body yworks bodyworks bodyworks bodywork bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks yworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks Bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks
|
|
|
- Erika West
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Bodyworks Your guide to understanding reproduction odyworks odyworks works yworks ork bodywork odyworks yworks yworks body
2 2 3 Bodyworks This leaflet will tell you all about the reproductive system in men and women. It s particularly useful if you want to understand: how the reproductive organs work the menstrual cycle (ovulation and periods) what s involved in conception (getting pregnant) how contraception works to prevent pregnancy. Women s bodies The reproductive system in women is made up of external and internal organs.these are found in the lower abdomen, the part of the body below the umbilicus (tummy button). This area is often referred to as the pelvic area. They include: The external organs vaginal entrance (opening) labia (vaginal lips) clitoris. The external organs are known as the vulva. The internal organs uterus (womb) fallopian tubes ovaries vagina cervix Contents Women s bodies...3 The female reproductive organs outside the body...4 The female reproductive organs inside the body...4 The menstrual cycle...6 Men s bodies...10 The male reproductive organs...10 Conception (getting pregnant)...13 Pregnancy...16 The pregnancy test...16 It s all in the genes...17 Making sense of contraception and sexual health..18 How do I find out about sexual health?...18 Emergency contraception...19 Sexually transmitted infections...19 How fpa can help you...20 A final word...20
3 4 5 The female reproductive organs outside the body The vulva includes the opening to the vagina, the inner and outer lips (called labia) and the clitoris. The external part of the clitoris is found towards the front of the vulva, it is highly sensitive and when stimulated can make women feel sexually aroused and lead to orgasm. Hormones and eggs did you know? The female sex hormones, estrogen and progesterone, are responsible for female characteristics such as body shape, developing breasts, periods and controlling the menstrual cycle. When a woman reaches puberty she will have up to 1 million eggs in her ovaries. During a woman s reproductive life only about eggs will actually be released at ovulation. As a woman gets older (over 30 years) the number and quality of her eggs declines making conception more difficult. An egg is less than 1/8 of the size of a grain of sand invisible to the naked eye. The fallopian tubes The two fallopian tubes are found on each side of the uterus, near the ovaries.these are tiny tubes only as wide inside as a thick human hair and just 10cm long! The funnel-like ends of the fallopian tubes pick up the egg released by the ovary and carry it to the uterus.tiny, microscopic hairs line the inside of the fallopian tubes and help move the egg along.the inside of the tube is very delicate and can very easily be damaged or blocked by infection. The uterus The uterus is made of muscle. It s about the size and shape of an upside down pear, hollow and very stretchy. This is where the baby develops if a woman becomes pregnant.the uterus can stretch to hold a baby and shrink more or less back to its pre-pregnancy size after the baby is born. The female reproductive organs inside the body Ovaries Women have two ovaries, one on each side of the uterus. Ovaries are the size and shape of almonds and they contain ova (eggs) in structures called follicles. The ovaries also produce the two female sex hormones estrogen and progesterone. ovary cervix fallopian tube uterus (womb) vagina
4 6 7 The cervix The lower part of the uterus which connects to the vagina is called the cervix. Sperm released by the man during sex swim from the vagina through the cervix to reach an egg. The cervix contains small glands which produce secretions called mucus.this alters in texture and amount during a woman s menstrual cycle. In her fertile phase (the time around ovulation when an ovary releases an egg) it changes from being thick, sticky and creamy in colour to being clearer, wetter, and more stretchy like raw egg white. These changes allow sperm to pass through the cervix and reach the egg more easily. When a woman is pregnant, the cervix becomes plugged with very thick mucus to protect the developing baby from infection. Vagina The vagina is a muscular tube 7 10cm long which leads from the cervix to the vaginal opening (vulva). The vaginal opening is between the legs, between the urethra (the tube women pee through) at the front and the anus at the back. The vagina tilts upward and towards the small of the back. It has glands which produce lubricating secretions when women are sexually aroused to help the penis enter the vagina (penetration). Like the uterus, the vaginal walls are stretchy, allowing it to hold a tampon and stretch around a penis during sex, or a baby during delivery. The menstrual cycle The menstrual cycle is the process during which an egg develops and is released from the ovaries, and the lining of the uterus prepares for a possible pregnancy. If a woman does not become pregnant the lining of the uterus is shed, as her period. uterus cervix fallopian tube endometrium cervical canal vagina These events are caused by hormones chemical messengers which travel around the body in the blood stream. How long does the cycle take? The number of days in the menstrual cycle is calculated from the first day of the period to the day before the start of the next period. The average length of the menstrual cycle is around 28 days, although many women have longer or shorter cycles and this is normal. ovary What happens during the menstrual cycle? The first day of the period is known as day one of the cycle. When a woman has her period about 20 eggs start to develop in the ovary.
5 8 9 The hormone estrogen causes the lining of the uterus (endometrium) to start to thicken in preparation for a fertilised egg. It also causes the mucus in the cervix to become thinner, wetter and more stretchy, allowing sperm to reach an egg more easily. Day 28 Day 1 Menstruation (period) Regardless of how long or short a woman s cycle is, ovulation (egg release from an ovary) will usually happen around days before the start of her next period. However, the time from the first day of the period to ovulation can vary between women. Post-Ovulation Pre-Ovulation Occasionally, more than one egg is released (if this happens it will occur within 24 hours of the first egg being released). If more than one egg is fertilised it can lead to a multiple pregnancy such as twins. Ovulation triggers the production of a second hormone, progesterone. This prepares the lining of the uterus even further, ensuring that it is spongy, thick and full of nutrients so that a fertilised egg can settle or implant into it. After ovulation the cervical mucus goes back to being thick and sticky. If the egg is not fertilised it will be reabsorbed naturally by the body, the level of hormones falls, and this menstrual cycle comes to an end. The cycle then begins again.the lining of the uterus breaks down and is shed through the vagina as a period, also called menstruation. Day 16 Day 10 Ovulation Periods did you know? Some menstrual cycles can be as short as 21 days and some as long as 40 days. Some women have menstrual cycles that vary in length from month to month. The amount and quality of cervical secretions will vary from woman to woman and also from one cycle to the next. The average amount of menstrual blood lost in a period is 3 5 tablespoons. A period usually lasts between 3 7 days. Women living together often find that they have their periods at the same time. Some women have pain around ovulation Mittelschmerz this means middle pain.
6 10 11 Men s bodies Unlike women s reproductive organs, men s reproductive organs are found entirely outside the body. The male reproductive organs Testicles and scrotum The testicles (balls) are the male equivalent of a woman s ovaries. It is inside these that sperm are made and important male hormones produced. There are two testicles, roughly the size of small plums, and they are protected in a soft pouch of skin called the scrotum. The scrotum hangs outside the body just behind the penis and between the legs.this helps the testicles keep cool the average body temperature (37 C) is too hot to produce healthy sperm.they are very sensitive to heat and if they get too hot the scrotum drops down to cool off and when they are cold it shrinks closer to the body to keep warm. Male hormones Hormones are just as important for reproduction in men as they are in women.the testicles produce the male hormone testosterone. It is responsible for sperm production and growth and is important for male sex drive. It also controls male characteristics such as hair growth and the deepening of the voice. Sperm Inside each testicle are about 1,000 tightly coiled tubes. Individual sperm are continuously made in these tubes. The growing sperm travel along the tiny tubes to a larger coiled tube called the glans penis scrotum bladder urethra epididymis which is at the top of the testicle. Here they stay until they are fully mature and ready to be ejaculated. Ejaculation At ejaculation sperm passes along the vas deferens (sperm ducts) to the penis and out of the body through the urethra. On the way, fluid from the seminal vesicles and prostate gland is added to the sperm.this helps nourish and seminal vesicles ejaculatory duct prostate gland Cowper s gland vas deferens testicle epididymis
7 12 13 Sperm did you know? Boys start to produce sperm at puberty, the time when their body goes through changes from a boy to a man. It takes about 70 days for a sperm to be produced, but as production is a continuous process there is always plenty of fully mature sperm at any one time. Sperm are minute only 1/25mm long and 1/250mm wide, which is about a hundred times smaller than the female egg. Sperm are made up of three parts, a head containing the sex chromosomes, a middle which gives them the energy, and a tail for swimming. On average men produce around 150 1,000 million sperm everyday, so they are unlikely to run out. Sperm are excellent swimmers. With the right type of conditions the best swimmers are able to swim through the cervix into the uterus in about two minutes. Sperm are also survivors and can live for up to five days on average inside the woman s body but up to seven days if the conditions are right. Sperm production can be damaged by untreated sexually transmitted infections, excessive heat, alcohol, smoking or recreational drugs. transport them and gives semen (as it is now called) its white creamy appearance. The average ejaculation contains up to 300 million sperm and will fill a small teaspoon. The penis contains erectile tissue which fills with blood when a man is sexually aroused and causes an erection, making the penis longer and thicker. To prepare for ejaculation a small amount of lubricating fluid, known as pre-ejaculation fluid is produced from the Cowper s glands. This fluid leaks out of the penis before ejaculation and may contain sperm. When a man ejaculates, the muscles of the penis contract forcing the semen out of the penis in spurts. Straight after ejaculation the fluid is thick but it becomes more liquid after a few minutes this helps to release the sperm. Conception (getting pregnant) Conception is a process that begins with fertilisation and ends with implantation. For fertilisation to take place an egg needs to meet a sperm usually through a man and woman having sex. When the ovary releases the egg, it is picked up by the fallopian tube where it can be fertilised by the sperm. Sperm are able to wait around in the uterus and fallopian tube until the egg is released. Small beating hairs and tiny wave-like contractions help the egg travel along the fallopian tube where it may meet a sperm within minutes or hours of being released from one of the ovaries.the egg only lives for up to 24 hours so it increases the chance of pregnancy if the sperm are ready and waiting. If you have sex 2 3 times a week you will help ensure there is always sperm waiting.
8 14 15 Only a smaller number of sperm will actually survive the trip to the fallopian tubes and finally only one sperm will actually enter the egg. The sperm attaches itself to the egg and produces a special substance which dissolves the outer coat of the egg. Once it has entered, a quick repair of the egg coating means that no other sperm can get in. Once the sperm is fully inside the egg, fertilisation has taken place. about 3 4 days later: the fertilised egg is now 64 separate cells 5 6 days later: the embryo floats in the womb about days later: the fertilised egg splits into two cells about two days later: the cells divide again The fertilised egg is wafted down the fallopian tube to the ready-prepared uterus. Here, the embryo settles and over a few days attaches itself to the thick, nutritious lining. Implantation has now taken place, conception is complete and the pregnancy begins. The time from ovulation to implantation is around ten days. Once the pregnancy has begun, the pregnancy hormone human chorionic gonadotrophin (hcg) begins to be produced. Sometimes a pregnancy develops outside the uterus, usually in the fallopian tube. This is called an ectopic pregnancy. womb ovary the embryo starts to embed itself in the womb wall.this is around 10 days after ovulation and pregnancy begins fallopian tube cervix vagina START HERE ovulation occurs; an egg is released from the ovary into the fallopian tube. It lives for up to 24 hours, if unprotected sex has taken place sperm surround the egg. One breaks through to fertilise it.
9 16 17 Conception did you know? Conception is a process that starts with fertilisation and ends with implantation. It takes about three hours for the sperm to fully enter the egg. The egg can be fertilised by sperm that have been ejaculated up to seven days before. The egg has special places on the outside coat that attract the sperm. It takes a couple an average of 3 6 months to conceive, if they are having sex frequently (2 3 times per week) during their fertile time. Women over 30 years old may take longer to conceive. Women who are either very underweight or very overweight may have more difficulties conceiving. An average pregnancy lasts 280 days. Pregnancy The pregnancy test The earliest and most reliable sign of pregnancy for women with a regular menstrual cycle is a missed period. Sometimes women who are pregnant have a shorter or lighter period than normal. A woman can carry out a pregnancy test from the first day of a missed period. Some tests suggest that pregnancy tests can be carried out earlier than this, but the effectiveness of this varies. For women who don t have regular periods, the earliest time to do a test is 21 days from the last time that they had unprotected sex. For some women the test does not show positive until their period is at least a week late. Pregnancy tests look for the pregnancy hormone hcg which is found in the urine of pregnant women. A positive test is almost always correct. But women can sometimes get a negative result if the test is carried out too early or not correctly, even though they may be pregnant. It s all in the genes How a baby looks is determined by the genes it inherits from its parents. Genes are contained in chromosomes tiny thread like structures and each chromosome contains thousands of genes. It is these genes that determine your height, build, blood group, and eye and hair colour. Some characteristics will be inherited from the mother and some from the father. So how is the sex of the baby decided? An egg has 22 chromosomes and one sex chromosome known as the X chromosome. A sperm also has 22 chromosomes and one sex chromosome which can either be an X or a Y chromosome. It is the sperm s chromosome that determines the sex of the baby. A simple way to look at it is like this: If the egg is fertilised by a sperm containing an X chromosome the baby will be female. Mother X + Father X = XX = Female If the sperm contains a Y chromosome the baby will be male. Mother X + Father Y = XY = Male. To date, there is no reliable scientific evidence to support claims made for choosing the sex of the baby, such as when you have sex, sexual positions or diet.
10 18 19 Making sense of contraception and sexual health Understanding how your body works can help you and your partner to plan a pregnancy or to avoid one. There are many different methods of contraception which suit people at different times of their lives. They all work in different ways, either by preventing or affecting ovulation, stopping fertilisation by preventing the sperm from meeting the egg, or by identifying the fertile and infertile times of the menstrual cycle. fpa produces a range of easy-to-read booklets about contraception, common sexually transmitted infections, pregnancy choices, abortion and planning a pregnancy. For more information visit or call the fpa helpline (see back cover). How do I find out about sexual health? Services are free for women and men of all ages through the National Health Service. You can find out about all sexual health services from sexual health direct, run by fpa, on or at You can find details of general practices and pharmacies in England at and in Wales at In Scotland you can find details of general practices at In England and Wales you can also call NHS Direct on and in Scotland NHS 24 on In Northern Ireland call fpa s helpline on or for details of general practices see You can also get details of your nearest contraception, genitourinary medicine (GUM) or sexual health clinic from a telephone directory, health centre, local pharmacy, hospital, midwife, health visitor or advice centre. You can get details of GUM or sexual health clinics from the Sexual Health Line on or at You can find details of young people s services from Brook on or from Sexwise on , or at Emergency contraception If you have had sex without using contraception or think your method might have failed there are two emergency methods you can use. The emergency hormonal pill must be taken up to three days (72 hours) after sex. It is more effective, the earlier it is taken after sex. An IUD must be fitted up to five days after sex, or up to five days after the earliest time you could have released an egg (ovulation). Ask your doctor or nurse about getting emergency pills in advance, just in case you need them. Sexually transmitted infections Most methods of contraception do not protect you from sexually transmitted infections. Male and female condoms, when used correctly and consistently, can help protect against sexually transmitted infections. Diaphragms and caps may also protect against some sexually transmitted infections. If you can, avoid using condoms containing Nonoxinol 9 (spermicidally lubricated), as this does not protect against HIV and may even increase the risk of infection.
11 How fpa can help you sexual health direct is a nationwide service run by fpa. It provides: confidential information and advice and a wide range of booklets on individual methods of contraception, common sexually transmitted infections, pregnancy choices, abortion and planning a pregnancy details of contraception clinics, sexual health clinics and genitourinary medicine (GUM) clinics. fpa helplines England helpline am to 6pm Monday to Friday b bod bb body 9am to 5pm Monday to Thursday, 9am to 4.30pm Friday Northern Ireland helpline or visit fpa s website A final word This booklet can only give you basic information about the body.the information in this booklet is based on evidence-guided research from the World Health Organization and The Faculty of Sexual and Reproductive Healthcare of the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists. Different people may give you different advice on certain points. All methods of contraceptionwb come with a Patient Information Leaflet which provides detailed information about the method. Remember contact your doctor, practice nurse or a contraception clinic if you are worried or unsure about anything. bod body Registered charity number Supported by the Department of Health. fpa April 2008 ISBN:
bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks odyworks bodyworks bodywor bodyworks yworks bodyworks bodyworks bodywork bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks odyworks body
 Bodyworks Your guide to understanding reproduction orksody odyworks body bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks dyworks ork bodywor odyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodywork
Bodyworks Your guide to understanding reproduction orksody odyworks body bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks dyworks ork bodywor odyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodywork
IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD the IUD. the IUD. the the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD.
 your guide to Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you I the IUD 2 3 The intrauterine device (IUD) An IUD is a small plastic and copper device that is put into your uterus (womb).
your guide to Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you I the IUD 2 3 The intrauterine device (IUD) An IUD is a small plastic and copper device that is put into your uterus (womb).
IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. the IUD. your guide to
 your guide to Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you IUD he the the the 2 3 The intrauterine device (IUD) An IUD is a small plastic and copper device that is put into your
your guide to Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you IUD he the the the 2 3 The intrauterine device (IUD) An IUD is a small plastic and copper device that is put into your
l family plan natural natural family p natural family planning ily natural family plannin natural fami atural family planning your guide to
 your guide to natural family planning Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you natural family pla al family plannin natural family planning natural family plann atural fam natural
your guide to natural family planning Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you natural family pla al family plannin natural family planning natural family plann atural fam natural
the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD your guide to
 your guide to Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you IUD IUD the e IUD IU IUD the IUD 2 The intrauterine device (IUD) An IUD is a small plastic and copper device that is put
your guide to Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you IUD IUD the e IUD IU IUD the IUD 2 The intrauterine device (IUD) An IUD is a small plastic and copper device that is put
progestog progestogen stogen-only pill progestogen progestogen-only pill he progestogen-only pill progestogen-onl progestogen-o the progestogenonly
 your guide to the progestogenonly pill Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you the progestogen rogestogen-only the progestogen-only pill progestogen-only pill stogen-only progestoge
your guide to the progestogenonly pill Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you the progestogen rogestogen-only the progestogen-only pill progestogen-only pill stogen-only progestoge
Lesson Plan Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I
 Lesson Plan Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I TOPIC: Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I SUBJECT: Life Skills TARGET AGE RANGE: 9 15 TIME: 45 minutes IDEAL NUMBER OF LEARNERS:
Lesson Plan Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I TOPIC: Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I SUBJECT: Life Skills TARGET AGE RANGE: 9 15 TIME: 45 minutes IDEAL NUMBER OF LEARNERS:
implant contraceptiv contraceptive contraceptive raceptiv contraceptive implant contraceptive contraceptive ontraceptive implant ontraceptive im
 your guide to the contraceptive implant Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you contra ontraceptive im contraceptive implant mpl ceptive contraceptive contracepti ntraceptive
your guide to the contraceptive implant Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you contra ontraceptive im contraceptive implant mpl ceptive contraceptive contracepti ntraceptive
Understanding Fertility
 Understanding Fertility 6 Introduction The word fertile means the ability to become pregnant or to cause pregnancy. Basic knowledge of both the male and female reproductive systems is important for understanding
Understanding Fertility 6 Introduction The word fertile means the ability to become pregnant or to cause pregnancy. Basic knowledge of both the male and female reproductive systems is important for understanding
ency emergency contra-
 your guide to emergency contraception Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you emergency cont gency contrace emergency contraception ency emergency contra- emergen mergency contraception
your guide to emergency contraception Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you emergency cont gency contrace emergency contraception ency emergency contra- emergen mergency contraception
injections injections injections injections injections injection injections injections injections tions njections injections injections injections
 your guide to contraceptive Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you ions ections injection njections injection tions 2 Contraceptive Contraceptive contain a progestogen hormone
your guide to contraceptive Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you ions ections injection njections injection tions 2 Contraceptive Contraceptive contain a progestogen hormone
Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS AND THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE
 Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS AND THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE Learning Objectives By the end of this unit, the learner should be able to: Explain the importance of understanding the male and female reproductive
Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS AND THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE Learning Objectives By the end of this unit, the learner should be able to: Explain the importance of understanding the male and female reproductive
Female Reproductive System. Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued
 Female Reproductive System Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System Female produce ovum or egg cells. The egg (ovum) cell is the female sex cell. Female Reproductive
Female Reproductive System Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System Female produce ovum or egg cells. The egg (ovum) cell is the female sex cell. Female Reproductive
contraception contraception contraception contracepti contraception contraception contraception aception contraception contraception contraception
 your guide to Helping you choose the method of that is best for you raception aception contracept contracepti contracep contracepti Your guide to This leaflet shows the available contraceptive methods,
your guide to Helping you choose the method of that is best for you raception aception contracept contracepti contracep contracepti Your guide to This leaflet shows the available contraceptive methods,
EVERY LIVING THING has a number of
 Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproductive Systems EVERY LIVING THING has a number of organ systems operating to perform specific functions. If you were to examine one of these systems, you would observe
Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproductive Systems EVERY LIVING THING has a number of organ systems operating to perform specific functions. If you were to examine one of these systems, you would observe
Male Infertility. Penis. Epididymis
 Male Infertility Introduction Infertility is a term used when a man is unable to get a woman pregnant. But the term is only used after at least one year of trying. Infertility is a common problem. About
Male Infertility Introduction Infertility is a term used when a man is unable to get a woman pregnant. But the term is only used after at least one year of trying. Infertility is a common problem. About
Anatomy of Male Reproductive System
 Anatomy of Male Reproductive System A. Reproductive Systems 1. Gonads: primary sex organs a. Produce gametes b. Produce hormones c. Male Gonads: testes d. Female Gonads: ovaries 2. Gametes: sex cells a.
Anatomy of Male Reproductive System A. Reproductive Systems 1. Gonads: primary sex organs a. Produce gametes b. Produce hormones c. Male Gonads: testes d. Female Gonads: ovaries 2. Gametes: sex cells a.
after you ve had you after you ve had your baby after you ve after you ve had your baby fter you ve had your baby after contraceptive choices
 your guide to contraceptive choices after you ve had your baby Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you after you ve had you ve had your bab after you ve had your baby after
your guide to contraceptive choices after you ve had your baby Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you after you ve had you ve had your bab after you ve had your baby after
Reproduction Multiple Choice questions
 Reproduction Multiple Choice questions 1. In mammals that are seasonal breeders, females are receptive only once a year. This is called A) a follicular cycle B) an estrous cycle C) a menstrual cycle D)
Reproduction Multiple Choice questions 1. In mammals that are seasonal breeders, females are receptive only once a year. This is called A) a follicular cycle B) an estrous cycle C) a menstrual cycle D)
2. What muscle pulls the testis down into the scrotum during development?
 Anatomy & Physiology Reproductive System Worksheet Male 1. Put the following structures in order from testis to urethra: ductus deferens, rete testis, epididymus, seminiferous tubules 1) 2) 3) 4) 2. What
Anatomy & Physiology Reproductive System Worksheet Male 1. Put the following structures in order from testis to urethra: ductus deferens, rete testis, epididymus, seminiferous tubules 1) 2) 3) 4) 2. What
STUDENT S WORKSHEETS. Eva M. Zamudio Zamudio
 STUDENT S WORKSHEETS January April 2009 HUMAN LIFE CYCLE HANDOUT 1 1. Write the name of each stage in the right order: retirement adolescence babyhood adulthood - childhood 2. What stage does it belong
STUDENT S WORKSHEETS January April 2009 HUMAN LIFE CYCLE HANDOUT 1 1. Write the name of each stage in the right order: retirement adolescence babyhood adulthood - childhood 2. What stage does it belong
Sexual reproduction in humans
 Sexual reproduction in humans Name: WHY DO HUMANS NEED TO REPRODUCE? The reason humans reproduce is to have children so that our species can continue to exist. Humans reproduce sexually, which means like
Sexual reproduction in humans Name: WHY DO HUMANS NEED TO REPRODUCE? The reason humans reproduce is to have children so that our species can continue to exist. Humans reproduce sexually, which means like
Sterilisation for women and men: what you need to know
 Sterilisation for women and men: what you need to know Published January 2004 by the RCOG Contents Page number Key points 1 About this information 2 What are tubal occlusion and vasectomy? 2 What do I
Sterilisation for women and men: what you need to know Published January 2004 by the RCOG Contents Page number Key points 1 About this information 2 What are tubal occlusion and vasectomy? 2 What do I
Gonorrhoea. Looking after your sexual health
 Gonorrhoea Looking after your sexual health 2 Gonorrhoea Gonorrhoea is a bacterial sexually transmitted infection (STI). It can be painful and can cause serious health problems such as infertility in both
Gonorrhoea Looking after your sexual health 2 Gonorrhoea Gonorrhoea is a bacterial sexually transmitted infection (STI). It can be painful and can cause serious health problems such as infertility in both
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Menstruation
 Menstruation WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Menstruation is a normal and healthy part of growing up. The discharge of blood and tissue from the lining of your uterus each
Menstruation WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Menstruation is a normal and healthy part of growing up. The discharge of blood and tissue from the lining of your uterus each
pregnant pregnant pregnant pregnant pregnan pregnant ant pregnant pregnant pregnant egnant pregnant pregnant pregnant pregnant pregna
 Pregnant and don t know what to do? A guide to your options pregna regnant ant pregnan egnant 2 3 Are you but not sure you want to have the baby? Do you need more information about the options available
Pregnant and don t know what to do? A guide to your options pregna regnant ant pregnan egnant 2 3 Are you but not sure you want to have the baby? Do you need more information about the options available
Trichomonas vaginalis. Looking after your sexual health
 Trichomonas vaginalis Looking after your sexual health 2 3 Trichomonas vaginalis Trichomonas vaginalis is a sexually transmitted infection (STI). It is sometimes referred to as trichomonas or trichomoniasis,
Trichomonas vaginalis Looking after your sexual health 2 3 Trichomonas vaginalis Trichomonas vaginalis is a sexually transmitted infection (STI). It is sometimes referred to as trichomonas or trichomoniasis,
Chlamydia. Looking after your sexual health
 Chlamydia Looking after your sexual health 2 Chlamydia Chlamydia is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections (STIs). It is very easy to treat and cure. Up to one in 10 sexually active young
Chlamydia Looking after your sexual health 2 Chlamydia Chlamydia is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections (STIs). It is very easy to treat and cure. Up to one in 10 sexually active young
Growing up what s it all about?
 4YOU Growing up what s it all about? GROWING UP... WHAT S HAPPENING? You may have noticed things about yourself and your friends that are starting to change. Changing bodies, changing feelings, changing
4YOU Growing up what s it all about? GROWING UP... WHAT S HAPPENING? You may have noticed things about yourself and your friends that are starting to change. Changing bodies, changing feelings, changing
condoms condoms male and fe male and female cond male and female condoms male and female male an male and female male and condoms
 your guide to male and female condoms Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you and male condoms female and female condom con dom male and female male an ale and female condoms
your guide to male and female condoms Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you and male condoms female and female condom con dom male and female male an ale and female condoms
abortion abortion abortion abortion abortion abortion abortion on abortio abortion ortion abortion abortion abortion abortion abortio
 Abortion Your questions answered abortio bortion ion ortion on abortio 2 Are you pregnant but not sure you want to have the baby? Do you need more information about your pregnancy choices? Unplanned pregnancy
Abortion Your questions answered abortio bortion ion ortion on abortio 2 Are you pregnant but not sure you want to have the baby? Do you need more information about your pregnancy choices? Unplanned pregnancy
The Menstrual Cycle, Hormones and Fertility Treatment
 The Menstrual Cycle, Hormones and Fertility Treatment How many of us understand how our monthly cycle works? Every 28 days (or thereabouts), between the ages of around 13 and 51, a woman will release a
The Menstrual Cycle, Hormones and Fertility Treatment How many of us understand how our monthly cycle works? Every 28 days (or thereabouts), between the ages of around 13 and 51, a woman will release a
vagina vaginal r vaginal ring vaginal vaginal ring aginal ring vaginal ring vaginal ring vaginal ring the contraceptive vaginal rin vaginal ring
 your guide to the contraceptive vaginal ring Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you vagina vaginal ring vaginal r vaginal ring vaginal ring vaginal rin vaginal aginal ring
your guide to the contraceptive vaginal ring Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you vagina vaginal ring vaginal r vaginal ring vaginal ring vaginal rin vaginal aginal ring
Reproductive System Grades 9 and 10, Lesson #3
 Reproductive System Grades 9 and 10, Lesson #3 Time Needed One class period Student Learning Objectives To be able to 1. Locate and spell at least 75% of the parts of the male and female reproductive systems,
Reproductive System Grades 9 and 10, Lesson #3 Time Needed One class period Student Learning Objectives To be able to 1. Locate and spell at least 75% of the parts of the male and female reproductive systems,
Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment
 Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment Information for you Information for you Published August 2010 Published in August 2010 (next review date: 2014) Acute What is pelvic inflammatory
Acute pelvic inflammatory disease: tests and treatment Information for you Information for you Published August 2010 Published in August 2010 (next review date: 2014) Acute What is pelvic inflammatory
Reproductive System. from the Human Body System Series. catalog # 3322. Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING
 Reproductive System from the Human Body System Series catalog # 3322 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560 Sherman Avenue Suite 100 Evanston, IL 60201 1-800-323-9084 24-Hour Fax No. 847-328-6706
Reproductive System from the Human Body System Series catalog # 3322 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560 Sherman Avenue Suite 100 Evanston, IL 60201 1-800-323-9084 24-Hour Fax No. 847-328-6706
How to Find Out What s Wrong A BASIC GUIDE TO MALE. A doctor s guide for patients developed by the American Urological Association, Inc.
 A BASIC GUIDE TO MALE How to Find Out What s Wrong A doctor s guide for patients developed by the American Urological Association, Inc. Based on the AUA Best Practice Policy and ASRM Practice Committee
A BASIC GUIDE TO MALE How to Find Out What s Wrong A doctor s guide for patients developed by the American Urological Association, Inc. Based on the AUA Best Practice Policy and ASRM Practice Committee
Birth Control Options
 1 of 5 6/2/2014 9:46 AM Return to Web version Birth Control Options What is contraception? Contraception means preventing pregnancy, also called birth control. Most people know about options such as birth
1 of 5 6/2/2014 9:46 AM Return to Web version Birth Control Options What is contraception? Contraception means preventing pregnancy, also called birth control. Most people know about options such as birth
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Birth Control Pills
 Birth Control Pills WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Birth control pills (also called oral contraceptives or "the pill") are used by millions of women in the United States to
Birth Control Pills WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Birth control pills (also called oral contraceptives or "the pill") are used by millions of women in the United States to
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
 Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
HPV is very common and usually clears up on its own
 What is HPV? All cervical cancers are linked to a very common virus called the human papillomavirus or HPV. HPV usually doesn t cause any harm and most people will be infected with it at some point in
What is HPV? All cervical cancers are linked to a very common virus called the human papillomavirus or HPV. HPV usually doesn t cause any harm and most people will be infected with it at some point in
How Your Fertility Works
 How Your Fertility Works These pages give a simple explanation of how male and female fertility work and complement each other, enabling couples to plan, space and limit family size, without using any
How Your Fertility Works These pages give a simple explanation of how male and female fertility work and complement each other, enabling couples to plan, space and limit family size, without using any
Oral sex. Looking after your sexual health
 Oral sex Looking after your sexual health 2 What is this booklet about? This booklet gives you information about oral sex, the risk of getting and passing on sexually transmitted infections through oral
Oral sex Looking after your sexual health 2 What is this booklet about? This booklet gives you information about oral sex, the risk of getting and passing on sexually transmitted infections through oral
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System
 Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System External genitalia (can be seen on the body surface) penis scrotum Internal genitalia (can t be seen on the body surface) sperm producing organs testes ducts that
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System External genitalia (can be seen on the body surface) penis scrotum Internal genitalia (can t be seen on the body surface) sperm producing organs testes ducts that
Page 1. 1. The production of monoploid cells by spermatogenesis occurs in (1) zygotes (3) ovaries (2) testes (4) meristems
 1. The production of monoploid cells by spermatogenesis occurs in (1) zygotes (3) ovaries (2) testes (4) meristems Base your answers to questions 2 and 3 on the diagram below of the female reproductive
1. The production of monoploid cells by spermatogenesis occurs in (1) zygotes (3) ovaries (2) testes (4) meristems Base your answers to questions 2 and 3 on the diagram below of the female reproductive
Anatomy and Physiology of Human Reproduction. Module 10a
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
Copper intra-uterine device (IUD)
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Copper intra-uterine device (IUD) Page What is an inter-uterine device? 3 How does it work? 4 Would an IUD be suitable for me? 5 Are there any risks or complications?
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Copper intra-uterine device (IUD) Page What is an inter-uterine device? 3 How does it work? 4 Would an IUD be suitable for me? 5 Are there any risks or complications?
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Endometriosis
 Endometriosis WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The lining of the uterus is called the endometrium. Sometimes, endometrial tissue grows elsewhere in the body. When this happens
Endometriosis WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The lining of the uterus is called the endometrium. Sometimes, endometrial tissue grows elsewhere in the body. When this happens
patch contracep raceptiv contraceptive patch contraceptive patch contraceptiv patch contraceptive patch tch ontraceptive atch contraceptive p
 your guide to the contraceptive patch Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you contra ontraceptive pat contraceptive patch contraceptive patch ceptive patc atch contrace contracept
your guide to the contraceptive patch Helping you choose the method of contraception that is best for you contra ontraceptive pat contraceptive patch contraceptive patch ceptive patc atch contrace contracept
FERTILITY AND AGE. Introduction. Fertility in the later 30's and 40's. Am I fertile?
 FERTILITY AND AGE Introduction Delaying pregnancy is a common choice for women in today's society. The number of women in their late 30s and 40s attempting pregnancy and having babies has increased in
FERTILITY AND AGE Introduction Delaying pregnancy is a common choice for women in today's society. The number of women in their late 30s and 40s attempting pregnancy and having babies has increased in
Genital warts. Looking after your sexual health
 Genital warts Looking after your sexual health 2 Genital warts Genital warts are the most common viral sexually transmitted infection (STI). They are caused by the human papilloma virus (HPV) which can
Genital warts Looking after your sexual health 2 Genital warts Genital warts are the most common viral sexually transmitted infection (STI). They are caused by the human papilloma virus (HPV) which can
Abortion. just so you know
 Abortion just so you know Abortion can arouse strong feelings. This booklet aims to: help you understand more about abortion give you information about abortion that could help you, or someone you know,
Abortion just so you know Abortion can arouse strong feelings. This booklet aims to: help you understand more about abortion give you information about abortion that could help you, or someone you know,
Here we will talk about:
 Here we will talk about: What is puberty? When changes happen to boys? What are the sex organs? What are erections and why do they happen? For more information you can visit: What s Happening? What is
Here we will talk about: What is puberty? When changes happen to boys? What are the sex organs? What are erections and why do they happen? For more information you can visit: What s Happening? What is
THE WELL. Intrauterine Contraceptive Devices WOMAN CENTRE
 THE WELL WOMAN CENTRE Intrauterine Contraceptive Devices INTRAUTERINE CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES How does the Mirena work? How effective is the Mirena? What are the advantages of the Mirena? What are the disadvantages
THE WELL WOMAN CENTRE Intrauterine Contraceptive Devices INTRAUTERINE CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES How does the Mirena work? How effective is the Mirena? What are the advantages of the Mirena? What are the disadvantages
LEARNER OUTCOME 1 W-5.3:
 GRADE 5 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY LESSON 4 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Lesson 4 GRADE 5 LEARNER OUTCOME W-5.3: Identify the basic components of the human reproductive system, and describe the basic functions of the
GRADE 5 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY LESSON 4 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Lesson 4 GRADE 5 LEARNER OUTCOME W-5.3: Identify the basic components of the human reproductive system, and describe the basic functions of the
Explore and Discover... Human growth. You have been asked to write a short leaflet for young people about growing up and puberty. Teacher information
 You have been asked to write a short leaflet for young people about growing up and puberty. Explore and Discover... Teacher information Gallery visited Human Biology Suitable for Key Stage 3 (ages 11 to
You have been asked to write a short leaflet for young people about growing up and puberty. Explore and Discover... Teacher information Gallery visited Human Biology Suitable for Key Stage 3 (ages 11 to
This is Jaydess. Patient Information. What is Jaydess? How does Jaydess work?
 , Patient Information This is Jaydess We hope that this brochure will answer your questions and concerns about Jaydess. What is Jaydess? Jaydess is an intrauterine device consisting of a hormone capsule
, Patient Information This is Jaydess We hope that this brochure will answer your questions and concerns about Jaydess. What is Jaydess? Jaydess is an intrauterine device consisting of a hormone capsule
Effective long-lasting strategy to prevent unintended pregnancy. The intrauterine system for contraception after abortion.
 Effective long-lasting strategy to prevent unintended pregnancy. The intrauterine system for contraception after abortion. After the abortion I started re-thinking my birth control method. I am looking
Effective long-lasting strategy to prevent unintended pregnancy. The intrauterine system for contraception after abortion. After the abortion I started re-thinking my birth control method. I am looking
Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system.
 Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
All methods of birth control are MUCH SAFER than being pregnant! If 100 women use each method for a year, how many of them get pregnant?
 The Correct Use of Birth Control: In order for any method of birth control to be effective, it must be used correctly ALL THE TIME. This means: One condom every time you have sex One pill every day One
The Correct Use of Birth Control: In order for any method of birth control to be effective, it must be used correctly ALL THE TIME. This means: One condom every time you have sex One pill every day One
Syphilis. Looking after your sexual health
 Syphilis Looking after your sexual health 2 Syphilis Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection (STI). It is not as common as some sexually transmitted infections but if left untreated it can cause very
Syphilis Looking after your sexual health 2 Syphilis Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection (STI). It is not as common as some sexually transmitted infections but if left untreated it can cause very
How does it all work?
 PREGNANCY How does it all work? How does it all work? reproductive organs bladder seminal vesicle prostate gland sperm duct epididymis testicle urethra fallopian tube uterus (womb) fallopian tube bladder
PREGNANCY How does it all work? How does it all work? reproductive organs bladder seminal vesicle prostate gland sperm duct epididymis testicle urethra fallopian tube uterus (womb) fallopian tube bladder
BREAST CANCER. How to spot the signs and symptoms and reduce your risk. cruk.org
 BREAST CANCER How to spot the signs and symptoms and reduce your risk cruk.org Breast cancer is the most common cancer in the UK. Around 8 in 10 breast cancer cases are in women aged 50 and over. Men can
BREAST CANCER How to spot the signs and symptoms and reduce your risk cruk.org Breast cancer is the most common cancer in the UK. Around 8 in 10 breast cancer cases are in women aged 50 and over. Men can
Glossary. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty.
 Glossary amenorrhea - absence or cessation of menstrual periods. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty. A amenorrhea, secondary - due to some physical
Glossary amenorrhea - absence or cessation of menstrual periods. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty. A amenorrhea, secondary - due to some physical
Timing is everything. Ovulation Tracking. Patient Information Booklet
 Timing is everything Ovulation Tracking Patient Information Booklet Contents Getting pregnant naturally 3 Getting pregnant the basics 3 What is ovulation? 3 Menstrual cycle 4 When does ovulation take place?
Timing is everything Ovulation Tracking Patient Information Booklet Contents Getting pregnant naturally 3 Getting pregnant the basics 3 What is ovulation? 3 Menstrual cycle 4 When does ovulation take place?
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma)
 Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
Reproductive System. Anatomy of Male Reproductive System
 Function: producing offspring Reproductive System propagation of the species in terms of evolution the only reason all the other systems exist only major system that doesn t work continuously only activated
Function: producing offspring Reproductive System propagation of the species in terms of evolution the only reason all the other systems exist only major system that doesn t work continuously only activated
Puberty is the name given to the physical changes that happen between childhood and adulthood
 LENScience 09-501-A3 Growing Up! A resource for Science Classes Growing Up! As a human you are going to spend a life time growing and changing. It all started at the time of fertilisation, or conception,
LENScience 09-501-A3 Growing Up! A resource for Science Classes Growing Up! As a human you are going to spend a life time growing and changing. It all started at the time of fertilisation, or conception,
Sexuality after your Spinal Cord Injury
 Sexuality after your Spinal Cord Injury Introduction Spinal Cord Injury (SCI) affects to varying degrees the mechanics and sensations of sex and sexuality. Some people think that spinal injury means an
Sexuality after your Spinal Cord Injury Introduction Spinal Cord Injury (SCI) affects to varying degrees the mechanics and sensations of sex and sexuality. Some people think that spinal injury means an
Ask us about LARC. LARC stands for Long Acting Reversible Contraception. Types of LARC are: Contraceptive implant IUS IUD Contraceptive injection
 Ask us about LARC LARC stands for Long Acting Reversible Contraception. Types of LARC are: Contraceptive implant IUS IUD Contraceptive injection visit our website Long Acting Reversible Contraception (LARC)
Ask us about LARC LARC stands for Long Acting Reversible Contraception. Types of LARC are: Contraceptive implant IUS IUD Contraceptive injection visit our website Long Acting Reversible Contraception (LARC)
HIV. Looking after your sexual health
 HIV Looking after your sexual health 2 HIV HIV stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus. Once someone is infected with HIV the virus will remain in their body for the rest of their life. There is currently
HIV Looking after your sexual health 2 HIV HIV stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus. Once someone is infected with HIV the virus will remain in their body for the rest of their life. There is currently
Age and Fertility. A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES
 Age and Fertility A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient Education Committee and the Publications
Age and Fertility A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient Education Committee and the Publications
Reproduction and its Hormonal Control
 Reproduction and its Hormonal Control Page 1 Reproduction and its Hormonal Control Different mammals have different patterns of reproduction Eg mammals, rats and mice can breed all year round, whereas
Reproduction and its Hormonal Control Page 1 Reproduction and its Hormonal Control Different mammals have different patterns of reproduction Eg mammals, rats and mice can breed all year round, whereas
LEARNER OUTCOME 1 W-6.3:
 GRADE 6 FETAL DEVELOPMENT LESSON 2 FETAL DEVELOPMENT Lesson 2 GRADE 6 LEARNER OUTCOME W-6.3: Identify and describe the stages and factors that can affect human development from conception through birth.
GRADE 6 FETAL DEVELOPMENT LESSON 2 FETAL DEVELOPMENT Lesson 2 GRADE 6 LEARNER OUTCOME W-6.3: Identify and describe the stages and factors that can affect human development from conception through birth.
About the Uterus. Hysterectomy may be done to treat conditions that affect the uterus. Some reasons a hysterectomy may be needed include:
 Hysterectomy removal of the uterus is a way of treating problems that affect the uterus. Many conditions can be cured with hysterectomy. Because it is major surgery, your doctor may suggest trying other
Hysterectomy removal of the uterus is a way of treating problems that affect the uterus. Many conditions can be cured with hysterectomy. Because it is major surgery, your doctor may suggest trying other
Artificial insemination with donor sperm
 Artificial insemination with donor sperm Ref. 123 / 2009 Reproductive Medicine Unit Servicio de Medicina de la Reproducción Gran Vía Carlos III 71-75 08028 Barcelona Tel. (+34) 93 227 47 00 Fax. (+34)
Artificial insemination with donor sperm Ref. 123 / 2009 Reproductive Medicine Unit Servicio de Medicina de la Reproducción Gran Vía Carlos III 71-75 08028 Barcelona Tel. (+34) 93 227 47 00 Fax. (+34)
it right? activity (page 4) to highlight ethical issues associated with IVF
 IN VITRO FERTILIZATION I V F In some cases, a sperm is directly injected into an egg IVF: THE MEETING OF SPERM AND EGG IN GLASS Louise Brown, the first test tube baby was born in 1978. Since then, there
IN VITRO FERTILIZATION I V F In some cases, a sperm is directly injected into an egg IVF: THE MEETING OF SPERM AND EGG IN GLASS Louise Brown, the first test tube baby was born in 1978. Since then, there
What s GoinG on? your guide to growing up. (for boys and girls)
 What s GoinG on? your guide to growing up (for boys and girls) introduction Changes as you get older This is a booklet about growing up. As you get older you ll notice that your body changes and you develop
What s GoinG on? your guide to growing up (for boys and girls) introduction Changes as you get older This is a booklet about growing up. As you get older you ll notice that your body changes and you develop
Assignment Discovery Online Curriculum
 Assignment Discovery Online Curriculum Lesson title: In Vitro Fertilization Grade level: 9-12, with adaptation for younger students Subject area: Life Science Duration: Two class periods Objectives: Students
Assignment Discovery Online Curriculum Lesson title: In Vitro Fertilization Grade level: 9-12, with adaptation for younger students Subject area: Life Science Duration: Two class periods Objectives: Students
Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1
 Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1 1. Which two glands in the diagram produce gametes? A. glands A and B B. glands B and E C. glands C and F D. glands E and F 2. Base your answer
Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1 1. Which two glands in the diagram produce gametes? A. glands A and B B. glands B and E C. glands C and F D. glands E and F 2. Base your answer
Getting Pregnant: The Natural Approach Revealing the Secrets to Increase Your Fertility
 Getting Pregnant: The Natural Approach Revealing the Secrets to Increase Your Fertility Page 1 Contents Introduction 3 Part I Understanding Fertility and Infertility Chapter 1: What is Fertility? 4 - Signs
Getting Pregnant: The Natural Approach Revealing the Secrets to Increase Your Fertility Page 1 Contents Introduction 3 Part I Understanding Fertility and Infertility Chapter 1: What is Fertility? 4 - Signs
Gynaecology FAQ s. Correspondence address: 204 Fulham Road London SW10 9PJ Email: enquiries@missayida.com Tel: 02077514489
 Gynaecology FAQ s Why is the cervical screening test important? Cervical cancer is not uncommon. In recent years the number of cases has fallen due to cervical screening tests. However, there are still
Gynaecology FAQ s Why is the cervical screening test important? Cervical cancer is not uncommon. In recent years the number of cases has fallen due to cervical screening tests. However, there are still
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
 Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome What is Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome? Polycystic ovary syndrome (or PCOS) is a common condition affecting 3 to 5% of women of reproductive age. It is linked with hormonal imbalances,
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome What is Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome? Polycystic ovary syndrome (or PCOS) is a common condition affecting 3 to 5% of women of reproductive age. It is linked with hormonal imbalances,
vasectomy your questions answered
 vasectomy your questions answered About Marie Stopes International Marie Stopes International is one of the UK s most respected names in sexual health. Each year, our nine centres across the UK help over
vasectomy your questions answered About Marie Stopes International Marie Stopes International is one of the UK s most respected names in sexual health. Each year, our nine centres across the UK help over
Grade 6, Theme Three
 Family Letter Grade 6, Theme Three Dear Family, We are ready to begin Theme Three of Fully Alive, our Family Life program. Because the partnership of home, church, and school is so important, this letter
Family Letter Grade 6, Theme Three Dear Family, We are ready to begin Theme Three of Fully Alive, our Family Life program. Because the partnership of home, church, and school is so important, this letter
Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle
 Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle Q: What is menstruation? A: Menstruation is a woman s monthly bleeding, also called a period. When you menstruate, your body is shedding the lining of the uterus (womb).
Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle Q: What is menstruation? A: Menstruation is a woman s monthly bleeding, also called a period. When you menstruate, your body is shedding the lining of the uterus (womb).
Let s talk aboutpuberty
 Let s talk aboutpuberty A booklet about growing up for young people who have a learning disability This booklet will tell you about what happens to your body as you grow up. This is called Puberty. A2
Let s talk aboutpuberty A booklet about growing up for young people who have a learning disability This booklet will tell you about what happens to your body as you grow up. This is called Puberty. A2
What could endometriosis mean for me?
 Endometriosis: what you need to know Published November 2007 What is endometriosis? Endometriosis is a very common condition where cells of the lining of the womb (the endometrium) are found elsewhere,
Endometriosis: what you need to know Published November 2007 What is endometriosis? Endometriosis is a very common condition where cells of the lining of the womb (the endometrium) are found elsewhere,
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System
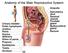 Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System External genitalia (can be seen on the body surface) penis scrotum Internal genitalia (can t be seen on the body surface)
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System External genitalia (can be seen on the body surface) penis scrotum Internal genitalia (can t be seen on the body surface)
male sexual dysfunction
 male sexual dysfunction lack of desire Both men and women often lose interest in sex during cancer treatment, at least for a time. At first, concern for survival is so overwhelming that sex is far down
male sexual dysfunction lack of desire Both men and women often lose interest in sex during cancer treatment, at least for a time. At first, concern for survival is so overwhelming that sex is far down
Thrush and Bacterial vaginosis. Looking after your sexual health
 Thrush and Bacterial vaginosis Looking after your sexual health 2 Thrush and Bacterial vaginosis Thrush is an infection that is caused by a yeast fungus. It is not a sexually transmitted infection but
Thrush and Bacterial vaginosis Looking after your sexual health 2 Thrush and Bacterial vaginosis Thrush is an infection that is caused by a yeast fungus. It is not a sexually transmitted infection but
Information for you Abortion care
 Information for you Abortion care Published in February 2012 This information is for you if you are considering having an abortion. It tells you: how you can access abortion services the care you can expect
Information for you Abortion care Published in February 2012 This information is for you if you are considering having an abortion. It tells you: how you can access abortion services the care you can expect
what is an abortion where can I go for help? SAMPLE do my parents have to know?
 where can I go for help? what is an abortion? ask brook about abortion do my parents have to know? ask brook about abortion Finding out that you re pregnant might just be the news that you ve been waiting
where can I go for help? what is an abortion? ask brook about abortion do my parents have to know? ask brook about abortion Finding out that you re pregnant might just be the news that you ve been waiting
Planning a pregnancy
 Planning a pregnancy 2 Do you want to start trying for a baby? Are you worried you won t be able to get pregnant? Are you trying to get pregnant, but it hasn t happened yet? This booklet explains how
Planning a pregnancy 2 Do you want to start trying for a baby? Are you worried you won t be able to get pregnant? Are you trying to get pregnant, but it hasn t happened yet? This booklet explains how
Treating Localized Prostate Cancer A Review of the Research for Adults
 Treating Localized Prostate Cancer A Review of the Research for Adults Is this information right for me? Yes, this information is right for you if: Your doctor * said all tests show you have localized
Treating Localized Prostate Cancer A Review of the Research for Adults Is this information right for me? Yes, this information is right for you if: Your doctor * said all tests show you have localized
VASECTOMY. Information Leaflet. Your Health. Our Priority.
 VASECTOMY Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 5 What is a vasectomy? A vasectomy involves cutting the two tubes (vas deferens) that carry sperm from your testicles to your penis. A
VASECTOMY Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 5 What is a vasectomy? A vasectomy involves cutting the two tubes (vas deferens) that carry sperm from your testicles to your penis. A
Understanding Endometriosis - Information Pack
 What is endometriosis? Endometriosis (pronounced en- doh mee tree oh sis) is the name given to the condition where cells like the ones in the lining of the womb (uterus) are found elsewhere in the body.
What is endometriosis? Endometriosis (pronounced en- doh mee tree oh sis) is the name given to the condition where cells like the ones in the lining of the womb (uterus) are found elsewhere in the body.
Dealing with Erectile Dysfunction During and After Prostate Cancer Treatment For You and Your Partner
 Dealing with Erectile Dysfunction During and After Prostate Cancer Treatment For You and Your Partner The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your
Dealing with Erectile Dysfunction During and After Prostate Cancer Treatment For You and Your Partner The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your
Saint Mary s Hospital. Ovarian Cysts. Information For Patients
 Saint Mary s Hospital Ovarian Cysts Information For Patients 2 Contents Welcome 4 What are ovarian cysts? 4 How common are ovarian cysts? 6 Ovarian cysts and fertility 6 What are the symptoms of ovarian
Saint Mary s Hospital Ovarian Cysts Information For Patients 2 Contents Welcome 4 What are ovarian cysts? 4 How common are ovarian cysts? 6 Ovarian cysts and fertility 6 What are the symptoms of ovarian
