Pearls in Cosmetic Oculofacial Plastic Surgery
|
|
|
- Ashlynn Reynolds
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 2 Pearls in Cosmetic Oculofacial Plastic Surgery Jonathan A. Hoenig 2 Core Messages Analyze the Face in Layers: Aging occurs in the skin, muscle, fat, and bony layers. The key for successful and consistent results is to define the anatomic problem and select procedures that address these problems. Do not sacrifice function for beauty. It is imperative that the patient and surgeon come to an understanding that function always supersedes beauty. The eyelids are unique in that they serve a vital function: to protect the eye. It is sometimes difficult for the patient to understand that, for example, the wrinkles that are still present after surgery are in actuality the skin necessary for eyelid closure. Endoscopic Brow Lift: The goal of a brow lift is less about lifting and more about contouring the shape of the brow. In women, the brow is elevated in a superior/medial vector. In men, the brow is elevated superiorly so that the brow becomes straight and forms a T configuration with the nose. Upper Blepharoplasty: An upper blepharoplasty procedure cannot cure brow ptosis. If the brow is ptotic, correct the brow. The goal of upper blepharoplasty is definition and subbrow fullness. Blepharoplasty is not about how much skin and fat you take out but how much tissue you leave in. Preserving the pretarsal and preseptal orbicularis is necessary for proper eyelid function. Lower Blepharoplasty: The goal of lower blepharoplasty is restoration of the youthful contour of the eyelid and midface. This consists of a vertically short lower eyelid and a full, convex midface. Analysis of the lower eyelid involves the relationship between the globe and inferior orbital rim projection, orbital fat protrusion, and midfacial fat loss and skin elasticity versus excess. 2.1 General Introduction Twenty years ago, life for the oculoplastic surgeon was relatively simple. If a patient presented with a problem, there were limited options to address the problem. As surgeons, we were good at removing tissue: fat, muscle, and skin. For example, if a patient presented with lower eyelid bags, the fat was always removed, while the skin would either be removed or be resurfaced. Most patients were treated in a similar manner despite significant anatomic differences. Most surgeons and patients were relatively happy with the surgical results. The reality is that we did not know any better. Then came the Internet. The Internet allowed patients and physicians to share and gather information. We all became more sophisticated. A variety of injectable fillers came on the market. Our whole philosophy of the aging process suddenly changed. Today, we are blessed with an array of options to rejuvenate the periocular region. There are multiple surgical and nonsurgical options. However, with all the various options, confusion ensues. What technique do we use to rejuvenate the lower eyelids? Do we use filler or fat? Who needs a transcutaneous blepharoplasty, and who is a better candidate for a transconjunctival incision? I often hear, What about a midface lift, doctor? My friend read on the Internet that to fix lower eyelid bags you need to put in an orbital rim implant. How about a laser or a peel? The combination of solutions can get dizzying. This chapter summarizes my personal experience and philosophy on what techniques seem to be the most effective. Many of these ideas are based on work described by others. The purpose of this chapter is to show the reader and surgeon my path through the mountain of options that are now available. The chapter is organized into sections for brow lifts, upper blepharoplasty, and lower
2 22 2 Pearls in Cosmetic Oculofacial Plastic Surgery 2 blepharoplasty (which also includes information on fillers and midface augmentation). 2.2 The Aging Process and Facial Analysis The face is created in layers. The sturdiest of these layers is the skeletal bones. The contour and configuration of these bones truly defines the facial shape and soft tissue positions. In many instances, prominent bony contours act as a scaffold and prevent soft tissue descent. This is an important concept since augmenting the bones and deep tissues with implants, fat, or fillers will lift the face to some degree (Fig. 2.1). The outermost layer of the face is the skin, which bears the brunt of environmental exposure. Between the bones and skin lay fat and muscular layers. In general, there are superficial and deep muscular layers known as the SMAS (superficial musculoaponeurotic system) and DMAS (deep musculoaponeurotic system) [32, 31, 46]. Aging occurs in all four layers: bone, muscle, fat, and skin. As we age, we lose bone around the eyes and mouth [30]. The vertical height of the orbit elongates, and the inferior orbital rim and maxillary face retrude [35]. There is also loss of bone in the mandible, and it also has a loss of its vertical dimension (Fig. 2.2). The muscles of the face stretch and become ptotic, resulting in jowls and neck laxity. There is loss of fat in the eyelid region, cheeks, and buccal space (Fig. 2.3). Some patients gain fat in the jowl region and neck. Finally, the skin undergoes significant changes [25]. The skin thins by losing dermal thickness. The dermal collagen becomes irregular and disorganized. Clinically, the skin has an increase in pigmented spots and wrinkles. Analyzing the face in layers and defining the problem in each layer is paramount to designing a specific individualized solution for each patient. This approach allows the surgeon to decide which procedure and treatment are needed for each patient. I like to compare facial surgery to building a house. When a house is constructed or repaired, the contractor looks at the foundation, internal beams, walls, and finally the paint. This is analogous to Fig. 2.2 Loss of bone in the mandible contributes to the appearance of a jowl (arrow). This prejowl sulcus is often due to loss of bone in this region a b Fig. 2.1 (a and b) Two patients who are of the same age. Patients with prominent bony contour have less soft tissue ptosis. The heart-shaped face is considered more youthful than the rectangular-shaped face
3 2.3 Endoscopic Brow Lift 23 a b Fig. 2.3 (a) Overall loss of facial fat, especially in the temples, buccal space, and jawline. (b) Loss of fat in the periorbital region with gain of fat in the submentum the face: We analyze the bones, muscles, fat, and skin. We all understand the concept that rebuilding the foundation of the house does little for the outside paint. Similarly, removing protruding eyelid fat in a patient with significant skin changes does little to improve the skin. I find it helpful to have workup sheets available for the evaluation of the patient. This forces the surgeon to analyze the various layers and come up with specific solutions. Table 2.1 is an example of my facial analysis workup sheet. Summary for the Clinician Analyze the face in layers: skin, muscle fat, and bone. Remember, aging occurs in all of these layers. A prominent underlying skeleton acts as a scaffold to support the soft tissue. Define the problem. Design a solution that addresses the specific anatomic abnormality. 2.3 Endoscopic Brow Lift Introduction The reestablishment of the structural integrity of the eyebrow is fundamental to achieving an aesthetically acceptable surgical result for cosmetic and functional periocular surgery [41]. Patients often present to the aesthetic surgeon complaining of excess upper eyelid skin and request blepharoplasty. However, when the eyebrows are raised to their normal position, there is often less redundant upper eyelid skin than anticipated, and the required amount of skin removal during blepharoplasty is significantly reduced [40, 47]. Malposition of the eyebrows can often be overlooked. Many patients reflexively raise the eyebrows with their frontalis muscles to lift the eyebrow and eyelid tissue out of the visual axis. These patients develop furrows in the forehead region due to the constant contraction of the frontalis muscles (Fig. 2.4). It is the surgeon s task to ensure that the patient s frontalis muscles are completely relaxed prior to assessing the eyebrow position and excess upper eyelid skin. The eyebrow region ages by deflation as well as descent. As we age, we lose volume in the subbrow fat pad known as the ROOF (retro orbicularis oculi fat) [29]. This deflation contributes to the hooding that occurs in the brow and upper eyelid region (Fig. 2.5). The forehead and eyebrows are also under the constant influence of downward forces of both gravity and the periorbital protractor muscles (orbicularis oculi, procerus, and corrugator and depressor supercilii). These downward forces are opposed by the elevating action of the frontalis muscle. In time, this constant tug-of-war between the downward and upward forces leads to a series of wrinkles in the forehead and downward displacement of the eyebrows and eyelids. The lateral portion of the brow tends to descend in an inferomedial vector due in part to the lack of frontalis muscle in this
4 24 2 Pearls in Cosmetic Oculofacial Plastic Surgery Table 2.1. Jonathan Hoenig, M.D. New Patient Consultation 2 CHIEF COMPLAINT HISTORY OF PRESENT ILLNESS: MAJOR CONCERNS: PHYSICAL EXAMINATION Scalp: Hair Density Length of Forehead CM Forehead: Brow Ptosis Forehead Rhytids: Glabella Rhytids Solar Damage: Bony Contour: Normal Abnormal EYELIDS: Ptosis: None OD OS PF LF MRD 1 Responds to Neosynephrine Lower Eyelids: Laxity: None OD OS Retraction: None OD mm OS mm Fat Herniation: None OD OS Orbicularis Strength: Upper Eyelid: OD OS Lower Eyelid OD OS Periorbital Rhytids: Static: OD OS Dynamic: OD OS EYELID cont. Skin Excess: Upper OD OS Lower OD OS Other: Ectropion Entropion Lesions: PHOTOS/DRAWINGS
5 2.3 Endoscopic Brow Lift 25 Table 2.1. (continued) MIDFACE Infraorbital bony status: Normal Hypoplasia Infraorbital Soft Tissue Dent None Central Midfacial Contour Lateral Midfacial Contour Festoons: None Preseptal Orbital Malar Mounds NASOLABIAL FOLD Right: Left: JOWLS Right: Left: PARACHUTE Right: Left: NECK LIPOMATOSIS Right: Left: PLATYSMAL BANDS Right: Left: SKIN LAXITY Right: Left: MIMETIC MUSCLE STRENGTH/NEURO SENSORY Frontal: R L V-1 Normal Abnormal Zygomatic: R L V-2 Normal Abnormal Buccal R L V-3 Normal Abnormal Mandibular R L G Auricular Normal Abnormal SKIN Fitzpatrick Classification Glagou Classification Lentigines Actinic Keratoses: Acne Vulgaris: Acne Rosacea Scars: Pigmentary Disturbances IMPRESSION: PLAN: Common Risks Bleeding Bruising Scarring Submandibular Gland Ptosis Change of Vision Loss of Vision Eyelid Malposition Tearing Persistent Wrinkles Persistent Swelling Changes in Skin Color Asymmetry Change in Shape of Eyes or Face Persistent Droopiness Loss of Fat Infection Contour Irregularities Need for Additional fat Skin Necrosis Persistent Neck Prominence Visible Submandibular Glands Extrusion or Infection of Implant Sensory and Motor Nerve Damage Loss of Hair Persistent Droopiness Unrealized Expectations portion of the brow as well as the sphincter action of the orbicularis oculi muscles [14]. There are many methods to raise the ptotic brow [19]. However, it is important for the surgeon to understand that the purpose of a brow lift is partly to raise the brow but more important to reshape the contour of the brow. Most female patients benefit from elevation of the lateral half of the brow only, thereby restoring the youthful arch of the brow. Men, on the other hand, require a straight brow that is less arched and sits lower than the female brow. The endoscopic forehead lift has now become the most popular method of raising the eyebrows and forehead.
6 26 2 Pearls in Cosmetic Oculofacial Plastic Surgery Endoscopic Browlift Anesthesia Pearls 2 Many facial surgical procedures can be performed under local anesthesia. The endoscopic brow lift, however, is typically performed with intravenous sedation due to the difficulty in anesthetizing the glabella region. Fig. 2.4 This patient has significant dermatochalasis, eyelid ptosis, and brow ptosis. The brow ptosis can be overlooked since the patient reflexively raises his eyebrows to pull the skin out of his visual axis. Note the deep wrinkles of his forehead. The horizontal lines are due to frontalis contraction. The vertical lines are sleep lines. These lines form when a pillow pushes his forehead tissues medially when sleeping face down (a) Avoid Bleeding: Use ml of tumescent anesthesia [24] to balloon up the scalp and forehead tissues. This compresses the blood vessels, separates out the layers, and reduces the chances of bleeding and nerve damage. The anesthetic is placed in a ring pattern starting from just above the ears, across the coronal line, and across the brows. (b) Tractional Nerve Pain: As the brow is released and elevated, there is traction on the sensory nerves. The traction extends to the posterior orbit, and the patient will feel pain and will be quite uncomfortable. To avoid the pain, perform supraorbital, supratrochlear, zygomaticotemporal, and zygomaticofacial nerve blocks with Septocaine or Marcaine. Extend the supraorbital block into the anterior, superior orbit. (c) Decrease the Amount of Sedatives: Have the anesthesiologist sedate the patient with propofol and then add mg ketamine IV [2]. The ketamine will act synergistically with the propofol and allow the anesthesiologist to use less sedative. Giving the propofol first will reduce the potential ketamine side effect of bad dreams Endoscopic Browlift Surgical Procedure Pearls Fig. 2.5 Deflation of the sub-brow fat pad (ROOF) contributes to the aging appearance of the brow. Reinflation of this region restores the more youthful three-dimensional contour of the eyebrow This procedure can achieve elevation of the eyebrows and reduction of forehead furrows and glabellar folds. The aesthetic success of the endoscopic approach is similar to a coronal lift without the need for a large incision. Pearls of the endoscopic lift are separated into three sections: anesthesia, surgical procedure, and postoperative care. (a) Vertical Incisions: Make all the incisions vertical and not horizontal. Vertical incisions, unlike horizontal ones, are almost never visible [19] (Fig. 2.6). (b) Lacrimal Retractors: Use a lacrimal retractor to keep the incisions open. The retractors will compress the edge of the incisions, thereby reducing the bleeding. The retractors make it easy to insert the endoscope and prevent blood from getting on the lens (Fig. 2.7). (c) Blind Dissection: 90% of the surgery can be performed without the use of an endoscope. Blind, subperiosteal dissection can be performed centrally until 2 cm above the brow. Laterally, dissection along the deep temporalis fascia can be performed easily with just headlight illumination. (d) Periosteal Elevators: A suction elevator with a lipdown configuration is an excellent tool to dissect along the deep temporalis fascia and for the blind subperiosteal dissection (Fig. 2.8).
7 2.3 Endoscopic Brow Lift 27 Fig. 2.6 Five vertical incisions are typically made in the temples and central and paracentral scalp Fig. 2.8 Elevators with a downward curvature help dissect in the subperiosteal plane pull is determined. In general, the brow is pulled posteriorly and shifted medially. This allows elevation of the tail of the brow without getting the surprised look. (h) Fat Transfer: Aging of the brow is mostly due to ptosis but also can be due to deflation of the subbrow fat pad. Adding fat in the subbrow plane will restore the three-dimensional contour of the brow and give a more natural look [26] (Fig. 2.10) Endoscopic Browlift Postoperative Care Pearls Fig. 2.7 Standard lacrimal retractors are used to keep the scalp incisions open, which reduces bleeding and prevents hair from getting dragged into the wound (e) Adequate Release: The key to getting a good lift is to free the attachments of the brow along the lateral orbit [45]. Superiolateral to the lateral canthus, a tendonous attachment of the orbicularis is noted. Use a standard facelift scissors to cut this tendon. This will elevate the lateral brow. (f) The Central Brow: Do not overelevate the central brow. This will result in a surprised look. Aggressive release or excision of the corrugator muscle will cause the medial brow to drift upward. I usually do not cut the periosteum medial to the supratrochlear nerves (Fig. 2.9). (g) Up-and-In Vector: After the entire scalp is mobile and the brow is ready for fixation, the direction of (a) Postop Nausea: Nausea after a brow lift is often attributed to the anesthesia. I find that patients with a short forehead (short distance between the brows and the hairline) are more likely to get nauseous no matter what kind of anesthesia is used. Identify these patients prior to surgery and give them antiemetics. I ask the patients to place a scopolamine patch in the posterior auricular region a day before surgery and keep it in place for 48 h [27]. (b) Dressings: Head wraps or other pressure dressings do little to prevent swelling or bruising. All they do is make the patient feel uncomfortable. A loose dressing can be used to hold drains in place, if used. (c) Drains: I rarely use drains. However, when there is some oozing of the veins in the supraorbital region, a small drain is used and will reduce the bruising. I use a modified butterfly tubing, in which I cut additional small holes along the length of the tube. The butterfly tube is placed just above the brow and is brought out through the temporal incision.
8 28 2 Pearls in Cosmetic Oculofacial Plastic Surgery a b 2 Fig. 2.9 (a) Pre operative photo of brow lift patient. The goal of surgery in the early to mid 1990 s was to release the entire brow and pull the brow as high as possible. (b) Release of the central glabella periosteum and aggressive resection of the procerus muscle lead to over-elevation of the central brow a b c d Fig (a and b) Pre and post-operative photos of patient who underwent brow lift, blepharoplasty with insertion of fat to the sub-brow region. (c and d): Pre and post-operative photos of patient who underwent brow lift, insertion of fat to the sub-brow region without a blepharoplasty
9 2.4 Upper Blepharoplasty 29 It is then attached to a red-top blood collection tube. (d) Showering: Have patients shower and wash their hair on postop day 2. This will get the incisions clean and make the patients feel much better. (e) Strict Salt Avoidance: Canned foods, Asian food, and Mexican food all have high sodium content. Eating these in the early postop period will result in a lot of swelling. (f) Sleeping Pattern: Have patients sleep on the back for the first 2 weeks after surgery. Sleeping on the side or on the stomach will cause the edema to settle in the eye region. A cervical pillow, available at most back stores, will help the patients unaccustomed to sleeping on the back. (g) Botox : Inject Botox in the glabella region within the first week of surgery. This will weaken the brow depressors and prevent the brow from getting pulled down during the first 3 months after surgery. This will increase the longevity of the browlift results [4]. During the first postoperative week, the brow and forehead region is typically numb, and the patients do not mind the injections. Summary for the Clinician: Endoscopic Brow Lift Tumesce the incisions and supraorbital region. Use Septocaine for nerve blocks, propofol and ketamine intravenously. Make short, vertical incisions. Add volume: Learn how to inject fat. Shift the forehead up and in. Botox the brow depressors postop. Identify the short-forehead patients; have them use scopolamine. 2.4 Upper Blepharoplasty Introduction The upper eyelid forms the lowest portion of the forehead/eyebrow/eyelid continuum. As noted, it is extremely important to take into account brow position before deciding on the degree of laxity of the upper eyelids. The eyelids are unique in that they are regarded in both their aesthetic and functional sense. It is imperative that the surgeon prioritize function over beauty Patient Evaluation Patients presenting for blepharoplasty are evaluated in a similar manner to those patients presenting for brow lift. The eyelids are evaluated in layers: skin, muscle, fat, and bone. The skin of the eyelid is extremely thin and stretches over time. When considering the amount of skin that is redundant, it is important to keep in mind that there is a minimal amount of skin that is necessary to ensure proper eyelid function [39]. Patients with prominent eyes will require more skin since the eyelid has to cover a greater convex surface. It is also imperative that the surgeon keep in mind that the degree of dermatochalasis is based on brow position. Due to gravitational effects, the position of the eyebrow will be lower when the patient is upright. When the patient is supine, the brow will be in a higher position, thus requiring more skin for the eyelids to close properly. This is the reason why many patients who seem to have enough eyelid skin when we evaluate them in our office actually have nocturnal lagophthalmus. The most important concept in blepharoplasty is not about how much skin you take out but how much you leave. Remember also that a blepharoplasty cannot cure brow ptosis. The orbicularis oculi is separated into three portions: pretarsal, preseptal, and orbital. The pretarsal and preseptal portions of the eyelid are needed for proper eyelid closure [36]. Removal of too much orbicularis oculi muscle will affect blinking and lead to dry eyes. For this reason, currently we remove less muscle during blepharoplasty than we did in the past. The upper eyelid fat pockets contribute to the fullness of the upper eyelids [34]. In decades past, a hollow upper lid with a high lid crease was considered aesthetically pleasing. Fullness is now in vogue and considered a sign of youth. It is the role of the surgeon to decide how much upper eyelid fat to remove. In general, I remove a moderate amount of the medial fat pad while removing little to none of the central eyelid fat pad. The sub-brow fat pad known as the ROOF is evaluated. As we age, there is deflation of this fat, which contributes to the apparent redundancy of the eyebrow and eyelid skin. Reinflating this fat pad improves the threedimensional contours of the brow and eyelids. Hyaluronic acid fillers and fat are often used as substrates [10]. The bones of the orbit consist of the zygoma and the frontal bone. It is important to carefully evaluate the bony contour of the superior orbit. Asymmetries are noted as well as convexities and concavities of the bone. The larger the bone is, the greater the foundational effects the bone exerts on the overlying soft tissue. Thus, it is common to
10 30 2 Pearls in Cosmetic Oculofacial Plastic Surgery 2 see one brow higher than another due to more prominent bone on the side with the higher eyebrow. These asymmetries are difficult to correct by manipulating the soft tissue. The only long-standing solution is to correct the bony asymmetry. Upper blepharoplasty is a technically simple surgery. There are only a handful of upper blepharoplasty techniques that are utilized [8]. However, blepharoplasty is often combined with other procedures, such as volume enhancement of the subbrow, brow-lifting and brow-stabilizing techniques, ptosis repair, lacrimal gland repositioning [23], and upper eyelid crease formation. Knowing when these adjunct procedures are necessary is the key to achieving great results. The pearls of upper blepharoplasty are separated into those for anesthesia and procedures Upper Blepharoplasty Anesthesia Pearls Upper blepharoplasty can easily be performed under local anesthesia. For patients who are anxious, 10 mg of diazepam is given orally 45 min prior to surgery [18]. I find it helpful for the patients to cooperate during surgery by opening and closing their eyes. (a) Topical Anesthesia: Use a topical anesthetic to blunt the pain of the local injection [33]. A combination of tetracaine, lidocaine, and prilocaine cream is placed on the eyelid for 30 min prior to the procedure. (b) Local Anesthetic Choice: I prefer to use articaine (Septocaine) to inject the upper eyelids. Articaine is a dental anesthetic that is ph balanced and stings much less than lidocaine. It gives a dense block and is longer lasting than lidocaine. However, it takes several minutes to take effect. (c) Timing of Local Anesthetic Injection: I prefer to inject the local anesthetic prior to marking the upper eyelid. This puts the skin on stretch and gives me an accurate idea of the amount of eyelid skin. Since the pretarsal skin is on stretch, the location of the anticipated lid crease becomes more accurate Upper Blepharoplasty Surgical Procedure Pearls (a) Marking: The proposed new lid crease height is marked with a thin marking pen. The proposed skin incision is an ellipse that is greater in vertical dimension laterally. Typically in women, the inferior portion of the incision is marked at 9 10 mm. In a man, it is marked at 8 mm. In an Asian, depending on the tarsal height, it is 6 7 mm [6]. The inferior border of the eyebrow skin is marked. The eyebrow skin is thicker than the eyelid skin, and the junction between the eyebrow and eyelid skin can be easily determined. Do not use the inferior brow cilia as a guide since many women pluck these hairs. Measure mm inferior to the eyebrow/eyelid junction. This point will be the superior portion of the incision. This will guarantee that a minimum of mm of eyelid skin will be left in the eyelid after the blepharoplasty. In a more prominent eye, more skin is left than a deeper-set eye. (b) Skin/Muscle Excision: Traditionally, blepharoplasty involved removing the same amount of skin and muscle, usually in an en bloc fashion. Currently, none or a minimal amount of orbicularis oculi is removed. Thus, the skin is first excised and dissected off of the underlying muscle. If the goal of surgery is to volumize the region inferior to the superior orbital rim, no muscle is removed [8]. Fat can also be injected in the subbrow region. If a more sculpted look is desired, a small portion of the preseptal orbicularis is removed across the eyelid, usually more in the lateral portion of the lid. (c) Crease Formation in the Lateral Third of the Lid: Defining the contour of the lateral portion of the lid is key to achieving aesthetically acceptable results in blepharoplasty. In patients with brow ptosis, elevating the lateral portion of the brow will improve the contour of the lateral portion of the lid. In patients with minimal brow ptosis or those who refuse a brow lift, redefining the contour of the orbital rim will mitigate the illusion of hooding. This can be achieved by suturing the superior cut edge of the orbicularis to the arcus marginalis in the lateral third of the lid [50]. These sutures support the subbrow fat pad and invaginate the skin and orbicularis so that they follow the contour of the orbital rim (Fig. 2.11). (d) Management of Excess Lateral Skin: Often, there is excess skin in the lateral portion of the lid. To address this dog-ear, many surgeons extend the incision laterally toward the thicker lateral canthal skin. However, dissection and skin excision in the thick lateral orbital region often result in a visible scar. To manage the extra skin an M- plasty is used that reduces the length of the extended scar by 50% [1, 7, 47] (Fig. 2.12). (e) Volumizing the Brow: Increasing the volume of the brow results in a more aesthetically pleasing contour of the upper eyelid. The deflation of the subbrow fat pad contributes to the dermatochalasis of the upper
11 2.4 Upper Blepharoplasty 31 a b c d e f g h Fig (a, b, and c) The arcus marginalis is identified, and a suture is placed between the arcus and the superior cut edge of the orbicularis. (d) A second buried suture is placed laterally. (e) These sutures stabilize the brow and prevent descent. (f) The wound is closed. (g, h) Pre- and postoperative results of patient undergoing this procedure eyelid. Fat is suctioned from a donor region, usually the abdomen, and ml of fat are injected into the subbrow region through the open blepharoplasty incision (Fig. 2.13). (f) Do Not Neglect the Ptosis: Upper eyelid ptosis not only results in drooping of the upper eyelid but also changes in the lid crease as well as changes in the brow position. When patients have upper eyelid ptosis, they compensate for the ptosis by raising their eyebrows. This must be taken into account prior to undertaking a blepharoplasty. Furthermore, addressing the ptosis will add fullness to the upper eyelids. In general, it is easier and more predictable to perform a posterior ptosis repair than an anterior ptosis repair. If a patient responds to epinephrine, then he or she is a candidate for the posterior approach [37] (Fig. 2.14).
12 32 2 Pearls in Cosmetic Oculofacial Plastic Surgery a b M Plasty Ellipse 2 c d Fig (a) Upper blepharoplasty incision closed with lateral M plasty. (b) The M plasty reduces the scar length by 50% compared to a standard ellipse. (c and d) Pre- and postoperative patient who underwent upper blepharoplasty. The patient has excess lateral skin, which would force the incision to extend lateral to the canthus. The M plasty keeps the scar within the orbital region a b c Fig (a) Fat is transferred to the suborbicularis region of the subbrow with multiple passes using a cannula. (b and c) Pre- and postoperative results of blepharoplasty and fat transfer
13 2.5 Lower Blepharoplasty, Fillers, and Midface Augmentation 33 a b Fig Pre- and postoperative internal ptosis repair. Note the improvement in the hollowness of the upper lid and improvement of the lid crease Summary for the Clinician: Upper Blepharoplasty Remember: The upper eyelid is a continuum of the forehead. You cannot cure brow ptosis with a blepharoplasty. Preserve the orbicularis. Leave at least 23 mm of skin. Add volume: Use fat to augment the subbrow region. 2.5 Lower Blepharoplasty, Fillers, and Midface Augmentation Introduction The lower eyelid forms the upper portion of the eyelid/ midface continuum. The midface contributes to the overall contour and shape of the eyelids. Ideally, the lower eyelid follows the contour of the globe until it reaches the inferior orbital rim. At this point, there is a slight concavity. As we follow the lid inferiorly, it becomes more convex. As we age, however, the lower eyelid lengthens, and the concavities and convexities change [15]. The goal of lower blepharoplasty is to restore the youthful contour of the lower eyelid and midface [20, 21] (Fig. 2.15). Lower blepharoplasty is not about removing fat, skin, or muscle. Removal of this tissue may be a means to achieve this goal but not its primary purpose. The lower eyelids are unique in that they are regarded in both their aesthetic and functional senses. It is imperative that the surgeon prioritize function over beauty Patient Evaluation Patients presenting for blepharoplasty are evaluated in a similar manner to those patients presenting for all other facial procedures. The eyelids are evaluated in layers: skin, muscle, fat, and bone. The skin of the eyelid is extremely thin and stretches over time. When considering the amount of skin that is redundant, it is important to keep in mind that there is a minimum amount of skin that is necessary to ensure proper eyelid function. Patients are evaluated by putting the lower eyelid on maximal stretch. This involves having the patient open his or her mouth and looking up. The degree of skin excess is then assessed. Again, patients with prominent eyes will require more skin since the eyelid has to cover a greater convex surface. It is important to differentiate between loss of skin elasticity and actual skin excess. Loss of skin elasticity will result in rhytids, and skin may appear redundant. It is tempting to remove this skin. However, removal of this skin may result in lid retraction if there is truly no skin excess. It is often better to laser or peel the skin to improve the elasticity than to remove the skin (Fig. 2.16).
14 34 2 Pearls in Cosmetic Oculofacial Plastic Surgery a b 2 c d Fig (a, b) The youthful eyelid/midface complex involves a short eyelid and a single midfacial convexity. (c, d) The aged midface involves a long lower eyelid and a double convexity of the midface
15 2.5 Lower Blepharoplasty, Fillers, and Midface Augmentation 35 a b c Fig (a) Patient appears to have extra lower eyelid skin (b) Excess lower eyelid skin determination: maximal skin stretch can be achieved by having patients open their mouth while looking up. (c) When the skin is in maximal stretch there is little excess noted Laxity of the orbicularis results in sagging of the lower eyelid and a generalized aged appearance. The pretarsal and preseptal orbicularis are vital for proper eyelid function and position. Laxity of the orbicularis results in bowing of the lower eyelid, lid retraction, and festoon formation [12]. Traditional lower blepharoplasty involved removal of preseptal orbicularis and skin. The removal of this vital muscle invariably resulted in lid retraction to some degree. In some cases, the lids became cicatrized to the orbital rim, resulting in severe retraction and ectropion (Fig. 2.17). Once the muscle was removed, it was difficult to attain proper lid height and contour without extensive surgery, such as midface lifting or insertion of hard palate grafts [38]. As oculoplastic surgeons, we manage many of the complications of lower blepharoplasty. In the 1980s, the trend toward limited skin and muscle excision emerged, and transconjunctival blepharoplasty became popular [3] (Fig. 2.18). The transconjunctival blepharoplasty, however, only addressed the orbital fat and neglected the orbicularis laxity. The addition of pinch skin removal or laser resurfacing of the skin improved the skin but still did not address the underlying orbicularis [5]. Currently, in patients with skin and orbicularis issues, an orbicularis oculi plication blepharoplasty is performed. This procedure is described in Section Protrusion of the orbital fat results in fullness of the eyelids above the inferior orbital rim. This fullness is exacerbated by concavities of the midface, where loss of the suborbicularis oculi fat (SOOF) is common. I like to give the following analogy to the patients: The eyelid/ Fig Severe lid retraction and ectropion resulting from aggressive removal of skin and orbicularis during transcutaneous blepharoplasty midface is similar to a hill and a valley. If one is standing in a deep valley next to a hill, then the hill will appear higher. Once the valley is filled, the hill appears less high. Thus, removal of protruding fat (hill) in the face of a concavity inferior to the fat (valley) will create an even larger
16 36 2 Pearls in Cosmetic Oculofacial Plastic Surgery a 2 b Fig (a and b) Transconjunctival blepharoplasty combined with laser resurfacing: Pre and Postoperative photos Fig This patient has mild fat protrusion and significant infraorbital hollowness. The concavity extends from the medial to lateralmost portion of the eyelid. Removal of protruding orbital fat in this patient will make the hollowness worse concavity (greater valley). It is imperative that the blepharoplasty surgeon evaluate the contours of the lower eyelid and decide if fat removal, fat addition, or fat repositioning is indicated (Fig. 2.19). The inferior orbital rim and bony midface are evaluated. The contours of these bones significantly contribute to eyelid position [13]. The relationship between the anterior corneal surface and the inferior orbital rim is evaluated in the sagittal plane. Patients are grouped into three categories: negative vector (the globe projects anterior to the rim), neutral vector (the globe is in line with the inferior rim), and positive vector (the globe projects posterior to the rim) [11] (Fig. 2.20). Patients with a negative vector configuration have less midfacial support and are more at risk for lid malpositions and contour irregularities after transconjunctival fat removal or transcutaneous blepharoplasty. Patients with prominent eyes and severe negative vector configuration may benefit from midface implants and a midface lift (Fig. 2.21). The question of fat removal versus fat preservation and repositioning is daunting [17]. I have abided by the following general principals and have managed to get consistent results: In patients with a prominent eye, negative vector, and orbital fat protrusion, a fat-repositioning procedure is performed [42]. In patients with a deeperset eye, positive vector, and orbital fat protrusion, fat removal is acceptable (Table 2.2). The lower eyelids are probably the most difficult region of the face to rejuvenate. Attaining excellent and consistent results in lower eyelid surgery is dependent on proper evaluation of the anatomic problems and proper solutions to address these problems. Since there are so many anatomic variations among patients, there are multiple procedures that are available for lower eyelid rejuvenation. Often, a patient may require multiple procedures within the context of blepharoplasty to address each anatomic abnormality. For example, lower lid fat repositioning may be combined with orbicularis suspension and skin excision. Transconjunctival blepharoplasty may be combined with hyaluronic fillers and a chemical peel [22]. The pearls of lower blepharoplasty are separated into anesthesia and procedure sections.
17 2.5 Lower Blepharoplasty, Fillers, and Midface Augmentation 37 a b c Fig (a, b, and c) From left to right: positive vector, neutral vector, and negative vector. The negative vector patients are more at risk of complications of blepharoplasty. Fat is rarely removed in these patients. Fat repositioning or midface augmentation is more effective Lower Blepharoplasty Anesthesia Pearls Lower blepharoplasty is usually performed under local anesthesia with or without intravenous sedation. Patients who prefer to have the procedure in the office are given 10 mg of diazepam orally 45 min prior to surgery. I find it necessary for the patients to cooperate during surgery by opening and closing the mouth (for skin excision) and moving the eyes. Fig Severe midface retrusion with a very prominent eye. This patient would benefit from a midface lift with implants (a) Topical Anesthesia: A combination of tetracaine, lidocaine, and prilocaine cream is placed on the eyelid for 30 min prior to the procedure. (b) Local Anesthetic Selection: Similar to the upper eyelids, I prefer to use articaine as the anesthetic when injecting the lower eyelids [43]. Articaine gives a dense block and even allows me to perform midface dissection with minimal discomfort. Due to potential permanent paresthesia, articaine should not be injected directly into the nerve or the region of the infraorbital foramen. Table 2.2 Fat Removal Neutral or Positive Vector(Bone) Good SOOF and Subcutaneous Fat layers(fat) Can be Combined with Orbicularis Lifting(Muscle) Can Be Combined with Skin Excision or Resurfacing(Skin) Pure Transconjunctical Blepharoplasty Represents only 10 to 15% of My Cases Fat Transposition Negative Vector(Bone) Thin SOOF and Subcutaneous Fat layers(fat) Abundant Extruding Orbital Fat Can be Combined with Orbicularis Lifting(Muscle) Can Be Combined with Skin Excision or Resurfacing(Skin) Pure Transconjunctical Blepharoplasty Represents 15% of Cases
18 38 2 Pearls in Cosmetic Oculofacial Plastic Surgery Lower Blepharoplasty Surgical Procedure Pearls (a) Infralash Muscle Plication Blepharoplasty: This procedure is a modification of that described by Fagien [9]. Patients with true excess skin and laxity of the orbicularis are candidates for this procedure. The procedure is also useful in the management of festoons. Step 1: The lower eyelid skin and muscle are reinjected with dilute lidocaine with epinephrine to balloon up the skin. Step 2: Two traction sutures are placed through the gray line of the lower eyelid. The sutures are clamped to the towels on the forehead, thereby putting the lower eyelid on stretch. Step 3: A number 15 blade is used to make an incision from medial to lateral. Laterally, the incision extends about a centimeter and is angled slightly inferiorly. It can be hidden in a rhytid in this region. Step 4: The assistant places two fingers on the skin of the lower eyelid/cheek junction, thereby putting the eyelid on maximal stretch. Step 5: Scissors are used to dissect the skin off the underlying muscle. The dissection proceeds until the inferior orbital rim is reached. It is important to stay superficial and not to damage the underlying muscle. Pinpoint bleeding is cauterized at this point. If fat reposition or fat excision is necessary, it is performed at this point of the procedure. A small horizontal incision is made through the orbicularis, and the septum is buttonholed. Midface dissection can easily be performed through this small hole. Fat excision is also quite easy to perform through this hole. After the fat manipulation is completed, the orbicularis is closed with several 6 0 buried Vicryl sutures. The traction sutures are now released. Step 6: The degree of lower eyelid laxity is assessed. In 70% of cases, a lateral canthal plication suture is placed to tighten the lower eyelid margin. If severe laxity exists, a tarsal strip is performed. It is imperative that the lower eyelid hug the globe. The suture is replaced until the proper tension and proper position of the eyelid are achieved. Step 7: The orbicularis is grasped at a point inferomedial to the canthus. The muscle is then pulled superolateral and folded on itself. If this elevates the orbicularis in the desired manner, a buried, 5 0 PDS suture is then placed from this portion of the orbicularis to the periosteum just lateral to the canthus. Multiple sutures are placed progressively laterally, thereby securing the orbicularis to the periosteum. The imbrication of the orbicularis adds fullness to the lateral lower eyelid, where a crescent typically forms during the aging process. Step 8: The skin is pulled superiorly and laterally, and the patient is asked to open his or her mouth and look superiorly. A pilot cut is then made through the skin at the lateral canthal region. Skin is conservatively excised lateral to medial. Very little skin is excised medially. The skin is then closed in the subciliary region. The skin lateral to the canthus is similarly excised. If a dog-ear is noted, an M-plasty can be performed (Fig. 2.22). (b) Transconjunctival Fat Repositioning: The transconjunctival approach for fat repositioning is utilized in patients with minimal or no skin/muscle issues. The techniques of fat repositioning have been described in the past [16, 17, 28]. The following are some tips that will make the procedure easier (Fig. 2.23): Step 1: A transconjunctival incision is made with a fine-tipped cautery. The incision extends through the lower eyelid retractors. Step 2: Cotton-tipped applicators are used to dissect to the inferior orbital rim. The arcus marginalis becomes visible. If the lateral fat pocket is prolapsing but is not large enough to reposition, it is excised at this point in the surgery. Step 3: The cutting cautery is then used to cut through the arcus marginalis. Step 4: A Senn retractor is helpful for the midface dissection. The dissection plane is a combination of preperiosteal and subperiosteal. Subperiosteal dissection proceeds for about 1.5 cm medial and lateral to the location of the infraorbital nerve. It is not necessary to disinsert the origin of the levator labii superioris muscle that overlies the infraorbital nerve. Blunt dissection with cotton-tipped applicators is performed on the anterior surface of the muscle. Step 5: The fat pockets are dissected free from their attachments to create a rectangular pedicle. Two 4 0 gut sutures are tied together. The suture is passed through the leading edge of the fat and locked at the medial and lateral poles (similar to what is performed in strabismus surgery).
19 2.5 Lower Blepharoplasty, Fillers, and Midface Augmentation 39 a b c d e f g h i Fig (a) The lid is put on stretch with a traction suture placed through the margin. (b) A skin flap created until the orbital rim is reached (c) A suture is placed to plicate the canthal tendon (d) Orbicularis muscle is pulled superior/lateral and sutured to the periosteum. Several sutures are sequentially placed. (d) Excess skin is removed by making a pilot cut at the canthus. The excess skin is removed medial and lateral to this vertical incision after having the patient look up and open their mouth (f and g) Pre- and postoperative patient who underwent muscle plication blepharoplasty (h and i) Pre- and post operative patient who underwent muscle plication blephaoplasty, fat injections and upper blepharoplasty Step 6: The suture is then passed through the midface tissues and exits the skin. It is tied over a Telfa bolster. The medial, the central, and if necessary the lateral fat pockets are rotated into place as described. After the sutures are placed, it is important to check for ocular motility. If too much tension is placed on the fat, dimpling occurs on the exit site of the suture in attempted downgaze. If this occurs, the fat is further freed from its attachments until no movement is noted on the skin. Step 7: I find it helpful to place Microfoam tape on the lower eyelids and keep it in place for 5 to 7 days. This significantly reduces swelling and bruising. The tape and sutures are cut on the seventh postoperative day. (c) Lower Eyelid Fillers or Fat: Many patients now present wanting a quick fix to their problems with minimal downtime and low chance of complications. The introduction of the hyaluronic acid fillers (e.g., Restylane, Juvederm ) has allowed us to achieve these goals. The purpose of the lower eyelid fillers is to fill in the concavities of the infraorbital region [44]. This region begins at the inferior orbital rim and ends inferiorly at the lid cheek junction. Medially, the skin is extremely thin and is often discolored. The dark circles that many patients complain about are due to
20 40 2 Pearls in Cosmetic Oculofacial Plastic Surgery a b c 2 d e f g h i Fig Transconjunctival approach for fat repositioning. (a) Surgeon s view. Orbital fat is pushed posteriorly and the arcus marginalis is visualized. (b) Subperiosteal dissection is performed. (c) Medial and lateral pockets are dissected, and a double-armed 4 0 gut suture is passed along the leading edge with locking bites at the medial and lateral poles. (d) Senn retractor is placed in the subperiosteal pocket (e) Sutures are brought out through the skin and tied over a telfa bolster. (f and g) Pre- and postoperative photos of patient who underwent transconjunctival fat repositioning. (h and i) Pre- and postoperative photos of another patient who underwent transconjunctival fat repositioning the red color of the orbicularis muscle that shines through the thin, tan skin. The combination of these colors gives a purple appearance. There is minimal or no SOOF in this region of the eyelid. As we proceed laterally, the skin thickens slightly. Many patients have an indentation in the inferolateral portion of the lid. It is important that the patients understand that the filler will only fill in the concavity (valley). It may camouflage the protruding fat (hill) but will not remove it.
21 2.5 Lower Blepharoplasty, Fillers, and Midface Augmentation Choice of Fillers: I prefer to use Restylane under the eyes since clinically Restylane appears to be less hydrophilic than Juvederm. One of the problems with the hyaluronic fillers is that they absorb fluid. In some patients, a secondary fluid bag can develop inferior to where the filler is placed. This seems to occur less with Restylane than with Juvederm. 2. Anesthesia: I prefer to use a topical anesthetic that consists of lidocaine, tetracaine, and prilocaine. The anesthetic is placed on the lower eyelids and left in place for 20 min. Some patients will swell from the local anesthetic, which may result in a false sense of fullness. 3. Needle Choice: The Restylane box comes with a 30-gauge needle. I prefer to use a 32-gauge needle since it allows me to be more precise with the amount of filler that I place. It takes greater pressure to inject through a 32-gauge needle. The needle must be securely tightened to the syringe so it does not pop off during the injection. 4. Vertical Strands: The Restylane is injected vertically from the superior portion of the cheek to the lower eyelid. Multiple vertical strands are placed deep to the orbicularis. In patients with a deep tear trough deformity, a small amount of filler is placed directly under the skin (Fig. 2.24). 5. Undercorrect: It is important that one undercorrect the lower eyelid region. The filler will absorb fluid and puff out over the first few weeks after the filler is placed. I typically have the patient return in 2 3 weeks and place a little more filler if necessary (Fig. 2.25). 6. Avoid Bruising: As with all procedures, we ask our patients to refrain from aspirin products, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications, fish oils, and other herbal supplements for 10 days prior to the procedure. 7. Postprocedure Management: Patients are asked to avoid salt and high-sodium foods and to sleep on the back. At the 2-week follow-up visit, the eyelids are reassessed. If there are contour irregularities due to too much filler placement, dilute hyaluronidase can be used. I like to dilute the hyaluronidase and mold the filler. Full-strength hyaluronidase will take away all of the filler, which is unnecessary. (d) Midface Implants: There are many patients who present for lower eyelid bags who have significant midface retrusion. These patients have prominent globes, inferior orbital rim recession, or midfacial concavities (Fig. 2.26). Fig Restylane is placed from the thicker cheek skin to the eyelid. Vertical strands are placed deep to the orbicularis These patients appear to have significant bags of their lower eyelids. However, when the face is analyzed, one realizes that the protruding fat is in the same sagittal plane as the anterior corneal surface. The abnormality lies in the recessed inferior orbital rim and midface. Thus, the abnormality is a bony one. The best management of this problem is to augment the inferior orbital rim and midface [11, 48]. There are several implants that are available. The implants vary in thickness and material. The solid silicone tear trough implant (Implantech) is used in patients with a moderate tear trough deformity and thin skin. The implant is inserted subperiosteally, and the midface tissues are elevated over the implant. The medpore (Porex) orbital rim implants have a greater anterior projection. They come in several designs and sizes and vary depending on the degree of cheek augmentation [49]. They are also inserted subperiosteally and are secured in place with screw fixation, and the midface is elevated over the implant (Fig. 2.27).
22 42 2 Pearls in Cosmetic Oculofacial Plastic Surgery a b 2 Fig (a) Photo prior to Restylane to lower eyelids. (b) Photo of Restylane to lower eyelids with overcorrection on the left side. There is fullness medially just inferior to the tear trough region a b Fig (a) Significant midface retrusion: The globe is a centimeter anterior to the inferior orbital rim. (b) Lower midface concavity: The inferior orbital rim is in a good position, while the subrim is deficient
23 2.5 Lower Blepharoplasty, Fillers, and Midface Augmentation 43 a b c d Fig (a and b) Pre and post-operative photos of patient who underwent midface implants and midface lift. (c and d) Pre and post-operative photos of another patient who underwent midface implants and lift
24 44 2 Pearls in Cosmetic Oculofacial Plastic Surgery 2 Summary for the Clinician: Lower Blepharoplasty Define the anatomic abnormality: think layers. Learn how to do peels. To add volume use filler fat or implants. It is okay to excise skin but not muscle. Reposition fat in negative vector patients. For a bony abnormality, think a bony solution: implant. References 1. Asken S (1994) A modified M plasty. J Derm Surg Oncol 12(4): Badrinath S, Avramov MN, Shadrick M, et al. (2000) The use of ketamine-propofol combination during monitored anesthesia care. Anesth Analg 90: Baylis HI, Long JA, Groth MJ (1989) Transconjunctival lower eyelid blepharoplasty. Technique and complications. Ophthalmology 96(7): Carruthers, J Carruthers A (2009) The adjunctive usage of botulinum toxin. Derm Surg 24(11): Carter SR, Seiff SR, Choo PH, Vallabhanath P (2001) Lower eyelid laser rejuvenation: a randomized, prospective clinical study. Ophthalmol 108(3): Chen WP (1987) Asian blepharoplasty. J Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 3: Courtiss EH, Webster RC, White MF (1974) Use of double W plasty in upper blepharoplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 53(1): Fagien S (2002) Adavanced rejuvenate upper blepharoplasty. Enhancing aesthetics of the upper periorbita. Plast Reconstr Surg 110: Fagien S (2007) Lower blepharoplasty: blending the lid cheek junction with orbicularis muscle and lateral retinacular suspension. In: Fagien S (ed) Putterman s cosmetic and oculoplastic surgery. Elsevier, New York, Chap Finn J, Cox S (2007) Fillers in the periorbital complex. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am 15(1): Flowers RS (1993) Tear trough implants for the correction of tear trough deformity. Clin Plast Surg 20(3): Furnas DW (1993) Festoons, mounds and bags of the eyelids and cheek. Clin Plast Surg 20(2): Goldberg RA, Relan A, Hoenig JA (1999) Relationship of the eye to the bony orbit, with clinical applications. Aust N Z J Ophthalmol 6: Gunter JP, Antrobus SD (1997) Aesthetic analysis of the eyebrows. Plast Reconstr Surg 99: Hamra SR (1992) Repositioning of the orbicularis oculi muscle in composite rhytidectomy. Plast Reconstr Surg 90: Hamra ST ( 1995) Arcus marginalis release and orbital fat repositioning in midface rejuvenation. Plast Reconstr Surg 92(2): Hamra ST (1996). The role of orbital fat preservation in facial aesthetic surgery. A new concept. Clin Plast Surg 23(1): Harley DH, Collins DR (2008) Patient satisfaction after blepharoplasty performed as office surgery using oral medication with the patient under local anesthesia. Aesthetic Plast Surg 32(1): Hoenig JA (2005) Comprehensive management of eyebrow and forehead ptosis. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 38: Hoenig JA, Shorr, NS, Shorr J (1997) The suborbicularis oculi fat in aesthetic and reconstructive surgery. Int Ophthalmol Clin 37: Hoenig JA, Shorr NS, Goldberg R (1998) The versatile SOOF lift in oculoplastic surgery. Facial Plast Clin 6(2): Hoenig JA, Shorr NS, Morrow DM (2007) Chemical peel: eyelid and facial skin rejuvenation. In: Fagien S (ed) Putterman s cosmetic and oculoplastic surgery. Elsevier, New York, Chap Horton CE, Carraway JH, Potenza AD (1978) Treatment of a lacrimal gland bulge in blepharoplasty by repositioning the lacrimal gland. Plast Reconstr Surg 61(5): Klein JA (1990) Tumescent technique for regional anesthesia permits lidocaine dose of 35 mg/kg for liposuction. J Dermatol Surg Oncol 16: Kligman AM, Lauker RM (1988) Cutaneous aging: the difference between intrinsic aging and photoaging. J Cutan Aging Cosmet Dermatol 1: Kranendonk S, Obagi S (2007) Autologous fat transfer for periorbital rejuvenation: indications, techniques and complications. Dermatol Surg 33(5): Kranke P, Morin A, Roewer N, et al (2002) The efficacy and safety of transdermal scopolamine for the prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting: a quantitative systemic review. Anesth Analg 95: Loeb R (1981) Fat pad sliding and fat grafting for leveling lid depressions. Clin Plast Surg 8: May JW, Fearson J, Zingarelli P (1990) Retro-orbicularis oculi fat (ROOF) resection on aesthetic blepharoplasty a six year study in 63 patients. Plast Reconstr Surg 86: Mendelson BC, Hartley W, Scott, M (2007) Age-related changes of the orbit and midcheek and implications for facial rejuvenation. Aesthetic Plast Surg 31: Millard JF, Cornette de St Cyr B, Sheflan M (1991) The subperiosteal bicoronal approach to total facelifting: the DMAS deep musculoaponeurotic system. Aesthetic Plast Surg 15:
25 References Mitz V, Peyronie M (1976) The superficial musculoaponeurtic system (SMAS) in the parotid and cheek area. Plast Reconstr Surg 58: Moody BR, Hold JB (2006) Anesthesia for office-based oculoplastic surgery. Dermatol Surg 31(7): Persichetti P, Di Lella F, Delfino F (2004) Adipose compartments of the upper eyelid: anatomy applied to blepharoplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 113: Pessa JE (2000) An algorithm of facial aging: verification of Lambros s theory by three dimensional stereolithography, with reference to the pathogenesis of midfacial aging, sclera show, and the lateral suborbital tera trough deformity. Plast Reconstr Surg 106: Porter JD, Burns LA, May PJ (1989) Morphological substrate for eyelid movements: Innervation and structure of primate levator palpebrae superioris and orbicularis oculi muscles. J Comp Neurol 287: Putterman AM, Urist MJ (1975) Muller s muscle-conjunctival resection: technique for treatment of blepharoptosis. Arch Ophthalmol 93: Shorr NS (1997) Madame butterfly procedure: total lower eyelid reconstruction in three layers utilizing a hard palate graft: management of the unhappy post-blepharoplasty patient with round eye and sclera show. Int J Aesthetic Restor Surg 3: Shorr NS, Cohen MS (1991) Cosmetic blepharoplasty. Ophthalmol Clin North Am 4(1): Shorr N, Enzer Y (1992) Considerations in aesthetic surgery. J Dermatol Surg Oncol 18: Shorr N, Hoenig JA (1995) Brow lift. In: Levine M (ed) Manual of oculoplastic surgery. Butterworth-Heinrmann, Newton, MA 42. Shorr N, Hoenig JA, Goldberg RA (1999) Fat preservation to rejuvenate the lower eyelid. Arch Facial Plast Surg 1(1): Steele EA, Ng JD, Poissant TM, et al. (2009) Comparison of injection pain of articaine and lidocaine in eyelid surgery. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 25(1): Steinsapir KD, Steinsapir SM (2006) Deep-fill hyaluronic acid for the temporary treatment of the naso-jugal groove: a report of 303 consecutive treatments. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 22(5): Steinsapir K, Shorr N, Hoenig JA, et al. (1998) Endoscopic forehead lift. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 14: Stuzin JM, Baker TJ, Gordon HL (1992) The relationship of the superficial and deep facial fascias: the relevance to rhytidectomy and aging. Plast Reconstr Surg 89: Webster RC, Fanous N, Smith RC (1979) Blepharoplasty: when to combine it with eyebrow, temple or coronal lift. J Otolaryngol 8: Yaremchuk MJ (2001) Infraorbital rim augmentation. Plast Reconstr Surg 107(6): Yaremchuk MJ (2005) Making the concave midface convex. Aesthetic Plast Surg 29(3) Zarem HA, Resnick JL, Carr RM, Wooton DG (1997) Browpexy: lateral orbicularis muscle fixation as an adjunct to upper blepharoplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 10:
26
Blepharoplasty & Cosmetic eyelid surgery
 Our cosmetic surgery team at The USF Eye Institute offers a wide variety of cosmetic procedures of the eyelids and face with the goal of obtaining a natural and rejuvenated appearance. Dr.Leyngold has
Our cosmetic surgery team at The USF Eye Institute offers a wide variety of cosmetic procedures of the eyelids and face with the goal of obtaining a natural and rejuvenated appearance. Dr.Leyngold has
5 Upper eyelid blepharoplasty
 5 Upper eyelid blepharoplasty INSTRUMENTS Marking pen No. 15 scalpel blade Blade handle Castroviejo needle holder Castroviejo calipers 0.5 fixation forceps Westcott scissors 6-0 prolene suture Bovie cautery
5 Upper eyelid blepharoplasty INSTRUMENTS Marking pen No. 15 scalpel blade Blade handle Castroviejo needle holder Castroviejo calipers 0.5 fixation forceps Westcott scissors 6-0 prolene suture Bovie cautery
Evaluation of the Cosmetic Patient
 APC Ophthalmology Conference Evaluation of the Cosmetic Patient David K. Isaacs, M.D. Clinical instructor Loma Linda University Clinial Staff Attending UCLA/Jules Stein Eye Institute Lecture Agenda Review
APC Ophthalmology Conference Evaluation of the Cosmetic Patient David K. Isaacs, M.D. Clinical instructor Loma Linda University Clinial Staff Attending UCLA/Jules Stein Eye Institute Lecture Agenda Review
Open and Endoscopic Forehead Lift. Plastic Surgery. For All Brow and Forehead Lift Procedures. Revolutionizing. Soft-Tissue Fixation
 Plastic Surgery Open and Endoscopic Forehead Lift For All Brow and Forehead Lift Procedures Revolutionizing Soft-Tissue Fixation DESIGNED FOR SIMPLICITY AND PREDICTABILITY The versatile design can be applied
Plastic Surgery Open and Endoscopic Forehead Lift For All Brow and Forehead Lift Procedures Revolutionizing Soft-Tissue Fixation DESIGNED FOR SIMPLICITY AND PREDICTABILITY The versatile design can be applied
Blepharoplasty - Eyelid Surgery
 Blepharoplasty - Eyelid Surgery Introduction Eyelid surgery repairs sagging or drooping eyelids. The surgery is also known as blepharoplasty, or an eyelid lift. Sagging or drooping eyelids happen naturally
Blepharoplasty - Eyelid Surgery Introduction Eyelid surgery repairs sagging or drooping eyelids. The surgery is also known as blepharoplasty, or an eyelid lift. Sagging or drooping eyelids happen naturally
Facial Nerve Paralysis: Management of the Eye
 Facial Nerve Paralysis: Management of the Eye Facial Nerve Paralysis: Management of the Eye Introduction Anatomy Options Discussion of Literature Introduction-Facial Nerve Paralysis Functional and cosmetic
Facial Nerve Paralysis: Management of the Eye Facial Nerve Paralysis: Management of the Eye Introduction Anatomy Options Discussion of Literature Introduction-Facial Nerve Paralysis Functional and cosmetic
Lid Surgery (Blepharoplasty)
 Lid Surgery (Blepharoplasty) Blepharoplasty Blepharoplasty surgery involves the removal or redistribution of eyelid tissue. These tissues include skin, muscle and fat, all of which undergo changes with
Lid Surgery (Blepharoplasty) Blepharoplasty Blepharoplasty surgery involves the removal or redistribution of eyelid tissue. These tissues include skin, muscle and fat, all of which undergo changes with
How To Improve Your Looks with Plastic Surgery
 How To Improve Your Looks with Plastic Surgery By Daniel Becker Plastic surgery is a special type of surgery that involves both a person's appearance and his or her ability to function. Plastic surgeons
How To Improve Your Looks with Plastic Surgery By Daniel Becker Plastic surgery is a special type of surgery that involves both a person's appearance and his or her ability to function. Plastic surgeons
Raising the suborbicularis oculi fat (SOOF): its role in chronic facial palsy
 Br J Ophthalmol 2;84:141 146 141 Raising the suborbicularis oculi fat (SOOF): its role in chronic facial palsy Jane M Olver Western Eye Hospital, Marylebone Road, London NW1 5YE and Eye Department, Charing
Br J Ophthalmol 2;84:141 146 141 Raising the suborbicularis oculi fat (SOOF): its role in chronic facial palsy Jane M Olver Western Eye Hospital, Marylebone Road, London NW1 5YE and Eye Department, Charing
ABDOMINOPLASTY - FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS (FAQs)
 Executive Level E1, Excen Centre, 119 Willoughby Road, Crows Nest 2065 Tel: 02 9817 7585 www.mycosmeticclinic.net AFFORDABILITY WITH EXCELLENCE Liposuction Breast Augmentation Abdominoplasty Eyelids Surgery
Executive Level E1, Excen Centre, 119 Willoughby Road, Crows Nest 2065 Tel: 02 9817 7585 www.mycosmeticclinic.net AFFORDABILITY WITH EXCELLENCE Liposuction Breast Augmentation Abdominoplasty Eyelids Surgery
How To Harvest Fat From The Infratemporal Fossila
 Techniques in Cosmetic Surgery Harvesting Fat from the Infratemporal Fossa Bahman Guyuron, M.D., and Kevin Rose, M.D. Cleveland, Ohio As part of forehead rejuvenation and surgical treatment of migraine
Techniques in Cosmetic Surgery Harvesting Fat from the Infratemporal Fossa Bahman Guyuron, M.D., and Kevin Rose, M.D. Cleveland, Ohio As part of forehead rejuvenation and surgical treatment of migraine
Thyroid Eye Disease. Anatomy: There are 6 muscles that move your eye.
 Thyroid Eye Disease Your doctor thinks you have thyroid orbitopathy. This is an autoimmune condition where your body's immune system is producing factors that stimulate enlargement of the muscles that
Thyroid Eye Disease Your doctor thinks you have thyroid orbitopathy. This is an autoimmune condition where your body's immune system is producing factors that stimulate enlargement of the muscles that
Open and Endoscopic Forehead Lift. Plastic Surgery. For All Brow and Forehead Lift Procedures. Revolutionizing. Soft-Tissue Fixation
 Plastic Surgery Open and Endoscopic Forehead Lift For All Brow and Forehead Lift Procedures Revolutionizing Soft-Tissue Fixation DESIGNED FOR SIMPLICITY AND PREDICTABILITY The versatile design can be applied
Plastic Surgery Open and Endoscopic Forehead Lift For All Brow and Forehead Lift Procedures Revolutionizing Soft-Tissue Fixation DESIGNED FOR SIMPLICITY AND PREDICTABILITY The versatile design can be applied
Corporate Medical Policy Reconstructive Eyelid Surgery and Brow Lift
 Corporate Medical Policy Reconstructive Eyelid Surgery and Brow Lift File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: reconstructive_eyelid_surgery_and_brow_lift 1/2000 9/2015 9/2016
Corporate Medical Policy Reconstructive Eyelid Surgery and Brow Lift File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: reconstructive_eyelid_surgery_and_brow_lift 1/2000 9/2015 9/2016
F ORUM. Special Topic. Facial Reshaping Using Minimally Invasive Methods
 Special Topic Facial Reshaping Using Minimally Invasive Methods Q1 Richard Ellenbogen, MD; Gary Motykie, MD; nthony Youn, MD; Steven Svehlak, MD; and Dan Yamini, MD Dr. Ellenbogen, Dr. Motykie, Dr. Yamini,
Special Topic Facial Reshaping Using Minimally Invasive Methods Q1 Richard Ellenbogen, MD; Gary Motykie, MD; nthony Youn, MD; Steven Svehlak, MD; and Dan Yamini, MD Dr. Ellenbogen, Dr. Motykie, Dr. Yamini,
Cosmetic Eyelid Surgery & Blepharoplasty (Eye Bag Removal)
 MR DAVID CHEUNG Consultant Ophthalmic and Oculoplastic Surgeon Contact Info NHS: Sandwell General Hospital, Birmingham PA: Denise Kaur 0121 507 3165 Russells Hall Hospital, Dudley : PA Jo Gough: 01384
MR DAVID CHEUNG Consultant Ophthalmic and Oculoplastic Surgeon Contact Info NHS: Sandwell General Hospital, Birmingham PA: Denise Kaur 0121 507 3165 Russells Hall Hospital, Dudley : PA Jo Gough: 01384
Cosmetic blepharoplasty
 Atlas Oral Maxillofacial Surg Clin N Am 12 (2004) 91 130 Cosmetic blepharoplasty Joseph Niamtu, III, DDS Oral/Maxillofacial and Cosmetic Facial Surgery, 10230 Cherokee Road, Richmond, VA 23235, USA It
Atlas Oral Maxillofacial Surg Clin N Am 12 (2004) 91 130 Cosmetic blepharoplasty Joseph Niamtu, III, DDS Oral/Maxillofacial and Cosmetic Facial Surgery, 10230 Cherokee Road, Richmond, VA 23235, USA It
Give us a table of facelift complications. How would you treat each? Answers from Cummings:
 Give us a table of facelift complications. How would you treat each? Answers from Cummings: Hematoma The most common perioperative complication of rhytidectomy is hematoma, which occurs in 1% to 10% of
Give us a table of facelift complications. How would you treat each? Answers from Cummings: Hematoma The most common perioperative complication of rhytidectomy is hematoma, which occurs in 1% to 10% of
Aestheticare Cosmetic Surgery Institute Dr. Ronald E. Moser 30260 Rancho Viejo Rd. San Juan Capistrano, CA 92675 (800) 662-1055
 Breast augmentation, or augmentation mammoplasty, is one of the most common plastic surgery procedures performed today. Over time, factors such as age, genetics, pregnancy, weight changes, sun exposure,
Breast augmentation, or augmentation mammoplasty, is one of the most common plastic surgery procedures performed today. Over time, factors such as age, genetics, pregnancy, weight changes, sun exposure,
Dermatochalasis is the crepey, wrinkled, Surgical Treatment Options for Lower Eyelid Aging. Cosmetic Technique. Joe Niamtu III, DMD
 Cosmetic Technique Surgical Treatment Options for Lower Eyelid Aging Joe Niamtu III, DMD The lower eyelid and associated anatomy represent a complex structure that is key in facial aging and rejuvenation.
Cosmetic Technique Surgical Treatment Options for Lower Eyelid Aging Joe Niamtu III, DMD The lower eyelid and associated anatomy represent a complex structure that is key in facial aging and rejuvenation.
Eyelid Surgery - Lower
 Eyelid Surgery - Lower Are your eyes still one of the most striking features on your face? Do they convey your actual emotions and inner vitality, or do they make you appear fatigued, sad, or older than
Eyelid Surgery - Lower Are your eyes still one of the most striking features on your face? Do they convey your actual emotions and inner vitality, or do they make you appear fatigued, sad, or older than
Cheekbone (zygoma) and/or eye socket (orbit) fracture surgery
 Ambulatory Care & Local Networks Cheekbone (zygoma) and/or eye socket (orbit) fracture surgery Information for patients You have been treated in the Emergency Department for a broken (fractured) cheekbone
Ambulatory Care & Local Networks Cheekbone (zygoma) and/or eye socket (orbit) fracture surgery Information for patients You have been treated in the Emergency Department for a broken (fractured) cheekbone
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Transconjunctival Lower Blepharoplasty. A Retrospective Comparison of Transposing Fat to the Subperiosteal vs Supraperiosteal Planes
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Transconjunctival Lower Blepharoplasty With Fat Repositioning A Retrospective Comparison of Transposing Fat to the Subperiosteal vs Supraperiosteal Planes Donald B. Yoo, MD; Grace Lee
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Transconjunctival Lower Blepharoplasty With Fat Repositioning A Retrospective Comparison of Transposing Fat to the Subperiosteal vs Supraperiosteal Planes Donald B. Yoo, MD; Grace Lee
Upper Eyelid Gold Weight Implantation in the Asian Patient with Facial Paralysis
 Upper Eyelid Gold Weight Implantation in the Asian Patient with Facial Paralysis Phillip H. Choo, M.D., Susan R. Carter, M.D., and Stuart R. Seiff, M.D. Sacramento and San Francisco, Calif. Patients with
Upper Eyelid Gold Weight Implantation in the Asian Patient with Facial Paralysis Phillip H. Choo, M.D., Susan R. Carter, M.D., and Stuart R. Seiff, M.D. Sacramento and San Francisco, Calif. Patients with
Orthopaedic Spine Center. Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) Normal Discs
 Orthopaedic Spine Center Graham Calvert MD James Woodall MD PhD Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) Normal Discs The cervical spine consists of the bony vertebrae, discs, nerves and other structures.
Orthopaedic Spine Center Graham Calvert MD James Woodall MD PhD Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) Normal Discs The cervical spine consists of the bony vertebrae, discs, nerves and other structures.
Traumatic Primary Eyelid and Facial Laceration Repair. Riva Lee Asbell Philadelphia, PA
 Traumatic Primary Eyelid and Facial Laceration Repair Riva Lee Asbell Philadelphia, PA I INTRODUCTION I always have to work a little harder when coding for traumatic eyelid and facial repairs. There is
Traumatic Primary Eyelid and Facial Laceration Repair Riva Lee Asbell Philadelphia, PA I INTRODUCTION I always have to work a little harder when coding for traumatic eyelid and facial repairs. There is
Ptosis. Patient Information - Adnexal
 Patient Information - Adnexal Ptosis What is ptosis? Ptosis is the medical name for the drooping of the upper eyelid, which can happen in one or both eyes. A low upper lid can interfere with vision by
Patient Information - Adnexal Ptosis What is ptosis? Ptosis is the medical name for the drooping of the upper eyelid, which can happen in one or both eyes. A low upper lid can interfere with vision by
S UPPLEMENT. The Anatomy of the Aging Face: Volume Loss and Changes in 3-Dimensional Topography
 The Anatomy of the Aging Face: Volume Loss and Changes in 3-Dimensional Topography Sydney R. Coleman, MD; Rajiv Grover, BSc, MB BS, MD, FRCS (Plast) Dr. Coleman is Assistant Professor of Plastic Surgery
The Anatomy of the Aging Face: Volume Loss and Changes in 3-Dimensional Topography Sydney R. Coleman, MD; Rajiv Grover, BSc, MB BS, MD, FRCS (Plast) Dr. Coleman is Assistant Professor of Plastic Surgery
Upper blepharoplasty is one of the most common cosmetic. The Sigmoid Upper Eyelid Blepharoplasty: Redefining Beauty. John P. Fezza, M.D.
 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE The Sigmoid Upper Eyelid Blepharoplasty: Redefining Beauty John P. Fezza, M.D. * *Center for Sight, Sarasota; and Department of Ophthalmology, University of South Florida, Tampa, Florida,
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE The Sigmoid Upper Eyelid Blepharoplasty: Redefining Beauty John P. Fezza, M.D. * *Center for Sight, Sarasota; and Department of Ophthalmology, University of South Florida, Tampa, Florida,
Chapter 11. Everting skin edges
 Chapter 11 PRIMARY WOUND CLOSURE KEY FIGURE: Everting skin edges In primary wound closure, the skin edges of the wound are sutured together to close the defect. Whenever possible and practical, primary
Chapter 11 PRIMARY WOUND CLOSURE KEY FIGURE: Everting skin edges In primary wound closure, the skin edges of the wound are sutured together to close the defect. Whenever possible and practical, primary
ADVANCED SUTURING WORKSHOP ANN BECKER, APRN-CNP; TONI PRATT-REID, APRN-CNP
 ADVANCED SUTURING WORKSHOP ANN BECKER, APRN-CNP; TONI PRATT-REID, APRN-CNP SUTURING WORKSHOP! The technique of suturing, as a method for closing cutaneous wounds has been a part of medicine for hundreds
ADVANCED SUTURING WORKSHOP ANN BECKER, APRN-CNP; TONI PRATT-REID, APRN-CNP SUTURING WORKSHOP! The technique of suturing, as a method for closing cutaneous wounds has been a part of medicine for hundreds
a guide to understanding crouzon syndrome a publication of children s craniofacial association
 a guide to understanding crouzon syndrome a publication of children s craniofacial association a guide to understanding crouzon syndrome this parent s guide to Crouzon syndrome is designed to answer questions
a guide to understanding crouzon syndrome a publication of children s craniofacial association a guide to understanding crouzon syndrome this parent s guide to Crouzon syndrome is designed to answer questions
Tissue Reinforcement with Strattice Reconstructive Tissue Matrix following Correction of Severe Breast Deformity
 Tissue Reinforcement with Strattice Reconstructive Tissue Matrix following Correction of Severe Breast Deformity Robert Cohen, MD, FACS* Paradise Valley, AZ Case summary A 41-year old woman with a history
Tissue Reinforcement with Strattice Reconstructive Tissue Matrix following Correction of Severe Breast Deformity Robert Cohen, MD, FACS* Paradise Valley, AZ Case summary A 41-year old woman with a history
DERMATOLOGY & COSMETIC LASER CENTER
 DERMATOLOGY & COSMETIC LASER CENTER MEET DR. NATALIE H. DANIELS Practicing medical, cosmetic, and surgical dermatology is my passion, which is why I m committed to the total health of my patients skin.
DERMATOLOGY & COSMETIC LASER CENTER MEET DR. NATALIE H. DANIELS Practicing medical, cosmetic, and surgical dermatology is my passion, which is why I m committed to the total health of my patients skin.
Abdominal Pedicle Flaps To The Hand And Forearm John C. Kelleher M.D., F.A.C.S.
 Abdominal Pedicle Flaps To The Hand And Forearm John C. Kelleher M.D., F.A.C.S. Global-HELP Publications Chapter Eight: TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR FORMATION OF A TUBED PEDICLE FLAP Creating a tube pedicle
Abdominal Pedicle Flaps To The Hand And Forearm John C. Kelleher M.D., F.A.C.S. Global-HELP Publications Chapter Eight: TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR FORMATION OF A TUBED PEDICLE FLAP Creating a tube pedicle
The Smooth Tuck Procedure
 The Smooth Tuck Procedure plastic surgery AN ALTERNATIVE APPROACH TO ABDOMINAL CONTOURING FOR THE OVERWEIGHT PATIENT atnt By Matthew R. Schulman, M.D. Body fat on an adult tends to increase gradually over
The Smooth Tuck Procedure plastic surgery AN ALTERNATIVE APPROACH TO ABDOMINAL CONTOURING FOR THE OVERWEIGHT PATIENT atnt By Matthew R. Schulman, M.D. Body fat on an adult tends to increase gradually over
Michael A. Boss, M.D. FMH Plastic, Reconstructive und Aesthetic Surgery
 Michael A. Boss, M.D. FMH Plastic, Reconstructive und Aesthetic Surgery Boss Aesthetic Center Schauplatzgasse 23 CH-3011 Bern Switzerland +41 31 311 7691 www.aesthetic-center.com B r e a s t A u g m e
Michael A. Boss, M.D. FMH Plastic, Reconstructive und Aesthetic Surgery Boss Aesthetic Center Schauplatzgasse 23 CH-3011 Bern Switzerland +41 31 311 7691 www.aesthetic-center.com B r e a s t A u g m e
Hydrogel Competence in Eye Surgery
 Hydrogel Competence in Eye Surgery Self-inflating tissue expander osmed self-inflating tissue expanders are made of a specially developed hydrogel that uses the osmotic principle to gain volume. These
Hydrogel Competence in Eye Surgery Self-inflating tissue expander osmed self-inflating tissue expanders are made of a specially developed hydrogel that uses the osmotic principle to gain volume. These
WEIGHT LOSS. ThePlasticDoc.com
 WEIGHT LOSS ThePlasticDoc.com The brochure you have been provided contains nudity. If you are offended by such material or are not at least 18 years of age, please do not read further. WEIGHT LOSS SURGERY
WEIGHT LOSS ThePlasticDoc.com The brochure you have been provided contains nudity. If you are offended by such material or are not at least 18 years of age, please do not read further. WEIGHT LOSS SURGERY
Thyroid eye disease (TED) Synonyms: Graves ophthalmopathy, thyroid ophthalmopathy, thyroid associated ophthalmopathy
 Thyroid eye disease (TED) Synonyms: Graves ophthalmopathy, thyroid ophthalmopathy, thyroid associated ophthalmopathy This information leaflet briefly covers the following issues in TED: What is TED? When
Thyroid eye disease (TED) Synonyms: Graves ophthalmopathy, thyroid ophthalmopathy, thyroid associated ophthalmopathy This information leaflet briefly covers the following issues in TED: What is TED? When
Cosmetic Laser Procedures and Facial Contouring with Injectables. 2009, American Society for Aesthetic Plastic Surgery
 Cosmetic Laser Procedures and Facial Contouring with Injectables Stuart B. Kincaid, MD, F.A.C.S. San Diego/La Jolla Office 8929 University Center Lane, Ste. 201 San Diego, California 92122 Phone: 858-450-4199
Cosmetic Laser Procedures and Facial Contouring with Injectables Stuart B. Kincaid, MD, F.A.C.S. San Diego/La Jolla Office 8929 University Center Lane, Ste. 201 San Diego, California 92122 Phone: 858-450-4199
Breast Augmentation. If you are dissatisfied with your breast size, augmentation surgery is a choice to consider. Breast augmentation can:
 Breast Augmentation What is Breast Augmentation? Also known as augmentation mammaplasty, breast augmentation involves using implants to fulfill your desire for fuller breasts or to restore breast volume
Breast Augmentation What is Breast Augmentation? Also known as augmentation mammaplasty, breast augmentation involves using implants to fulfill your desire for fuller breasts or to restore breast volume
ACCEPTABLE OPERATIVE REPORT # 1
 ACCEPTABLE OPERATIVE REPORT # 1 This operative report follows the standards set by The Joint Commission and AAAHC for sufficient information to: identify the patient support the diagnosis justify the treatment
ACCEPTABLE OPERATIVE REPORT # 1 This operative report follows the standards set by The Joint Commission and AAAHC for sufficient information to: identify the patient support the diagnosis justify the treatment
Body Jet - Water Assisted Liposuction
 Steven L. Ringler, MD, FACS Introducing: SmartLipo Triplex Laser-BodySculpting Body Jet - Water Assisted Liposuction CoolSculpting by Zeltiq *Experience Exceptional - Dr. Steven L. Ringler and The Center
Steven L. Ringler, MD, FACS Introducing: SmartLipo Triplex Laser-BodySculpting Body Jet - Water Assisted Liposuction CoolSculpting by Zeltiq *Experience Exceptional - Dr. Steven L. Ringler and The Center
Thyroid eye disease (TED)
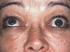 Thyroid eye disease (TED) Mr David H Verity, MD MA FRCOphth Consultant Ophthalmic Surgeon Synonyms: Graves ophthalmopathy, thyroid ophthalmopathy, thyroid associated ophthalmopathy This information leaflet
Thyroid eye disease (TED) Mr David H Verity, MD MA FRCOphth Consultant Ophthalmic Surgeon Synonyms: Graves ophthalmopathy, thyroid ophthalmopathy, thyroid associated ophthalmopathy This information leaflet
Basal Cell Carcinoma Affecting the Eye Your Treatment Explained
 Basal Cell Carcinoma Affecting the Eye Your Treatment Explained Patient Information Introduction This booklet is designed to give you information about having a Basal Cell Carcinoma near your eye and the
Basal Cell Carcinoma Affecting the Eye Your Treatment Explained Patient Information Introduction This booklet is designed to give you information about having a Basal Cell Carcinoma near your eye and the
Minor Lid Surgery. Information for patients
 Minor Lid Surgery Information for patients This leaflet has been produced to give you information about the problems you have been having with your eyelid. If you have any questions or require further
Minor Lid Surgery Information for patients This leaflet has been produced to give you information about the problems you have been having with your eyelid. If you have any questions or require further
Current Techniques in Aesthetic Oculoplastic Surgery.
 176 Current Techniques in Aesthetic Oculoplastic Surgery. AK Grover, Shilpa Taneja, Shaloo Bageja Department of Ophthalmology, Sir Ganga Ram Hospital, Rajinder Nagar, New Delhi, India Abstract: Aesthetic
176 Current Techniques in Aesthetic Oculoplastic Surgery. AK Grover, Shilpa Taneja, Shaloo Bageja Department of Ophthalmology, Sir Ganga Ram Hospital, Rajinder Nagar, New Delhi, India Abstract: Aesthetic
Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery
 Chapter 1 Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery 1 H.M. Mayer Primum non nocere First do no harm In the long history of surgery it always has been a basic principle to restrict the iatrogenic trauma done to
Chapter 1 Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery 1 H.M. Mayer Primum non nocere First do no harm In the long history of surgery it always has been a basic principle to restrict the iatrogenic trauma done to
Descemet s Stripping Endothelial Keratoplasty (DSEK)
 Descemet s Stripping Endothelial Keratoplasty (DSEK) Your doctor has decided that you will benefit from a corneal transplant operation. This handout will explain your options to you. It explains the differences
Descemet s Stripping Endothelial Keratoplasty (DSEK) Your doctor has decided that you will benefit from a corneal transplant operation. This handout will explain your options to you. It explains the differences
X-Plain Trigeminal Neuralgia Reference Summary
 X-Plain Trigeminal Neuralgia Reference Summary Introduction Trigeminal neuralgia is a condition that affects about 40,000 patients in the US every year. Its treatment mostly involves the usage of oral
X-Plain Trigeminal Neuralgia Reference Summary Introduction Trigeminal neuralgia is a condition that affects about 40,000 patients in the US every year. Its treatment mostly involves the usage of oral
Kensington Eye Center 4701 Randolph Road, #G-2 Rockville, MD 20852 (301) 881-5701 www.keceyes.com
 Kensington Eye Center 4701 Randolph Road, #G-2 Rockville, MD 20852 (301) 881-5701 www.keceyes.com Natasha L. Herz, MD INFORMED CONSENT FOR DESCEMET S STRIPPING and AUTOMATED ENDOTHELIAL KERATOPLASTY (DSAEK)
Kensington Eye Center 4701 Randolph Road, #G-2 Rockville, MD 20852 (301) 881-5701 www.keceyes.com Natasha L. Herz, MD INFORMED CONSENT FOR DESCEMET S STRIPPING and AUTOMATED ENDOTHELIAL KERATOPLASTY (DSAEK)
Laser and Cosmetic Center
 Laser and Cosmetic Center A Patient s Guide to Cosmetic Dermatology WELCOME Experts You Can Trust The Massachusetts General Hospital Dermatology Laser and Cosmetic Center s depth of experience is unmatched.
Laser and Cosmetic Center A Patient s Guide to Cosmetic Dermatology WELCOME Experts You Can Trust The Massachusetts General Hospital Dermatology Laser and Cosmetic Center s depth of experience is unmatched.
X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary
 X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary Introduction A Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter, or subclavian line, is a long thin hollow tube inserted in a vein under the
X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary Introduction A Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter, or subclavian line, is a long thin hollow tube inserted in a vein under the
INFORMED CONSENT BLEPHAROPLASTY SURGERY
 INFORMED CONSENT BLEPHAROPLASTY SURGERY INSTRUCTIONS This is informed-consent document which had been prepared to help your plastic surgeon inform you about blepharoplasty surgery, its risks, and alternative
INFORMED CONSENT BLEPHAROPLASTY SURGERY INSTRUCTIONS This is informed-consent document which had been prepared to help your plastic surgeon inform you about blepharoplasty surgery, its risks, and alternative
Tucson Eye Care, PC. Informed Consent for Cataract Surgery And/Or Implantation of an Intraocular Lens
 Tucson Eye Care, PC Informed Consent for Cataract Surgery And/Or Implantation of an Intraocular Lens INTRODUCTION This information is provided so that you may make an informed decision about having eye
Tucson Eye Care, PC Informed Consent for Cataract Surgery And/Or Implantation of an Intraocular Lens INTRODUCTION This information is provided so that you may make an informed decision about having eye
Integumentary System Individual Exercises
 Integumentary System Individual Exercises 1. A physician performs an incision and drainage of a subcutaneous abscess in his office for a particularly uncooperative established patient. How should this
Integumentary System Individual Exercises 1. A physician performs an incision and drainage of a subcutaneous abscess in his office for a particularly uncooperative established patient. How should this
Bankart Repair using the Smith & Nephew BIORAPTOR 2.9 Suture Anchor
 Shoulder Series Technique Guide *smith&nephew BIORAPTOR 2.9 Suture Anchor Bankart Repair using the Smith & Nephew BIORAPTOR 2.9 Suture Anchor Gary M. Gartsman, M.D. Introduction Arthroscopic studies of
Shoulder Series Technique Guide *smith&nephew BIORAPTOR 2.9 Suture Anchor Bankart Repair using the Smith & Nephew BIORAPTOR 2.9 Suture Anchor Gary M. Gartsman, M.D. Introduction Arthroscopic studies of
Shoulder Arthroscopy
 Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Shoulder Arthroscopy Arthroscopy is a procedure that orthopaedic surgeons use to inspect, diagnose, and repair problems inside a joint. The word
Copyright 2011 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Shoulder Arthroscopy Arthroscopy is a procedure that orthopaedic surgeons use to inspect, diagnose, and repair problems inside a joint. The word
How To Use A Botox
 BTFR-04(17-28) 7/23/03 5:43 PM Page 17 4 Preparation,storage and injection technique NEVER handle botulinum toxin without surgical gloves. PRESENTATION Botox Botox is delivered in an insulated container.
BTFR-04(17-28) 7/23/03 5:43 PM Page 17 4 Preparation,storage and injection technique NEVER handle botulinum toxin without surgical gloves. PRESENTATION Botox Botox is delivered in an insulated container.
MOHS MICROGRAPHIC SURGERY
 MOHS MICROGRAPHIC SURGERY UMass Memorial Medical Center 55 Lake Avenue North Worcester, MA 01655 (508) 856-1666 Dr. Mary Maloney This booklet is intended to explain Mohs surgery to you. It is not, however,
MOHS MICROGRAPHIC SURGERY UMass Memorial Medical Center 55 Lake Avenue North Worcester, MA 01655 (508) 856-1666 Dr. Mary Maloney This booklet is intended to explain Mohs surgery to you. It is not, however,
Pretarsal Fixation of Gold Weights in Facial Nerve Palsy
 Ophthalmic Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 5(2): 104-109. 1989. 104 1989 Raven Press, Ltd., New York Pretarsal Fixation of Gold Weights in Facial Nerve Palsy Stuart R. Seiff, M.D., John H. Sullivan,
Ophthalmic Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 5(2): 104-109. 1989. 104 1989 Raven Press, Ltd., New York Pretarsal Fixation of Gold Weights in Facial Nerve Palsy Stuart R. Seiff, M.D., John H. Sullivan,
Preparing to Suture. 6 th Annual Pediatric Advanced Practice Conference Tuesday, February 9, 2016 1:30 pm. Workshop B: Suturing for Beginners
 Preparing to Suture Kristen Devick, MPAS, PA-C University of Colorado Department of Emergency Medicine NONE! Skin Anatomy Trott, 2012, p.11 Preparing to suture Initial evaluation Hemostasis Anesthesia
Preparing to Suture Kristen Devick, MPAS, PA-C University of Colorado Department of Emergency Medicine NONE! Skin Anatomy Trott, 2012, p.11 Preparing to suture Initial evaluation Hemostasis Anesthesia
Hard work. PAL will take you. can get you 90% of the way there. over the finish line. Results instead of hype.
 Hard work can get you 90% of the way there. PAL will take you over the finish line. Results instead of hype. Power-Assisted Liposuction (PAL) offers meaningful patient benefits. Less bruising, swelling
Hard work can get you 90% of the way there. PAL will take you over the finish line. Results instead of hype. Power-Assisted Liposuction (PAL) offers meaningful patient benefits. Less bruising, swelling
Lateral Canthoplasty by the Micro-Mitek Anchor System: 10-Year Review of 96 Patients
 CRANIOMAXILLOFACIAL DEFORMITIES/COSMETIC SURGERY J Oral Maxillofac Surg 69:1745-1749, 2011 Lateral Canthoplasty by the Micro-Mitek Anchor System: 10-Year Review of 96 Patients Carmine Alfano, MD,* Stefano
CRANIOMAXILLOFACIAL DEFORMITIES/COSMETIC SURGERY J Oral Maxillofac Surg 69:1745-1749, 2011 Lateral Canthoplasty by the Micro-Mitek Anchor System: 10-Year Review of 96 Patients Carmine Alfano, MD,* Stefano
Facial Sports Injuries
 Facial Sports Injuries Playing catch, shooting hoops, bicycling on a scenic path or just kicking around a soccer ball have more in common than you may think. On the up side, these activities are good exercise
Facial Sports Injuries Playing catch, shooting hoops, bicycling on a scenic path or just kicking around a soccer ball have more in common than you may think. On the up side, these activities are good exercise
TOWN CENTER ORTHOPAEDIC ASSOCIATES P.C. Labral Tears
 Labral Tears The shoulder is your body s most flexible joint. It is designed to let the arm move in almost any direction. But this flexibility has a price, making the joint prone to injury. The shoulder
Labral Tears The shoulder is your body s most flexible joint. It is designed to let the arm move in almost any direction. But this flexibility has a price, making the joint prone to injury. The shoulder
Cosmetic Surgery Procedures
 Last Review Date: July 20, 2015 Number: MG.MM.AD.07cC2 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or primary care provider must submit to EmblemHealth
Last Review Date: July 20, 2015 Number: MG.MM.AD.07cC2 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or primary care provider must submit to EmblemHealth
SKIN CARE menu of services
 SKIN CARE menu of services your best you. There s no denying the confidence you can possess when you look as good as you feel. Allow the skin health specialists and staff at C H A R L O T T E P L A S T
SKIN CARE menu of services your best you. There s no denying the confidence you can possess when you look as good as you feel. Allow the skin health specialists and staff at C H A R L O T T E P L A S T
LIPOSUCTION. The Symbol of Excellence in Plastic Surgery. Anil P. Punjabi, M.D., D.D.S
 LIPOSUCTION Anil P. Punjabi, M.D., D.D.S The Symbol of Excellence in Plastic Surgery A public education service of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons and the American Society for Aesthetic Plastic
LIPOSUCTION Anil P. Punjabi, M.D., D.D.S The Symbol of Excellence in Plastic Surgery A public education service of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons and the American Society for Aesthetic Plastic
AESTHETICS. Appointment booking for new patients 15. Consultation Fee 60. Patch Test for Laser Treatments 60
 CONSULTATION AND PATCH TEST Appointment booking for new patients 15 Consultation Fee 60 Patch Test for Laser Treatments 60 The 15 deposit is redeemed from the 60 consultation fee The consultation fee is
CONSULTATION AND PATCH TEST Appointment booking for new patients 15 Consultation Fee 60 Patch Test for Laser Treatments 60 The 15 deposit is redeemed from the 60 consultation fee The consultation fee is
VARICOSE VEINS. Information Leaflet. Your Health. Our Priority. VTE Ambulatory Clinic Stepping Hill Hospital
 VARICOSE VEINS Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 7 Varicose Veins There are no accurate figures for the number of people with varicose veins. Some studies suggest that 3 in 100 people
VARICOSE VEINS Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 7 Varicose Veins There are no accurate figures for the number of people with varicose veins. Some studies suggest that 3 in 100 people
CONSENT FORM. Procedure: Descemet s Stripping Automated Endothelial Keratoplasty (DSAEK)
 CONSENT FORM Procedure: Descemet s Stripping Automated Endothelial Keratoplasty (DSAEK) Surgeon: Jeffrey W. Liu, M.D. Peninsula Laser Eye Medical Group 1174 Castro Street, Ste. 100 Mountain View, CA 94040
CONSENT FORM Procedure: Descemet s Stripping Automated Endothelial Keratoplasty (DSAEK) Surgeon: Jeffrey W. Liu, M.D. Peninsula Laser Eye Medical Group 1174 Castro Street, Ste. 100 Mountain View, CA 94040
BREAST AUGMENTATION PATIENT INFORMATION
 BREAST AUGMENTATION PATIENT INFORMATION Elizabeth J. Hall-Findlay, MD, FRCSC 340-317 Banff Avenue, Box 2009, Banff, Alberta, Canada T1L 1B7 403-762-2055 tel 403-762-8297 fax www.banffplasticsurgery.com
BREAST AUGMENTATION PATIENT INFORMATION Elizabeth J. Hall-Findlay, MD, FRCSC 340-317 Banff Avenue, Box 2009, Banff, Alberta, Canada T1L 1B7 403-762-2055 tel 403-762-8297 fax www.banffplasticsurgery.com
PHaSES: Practical Hands-on Surgical Education System
 U.S. Toll Free 866-GOLIMBS PHaSES Range PHaSES: Practical Hands-on Surgical Education System Limbs & Things is pleased to introduce the PHaSES Range. The range is based upon our well known basic & general
U.S. Toll Free 866-GOLIMBS PHaSES Range PHaSES: Practical Hands-on Surgical Education System Limbs & Things is pleased to introduce the PHaSES Range. The range is based upon our well known basic & general
Glaucoma filtration surgery (Tube surgery)
 Oxford Eye Hospital Glaucoma filtration surgery (Tube surgery) Information for patients page 2 This leaflet gives you information that will help you decide whether to have glaucoma tube surgery. You might
Oxford Eye Hospital Glaucoma filtration surgery (Tube surgery) Information for patients page 2 This leaflet gives you information that will help you decide whether to have glaucoma tube surgery. You might
Life After Weight Loss Program Patient Guide
 Life After Weight Loss Program Patient Guide The new you. Weight loss either through bariatric surgery or diet and exercise is truly a life changing event. You look and feel better. You are healthier.
Life After Weight Loss Program Patient Guide The new you. Weight loss either through bariatric surgery or diet and exercise is truly a life changing event. You look and feel better. You are healthier.
Titanium Wire with Barb and Needle. For canthal tendon procedures.
 Titanium Wire with Barb and Needle. For canthal tendon procedures. Technique Guide Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation Table of Contents Introduction Titanium Wire with Barb and Needle
Titanium Wire with Barb and Needle. For canthal tendon procedures. Technique Guide Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation Table of Contents Introduction Titanium Wire with Barb and Needle
MEDICAL MANAGEMENT POLICY
 TITLE: Scar Revision/Keloid PAGE: 1of 9 This Medical policy is not a guarantee of benefits or coverage, nor should it be deemed as medical advice. In the event of any conflict concerning benefit coverage,
TITLE: Scar Revision/Keloid PAGE: 1of 9 This Medical policy is not a guarantee of benefits or coverage, nor should it be deemed as medical advice. In the event of any conflict concerning benefit coverage,
Minimally Invasive Hip Replacement through the Direct Lateral Approach
 Surgical Technique INNOVATIONS IN MINIMALLY INVASIVE JOINT SURGERY Minimally Invasive Hip Replacement through the Direct Lateral Approach *smith&nephew Introduction Prosthetic replacement of the hip joint
Surgical Technique INNOVATIONS IN MINIMALLY INVASIVE JOINT SURGERY Minimally Invasive Hip Replacement through the Direct Lateral Approach *smith&nephew Introduction Prosthetic replacement of the hip joint
Ophthalmic Management of the Facial Palsy Patient
 Ophthalmic Management of the Facial Palsy Patient Philip L. Custer, M.D. 1 ABSTRACT The management of the ocular sequelae of facial palsy should be individualized for each patient. The patient s age, ocular
Ophthalmic Management of the Facial Palsy Patient Philip L. Custer, M.D. 1 ABSTRACT The management of the ocular sequelae of facial palsy should be individualized for each patient. The patient s age, ocular
Patient Information. Posterior Cervical Surgery. Here to help. Respond Deliver & Enable
 Here to help Our Health Information Centre (HIC) provides advice and information on a wide range of health-related topics. We also offer: Services for people with disabilities. Information in large print,
Here to help Our Health Information Centre (HIC) provides advice and information on a wide range of health-related topics. We also offer: Services for people with disabilities. Information in large print,
SERVICES. Cosmetic and Laser Surgery
 SERVICES Cosmetic and Laser Surgery Cosmetic and Laser Surgery at Lahey Outpatient Center, Lexington, uses the most advanced anti-aging treatments and technologies to restore the younger, more vibrant
SERVICES Cosmetic and Laser Surgery Cosmetic and Laser Surgery at Lahey Outpatient Center, Lexington, uses the most advanced anti-aging treatments and technologies to restore the younger, more vibrant
UNMH Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Clinical Privileges
 All new applicants must meet the following requirements as approved by the UNMH Board of Trustees effective: 09/26/2014 INSTRUCTIONS Applicant: Check off the "Requested" box for each privilege requested.
All new applicants must meet the following requirements as approved by the UNMH Board of Trustees effective: 09/26/2014 INSTRUCTIONS Applicant: Check off the "Requested" box for each privilege requested.
Breast Augmentation Information Sheet
 Breast Augmentation Information Sheet Are you thinking about Breast Augmentation? If you are considering surgery, Dr. Peterson wants you to be thoroughly informed about this procedure. Reading this brochure
Breast Augmentation Information Sheet Are you thinking about Breast Augmentation? If you are considering surgery, Dr. Peterson wants you to be thoroughly informed about this procedure. Reading this brochure
Posterior Cervical Decompression
 Posterior Cervical Decompression Spinal Unit Tel: 01473 702032 or 702097 Issue 2: January 2009 Following your recent MRI scan and consultation with your spinal surgeon, you have been diagnosed with a
Posterior Cervical Decompression Spinal Unit Tel: 01473 702032 or 702097 Issue 2: January 2009 Following your recent MRI scan and consultation with your spinal surgeon, you have been diagnosed with a
Melbourne Children s Eye Clinic. Strabismus Surgery for Children
 Melbourne Children s Eye Clinic Strabismus Surgery for Children Why operate on turned eyes? Surgery for turned eyes aims to improve the alignment of the eyes, that is, to make the eyes look straight. The
Melbourne Children s Eye Clinic Strabismus Surgery for Children Why operate on turned eyes? Surgery for turned eyes aims to improve the alignment of the eyes, that is, to make the eyes look straight. The
SILS. Port Insertion By Homero Rivas, MD, MBA, FACS. Single incision. Single port. Simple choice.
 SILS Port Insertion By Homero Rivas, MD, MBA, FACS Single incision. Single port. Simple choice. SILS Port Insertion By Homero Rivas, MD, MBA, FACS For the last 20 years, there has given surgical procedure.
SILS Port Insertion By Homero Rivas, MD, MBA, FACS Single incision. Single port. Simple choice. SILS Port Insertion By Homero Rivas, MD, MBA, FACS For the last 20 years, there has given surgical procedure.
Selinsgrove, Pennsylvania
 Selinsgrove, Pennsylvania Skin Care at FPC offers patients a wide array of aesthetic services and products in a relaxing and serene environment. Body Contouring Treatments Now you can have the body you
Selinsgrove, Pennsylvania Skin Care at FPC offers patients a wide array of aesthetic services and products in a relaxing and serene environment. Body Contouring Treatments Now you can have the body you
BREAST IMPLANTS (enlargement, augmentation) Dr. Benjamin Van Raalte TYPES OF IMPLANTS saline round implants high profiles low profile shaped
 BREAST IMPLANTS (enlargement, augmentation) Dr. Benjamin Van Raalte has 20 years of experience with breast enlargement including axillary incisions and gel implants. Dr. Van Raalte is the first Quad City
BREAST IMPLANTS (enlargement, augmentation) Dr. Benjamin Van Raalte has 20 years of experience with breast enlargement including axillary incisions and gel implants. Dr. Van Raalte is the first Quad City
Claims submission simplified for emergency dental procedure codes
 January 2002 No. 2002-02 PHC 1844 To: Dentists HMOs and Other Managed Care Programs Claims submission simplified for emergency dental procedure codes Effective immediately, both electronic and paper claims
January 2002 No. 2002-02 PHC 1844 To: Dentists HMOs and Other Managed Care Programs Claims submission simplified for emergency dental procedure codes Effective immediately, both electronic and paper claims
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY
 OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY NASOLABIAL FLAP FOR ORAL CAVITY RECONSTRUCTION Harry Wright, Scott Stephan, James Netterville Designed as a true myocutaneous flap pedicled
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY NASOLABIAL FLAP FOR ORAL CAVITY RECONSTRUCTION Harry Wright, Scott Stephan, James Netterville Designed as a true myocutaneous flap pedicled
Caring for a Tenckhoff Catheter
 Caring for a Tenckhoff Catheter UHN A Patient s Guide What is a Pleural Effusion? There is a small space between the outside of your lung and the chest wall (ribs). This space is called the pleural space.
Caring for a Tenckhoff Catheter UHN A Patient s Guide What is a Pleural Effusion? There is a small space between the outside of your lung and the chest wall (ribs). This space is called the pleural space.
Arthroscopic shoulder stabilisation. Patient Information to be retained by patient
 PLEASE PRINT WHOLE FORM DOUBLE SIDED ON YELLOW PAPER Patient Information to be retained by patient affix patient label Shoulder instability The shoulder is the most common joint in the body to dislocate.
PLEASE PRINT WHOLE FORM DOUBLE SIDED ON YELLOW PAPER Patient Information to be retained by patient affix patient label Shoulder instability The shoulder is the most common joint in the body to dislocate.
Arthroscopic Shoulder Procedures. David C. Neuschwander MD. Shoulder Instability. Allegheny Health Network Orthopedic Associates of Pittsburgh
 Arthroscopic Shoulder Procedures David C. Neuschwander MD Allegheny Health Network Orthopedic Associates of Pittsburgh Shoulder Instability Anterior Instability Posterior Instability Glenohumeral Joint
Arthroscopic Shoulder Procedures David C. Neuschwander MD Allegheny Health Network Orthopedic Associates of Pittsburgh Shoulder Instability Anterior Instability Posterior Instability Glenohumeral Joint
EYE MUSCLE SURGERY. I am on staff and perform surgery at the following facilities: HCA Gulf Coast Surgery Center of Bradenton
 1 EYE MUSCLE SURGERY Prepared by Scott E. Silverman, M.D. Strabismus is a misalignment of the eyes. The eyes may cross or drift up or out. Strabismus may be present from birth or may develop in childhood.
1 EYE MUSCLE SURGERY Prepared by Scott E. Silverman, M.D. Strabismus is a misalignment of the eyes. The eyes may cross or drift up or out. Strabismus may be present from birth or may develop in childhood.
LASIK What is LASIK? Am I a good candidate for LASIK? What happens before surgery? How is LASIK done?
 LASIK What is LASIK? Laser assisted in situ keratomileusis, or LASIK, is an outpatient surgical procedure used to treat myopia (nearsightedness), hyperopia (farsightedness), and astigmatism. With LASIK,
LASIK What is LASIK? Laser assisted in situ keratomileusis, or LASIK, is an outpatient surgical procedure used to treat myopia (nearsightedness), hyperopia (farsightedness), and astigmatism. With LASIK,
THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME
 THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME The Problem The term thoracic outlet syndrome is used to describe a condition of compression of the nerves and/or blood vessels in the region around the neck and collarbone, called
THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME The Problem The term thoracic outlet syndrome is used to describe a condition of compression of the nerves and/or blood vessels in the region around the neck and collarbone, called
