PII S (01)
|
|
|
- Hector Green
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PII S (01) Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys., Vol. 52, No. 5, pp , 2002 Copyright 2002 Elsevier Science Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved /02/$ see front matter CLINICAL INVESTIGATION Central Nervous System 1 H-MRS IN VIVO PREDICTS THE EARLY TREATMENT OUTCOME OF POSTOPERATIVE RADIOTHERAPY FOR MALIGNANT GLIOMAS RAFAL TARNAWSKI, M.D., PH.D.,* MARIA SOKOL, PH.D., PIOTR PIENIAZEK, M.D., PH.D., BOGUSLAW MACIEJEWSKI, M.D., PH.D.,* JERZY WALECKI, M.D., PH.D., LESZEK MISZCZYK, M.D., PH.D.,* AND TERESA KRUPSKA, M.D.* Departments of *Radiotherapy and Radiology, Centre of Oncology Maria Sklodowska Curie Institute Branch in Gliwice, Gliwice, Poland; Department of Radiology, Medical University of Bialystok, Bialystok, Poland Purpose: To analyze prospectively the prognostic significance of 1 H magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) in vivo recorded from the tumor bed of patients after surgery for malignant glioma. Methods and Materials: Fifty-one patients aged years were examined using a MRI/MRS system (Elscint 2T Prestige). Of the 51 patients, 33 had Grade 3 gliomas and 18 had glioblastomas. MRI-localized 1 HMR spectra were acquired using a single-voxel, double-spin-echo sequence. Relative intensities of the signals (choline, creatine [Cr] N-acetyl aspartate [NAA], myo-inositol, lactate, and lipids) were obtained by numeric integration of fitted signals. Two voxels were examined, one located at the tumor bed and the second distant to the tumor bed. All patients were irradiated to 60 Gy using three-dimensional conformal noncoplanar techniques to 60 Gy. Results: MRS in vivo in patients after brain tumor surgery revealed a statistically significant decrease in the NAA/Cr ratio and increases in the choline/creatine (Cr), choline/naa, and myo-inosytol/cr ratios. The intensive signals of lactate and lipids appeared in spectrum. Survival correlated strongly with tumor grade and patient age but the strongest prognostic factor was the lactate/naa ratio. For lactate/naa values >2.0 (intensive lactate signal) the 1-year survival rate was 20%, and for lactate/naa values <2.0, the 1-year survival rate was 85%. Conclusion: A new diagnostic tool demonstrated ability to distinguish between patients with a favorable prognosis and those who will die within 1 year Elsevier Science Inc. NMR spectroscopy, Brain tumors, Prognostic factors, Hypoxia. INTRODUCTION Primary brain tumors are a very diverse group of diseases. Despite many clinical trials conducted during the past decades, no improvement has occurred in the treatment outcome (1 3). Both clinical and basic research have shown that the main reason for the poor prognosis is the biologic heterogeneity of brain tumors. This heterogeneity, together with radioresistance and questionable surgical macroscopic or microscopic margins, is the reason most anaplastic tumors are incurable with conventional multidisciplinary treatment. An improvement in patient survival might be achieved by the identification of molecular or metabolic prognostic factors and treatment individualization. Because brain tumors are inaccessible for clinical examination, imaging of the central nervous system with MRI is irreplaceable in the diagnostic workup. Postoperative disruption of the blood brain barrier limits the value of both CT and MRI in the early differentiation of neoplastic tissue remnants and postoperative changes (4). Reprint requests to: Rafal Tarnawski, M.D., Ph.D., Centre of Oncology, Maria Sklodowska-Curie Institute Branch in Gliwice, Wyb. Armii Krajowej 15, Gliwice Poland. Tel: ; Fax: ; [email protected] This research was partly supported by KBN (Polish Committee Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy (MRS) in vivo allows for insight in the tissue metabolic profiles by analysis of the NMR spectrum. The pattern of metabolic changes may potentially be helpful in basic and applied research. The aim of this work was to evaluate MRS findings in vivo as predictive or prognostic factors for postoperative radiotherapy (RT) for malignant gliomas. The studies of the prognostic importance of MRS are sparse and fragmentary. Most research has been applied to spectroscopy of brain tumors before surgery. In the case of multidisciplinary treatment, an analysis of the tumor bed might be more informative, because the macroscopic or microscopic remnants of tumor might be present and detected. Localized MRS enables studies of the tumor bed regions that are most suspected of active malignancy. METHODS AND MATERIALS The study group consisted of 51 patients (35 men and 16 women, age range years, mean 47) treated with of Scientific Research), No. 8-T11E Acknowledgments We thank the anonymous referees whose comments made essential improvements in this paper. Received Apr 28, 2001, and in revised form Nov 1, Accepted for publication Nov 12,
2 1272 I. J. Radiation Oncology Biology Physics Volume 52, Number 5, 2002 Table 1. Averaged relative concentration of metabolites for tumor bed and controls NAA/Cr Cho/Cr mi/cr Cho/NAA Lac/NAA Lip/NAA Tumor bed * * * * * Control (C1) * Control (C2) Abbreviations: NAA N-acetyl aspartate; Cr creatine; Cho choline; mi myo-inositol; Lac lactate; Lip lipid; (C1) control group, spectroscopic measurement from the uninvolved opposite brain lobe; C2 control group of 30 healthy volunteers. * Highly significant. Significant. Not significant. postoperative RT at the Center of Oncology Maria Sklodowska-Curie Memorial Institute Branch in Gliwice. All patients had good neurologic status and qualified for radical postoperative RT. Twenty-nine patients underwent total resection and 22 partial resection. Of the 51 tumors, 33 were anaplastic glial tumors and 18 were glioblastomas. Patients were treated with conformal three-dimensional techniques using 6 20 MV photons. The dose per fraction was 2 Gy, and the total dose was 60 Gy for all patients. Patients did not receive adjuvant chemotherapy. All consecutive patients with high-grade gliomas and good performance status who had been referred by neurosurgeons for RT were included in this study. MRI and MRS of the tumor bed were performed before RT. The first control group (C1) consisted of spectroscopic measurements from the uninvolved opposite brain lobe and the second control group (C2) consisted of 30 healthy volunteers (5). The interval between surgery and MRI was days (mean 41). Patients were followed using MRI scans 1, 4, and 9 months after treatment. After 9 months of follow-up, MRI was scheduled every 6 months. The spectra were registered from a region of altered MR signal on pilot imaging sequences, avoiding fluid spaces. MRI-localized 1 HMR spectra (using Elscint 2T Prestige operating at the field strength of 2T) were acquired using a single-voxel, double-spin-echo PRESS sequence with the parameters: TR 1500 ms, TE 35 ms, 200 acquisitions, for a voxel volume of cm 3. The spectra recording was preceded by the global and local shimming procedure. For each patient, the spectra were obtained from at least two regions of interest. The first was located at the tumor site and was placed at the operation field edge or at the region of altered MRI appearance suggestive of tumor remnants. The other control voxel was placed at the opposite uninvolved lobe. The spectra were postprocessed with the automatic fitting in the frequency domain. The relative intensities of the signals caused by N-acetyl aspartate (NAA), choline-based compounds (Cho), myo-inositol (mi), lactate (Lac), and lipids (Lip) were obtained by numeric integration of the fitted signals. Statistical analysis The statistical difference between the means was calculated using the Mann Whitney U test. The statistical significance between survival curves was calculated using the modified Peto test. Patient survival was scored as the time after the end of RT. Cutoff levels for the metabolite ratios used in the survival analysis were calculated using the maximum-likelihood estimation and logistic model. Cox regression analysis was used for multivariate survival analysis. RESULTS All spectrum parameters registered from the tumor bed were statistically significantly different from those obtained from the control uninvolved lobe (control group C1) and from the spectrum of healthy volunteers (control group C2) (Table 1). The NAA/Cr ratio was lower compared with the control values, and the Cho/Cr, Cho/NAA, and mi/cr ratios were higher. In contrast to the spectra of healthy brain tissue (control group C2), the spectra recorded from the tumor bed reveal strong signals of Lac and Lip, reflected in the high values of the Lac/NAA and Lip/NAA ratios. Interestingly, the NAA/Cr ratio from the uninvolved lobe (control group C1) was also significantly lower than the normal value. MRI was scored as positive if the contrast enhancement had been registered in the tumor bed (MRI ). For the entire partial resection group, contrast enhancement was observed, but in the total resection group, only 9 patients had MRI scans without contrast enhancement in the tumor bed (MRI ). It should be noted, however, that differentiation between postoperative enhancement and tumor is frequently difficult and may have led to an overestimation of the MRI group. The correlation between the MRS parameters from the tumor bed with tumor grade and contrast enhancement on MRI is shown in Table 2. Lac/NAA and Lip/NAA ratios were significantly increased for Grade 4 tumors and for the patients from the MRI group, but the values were widely scattered. No correlation was found between the MRS parameters and the time from surgery. Patient survival correlated with tumor grade (Fig. 1) and patient age (Fig. 2). However, the extent of resection did not correlate with patient survival (Fig. 3), although it did correlate with the MRI results (Fig. 4).
3 Postoperative 1 H-MRS predicts survival in malignant glioma R. TARNAWSKI et al Table 2. Correlation between MRS parameters from tumor bed with tumor grade and contrast enhancement in MRI Tumor bed NAA/Cr Cho/Cr mi/cr Cho/NAA Lac/NAA Lip/NAA Anaplastic astrocytomas glioblastoma * * * * MRI MRI * * * * Abbreviations as in Table 1. * Not significant. Highly significant. Significant. The cutoff levels used for survival analysis were calculated using logistic regression analysis. It was found that a Lac/NAA ratio of 2 and a Lip/NAA ratio of 2 were the cutoff levels with the best predictive value. Patient survival correlated significantly with the Lac/NAA (Fig. 5) and Lip/NAA (Fig. 6) ratios. To exclude the confounding influence of tumor grade, survival was calculated for Grade 3 tumors and the Lac/NAA ratio (Fig. 7). The forward stepwise multivariate Cox regression analysis involving all the parameters of the MRS spectrum and the known prognostic factors such as age, grade, and extent of surgery, resulted in finding the Lac/NAA ratio and patient age as the two most important predictors of treatment outcome (Table 3). The other parameters were excluded by stepwise procedure. DISCUSSION Patients with malignant gliomas have an extremely bad prognosis. The diffusely infiltrative tumor growth and the site of primary tumor close to important centers of the central nervous system generally preclude radical excision (1). Patient survival depends on both the aggressiveness of the disease and the ability of postoperative treatment to sterilize the tumor. We chose to study the prognostic importance of MRS after surgical tumor excision. Although postoperative changes may potentially change the results of MRS, we did not observe any correlation between the time after surgery and the results of MRS. In this case, MRS may reflect the metabolism of tumor remnants. After a partial resection of tumor, MRS reflects the metabolism of the tumor, and after total resection, it reflects the metabolism of the surgical margins. MRS in vivo for patients after surgery because of brain tumor revealed statistically significant decreases in the NAA/Cr ratio and increases in the Cho/Cr, Cho/NAA, and mi/cr ratios. The intensive signals of Lac and Lip appeared in the spectrum. The Lac/NAA ratio was found to be the strongest independent prognostic and predictive factor for patient survival. For values of Lac/NAA 2.0 (intensive Lac signal), the 1-year survival rate was 30%, and none of those patients were alive 2 years after treatment. For the values of Lac/ NAA 2.0, the 2-year survival rate was close to 80%. Although the Lac/NAA ratio correlated strongly with the Fig. 1. Overall survival correlated significantly with tumor grade Solid line, Grade 3; dotted line, glioblastoma. Fig. 2. Overall survival correlated with patient age. Solid line, age 40 years; dashed line, age 40 and 55 years; and dotted/no line, age 55 years.
4 1274 I. J. Radiation Oncology Biology Physics Volume 52, Number 5, 2002 Fig. 3. Extent of operation (total [solid line] vs. partial [dotted line] resection) did not correlate with patient survival. histologic findings and MRI, its prognostic importance was high in the subgroup of patients with Grade 3 tumors and the group of patients with contrast enhancement on MRI. The forward stepwise multivariate analysis found the Lac/ NAA ratio and patient age to be the most important predictors of treatment outcome. Although the latest MRI techniques are able to provide an excellent depiction of abnormalities in soft tissue morphology, they are frequently unable to distinguish treatmentinduced changes from recurrent or residual tumor. For an assessment of the response to therapy, it is therefore important to use functional imaging modalities such as positron emission tomography and MRS (4). Large randomized trials have established the clinical prognostic factors influencing the survival of patients with malignant gliomas (6 8). The most important factors are Fig. 5. Survival curves for the patients with different intensities of Lac signal. A Lac/NAA cutoff level of 2 was calculated using logistic regression analysis. Patient survival correlated highly with Lac signal intensity. Solid line, Lac/NAA 2; dotted line, Lac/ NAA 2. age, neurologic performance status, extent of resection, and the presence of enhancement on CT or MRI. Unfortunately, these factors are not sufficient for individualization of treatment. More importantly, functional imaging such as localized MRS may be helpful in delineation of a boost region. Because postoperative MRS studies of the brain are sparse (9, 10), we can only discuss our findings with regard to the preoperative parameters. 1 H-MRS of the brain consists of several signals that may be resolved and quantified. The NAA signal derives from the COOCH3 group of N-acetyl aspartate, the amino acid Fig. 4. Patients with contrast enhancement (dotted line) on MRI had significantly shorter survival times compared with those without contrast enhancement (solid line). Fig. 6. Survival curves for the patients with different intensities of Lip signal. A Lip/NAA cutoff level of 2 was calculated using logistic regression analysis. Patient survival correlated highly with Lip signal intensity. Solid line, Lip/NAA 2; dotted line, Lip/ NAA 2.
5 Postoperative 1 H-MRS predicts survival in malignant glioma R. TARNAWSKI et al Table 3. Results of forward stepwise multivariate Cox regression analysis Parameter Estimate Standard error p RR Lac/NAA ratio Age Abbreviations: Lac lactate; NAA N-acetyl aspartate; RR relative risk. Strongest prognostic factors were Lac/NAA ratio and patient age; the other parameters were excluded by the stepwise procedure. Fig. 7. Survival curves for patients with different intensities of Lac signal in the group with anaplastic astrocytomas (excluding glioblastomas). Patient survival correlated highly with Lac signal intensity. Solid line, Lac/NAA 2; dotted line, Lac/NAA 2. that is present primarily in neurons. A decrease in the NAA level is usually interpreted as due to a reduction in the number of neurons (11). Novel studies have revealed, however, that a decreased intensity of the COOCH3 group signal may reflect lower functional activity of neurons in response to stress or injury (12). On the other hand, the elevation of the Cho/Cr, Cho/NAA, and mi/cr ratios is explained by the proliferation of glial cells (13). Both Cho and mi are thought to be products of myelin degradation (14). Lac and Lip are not present in normal spectrum; however, the presence of both metabolites in pathologic tissue has been frequently highlighted by many authors (15 19). The Lac signal rises whenever the Lac-producing anaerobic glycolytic pathway exceeds the capacity of the Lac-catabolizing respiratory pathways or when the cellular capacity for exporting Lac to the bloodstream is impaired. Another reason for Lac presence is an impairment of mitochondrial function due to hypoxia. Lac is also thought to be found frequently in malignant gliomas. Similarly, mobile Lip are more likely to be present in higher grade tumors than in lower grade ones (15). Lip signals are not seen in normal spectrum because of severe broadening resulting from restricted mobility of Lip molecules involved in cell membrane formation. When cell membranes become disrupted for any reason mobile lipids signals may be resolved in spectrum. Recently, it was confirmed that the Lip signals not only increase progressively with tumor grade (16, 17) but that there is also a correlation between the fraction of microscopic necrosis and their integral intensity, as observed ex vivo using 1 H-MRS (18). Similarly, it has been shown that Lac signals are present in high-grade astrocytomas and absent in most lowgrade gliomas (19). The close correlation of the Lac and Lip concentrations suggests that the mechanisms of their increase are similar. In summary, we have found an unexpectedly high correlation between patient survival and Lac signal intensity. It is possible that postoperative MRS reflects the metabolism of the postoperative site. Factors such as hypoxia, blood brain barrier disruption, edema, demyelinization, and inflammatory responses may change brain metabolic function, resulting in changes in the MRS signals (5). The poor outcome of patients with strong Lac signals may be explained by the decreased radiosensitivity in the presence of hypoxia. Clearly, additional review with a large population will improve the multivariate analysis, important in not only dissecting out the influence of histologic grade and age, but also in the degree of residual tumor seen on MRI. REFERENCES 1. Sheline GE. Radiotherapy for high grade gliomas. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 1990;18: Fallai C, Olmi P. Hyperfractionated and accelerated radiation therapy in central nervous system (malignant gliomas, pediatric tumors, and brain metastases). Radiother Oncol 1997;43: Werner-Wasik M, Scott CB, Nelson DF, et al. Final report of phase I/II trial of hyperfractionated and accelerated hyperfractionated radiation therapy with carmustine for adult with supratentorial malignant gliomas. Cancer 1995;77: Nelson SJ. Imaging of brain tumors after therapy. Neuroimag Clin North Am 1999;9: Walecki J, Sok&slash;ó M, Pienia żek P, et al. Role of short TE 1H-MR spectroscopy in monitoring of post-operation irradiated patients. Eur J Radiol 1999;30: Davis FG, McCarty MJ, Freels S, et al. The conditional probability of survival of patients with primary malignant brain tumors. Cancer 1999;85: Nelson DF, Nelson JS, Davis DR, et al. Survival and prognosis of patients with atypical or anaplastic features. J Neurooncol 1985;3: Scott CB, Scarantino C, Urtasun R, et al. Validation and predictive power of Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) recursive partitioning analysis classes for malignant glioma patients: A report using RTOG Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 1998;40:51 55.
6 1276 I. J. Radiation Oncology Biology Physics Volume 52, Number 5, Girard N, Wang ZJ, Erbetta A, et al. Prognostic value of proton MR spectroscopy of cerebral hemisphere tumors in children. Neuroradiology 1998;40: Lazareff JA, Gupta RK, Alger J. Variation of post-treatment H-MRSI choline intensity in pediatric gliomas. J Neurooncol 1999;41: Bates TE, Stangward M, Keelan J, et al. Inhibition of N- acetylaspartate production: Implications for 1 H MRS studies in vivo. Neuro Rep 1996;7: Estève F, Rubin C, Grand S, et al. Transient metabolic changes observed with proton MR spectroscopy in normal human brain after radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 1998;40: Barbarella G, Ricci R, Pirini G, et al. In vivo single voxel 1H MRS of glial brain tumors: Correlation with tissue histology and in vitro MRS. Int J Oncol 1998;12: Ross BD. Biochemical considerations in 1 H spectroscopy: Glutamate and glutamine, myo-inositol and related metabolites. NMR Biomed 1991;4: Tien RD, Lai PH, Smith JS, et al. Single-voxel proton brain spectroscopy exam (PROBE/SV) in patients with primary brain tumors. Am J Radiol 1996;167: Negendank W, Sauter R. Intratumoral lipids in 1H MRS in vivo in brain tumors: Experience of the Siemens cooperative clinical trial. Anticancer Res 1996;16: Negendank WG, Sauter R, Brown TR, et al. Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in patients with glial tumors: A multicenter study. J Neurosurg 1996;84: Kuesel AC, Briere KM, Halliday WC, et al. Mobile lipid accumulation in necrotic tissue of high grade astrocytomas. Anticancer Res 1996;16: Heesters MA, Kamman RL, Mooyaart EL, et al. Localized proton spectroscopy of inoperable brain gliomas: Response to radiation therapy. J Neurooncol 1993;17:27 35.
Brain Tumor Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Brain Tumor Treatment Brain Tumors Overview A brain tumor is a group of abnormal cells that grows in or around the brain. Tumors can directly destroy healthy brain cells. They can
Scan for mobile link. Brain Tumor Treatment Brain Tumors Overview A brain tumor is a group of abnormal cells that grows in or around the brain. Tumors can directly destroy healthy brain cells. They can
A new score predicting the survival of patients with spinal cord compression from myeloma
 A new score predicting the survival of patients with spinal cord compression from myeloma (1) Sarah Douglas, Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Lubeck, Germany; [email protected] (2) Steven
A new score predicting the survival of patients with spinal cord compression from myeloma (1) Sarah Douglas, Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Lubeck, Germany; [email protected] (2) Steven
Detection and staging of recurrent prostate cancer is still one of the important clinical problems in prostate cancer. A rise in PSA or biochemical
 Summary. 111 Detection and staging of recurrent prostate cancer is still one of the important clinical problems in prostate cancer. A rise in PSA or biochemical recurrence (BCR) is the first sign of recurrent
Summary. 111 Detection and staging of recurrent prostate cancer is still one of the important clinical problems in prostate cancer. A rise in PSA or biochemical recurrence (BCR) is the first sign of recurrent
Historical Basis for Concern
 Androgens After : Are We Ready? Mohit Khera, MD, MBA Assistant Professor of Urology Division of Male Reproductive Medicine and Surgery Scott Department of Urology Baylor College of Medicine Historical
Androgens After : Are We Ready? Mohit Khera, MD, MBA Assistant Professor of Urology Division of Male Reproductive Medicine and Surgery Scott Department of Urology Baylor College of Medicine Historical
Current Status and Perspectives of Radiation Therapy for Breast Cancer
 Breast Cancer Current Status and Perspectives of Radiation Therapy for Breast Cancer JMAJ 45(10): 434 439, 2002 Masahiro HIRAOKA, Masaki KOKUBO, Chikako YAMAMOTO and Michihide MITSUMORI Department of Therapeutic
Breast Cancer Current Status and Perspectives of Radiation Therapy for Breast Cancer JMAJ 45(10): 434 439, 2002 Masahiro HIRAOKA, Masaki KOKUBO, Chikako YAMAMOTO and Michihide MITSUMORI Department of Therapeutic
BEYOND 18 F-FDG: INTRODUCTION TO NEW RADIOPHARMACEUTICALS
 BEYOND F-FDG: INTRODUCTION TO NEW RADIOPHARMACEUTICALS Asti Mattia Nuclear Medicine Department Santa Maria Nuova Hospital, Reggio Emilia, Italy SUMMARY: F-Labelled Choline analogues. Comparison between
BEYOND F-FDG: INTRODUCTION TO NEW RADIOPHARMACEUTICALS Asti Mattia Nuclear Medicine Department Santa Maria Nuova Hospital, Reggio Emilia, Italy SUMMARY: F-Labelled Choline analogues. Comparison between
TITLE: Comparison of the dosimetric planning of partial breast irradiation with and without the aid of 3D virtual reality simulation (VRS) software.
 SAMPLE CLINICAL RESEARCH APPLICATION ABSTRACT: TITLE: Comparison of the dosimetric planning of partial breast irradiation with and without the aid of 3D virtual reality simulation (VRS) software. Hypothesis:
SAMPLE CLINICAL RESEARCH APPLICATION ABSTRACT: TITLE: Comparison of the dosimetric planning of partial breast irradiation with and without the aid of 3D virtual reality simulation (VRS) software. Hypothesis:
Chapter 10. Summary & Future perspectives
 Summary & Future perspectives 123 Multiple sclerosis is a chronic disorder of the central nervous system, characterized by inflammation and axonal degeneration. All current therapies modulate the peripheral
Summary & Future perspectives 123 Multiple sclerosis is a chronic disorder of the central nervous system, characterized by inflammation and axonal degeneration. All current therapies modulate the peripheral
The Brain and Spine CenTer
 The Br ain and Spine Center Choosing the right treatment partner is important for patients facing tumors involving the brain, spine or skull base. The Brain and Spine Center at The University of Texas
The Br ain and Spine Center Choosing the right treatment partner is important for patients facing tumors involving the brain, spine or skull base. The Brain and Spine Center at The University of Texas
Management of low grade glioma s: update on recent trials
 Management of low grade glioma s: update on recent trials M.J. van den Bent The Brain Tumor Center at Erasmus MC Cancer Center Rotterdam, the Netherlands Low grades Female, born 1976 1 st seizure 2005,
Management of low grade glioma s: update on recent trials M.J. van den Bent The Brain Tumor Center at Erasmus MC Cancer Center Rotterdam, the Netherlands Low grades Female, born 1976 1 st seizure 2005,
NEW HYBRID IMAGING TECHNOLOGY MAY HAVE BIG POTENTIAL FOR IMPROVING DIAGNOSIS OF PROSTATE CANCER
 Media Release April 7, 2009 For Immediate Release NEW HYBRID IMAGING TECHNOLOGY MAY HAVE BIG POTENTIAL FOR IMPROVING DIAGNOSIS OF PROSTATE CANCER London, Ontario Improved hybrid imaging techniques developed
Media Release April 7, 2009 For Immediate Release NEW HYBRID IMAGING TECHNOLOGY MAY HAVE BIG POTENTIAL FOR IMPROVING DIAGNOSIS OF PROSTATE CANCER London, Ontario Improved hybrid imaging techniques developed
L Lang-Lazdunski, A Bille, S Marshall, R Lal, D Landau, J Spicer
 Pleurectomy/decortication, hyperthermic pleural lavage with povidone-iodine and systemic chemotherapy in malignant pleural mesothelioma. A 10-year experience. L Lang-Lazdunski, A Bille, S Marshall, R Lal,
Pleurectomy/decortication, hyperthermic pleural lavage with povidone-iodine and systemic chemotherapy in malignant pleural mesothelioma. A 10-year experience. L Lang-Lazdunski, A Bille, S Marshall, R Lal,
Table of Contents. Data Supplement 1: Summary of ASTRO Guideline Statements. Data Supplement 2: Definition of Terms
 Definitive and Adjuvant Radiotherapy in Locally Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline Endorsement of the American Society for Radiation
Definitive and Adjuvant Radiotherapy in Locally Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline Endorsement of the American Society for Radiation
Brain Cancer. This reference summary will help you understand how brain tumors are diagnosed and what options are available to treat them.
 Brain Cancer Introduction Brain tumors are not rare. Thousands of people are diagnosed every year with tumors of the brain and the rest of the nervous system. The diagnosis and treatment of brain tumors
Brain Cancer Introduction Brain tumors are not rare. Thousands of people are diagnosed every year with tumors of the brain and the rest of the nervous system. The diagnosis and treatment of brain tumors
Radioterapia panencefalica. Umberto Ricardi
 Radioterapia panencefalica Umberto Ricardi Background Systemic disease to the brain is unfortunately a quite common event Radiotherapy, especially with the great technical development during the past decades,
Radioterapia panencefalica Umberto Ricardi Background Systemic disease to the brain is unfortunately a quite common event Radiotherapy, especially with the great technical development during the past decades,
Radiation Therapy in the Treatment of
 Lung Cancer Radiation Therapy in the Treatment of Lung Cancer JMAJ 46(12): 537 541, 2003 Kazushige HAYAKAWA Professor and Chairman, Department of Radiology, Kitasato University School of Medicine Abstract:
Lung Cancer Radiation Therapy in the Treatment of Lung Cancer JMAJ 46(12): 537 541, 2003 Kazushige HAYAKAWA Professor and Chairman, Department of Radiology, Kitasato University School of Medicine Abstract:
Multimodality imaging of brain tumours: High Grade Brain Tumours
 20th Advance Course Multimodality imaging of brain tumours: High Grade Brain Tumours Àlex Rovira Unitat de Ressonància Magnètica Servei de Radiologia Hospital Vall d Hebron. Barcelona. alex.rovira@idi
20th Advance Course Multimodality imaging of brain tumours: High Grade Brain Tumours Àlex Rovira Unitat de Ressonància Magnètica Servei de Radiologia Hospital Vall d Hebron. Barcelona. alex.rovira@idi
Implementation Date: April 2015 Clinical Operations
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guideline PROSTATE CANCER Original Date: March 2011 Page 1 of 5 Radiation Oncology Last Review Date: March 2015 Guideline Number: NIA_CG_124 Last Revised Date:
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guideline PROSTATE CANCER Original Date: March 2011 Page 1 of 5 Radiation Oncology Last Review Date: March 2015 Guideline Number: NIA_CG_124 Last Revised Date:
AMERICAN BRAIN TUMOR ASSOCIATION. Ependymoma
 AMERICAN BRAIN TUMOR ASSOCIATION Ependymoma ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ABOUT THE AMERICAN BRAIN TUMOR ASSOCIATION Founded in 1973, the American Brain Tumor Association (ABTA) was the first national nonprofit organization
AMERICAN BRAIN TUMOR ASSOCIATION Ependymoma ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ABOUT THE AMERICAN BRAIN TUMOR ASSOCIATION Founded in 1973, the American Brain Tumor Association (ABTA) was the first national nonprofit organization
In Practice Whole Body MR for Visualizing Metastatic Prostate Cancer
 In Practice Whole Body MR for Visualizing Metastatic Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer in men worldwide, accounting for 15% of all new cancer cases. 1 Great strides have
In Practice Whole Body MR for Visualizing Metastatic Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer in men worldwide, accounting for 15% of all new cancer cases. 1 Great strides have
Lung Cancer Treatment Guidelines
 Updated June 2014 Derived and updated by consensus of members of the Providence Thoracic Oncology Program with the aid of evidence-based National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) national guidelines,
Updated June 2014 Derived and updated by consensus of members of the Providence Thoracic Oncology Program with the aid of evidence-based National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) national guidelines,
PRIMARY GLIOMA (oligodendroglioma, astrocytoma, oligodendroglioma, oligoastrocytoma, including anaplastic, gliosarcoma and glioblastoma multiforme)
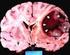 Protocol for Planning and Treatment The process to be followed when a course of chemotherapy is required to treat: PRIMARY GLIOMA (oligodendroglioma, astrocytoma, oligodendroglioma, oligoastrocytoma, including
Protocol for Planning and Treatment The process to be followed when a course of chemotherapy is required to treat: PRIMARY GLIOMA (oligodendroglioma, astrocytoma, oligodendroglioma, oligoastrocytoma, including
Prostate Cancer. Treatments as unique as you are
 Prostate Cancer Treatments as unique as you are UCLA Prostate Cancer Program Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer among men. The UCLA Prostate Cancer Program brings together the elements essential
Prostate Cancer Treatments as unique as you are UCLA Prostate Cancer Program Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer among men. The UCLA Prostate Cancer Program brings together the elements essential
Stomach (Gastric) Cancer. Prof. M K Mahajan ACDT & RC Bathinda
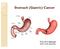 Stomach (Gastric) Cancer Prof. M K Mahajan ACDT & RC Bathinda Gastric Cancer Role of Radiation Layers of the Stomach Mucosa Submucosa Muscularis Serosa Stomach and Regional Lymph Nodes Stomach and Regional
Stomach (Gastric) Cancer Prof. M K Mahajan ACDT & RC Bathinda Gastric Cancer Role of Radiation Layers of the Stomach Mucosa Submucosa Muscularis Serosa Stomach and Regional Lymph Nodes Stomach and Regional
The 4Kscore blood test for risk of aggressive prostate cancer
 The 4Kscore blood test for risk of aggressive prostate cancer Prostate cancer tests When to use the 4Kscore Test? Screening Prior to 1 st biopsy Prior to negative previous biopsy Prognosis in Gleason 6
The 4Kscore blood test for risk of aggressive prostate cancer Prostate cancer tests When to use the 4Kscore Test? Screening Prior to 1 st biopsy Prior to negative previous biopsy Prognosis in Gleason 6
Robert Bristow MD PhD FRCPC
 Robert Bristow MD PhD FRCPC Clinician-Scientist and Professor, Radiation Oncology and Medical Biophysics, University of Toronto and Ontario Cancer Institute/ (UHN) Head, PMH-CFCRI Prostate Cancer Research
Robert Bristow MD PhD FRCPC Clinician-Scientist and Professor, Radiation Oncology and Medical Biophysics, University of Toronto and Ontario Cancer Institute/ (UHN) Head, PMH-CFCRI Prostate Cancer Research
Principles of Radiation Therapy A Bapsi Chakravarthy, MD Associate e P rofessor Professor Radiation Oncology
 Principles of Radiation Therapy A Bapsi Chakravarthy, MD Associate Professor Radiation Oncology Disclosure Information I have no financial relationships to disclose relevant to the conten of this presentation.
Principles of Radiation Therapy A Bapsi Chakravarthy, MD Associate Professor Radiation Oncology Disclosure Information I have no financial relationships to disclose relevant to the conten of this presentation.
AMERICAN BRAIN TUMOR ASSOCIATION. Proton Therapy
 AMERICAN BRAIN TUMOR ASSOCIATION Proton Therapy Acknowledgements About the American Brain Tumor Association Founded in 1973, the American Brain Tumor Association (ABTA) was the first national nonprofit
AMERICAN BRAIN TUMOR ASSOCIATION Proton Therapy Acknowledgements About the American Brain Tumor Association Founded in 1973, the American Brain Tumor Association (ABTA) was the first national nonprofit
False positive PET in lymphoma
 False positive PET in lymphoma Thomas Krause Introduction and conclusion 2 3 Introduction 4 FDG-PET in staging of lymphoma 34 studies with 2227 Patients CT FDG-PET Sensitivity 63 % 89 % (58%-100%) (63%-100%)
False positive PET in lymphoma Thomas Krause Introduction and conclusion 2 3 Introduction 4 FDG-PET in staging of lymphoma 34 studies with 2227 Patients CT FDG-PET Sensitivity 63 % 89 % (58%-100%) (63%-100%)
MRI for Paediatric Surgeons
 MRI for Paediatric Surgeons Starship David Perry Paediatric Radiologist Starship Children s Hospital CHILDREN S HEALTH What determines the brightness of a pixel in MRI? i.e. What determines the strength
MRI for Paediatric Surgeons Starship David Perry Paediatric Radiologist Starship Children s Hospital CHILDREN S HEALTH What determines the brightness of a pixel in MRI? i.e. What determines the strength
Radiation therapy involves using many terms you may have never heard before. Below is a list of words you could hear during your treatment.
 Dictionary Radiation therapy involves using many terms you may have never heard before. Below is a list of words you could hear during your treatment. Applicator A device used to hold a radioactive source
Dictionary Radiation therapy involves using many terms you may have never heard before. Below is a list of words you could hear during your treatment. Applicator A device used to hold a radioactive source
Glioblastoma (cancer affecting the brain) A guide for journalists on glioblastoma and its treatment
 Glioblastoma (cancer affecting the brain) A guide for journalists on glioblastoma and its treatment Section 1 Glioblastoma Section 2 Epidemiology and prognosis Section 3 Treatment Contents Contents 2 3
Glioblastoma (cancer affecting the brain) A guide for journalists on glioblastoma and its treatment Section 1 Glioblastoma Section 2 Epidemiology and prognosis Section 3 Treatment Contents Contents 2 3
What is Glioblastoma? How is GBM classified according to the WHO Grading System? What risk factors pertain to GBM?
 GBM (English) What is Glioblastoma? Glioblastoma or glioblastoma multiforme is one of the most common brain tumors accounting for approximately 12 to 15 percent of all brain tumors. The name of the tumor
GBM (English) What is Glioblastoma? Glioblastoma or glioblastoma multiforme is one of the most common brain tumors accounting for approximately 12 to 15 percent of all brain tumors. The name of the tumor
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF LUNG CANCER
 GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF LUNG CANCER BY Ali Shamseddine, MD (Coordinator); [email protected] Fady Geara, MD Bassem Shabb, MD Ghassan Jamaleddine, MD CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR THE TREATMENT
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF LUNG CANCER BY Ali Shamseddine, MD (Coordinator); [email protected] Fady Geara, MD Bassem Shabb, MD Ghassan Jamaleddine, MD CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR THE TREATMENT
Small Cell Lung Cancer
 Small Cell Lung Cancer Types of Lung Cancer Non-small cell carcinoma (NSCC) (87%) Adenocarcinoma (38%) Squamous cell (20%) Large cell (5%) Small cell carcinoma (13%) Small cell lung cancer is virtually
Small Cell Lung Cancer Types of Lung Cancer Non-small cell carcinoma (NSCC) (87%) Adenocarcinoma (38%) Squamous cell (20%) Large cell (5%) Small cell carcinoma (13%) Small cell lung cancer is virtually
Prostate cancer is the most common cause of death from cancer in men over age 75. Prostate cancer is rarely found in men younger than 40.
 A.D.A.M. Medical Encyclopedia. Prostate cancer Cancer - prostate; Biopsy - prostate; Prostate biopsy; Gleason score Last reviewed: October 2, 2013. Prostate cancer is cancer that starts in the prostate
A.D.A.M. Medical Encyclopedia. Prostate cancer Cancer - prostate; Biopsy - prostate; Prostate biopsy; Gleason score Last reviewed: October 2, 2013. Prostate cancer is cancer that starts in the prostate
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم
 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Updates in Mesothelioma By Samieh Amer, MD Professor of Cardiothoracic Surgery Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University History Wagner and his colleagues (1960) 33 cases of mesothelioma
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Updates in Mesothelioma By Samieh Amer, MD Professor of Cardiothoracic Surgery Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University History Wagner and his colleagues (1960) 33 cases of mesothelioma
HADRON THERAPY FOR CANCER TREATMENT
 HADRON THERAPY FOR CANCER TREATMENT Seminar presented by Arlene Lennox at Fermilab on Nov 21, 2003 CANCER STAGES LOCAL TUMOR REGIONAL METASTASIS SYSTEMIC DISEASE CANCER TREATMENT SURGERY RADIATION THERAPY
HADRON THERAPY FOR CANCER TREATMENT Seminar presented by Arlene Lennox at Fermilab on Nov 21, 2003 CANCER STAGES LOCAL TUMOR REGIONAL METASTASIS SYSTEMIC DISEASE CANCER TREATMENT SURGERY RADIATION THERAPY
PET/CT in Lung Cancer
 PET/CT in Lung Cancer Rodolfo Núñez Miller, M.D. Nuclear Medicine and Diagnostic Imaging Section Division of Human Health International Atomic Energy Agency Vienna, Austria GLOBOCAN 2012 #1 #3 FDG-PET/CT
PET/CT in Lung Cancer Rodolfo Núñez Miller, M.D. Nuclear Medicine and Diagnostic Imaging Section Division of Human Health International Atomic Energy Agency Vienna, Austria GLOBOCAN 2012 #1 #3 FDG-PET/CT
Us TOO University Presents: Understanding Diagnostic Testing
 Us TOO University Presents: Understanding Diagnostic Testing for Prostate Cancer Patients Today s speaker is Manish Bhandari, MD Program moderator is Pam Barrett, Us TOO International Made possible by
Us TOO University Presents: Understanding Diagnostic Testing for Prostate Cancer Patients Today s speaker is Manish Bhandari, MD Program moderator is Pam Barrett, Us TOO International Made possible by
Prostatectomy, pelvic lymphadenect. Med age 63 years Mean followup 53 months No other cancer related therapy before recurrence. Negative.
 Adjuvante und Salvage Radiotherapie Ludwig Plasswilm Klinik für Radio-Onkologie, KSSG CANCER CONTROL WITH RADICAL PROSTATECTOMY ALONE IN 1,000 CONSECUTIVE PATIENTS 1983 1998 Clinical stage T1 and T2 Mean
Adjuvante und Salvage Radiotherapie Ludwig Plasswilm Klinik für Radio-Onkologie, KSSG CANCER CONTROL WITH RADICAL PROSTATECTOMY ALONE IN 1,000 CONSECUTIVE PATIENTS 1983 1998 Clinical stage T1 and T2 Mean
Understanding ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and deciding about treatment
 Understanding ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and deciding about treatment Developed by National Breast and Ovarian Cancer Centre Funded by the Australian Government Department of Health and Ageing Understanding
Understanding ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and deciding about treatment Developed by National Breast and Ovarian Cancer Centre Funded by the Australian Government Department of Health and Ageing Understanding
Accelerated hemithoracic radiation followed by extrapleural pneumonectomy for malignant pleural mesothelioma
 Accelerated hemithoracic radiation followed by extrapleural pneumonectomy for malignant pleural mesothelioma Marc de Perrot, Ronald Feld, Natasha B Leighl, Andrew Hope, Thomas K Waddell, Shaf Keshavjee,
Accelerated hemithoracic radiation followed by extrapleural pneumonectomy for malignant pleural mesothelioma Marc de Perrot, Ronald Feld, Natasha B Leighl, Andrew Hope, Thomas K Waddell, Shaf Keshavjee,
Our Facility. Advanced clinical center with the newest and highly exact technology for treatment of patients with cancer pencil beam
 PTC Czech The main goal of radiotherapy is to irreversibly damage tumor cells, whereas the cells of healthy tissue are damaged only reversibly or not at all. Proton therapy currently comes closest to this
PTC Czech The main goal of radiotherapy is to irreversibly damage tumor cells, whereas the cells of healthy tissue are damaged only reversibly or not at all. Proton therapy currently comes closest to this
Loco-regional Recurrence
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer AGO AGO e. e. V. V. Loco-regional Recurrence Loco-regional Recurrence Version 2002: Brunnert / Simon Versions 2003 2012: Audretsch
Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer AGO AGO e. e. V. V. Loco-regional Recurrence Loco-regional Recurrence Version 2002: Brunnert / Simon Versions 2003 2012: Audretsch
Clinical Trial Design. Sponsored by Center for Cancer Research National Cancer Institute
 Clinical Trial Design Sponsored by Center for Cancer Research National Cancer Institute Overview Clinical research is research conducted on human beings (or on material of human origin such as tissues,
Clinical Trial Design Sponsored by Center for Cancer Research National Cancer Institute Overview Clinical research is research conducted on human beings (or on material of human origin such as tissues,
Guidelines for the treatment of breast cancer with radiotherapy
 London Cancer Guidelines for the treatment of breast cancer with radiotherapy March 2013 Review March 2014 Version 1.0 Contents 1. Introduction... 3 2. Indications and dosing schedules... 3 2.1. Ductal
London Cancer Guidelines for the treatment of breast cancer with radiotherapy March 2013 Review March 2014 Version 1.0 Contents 1. Introduction... 3 2. Indications and dosing schedules... 3 2.1. Ductal
Analysis of Prostate Cancer at Easter Connecticut Health Network Using Cancer Registry Data
 The 2014 Cancer Program Annual Public Reporting of Outcomes/Annual Site Analysis Statistical Data from 2013 More than 70 percent of all newly diagnosed cancer patients are treated in the more than 1,500
The 2014 Cancer Program Annual Public Reporting of Outcomes/Annual Site Analysis Statistical Data from 2013 More than 70 percent of all newly diagnosed cancer patients are treated in the more than 1,500
Colorectal Cancer Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Colorectal Cancer Treatment Colorectal cancer overview Colorectal cancer, also called large bowel cancer, is the term used to describe malignant tumors found in the colon and rectum.
Scan for mobile link. Colorectal Cancer Treatment Colorectal cancer overview Colorectal cancer, also called large bowel cancer, is the term used to describe malignant tumors found in the colon and rectum.
Case Report. Central Neurocytoma. Fotis Souslian, MD; Dino Terzic, MD; Ramachandra Tummala, MD. Department of Neurosurgery, University of Minnesota
 1 Case Report Central Neurocytoma Fotis, MD; Dino Terzic, MD; Ramachandra Tummala, MD Department of Neurosurgery, University of Minnesota Case This is a previously healthy 20 year old female, with 3 months
1 Case Report Central Neurocytoma Fotis, MD; Dino Terzic, MD; Ramachandra Tummala, MD Department of Neurosurgery, University of Minnesota Case This is a previously healthy 20 year old female, with 3 months
High-Grade Cerebral Glioma Characterization: Usefulness of MR Spectroscopy and Perfusion Imaging Associated Evaluation
 The Neuroradiology Journal 25: 57-66, 2012 www.centauro.it High-Grade Cerebral Glioma Characterization: Usefulness of MR Spectroscopy and Perfusion Imaging Associated Evaluation I. Aprile 1, C. Torni 1,
The Neuroradiology Journal 25: 57-66, 2012 www.centauro.it High-Grade Cerebral Glioma Characterization: Usefulness of MR Spectroscopy and Perfusion Imaging Associated Evaluation I. Aprile 1, C. Torni 1,
Radiotherapy in locally advanced & metastatic NSC lung cancer
 Radiotherapy in locally advanced & metastatic NSC lung cancer Dr Raj Hegde. MD. FRANZCR Consultant Radiation Oncologist. William Buckland Radiotherapy Centre. Latrobe Regional Hospital. Locally advanced
Radiotherapy in locally advanced & metastatic NSC lung cancer Dr Raj Hegde. MD. FRANZCR Consultant Radiation Oncologist. William Buckland Radiotherapy Centre. Latrobe Regional Hospital. Locally advanced
IBA Proton Therapy. Biomed days 2015. Vincent Bossier. System Architect [email protected]. Protect, Enhance and Save Lives
 Vincent Bossier System Architect [email protected] IBA Proton Therapy Biomed days 2015 Protect, Enhance and Save Lives 1 Agenda AN INTRODUCTION TO IBA WHY PROTON THERAPY CLINICAL WORKFLOW TREATMENT
Vincent Bossier System Architect [email protected] IBA Proton Therapy Biomed days 2015 Protect, Enhance and Save Lives 1 Agenda AN INTRODUCTION TO IBA WHY PROTON THERAPY CLINICAL WORKFLOW TREATMENT
CHILDHOOD CANCER SURVIVOR STUDY Analysis Concept Proposal
 CHILDHOOD CANCER SURVIVOR STUDY Analysis Concept Proposal 1. STUDY TITLE: Longitudinal Assessment of Chronic Health Conditions: The Aging of Childhood Cancer Survivors 2. WORKING GROUP AND INVESTIGATORS:
CHILDHOOD CANCER SURVIVOR STUDY Analysis Concept Proposal 1. STUDY TITLE: Longitudinal Assessment of Chronic Health Conditions: The Aging of Childhood Cancer Survivors 2. WORKING GROUP AND INVESTIGATORS:
Case Number: RT2009-124(M) Potential Audiences: Intent Doctor, Oncology Special Nurse, Resident Doctor
 Renal Cell Carcinoma of the Left Kidney Post Radical Surgery with pt4 Classification with Multiple Lung and Single Brain Metastases: the Role and Treatment Consideration of Radiotherapy Case Number: RT2009-124(M)
Renal Cell Carcinoma of the Left Kidney Post Radical Surgery with pt4 Classification with Multiple Lung and Single Brain Metastases: the Role and Treatment Consideration of Radiotherapy Case Number: RT2009-124(M)
ALCHEMIST (Adjuvant Lung Cancer Enrichment Marker Identification and Sequencing Trials)
 ALCHEMIST (Adjuvant Lung Cancer Enrichment Marker Identification and Sequencing Trials) 3 Integrated Trials Testing Targeted Therapy in Early Stage Lung Cancer Part of NCI s Precision Medicine Effort in
ALCHEMIST (Adjuvant Lung Cancer Enrichment Marker Identification and Sequencing Trials) 3 Integrated Trials Testing Targeted Therapy in Early Stage Lung Cancer Part of NCI s Precision Medicine Effort in
Current and Future Trends in Proton Treatment of Prostate Cancer
 Current and Future Trends in Proton Treatment of Prostate Cancer Reinhard W. Schulte Assistant Professor Department of Radiation Medicine Loma Linda University Medical Center Loma Linda, CA, USA Outline
Current and Future Trends in Proton Treatment of Prostate Cancer Reinhard W. Schulte Assistant Professor Department of Radiation Medicine Loma Linda University Medical Center Loma Linda, CA, USA Outline
Treatment of Small Cell Lung Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Endorsement of the American College of Chest Physicians (ACCP) Guideline
 Treatment of Small Cell Lung Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Endorsement of the American College of Chest Physicians (ACCP) Guideline An ASCO Endorsement of Treatment of Small Cell Lung Cancer:
Treatment of Small Cell Lung Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Endorsement of the American College of Chest Physicians (ACCP) Guideline An ASCO Endorsement of Treatment of Small Cell Lung Cancer:
Current Status and Future Direction of Proton Beam Therapy
 Current Status and Future Direction of Proton Beam Therapy National Cancer Center Hospital East Division of Radiation Oncology and Particle Therapy Tetsuo Akimoto Comparison of status of particle therapy
Current Status and Future Direction of Proton Beam Therapy National Cancer Center Hospital East Division of Radiation Oncology and Particle Therapy Tetsuo Akimoto Comparison of status of particle therapy
ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS)
 Understanding ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and deciding about treatment Understanding ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and deciding about treatment Developed by National Breast and Ovarian Cancer Centre
Understanding ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and deciding about treatment Understanding ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and deciding about treatment Developed by National Breast and Ovarian Cancer Centre
Management of Postmenopausal Women with T1 ER+ Tumors: Options and Tradeoffs. Case Study. Surgery. Lumpectomy and Radiation
 Management of Postmenopausal Women with T1 ER+ Tumors: Options and Tradeoffs Michael Alvarado, MD Associate Professor of Surgery University of California San Francisco Case Study 59 yo woman with new palpable
Management of Postmenopausal Women with T1 ER+ Tumors: Options and Tradeoffs Michael Alvarado, MD Associate Professor of Surgery University of California San Francisco Case Study 59 yo woman with new palpable
SUNY DOWNSTATE MEDICAL CENTER SURGERY GRAND ROUNDS February 28, 2013 VERENA LIU, MD ROSEANNA LEE, MD
 SUNY DOWNSTATE MEDICAL CENTER SURGERY GRAND ROUNDS February 28, 2013 VERENA LIU, MD ROSEANNA LEE, MD Case Presentation 35 year old male referred from PMD with an asymptomatic palpable right neck mass PMH/PSH:
SUNY DOWNSTATE MEDICAL CENTER SURGERY GRAND ROUNDS February 28, 2013 VERENA LIU, MD ROSEANNA LEE, MD Case Presentation 35 year old male referred from PMD with an asymptomatic palpable right neck mass PMH/PSH:
New Approaches to Neuroimaging of Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy. Alexandra Binnie, HMS III Gillian Lieberman, M.D.
 New Approaches to Neuroimaging of Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy Alexandra Binnie, HMS III Gillian Lieberman, M.D. What is Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy (PML)? A demyelinating
New Approaches to Neuroimaging of Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy Alexandra Binnie, HMS III Gillian Lieberman, M.D. What is Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy (PML)? A demyelinating
Brain Tumor 101. Shanna Armstrong, RN Neuro Oncology Nurse Clinician UC Brain Tumor Center
 Brain Tumor 101 Shanna Armstrong, RN Neuro Oncology Nurse Clinician UC Brain Tumor Center Objectives Identify the different parts of the brain Describe how each part of the brain works Connect each part
Brain Tumor 101 Shanna Armstrong, RN Neuro Oncology Nurse Clinician UC Brain Tumor Center Objectives Identify the different parts of the brain Describe how each part of the brain works Connect each part
Targeted Therapy What the Surgeon Needs to Know
 Targeted Therapy What the Surgeon Needs to Know AATS Focus in Thoracic Surgery 2014 David R. Jones, M.D. Professor & Chief, Thoracic Surgery Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center I have no disclosures
Targeted Therapy What the Surgeon Needs to Know AATS Focus in Thoracic Surgery 2014 David R. Jones, M.D. Professor & Chief, Thoracic Surgery Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center I have no disclosures
The Center for Prostate Cancer. Personalized Treatment. Clinical Excellence.
 The Center for Prostate Cancer Personalized Treatment. Clinical Excellence. The Center for Prostate Cancer Leaders in Prostate Cancer Treatment and Research The Center for Prostate Cancer at the North
The Center for Prostate Cancer Personalized Treatment. Clinical Excellence. The Center for Prostate Cancer Leaders in Prostate Cancer Treatment and Research The Center for Prostate Cancer at the North
Advanced MRI methods in diagnostics of spinal cord pathology
 Advanced MRI methods in diagnostics of spinal cord pathology Stanisław Kwieciński Department of Magnetic Resonance MR IMAGING LAB MRI /MRS IN BIOMEDICAL RESEARCH ON HUMANS AND ANIMAL MODELS IN VIVO Equipment:
Advanced MRI methods in diagnostics of spinal cord pathology Stanisław Kwieciński Department of Magnetic Resonance MR IMAGING LAB MRI /MRS IN BIOMEDICAL RESEARCH ON HUMANS AND ANIMAL MODELS IN VIVO Equipment:
Moving Beyond RECIST
 Moving Beyond RECIST Ihab R. Kamel, M.D., Ph.D. [email protected] Associate Professor Clinical Director, MRI Department of Radiology The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Outline Standard measures
Moving Beyond RECIST Ihab R. Kamel, M.D., Ph.D. [email protected] Associate Professor Clinical Director, MRI Department of Radiology The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Outline Standard measures
AMERICAN BRAIN TUMOR ASSOCIATION. Meningioma
 AMERICAN BRAIN TUMOR ASSOCIATION Meningioma AcKnoWLeDGemenTs about the american BraIn tumor association Founded in 1973, the American Brain Tumor Association (ABTA) was the first national nonprofit organization
AMERICAN BRAIN TUMOR ASSOCIATION Meningioma AcKnoWLeDGemenTs about the american BraIn tumor association Founded in 1973, the American Brain Tumor Association (ABTA) was the first national nonprofit organization
Corporate Medical Policy Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) of the Prostate
 Corporate Medical Policy Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) of the Prostate File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: intensity_modulated_radiation_therapy_imrt_of_the_prostate
Corporate Medical Policy Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) of the Prostate File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: intensity_modulated_radiation_therapy_imrt_of_the_prostate
Local control in ductal carcinoma in situ treated by excision alone: incremental benefit of larger margins
 The American Journal of Surgery 190 (2005) 521 525 George Peter s Award Winner Local control in ductal carcinoma in situ treated by excision alone: incremental benefit of larger margins Heather R. MacDonald,
The American Journal of Surgery 190 (2005) 521 525 George Peter s Award Winner Local control in ductal carcinoma in situ treated by excision alone: incremental benefit of larger margins Heather R. MacDonald,
Radiation Oncology Nursing Care. Helen Lusby Radiation Oncology Nurse BAROC 2012
 Radiation Oncology Nursing Care Helen Lusby Radiation Oncology Nurse BAROC 2012 Definitions Radiation Therapy: Treatment of cancer using x- ray particles that cause ionisation within the cells. External
Radiation Oncology Nursing Care Helen Lusby Radiation Oncology Nurse BAROC 2012 Definitions Radiation Therapy: Treatment of cancer using x- ray particles that cause ionisation within the cells. External
Potential Benefits of Proton Therapy in Clinic
 Potential Benefits of Proton Therapy in Clinic Simone Pieplenbosch Proton therapy offers great potential in cancer treatment compared with the conventional photon therapy. The advantages of the unique
Potential Benefits of Proton Therapy in Clinic Simone Pieplenbosch Proton therapy offers great potential in cancer treatment compared with the conventional photon therapy. The advantages of the unique
Management of spinal cord compression
 Management of spinal cord compression (SUMMARY) Main points a) On diagnosis, all patients should receive dexamethasone 10mg IV one dose, then 4mg every 6h. then switched to oral dose and tapered as tolerated
Management of spinal cord compression (SUMMARY) Main points a) On diagnosis, all patients should receive dexamethasone 10mg IV one dose, then 4mg every 6h. then switched to oral dose and tapered as tolerated
Proton Therapy Center Czech
 Proton Therapy Center Czech The main goal of radiotherapy is to irreversibly damage tumor cells, whereas the cells of healthy tissue are damaged only reversibly or not at all. Proton therapy currently
Proton Therapy Center Czech The main goal of radiotherapy is to irreversibly damage tumor cells, whereas the cells of healthy tissue are damaged only reversibly or not at all. Proton therapy currently
Update on thyroid cancer surveillance and management of recurrent disease. Minimally invasive thyroid surgery
 Update on thyroid cancer surveillance and management of recurrent disease Minimally invasive thyroid surgery July 2006 Michael W. Yeh, MD Program Director, Endocrine Surgery Assistant Professor, David
Update on thyroid cancer surveillance and management of recurrent disease Minimally invasive thyroid surgery July 2006 Michael W. Yeh, MD Program Director, Endocrine Surgery Assistant Professor, David
There must be an appropriate administrative structure for each residency program.
 Specific Standards of Accreditation for Residency Programs in Radiation Oncology 2015 VERSION 3.0 INTRODUCTION The purpose of this document is to provide program directors and surveyors with an interpretation
Specific Standards of Accreditation for Residency Programs in Radiation Oncology 2015 VERSION 3.0 INTRODUCTION The purpose of this document is to provide program directors and surveyors with an interpretation
RESEARCH EDUCATE ADVOCATE. Just Diagnosed with Melanoma Now What?
 RESEARCH EDUCATE ADVOCATE Just Diagnosed with Melanoma Now What? INTRODUCTION If you are reading this, you have undergone a biopsy (either of a skin lesion or a lymph node) or have had other tests in which
RESEARCH EDUCATE ADVOCATE Just Diagnosed with Melanoma Now What? INTRODUCTION If you are reading this, you have undergone a biopsy (either of a skin lesion or a lymph node) or have had other tests in which
MesoPDT. Photodynamic Therapy for malignant pleural mesothelioma ONCO-THAI. Image Assisted Laser Therapy for Oncology
 MesoPDT Photodynamic Therapy for malignant pleural mesothelioma ONCO-THAI Image Assisted Laser Therapy for Oncology Unité Inserm ONCO-THAI «Image Assisted Laser Therapy for Oncology» Inserm ONCO-THAI "Image
MesoPDT Photodynamic Therapy for malignant pleural mesothelioma ONCO-THAI Image Assisted Laser Therapy for Oncology Unité Inserm ONCO-THAI «Image Assisted Laser Therapy for Oncology» Inserm ONCO-THAI "Image
The Science behind Proton Beam Therapy
 The Science behind Proton Beam Therapy Anthony Zietman MD Shipley Professor of Radiation Oncology Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Principles underlying Radiotherapy Radiation related
The Science behind Proton Beam Therapy Anthony Zietman MD Shipley Professor of Radiation Oncology Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Principles underlying Radiotherapy Radiation related
OBJECTIVES By the end of this segment, the community participant will be able to:
 Cancer 101: Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Linda U. Krebs, RN, PhD, AOCN, FAAN OCEAN Native Navigators and the Cancer Continuum (NNACC) (NCMHD R24MD002811) Cancer 101: Diagnosis & Staging (Watanabe-Galloway
Cancer 101: Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Linda U. Krebs, RN, PhD, AOCN, FAAN OCEAN Native Navigators and the Cancer Continuum (NNACC) (NCMHD R24MD002811) Cancer 101: Diagnosis & Staging (Watanabe-Galloway
The Di Bella Method (DBM) improves Survival, Objective Response and Performance Status in Breast Cancer
 BIT's 4th World Cancer Congress 2011 People s Republic of China Dalian The Di Bella Method (DBM) improves Survival, Objective Response and Performance Status in treated with DBM therapy Retrospective observational
BIT's 4th World Cancer Congress 2011 People s Republic of China Dalian The Di Bella Method (DBM) improves Survival, Objective Response and Performance Status in treated with DBM therapy Retrospective observational
THYROID CANCER. I. Introduction
 THYROID CANCER I. Introduction There are over 11,000 new cases of thyroid cancer each year in the US. Females are more likely to have thyroid cancer than men by a ratio of 3:1, and it is more common in
THYROID CANCER I. Introduction There are over 11,000 new cases of thyroid cancer each year in the US. Females are more likely to have thyroid cancer than men by a ratio of 3:1, and it is more common in
Supportive Care For Patients With High-Grade Glioma (primary brain tumours) Dr Susan Catt & Professor Lesley Fallowfield
 Supportive Care For Patients With High-Grade Glioma (primary brain tumours) Dr Susan Catt & Professor Lesley Fallowfield Partners Mr Giles Critchley Consultant Neurosurgeon Hurstwood Park Neurological
Supportive Care For Patients With High-Grade Glioma (primary brain tumours) Dr Susan Catt & Professor Lesley Fallowfield Partners Mr Giles Critchley Consultant Neurosurgeon Hurstwood Park Neurological
Disease/Illness GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER. What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? www.simpsonmillar.co.uk Telephone 0844 858 3200
 GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) for Thyroid Cancer
 Thyroid Science 5(1):CLS1-8, 2010 www.thyroidscience.com Clinical and Laboratory Studies Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) for Thyroid Cancer 1 2 5 Aruna Turaka, MD, Tianyu Li, MS, Jian Q. Yu,
Thyroid Science 5(1):CLS1-8, 2010 www.thyroidscience.com Clinical and Laboratory Studies Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) for Thyroid Cancer 1 2 5 Aruna Turaka, MD, Tianyu Li, MS, Jian Q. Yu,
Tricia Cox on 7/18/2012 at Oncology Center. Sarah Randolf. Female
 SAMPLE This Survivorship Care Plan will facilitate cancer care following active treatment. It may include important contact information, a treatment summary, recommendations for follow-up care testing,
SAMPLE This Survivorship Care Plan will facilitate cancer care following active treatment. It may include important contact information, a treatment summary, recommendations for follow-up care testing,
Clinical Trials and Radiation Treatment. Gerard Morton Odette Cancer Centre Sunnybrook Research Institute University of Toronto
 Clinical Trials and Radiation Treatment Gerard Morton Odette Cancer Centre Sunnybrook Research Institute University of Toronto What I will cover.. A little about radiation treatment The clinical trials
Clinical Trials and Radiation Treatment Gerard Morton Odette Cancer Centre Sunnybrook Research Institute University of Toronto What I will cover.. A little about radiation treatment The clinical trials
PROTON THERAPY FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
 PROTON THERAPY FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS Table of contents 1. What is cancer?... 2 2. How is cancer treated?... 3 3. What is proton therapy?... 4 4. What are the clinical benefits of proton therapy?...
PROTON THERAPY FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS Table of contents 1. What is cancer?... 2 2. How is cancer treated?... 3 3. What is proton therapy?... 4 4. What are the clinical benefits of proton therapy?...
The TV Series. www.healthybodyhealthymind.com INFORMATION TELEVISION NETWORK
 The TV Series www.healthybodyhealthymind.com Produced By: INFORMATION TELEVISION NETWORK ONE PARK PLACE 621 NW 53RD ST BOCA RATON, FL 33428 1-800-INFO-ITV www.itvisus.com 2005 Information Television Network.
The TV Series www.healthybodyhealthymind.com Produced By: INFORMATION TELEVISION NETWORK ONE PARK PLACE 621 NW 53RD ST BOCA RATON, FL 33428 1-800-INFO-ITV www.itvisus.com 2005 Information Television Network.
