Severe Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
|
|
|
- Charity Hampton
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Severe Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) University of Cincinnati Neuroscience Institute NEUROTRAUMA CENTER OVERVIEW Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) is any injury that results from a blow or jolt to the head from blunt or penetrating trauma. TBI can be the result of any blunt head injury, but common causes include falls, sports injuries, vehicle accidents and assault. There are different degrees of head injury ranging from a mild concussion, which requires symptom monitoring and rest, to a severe TBI, which could require hospitalization and/or surgery. high pressure this bleed can grow quickly, resulting in a rapid decrease in a patient s consciousness. Intracranial hematoma (ICH) is bleeding within the brain tissue. Although we describe these as individual injuries, it is rare for a patient to suffer only one type of injury. It is more common for a patient to have a combination of injuries, all of which may have different levels of severity. This makes questions like, what part of the brain is hurt? extremely difficult to answer, as it is usually not just one area. What is a traumatic brain injury? TBI is an injury to the head resulting from blunt or penetrating trauma. The initial injury is known as the primary injury.primary injuries can affect the entire brain (diffuse injuries) or a specific section (focal injuries). Types of diffuse injuries: Concussions are mild head injuries that can cause brief loss of consciousness without brain tissue injury. Diffuse axonal injury (DAI) is commonly referred to as shear injury. This is an injury that occurs when the brain quickly moves back and forth inside the skull damaging the cells that carry information throughout the brain. This disrupts how the brain normally communicates information and can result in changes in a patient s consciousness. Traumatic subarachnoid hemorrhage is caused from bleeding on the surface of the brain. Types of focal injuries: A cerebral contusion is a bruise on the brain tissue. A subdural hematoma (SDH) is bleeding that occurs under the dura, or layer of tissue that surrounds the brain. Tearing of veins or vessels that deliver the blood back to the heart is often the cause this type of bleeding. An epidural hematoma (EDH) is a blood clot that forms on top of the dura, below the skull. Arteries that supply blood from the heart most commonly cause this type of bleed. Because the blood within the arteries travels at a figure 1 Secondary injury is an injury that occurs as a result of the body s response to the primary injury. The inflammatory response of a brain injury causes extra fluid to collect in the brain in an attempt to heal the injury. In other areas of the body swelling (edema) is a good response; however it can be dangerous in the brain, where space is limited by the skull. The swelling causes injury to parts of the brain that were not initially injured, resulting in secondary brain injury. This swelling happens gradually and can occur up to 5 days after the primary injury. Nurses and doctors in the Neuroscience Intensive Care Unit (NSICU) will monitor patients closely for signs of cerebral edema, or swelling of the brain tissue, by analyzing their responsiveness and exam results. One type of technology that is used to show swelling of the brain is an intracranial pressure (ICP) monitor. The monitor is placed inside the brain to measure pressure inside the head, and gives the NSICU team the ability to intervene if the pressure level rises above normal.
2 Diffuse injuries, like concussion or DAI will typically cause an overall decreased level of consciousness. Focal injuries, like ICH or cerebral contusion, will trigger symptoms based on the area of the brain that is affected. Every patient is unique and some injuries involve more than one area of the brain, making it difficult to predict which specific symptoms a patient will experience. What are the symptoms of traumatic brain injury? Depending on the type and location of the injury, a patient s symptoms may include: Loss of consciousness Sleep disturbances Confusion and disorientation Dizziness/loss of balance Memory loss/amnesia Irritability/emotional Fatigue disturbances Headaches Feelings of depression Visual problems Seizures Poor attention/concentration Vomiting How is a diagnosis made? When a patient is brought to the emergency room with a head injury, doctors will learn as much as possible about his or her symptoms and how the injury occurred. The person s condition is assessed quickly to determine the extent of injury. A Glasgow Coma Score (GCS) is a coma score that is used to assess a patient s level of consciousness. The GCS has three categories that are scored based on a patient s responsiveness. The categories consist of the patient s ability to: Open his or her eyes Respond appropriately to orientation questions like, what is your name? and what is the date today? Follow commands like holding up two fingers or responding to painful stimulation A number is assigned to each category based on a patient s performance and the scores are added together to get the total GCS score. The scores range from 3 to 15 and help determine if a patient has a mild, moderate or severe brain injury. A mild TBI scores anywhere from 13-15, a moderate TBI scores from 9-12 and a severe TBI scores anything below 9. Other tests may also be used to assess a patient s injury: A Computed Tomography (CT) Scan uses X-rays and a computer to create images of the brain at the time of injury to quickly diagnose the type, location and extent of injury. CT scans are used throughout recovery to evaluate the injury and help guide the decision-making in a patient s care. A Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) uses a magnet, radio waves and a computer to create images of the brain and is used to further define the extent of injury. The MRI can detect more subtle changes in the brain that cannot be seen on the CT scan. These tests are not used in emergency situations because they can take anywhere from minutes to complete. What treatments are available? Mild TBI usually requires rest and medication to relieve symptoms, while moderate to severe TBI require intensive care in a hospital bed. Bleeding and swelling in the brain can become an emergency that requires surgery. However, there are times when a patient does not require surgery and can be safely monitored in the NSICU. The goals of treatment are to stabilize a critically ill patient, minimize secondary brain injury and complications, and facilitate the patient s transition to a recovery environment. The care of critically ill patients with a TBI is overseen by a neurosurgical team and a neurointensivist, a specialty-trained physician who coordinates the patient s neurological and medical care. Seeing a patient who has suffered a severe TBI can be shocking. It is possible that your loved one s appearance will be altered because of facial injury and equipment that is used for monitoring. Numerous tubes, lines and equipment are used to closely monitor his or her heart rate, blood pressure and other critical body functions. Medication Sedation and pain After a head injury it may be necessary to keep a patient sedated with medications. The dosage of medications can be altered quickly in order to awaken a patient. Because patients usually have additional injuries, pain medication is given to keep them comfortable. Controlling intracranial pressure Some medications are used to control pressure within the brain. They work by drawing the extra water out of the brain cells and into the blood vessels, allowing the kidneys to filter it out of the blood. Preventing seizures Patients who have had a moderate to severe TBI are at higher risk of having seizures during the first week after their injury. Patients are given an antiseizure medication to prevent seizures from occurring during their hospital stay. Preventing infection Although every attempt is made to prevent infection while your loved one is in the hospital, the risk is always present. Any device placed within the patient has the potential to introduce a microbe that can cause an infection. If an infection is suspected, a test will be sent to a laboratory for analysis. If an infection is present, it will be treated with appropriate antibiotics.
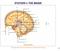
3 Diffuse injuries, like concussion or DAI will typically cause an overall decreased level of consciousness. Focal injuries, like ICH or cerebral contusion, will trigger symptoms based on the area of the brain that is affected. Every patient is unique and some injuries involve more than one area of the brain, making it difficult to predict which specific symptoms a patient will experience. IMPACT OF A BRAIN INJURY Lobes of the Brain Cerebrum Key Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Occipital lobe Temporal lobe Cerebellum HEALTHY BRAIN Frontal lobe Personality and emotions Intelligence Attention and concentration Judgment Body movement (motor strip) Problem solving Speech (speaking & writing) Sense of smell Parietal lobe Sense of touch, pain and temperature (sensory strip) Distinguishing size, shape and color Spatial perception Visual perception Occipital lobe Vision Temporal lobe Speech (understanding language) Memory Hearing Sequencing Organization Cerebellum Balance Coordination Brainstem Breathing Heart rate Alertness and consciousness Brain Stem INJURED BRAIN Changes in social behavior and personality Mood swings, irritability, impulsiveness Repetition of a single thought Unable to focus on a task Impaired judgment Loss of movement (paralysis) Difficulty with problem solving Difficulty with language; can t get the words out (aphasia) Loss of smell Loss of appetite Lack of awareness or neglect of certain body parts Difficulty distinguishing left from right Difficulties with hand-eye coordination Problems with reading, writing, drawing and naming Difficulty with mathematics Defects in vision or blind spots Blurred vision Visual illusions/hallucinations Difficulty reading and writing Difficulty understanding language and speaking (aphasia) Difficulty recognizing faces Difficulty identifying/naming objects Problems with short-term and long-term memory Changes in sexual behavior Increase in aggressive behavior Difficulty walking Difficulty coordinating fine movements Tremors Dizziness (vertigo) Slurred speech Changes in breathing Difficulty swallowing food and water (dysphagia) Problems with balance and movement Dizziness and nausea (vertigo)
4 EQUIPMENT IN YOUR ROOM The picture below shows the equipment that might be in our patient rooms. Please ask your nurse if you have questions about any of the technology in your room. Intracranial Pressure (ICP) monitor: a probe inserted through the skull into the brain to measure pressure; may also be used to drain fluid. Bedside monitor: a TV-like screen that displays heart rate, oxygen saturation, blood pressure, and other vital signs. Intravenous (IV) pump: delivers fluids and medications through a tube inserted into a vein. Ventilator: provides oxygen and assists or totally breathes for the patient through an endotracheal tube or tracheostomy inserted into the windpipe. EEG box / electrodes: connection for multiple sensors attached to the scalp that record brain electrical activity. Feeding pump: provides liquid food to the stomach through the Enteroflex tube. Enteroflex tube: a small tube placed through the nose into the stomach; provides food or removes contents from stomach. Licox: measures oxygen levels in the brain. Hemedex monitor: measures blood flow in specific areas of the brain. Mayfield Clinic Central line: a catheter inserted into a large, deep vein to deliver medication and draw blood. Compression boots: prevent blood clots from forming in the leg veins by periodically squeezing the leg muscles. Electroencephalography (EEG): a machine that records electrical activity of the brain. It monitors for seizures, the effects of sedation, and worsening brain function. Pulse oximeter: a probe attached to the end of a finger or toe; measures the blood oxygen level. Foley catheter: a tube inserted into the bladder to collect and measure urine. Restraints: soft cloth ties that hold the patient's arms; prevents the patient from pulling out tubes.
5 Recovery & Prevention The recovery process varies by patient depending on the severity of the injury, but typically progresses through 3 stages: coma, confusion/amnesia and recovery. The Family s Role Family members often express feelings of helplessness when their loved one is in the NSICU. You are not alone. Please take care of yourself and use your energy wisely. Surgery Surgery is sometimes necessary to repair skull fractures, repair bleeding vessels or remove large blood clots. It is also performed to relieve extremely high intracranial pressure. Craniotomy is a procedure that involves removing a section of skull bone in order to access the brain. After the intended procedure is completed the bone is replaced and secured in place. (figure 2) Craniectomy is the removal of a portion of the skull bone to allow room for the brain to swell. This procedure is typically done when a patient has a large amount of damage to an area of the brain and the swelling becomes life-threatening. When the pressure returns to a normal level the bone can be replaced with a procedure called a cranioplasty. Some procedures may be necessary to aid in a patient s recovery. These procedures help patients transition their care from the NSICU to an area where less monitoring is appropriate. These procedures are not always needed, however when they are needed they are not always permanent. As a patient recovers, and if it s medically appropriate, the devices can be removed. figure 2 Tracheotomy is a procedure that involves making a small incision in the patient s neck to place a breathing tube into the windpipe. A ventilator, or breathing machine, will then be connected to assist the patient with normal breathing. Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy (PEG) Tube is a feeding tube that is inserted directly into the stomach through the abdominal wall. A small camera is placed down the patient s throat into the stomach to aid with the procedure and to ensure correct placement of the PEG tube. Visiting hours are limited in the NSICU. Patients with neurological problems often need quiet surroundings, and may become too excited by touching, music, talking or loud noises. Our staff asks for no more than 2 visitors in a patient room at a time. Too much excitement may cause harmful changes in your loved one s vital signs. The bedside nurse will guide you on the appropriate amount of stimulation a patient can tolerate, and may ask that visitors leave the room at times. Rehabilitation Patients are discharged from the hospital when their condition has stabilized and they no longer require intensive care. After discharge a patient is likely to go to one of the following facilities: A long-term acute care (LTAC) facility is a place for patients who have stabilized from their initial head injury, but still require a ventilator or frequent nursing care. Many patients are discharged to an LTAC after their injury to continue being weaned from the ventilator. Once off the ventilator, they can be moved to a rehabilitation or skilled nursing facility where they will continue their recovery. A rehabilitation facility is a place for patients who do not require a ventilator, but still require help with basic daily activities. Physical and occupational therapists work with patients to help them achieve their maximum potential for recovery. Rehab facilities are either Acute Inpatient Rehab that requires patients to participate in 3 hours or more of rehab a day or a Skilled Nursing Facility (SNF) that will provide 1-3 hours of rehab a day depending on what the patient can tolerate. Prevention Tips to reduce the risk for a head injury: Always wear your helmet when riding a bicycle, motorcycle, skateboard or all-terrain vehicle. Never drive under the influence of alcohol or drugs. Always wear your seatbelt and ensure that children are secured in the appropriate child safety seats. (continued)
6 Avoid falls in the home by keeping unsecured items off the floor, installing safety features such as non-slip mats in the bathtub, handrails on stairways and keeping items off the stairs. Avoid falls by participating in an exercise program to increase strength, balance and coordination. Store firearms in a locked cabinet with bullets in a separate location. Wear protective headgear while playing sports. Resources: The Brain Injury Association of Ohio Sources: 1. Brain Trauma Foundation: Guidelines for the Management of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury. J Neurotrauma 24 Suppl 1:S1-106, Johnson G. Traumatic Brain Injury Survival Guide, Updated: Reviewed by: Erin Silva, CNP; Norberto Andaluz, MD This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Always follow your healthcare professional s instructions 4/14
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
 Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Overview Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is sudden damage to the brain caused by a blow or jolt to the head. Common causes include car or motorcycle crashes, falls, sports injuries,
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Overview Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is sudden damage to the brain caused by a blow or jolt to the head. Common causes include car or motorcycle crashes, falls, sports injuries,
Types of Brain Injury
 Types of Brain Injury The bones of your skull are hard and they protect your brain. Your brain is soft, like firm Jell-O. When your head moves, your brain moves inside your skull. When your head is hit
Types of Brain Injury The bones of your skull are hard and they protect your brain. Your brain is soft, like firm Jell-O. When your head moves, your brain moves inside your skull. When your head is hit
Brain Injury Education
 Memorial Hermann mischer neuroscience institute Brain Injury Education texas medical center Table of Contents 1 Introduction 3 What Is a Brain Injury? 4 Types of Brain Injury 6 Meet Our Directors and Attending
Memorial Hermann mischer neuroscience institute Brain Injury Education texas medical center Table of Contents 1 Introduction 3 What Is a Brain Injury? 4 Types of Brain Injury 6 Meet Our Directors and Attending
Functions of the Brain
 Objectives 0 Participants will be able to identify 4 characteristics of a healthy brain. 0 Participants will be able to state the functions of the brain. 0 Participants will be able to identify 3 types
Objectives 0 Participants will be able to identify 4 characteristics of a healthy brain. 0 Participants will be able to state the functions of the brain. 0 Participants will be able to identify 3 types
Diuretics: You may get diuretic medicine to help decrease swelling in your brain. This may help your brain get better blood flow.
 Hemorrhagic Stroke GENERAL INFORMATION: What is a hemorrhagic stroke? A hemorrhagic stroke happens when a blood vessel in the brain bursts. This may happen if the blood vessel wall is weak, or sometimes
Hemorrhagic Stroke GENERAL INFORMATION: What is a hemorrhagic stroke? A hemorrhagic stroke happens when a blood vessel in the brain bursts. This may happen if the blood vessel wall is weak, or sometimes
Traumatic brain injury (TBI)
 Traumatic brain injury (TBI) A topic in the Alzheimer s Association series on understanding dementia. About dementia Dementia is a condition in which a person has significant difficulty with daily functioning
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) A topic in the Alzheimer s Association series on understanding dementia. About dementia Dementia is a condition in which a person has significant difficulty with daily functioning
Background on Brain Injury
 CHAPTER 1 Background on Brain Injury In this chapter, you will: Read about Alberta s definition of Acquired Brain Injury and how that affects which supports you will be able to access. Learn about the
CHAPTER 1 Background on Brain Injury In this chapter, you will: Read about Alberta s definition of Acquired Brain Injury and how that affects which supports you will be able to access. Learn about the
Traumatic Brain Injury and Incarceration. Objectives. Traumatic Brain Injury. Which came first, the injury or the behavior?
 Traumatic Brain Injury and Incarceration Which came first, the injury or the behavior? Barbara Burchell Curtis RN, MSN Objectives Upon completion of discussion, participants should be able to Describe
Traumatic Brain Injury and Incarceration Which came first, the injury or the behavior? Barbara Burchell Curtis RN, MSN Objectives Upon completion of discussion, participants should be able to Describe
Recovering from a Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (MTBI)
 Recovering from a Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (MTBI) What happened? You have a Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (MTBI), which is a very common injury. Some common ways people acquire this type of injury are
Recovering from a Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (MTBI) What happened? You have a Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (MTBI), which is a very common injury. Some common ways people acquire this type of injury are
What Is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)?
 What Is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D., Chair 1 What
What Is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D., Chair 1 What
A patient guide to mild traumatic brain injury
 A patient guide to mild traumatic brain injury Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
A patient guide to mild traumatic brain injury Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
brain injury take care of yourself. we ll take care of the rest.
 take care of yourself. we ll take care of the rest. common injuries While injuries to the head do not always result in damage to the brain, it s important to note the most common forms of head trauma that
take care of yourself. we ll take care of the rest. common injuries While injuries to the head do not always result in damage to the brain, it s important to note the most common forms of head trauma that
PE finding: Left side extremities mild weakness No traumatic wound No bloody otorrhea, nor rhinorrhea
 Case report A 82-year-old man was suffered from sudden onset spasm of extremities then he fell down to the ground with loss of consciousness. He recovered his consciousness 7-8 mins later but his conscious
Case report A 82-year-old man was suffered from sudden onset spasm of extremities then he fell down to the ground with loss of consciousness. He recovered his consciousness 7-8 mins later but his conscious
Table of contents Topic Page
 Table of contents Topic Page Introduction 1 What is an acquired brain injury? 3 What type of damage has occurred? 4 How much damage has occurred? 5 What tests will my child need? 7 What happens when the
Table of contents Topic Page Introduction 1 What is an acquired brain injury? 3 What type of damage has occurred? 4 How much damage has occurred? 5 What tests will my child need? 7 What happens when the
Brain Injury Association National Help Line: 1-800-444-6443 Brain Injury Association Web site: www.biausa.org Centers for Disease Control and
 Brain Injury Association National Help Line: 1-800-444-6443 Brain Injury Association Web site: www.biausa.org Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Web site: www.cdc.gov/ncipc/tbi Contents About Brain
Brain Injury Association National Help Line: 1-800-444-6443 Brain Injury Association Web site: www.biausa.org Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Web site: www.cdc.gov/ncipc/tbi Contents About Brain
BINSA Information on Brain Injury
 Acquired Brain Injury (ABI) There are a number of ways an individual can suffer an acquired brain injury (ABI) Figure one - ABI causes Significant causes of ABI Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Traumatic Brain
Acquired Brain Injury (ABI) There are a number of ways an individual can suffer an acquired brain injury (ABI) Figure one - ABI causes Significant causes of ABI Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Traumatic Brain
Staff, please note that the Head Injury Routine is included on page 3.
 Staff, please note that the Head Injury Routine is included on page 3. This booklet explains what can happen after a concussion, how to get better and where to go for more information and help if needed.
Staff, please note that the Head Injury Routine is included on page 3. This booklet explains what can happen after a concussion, how to get better and where to go for more information and help if needed.
Head Injury in Children
 Head Injury in Children The worst fear of every parent is to receive news that your child has been injured in an accident. Unfortunately, in our society, accidental injuries have become the leading threat
Head Injury in Children The worst fear of every parent is to receive news that your child has been injured in an accident. Unfortunately, in our society, accidental injuries have become the leading threat
Homework Help Stroke
 The Brain & Strokes Your brain is the most complex organ in your body. It is the command centre for everything you do, think, sense and say! It has over 100 billion special nerve cells called neurons.
The Brain & Strokes Your brain is the most complex organ in your body. It is the command centre for everything you do, think, sense and say! It has over 100 billion special nerve cells called neurons.
The Petrylaw Lawsuits Settlements and Injury Settlement Report
 The Petrylaw Lawsuits Settlements and Injury Settlement Report TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURIES How Minnesota Juries Decide the Value of Pain and Suffering in Brain Injury Cases The Petrylaw Lawsuits Settlements
The Petrylaw Lawsuits Settlements and Injury Settlement Report TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURIES How Minnesota Juries Decide the Value of Pain and Suffering in Brain Injury Cases The Petrylaw Lawsuits Settlements
How To Understand The Effects Of Mild Traumatic Brain Injury
 Knowing about your Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Knowing about mild TBI There is a distinction between visible injuries to the scalp ( Head Injuries ) and internal injuries to the brain itself ( Traumatic
Knowing about your Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Knowing about mild TBI There is a distinction between visible injuries to the scalp ( Head Injuries ) and internal injuries to the brain itself ( Traumatic
6.0 Management of Head Injuries for Maxillofacial SHOs
 6.0 Management of Head Injuries for Maxillofacial SHOs As a Maxillofacial SHO you are not required to manage established head injury, however an awareness of the process is essential when dealing with
6.0 Management of Head Injuries for Maxillofacial SHOs As a Maxillofacial SHO you are not required to manage established head injury, however an awareness of the process is essential when dealing with
HEAD INJURIES V S U H E A L T H C E N T E R V A L D O S T A S T A T E U N I V E R S I T Y F A L L 2 0 1 2
 HEAD INJURIES V S U H E A L T H C E N T E R V A L D O S T A S T A T E U N I V E R S I T Y F A L L 2 0 1 2 LET S TALK ABOUT BRAIN INJURIES! Traumatic head injury affects more than 1.7 million people in
HEAD INJURIES V S U H E A L T H C E N T E R V A L D O S T A S T A T E U N I V E R S I T Y F A L L 2 0 1 2 LET S TALK ABOUT BRAIN INJURIES! Traumatic head injury affects more than 1.7 million people in
Module 1: The Brain and the Central Nervous System (CNS)
 Module 1: The Brain and the Central Nervous System (CNS) By the end of this unit, the learner will be able to: Describe the anatomy of the brain and the central nervous system Identify regions of the brain
Module 1: The Brain and the Central Nervous System (CNS) By the end of this unit, the learner will be able to: Describe the anatomy of the brain and the central nervous system Identify regions of the brain
Ischaemic stroke 85% (85 in every 100 strokes)
 UNDERSTANDING STROKE DUE TO INTRACEREBRAL HAEMORRHAGE This factsheet provides information for people who have had a stroke due to an intracerebral (bleed in the brain) and for their families and carers.
UNDERSTANDING STROKE DUE TO INTRACEREBRAL HAEMORRHAGE This factsheet provides information for people who have had a stroke due to an intracerebral (bleed in the brain) and for their families and carers.
What You Should Know About Cerebral Aneurysms
 What You Should Know About Cerebral Aneurysms From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Interventions Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Radiology Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D.,
What You Should Know About Cerebral Aneurysms From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Interventions Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Radiology Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D.,
Traumatic Brain Injury Lawsuit
 Traumatic Brain Injury Lawsuit D Legal Guide Simple Step-By-Step Guide to Your Brain & Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) [Type text] Distributed By: www.downtownlalw.com A Simple Step-by-Step Guide to your
Traumatic Brain Injury Lawsuit D Legal Guide Simple Step-By-Step Guide to Your Brain & Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) [Type text] Distributed By: www.downtownlalw.com A Simple Step-by-Step Guide to your
Basic Brain Information
 Basic Brain Information Brain facts Your brain weighs about 3lbs, or just under 1.5Kg It has the texture of blancmange Your brain is connected to your spinal cord by the brain stem Behind your brain stem
Basic Brain Information Brain facts Your brain weighs about 3lbs, or just under 1.5Kg It has the texture of blancmange Your brain is connected to your spinal cord by the brain stem Behind your brain stem
Concussion Management Return to Play Protocol
 Concussion Management Return to Play Protocol Returning to play following a concussion involves a stepwise progression once the individual is symptom free. There are many risks to premature return to play
Concussion Management Return to Play Protocol Returning to play following a concussion involves a stepwise progression once the individual is symptom free. There are many risks to premature return to play
Head Injury, Age 4 and Older
 Head Injury, Age 4 and Older Table of Contents Topic Overview Check Your Symptoms Home Treatment Prevention Preparing For Your Appointment Related Information Credits Topic Overview Head injury Most injuries
Head Injury, Age 4 and Older Table of Contents Topic Overview Check Your Symptoms Home Treatment Prevention Preparing For Your Appointment Related Information Credits Topic Overview Head injury Most injuries
Epidural Continuous Infusion. Patient information Leaflet
 Epidural Continuous Infusion Patient information Leaflet April 2015 Introduction You may already know that epidural s are often used to treat pain during childbirth. This same technique can also used as
Epidural Continuous Infusion Patient information Leaflet April 2015 Introduction You may already know that epidural s are often used to treat pain during childbirth. This same technique can also used as
1 of 6 1/22/2015 10:06 AM
 1 of 6 1/22/2015 10:06 AM 2 of 6 1/22/2015 10:06 AM This cross-section view of the shoulder socket shows a typical SLAP tear. Injuries to the superior labrum can be caused by acute trauma or by repetitive
1 of 6 1/22/2015 10:06 AM 2 of 6 1/22/2015 10:06 AM This cross-section view of the shoulder socket shows a typical SLAP tear. Injuries to the superior labrum can be caused by acute trauma or by repetitive
B U R T & D A V I E S PERSONAL INJURY LAWYERS
 TRANSPORT ACCIDENT LAW - TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY Traumatic Brain Injury ( TBI ) is a common injury in transport accidents. TBI s are probably the most commonly undiagnosed injuries in a hospital setting.
TRANSPORT ACCIDENT LAW - TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY Traumatic Brain Injury ( TBI ) is a common injury in transport accidents. TBI s are probably the most commonly undiagnosed injuries in a hospital setting.
Delirium. The signs of delirium are managed by treating the underlying cause of the medical condition causing the delirium.
 Delirium Introduction Delirium is a complex symptom where a person becomes confused and shows significant changes in behavior and mental state. Signs of delirium include problems with attention and awareness,
Delirium Introduction Delirium is a complex symptom where a person becomes confused and shows significant changes in behavior and mental state. Signs of delirium include problems with attention and awareness,
HEAD INJURY Discharge Instructions
 Hospital Copy NEUROSURGICAL CONSULTANTS, INC. www.neurosurgical-consult.com MICHAEL GIEGER, ABNS MICHAEL H. FREED, M.D., FACS, ABNS MARC H. FRIEDBERG, M.D., Ph.D., FACS, ABNS LINDEN BUILDING FIRST FLOOR
Hospital Copy NEUROSURGICAL CONSULTANTS, INC. www.neurosurgical-consult.com MICHAEL GIEGER, ABNS MICHAEL H. FREED, M.D., FACS, ABNS MARC H. FRIEDBERG, M.D., Ph.D., FACS, ABNS LINDEN BUILDING FIRST FLOOR
Brain Tumor 101. Shanna Armstrong, RN Neuro Oncology Nurse Clinician UC Brain Tumor Center
 Brain Tumor 101 Shanna Armstrong, RN Neuro Oncology Nurse Clinician UC Brain Tumor Center Objectives Identify the different parts of the brain Describe how each part of the brain works Connect each part
Brain Tumor 101 Shanna Armstrong, RN Neuro Oncology Nurse Clinician UC Brain Tumor Center Objectives Identify the different parts of the brain Describe how each part of the brain works Connect each part
Head Injury. Dr Sally McCarthy Medical Director ECI
 Head Injury Dr Sally McCarthy Medical Director ECI Head injury in the emergency department A common presentation 80% Mild Head Injury = GCS 14 15 10% Moderate Head Injury = GCS 9 13 10% Severe Head Injury
Head Injury Dr Sally McCarthy Medical Director ECI Head injury in the emergency department A common presentation 80% Mild Head Injury = GCS 14 15 10% Moderate Head Injury = GCS 9 13 10% Severe Head Injury
TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY (TBI)
 Background: Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) is one of the leading causes of trauma related disability and death in the U.S. TBIs can occur as either blunt, penetrating, or a combination of both depending
Background: Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) is one of the leading causes of trauma related disability and death in the U.S. TBIs can occur as either blunt, penetrating, or a combination of both depending
X-Plain Hip Replacement Surgery - Preventing Post Op Complications Reference Summary
 X-Plain Hip Replacement Surgery - Preventing Post Op Complications Reference Summary Introduction Severe arthritis in the hip can lead to severe pain and inability to walk. To relieve the pain and improve
X-Plain Hip Replacement Surgery - Preventing Post Op Complications Reference Summary Introduction Severe arthritis in the hip can lead to severe pain and inability to walk. To relieve the pain and improve
Head Injury in Infants, Children and Adults: Triage, Assessment, Investigation and Early Management
 Head Injury in Infants, Children and Adults: Triage, Assessment, Investigation and Early Management Information for people who have injured their head, their families and carers NICE Guideline (Patient
Head Injury in Infants, Children and Adults: Triage, Assessment, Investigation and Early Management Information for people who have injured their head, their families and carers NICE Guideline (Patient
It s Just a Concussion, right?
 Head Injury It s Just a Concussion, right? July 2015, 1 hour Introcuction - What is Traumatic Brain Injury? Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) is defined as a blow or jolt to the head, or penetration of the
Head Injury It s Just a Concussion, right? July 2015, 1 hour Introcuction - What is Traumatic Brain Injury? Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) is defined as a blow or jolt to the head, or penetration of the
TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY
 1 TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY WHAT IS IT? Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) is caused by impact to the head in turn causes damage to the brain. TBI can happen at the time of the impact or later on. The injury may
1 TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY WHAT IS IT? Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) is caused by impact to the head in turn causes damage to the brain. TBI can happen at the time of the impact or later on. The injury may
Concussion Guidance for the General Public
 CONCUSSION FACTS A concussion is a brain injury. All concussions are serious. Concussions can occur without loss of consciousness. All athletes with any symptoms following a head injury must be removed
CONCUSSION FACTS A concussion is a brain injury. All concussions are serious. Concussions can occur without loss of consciousness. All athletes with any symptoms following a head injury must be removed
Mild Brain Injury Recovery
 2011 Mild Brain Injury Recovery Mild Brain Injury Recovery What is a mild brain injury? A brain injury is often caused by trauma to the head for any reason. If you had a change in your level of consciousness,
2011 Mild Brain Injury Recovery Mild Brain Injury Recovery What is a mild brain injury? A brain injury is often caused by trauma to the head for any reason. If you had a change in your level of consciousness,
Herniated Disk. This reference summary explains herniated disks. It discusses symptoms and causes of the condition, as well as treatment options.
 Herniated Disk Introduction Your backbone, or spine, has 24 moveable vertebrae made of bone. Between the bones are soft disks filled with a jelly-like substance. These disks cushion the vertebrae and keep
Herniated Disk Introduction Your backbone, or spine, has 24 moveable vertebrae made of bone. Between the bones are soft disks filled with a jelly-like substance. These disks cushion the vertebrae and keep
Anatomy of the Brain: The Basics... 3. Scales, Tests and Diagnostic Measures... 6. Glossary of Terms You May Hear... 9
 Table of Contents Brain Injury: Basic Facts... 1 Anatomy of the Brain: The Basics... 3 Scales, Tests and Diagnostic Measures... 6 Glossary of Terms You May Hear... 9 Questions Families Should Ask Their...
Table of Contents Brain Injury: Basic Facts... 1 Anatomy of the Brain: The Basics... 3 Scales, Tests and Diagnostic Measures... 6 Glossary of Terms You May Hear... 9 Questions Families Should Ask Their...
IF IN DOUBT, SIT THEM OUT.
 IF IN DOUBT, SIT THEM OUT. Scottish Sports Concussion Guidance: Grassroots sport and general public Modified from World Rugby s Guidelines on Concussion Management for the General Public Introduction The
IF IN DOUBT, SIT THEM OUT. Scottish Sports Concussion Guidance: Grassroots sport and general public Modified from World Rugby s Guidelines on Concussion Management for the General Public Introduction The
The science of medicine. The compassion to heal.
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES OF THE HEART The science of medicine. The compassion to heal. This teaching booklet is designed to introduce you to electrophysiology studies of the heart.
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES OF THE HEART The science of medicine. The compassion to heal. This teaching booklet is designed to introduce you to electrophysiology studies of the heart.
Electroconvulsive Therapy - ECT
 Electroconvulsive Therapy - ECT Introduction Electroconvulsive therapy, or ECT, is a safe and effective treatment that may reduce symptoms related to depression or mental illness. During ECT, certain parts
Electroconvulsive Therapy - ECT Introduction Electroconvulsive therapy, or ECT, is a safe and effective treatment that may reduce symptoms related to depression or mental illness. During ECT, certain parts
Concussion Management Program for Red Bank Catholic High School Athletic Department
 Concussion Management Program for Red Bank Catholic High School Athletic Department *This document should be used as a framework for a successful concussion management program but is not intended to replace
Concussion Management Program for Red Bank Catholic High School Athletic Department *This document should be used as a framework for a successful concussion management program but is not intended to replace
X-Plain Trigeminal Neuralgia Reference Summary
 X-Plain Trigeminal Neuralgia Reference Summary Introduction Trigeminal neuralgia is a condition that affects about 40,000 patients in the US every year. Its treatment mostly involves the usage of oral
X-Plain Trigeminal Neuralgia Reference Summary Introduction Trigeminal neuralgia is a condition that affects about 40,000 patients in the US every year. Its treatment mostly involves the usage of oral
The FacTs: * All concussions are serious. A Fact Sheet for School Nurses
 A Fact Sheet for School Nurses Assess the situation Be alert for signs and symptoms Contact a health care professional The FacTs: * All concussions are serious. * Most concussions occur without loss of
A Fact Sheet for School Nurses Assess the situation Be alert for signs and symptoms Contact a health care professional The FacTs: * All concussions are serious. * Most concussions occur without loss of
Mild head injury: How mild is it?
 Mild head injury: How mild is it? Carly Dutton; Gemma Foster & Stephen Spoors Sunderland and Gateshead Community Acquired Brain Injury Service (CABIS), Northumberland, Tyne and Wear NHS Foundation Trust
Mild head injury: How mild is it? Carly Dutton; Gemma Foster & Stephen Spoors Sunderland and Gateshead Community Acquired Brain Injury Service (CABIS), Northumberland, Tyne and Wear NHS Foundation Trust
COMPREHENSIVE CHILDREN S INJURY CENTER (CCIC) Head Injury Clinic A GUIDE TO CONCUSSIONS & MILD TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURIES
 COMPREHENSIVE CHILDREN S INJURY CENTER (CCIC) Head Injury Clinic A GUIDE TO CONCUSSIONS & MILD TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURIES Concussions and What is a concussion? DIAGNOSIS Traumatic Brain Injuries A concussion
COMPREHENSIVE CHILDREN S INJURY CENTER (CCIC) Head Injury Clinic A GUIDE TO CONCUSSIONS & MILD TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURIES Concussions and What is a concussion? DIAGNOSIS Traumatic Brain Injuries A concussion
Steps to getting a diagnosis: Finding out if it s Alzheimer s Disease.
 Steps to getting a diagnosis: Finding out if it s Alzheimer s Disease. Memory loss and changes in mood and behavior are some signs that you or a family member may have Alzheimer s disease. If you have
Steps to getting a diagnosis: Finding out if it s Alzheimer s Disease. Memory loss and changes in mood and behavior are some signs that you or a family member may have Alzheimer s disease. If you have
http://images.tutorvista.com/content/control5coordination/human5brain.jpeg!! 387
 http://images.tutorvista.com/content/control5coordination/human5brain.jpeg!! 387! 388! http://my.fresnounified.org/personal/lygonza/gonzalez/neuron/neuron5synapse%20communication.png!! http://www.urbanchildinstitute.org/sites/all/files/databooks/2011/ch15fg25communication5between5neurons.jpg!!
http://images.tutorvista.com/content/control5coordination/human5brain.jpeg!! 387! 388! http://my.fresnounified.org/personal/lygonza/gonzalez/neuron/neuron5synapse%20communication.png!! http://www.urbanchildinstitute.org/sites/all/files/databooks/2011/ch15fg25communication5between5neurons.jpg!!
Orthopaedic Spine Center. Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) Normal Discs
 Orthopaedic Spine Center Graham Calvert MD James Woodall MD PhD Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) Normal Discs The cervical spine consists of the bony vertebrae, discs, nerves and other structures.
Orthopaedic Spine Center Graham Calvert MD James Woodall MD PhD Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) Normal Discs The cervical spine consists of the bony vertebrae, discs, nerves and other structures.
Understanding. Spinal Cord Injury. Tasha, injured in 1997.
 Understanding Spinal Cord Injury Tasha, injured in 1997. What Is Spinal Cord Injury? The spinal cord is the part of the central nervous system that contains the body s longest nerve fibers. It serves as
Understanding Spinal Cord Injury Tasha, injured in 1997. What Is Spinal Cord Injury? The spinal cord is the part of the central nervous system that contains the body s longest nerve fibers. It serves as
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH)
 A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
RECOGNISE AND REMOVE
 RECOGNISE AND REMOVE Remember the 4 R s of concussion management: RECOGNISE REMOVE RECOVER RETURN Identifying concussion is not always easy, and players may not exhibit the signs or symptoms immediately
RECOGNISE AND REMOVE Remember the 4 R s of concussion management: RECOGNISE REMOVE RECOVER RETURN Identifying concussion is not always easy, and players may not exhibit the signs or symptoms immediately
.org. Herniated Disk in the Lower Back. Anatomy. Description
 Herniated Disk in the Lower Back Page ( 1 ) Sometimes called a slipped or ruptured disk, a herniated disk most often occurs in your lower back. It is one of the most common causes of low back pain, as
Herniated Disk in the Lower Back Page ( 1 ) Sometimes called a slipped or ruptured disk, a herniated disk most often occurs in your lower back. It is one of the most common causes of low back pain, as
Dizziness and Vertigo
 Dizziness and Vertigo Introduction When you are dizzy, you may feel lightheaded or lose your balance. If you also feel that the room is spinning, you may have vertigo. Vertigo is a type of severe dizziness.
Dizziness and Vertigo Introduction When you are dizzy, you may feel lightheaded or lose your balance. If you also feel that the room is spinning, you may have vertigo. Vertigo is a type of severe dizziness.
Patient Information. Anterior Cervical Surgery. Here to help. Respond Deliver & Enable
 Here to help Our Health Information Centre (HIC) provides advice and information on a wide range of health-related topics. We also offer: Services for people with disabilities. Information in large print,
Here to help Our Health Information Centre (HIC) provides advice and information on a wide range of health-related topics. We also offer: Services for people with disabilities. Information in large print,
Revised 10-4-10 Bethel Park s Sports Concussion and Closed Head Injury Protocol and Procedures for Student-Athletes
 Bethel Park s Sports Concussion and Closed Head Injury Protocol and Procedures for Student-Athletes If the Certified Athletic Trainer of Bethel Park School District has a concern that a student-athlete
Bethel Park s Sports Concussion and Closed Head Injury Protocol and Procedures for Student-Athletes If the Certified Athletic Trainer of Bethel Park School District has a concern that a student-athlete
.org. Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine. Cause. Description
 Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Page ( 1 ) Spinal fractures can vary widely in severity. While some fractures are very serious injuries that require emergency treatment, other fractures can
Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Page ( 1 ) Spinal fractures can vary widely in severity. While some fractures are very serious injuries that require emergency treatment, other fractures can
Total Abdominal Hysterectomy
 What is a total abdominal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through an abdominal incision (either an up and down or bikini cut). Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient.
What is a total abdominal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through an abdominal incision (either an up and down or bikini cut). Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient.
Long Term Tube Feeding. Sunnybrook. A Guide for Patients and Substitute Decision Makers VETERANS & COMMUNITY
 Long Term Tube Feeding A Guide for Patients and Substitute Decision Makers Sunnybrook VETERANS & COMMUNITY Sunnybrook VETERANS & COMMUNITY This brochure has been produced by: Sunnybrook Health Sciences
Long Term Tube Feeding A Guide for Patients and Substitute Decision Makers Sunnybrook VETERANS & COMMUNITY Sunnybrook VETERANS & COMMUNITY This brochure has been produced by: Sunnybrook Health Sciences
CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFT & HEART VALVE SURGERY
 CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFT & HEART VALVE SURGERY www.cpmc.org/learning i learning about your health What to Expect During Your Hospital Stay 1 Our Team: Our cardiac surgery specialty team includes nurses,
CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFT & HEART VALVE SURGERY www.cpmc.org/learning i learning about your health What to Expect During Your Hospital Stay 1 Our Team: Our cardiac surgery specialty team includes nurses,
Total Vaginal Hysterectomy
 What is a total vaginal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through the vagina. Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient. Why is this surgery used? To treat disease of
What is a total vaginal hysterectomy? Is the removal of the uterus and cervix through the vagina. Removal of the ovaries and tubes depends on the patient. Why is this surgery used? To treat disease of
BINSA Information on Mild Traumatic Brain Injury
 Mild traumatic brain injuries (MTBI) occur through sporting, car and workplace accidents. Mild brain injury is not easily diagnosed. This fact sheet explains how it may be recognised and assessed, and
Mild traumatic brain injuries (MTBI) occur through sporting, car and workplace accidents. Mild brain injury is not easily diagnosed. This fact sheet explains how it may be recognised and assessed, and
CONCUSSION AND HEAD INJURY AWARENESS POLICY TRAINING C I T Y O F S O U T H J O R D A N 9 / 2 0 1 1
 CONCUSSION AND HEAD INJURY AWARENESS POLICY TRAINING C I T Y O F S O U T H J O R D A N 9 / 2 0 1 1 UTAH STATE LEGISLATION 2011 General Legislative Session House Bill 204: Enacts the Protection of Athletes
CONCUSSION AND HEAD INJURY AWARENESS POLICY TRAINING C I T Y O F S O U T H J O R D A N 9 / 2 0 1 1 UTAH STATE LEGISLATION 2011 General Legislative Session House Bill 204: Enacts the Protection of Athletes
Injury Law Center HEAD INJURY. Head injuries can be caused by car crashes, sports injuries, falls, workplace injuries and assaults.
 Injury Law Center Note: This information is provided to give you a basic understanding of the injury. It is not intended as medical advice. You should consult a qualified medical provider. Description
Injury Law Center Note: This information is provided to give you a basic understanding of the injury. It is not intended as medical advice. You should consult a qualified medical provider. Description
Advance Health Care Planning: Making Your Wishes Known
 Page 1 of 26 Advance Health Care Planning: Making Your Wishes Known Page 2 of 26 What s Inside Why Health Care Planning Is Important... 2 What You Can Do... 4 Work through the advance health care planning
Page 1 of 26 Advance Health Care Planning: Making Your Wishes Known Page 2 of 26 What s Inside Why Health Care Planning Is Important... 2 What You Can Do... 4 Work through the advance health care planning
Brain Tumor Center. A Team Approach to Treating Brain Tumors
 Brain Tumor Center A Team Approach to Treating Brain Tumors Introducing Our Brain Tumor Center Making an appointment with the Brain Tumor Center at the Center for Advanced Medicine is the important first
Brain Tumor Center A Team Approach to Treating Brain Tumors Introducing Our Brain Tumor Center Making an appointment with the Brain Tumor Center at the Center for Advanced Medicine is the important first
Acute Low Back Pain. North American Spine Society Public Education Series
 Acute Low Back Pain North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Acute Low Back Pain? Acute low back pain (LBP) is defined as low back pain present for up to six weeks. It may be experienced
Acute Low Back Pain North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Acute Low Back Pain? Acute low back pain (LBP) is defined as low back pain present for up to six weeks. It may be experienced
Urinary Diversion: Ileovesicostomy/Ileal Loop/Colon Loop
 Urinary Diversion: Ileovesicostomy/Ileal Loop/Colon Loop Why do I need this surgery? A urinary diversion is a surgical procedure that is performed to allow urine to safely pass from the kidneys into a
Urinary Diversion: Ileovesicostomy/Ileal Loop/Colon Loop Why do I need this surgery? A urinary diversion is a surgical procedure that is performed to allow urine to safely pass from the kidneys into a
X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary
 X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary Introduction A Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter, or subclavian line, is a long thin hollow tube inserted in a vein under the
X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary Introduction A Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter, or subclavian line, is a long thin hollow tube inserted in a vein under the
Traumatic Head Injuries
 Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Traumatic Head Injuries Major contributing cause of trauma deaths Many survivors have permanent disability Commonly occurs in young adults (mostly males) Spokane County EMS
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Traumatic Head Injuries Major contributing cause of trauma deaths Many survivors have permanent disability Commonly occurs in young adults (mostly males) Spokane County EMS
Traumatic brain injury (TBI), caused either by blunt force or acceleration/
 Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Carol A. Waldmann, MD Traumatic brain injury (TBI), caused either by blunt force or acceleration/ deceleration forces, is common in the general population. Homeless persons
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Carol A. Waldmann, MD Traumatic brain injury (TBI), caused either by blunt force or acceleration/ deceleration forces, is common in the general population. Homeless persons
Open Discectomy. North American Spine Society Public Education Series
 Open Discectomy North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Open Discectomy? Open discectomy is the most common surgical treatment for ruptured or herniated discs of the lumbar spine.
Open Discectomy North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Open Discectomy? Open discectomy is the most common surgical treatment for ruptured or herniated discs of the lumbar spine.
Degree of Intervention
 Inglewood Care Centre Degree of Intervention Handbook for Residents and Families Index Introduction..................................................... 2 Beliefs, Values, and Wishes.........................................
Inglewood Care Centre Degree of Intervention Handbook for Residents and Families Index Introduction..................................................... 2 Beliefs, Values, and Wishes.........................................
TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY AND DOMESTIC VIOLENCE
 TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY AND DOMESTIC VIOLENCE Women who are abused often suffer injury to their head, neck, and face. The high potential for women who are abused to have mild to severe Traumatic Brain Injury
TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY AND DOMESTIC VIOLENCE Women who are abused often suffer injury to their head, neck, and face. The high potential for women who are abused to have mild to severe Traumatic Brain Injury
Post-Concussion Syndrome
 Post-Concussion Syndrome Anatomy of the injury: The brain is a soft delicate structure encased in our skull, which protects it from external damage. It is suspended within the skull in a liquid called
Post-Concussion Syndrome Anatomy of the injury: The brain is a soft delicate structure encased in our skull, which protects it from external damage. It is suspended within the skull in a liquid called
Ronald G. Riechers, II, M.D. Medical Director, Polytrauma Team Cleveland VAMC Assistant Professor Department of Neurology Case Western Reserve
 Ronald G. Riechers, II, M.D. Medical Director, Polytrauma Team Cleveland VAMC Assistant Professor Department of Neurology Case Western Reserve University The opinions or assertions contained herein are
Ronald G. Riechers, II, M.D. Medical Director, Polytrauma Team Cleveland VAMC Assistant Professor Department of Neurology Case Western Reserve University The opinions or assertions contained herein are
Epidurals for pain relief after surgery
 Epidurals for pain relief after surgery This information leaflet is for anyone who may benefit from an epidural for pain relief after surgery. We hope it will help you to ask questions and direct you to
Epidurals for pain relief after surgery This information leaflet is for anyone who may benefit from an epidural for pain relief after surgery. We hope it will help you to ask questions and direct you to
X-Plain Inguinal Hernia Repair Reference Summary
 X-Plain Inguinal Hernia Repair Reference Summary Introduction Hernias are common conditions that affect men and women of all ages. Your doctor may recommend a hernia operation. The decision whether or
X-Plain Inguinal Hernia Repair Reference Summary Introduction Hernias are common conditions that affect men and women of all ages. Your doctor may recommend a hernia operation. The decision whether or
Traumatic Brain Injury. Working with persons with traumatic brain injury (TBI) in the community.
 Traumatic Brain Injury Working with persons with traumatic brain injury (TBI) in the community. Fact or Fiction about Brain Injury 1. Traumatic brain injury is caused by a disease. 2. Children are more
Traumatic Brain Injury Working with persons with traumatic brain injury (TBI) in the community. Fact or Fiction about Brain Injury 1. Traumatic brain injury is caused by a disease. 2. Children are more
Bleeding in the brain haemorrhagic stroke
 Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Bleeding in the brain haemorrhagic stroke Most strokes are caused by a blockage in an artery leading to the brain an ischaemic stroke. However, about
Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Bleeding in the brain haemorrhagic stroke Most strokes are caused by a blockage in an artery leading to the brain an ischaemic stroke. However, about
Recto-vaginal Fistula Repair
 What is a recto-vaginal fistula repair? Rectovaginal fistula repair is a procedure in which the healthy tissue between the rectum and vagina is closed in multiple tissue layers. An incision is made either
What is a recto-vaginal fistula repair? Rectovaginal fistula repair is a procedure in which the healthy tissue between the rectum and vagina is closed in multiple tissue layers. An incision is made either
Cycling-related Traumatic Brain Injury 2011
 Cycling-related Traumatic Brain Injury 2011 The Chinese University of Hong Kong Division of Neurosurgery, Department of Surgery Accident & Emergency Medicine Academic Unit Jockey Club School of Public
Cycling-related Traumatic Brain Injury 2011 The Chinese University of Hong Kong Division of Neurosurgery, Department of Surgery Accident & Emergency Medicine Academic Unit Jockey Club School of Public
Recommended time for assessment:
 Recommended time for assessment: Basic Intermediate Advanced FIMTM: (see attachment 1) - Entry to rehab - Discharge rehab - 1 month post injury - 3 months post injury NSI: (see attachment 2) - Entry to
Recommended time for assessment: Basic Intermediate Advanced FIMTM: (see attachment 1) - Entry to rehab - Discharge rehab - 1 month post injury - 3 months post injury NSI: (see attachment 2) - Entry to
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO CARDIAC CATHETERIZATION
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO CARDIAC CATHETERIZATION The science of medicine. The compassion to heal. This teaching booklet is designed to introduce you to cardiac catheterization. In the following pages, we will
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO CARDIAC CATHETERIZATION The science of medicine. The compassion to heal. This teaching booklet is designed to introduce you to cardiac catheterization. In the following pages, we will
Quality Measures for Long-stay Residents Percent of residents whose need for help with daily activities has increased.
 Quality Measures for Long-stay Residents Percent of residents whose need for help with daily activities has increased. This graph shows the percent of residents whose need for help doing basic daily tasks
Quality Measures for Long-stay Residents Percent of residents whose need for help with daily activities has increased. This graph shows the percent of residents whose need for help doing basic daily tasks
Parkinson s Disease (PD)
 Parkinson s Disease (PD) Parkinson s disease (PD) is a movement disorder that worsens over time. About 1 in 100 people older than 60 has Parkinson s. The exact cause of PD is still not known, but research
Parkinson s Disease (PD) Parkinson s disease (PD) is a movement disorder that worsens over time. About 1 in 100 people older than 60 has Parkinson s. The exact cause of PD is still not known, but research
CHAPTER 6 HEAD INJURY AND UNCONSCIOUSNESS
 CHAPTER 6 HEAD INJURY AND UNCONSCIOUSNESS BRAIN INJURY Injury to the brain is one of the more serious outcomes that occur due to injury or illness. The first aider plays a major role in limiting damage
CHAPTER 6 HEAD INJURY AND UNCONSCIOUSNESS BRAIN INJURY Injury to the brain is one of the more serious outcomes that occur due to injury or illness. The first aider plays a major role in limiting damage
The Clinical Evaluation of the Comatose Patient in the Emergency Department
 The Clinical Evaluation of the Comatose Patient in the Emergency Department patients with altered mental status (AMS) and coma. treat patients who present to the Emergency Department with altered mental
The Clinical Evaluation of the Comatose Patient in the Emergency Department patients with altered mental status (AMS) and coma. treat patients who present to the Emergency Department with altered mental
Pain Management after Surgery Patient Information Booklet
 Pain Management after Surgery Patient Information Booklet PATS 509-15-05 Your Health Care Be Involved Be involved in your healthcare. Speak up if you have questions or concerns about your care. Tell a
Pain Management after Surgery Patient Information Booklet PATS 509-15-05 Your Health Care Be Involved Be involved in your healthcare. Speak up if you have questions or concerns about your care. Tell a
X-Plain Preparing For Surgery Reference Summary
 X-Plain Preparing For Surgery Reference Summary Introduction More than 25 million surgical procedures are performed each year in the US. This reference summary will help you prepare for surgery. By understanding
X-Plain Preparing For Surgery Reference Summary Introduction More than 25 million surgical procedures are performed each year in the US. This reference summary will help you prepare for surgery. By understanding
Surgical removal of fibroids through an abdominal incision-either up and down or bikini cut. The uterus and cervix are left in place.
 What is an abdominal myomectomy? Surgical removal of fibroids through an abdominal incision-either up and down or bikini cut. The uterus and cervix are left in place. When is this surgery used? Treatment
What is an abdominal myomectomy? Surgical removal of fibroids through an abdominal incision-either up and down or bikini cut. The uterus and cervix are left in place. When is this surgery used? Treatment
X-Plain Perforated Ear Drum Reference Summary
 X-Plain Perforated Ear Drum Reference Summary Introduction Perforated eardrum is a common condition. The eardrum is a thin layer of tissue at the end of the ear canal inside the ear. Eardrum perforations
X-Plain Perforated Ear Drum Reference Summary Introduction Perforated eardrum is a common condition. The eardrum is a thin layer of tissue at the end of the ear canal inside the ear. Eardrum perforations
