Multiple Sclerosis 2012 Genzyme Corporation, a Sanofi company. Brought All rights to reserved. you by www.msatrium.com, MS.US.PO876.1012 your gateway to MS knowledge.
Accuracy in Space and Time: Diagnosing Multiple Sclerosis 2012 Genzyme Corporation, a Sanofi company. Brought All rights to reserved. you by www.msatrium.com, MS.US.PO876.1012 your gateway to MS knowledge.
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE. Proposed Health Technology Appraisal
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Proposed Health Technology Appraisal Daclizumab for treating relapsing-remitting multiple Draft scope (pre-referral) Draft remit/appraisal objective To
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Proposed Health Technology Appraisal Daclizumab for treating relapsing-remitting multiple Draft scope (pre-referral) Draft remit/appraisal objective To
Teriflunomide (Aubagio) 14mg once daily tablet
 Teriflunomide (Aubagio) 14mg once daily tablet Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Your Consultant Neurologist has suggested that you may benefit from treatment with Teriflunomide. The decision
Teriflunomide (Aubagio) 14mg once daily tablet Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Your Consultant Neurologist has suggested that you may benefit from treatment with Teriflunomide. The decision
NEW DIRECTION IN THE IMPROVEMENT OF CLINICAL CONDITIONS IN MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS PATIENTS By F. De Silvestri, E. Romani, A. Grasso
 NEW DIRECTION IN THE IMPROVEMENT OF CLINICAL CONDITIONS IN MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS PATIENTS By F. De Silvestri, E. Romani, A. Grasso Introduction Multiple sclerosis (MS), in its many and varied clinical forms,
NEW DIRECTION IN THE IMPROVEMENT OF CLINICAL CONDITIONS IN MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS PATIENTS By F. De Silvestri, E. Romani, A. Grasso Introduction Multiple sclerosis (MS), in its many and varied clinical forms,
Cerebral palsy can be classified according to the type of abnormal muscle tone or movement, and the distribution of these motor impairments.
 The Face of Cerebral Palsy Segment I Discovering Patterns What is Cerebral Palsy? Cerebral palsy (CP) is an umbrella term for a group of non-progressive but often changing motor impairment syndromes, which
The Face of Cerebral Palsy Segment I Discovering Patterns What is Cerebral Palsy? Cerebral palsy (CP) is an umbrella term for a group of non-progressive but often changing motor impairment syndromes, which
Recruitment Start date: April 2010 End date: Recruitment will continue until enrolment is fully completed
 Apitope study The study drug (ATX-MS-1467) is a new investigational drug being tested as a potential treatment for relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis (RMS). The term investigational drug means it has
Apitope study The study drug (ATX-MS-1467) is a new investigational drug being tested as a potential treatment for relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis (RMS). The term investigational drug means it has
Patient Group Input to CADTH
 Patient Group Input to CADTH Section 1 General Information Name of the drug CADTH is reviewing and indication(s) of interest Name of patient group/author of submission Patient group s contact information:
Patient Group Input to CADTH Section 1 General Information Name of the drug CADTH is reviewing and indication(s) of interest Name of patient group/author of submission Patient group s contact information:
Medication Policy Manual. Topic: Aubagio, teriflunomide Date of Origin: November 9, 2012
 Medication Policy Manual Policy No: dru283 Topic: Aubagio, teriflunomide Date of Origin: November 9, 2012 Committee Approval Date: December 11, 2015 Next Review Date: December 2016 Effective Date: January
Medication Policy Manual Policy No: dru283 Topic: Aubagio, teriflunomide Date of Origin: November 9, 2012 Committee Approval Date: December 11, 2015 Next Review Date: December 2016 Effective Date: January
Cerebral Palsy. 1995-2014, The Patient Education Institute, Inc. www.x-plain.com nr200105 Last reviewed: 06/17/2014 1
 Cerebral Palsy Introduction Cerebral palsy, or CP, can cause serious neurological symptoms in children. Thousands of children are diagnosed with cerebral palsy every year. This reference summary explains
Cerebral Palsy Introduction Cerebral palsy, or CP, can cause serious neurological symptoms in children. Thousands of children are diagnosed with cerebral palsy every year. This reference summary explains
Multiple Sclerosis Ireland, September 2013. Contents Summary 2 Commentary 3 Recommendations 5 Information on MS 6 Personal testimonies 9
 Submission to the Department of Health Consultation on Draft Misuse of Drugs (Amendment) Regulations 2013 which will amend the Misuse of Drugs Regulations, 1988 Multiple Sclerosis Ireland, September 2013
Submission to the Department of Health Consultation on Draft Misuse of Drugs (Amendment) Regulations 2013 which will amend the Misuse of Drugs Regulations, 1988 Multiple Sclerosis Ireland, September 2013
Acute Myeloid Leukemia
 Acute Myeloid Leukemia Introduction Leukemia is cancer of the white blood cells. The increased number of these cells leads to overcrowding of healthy blood cells. As a result, the healthy cells are not
Acute Myeloid Leukemia Introduction Leukemia is cancer of the white blood cells. The increased number of these cells leads to overcrowding of healthy blood cells. As a result, the healthy cells are not
SOUTH TAMPA MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS CENTER
 SOUTH TAMPA MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS CENTER PATIENT/CARE GIVER QUESTIONNAIRE DEMOGRAPHIC INFORMATION Patient's Name: City: State: Zip Code: Phone: Marital Status: Spouse/Care Giver Name: Phone (H) (W) Occupation:
SOUTH TAMPA MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS CENTER PATIENT/CARE GIVER QUESTIONNAIRE DEMOGRAPHIC INFORMATION Patient's Name: City: State: Zip Code: Phone: Marital Status: Spouse/Care Giver Name: Phone (H) (W) Occupation:
INTRODUCTION Thrombophilia deep vein thrombosis DVT pulmonary embolism PE inherited thrombophilia
 INTRODUCTION Thrombophilia (Hypercoagulability) is a condition in which a person forms blood clots more than normal. Blood clots may occur in the arms or legs (e.g., deep vein thrombosis DVT), the lungs
INTRODUCTION Thrombophilia (Hypercoagulability) is a condition in which a person forms blood clots more than normal. Blood clots may occur in the arms or legs (e.g., deep vein thrombosis DVT), the lungs
