Basic Thin Film and XRPD Analysis
|
|
|
- Clifford Wiggins
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Basic Thin Film and XRPD Analysis with the Point Detector on the Rigaku Smartlab Multipurpose Diffractometer Scott A Speakman, Ph.D Center for Materials Science and Engineering at MIT For help in the X-ray Lab, contact Charles Settens settens@mit.edu The Rigaku SmartLab is a multipurpose diffractometer with a wide variety of optics and sample stages that are available. Fast data collection is enabled by a 9 kw rotating anode source which produces a high flux of X-ray intensity. The data collection program for the SmartLab is called SmartLab Guidance. When you select a package from SmartLab Guidance, it will guide you through the process of configuring the instrument, aligning the sample, and collecting data. This mode of operation is slightly slower than a fully manual operation of the instrument, but it means that you are more empowered to collect data from your sample in a variety of configurations. This SOP will walk you through using the Smartlab with the Scintillation Point Detector in either Bragg-Brentano or Parallel Beam mode. This mode of data collection is best suited for thin film analysis, though it can also be used for analysis of powders. I. Configure the Instrument pg II. Write a Measurement Program pg III. Run the Measurement Program pg IV. When You are Done pg Appendix A. Terms and Conventions pg Revised 9 February 2014 Page 1 of 20
2 Rigaku Smartlab Operation Checklist 1. Engage the Smartlab in Coral 2. Start the program SmartLab Guidance 3. Assess instrument status and safety a. Is the generator on? b. Is the shutter open? 4. If the generator is off, then turn it on. Turn the generator up to full power, 45 kv and 200mA 5. Select a measurement package 6. Align the instrument optics 7. Load and align your sample 8. Run the package measurement 9. When finished a. Determine if someone is using the SmartLab later the same day. i. If someone is using the SmartLab later the same day, then turn the generator power down to its stand-by level, 20 kv and 10 ma ii. If no one is using the SmartLab later the same day, then turn the generator off b. Retrieve your sample c. Clean the sample stage and sample holders d. Copy your data to a secure location e. Disengage the Smartlab in Coral Revised 9 February 2014 Page 2 of 20
3 Managing the Rotating Anode Generator When the Smartlab is not being used for an extended period, the rotating anode generator should be turned off to conserve the life of the anode and filament. When the rotating anode generator is first turned on, the instrument requires 20 minutes to warmup before it is ready for use. Therefore, use the following guidelines for turning the rotating anode generator on and off: 1. If you are going to be the first person to use the instrument for the day, plan to turn the instrument on 20 minutes before you will start using it. a. If you contact SEF staff ahead of time, we will try to turn the instrument on first thing in the morning so that the instrument will be ready when you arrive to use it. b. You do not have to engage the Smartlab in Coral while the generator is warming up. You only need to engage the Smartlab in Coral when you start aligning the instrument and getting it ready for your measurement. 2. When you are done using the instrument, look at the schedule in Coral. a. If someone else is using the instrument after you that same day, then just turn the power down to standby mode (20 kv and 10 ma) do not turn the generator off. b. If nobody else is using the instrument after you that same day, then turn the generator off. 3. Never turn the instrument off from the front panel unless there is an emergency. This would stop the turbopump in addition to turning off the generator. The instrument would then require 1+ hours to turn back on. a. When you turn the generator off from the Smartlab Guidance software, only the X-ray source is turned off. The turbopump continues to run to maintain a good vacuum in the X-ray source. Revised 9 February 2014 Page 3 of 20
4 I. Configure the Instrument 1. ENGAGE THE SMARTLAB IN CORAL 2. START THE SMARTLAB GUIDANCE SOFTWARE a. If SmartLab Guidance is not running, then start it. Log-in using the account: i. Login name: CMSE ii. Leave the Password blank iii. Click OK 3. ASSESS INSTRUMENT STATUS AND SAFETY 1. Main panel Panel used to start and stop SmartLab. 2. Operating panel Panel used to turn the internal light on/off. 3. Door Can be safely opened when shutter is closed. 4. X-ray warning lamp Lights when x-rays are generated. 5. Door-lock button Lock/Unlock the door a. Determine if the generator is on. i. The X-ray warning lamp, which is labeled X-rays ON (number 4 in the figure above), will be lit if the generator is on. ii. If the generator is not on, proceed to step 3d on the next page for instructions iii. If the generator is on, then you will need to: 1. evaluate the instrument status, as described below 2. set the generator to maximum power as described on the next page, step 3c b. Determine if a run is in progress. i. The Hardware Control window (pictured right) will tell you if an alignment or measurement is in progress. ii. You can look at the History to see when the scan started and the Measurement Window to see how long the scan was supposed to take in order to judge when the scan will be finished. iii. If a measurement is in progress, either let it finish or stop it 1. To stop a scan, click on the Abort button. 2. Data are not saved automatically when you abort a scan. You should manually save the data that was collected. a. Go to the menu File > Save As b. If the data is yours, then save it in your folder. c. If the data is somebody else s, then save it in the folder c:\temp\aborted scans. Name the file with the date and time. iv. If no scan is in progress, proceed to step c, setting the generator to maximum power Revised 9 February 2014 Page 4 of 20
5 c. Set Generator Power to Maximum i. If the generator was already turned on when you arrived in the lab, then you need to make sure that the generator is at full power ii. Go to the menu Control > XG Control iii. Set the voltage to 45 kv iv. Set the current to 200 ma v. Click the Set button. vi. Click the Close button to close the window vii. Review instructions for opening the instrument doors, then proceed to the next page. d. Turn on the SmartLab Generator (if it is off) i. Click on the Startup button in the left-hand pane of the SmartLab Guidance software. ii. The Startup dialog box will open. In that box: 1. Make sure that the Timer box is NOT checked. 2. Select Use everyday in the Generator usage: drop-down 3. Select Hold in the XG set: drop-down menu 4. Click the Execute button. iii. A separate Hardware Control window (pictured right) will open which will countdown the time remaining during the Aging process. That window will close when the instrument is ready for use. iv. It will take 18 minutes for the instrument to warm up when it is first turned on. e. To OPEN and CLOSE the Instrument Doors i. Make sure that the shutter is closed 1. If the shutter is open, the red shutter open LED on the X- ray tube tower will be lit (shown to the right). 2. If the shutter is closed, you are safe from X-ray exposure even when the generator is on. Proceed to the step ii. 3. If the shutter is open, determine if a measurement is in progress. The Hardware Control window (pictured right) will tell you if an alignment or measurement is in progress. a. If a measurement is in progress, follow the instructions in step b on page 4 to stop the scan and save the data. b. If a measurement is not in progress and the shutter is open, something is wrong. Contact SEF staff for help. ii. Press the Door Lock button on the left door (number 5 in the illustration on page 4) iii. The Door Lock button will light up. Wait until it starts blinking before you try to open the door. The instrument is making sure it is safe before it unlocks the doors. iv. When the Door Lock button begins to flash the door is unlocked. v. GENTLY Slide the doors open. vi. When you are done, GENTLY slide the doors closed vii. Press the Door Lock button to lock the doors again. Revised 9 February 2014 Page 5 of 20
6 4. SELECT A MEASUREMENT PACKAGE a. In the measurement pane, select either a Preinstalled or a User Defined measurement. i. If you need assistance deciding which measurement is best for your sample, contact SEF staff. ii. Certain measurements ask you to perform hardware changes that require additional training. Do not attempt to change hardware that is unfamiliar to you! If you would like to be trained to use new hardware, contact SEF staff. b. The packages that you can run after completing the Basic Smartlab training are: User-Defined Measurements BB coupled scan PB-PSA coupled scan PB-PSA GIXD Variable Slit-BB XRR PB-medium resolution Preinstalled Measurements Reflectivity (medium resolution PB) Rocking Curve/Reciprocal Space Map (medium resolution PB) Quick Theta/2-Theta Scan (Bragg-Brentano focusing) Precise Theta/2-Theta Scan (Bragg-Brentano focusing) General (Bragg-Brentano focusing) Quick Theta/2-Theta Scan (medium resolution PB/PSA) Precise Theta/2-Theta Scan (medium resolution PB/PSA) General (medium resolution PB/PSA) Reflection SAXS (medium resolution PB) Residual Stress (medium resolution PB/PSA) Phase analysis of thick polycrystalline samples. Phase analysis of polycrystalline samplesespecially those with rough uneven surfaces or when tilting to study preferred orientation Phase analysis of thin polycrystalline films or depth profiling of surfaces. Does not work for samples with preferred orientation. Phase analysis of thin polycrystalline samples. Analysis of thin film thickness and roughness. Don t use this package- it misaligns the sample. Use the macro instead. Evaluate texture or quality of thin film Phase analysis of polycrystalline samples- works best for thick samples with smooth flat surfaces Phase analysis of polycrystalline samples- works best for thin films or samples with rough uneven surfaces Small angle scattering analysis of thin film Residual stress analysis of non-textured samples The Bragg-Brentano (BB) geometry uses a divergent X-ray beam and parafocusing optics. Incident angle (omega) and diffraction angle (2theta) must be coupled, so that ω=½*2θ. o This provides the best angular resolution for diffraction data If the divergence limiting slit is fixed, then the X-ray beam width decreases during the measurement. For thin films, this will result in a loss of intensity at higher angles. If a variable divergence slit is used, then the divergence aperture will change during the scan in order to maintain a constant X-ray beam width. This will avoid the loss of intensity at high angles from thin films. The Parallel-Beam (PB) geometry uses a Gobel mirror to focus the divergent X-ray beam into a nearly parallel X-ray beam (very low divergence). This allows the incident angle (omega) and the diffraction angle (2theta) to be decoupled. Scans can be executed with a fixed incident angle, allowing for Grazing Incident X-Ray Diffraction (GIXD). o GIXD allows the X-ray beam to be focuses in the surface of the sample, increasing the amount of signal that comes from the thin film or sample surface. o GIXD does not work well for textured thin films. Scans can also be executed with a set angular offset, such that ω=½*2θ+τ. This allows different directions in the sample to be probed. Revised 9 February 2014 Page 6 of 20
7 c. When you select a measurement, a flow chart will appear with the steps required to execute that measurement. There are always at least three steps: i. Optics Alignment ii. Sample Alignment iii. Measurement d. You have two different ways that you can choose to execute the package: i. This SOP assumes that you will individual execute each step. You will manually proceed from one step to the next. 1. Select each step by clicking on the box in the guidance software. 2. Set the parameters, 3. Click Execute to run the step. 4. Close the dialog when the step is finished. ii. You can also set all parameters and then Run the measurement in a semi-automated fashion. This mode of operation is not covered in this manual. 5. OPTICS ALIGNMENT a. In the Package window, click on the Optics Alignment part. b. Decide whether or not you want to run the full alignment. In the window that opens: i. If you do not want to run the full alignment, then check the box says either Change optics (quick alignment only) or Change optics without alignment. 1. This will usually collect data with over 90% efficiency. Sometimes you might observe that the quick alignment fails and then you have to run the full alignment. ii. If you want to run the full alignment, do not check this box. 1. The instrument will take 5 to 10 minutes to align all of the optics to provide maximum possible efficiency. You might want to do this if you are performing a difficult or demanding measurement. iii. Click the Execute button. c. The instrument will spend a couple of minutes reading the current instrument configuration and will then produce a guidance window to tell you what physical pieces to change. Revised 9 February 2014 Page 7 of 20
8 d. The default configuration is the medium resolution parallel beam (PB) or Bragg-Brentano focusing configuration. Assuming that is the configuration that you are starting from, the guidance will look like: e. To change the selection slit i. The Bragg Brentano (BB) selection slit is labeled BB on the end. The Parallel Beam (PB) selection slit is labeled PB on the end. ii. Pull the slit straight out and then insert the other slit f. To insert the height reference sample plate and the Center_slit i. The height reference sample plate may already be on the sample stage. Otherwise, the wafer sample plate is probably mounted (pictured below) Height reference sample plate wafer sample plate Sample spacer Revised 9 February 2014 Page 8 of 20
9 ii. If the wafer sample plate is mounted, rotate it CCW to loosen. Then lift the wafer sample plate off of the adapter. iii. If there is a sample spacer mounted, press in on the bar indicated by the arrow below and then turn the spacer CCW to loosen it. Then lift spacer off of the adapter. iv. To put the height reference plate onto the sample stage adapter 1. Line up the screws on the reference plate to the large holes on the adapter, as indicated by the arrows on the figure below 2. Then turn the height reference plate CW to lock it in place. v. Then insert the center slit (pictured below) into the height reference plate. 1. The center slit is labeled on the bottom 2. The center slit will be secured by the clips below the alignment block of the reference plate. 3. The guides on the side of the center slit will make sure that it is properly centered Revised 9 February 2014 Page 9 of 20
10 g. You may have to change the optics in the ROD adaptor and RPS adaptor, on the detector side of the instrument. i. Parts that fit in the ROD adaptor are labeled with a red + ii. Parts that fit in the RPS adaptor are labeled with a red X iii. To change the optics in the adaptor 1. Use the 2.5mm Allen wrench to loosen the set screw. Do not completely remove the screw. 2. Remove the optic and put it in the glass cabinet. 3. Gently insert the correct optic. a. Some optics can be used multiple ways. The label for the desired mode should be facing towards you. 4. Tighten the set screw so that it is barely snug. Do not overtighten the screw. h. When all components have been changed as instructed by the Guidance software, click OK to close the guidance dialogue window. i. The system will now update the configuration and may align some or all of the optics. During this process, the Hardware Control window will indicate the status of the alignment. j. If preparing for a PB/PSA measurement, part way through the alignment the system might prompt you to change the optic(s) in the ROD and/or RPS adaptors. k. When the alignment is done, the Hardware Control window will close. l. Then click OK on the Optics Alignment window to close it. 6. SAMPLE ALIGNMENT a. You have two options to load your sample in to the instrument i. Load the sample in to a rectangular Rigaku sample holder. 1. Use a glass sample holder for powders. You can select from a well that is 0.2mm deep or 0.5mm deep. 2. Use the aluminum sample holder for solid samples. 3. These are stored in the blue bin on the counter by the sink. Please do not remove sample holders from the lab- they are there for everybody to share!! 4. You will remove the center slit and place the sample holder in the height reference sample plate (pictured on page 9). The sample will not have to be aligned. ii. Put the sample on a wafer sample plate. 1. This is best for coatings on substrates and powder on a ZBH. 2. The sample will be aligned by bisecting the beam. 3. If your sample is less than 20mm x 20mm, you should put a glass slide underneath it, otherwise you may see signal from the sample stage. Revised 9 February 2014 Page 10 of 20
11 b. In the Package window, select the Sample Alignment part. i. The Sample Alignment window will open. Direction of X-ray beam Sample thickness Sample width c. Select the radio button for the sample alignment technique you want to use. You will usually use the Flat sample option: i. Select Flat sample as long as you are using the wafer sample plate and if your sample is flat and larger than 10mm x 10 mm. Always select it if you are doing a GIXD scan ii. Select Use the height reference sample plate (no height alignment) if you are using a Rigaku sample holder loaded into the height reference sample plate. iii. Select Curved sample (Z scan only) if you are using the wafer sample plate and your sample has either a curved surface OR if your sample is smaller than 10mm x 10mm at its smallest dimension in the X-ray beam. d. If you select Flat sample or Curved sample, you will be prompted to enter your sample thickness in the Sample thickness (mm) dialog box. If you are setting your sample on a glass slide, include the glass slide thickness in the number. e. There is a difference in the procedure depending on if you are using BB and PB-PSA i. If using BB optics, just select the Run recommended sequence radio button. 1. Enter your total Sample Thickness in the appropriate box if using Flat Sample or Curved Sample alignments. ii. If using PB-PSA optics, you must customize the alignment scan. 1. Select the Customize Conditions radio button 2. Click on the Customize button 3. The Customize window will open 4. Select the Flat sample radio button 5. Enter the approximate thickness of your sample in the Sample thickness (mm) box. 6. Change the IS (mm) value to mm 7. Click OK. The Customize window will close. f. Click Execute to run the sample alignment. Revised 9 February 2014 Page 11 of 20
12 g. The software will instruct you to change the sample stage and to load the sample. i. Follow the instructions on the screen. ii. The software will instruct you to change the sample stage. 1. The software cannot automatically detect the sample stage that is installed, so it will always tell you which one you have to use. 2. If you must change the sample stage, follow the illustrated instructions pages When selecting the correct Sample Spacer, refer to the numbers in black. Ignore the numbers in red. iii. If using PB-PSA optics, always use the PSA. Do not use the 0.5 PSA as the software recommends. You will have to remove both the ROD and RPS optics in order to install the PSA (it is a large optic and takes up both spaces). Only tighten the set screw in the ROD adapter (marked with a red +) iv. While you are loading the sample, you should change the IS_L slit if necessary. Because of a flaw in the software, SmartLab Guidance will not properly instruct you to change this slit. You must remember to change it yourself. 1. The IS_L is used to match the X-ray beam length to your sample height. The Rigaku convention for naming these directions is unusual, so see the diagram below. 2. The IS_L slit should be at least 20% smaller than your sample. We usually use the 10mm IS_L and nothing larger. If your sample is smaller than 12mm, however, you should change the IS_L. For example, if your sample has a sample height of 10mm, you should use the 5 mm IS_L. The available IS_L slit sizes are 15, 10, 5, and 2 mm. 3. Change the IS_L (circled in red below) with one of the correct size. Direction of X-ray beam Sample thickness Sample width v. Remove the K-beta filter, if present. This is located in the first slit position on the detector side Revised 9 February 2014 Page 12 of 20
13 vi. Close the enclosure doors. vii. Click OK in the Guidance dialog. h. While the sample is being aligned, the Hardware Control window will indicate the status of the alignment. i. When alignment is done, the Hardware Control window will close. j. When the alignment is done, look at the scans to make sure that they executed properly i. Look at the Z-scan. The intensity should start at a maximum value, then reduce to zero as the sample begins to block the X-ray beam. The optimal Z position for the sample is when it makes the intensity equal to ½ I max. ii. Look at the Omega scans (only available if you ran selected Flat Sample for the alignment). 1. The omega scan should have a well-defined maximum iii. If these alignment scans do not look like the executed properly, see Appendix B for suggestions on how to correct the alignment. Counts Z-scan Omega scan Revised 9 February 2014 Page 13 of 20
14 7. RUN THE MEASUREMENT a. Click on the General Measurement part in the Guidance flowchart. b. The General Measurement window will open. i. The window will look slightly different depending on if you are running in Bragg- Brentano (BB) mode or in Parallel-Beam (PB) mode. Bragg-Brentano (BB) dialog box Parallel-beam (PB) dialog box c. Click on the [ ] button to open the Save As dialog to set the folder and filename for the data to be saved to. Click the Save button once that information is set. d. Click on the Read Current Slits button to load the current optics in to the entries for Soller/PSC (deg), IS L (mm), PSA (deg), and Soller (deg). These optics are listed in the order that they appear in the instrument, going to from the x-ray tube (on the left) to the detector (on the right). For example, the first Soller slit listed is the incident-beam side Soller slit and the second Soller slit listed is the diffracted-beam side Soller slit. e. Change these optics as desired. The recommended settings for PSA and the second Soller slit will be different depending on if you are using BB or PB-PSA optics. i. Soller/PSC (deg) is the incident Soller slit. For BB optics, this should be 5 deg. Sometimes it might be set to 2.5 deg. It is better to make the diffracted-beam side Soller slit smaller rather than this incident-beam Soller slit smaller if you want to reduce peak asymmetry of very low angle peaks (below 20 deg 2theta). For PB-PSA optics using the deg PSA (which is usual), this is your only Soller slit. Set it to: 5 deg for more intensity 2.5 deg for better precision 0.5 deg for highly precise quantitative analysis or to reduce asymmetry of peaks below 15 deg 2theta. If you are using a larger PSA, then follow the recommendations for the BB optics. ii. IS L (mm) is the beam length limiting slit, which is used to match the length of the X-ray beam to the height or your sample. Be sure to refer to the figure on page 12 for direction conventions on the Rigaku. Select a slit (15, 10, 5, or 2 mm) that is slightly narrower than your sample. Revised 9 February 2014 Page 14 of 20
15 iii. PSA (deg) is the parallel slit analyzer. For BB optics, this should be set Open. For PB-PSA optics, this will normally be set to deg. This can be set to 0.5 or 1 deg for more intensity, but the peak resolution will be very poor. iv. Soller (deg) is the diffracted beam Soller slit. For BB optics: For PB-PSA optics: 5 deg for more intensity If using the PSA (which is most 2.5 deg for better precision typical), then set this to None 0.5 deg for highly precise quantitative analysis or to reduce asymmetry of peaks below 15 deg 2theta. If using a larger PSA, then follow the recommendations for the BB optic. This should be 5 deg or 2.5 deg if using. f. In the area Monochromization for the BB optics, select K beta filter method unless you are using the diffracted beam monochromator. i. The monochromator is useful to filter out unwanted wavelengths of radiation including fluoresced X-rays. This will greatly improve your signal-to-noise ratio, especially for samples that contain high concentrations of Fe and/or Co. ii. You can only use the monochromator if you have received special training and authorization. See SEF staff if you are interested. iii. If you want to use the monochromator with the PB-PSA optics, a different approach will be required. See SEF staff for help. g. Set your Measurement conditions h. You can check one row to perform one measurement or you can check multiple rows to run several measurements on the same sample. Check each row of measurements you want to execute. i. Multiple scans will be saved to the same file. i. Enter your measurement parameters i. Scan Axis: 1. Select Theta/2Theta for a coupled scan using the conventional Bragg-Brentano geometry where omega must be equal to ½*2Theta. 2. Select 2Theta/Omega for a coupled scan with a tilt offset, such that omega= ½*2theta + offset 3. Select 2Theta for a GIXD measurement ii. Mode is almost always Continuous iii. Range is usually Absolute iv. Enter the Start and Stop values appropriate for the scan range required for your measurement. v. Step is usually 0.02 deg vi. Speed is usually a value from 0.5 to 5 deg/min. Revised 9 February 2014 Page 15 of 20
16 vii. The next four columns will set the computer controlled optics. These are: 1. IS is the incident slit. a. You can change the units for this slit using the drop-down menu underneath the column label (deg or mm). b. This slit will determine the width of the X-ray beam (see page 12 for Rigaku naming conventions for directions). You do not want the beam to be wider than your sample. 2. RS1 is the anti-scatter slit. a. You can change the units for this slit using the drop-down menu underneath the column label (deg or mm). 3. RS2 is the receiving slit 4. Attenuator is an attenuation foil that will reduce X-ray beam intensity if it might become so intense that it could damage the detector viii. These optics will be set differently for BB coupled scans, PB-PSA coupled scans, and PB-PSA GIXD scans. Note that the units are written differently for different scan conditions! IS RS1 RS2 BB coupled scan PB-PSA coupled scan PB-PSA GIXD scan 0.25 to 2/3 deg is normal. Use a smaller slit for lower angle data or more precision. 0.5 to 2 mm is normal. Use a smaller slit for lower angle data to 0.2 mm is normal. This should be the same as the IS slit. 10mm 10mm 0.3mm is normal. Use smaller for more precise data (with less intensity). Never use smaller than 0.1mm. Use larger (up to 0.6mm) for more intensity at the cost of resolution. Useful for amorphous or nanocrystalline materials where peak width is determined by the sample, not the instrument. 10mm 10mm If using the parallel-beam (PB) optics, the X-ray beam width can be calculated as If using Bragg-Brentano (BB) optics, the X-ray beam width can be calculated using the excel spreadsheet Rigaku SmartLab Beam Width Calculator.xslx The depth of penetration of the X-rays into your sample can be calculated using the MAC Calculator in HighScore Plus. See the HighScore Plus Guide.docx for instructions. ix. The Attenuator should be set to Open, unless your sample includes a single crystal substrate. Then it should be set to Automatic. This is important to protect the detector. x. If running a BB scan, you must make sure that Voltage is set to 45 kv and Current is set to 200 ma. xi. Click on the Set button in the Options column to open the dialog for angular offsets. Revised 9 February 2014 Page 16 of 20
17 xii. The Action column for Phi and 2ThetaChi should almost always be set to None. xiii. The other Action columns will be set differently depending on your optics and measurement type. 1. If you are collecting a coupled scan from a sample that does not include a single crystal substrate, using either the BB optics or the PB-PSA optics, then the Action column for both 2Theta and Omega should be set to None. 2. If you are collecting a GIXD measurement using PB-PSA optics, then: a. the Action column for Omega should be set to Move to origin. b. The Origin(Center) value will be the omega angle for your GIXD measurement. i. This is usually a value from 0.5 to 2 deg. ii. The shallower the angle, the more the x-ray beam is focused in the surface of the sample. 3. For a 2theta/omega coupled scan, you can set a tilt offset. a. This is useful for avoiding the single crystal peak from a single crystal substrate. This works with either BB or PB-PSA optics. set i. Set the Action column for 2Theta and Omega to Move to Origin, ii. enter the starting value of the scan for the 2Theta Origin(Center) iii. enter a value of ½*2Theta+Offset for omega Origin(Center). A typical offset is 1deg. b. This can be used with PB-PSA optics to probe in a different direction rather than normal to the substrate. i. Set the Action column for 2Theta and Omega to Move to Origin, ii. enter the starting value of the scan for the 2Theta Origin(Center) iii. enter a value of ½*2Theta+Offset for omega Origin(Center). The offset will dictate the tilt, t, of your analysis. xiv. Click close xv. When ready to collect data, click Execute xvi. A dialog will ask if you want to change the optics from those written in the program. Click NO xvii. Change optics as instructed by the SmartLab Guidance software Revised 9 February 2014 Page 17 of 20
18 IV. When You are Done 1. When the measurement finishes: a. Your data are automatically saved b. The shutter is automatically closed 2. Look to see if anybody is using the instrument after you. a. If somebody is using the instrument later that day, then turn down the generator power to 20 kv and 10 ma i. Go to the menu Control > XG Control ii. Enter 20 kv for the Voltage and 10 ma for the Current iii. Click the Set button. b. If nobody is using the instrument later that day, then turn the generator off. i. Click the Shutdown button from the packages menu. ii. Click Execute 3. Remove your sample and clean up. 4. Disengage the Smartlab in Coral Appendix A. Terms and Conventions Used Terms Used to Denote an Action In this guide there are several terms that indicate an action. Click Press the left mouse button and quickly release it. Double-click Press the mouse button twice (quickly) on an icon, item, file, etc. Right-click Press the right mouse button and quickly release it. Check/Uncheck Click in a check box ( ) to check it or uncheck it Enter Type in information. This can be either text or numerical data. Press Press a key on the keyboard, or a push-button in a window. Select Move the mouse cursor to the option you want and click the left mouse button. Toggle Press Switch between parameters or states (for example: On-Off-On). In the examples in this Guide we terminate most actions by saying press ; you can usually press the Enter key instead. Revised 9 February 2014 Page 18 of 20
19 Appendix B. Things to try if the Sample Alignment doesn t work correctly Counts a. When the alignment is done, look at the scans to make sure that they executed properly i. Look at the Z-scan. The intensity should start at a maximum value, then reduce to zero as the sample begins to block the X-ray beam. The optimal Z position for the sample is when it makes the intensity equal to ½ I max. I max ½ I max The optimal Z value reduces the X-ray beam intensity to ½ I max indicating that the sample is bisecting the X-ray beam. 0 I min =0 1. If I min does not equal zero, then the X-ray beam is wider than the sample. The automatic alignment performed by the software will be wrong. You will need to manually calculate the optimal Z value. 2. The optimal Z value reduces the X-ray beam intensity to ½ (I max -I min ) + I min 3. Drive the Z axis to the optimal value by: a. Select the menu Control > Manual Control b. The Manual Control window will open c. Select Z from the list on the left d. In the upper center of the window is the area Move conditions e. Enter the optimal Z value in the To: box. Then click the Move button. f. Click Close to close the window ii. Look at the Omega scans (only available if you ran selected Flat Sample for the alignment). 1. The omega scan should have a well-defined maximum Revised 9 February 2014 Page 19 of 20
20 a. If the sample does not have a well-defined maximum, re-run the sample alignment using the Curved sample (Z scan only) option. 2. The software will mark with an x the position that it identified as the optimal value. Make sure that the marked position is close to what you would select as the center of gravity of the peak. If it does not: a. Use the mouse cursor to determine what you think the optimal omega value is. b. Drive the Z axis to the optimal value by: i. Select the menu Control > Manual Control ii. The Manual Control window will open iii. Select Omega from the list on the left iv. In the upper center of the window is the area Move conditions v. Enter the optimal omega value in the To: box. Then click the Move button. vi. Click Close to close the window. c. Then re-run the sample alignment using the Curved sample (Z scan only) option. Omega scan i. When the alignment is done, click OK to close the Sample Alignment window. Revised 9 February 2014 Page 20 of 20
Hitachi U-4100 UV-vis-NIR spectrophotometer (341-F)
 Hitachi U-4100 UV-vis-NIR spectrophotometer (341-F) Please contact Dr. Amanda Young for training requests and assistance: 979-862-6845, amandayoung@tamu.edu Hardware Our spectrophotometer is made up of
Hitachi U-4100 UV-vis-NIR spectrophotometer (341-F) Please contact Dr. Amanda Young for training requests and assistance: 979-862-6845, amandayoung@tamu.edu Hardware Our spectrophotometer is made up of
Rigaku XRD-System Instruction Manual v4/19/03. The Krishnan Group/Wilcox 132, University of Washington
 Rigaku XRD-System Instruction Manual v4/19/03 The Krishnan Group/Wilcox 132, University of Washington Contents: - General information - Safety - How to turn on the X-rays - How to turn off the X-rays -
Rigaku XRD-System Instruction Manual v4/19/03 The Krishnan Group/Wilcox 132, University of Washington Contents: - General information - Safety - How to turn on the X-rays - How to turn off the X-rays -
X-ray thin-film measurement techniques
 Technical articles X-ray thin-film measurement techniques II. Out-of-plane diffraction measurements Toru Mitsunaga* 1. Introduction A thin-film sample is two-dimensionally formed on the surface of a substrate,
Technical articles X-ray thin-film measurement techniques II. Out-of-plane diffraction measurements Toru Mitsunaga* 1. Introduction A thin-film sample is two-dimensionally formed on the surface of a substrate,
Applications of New, High Intensity X-Ray Optics - Normal and thin film diffraction using a parabolic, multilayer mirror
 Applications of New, High Intensity X-Ray Optics - Normal and thin film diffraction using a parabolic, multilayer mirror Stephen B. Robie scintag, Inc. 10040 Bubb Road Cupertino, CA 95014 Abstract Corundum
Applications of New, High Intensity X-Ray Optics - Normal and thin film diffraction using a parabolic, multilayer mirror Stephen B. Robie scintag, Inc. 10040 Bubb Road Cupertino, CA 95014 Abstract Corundum
Using the Bruker Tracer III-SD Handheld X-Ray Fluorescence Spectrometer using PC Software for Data Collection
 Using the Bruker Tracer III-SD Handheld X-Ray Fluorescence Spectrometer using PC Software for Data Collection Scott A Speakman, Ph.D Center for Materials Science and Engineering at MIT speakman@mit.edu
Using the Bruker Tracer III-SD Handheld X-Ray Fluorescence Spectrometer using PC Software for Data Collection Scott A Speakman, Ph.D Center for Materials Science and Engineering at MIT speakman@mit.edu
Atomic Force Microscope
 Atomic Force Microscope (Veeco Nanoman) User Manual Basic Operation 4 th Edition Aug 2012 NR System Startup If the system is currently ON To start the NanoScope software, double-click the NanoScope startup
Atomic Force Microscope (Veeco Nanoman) User Manual Basic Operation 4 th Edition Aug 2012 NR System Startup If the system is currently ON To start the NanoScope software, double-click the NanoScope startup
1. Installing The Monitoring Software
 SD7000 Digital Microphone Monitor Software manual Table of Contents 1. Installing The Monitor Software 1.1 Setting Up Receivers For Monitoring 1.2 Running The Application 1.3 Shutdown 2. The Detail Monitoring
SD7000 Digital Microphone Monitor Software manual Table of Contents 1. Installing The Monitor Software 1.1 Setting Up Receivers For Monitoring 1.2 Running The Application 1.3 Shutdown 2. The Detail Monitoring
Create a Poster Using Publisher
 Contents 1. Introduction 1. Starting Publisher 2. Create a Poster Template 5. Aligning your images and text 7. Apply a background 12. Add text to your poster 14. Add pictures to your poster 17. Add graphs
Contents 1. Introduction 1. Starting Publisher 2. Create a Poster Template 5. Aligning your images and text 7. Apply a background 12. Add text to your poster 14. Add pictures to your poster 17. Add graphs
Appendix A How to create a data-sharing lab
 Appendix A How to create a data-sharing lab Creating a lab involves completing five major steps: creating lists, then graphs, then the page for lab instructions, then adding forms to the lab instructions,
Appendix A How to create a data-sharing lab Creating a lab involves completing five major steps: creating lists, then graphs, then the page for lab instructions, then adding forms to the lab instructions,
Software for Producing Rack Layouts and Purchase Orders
 1 Software for Producing Rack Layouts and Purchase Orders Welcome to RackTools: software that makes it simple and quick to specify Middle Atlantic Products. RackTools has been designed with one purpose
1 Software for Producing Rack Layouts and Purchase Orders Welcome to RackTools: software that makes it simple and quick to specify Middle Atlantic Products. RackTools has been designed with one purpose
Beckman Coulter DTX 880 Multimode Detector Bergen County Technical Schools Stem Cell Lab
 Beckman Coulter DTX 880 Multimode Detector Bergen County Technical Schools Stem Cell Lab Room 213 Beckman Coulter DTX 880 Multimode Detector Information The Beckman Coulter DTX 880 Multimode Detector is
Beckman Coulter DTX 880 Multimode Detector Bergen County Technical Schools Stem Cell Lab Room 213 Beckman Coulter DTX 880 Multimode Detector Information The Beckman Coulter DTX 880 Multimode Detector is
Introduction to Powder X-Ray Diffraction History Basic Principles
 Introduction to Powder X-Ray Diffraction History Basic Principles Folie.1 History: Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen discovered 1895 the X-rays. 1901 he was honoured by the Noble prize for
Introduction to Powder X-Ray Diffraction History Basic Principles Folie.1 History: Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen discovered 1895 the X-rays. 1901 he was honoured by the Noble prize for
Using Excel to find Perimeter, Area & Volume
 Using Excel to find Perimeter, Area & Volume Level: LBS 4 V = lwh Goal: To become familiar with Microsoft Excel by entering formulas into a spreadsheet in order to calculate the perimeter, area and volume
Using Excel to find Perimeter, Area & Volume Level: LBS 4 V = lwh Goal: To become familiar with Microsoft Excel by entering formulas into a spreadsheet in order to calculate the perimeter, area and volume
SECTION 5: Finalizing Your Workbook
 SECTION 5: Finalizing Your Workbook In this section you will learn how to: Protect a workbook Protect a sheet Protect Excel files Unlock cells Use the document inspector Use the compatibility checker Mark
SECTION 5: Finalizing Your Workbook In this section you will learn how to: Protect a workbook Protect a sheet Protect Excel files Unlock cells Use the document inspector Use the compatibility checker Mark
ScanPro 3000 High Definition Microfilm Scanner. Help Guide
 ScanPro 3000 High Definition Microfilm Scanner Help Guide Table of Contents Getting Started 3 Loading the Film 4-5 Viewing Your Film 6-7 Motorized Roll Film Control 6 Crop Box 7 Using the Toolbar Controls
ScanPro 3000 High Definition Microfilm Scanner Help Guide Table of Contents Getting Started 3 Loading the Film 4-5 Viewing Your Film 6-7 Motorized Roll Film Control 6 Crop Box 7 Using the Toolbar Controls
Creating a Poster in PowerPoint 2010. A. Set Up Your Poster
 View the Best Practices in Poster Design located at http://www.emich.edu/training/poster before you begin creating a poster. Then in PowerPoint: (A) set up the poster size and orientation, (B) add and
View the Best Practices in Poster Design located at http://www.emich.edu/training/poster before you begin creating a poster. Then in PowerPoint: (A) set up the poster size and orientation, (B) add and
1051-232 Imaging Systems Laboratory II. Laboratory 4: Basic Lens Design in OSLO April 2 & 4, 2002
 05-232 Imaging Systems Laboratory II Laboratory 4: Basic Lens Design in OSLO April 2 & 4, 2002 Abstract: For designing the optics of an imaging system, one of the main types of tools used today is optical
05-232 Imaging Systems Laboratory II Laboratory 4: Basic Lens Design in OSLO April 2 & 4, 2002 Abstract: For designing the optics of an imaging system, one of the main types of tools used today is optical
Introduction to X-Ray Powder Diffraction Data Analysis
 Introduction to X-Ray Powder Diffraction Data Analysis Center for Materials Science and Engineering at MIT http://prism.mit.edu/xray An X-ray diffraction pattern is a plot of the intensity of X-rays scattered
Introduction to X-Ray Powder Diffraction Data Analysis Center for Materials Science and Engineering at MIT http://prism.mit.edu/xray An X-ray diffraction pattern is a plot of the intensity of X-rays scattered
LS-1 Series Tungsten Halogen Light Sources Installation and Operation Instructions
 LS-1 Series Tungsten Halogen Light Sources Installation and Operation Instructions Description The LS-1 Series of tungsten halogen light sources are versatile, white-light lamps optimized for use in the
LS-1 Series Tungsten Halogen Light Sources Installation and Operation Instructions Description The LS-1 Series of tungsten halogen light sources are versatile, white-light lamps optimized for use in the
Microsoft Excel 2010 Charts and Graphs
 Microsoft Excel 2010 Charts and Graphs Email: training@health.ufl.edu Web Page: http://training.health.ufl.edu Microsoft Excel 2010: Charts and Graphs 2.0 hours Topics include data groupings; creating
Microsoft Excel 2010 Charts and Graphs Email: training@health.ufl.edu Web Page: http://training.health.ufl.edu Microsoft Excel 2010: Charts and Graphs 2.0 hours Topics include data groupings; creating
PowerWorld Simulator
 PowerWorld Simulator Quick Start Guide 2001 South First Street Champaign, Illinois 61820 +1 (217) 384.6330 support@powerworld.com http://www.powerworld.com Purpose This quick start guide is intended to
PowerWorld Simulator Quick Start Guide 2001 South First Street Champaign, Illinois 61820 +1 (217) 384.6330 support@powerworld.com http://www.powerworld.com Purpose This quick start guide is intended to
CATIA Functional Tolerancing & Annotation TABLE OF CONTENTS
 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction...1 Functional Tolerancing and Annotation...2 Pull-down Menus...3 Insert...3 Functional Tolerancing and Annotation Workbench...4 Bottom Toolbar Changes...5 3D Grid Toolbar...5
TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction...1 Functional Tolerancing and Annotation...2 Pull-down Menus...3 Insert...3 Functional Tolerancing and Annotation Workbench...4 Bottom Toolbar Changes...5 3D Grid Toolbar...5
Using Microsoft Project 2000
 Using MS Project Personal Computer Fundamentals 1 of 45 Using Microsoft Project 2000 General Conventions All text highlighted in bold refers to menu selections. Examples would be File and Analysis. ALL
Using MS Project Personal Computer Fundamentals 1 of 45 Using Microsoft Project 2000 General Conventions All text highlighted in bold refers to menu selections. Examples would be File and Analysis. ALL
WAVELENGTH OF LIGHT - DIFFRACTION GRATING
 PURPOSE In this experiment we will use the diffraction grating and the spectrometer to measure wavelengths in the mercury spectrum. THEORY A diffraction grating is essentially a series of parallel equidistant
PURPOSE In this experiment we will use the diffraction grating and the spectrometer to measure wavelengths in the mercury spectrum. THEORY A diffraction grating is essentially a series of parallel equidistant
5. Tutorial. Starting FlashCut CNC
 FlashCut CNC Section 5 Tutorial 259 5. Tutorial Starting FlashCut CNC To start FlashCut CNC, click on the Start button, select Programs, select FlashCut CNC 4, then select the FlashCut CNC 4 icon. A dialog
FlashCut CNC Section 5 Tutorial 259 5. Tutorial Starting FlashCut CNC To start FlashCut CNC, click on the Start button, select Programs, select FlashCut CNC 4, then select the FlashCut CNC 4 icon. A dialog
Creating Interactive PDF Forms
 Creating Interactive PDF Forms Using Adobe Acrobat X Pro Information Technology Services Outreach and Distance Learning Technologies Copyright 2012 KSU Department of Information Technology Services This
Creating Interactive PDF Forms Using Adobe Acrobat X Pro Information Technology Services Outreach and Distance Learning Technologies Copyright 2012 KSU Department of Information Technology Services This
Education Solutions Development, Inc. APECS Navigation: Business Systems Getting Started Reference Guide
 Education Solutions Development, Inc. APECS Navigation: Business Systems Getting Started Reference Guide March 2013 Education Solutions Development, Inc. What s Inside The information in this reference
Education Solutions Development, Inc. APECS Navigation: Business Systems Getting Started Reference Guide March 2013 Education Solutions Development, Inc. What s Inside The information in this reference
BODY-12, Door Handle - Removal, Installation, and Adjustment
 Introduction BODY-12, Door Handle - Removal, Installation, and Adjustment There are many different procedures floating around describing how to replace the door handles on a 944 and every one of them will
Introduction BODY-12, Door Handle - Removal, Installation, and Adjustment There are many different procedures floating around describing how to replace the door handles on a 944 and every one of them will
Decision Support AITS University Administration. Web Intelligence Rich Client 4.1 User Guide
 Decision Support AITS University Administration Web Intelligence Rich Client 4.1 User Guide 2 P age Web Intelligence 4.1 User Guide Web Intelligence 4.1 User Guide Contents Getting Started in Web Intelligence
Decision Support AITS University Administration Web Intelligence Rich Client 4.1 User Guide 2 P age Web Intelligence 4.1 User Guide Web Intelligence 4.1 User Guide Contents Getting Started in Web Intelligence
Speed-Mat Rectangle Cutter
 Speed-Mat Rectangle Cutter 1 Honeycomb baseboard. 2 Left hold down. 14 3 Bottom hold down. 4 4 Left / right rule. 8 5 8 5 Left / right rule pointer. 1 6 Top / bottom rule. 7 Top / bottom rule pointer.
Speed-Mat Rectangle Cutter 1 Honeycomb baseboard. 2 Left hold down. 14 3 Bottom hold down. 4 4 Left / right rule. 8 5 8 5 Left / right rule pointer. 1 6 Top / bottom rule. 7 Top / bottom rule pointer.
Window Glass Design 5 According to ASTM E 1300
 A User s Guide to: Window Glass Design 5 According to ASTM E 1300 A product of: 1 Table of Contents Table of Contents List of Figures Chapter 1: Window Glass Design 5 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Features ii iv
A User s Guide to: Window Glass Design 5 According to ASTM E 1300 A product of: 1 Table of Contents Table of Contents List of Figures Chapter 1: Window Glass Design 5 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Features ii iv
13 Managing Devices. Your computer is an assembly of many components from different manufacturers. LESSON OBJECTIVES
 LESSON 13 Managing Devices OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you will be able to: 1. Open System Properties. 2. Use Device Manager. 3. Understand hardware profiles. 4. Set performance options. Estimated
LESSON 13 Managing Devices OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you will be able to: 1. Open System Properties. 2. Use Device Manager. 3. Understand hardware profiles. 4. Set performance options. Estimated
FrontPage 2003: Forms
 FrontPage 2003: Forms Using the Form Page Wizard Open up your website. Use File>New Page and choose More Page Templates. In Page Templates>General, choose Front Page Wizard. Click OK. It is helpful if
FrontPage 2003: Forms Using the Form Page Wizard Open up your website. Use File>New Page and choose More Page Templates. In Page Templates>General, choose Front Page Wizard. Click OK. It is helpful if
A Quick Start Guide to Using PowerPoint For Image-based Presentations
 A Quick Start Guide to Using PowerPoint For Image-based Presentations By Susan Jane Williams & William Staffeld, Knight Visual Resources Facility College of Architecture, Art and Planning Cornell University.
A Quick Start Guide to Using PowerPoint For Image-based Presentations By Susan Jane Williams & William Staffeld, Knight Visual Resources Facility College of Architecture, Art and Planning Cornell University.
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS Nikon TiE Deconvolution Microscope CCRB 1-220G
 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS Nikon TiE Deconvolution Microscope CCRB 1-220G Conventions Through these notes bold font refers to a software button and italics refer to a hardware switch. The software makes extensive
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS Nikon TiE Deconvolution Microscope CCRB 1-220G Conventions Through these notes bold font refers to a software button and italics refer to a hardware switch. The software makes extensive
Quick Start Guide See Inside for Use and Safety Information
 3 rd Generation Personal 3D Printer Quick Start Guide See Inside for Use and Safety Information The USB Mass Storage Device Contains the User Guide and Quick Start Guide in other Languages Congratulations
3 rd Generation Personal 3D Printer Quick Start Guide See Inside for Use and Safety Information The USB Mass Storage Device Contains the User Guide and Quick Start Guide in other Languages Congratulations
Connect and Project: Using a Video Projector in the Classroom
 Connect and Project: Using a Video Projector in the Classroom Apple and Dell Laptops User Guide Training Module Version Date: 7/2008 1 Connect and Project: Using a Video Projector in the Classroom Video
Connect and Project: Using a Video Projector in the Classroom Apple and Dell Laptops User Guide Training Module Version Date: 7/2008 1 Connect and Project: Using a Video Projector in the Classroom Video
Content Author's Reference and Cookbook
 Sitecore CMS 6.5 Content Author's Reference and Cookbook Rev. 110621 Sitecore CMS 6.5 Content Author's Reference and Cookbook A Conceptual Overview and Practical Guide to Using Sitecore Table of Contents
Sitecore CMS 6.5 Content Author's Reference and Cookbook Rev. 110621 Sitecore CMS 6.5 Content Author's Reference and Cookbook A Conceptual Overview and Practical Guide to Using Sitecore Table of Contents
LESSON 7: IMPORTING AND VECTORIZING A BITMAP IMAGE
 LESSON 7: IMPORTING AND VECTORIZING A BITMAP IMAGE In this lesson we ll learn how to import a bitmap logo, transform it into a vector and perform some editing on the vector to clean it up. The concepts
LESSON 7: IMPORTING AND VECTORIZING A BITMAP IMAGE In this lesson we ll learn how to import a bitmap logo, transform it into a vector and perform some editing on the vector to clean it up. The concepts
Chapter 7: Basics of X-ray Diffraction
 Providing Solutions To Your Diffraction Needs. Chapter 7: Basics of X-ray Diffraction Scintag has prepared this section for use by customers and authorized personnel. The information contained herein is
Providing Solutions To Your Diffraction Needs. Chapter 7: Basics of X-ray Diffraction Scintag has prepared this section for use by customers and authorized personnel. The information contained herein is
House Design Tutorial
 Chapter 2: House Design Tutorial This House Design Tutorial shows you how to get started on a design project. The tutorials that follow continue with the same plan. When we are finished, we will have created
Chapter 2: House Design Tutorial This House Design Tutorial shows you how to get started on a design project. The tutorials that follow continue with the same plan. When we are finished, we will have created
X-ray diffraction techniques for thin films
 X-ray diffraction techniques for thin films Rigaku Corporation Application Laboratory Takayuki Konya 1 Today s contents (PM) Introduction X-ray diffraction method Out-of-Plane In-Plane Pole figure Reciprocal
X-ray diffraction techniques for thin films Rigaku Corporation Application Laboratory Takayuki Konya 1 Today s contents (PM) Introduction X-ray diffraction method Out-of-Plane In-Plane Pole figure Reciprocal
Now part of ALLSCRIPTS. HealthMatics EMR Input Manager
 Now part of ALLSCRIPTS HealthMatics EMR Input Manager May 9, 2006 Statement of Confidentiality The information contained herein is proprietary and confidential to A 4 HEALTH SYSTEMS. No part of this document
Now part of ALLSCRIPTS HealthMatics EMR Input Manager May 9, 2006 Statement of Confidentiality The information contained herein is proprietary and confidential to A 4 HEALTH SYSTEMS. No part of this document
RIGAKU MINIFLEX II. Standard Operating Procedure (SOP)
 RIGAKU MINIFLEX II Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) Contact Information Rigaku Americas Tel: 1-888-362-2324 Email: support@rigaku.com Dr. Mas Subramanian Weniger Hall 339 Phone: (541) 737-8235 Phone
RIGAKU MINIFLEX II Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) Contact Information Rigaku Americas Tel: 1-888-362-2324 Email: support@rigaku.com Dr. Mas Subramanian Weniger Hall 339 Phone: (541) 737-8235 Phone
Using Mail Merge in Microsoft Word 2003
 Using Mail Merge in Microsoft Word 2003 Mail Merge Created: 12 April 2005 Note: You should be competent in Microsoft Word before you attempt this Tutorial. Open Microsoft Word 2003 Beginning the Merge
Using Mail Merge in Microsoft Word 2003 Mail Merge Created: 12 April 2005 Note: You should be competent in Microsoft Word before you attempt this Tutorial. Open Microsoft Word 2003 Beginning the Merge
Microsoft Word defaults to left justified (aligned) paragraphs. This means that new lines automatically line up with the left margin.
 Microsoft Word Part 2 Office 2007 Microsoft Word 2007 Part 2 Alignment Microsoft Word defaults to left justified (aligned) paragraphs. This means that new lines automatically line up with the left margin.
Microsoft Word Part 2 Office 2007 Microsoft Word 2007 Part 2 Alignment Microsoft Word defaults to left justified (aligned) paragraphs. This means that new lines automatically line up with the left margin.
Zeiss 780 Training Notes
 Zeiss 780 Training Notes 780 Start Up Sequence Do you need the argon laser, 458,488,514nm lines? No Turn on the Systems PC Switch Turn on Main Power Switch Yes Turn on the laser main power switch and turn
Zeiss 780 Training Notes 780 Start Up Sequence Do you need the argon laser, 458,488,514nm lines? No Turn on the Systems PC Switch Turn on Main Power Switch Yes Turn on the laser main power switch and turn
Quick Guide for Data Collection on the NIU Bruker Smart CCD
 Quick Guide for Data Collection on the NIU Bruker Smart CCD 1. Create a new project 2. Optically align the crystal 3. Take rotation picture 4. Collect matrix to determine unit cell 5. Refine unit cell
Quick Guide for Data Collection on the NIU Bruker Smart CCD 1. Create a new project 2. Optically align the crystal 3. Take rotation picture 4. Collect matrix to determine unit cell 5. Refine unit cell
6) How wide must a narrow slit be if the first diffraction minimum occurs at ±12 with laser light of 633 nm?
 Test IV Name 1) In a single slit diffraction experiment, the width of the slit is 3.1 10-5 m and the distance from the slit to the screen is 2.2 m. If the beam of light of wavelength 600 nm passes through
Test IV Name 1) In a single slit diffraction experiment, the width of the slit is 3.1 10-5 m and the distance from the slit to the screen is 2.2 m. If the beam of light of wavelength 600 nm passes through
Microsoft Migrating to PowerPoint 2010 from PowerPoint 2003
 In This Guide Microsoft PowerPoint 2010 looks very different, so we created this guide to help you minimize the learning curve. Read on to learn key parts of the new interface, discover free PowerPoint
In This Guide Microsoft PowerPoint 2010 looks very different, so we created this guide to help you minimize the learning curve. Read on to learn key parts of the new interface, discover free PowerPoint
MAINTENANCE & TROUBLESHOOTING
 MAINTENANCE & TROUBLESHOOTING This section describes how to: clean the lens clean the fan intake filter replace the projection lamp replace the batteries in the remote control use the Kensington lock feature
MAINTENANCE & TROUBLESHOOTING This section describes how to: clean the lens clean the fan intake filter replace the projection lamp replace the batteries in the remote control use the Kensington lock feature
Quick Start Tutorial Metric version
 Quick Start Tutorial Metric version 1996-2009 Cadsoft Corporation. No part of this guide or the accompanying software may be reproduced or transmitted, electronically or mechanically, without written permission
Quick Start Tutorial Metric version 1996-2009 Cadsoft Corporation. No part of this guide or the accompanying software may be reproduced or transmitted, electronically or mechanically, without written permission
KPN SMS mail. Send SMS as fast as e-mail!
 KPN SMS mail Send SMS as fast as e-mail! Quick start Start using KPN SMS mail in 5 steps If you want to install and use KPN SMS mail quickly, without reading the user guide, follow the next five steps.
KPN SMS mail Send SMS as fast as e-mail! Quick start Start using KPN SMS mail in 5 steps If you want to install and use KPN SMS mail quickly, without reading the user guide, follow the next five steps.
Excel 2003 A Beginners Guide
 Excel 2003 A Beginners Guide Beginner Introduction The aim of this document is to introduce some basic techniques for using Excel to enter data, perform calculations and produce simple charts based on
Excel 2003 A Beginners Guide Beginner Introduction The aim of this document is to introduce some basic techniques for using Excel to enter data, perform calculations and produce simple charts based on
Everyday Excel Stuff Excel Day Planner Organizer Reference Guide
 Everyday Excel Stuff Excel Day Planner Organizer Reference Guide Opening & Saving the Excel Day Planner... 2 1. Opening the Day Planner...2 2. Saving the Day Planner...2 Daily Task Sheet... 2 1. Entering
Everyday Excel Stuff Excel Day Planner Organizer Reference Guide Opening & Saving the Excel Day Planner... 2 1. Opening the Day Planner...2 2. Saving the Day Planner...2 Daily Task Sheet... 2 1. Entering
Getting Started with Excel 2008. Table of Contents
 Table of Contents Elements of An Excel Document... 2 Resizing and Hiding Columns and Rows... 3 Using Panes to Create Spreadsheet Headers... 3 Using the AutoFill Command... 4 Using AutoFill for Sequences...
Table of Contents Elements of An Excel Document... 2 Resizing and Hiding Columns and Rows... 3 Using Panes to Create Spreadsheet Headers... 3 Using the AutoFill Command... 4 Using AutoFill for Sequences...
Data Warehouse. Business Objects
 Data Warehouse Business Objects Power User: Querying [DW POWER USER] The data warehouse, at Booth, is used to store, retrieve and create reports for data at Booth. The first release of the warehouse contains
Data Warehouse Business Objects Power User: Querying [DW POWER USER] The data warehouse, at Booth, is used to store, retrieve and create reports for data at Booth. The first release of the warehouse contains
Lesson 7 - Creating Animation II
 Lesson 7 - Creating Animation II A. Motion-Tweened Animation With motion tweening, you can easily create motion effects for the objects in your Flash movies. Kites flying, balls bouncing, rocks rolling
Lesson 7 - Creating Animation II A. Motion-Tweened Animation With motion tweening, you can easily create motion effects for the objects in your Flash movies. Kites flying, balls bouncing, rocks rolling
Microsoft Excel 2013 Tutorial
 Microsoft Excel 2013 Tutorial TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Getting Started Pg. 3 2. Creating A New Document Pg. 3 3. Saving Your Document Pg. 4 4. Toolbars Pg. 4 5. Formatting Pg. 6 Working With Cells Pg. 6 Changing
Microsoft Excel 2013 Tutorial TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Getting Started Pg. 3 2. Creating A New Document Pg. 3 3. Saving Your Document Pg. 4 4. Toolbars Pg. 4 5. Formatting Pg. 6 Working With Cells Pg. 6 Changing
Integrated Accounting System for Mac OS X
 Integrated Accounting System for Mac OS X Program version: 6.3 110401 2011 HansaWorld Ireland Limited, Dublin, Ireland Preface Standard Accounts is a powerful accounting system for Mac OS X. Text in square
Integrated Accounting System for Mac OS X Program version: 6.3 110401 2011 HansaWorld Ireland Limited, Dublin, Ireland Preface Standard Accounts is a powerful accounting system for Mac OS X. Text in square
Excel macros made easy
 IT Training Excel macros made easy Jane Barrett, IT Training & Engagement Team Information System Services Version 1.1 Scope Learning outcomes Understand the concept of what a macro is and what it does.
IT Training Excel macros made easy Jane Barrett, IT Training & Engagement Team Information System Services Version 1.1 Scope Learning outcomes Understand the concept of what a macro is and what it does.
Getting Started Guide
 Getting Started Guide Mulberry IMAP Internet Mail Client Versions 3.0 & 3.1 Cyrusoft International, Inc. Suite 780 The Design Center 5001 Baum Blvd. Pittsburgh PA 15213 USA Tel: +1 412 605 0499 Fax: +1
Getting Started Guide Mulberry IMAP Internet Mail Client Versions 3.0 & 3.1 Cyrusoft International, Inc. Suite 780 The Design Center 5001 Baum Blvd. Pittsburgh PA 15213 USA Tel: +1 412 605 0499 Fax: +1
Introduction to Autodesk Inventor for F1 in Schools
 Introduction to Autodesk Inventor for F1 in Schools F1 in Schools Race Car In this course you will be introduced to Autodesk Inventor, which is the centerpiece of Autodesk s digital prototyping strategy
Introduction to Autodesk Inventor for F1 in Schools F1 in Schools Race Car In this course you will be introduced to Autodesk Inventor, which is the centerpiece of Autodesk s digital prototyping strategy
Introduction to Microsoft Excel 2010
 Introduction to Microsoft Excel 2010 Screen Elements Quick Access Toolbar The Ribbon Formula Bar Expand Formula Bar Button File Menu Vertical Scroll Worksheet Navigation Tabs Horizontal Scroll Bar Zoom
Introduction to Microsoft Excel 2010 Screen Elements Quick Access Toolbar The Ribbon Formula Bar Expand Formula Bar Button File Menu Vertical Scroll Worksheet Navigation Tabs Horizontal Scroll Bar Zoom
TRIMMING UNIT/DIAMOND MACHINE TST.13
 TRIMMING UNIT/DIAMOND MACHINE TST.13 REFERENCE BOOK rel. 02.15 TRIMMING UNIT/DIAMOND MACHINE TST.13 REL. 02.15 ENGLISH LANGUAGE 1 MACHINE DESCRIPTION TST.13 was designed and built for processing methacrylate.
TRIMMING UNIT/DIAMOND MACHINE TST.13 REFERENCE BOOK rel. 02.15 TRIMMING UNIT/DIAMOND MACHINE TST.13 REL. 02.15 ENGLISH LANGUAGE 1 MACHINE DESCRIPTION TST.13 was designed and built for processing methacrylate.
Laboratory Designed Abutment. Optimization By Design
 The Laboratory Designed Abutment Optimization By Design Table Of Contents Instructions For Scanning The Laboratory Designed Abutment.... 1 Pouring The Model And Cast... 1 Starting The Scanner.... 1 Calibrating
The Laboratory Designed Abutment Optimization By Design Table Of Contents Instructions For Scanning The Laboratory Designed Abutment.... 1 Pouring The Model And Cast... 1 Starting The Scanner.... 1 Calibrating
EPSON SCANNING TIPS AND TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE Epson Perfection 3170 Scanner
 EPSON SCANNING TIPS AND TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE Epson Perfection 3170 Scanner SELECT A SUITABLE RESOLUTION The best scanning resolution depends on the purpose of the scan. When you specify a high resolution,
EPSON SCANNING TIPS AND TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE Epson Perfection 3170 Scanner SELECT A SUITABLE RESOLUTION The best scanning resolution depends on the purpose of the scan. When you specify a high resolution,
Correcting the Lateral Response Artifact in Radiochromic Film Images from Flatbed Scanners
 Correcting the Lateral Response Artifact in Radiochromic Film Images from Flatbed Scanners Background The lateral response artifact (LRA) in radiochromic film images from flatbed scanners was first pointed
Correcting the Lateral Response Artifact in Radiochromic Film Images from Flatbed Scanners Background The lateral response artifact (LRA) in radiochromic film images from flatbed scanners was first pointed
Project Setup and Data Management Tutorial
 Project Setup and Heavy Construction Edition Version 1.20 Corporate Office Trimble Navigation Limited Engineering and Construction Division 5475 Kellenburger Road Dayton, Ohio 45424-1099 U.S.A. Phone:
Project Setup and Heavy Construction Edition Version 1.20 Corporate Office Trimble Navigation Limited Engineering and Construction Division 5475 Kellenburger Road Dayton, Ohio 45424-1099 U.S.A. Phone:
Gestation Period as a function of Lifespan
 This document will show a number of tricks that can be done in Minitab to make attractive graphs. We work first with the file X:\SOR\24\M\ANIMALS.MTP. This first picture was obtained through Graph Plot.
This document will show a number of tricks that can be done in Minitab to make attractive graphs. We work first with the file X:\SOR\24\M\ANIMALS.MTP. This first picture was obtained through Graph Plot.
Universal Simple Control, USC-1
 Universal Simple Control, USC-1 Data and Event Logging with the USB Flash Drive DATA-PAK The USC-1 universal simple voltage regulator control uses a flash drive to store data. Then a propriety Data and
Universal Simple Control, USC-1 Data and Event Logging with the USB Flash Drive DATA-PAK The USC-1 universal simple voltage regulator control uses a flash drive to store data. Then a propriety Data and
Using Microsoft Word. Working With Objects
 Using Microsoft Word Many Word documents will require elements that were created in programs other than Word, such as the picture to the right. Nontext elements in a document are referred to as Objects
Using Microsoft Word Many Word documents will require elements that were created in programs other than Word, such as the picture to the right. Nontext elements in a document are referred to as Objects
Detector transparent with Color Inserts. FAA 500 TR P Trim Ring transparent with Color Inserts. FCA 500 / FCA 500 E Detector Bases
 Detector Color Detector transparent with Color Inserts FAA 500 TR W Trim Ring FAA 500 TR P Trim Ring transparent with Color Inserts FAA 500 BB Ceiling Mount Back Box FCA 500 / FCA 500 E Detector Bases
Detector Color Detector transparent with Color Inserts FAA 500 TR W Trim Ring FAA 500 TR P Trim Ring transparent with Color Inserts FAA 500 BB Ceiling Mount Back Box FCA 500 / FCA 500 E Detector Bases
A Beginner s Guide to PowerPoint 2010
 A Beginner s Guide to PowerPoint 2010 I. The Opening Screen You will see the default opening screen is actually composed of three parts: 1. The Slides/Outline tabs on the left which displays thumbnails
A Beginner s Guide to PowerPoint 2010 I. The Opening Screen You will see the default opening screen is actually composed of three parts: 1. The Slides/Outline tabs on the left which displays thumbnails
TABLE OF CONTENTS. INTRODUCTION... 5 Advance Concrete... 5 Where to find information?... 6 INSTALLATION... 7 STARTING ADVANCE CONCRETE...
 Starting Guide TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... 5 Advance Concrete... 5 Where to find information?... 6 INSTALLATION... 7 STARTING ADVANCE CONCRETE... 7 ADVANCE CONCRETE USER INTERFACE... 7 Other important
Starting Guide TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... 5 Advance Concrete... 5 Where to find information?... 6 INSTALLATION... 7 STARTING ADVANCE CONCRETE... 7 ADVANCE CONCRETE USER INTERFACE... 7 Other important
Excel Project Creating a Stock Portfolio Simulation
 Background Vocabulary Excel Project Creating a Stock Portfolio Simulation 1. What is a stock? A stock is a share in the ownership of a corporation, a large business organization. A stock, also, represents
Background Vocabulary Excel Project Creating a Stock Portfolio Simulation 1. What is a stock? A stock is a share in the ownership of a corporation, a large business organization. A stock, also, represents
Chapter 1. Creating Sketches in. the Sketch Mode-I. Evaluation chapter. Logon to www.cadcim.com for more details. Learning Objectives
 Chapter 1 Creating Sketches in Learning Objectives the Sketch Mode-I After completing this chapter you will be able to: Use various tools to create a geometry. Dimension a sketch. Apply constraints to
Chapter 1 Creating Sketches in Learning Objectives the Sketch Mode-I After completing this chapter you will be able to: Use various tools to create a geometry. Dimension a sketch. Apply constraints to
Task Force on Technology / EXCEL
 Task Force on Technology EXCEL Basic terminology Spreadsheet A spreadsheet is an electronic document that stores various types of data. There are vertical columns and horizontal rows. A cell is where the
Task Force on Technology EXCEL Basic terminology Spreadsheet A spreadsheet is an electronic document that stores various types of data. There are vertical columns and horizontal rows. A cell is where the
Migrating to Excel 2010 from Excel 2003 - Excel - Microsoft Office 1 of 1
 Migrating to Excel 2010 - Excel - Microsoft Office 1 of 1 In This Guide Microsoft Excel 2010 looks very different, so we created this guide to help you minimize the learning curve. Read on to learn key
Migrating to Excel 2010 - Excel - Microsoft Office 1 of 1 In This Guide Microsoft Excel 2010 looks very different, so we created this guide to help you minimize the learning curve. Read on to learn key
SQL Server 2005: Report Builder
 SQL Server 2005: Report Builder Table of Contents SQL Server 2005: Report Builder...3 Lab Setup...4 Exercise 1 Report Model Projects...5 Exercise 2 Create a Report using Report Builder...9 SQL Server 2005:
SQL Server 2005: Report Builder Table of Contents SQL Server 2005: Report Builder...3 Lab Setup...4 Exercise 1 Report Model Projects...5 Exercise 2 Create a Report using Report Builder...9 SQL Server 2005:
Navios Quick Reference
 Navios Quick Reference Purpose: The purpose of this Quick Reference is to provide a simple step by step outline of the information needed to perform various tasks on the system. We begin with basic tasks
Navios Quick Reference Purpose: The purpose of this Quick Reference is to provide a simple step by step outline of the information needed to perform various tasks on the system. We begin with basic tasks
Complete. PCB Design Using. NI Multisim, NI Ultiboard, LPKF CircuitCAM and BoardMaster. pg. 1. Wei Siang Pee
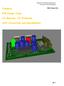 Complete Wei Siang Pee PCB Design Using NI Multisim, NI Ultiboard, LPKF CircuitCAM and BoardMaster pg. 1 Introduction Multisim equips educators, students, and professionals with the tools to analyze circuit
Complete Wei Siang Pee PCB Design Using NI Multisim, NI Ultiboard, LPKF CircuitCAM and BoardMaster pg. 1 Introduction Multisim equips educators, students, and professionals with the tools to analyze circuit
If you know exactly how you want your business forms to look and don t mind
 appendix e Advanced Form Customization If you know exactly how you want your business forms to look and don t mind detail work, you can configure QuickBooks forms however you want. With QuickBooks Layout
appendix e Advanced Form Customization If you know exactly how you want your business forms to look and don t mind detail work, you can configure QuickBooks forms however you want. With QuickBooks Layout
Project 1 - Business Proposal (PowerPoint)
 Project 1 - Business Proposal (PowerPoint) extraordinary faculty, inquisitive and talented students, a constant striving to build upon and expand historical strengths, the vision to anticipate the future,
Project 1 - Business Proposal (PowerPoint) extraordinary faculty, inquisitive and talented students, a constant striving to build upon and expand historical strengths, the vision to anticipate the future,
Introduction to dobe Acrobat XI Pro
 Introduction to dobe Acrobat XI Pro Introduction to Adobe Acrobat XI Pro is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License. To view a copy of this
Introduction to dobe Acrobat XI Pro Introduction to Adobe Acrobat XI Pro is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License. To view a copy of this
Entourage - an Introduction to E-mail
 Entourage - an Introduction to E-mail Version 2004 for Macintosh Table of Contents What is Entourage Starting Entourage The Navigation Pane Getting Help Creating and Sending a Message Using the UI Exchange
Entourage - an Introduction to E-mail Version 2004 for Macintosh Table of Contents What is Entourage Starting Entourage The Navigation Pane Getting Help Creating and Sending a Message Using the UI Exchange
Getting Started Guide
 Getting Started Guide Mulberry Internet Email/Calendar Client Version 4.0 Cyrus Daboo Pittsburgh PA USA mailto:mulberry@mulberrymail.com http://www.mulberrymail.com/ Information in this document is subject
Getting Started Guide Mulberry Internet Email/Calendar Client Version 4.0 Cyrus Daboo Pittsburgh PA USA mailto:mulberry@mulberrymail.com http://www.mulberrymail.com/ Information in this document is subject
Atomic Force Microscope and Magnetic Force Microscope Background Information
 Atomic Force Microscope and Magnetic Force Microscope Background Information Lego Building Instructions There are several places to find the building instructions for building the Lego models of atomic
Atomic Force Microscope and Magnetic Force Microscope Background Information Lego Building Instructions There are several places to find the building instructions for building the Lego models of atomic
Kitchen and Bath Design Tutorial
 Adding Cabinets Chapter 5: Kitchen and Bath Design Tutorial This tutorial continues where the Materials Tutorial left off. You should save this tutorial using a new name to archive your previous work.
Adding Cabinets Chapter 5: Kitchen and Bath Design Tutorial This tutorial continues where the Materials Tutorial left off. You should save this tutorial using a new name to archive your previous work.
Microsoft Migrating to Word 2010 from Word 2003
 In This Guide Microsoft Word 2010 looks very different, so we created this guide to help you minimize the learning curve. Read on to learn key parts of the new interface, discover free Word 2010 training,
In This Guide Microsoft Word 2010 looks very different, so we created this guide to help you minimize the learning curve. Read on to learn key parts of the new interface, discover free Word 2010 training,
SECTION 2-1: OVERVIEW SECTION 2-2: FREQUENCY DISTRIBUTIONS
 SECTION 2-1: OVERVIEW Chapter 2 Describing, Exploring and Comparing Data 19 In this chapter, we will use the capabilities of Excel to help us look more carefully at sets of data. We can do this by re-organizing
SECTION 2-1: OVERVIEW Chapter 2 Describing, Exploring and Comparing Data 19 In this chapter, we will use the capabilities of Excel to help us look more carefully at sets of data. We can do this by re-organizing
OxySense Gen III Operations Manual
 OxySense Gen III Operations Manual OxySense GEN III 300 Series OxySense GEN III 5000 Series COMPLIES WITH ASTM 2714-08 OxySense, Inc. 13111 North Central Expressway, Suite 440 Dallas, Texas 75243 Phone
OxySense Gen III Operations Manual OxySense GEN III 300 Series OxySense GEN III 5000 Series COMPLIES WITH ASTM 2714-08 OxySense, Inc. 13111 North Central Expressway, Suite 440 Dallas, Texas 75243 Phone
149mm. Walk-Thru Assembly Gate. MODEL NO: 1161, 1167 Owner s Manual. www.regalo-baby.com
 149mm 210mm Walk-Thru Assembly Gate MODEL NO: 1161, 1167 Owner s Manual READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE ASSEMBLY AND USE OF GATE. KEEP INSTRUCTIONS FOR FUTURE USE. www.regalo-baby.com... Regalo International,
149mm 210mm Walk-Thru Assembly Gate MODEL NO: 1161, 1167 Owner s Manual READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE ASSEMBLY AND USE OF GATE. KEEP INSTRUCTIONS FOR FUTURE USE. www.regalo-baby.com... Regalo International,
Becton-Dickinson FACSCalibur Flow Cytometer Instructions
 Start-up 1. Turn on flow cytometer by pushing green button on right side of instrument, toward the back. Give it 30 minutes to warm up before collecting data. 2. Turn on monitor. 3. Turn on computer. If
Start-up 1. Turn on flow cytometer by pushing green button on right side of instrument, toward the back. Give it 30 minutes to warm up before collecting data. 2. Turn on monitor. 3. Turn on computer. If
POWERPOINT BASICS: MICROSOFT OFFICE 2013
 University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill Libraries Carrboro Cybrary Chapel Hill Public Library Durham County Public Library POWERPOINT BASICS: MICROSOFT OFFICE 2013 GETTING STARTED PAGE 02 Prerequisites
University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill Libraries Carrboro Cybrary Chapel Hill Public Library Durham County Public Library POWERPOINT BASICS: MICROSOFT OFFICE 2013 GETTING STARTED PAGE 02 Prerequisites
TimeValue Software Due Date Tracking and Task Management Software
 User s Guide TM TimeValue Software Due Date Tracking and Task Management Software File In Time Software User s Guide Copyright TimeValue Software, Inc. (a California Corporation) 1992-2010. All rights
User s Guide TM TimeValue Software Due Date Tracking and Task Management Software File In Time Software User s Guide Copyright TimeValue Software, Inc. (a California Corporation) 1992-2010. All rights
EXPERIMENT O-6. Michelson Interferometer. Abstract. References. Pre-Lab
 EXPERIMENT O-6 Michelson Interferometer Abstract A Michelson interferometer, constructed by the student, is used to measure the wavelength of He-Ne laser light and the index of refraction of a flat transparent
EXPERIMENT O-6 Michelson Interferometer Abstract A Michelson interferometer, constructed by the student, is used to measure the wavelength of He-Ne laser light and the index of refraction of a flat transparent
Introduction to MS WINDOWS XP
 Introduction to MS WINDOWS XP Mouse Desktop Windows Applications File handling Introduction to MS Windows XP 2 Table of Contents What is Windows XP?... 3 Windows within Windows... 3 The Desktop... 3 The
Introduction to MS WINDOWS XP Mouse Desktop Windows Applications File handling Introduction to MS Windows XP 2 Table of Contents What is Windows XP?... 3 Windows within Windows... 3 The Desktop... 3 The
Site Maintenance. Table of Contents
 Site Maintenance Table of Contents Adobe Contribute How to Install... 1 Publisher and Editor Roles... 1 Editing a Page in Contribute... 2 Designing a Page... 4 Publishing a Draft... 7 Common Problems...
Site Maintenance Table of Contents Adobe Contribute How to Install... 1 Publisher and Editor Roles... 1 Editing a Page in Contribute... 2 Designing a Page... 4 Publishing a Draft... 7 Common Problems...
Understand the Sketcher workbench of CATIA V5.
 Chapter 1 Drawing Sketches in Learning Objectives the Sketcher Workbench-I After completing this chapter you will be able to: Understand the Sketcher workbench of CATIA V5. Start a new file in the Part
Chapter 1 Drawing Sketches in Learning Objectives the Sketcher Workbench-I After completing this chapter you will be able to: Understand the Sketcher workbench of CATIA V5. Start a new file in the Part
