SEMI-AUTOMATED CLASSIFICATION OF URBAN AREAS BY MEANS OF HIGH RESOLUTION RADAR DATA
|
|
|
- Rosemary Walsh
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SEMI-AUTOMATED CLASSIFICATION OF URBAN AREAS BY MEANS OF HIGH RESOLUTION RADAR DATA T. Esch, A. Roth German Aerospace Center DLR, German Remote Sensing Data Center DFD, Wessling, Germany- (Thomas.Esch, Commission VI, WG VI/4 KEY WORDS: High Resolution SAR, Urban Areas, Detection, Contextual Analysis, Texture, Automation ABSTRACT: Almost two thirds of the world s population will live in cities by Thus, human settlements typify the most dynamic regions on earth. To cope with this development urban planning and management requires up-to-date information about the various processes taking place within the urbanised zones. As radar remote sensing allows for the collection of areal data under almost all weather and environmental conditions it is predestined for a frequent and near-term retrieval of geo-information. In view of the future TerraSAR-X mission the German Remote Sensing Data Center (DFD) researches into the potential use of high resolution radar imagery. In this context our main objective is to develop concepts for a mostly automated detection and analysis of human settlements by means of high resolution SAR data. The studies are based on multi-frequency single-, dual- and quadpolarised SAR data recorded by the airborne Experimental Synthetic Aperture Radar (E-SAR) system of the German Aerospace Center (DLR). This paper presents first results of an object-oriented approach towards a semi-automated identification of built-up areas based on single-polarised E-SAR X-band imagery. The basic concept includes an optimised speckle suppression procedure in order to improve and stabilise subsequent image analysis as well as the development of an object-oriented classification scheme for an automated detection of built-up areas from high resolution X-band imagery. The developed concept for a semi-automated extraction of urban areas from single polarised X-band data yields promising results. Built-up areas could be detected with an accuracy of 86%, 85% and 91% for three flight tracks. While the main body of the settlements could be identified with an accuracy of more than 90% inaccuracies were mainly associated with flanking parks, recreation areas and allotments. 1. INTRODUCTION Numerous studies have focused on the utilisation of satellite imagery to analyse human settlements, monitor urban sprawl or map urban land use patterns and infrastructure. Most of these applications deal with an analysis of regional or local phenomena based on spectral characteristics or indices derived from high resolution optical satellite imagery (Ehrlich, Lavalle, Schillinger, 1999; Masek, Lindsay, Goward, 2000; Ridd, Liu, 1998). In the context of urban applications radar imagery has played a minor role since the strong dependence of radar reflectance on geometrical characteristics of the illuminated scene has hampered its interpretation significantly. In radar images the agglomeration of di- and trihedral corner reflectors in urban environments makes these regions standing out as clusters of more or less bright signal returns. This effect has been used for monitoring the urban footprint and subsequently estimating socio-economic characteristics (Haack, 1984; Henderson, Xia, 1998). In this regard polarised and/or multifrequency radar data have proven to be particularly valuable. Radar imagery has also been used successfully in combination with optical data (Forster, Ticehurst, 1994; Weydahl, Becquey, Tollefsen, 1995). The strong dependence of the signal return on the geometrical properties of the illuminated objects results in an ambiguity of its intensity signature with respect to its physical characteristics. This demands the use of alternative features for a distinct classification. The applicability of textural information in urban applications has already been shown for optical and radar based imagery (Henderson, Xia, 1998; Kressler, Steinnocher, 2001; Ryherd, Woodcock, 1996). While most of these analyses were based on conventional pixel-based techniques recent studies have increasingly focused on object-oriented approaches (De Kok, Wever, Fockelmann, 2003; Kressler, Steinnocher, Kim, 2002; Hofman, 2001). These more sophisticated techniques provide possibilities to describe and utilise the geometric, textural and especially contextual properties of the real-world objects in the classification process. With the perspective of the future TerraSAR-X satellite (Roth, 2003) this study aims at the development of a concept for the automated extraction of built-up areas based on high resolution, single polarised X-band imagery. The main emphasis is placed on both, the improvement of image pre-processing with respect to a subsequent object oriented image analysis and the development of a robust classification scheme for a mostly automated identification of human settlements. In the first part of this paper an overview on the methodological concept is given. Then preliminary results of the developed approach are shown. Finally an outlook on the further research is given. 2. METHODOLOGY This section provides a description of the method to detect built-up areas on the basis of high resolution single-polarised X- band imagery automatically.
2 2.1 Basic Concept The methodology consists of two main steps: the preparation of the initial data including speckle suppression and the generation of an additional texture layer the image segmentation and classification. Subsequent to an initial speckle suppression by means of an optimised filtering technique a texture layer is generated. Along with the despeckled intensity image this texture layer is used for the segmentation of the data set. The classification itself is based on the despeckled intensity image and the original data. Both, the image segmentation and the classification are performed on the basis of the object-oriented image analysis software ecognition (Baatz & Schäpe, 1999). This technique partitions the complete scene into groups of spectrally similar pixels by means of an image segmentation to form image objects on an arbitrary number of scale levels. The analysis of these objects instead of single pixels is particularly applicable for the classification of very high resolution imagery. It facilitates the distinction between different structures and their function by considering spectral, geometric and textural characteristics along with information about properties of the area surrounding the image objects. Moreover the objectoriented approach is capable of displaying different objects in a single image at various scales. With respect to radar imagery the initial segmentation also helps to reduce the effects of radar speckle because the intensity of the generated segments results from an averaging of the underlying pixel values. Subsequent to image segmentation a knowledge base is created. This knowledge base defines both, the classes to be identified and the according features for their description and classification. The rules for the class description might include spectral and textural characteristics of the objects, the hierarchical context of the segments or the relationship between neighbouring objects. According to these predefined rules the image is analysed and classified by means of fuzzy logic or a nearest neighbour algorithm (Baatz & Schäpe, 1999). Each step performed during the image analysis can be stored in a separate protocol which might then be applied to other data automatically. 2.2 Test Site and Data Set 3.1 Data preparation 3. SETTLEMENT DETECTION In initial experiments it became apparent that a segmentation based solely on the initial intensity image is difficult. First, significantly textured medium- or small-scale structures are often not recognised or reconstructed by the segmentation. At a low segmentation level consisting of small image objects these structures are often split up into several individual segments with distinctively differing backscatter values. Increasing the size of the objects frequently results in a fusion of the textured segments with those adjacent objects, whose backscatter is quite similar. Sometimes the structure isn t even noticed at all. Moreover the shape of the resulting image objects is frayed and does not follow the actual boundaries satisfactory. As a proper image segmentation is crucial for the subsequent classification we improved this work step by supplementing the intensity information with an additional texture layer (Mean Euclidian Distance) calculated for the intensity image. Since the speckle effect clearly constricts the computation of a meaningful texture the speckle of the initial intensity image has to be minimised first. Strong speckle suppression with conventional speckle filters smoothes edges to a certain degree. Thus, we developed an optimised filtering technique to preserve major edges while significantly smoothing homogeneous areas. This moving window filter represents a combination of a selective mean filter and a conventional Lee Sigma approach. The effect of this filter is shown in Figure 1. A The X-band SAR imagery was acquired over the German cities of Ludwigshafen and Mannheim in May 2003 by the airborne Experimental Synthetic Aperture Radar (E-SAR) system of the DLR (Moreira, Spielbauer, Pötzsch, 1994). Both cities are in the Rhine-Neckar region, which represents Germany s 7 th largest conurbation. During the flight campaign single polarised X-band, dualpolarised C-band and fully polarimetric L-band data was recorded along three flight tracks featuring a depression angle of Each track covers an area of 3x10km in a spatial resolution of 2-3m. The recorded images feature a large variety of urban, suburban and agricultural structures. In order to validate the image classification some classes of a biodiversity GIS vector layer updated in 2000 were merged into a data set showing the built-up areas within the specified region. This data base was complemented by additional aerial photographs recorded during the radar flight campaign. B Figure 1. Speckle Suppression (A: original ; B: filtered)
3 3.2 Object-oriented image analysis Image Segmentation The despeckled intensity image and the generated texture layer are used for the segmentation procedure described in this section. In various tests we found that slightly different input images resulted in significantly different segmentations of the scenes, even though the segmentation settings were identical. As this severely restricts the ability to automate the classification process a first classification phase is interposed. The goal of this phase is to create comparable image objects on a specified segmentation level, independently of the input image characteristics. This is achieved by iteratively performing a classification based border optimisation on an initial, relatively coarse image object level. For that purpose a set of sub-levels with constantly decreasing segment size is generated underneath the initial image object level. Then for each segment of the new layers it is successively tested whether its intensity value significantly diverges from both, its respective super-object located at the initial segmentation level and its directly adjacent segments. If it does, it is classified as a significant substructure. Consequently, the appropriate super-object on the initial segmentation level is cut according to the shape of the identified structure. After the procedure has finished, only the initial, henceforth trimmed image object level is retained for further analysis. The effect of this adjustment is illustrated by Figure 2. The optimised level serves as the basis for the actual classification. Additionally, a level with small objects is created underneath this base level and another one with very large segments is generated above. The newly generated fine level is best suited for the characterisation of single small-scale structures like houses or roads, while the segments of the third, coarse level cover large areas. Thus they represent complete quarters, agricultural fields or forest stands optimally. The described image segmentation finally results in three image object levels Image classification The images are then classified according to a set of class rules collected in a rule base. A key issue of the rule base development is the use of robust features for the class description. This is achieved by basing the classification procedure on textural and contextual features primarily. For the definition of the rule base the segments of the coarse level are analysed with respect to the spatial composition of the underlying small-scale structures using textural features, in particular Haralick parameters (Haralick, 1979). Moreover the shape of these segments is utilised, e.g. to separate built-up areas from spectrally and texturally alike agricultural fields. The latter are typically by far more symmetric and uniform in shape. The fine segments of the lowest level are classified to characterise small-scale urban structures like houses, other significant scatterers or shadows. They are mainly defined on the basis of their intensity, their difference in brightness to the surrounding objects and the composition of the neighbouring area. In addition, the textural and shape-related characteristics of the appropriate super ordinate segment situated at the coarse level are considered by obtaining the according information from the segments of the third level. The information provided by the fine and the coarse level are then combined at the initial medium level to calculate the final settlement mask. 1a 2a 1b 2b Figure 2. Adjustment of image objects shown for two differing input segmentations (a: initial; b: optimized )
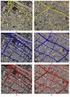
4 4. RESULTS The rule base developed on the basis of small subsets is applied to each of the three flight track images to determine the transferability of the classification scheme. The outcome is validated by comparing the classification to the reference GIS data set and the aerial photographs based on 500 randomly distributed control points. Since the vector data isn t available for all of the area covered, the accuracy for the respective regions is determined solely by a comparison to the aerial photographs. The result shows that the built-up areas can be identified with an overall accuracy of 86% for track 1, 85% for track 2 and 91% for track three. The classification for flight track 1 is illustrated in Figure 3 along with the reference vector data on its right. It can be seen that the main body of the settlements shown red in the reference map - is detected very accurately. These areas could be classified with an accuracy of more than 90%. This promising result can be traced back to the fact that these zones contain quite characteristic features like high texture, significant spectral difference of the single structures to their neighbours and the existence of multiple strong scatterers and shadow areas. In this manner even recently built-up development areas could be identified, which are not yet included in the reference data (see blue arrows in Figure 3). Errors occurred mainly in the context of highly structured areas possessing diverse strong scatterers and significant shadow, e.g. non-urban street crossings surrounded by groups of trees. The most significant false assignments occurred in recreation areas or allotments flanking the settlements. These zones - represented by greenish colours in the reference map - could only be identified when featuring significant texture along with the existence of some bright scatterers. Those spots situated in the far range region of the image lack these conditions due to the decreasing influence of surface roughness in far range. Consequently, these areas appear as dark, smooth zones without significant scatters. Thus, they can not generally be separated from areas in mid- and near-range featuring a significantly lower meso-scale roughness in reality. In mid- and near range the recreation areas and allotments possess the same characteristics as smaller forest stands, groups of trees or rough agricultural fields consequently these zones remain unclassified. 5. CONCLUSIONS The study has shown the applicability of high resolution, single polarised X-band imagery for the detection of built-up areas. Nevertheless, the significant variation of radar backscatter along the surface of a single structure (e.g. a building), the interaction of the scattered waves with multiple objects, the range-dependant effects of surface roughness and the visibility of objects subject to the line of sight result in considerable ambiguities of the recorded signature. Thus, the intensity information has to be analysed in consideration of its spatial context including the attributes of the surrounding objects as well as the characteristics of the super ordinate structure instead of solely regarding the backscatter signal. The object-oriented approach has proven to be very efficient as it provides multiple tools and features to address textural, contextual and hierarchical properties of image structures. 6. FUTURE PERSPECTIVES A first future goal is the improvement of the presented classification scheme in view of a more accurate detection of recreation areas, parks and allotments. In addition the development of comparable procedures for single-polarised C- and L-band imagery is designated. A second field of study will be dealing with the potential improvements associated with an analysis based on a combination of single-polarised X- and L-band data (multifrequency analysis). Finally the integration of polarimetric decomposition properties considering the quad-polarised L- band data is planned. REFERENCES Baatz, M., Schäpe, A., Object-Oriented and Multi-Scale Image Analysis in Semantic Networks. In: Proc. of the 2nd International Symposium on Operationalization of Remote Sensing, August 16-20, Enschede. ITC. De Kok, R., Wever, T., Fockelmann, R., Analysis of urban structure and development applying procedures for automatic mapping of large area data. In: Carstens, J. (Ed.): Remote Sensing of Urban Areas 2003, Ehrlich, D., Lavalle, C., Schillinger, S., Monitoring the Evolution of Europe s Urban Landscapes. In: Proc. of the IGARSS'99 in Hamburg. Vol. III, pp Forster, B.C., Ticehurst, C., Urban Morphology Measures from Optical and RADAR Remotely Sensed Data Some Preliminary Results. Proc. ISPRS Commission VII Symp., Sept Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, Vol. 30, Part 7b, pp Haack, B., L- and X-Band Like- and Cross-Polarized Synthetic Aperture Radar for Investigating Urban Environments. Photogram. Eng. & Remote Sensing, Vol.50, No.10, pp Haralick, R. M., Statistical and structural approaches to texture. Proceedings IEEE, Vol. 67, no.5, pp Henderson, F.M., Xia, Z.G., Radar Applications in Urban Analysis, Settlement Detection and Population Analysis. Principles and Applications of Imaging Radar (F.M. Henderson and A.J. Lewis, eds.), Chapter 15. New York, pp Hofman, P., Detecting urban features from IKONOS data using an object oriented approach. In: Remote Sensing & Photogrammetry Society (Ed.): Proceedings of the First Annual Conference of the Remote Sensing & Remote Sensing Society, Kressler, F., Steinnocher, K., Monitoring urban development using satellite images. In: Jürgens, C. (Ed.).: Remote Sensing of Urban Areas. Regensburger Geographische Schriften, Heft 35, Kressler, F., Steinnocher, K., Kim, Y., Urban land cover mapping from Kompsat EOC panchromatic images using an object-oriented classification approach. In: Proceedings of the Third International Symposium Remote Sensing of Urban Areas, Vol. 1, ISBN X, pp , Istanbul, June, 2002.
5 Masek, J.G., Lindsay, F.E., Goward, S.N., Dynamics of urban growth in Washington DC metropolitan area from Landsat observations. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 21(18), pp Moreira, A., Spielbauer, R., Pötzsch, W., Conceptual Design, Performance Analysis and Results of the High Resolution Real-Time Processor of the DLR Airborne SAR System. In: Proceedings of IGARSS'94, Pasadena (USA). Ridd, M.K., Liu, J A comparison of four algorithms for change detection in an urban environment. Remote Sensing of Environment. 63, pp GRSS/ISPRS Workshop on Remote Sensing and Data Fusion over Urban Areas, Berlin, Germany, pp. 4-7 Ryherd, S., Woodcock, C., Combining Spectral and Texture Data in the Segmentation of Remotely Sensed Images. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, vol. 62, no. 2, Weydahl, D.J., Becquey, X., Tollefsen, T., Combining ERS-1 SAR with optical satellite data over urban areas, International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, IGARSS '95. Quantitative Remote Sensing for Science and Applications, Vol.3, pp Roth A., TerraSAR-X: A New Perspective for Scientific Use of High Resolution Spaceborne SAR Data. In: Proc. of 2 nd N 0 1 kilometers Figure 3. Detected settlements for flight track 1 (orange: built-up area ; greenish: shadow, road) and reference data set (red: main body of settlement; green: recreation area, allotment, park) ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS The municipalities of Ludwigshafen and Mannheim as well as the regional planning association Raumordnungsverband Rhein-Neckar supported this research by means of a fruitful cooperation and the supply of various reference information.
Comparison of ALOS-PALSAR and TerraSAR-X Data in terms of Detecting Settlements First Results
 ALOS 2008 Symposium, 3-7 November Rhodes, Greece Comparison of ALOS-PALSAR and TerraSAR-X Data in terms of Detecting Settlements First Results Thomas Esch*, Achim Roth*, Michael Thiel, Michael Schmidt*,
ALOS 2008 Symposium, 3-7 November Rhodes, Greece Comparison of ALOS-PALSAR and TerraSAR-X Data in terms of Detecting Settlements First Results Thomas Esch*, Achim Roth*, Michael Thiel, Michael Schmidt*,
DEVELOPMENT OF A SUPERVISED SOFTWARE TOOL FOR AUTOMATED DETERMINATION OF OPTIMAL SEGMENTATION PARAMETERS FOR ECOGNITION
 DEVELOPMENT OF A SUPERVISED SOFTWARE TOOL FOR AUTOMATED DETERMINATION OF OPTIMAL SEGMENTATION PARAMETERS FOR ECOGNITION Y. Zhang* a, T. Maxwell, H. Tong, V. Dey a University of New Brunswick, Geodesy &
DEVELOPMENT OF A SUPERVISED SOFTWARE TOOL FOR AUTOMATED DETERMINATION OF OPTIMAL SEGMENTATION PARAMETERS FOR ECOGNITION Y. Zhang* a, T. Maxwell, H. Tong, V. Dey a University of New Brunswick, Geodesy &
An Assessment of the Effectiveness of Segmentation Methods on Classification Performance
 An Assessment of the Effectiveness of Segmentation Methods on Classification Performance Merve Yildiz 1, Taskin Kavzoglu 2, Ismail Colkesen 3, Emrehan K. Sahin Gebze Institute of Technology, Department
An Assessment of the Effectiveness of Segmentation Methods on Classification Performance Merve Yildiz 1, Taskin Kavzoglu 2, Ismail Colkesen 3, Emrehan K. Sahin Gebze Institute of Technology, Department
Pixel-based and object-oriented change detection analysis using high-resolution imagery
 Pixel-based and object-oriented change detection analysis using high-resolution imagery Institute for Mine-Surveying and Geodesy TU Bergakademie Freiberg D-09599 Freiberg, Germany imgard.niemeyer@tu-freiberg.de
Pixel-based and object-oriented change detection analysis using high-resolution imagery Institute for Mine-Surveying and Geodesy TU Bergakademie Freiberg D-09599 Freiberg, Germany imgard.niemeyer@tu-freiberg.de
Information Contents of High Resolution Satellite Images
 Information Contents of High Resolution Satellite Images H. Topan, G. Büyüksalih Zonguldak Karelmas University K. Jacobsen University of Hannover, Germany Keywords: satellite images, mapping, resolution,
Information Contents of High Resolution Satellite Images H. Topan, G. Büyüksalih Zonguldak Karelmas University K. Jacobsen University of Hannover, Germany Keywords: satellite images, mapping, resolution,
Multiscale Object-Based Classification of Satellite Images Merging Multispectral Information with Panchromatic Textural Features
 Remote Sensing and Geoinformation Lena Halounová, Editor not only for Scientific Cooperation EARSeL, 2011 Multiscale Object-Based Classification of Satellite Images Merging Multispectral Information with
Remote Sensing and Geoinformation Lena Halounová, Editor not only for Scientific Cooperation EARSeL, 2011 Multiscale Object-Based Classification of Satellite Images Merging Multispectral Information with
- 107 - DETECTING INFORMAL SETTLEMENTS FROM IKONOS IMAGE DATA USING METHODS OF OBJECT ORIENTED IMAGE ANALYSIS AN EXAMPLE FROM CAPE TOWN (SOUTH AFRICA)
 - 107 - DETECTING INFORMAL SETTLEMENTS FROM IKONOS IMAGE DATA USING METHODS OF OBJECT ORIENTED IMAGE ANALYSIS AN EXAMPLE FROM CAPE TOWN (SOUTH AFRICA) Peter HOFMANN - DEFiNiENS AG Rindermarkt 7 D-80331
- 107 - DETECTING INFORMAL SETTLEMENTS FROM IKONOS IMAGE DATA USING METHODS OF OBJECT ORIENTED IMAGE ANALYSIS AN EXAMPLE FROM CAPE TOWN (SOUTH AFRICA) Peter HOFMANN - DEFiNiENS AG Rindermarkt 7 D-80331
MULTI-SCALE ANALYSIS OF C-BAND SAR DATA FOR LAND USE MAPPING ISSUES
 MULTI-SCALE ANALYSIS OF C-BAND SAR DATA FOR LAND USE MAPPING ISSUES Tanja Riedel, Christian Thiel and Christiane Schmullius Friedrich-Schiller-University, Earth Observation, Jena, Germany; Tanja.Riedel@uni-jena.de
MULTI-SCALE ANALYSIS OF C-BAND SAR DATA FOR LAND USE MAPPING ISSUES Tanja Riedel, Christian Thiel and Christiane Schmullius Friedrich-Schiller-University, Earth Observation, Jena, Germany; Tanja.Riedel@uni-jena.de
COMPARISON OF OBJECT BASED AND PIXEL BASED CLASSIFICATION OF HIGH RESOLUTION SATELLITE IMAGES USING ARTIFICIAL NEURAL NETWORKS
 COMPARISON OF OBJECT BASED AND PIXEL BASED CLASSIFICATION OF HIGH RESOLUTION SATELLITE IMAGES USING ARTIFICIAL NEURAL NETWORKS B.K. Mohan and S. N. Ladha Centre for Studies in Resources Engineering IIT
COMPARISON OF OBJECT BASED AND PIXEL BASED CLASSIFICATION OF HIGH RESOLUTION SATELLITE IMAGES USING ARTIFICIAL NEURAL NETWORKS B.K. Mohan and S. N. Ladha Centre for Studies in Resources Engineering IIT
DETECTION OF URBAN FEATURES AND MAP UPDATING FROM SATELLITE IMAGES USING OBJECT-BASED IMAGE CLASSIFICATION METHODS AND INTEGRATION TO GIS
 Proceedings of the 4th GEOBIA, May 79, 2012 Rio de Janeiro Brazil. p.315 DETECTION OF URBAN FEATURES AND MAP UPDATING FROM SATELLITE IMAGES USING OBJECTBASED IMAGE CLASSIFICATION METHODS AND INTEGRATION
Proceedings of the 4th GEOBIA, May 79, 2012 Rio de Janeiro Brazil. p.315 DETECTION OF URBAN FEATURES AND MAP UPDATING FROM SATELLITE IMAGES USING OBJECTBASED IMAGE CLASSIFICATION METHODS AND INTEGRATION
Environmental Remote Sensing GEOG 2021
 Environmental Remote Sensing GEOG 2021 Lecture 4 Image classification 2 Purpose categorising data data abstraction / simplification data interpretation mapping for land cover mapping use land cover class
Environmental Remote Sensing GEOG 2021 Lecture 4 Image classification 2 Purpose categorising data data abstraction / simplification data interpretation mapping for land cover mapping use land cover class
Research On The Classification Of High Resolution Image Based On Object-oriented And Class Rule
 Research On The Classification Of High Resolution Image Based On Object-oriented And Class Rule Li Chaokui a,b, Fang Wen a,b, Dong Xiaojiao a,b a National-Local Joint Engineering Laboratory of Geo-Spatial
Research On The Classification Of High Resolution Image Based On Object-oriented And Class Rule Li Chaokui a,b, Fang Wen a,b, Dong Xiaojiao a,b a National-Local Joint Engineering Laboratory of Geo-Spatial
UPDATING OBJECT FOR GIS DATABASE INFORMATION USING HIGH RESOLUTION SATELLITE IMAGES: A CASE STUDY ZONGULDAK
 UPDATING OBJECT FOR GIS DATABASE INFORMATION USING HIGH RESOLUTION SATELLITE IMAGES: A CASE STUDY ZONGULDAK M. Alkan 1, *, D. Arca 1, Ç. Bayik 1, A.M. Marangoz 1 1 Zonguldak Karaelmas University, Engineering
UPDATING OBJECT FOR GIS DATABASE INFORMATION USING HIGH RESOLUTION SATELLITE IMAGES: A CASE STUDY ZONGULDAK M. Alkan 1, *, D. Arca 1, Ç. Bayik 1, A.M. Marangoz 1 1 Zonguldak Karaelmas University, Engineering
RESOLUTION MERGE OF 1:35.000 SCALE AERIAL PHOTOGRAPHS WITH LANDSAT 7 ETM IMAGERY
 RESOLUTION MERGE OF 1:35.000 SCALE AERIAL PHOTOGRAPHS WITH LANDSAT 7 ETM IMAGERY M. Erdogan, H.H. Maras, A. Yilmaz, Ö.T. Özerbil General Command of Mapping 06100 Dikimevi, Ankara, TURKEY - (mustafa.erdogan;
RESOLUTION MERGE OF 1:35.000 SCALE AERIAL PHOTOGRAPHS WITH LANDSAT 7 ETM IMAGERY M. Erdogan, H.H. Maras, A. Yilmaz, Ö.T. Özerbil General Command of Mapping 06100 Dikimevi, Ankara, TURKEY - (mustafa.erdogan;
WATER BODY EXTRACTION FROM MULTI SPECTRAL IMAGE BY SPECTRAL PATTERN ANALYSIS
 WATER BODY EXTRACTION FROM MULTI SPECTRAL IMAGE BY SPECTRAL PATTERN ANALYSIS Nguyen Dinh Duong Department of Environmental Information Study and Analysis, Institute of Geography, 18 Hoang Quoc Viet Rd.,
WATER BODY EXTRACTION FROM MULTI SPECTRAL IMAGE BY SPECTRAL PATTERN ANALYSIS Nguyen Dinh Duong Department of Environmental Information Study and Analysis, Institute of Geography, 18 Hoang Quoc Viet Rd.,
Modelling, Extraction and Description of Intrinsic Cues of High Resolution Satellite Images: Independent Component Analysis based approaches
 Modelling, Extraction and Description of Intrinsic Cues of High Resolution Satellite Images: Independent Component Analysis based approaches PhD Thesis by Payam Birjandi Director: Prof. Mihai Datcu Problematic
Modelling, Extraction and Description of Intrinsic Cues of High Resolution Satellite Images: Independent Component Analysis based approaches PhD Thesis by Payam Birjandi Director: Prof. Mihai Datcu Problematic
RULE INHERITANCE IN OBJECT-BASED IMAGE CLASSIFICATION FOR URBAN LAND COVER MAPPING INTRODUCTION
 RULE INHERITANCE IN OBJECT-BASED IMAGE CLASSIFICATION FOR URBAN LAND COVER MAPPING Ejaz Hussain, Jie Shan {ehussain, jshan}@ecn.purdue.edu} Geomatics Engineering, School of Civil Engineering, Purdue University
RULE INHERITANCE IN OBJECT-BASED IMAGE CLASSIFICATION FOR URBAN LAND COVER MAPPING Ejaz Hussain, Jie Shan {ehussain, jshan}@ecn.purdue.edu} Geomatics Engineering, School of Civil Engineering, Purdue University
Object based image analysis of high resolution data in the alpine forest area
 Object based image analysis of high resolution data in the alpine forest area R. de Kok, T. Schneider, M. Baatz, U. Ammer Lehrstuhl für Landnutzungsplanung und Naturschutz, am Hochanger 13, 85354 Freising
Object based image analysis of high resolution data in the alpine forest area R. de Kok, T. Schneider, M. Baatz, U. Ammer Lehrstuhl für Landnutzungsplanung und Naturschutz, am Hochanger 13, 85354 Freising
A COMPARISON OF THE PERFORMANCE OF PIXEL-BASED AND OBJECT-BASED CLASSIFICATIONS OVER IMAGES WITH VARIOUS SPATIAL RESOLUTIONS
 A COMPARISON OF THE PERFORMANCE OF PIXEL-BASED AND OBJECT-BASED CLASSIFICATIONS OVER IMAGES WITH VARIOUS SPATIAL RESOLUTIONS Y. Gao a, *, J.F. Mas a a Centro de Investigaciones en Geografía Ambiental,
A COMPARISON OF THE PERFORMANCE OF PIXEL-BASED AND OBJECT-BASED CLASSIFICATIONS OVER IMAGES WITH VARIOUS SPATIAL RESOLUTIONS Y. Gao a, *, J.F. Mas a a Centro de Investigaciones en Geografía Ambiental,
Let s SAR: Mapping and monitoring of land cover change with ALOS/ALOS-2 L-band data
 Let s SAR: Mapping and monitoring of land cover change with ALOS/ALOS-2 L-band data Rajesh Bahadur THAPA, Masanobu SHIMADA, Takeshi MOTOHKA, Manabu WATANABE and Shinichi rajesh.thapa@jaxa.jp; thaparb@gmail.com
Let s SAR: Mapping and monitoring of land cover change with ALOS/ALOS-2 L-band data Rajesh Bahadur THAPA, Masanobu SHIMADA, Takeshi MOTOHKA, Manabu WATANABE and Shinichi rajesh.thapa@jaxa.jp; thaparb@gmail.com
Automatic Change Detection in Very High Resolution Images with Pulse-Coupled Neural Networks
 1 Automatic Change Detection in Very High Resolution Images with Pulse-Coupled Neural Networks Fabio Pacifici, Student Member, IEEE, and Fabio Del Frate, Member, IEEE Abstract A novel approach based on
1 Automatic Change Detection in Very High Resolution Images with Pulse-Coupled Neural Networks Fabio Pacifici, Student Member, IEEE, and Fabio Del Frate, Member, IEEE Abstract A novel approach based on
Object-Oriented Approach of Information Extraction from High Resolution Satellite Imagery
 IOSR Journal of Computer Engineering (IOSR-JCE) e-issn: 2278-0661,p-ISSN: 2278-8727, Volume 17, Issue 3, Ver. IV (May Jun. 2015), PP 47-52 www.iosrjournals.org Object-Oriented Approach of Information Extraction
IOSR Journal of Computer Engineering (IOSR-JCE) e-issn: 2278-0661,p-ISSN: 2278-8727, Volume 17, Issue 3, Ver. IV (May Jun. 2015), PP 47-52 www.iosrjournals.org Object-Oriented Approach of Information Extraction
A tiered reconnaissance approach toward flood monitoring utilising multi-source radar and optical data
 5 th International Workshop on Remote Sensing for Disaster Response A tiered reconnaissance approach toward flood monitoring utilising multi-source radar and optical data Anneley McMillan Dr. Beverley
5 th International Workshop on Remote Sensing for Disaster Response A tiered reconnaissance approach toward flood monitoring utilising multi-source radar and optical data Anneley McMillan Dr. Beverley
ANALYSIS OF SETTLEMENT STRUCTURE BY MEANS OF HIGH RESOLUTION SATELLITE IMAGERY
 Schmitt et al. 557 ANALYSIS OF SETTLEMENT STRUCTURE BY MEANS OF HIGH RESOLUTION SATELLITE IMAGERY Ursula SCHMITT*, Wolfgang SULZER**, Mathias SCHARDT* *JOANNEUM RESEARCH, Institute of Digital Image Processing,
Schmitt et al. 557 ANALYSIS OF SETTLEMENT STRUCTURE BY MEANS OF HIGH RESOLUTION SATELLITE IMAGERY Ursula SCHMITT*, Wolfgang SULZER**, Mathias SCHARDT* *JOANNEUM RESEARCH, Institute of Digital Image Processing,
Synthetic Aperture Radar: Principles and Applications of AI in Automatic Target Recognition
 Synthetic Aperture Radar: Principles and Applications of AI in Automatic Target Recognition Paulo Marques 1 Instituto Superior de Engenharia de Lisboa / Instituto de Telecomunicações R. Conselheiro Emídio
Synthetic Aperture Radar: Principles and Applications of AI in Automatic Target Recognition Paulo Marques 1 Instituto Superior de Engenharia de Lisboa / Instituto de Telecomunicações R. Conselheiro Emídio
Multi-resolution, object-oriented fuzzy analysis of remote sensing data for GIS-ready information
 ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry & Remote Sensing 58 (2004) 239 258 www.elsevier.com/locate/isprsjprs Multi-resolution, object-oriented fuzzy analysis of remote sensing data for GIS-ready information Ursula
ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry & Remote Sensing 58 (2004) 239 258 www.elsevier.com/locate/isprsjprs Multi-resolution, object-oriented fuzzy analysis of remote sensing data for GIS-ready information Ursula
Sub-pixel mapping: A comparison of techniques
 Sub-pixel mapping: A comparison of techniques Koen C. Mertens, Lieven P.C. Verbeke & Robert R. De Wulf Laboratory of Forest Management and Spatial Information Techniques, Ghent University, 9000 Gent, Belgium
Sub-pixel mapping: A comparison of techniques Koen C. Mertens, Lieven P.C. Verbeke & Robert R. De Wulf Laboratory of Forest Management and Spatial Information Techniques, Ghent University, 9000 Gent, Belgium
A System of Shadow Detection and Shadow Removal for High Resolution Remote Sensing Images
 A System of Shadow Detection and Shadow Removal for High Resolution Remote Sensing Images G.Gayathri PG student, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Parisutham Institute of Technology and Science,
A System of Shadow Detection and Shadow Removal for High Resolution Remote Sensing Images G.Gayathri PG student, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Parisutham Institute of Technology and Science,
Digital Remote Sensing Data Processing Digital Remote Sensing Data Processing and Analysis: An Introduction and Analysis: An Introduction
 Digital Remote Sensing Data Processing Digital Remote Sensing Data Processing and Analysis: An Introduction and Analysis: An Introduction Content Remote sensing data Spatial, spectral, radiometric and
Digital Remote Sensing Data Processing Digital Remote Sensing Data Processing and Analysis: An Introduction and Analysis: An Introduction Content Remote sensing data Spatial, spectral, radiometric and
AUTOMATIC BUILDING DETECTION BASED ON SUPERVISED CLASSIFICATION USING HIGH RESOLUTION GOOGLE EARTH IMAGES
 AUTOMATIC BUILDING DETECTION BASED ON SUPERVISED CLASSIFICATION USING HIGH RESOLUTION GOOGLE EARTH IMAGES Salar Ghaffarian, Saman Ghaffarian Department of Geomatics Engineering, Hacettepe University, 06800
AUTOMATIC BUILDING DETECTION BASED ON SUPERVISED CLASSIFICATION USING HIGH RESOLUTION GOOGLE EARTH IMAGES Salar Ghaffarian, Saman Ghaffarian Department of Geomatics Engineering, Hacettepe University, 06800
THE OBJECT-BASED APPROACH FOR URBAN LAND USE CLASSIFICATION USING HIGH RESOLUTION SATELLITE IMAGERY (A CASE STUDY ZANJAN CITY)
 Proceedings of the 4th GEOBIA, May 7-9, 2012 - Rio de Janeiro - Brazil. p.678 THE OBJECT-BASED APPROACH FOR URBAN LAND USE CLASSIFICATION USING HIGH RESOLUTION SATELLITE IMAGERY (A CASE STUDY ZANJAN CITY)
Proceedings of the 4th GEOBIA, May 7-9, 2012 - Rio de Janeiro - Brazil. p.678 THE OBJECT-BASED APPROACH FOR URBAN LAND USE CLASSIFICATION USING HIGH RESOLUTION SATELLITE IMAGERY (A CASE STUDY ZANJAN CITY)
River Flood Damage Assessment using IKONOS images, Segmentation Algorithms & Flood Simulation Models
 River Flood Damage Assessment using IKONOS images, Segmentation Algorithms & Flood Simulation Models Steven M. de Jong & Raymond Sluiter Utrecht University Corné van der Sande Netherlands Earth Observation
River Flood Damage Assessment using IKONOS images, Segmentation Algorithms & Flood Simulation Models Steven M. de Jong & Raymond Sluiter Utrecht University Corné van der Sande Netherlands Earth Observation
A PHOTOGRAMMETRIC APPRAOCH FOR AUTOMATIC TRAFFIC ASSESSMENT USING CONVENTIONAL CCTV CAMERA
 A PHOTOGRAMMETRIC APPRAOCH FOR AUTOMATIC TRAFFIC ASSESSMENT USING CONVENTIONAL CCTV CAMERA N. Zarrinpanjeh a, F. Dadrassjavan b, H. Fattahi c * a Islamic Azad University of Qazvin - nzarrin@qiau.ac.ir
A PHOTOGRAMMETRIC APPRAOCH FOR AUTOMATIC TRAFFIC ASSESSMENT USING CONVENTIONAL CCTV CAMERA N. Zarrinpanjeh a, F. Dadrassjavan b, H. Fattahi c * a Islamic Azad University of Qazvin - nzarrin@qiau.ac.ir
The Role of SPOT Satellite Images in Mapping Air Pollution Caused by Cement Factories
 The Role of SPOT Satellite Images in Mapping Air Pollution Caused by Cement Factories Dr. Farrag Ali FARRAG Assistant Prof. at Civil Engineering Dept. Faculty of Engineering Assiut University Assiut, Egypt.
The Role of SPOT Satellite Images in Mapping Air Pollution Caused by Cement Factories Dr. Farrag Ali FARRAG Assistant Prof. at Civil Engineering Dept. Faculty of Engineering Assiut University Assiut, Egypt.
A remote sensing instrument collects information about an object or phenomenon within the
 Satellite Remote Sensing GE 4150- Natural Hazards Some slides taken from Ann Maclean: Introduction to Digital Image Processing Remote Sensing the art, science, and technology of obtaining reliable information
Satellite Remote Sensing GE 4150- Natural Hazards Some slides taken from Ann Maclean: Introduction to Digital Image Processing Remote Sensing the art, science, and technology of obtaining reliable information
Remote Sensing and Land Use Classification: Supervised vs. Unsupervised Classification Glen Busch
 Remote Sensing and Land Use Classification: Supervised vs. Unsupervised Classification Glen Busch Introduction In this time of large-scale planning and land management on public lands, managers are increasingly
Remote Sensing and Land Use Classification: Supervised vs. Unsupervised Classification Glen Busch Introduction In this time of large-scale planning and land management on public lands, managers are increasingly
OBJECT ORIENTED ANALYSIS AND SEMANTIC NETWORK FOR HIGH RESOLUTION IMAGE CLASSIFICATION
 OBJECT ORIENTED ANALYSIS AND SEMANTIC NETWORK FOR HIGH RESOLUTION IMAGE CLASSIFICATION 1 ALZIR FELIPPE B. ANTUNES 2 CHRISTEL LINGNAU 1 JORGE CENTENO DA SILVA 1 UFPR- Universidade Federal do Paraná Departamento
OBJECT ORIENTED ANALYSIS AND SEMANTIC NETWORK FOR HIGH RESOLUTION IMAGE CLASSIFICATION 1 ALZIR FELIPPE B. ANTUNES 2 CHRISTEL LINGNAU 1 JORGE CENTENO DA SILVA 1 UFPR- Universidade Federal do Paraná Departamento
Digital image processing
 746A27 Remote Sensing and GIS Lecture 4 Digital image processing Chandan Roy Guest Lecturer Department of Computer and Information Science Linköping University Digital Image Processing Most of the common
746A27 Remote Sensing and GIS Lecture 4 Digital image processing Chandan Roy Guest Lecturer Department of Computer and Information Science Linköping University Digital Image Processing Most of the common
Calculation of Minimum Distances. Minimum Distance to Means. Σi i = 1
 Minimum Distance to Means Similar to Parallelepiped classifier, but instead of bounding areas, the user supplies spectral class means in n-dimensional space and the algorithm calculates the distance between
Minimum Distance to Means Similar to Parallelepiped classifier, but instead of bounding areas, the user supplies spectral class means in n-dimensional space and the algorithm calculates the distance between
Geospatial intelligence and data fusion techniques for sustainable development problems
 Geospatial intelligence and data fusion techniques for sustainable development problems Nataliia Kussul 1,2, Andrii Shelestov 1,2,4, Ruslan Basarab 1,4, Sergii Skakun 1, Olga Kussul 2 and Mykola Lavreniuk
Geospatial intelligence and data fusion techniques for sustainable development problems Nataliia Kussul 1,2, Andrii Shelestov 1,2,4, Ruslan Basarab 1,4, Sergii Skakun 1, Olga Kussul 2 and Mykola Lavreniuk
Template-based Eye and Mouth Detection for 3D Video Conferencing
 Template-based Eye and Mouth Detection for 3D Video Conferencing Jürgen Rurainsky and Peter Eisert Fraunhofer Institute for Telecommunications - Heinrich-Hertz-Institute, Image Processing Department, Einsteinufer
Template-based Eye and Mouth Detection for 3D Video Conferencing Jürgen Rurainsky and Peter Eisert Fraunhofer Institute for Telecommunications - Heinrich-Hertz-Institute, Image Processing Department, Einsteinufer
SAMPLE MIDTERM QUESTIONS
 Geography 309 Sample MidTerm Questions Page 1 SAMPLE MIDTERM QUESTIONS Textbook Questions Chapter 1 Questions 4, 5, 6, Chapter 2 Questions 4, 7, 10 Chapter 4 Questions 8, 9 Chapter 10 Questions 1, 4, 7
Geography 309 Sample MidTerm Questions Page 1 SAMPLE MIDTERM QUESTIONS Textbook Questions Chapter 1 Questions 4, 5, 6, Chapter 2 Questions 4, 7, 10 Chapter 4 Questions 8, 9 Chapter 10 Questions 1, 4, 7
Generation of Cloud-free Imagery Using Landsat-8
 Generation of Cloud-free Imagery Using Landsat-8 Byeonghee Kim 1, Youkyung Han 2, Yonghyun Kim 3, Yongil Kim 4 Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Seoul National University (SNU), Seoul,
Generation of Cloud-free Imagery Using Landsat-8 Byeonghee Kim 1, Youkyung Han 2, Yonghyun Kim 3, Yongil Kim 4 Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Seoul National University (SNU), Seoul,
Extraction of Satellite Image using Particle Swarm Optimization
 Extraction of Satellite Image using Particle Swarm Optimization Er.Harish Kundra Assistant Professor & Head Rayat Institute of Engineering & IT, Railmajra, Punjab,India. Dr. V.K.Panchal Director, DTRL,DRDO,
Extraction of Satellite Image using Particle Swarm Optimization Er.Harish Kundra Assistant Professor & Head Rayat Institute of Engineering & IT, Railmajra, Punjab,India. Dr. V.K.Panchal Director, DTRL,DRDO,
Map World Forum Hyderabad, India Introduction: High and very high resolution space images: GIS Development
 Very high resolution satellite images - competition to aerial images Dr. Karsten Jacobsen Leibniz University Hannover, Germany jacobsen@ipi.uni-hannover.de Introduction: Very high resolution images taken
Very high resolution satellite images - competition to aerial images Dr. Karsten Jacobsen Leibniz University Hannover, Germany jacobsen@ipi.uni-hannover.de Introduction: Very high resolution images taken
An Automatic and Accurate Segmentation for High Resolution Satellite Image S.Saumya 1, D.V.Jiji Thanka Ligoshia 2
 An Automatic and Accurate Segmentation for High Resolution Satellite Image S.Saumya 1, D.V.Jiji Thanka Ligoshia 2 Assistant Professor, Dept of ECE, Bethlahem Institute of Engineering, Karungal, Tamilnadu,
An Automatic and Accurate Segmentation for High Resolution Satellite Image S.Saumya 1, D.V.Jiji Thanka Ligoshia 2 Assistant Professor, Dept of ECE, Bethlahem Institute of Engineering, Karungal, Tamilnadu,
CROP CLASSIFICATION WITH HYPERSPECTRAL DATA OF THE HYMAP SENSOR USING DIFFERENT FEATURE EXTRACTION TECHNIQUES
 Proceedings of the 2 nd Workshop of the EARSeL SIG on Land Use and Land Cover CROP CLASSIFICATION WITH HYPERSPECTRAL DATA OF THE HYMAP SENSOR USING DIFFERENT FEATURE EXTRACTION TECHNIQUES Sebastian Mader
Proceedings of the 2 nd Workshop of the EARSeL SIG on Land Use and Land Cover CROP CLASSIFICATION WITH HYPERSPECTRAL DATA OF THE HYMAP SENSOR USING DIFFERENT FEATURE EXTRACTION TECHNIQUES Sebastian Mader
Monitoring of Arctic Conditions from a Virtual Constellation of Synthetic Aperture Radar Satellites
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Monitoring of Arctic Conditions from a Virtual Constellation of Synthetic Aperture Radar Satellites Hans C. Graber RSMAS
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Monitoring of Arctic Conditions from a Virtual Constellation of Synthetic Aperture Radar Satellites Hans C. Graber RSMAS
Hydrographic Surveying using High Resolution Satellite Images
 Hydrographic Surveying using High Resolution Satellite Images Petra PHILIPSON and Frida ANDERSSON, Sweden Key words: remote sensing, high resolution, hydrographic survey, depth estimation. SUMMARY The
Hydrographic Surveying using High Resolution Satellite Images Petra PHILIPSON and Frida ANDERSSON, Sweden Key words: remote sensing, high resolution, hydrographic survey, depth estimation. SUMMARY The
How To Write A Call To Action For Terrasar-X
 Doc.: TX-PGS-PL-4127 TerraSAR-X Announcement of Opportunity: Utilization of the TerraSAR-X Archive 1 Page: 2 of 11 TABLE OF CONTENTS TERRASAR-X... 1 ANNOUNCEMENT OF OPPORTUNITY: UTILIZATION OF THE TERRASAR-X
Doc.: TX-PGS-PL-4127 TerraSAR-X Announcement of Opportunity: Utilization of the TerraSAR-X Archive 1 Page: 2 of 11 TABLE OF CONTENTS TERRASAR-X... 1 ANNOUNCEMENT OF OPPORTUNITY: UTILIZATION OF THE TERRASAR-X
PIMAR PROJECT - MONITORING THE ATLANTIC RAINFOREST REMNANTS AND THE URBAN GROWTH OF THE RIO DE JANEIRO CITY (BRAZIL) THROUGH REMOTE SENSING
 PIMAR PROJECT - MONITORING THE ATLANTIC RAINFOREST REMNANTS AND THE URBAN GROWTH OF THE RIO DE JANEIRO CITY (BRAZIL) THROUGH REMOTE SENSING D. P. Cintra a, *, T. Novack b, L. F. G. Rego a, G. A. O. P.
PIMAR PROJECT - MONITORING THE ATLANTIC RAINFOREST REMNANTS AND THE URBAN GROWTH OF THE RIO DE JANEIRO CITY (BRAZIL) THROUGH REMOTE SENSING D. P. Cintra a, *, T. Novack b, L. F. G. Rego a, G. A. O. P.
Monitoring of Arctic Conditions from a Virtual Constellation of Synthetic Aperture Radar Satellites
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Monitoring of Arctic Conditions from a Virtual Constellation of Synthetic Aperture Radar Satellites Hans C. Graber RSMAS
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Monitoring of Arctic Conditions from a Virtual Constellation of Synthetic Aperture Radar Satellites Hans C. Graber RSMAS
EDGE-PRESERVING SMOOTHING OF HIGH-RESOLUTION IMAGES WITH A PARTIAL MULTIFRACTAL RECONSTRUCTION SCHEME
 EDGE-PRESERVING SMOOTHING OF HIGH-RESOLUTION IMAGES WITH A PARTIAL MULTIFRACTAL RECONSTRUCTION SCHEME Jacopo Grazzini, Antonio Turiel and Hussein Yahia Air Project Departament de Física Fondamental INRIA
EDGE-PRESERVING SMOOTHING OF HIGH-RESOLUTION IMAGES WITH A PARTIAL MULTIFRACTAL RECONSTRUCTION SCHEME Jacopo Grazzini, Antonio Turiel and Hussein Yahia Air Project Departament de Física Fondamental INRIA
DETECTING LANDUSE/LANDCOVER CHANGES ALONG THE RING ROAD IN PESHAWAR CITY USING SATELLITE REMOTE SENSING AND GIS TECHNIQUES
 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Full length Research Paper -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Full length Research Paper -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Department of Mechanical Engineering, King s College London, University of London, Strand, London, WC2R 2LS, UK; e-mail: david.hann@kcl.ac.
 INT. J. REMOTE SENSING, 2003, VOL. 24, NO. 9, 1949 1956 Technical note Classification of off-diagonal points in a co-occurrence matrix D. B. HANN, Department of Mechanical Engineering, King s College London,
INT. J. REMOTE SENSING, 2003, VOL. 24, NO. 9, 1949 1956 Technical note Classification of off-diagonal points in a co-occurrence matrix D. B. HANN, Department of Mechanical Engineering, King s College London,
High Resolution Digital Surface Models and Orthoimages for Telecom Network Planning
 Renouard, Lehmann 241 High Resolution Digital Surface Models and Orthoimages for Telecom Network Planning LAURENT RENOUARD, S ophia Antipolis FRANK LEHMANN, Berlin ABSTRACT DLR of Germany and ISTAR of
Renouard, Lehmann 241 High Resolution Digital Surface Models and Orthoimages for Telecom Network Planning LAURENT RENOUARD, S ophia Antipolis FRANK LEHMANN, Berlin ABSTRACT DLR of Germany and ISTAR of
Review for Introduction to Remote Sensing: Science Concepts and Technology
 Review for Introduction to Remote Sensing: Science Concepts and Technology Ann Johnson Associate Director ann@baremt.com Funded by National Science Foundation Advanced Technological Education program [DUE
Review for Introduction to Remote Sensing: Science Concepts and Technology Ann Johnson Associate Director ann@baremt.com Funded by National Science Foundation Advanced Technological Education program [DUE
POTENTIAL OF MANUAL AND AUTOMATIC FEATURE EXTRACTION FROM HIGH RESOLUTION SPACE IMAGES IN MOUNTAINOUS URBAN AREAS
 POTENTIAL OF MANUAL AND AUTOMATIC FEATURE EXTRACTION FROM HIGH RESOLUTION SPACE IMAGES IN MOUNTAINOUS URBAN AREAS H. Topan a, *, M. Oruç a, K. Jacobsen b a ZKU, Engineering Faculty, Dept. of Geodesy and
POTENTIAL OF MANUAL AND AUTOMATIC FEATURE EXTRACTION FROM HIGH RESOLUTION SPACE IMAGES IN MOUNTAINOUS URBAN AREAS H. Topan a, *, M. Oruç a, K. Jacobsen b a ZKU, Engineering Faculty, Dept. of Geodesy and
AUTOMATIC CROWD ANALYSIS FROM VERY HIGH RESOLUTION SATELLITE IMAGES
 In: Stilla U et al (Eds) PIA11. International Archives of Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences 38 (3/W22) AUTOMATIC CROWD ANALYSIS FROM VERY HIGH RESOLUTION SATELLITE IMAGES
In: Stilla U et al (Eds) PIA11. International Archives of Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences 38 (3/W22) AUTOMATIC CROWD ANALYSIS FROM VERY HIGH RESOLUTION SATELLITE IMAGES
DIGITAL ELEVATION MODEL DATABASE W42 - A SCALABLE SYSTEM FOR SPATIAL DATA
 DIGITAL ELEVATION MODEL DATABASE W42 - A SCALABLE SYSTEM FOR SPATIAL DATA M. Habermeyer, U. Marschalk, A. Roth German Aerospace Center (DLR),German Remote Sensing Data Center (DFD) 82234 Wessling, Germany,(martin.habermeyer,ursula.marschalk,achim.roth)@dlr.de
DIGITAL ELEVATION MODEL DATABASE W42 - A SCALABLE SYSTEM FOR SPATIAL DATA M. Habermeyer, U. Marschalk, A. Roth German Aerospace Center (DLR),German Remote Sensing Data Center (DFD) 82234 Wessling, Germany,(martin.habermeyer,ursula.marschalk,achim.roth)@dlr.de
APPLICATION OF MULTITEMPORAL LANDSAT DATA TO MAP AND MONITOR LAND COVER AND LAND USE CHANGE IN THE CHESAPEAKE BAY WATERSHED
 APPLICATION OF MULTITEMPORAL LANDSAT DATA TO MAP AND MONITOR LAND COVER AND LAND USE CHANGE IN THE CHESAPEAKE BAY WATERSHED S. J. GOETZ Woods Hole Research Center Woods Hole, Massachusetts 054-096 USA
APPLICATION OF MULTITEMPORAL LANDSAT DATA TO MAP AND MONITOR LAND COVER AND LAND USE CHANGE IN THE CHESAPEAKE BAY WATERSHED S. J. GOETZ Woods Hole Research Center Woods Hole, Massachusetts 054-096 USA
Classification-based vehicle detection in highresolution
 Classification-based vehicle detection in highresolution satellite images Line Eikvil, Lars Aurdal and Hans Koren Norwegian Computing Center P.O. Box 114, Blindern NO-0314 Oslo, Norway Tel: +47 22 85 25
Classification-based vehicle detection in highresolution satellite images Line Eikvil, Lars Aurdal and Hans Koren Norwegian Computing Center P.O. Box 114, Blindern NO-0314 Oslo, Norway Tel: +47 22 85 25
Some elements of photo. interpretation
 Some elements of photo Shape Size Pattern Color (tone, hue) Texture Shadows Site Association interpretation Olson, C. E., Jr. 1960. Elements of photographic interpretation common to several sensors. Photogrammetric
Some elements of photo Shape Size Pattern Color (tone, hue) Texture Shadows Site Association interpretation Olson, C. E., Jr. 1960. Elements of photographic interpretation common to several sensors. Photogrammetric
MODIS IMAGES RESTORATION FOR VNIR BANDS ON FIRE SMOKE AFFECTED AREA
 MODIS IMAGES RESTORATION FOR VNIR BANDS ON FIRE SMOKE AFFECTED AREA Li-Yu Chang and Chi-Farn Chen Center for Space and Remote Sensing Research, National Central University, No. 300, Zhongda Rd., Zhongli
MODIS IMAGES RESTORATION FOR VNIR BANDS ON FIRE SMOKE AFFECTED AREA Li-Yu Chang and Chi-Farn Chen Center for Space and Remote Sensing Research, National Central University, No. 300, Zhongda Rd., Zhongli
Development of a remote sensing based land barometer for sustainable land use management
 Bilateral German-Polish REFINA workshop Research and model projects on suburbanization and land consumption Development of a remote sensing based land barometer for sustainable land use management Thomas
Bilateral German-Polish REFINA workshop Research and model projects on suburbanization and land consumption Development of a remote sensing based land barometer for sustainable land use management Thomas
ANALYSIS OF X-BAND POLARIMETRIC SAR DATA FOR THE DERIVATION OF THE SURFACE ROUGHNESS OVER BARE AGRICULTURAL FIELDS
 ANALYSIS OF X-BAND POLARIMETRIC SAR DATA FOR THE DERIVATION OF THE SURFACE ROUGHNESS OVER BARE AGRICULTURAL FIELDS Nicolas Baghdadi, Noha Holah, Pascale Dubois-Fernandez 2, Laurent Prévot 3, Steven Hosford,
ANALYSIS OF X-BAND POLARIMETRIC SAR DATA FOR THE DERIVATION OF THE SURFACE ROUGHNESS OVER BARE AGRICULTURAL FIELDS Nicolas Baghdadi, Noha Holah, Pascale Dubois-Fernandez 2, Laurent Prévot 3, Steven Hosford,
ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF THE HOUGH TRANSFORMATION IN THE FRAME OF AUTOMATED BUILDING EXTRACTION
 ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF THE HOUGH TRANSFORMATION IN THE FRAME OF AUTOMATED BUILDING EXTRACTION G. Vozikis a,*, J.Jansa b a GEOMET Ltd., Faneromenis 4 & Agamemnonos 11, GR - 15561 Holargos, GREECE
ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF THE HOUGH TRANSFORMATION IN THE FRAME OF AUTOMATED BUILDING EXTRACTION G. Vozikis a,*, J.Jansa b a GEOMET Ltd., Faneromenis 4 & Agamemnonos 11, GR - 15561 Holargos, GREECE
CLASSIFICATION OF URBAN SETTLEMENTS TYPES BASED ON SPACE-BORNE SAR DATASETS
 CLASSIFICATION OF URBAN SETTLEMENTS TYPES BASED ON SPACE-BORNE SAR DATASETS T. Novack *, U. Stilla Technische Universitaet Muenchen, Faculty of Civil, Geo and Environmental Engineering, 80333 Munich, Germany
CLASSIFICATION OF URBAN SETTLEMENTS TYPES BASED ON SPACE-BORNE SAR DATASETS T. Novack *, U. Stilla Technische Universitaet Muenchen, Faculty of Civil, Geo and Environmental Engineering, 80333 Munich, Germany
VCS REDD Methodology Module. Methods for monitoring forest cover changes in REDD project activities
 1 VCS REDD Methodology Module Methods for monitoring forest cover changes in REDD project activities Version 1.0 May 2009 I. SCOPE, APPLICABILITY, DATA REQUIREMENT AND OUTPUT PARAMETERS Scope This module
1 VCS REDD Methodology Module Methods for monitoring forest cover changes in REDD project activities Version 1.0 May 2009 I. SCOPE, APPLICABILITY, DATA REQUIREMENT AND OUTPUT PARAMETERS Scope This module
ENVI THE PREMIER SOFTWARE FOR EXTRACTING INFORMATION FROM GEOSPATIAL IMAGERY.
 ENVI THE PREMIER SOFTWARE FOR EXTRACTING INFORMATION FROM GEOSPATIAL IMAGERY. ENVI Imagery Becomes Knowledge ENVI software uses proven scientific methods and automated processes to help you turn geospatial
ENVI THE PREMIER SOFTWARE FOR EXTRACTING INFORMATION FROM GEOSPATIAL IMAGERY. ENVI Imagery Becomes Knowledge ENVI software uses proven scientific methods and automated processes to help you turn geospatial
Outline. Multitemporal high-resolution image classification
 IGARSS-2011 Vancouver, Canada, July 24-29, 29, 2011 Multitemporal Region-Based Classification of High-Resolution Images by Markov Random Fields and Multiscale Segmentation Gabriele Moser Sebastiano B.
IGARSS-2011 Vancouver, Canada, July 24-29, 29, 2011 Multitemporal Region-Based Classification of High-Resolution Images by Markov Random Fields and Multiscale Segmentation Gabriele Moser Sebastiano B.
Field Techniques Manual: GIS, GPS and Remote Sensing
 Field Techniques Manual: GIS, GPS and Remote Sensing Section A: Introduction Chapter 1: GIS, GPS, Remote Sensing and Fieldwork 1 GIS, GPS, Remote Sensing and Fieldwork The widespread use of computers
Field Techniques Manual: GIS, GPS and Remote Sensing Section A: Introduction Chapter 1: GIS, GPS, Remote Sensing and Fieldwork 1 GIS, GPS, Remote Sensing and Fieldwork The widespread use of computers
Developments toward a European Land Monitoring Framework. Geoff Smith. Seminar 2 nd December, 2015 Department of Geography, University of Cambridge
 Developments toward a European Land Monitoring Framework Geoff Smith Specto Natura Limited Enable clients to deliver useful, accurate and reliable environmental information from EO. Positioned at the interface
Developments toward a European Land Monitoring Framework Geoff Smith Specto Natura Limited Enable clients to deliver useful, accurate and reliable environmental information from EO. Positioned at the interface
CLASSIFICATION ACCURACY INCREASE USING MULTISENSOR DATA FUSION
 CLASSIFICATION ACCURACY INCREASE USING MULTISENSOR DATA FUSION Aliaksei Makarau, Gintautas Palubinskas, and Peter Reinartz German Aerospace Center (DLR) German Remote Sensing Data Center (DFD) bzw. Remote
CLASSIFICATION ACCURACY INCREASE USING MULTISENSOR DATA FUSION Aliaksei Makarau, Gintautas Palubinskas, and Peter Reinartz German Aerospace Center (DLR) German Remote Sensing Data Center (DFD) bzw. Remote
MULTIPURPOSE USE OF ORTHOPHOTO MAPS FORMING BASIS TO DIGITAL CADASTRE DATA AND THE VISION OF THE GENERAL DIRECTORATE OF LAND REGISTRY AND CADASTRE
 MULTIPURPOSE USE OF ORTHOPHOTO MAPS FORMING BASIS TO DIGITAL CADASTRE DATA AND THE VISION OF THE GENERAL DIRECTORATE OF LAND REGISTRY AND CADASTRE E.ÖZER, H.TUNA, F.Ç.ACAR, B.ERKEK, S.BAKICI General Directorate
MULTIPURPOSE USE OF ORTHOPHOTO MAPS FORMING BASIS TO DIGITAL CADASTRE DATA AND THE VISION OF THE GENERAL DIRECTORATE OF LAND REGISTRY AND CADASTRE E.ÖZER, H.TUNA, F.Ç.ACAR, B.ERKEK, S.BAKICI General Directorate
Segmentation of building models from dense 3D point-clouds
 Segmentation of building models from dense 3D point-clouds Joachim Bauer, Konrad Karner, Konrad Schindler, Andreas Klaus, Christopher Zach VRVis Research Center for Virtual Reality and Visualization, Institute
Segmentation of building models from dense 3D point-clouds Joachim Bauer, Konrad Karner, Konrad Schindler, Andreas Klaus, Christopher Zach VRVis Research Center for Virtual Reality and Visualization, Institute
AUTOMATIC CLASSIFICATION OF LAND COVER FEATURES WITH HIGH RESOLUTION IMAGERY AND LIDAR DATA: AN OBJECT-ORIENTED APPROACH
 Sohel Syed, Paul Dare and Simon Jones. Automatic classification of land cover features with high resolution imagery and lidar data: an objectoriented approach. Proceedings of SSC2005 Spatial Intelligence,
Sohel Syed, Paul Dare and Simon Jones. Automatic classification of land cover features with high resolution imagery and lidar data: an objectoriented approach. Proceedings of SSC2005 Spatial Intelligence,
SEMANTIC LABELLING OF URBAN POINT CLOUD DATA
 SEMANTIC LABELLING OF URBAN POINT CLOUD DATA A.M.Ramiya a, Rama Rao Nidamanuri a, R Krishnan a Dept. of Earth and Space Science, Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology, Thiruvananthapuram,Kerala
SEMANTIC LABELLING OF URBAN POINT CLOUD DATA A.M.Ramiya a, Rama Rao Nidamanuri a, R Krishnan a Dept. of Earth and Space Science, Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology, Thiruvananthapuram,Kerala
Active and Passive Microwave Remote Sensing
 Active and Passive Microwave Remote Sensing Passive remote sensing system record EMR that was reflected (e.g., blue, green, red, and near IR) or emitted (e.g., thermal IR) from the surface of the Earth.
Active and Passive Microwave Remote Sensing Passive remote sensing system record EMR that was reflected (e.g., blue, green, red, and near IR) or emitted (e.g., thermal IR) from the surface of the Earth.
Monitoring a Changing Environment with Synthetic Aperture Radar. Alaska Satellite Facility National Park Service Don Atwood
 Monitoring a Changing Environment with Synthetic Aperture Radar Don Atwood Alaska Satellite Facility 1 Entering the SAR Age 2 SAR Satellites RADARSAT-1 Launched 1995 by CSA 5.6 cm (C-Band) HH Polarization
Monitoring a Changing Environment with Synthetic Aperture Radar Don Atwood Alaska Satellite Facility 1 Entering the SAR Age 2 SAR Satellites RADARSAT-1 Launched 1995 by CSA 5.6 cm (C-Band) HH Polarization
The Scientific Data Mining Process
 Chapter 4 The Scientific Data Mining Process When I use a word, Humpty Dumpty said, in rather a scornful tone, it means just what I choose it to mean neither more nor less. Lewis Carroll [87, p. 214] In
Chapter 4 The Scientific Data Mining Process When I use a word, Humpty Dumpty said, in rather a scornful tone, it means just what I choose it to mean neither more nor less. Lewis Carroll [87, p. 214] In
The premier software for extracting information from geospatial imagery.
 Imagery Becomes Knowledge ENVI The premier software for extracting information from geospatial imagery. ENVI Imagery Becomes Knowledge Geospatial imagery is used more and more across industries because
Imagery Becomes Knowledge ENVI The premier software for extracting information from geospatial imagery. ENVI Imagery Becomes Knowledge Geospatial imagery is used more and more across industries because
3198 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON GEOSCIENCE AND REMOTE SENSING, VOL. 48, NO. 8, AUGUST 2010 0196-2892/$26.00 2010 IEEE
 3198 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON GEOSCIENCE AND REMOTE SENSING, VOL. 48, NO. 8, AUGUST 2010 Rule-Based Classification of a Very High Resolution Image in an Urban Environment Using Multispectral Segmentation Guided
3198 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON GEOSCIENCE AND REMOTE SENSING, VOL. 48, NO. 8, AUGUST 2010 Rule-Based Classification of a Very High Resolution Image in an Urban Environment Using Multispectral Segmentation Guided
INTRA-URBAN LAND COVER CLASSIFICATION FROM HIGH-RESOLUTION IMAGES USING THE C4.5 ALGORITHM
 INTRA-URBAN LAND COVER CLASSIFICATION FROM HIGH-RESOLUTION IMAGES USING THE C4.5 ALGORITHM C. M. D. Pinho a, F. C. Silva a, L. M. C. Fonseca, *, A. M. V. Monteiro a a Image Processing Division, Brazil's
INTRA-URBAN LAND COVER CLASSIFICATION FROM HIGH-RESOLUTION IMAGES USING THE C4.5 ALGORITHM C. M. D. Pinho a, F. C. Silva a, L. M. C. Fonseca, *, A. M. V. Monteiro a a Image Processing Division, Brazil's
Radar images Università di Pavia Fabio Dell Acqua Gruppo di Telerilevamento
 Radar images Radar images radar image DNs linked to backscattered field Backscattered field depends on wave-target interaction, with different factors relevant to it: within-pixel coherent combination
Radar images Radar images radar image DNs linked to backscattered field Backscattered field depends on wave-target interaction, with different factors relevant to it: within-pixel coherent combination
The Idiots Guide to GIS and Remote Sensing
 The Idiots Guide to GIS and Remote Sensing 1. Picking the right imagery 1 2. Accessing imagery 1 3. Processing steps 1 a. Geocorrection 2 b. Processing Landsat images layerstacking 4 4. Landcover classification
The Idiots Guide to GIS and Remote Sensing 1. Picking the right imagery 1 2. Accessing imagery 1 3. Processing steps 1 a. Geocorrection 2 b. Processing Landsat images layerstacking 4 4. Landcover classification
AMONG the region-based approaches for segmentation,
 40 IEEE GEOSCIENCE AND REMOTE SENSING LETTERS, VOL. 3, NO. 1, JANUARY 2006 Classification of Remote Sensing Images From Urban Areas Using a Fuzzy Possibilistic Model Jocelyn Chanussot, Senior Member, IEEE,
40 IEEE GEOSCIENCE AND REMOTE SENSING LETTERS, VOL. 3, NO. 1, JANUARY 2006 Classification of Remote Sensing Images From Urban Areas Using a Fuzzy Possibilistic Model Jocelyn Chanussot, Senior Member, IEEE,
Spectral Response for DigitalGlobe Earth Imaging Instruments
 Spectral Response for DigitalGlobe Earth Imaging Instruments IKONOS The IKONOS satellite carries a high resolution panchromatic band covering most of the silicon response and four lower resolution spectral
Spectral Response for DigitalGlobe Earth Imaging Instruments IKONOS The IKONOS satellite carries a high resolution panchromatic band covering most of the silicon response and four lower resolution spectral
Noise estimation in remote sensing imagery using data masking
 INT. J. REMOTE SENSING, 2003, VOL. 24, NO. 4, 689 702 Noise estimation in remote sensing imagery using data masking B. R. CORNER, R. M. NARAYANAN* and S. E. REICHENBACH Department of Electrical Engineering,
INT. J. REMOTE SENSING, 2003, VOL. 24, NO. 4, 689 702 Noise estimation in remote sensing imagery using data masking B. R. CORNER, R. M. NARAYANAN* and S. E. REICHENBACH Department of Electrical Engineering,
DEVELOPMENT OF SETTLEMENT FRAGMENTATION INDICES FOR ENERGY INFRASTRUCTURE COST ASSESSMENT IN AUSTRIA
 DEVELOPMENT OF SETTLEMENT FRAGMENTATION INDICES FOR ENERGY INFRASTRUCTURE COST ASSESSMENT IN AUSTRIA Thomas Blaschke a, Gerald Griesebner a, Manfred Mittlböck b a ZGIS, Department of Geography und Geoinformatics,
DEVELOPMENT OF SETTLEMENT FRAGMENTATION INDICES FOR ENERGY INFRASTRUCTURE COST ASSESSMENT IN AUSTRIA Thomas Blaschke a, Gerald Griesebner a, Manfred Mittlböck b a ZGIS, Department of Geography und Geoinformatics,
THEMATIC ACCURACY ASSESSMENT FOR OBJECT BASED CLASSIFICATION IN AGRICULTURE AREAS: COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF SELECTED APPROACHES
 THEMATIC ACCURACY ASSESSMENT FOR OBJECT BASED CLASSIFICATION IN AGRICULTURE AREAS: COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF SELECTED APPROACHES J. Chmiel, A. Fijałkowska Warsaw University of Technology, Faculty of Geodesy
THEMATIC ACCURACY ASSESSMENT FOR OBJECT BASED CLASSIFICATION IN AGRICULTURE AREAS: COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF SELECTED APPROACHES J. Chmiel, A. Fijałkowska Warsaw University of Technology, Faculty of Geodesy
DATA VISUALIZATION GABRIEL PARODI STUDY MATERIAL: PRINCIPLES OF GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS AN INTRODUCTORY TEXTBOOK CHAPTER 7
 DATA VISUALIZATION GABRIEL PARODI STUDY MATERIAL: PRINCIPLES OF GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS AN INTRODUCTORY TEXTBOOK CHAPTER 7 Contents GIS and maps The visualization process Visualization and strategies
DATA VISUALIZATION GABRIEL PARODI STUDY MATERIAL: PRINCIPLES OF GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS AN INTRODUCTORY TEXTBOOK CHAPTER 7 Contents GIS and maps The visualization process Visualization and strategies
The Application of Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) to Natural Resource Damage Assessment
 The Application of Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) to Natural Resource Damage Assessment George Graettinger, GIS Project Manager Jay Coady, Nicolas Eckhardt, Mathew Dorsey, and Paul Whelan NOAA s Ocean
The Application of Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) to Natural Resource Damage Assessment George Graettinger, GIS Project Manager Jay Coady, Nicolas Eckhardt, Mathew Dorsey, and Paul Whelan NOAA s Ocean
PIXEL-LEVEL IMAGE FUSION USING BROVEY TRANSFORME AND WAVELET TRANSFORM
 PIXEL-LEVEL IMAGE FUSION USING BROVEY TRANSFORME AND WAVELET TRANSFORM Rohan Ashok Mandhare 1, Pragati Upadhyay 2,Sudha Gupta 3 ME Student, K.J.SOMIYA College of Engineering, Vidyavihar, Mumbai, Maharashtra,
PIXEL-LEVEL IMAGE FUSION USING BROVEY TRANSFORME AND WAVELET TRANSFORM Rohan Ashok Mandhare 1, Pragati Upadhyay 2,Sudha Gupta 3 ME Student, K.J.SOMIYA College of Engineering, Vidyavihar, Mumbai, Maharashtra,
A Novel Method to Improve Resolution of Satellite Images Using DWT and Interpolation
 A Novel Method to Improve Resolution of Satellite Images Using DWT and Interpolation S.VENKATA RAMANA ¹, S. NARAYANA REDDY ² M.Tech student, Department of ECE, SVU college of Engineering, Tirupati, 517502,
A Novel Method to Improve Resolution of Satellite Images Using DWT and Interpolation S.VENKATA RAMANA ¹, S. NARAYANA REDDY ² M.Tech student, Department of ECE, SVU college of Engineering, Tirupati, 517502,
3D Model of the City Using LiDAR and Visualization of Flood in Three-Dimension
 3D Model of the City Using LiDAR and Visualization of Flood in Three-Dimension R.Queen Suraajini, Department of Civil Engineering, College of Engineering Guindy, Anna University, India, suraa12@gmail.com
3D Model of the City Using LiDAR and Visualization of Flood in Three-Dimension R.Queen Suraajini, Department of Civil Engineering, College of Engineering Guindy, Anna University, India, suraa12@gmail.com
Remote Sensing an Introduction
 Remote Sensing an Introduction Seminar: Space is the Place Referenten: Anica Huck & Michael Schlund Remote Sensing means the observation of, or gathering information about, a target by a device separated
Remote Sensing an Introduction Seminar: Space is the Place Referenten: Anica Huck & Michael Schlund Remote Sensing means the observation of, or gathering information about, a target by a device separated
An Energy-Based Vehicle Tracking System using Principal Component Analysis and Unsupervised ART Network
 Proceedings of the 8th WSEAS Int. Conf. on ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE, KNOWLEDGE ENGINEERING & DATA BASES (AIKED '9) ISSN: 179-519 435 ISBN: 978-96-474-51-2 An Energy-Based Vehicle Tracking System using Principal
Proceedings of the 8th WSEAS Int. Conf. on ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE, KNOWLEDGE ENGINEERING & DATA BASES (AIKED '9) ISSN: 179-519 435 ISBN: 978-96-474-51-2 An Energy-Based Vehicle Tracking System using Principal
TerraColor White Paper
 TerraColor White Paper TerraColor is a simulated true color digital earth imagery product developed by Earthstar Geographics LLC. This product was built from imagery captured by the US Landsat 7 (ETM+)
TerraColor White Paper TerraColor is a simulated true color digital earth imagery product developed by Earthstar Geographics LLC. This product was built from imagery captured by the US Landsat 7 (ETM+)
Satellite Monitoring of Urbanization in Megacities
 Satellite Monitoring of Urbanization in Megacities Yifang Ban Professor of Geoinformatics Department of Urban Planning & Environment KTH Royal Institute of Technology Stockholm, Sweden Introduction In
Satellite Monitoring of Urbanization in Megacities Yifang Ban Professor of Geoinformatics Department of Urban Planning & Environment KTH Royal Institute of Technology Stockholm, Sweden Introduction In
