Muscle spasm Diminished bowel sounds Nausea/vomiting
|
|
|
- Della Skinner
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 Chapter 28: Abdomen and Genitalia Injuries 2 Abdominal Injuries Abdomen is major body cavity extending from to pelvis. Contains organs that make up digestive, urinary, and genitourinary systems. 8% of significant trauma involves the abdomen. Injuries to the abdomen that go unrecognized or are not repaired in are a leading cause of traumatic death. 3 Abdominal Quadrants Right upper quadrant (RUQ) _, gallbladder, duodenum, pancreas Left upper quadrant (LUQ) Stomach and Left lower quadrant (LLQ) Descending colon, left half of transverse colon Right lower quadrant (RLQ) Large and small intestine, the 4 Abdominal Quadrants 5 Hollow Organs in the Abdominal Cavity Structures through which materials pass Stomach, intestines, ureters, Most contain digested food,, or bile 6 Peritonitis Inflammation of the of the abdomen Caused by ruptured hollow organs spilling content into the peritoneal cavity Can lead to a lethal 7 S/S of Peritonitis Abdominal pain Muscle spasm Diminished bowel sounds Nausea/vomiting 8 Solid Organs in the Abdominal Cavity Solid masses of Perform chemical work of the body: enzyme production, blood cleansing, energy production Because of rich blood supply, can be severe. 9 Liver The liver is the organ in abdomen. Vascular, can lead to Often injured by fractured lower right rib or penetrating trauma
2 Often injured by fractured lower right rib or penetrating trauma 10 Spleen and Pancreas and prone to heavy bleeding Spleen is often injured. Motor vehicle collisions Steering wheel trauma from heights Bicycle and motorcycle accidents involving handlebars 11 Kidneys and Diaphragm Kidneys Can cause significant blood loss Common finding is blood in urine (). 12 Injuries of the Abdomen injury Severe blows that damage the abdomen without breaking the skin injury Foreign body enters the abdomen and opens the peritoneal cavity to the outside 13 Signs and Symptoms of Abdominal Injury Pain Decreased blood pressure Pale, cool, moist A firm abdomen on palpation 14 Evaluating Abdominal Injuries Determine the type of injury, extent of damage, and presence of. Keep airway clear and watch for vomiting. Place the patient supine with knees bent. Obtain baseline vitals. Follow. Inspect abdomen for wounds. any impaled objects. 15 Blunt Abdominal Wounds Severe bruises of the abdominal wall Laceration of the liver and spleen of the intestine in the mesentery 16 Care of Blunt Abdominal Wounds Place patient on. Protect airway.
3 Place patient on. Protect airway. Monitor vital signs. Administer oxygen. Treat for. Provide prompt transport. 17 Seat Belts and Airbags Prevent many injuries and save lives If used inappropriately, seat belts may cause injuries. airbags provide protection only during headon collisions. Airbags must be used in conjunction with 18 Seat Belt Positions The proper position of a seat belt is below the superior iliac spines and against the hip joints (C). A and B show incorrect positions. 19 Care for Penetrating Injuries Inspect patient s back and sides for wounds. Apply a dry, sterile dressing to all open wounds. If the penetrating object is still in place, apply a bandage around it to control bleeding and minimize movement. 20 Abdominal Evisceration Internal organs or fat protrude through the open wound. Never organs. Cover the organs with a moist gauze, then secure with a dressing. Organs must be kept warm and. Transport promptly. 21 Treatment for Evisceration 22 Genitourinary System Controls reproductive functions and discharge Generally considered together Male genitalia lie pelvic cavity. Except prostate gland and seminal vesicles Female genitalia lie pelvic cavity. Except vulva, clitoris, labia 23 Anatomy of the Genitourinary System 24 Female Reproductive System 25 Male Reproductive System 26 Injuries to the Kidneys (1 of 2) Suspect kidney damage if patient has a history or physical evidence of: Abrasion, laceration, or contusion in the
4 Suspect kidney damage if patient has a history or physical evidence of: Abrasion, laceration, or contusion in the A penetrating wound in the region of the rib cage or upper abdomen on either side of the lower rib cage or of the lower thoracic or lumbar vertebrae A hematoma in the flank region 27 Injuries to the Kidneys (2 of 2) Kidney injuries may result from a blow, such as in a tackle in football. 28 Injury of the Urinary Bladder (1 of 2) Either a blunt or penetrating injury can rupture the bladder. will spill into the surrounding tissues. Suspect if you see at the urethral opening or physical signs of trauma on the lower abdomen, pelvis, or perineum. Monitor vitals signs. The presence of associated injuries or shock will dictate the urgency of transport. 29 Injury of the Urinary Bladder (2 of 2) Fracture of the can result in a laceration of the bladder. 30 Care for Injury to the External Male Genitalia (1 of 3) These injuries are very but rarely are life threatening. Should never take priority over more severe injuries Make the patient. Use sterile moist compresses to cover areas stripped of skin. 31 Care for Injury to the External Male Genitalia (2 of 3) Apply direct pressure to control bleeding. Never manipulate any objects or objects incarcerating the penis. Identify and bring avulsed parts to the hospital. Be. 32 Care for Injury to the External Male Genitalia (3 of 3) Zipper Trauma If only 1 or 2 teeth caught, zipper ends and pull apart If more than 2 teeth caught, cut out zipper and leave on the patient Blunt Trauma Causes swelling, apply Can cause rupture of testicle and blood in scrotum 33 Care for Injuries of the Female Genitalia (2 of 3) Female internal genitalia is well protected and usually not injured. The exception is the pregnant which is
5 Female internal genitalia is well protected and usually not injured. The exception is the pregnant which is vulnerable to both blunt and penetrating injuries. Keep in mind that the unborn child is also at risk. Expect to see signs and symptoms of. Provide all necessary support. Transport promptly. 34 Care for Injuries of the Female Genitalia (3 of 3) Injuries to the external genitalia are very painful but not life threatening. Treat lacerations, abrasions, and avulsions with, sterile compresses. Use local pressure and a -type bandage to hold the dressing in place. 35 Care for Injuries of the Female Genitalia (3 of 3) The urgency of transport will be determined by the associated injuries, amount of hemorrhage, and the presence of. Do not put dressings in the. Comfort patient and transport Leave any foreign bodies in place after stabilizing with bandages. 36 Rectal Bleeding Common complaint Blood may appear in undergarments or may be passed during a bowel movement. Can be caused by sexual assault, hemorrhoids, colitis, or ulcers of the digestive tract bleeding should never be passed off as something minor. Pack the between the buttocks with compresses and consult with medical control. 37 Sexual Assault Do not genitalia unless there is obvious bleeding. The patient should not wash the area, douche, defecate, eat, or drink until examined. Offer to call the local rape crisis center. carefully and preserve evidence. Use same gender EMT if possible
Aehlert: Paramedic Practice Today PowerPoint Lecture Notes Chapter 50: Abdominal Trauma
 Aehlert: Paramedic Practice Today PowerPoint Lecture Notes Chapter 50: Abdominal Trauma Chapter 50 Abdominal Trauma 1 Describe the epidemiology, including morbidity, mortality rates, and prevention strategies,
Aehlert: Paramedic Practice Today PowerPoint Lecture Notes Chapter 50: Abdominal Trauma Chapter 50 Abdominal Trauma 1 Describe the epidemiology, including morbidity, mortality rates, and prevention strategies,
United States Department of Transportation National Highway Traffic Safety Administration Paramedic: National Standard Curriculum 1
 UNIT TERMINAL OBJECTIVE 4-8 At the completion of this unit, the paramedic student will be able to integrate pathophysiologic principles and the assessment findings to formulate a field impression and implement
UNIT TERMINAL OBJECTIVE 4-8 At the completion of this unit, the paramedic student will be able to integrate pathophysiologic principles and the assessment findings to formulate a field impression and implement
BLUNT TORSO INJURY FROM IMPACT OR DECELERATION HAS ABDOMINAL SOLID ORGAN TRAUMA UNTIL PROVEN OTHERWISE
 Abdominal and Pelvic Trauma In the primary survey, the circulation part includes thinking about the abdomen as a source of occult hemorrhage The OBVIOUS THING is a penetrating abdominal injury Generally
Abdominal and Pelvic Trauma In the primary survey, the circulation part includes thinking about the abdomen as a source of occult hemorrhage The OBVIOUS THING is a penetrating abdominal injury Generally
Introduction. Physiology of the Abdomen. Anatomy & Physiology. Abdominal Pain Introduction (2 of 2) Gastrointestional and Urologic Emergencies
 Gastrointestional and Urologic Emergencies Introduction Abdominal pain is a common complaint. Cause of abdominal pain is often difficult to determine. As an EMT: You do not need to determine exact cause.
Gastrointestional and Urologic Emergencies Introduction Abdominal pain is a common complaint. Cause of abdominal pain is often difficult to determine. As an EMT: You do not need to determine exact cause.
X-Plain Inguinal Hernia Repair Reference Summary
 X-Plain Inguinal Hernia Repair Reference Summary Introduction Hernias are common conditions that affect men and women of all ages. Your doctor may recommend a hernia operation. The decision whether or
X-Plain Inguinal Hernia Repair Reference Summary Introduction Hernias are common conditions that affect men and women of all ages. Your doctor may recommend a hernia operation. The decision whether or
Guide to Abdominal or Gastroenterological Surgery Claims
 What are the steps towards abdominal surgery? Investigation and Diagnosis It is very important that all necessary tests are undertaken to investigate the patient s symptoms appropriately and an accurate
What are the steps towards abdominal surgery? Investigation and Diagnosis It is very important that all necessary tests are undertaken to investigate the patient s symptoms appropriately and an accurate
EYE, EAR, NOSE, and THROAT INJURIES
 T6 EYE, EAR, NOSE, and THROAT INJURIES Management of injuries of the eyes, ears, nose, and throat focuses on airway management and initial stabilization of the injury. Bilateral comparisons can assist
T6 EYE, EAR, NOSE, and THROAT INJURIES Management of injuries of the eyes, ears, nose, and throat focuses on airway management and initial stabilization of the injury. Bilateral comparisons can assist
Gunshot wounds. Warning: This presentation has extremely graphic pictures! Richard P. Kness, EMT- P
 Gunshot wounds Warning: This presentation has extremely graphic pictures! Richard P. Kness, EMT- P Objectives After this lesson the student will be able to: List scene safety issues Describe procedures
Gunshot wounds Warning: This presentation has extremely graphic pictures! Richard P. Kness, EMT- P Objectives After this lesson the student will be able to: List scene safety issues Describe procedures
Figure 9-2. Abdominal and Genitourinary. Internal Anatomy. Deep Internal Anatomy. Abdominal Anatomy & Physiology. Abdominal Surface Landmarks
 Figure 9-2. Abdominal and Genitourinary Abdominal Surface Landmarks Myung-Hee Pak, RN, MSN, CNS Internal Anatomy Deep Internal Anatomy Pat Thomas, 2006. Pat Thomas, 2006. Abdominal Anatomy & Organs of
Figure 9-2. Abdominal and Genitourinary Abdominal Surface Landmarks Myung-Hee Pak, RN, MSN, CNS Internal Anatomy Deep Internal Anatomy Pat Thomas, 2006. Pat Thomas, 2006. Abdominal Anatomy & Organs of
Injury Law Center OTHER INJURIES
 Injury Law Center Note: This information is provided to give you a basic understanding of the injury. It is not intended as medical advice. You should consult a qualified medical provider. OTHER INJURIES
Injury Law Center Note: This information is provided to give you a basic understanding of the injury. It is not intended as medical advice. You should consult a qualified medical provider. OTHER INJURIES
Abdomen X-Ray (AXR) Collimation is ideally from diaphragms to lower border of the symphysis pubis and the lateral skin margins.
 Abdomen X-Ray (AXR) Collimation is ideally from diaphragms to lower border of the symphysis pubis and the lateral skin margins. LMP of child-bearing age female patients should be checked. 1. Acute abdomen
Abdomen X-Ray (AXR) Collimation is ideally from diaphragms to lower border of the symphysis pubis and the lateral skin margins. LMP of child-bearing age female patients should be checked. 1. Acute abdomen
UNIT 1 BODY PLAN AND ORGANIZATION LECTURE
 UNIT 1 BODY PLAN AND ORGANIZATION LECTURE 1.03 CONTRAST THE SCIENCES OF ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY A. Anatomy Anatomy is the scientific study of structures and the relationship of.. structures to each other.
UNIT 1 BODY PLAN AND ORGANIZATION LECTURE 1.03 CONTRAST THE SCIENCES OF ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY A. Anatomy Anatomy is the scientific study of structures and the relationship of.. structures to each other.
Range of Injury Scale Values
 Range of Injury Scale Values Civil Liability Regulations 2014 SCHEDULE 4 Range of Injury Scale Values (summary) Item Injury ISV Range Part 1-Central Nervous System and Head Injuries 1 Quadriplegia 75 100
Range of Injury Scale Values Civil Liability Regulations 2014 SCHEDULE 4 Range of Injury Scale Values (summary) Item Injury ISV Range Part 1-Central Nervous System and Head Injuries 1 Quadriplegia 75 100
10 Common Questions Answers SBO
 10 Common Questions Answers SBO 1 What is Small Bowel Obstruction (SBO)? After food passes through our stomach, it soon arrives in our intestines, starting at the small bowel. This tube-like organ meanders
10 Common Questions Answers SBO 1 What is Small Bowel Obstruction (SBO)? After food passes through our stomach, it soon arrives in our intestines, starting at the small bowel. This tube-like organ meanders
X-Plain Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Vascular Surgery Reference Summary
 X-Plain Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Vascular Surgery Reference Summary Ballooning of the aorta, also known as an "abdominal aortic aneurysm," can lead to life threatening bleeding. Doctors may recommend
X-Plain Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Vascular Surgery Reference Summary Ballooning of the aorta, also known as an "abdominal aortic aneurysm," can lead to life threatening bleeding. Doctors may recommend
Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA
 Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA 4671 S. Congress Avenue, Lake Worth, FL 33461 561.434.0111 4631 N. Congress Avenue, Suite 102, West Palm Beach, FL 33407 Urinary Tract Infection About one of every
Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA 4671 S. Congress Avenue, Lake Worth, FL 33461 561.434.0111 4631 N. Congress Avenue, Suite 102, West Palm Beach, FL 33407 Urinary Tract Infection About one of every
KEYHOLE HERNIA SURGERY
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage a hernia or abdominal pain. All decisions about the management of a hernia must be made in conjunction with your Physician
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage a hernia or abdominal pain. All decisions about the management of a hernia must be made in conjunction with your Physician
Urinary Tract Infections
 1 Infections in the urinary tract are relatively common. These infections are often referred to as bladder infections. They are also known as UTI s or urinary tract infections. When an infection is confined
1 Infections in the urinary tract are relatively common. These infections are often referred to as bladder infections. They are also known as UTI s or urinary tract infections. When an infection is confined
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY
 ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
CHAPTER 5 PELVIC FRACTURES AND CRUSH INJURIES OF THE BLADDER 113
 PELVIC FRACTURES AND CRUSH INJURIES OF THE BLADDER 113 CHAPTER 5 PELVIC FRACTURES AND CRUSH INJURIES OF THE BLADDER GU Tract Ch 2 Ch 3 Ch 4,5 Ch 6,7,8,11 Ch 8,9 Ch 8,9 Ch 8,10 Structure Kidney Ureter Bladder
PELVIC FRACTURES AND CRUSH INJURIES OF THE BLADDER 113 CHAPTER 5 PELVIC FRACTURES AND CRUSH INJURIES OF THE BLADDER GU Tract Ch 2 Ch 3 Ch 4,5 Ch 6,7,8,11 Ch 8,9 Ch 8,9 Ch 8,10 Structure Kidney Ureter Bladder
12/5/2012. Introduction. Head, Neck, and Spine Injuries. Recognizing and Caring for Serious Head, Neck and Back Injuries
 Head, Neck, and Spine Injuries Identify the most common causes of head, neck and spinal injuries. List 10 situations that might indicate serious head, neck and spinal injuries. List the signals of head,
Head, Neck, and Spine Injuries Identify the most common causes of head, neck and spinal injuries. List 10 situations that might indicate serious head, neck and spinal injuries. List the signals of head,
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
 Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Removal of Gall Bladder Page 12 Patient Information Further Information We endeavour to provide an excellent service at all times, but should you have any concerns please,
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Removal of Gall Bladder Page 12 Patient Information Further Information We endeavour to provide an excellent service at all times, but should you have any concerns please,
CHAPTER 32 QUIZ. Handout 32-1. Write the letter of the best answer in the space provided.
 Handout 32-1 QUIZ Write the letter of the best answer in the space provided. 1. All of the following are signs and symptoms in patients with spinal injuries except A. paralysis. C. hyperglycemia. B. priapism.
Handout 32-1 QUIZ Write the letter of the best answer in the space provided. 1. All of the following are signs and symptoms in patients with spinal injuries except A. paralysis. C. hyperglycemia. B. priapism.
Organ Systems Overview
 E x e r c i s e 2 Organ Systems Overview Time Allotment: 1½ hours (rat dissection: 1 hour; if performing reproductive system dissection, ½ hour each for male and female; dissectible human torso model:
E x e r c i s e 2 Organ Systems Overview Time Allotment: 1½ hours (rat dissection: 1 hour; if performing reproductive system dissection, ½ hour each for male and female; dissectible human torso model:
Care and Problems of the Digestive System. Chapter 18 Lesson 2
 Care and Problems of the Digestive System Chapter 18 Lesson 2 Care of the Digestive System Good eating habits are the best way to avoid or minimize digestive system problems. Eat a variety of foods Avoid
Care and Problems of the Digestive System Chapter 18 Lesson 2 Care of the Digestive System Good eating habits are the best way to avoid or minimize digestive system problems. Eat a variety of foods Avoid
Eating, pooping, and peeing THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Ingested food is not technically in the body until it is absorbed so it needs to be: Mechanically and chemically reduced Transported by the blood to the cells Large portions are not
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Ingested food is not technically in the body until it is absorbed so it needs to be: Mechanically and chemically reduced Transported by the blood to the cells Large portions are not
.org. Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine. Cause. Description
 Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Page ( 1 ) Spinal fractures can vary widely in severity. While some fractures are very serious injuries that require emergency treatment, other fractures can
Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Page ( 1 ) Spinal fractures can vary widely in severity. While some fractures are very serious injuries that require emergency treatment, other fractures can
Digestive System AKA. GI System. Overview. GI Process Process Includes. G-I Tract Alimentary Canal
 Digestive System AKA G-I Tract Alimentary Canal Overview GI System Consists of Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, anus About 30 in length Accessory Organs Teeth, tongue,
Digestive System AKA G-I Tract Alimentary Canal Overview GI System Consists of Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, anus About 30 in length Accessory Organs Teeth, tongue,
TRAUMA SURGERY Dr. Michal Cheatham Orlando Regional Health PGY-4
 ROTATION LIAISON: INSTITUTION: LEVEL(S): TRAUMA SURGERY Dr. Michal Cheatham Orlando Regional Health PGY-4 I. GENERAL INFORMATION The General Surgery Department at Orlando Regional Health has three full
ROTATION LIAISON: INSTITUTION: LEVEL(S): TRAUMA SURGERY Dr. Michal Cheatham Orlando Regional Health PGY-4 I. GENERAL INFORMATION The General Surgery Department at Orlando Regional Health has three full
10 Instructions Pregnant Women Should Follow for Safe and Effective Use of Medication
 10 Instructions Pregnant Women Should Follow for Safe and Effective Use of Medication 1. Check whether or not you are pregnant before taking medicines. Fertile women should check whether or not they could
10 Instructions Pregnant Women Should Follow for Safe and Effective Use of Medication 1. Check whether or not you are pregnant before taking medicines. Fertile women should check whether or not they could
Spinal Cord Injury Education. An Overview for Patients, Families, and Caregivers
 Spinal Cord Injury Education An Overview for Patients, Families, and Caregivers Spinal Cord Anatomy A major component of the Central Nervous System (CNS) It is 15 to 16 inches long, and weighs 1 to 2 ounces
Spinal Cord Injury Education An Overview for Patients, Families, and Caregivers Spinal Cord Anatomy A major component of the Central Nervous System (CNS) It is 15 to 16 inches long, and weighs 1 to 2 ounces
Acute abdominal conditions Key Points
 7 Acute abdominal conditions Key Points 7.1 ASSESSMENT AND DIAGNOSIS Referred abdominal pain Fore gut pain (stomach, duodenum, gall bladder) is referred to the upper abdomen Mid gut pain (small intestine,
7 Acute abdominal conditions Key Points 7.1 ASSESSMENT AND DIAGNOSIS Referred abdominal pain Fore gut pain (stomach, duodenum, gall bladder) is referred to the upper abdomen Mid gut pain (small intestine,
Laparoscopic Repair of Hernias. A simple guide to help answer your questions
 Laparoscopic Repair of Hernias A simple guide to help answer your questions What is a hernia? A hernia is defined as a hole or defect in the abdominal (belly) wall. A hernia can either be congenital (a
Laparoscopic Repair of Hernias A simple guide to help answer your questions What is a hernia? A hernia is defined as a hole or defect in the abdominal (belly) wall. A hernia can either be congenital (a
I. The basic function of the digestive system is
 Chapter 15, Digestive System - ANATOMY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM I. The basic function of the digestive system is. This process is called. II. List 2 other names for the digestive tract: A. B. III. The digestive
Chapter 15, Digestive System - ANATOMY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM I. The basic function of the digestive system is. This process is called. II. List 2 other names for the digestive tract: A. B. III. The digestive
FEMALE ANATOMY. the Functions of the Female Organs
 FEMALE ANATOMY the Functions of the Female Organs An educational video for every woman who is told she needs pelvic surgery, including exploratory surgery or removal of the uterus, fallopian tubes, or
FEMALE ANATOMY the Functions of the Female Organs An educational video for every woman who is told she needs pelvic surgery, including exploratory surgery or removal of the uterus, fallopian tubes, or
Module 8: Soft Tissue Trauma
 1. Which of the following is a major function of the skin? a. Excretion of wastes b. Protection from the environment c. Temperature regulation d. All of the above 2. Which of the following is the outermost
1. Which of the following is a major function of the skin? a. Excretion of wastes b. Protection from the environment c. Temperature regulation d. All of the above 2. Which of the following is the outermost
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES
 BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer
 Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Introduction Cancer of the prostate is the most common form of cancer that affects men. About 240,000 American men are diagnosed with prostate cancer every year. Your
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Introduction Cancer of the prostate is the most common form of cancer that affects men. About 240,000 American men are diagnosed with prostate cancer every year. Your
LEADING CAUSE OF DEATH FOR PERSONS UNDER 39 YEARS OLD RESPONSIBLE FOR MORE THAN 150,000 DEATHS EACH YEAR, NEIGHBORHOOD OF 50,000000 ON HIGHWAYS
 THE KINETICS OF T MAX BORNSTEIN, NREMTP OLD DOMINION OMINION EMS A EMS ALLIANCE DIRECTOR PRINCE GEORGE FIRE (RETIRED) OF TRAUMA IRE/EMS BASIC TRAUMA F RAUMA FACTS LEADING CAUSE OF DEATH FOR PERSONS UNDER
THE KINETICS OF T MAX BORNSTEIN, NREMTP OLD DOMINION OMINION EMS A EMS ALLIANCE DIRECTOR PRINCE GEORGE FIRE (RETIRED) OF TRAUMA IRE/EMS BASIC TRAUMA F RAUMA FACTS LEADING CAUSE OF DEATH FOR PERSONS UNDER
Nursing. Management of Spinal Trauma. Content. Objectives. Objectives
 7 cervical vertebrae Content 12 thoracic vertebrae Nursing 5 sacral vertebrae Management of Spinal Trauma Kwai Fung Betty Siu Ward Manager O&T Dept TKOH Date : 22nd April 2007 5 lumbar vertebrae 4 coccygeal
7 cervical vertebrae Content 12 thoracic vertebrae Nursing 5 sacral vertebrae Management of Spinal Trauma Kwai Fung Betty Siu Ward Manager O&T Dept TKOH Date : 22nd April 2007 5 lumbar vertebrae 4 coccygeal
EVERY LIVING THING has a number of
 Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproductive Systems EVERY LIVING THING has a number of organ systems operating to perform specific functions. If you were to examine one of these systems, you would observe
Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproductive Systems EVERY LIVING THING has a number of organ systems operating to perform specific functions. If you were to examine one of these systems, you would observe
REGIONAL INJURIES (LECTURE III) INJURIES TO SPINE, NECK, CHEST, ABDOMEN AND PELVIS.
 REGIONAL INJURIES (LECTURE III) INJURIES TO SPINE, NECK, CHEST, ABDOMEN AND PELVIS. LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture, last in the series of regional injuries, the students will be knowing
REGIONAL INJURIES (LECTURE III) INJURIES TO SPINE, NECK, CHEST, ABDOMEN AND PELVIS. LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture, last in the series of regional injuries, the students will be knowing
MRC Medical Jeopardy Feud List of Treatments for Possible Injuries/Conditions
 List of Treatments for Possible Injuries/Conditions A. Apply cold compresses to affected area; elevate the area to reduce swelling and possible bleeding B. Apply direct pressure to wound area with sterile
List of Treatments for Possible Injuries/Conditions A. Apply cold compresses to affected area; elevate the area to reduce swelling and possible bleeding B. Apply direct pressure to wound area with sterile
The Abbreviated Injury Scale (AIS) A brief introduction
 The Abbreviated Injury Scale (AIS) A brief introduction Abbreviated Injury Scale 1990 Revision Update 98 The Abbreviated Injury Scale produced by: Association for the Advancement of Automotive Medicine
The Abbreviated Injury Scale (AIS) A brief introduction Abbreviated Injury Scale 1990 Revision Update 98 The Abbreviated Injury Scale produced by: Association for the Advancement of Automotive Medicine
Location: Clinical Practice Manual
 Subject: Area: Classification: Relevant to: Bladder Management Clinical Practice All Clinical Staff Implementation Date: March 2001 Review Date: March 2004 Responsible for Review: Approved by: Distribution:
Subject: Area: Classification: Relevant to: Bladder Management Clinical Practice All Clinical Staff Implementation Date: March 2001 Review Date: March 2004 Responsible for Review: Approved by: Distribution:
Certified Athletic trainers should follow a 10-step process of evaluation for orthopedic injuries, which includes but is not limited to:
 Acute Care Policy Acute Care Policy and Procedures Athletic training students within Winona State University s Athletic Training Education Program have the opportunity to evaluate acute athletic injuries
Acute Care Policy Acute Care Policy and Procedures Athletic training students within Winona State University s Athletic Training Education Program have the opportunity to evaluate acute athletic injuries
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION
 CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
RP0807 - PERFORM SPLINTING TECHNIQUES
 RP0807 - PERFORM SPLINTING TECHNIQUES TERMINAL LEARNING OBJECTIVE. 1. Without the aid of references, given a casualty and standard combat lifesaver medical equipment set, perform splinting techniques,
RP0807 - PERFORM SPLINTING TECHNIQUES TERMINAL LEARNING OBJECTIVE. 1. Without the aid of references, given a casualty and standard combat lifesaver medical equipment set, perform splinting techniques,
NR 23 Assessment of the Abdomen
 The Abdomen NR 23 Assessment of the Abdomen Abdominal Cavity The body systems in the abdomen Gastrointestinal Urinary Reproductive Vascular The Gastrointestional System Alimentary canal Mouth Pharynx Tongue
The Abdomen NR 23 Assessment of the Abdomen Abdominal Cavity The body systems in the abdomen Gastrointestinal Urinary Reproductive Vascular The Gastrointestional System Alimentary canal Mouth Pharynx Tongue
Bladder Catheterization
 Approved by: Bladder Catheterization Gail Cameron Senior Director, Operations, Maternal, Neonatal & Child Health Programs Dr. Ensenat Medical Director, Neonatology Neonatal Nursery Policy & Procedures
Approved by: Bladder Catheterization Gail Cameron Senior Director, Operations, Maternal, Neonatal & Child Health Programs Dr. Ensenat Medical Director, Neonatology Neonatal Nursery Policy & Procedures
CHAPTER 6 HEAD INJURY AND UNCONSCIOUSNESS
 CHAPTER 6 HEAD INJURY AND UNCONSCIOUSNESS BRAIN INJURY Injury to the brain is one of the more serious outcomes that occur due to injury or illness. The first aider plays a major role in limiting damage
CHAPTER 6 HEAD INJURY AND UNCONSCIOUSNESS BRAIN INJURY Injury to the brain is one of the more serious outcomes that occur due to injury or illness. The first aider plays a major role in limiting damage
THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME & BRACHIAL PLEXUS INJURIES
 THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME & BRACHIAL PLEXUS INJURIES I. THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME TOS is a compression of nerves or blood vessels, or both, in the thoracic outlet region, which is the space between the collarbone
THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME & BRACHIAL PLEXUS INJURIES I. THORACIC OUTLET SYNDROME TOS is a compression of nerves or blood vessels, or both, in the thoracic outlet region, which is the space between the collarbone
Laparoscopic Surgery of the Colon and Rectum (Large Intestine) A Simple Guide to Help Answer Your Questions
 Laparoscopic Surgery of the Colon and Rectum (Large Intestine) A Simple Guide to Help Answer Your Questions What are the Colon and Rectum? The colon and rectum together make up the large intestine. After
Laparoscopic Surgery of the Colon and Rectum (Large Intestine) A Simple Guide to Help Answer Your Questions What are the Colon and Rectum? The colon and rectum together make up the large intestine. After
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy (Removal of the Gallbladder)
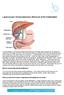 Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy (Removal of the Gallbladder) The gall bladder is a small pear-shaped organ that lies in the right upper quadrant of your abdomen under your liver (under your ribs). The liver
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy (Removal of the Gallbladder) The gall bladder is a small pear-shaped organ that lies in the right upper quadrant of your abdomen under your liver (under your ribs). The liver
Learning Objectives. Introduction to Medical Careers. Vocabulary: Chapter 16 FACTS. Functions. Organs. Digestive System Chapter 16
 Learning Objectives Introduction to Medical Careers Digestive System Chapter 16 Define at least 10 terms relating to the digestive Describe the four functions of the digestive Identify different structures
Learning Objectives Introduction to Medical Careers Digestive System Chapter 16 Define at least 10 terms relating to the digestive Describe the four functions of the digestive Identify different structures
Foley Catheter Placement
 Foley Catheter Placement Indications for a Foley Catheter Retention of urine leading to urinary hesitancy, straining to urinate, decrease in size and force of the urinary stream, interruption of urinary
Foley Catheter Placement Indications for a Foley Catheter Retention of urine leading to urinary hesitancy, straining to urinate, decrease in size and force of the urinary stream, interruption of urinary
Contact your Doctor or Nurse for more information.
 A spinal cord injury is damage to your spinal cord that affects your movement, feeling, or the way your organs work. The injury can happen by cutting, stretching, or swelling of the spinal cord. Injury
A spinal cord injury is damage to your spinal cord that affects your movement, feeling, or the way your organs work. The injury can happen by cutting, stretching, or swelling of the spinal cord. Injury
Welcome back. Today, we embark on Lesson 6 where we ll study the human digestive system.
 Basic Human Anatomy Lesson 6: The Human Digestive System Welcome back. Today, we embark on Lesson 6 where we ll study the human digestive system. After completing this lesson, you should be able to define
Basic Human Anatomy Lesson 6: The Human Digestive System Welcome back. Today, we embark on Lesson 6 where we ll study the human digestive system. After completing this lesson, you should be able to define
CHOC CHILDREN SUROLOGY CENTER. Constipation
 Constipation What is constipation? Constipation is a condition in which a person has uncomfortable or infrequent bowel movements. Generally, a person is considered to be constipated when bowel movements
Constipation What is constipation? Constipation is a condition in which a person has uncomfortable or infrequent bowel movements. Generally, a person is considered to be constipated when bowel movements
5. Secretion: release of water, acids. Enzymes, buffers by digestive tract.
 Digestive System CH-16 Lecture topics Functions of the digestive system: p. 488. 1. Ingestion: Taking food in 2. Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal p.490. voluntary: swalloing : skeletal
Digestive System CH-16 Lecture topics Functions of the digestive system: p. 488. 1. Ingestion: Taking food in 2. Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal p.490. voluntary: swalloing : skeletal
Anatomy of Male Reproductive System
 Anatomy of Male Reproductive System A. Reproductive Systems 1. Gonads: primary sex organs a. Produce gametes b. Produce hormones c. Male Gonads: testes d. Female Gonads: ovaries 2. Gametes: sex cells a.
Anatomy of Male Reproductive System A. Reproductive Systems 1. Gonads: primary sex organs a. Produce gametes b. Produce hormones c. Male Gonads: testes d. Female Gonads: ovaries 2. Gametes: sex cells a.
Facial Sports Injuries
 Facial Sports Injuries Playing catch, shooting hoops, bicycling on a scenic path or just kicking around a soccer ball have more in common than you may think. On the up side, these activities are good exercise
Facial Sports Injuries Playing catch, shooting hoops, bicycling on a scenic path or just kicking around a soccer ball have more in common than you may think. On the up side, these activities are good exercise
Inguinal Hernia (Female)
 Inguinal Hernia (Female) WHAT IS AN INGUINAL HERNIA? 2 WHAT CAUSES AN INGUINAL HERNIA? 2 WHAT DOES TREATMENT / MANAGEMENT INVOLVE? 3 DAY SURGERY MANAGEMENT 3 SURGICAL REPAIR 4 WHAT ARE THE RISKS/COMPLICATIONS
Inguinal Hernia (Female) WHAT IS AN INGUINAL HERNIA? 2 WHAT CAUSES AN INGUINAL HERNIA? 2 WHAT DOES TREATMENT / MANAGEMENT INVOLVE? 3 DAY SURGERY MANAGEMENT 3 SURGICAL REPAIR 4 WHAT ARE THE RISKS/COMPLICATIONS
Bladder reconstruction (neo-bladder)
 Bladder reconstruction (neo-bladder) We have written this leaflet to help you understand about your operation. It is designed to help you answer any questions you may have. The leaflet contains the following
Bladder reconstruction (neo-bladder) We have written this leaflet to help you understand about your operation. It is designed to help you answer any questions you may have. The leaflet contains the following
Surgical removal of fibroids through an abdominal incision-either up and down or bikini cut. The uterus and cervix are left in place.
 What is an abdominal myomectomy? Surgical removal of fibroids through an abdominal incision-either up and down or bikini cut. The uterus and cervix are left in place. When is this surgery used? Treatment
What is an abdominal myomectomy? Surgical removal of fibroids through an abdominal incision-either up and down or bikini cut. The uterus and cervix are left in place. When is this surgery used? Treatment
Identifying Victims of Abuse and Neglect
 Wesley Medical Center Wichita, Kansas Identifying Victims of Abuse and Neglect Department of Staff Development August, 2008 Identifying Victims of Abuse and Neglect Objectives Define the major types of
Wesley Medical Center Wichita, Kansas Identifying Victims of Abuse and Neglect Department of Staff Development August, 2008 Identifying Victims of Abuse and Neglect Objectives Define the major types of
Lumbar Laminectomy and Interspinous Process Fusion
 Lumbar Laminectomy and Interspinous Process Fusion Introduction Low back and leg pain caused by pinched nerves in the back is a common condition that limits your ability to move, walk, and work. This condition
Lumbar Laminectomy and Interspinous Process Fusion Introduction Low back and leg pain caused by pinched nerves in the back is a common condition that limits your ability to move, walk, and work. This condition
NEEDLE THORACENTESIS Pneumothorax / Hemothorax
 NEEDLE THORACENTESIS Pneumothorax / Hemothorax By: Steven Jones, NREMT-P Pneumothorax Pneumothorax is a collection of air or gas in the pleural space of the lung, causing the lung to collapse. Pneumothorax
NEEDLE THORACENTESIS Pneumothorax / Hemothorax By: Steven Jones, NREMT-P Pneumothorax Pneumothorax is a collection of air or gas in the pleural space of the lung, causing the lung to collapse. Pneumothorax
Head & Spinal Trauma. Lesson Goal. Lesson Objectives 9/10/2012
 Head & Spinal Trauma Lesson Goal Learn assessment of patients with head or spinal injuries and how to treat those injuries Lesson Objectives State nervous system components List central nervous system
Head & Spinal Trauma Lesson Goal Learn assessment of patients with head or spinal injuries and how to treat those injuries Lesson Objectives State nervous system components List central nervous system
Abdominal Wall Pain. What is Abdominal Wall Pain?
 Abdominal Wall Pain What is Abdominal Wall Pain? Abdominal Wall Pain is a syndrome (an experience) of abdominal pain that can occur at any time of life and is not unique to children. It is diagnosed by
Abdominal Wall Pain What is Abdominal Wall Pain? Abdominal Wall Pain is a syndrome (an experience) of abdominal pain that can occur at any time of life and is not unique to children. It is diagnosed by
MEDICAL MALPRACTICE CASE RESULTS
 CASE RESULTS INFORMATION Please note that every case is different and these verdicts and settlements, while accurate, do not represent what we may obtain for you in your case. Nor does it mean that we
CASE RESULTS INFORMATION Please note that every case is different and these verdicts and settlements, while accurate, do not represent what we may obtain for you in your case. Nor does it mean that we
Pancreatic Cancer Information for patients and their families
 Pancreatic Cancer Information for patients and their families This handout answers common questions that are often asked by our patients and families. The information in this booklet is what we talked
Pancreatic Cancer Information for patients and their families This handout answers common questions that are often asked by our patients and families. The information in this booklet is what we talked
Table of Contents. Summary of Tupler Technique Program... 2. How the Program Works... 3. Checking for Diastasis... 4. Splinting Tips...
 Tips Table of Contents Summary of Tupler Technique Program... 2 How the Program Works... 3 Checking for Diastasis... 4 Splinting Tips... 5-6 Exercise Tips... 7-8 Other Tips... 9 Ongoing Support with the
Tips Table of Contents Summary of Tupler Technique Program... 2 How the Program Works... 3 Checking for Diastasis... 4 Splinting Tips... 5-6 Exercise Tips... 7-8 Other Tips... 9 Ongoing Support with the
2. Does the patient have one of the following appropriate indications for placing indwelling urinary catheters?
 A. Decision to Insert a Urinary Catheter: 1. Before placing an indwelling catheter, please consider if these alternatives would be more appropriate: Bladder scanner: to assess and confirm urinary retention,
A. Decision to Insert a Urinary Catheter: 1. Before placing an indwelling catheter, please consider if these alternatives would be more appropriate: Bladder scanner: to assess and confirm urinary retention,
Low Back Injury in the Industrial Athlete: An Anatomic Approach
 Low Back Injury in the Industrial Athlete: An Anatomic Approach Earl J. Craig, M.D. Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Epidemiology
Low Back Injury in the Industrial Athlete: An Anatomic Approach Earl J. Craig, M.D. Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Epidemiology
THE KIDNEY. Bulb of penis Abdominal aorta Scrotum Adrenal gland Inferior vena cava Urethra Corona glandis. Kidney. Glans penis Testicular vein
 29 THE KIDNEY 9. Recurrent urinary tract infections Recurrent urinary tract infections The urinary tract consists of the urethra, the bladder, the ureters, the kidneys and in men the prostate gland. An
29 THE KIDNEY 9. Recurrent urinary tract infections Recurrent urinary tract infections The urinary tract consists of the urethra, the bladder, the ureters, the kidneys and in men the prostate gland. An
ICD-9-CM coding for patients with Spinal Cord Injury*
 ICD-9-CM coding for patients with Spinal Cord Injury* indicates intervening codes have been left out of this list. OTHER DISORDERS OF THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM (340-349) 344 Other paralytic syndromes
ICD-9-CM coding for patients with Spinal Cord Injury* indicates intervening codes have been left out of this list. OTHER DISORDERS OF THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM (340-349) 344 Other paralytic syndromes
Bile Duct Diseases and Problems
 Bile Duct Diseases and Problems Introduction A bile duct is a tube that carries bile between the liver and gallbladder and the intestine. Bile is a substance made by the liver that helps with digestion.
Bile Duct Diseases and Problems Introduction A bile duct is a tube that carries bile between the liver and gallbladder and the intestine. Bile is a substance made by the liver that helps with digestion.
Gallbladder Diseases and Problems
 Gallbladder Diseases and Problems Introduction Your gallbladder is a pear-shaped organ under your liver. It stores bile, a fluid made by your liver to digest fat. There are many diseases and problems that
Gallbladder Diseases and Problems Introduction Your gallbladder is a pear-shaped organ under your liver. It stores bile, a fluid made by your liver to digest fat. There are many diseases and problems that
Forensic Examination
 Forensic Examination _ _ 4 purposes of forensic evidence To identify the assailant To confirm recent sexual contact To establish force or threat To corroborate the victim s story When to obtain a forensic
Forensic Examination _ _ 4 purposes of forensic evidence To identify the assailant To confirm recent sexual contact To establish force or threat To corroborate the victim s story When to obtain a forensic
Laparoscopic Colectomy. What do I need to know about my laparoscopic colorectal surgery?
 Laparoscopic Colectomy What do I need to know about my laparoscopic colorectal surgery? Traditionally, colon & rectal surgery requires a large, abdominal and/or pelvic incision, which often requires a
Laparoscopic Colectomy What do I need to know about my laparoscopic colorectal surgery? Traditionally, colon & rectal surgery requires a large, abdominal and/or pelvic incision, which often requires a
Medical Surgical Procedures - Laparoscopy
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
 Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Gallbladder removal is one of the most commonly performed surgical procedures in the United States. Today,gallbladder surgery is performed laparoscopically. The medical name
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Gallbladder removal is one of the most commonly performed surgical procedures in the United States. Today,gallbladder surgery is performed laparoscopically. The medical name
First Responder (FR) and Emergency Medical Responder (EMR) Progress Log
 First Responder (FR) and Emergency Medical Responder (EMR) Progress Log Note: Those competencies that are for EMR only are denoted by boldface type. For further details on the National Occupational Competencies
First Responder (FR) and Emergency Medical Responder (EMR) Progress Log Note: Those competencies that are for EMR only are denoted by boldface type. For further details on the National Occupational Competencies
Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions
 Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions Goals: Define the anatomical position, including the application of the terms right and left. List and correctly use the major directional terms used in anatomy.
Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions Goals: Define the anatomical position, including the application of the terms right and left. List and correctly use the major directional terms used in anatomy.
Normal bladder function. Aging of the bladder and urethra
 SECTION 10 Bladder and bowel control (continence) Section overview This section looks at: Normal bladder function Stroke and loss of bladder control (incontinence) Normal bowel function Stroke and bowel
SECTION 10 Bladder and bowel control (continence) Section overview This section looks at: Normal bladder function Stroke and loss of bladder control (incontinence) Normal bowel function Stroke and bowel
State of New Hampshire Department of Safety Division of Fire Standards and Training & Emergency Medical Services
 State of New Hampshire Department of Safety Division of Fire Standards and Training & Emergency Medical Services September 2013 PATIENT ASSESSMENT / MANAGEMENT - TRAUMA Time allowed: 10 minutes SCENARIO
State of New Hampshire Department of Safety Division of Fire Standards and Training & Emergency Medical Services September 2013 PATIENT ASSESSMENT / MANAGEMENT - TRAUMA Time allowed: 10 minutes SCENARIO
Patient Guide. Sacroiliac Joint Pain
 Patient Guide Sacroiliac Joint Pain Anatomy Where is the Sacroiliac Joint? The sacroiliac joint (SIJ) is located at the bottom end of your spine, where the "tailbone" (sacrum) joins the pelvis (ilium).
Patient Guide Sacroiliac Joint Pain Anatomy Where is the Sacroiliac Joint? The sacroiliac joint (SIJ) is located at the bottom end of your spine, where the "tailbone" (sacrum) joins the pelvis (ilium).
Medical Specialties Guide
 Medical Specialties Guide Allergy And Immunology Specialists in this field treat disorders related to how the body reacts to foreign substances. They treat such things as seasonal allergies, eczema, asthma,
Medical Specialties Guide Allergy And Immunology Specialists in this field treat disorders related to how the body reacts to foreign substances. They treat such things as seasonal allergies, eczema, asthma,
Magic School Bus Digestive System Brainpop Digestive System
 The Digestive System Magic School Bus Digestive System Brainpop Digestive System 1 Functions of the Digestive System: 1. Break up food into smaller pieces 2. Absorbing nutrients into the blood 3. Excreting
The Digestive System Magic School Bus Digestive System Brainpop Digestive System 1 Functions of the Digestive System: 1. Break up food into smaller pieces 2. Absorbing nutrients into the blood 3. Excreting
Nature of Accident Nature of Injury Body Part Code Table
 Nature of Accident Burn or Scald; Heat or Cold Exposure Contact With Chemicals 01 Hot Objects or Substances (Contact with Hot Objects) 02 Temperature Extremes 03 Fire or Flame 04 Steam or Hot Fluids 05
Nature of Accident Burn or Scald; Heat or Cold Exposure Contact With Chemicals 01 Hot Objects or Substances (Contact with Hot Objects) 02 Temperature Extremes 03 Fire or Flame 04 Steam or Hot Fluids 05
Glossary. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty.
 Glossary amenorrhea - absence or cessation of menstrual periods. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty. A amenorrhea, secondary - due to some physical
Glossary amenorrhea - absence or cessation of menstrual periods. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty. A amenorrhea, secondary - due to some physical
About the Uterus. Hysterectomy may be done to treat conditions that affect the uterus. Some reasons a hysterectomy may be needed include:
 Hysterectomy removal of the uterus is a way of treating problems that affect the uterus. Many conditions can be cured with hysterectomy. Because it is major surgery, your doctor may suggest trying other
Hysterectomy removal of the uterus is a way of treating problems that affect the uterus. Many conditions can be cured with hysterectomy. Because it is major surgery, your doctor may suggest trying other
Coccydynia. (Coccyx Pain) Information for patients. Outpatients Physiotherapy Tel: 01473 703312
 Information for patients Coccydynia (Coccyx Pain) Outpatients Physiotherapy Tel: 01473 703312 DPS ref: 4508-12(RP) Issue 1: February 2013 Review date: January 2016 The Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust, 2013.
Information for patients Coccydynia (Coccyx Pain) Outpatients Physiotherapy Tel: 01473 703312 DPS ref: 4508-12(RP) Issue 1: February 2013 Review date: January 2016 The Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust, 2013.
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin
 Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
Femoral Hernia Repair
 Femoral Hernia Repair WHAT IS A FEMORAL HERNIA REPAIR? 2 WHAT CAUSES A FEMORAL HERNIA? 2 WHAT DOES TREATMENT/ MANAGEMENT INVOLVE? 3 DAY SURGERY MANAGEMENT 3 SURGICAL REPAIR 4 WHAT ARE THE RISKS/COMPLICATIONS
Femoral Hernia Repair WHAT IS A FEMORAL HERNIA REPAIR? 2 WHAT CAUSES A FEMORAL HERNIA? 2 WHAT DOES TREATMENT/ MANAGEMENT INVOLVE? 3 DAY SURGERY MANAGEMENT 3 SURGICAL REPAIR 4 WHAT ARE THE RISKS/COMPLICATIONS
Biliary Stone Disease
 Biliary Stone Disease Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm You have
Biliary Stone Disease Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm You have
Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus
 Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy & Physiology
Introduction to A&P (Chapter 1) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy & Physiology
