VNA Level II Module 5: Therapeutic Nutrition- Kidney Disease
|
|
|
- Lester Mosley
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 VNA Level II Module 5: Therapeutic Nutrition- Learning Objectives After completing this module, your basic understanding should include: What the kidneys do and how disease can affect their function. The importance of proper pet nutrition to minimize kidney disease. The value of screening senior pets for kidney disease. How early intervention with Hill s Prescription Diet k/d Canine pet foods may help lead to a longer, better quality of life for dogs with chronic renal failure. The benefits of Hill s Prescription Diet k/d Canine and k/d Feline pet foods. Your progress is saved. Slide 1 of 23
2 Introduction Having completed all of Level I, and Modules 1, 2, 3 and 4 in Level II, you should have a good understanding of the importance of proper pet nutrition the pet s entire life. Just because a client may have not seemed interested one or more times to nutritional recommendations, it is still important to discuss proper pet nutrition on every pet owner visit (and ideally recorded in the pet s medical record). Many of us often need reminders, so as an advocate for the pet s best interest and as requested by the veterinarian, you may have many opportunities to revisit critical wellness issues with pet owners. This approach to reinforcing the veterinarian s recommendations is part of the veterinary team concept. There are times though, when a pet owner might not heed advice, was never even told about proper nutrition, was told only once, or the pet, for any number of reasons, develops medical problems regardless of the plane of nutrition or care. These are prime areas where therapeutic nutrition should be considered a vital part of treatment and long-term management. Depending on certain circumstances, such as the cause, severity and progression of the disease, many pets can substantially benefit from nutritional intervention as part of the treatment regime. Therapeutic nutrition should ALWAYS be considered in patient care! Your progress is saved. Slide 2 of 23
3 Introduction Hill s Pet Nutrition, Inc. has 34+ Prescription Diet pet food formulas, and more than 100 packaging configurations for the veterinary profession to rely upon. In this Veterinary Nutritional Advocate educational experience, it would be difficult to cover each product and the conditions the food helps manage, in any kind of detail. Therefore, in the next four modules, we ll concentrate on four main areas:, Weight Management, Gastrointestinal Problems and Lower Urinary Tract Diseases. These issues often constitute a substantial percentage of veterinary practice medical caseloads. You ll be able to use the nutritional therapy concepts discussed in these modules, and apply them to a myriad of other situations needing nutritional intervention and support with Hill s Prescription Diets products. Proper nutrition is a critical element for managing cats and dogs with kidney (renal) disease, often helping to enhance the pet s quality and length of life. Because the requirements for protein, minerals, and some other nutrients change markedly during progressive kidney disease, the role of nutrition is paramount. After the veterinarian makes a SPECIFIC product recommendation to the client, the veterinary health care team needs to effectively communicate the critical importance, (and adherence) to nutritional therapy. This is usually a traumatic time for the pet owner, so your ability to reassuringly reinforce the veterinarian s protocol will be vital. This module of VNA is designed to provide you with a variety of communication points, to help you convey the importance of proper pet nutrition to clients whose pets have kidney disease. Specifically, we ll focus on Hill s Prescription Diet k/d Canine and k/d Feline products. Your progress is saved. Slide 3 of 23
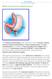
4 What Are The Kidneys And What Do They Do? The kidneys are part of a pet s urinary tract. The urinary tract consists of two kidneys, two ureters that connect the kidneys to the urinary bladder, and the urethra, the tube through which urine leaves the body, (see Figure 1). Normal dog and cat kidneys are bean-shaped, smooth, and are found under the backbone just beneath the last ribs and first few lumbar vertebrae. Figure 1. Parts of the canine and feline urinary tract. Your progress is saved. Slide 4 of 23
5 What Are The Kidneys And What Do They Do? In resting pets, one-fourth of the blood pumped by the heart goes to the kidneys. In the kidneys, blood is pumped through a complex network of blood vessels that serve to decrease blood pressure and allow for controlled filtering of the blood and formation of urine. The functional unit of the kidney is called a nephron. Each nephron consists of a cup-like structure called the glomerulus and a long thin tube lined by cells that have various functions. These tubes are called tubules. A thin delicate membrane called the glomerular membrane can be found at the end of the blood vessels in glomerulus. This membrane acts as a sieve, retaining cells and large protein molecules, but letting through water and other plasma components. The cells lining the tubules recover 99% of the water, salt, and vital nutrients filtered by the glomerular membrane, leaving behind metabolic waste products in the urine. This process also allows the kidneys to make small changes in body fluid composition by altering the amount of salt, acid, or alkali excreted or retained, depending on the body s need. The tubules combine to form the ureters mentioned above. Figure 2. The main function of the kidney is to filter the blood. In resting pets, one-fourth of the blood pumped by the heart goes to the kidneys. In the kidneys, blood is pumped through a complex network of blood vessels that serve to decrease blood pressure and allow for controlled filtering of the blood and formation of urine. Your progress is saved. Slide 5 of 23
6 The kidneys are vital organs that perform numerous metabolic tasks. The main functions include filtering and excreting the waste products of metabolism, regulating the body s concentration of water and salt, maintaining a slightly alkaline body environment, reabsorbing molecules needed by the body (for example, glucose, amino acids, and vitamins), and secreting various hormones. The kidneys eliminate urea and other waste products that result from the breakdown of dietary protein; the higher the protein content in the diet, the more waste products that must be eliminated. A brief summary of kidney functions: What Are The Kidneys And What Do They Do? Maintenance of body composition. Recall that the body of dogs and cats is composed mostly of water (See Level I, Module 1: Nutrients). The kidneys function to regulate how much water and minerals are excreted as urine or retained by the body. These minerals include sodium, potassium, chloride, calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus. By regulating water and mineral levels, the kidneys control body fluid levels and their composition. The kidneys also help maintain body acid levels within a narrow range. The main functions of the kidney include excreting waste products of metabolism, regulating the body s concentration of water and salt, maintaining a slightly alkaline body environment, reabsorbing vital body molecules, and secreting various hormones. The nephron is the functional unit of the kidney. Clinical signs of chronic kidney disease don t appear until at least threefourths of kidney function has been lost, usually over several months to years. Your progress is saved. Slide 6 of 23
7 What Are The Kidneys And What Do They Do? Excretion of body wastes and foreign substances. The kidneys excrete many drugs in the urine, ensuring that harmful levels do not accumulate in the body. Also, the kidneys rid the body of many by-products of normal body metabolism. As one example, the kidneys excrete urea, a byproduct of protein metabolism. Production and secretion of proteins called hormones. These proteins help control salt balance and blood pressure, red blood cell production, and calcium and phosphorus balance. Optimal function of every organ in the body depends on control of fluid composition and levels within appropriate ranges. The kidneys correct fluctuations in body fluid composition and levels that result from food intake, metabolism, environmental factors, and medical therapy. Your progress is saved. Slide 7 of 23
8 Detecting Kidney Failure Kidney failure occurs when the kidneys can t perform their functions. As a result, waste products and excess water accumulate in the body, causing clinical signs and abnormal laboratory results (see below). Clinical signs of chronic kidney disease don t appear until at least three-fourths of kidney function has been lost. There are two types of kidney failure seen in veterinary practice: acute (short term) and chronic (long term). Heart failure, extreme dehydration, some drugs and toxins (i.e., antifreeze containing ethylene glycol), or obstruction of the urinary tract (for example, a urinary bladder stone that lodges in the urethra preventing urination) are some of the more common causes of acute kidney failure. Acute kidney failure may or may not be reversed by medical therapy or surgical intervention, and may or may not progress to chronic kidney failure (CRF, where the R refers to renal, [kidney]). The rest of this module focuses on CRF. Figure 3. Effects of Chronic. Source: Hills Atlas of Veterinary Clinical Anatomy CRF is characterized by an inability of the kidneys to perform normal functions due to progressive loss of nephrons over months to years. Although many diseases and conditions can initiate CRF including diabetes mellitus, infection, injury, exposure to toxins, and conditions such as high blood pressure, in some cases, it isn t possible to determine the underlying cause. CRF is life-threatening and always progresses, ultimately causing death. Your progress is saved. Slide 8 of 23
9 Detecting Kidney Failure Regardless of the cause, in CRF the kidneys are unable to properly filter blood and perform their many functions. Metabolic waste products and extra fluids accumulate, and the chemical composition of the body becomes unbalanced. As a result, pets with CRF may develop weakened bones (impaired calcium and phosphorus metabolism), have difficulty controlling blood pressure (which further damages kidney function), and develop anemia (due to a lack of the kidney hormone that stimulates red blood cell production). Make sure pet owners with older dogs and cats, periodically monitor the pet s water intake and urinations. Normal Renal function Renal Damage Loss of Renal reserve Renal Insuffucuency Azotemia Uremia Death Figure 4. Natural progression of kidney disease. Your progress is saved. Slide 9 of 23
10 Detecting Kidney Failure Pet owners may first note their pet drinks more water, (polydipsia) and needs to urinate more often, (polyuria) possibly having urinary accidents in the house, especially at night. Other clinical signs of CRF often include appetite loss, weight loss, weakness, vomiting, diarrhea, foul mouth odor, decreased water intake and urine output, (later stages), seizures, and a tendency to bleed easily. These symptoms can also mimic other disease signs. Blindness may be present if high blood pressure has been present for a prolonged period. Physical examination may reveal dehydration, malnutrition, oral ulcers, joint pain, facial swellings, abnormal retinas (an internal eye structure), and kidneys of abnormal size (usually smaller). Your progress is saved. Slide 10 of 23
11 Detecting Kidney Failure If the veterinarian suspects kidney disease, he or she may request that the veterinary technician collect blood and urine samples for testing. Blood levels of urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine may be elevated, indicating the kidneys are unable to adequately filter wastes from the blood. Likewise, potassium, calcium, phosphorus, glucose, and protein levels may be abnormal. Evaluation of a blood sample may indicate inflammation, anemia, or both. Blood pressure measurements may be abnormally high. Radiographs and ultrasound may show changes in the size, shape, or position of the kidneys. Senior dogs and cats should be screened for kidney disease at least annually. It is now recommended that veterinarians begin conducting kidney screenings on cats, and small, medium and large size dogs, beginning at seven years of age, and beginning at five years of age for giant breed dogs. Kidney screening should always be conducted earlier if the veterinarian suspects a problem. Recommended tests include a complete urinalysis, complete biochemistry profile, and microalbuminuria. Testing for microalbuminuria is particularly important; a blood protein called albumin may leak through the glomerulus of the kidney and appear in the urine where it can be detected. This finding may be present before results of other lab tests become abnormal, and thus be an indicator of early kidney damage. Early detection-even before clinical signs occur-and proper nutrition, may improve the length and quality of life for pets with kidney disease. Your progress is saved. Slide 11 of 23
12 Risk Factors For Kidney Failure In client surveys, kidney disease was the second most common cause of death in cats, (after cancer) and the third most common cause in dogs, after cancer and heart disease (Morris Animal Foundation Animal Health Survey, 1998). In yet another survey, approximately 20% of 1,600 pet dogs over 5 years of age had abnormally elevated kidney function tests (Leibetseder J, Neufeld K. Dogs with chronic renal failure. Proc. WSAVA, 1991; ). CRF becomes more common in cats and dogs with advancing age. Other risk factors for CRF include: Breed. Some canine and feline breeds are more likely to develop familial forms of kidney disease. Dog breeds include Lhasa apsos, Shih Tzus, Doberman pinschers, and golden retrievers. Cat breeds include Maine coon, Abyssinian, Siamese, Russian blue and Burmese. Urinary tract infections. Drug therapy. Some antimicrobial and analgesic agents (among other drugs) may predispose to kidney disease. Poor blood flow. Shock, heart disease, and blood loss can cause kidney damage. Diabetes mellitus. High blood pressure. Your progress is saved. Slide 12 of 23
13 Treating Kidney Failure Although CRF can t be cured, it is possible to control the clinical signs, reduce complications, and slow the disease s progression. These measures may improve the quality and length of an affected pet s life. The underlying disease and its complications should be controlled if possible. For more than 50 years, a cornerstone of managing pets with CRF has been dietary modification. Unlike carbohydrates and fats, excess protein is not stored in the body, but rather, it is degraded to form urea and other nitrogen-containing substances that must be eliminated by the kidneys. Also, foods containing high levels of protein contain more phosphorus, hydrogen ions (which contribute to body acidity), and inorganic ions than low-protein foods. Consequently, CRF patients consuming excessive dietary protein will accumulate nitrogen-containing wastes, resulting in a life-threatening syndrome called uremia. For more than 50 years, dietary modification has been the cornerstone of managing CRF. Limiting dietary protein and phosphorus intake helps correct many clinical signs and metabolic complications of uremia. Many years ago, investigators in human and veterinary medicine discovered that limiting dietary protein and phosphorus intake would help correct many clinical signs and metabolic complications of uremia in people and pets. This finding helped formulate the goals of nutritional therapy for CRF: Ensure sufficient caloric intake to prevent malnutrition Limit accumulation of nitrogen-containing wastes and metabolic disturbances associated with uremia Slow progression of CRF, if possible. Your progress is saved. Slide 13 of 23
14 Treating Kidney Failure Other therapy often prescribed for pets with CRF include: Fluid therapy to treat dehydration and correct electrolyte imbalances Drugs to control nausea and vomiting Drugs called intestinal phosphate binders to help correct high blood phosphorus levels A hormone called erythropoietin to treat anemia Drugs to treat high blood pressure Antibacterial drugs to treat infections Surgery to correct anatomic defects Drugs to decrease blood levels of a protein called parathyroid hormone. Hemodialysis, a blood-filtering procedure, and even kidney transplants are performed at some veterinary referral centers. Your progress is saved. Slide 14 of 23
15 Features And Benefits Of Prescription Diet k/d Canine And k/d Feline Dr. Mark Morris, Sr. began working on the first veterinary therapeutic dog food in the late 1930s. This food was of great benefit to one of the first Seeing Eye Dogs in America, Buddy, and of course her owner, Morris Frank! Buddy was suffering from CRF. This food was called Raritan Ration B and contained ingredients to lessen the workload on Buddy s kidneys. Raritan Ration B evolved into Prescription Diet k/d Canine, which was first introduced to veterinarians in Prescription Diet k/d Feline was subsequently added as a nutritional aid for cats with CRF. Tables 1 and 2 show selected product features and benefits of Prescription Diet k/d Canine and k/d Feline to help you better communicate with pet owners. Remember, benefits answer a potential so what? and are considered the advantages the features deliver. Figure 5. Dr. Mark Morris Sr. developed the first therapeutic veterinary food. As a result, Hill s Pet Nutrition, Inc. came to be. Figure 6. Morris Frank and his companion, Buddy, one of the first seeing eye dogs in America. Your progress is saved. Slide 15 of 23
16 Features And Benefits Of Prescription Diet k/d Canine And k/d Feline Table 1. Features and Benefits of Prescription Diet k/d Canine.* Features Very low phosphorus Low protein Low sodium Increased dietary buffering capacity Target urine ph: Added potassium citrate High soluble dietary fiber High omega-3 fatty acids High non-protein calories Benefits Helps maintain healthy renal function Limits accumulation of waste products Helps maintain normal blood pressure Helps maintain normal acid-base balance Helps prevent muscle wasting Helps maintain normal acid-base balance Helps maintain normal acid-base balance and limit accumulation of waste products Helps reduce urinary nitrogen excretion Helps improve renal blood flow Helps prevent malnutrition *Source: Hill s Key to Clinical Nutrition. Your progress is saved. Slide 16 of 23
17 Features And Benefits Of Prescription Diet k/d Canine And k/d Feline Table 2. Features and Benefits of Prescription Diet k/d Feline.* Features Very low phosphorus Low protein Low sodium Increased dietary buffering capacity Target urine ph: High B vitamins Added soluble dietary fiber High omega-3 fatty acids High non-protein calories Benefits Helps maintain healthy renal function Limits accumulation of waste products Helps maintain normal blood pressure Helps maintain normal acid-base balance Helps prevent muscle wasting Helps maintain normal acid-base balance Helps avoid losses caused by excess urine production Helps reduce urinary nitrogen excretion Helps improve renal blood flow Helps prevent malnutrition *Source: Hill s Key to Clinical Nutrition. Your progress is saved. Slide 17 of 23
18 Features And Benefits Of Prescription Diet k/d Canine And k/d Feline Some general benefits also include: Cost effective on a daily feeding basis. Balanced nutrition and great taste, to optimize the feeding experience. Canned and dry formulations. Dogs may be able to have Prescription Diet Canine Treats, which are low in calories and minerals. The pet owner is less likely to feed other snacks. 100% Guarantee on all Hill s Prescription Diet products: Hill s guarantees Prescription Diet brand pet food for quality, consistency and taste. If you are not completely satisfied with any purchase of Prescription Diet brand pet food for these reasons, simply return the unused portion to your veterinarian for a full refund or replacement. (Hill s will reimburse the practice). Keep in mind also, that there are a number of benefits to your practice regarding the sale of Prescription Diet brand pet foods. Examples include: More frequent client visits (bonding), the comfort of knowing you are providing an important part of disease therapy, ability to interact with the pet owner and answer questions, further educating the client on issues not adequately covered during exams, reinforce previous recommendations, the opportunity to promote other appropriate products and services, the profitability of Prescription Diet brand pet foods to the practice Your progress is saved. Slide 18 of 23
19 Features And Benefits Of Prescription Diet k/d Canine And k/d Feline A clinical study published in 2002 demonstrated that dogs fed k/d Canine lived twice as long and had 50% fewer clinical signs than dogs fed a typical adult dog food. Over the years, Prescription Diet kidney foods have been reformulated to incorporate the latest veterinary research. In a clinical study published in 2002, investigators found that feeding Prescription Diet k/d Canine dry was beneficial in reducing clinical signs and improving survival time in dogs with mild to moderate spontaneous renal failure compared to feeding a typical adult dog food. Your progress is saved. Slide 19 of 23
20 Features And Benefits Of Prescription Diet k/d Canine And k/d Feline Dogs with CRF fed k/d Canine lived twice as long and exhibited 50% fewer clinical signs than dogs fed the typical adult dog food. The authors concluded that initiation of treatment with k/d Canine would benefit dogs with serum creatinine concentrations equal to or greater than 2.0 mg/dl (Jacob F, et al. Clinical evaluation of dietary modification for treatment of spontaneous chronic renal failure in dogs. JAVMA 2002; 220: ). Many dogs with creatinine values this low do not yet suffer from clinical signs of kidney disease, underscoring the need for early detection. Prescription Diet k/d Canine is the only pet food demonstrated to help improve the life expectancy of dogs with kidney disease. It is prudent that proper nutrition begin early in the course of the disease, ideally long before the onset of clinical signs, and that no other foods be fed. Remind clients to always ensure that fresh clean water be available for pets with CRF. Your progress is saved. Slide 20 of 23
21 Monitoring Crf Patients Because CRF is a progressive, incurable disorder, dogs and cats with CRF should be monitored at regular intervals, depending on the severity of their disease and the therapy prescribed. Initially, pets may need to be checked every week, especially if drugs are given to increase red blood cell production or control parathyroid gland activity. Even pets with well-controlled CRF may need to be evaluated every one to three months. Blood and urine tests will likely be a part of most evaluations. Owners of CRF pets may, unfortunately, feed inappropriate foods and treats. The result may be an increased number of clinical signs (reduced quality of life) and/or premature death of the pet. Communicate the importance of strict adherence to the veterinarian s therapeutic plan, including the food. You can support the client s efforts by ensuring that they keep their appointments and purchase Prescription Diet k/d Canine or k/d Feline as recommended, on an ongoing basis. It is usually necessary to limit the kidney disease patient s access to other people and animal food (for example, a dog having access to cat food). Feeding location and presentation are important. Timid pets should be fed in a quiet place. Cats should not be fed in a loud environment. Placing small quantities of the food in a patient s mouth or on its paws to stimulate licking or swallowing (hand feeding) may facilitate eating. Your progress is saved. Slide 21 of 23
22 Monitoring Crf Patients Food aversion (avoiding a food) is possible if a nauseated animal is force-fed or if a painful or unpleasant experience is associated with feeding. Disagreeable medications (for example, intestinal phosphate binders) should not be mixed with Prescription Diet k/d Canine or k/d Feline. Managing underlying abnormalities in fluid, electrolyte, and acid-base balance will help minimize nausea and vomiting. Consider using Prescription Diet k/d Canine and k/d Feline, foods intended for long-term management of CRF, should not be offered during periods of nausea and vomiting to prevent possible food aversions. Do not use foods intended for longterm management of CRF, if the pet is nauseated. Doing so may cause the pet to develop a food aversion, making it even more difficult to manage CRF. Your progress is saved. Slide 22 of 23
23 Summary Chronic is an irreversible, progressive disorder that affects many dogs and cats for a variety of reasons. Although kidney disease is especially common in older pets, earlier stages of it can often be diagnosed when pets are about 7 years of age. Therefore, screening protocols are especially important for early diagnosis, when dietary intervention may help CRF patients live longer, healthier lives. Helping place the pet on the proper food, and having the owner adhere to your instructions, will allow you to experience the Family-Pet-Veterinary Team Bond in a special way. No doubt, the pet and the pet owner will be very appreciative of your efforts! Are You Ready? To continue, you will need to complete the quiz for this module. When you are ready, click on the forward arrow below to take you to the quiz. Your progress is saved. Slide 23 of 23
Your Kidneys: Master Chemists of the Body
 Your Kidneys: Master Chemists of the Body www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes
Your Kidneys: Master Chemists of the Body www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes
GFR (Glomerular Filtration Rate) A Key to Understanding How Well Your Kidneys Are Working
 GFR (Glomerular Filtration Rate) A Key to Understanding How Well Your Kidneys Are Working www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National
GFR (Glomerular Filtration Rate) A Key to Understanding How Well Your Kidneys Are Working www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National
DIABETES. Eyes, Heart, Nerves, Feet, and Kidneys. www.kidney.org
 DIABETES Eyes, Heart, Nerves, Feet, and Kidneys www.kidney.org About the Information in this Booklet Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation (NKF) offers guidelines and commentaries that help
DIABETES Eyes, Heart, Nerves, Feet, and Kidneys www.kidney.org About the Information in this Booklet Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation (NKF) offers guidelines and commentaries that help
Diabetes and kidney disease. The foundation of kidney care.
 Diabetes and kidney disease The foundation of kidney care. T H E K I D N E Y F O U N D A T I O N O F C A N A D A 1 Diabetes and kidney disease What is diabetes? Diabetes is a disease that is caused by
Diabetes and kidney disease The foundation of kidney care. T H E K I D N E Y F O U N D A T I O N O F C A N A D A 1 Diabetes and kidney disease What is diabetes? Diabetes is a disease that is caused by
InDependent Diabetes Trust
 InDependent Diabetes Trust Kidneys and Diabetes Updated July 2015 Registered Company Number 3148360 Registered Charity No 1058284 Contents Introduction Healthy Kidneys Kidney disease and diabetes The use
InDependent Diabetes Trust Kidneys and Diabetes Updated July 2015 Registered Company Number 3148360 Registered Charity No 1058284 Contents Introduction Healthy Kidneys Kidney disease and diabetes The use
1333 Plaza Blvd, Suite E, Central Point, OR 97502 * www.mountainviewvet.net
 1333 Plaza Blvd, Suite E, Central Point, OR 97502 * www.mountainviewvet.net Diabetes Mellitus (in cats) Diabetes, sugar Affected Animals: Most diabetic cats are older than 10 years of age when they are
1333 Plaza Blvd, Suite E, Central Point, OR 97502 * www.mountainviewvet.net Diabetes Mellitus (in cats) Diabetes, sugar Affected Animals: Most diabetic cats are older than 10 years of age when they are
Kidney or renal disease
 Kidney or renal disease VETERINARY GUIDE 6 The kidneys are responsible for filtering waste products out of the blood to form urine. Disease of the kidneys is one of the most common problems affecting middle-aged
Kidney or renal disease VETERINARY GUIDE 6 The kidneys are responsible for filtering waste products out of the blood to form urine. Disease of the kidneys is one of the most common problems affecting middle-aged
Kidney Disease WHAT IS KIDNEY DISEASE? TESTS TO DETECT OR DIAGNOSE KIDNEY DISEASE TREATMENT STRATEGIES FOR KIDNEY DISEASE
 Kidney Disease WHAT IS KIDNEY DISEASE? Kidney disease is when your kidneys are damaged and not functioning as they should. When kidney disease is not going away it is called chronic kidney disease or CKD.
Kidney Disease WHAT IS KIDNEY DISEASE? Kidney disease is when your kidneys are damaged and not functioning as they should. When kidney disease is not going away it is called chronic kidney disease or CKD.
High Blood Pressure and Chronic Kidney Disease. For People With CKD Stages 1 4
 High Blood Pressure and Chronic Kidney Disease For People With CKD Stages 1 4 National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative (NKF-KDOQI ) The National Kidney Foundation s Kidney
High Blood Pressure and Chronic Kidney Disease For People With CKD Stages 1 4 National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative (NKF-KDOQI ) The National Kidney Foundation s Kidney
Chapter 23. Composition and Properties of Urine
 Chapter 23 Composition and Properties of Urine Composition and Properties of Urine urinalysis the examination of the physical and chemical properties of urine appearance - clear, almost colorless to deep
Chapter 23 Composition and Properties of Urine Composition and Properties of Urine urinalysis the examination of the physical and chemical properties of urine appearance - clear, almost colorless to deep
MANAGING ANEMIA. When You Have Kidney Disease or Kidney Failure. www.kidney.org
 MANAGING ANEMIA When You Have Kidney Disease or Kidney Failure www.kidney.org About the Information in this Booklet Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation (NKF) offers guidelines and commentaries
MANAGING ANEMIA When You Have Kidney Disease or Kidney Failure www.kidney.org About the Information in this Booklet Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation (NKF) offers guidelines and commentaries
High Blood pressure and chronic kidney disease
 High Blood pressure and chronic kidney disease For People with CKD Stages 1 4 www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney
High Blood pressure and chronic kidney disease For People with CKD Stages 1 4 www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney
Chronic Kidney Disease and Diabetes
 Anyone with diabetes can get kidney disease. Diabetes and high blood pressure are the most common causes of kidney disease, and people often have both. Chronic (long term) kidney disease (CKD) caused by
Anyone with diabetes can get kidney disease. Diabetes and high blood pressure are the most common causes of kidney disease, and people often have both. Chronic (long term) kidney disease (CKD) caused by
Published on: 07/04/2015 Page 1 of 5
 Bladder Stones A DNA test for Hyperunicosuria (HUU) to find the gene which is implicated in the development of URATE stones has been developed which work with Bulldogs and many other breeds including Black
Bladder Stones A DNA test for Hyperunicosuria (HUU) to find the gene which is implicated in the development of URATE stones has been developed which work with Bulldogs and many other breeds including Black
LECTURE 1 RENAL FUNCTION
 LECTURE 1 RENAL FUNCTION Components of the Urinary System 2 Kidneys 2 Ureters Bladder Urethra Refer to Renal System Vocabulary in your notes Figure 2-1,page10 Kidney Composition Cortex Outer region Contains
LECTURE 1 RENAL FUNCTION Components of the Urinary System 2 Kidneys 2 Ureters Bladder Urethra Refer to Renal System Vocabulary in your notes Figure 2-1,page10 Kidney Composition Cortex Outer region Contains
Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones. Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke
 Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke Nephrology vs. Urology Nephrologist a physician who has been trained in the diagnosis
Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke Nephrology vs. Urology Nephrologist a physician who has been trained in the diagnosis
How To Know If Your Cat Is Healthy And Happy
 Senior Cat Care As cats get older, they can experience many changes in their bodies. Not all cats will have these changes at the same time in their lives but we can categorize their life stages. Stage
Senior Cat Care As cats get older, they can experience many changes in their bodies. Not all cats will have these changes at the same time in their lives but we can categorize their life stages. Stage
483.25(i) Nutrition (F325) Surveyor Training: Interpretive Guidance Investigative Protocol
 483.25(i) Nutrition (F325) Surveyor Training: 1 With regard to the revised guidance F325 Nutrition, there have been significant changes. Specifically, F325 and F326 were merged. However, the regulatory
483.25(i) Nutrition (F325) Surveyor Training: 1 With regard to the revised guidance F325 Nutrition, there have been significant changes. Specifically, F325 and F326 were merged. However, the regulatory
Nutrition and Chronic Kidney Disease
 Nutrition and Chronic Kidney Disease I have been told I have early kidney failure. What does this mean? What can I expect? This means that your kidneys are not doing as good a job as they should to help
Nutrition and Chronic Kidney Disease I have been told I have early kidney failure. What does this mean? What can I expect? This means that your kidneys are not doing as good a job as they should to help
Select the one that is the best answer:
 MQ Kidney 1 Select the one that is the best answer: 1) n increase in the concentration of plasma potassium causes increase in: a) release of renin b) secretion of aldosterone c) secretion of H d) release
MQ Kidney 1 Select the one that is the best answer: 1) n increase in the concentration of plasma potassium causes increase in: a) release of renin b) secretion of aldosterone c) secretion of H d) release
The digestive system eliminated waste from the digestive tract. But we also need a way to eliminate waste from the rest of the body.
 Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system 1
Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system 1
Information for Childhood Cancer Survivors. Kidney Problems
 Kidney problems Some chemotherapy drugs can affect the kidneys. The kidneys break down and remove many chemotherapy drugs from the body. When chemotherapy drugs get broken down, they may make products
Kidney problems Some chemotherapy drugs can affect the kidneys. The kidneys break down and remove many chemotherapy drugs from the body. When chemotherapy drugs get broken down, they may make products
What is Geriatric? Geriatric Nutrition of Companion Animals. Age Chart. Diseases Associated with Older Pets
 Geriatric Nutrition of Companion Animals What is Geriatric? Aging is a biologic process that results in progressive reduction of one s ability to maintain oneself under stress, leading to increased vulnerability
Geriatric Nutrition of Companion Animals What is Geriatric? Aging is a biologic process that results in progressive reduction of one s ability to maintain oneself under stress, leading to increased vulnerability
Chronic Kidney Disease
 Page 1 of 6 Chronic Kidney Disease Chronic kidney disease (CKD) means that your kidneys are not working as well as they once did. Various conditions can cause CKD. Severity can vary but most cases are:
Page 1 of 6 Chronic Kidney Disease Chronic kidney disease (CKD) means that your kidneys are not working as well as they once did. Various conditions can cause CKD. Severity can vary but most cases are:
X-Plain Kidney Stones Reference Summary
 X-Plain Kidney Stones Reference Summary Introduction Kidney stones are fairly common. Although they can be very painful, they are treatable, and in many cases preventable. This reference summary will help
X-Plain Kidney Stones Reference Summary Introduction Kidney stones are fairly common. Although they can be very painful, they are treatable, and in many cases preventable. This reference summary will help
Chapter 2 What Is Diabetes?
 Chapter 2 What Is Diabetes? TYPE 1 (INSULIN-DEPENDENT) DIABETES Type 1 (also known as insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus [IDDM] or juvenile or childhood) diabetes is the most common type found in children
Chapter 2 What Is Diabetes? TYPE 1 (INSULIN-DEPENDENT) DIABETES Type 1 (also known as insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus [IDDM] or juvenile or childhood) diabetes is the most common type found in children
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology. Chapter 15. The Urinary System. Slides 15.1 15.20. Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L.
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 15 The Urinary System Slides 15.1 15.20 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Functions of the Urinary System Elimination
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 15 The Urinary System Slides 15.1 15.20 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Functions of the Urinary System Elimination
Identifying and treating long-term kidney problems (chronic kidney disease)
 Understanding NICE guidance Information for people who use NHS services Identifying and treating long-term kidney problems (chronic kidney disease) NICE clinical guidelines advise the NHS on caring for
Understanding NICE guidance Information for people who use NHS services Identifying and treating long-term kidney problems (chronic kidney disease) NICE clinical guidelines advise the NHS on caring for
Bariatric Patients, Nutritional Intervention for
 SKILL COMPETENCY CHECKLIST Bariatric Patients, Nutritional Intervention for Link to Dietitian Practice and Skill Standard Met/Initials Prerequisite Skills Competency Areas Knowledge of how to conduct a
SKILL COMPETENCY CHECKLIST Bariatric Patients, Nutritional Intervention for Link to Dietitian Practice and Skill Standard Met/Initials Prerequisite Skills Competency Areas Knowledge of how to conduct a
High Blood Pressure and Chronic Kidney Disease
 High Blood Pressure and Chronic Kidney Disease For People with CKD Stages 1 4 www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney
High Blood Pressure and Chronic Kidney Disease For People with CKD Stages 1 4 www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney
Managing Anemia When You Are on Dialysis. Stage 5
 Managing Anemia When You Are on Dialysis Stage 5 What is anemia? Anemia happens when your red blood cells are in short supply. Red blood cells carry oxygen from your lungs to all parts of your body, giving
Managing Anemia When You Are on Dialysis Stage 5 What is anemia? Anemia happens when your red blood cells are in short supply. Red blood cells carry oxygen from your lungs to all parts of your body, giving
Acid-Base Balance and the Anion Gap
 Acid-Base Balance and the Anion Gap 1. The body strives for electrical neutrality. a. Cations = Anions b. One of the cations is very special, H +, and its concentration is monitored and regulated very
Acid-Base Balance and the Anion Gap 1. The body strives for electrical neutrality. a. Cations = Anions b. One of the cations is very special, H +, and its concentration is monitored and regulated very
Chapter 48. Nutrients in Food. Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids. Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids, continued
 Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids The three nutrients needed by the body in the greatest amounts are carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Nutrients in Food All of these nutrients are called organic compounds,
Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids The three nutrients needed by the body in the greatest amounts are carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Nutrients in Food All of these nutrients are called organic compounds,
Nutrition and Chronic Kidney Disease
 Nutrition and Chronic Kidney Disease National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative (NKF-K/DOQI TM ) The National Kidney Foundation is developing guidelines for clinical care to
Nutrition and Chronic Kidney Disease National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative (NKF-K/DOQI TM ) The National Kidney Foundation is developing guidelines for clinical care to
Understanding Treatment Options for Renal Therapy
 Understanding Treatment Options for Renal Therapy Kidney failure happens to many different people for many different reasons 1 What causes kidney failure? Diabetes Chronic infection High blood pressure
Understanding Treatment Options for Renal Therapy Kidney failure happens to many different people for many different reasons 1 What causes kidney failure? Diabetes Chronic infection High blood pressure
CHAPTER 20: URINARY SYSTEM
 OBJECTIVES: 1. Name the major function of the urinary system, and name and locate (on a diagram) the organs that compose the system. 2. Explain what the term renal refers to. 3. Define the term retroperitoneal.
OBJECTIVES: 1. Name the major function of the urinary system, and name and locate (on a diagram) the organs that compose the system. 2. Explain what the term renal refers to. 3. Define the term retroperitoneal.
DIALYSIS COMPACT. The function, diseases and treatments for the human kidney.
 DIALYSIS COMPACT The function, diseases and treatments for the human kidney. Content 3 Editorial 4 What do healthy kidneys accomplish? 5 What causes kidney disease? 6 What effects does kidney disease have?
DIALYSIS COMPACT The function, diseases and treatments for the human kidney. Content 3 Editorial 4 What do healthy kidneys accomplish? 5 What causes kidney disease? 6 What effects does kidney disease have?
UTI CAT FOOD COMPARISON CHART
 UTI CAT FOOD COMPARISON CHART believes that urinary tract infections, crystals and kidney problems in today s cat are due mainly to excessive minerals consumed by our cats as they age. Once you cat reaches
UTI CAT FOOD COMPARISON CHART believes that urinary tract infections, crystals and kidney problems in today s cat are due mainly to excessive minerals consumed by our cats as they age. Once you cat reaches
Renal Topics 1) renal function 2) renal system 3) urine formation 4) urine & urination 5) renal diseases
 Renal Topics 1) renal function 2) renal system 3) urine formation 4) urine & urination 5) renal diseases 1/9/2015 Renal Biology - Sandra Hsu 1 Renal Functions 1) excrete metabolic wastes (blood cleaning)
Renal Topics 1) renal function 2) renal system 3) urine formation 4) urine & urination 5) renal diseases 1/9/2015 Renal Biology - Sandra Hsu 1 Renal Functions 1) excrete metabolic wastes (blood cleaning)
URINARY CATHETER CARE
 URINARY CATHETER CARE INTRODUCTION Urinary catheter care is a very important skill, and it is a skill that many certified nursing assistants (CNAs) must know. Competence at providing urinary catheter care
URINARY CATHETER CARE INTRODUCTION Urinary catheter care is a very important skill, and it is a skill that many certified nursing assistants (CNAs) must know. Competence at providing urinary catheter care
Diet and haemodialysis
 Diet and haemodialysis This leaflet is for patients with kidney disease who are receiving haemodialysis treatment. If you have any further questions, please contact us using the details below and on the
Diet and haemodialysis This leaflet is for patients with kidney disease who are receiving haemodialysis treatment. If you have any further questions, please contact us using the details below and on the
Peritoneal dialysis all you need to know about your blood results
 Peritoneal dialysis all you need to know about your blood results Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Peritoneal dialysis all you need to know about your blood results Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Diagnostics: Page 2 of 5
 Proteinuria Proteinuria is a condition in which there are increased amounts of protein in the urine. There are a number of different diseases which can result in proteinuria. In the early stages of the
Proteinuria Proteinuria is a condition in which there are increased amounts of protein in the urine. There are a number of different diseases which can result in proteinuria. In the early stages of the
Diabetic Ketoacidosis: When Sugar Isn t Sweet!!!
 Diabetic Ketoacidosis: When Sugar Isn t Sweet!!! W Ricks Hanna Jr MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics University of Tennessee Health Science Center LeBonheur Children s Hospital Introduction Diabetes
Diabetic Ketoacidosis: When Sugar Isn t Sweet!!! W Ricks Hanna Jr MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics University of Tennessee Health Science Center LeBonheur Children s Hospital Introduction Diabetes
Adams Memorial Hospital Decatur, Indiana EXPLANATION OF LABORATORY TESTS
 Adams Memorial Hospital Decatur, Indiana EXPLANATION OF LABORATORY TESTS Your health is important to us! The test descriptions listed below are for educational purposes only. Laboratory test interpretation
Adams Memorial Hospital Decatur, Indiana EXPLANATION OF LABORATORY TESTS Your health is important to us! The test descriptions listed below are for educational purposes only. Laboratory test interpretation
Ureteroscopy with Laser Lithotripsy
 Ureteroscopy with Laser Lithotripsy Introduction Kidney stones are fairly common. Although kidney stones can be very painful, they are treatable, and in many cases preventable. Your doctor may recommend
Ureteroscopy with Laser Lithotripsy Introduction Kidney stones are fairly common. Although kidney stones can be very painful, they are treatable, and in many cases preventable. Your doctor may recommend
Feline Cystitis (Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease)
 Feline Cystitis (Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease) The term "cystitis" literally means inflammation of the urinary bladder. Although this term is rather general, there is a common form of cystitis that
Feline Cystitis (Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease) The term "cystitis" literally means inflammation of the urinary bladder. Although this term is rather general, there is a common form of cystitis that
Is a kidney transplant right for me?
 Is a kidney transplant right for me? Your guide to the transplant process www.esrdncc.org Contents Introduction 3 What is a Transplant Center? 4 What is the Waiting List? 5 What Happens After the Surgery?
Is a kidney transplant right for me? Your guide to the transplant process www.esrdncc.org Contents Introduction 3 What is a Transplant Center? 4 What is the Waiting List? 5 What Happens After the Surgery?
Kidney Stones. This reference summary will help you understand kidney stones and how to treat and prevent them. Kidney
 Introduction A kidney stone is a solid piece of material that forms in the kidney from substances in the urine. Kidney stones are fairly common. Although kidney stones can be painful, they are treatable.
Introduction A kidney stone is a solid piece of material that forms in the kidney from substances in the urine. Kidney stones are fairly common. Although kidney stones can be painful, they are treatable.
Weight-Loss Surgery for Adults With Diabetes or Prediabetes Who Are at the Lower Levels of Obesity
 Weight-Loss Surgery for Adults With Diabetes or Prediabetes Who Are at the Lower Levels of Obesity A Review of the Research for Adults With a BMI Between 30 and 35 Is This Information Right for Me? If
Weight-Loss Surgery for Adults With Diabetes or Prediabetes Who Are at the Lower Levels of Obesity A Review of the Research for Adults With a BMI Between 30 and 35 Is This Information Right for Me? If
Endocrine System: Practice Questions #1
 Endocrine System: Practice Questions #1 1. Removing part of gland D would most likely result in A. a decrease in the secretions of other glands B. a decrease in the blood calcium level C. an increase in
Endocrine System: Practice Questions #1 1. Removing part of gland D would most likely result in A. a decrease in the secretions of other glands B. a decrease in the blood calcium level C. an increase in
Evidence-based Nutritional Decisions for Chronic Kidney Disease. Dr Delisa Appleton BVSc (Hons) PhD
 Evidence-based Nutritional Decisions for Chronic Kidney Disease Dr Delisa Appleton BVSc (Hons) PhD Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a common clinical diagnosis, particularly in older cats and dogs, and
Evidence-based Nutritional Decisions for Chronic Kidney Disease Dr Delisa Appleton BVSc (Hons) PhD Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a common clinical diagnosis, particularly in older cats and dogs, and
UCSF Kidney Transplant Symposium 2012
 UCSF Kidney Transplant Symposium 2012 Nutrition Fitness in Kidney Transplant Mary Ellen DiPaola, RD, CDE UCSF Outpatient Dietitian Goal of Nutrition Fitness for Transplant Nutritional guidance of pre-
UCSF Kidney Transplant Symposium 2012 Nutrition Fitness in Kidney Transplant Mary Ellen DiPaola, RD, CDE UCSF Outpatient Dietitian Goal of Nutrition Fitness for Transplant Nutritional guidance of pre-
Multiple Myeloma. This reference summary will help you understand multiple myeloma and its treatment options.
 Multiple Myeloma Introduction Multiple myeloma is a type of cancer that affects white blood cells. Each year, thousands of people find out that they have multiple myeloma. This reference summary will help
Multiple Myeloma Introduction Multiple myeloma is a type of cancer that affects white blood cells. Each year, thousands of people find out that they have multiple myeloma. This reference summary will help
How do Patients Take THE GIFT from Mother Earth, BEST FULVIC and Humic and Fulvic Based Supplements?
 How do Patients Take THE GIFT from Mother Earth, BEST FULVIC and Humic and Fulvic Based Supplements? Patients typically start taking THE GIFT from Mother Earth. THE GIFT from Mother Earth is a highly-concentrated
How do Patients Take THE GIFT from Mother Earth, BEST FULVIC and Humic and Fulvic Based Supplements? Patients typically start taking THE GIFT from Mother Earth. THE GIFT from Mother Earth is a highly-concentrated
Pyelonephritis: Kidney Infection
 Pyelonephritis: Kidney Infection National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is pyelonephritis? Pyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis: Kidney Infection National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is pyelonephritis? Pyelonephritis
Bulimia Nervosa. This reference summary explains bulimia. It covers symptoms and causes of the condition, as well as treatment options.
 Bulimia Nervosa Introduction Bulimia nervosa, or bulimia, is an eating disorder. A person with bulimia eats a large amount of food in a short amount of time. To prevent weight gain, the person then purges.
Bulimia Nervosa Introduction Bulimia nervosa, or bulimia, is an eating disorder. A person with bulimia eats a large amount of food in a short amount of time. To prevent weight gain, the person then purges.
Congestive Heart Failure Dogs
 Congestive Heart Failure Dogs Congestive heart failure (CHF) is caused by an abnormality in the structure or function of the heart. Because of this abnormality, the heart is unable to adequately pump blood
Congestive Heart Failure Dogs Congestive heart failure (CHF) is caused by an abnormality in the structure or function of the heart. Because of this abnormality, the heart is unable to adequately pump blood
MEDICATION GUIDE ACTOPLUS MET (ak-tō-plus-met) (pioglitazone hydrochloride and metformin hydrochloride) tablets
 MEDICATION GUIDE (ak-tō-plus-met) (pioglitazone hydrochloride and metformin hydrochloride) tablets Read this Medication Guide carefully before you start taking and each time you get a refill. There may
MEDICATION GUIDE (ak-tō-plus-met) (pioglitazone hydrochloride and metformin hydrochloride) tablets Read this Medication Guide carefully before you start taking and each time you get a refill. There may
LYMPHOMA IN DOGS. Diagnosis/Initial evaluation. Treatment and Prognosis
 LYMPHOMA IN DOGS Lymphoma is a relatively common cancer in dogs. It is a cancer of lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) and lymphoid tissues. Lymphoid tissue is normally present in many places in the
LYMPHOMA IN DOGS Lymphoma is a relatively common cancer in dogs. It is a cancer of lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) and lymphoid tissues. Lymphoid tissue is normally present in many places in the
Liver Function Essay
 Liver Function Essay Name: Quindoline Ntui Date: April 20, 2009 Professor: Dr. Danil Hammoudi Class: Anatomy and Physiology 2 Liver function The human body consist of many highly organize part working
Liver Function Essay Name: Quindoline Ntui Date: April 20, 2009 Professor: Dr. Danil Hammoudi Class: Anatomy and Physiology 2 Liver function The human body consist of many highly organize part working
TOTAL PROTEIN FIBRINOGEN
 UNIT: Proteins 16tproteins.wpd Task Determination of Total Protein, Albumin and Globulins Objectives Upon completion of this exercise, the student will be able to: 1. Explain the ratio of albumin and globulin
UNIT: Proteins 16tproteins.wpd Task Determination of Total Protein, Albumin and Globulins Objectives Upon completion of this exercise, the student will be able to: 1. Explain the ratio of albumin and globulin
Interpretation of Laboratory Values
 Interpretation of Laboratory Values Konrad J. Dias PT, DPT, CCS Overview Electrolyte imbalances Renal Function Tests Complete Blood Count Coagulation Profile Fluid imbalance Sodium Electrolyte Imbalances
Interpretation of Laboratory Values Konrad J. Dias PT, DPT, CCS Overview Electrolyte imbalances Renal Function Tests Complete Blood Count Coagulation Profile Fluid imbalance Sodium Electrolyte Imbalances
Haemodialysis Blood Results
 Haemodialysis Blood Results Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient information leaflets.htm Introduction
Haemodialysis Blood Results Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient information leaflets.htm Introduction
Water Homeostasis. Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.
 Water Homeostasis Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) 1. Water Homeostasis The body maintains a balance of water intake
Water Homeostasis Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) 1. Water Homeostasis The body maintains a balance of water intake
ACID- BASE and ELECTROLYTE BALANCE. MGHS School of EMT-Paramedic Program 2011
 ACID- BASE and ELECTROLYTE BALANCE MGHS School of EMT-Paramedic Program 2011 ACID- BASE BALANCE Ions balance themselves like a see-saw. Solutions turn into acids when concentration of hydrogen ions rises
ACID- BASE and ELECTROLYTE BALANCE MGHS School of EMT-Paramedic Program 2011 ACID- BASE BALANCE Ions balance themselves like a see-saw. Solutions turn into acids when concentration of hydrogen ions rises
EXECUTIVE BLOOD WORK PANEL
 EXECUTIVE BLOOD WORK PANEL Below is a list of all blood and urine testing done on the day of your Executive Medical. MALE Serum Glucose Random Serum Glucose Fasting Creatinine Uric Acid Sodium Potassium
EXECUTIVE BLOOD WORK PANEL Below is a list of all blood and urine testing done on the day of your Executive Medical. MALE Serum Glucose Random Serum Glucose Fasting Creatinine Uric Acid Sodium Potassium
What is the Sleeve Gastrectomy?
 What is the Sleeve Gastrectomy? The Sleeve Gastrectomy (also referred to as the Gastric Sleeve, Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy, Partial Gastrectomy, or Tube Gastrectomy) is a relatively new procedure for
What is the Sleeve Gastrectomy? The Sleeve Gastrectomy (also referred to as the Gastric Sleeve, Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy, Partial Gastrectomy, or Tube Gastrectomy) is a relatively new procedure for
2. What Should Advocates Know About Diabetes? O
 2. What Should Advocates Know About Diabetes? O ften a school district s failure to properly address the needs of a student with diabetes is due not to bad faith, but to ignorance or a lack of accurate
2. What Should Advocates Know About Diabetes? O ften a school district s failure to properly address the needs of a student with diabetes is due not to bad faith, but to ignorance or a lack of accurate
NHRMC General Surgery Specialists. Minimally Invasive Gastrointestinal Surgery Phone: 910-662-9300 Fax: 910-662-9303
 Minimally Invasive Gastrointestinal Surgery Phone: 910-662-9300 Fax: 910-662-9303 W. Borden Hooks III, MD 1725 New Hanover Medical Park Drive Wilmington, NC 28403 Thank you for choosing NHRMC General Surgery
Minimally Invasive Gastrointestinal Surgery Phone: 910-662-9300 Fax: 910-662-9303 W. Borden Hooks III, MD 1725 New Hanover Medical Park Drive Wilmington, NC 28403 Thank you for choosing NHRMC General Surgery
NUTRITION AND HEMODIALYSIS
 NUTRITION AND HEMODIALYSIS www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative
NUTRITION AND HEMODIALYSIS www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative
Less stress for you and your pet
 Less stress for you and your pet Canine hyperadrenocorticism Category: Canine Cushing s disease, Cushing s syndrome Affected Animals: Although dogs of almost every age have been reported to have Cushing
Less stress for you and your pet Canine hyperadrenocorticism Category: Canine Cushing s disease, Cushing s syndrome Affected Animals: Although dogs of almost every age have been reported to have Cushing
The Family Library. Understanding Diabetes
 The Family Library Understanding Diabetes What is Diabetes? Diabetes is caused when the body has a problem in making or using insulin. Insulin is a hormone secreted by the pancreas and is needed for the
The Family Library Understanding Diabetes What is Diabetes? Diabetes is caused when the body has a problem in making or using insulin. Insulin is a hormone secreted by the pancreas and is needed for the
The University of Hong Kong Department of Surgery Division of Esophageal and Upper Gastrointestinal Surgery
 Program Overview The University of Hong Kong Department of Surgery Division of Esophageal and Upper Gastrointestinal Surgery Weight Control and Metabolic Surgery Program The Weight Control and Metabolic
Program Overview The University of Hong Kong Department of Surgery Division of Esophageal and Upper Gastrointestinal Surgery Weight Control and Metabolic Surgery Program The Weight Control and Metabolic
WHAT IS DIABETES MELLITUS? CAUSES AND CONSEQUENCES. Living your life as normal as possible
 WHAT IS DIABETES MELLITUS? CAUSES AND CONSEQUENCES DEDBT01954 Lilly Deutschland GmbH Werner-Reimers-Straße 2-4 61352 Bad Homburg Living your life as normal as possible www.lilly-pharma.de www.lilly-diabetes.de
WHAT IS DIABETES MELLITUS? CAUSES AND CONSEQUENCES DEDBT01954 Lilly Deutschland GmbH Werner-Reimers-Straße 2-4 61352 Bad Homburg Living your life as normal as possible www.lilly-pharma.de www.lilly-diabetes.de
Eating Disorders. 1995-2012, The Patient Education Institute, Inc. www.x-plain.com mhf70101 Last reviewed: 06/29/2012 1
 Eating Disorders Introduction Eating disorders are illnesses that cause serious changes in a person s daily diet. This can include not eating enough food or overeating. Eating disorders affect about 70
Eating Disorders Introduction Eating disorders are illnesses that cause serious changes in a person s daily diet. This can include not eating enough food or overeating. Eating disorders affect about 70
HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE AND YOUR KIDNEYS
 HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE AND YOUR KIDNEYS www.kidney.org About the Information in this Booklet Did you know that the National Kidney (NKF) Foundation offers guidelines and commentaries that help your healthcare
HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE AND YOUR KIDNEYS www.kidney.org About the Information in this Booklet Did you know that the National Kidney (NKF) Foundation offers guidelines and commentaries that help your healthcare
Eating, pooping, and peeing THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Ingested food is not technically in the body until it is absorbed so it needs to be: Mechanically and chemically reduced Transported by the blood to the cells Large portions are not
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Ingested food is not technically in the body until it is absorbed so it needs to be: Mechanically and chemically reduced Transported by the blood to the cells Large portions are not
Chapter 25: Metabolism and Nutrition
 Chapter 25: Metabolism and Nutrition Chapter Objectives INTRODUCTION 1. Generalize the way in which nutrients are processed through the three major metabolic fates in order to perform various energetic
Chapter 25: Metabolism and Nutrition Chapter Objectives INTRODUCTION 1. Generalize the way in which nutrients are processed through the three major metabolic fates in order to perform various energetic
Hemodialysis: What You Need to Know
 Hemodialysis: What You Need to Know Healthy kidneys clean your blood and remove extra fluid in the form of urine. They also make hormones your body needs for some important functions. When kidney failure
Hemodialysis: What You Need to Know Healthy kidneys clean your blood and remove extra fluid in the form of urine. They also make hormones your body needs for some important functions. When kidney failure
Dehydration & Overhydration. Waseem Jerjes
 Dehydration & Overhydration Waseem Jerjes Dehydration 3 Major Types Isotonic - Fluid has the same osmolarity as plasma Hypotonic -Fluid has fewer solutes than plasma Hypertonic-Fluid has more solutes than
Dehydration & Overhydration Waseem Jerjes Dehydration 3 Major Types Isotonic - Fluid has the same osmolarity as plasma Hypotonic -Fluid has fewer solutes than plasma Hypertonic-Fluid has more solutes than
Diet for Kidney Stone Prevention
 Diet for Kidney Stone Prevention National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH How does diet affect the risk
Diet for Kidney Stone Prevention National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH How does diet affect the risk
FAILURE TO THRIVE What Is Failure to Thrive?
 FAILURE TO THRIVE The first few years of life are a time when most children gain weight and grow much more rapidly than they will later on. Sometimes, however, babies and children don't meet expected standards
FAILURE TO THRIVE The first few years of life are a time when most children gain weight and grow much more rapidly than they will later on. Sometimes, however, babies and children don't meet expected standards
Bile Duct Diseases and Problems
 Bile Duct Diseases and Problems Introduction A bile duct is a tube that carries bile between the liver and gallbladder and the intestine. Bile is a substance made by the liver that helps with digestion.
Bile Duct Diseases and Problems Introduction A bile duct is a tube that carries bile between the liver and gallbladder and the intestine. Bile is a substance made by the liver that helps with digestion.
Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease (FLUTD)
 Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease (FLUTD) VETERINARY GUIDE 2 What is FLUTD? FLUTD describes a collection of common conditions that affect the bladder and/or urethra the narrow tube that carries urine
Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease (FLUTD) VETERINARY GUIDE 2 What is FLUTD? FLUTD describes a collection of common conditions that affect the bladder and/or urethra the narrow tube that carries urine
Nutritional Support of the Burn Patient
 Nutritional Support of the Burn Patient Objectives To understand the principles of normal nutrient utilization and the abnormalities caused by burn injury To be able to assess nutrient needs To be able
Nutritional Support of the Burn Patient Objectives To understand the principles of normal nutrient utilization and the abnormalities caused by burn injury To be able to assess nutrient needs To be able
Hepatic Encephalopathy (Brain Disorder Secondary to Liver Disease) Basics
 Hepatic Encephalopathy (Brain Disorder Secondary to Liver Disease) Basics OVERVIEW Hepatic refers to the liver; encephalopathy is the medical term for any disorder of the brain Disorder affecting the central
Hepatic Encephalopathy (Brain Disorder Secondary to Liver Disease) Basics OVERVIEW Hepatic refers to the liver; encephalopathy is the medical term for any disorder of the brain Disorder affecting the central
QUALITY OF LIFE WITH DIABETES AND CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE
 QUALITY OF LIFE WITH DIABETES AND CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation's Kidney
QUALITY OF LIFE WITH DIABETES AND CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation's Kidney
Treatment Recommendations for CKD in Cats (2015)
 All treatments for chronic kidney disease (CKD) need to be tailored to the individual patient. The following recommendations are useful starting points for the majority of cats at each stage. Serial monitoring
All treatments for chronic kidney disease (CKD) need to be tailored to the individual patient. The following recommendations are useful starting points for the majority of cats at each stage. Serial monitoring
The Anorexic Cat For this reason, any cat that stops eating for any reason is considered an emergency situation.
 The Anorexic Cat Introduction Any cat that stops eating (anorexic) or begins to eat much less than their normal amount should be seen by a veterinarian right away. The primary reason why a cat stops eating
The Anorexic Cat Introduction Any cat that stops eating (anorexic) or begins to eat much less than their normal amount should be seen by a veterinarian right away. The primary reason why a cat stops eating
SEARCHING FOR A COMPLIMENT FOR CANCER Part 1 Nutrition and Cancer
 SEARCHING FOR A COMPLIMENT FOR CANCER Part 1 Nutrition and Cancer Donna M. Raditic DVM, DACVN, CVA Clinical Assistant Professor Integrative Medicine Nutrition Service The University of Tennessee College
SEARCHING FOR A COMPLIMENT FOR CANCER Part 1 Nutrition and Cancer Donna M. Raditic DVM, DACVN, CVA Clinical Assistant Professor Integrative Medicine Nutrition Service The University of Tennessee College
Problems of the Digestive System
 The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists f AQ FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS FAQ120 WOMEN S HEALTH Problems of the Digestive System What are some common digestive problems? What is constipation?
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists f AQ FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS FAQ120 WOMEN S HEALTH Problems of the Digestive System What are some common digestive problems? What is constipation?
Week 30. Water Balance and Minerals
 Week 30 Water Balance and Minerals Water: more vital to life than food involved in almost every body function is not stored--excreted daily largest single constituent of the human body, averaging 60% of
Week 30 Water Balance and Minerals Water: more vital to life than food involved in almost every body function is not stored--excreted daily largest single constituent of the human body, averaging 60% of
Assessment of Dietary Management of Patient during Dialysis
 Assessment of Dietary Management of Patient during Dialysis Shadia Mohamed 1, Amani Lafe Abdullah 2 1,2 University of Hail, Saudi Arabia Abstract: Inadequate dietary intake is a major determinant of malnutrition
Assessment of Dietary Management of Patient during Dialysis Shadia Mohamed 1, Amani Lafe Abdullah 2 1,2 University of Hail, Saudi Arabia Abstract: Inadequate dietary intake is a major determinant of malnutrition
X-Plain Diabetes - Introduction Reference Summary
 X-Plain Diabetes - Introduction Reference Summary Introduction Diabetes is a disease that affects millions of Americans every year. Your doctor may have informed you that you have diabetes. Although there
X-Plain Diabetes - Introduction Reference Summary Introduction Diabetes is a disease that affects millions of Americans every year. Your doctor may have informed you that you have diabetes. Although there
PHOSPHATE-SANDOZ Tablets (High dose phosphate supplement)
 1 PHOSPHATE-SANDOZ Tablets (High dose phosphate supplement) PHOSPHATE-SANDOZ PHOSPHATE-SANDOZ Tablets are a high dose phosphate supplement containing sodium phosphate monobasic. The CAS registry number
1 PHOSPHATE-SANDOZ Tablets (High dose phosphate supplement) PHOSPHATE-SANDOZ PHOSPHATE-SANDOZ Tablets are a high dose phosphate supplement containing sodium phosphate monobasic. The CAS registry number
NUTRITION OF THE BODY
 5 Training Objectives:! Knowledge of the most important function of nutrients! Description of both, mechanism and function of gluconeogenesis! Knowledge of the difference between essential and conditionally
5 Training Objectives:! Knowledge of the most important function of nutrients! Description of both, mechanism and function of gluconeogenesis! Knowledge of the difference between essential and conditionally
Introduction. Introduction Nutritional Requirements. Six Major Classes of Nutrients. Water 12/1/2011. Regional Hay School -- Bolivar, MO 1
 Cattle and Horse Nutrition Dona Goede Livestock Specialist Introduction Many health, reproductive and production problems can be prevented with good nutrition. Poor nutrition results in: Poor conception
Cattle and Horse Nutrition Dona Goede Livestock Specialist Introduction Many health, reproductive and production problems can be prevented with good nutrition. Poor nutrition results in: Poor conception
Vitreo-Retinal and Macular Degeneration Frequently Asked Questions
 Vitreo-Retinal and Macular Degeneration Frequently Asked Questions What is a Vitreo-Retinal specialist? Retinal specialists are eye physicians and surgeons who focus on diseases in the back of the eye
Vitreo-Retinal and Macular Degeneration Frequently Asked Questions What is a Vitreo-Retinal specialist? Retinal specialists are eye physicians and surgeons who focus on diseases in the back of the eye
Quality Measures for Long-stay Residents Percent of residents whose need for help with daily activities has increased.
 Quality Measures for Long-stay Residents Percent of residents whose need for help with daily activities has increased. This graph shows the percent of residents whose need for help doing basic daily tasks
Quality Measures for Long-stay Residents Percent of residents whose need for help with daily activities has increased. This graph shows the percent of residents whose need for help doing basic daily tasks
