Lab 2.5.1: Basic Switch Configuration
|
|
|
- Andra Watkins
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway PC1 NIC PC2 NIC S1 VLAN Learning Objectives Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to: Cable a network according to the topology diagram Clear an existing configuration on a switch Examine and verify the default configuration Create a basic switch configuration, including a name and an IP address Configure passwords to ensure that access to the CLI is secured Configure switch port speed and duplex properties for an interface Configure basic switch port security Manage the MAC address table Assign static MAC addresses Add and move hosts on a switch Scenario In this lab, you will examine and configure a standalone LAN switch. Although a switch performs basic functions in its default out-of-the-box condition, there are a number of parameters that a network administrator should modify to ensure a secure and optimized LAN. This lab introduces you to the basics of switch configuration. All contents are Copyright Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 1 of 14
2 Task 1: Cable, Erase, and Reload the Switch Step 1: Cable a network. Cable a network that is similar to the one in the topology diagram. Create a console connection to the switch. If necessary, refer to Lab on how to create a console connection. You can use any current switch in your lab as long as it has the required interfaces shown in the topology. The output shown in this lab is from a 2960 switch. If you use other switches, the switch outputs and interface descriptions may appear different. Note: PC2 is not initially connected to the switch. It is only used in Task 5. Step 2: Clear the configuration on the switch. Clear the configuration on the switch using the procedure in Appendix 1. Task 2: Verify the Default Switch Configuration Step 1: Enter privileged mode. You can access all the switch commands in privileged mode. However, because many of the privileged commands configure operating parameters, privileged access should be password-protected to prevent unauthorized use. You will set passwords in Task 3. The privileged EXEC command set includes those commands contained in user EXEC mode, as well as the configure command through which access to the remaining command modes are gained. Enter privileged EXEC mode by entering the enable command. Switch>enable Switch# Notice that the prompt changed in the configuration to reflect privileged EXEC mode. Step 2: Examine the current switch configuration. Examine the current running configuration file. Switch#show running-config How many Fast Ethernet interfaces does the switch have? How many Gigabit Ethernet interfaces does the switch have? What is the range of values shown for the vty lines? Examine the current contents of NVRAM: Switch#show startup-config startup-config is not present Why does the switch give this response? Examine the characteristics of the virtual interface VLAN1: Switch#show interface vlan1 All contents are Copyright Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 2 of 14
3 Is there an IP address set on the switch? What is the MAC address of this virtual switch interface? Is this interface up? Now view the IP properties of the interface: Switch#show ip interface vlan1 What output do you see? Step 3: Display Cisco IOS information. Examine the following version information that the switch reports. Switch#show version What is the Cisco IOS version that the switch is running? What is the system image filename? What is the base MAC address of this switch? Step 4: Examine the Fast Ethernet interfaces. Examine the default properties of the Fast Ethernet interface used by PC1. Switch#show interface fastethernet 0/18 Is the interface up or down? What event would make an interface go up? What is the MAC address of the interface? What is the speed and duplex setting of the interface? Step 5: Examine VLAN information. Examine the default VLAN settings of the switch. Switch#show vlan What is the name of VLAN 1? Which ports are in this VLAN? Is VLAN 1 active? What type of VLAN is the default VLAN? Step 6 Examine flash memory. Issue one of the following commands to examine the contents of the flash directory. Switch#dir flash: or Switch#show flash Which files or directories are found? All contents are Copyright Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 3 of 14
4 Files have a file extension, such as.bin, at the end of the filename. Directories do not have a file extension. To examine the files in a directory, issue the following command using the filename displayed in the output of the previous command: Switch#dir flash:c2960-lanbase-mz see3 The output should look similar to this: Directory of flash:/c2960-lanbase-mz see3/ 6 drwx 4480 Mar :04:42 +00:00 html 618 -rwx Mar :06:06 +00:00 c2960-lanbase-mz see3.bin 619 -rwx 457 Mar :06:06 +00:00 info bytes total ( bytes free) What is the name of the Cisco IOS image file? Step 7: Examine the startup configuration file. To view the contents of the startup configuration file, issue the show startup-config command in privileged EXEC mode. Switch#show startup-config startup-config is not present Why does this message appear? Let s make one configuration change to the switch and then save it. Type the following commands: Switch#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Switch(config)#hostname S1 S1(config)#exit S1# To save the contents of the running configuration file to non-volatile RAM (NVRAM), issue the the command copy running-config startup-config. Switch#copy running-config startup-config Destination filename [startup-config]? (enter) Building configuration... [OK] Note: This command is easier to enter by using the copy run start abbreviation. Now display the contents of NVRAM using the show startup-config command. S1#show startup-config Using 1170 out of bytes! version 12.2 no service pad service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password-encryption! hostname S1! <output omitted> All contents are Copyright Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 4 of 14
5 The current configuration has been written to NVRAM. Task 3: Create a Basic Switch Configuration Step 1: Assign a name to the switch. In the last step of the previous task, you configured the hostname. Here's a review of the commands used. S1#configure terminal S1(config)#hostname S1 S1(config)#exit Step 2: Set the access passwords. Enter config-line mode for the console. Set the login password to cisco. Also configure the vty lines 0 to 15 with the password cisco. S1#configure terminal Enter the configuration commands, one for each line. When you are finished, return to global configuration mode by entering the exit command or pressing Ctrl-Z. S1(config)#line console 0 S1(config-line)#password cisco S1(config-line)#login S1(config-line)#line vty 0 15 S1(config-line)#password cisco S1(config-line)#login S1(config-line)#exit Why is the login command required? Step 3. Set the command mode passwords. Set the enable secret password to class. This password protects access to privileged EXEC mode. S1(config)#enable secret class Step 4. Configure the Layer 3 address of the switch. Before you can manage S1 remotely from PC1, you need to assign the switch an IP address. The default configuration on the switch is to have the management of the switch controlled through VLAN 1. However, a best practice for basic switch configuration is to change the management VLAN to a VLAN other than VLAN 1. The implications and reasoning behind this action are explained in the next chapter. For management purposes, we will use VLAN 99. The selection of VLAN 99 is arbitrary and in no way implies you should always use VLAN 99. First, you will create the new VLAN 99 on the switch. Then you will set the IP address of the switch to with a subnet mask of on the internal virtual interface VLAN 99. S1(config)#vlan 99 S1(config-vlan)#exit S1(config)#interface vlan99 %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Vlan99, changed state to down S1(config-if)#ip address S1(config-if)#no shutdown All contents are Copyright Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 5 of 14
6 S1(config-if)#exit S1(config)# Notice that the VLAN 99 interface is in the down state even though you entered the command no shutdown. The interface is currently down because no switchports are assigned to VLAN 99. Assign all user ports to VLAN 99. S1#configure terminal S1(config)#interface range fa0/1-24 S1(config-if-range)#switchport access vlan 99 S1(config-if-range)#exit S1(config-if-range)# %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Vlan1, changed state to down %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Vlan99, changed state to up It is beyond the scope of this lab to fully explore VLANs. This subject is discussed in greater detail in the next chapter. However, to establish connectivity between the host and the switch, the ports used by the host must be in the same VLAN as the switch. Notice in the above output that VLAN 1 interface goes down because none of the ports are assigned to VLAN 1. After a few seconds, VLAN 99 will come up because at least one port is now assigned to VLAN 99. Step 5: Set the switch default gateway. S1 is a layer 2 switch, so it makes forwarding decisions based on the Layer 2 header. If multiple networks are connected to a switch, you need to specify how the switch forwards the internetwork frames, because the path must be determined at Layer three. This is done by specifying a default gateway address that points to a router or Layer 3 switch. Although this activity does not include an external IP gateway, assume that you will eventually connect the LAN to a router for external access. Assuming that the LAN interface on the router is , set the default gateway for the switch. S1(config)#ip default-gateway S1(config)#exit Step 6: Verify the management LANs settings. Verify the interface settings on VLAN 99. S1#show interface vlan 99 Vlan99 is up, line protocol is up Hardware is EtherSVI, address is 001b ec1 (bia 001b ec1) Internet address is /24 MTU 1500 bytes, BW Kbit, DLY 10 usec, reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255 Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00 Last input 00:00:06, output 00:03:23, output hang never Last clearing of "show interface" counters never Input queue: 0/75/0/0 (size/max/drops/flushes); Total output drops: 0 Queueing strategy: fifo Output queue: 0/40 (size/max) 5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec 5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec 4 packets input, 1368 bytes, 0 no buffer Received 0 broadcasts (0 IP multicast) 0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles 0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored 1 packets output, 64 bytes, 0 underruns 0 output errors, 0 interface resets 0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out All contents are Copyright Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 6 of 14
7 What is the bandwidth on this interface? What are the VLAN states? VLAN1 is Line protocol is What is the queuing strategy? Step 7: Configure the IP address and default gateway for PC1. Set the IP address of PC1 to , with a subnet mask of Configure a default gateway of (If needed, refer to Lab to configure the PC NIC.) Step 8: Verify connectivity. To verify the host and switch are correctly configured, ping the IP address of the switch ( ) from PC1. Was the ping successful? If not, troubleshoot the switch and host configuration. Note that this may take a couple of tries for the pings to succeed. Step 9: Configure the port speed and duplex settings for a Fast Ethernet interface. Configure the duplex and speed settings on Fast Ethernet 0/18. Use the end command to return to privileged EXEC mode when finished. S1#configure terminal S1(config)#interface fastethernet 0/18 S1(config-if)#speed 100 S1(config-if)#duplex full S1(config-if)#end %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/18, changed state to down %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Vlan99, changed state to down %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface FastEthernet0/18, changed state to down %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface FastEthernet0/18, changed state to up %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/18, changed state to up %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Vlan99, changed state to up The line protocol for both interface FastEthernet 0/18 and interface VLAN 99 will temporarily go down. The default on the Ethernet interface of the switch is auto-sensing, so it automatically negotiates optimal settings. You should set duplex and speed manually only if a port must operate at a certain speed and duplex mode. Manually configuring ports can lead to duplex mismatches, which can significantly degrade performance. Verify the new duplex and speed settings on the Fast Ethernet interface. S1#show interface fastethernet 0/18 FastEthernet0/18 is up, line protocol is up (connected) Hardware is Fast Ethernet, address is 001b e92 (bia 001b e92) MTU 1500 bytes, BW Kbit, DLY 100 usec, reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255 Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set Keepalive set (10 sec) Full-duplex, 100Mb/s, media type is 10/100BaseTX input flow-control is off, output flow-control is unsupported ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00 Last input never, output 00:00:01, output hang never Last clearing of "show interface" counters never Input queue: 0/75/0/0 (size/max/drops/flushes); Total output drops: 0 All contents are Copyright Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 7 of 14
8 Queueing strategy: fifo Output queue: 0/40 (size/max) 5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec 5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec 265 packets input, bytes, 0 no buffer Received 265 broadcasts (0 multicast) 0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles 0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored 0 watchdog, 32 multicast, 0 pause input 0 input packets with dribble condition detected 4109 packets output, bytes, 0 underruns 0 output errors, 0 collisions, 1 interface resets 0 babbles, 0 late collision, 0 deferred 0 lost carrier, 0 no carrier, 0 PAUSE output 0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out Step 10: Save the configuration. You have completed the basic configuration of the switch. Now back up the running configuration file to NVRAM to ensure that the changes made will not be lost if the system is rebooted or loses power. S1#copy running-config startup-config Destination filename [startup-config]?[enter] Building configuration... [OK] S1# Step 11: Examine the startup configuration file. To see the configuration that is stored in NVRAM, issue the show startup-config command from privileged EXEC mode. S1#show startup-config Are all the changes that were entered recorded in the file? Task 4: Managing the MAC Address Table Step 1: Record the MAC addresses of the hosts. Determine and record the Layer 2 (physical) addresses of the PC network interface cards using the following commands: Start > Run > cmd > ipconfig /all PC1: PC2: Step 2: Determine the MAC addresses that the switch has learned. Display the MAC addresses using the show mac-address-table command in privileged EXEC mode. S1#show mac-address-table How many dynamic addresses are there? How many MAC addresses are there in total? Do the dynamic MAC addresses match the host MAC addresses? All contents are Copyright Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 8 of 14
9 Step 3: List the show mac-address-table options. S1#show mac-address-table? How many options are available for the show mac-address-table command? Show only the MAC addresses from the table that were learned dynamically. S1#show mac-address-table address <PC1 MAC here> How many dynamic addresses are there? Step 4: Clear the MAC address table. To remove the existing MAC addresses, use the clear mac-address-table command from privileged EXEC mode. S1#clear mac-address-table dynamic Step 5: Verify the results. Verify that the MAC address table was cleared. S1#show mac-address-table How many static MAC addresses are there? How many dynamic addresses are there? Step 6: Examine the MAC table again. More than likely, an application running on your PC1 has already sent a frame out the NIC to S1. Look at the MAC address table again in privileged EXEC mode to see if S1 has relearned the MAC address for PC1 S1#show mac-address-table How many dynamic addresses are there? Why did this change from the last display? If S1 has not yet relearned the MAC address for PC1, ping the VLAN 99 IP address of the switch from PC1 and then repeat Step 6. Step 7: Set up a static MAC address. To specify which ports a host can connect to, one option is to create a static mapping of the host MAC address to a port. Set up a static MAC address on Fast Ethernet interface 0/18 using the address that was recorded for PC1 in Step 1 of this task. The MAC address 00e is used as an example only. You must use the MAC address of your PC1, which is different than the one given here as an example. S1(config)#mac-address-table static 00e interface fastethernet 0/18 vlan 99 All contents are Copyright Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 9 of 14
10 Step 8: Verify the results. Verify the MAC address table entries. S1#show mac-address-table How many total MAC addresses are there? How many static addresses are there? Step 10: Remove the static MAC entry. To complete the next task, it will be necessary to remove the static MAC address table entry. Enter configuration mode and remove the command by putting a no in front of the command string. Note: The MAC address 00e is used in the example only. Use the MAC address for your PC1. S1(config)#no mac-address-table static 00e interface fastethernet 0/18 vlan 99 Step 10: Verify the results. Verify that the static MAC address has been cleared. S1#show mac-address-table How many total static MAC addresses are there? Task 5 Configuring Port Security Step 1: Configure a second host. A second host is needed for this task. Set the IP address of PC2 to , with a subnet mask of and a default gateway of Do not connect this PC to the switch yet. Step 2: Verify connectivity. Verify that PC1 and the switch are still correctly configured by pinging the VLAN 99 IP address of the switch from the host. Were the pings successful? If the answer is no, troubleshoot the host and switch configurations. Step 3: Copy the host MAC addresses. Write down the MAC addresses from Task 4, Step 1. PC1 PC2 Step 4: Determine which MAC addresses that the switch has learned. Display the learned MAC addresses using the show mac-address-table command in privileged EXEC mode. S1#show mac-address-table All contents are Copyright Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 10 of 14
11 How many dynamic addresses are there? Do the MAC addresses match the host MAC addresses? Step 5: List the port security options. Explore the options for setting port security on interface Fast Ethernet 0/18. S1# configure terminal S1(config)#interface fastethernet 0/18 S1(config-if)#switchport port-security? aging Port-security aging commands mac-address Secure mac address maximum Max secure addresses violation Security violation mode <cr> S1(config-if)#switchport port-security Step 6: Configure port security on an access port. Configure switch port Fast Ethernet 0/18 to accept only two devices, to learn the MAC addresses of those devices dynamically, and to block traffic from invalid hosts if a violation occurs. S1(config-if)#switchport mode access S1(config-if)#switchport port-security S1(config-if)#switchport port-security maximum 2 S1(config-if)#switchport port-security mac-address sticky S1(config-if)#switchport port-security violation protect S1(config-if)#exit Step 7: Verify the results. Show the port security settings. S1#show port-security How many secure addresses are allowed on Fast Ethernet 0/18? What is the security action for this port? Step 8: Examine the running configuration file. S1#show running-config Are there statements listed that directly reflect the security implementation of the running configuration? Step 9: Modify the post security settings on a port. On interface Fast Ethernet 0/18, change the port security maximum MAC address count to 1 and to shut down if a violation occurs. S1(config-if)#switchport port-security maximum 1 S1(config-if)#switchport port-security violation shutdown Step 10: Verify the results. Show the port security settings. All contents are Copyright Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 11 of 14
12 S1#show port-security Have the port security settings changed to reflect the modifications in Step 9? Ping the VLAN 99 address of the switch from PC1 to verify connectivity and to refresh the MAC address table. You should now see the MAC address for PC1 stuck to the running configuration. S1#show run Building configuration... <output omitted>! interface FastEthernet0/18 switchport access vlan 99 switchport mode access switchport port-security switchport port-security mac-address sticky switchport port-security mac-address sticky 00e speed 100 duplex full! <output omitted> Step 11: Introduce a rogue host. Disconnect PC1 and connect PC2 to port Fast Ethernet 0/18. Ping the VLAN 99 address from the new host. Wait for the amber link light to turn green. Once it turns green, it should almost immediately turn off. Record any observations: Step 12: Show port configuration information. To see the configuration information for just Fast Ethernet port 0/18, issue the following command in privileged EXEC mode: S1#show interface fastethernet 0/18 What is the state of this interface? Fast Ethernet0/18 is Line protocol is Step 13: Reactivate the port. If a security violation occurs and the port is shut down, you can use the no shutdown command to reactivate it. However, as long as the rogue host is attached to Fast Ethernet 0/18, any traffic from the host disables the port. Reconnect PC1 to Fast Ethernet 0/18, and enter the following commands on the switch: S1# configure terminal S1(config)#interface fastethernet 0/18 S1(config-if)# no shutdown S1(config-if)#exit Note: Some IOS version may require a manual shutdown command before entering the no shutdown command. All contents are Copyright Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 12 of 14
13 Step 14: Cleanup Unless directed otherwise, clear the configuration on the switches, turn off the power to the host computer and switches, and remove and store the cables. Appendix 1 Erasing and Reloading the Switch For the majority of the labs in Exploration 3, it is necessary to start with an unconfigured switch. Using a switch with an existing configuration may produce unpredictable results. These instructions show you how to prepare the switch prior to starting the lab. These instructions are for the 2960 switch; however, the procedure for the 2900 and 2950 switches is the same. Step 1: Enter privileged EXEC mode by typing the enable command. If prompted for a password, enter class. If that does not work, ask the instructor. Switch>enable Step 2: Remove the VLAN database information file. Switch#delete flash:vlan.dat Delete filename [vlan.dat]?[enter] Delete flash:vlan.dat? [confirm] [Enter] If there is no VLAN file, this message is displayed: %Error deleting flash:vlan.dat (No such file or directory) Step 3: Remove the switch startup configuration file from NVRAM. Switch#erase startup-config The responding line prompt will be: Erasing the nvram filesystem will remove all files! Continue? [confirm] Press Enter to confirm. The response should be: Erase of nvram: complete Step 4: Check that the VLAN information was deleted. Verify that the VLAN configuration was deleted in Step 2 using the show vlan command. If the VLAN information was successfully deleted in Step 2, go to Step 5 and restart the switch using the reload command. If previous VLAN configuration information is still present (other than the default management VLAN 1), you must power-cycle the switch (hardware restart ) instead of issuing the reload command. To powercycle the switch, remove the power cord from the back of the switch or unplug it, and then plug it back in. Step 5: Restart the software. Note: This step is not necessary if the switch was restarted using the power-cycle method. At the privileged EXEC mode prompt, enter the reload command. Switch(config)#reload The responding line prompt will be: All contents are Copyright Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 13 of 14
14 System configuration has been modified. Save? [yes/no]: Type n and then press Enter. The responding line prompt will be: Proceed with reload? [confirm] [Enter] The first line of the response will be: Reload requested by console. After the switch has reloaded, the line prompt will be: Would you like to enter the initial configuration dialog? [yes/no]: Type n and then press Enter. The responding line prompt will be: Press RETURN to get started! [Enter] All contents are Copyright Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 14 of 14
Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI
 Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Serial 0/0/0 (DCE) 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 FastEthernet 0/0 172.16.0.1 255.255.0.0
Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Serial 0/0/0 (DCE) 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 FastEthernet 0/0 172.16.0.1 255.255.0.0
Lab 6.2.3 Managing the MAC Address Table
 Lab 6.2.3 Managing the MAC Address Table Objective Create a basic switch configuration. Manage the switch MAC table. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in the diagram. The configuration
Lab 6.2.3 Managing the MAC Address Table Objective Create a basic switch configuration. Manage the switch MAC table. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in the diagram. The configuration
Configuring Link Aggregation
 10 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure link aggregation for the ML-Series cards, both EtherChannel and packet-over-sonet/sdh (POS) channel. For additional information about the Cisco IOS commands
10 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure link aggregation for the ML-Series cards, both EtherChannel and packet-over-sonet/sdh (POS) channel. For additional information about the Cisco IOS commands
Lab 5.5.4 Configuring the Cisco 2960 Switch
 Lab 5.5.4 Configuring the Cisco 2960 Switch Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port S1 CustomerSwitch VLAN 1 192.168.1.5 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 N/A R1 CustomerRouter
Lab 5.5.4 Configuring the Cisco 2960 Switch Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port S1 CustomerSwitch VLAN 1 192.168.1.5 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 N/A R1 CustomerRouter
Lab 3.5.1: Basic VLAN Configuration (Instructor Version)
 (Instructor Version) Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0
(Instructor Version) Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0
Configuring the Switch for the Firewall Services Module
 CHAPTER 2 Configuring the Switch for the Firewall Services Module This chapter describes how to configure the Catalyst 6500 series switch or the Cisco 7600 series router for use with the FWSM. Before completing
CHAPTER 2 Configuring the Switch for the Firewall Services Module This chapter describes how to configure the Catalyst 6500 series switch or the Cisco 7600 series router for use with the FWSM. Before completing
Lab - Using IOS CLI with Switch MAC Address Tables
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12
Configuring InterVLAN Routing and ISL/802.1Q Trunking on Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL/2940/2950/2970 Series Switches Using an External Router
 Configuring InterVLAN Routing and ISL/802.1Q Trunking on Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL/2940/2950/2970 Series Switches Using an External Router Document ID: 14976 Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites
Configuring InterVLAN Routing and ISL/802.1Q Trunking on Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL/2940/2950/2970 Series Switches Using an External Router Document ID: 14976 Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites
Lab 1.2.3 Review of Basic Router Configuration with RIP. Objective. Background / Preparation. General Configuration Tips
 Lab 1.2.3 Review of Basic Router Configuration with RIP Objective Cable and configure workstations and routers Setup IP addressing scheme using Class B networks Configure Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
Lab 1.2.3 Review of Basic Router Configuration with RIP Objective Cable and configure workstations and routers Setup IP addressing scheme using Class B networks Configure Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths
 Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths Objective Configure Load balance across multiple paths. Observe the load balancing process. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in the
Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths Objective Configure Load balance across multiple paths. Observe the load balancing process. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in the
Lab 5.3.9b Managing Router Configuration Files Using TFTP
 Lab 5.3.9b Managing Router Configuration Files Using TFTP Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Download and install TFTP server software.
Lab 5.3.9b Managing Router Configuration Files Using TFTP Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Download and install TFTP server software.
Lab 4.2.4 Advanced Telnet Operations
 Lab 4.2.4 Advanced Telnet Operations Objective Use the telnet command to remotely access other routers. Verify that the application layer between the source and the destination is working properly. Suspend
Lab 4.2.4 Advanced Telnet Operations Objective Use the telnet command to remotely access other routers. Verify that the application layer between the source and the destination is working properly. Suspend
3.1 Connecting to a Router and Basic Configuration
 3.1 Connecting to a Router and Basic Configuration Objective This lab will focus on the ability to connect a PC to a router in order to establish a console session and observe the user interface. A console
3.1 Connecting to a Router and Basic Configuration Objective This lab will focus on the ability to connect a PC to a router in order to establish a console session and observe the user interface. A console
Procedure: You can find the problem sheet on Drive D: of the lab PCs. Part 1: Router & Switch
 University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Computer Engineering Department Computer Networks Laboratory 907528 Lab. 2 Network Devices & Packet Tracer Objectives 1. To become familiar with
University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Computer Engineering Department Computer Networks Laboratory 907528 Lab. 2 Network Devices & Packet Tracer Objectives 1. To become familiar with
Course "Netzwerke" LAB 2 Basic Router Configuration
 Course "Netzwerke" LAB 2 Basic Router Configuration Learning Objectives Review of previously learned skills. Basic IOS Command Line Interface operation. Basic Router configuration. Verification and testing
Course "Netzwerke" LAB 2 Basic Router Configuration Learning Objectives Review of previously learned skills. Basic IOS Command Line Interface operation. Basic Router configuration. Verification and testing
Connect the Host to attach to Fast Ethernet switch port Fa0/2. Configure the host as shown in the topology diagram above.
 Lab 1.2.2 Capturing and Analyzing Network Traffic Host Name IP Address Fa0/0 Subnet Mask IP Address S0/0/0 Subnet Mask Default Gateway RouterA 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 192.168.1.1 (DCE) 255.255.255.0 N/A
Lab 1.2.2 Capturing and Analyzing Network Traffic Host Name IP Address Fa0/0 Subnet Mask IP Address S0/0/0 Subnet Mask Default Gateway RouterA 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 192.168.1.1 (DCE) 255.255.255.0 N/A
Lab 4.1.4 Creating a Network Map using CDP Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 4.1.4 Creating a Network Map using CDP Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) commands to get information about neighboring network devices. Background/Preparation CDP
Lab 4.1.4 Creating a Network Map using CDP Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) commands to get information about neighboring network devices. Background/Preparation CDP
Chapter 2 Reading Organizer
 Chapter 2 Reading Organizer After completion of this chapter, you should be able to: Explain the advantages and disadvantages of static routing Configure initial settings on a Cisco switch Configure switch
Chapter 2 Reading Organizer After completion of this chapter, you should be able to: Explain the advantages and disadvantages of static routing Configure initial settings on a Cisco switch Configure switch
How To Configure A Cisco Router With A Cio Router
 CHAPTER 1 This chapter provides procedures for configuring the basic parameters of your Cisco router, including global parameter settings, routing protocols, interfaces, and command-line access. It also
CHAPTER 1 This chapter provides procedures for configuring the basic parameters of your Cisco router, including global parameter settings, routing protocols, interfaces, and command-line access. It also
Lab 8.4.3a Managing Cisco IOS Images with TFTP
 Lab 8.4.3a Managing Cisco IOS Images with TFTP Host Device Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Analyze the Cisco IOS image and router flash memory.
Lab 8.4.3a Managing Cisco IOS Images with TFTP Host Device Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Analyze the Cisco IOS image and router flash memory.
Objectives. Router as a Computer. Router components and their functions. Router components and their functions
 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public Objectives Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1 Identify a router as a computer with an OS and
2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public Objectives Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1 Identify a router as a computer with an OS and
Configuring a Leased Line
 CHAPTER 4 Configuring a Leased Line The configuration in this chapter describes how to configure a Cisco 1700 router for IP and IPX over a synchronous serial line. Before You Begin The configuration in
CHAPTER 4 Configuring a Leased Line The configuration in this chapter describes how to configure a Cisco 1700 router for IP and IPX over a synchronous serial line. Before You Begin The configuration in
Note: This case study utilizes Packet Tracer. Please see the Chapter 5 Packet Tracer file located in Supplemental Materials.
 Note: This case study utilizes Packet Tracer. Please see the Chapter 5 Packet Tracer file located in Supplemental Materials. CHAPTER 5 OBJECTIVES Configure a router with an initial configuration. Use the
Note: This case study utilizes Packet Tracer. Please see the Chapter 5 Packet Tracer file located in Supplemental Materials. CHAPTER 5 OBJECTIVES Configure a router with an initial configuration. Use the
Lab 2.3.2 Configuring OSPF with Loopback Addresses
 Lab 2.3.2 Configuring OSPF with Loopback Addresses Objective Configure routers with a Class C IP addressing scheme. Observe the election process for designated routers (DR) and backup designated routers
Lab 2.3.2 Configuring OSPF with Loopback Addresses Objective Configure routers with a Class C IP addressing scheme. Observe the election process for designated routers (DR) and backup designated routers
Lab 3.1.2 Creating a Logical Network Diagram
 Lab 3.1.2 Creating a Logical Network Diagram Objectives Use router and switch commands to obtain information about an existing network. Use Cisco Network Assistant to obtain information about an existing
Lab 3.1.2 Creating a Logical Network Diagram Objectives Use router and switch commands to obtain information about an existing network. Use Cisco Network Assistant to obtain information about an existing
Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths Instructor Version 2500 Objective onfigure Load balance across multiple paths. Observe the load balancing process. Background/Preparation able a network similar
Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths Instructor Version 2500 Objective onfigure Load balance across multiple paths. Observe the load balancing process. Background/Preparation able a network similar
- Switch Port Configuration -
 1 Cisco Operating Systems - Switch Port Configuration - Cisco offers two brands of network switches: Catalyst Cisco s flagship switching platform, with a large selection of models spanning access, distribution,
1 Cisco Operating Systems - Switch Port Configuration - Cisco offers two brands of network switches: Catalyst Cisco s flagship switching platform, with a large selection of models spanning access, distribution,
Skills Assessment Student Training Exam
 Skills Assessment Student Training Exam Topology Assessment Objectives Part 1: Initialize Devices (8 points, 5 minutes) Part 2: Configure Device Basic Settings (28 points, 30 minutes) Part 3: Configure
Skills Assessment Student Training Exam Topology Assessment Objectives Part 1: Initialize Devices (8 points, 5 minutes) Part 2: Configure Device Basic Settings (28 points, 30 minutes) Part 3: Configure
Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI
 Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP address Subnet mask R1 R1 Serial 0/0/0 (DCE) 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 FastEthernet 0/0 172.16.0.1 255.255.0.0
Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP address Subnet mask R1 R1 Serial 0/0/0 (DCE) 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 FastEthernet 0/0 172.16.0.1 255.255.0.0
Lab 5.3.7 Configuring DHCP with SDM and the Cisco IOS CLI
 Lab 5.3.7 Configuring DHCP with SDM and the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 Customer Serial 0/0/1 (DTE) 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 Fast Ethernet 0/0 192.168.1.1
Lab 5.3.7 Configuring DHCP with SDM and the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 Customer Serial 0/0/1 (DTE) 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 Fast Ethernet 0/0 192.168.1.1
section examines how to configure leased lines between two routers using HDLC and PPP.
 4357ix.fm Page 620 Thursday, August 25, 2011 11:22 AM This chapter covers the following subjects: Configuring Point-to-Point WANs: This section examines how to configure leased lines between two routers
4357ix.fm Page 620 Thursday, August 25, 2011 11:22 AM This chapter covers the following subjects: Configuring Point-to-Point WANs: This section examines how to configure leased lines between two routers
CCNA Exploration 4.0.5.0 Routing Protocols and Concepts Student Lab Manual
 4.0.5.0 Routing Protocols and Concepts Student Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution
4.0.5.0 Routing Protocols and Concepts Student Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution
Lab 3 Routing Information Protocol (RIPv1) on a Cisco Router Network
 Lab 3 Routing Information Protocol (RIPv1) on a Cisco Router Network CMPE 150 Fall 2005 Introduction Today you are going to be thrown into using Cisco s Internetwork Operating System (IOS) to configure
Lab 3 Routing Information Protocol (RIPv1) on a Cisco Router Network CMPE 150 Fall 2005 Introduction Today you are going to be thrown into using Cisco s Internetwork Operating System (IOS) to configure
Configuring the Switch with the CLI-Based Setup Program
 APPENDIX D Configuring the Switch with the CLI-Based Setup Program This appendix provides a command-line interface (CLI)-based setup procedure for a standalone switch. For product overview information,
APPENDIX D Configuring the Switch with the CLI-Based Setup Program This appendix provides a command-line interface (CLI)-based setup procedure for a standalone switch. For product overview information,
Lab 2 - Basic Router Configuration
 CS326 Fall 2001 Room: PAI 5.48 Name: Lab 2 - Basic Router Configuration In this lab you will learn: the various configuration modes of Cisco 2621 routers how to set up IP addresses for such routers how
CS326 Fall 2001 Room: PAI 5.48 Name: Lab 2 - Basic Router Configuration In this lab you will learn: the various configuration modes of Cisco 2621 routers how to set up IP addresses for such routers how
Configuring Port Security
 32 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure port security on Catalyst 4500 series switches. It provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. Note For complete syntax and usage information
32 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure port security on Catalyst 4500 series switches. It provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. Note For complete syntax and usage information
Basic Wireless Configuration
 Basic Wireless Configuration Topology Diagram Learning Objectives Configure options in the Linksys Setup tab. Configure options in the Linksys Wireless tab. Configure options in the Linksys Administration
Basic Wireless Configuration Topology Diagram Learning Objectives Configure options in the Linksys Setup tab. Configure options in the Linksys Wireless tab. Configure options in the Linksys Administration
Lab: Basic Router Configuration
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Def. Gateway R1 Fa0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R2 Fa0/0 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Def. Gateway R1 Fa0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R2 Fa0/0 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Configuring Port Security
 CHAPTER 62 This chapter describes how to configure the port security feature. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, see the Cisco IOS Master List, at this URL:
CHAPTER 62 This chapter describes how to configure the port security feature. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, see the Cisco IOS Master List, at this URL:
LAB Configuring NAT. Objective. Background/Preparation
 LAB Configuring NAT Objective Configure a router to use network address translation (NAT) to convert internal IP addresses, typically private addresses, into outside public addresses. Configure static
LAB Configuring NAT Objective Configure a router to use network address translation (NAT) to convert internal IP addresses, typically private addresses, into outside public addresses. Configure static
APOSTILA DE REDES DE COMPUTADORES PARTE VI SWITCH
 APOSTILA DE REDES DE COMPUTADORES PARTE VI SWITCH 1 1. Criando um Banner de Login REDE DE COMPUTADORES VI SALESIANO#conf t SALESIANO(config)#banner motd c Enter TEXT message. End with the character 'c'.
APOSTILA DE REDES DE COMPUTADORES PARTE VI SWITCH 1 1. Criando um Banner de Login REDE DE COMPUTADORES VI SALESIANO#conf t SALESIANO(config)#banner motd c Enter TEXT message. End with the character 'c'.
Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding. Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1
 Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1 1 1 Objectives Identify a router as a computer with an OS and hardware designed for the routing process. Demonstrate
Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1 1 1 Objectives Identify a router as a computer with an OS and hardware designed for the routing process. Demonstrate
CISCO ROUTERLAR İLE ISDN BRI DATA HABERLEŞMESİ UYGULAMASI
 CISCO ROUTERLAR İLE ISDN BRI DATA HABERLEŞMESİ UYGULAMASI Gökhan AKIN İTÜ 2003 TOPOLOJİ: İSTENENLER: 1. Topolojiyi Legacy DDR tekniği ile kurunuz. 2. Aynõ Topolojiyi Dialer Profile tekniğini kullanarak
CISCO ROUTERLAR İLE ISDN BRI DATA HABERLEŞMESİ UYGULAMASI Gökhan AKIN İTÜ 2003 TOPOLOJİ: İSTENENLER: 1. Topolojiyi Legacy DDR tekniği ile kurunuz. 2. Aynõ Topolojiyi Dialer Profile tekniğini kullanarak
Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, Configuring EtherChannel Instructor Version
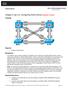 Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, Configuring EtherChannel Instructor Version Topology Objective Background Configure EtherChannel. Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer switches are Catalyst
Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, Configuring EtherChannel Instructor Version Topology Objective Background Configure EtherChannel. Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer switches are Catalyst
Router Lab Reference Guide
 Router Lab Reference Guide 1 PURPOSE AND GOALS The routing lab allows testing different IP-related protocols and solutions in a close to live environment. You can learn how to configure Cisco routers and
Router Lab Reference Guide 1 PURPOSE AND GOALS The routing lab allows testing different IP-related protocols and solutions in a close to live environment. You can learn how to configure Cisco routers and
Applicazioni Telematiche
 Angelo Coiro Laboratorio Applicazioni Telematiche L emulatore Packet Tracer Packet Tracer Cisco Packet Tracer is an academic software that allows to emulate Cisco devices Packet Tracer can be used for
Angelo Coiro Laboratorio Applicazioni Telematiche L emulatore Packet Tracer Packet Tracer Cisco Packet Tracer is an academic software that allows to emulate Cisco devices Packet Tracer can be used for
Lab 4.5.2 Diagramming Intranet Traffic Flows
 Lab 4.5.2 Diagramming Intranet Traffic Flows Objective Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Business Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 FC-CPE-1 Fa0/1 172.17.0.1 Fa0/0 10.0.0.1
Lab 4.5.2 Diagramming Intranet Traffic Flows Objective Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Business Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 FC-CPE-1 Fa0/1 172.17.0.1 Fa0/0 10.0.0.1
Chapter 8 Lab B: Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client
 Chapter 8 Lab B: Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client Topology Note: ISR G2 devices have Gigabit Ethernet interfaces instead of FastEthernet Interfaces. All contents are Copyright 1992 2012
Chapter 8 Lab B: Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client Topology Note: ISR G2 devices have Gigabit Ethernet interfaces instead of FastEthernet Interfaces. All contents are Copyright 1992 2012
Lab 5.3.8 Configuring PAT with SDM and Static NAT using Cisco IOS Commands
 Lab 5.3.8 Configuring PAT with SDM and Static NAT using Cisco IOS Commands Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 CustomerRouter Serial 0/0/0 (DTE) 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 Fast Ethernet
Lab 5.3.8 Configuring PAT with SDM and Static NAT using Cisco IOS Commands Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 CustomerRouter Serial 0/0/0 (DTE) 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 Fast Ethernet
Lab 3.10.2 Use Network Inspector to Observe STP Behavior
 Lab 3.10.2 Use Network Inspector to Observe STP Behavior Objective The purpose of this lab is to observe STP behavior with the Network Inspector switch trace feature. Scenario A new switched network has
Lab 3.10.2 Use Network Inspector to Observe STP Behavior Objective The purpose of this lab is to observe STP behavior with the Network Inspector switch trace feature. Scenario A new switched network has
Objectives Understand Cisco IOS system architecture components. Work with the Cisco IOS Command Line Interface (CLI) and common commands.
 Objectives Understand Cisco IOS system architecture components. Work with the Cisco IOS Command Line Interface (CLI) and common commands. Learn about Cisco IOS troubleshooting techniques. Understand upgrading
Objectives Understand Cisco IOS system architecture components. Work with the Cisco IOS Command Line Interface (CLI) and common commands. Learn about Cisco IOS troubleshooting techniques. Understand upgrading
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and
 This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNP: Optimizing
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNP: Optimizing
PA-MC-T3 Multi-Channel T3 Synchronous Serial Port Adapter Enhancement
 PA-MC-T3 Multi-Channel T3 Synchronous Serial Port Adapter Enhancement This feature module describes the PA-MC-T3 Multi-Channel T3 port adapter (PA-MC-T3 [=]), which can now be configured as either customer
PA-MC-T3 Multi-Channel T3 Synchronous Serial Port Adapter Enhancement This feature module describes the PA-MC-T3 Multi-Channel T3 port adapter (PA-MC-T3 [=]), which can now be configured as either customer
ICND1-100-101 IOS CLI Study Guide (CCENT)
 ICND1-100-101 IOS CLI Study Guide (CCENT) Hostname: 2. hostname SW1 SWITCH CONFIGURATION Mgmt IP: 2. interface vlan 1 3. ip address 10.0.0.2 4. no shut Gateway: 2. ip default-gateway 10.0.0.1 Local User/Pwd:
ICND1-100-101 IOS CLI Study Guide (CCENT) Hostname: 2. hostname SW1 SWITCH CONFIGURATION Mgmt IP: 2. interface vlan 1 3. ip address 10.0.0.2 4. no shut Gateway: 2. ip default-gateway 10.0.0.1 Local User/Pwd:
Lab 11.5.6.1 Configure Syslog on AP
 Lab 11.5.6.1 Configure Syslog on AP Estimated Time: 25 minutes Number of Team Members: Students will work in teams of two. Objective In this lab, students will configure and use syslog logging to monitor
Lab 11.5.6.1 Configure Syslog on AP Estimated Time: 25 minutes Number of Team Members: Students will work in teams of two. Objective In this lab, students will configure and use syslog logging to monitor
Connecting to the Firewall Services Module and Managing the Configuration
 CHAPTER 3 Connecting to the Firewall Services Module and This chapter describes how to access the command-line interface and work with the configuration. This chapter includes the following sections: Connecting
CHAPTER 3 Connecting to the Firewall Services Module and This chapter describes how to access the command-line interface and work with the configuration. This chapter includes the following sections: Connecting
Lab 4.1.2 Characterizing Network Applications
 Lab 4.1.2 Characterizing Network Applications Objective Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Business Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 FC-CPE-1 Fa0/1 172.17.0.1 Fa0/0 10.0.0.1
Lab 4.1.2 Characterizing Network Applications Objective Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Business Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 FC-CPE-1 Fa0/1 172.17.0.1 Fa0/0 10.0.0.1
CCT vs. CCENT Skill Set Comparison
 Operation of IP Data Networks Recognize the purpose and functions of various network devices such as Routers, Switches, Bridges and Hubs Select the components required to meet a given network specification
Operation of IP Data Networks Recognize the purpose and functions of various network devices such as Routers, Switches, Bridges and Hubs Select the components required to meet a given network specification
Computer Networks I Laboratory Exercise 1
 Computer Networks I Laboratory Exercise 1 The lab is divided into two parts where the first part is a basic PC network TCP/IP configuration and connection to the Internet. The second part is building a
Computer Networks I Laboratory Exercise 1 The lab is divided into two parts where the first part is a basic PC network TCP/IP configuration and connection to the Internet. The second part is building a
Felix Rohrer. PT Activity 7.5.3: Troubleshooting Wireless WRT300N. Topology Diagram
 Felix Rohrer PT Activity 7.5.3: Troubleshooting Wireless WRT300N Topology Diagram All contents are Copyright 1992 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Felix Rohrer PT Activity 7.5.3: Troubleshooting Wireless WRT300N Topology Diagram All contents are Copyright 1992 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 3600 and 3800 Series Routers
 Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 3600 and 3800 Series Routers Document ID: 22189 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions Step by Step Procedure
Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 3600 and 3800 Series Routers Document ID: 22189 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions Step by Step Procedure
How To Configure InterVLAN Routing on Layer 3 Switches
 How To Configure InterVLAN Routing on Layer 3 Switches Document ID: 41860 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure InterVLAN Routing Task Step by Step Instructions
How To Configure InterVLAN Routing on Layer 3 Switches Document ID: 41860 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure InterVLAN Routing Task Step by Step Instructions
Objectives. Background. Required Resources. CCNA Security
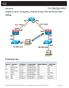 Chapter 8 Lab B, Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client Topology IP Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 FA0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Chapter 8 Lab B, Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client Topology IP Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 FA0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Lab Configuring Syslog and NTP (Instructor Version)
 (Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
(Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
Cisco Configuration Professional Quick Start Guide
 Cisco Configuration Professional Quick Start Guide April 29, 2011 This document explains how to start using Cisco Configuration Professional Express (Cisco CP Express) and Cisco Configuration Professional
Cisco Configuration Professional Quick Start Guide April 29, 2011 This document explains how to start using Cisco Configuration Professional Express (Cisco CP Express) and Cisco Configuration Professional
Lab 4.5.4 Diagramming External Traffic Flows
 Lab 4.5.4 Diagramming External Traffic Flows Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Business Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 R2 R3 FC-CPE-1 FC-CPE-2 ISP Fa0/1 172.17.0.1
Lab 4.5.4 Diagramming External Traffic Flows Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Business Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 R2 R3 FC-CPE-1 FC-CPE-2 ISP Fa0/1 172.17.0.1
About This Guide. Document Objectives. Audience
 About This Guide This preface describes the objectives, audience, organization, and conventions of the Cisco 1600 Series Software Configuration Guide. Cisco documentation and additional literature are
About This Guide This preface describes the objectives, audience, organization, and conventions of the Cisco 1600 Series Software Configuration Guide. Cisco documentation and additional literature are
Lab 1.4.1 Introductory Lab 1 - Getting Started and Building Start.txt
 Lab 1.4.1 Introductory Lab 1 - Getting Started and Building Start.txt Objective This lab may introduce new CCNP lab equipment and certain IOS features. This introductory activity also describes how to
Lab 1.4.1 Introductory Lab 1 - Getting Started and Building Start.txt Objective This lab may introduce new CCNP lab equipment and certain IOS features. This introductory activity also describes how to
CISCO CATALYST 3550 Series Switches
 CISCO CATALYST 3550 Series Switches The switches that belong to this series are stackable and are multilayer switches that provide QoS, high availability and security that are responsible for enhancing
CISCO CATALYST 3550 Series Switches The switches that belong to this series are stackable and are multilayer switches that provide QoS, high availability and security that are responsible for enhancing
Lab 8.4.3b Managing Cisco IOS images with ROMMON and TFTP
 Lab 8.4.3b Managing Cisco IOS images with ROMMON and TFTP Host Device Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Analyze the Cisco IOS image and router
Lab 8.4.3b Managing Cisco IOS images with ROMMON and TFTP Host Device Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Analyze the Cisco IOS image and router
LAB THREE STATIC ROUTING
 LAB THREE STATIC ROUTING In this lab you will work with four different network topologies. The topology for Parts 1-4 is shown in Figure 3.1. These parts address router configuration on Linux PCs and a
LAB THREE STATIC ROUTING In this lab you will work with four different network topologies. The topology for Parts 1-4 is shown in Figure 3.1. These parts address router configuration on Linux PCs and a
Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway
 Felix Rohrer Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1 S2 VLAN 99 192.168.99.12 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1
Felix Rohrer Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1 S2 VLAN 99 192.168.99.12 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1
Fundamentals of Switching
 1 CCNA 640-801 Exam Notes - Fundamentals of Switching CCNA 640-801 Exam Notes Fundamentals of Switching 1. LAN Segmentation 1.1 In a collision domain, a frame sent by a device can cause collision with
1 CCNA 640-801 Exam Notes - Fundamentals of Switching CCNA 640-801 Exam Notes Fundamentals of Switching 1. LAN Segmentation 1.1 In a collision domain, a frame sent by a device can cause collision with
Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 806, 826, 827, 828, 831, 836, 837 and 881 Series Routers
 Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 806, 826, 827, 828, 831, 836, 837 and 881 Series Routers Document ID: 12065 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions
Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 806, 826, 827, 828, 831, 836, 837 and 881 Series Routers Document ID: 12065 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions
Basic Router and Switch Instructions (Cisco Devices)
 Basic Router and Switch Instructions (Cisco Devices) Basic Device Connection 1. Connect to the device via the console cable (light blue cable) and the use of a terminal program (Windows Hyperterminal,
Basic Router and Switch Instructions (Cisco Devices) Basic Device Connection 1. Connect to the device via the console cable (light blue cable) and the use of a terminal program (Windows Hyperterminal,
Configuring PROFINET
 CHAPTER 9 This chapter describes how to configure the PROFINET feature on the Cisco IE 3000 switch. Understanding PROFINET, page 9-1, page 9-4 Displaying the PROFINET Configuration, page 9-5 Troubleshooting
CHAPTER 9 This chapter describes how to configure the PROFINET feature on the Cisco IE 3000 switch. Understanding PROFINET, page 9-1, page 9-4 Displaying the PROFINET Configuration, page 9-5 Troubleshooting
http://computernetworkingnotes.com/ccna-study-guide/cisco-ios-naming-convention-explainedwith-examples.html
 IOS is the most critical part of any cisco device. We should always keep a backup copy of IOS to deal with any unwanted situation. In this article I will explain the backup and restore process of IOS in
IOS is the most critical part of any cisco device. We should always keep a backup copy of IOS to deal with any unwanted situation. In this article I will explain the backup and restore process of IOS in
Lab 8.3.1.2 Configure Basic AP Security through IOS CLI
 Lab 8.3.1.2 Configure Basic AP Security through IOS CLI Estimated Time: 30 minutes Number of Team Members: Students will work in teams of two. Objective In this lab, the student will learn the following
Lab 8.3.1.2 Configure Basic AP Security through IOS CLI Estimated Time: 30 minutes Number of Team Members: Students will work in teams of two. Objective In this lab, the student will learn the following
Configuring a Cisco 2509-RJ Terminal Router
 created by: Rainer Bemsel Version 1.0 Dated: Dec/08/2012 For my Cisco LAB, I ve purchased a used Cisco 2509-RJ with RJ45-RJ45 roll-over cables. This TechTip shows my configuration setup, so you can easily
created by: Rainer Bemsel Version 1.0 Dated: Dec/08/2012 For my Cisco LAB, I ve purchased a used Cisco 2509-RJ with RJ45-RJ45 roll-over cables. This TechTip shows my configuration setup, so you can easily
How To Install An At-S100 (Geo) On A Network Card (Geoswitch)
 AT-S100 Version 1.0.3 Patch 1 Management Software for the AT-9000/28 Managed Layer 2 GE ecoswitch and AT-9000/28SP Managed Layer 2 GE ecoswitch Software Release Notes Please read this document before you
AT-S100 Version 1.0.3 Patch 1 Management Software for the AT-9000/28 Managed Layer 2 GE ecoswitch and AT-9000/28SP Managed Layer 2 GE ecoswitch Software Release Notes Please read this document before you
Configuring the Firewall Management Interface
 Configuring the Firewall Management Interface The firewall management interface can be configured under each firewall context to provide a virtualized management interface (see Figure 7). The management
Configuring the Firewall Management Interface The firewall management interface can be configured under each firewall context to provide a virtualized management interface (see Figure 7). The management
Cisco - Configure the 1721 Router for VLANs Using a Switch Module (WIC-4ESW)
 Page 1 of 20 Configure the 1721 Router for VLANs Using a Switch Module (WIC-4ESW) Document ID: 50036 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Network Diagram The Role of Switched
Page 1 of 20 Configure the 1721 Router for VLANs Using a Switch Module (WIC-4ESW) Document ID: 50036 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Network Diagram The Role of Switched
CCNA R&S: Introduction to Networks. Chapter 5: Ethernet
 CCNA R&S: Introduction to Networks Chapter 5: Ethernet 5.0.1.1 Introduction The OSI physical layer provides the means to transport the bits that make up a data link layer frame across the network media.
CCNA R&S: Introduction to Networks Chapter 5: Ethernet 5.0.1.1 Introduction The OSI physical layer provides the means to transport the bits that make up a data link layer frame across the network media.
Basic Configuration of the Cisco 12000 Series Internet Router
 CHAPTER 2 Basic Configuration of the Cisco 12000 Series Internet Router This chapter describes how to boot and configure the Cisco 12000 Series Internet Router. It discusses the following subjects: Cisco
CHAPTER 2 Basic Configuration of the Cisco 12000 Series Internet Router This chapter describes how to boot and configure the Cisco 12000 Series Internet Router. It discusses the following subjects: Cisco
Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing
 Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing Topology Objectives Background Review a basic EIGRP configuration. Explore the EIGRP topology table. Identify successors, feasible successors, and feasible distances.
Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing Topology Objectives Background Review a basic EIGRP configuration. Explore the EIGRP topology table. Identify successors, feasible successors, and feasible distances.
Lab 5-5 Configuring the Cisco IOS DHCP Server
 Lab 5-5 Configuring the Cisco IOS DHCP Server Learning Objectives Configure and verify the operation of the Cisco IOS DHCP server Configure an IP Helper address Review the EIGRP configuration Topology
Lab 5-5 Configuring the Cisco IOS DHCP Server Learning Objectives Configure and verify the operation of the Cisco IOS DHCP server Configure an IP Helper address Review the EIGRP configuration Topology
Management Software. Web Browser User s Guide AT-S106. For the AT-GS950/48 Gigabit Ethernet Smart Switch. Version 1.0.0. 613-001339 Rev.
 Management Software AT-S106 Web Browser User s Guide For the AT-GS950/48 Gigabit Ethernet Smart Switch Version 1.0.0 613-001339 Rev. A Copyright 2010 Allied Telesis, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of
Management Software AT-S106 Web Browser User s Guide For the AT-GS950/48 Gigabit Ethernet Smart Switch Version 1.0.0 613-001339 Rev. A Copyright 2010 Allied Telesis, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of
What is VLAN Routing?
 Application Note #38 February 2004 What is VLAN Routing? This Application Notes relates to the following Dell product(s): 6024 and 6024F 33xx Abstract Virtual LANs (VLANs) offer a method of dividing one
Application Note #38 February 2004 What is VLAN Routing? This Application Notes relates to the following Dell product(s): 6024 and 6024F 33xx Abstract Virtual LANs (VLANs) offer a method of dividing one
Configuring System Message Logging
 CHAPTER 1 This chapter describes how to configure system message logging on the Cisco 4700 Series Application Control Engine (ACE) appliance. Each ACE contains a number of log files that retain records
CHAPTER 1 This chapter describes how to configure system message logging on the Cisco 4700 Series Application Control Engine (ACE) appliance. Each ACE contains a number of log files that retain records
Configuring Network Load Balancing for vethernet
 Configuring Network Load Balancing for vethernet This chapter contains the following sections: Information About Microsoft Network Load Balancing, page 1 Guidelines and Limitations, page 1 Configuring
Configuring Network Load Balancing for vethernet This chapter contains the following sections: Information About Microsoft Network Load Balancing, page 1 Guidelines and Limitations, page 1 Configuring
CCNA Discovery 4.0.3.0 Networking for Homes and Small Businesses Student Packet Tracer Lab Manual
 4.0.3.0 Networking for Homes and Small Businesses Student Packet Tracer Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial
4.0.3.0 Networking for Homes and Small Businesses Student Packet Tracer Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial
GLBP - Gateway Load Balancing Protocol
 GLBP - Gateway Load Balancing Protocol Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) protects data traffic from a failed router or circuit, like Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) and Virtual Router Redundancy
GLBP - Gateway Load Balancing Protocol Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) protects data traffic from a failed router or circuit, like Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) and Virtual Router Redundancy
ENetwork Basic Configuration PT Practice SBA
 ENetwork Basic Configuration PT Practice SBA A few things to keep in mind while completing this activity: 1. Do not use the browser Back button or close or reload any exam windows during the exam. 2. Do
ENetwork Basic Configuration PT Practice SBA A few things to keep in mind while completing this activity: 1. Do not use the browser Back button or close or reload any exam windows during the exam. 2. Do
Using Cisco IOS Software
 Using Cisco IOS Software This chapter provides helpful tips for understanding and configuring Cisco IOS software using the command-line interface (CLI). It contains the following sections: Understanding
Using Cisco IOS Software This chapter provides helpful tips for understanding and configuring Cisco IOS software using the command-line interface (CLI). It contains the following sections: Understanding
LAB MANUAL for Computer Network
 LAB MANUAL for Computer Network CSE-310 F Computer Network Lab L T P - - 3 Class Work : 25 Marks Exam : 25 MARKS Total : 50 Marks This course provides students with hands on training regarding the design,
LAB MANUAL for Computer Network CSE-310 F Computer Network Lab L T P - - 3 Class Work : 25 Marks Exam : 25 MARKS Total : 50 Marks This course provides students with hands on training regarding the design,
Chapter 7 Configuring Trunk Groups and Dynamic Link Aggregation
 Chapter 7 Configuring Trunk Groups and Dynamic Link Aggregation This chapter describes how to configure trunk groups and 802.3ad link aggregation. Trunk groups are manually-configured aggregate links containing
Chapter 7 Configuring Trunk Groups and Dynamic Link Aggregation This chapter describes how to configure trunk groups and 802.3ad link aggregation. Trunk groups are manually-configured aggregate links containing
Configuring DHCP Snooping and IP Source Guard
 CHAPTER 19 This chapter describes how to configure Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) snooping and IP Source Guard on Catalyst 4500 series switches. It provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration
CHAPTER 19 This chapter describes how to configure Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) snooping and IP Source Guard on Catalyst 4500 series switches. It provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration
PT Activity: Configure Cisco Routers for Syslog, NTP, and SSH Operations
 PT Activity: Configure Cisco Routers for Syslog, NTP, and SSH Operations Instructor Version Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 FA0/1
PT Activity: Configure Cisco Routers for Syslog, NTP, and SSH Operations Instructor Version Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 FA0/1
Lab 4.2.3 Analyzing Network Traffic
 Lab 4.2.3 Analyzing Network Traffic Objective Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Network Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 FC-CPE-1 Fa0/1 172.17.0.1 Fa0/0 10.0.0.1 255.255.0.0
Lab 4.2.3 Analyzing Network Traffic Objective Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Network Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 FC-CPE-1 Fa0/1 172.17.0.1 Fa0/0 10.0.0.1 255.255.0.0
Networking Guide Redwood Manager 3.0 August 2013
 Networking Guide Redwood Manager 3.0 August 2013 Table of Contents 1 Introduction... 3 1.1 IP Addresses... 3 1.1.1 Static vs. DHCP... 3 1.2 Required Ports... 4 2 Adding the Redwood Engine to the Network...
Networking Guide Redwood Manager 3.0 August 2013 Table of Contents 1 Introduction... 3 1.1 IP Addresses... 3 1.1.1 Static vs. DHCP... 3 1.2 Required Ports... 4 2 Adding the Redwood Engine to the Network...
