Assumption-free analysis of quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) data
|
|
|
- Christian Hoover
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Neuroscience Letters 339 (2003) Assumption-free analysis of quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) data Christian Ramakers a,b, Jan M. Ruijter a, *, Ronald H. Lekanne Deprez a, Antoon F.M. Moorman a a Department of Anatomy and Embryology K2-283, Experimental and Molecular Cardiology Group, Academic Medical Centre, University of Amsterdam, Meibergdreef 15, 1105 AZ Amsterdam, The Netherlands b Department of Cardiology, University Hospital Maastricht, Cardiovascular Research Institute Maastricht, Maastricht, The Netherlands Received 22 November 2002; received in revised form 4 December 2002; accepted 5 December 2002 Abstract Quantification of mrnas using real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) by monitoring the product formation with the fluorescent dye SYBR Green I is being extensively used in neurosciences, developmental biology, and medical diagnostics. Most PCR data analysis procedures assume that the PCR efficiency for the amplicon of interest is constant or even, in the case of the comparative C t method, equal to 2. The latter method already leads to a 4-fold error when the PCR efficiencies vary over just a 0.04 range. PCR efficiencies of amplicons are usually calculated from standard curves based on either known RNA inputs or on dilution series of a reference cdna sample. In this paper we show that the first approach can lead to PCR efficiencies that vary over a 0.2 range, whereas the second approach may be off by Therefore, we propose linear regression on the Log(fluorescence) per cycle number data as an assumption-free method to calculate starting concentrations of mrnas and PCR efficiencies for each sample. A computer program to perform this calculation is available on request ( bioinfo@amc.uva.nl; subject: LinRegPCR). q 2003 Elsevier Science Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved. Keywords: mrna quantification; Quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR); Real-time PCR; SYBR w green I; PCR efficiency; Linear regression; Standard curve method; Comparative C t method Recent developments in polymerase chain reaction (PCR) combined with new fluorescent techniques have led to the introduction of quantitative or real-time PCR [1,9]. This technique is extensively used in neurosciences, developmental biology and medical diagnostics and is preferred over other quantitative PCR methods because it does not rely on end-point analyzes, which can be misleading due to product inhibition, enzyme instability and a decrease of reaction components in time [2]. Quantification of cdna in real-time PCR in combination with the double stranded DNA specific dye SYBR w Green I is based on the monitoring of the increasing fluorescence intensity after each PCR cycle. This SYBR green I monitoring is available in all quantitative PCR systems. All currently used data analysis methods are based on determining the threshold cycle (C t ), which is the fractional cycle number at which a fixed amount of DNA is formed. All calculations assume * Corresponding author. Tel.: þ ; fax: þ addresses: j.m.ruijter@amc.uva.nl (J.M. Ruijter), c.r. ramakers@amc.uva.nl (C. Ramakers). that the PCR efficiency of the amplicon of interest is constant over time and has the same value in all studied samples. The comparative C t method even assumes this constant efficiency to be equal to 2 for the target and the reference amplicon [6]. With this method, the amount of target amplicon X in sample S, normalized to an endogenous reference R and related to a control sample C is calculated as 2 {(2 C t X,S 2CR,S) t 2(CX,C t 2CR,C )} t, resulting in the fold difference between sample and control. However, it has been reported that PCR efficiencies of target and reference amplicons can vary over a range of [3]. When this variation in PCR efficiency is taken into account, it can easily be calculated that a real 10-fold difference can turn up as any value between 0.7 and 210 (Table 1). Even with a 0.04 range in PCR efficiencies (from 1.78 to 1.82) already a 4-fold error in fold-difference will occur. This shows that the comparative C t method is very sensitive to variations in PCR efficiency. Alternatives, that include separate PCR efficiencies for target and reference amplicons but still assume /03/$ - see front matter q 2003 Elsevier Science Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved. doi: /s (02)
2 C. Ramakers et al. / Neuroscience Letters 339 (2003) Table 1 Illustration of the effect of unequal PCR efficiencies on the result of the comparative C t method a Sample Control Fold difference Amplicon X Reference Amplicon X Reference N ! Input: 10 E C t ! Obs: 212 E C t ! Obs: 12 E C t ! Obs: 0.7 a With this method, the fold difference defined as the amount of target amplicon X in sample S, normalized to an endogenous reference R and related to a control sample C can be calculated as 2 {(2CtX,S 2Ct R,S )2(Ct X,C 2Ct R,C )}. With an input 10-fold difference (N 0 line) and PCR efficiencies ranging from 1.8 to 2.0 (E lines) the fractional number of cycles needed to reach a threshold of 50 (N t ) can be calculated as C t ¼ {Log(N t ) 2 Log(N 0 )}/Log(E). From these threshold cycles the observed (Obs) fold difference can be calculated [6]. constant efficiencies in all samples, have been published [3, 7]. These alternatives rely on standard curves for the estimation of these PCR efficiencies. The standard curve method is usually based on the C t values of either an input series of known RNA concentrations in the reverse transcription or a dilution series of a reference cdna sample [6]. The equation for PCR kinetics (N C ¼ N 0 Eff C ) states that the amount of product after C cycles (N C ) is equal to the starting concentration (N 0 ) times the efficiency (Eff) to the power C. This equation can be converted into the form C t ¼ Log(N C )/Log(Eff) 2 {1/ Log(Eff)} Log(N 0 ) which is a linear relation between C t and Log(N 0 ) when N C is fixed and only when the efficiency is constant. The standard curve is constructed by fitting this equation to the Log(N 0 ) and C t values for a known series of N 0. The PCR efficiency is then calculated from the slope of the standard curve (Eff ¼ 10 21/slope ). However, in most applications of real-time PCR the standard curve-derived PCR efficiencies are not used. The standard curve is only used as a calibration curve to estimate the starting concentrations of unknown samples. We scrutinized the use of standard curves for estimating PCR efficiencies by reviewing the two approaches for creating standard curves: (1) the use of (duplicate) serial dilutions of one of the cdna samples under investigation; and (2) the use of a (duplicate) series of increasing amounts of total RNA as input in the reverse transcription [6]. When the standard curve is based on the serial dilution of a single cdna sample the chance exists that the sample used to generate this standard curve is contaminated with for example salt, phenol, chloroform and/or ethanol resulting in a lower-than-expected PCR efficiency. However, dilution of this sample will also dilute the poison and decrease its effect on the PCR reaction, thereby increasing the PCR efficiency with each dilution step. A computer calculation of this dilution effect (Fig. 1) clearly shows that there is no direct relation between the individual PCR efficiencies (E diluted, ) and the standard-curve-derived PCR efficiency (1.91). In this example the latter efficiency deviates 0.26 from the PCR efficiency of the undiluted reference sample and probably from all other samples prepared in the same way. Only when the individual PCR efficiencies of the standard curve samples are checked, a poisoned standard curve can be unmasked. In the second approach, the standard curve is based on a series of increasing amounts of total RNA as input in the reverse transcription. To this end, six different concentrations of left ventricular total RNA of a mongrel dog were measured in triplicate. This experimental set-up enabled us to do a sub-sampling experiment and to construct two series of 3 6 ( ¼ 729) standard curves: one series based on six single data points per curve and another series based on six duplicate data points per curve. The frequency distributions of all slopes and calculated PCR efficiencies of these two series of standard curves are shown in Fig. 2. The calculated PCR efficiencies for standard curves based on single data points vary between 1.81 and 2.02; the use of duplicates halves this range (Fig. 2). In summary, the comparative C t method and the standard curve rely heavily on the assumption that in all samples the PCR efficiency of each amplicon is constant. To by-pass this assumption in the analysis of quantitative PCR data, the fluorescence measured per cycle of each sample can be used. This alternative approach is based on linearization of the basic formula for exponential PCR amplification by taking the logarithm on both sides of the equation resulting in Log(N C ) ¼ Log(N 0 ) þ Log(Eff) C. The N C and C are measured fluorescence data and cycle number, respectively. The log-linear part of the PCR data can be determined for each sample by selecting a lower and an upper limit of a window-of-linearity (Fig. 3). Linear regression analysis is then used to calculate the intercept and the slope, Log (N 0 )
3 64 C. Ramakers et al. / Neuroscience Letters 339 (2003) Fig. 1. Computer simulation showing the influence of a poison in the cdna sample that is serially diluted to construct a standard curve. Input gives the parameters used in the simulation. E max represents the maximum PCR efficiency and E actual the actual PCR efficiency due to a loss in PCR efficiency (E lost ). A fraction D of this loss is due to a poison that can be diluted, leaving a fraction U that cannot be diluted (U ¼ 1 2 D). Simulation shows the dilutions with the resulting N 0 values. The effect of the dilution on the PCR efficiency can be calculated with: E ¼ E max 2 U E lost 2 (D/dilution) E lost. This calculation is carried out for a situation in which part of the loss is due to a poison that can be diluted (column 3, E diluted ) and for a situation in which the loss in efficiency is due to factors, which cannot be diluted (column 5, E constant ). For both, the fractional number of cycles needed in each sample to reach the crossing line level of 2 (C 2 ¼ {Log(2) 2 Log(N 0 )}/Log(E)) is calculated in columns 4 and 6, respectively. The resulting threshold cycles (C 2 ) are plotted against the Log(N 0 ). Linear regression analysis of the poisoned standard curve (open circles) shows perfect linearity (R 2 ¼ 1). Result shows that the different slopes of the standard curves translate into significantly different calculated PCR efficiencies. Note that ultimate dilution of the poisoned sample would give an E diluted of and Log(Eff), respectively, from the straight line that fits best to the included data points. The starting concentration follows directly from the intercept of this linear regression line (N 0 ¼ 10 intercept ), and is expressed in terms of SYBR Green I fluorescence. The individual PCR efficiency follows from the slope of the linear regression line (Eff ¼ 10 slope ) and can be used as a quality check to exclude possible Fig. 2. Sub-sampling experiment to estimate the variability of the PCR efficiencies calculated from the slope of the standard curve. Six different concentrations of left ventricular total RNA of a mongrel dog (0.065, 0.13, 0.26, 0.65, 1.3, and 2.6 mg/50 ml) were reverse transcribed. In the real-time PCR, 1.3 ml of cdna was used to amplify a 273 bp GAPDH amplicon using dog specific primers [8]. Details regarding reverse transcription and real-time PCR protocols have been previously published [4]. Based on samples in which reverse transcriptase enzyme was omitted during reverse transcription, genomic DNA contamination of the samples was estimated to be less than the quantified cdna levels and was therefore considered to be negligible. All cdnas were quantified in triplicate. The graph shows the frequency distribution of PCR efficiencies that can be calculated from the slopes (Eff ¼ 10 1/slope ) of 729 standard curves constructed from all possible permutations of the six times three RNA inputs (light bars). These PCR efficiencies range from 1.81 to When the three possible duplicate observations per triplicate are used, the range of the distribution is reduced to (dark bars). The correlation coefficient squared (R 2 ) in both sets of calibration curves ranged from 0.98 to 1.00 indicating almost perfect linearity of all curves. contaminated samples. To ensure unambiguous selection of data points within the window-of-linearity, an iterative algorithm is formulated to search for lines consisting of at least 4 and no more than six data points with the highest R 2 value and a slope close to the maximum slope. The above algorithm gives the best correlation between the known input and the observed N 0 value as was tested in a large number of dilution series. Using lines with only three data points gives inconsistent N 0 values whereas longer lines may be biased by inclusion of below-detection-limit and/or plateau phase points. The slope criterion is included in the algorithm to avoid fitting in the plateau phase. Note that this algorithm provides an adequate window-of-linearity for most if not all of the samples. However, visual inspection of all amplification curves remains necessary to identify deviating samples that require an individual window or may have to be excluded. A computer program that implements the linear regression analysis of real-time PCR data and the described algorithm, as well as the possibility to interactively draw a window-of-linearity, is available by automatic request ( bioinfo@amc.uva.nl; subject: LinRegPCR). This program is compatible with exported data
4 C. Ramakers et al. / Neuroscience Letters 339 (2003) our proposed linear regression approach over this non-linear curve fit. The use of the Log(fluorescence) versus cycle number plot in the linear regression approach enables more reliable identification of below-detection-limit noise points and of data points that are no longer in the straight log-linear phase of the PCR reaction, both of which can not easily be identified in a non-logarithmic graph (Fig. 3: fluorescence versus Cycle number graphs). Furthermore, the use of all points in the log-linear phase with linear regression not only gives a more reliable measure for the slope of the regression line and thus for the PCR efficiency, but also provides the correlation coefficient as a measure for the goodness of fit. The main advantage of the linear regression approach is that an estimate of the N 0, the initial number of molecules, can directly be calculated from the intercept parameter of the regression line. In conclusion, the poison simulation as well as the subsampling experiment demonstrates that systematic and random differences in PCR efficiencies of individual samples make the standard curve an unreliable tool for quantification of mrna levels. On the other hand, the linear regression approach enables the straightforward estimation and direct comparison of N 0 values between samples and between target and reference amplicons without the need to assume equal PCR efficiencies. This greatly simplifies the calculation involved in real time PCR analyzes and enables an independent estimation of mrna contents in single samples. This may be of special importance when low quantities have to be reliably measured in small tissue samples as in fields of neuroscience and medical diagnostics. Fig. 3. Illustration of the linear regression calculations implemented in a Microsoft Excel w spreadsheet for determining starting concentrations and PCR efficiencies per sample. The cycle number fluorescence data pairs are imported at starting position A2. Only data of one sample are shown with cycle number and fluorescence in columns A and B, rows 4 till 43. The IF-statements in rows 48 till 87 filter those data points that fall in the socalled window-of-linearity, determined by setting the values in the anchored cells B$45 and B$46. These values can be changed interactively. Once the window-of-linearity is established a regression line is fitted to the included data points. The functions in cells B89, B90 and B91 calculate the R 2, slope and the intercept, respectively. Finally, in cells B93 and B94 the PCR efficiency ( ¼ 10 slope ) and N 0 ( ¼ 10 intercept ) are calculated. A Microsoft Windows w program to perform these calculations is available by automatic request ( bioinfo@amc.uva.nl; subject: LinRegPCR). from the LightCycler e system (Roche) as well as the ABI Prism w systems (Applied Biosystems). It has been proposed recently [5] to determine the PCR efficiency of each sample from the amount of fluorescence (N A and N B ) and the number of cycles (C A and C B ) at two arbitrary thresholds A and B along the exponential phase using the equation: E ¼ (N A /N B ) 1/(C A 2C B ) (note that the symbols are adapted to the ones used in this letter and that a mistake in the exponent of the equation which appears in the original paper is corrected). There are several advantages of Acknowledgements We would like to thank Dr Marc Vos, Department of Cardiology, Academic Hospital Maastricht, and Dr Onno Bakker, Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Academic Medical Center, Amsterdam for their constructive support. This research is partly supported by the Netherlands Heart Foundation, grant NHS (CR) and NHS (RHLD) (AFMM). References [1] U.E.M. Gibson, C.A. Heid, P.M. Williams, A novel method for real time quantitative RT-PCR, Genome Res. 6 (1996) [2] P. Kains, The PCR plateau phase towards an understanding of its limitations, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1494 (2000) [3] W. Kamphuis, A. Schneemann, L.M. Van Beek, A.B. Smit, P.F.J. Hoyng, E. Koya, Prostanoid receptor gene expression profile in human trabecular meshwork: a quantitative real-time PCR approach, Invest. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 42 (2001) [4] R.H. Lekanne Deprez, A.C. Fijnvandraat, J.M. Ruijter, A.F.M. Moorman, Sensitivity and accuracy of quantitative real-time PCR
5 66 C. Ramakers et al. / Neuroscience Letters 339 (2003) using SYBR green I depend on cdna synthesis conditions, Anal. Biochem. 307 (2002) [5] W. Liu, D.A. Saint, A new quantitative method of real time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction assay based on simulation of polymerase chain reaction kinetics, Anal. Biochem. 302 (2002) [6] Livak, K.J., ABI Prism 7700 Sequence Detection System. User bulletin 2, PE Applied Biosystems (2001). [7] J. Meijerink, C. Mandigers, L. van de Locht, E. Goodsaid, J. Raemakers, A novel method to compensate for different amplification efficiencies between patient DNA samples in quantitative real-time PCR, J. Mol. Diagn. 3 (2001) [8] S.C. Verduyn, C. Ramakers, G. Snoep, J.D.M. Leunissen, H.J.J. Wellens, M.A. Vos, Time course of structural adaptations in chronic AV block dogs: evidence for differential ventricular remodeling, Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 280 (2001) H2882 H2890. [9] C.T. Wittwer, K.M. Ririe, R.V. Andrew, D.A. David, R.A. Gundry, U.J. Balis, The LightCyclere: a microvolume multisample fluorimeter with rapid temperature control, Biotechniques 22 (1997)
Gene Expression Assays
 APPLICATION NOTE TaqMan Gene Expression Assays A mpl i fic ationef ficienc yof TaqMan Gene Expression Assays Assays tested extensively for qpcr efficiency Key factors that affect efficiency Efficiency
APPLICATION NOTE TaqMan Gene Expression Assays A mpl i fic ationef ficienc yof TaqMan Gene Expression Assays Assays tested extensively for qpcr efficiency Key factors that affect efficiency Efficiency
Introduction To Real Time Quantitative PCR (qpcr)
 Introduction To Real Time Quantitative PCR (qpcr) SABiosciences, A QIAGEN Company www.sabiosciences.com The Seminar Topics The advantages of qpcr versus conventional PCR Work flow & applications Factors
Introduction To Real Time Quantitative PCR (qpcr) SABiosciences, A QIAGEN Company www.sabiosciences.com The Seminar Topics The advantages of qpcr versus conventional PCR Work flow & applications Factors
Essentials of Real Time PCR. About Sequence Detection Chemistries
 Essentials of Real Time PCR About Real-Time PCR Assays Real-time Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is the ability to monitor the progress of the PCR as it occurs (i.e., in real time). Data is therefore collected
Essentials of Real Time PCR About Real-Time PCR Assays Real-time Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is the ability to monitor the progress of the PCR as it occurs (i.e., in real time). Data is therefore collected
Real-Time PCR Vs. Traditional PCR
 Real-Time PCR Vs. Traditional PCR Description This tutorial will discuss the evolution of traditional PCR methods towards the use of Real-Time chemistry and instrumentation for accurate quantitation. Objectives
Real-Time PCR Vs. Traditional PCR Description This tutorial will discuss the evolution of traditional PCR methods towards the use of Real-Time chemistry and instrumentation for accurate quantitation. Objectives
REAL TIME PCR SYBR GREEN
 REAL TIME PCR SYBR GREEN 1 THE PROBLEM NEED TO QUANTITATE DIFFERENCES IN mrna EXPRESSION SMALL AMOUNTS OF mrna LASER CAPTURE SMALL AMOUNTS OF TISSUE PRIMARY CELLS PRECIOUS REAGENTS 2 THE PROBLEM QUANTITATION
REAL TIME PCR SYBR GREEN 1 THE PROBLEM NEED TO QUANTITATE DIFFERENCES IN mrna EXPRESSION SMALL AMOUNTS OF mrna LASER CAPTURE SMALL AMOUNTS OF TISSUE PRIMARY CELLS PRECIOUS REAGENTS 2 THE PROBLEM QUANTITATION
REAL TIME PCR USING SYBR GREEN
 REAL TIME PCR USING SYBR GREEN 1 THE PROBLEM NEED TO QUANTITATE DIFFERENCES IN mrna EXPRESSION SMALL AMOUNTS OF mrna LASER CAPTURE SMALL AMOUNTS OF TISSUE PRIMARY CELLS PRECIOUS REAGENTS 2 THE PROBLEM
REAL TIME PCR USING SYBR GREEN 1 THE PROBLEM NEED TO QUANTITATE DIFFERENCES IN mrna EXPRESSION SMALL AMOUNTS OF mrna LASER CAPTURE SMALL AMOUNTS OF TISSUE PRIMARY CELLS PRECIOUS REAGENTS 2 THE PROBLEM
Data Analysis on the ABI PRISM 7700 Sequence Detection System: Setting Baselines and Thresholds. Overview. Data Analysis Tutorial
 Data Analysis on the ABI PRISM 7700 Sequence Detection System: Setting Baselines and Thresholds Overview In order for accuracy and precision to be optimal, the assay must be properly evaluated and a few
Data Analysis on the ABI PRISM 7700 Sequence Detection System: Setting Baselines and Thresholds Overview In order for accuracy and precision to be optimal, the assay must be properly evaluated and a few
Real time and Quantitative (RTAQ) PCR. so I have an outlier and I want to see if it really is changed
 Real time and Quantitative (RTAQ) PCR or.. for this audience so I have an outlier and I want to see if it really is changed Nigel Walker, Ph.D. Laboratory of Computational Biology and Risk Analysis, Environmental
Real time and Quantitative (RTAQ) PCR or.. for this audience so I have an outlier and I want to see if it really is changed Nigel Walker, Ph.D. Laboratory of Computational Biology and Risk Analysis, Environmental
Real-time PCR: Understanding C t
 APPLICATION NOTE Real-Time PCR Real-time PCR: Understanding C t Real-time PCR, also called quantitative PCR or qpcr, can provide a simple and elegant method for determining the amount of a target sequence
APPLICATION NOTE Real-Time PCR Real-time PCR: Understanding C t Real-time PCR, also called quantitative PCR or qpcr, can provide a simple and elegant method for determining the amount of a target sequence
2.500 Threshold. 2.000 1000e - 001. Threshold. Exponential phase. Cycle Number
 application note Real-Time PCR: Understanding C T Real-Time PCR: Understanding C T 4.500 3.500 1000e + 001 4.000 3.000 1000e + 000 3.500 2.500 Threshold 3.000 2.000 1000e - 001 Rn 2500 Rn 1500 Rn 2000
application note Real-Time PCR: Understanding C T Real-Time PCR: Understanding C T 4.500 3.500 1000e + 001 4.000 3.000 1000e + 000 3.500 2.500 Threshold 3.000 2.000 1000e - 001 Rn 2500 Rn 1500 Rn 2000
QPCR Applications using Stratagene s Mx Real-Time PCR Platform
 QPCR Applications using Stratagene s Mx Real-Time PCR Platform Dan Schoeffner, Ph.D Field Applications Scientist Dan.Schoeffner@Stratagene.com Tech. Services 800-894-1304 Polymerase Chain Reaction Melt
QPCR Applications using Stratagene s Mx Real-Time PCR Platform Dan Schoeffner, Ph.D Field Applications Scientist Dan.Schoeffner@Stratagene.com Tech. Services 800-894-1304 Polymerase Chain Reaction Melt
Factors Influencing Multiplex Real-Time PCR
 APPLICATION NOTE Multiplex Real-Time PCR Factors Influencing Multiplex Real-Time PCR Introduction Multiplex PCR is the simultaneous amplification of more than one target sequence in a single reaction [1].
APPLICATION NOTE Multiplex Real-Time PCR Factors Influencing Multiplex Real-Time PCR Introduction Multiplex PCR is the simultaneous amplification of more than one target sequence in a single reaction [1].
Thermo Scientific DyNAmo cdna Synthesis Kit for qrt-pcr Technical Manual
 Thermo Scientific DyNAmo cdna Synthesis Kit for qrt-pcr Technical Manual F- 470S 20 cdna synthesis reactions (20 µl each) F- 470L 100 cdna synthesis reactions (20 µl each) Table of contents 1. Description...
Thermo Scientific DyNAmo cdna Synthesis Kit for qrt-pcr Technical Manual F- 470S 20 cdna synthesis reactions (20 µl each) F- 470L 100 cdna synthesis reactions (20 µl each) Table of contents 1. Description...
SYBR Green Realtime PCR Master Mix -Plus-
 Instruction manual SYBR Green Realtime PCR Master Mix -Plus- 0810 F0925K SYBR Green Realtime PCR Master Mix -Plus- Contents QPK-212T 1mLx1 QPK-212 1mLx5 Store at -20 C, protected from light [1] Introduction
Instruction manual SYBR Green Realtime PCR Master Mix -Plus- 0810 F0925K SYBR Green Realtime PCR Master Mix -Plus- Contents QPK-212T 1mLx1 QPK-212 1mLx5 Store at -20 C, protected from light [1] Introduction
Validating Microarray Data Using RT 2 Real-Time PCR Products
 Validating Microarray Data Using RT 2 Real-Time PCR Products Introduction: Real-time PCR monitors the amount of amplicon as the reaction occurs. Usually, the amount of product is directly related to the
Validating Microarray Data Using RT 2 Real-Time PCR Products Introduction: Real-time PCR monitors the amount of amplicon as the reaction occurs. Usually, the amount of product is directly related to the
User Bulletin #2 ABI PRISM 7700 Sequence Detection System
 User Bulletin #2 ABI PRISM 7700 Sequence Detection System December 11, 1997 (updated 10/2001) SUBJECT: Relative Quantitation of Gene Expression Introduction Amplification of an endogenous control may be
User Bulletin #2 ABI PRISM 7700 Sequence Detection System December 11, 1997 (updated 10/2001) SUBJECT: Relative Quantitation of Gene Expression Introduction Amplification of an endogenous control may be
qstar mirna qpcr Detection System
 qstar mirna qpcr Detection System Table of Contents Table of Contents...1 Package Contents and Storage Conditions...2 For mirna cdna synthesis kit...2 For qstar mirna primer pairs...2 For qstar mirna qpcr
qstar mirna qpcr Detection System Table of Contents Table of Contents...1 Package Contents and Storage Conditions...2 For mirna cdna synthesis kit...2 For qstar mirna primer pairs...2 For qstar mirna qpcr
Quantifiler Human DNA Quantification Kit Quantifiler Y Human Male DNA Quantification Kit
 Product Bulletin Human Identification Quantifiler Human DNA Quantification Kit Quantifiler Y Human Male DNA Quantification Kit The Quantifiler kits produce reliable and reproducible results, helping to
Product Bulletin Human Identification Quantifiler Human DNA Quantification Kit Quantifiler Y Human Male DNA Quantification Kit The Quantifiler kits produce reliable and reproducible results, helping to
DNA Integrity Number (DIN) For the Assessment of Genomic DNA Samples in Real-Time Quantitative PCR (qpcr) Experiments
 DNA Integrity Number () For the Assessment of Genomic DNA Samples in Real-Time Quantitative PCR (qpcr) Experiments Application Note Nucleic Acid Analysis Author Arunkumar Padmanaban Agilent Technologies,
DNA Integrity Number () For the Assessment of Genomic DNA Samples in Real-Time Quantitative PCR (qpcr) Experiments Application Note Nucleic Acid Analysis Author Arunkumar Padmanaban Agilent Technologies,
Fluorescent dyes for use with the
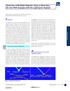 Detection of Multiple Reporter Dyes in Real-time, On-line PCR Analysis with the LightCycler System Gregor Sagner, Cornelia Goldstein, and Rob van Miltenburg Roche Molecular Biochemicals, Penzberg, Germany
Detection of Multiple Reporter Dyes in Real-time, On-line PCR Analysis with the LightCycler System Gregor Sagner, Cornelia Goldstein, and Rob van Miltenburg Roche Molecular Biochemicals, Penzberg, Germany
Quantitative Real Time PCR Protocol. Stack Lab
 Quantitative Real Time PCR Protocol Stack Lab Overview Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qpcr) differs from regular PCR by including in the reaction fluorescent reporter molecules that
Quantitative Real Time PCR Protocol Stack Lab Overview Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qpcr) differs from regular PCR by including in the reaction fluorescent reporter molecules that
MystiCq microrna cdna Synthesis Mix Catalog Number MIRRT Storage Temperature 20 C
 microrna cdna Synthesis Mix Catalog Number MIRRT Storage Temperature 20 C Product Description The microrna cdna Synthesis Mix has been designed to easily convert micrornas into cdna templates for qpcr
microrna cdna Synthesis Mix Catalog Number MIRRT Storage Temperature 20 C Product Description The microrna cdna Synthesis Mix has been designed to easily convert micrornas into cdna templates for qpcr
Technical Note. Roche Applied Science. No. LC 18/2004. Assay Formats for Use in Real-Time PCR
 Roche Applied Science Technical Note No. LC 18/2004 Purpose of this Note Assay Formats for Use in Real-Time PCR The LightCycler Instrument uses several detection channels to monitor the amplification of
Roche Applied Science Technical Note No. LC 18/2004 Purpose of this Note Assay Formats for Use in Real-Time PCR The LightCycler Instrument uses several detection channels to monitor the amplification of
Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real- Time Quantitative PCR and the 2 C T Method
 METHODS 25, 402 408 (2001) doi:10.1006/meth.2001.1262, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real- Time Quantitative PCR and the 2 C T Method
METHODS 25, 402 408 (2001) doi:10.1006/meth.2001.1262, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real- Time Quantitative PCR and the 2 C T Method
RT 2 Profiler PCR Array: Web-Based Data Analysis Tutorial
 RT 2 Profiler PCR Array: Web-Based Data Analysis Tutorial Samuel J. Rulli, Jr., Ph.D. qpcr-applications Scientist Samuel.Rulli@QIAGEN.com Pathway Focused Research from Sample Prep to Data Analysis! -2-
RT 2 Profiler PCR Array: Web-Based Data Analysis Tutorial Samuel J. Rulli, Jr., Ph.D. qpcr-applications Scientist Samuel.Rulli@QIAGEN.com Pathway Focused Research from Sample Prep to Data Analysis! -2-
Mir-X mirna First-Strand Synthesis Kit User Manual
 User Manual Mir-X mirna First-Strand Synthesis Kit User Manual United States/Canada 800.662.2566 Asia Pacific +1.650.919.7300 Europe +33.(0)1.3904.6880 Japan +81.(0)77.543.6116 Clontech Laboratories, Inc.
User Manual Mir-X mirna First-Strand Synthesis Kit User Manual United States/Canada 800.662.2566 Asia Pacific +1.650.919.7300 Europe +33.(0)1.3904.6880 Japan +81.(0)77.543.6116 Clontech Laboratories, Inc.
PATHOGEN DETECTION SYSTEMS BY REAL TIME PCR. Results Interpretation Guide
 PATHOGEN DETECTION SYSTEMS BY REAL TIME PCR Results Interpretation Guide Pathogen Detection Systems by Real Time PCR Microbial offers real time PCR based systems for the detection of pathogenic bacteria
PATHOGEN DETECTION SYSTEMS BY REAL TIME PCR Results Interpretation Guide Pathogen Detection Systems by Real Time PCR Microbial offers real time PCR based systems for the detection of pathogenic bacteria
Real-time quantitative RT -PCR (Taqman)
 Real-time quantitative RT -PCR (Taqman) Author: SC, Patti Lab, 3/03 This is performed as a 2-step reaction: 1. cdna synthesis from DNase 1-treated total RNA 2. PCR 1. cdna synthesis (Advantage RT-for-PCR
Real-time quantitative RT -PCR (Taqman) Author: SC, Patti Lab, 3/03 This is performed as a 2-step reaction: 1. cdna synthesis from DNase 1-treated total RNA 2. PCR 1. cdna synthesis (Advantage RT-for-PCR
PrimePCR Assay Validation Report
 Gene Information Gene Name Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID papillary renal cell carcinoma (translocation-associated) PRCC Human This gene
Gene Information Gene Name Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID papillary renal cell carcinoma (translocation-associated) PRCC Human This gene
CABIOS. Q-RT-PCR: data analysis software for measurement of gene expression by competitive RT-PCR
 CABIOS Vol. 73 no. 6 1997 Pages 587-591 Q-RT-PCR: data analysis software for measurement of gene expression by competitive RT-PCR Peter A. Doris 2, Amanda Hayward-Lester and Jon K. Hays Sr 1 Department
CABIOS Vol. 73 no. 6 1997 Pages 587-591 Q-RT-PCR: data analysis software for measurement of gene expression by competitive RT-PCR Peter A. Doris 2, Amanda Hayward-Lester and Jon K. Hays Sr 1 Department
DyNAmo cdna Synthesis Kit for qrt-pcr
 DyNAmo cdna Synthesis Kit for qrt-pcr Instruction manual F- 470S Sufficient for 20 cdna synthesis reactions (20 µl each) F- 470L Sufficient for 100 cdna synthesis reactions (20 µl each) Description...
DyNAmo cdna Synthesis Kit for qrt-pcr Instruction manual F- 470S Sufficient for 20 cdna synthesis reactions (20 µl each) F- 470L Sufficient for 100 cdna synthesis reactions (20 µl each) Description...
Mir-X mirna First-Strand Synthesis and SYBR qrt-pcr
 User Manual Mir-X mirna First-Strand Synthesis and SYBR qrt-pcr User Manual United States/Canada 800.662.2566 Asia Pacific +1.650.919.7300 Europe +33.(0)1.3904.6880 Japan +81.(0)77.543.6116 Clontech Laboratories,
User Manual Mir-X mirna First-Strand Synthesis and SYBR qrt-pcr User Manual United States/Canada 800.662.2566 Asia Pacific +1.650.919.7300 Europe +33.(0)1.3904.6880 Japan +81.(0)77.543.6116 Clontech Laboratories,
User Manual/Hand book. qpcr mirna Arrays ABM catalog # MA003 (human) and MA004 (mouse)
 User Manual/Hand book qpcr mirna Arrays ABM catalog # MA003 (human) and MA004 (mouse) Kit Components Cat. No. MA003...Human Whole Genome mirna qpcr Profiling Kit (-20 C) The following components are sufficient
User Manual/Hand book qpcr mirna Arrays ABM catalog # MA003 (human) and MA004 (mouse) Kit Components Cat. No. MA003...Human Whole Genome mirna qpcr Profiling Kit (-20 C) The following components are sufficient
Quando si parla di PCR quantitativa si intende:
 Quando si parla di PCR quantitativa si intende: A. Una PCR che produce grandi quantità di DNA B. Una PCR che emette quanti di luce C. Una PCR che quantifica il numero di molecole stampo presenti all inizio
Quando si parla di PCR quantitativa si intende: A. Una PCR che produce grandi quantità di DNA B. Una PCR che emette quanti di luce C. Una PCR che quantifica il numero di molecole stampo presenti all inizio
Highly specific and sensitive quantitation
 PRODUCT ULLETIN SYR Select Master Mix SYR Select Master Mix Highly specific and sensitive quantitation SYR Select Master Mix offers advanced performance at an affordable price. SYR Select Master Mix is
PRODUCT ULLETIN SYR Select Master Mix SYR Select Master Mix Highly specific and sensitive quantitation SYR Select Master Mix offers advanced performance at an affordable price. SYR Select Master Mix is
quantitative real-time PCR, grain, simplex DNA extraction: PGS0426 RT-PCR: PGS0494 & PGS0476
 BioScience quantitative real-time PCR, grain, simplex DNA extraction: PGS0426 RT-PCR: PGS0494 & PGS0476 This method describes a Real-time semi-quantitative TaqMan PCR procedure for the determination of
BioScience quantitative real-time PCR, grain, simplex DNA extraction: PGS0426 RT-PCR: PGS0494 & PGS0476 This method describes a Real-time semi-quantitative TaqMan PCR procedure for the determination of
PrimePCR Assay Validation Report
 Gene Information Gene Name sorbin and SH3 domain containing 2 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID SORBS2 Human Arg and c-abl represent the mammalian
Gene Information Gene Name sorbin and SH3 domain containing 2 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID SORBS2 Human Arg and c-abl represent the mammalian
Protocol. Introduction to TaqMan and SYBR Green Chemistries for Real-Time PCR
 Protocol Introduction to TaqMan and SYBR Green Chemistries for Real-Time PCR Copyright 2008, 2010 Applied Biosystems. All rights reserved. Ambion and Applied Biosystems products are for Research Use Only.
Protocol Introduction to TaqMan and SYBR Green Chemistries for Real-Time PCR Copyright 2008, 2010 Applied Biosystems. All rights reserved. Ambion and Applied Biosystems products are for Research Use Only.
CompleteⅡ 1st strand cdna Synthesis Kit
 Instruction Manual CompleteⅡ 1st strand cdna Synthesis Kit Catalog # GM30401, GM30402 Green Mountain Biosystems. LLC Web: www.greenmountainbio.com Tel: 800-942-1160 Sales: Sales@ greenmountainbio.com Support:
Instruction Manual CompleteⅡ 1st strand cdna Synthesis Kit Catalog # GM30401, GM30402 Green Mountain Biosystems. LLC Web: www.greenmountainbio.com Tel: 800-942-1160 Sales: Sales@ greenmountainbio.com Support:
HiPer RT-PCR Teaching Kit
 HiPer RT-PCR Teaching Kit Product Code: HTBM024 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5 Duration of Experiment: Protocol: 4 hours Agarose Gel Electrophoresis: 45 minutes Storage Instructions: The
HiPer RT-PCR Teaching Kit Product Code: HTBM024 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5 Duration of Experiment: Protocol: 4 hours Agarose Gel Electrophoresis: 45 minutes Storage Instructions: The
Stratagene QPCR Mouse Reference Total RNA
 Stratagene QPCR Mouse Reference Total RNA Instruction Manual Catalog #750600 Revision C.0 For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. 750600-12 LIMITED PRODUCT WARRANTY This warranty limits
Stratagene QPCR Mouse Reference Total RNA Instruction Manual Catalog #750600 Revision C.0 For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. 750600-12 LIMITED PRODUCT WARRANTY This warranty limits
Co Extra (GM and non GM supply chains: Their CO EXistence and TRAceability) Outcomes of Co Extra
 GM and non GM supply chains: Their CO EXistence and TRAceability Outcomes of Co Extra Comparison of different real time PCR chemistries and their suitability for detection and quantification of genetically
GM and non GM supply chains: Their CO EXistence and TRAceability Outcomes of Co Extra Comparison of different real time PCR chemistries and their suitability for detection and quantification of genetically
Guide to using the Bio Rad CFX96 Real Time PCR Machine
 Guide to using the Bio Rad CFX96 Real Time PCR Machine Kyle Dobbs and Peter Hansen Table of Contents Overview..3 Setup Reaction Guidelines 4 Starting up the Software 5 Setup Protocol on Software 6 Setup
Guide to using the Bio Rad CFX96 Real Time PCR Machine Kyle Dobbs and Peter Hansen Table of Contents Overview..3 Setup Reaction Guidelines 4 Starting up the Software 5 Setup Protocol on Software 6 Setup
mircute mirna qpcr Detection Kit (SYBR Green)
 mircute mirna qpcr Detection Kit (SYBR Green) For detection of mirna using real-time RT-PCR (SYBR Green I) www.tiangen.com QP110302 mircute mirna qpcr Detection Kit (SYBR Green) Kit Contents Cat. no. FP401
mircute mirna qpcr Detection Kit (SYBR Green) For detection of mirna using real-time RT-PCR (SYBR Green I) www.tiangen.com QP110302 mircute mirna qpcr Detection Kit (SYBR Green) Kit Contents Cat. no. FP401
ab185916 Hi-Fi cdna Synthesis Kit
 ab185916 Hi-Fi cdna Synthesis Kit Instructions for Use For cdna synthesis from various RNA samples This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Version 1 Last Updated 1
ab185916 Hi-Fi cdna Synthesis Kit Instructions for Use For cdna synthesis from various RNA samples This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Version 1 Last Updated 1
Generating ABI PRISM 7700 Standard Curve Plots in a Spreadsheet Program
 Generating ABI PRISM 7700 Standard Curve Plots in a Spreadsheet Program Overview The goal of this tutorial is to demonstrate the procedure through which analyzed data generated within an ABI PRISM 7700
Generating ABI PRISM 7700 Standard Curve Plots in a Spreadsheet Program Overview The goal of this tutorial is to demonstrate the procedure through which analyzed data generated within an ABI PRISM 7700
ONLINE SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL. Allele-Specific Expression of Angiotensinogen in Human Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue
 ONLINE SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Allele-Specific Expression of Angiotensinogen in Human Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue Sungmi Park 1, Ko-Ting Lu 1, Xuebo Liu 1, Tapan K. Chatterjee 2, Steven M. Rudich 3, Neal
ONLINE SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Allele-Specific Expression of Angiotensinogen in Human Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue Sungmi Park 1, Ko-Ting Lu 1, Xuebo Liu 1, Tapan K. Chatterjee 2, Steven M. Rudich 3, Neal
Calculating Nucleic Acid or Protein Concentration Using the GloMax Multi+ Microplate Instrument
 Calculating Nucleic Acid or Protein Concentration Using the GloMax Multi+ Microplate Instrument Technical Note INTRODUCTION Direct measurements of nucleic acid samples at OD 260 or protein samples at OD
Calculating Nucleic Acid or Protein Concentration Using the GloMax Multi+ Microplate Instrument Technical Note INTRODUCTION Direct measurements of nucleic acid samples at OD 260 or protein samples at OD
User Manual. CelluLyser Lysis and cdna Synthesis Kit. Version 1.4 Oct 2012 From cells to cdna in one tube
 User Manual CelluLyser Lysis and cdna Synthesis Kit Version 1.4 Oct 2012 From cells to cdna in one tube CelluLyser Lysis and cdna Synthesis Kit Table of contents Introduction 4 Contents 5 Storage 5 Additionally
User Manual CelluLyser Lysis and cdna Synthesis Kit Version 1.4 Oct 2012 From cells to cdna in one tube CelluLyser Lysis and cdna Synthesis Kit Table of contents Introduction 4 Contents 5 Storage 5 Additionally
RealStar HBV PCR Kit 1.0 11/2012
 RealStar HBV PCR Kit 1.0 11/2012 RealStar HBV PCR Kit 1.0 For research use only! (RUO) Product No.: 201003 96 rxns INS-201000-GB-02 Store at -25 C... -15 C November 2012 altona Diagnostics GmbH Mörkenstraße
RealStar HBV PCR Kit 1.0 11/2012 RealStar HBV PCR Kit 1.0 For research use only! (RUO) Product No.: 201003 96 rxns INS-201000-GB-02 Store at -25 C... -15 C November 2012 altona Diagnostics GmbH Mörkenstraße
Creating Standard Curves with Genomic DNA or Plasmid DNA Templates for Use in Quantitative PCR
 Creating Standard Curves with Genomic DNA or Plasmid DNA Templates for Use in Quantitative PCR Overview Genomic DNA (gdna) and plasmids containing cloned target sequences are commonly used as standards
Creating Standard Curves with Genomic DNA or Plasmid DNA Templates for Use in Quantitative PCR Overview Genomic DNA (gdna) and plasmids containing cloned target sequences are commonly used as standards
First Strand cdna Synthesis
 380PR 01 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name First Strand cdna Synthesis (Cat. # 786 812) think proteins! think G-Biosciences
380PR 01 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name First Strand cdna Synthesis (Cat. # 786 812) think proteins! think G-Biosciences
TITRATION OF raav (VG) USING QUANTITATIVE REAL TIME PCR
 Page 1 of 5 Materials DNase digestion buffer [13 mm Tris-Cl, ph7,5 / 5 mm MgCl2 / 0,12 mm CaCl2] RSS plasmid ptr-uf11 SV40pA Forward primer (10µM) AGC AAT AGC ATC ACA AAT TTC ACA A SV40pA Reverse Primer
Page 1 of 5 Materials DNase digestion buffer [13 mm Tris-Cl, ph7,5 / 5 mm MgCl2 / 0,12 mm CaCl2] RSS plasmid ptr-uf11 SV40pA Forward primer (10µM) AGC AAT AGC ATC ACA AAT TTC ACA A SV40pA Reverse Primer
Table of Contents. I. Description... 2. II. Kit Components... 2. III. Storage... 2. IV. 1st Strand cdna Synthesis Reaction... 3
 Table of Contents I. Description... 2 II. Kit Components... 2 III. Storage... 2 IV. 1st Strand cdna Synthesis Reaction... 3 V. RT-PCR, Real-time RT-PCR... 4 VI. Application... 5 VII. Preparation of RNA
Table of Contents I. Description... 2 II. Kit Components... 2 III. Storage... 2 IV. 1st Strand cdna Synthesis Reaction... 3 V. RT-PCR, Real-time RT-PCR... 4 VI. Application... 5 VII. Preparation of RNA
bitter is de pil Linos Vandekerckhove, MD, PhD
 4//24 Current HIV care HIV copies/ ml plasma Viral load Welcome to the Digital droplet PCR age! bitter is de pil Linos Vandekerckhove, MD, PhD Latent HIV reservoir Time at Ghent University Hospital 2 HIV
4//24 Current HIV care HIV copies/ ml plasma Viral load Welcome to the Digital droplet PCR age! bitter is de pil Linos Vandekerckhove, MD, PhD Latent HIV reservoir Time at Ghent University Hospital 2 HIV
RevertAid Premium First Strand cdna Synthesis Kit
 RevertAid Premium First Strand cdna Synthesis Kit #K1651, #K1652 CERTIFICATE OF ANALYSIS #K1651 Lot QUALITY CONTROL RT-PCR using 100 fg of control GAPDH RNA and GAPDH control primers generated a prominent
RevertAid Premium First Strand cdna Synthesis Kit #K1651, #K1652 CERTIFICATE OF ANALYSIS #K1651 Lot QUALITY CONTROL RT-PCR using 100 fg of control GAPDH RNA and GAPDH control primers generated a prominent
QUANTITATIVE RT-PCR. A = B (1+e) n. A=amplified products, B=input templates, n=cycle number, and e=amplification efficiency.
 QUANTITATIVE RT-PCR Application: Quantitative RT-PCR is used to quantify mrna in both relative and absolute terms. It can be applied for the quantification of mrna expressed from endogenous genes, and
QUANTITATIVE RT-PCR Application: Quantitative RT-PCR is used to quantify mrna in both relative and absolute terms. It can be applied for the quantification of mrna expressed from endogenous genes, and
BacReady TM Multiplex PCR System
 BacReady TM Multiplex PCR System Technical Manual No. 0191 Version 10112010 I Description.. 1 II Applications 2 III Key Features.. 2 IV Shipping and Storage. 2 V Simplified Procedures. 2 VI Detailed Experimental
BacReady TM Multiplex PCR System Technical Manual No. 0191 Version 10112010 I Description.. 1 II Applications 2 III Key Features.. 2 IV Shipping and Storage. 2 V Simplified Procedures. 2 VI Detailed Experimental
AP Physics 1 and 2 Lab Investigations
 AP Physics 1 and 2 Lab Investigations Student Guide to Data Analysis New York, NY. College Board, Advanced Placement, Advanced Placement Program, AP, AP Central, and the acorn logo are registered trademarks
AP Physics 1 and 2 Lab Investigations Student Guide to Data Analysis New York, NY. College Board, Advanced Placement, Advanced Placement Program, AP, AP Central, and the acorn logo are registered trademarks
Using Excel (Microsoft Office 2007 Version) for Graphical Analysis of Data
 Using Excel (Microsoft Office 2007 Version) for Graphical Analysis of Data Introduction In several upcoming labs, a primary goal will be to determine the mathematical relationship between two variable
Using Excel (Microsoft Office 2007 Version) for Graphical Analysis of Data Introduction In several upcoming labs, a primary goal will be to determine the mathematical relationship between two variable
Sequencing Library qpcr Quantification Guide
 Sequencing Library qpcr Quantification Guide FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Introduction 3 Quantification Workflow 4 Best Practices 5 Consumables and Equipment 6 Select Control Template 8 Dilute qpcr Control Template
Sequencing Library qpcr Quantification Guide FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Introduction 3 Quantification Workflow 4 Best Practices 5 Consumables and Equipment 6 Select Control Template 8 Dilute qpcr Control Template
Recombinant DNA & Genetic Engineering. Tools for Genetic Manipulation
 Recombinant DNA & Genetic Engineering g Genetic Manipulation: Tools Kathleen Hill Associate Professor Department of Biology The University of Western Ontario Tools for Genetic Manipulation DNA, RNA, cdna
Recombinant DNA & Genetic Engineering g Genetic Manipulation: Tools Kathleen Hill Associate Professor Department of Biology The University of Western Ontario Tools for Genetic Manipulation DNA, RNA, cdna
Plexor Systems Instrument Setup and Data Analysis for the Applied Biosystems 7300 and 7500 Real-Time PCR Systems
 Technical Manual Plexor Systems Instrument Setup and Data Analysis for the Applied Biosystems 7300 and 7500 Real-Time PCR Systems INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE OF PRODUCTS A4011, A4021, A4031, A4041, A4051 AND
Technical Manual Plexor Systems Instrument Setup and Data Analysis for the Applied Biosystems 7300 and 7500 Real-Time PCR Systems INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE OF PRODUCTS A4011, A4021, A4031, A4041, A4051 AND
Review of Chemical Equilibrium 7.51 September 1999. free [A] (µm)
![Review of Chemical Equilibrium 7.51 September 1999. free [A] (µm) Review of Chemical Equilibrium 7.51 September 1999. free [A] (µm)](/thumbs/40/21435474.jpg) Review of Chemical Equilibrium 7.51 September 1999 Equilibrium experiments study how the concentration of reaction products change as a function of reactant concentrations and/or reaction conditions. For
Review of Chemical Equilibrium 7.51 September 1999 Equilibrium experiments study how the concentration of reaction products change as a function of reactant concentrations and/or reaction conditions. For
Application Note. Biotechnology Explorer Crime Scene Investigator PCR Basics. Kit: A Real-Time PCR Extension
 Biotechnology Explorer Crime Scene Investigator PCR Basics Kit: Table of Contents Introduction.............................................. 2 Learning Objectives......................................
Biotechnology Explorer Crime Scene Investigator PCR Basics Kit: Table of Contents Introduction.............................................. 2 Learning Objectives......................................
Beginner s Guide to Real-Time PCR
 Beginner s Guide to Real-Time PCR 02 Real-time PCR basic principles PCR or the Polymerase Chain Reaction has become the cornerstone of modern molecular biology the world over. Real-time PCR is an advanced
Beginner s Guide to Real-Time PCR 02 Real-time PCR basic principles PCR or the Polymerase Chain Reaction has become the cornerstone of modern molecular biology the world over. Real-time PCR is an advanced
PreciseTM Whitepaper
 Precise TM Whitepaper Introduction LIMITATIONS OF EXISTING RNA-SEQ METHODS Correctly designed gene expression studies require large numbers of samples, accurate results and low analysis costs. Analysis
Precise TM Whitepaper Introduction LIMITATIONS OF EXISTING RNA-SEQ METHODS Correctly designed gene expression studies require large numbers of samples, accurate results and low analysis costs. Analysis
Reconstituting and Diluting Primers and TaqMan Probes
 Reconstituting and Diluting Primers and TaqMan Probes Introduction TaqMan primers are commonly shipped in a lyophilized state. TaqMan probes are sometimes shipped in the lyophilized state, but more often
Reconstituting and Diluting Primers and TaqMan Probes Introduction TaqMan primers are commonly shipped in a lyophilized state. TaqMan probes are sometimes shipped in the lyophilized state, but more often
Relative Quantification of mirna Target mrnas by Real-Time qpcr. 1 Introduction. Gene Expression Application Note No. 4
 Gene Expression Application Note No. 4 Relative Quantification of mirna Target mrnas by Real-Time qpcr Ute Ernst, Jitao David Zhang, Anja Irsigler, Stefan Wiemann, Ulrich Tschulena Division: Molecular
Gene Expression Application Note No. 4 Relative Quantification of mirna Target mrnas by Real-Time qpcr Ute Ernst, Jitao David Zhang, Anja Irsigler, Stefan Wiemann, Ulrich Tschulena Division: Molecular
Absolute Quantifi cation of Gene Expression using SYBR Green in the Eco Real-Time PCR System
 Absolute Quantifi cation of Gene Expression using SYBR Green in the Eco System Introduction Gene expression is the process by which genetic information is converted into a functional product. This process
Absolute Quantifi cation of Gene Expression using SYBR Green in the Eco System Introduction Gene expression is the process by which genetic information is converted into a functional product. This process
GenScript BloodReady TM Multiplex PCR System
 GenScript BloodReady TM Multiplex PCR System Technical Manual No. 0174 Version 20040915 I Description.. 1 II Applications 2 III Key Features.. 2 IV Shipping and Storage. 2 V Simplified Procedures. 2 VI
GenScript BloodReady TM Multiplex PCR System Technical Manual No. 0174 Version 20040915 I Description.. 1 II Applications 2 III Key Features.. 2 IV Shipping and Storage. 2 V Simplified Procedures. 2 VI
Absolute Quantification Getting Started Guide
 5 cdna Reverse Primer Oligo d(t) or random hexamer Synthesis of 1st cdna strand 3 5 cdna Applied Biosystems 7300/7500/7500 Fast Real-Time PCR System Absolute Quantification Getting Started Guide Introduction
5 cdna Reverse Primer Oligo d(t) or random hexamer Synthesis of 1st cdna strand 3 5 cdna Applied Biosystems 7300/7500/7500 Fast Real-Time PCR System Absolute Quantification Getting Started Guide Introduction
Speed Matters - Fast ways from template to result
 qpcr Symposium 2007 - Weihenstephan Speed Matters - Fast ways from template to result March 28, 2007 Dr. Thorsten Traeger Senior Scientist, Research and Development - 1 - Overview Ạgenda Fast PCR The Challenges
qpcr Symposium 2007 - Weihenstephan Speed Matters - Fast ways from template to result March 28, 2007 Dr. Thorsten Traeger Senior Scientist, Research and Development - 1 - Overview Ạgenda Fast PCR The Challenges
DNA Sequence Analysis
 DNA Sequence Analysis Two general kinds of analysis Screen for one of a set of known sequences Determine the sequence even if it is novel Screening for a known sequence usually involves an oligonucleotide
DNA Sequence Analysis Two general kinds of analysis Screen for one of a set of known sequences Determine the sequence even if it is novel Screening for a known sequence usually involves an oligonucleotide
Next Generation Sequencing
 Next Generation Sequencing Technology and applications 10/1/2015 Jeroen Van Houdt - Genomics Core - KU Leuven - UZ Leuven 1 Landmarks in DNA sequencing 1953 Discovery of DNA double helix structure 1977
Next Generation Sequencing Technology and applications 10/1/2015 Jeroen Van Houdt - Genomics Core - KU Leuven - UZ Leuven 1 Landmarks in DNA sequencing 1953 Discovery of DNA double helix structure 1977
Profiling of microrna in Blood Serum/Plasma. Guidelines for the mircury LNA TM Universal RT microrna PCR System
 Profiling of microrna in Blood Serum/Plasma Guidelines for the mircury LNA TM Universal RT microrna PCR System Table of Contents 2 Introduction.....................................................................................
Profiling of microrna in Blood Serum/Plasma Guidelines for the mircury LNA TM Universal RT microrna PCR System Table of Contents 2 Introduction.....................................................................................
A systematic guideline for developing the best real-time PCR primers
 Scientific article Lessons learned from designing assays for more than 14, genes George Quellhorst and Sam Rulli QIAGEN, 6951 Executive Way, Frederick, Maryland 213, USA Abstract: Primer design is the
Scientific article Lessons learned from designing assays for more than 14, genes George Quellhorst and Sam Rulli QIAGEN, 6951 Executive Way, Frederick, Maryland 213, USA Abstract: Primer design is the
SYBR Green PCR Master Mix and SYBR Green RT-PCR Reagents Kit
 USER GUIDE SYBR Green PCR Master Mix and SYBR Green RT-PCR Reagents Kit Catalog Number 4309155 (Master Mix) and 4306736 (RT-PCR Reagents Kit) Publication Part Number 4310251 Rev. G Revision Date September
USER GUIDE SYBR Green PCR Master Mix and SYBR Green RT-PCR Reagents Kit Catalog Number 4309155 (Master Mix) and 4306736 (RT-PCR Reagents Kit) Publication Part Number 4310251 Rev. G Revision Date September
South Carolina College- and Career-Ready (SCCCR) Probability and Statistics
 South Carolina College- and Career-Ready (SCCCR) Probability and Statistics South Carolina College- and Career-Ready Mathematical Process Standards The South Carolina College- and Career-Ready (SCCCR)
South Carolina College- and Career-Ready (SCCCR) Probability and Statistics South Carolina College- and Career-Ready Mathematical Process Standards The South Carolina College- and Career-Ready (SCCCR)
Current Standard: Mathematical Concepts and Applications Shape, Space, and Measurement- Primary
 Shape, Space, and Measurement- Primary A student shall apply concepts of shape, space, and measurement to solve problems involving two- and three-dimensional shapes by demonstrating an understanding of:
Shape, Space, and Measurement- Primary A student shall apply concepts of shape, space, and measurement to solve problems involving two- and three-dimensional shapes by demonstrating an understanding of:
Supplemental Material. Methods
 Supplemental Material Methods Measurement of lncrnas expression Total RNA was extracted from PAXgene TM tubes using the PAXgene blood RNA kit (Qiagen, Venlo, Netherlands) as described by the manufacturer.
Supplemental Material Methods Measurement of lncrnas expression Total RNA was extracted from PAXgene TM tubes using the PAXgene blood RNA kit (Qiagen, Venlo, Netherlands) as described by the manufacturer.
Dengue Virus subtypes 1,2 3 and 4. genesig Standard Kit. DNA testing. Everything... Everyone... Everywhere... 3 Untranslated Region (3 UTR) 150 tests
 TM Primerdesign Ltd TM Primerdesign Ltd Dengue Virus subtypes 1,2 3 and 4 3 Untranslated Region (3 UTR) genesig Standard Kit 150 tests DNA testing Everything... Everyone... Everywhere... For general laboratory
TM Primerdesign Ltd TM Primerdesign Ltd Dengue Virus subtypes 1,2 3 and 4 3 Untranslated Region (3 UTR) genesig Standard Kit 150 tests DNA testing Everything... Everyone... Everywhere... For general laboratory
qpcr Quantification Protocol Guide
 qpcr Quantification Protocol Guide FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Topics 3 Introduction 5 User-Supplied Consumables and Equipment 7 Select Template 8 Dilute qpcr Template 9 Dilute Libraries 10 Prepare Reaction
qpcr Quantification Protocol Guide FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Topics 3 Introduction 5 User-Supplied Consumables and Equipment 7 Select Template 8 Dilute qpcr Template 9 Dilute Libraries 10 Prepare Reaction
Power SYBR Green PCR Master Mix and Power SYBR Green RT-PCR Reagents Kit
 USER GUIDE Power SYBR Green PCR Master Mix and Power SYBR Green RT-PCR Reagents Kit Catalog Number 4368577, 4367659, 4367660, 4368706, 4368702, 4368708 (Master Mix) and 4368711 (RT-PCR Reagents Kit) Publication
USER GUIDE Power SYBR Green PCR Master Mix and Power SYBR Green RT-PCR Reagents Kit Catalog Number 4368577, 4367659, 4367660, 4368706, 4368702, 4368708 (Master Mix) and 4368711 (RT-PCR Reagents Kit) Publication
RT31-020 20 rxns. RT31-100 100 rxns TRANSCRIPTME Enzyme Mix (1) 40 µl 2 x 50 µl 5 x 40 µl
 Components RT31-020 20 rxns RT31-050 50 rxns RT31-100 100 rxns TRANSCRIPTME Enzyme Mix (1) 40 µl 2 x 50 µl 5 x 40 µl 2x RT Master Mix (2) 200 µl 2 x 250 µl 5 x 200 µl RNase H (E. coli) 20 µl 2 x 25 µl
Components RT31-020 20 rxns RT31-050 50 rxns RT31-100 100 rxns TRANSCRIPTME Enzyme Mix (1) 40 µl 2 x 50 µl 5 x 40 µl 2x RT Master Mix (2) 200 µl 2 x 250 µl 5 x 200 µl RNase H (E. coli) 20 µl 2 x 25 µl
Section 14 Simple Linear Regression: Introduction to Least Squares Regression
 Slide 1 Section 14 Simple Linear Regression: Introduction to Least Squares Regression There are several different measures of statistical association used for understanding the quantitative relationship
Slide 1 Section 14 Simple Linear Regression: Introduction to Least Squares Regression There are several different measures of statistical association used for understanding the quantitative relationship
Experiment 2 Kinetics II Concentration-Time Relationships and Activation Energy
 2-1 Experiment 2 Kinetics II Concentration-Time Relationships and Activation Energy Introduction: The kinetics of a decomposition reaction involving hydroxide ion and crystal violet, an organic dye used
2-1 Experiment 2 Kinetics II Concentration-Time Relationships and Activation Energy Introduction: The kinetics of a decomposition reaction involving hydroxide ion and crystal violet, an organic dye used
Description: Molecular Biology Services and DNA Sequencing
 Description: Molecular Biology s and DNA Sequencing DNA Sequencing s Single Pass Sequencing Sequence data only, for plasmids or PCR products Plasmid DNA or PCR products Plasmid DNA: 20 100 ng/μl PCR Product:
Description: Molecular Biology s and DNA Sequencing DNA Sequencing s Single Pass Sequencing Sequence data only, for plasmids or PCR products Plasmid DNA or PCR products Plasmid DNA: 20 100 ng/μl PCR Product:
All-in-One mirna qrt-pcr Reagent Kits For quantitative detection of mature mirna
 All-in-One mirna qrt-pcr Reagent Kits For quantitative detection of mature mirna All-in-One TM mirna First-Strand cdna Synthesis Kit AMRT-0020 (20 RT reactions), AMRT-0060 (60 RT reactions) Used in combination
All-in-One mirna qrt-pcr Reagent Kits For quantitative detection of mature mirna All-in-One TM mirna First-Strand cdna Synthesis Kit AMRT-0020 (20 RT reactions), AMRT-0060 (60 RT reactions) Used in combination
All-in-One First-Strand cdna Synthesis Kit
 All-in-One First-Strand cdna Synthesis Kit For reliable first-strand cdna synthesis from all RNA sources Cat. No. AORT-0020 (20 synthesis reactions) Cat. No. AORT-0050 (50 synthesis reactions) User Manual
All-in-One First-Strand cdna Synthesis Kit For reliable first-strand cdna synthesis from all RNA sources Cat. No. AORT-0020 (20 synthesis reactions) Cat. No. AORT-0050 (50 synthesis reactions) User Manual
TaqMan Fast Advanced Master Mix. Protocol
 TaqMan Fast Advanced Master Mix Protocol For Research Use Only. Not intended for any animal or human therapeutic or diagnostic use. Information in this document is subject to change without notice. APPLIED
TaqMan Fast Advanced Master Mix Protocol For Research Use Only. Not intended for any animal or human therapeutic or diagnostic use. Information in this document is subject to change without notice. APPLIED
Calibration and Linear Regression Analysis: A Self-Guided Tutorial
 Calibration and Linear Regression Analysis: A Self-Guided Tutorial Part 1 Instrumental Analysis with Excel: The Basics CHM314 Instrumental Analysis Department of Chemistry, University of Toronto Dr. D.
Calibration and Linear Regression Analysis: A Self-Guided Tutorial Part 1 Instrumental Analysis with Excel: The Basics CHM314 Instrumental Analysis Department of Chemistry, University of Toronto Dr. D.
QIAGEN Rotor Gene Q: Software V2.0
 QIAGEN Rotor Gene Q: Software V2.0 Instrument Setup Instructions for RT 2 Profiler PCR Arrays Preparation Before the Experiment (Presetting the Machine will save time for your run): Please make note of
QIAGEN Rotor Gene Q: Software V2.0 Instrument Setup Instructions for RT 2 Profiler PCR Arrays Preparation Before the Experiment (Presetting the Machine will save time for your run): Please make note of
miracle mirna qpcr Instruction Manual Store at -20 Version 3.0 (Aug.2013)
 miracle mirna qpcr Instruction Manual Store at -20 Version 3.0 (Aug.2013) Contents I. PRODUCT INTRODUCTION 1 A. OVERVIEW 1 B. KIT CONTENTS 1 1. REAGENT KITS 1 2. PRIMER SETS 3 3. MIRACLE ON CALL SCREEN
miracle mirna qpcr Instruction Manual Store at -20 Version 3.0 (Aug.2013) Contents I. PRODUCT INTRODUCTION 1 A. OVERVIEW 1 B. KIT CONTENTS 1 1. REAGENT KITS 1 2. PRIMER SETS 3 3. MIRACLE ON CALL SCREEN
Experiment #1, Analyze Data using Excel, Calculator and Graphs.
 Physics 182 - Fall 2014 - Experiment #1 1 Experiment #1, Analyze Data using Excel, Calculator and Graphs. 1 Purpose (5 Points, Including Title. Points apply to your lab report.) Before we start measuring
Physics 182 - Fall 2014 - Experiment #1 1 Experiment #1, Analyze Data using Excel, Calculator and Graphs. 1 Purpose (5 Points, Including Title. Points apply to your lab report.) Before we start measuring
Chem 405 Biochemistry Lab I Experiment 2 Quantitation of an unknown protein solution.
 Chem 405 Biochemistry Lab I Experiment 2 Quantitation of an unknown protein solution. Introduction: The determination of protein concentration is frequently required in biochemical work. Several methods
Chem 405 Biochemistry Lab I Experiment 2 Quantitation of an unknown protein solution. Introduction: The determination of protein concentration is frequently required in biochemical work. Several methods
User Manual Mouse Endogenous Control Gene Panel
 User Manual Mouse Endogenous Control Gene Panel Version 1.5 March 2008 For use in quantitative real-time PCR Mouse Endogenous Control Gene Panel Table of contents Background 4 Contents 4 Additionally required
User Manual Mouse Endogenous Control Gene Panel Version 1.5 March 2008 For use in quantitative real-time PCR Mouse Endogenous Control Gene Panel Table of contents Background 4 Contents 4 Additionally required
Troubleshooting Sequencing Data
 Troubleshooting Sequencing Data Troubleshooting Sequencing Data No recognizable sequence (see page 7-10) Insufficient Quantitate the DNA. Increase the amount of DNA in the sequencing reactions. See page
Troubleshooting Sequencing Data Troubleshooting Sequencing Data No recognizable sequence (see page 7-10) Insufficient Quantitate the DNA. Increase the amount of DNA in the sequencing reactions. See page
Correlation key concepts:
 CORRELATION Correlation key concepts: Types of correlation Methods of studying correlation a) Scatter diagram b) Karl pearson s coefficient of correlation c) Spearman s Rank correlation coefficient d)
CORRELATION Correlation key concepts: Types of correlation Methods of studying correlation a) Scatter diagram b) Karl pearson s coefficient of correlation c) Spearman s Rank correlation coefficient d)
New Technologies for Sensitive, Low-Input RNA-Seq. Clontech Laboratories, Inc.
 New Technologies for Sensitive, Low-Input RNA-Seq Clontech Laboratories, Inc. Outline Introduction Single-Cell-Capable mrna-seq Using SMART Technology SMARTer Ultra Low RNA Kit for the Fluidigm C 1 System
New Technologies for Sensitive, Low-Input RNA-Seq Clontech Laboratories, Inc. Outline Introduction Single-Cell-Capable mrna-seq Using SMART Technology SMARTer Ultra Low RNA Kit for the Fluidigm C 1 System
