EMERGENCY SITUATIONS
|
|
|
- Dwain Elliott
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EMERGENCY SITUATIONS Your priority is the treatment of injured persons. The types of injuries that could be incurred are numerous, however, three types require prompt attention: Blocked Airway or Stoppage of Breathing Most people can be saved if they start breathing on their own or artificially within two minutes. If breathing has been stopped for five minutes, there is only a 25% chance of saving the victim. (A basic CPR course is recommended for all school bus drivers). Severe Bleeding Sanitary napkins are very effective. If a person is bleeding profusely, shock or death may result quickly. Shock In shock, the vital body functions are depressed. Death may result if not treated promptly, even though the injury which caused the shock is not severe enough to cause death. Shock may result from injuries not readily apparent, or even without physical injury. Priority of Treatment A school bus crash may involve injury to a number of people. If several people are injured, and the scene permits you to begin treatment promptly, treat breathing first, then move quickly to those who are bleeding but still have a chance for survival. Then move to less urgent injuries. Except in situations of continuing danger or physical impracticality, treat a person where he is found and utilize those on the scene, including the victims, to assist in the treatment where feasible. In this way you can handle a number of injuries at once. It goes without saying that a collision scene is a very confusing place. Most people tend to run around trying to be helpful, but do not really know what to do. Therefore, it is essential that you be prepared to take control and establish priorities for action on the basis of three evaluations you make. Note: You, as a school bus driver, will be functional in a collision only if you remain conscious and alert. NEVER begin first aid treatment until the further safety of everyone is assured. General First Aid Principles There are a number of basic first aid principles that are applicable in every case, regardless of the nature of the injury. In carrying these out, you will do much to preserve the lives of the injured until the casualty or casualties are transported to medical attentions. The principles are: Arrange for Medical Attention - The best procedure to follow is to take the casualty or have him taken (if necessary, by ambulance) to the emergency room of the nearest hospital. - Speed is important because a major factor in saving lives and limbs of those who are seriously injured is early medical assessment. 75
2 Keep the Casualty Quietly at Rest - Particularly if badly injured of if the nature of the injuries is unknown. Organize Bystanders to Give Assistance - Some bystanders may have knowledge of first aid: others should be sent to obtain assistance or blankets, direct traffic, etc. Provide Warmth - It is important to keep the casualties warm by placing blankets, coats, etc. over and under them. Give Plenty of Reassurance - Fear and anxiety are frequently the most distressing aspects of traffic collision. Words of comfort help slightly, but an attitude of efficiency and calmness will do much more to give the casualty confidence and relieve high anxiety. - Determine the number of casualties and the severity of the injured (quick look at the group) - Send for the medical aid - Where there are multiple casualties, check each in turn for life threatening injuries, only treating those injuries as soon as found. A Airway B Not Breathing C Circulation severe bleeding and shock When all life threatening injuries are dealt with, you can then check for other injuries. - Be alert for changes - Hand over to medical help When you check each person, you can ask Where does it hurt?. If you get a response you will be able to tell if there is a good airway and if the breathing is effective. Control any obvious bleeding and do a rapid body survey (wet check) for hidden severe external and internal bleeding. Have them take a deep breath and cough. If they are able to, it is unlikely that they have serious chest injury. Have them pull in their stomach and blow out again. If there is no distress they are probably free from internal injury. Warm, rest, reassure and into the recovery position for shock. If breathing is ineffective, assess the rate and depth of breathing and assist if needed (see artificial respiration). If there is no response - Remember that unconsciousness is a breathing emergency. Open the airway using a head tilt chin lift if there is no suspected spinal injury, otherwise do a jaw thrust with NO head tilt. - Maintain the airway and check for breathing by looking at the chest, listening and feeling for breathing. - If effective, check for severe bleeding. - If ineffective, assist as needed. 76
3 - If NOT breathing, give two slow breaths, then check for pulse. If present, continue with artificial respiration. If absent start CPR or move on if there are multiple casualties. - Do a quick check and control severe bleeding - If you find any deformities, have the injured part steadied and supported until medical help takes over. Artificial Respiration - Open the airway and check for breathing by looking at the chest, listening at the nose and mouth and feeling with cheek and with hand on chest. If there is no breathing then pinch the nose and mouth-to-mouth seal. - Give two slow breaths. - Check the carotid pulse 5 to 10 seconds. - Continue breaths adults, one breath every 5 seconds children, one breath every 3 seconds. - Check pulse after one minute and every few minutes thereafter. - Continue artificial respiration until casualty is breathing unassisted or medical aid takes over, treat for severe bleeding and shock and check for other injuries. - Watch for changes in condition until handed over to medical aid. Severe Bleeding If you suspect internal bleeding send for medical help immediately. Signs - Sharp blows - Deep punctures - Crush injuries - Massive bruising - Bleeding from mouth, ears and/or nose - Coughed up frothy blood Symptoms Ask the casualty to take a deep breath and cough, if no pain, unlikely to have internal bleeding, serious chest injury or broken ribs. Ask the casualty to suck in and then blow out stomach; if no distress or harness in the area, then internal bleeding or injury is unlikely. 77
4 Treatment of Severe External Bleeding - Expose wound - Lie the casualty down or at rest - Elevate wound - Direct pressure applied to the wound To bring bleeding under control, follow these steps: - Apply direct, even pressure over wound with dressing if possible, use bare hand if necessary. - If blood soaks through dressing, do not remove but apply more dressing. - When bleeding has stopped, apply bandage. - Check skin temperature of limbs and nail beds for circulation. - Elevate limb above heart level, except where there is a possible fracture. - Treat for shock, monitor for circulation. If transporting, apply sling. Dressings: Control bleeding and prevent further infection. Must be sterile, absorbent, lint free, non-sticky and large enough to cover wound. Bandages: Hold dressings in place, maintain pressure over wound, support limb or joint, immobilize with a tie, belt, adhesive tape, scarf, pillowcase, tea towel, etc. Shock Shock is always present to some degree with any injury or illness (the casualty may not be aware that they are in shock). Shock is caused by loss of circulation. Even if the symptoms of shock are not evident, the casualty should be kept warm, quiet, at rest and re-assured. Signs: - Shallow rapid breathing - Weak and rapid pulse - Restlessness and anxiety - Gasping for air - Vomiting - Unconsciousness Symptoms: - Feels faint - Thirst - Nausea - Anxiety - Dizzy To treat for shock you must give timely efficient first aid. The casualty must be kept warm, calm and in the right recovery position for the type of injury. The recovery positions are as follows: 78
5 Suspected Spinal - Steady and support the head and neck, cover with blanket - Keep warm - Keep in position found Unconscious (no obvious injuries) - Recovery position - Wrapped or covered with blanket - Keep warm Conscious (with breathing difficulties) - Semi sitting, cover with blanket - Keep warm Conscious - Lying on back, elevate feet 15 to 30 cm - Loosen tight clothing With all these casualties, loosen tight clothing, handle gently, keep warm with blankets, give nothing by mouth but moisten lips if needed. At all times, reassure and be alert for changes in condition. Choking Ask if the casualty is choking; encourage them to keep coughing. If there is poor or no exchange of air (bluish skin, unable to speak or cough) do abdominal thrust: - Landmark make a fist and place midway between the navel and point where ribs meet in the chest and pull the fist into the casualty s abdominal area. - Repeat the thrust until airway clears or casualty becomes unconscious. - Send for medical help as soon as the casualty loses consciousness. With casualty on their back, open the mouth with a tongue-jaw lift, then finger sweep (on larger children or adults only) to try to find and dislodge the obstruction, then try to blow air in. If none goes in: - Landmark - Do five abdominal thrust (astride legs) - Repeat the sequence until successful - Treat for shock Always make sure that a medical doctor sees them if abdominal thrusts have been used. 79
6 Fainting If the bus is too hot, the students are overdressed or are reacting to the sight of blood, you will often have a person who feels faint or faints. If a casualty feels faint (due to reduced oxygen in the brain): Signs: - Pale - Sweating Symptoms: - Nausea - Dizziness Treatment: - Shock position - Fresh air - Loosen tight clothing at neck, chest and waist - Remove glasses - Make sure they are breathing If casualty has fainted: - Check breathing - Check for any injuries the casualty may have suffered from fainting - Recovery position - If not fully recovered within minutes, send for medical aid - Keep lying down for 10 to 15 minutes - Monitor breathing frequently Burns There are many different types of burns and each must be handled a little differently. The causes and treatments are as follows: Causes: - Electricity - Chemicals - Heat - Sun Severity: - How much of the body is burned - Location and depth - Casualty age and health Superficial: reddened skin, swelling, blistering, severe pain Deep: charred skin, little or no pain Treatment: - Do not apply lotions - Do not break blisters - Do not touch, breath or cough on burn - Do not remove any clothing stuck on burn - Do not cover with cotton wool 80
7 Heat Burns - Remove jewellery - Immerse burn in cool water until cool - Cover with sterile dressing - Secure the dressing - Send for medical aid - Treat for shock Chemical Burns - Brush off powdered chemicals before flushing - Remove affected clothing and flush with cool running water 10 to 15 minutes - Cover with moist sterile dressing - Send for medical aid - Treat for shock Electrical Burns - Turn off electricity before touching or approaching casualty - Call for an ambulance - There is often cardiac arrest, stopped breathing, fractures, dislocations and severe internal burns - Treat life threatening injuries Cover burns with clean dry dressings at point of entry and exit to prevent further infection. Continue to monitor casualty for changes while waiting for the ambulance. Poisoning There are many different types of poisons and many of the products we use daily can be poisonous in larger quantities. Poison: any substance that can harm or kill you if taken into the body. It can be: - Swallowed - Inhaled - Injected - Absorbed through the skin If you suspect poisoning act immediately. Quickly find out: - What poison - How much - How it entered the body - When it was taken Inform dispatch as quickly as possible. A very dangerous situation with a vehicle is the colorless, odorless gas known as carbon monoxide. If there is an undetected exhaust leak into the vehicle and there is not enough fresh air, the casualty will have some of the following symptoms: 81
8 Symptoms: - Headache, irritability, fatigue - Unconsciousness - Reddish discoloration of the skin Treatment: - Remove the casualty from the poisoning source and to fresh air - Give artificial respiration if breathing is weak - Keep the casualty warm and away from draft - Keep the casualty at rest, with the head slightly lower than the feet Cold Injuries Symptoms and Treatment of Cold Injuries Hypothermia is a term referring to the dangerous lowering of the body s core temperature. Contrary to popular belief, it can occur at above freezing temperatures in a relatively short time depending on age, size, dress, etc. It is progressive as shown in this chart. Signs Mild Moderate Severe Pulse Normal Slow and weak Weak or absent Breathing Normal Slow, shallow Slow or absent Appearance Mental State Shivering Slurred speech Clumsy, stumbles Conscious, withdrawn Shivering is violent or stopped Confused, sleepy, irrational Shivering has stopped Unconscious Treatment: - Handle gently - Remove from cold - Remove wet clothing - Gently warm (body heat and blankets) - Give warm sweet drink if conscious (no coffee or alcohol) - Do AR or CPR if needed - Remember to warm the body core rather than the limbs Frostbite is characterized by numbness of the affected area accompanied by a loss of coloration of the skin. While severe frostbite, involving damage to tissue, requires medical attention, it may be treated initially in the following manner: - Get the person into shelter and warmth if not already there - Remove anything constrictive from affected area (i.e. gloves, rings, boots) - Gradually warm area with warm dry covering or with body heat, gentle steady pressure - Do not warm if there is a danger of refreezing the area before receiving medical attention - Do not rub the affected area - Do not apply direct heat in any form - Remember that if the frostbite is severe, treat it gently and leave it frozen until medical help is obtained 82
9 General First Aid Introduction In this module, we want to review some general first aid principles that are considered basic knowledge for the school bus operator, as well as deal with the treatment of specific injuries mentioned, namely: - Blocked airway or stopped breathing - Severe bleeding - Shock This segment is NOT a first aid course and operators are encouraged to complete proper first aid training. This segment has been kept basic and deals with only those subjects that are considered critical. A number of first aid courses are offered which cover many more topics than this. It is strongly recommended that anyone interested in developing their first aid skills, enroll in a course in their local area. What is First Aid? First aid implies just what the name says. It embodies a number of principles that can be intelligently applied by the layman in almost any type of crash or emergency situation to care for the injured. Thus, it is a guide for practical action in emergency situations. It is by no means a substitute for medical assistance. If, in respect of a person who is ill, injured or unconscious as the result of a crash or other emergency, - A physician, professional medical assistant, or registered nurse voluntarily and without expectation of compensation or reward renders emergency medical services or first aid assistance and the services or assistance are not rendered at a hospital or other place having adequate medical facilities and equipment, or - A person other than a person mentioned in the clause before, voluntarily renders emergency first aid assistance and that assistance is rendered at the immediate scene of the crash or emergency, the physician, professional medical assistant, registered nurse or other person is not liable for damages for injuries to or the death of that person alleged to have been caused by an act or omission on his part in rendering the medical services or first aid assistance, unless it is established that the injuries or death were caused by gross negligence on their part. Diagnosing Injuries and Establishing Priorities for Treatment It may not be readily apparent after a collision from what a casualty is suffering. Offer to help but do not move the casualty if head/spinal injuries are suspected unless you have no choice (i.e. fire, dangerous or unsafe position). 83
Adult First Aid/CPR/AEd. Ready Reference
 Adult First Aid/CPR/AEd Ready Reference Contents Checking an Injured or Ill Adult 3 CPR 4 AED Adult or Child 5 Conscious Choking 7 Controlling External Bleeding 8 Burns 9 Poisoning 10 Head, Neck or Spinal
Adult First Aid/CPR/AEd Ready Reference Contents Checking an Injured or Ill Adult 3 CPR 4 AED Adult or Child 5 Conscious Choking 7 Controlling External Bleeding 8 Burns 9 Poisoning 10 Head, Neck or Spinal
HEAT ILLNESS PREVENTION PLAN FOR SUTTER COUNTY SUPERINTENDENT OF SCHOOLS
 HEAT ILLNESS PREVENTION PLAN FOR SUTTER COUNTY SUPERINTENDENT OF SCHOOLS TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.0 Purpose... 1 2.0 Heat Illness Prevention... 2 2.1 Heat Stroke... 2 2.2 Heat Exhaustion... 2 2.3 Heat Cramps...
HEAT ILLNESS PREVENTION PLAN FOR SUTTER COUNTY SUPERINTENDENT OF SCHOOLS TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.0 Purpose... 1 2.0 Heat Illness Prevention... 2 2.1 Heat Stroke... 2 2.2 Heat Exhaustion... 2 2.3 Heat Cramps...
CASAID THE AIMS OF FIRST AID, INCIDENT ACTION PLAN, INITIAL ASSESSMENT AND THE RECOVERY POSITION. Airway must be open so oxygen can enter the body.
 CASAID THE AIMS OF FIRST AID, INCIDENT ACTION PLAN, INITIAL ASSESSMENT AND THE RECOVERY POSITION The Aims of First Aid The aims of first aid (the three Ps) are to: Preserve the casualty s life. Prevent
CASAID THE AIMS OF FIRST AID, INCIDENT ACTION PLAN, INITIAL ASSESSMENT AND THE RECOVERY POSITION The Aims of First Aid The aims of first aid (the three Ps) are to: Preserve the casualty s life. Prevent
WET, COUGHING AND COLD NEAR RIVER BANK STUNG BY BEE CAUSING ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK TO WRIST
 GRIT IN EYE BROKEN LEG BONE WET, COUGHING AND COLD NEAR RIVER BANK STUNG BY BEE CAUSING ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK HEART ATTACK SUFFERING FROM SHOCK CHOKING SEVERE BLEEDING TO WRIST HYPOTHERMIA ANGINA Localised
GRIT IN EYE BROKEN LEG BONE WET, COUGHING AND COLD NEAR RIVER BANK STUNG BY BEE CAUSING ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK HEART ATTACK SUFFERING FROM SHOCK CHOKING SEVERE BLEEDING TO WRIST HYPOTHERMIA ANGINA Localised
EXTREME HEAT OR COLD
 Responsibility Never hesitate to call 911 Life Safety is most important! It is the responsibility of every individual to learn to recognize the warning signs of a medical emergency. Warning Signs and Symptoms
Responsibility Never hesitate to call 911 Life Safety is most important! It is the responsibility of every individual to learn to recognize the warning signs of a medical emergency. Warning Signs and Symptoms
FIRST AID TEST. 367 West Robles Ave Santa Rosa, CA 95407 707-206-9988. www.schoolbusing.com. Revised April 21, 2008 - 1 -
 FIRST AID TEST 367 West Robles Ave Santa Rosa, CA 95407 707-206-9988 www.schoolbusing.com Revised April 21, 2008-1 - West County Transportation Agency This test was developed to help school bus driver
FIRST AID TEST 367 West Robles Ave Santa Rosa, CA 95407 707-206-9988 www.schoolbusing.com Revised April 21, 2008-1 - West County Transportation Agency This test was developed to help school bus driver
First Aid Multiple Choice Test
 First Aid Multiple Choice Test Answer all 25 questions by circling the correct answer. This is an open-book test. Answers are contained in The Boy Scout Handbook. Patrol Troop 1. When making a 911 call,
First Aid Multiple Choice Test Answer all 25 questions by circling the correct answer. This is an open-book test. Answers are contained in The Boy Scout Handbook. Patrol Troop 1. When making a 911 call,
MRC Medical Jeopardy Feud List of Treatments for Possible Injuries/Conditions
 List of Treatments for Possible Injuries/Conditions A. Apply cold compresses to affected area; elevate the area to reduce swelling and possible bleeding B. Apply direct pressure to wound area with sterile
List of Treatments for Possible Injuries/Conditions A. Apply cold compresses to affected area; elevate the area to reduce swelling and possible bleeding B. Apply direct pressure to wound area with sterile
Heat Illnesses. Common Heat Rash Sites
 Heat Illnesses Introduction Heat illnesses happen when the body becomes too hot and cannot cool itself. There are several different types of heat-related illnesses. This includes heat cramps, heat exhaustion,
Heat Illnesses Introduction Heat illnesses happen when the body becomes too hot and cannot cool itself. There are several different types of heat-related illnesses. This includes heat cramps, heat exhaustion,
American Heart Association
 American Heart Association Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest April 2006 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST For BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses 2006 American Heart
American Heart Association Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest April 2006 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST For BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses 2006 American Heart
Heat Illness Prevention Program
 I. Policy Heat Illness Prevention Program Responsible Executive: Vice President for Administration and Finance Responsible Office: Environmental Health and Instructional Safety Originally Issued: February
I. Policy Heat Illness Prevention Program Responsible Executive: Vice President for Administration and Finance Responsible Office: Environmental Health and Instructional Safety Originally Issued: February
Emergency procedures instructions to farm staff
 Emergency procedures instructions to farm staff The first priority in the event of an emergency is for the safety of all people present. Emergency phone numbers Dial 111 for Fire/Police/Ambulance 1. Tell
Emergency procedures instructions to farm staff The first priority in the event of an emergency is for the safety of all people present. Emergency phone numbers Dial 111 for Fire/Police/Ambulance 1. Tell
Heat Illness Prevention Program
 Heat Illness Prevention Program I. Policy Employees working in outdoor places of employment or in other areas at times when the environmental risk factors for heat illness are present, are at risk for
Heat Illness Prevention Program I. Policy Employees working in outdoor places of employment or in other areas at times when the environmental risk factors for heat illness are present, are at risk for
American Red Cross First Aid EXAMPLE ANSWER SHEET
 American Red Cross First Aid Exam A IMPORTANT: Read all instructions before beginning the exam. INSTRUCTIONS: Do not write on this exam. Mark all answers in pencil on the separate answer sheet as directed
American Red Cross First Aid Exam A IMPORTANT: Read all instructions before beginning the exam. INSTRUCTIONS: Do not write on this exam. Mark all answers in pencil on the separate answer sheet as directed
CHAPTER 2 APPROACH TO THE INCIDENT
 CHAPTER 2 APPROACH TO THE INCIDENT Reassuring the casualty is very important in first aid and the best reassurance for both casualty and bystanders is a confident first aider taking decisive action. In
CHAPTER 2 APPROACH TO THE INCIDENT Reassuring the casualty is very important in first aid and the best reassurance for both casualty and bystanders is a confident first aider taking decisive action. In
Emergency Action Plans
 Emergency Action Plans Clearly the most effective way to deal with an injury- emergency is to plan ahead and to practice the appropriate procedures. An emergency action plan is a written plan of action
Emergency Action Plans Clearly the most effective way to deal with an injury- emergency is to plan ahead and to practice the appropriate procedures. An emergency action plan is a written plan of action
COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL. Effective Date: August 31, 2006
 COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SECTION Emergency Procedures POLICY NUMBER: 715 Effective Date: August 31, 2006 SUBJECT: EMERGENCY CARE OF HEMORRHAGE 1. PURPOSE: The management
COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SECTION Emergency Procedures POLICY NUMBER: 715 Effective Date: August 31, 2006 SUBJECT: EMERGENCY CARE OF HEMORRHAGE 1. PURPOSE: The management
Accident/Injury Reporting, Investigation, & Basic First Aid Plan
 Accident/Injury Reporting, Investigation, & Basic First Aid Plan Environmental Health, Safety, and Risk Management Department Box 6113, SFA Station Nacogdoches, Texas 75962-6113 Revised: January 2011 Purpose
Accident/Injury Reporting, Investigation, & Basic First Aid Plan Environmental Health, Safety, and Risk Management Department Box 6113, SFA Station Nacogdoches, Texas 75962-6113 Revised: January 2011 Purpose
CHAPTER 1 DISASTER FIRST AID INTRODUCTION
 CHAPTER 1 DISASTER FIRST AID INTRODUCTION This chapter will cover the following topics: Introduction: The basic concepts of providing disaster first aid and the equipment required to safely respond to
CHAPTER 1 DISASTER FIRST AID INTRODUCTION This chapter will cover the following topics: Introduction: The basic concepts of providing disaster first aid and the equipment required to safely respond to
Types of electrical injuries
 Types of electrical injuries Electrical injury is a term for all injuries caused by contact with electrical energy. Electrical contact can cause a wide variety of injuries involving most organ systems.
Types of electrical injuries Electrical injury is a term for all injuries caused by contact with electrical energy. Electrical contact can cause a wide variety of injuries involving most organ systems.
5420-R STUDENT HEALTH SERVICES REGULATION NORTH COLONIE CENTRAL SCHOOLS NEWTONVILLE, NEW YORK Emergency Procedures and Approved First Aid Methods
 STUDENT HEALTH SERVICES REGULATION NORTH COLONIE CENTRAL SCHOOLS NEWTONVILLE, NEW YORK Emergency Procedures and Approved First Aid Methods EMERGENCY PROCEDURES Contact parents and cooperate with them in
STUDENT HEALTH SERVICES REGULATION NORTH COLONIE CENTRAL SCHOOLS NEWTONVILLE, NEW YORK Emergency Procedures and Approved First Aid Methods EMERGENCY PROCEDURES Contact parents and cooperate with them in
CHAPTER 6 HEAD INJURY AND UNCONSCIOUSNESS
 CHAPTER 6 HEAD INJURY AND UNCONSCIOUSNESS BRAIN INJURY Injury to the brain is one of the more serious outcomes that occur due to injury or illness. The first aider plays a major role in limiting damage
CHAPTER 6 HEAD INJURY AND UNCONSCIOUSNESS BRAIN INJURY Injury to the brain is one of the more serious outcomes that occur due to injury or illness. The first aider plays a major role in limiting damage
Pesticide Harmful Effects And Emergency Response
 Pesticide Harmful Effects And Emergency Response Most pesticides are designed to harm or kill pests. Because some pests have systems similar to the human system, some pesticides also can harm or kill humans.
Pesticide Harmful Effects And Emergency Response Most pesticides are designed to harm or kill pests. Because some pests have systems similar to the human system, some pesticides also can harm or kill humans.
Objectives. Burn Assessment and Management. Questions Regarding the Case Study. Case Study. Patient Assessment. Patient Assessment
 Objectives Burn Assessment and Management Discuss the mechanisms and complications of a thermal burn, electrical burn and an inhalation burn Explain the factors to consider when determining the severity
Objectives Burn Assessment and Management Discuss the mechanisms and complications of a thermal burn, electrical burn and an inhalation burn Explain the factors to consider when determining the severity
Be Safe! Manage Heat Stress. Be Safe! Manage Heat Stress.
 Be Safe! Manage Heat Stress. Be Safe! Manage Heat Stress. Overview Workers who are exposed to extreme heat or work in hot environments may be at risk of heat stress. Exposure to extreme heat can result
Be Safe! Manage Heat Stress. Be Safe! Manage Heat Stress. Overview Workers who are exposed to extreme heat or work in hot environments may be at risk of heat stress. Exposure to extreme heat can result
Basic First Aid Tutorial
 Basic First Aid Tutorial 1 Overview: 1-Introduction 2-Emergency Response 3-Bleeding, Shock, & Soft-Tissue Injuries 4-Bone, Joint, & Muscle Injuries 5-Medical Emergencies 6-Heat & Cold-Related Illness/Injury
Basic First Aid Tutorial 1 Overview: 1-Introduction 2-Emergency Response 3-Bleeding, Shock, & Soft-Tissue Injuries 4-Bone, Joint, & Muscle Injuries 5-Medical Emergencies 6-Heat & Cold-Related Illness/Injury
American Heart Association. Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers
 American Heart Association Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest February 2001 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST for BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses 2001 American
American Heart Association Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest February 2001 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST for BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses 2001 American
Northwestern Health Sciences University. Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers
 Northwestern Health Sciences University Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest May 2005 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST for BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses Based
Northwestern Health Sciences University Basic Life Support for Healthcare Providers Pretest May 2005 This examination to be used only as a PRECOURSE TEST for BLS for Healthcare Providers Courses Based
Infant CPR. What You Need to Know. How to Do Infant CPR
 Infant CPR Infant CPR also called Cardiopulmonary resuscitation is emergency care given to a baby who has stopped breathing. This sheet has the steps for CPR for newborns or babies less than 1 year old.
Infant CPR Infant CPR also called Cardiopulmonary resuscitation is emergency care given to a baby who has stopped breathing. This sheet has the steps for CPR for newborns or babies less than 1 year old.
TakE Care in Hot & Cold Weather
 www.coned.com TakE Care in Hot & Cold Weather Preventing Hyperthermia and Hypothermia When it s Too Hot! Beating the heat is as much a part of summer as baseball and hot dogs. City residents are particularly
www.coned.com TakE Care in Hot & Cold Weather Preventing Hyperthermia and Hypothermia When it s Too Hot! Beating the heat is as much a part of summer as baseball and hot dogs. City residents are particularly
CPR/AED for Professional Rescuers and Health Care Providers HANDBOOK
 CPR/AED for Professional Rescuers and Health Care Providers HANDBOOK TABLE OF CONTENTS SECTION 1: THE PROFESSIONAL RESCUER The Duty to Respond 2 Preventing the Spread of Bloodborne Pathogens 3 Taking Action
CPR/AED for Professional Rescuers and Health Care Providers HANDBOOK TABLE OF CONTENTS SECTION 1: THE PROFESSIONAL RESCUER The Duty to Respond 2 Preventing the Spread of Bloodborne Pathogens 3 Taking Action
2. When temperature and wind chill falls below 35 degrees including the wind chill, students, are kept indoors.
 Weather /Environmental Guidelines Time spent outdoors is an important part of the school day. It is difficult to set guidelines that fit every circumstance and condition in regards to outside activities.
Weather /Environmental Guidelines Time spent outdoors is an important part of the school day. It is difficult to set guidelines that fit every circumstance and condition in regards to outside activities.
Heart information. CPR cardiopulmonary resuscitation
 Heart information CPR cardiopulmonary resuscitation Contents 3 What is CPR? 3 What is cardiac arrest? 4 Heart attack and cardiac arrest 4 Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) 5 Danger 6 Response 7 Send
Heart information CPR cardiopulmonary resuscitation Contents 3 What is CPR? 3 What is cardiac arrest? 4 Heart attack and cardiac arrest 4 Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) 5 Danger 6 Response 7 Send
Shift Commander: The senior ranking uniformed line officer at the DOC facility, most commonly a Sergeant, Lieutenant or Captain.
 I Index: Date Signed: 04/18/2015 Replaces : N/A Supersedes Dated: 05/21/2014 Affected Units: Adult Institutions Effective Date: 04/20/2015 Scheduled Revision Date: March 2016 Revision Number: 12 Office
I Index: Date Signed: 04/18/2015 Replaces : N/A Supersedes Dated: 05/21/2014 Affected Units: Adult Institutions Effective Date: 04/20/2015 Scheduled Revision Date: March 2016 Revision Number: 12 Office
Fainting - Syncope. This reference summary explains fainting. It discusses the causes and treatment options for the condition.
 Fainting - Syncope Introduction Fainting, also known as syncope, is a temporary loss of consciousness. It is caused by a drop in blood flow to the brain. You may feel dizzy, lightheaded or nauseous before
Fainting - Syncope Introduction Fainting, also known as syncope, is a temporary loss of consciousness. It is caused by a drop in blood flow to the brain. You may feel dizzy, lightheaded or nauseous before
PHYSICAL AGENT DATA SHEET
 Alaska Department of Labor and Workforce Development Labor Standards and Safety 3301 Eagle Street/PO Box 107022 Anchorage, Alaska 99510-7022 (907) 269-4955 PHYSICAL AGENT DATA SHEET COLD STRESS HYPOTHERMIA
Alaska Department of Labor and Workforce Development Labor Standards and Safety 3301 Eagle Street/PO Box 107022 Anchorage, Alaska 99510-7022 (907) 269-4955 PHYSICAL AGENT DATA SHEET COLD STRESS HYPOTHERMIA
EYE, EAR, NOSE, and THROAT INJURIES
 T6 EYE, EAR, NOSE, and THROAT INJURIES Management of injuries of the eyes, ears, nose, and throat focuses on airway management and initial stabilization of the injury. Bilateral comparisons can assist
T6 EYE, EAR, NOSE, and THROAT INJURIES Management of injuries of the eyes, ears, nose, and throat focuses on airway management and initial stabilization of the injury. Bilateral comparisons can assist
First Responder (FR) and Emergency Medical Responder (EMR) Progress Log
 First Responder (FR) and Emergency Medical Responder (EMR) Progress Log Note: Those competencies that are for EMR only are denoted by boldface type. For further details on the National Occupational Competencies
First Responder (FR) and Emergency Medical Responder (EMR) Progress Log Note: Those competencies that are for EMR only are denoted by boldface type. For further details on the National Occupational Competencies
Chapter 18 THERMAL INJURIES
 Chapter 18 THERMAL INJURIES Because of the range of environmental condition within which sports take place, various temperature-related health emergencies occur each year, some result in death. Most, if
Chapter 18 THERMAL INJURIES Because of the range of environmental condition within which sports take place, various temperature-related health emergencies occur each year, some result in death. Most, if
RECOGNISE AND REMOVE
 RECOGNISE AND REMOVE Remember the 4 R s of concussion management: RECOGNISE REMOVE RECOVER RETURN Identifying concussion is not always easy, and players may not exhibit the signs or symptoms immediately
RECOGNISE AND REMOVE Remember the 4 R s of concussion management: RECOGNISE REMOVE RECOVER RETURN Identifying concussion is not always easy, and players may not exhibit the signs or symptoms immediately
Epinephrine Administration Training for Unlicensed School Personnel
 Epinephrine Administration Training for Unlicensed School Personnel Management of Life-Threatening Allergies in the School Setting Dover and Sherborn Schools EpiPen Administration This program is designed
Epinephrine Administration Training for Unlicensed School Personnel Management of Life-Threatening Allergies in the School Setting Dover and Sherborn Schools EpiPen Administration This program is designed
All About Your Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC)
 All About Your Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) General Information Intravenous (IV) therapy is the delivery of fluid directly into a vein. An intravenous catheter is a hollow tube that is
All About Your Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) General Information Intravenous (IV) therapy is the delivery of fluid directly into a vein. An intravenous catheter is a hollow tube that is
& WHEN SHOULD I WORRY?
 WHEN SHOULD I WORRY? - Your guide to Coughs, Colds, Earache & Sore Throats Information For:- Who is this booklet for? Having an ill child can be a very scary experience for parents. If you understand more
WHEN SHOULD I WORRY? - Your guide to Coughs, Colds, Earache & Sore Throats Information For:- Who is this booklet for? Having an ill child can be a very scary experience for parents. If you understand more
Low Blood Pressure. This reference summary explains low blood pressure and how it can be prevented and controlled.
 Low Blood Pressure Introduction Low blood pressure, or hypotension, is when your blood pressure reading is 90/60 or lower. Some people have low blood pressure all of the time. In other people, blood pressure
Low Blood Pressure Introduction Low blood pressure, or hypotension, is when your blood pressure reading is 90/60 or lower. Some people have low blood pressure all of the time. In other people, blood pressure
American Red Cross CPR Adult EXAMPLE ANSWER SHEET
 American Red Cross CPR Adult IMPORTANT: Read all instructions before beginning the exam. INSTRUCTIONS: Do not write on this exam. Mark all answers in pencil on the separate answer sheet as directed by
American Red Cross CPR Adult IMPORTANT: Read all instructions before beginning the exam. INSTRUCTIONS: Do not write on this exam. Mark all answers in pencil on the separate answer sheet as directed by
Heat Production and Loss. Environmental Emergencies. Heat Regulation. Body Temperature Ranges. Focused Assessment: Your Patient: Heat Production
 Heat Production and Loss Environmental Emergencies Messing with Mother Nature Heat Production Basal Metabolism processes in the body that generate heat through nominal functions Activity, fever, metabolic
Heat Production and Loss Environmental Emergencies Messing with Mother Nature Heat Production Basal Metabolism processes in the body that generate heat through nominal functions Activity, fever, metabolic
Lighthouse IF YOU WERE THE DRIVER OF YOUR OWN VEHICLE, SOMEONE ELSE S VEHICLE OR A PASSENGER IN THE VEHICLE, ANSWER THIS SECTION COMPLETELY.
 Lighthouse Chiropractic IF YOU WERE THE DRIVER OF YOUR OWN VEHICLE, SOMEONE ELSE S VEHICLE OR A PASSENGER IN THE VEHICLE, ANSWER THIS SECTION COMPLETELY. Your Auto Insurance Company Name Address Policy
Lighthouse Chiropractic IF YOU WERE THE DRIVER OF YOUR OWN VEHICLE, SOMEONE ELSE S VEHICLE OR A PASSENGER IN THE VEHICLE, ANSWER THIS SECTION COMPLETELY. Your Auto Insurance Company Name Address Policy
Emergency Medical Dispatching (EMD)
 Goals: Emergency Medical Dispatching (EMD) This program has been specifically designed to know how to use and be able to practice scenarios for Emergency Medical Dispatching. Objectives: Can explain how
Goals: Emergency Medical Dispatching (EMD) This program has been specifically designed to know how to use and be able to practice scenarios for Emergency Medical Dispatching. Objectives: Can explain how
HEMOPHILIA WHAT SCHOOL PERSONNEL SHOULD KNOW
 HEMOPHILIA WHAT SCHOOL PERSONNEL SHOULD KNOW TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction p. 3 What Is Hemophilia p. 4 Common Bleeds p. 5 Superficial Bruising p. 8 Lacerations p. 8 Life-Threatening Bleeds p. 9 Sports
HEMOPHILIA WHAT SCHOOL PERSONNEL SHOULD KNOW TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction p. 3 What Is Hemophilia p. 4 Common Bleeds p. 5 Superficial Bruising p. 8 Lacerations p. 8 Life-Threatening Bleeds p. 9 Sports
Adult Choking and CPR Manual
 Adult Choking and CPR Manual 2009 Breath of Life Home Medical Equipment and Respiratory Services CHOKING Description: Choking is the coughing spasm and sputtering that happen when liquids or solids get
Adult Choking and CPR Manual 2009 Breath of Life Home Medical Equipment and Respiratory Services CHOKING Description: Choking is the coughing spasm and sputtering that happen when liquids or solids get
heatwave A GUIDE TO LOOKING AFTER YOURSELF AND OTHERS DURING HOT WEATHER
 heatwave A GUIDE TO LOOKING AFTER YOURSELF AND OTHERS DURING HOT WEATHER heatwave Most of us enjoy sunny weather, but extreme heat can seriously damage your health. During a heatwave, when temperatures
heatwave A GUIDE TO LOOKING AFTER YOURSELF AND OTHERS DURING HOT WEATHER heatwave Most of us enjoy sunny weather, but extreme heat can seriously damage your health. During a heatwave, when temperatures
IN CASE OF EMERGENCY. Emergency Telephone Number 112
 IN CASE OF EMERGENCY Emergency Telephone Number 112 Police, Fire, Ambulance Dial 112 in case of fire, medical emergency, serious or life threatening traffic or other accident. Tell the operator: What has
IN CASE OF EMERGENCY Emergency Telephone Number 112 Police, Fire, Ambulance Dial 112 in case of fire, medical emergency, serious or life threatening traffic or other accident. Tell the operator: What has
THERAPEUTIC USE OF HEAT AND COLD
 THERAPEUTIC USE OF HEAT AND COLD INTRODUCTION Heat and cold are simple and very effective therapeutic tools. They can be used locally or over the whole body, and the proper application of heat and cold
THERAPEUTIC USE OF HEAT AND COLD INTRODUCTION Heat and cold are simple and very effective therapeutic tools. They can be used locally or over the whole body, and the proper application of heat and cold
Head Injury, Age 4 and Older
 Head Injury, Age 4 and Older Table of Contents Topic Overview Check Your Symptoms Home Treatment Prevention Preparing For Your Appointment Related Information Credits Topic Overview Head injury Most injuries
Head Injury, Age 4 and Older Table of Contents Topic Overview Check Your Symptoms Home Treatment Prevention Preparing For Your Appointment Related Information Credits Topic Overview Head injury Most injuries
81 First Responder Respiratory
 81 First Responder Medical Scenarios Asthma Scenario: You are called to a local house for a woman with trouble breathing. You arrive to find a 67-year-old woman sitting upright in a chair. She states she
81 First Responder Medical Scenarios Asthma Scenario: You are called to a local house for a woman with trouble breathing. You arrive to find a 67-year-old woman sitting upright in a chair. She states she
The Family Library. Understanding Diabetes
 The Family Library Understanding Diabetes What is Diabetes? Diabetes is caused when the body has a problem in making or using insulin. Insulin is a hormone secreted by the pancreas and is needed for the
The Family Library Understanding Diabetes What is Diabetes? Diabetes is caused when the body has a problem in making or using insulin. Insulin is a hormone secreted by the pancreas and is needed for the
Heat Stress Training
 Heat Stress Training Agenda 1. What is Heat Stress - The Physiology - Heat Exhaustion (Symptoms and First Aid) - Heat Stroke (Symptoms and First Aid) - Other Conditions associated with Heat Stress 2. Who
Heat Stress Training Agenda 1. What is Heat Stress - The Physiology - Heat Exhaustion (Symptoms and First Aid) - Heat Stroke (Symptoms and First Aid) - Other Conditions associated with Heat Stress 2. Who
too hot! Heat Related Illness
 too hot! Heat Related Illness Participating in recreation and sport activities provides many benefits for children and can be a fun and enjoyable way to be physically active. However, when the temperature
too hot! Heat Related Illness Participating in recreation and sport activities provides many benefits for children and can be a fun and enjoyable way to be physically active. However, when the temperature
OPTIONAL LESSON Anaphylaxis and Epinephrine Auto-Injector
 OPTIONAL LESSON Anaphylaxis and Epinephrine Auto-Injector Lesson Length: 54 minutes GUIDANCE FOR THE INSTRUCTOR To complete this lesson and meet the lesson objectives, you must: Discuss all points in the
OPTIONAL LESSON Anaphylaxis and Epinephrine Auto-Injector Lesson Length: 54 minutes GUIDANCE FOR THE INSTRUCTOR To complete this lesson and meet the lesson objectives, you must: Discuss all points in the
2. (U4C2L3:F2) If your friend received a deep cut on her wrist, what would you do?
 Cadet Name: Date: 1. (U4C2L3:F1) Your friend receives a deep cut on her wrist while washing dishes. She asks for your help. How confident are you that you could provide appropriate aid? A) My friend is
Cadet Name: Date: 1. (U4C2L3:F1) Your friend receives a deep cut on her wrist while washing dishes. She asks for your help. How confident are you that you could provide appropriate aid? A) My friend is
3/24/2014. Waubonsee Community College Safety Day 2014. Why do we need a First Aid Program?
 Waubonsee Community College Safety Day 2014 Why do we need a First Aid Program? 4,383 workers were killed on the job in 2012 Total recordable non fatal cases: 2,976,400 in 2012 Cases involving days away
Waubonsee Community College Safety Day 2014 Why do we need a First Aid Program? 4,383 workers were killed on the job in 2012 Total recordable non fatal cases: 2,976,400 in 2012 Cases involving days away
First aid for seizures
 First aid for seizures What is epilepsy? Epilepsy is a tendency to have repeated seizures that begin in the brain. For most people with epilepsy their seizures will be controlled by medication. Around
First aid for seizures What is epilepsy? Epilepsy is a tendency to have repeated seizures that begin in the brain. For most people with epilepsy their seizures will be controlled by medication. Around
Staff, please note that the Head Injury Routine is included on page 3.
 Staff, please note that the Head Injury Routine is included on page 3. This booklet explains what can happen after a concussion, how to get better and where to go for more information and help if needed.
Staff, please note that the Head Injury Routine is included on page 3. This booklet explains what can happen after a concussion, how to get better and where to go for more information and help if needed.
American Red Cross Advisory Council on First Aid, Aquatics, Safety and Preparedness
 Copyright 2008 by The American National Red Cross All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced; stored in a retrieval system; or transmitted, in any form or by any means, electronic,
Copyright 2008 by The American National Red Cross All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced; stored in a retrieval system; or transmitted, in any form or by any means, electronic,
Scenario 2 Is it ever safe enough?
 IRECA BLS Competition 2011 Scenario 2 Is it ever safe enough? Team Name Captain Name Judge 1 Judge 2 The Event: You are dispatched to a shooting for two injured at a local bar. Witnesses have told police
IRECA BLS Competition 2011 Scenario 2 Is it ever safe enough? Team Name Captain Name Judge 1 Judge 2 The Event: You are dispatched to a shooting for two injured at a local bar. Witnesses have told police
NEW YORK STATE DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH BUREAU OF EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES
 NEW YORK STATE DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH BUREAU OF EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES TRAINING PROGRAM OUTLINE FOR UNLICENSED OR UNCERTIFIED PERSONNEL TO ADMINISTER EPINEPHRINE BY AUTO-INJECTOR IN LIFE-THREATENING
NEW YORK STATE DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH BUREAU OF EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES TRAINING PROGRAM OUTLINE FOR UNLICENSED OR UNCERTIFIED PERSONNEL TO ADMINISTER EPINEPHRINE BY AUTO-INJECTOR IN LIFE-THREATENING
Please Do Not Call 911
 The Last Hours of Life - What to Expect Names and Phone Numbers You May Need Name Phone Family Dr. Palliative Dr. After Hours Access Centre Visiting Nurse Hospice Clergy Funeral Contact Please Do Not Call
The Last Hours of Life - What to Expect Names and Phone Numbers You May Need Name Phone Family Dr. Palliative Dr. After Hours Access Centre Visiting Nurse Hospice Clergy Funeral Contact Please Do Not Call
Southern Stone County Fire Protection District Emergency Medical Protocols
 TITLE Pediatric Medical Assessment PM 2.4 Confirm scene safety Appropriate body substance isolation procedures Number of patients Nature of illness Evaluate the need for assistance B.L.S ABC s & LOC Focused
TITLE Pediatric Medical Assessment PM 2.4 Confirm scene safety Appropriate body substance isolation procedures Number of patients Nature of illness Evaluate the need for assistance B.L.S ABC s & LOC Focused
BROCKTON AREA MULTI-SERVICES, INC. MEDICAL PROCEDURE GUIDE. Date(s) Reviewed/Revised:
 Page 1 of 5 PROCEDURE FOR: MAP-certified staff and RN/LPN MAP-certified staff are to be trained in the use of epinephrine administration via pre-filled autoinjector devices(s) annually. Certified staff
Page 1 of 5 PROCEDURE FOR: MAP-certified staff and RN/LPN MAP-certified staff are to be trained in the use of epinephrine administration via pre-filled autoinjector devices(s) annually. Certified staff
Get the Facts About Tuberculosis Disease
 TB Get the Facts About Tuberculosis Disease What s Inside: Read this brochure today to learn how to protect your family and friends from TB. Then share it with people in your life. 2 Contents Get the facts,
TB Get the Facts About Tuberculosis Disease What s Inside: Read this brochure today to learn how to protect your family and friends from TB. Then share it with people in your life. 2 Contents Get the facts,
2 CHECKING AN INJURED OR ILL ATHLETE
 American Red Cross 2 CHECKING AN INJURED OR ILL ATHLETE ~~~'1'H ~.. 2 CHECKING AN INJURED OR III ATHLETE Checking the scene for safety and checking an injured or ill athlete is the first action to take,
American Red Cross 2 CHECKING AN INJURED OR ILL ATHLETE ~~~'1'H ~.. 2 CHECKING AN INJURED OR III ATHLETE Checking the scene for safety and checking an injured or ill athlete is the first action to take,
Adult, Child, and Infant Written Exam CPR Pro for the Professional Rescuer
 Adult, Child, and Infant Written Exam CPR Pro for the Professional Rescuer Instructions: Read each of the following questions carefully and then place an X over the correct answer on the separate answer
Adult, Child, and Infant Written Exam CPR Pro for the Professional Rescuer Instructions: Read each of the following questions carefully and then place an X over the correct answer on the separate answer
12/5/2012. Introduction. Head, Neck, and Spine Injuries. Recognizing and Caring for Serious Head, Neck and Back Injuries
 Head, Neck, and Spine Injuries Identify the most common causes of head, neck and spinal injuries. List 10 situations that might indicate serious head, neck and spinal injuries. List the signals of head,
Head, Neck, and Spine Injuries Identify the most common causes of head, neck and spinal injuries. List 10 situations that might indicate serious head, neck and spinal injuries. List the signals of head,
What Medical Emergencies Should a Dental Office be Prepared to Handle?
 What Medical Emergencies Should a Dental Office be Prepared to Handle? Gary Cuttrell, DDS, JD, University of NM Division of Dental Services Santiago Macias, MD, First Choice Community Healthcare Dentists
What Medical Emergencies Should a Dental Office be Prepared to Handle? Gary Cuttrell, DDS, JD, University of NM Division of Dental Services Santiago Macias, MD, First Choice Community Healthcare Dentists
Module 5 ADULT RECOvERY POSITION STEP 1 POSITION ThE victim
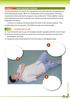 Module 5 ADULT RECOVERY POSITION The recovery position is used in the management of victims who are unresponsive but have breathing and pulse. When an unresponsive victim is lying supine, the airway may
Module 5 ADULT RECOVERY POSITION The recovery position is used in the management of victims who are unresponsive but have breathing and pulse. When an unresponsive victim is lying supine, the airway may
How To Care For A Sick Person
 39 How to Take Care of a Sick Person Sickness weakens the body. To gain strength and get well quickly, special care is needed. Medicines are often not necessary. But good care is always important. The
39 How to Take Care of a Sick Person Sickness weakens the body. To gain strength and get well quickly, special care is needed. Medicines are often not necessary. But good care is always important. The
MARYLAND STATE SCHOOL HEALTH SERVICES GUIDELINES
 Department of Health and Mental Hygiene Maryland State Department of Education Maryland State School Health Council MARYLAND STATE SCHOOL HEALTH SERVICES GUIDELINES Emergency Management Guidelines for
Department of Health and Mental Hygiene Maryland State Department of Education Maryland State School Health Council MARYLAND STATE SCHOOL HEALTH SERVICES GUIDELINES Emergency Management Guidelines for
Scout Skills... Simple First Aid
 Scout Skills... Simple First Aid Item Code FS315077 Aug/00 Edition no 2 (103851) 0845 300 1818 The practice of first aid is often said to be one of 'common sense' and in many ways this is true, for example,
Scout Skills... Simple First Aid Item Code FS315077 Aug/00 Edition no 2 (103851) 0845 300 1818 The practice of first aid is often said to be one of 'common sense' and in many ways this is true, for example,
Guide to Prevention of Heat Stress At Work
 Guide to Prevention of Heat Stress At Work WCB Website: www.wcb.pe.ca Toll free in Atlantic Canada: 1-800-237-5049 Feb, 2008 1 Prevention of Heat Stress at Work On Prince Edward Island illness from excess
Guide to Prevention of Heat Stress At Work WCB Website: www.wcb.pe.ca Toll free in Atlantic Canada: 1-800-237-5049 Feb, 2008 1 Prevention of Heat Stress at Work On Prince Edward Island illness from excess
CAMPSITE RISK ASSESSMENT. Risk mitigation and control measures: a practical guide for group leaders to manage general risk and hazards on tour
 CAMPSITE RISK ASSESSMENT mitigation and control measures: a practical guide for group leaders to manage general risk and hazards on tour CONTENTS 1. Introduction 2-3 2. Climbing Wall 4 3. Rock Climbing
CAMPSITE RISK ASSESSMENT mitigation and control measures: a practical guide for group leaders to manage general risk and hazards on tour CONTENTS 1. Introduction 2-3 2. Climbing Wall 4 3. Rock Climbing
BLS TREATMENT GUIDELINES - CARDIAC
 BLS TREATMENT GUIDELINES - CARDIAC CARDIOPULMONARY ARREST - NON-TRAUMATIC (SJ-B101) effective 07/01/99 Defibrillation CPR Apply S-AED and assess rhythm as trained. Defib as indicated Simultaneous OXYGEN:
BLS TREATMENT GUIDELINES - CARDIAC CARDIOPULMONARY ARREST - NON-TRAUMATIC (SJ-B101) effective 07/01/99 Defibrillation CPR Apply S-AED and assess rhythm as trained. Defib as indicated Simultaneous OXYGEN:
Biliary Drain. What is a biliary drain?
 Biliary Drain What is a biliary drain? A biliary drain is a tube to drain bile from your liver. It is put in by a doctor called an Interventional Radiologist. The tube or catheter is placed through your
Biliary Drain What is a biliary drain? A biliary drain is a tube to drain bile from your liver. It is put in by a doctor called an Interventional Radiologist. The tube or catheter is placed through your
HEAT-RELATED ILLNESS AND STUDENT ATHLETES. Diana L. Malone, Ph.D. Training & Consultation Coordinator
 HEAT-RELATED ILLNESS AND STUDENT ATHLETES Diana L. Malone, Ph.D. Training & Consultation Coordinator HEAT-RELATED ILLNESS Objectives: Factors that create HRI Stages of HRI Care Basic First Aid Protecting
HEAT-RELATED ILLNESS AND STUDENT ATHLETES Diana L. Malone, Ph.D. Training & Consultation Coordinator HEAT-RELATED ILLNESS Objectives: Factors that create HRI Stages of HRI Care Basic First Aid Protecting
EMERGENCY TREATMENT OF ANAPHYLAXIS EPINEPHRINE AUTO-INJECTOR
 I. GENERAL GUIDELINES EMERGENCY TREATMENT OF ANAPHYLAXIS EPINEPHRINE AUTO-INJECTOR A. PURPOSE To counteract a severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis) to a foreign substance as prescribed by the licensed
I. GENERAL GUIDELINES EMERGENCY TREATMENT OF ANAPHYLAXIS EPINEPHRINE AUTO-INJECTOR A. PURPOSE To counteract a severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis) to a foreign substance as prescribed by the licensed
EMT B Practice Test. Practice Questions:
 EMT B Practice Test Practice Questions: Questions 1 to 3 pertain to the following scenario: You and your partner are called to the home of a 75-year-old man complaining of severe pain in the chest and
EMT B Practice Test Practice Questions: Questions 1 to 3 pertain to the following scenario: You and your partner are called to the home of a 75-year-old man complaining of severe pain in the chest and
Basic First Aid for the Community and Workplace
 A M E R I C A N S A F E T Y & H E A LT H I N S T I T U T E Basic First Aid for the Community and Workplace Student Handbook This handbook serves as a reference guide for basic first aid. For the purpose
A M E R I C A N S A F E T Y & H E A LT H I N S T I T U T E Basic First Aid for the Community and Workplace Student Handbook This handbook serves as a reference guide for basic first aid. For the purpose
let s talk bleeds a bleed checklist for haemophilia patients
 let s talk bleeds a bleed checklist for haemophilia patients Specific signs of a bleed Watch for Bruising, with or without lumps Difference in the size of arms/legs Difference in movement in arms/legs
let s talk bleeds a bleed checklist for haemophilia patients Specific signs of a bleed Watch for Bruising, with or without lumps Difference in the size of arms/legs Difference in movement in arms/legs
Cardio-Pulmonary Resuscitation (CPR): A Decision Aid For. KGH Patients And Their Families
 Cardio-Pulmonary Resuscitation (CPR): A Decision Aid For KGH Patients And Their Families The goal of this pamphlet is to provide information about cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) so you can be adequately
Cardio-Pulmonary Resuscitation (CPR): A Decision Aid For KGH Patients And Their Families The goal of this pamphlet is to provide information about cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) so you can be adequately
For More Information: U.S. Department of Labor Occupational Safety and Health Administration 1-800-321-OSHA (6742) TTY 1-877-889-5627 www.osha.
 Acknowledgments: This Heat Illness Prevention Training Guide was adapted from materials developed by the Labor Occupational Health Program (LOHP), University of California, Berkeley. These materials are
Acknowledgments: This Heat Illness Prevention Training Guide was adapted from materials developed by the Labor Occupational Health Program (LOHP), University of California, Berkeley. These materials are
State Of Wisconsin Department of Military Affairs
 State Of Wisconsin Department of Military Affairs Division of Emergency Management Brian M. Satula Administrator Scott Walker Governor For more information contact: Tod Pritchard Lori Getter Office (608)
State Of Wisconsin Department of Military Affairs Division of Emergency Management Brian M. Satula Administrator Scott Walker Governor For more information contact: Tod Pritchard Lori Getter Office (608)
call 811 to get advice from a nurse, or have someone drive the patient to a hospital Emergency Department. Patients should NOT drive themselves.
 Taking Care at Home After Surgery This checklist is to help you and your support person know what to do after you go home following your surgery. If you are given instructions verbally or in writing by
Taking Care at Home After Surgery This checklist is to help you and your support person know what to do after you go home following your surgery. If you are given instructions verbally or in writing by
For the Patient: Paclitaxel injection Other names: TAXOL
 For the Patient: Paclitaxel injection Other names: TAXOL Paclitaxel (pak'' li tax' el) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a clear liquid that is injected into a vein. Tell your
For the Patient: Paclitaxel injection Other names: TAXOL Paclitaxel (pak'' li tax' el) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a clear liquid that is injected into a vein. Tell your
DRUG and ALCOHOL ABUSE
 M12 DRUG and ALCOHOL ABUSE EMS personnel must be aware that alcohol and drug ingestion can mask the symptoms of injury or illness. In addition, many injuries and illnesses can present as suspected alcohol
M12 DRUG and ALCOHOL ABUSE EMS personnel must be aware that alcohol and drug ingestion can mask the symptoms of injury or illness. In addition, many injuries and illnesses can present as suspected alcohol
FIRST AID FOR BASEBALL COACHES
 FIRST AID FOR BASEBALL COACHES Liability Issues. Do the right thing State provides qualified immunity Chapter 258 C, Section 13. Good Samaritan Law: No person who, in good faith, provides or obtains, or
FIRST AID FOR BASEBALL COACHES Liability Issues. Do the right thing State provides qualified immunity Chapter 258 C, Section 13. Good Samaritan Law: No person who, in good faith, provides or obtains, or
THE SHIP CAPTAIN S MEDICAL GUIDE
 THE SHIP CAPTAIN S MEDICAL GUIDE 5 Introduction When a ship is in port, or near to port where hospital and other expert medical attention are available, the first aid treatment necessary aboard ship is
THE SHIP CAPTAIN S MEDICAL GUIDE 5 Introduction When a ship is in port, or near to port where hospital and other expert medical attention are available, the first aid treatment necessary aboard ship is
Canine Tactical Combat Casualty Care
 Canine Tactical Combat Casualty Care The following C-TCC guidelines are based on human C-TCCC guidelines and the limited data available on combat injuries and field treatment of working dogs. These guideline
Canine Tactical Combat Casualty Care The following C-TCC guidelines are based on human C-TCCC guidelines and the limited data available on combat injuries and field treatment of working dogs. These guideline
WEEKLY SAFETY MEETING All Euramax Subsidiaries COLD WEATHER. Safety Meeting Contents. Meeting Notice. Leaders Guide. Employee Handout.
 Safety Meeting Contents Meeting Notice Leaders Guide Employee Handout Employee Quiz Meeting Sign-In Sheet Employee Puzzle PRIOR TO THE WEEKLY MEETING: - Post the meeting notice by the timeclock - Read
Safety Meeting Contents Meeting Notice Leaders Guide Employee Handout Employee Quiz Meeting Sign-In Sheet Employee Puzzle PRIOR TO THE WEEKLY MEETING: - Post the meeting notice by the timeclock - Read
Going home after an AV Fistula or AV Graft
 Going home after an AV Fistula or AV Graft TGH Information for patients and families During your hospital stay, your surgeon created an: AV Fistula AV Graft Read this booklet to learn: how to care for
Going home after an AV Fistula or AV Graft TGH Information for patients and families During your hospital stay, your surgeon created an: AV Fistula AV Graft Read this booklet to learn: how to care for
6. Do not hang up until told to do so by the emergency service 7. Make sure someone is available to direct the emergency service to the scene
 Emergency procedures Stop, think, act! The first priority in the event of an emergency is for the safety of all people present Raise the alarm Turn to the relevant page to confirm what to do Emergency
Emergency procedures Stop, think, act! The first priority in the event of an emergency is for the safety of all people present Raise the alarm Turn to the relevant page to confirm what to do Emergency
For the Patient: Dasatinib Other names: SPRYCEL
 For the Patient: Dasatinib Other names: SPRYCEL Dasatinib (da sa' ti nib) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. Tell your doctor if you have ever
For the Patient: Dasatinib Other names: SPRYCEL Dasatinib (da sa' ti nib) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. Tell your doctor if you have ever
