Describing the current state of health information management and sharing:
|
|
|
- Avis Cox
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 China-Finland e-health Partnership 1 (56) China-Finland e-health Partnership Research Project Report 1 Describing the current state of health information management and sharing: The case of maternity pathway in Weifang Community Health Centre and East Hospital, Shanghai, in 2007 Irmeli Luukkonen 1, Jiechen Jiang 1, Mikko Korpela 1, Anja Mursu 3, Juha Mykkänen 1, Joonas Mäkinen 2, Pirkko Nykänen 2, Antto Seppälä 2, Hellevi Ruonamaa 1, Hannu Virkanen 1 1 University of Kuopio, Healthcare Information Systems Research and Development (HIS R&D) Unit 2 University of Tampere, Department of Computer Sciences 3 Salivirta Oy University of Kuopio, Kuopio, Finland,
2 China-Finland e-health Partnership 2 (56) Table of contents 1. Introduction China-Finland e-health Partnership research project Theme Needs and Requirements: research methods and timetable Context Overview of healthcare organizations in Shanghai Managerial and statistical information flows between organizations Standards Maternity pathway Maternity pathway overview Maternity processes and related information in Weifang CHC and East Hospital Early pregnancy: Weifang CHC Late pregnancy and delivery: East Hospital After delivery: Weifang CHC, East Hospital and Maternity and Child Health Centre Information entities in the maternity pathway Digital information systems used in Weifang and East Hospital Information systems in Weifang CHC Information systems in East Hospital Development points and information sharing needs within the maternity pathway Development points and information sharing needs from the healthcare chain viewpoint Paper-based information sharing and overlapping information Lack of information transfer causes fragmented and isolated information Delay in or lack of information transfer causes many phone calls Duplicate work Information transfer is important for developing healthcare actors professional skills Generic needs Summary, discussion and further work... 54
3 China-Finland e-health Partnership 3 (56) Summary The China-Finland e-health Partnership is a joint research project between Finnish and Chinese counterparts. The aim of the project is to improve information sharing in healthcare. The project was approved as part of the bilateral governmental China-Finland Science and Technology Programme. The research institutions in Finland are the University of Kuopio (UKu, coordinator) and the University of Tampere (UTa). This project is organized with four main research themes: 1) Needs and requirements, 2) Architectures, interoperability and standards, 3) Data set definition for electronic health records, and 4) Evaluation. Within each theme, the Finnish counterparts research findings from the ZipIT ( SerAPI ( ehp Finland, and EBMeDS projects are applied to benefit the project. All the themes concentrate on the same case domain, to ensure better use of resources and mutual understanding of the pilot sites: the working groups and the projects counterparts. The maternity care chain, or maternity pathway, was selected as a case study, and two healthcare organizations, Weifang Community Health Centre (CHC) and East Hospital, were selected as target organizations in the Pudong New Area. Data were gathered mostly in empirical studies in the hospitals during November 2007 and January In this report the state of maternity care in Weifang CHC and East Hospital is studied from the viewpoint of the maternity healthcare chain, emphasizing healthcare professionals information needs in their work. In chapter 2 we provide basic information about the healthcare organizations, current information flows between them, and the health information standards used in the Shanghai area. In chapter 3, we describe a basic maternity pathway by identifying the main activities and actors in both case organizations. The information currently needed and used within the pathway is also described. In chapter 4 we discuss the aspects of information sharing that need developing. Most of the maternity-related information is paper based. In the Weifang CHC and East Hospital the basic HIS includes appointment management and invoicing systems; LIS, PACS, EPR and EHR are also used through doctors workstations. Some systems are integrated with each other inside the hospitals, but not all. Integration between different hospitals and between the hospital and CDC is also needed. Lack of integration often causes duplicate work and information inconsistency. The question of a unified personal ID also needs to be solved. This report serves as a starting point for guidelines for integrating Health Information Systems and for evaluating the solutions implemented.
4 China-Finland e-health Partnership 4 (56) Acknowledgements This paper is based on research conducted in the project China-Finland e-health Partnership (Cn-Fi ehp), funded in by the Finnish Agency for Technology and Innovation Tekes (grant no /07) as well as Conceptia Oy, ehit Oy, GoodIT Oy, Kuopio Innovation Oy, Mawell Oy, Mylab Oy and Tietotarha Oy. The project was implemented by the University of Kuopio, Healthcare information Systems Research and Development Unit, and the University of Tampere, Department of Computer Sciences. The 12th Joint Session under the Agreement on Scientific and Technological Cooperation between the People s Republic of China and the Republic of Finland, in Beijing on 24 May 2006, approved the Cn-Fi ehp project and its sister project Researching on the strategy of construction & evolution in digital hospital (Guidelines for information interoperability), by the Health Information Centre of Shanghai Municipal Health Bureau, to the Sino-Finnish Scientific and Technological Cooperation Programme as project no. AM12:08. The authors wish to gratefully acknowledge the invaluable contributions of the Health Information Centre of Shanghai Municipal Health Bureau, the Pudong Health Authority of the Social Development Bureau of the Pudong New Area District, all participants of the sister project and particularly members of staff of the Weifang Community Health Centre and the East Hospital. Abbreviations: BDSS CDC CHC CHIMA CHSI DICOM3 EHR EPR GP ICT HIBDSS HIS HL7 ISD MCH MOH PACS RHIN SMHB UKu UTa KTL Basic Data Set Standard Centre for Disease Control and Prevention Community Healthcare Centre Chinese Hospital Information Management Association Centre for Health Statistics Information (under MOH) Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine, version 3 -standard Electronic Health Record Electronic Patient Record General Practitioner (working in CHC) Information and Communication Technology Hospital Information Basic Data Set Standard Hospital Information System Health Level 7 standard Information Systems Development Maternity and Child HealthcareCentre Ministry of Health Picture Archiving and Communication System Regional Health Information Networks Shanghai Municipal Health Bureau University of Kuopio University of Tampere Kansanterveyslaitos, National Public Health Institute in Finland
5 China-Finland e-health Partnership 5 (56) 1. Introduction The China-Finland e-health Partnership was a Finnish and Chinese joint research project, which aimed to improve information sharing in healthcare. This report describes the current state and identifies aspects that need development in health information management and information sharing in the Case maternity pathway in the Weifang CHC and East Hospital. This report serves as a starting point for guidelines for integrating Health Information Systems and evaluating the solutions implemented. Data for this report were gathered mostly in field studies in the hospitals during November 2007 and January The report is organized as follows. The introduction provides background information about the China-Finland-eHealth Partnership project and presents the research flow. The results of the research are presented in the rest of the report. Chapter 2 gives an overview of Chinese Healthcare organizations and current information flows between them. Chapter 3 explains the maternity pathway and related information in details in the Weifang CHC and East Hospital, Chapter 4 identifies the aspects of information sharing in the maternity pathway that need development.. In chapter 5 we provide a summary and discussion China-Finland e-health Partnership research project China is the biggest fresh market for the e-health industry in the world. There are more than hospitals in China, about 500 of which are in the Shanghai Municipality (metropolitan area), which is the economically most advanced area. Currently about 85% of the hospitals nationwide have basic hospital management information systems and 15% are building clinical information systems; the figures are significantly higher in Shanghai. ICT in healthcare is developing very fast in China at present, especially electronic health record (EHR) systems and regional health information sharing. However, the large number of systems designed by different software companies and the lack of standards lead to information isolation and many projects in China are starting to study regional information sharing. For example, the main target of the Pudong New Area district government in Shanghai is to establish a regional health platform, based on the existing systems, to fulfil information sharing between all the healthcare organizations. For this purpose, they have established the Pudong project, the goal of which is to establish a regional health information platform for the pilot hospitals (East Hospital, Gong Li Hospital, Pudong MCH, Weifang CHC, Tang Qiao CHC, Lu Jiazui CHC and Pu Dong Birth Control Office). Since early 2006 the government of China has emphasized the role of primary care (Community Healthcare Centres) to address the inequality of access to healthcare services. Correspondingly, information sharing and regional health information networks (RHIN) are the hot topics for research and development. The joint China-Finland e-health research project was approved as part of the bilateral governmental China-Finland Science and Technology Programme. The Finnish research institutions involved are the University of Kuopio (UKu, coordinator) and the University of Tampere (UTa). The Finnish side of the project was funded by Finnish Funding Agency for Technology and Innovation, Tekes, and participating Finnish companies. The main goal of the Finnish project was to study the applicability of ISD methods, developed in previous research projects, in different socio-economic and cultural healthcare systems, comparing experiences in China and Finland. The research project contributed to the Pudong pilot project and aimed at generalizing the experiences for wider application. The research groups collaborated with the Information Centre of the Shanghai Municipal Health Bureau and the Social Development Bureau of the Pudong New Area District to analyze the needs for e-health systems, develop architectural guidelines and data standards, and evaluate the progress. The research groups also interacted with the National EHR Workgroups of the Chinese Ministry of Health. This project was organized with four main research themes: 1) Needs and requirements, 2) Architectures, interoperability and standards, 3) Data set definition for electronic health records,
6 China-Finland e-health Partnership 6 (56) and 4) Evaluation. Within each theme, the Finnish partners research results from ZipIT ( SerAPI ( ehp Finland, and EBMeDS projects were used in the project. All the themes concentrated on the same case domain, to ensure better use of resources and mutual understanding of the pilot sites, the working groups and project partners. The maternity care chain, or the maternity pathway, was selected for a case study, and two healthcare organizations, the Weifang Community Health Centre (CHC) and East Hospital, were selected as target organizations in the Pudong New area. The project main outcome is constructed from three reports, which are in line with each other: Report 1 ("Before"): Current situation of the case (Theme Needs and Requirements) Report 2 ("After"): Evaluation of the case after the implementation of the new system(s) (Theme Evaluation) Report 3 ("Future"): Principles of integrating regional and added-value applications to the existing base, with examples applied to the case (Theme Architectures, Interoperability and Standards). This report is the main outcome of the Needs and Requirements theme, a description of the current state of health information management and sharing in the Case maternity pathway in the Weifang CHC and East Hospital Theme Needs and Requirements: research methods and timetable The activity-driven needs analysis is based on the Activity-driven Information Systems Development Model, which was developed through action research and case studies in several practical ISD projects, hosted by different healthcare organizations in Finland. The emphasis of the model is on domain analysis and description, and requirements elicitation. The model has three levels of analysis and descriptions, traceable with each other: individual level (actions), group/activity level (work processes), and organizational level (network of activities). At each level the work, linked up with information system, is analyzed with different degrees of detail. The research was conducted in a participatory manner using workshops, story telling, interactive writing, and group interviews. In the analysis phases multidisciplinary (e.g. software engineering, ISD, and work development) knowledge was exploited to achieve results. Materials for this report were collected mostly in empirical studies in November 2007 in the Weifang CHC and East Hospital, and refined during January Some background and context information was collected from reports of previous trips and other documents. Several researchers workshops were held before and after the field studies to achieve mutual understanding of the case and the project goals from the viewpoint of different themes. The viewpoint of our participating companies was also an important input to our work. The main research activities of the Needs and Requirements theme are summarized in Table 1. The maternity pathway story is used to illustrate the maternity health care processes in different levels of description. The earlier versions of the same story were used to capture first the understanding of the Chinese maternity pathway, and further in interviews and walking trough the maternity pathway in the Weifang CHC and East Hospital. For the field studies, the story was translated into Chinese and used as a discussion facilitator. Unclear parts were clarified, and answers were used to complete the story.
7 China-Finland e-health Partnership 7 (56) Table 1. Research workflow and outputs of the Needs and Requirements theme Timeslot and phase Activity Output September - October: Starting project Reading, researchers workshops, interactive writing Pre-understanding about Chinese healthcare, maternity story with questions November: gathering data Interviews and maternity pathway walk through in Weifang CHC and East Hospital, other visits Gathered data December: analysis and reporting researchers analytical writing workshops, First draft of this report, field study reports, travel reports January: data gathering and validation February- May: analysis and reporting Workshop with companies, workshop with Shanghai partners, other visits researchers workshops, workshop with companies, analytical writing, completed data (questions answered) Report 1, baselines of report 2 and 3 2. Context There are three levels of governance in China: the national, municipal (e.g. Shanghai) and district levels (e.g. Pudong New Area). In this chapter we give an overview of healthcare organizations, managerial and statistical information flows and current standards and standardization activities in health information managing in Shanghai Overview of healthcare organizations in Shanghai Shanghai Health Administration is divided into 2 parts. One is the Shanghai Municipal Health Bureau (SMHB), which is in charge of making health policy and regulations, unifying the guidelines and standards etc. for the whole Shanghai Area. The other is the Shen Kang Hospital Authority, which is in charge of the management of most teaching hospitals at the third level in Shanghai, and it also grants funding for development projects. The Shen Kang Hospital Authority provides the funding for the Health Information System development project for these hospitals. There are 19 districts in Shanghai, and Pudong New Area is the biggest and leading district. Pudong was the first district to set up the Pudong Hospital Authority at the beginning of As a result, the Pudong Social Development Bureau has two Health Administrations to manage the health organizations in Pudong, the Health Sector of the Social Development Bureau and the Pudong Hospital Authority, which is in charge of all the 29 Community Health Centres in Pudong, and might manage all the general hospitals (second level) in Pudong in the next two years. There are three levels of hospitals: 1. Community Healthcare Centres (CHC, level 1, under which there are Community Health Stations), 2. General Hospitals (level 2), and
8 China-Finland e-health Partnership 8 (56) 3. Specialist Hospitals and Teaching Hospitals (both level 3). Citizens are free to choose a hospital of any level when they need health services. Major funding for hospitals comes from citizens payments (for doctor s visits, laboratory tests, drugs etc.). Only ~10 % of the funding comes from the government through the public health insurance organizations, which are found at municipal and national levels. Apart from these hospitals, there are four other main public health organizations in Pudong. The most important is the Centre for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), similar to the National Public Health Institute (KTL) in Finland, which is in charge of collecting public health data from hospitals and health Centres. The other three organizations are the Maternity & Child Healthcare Centre (MCH) (within the Maternity & Child Hospital), the Mental Healthcare Centre and the Health Supervision Institution. The Birth Control Office is the place where women who do not have residence in Shanghai can register when they are pregnant. The general network and relationships between the Healthcare Organizations in Pudong are shown in Figure 1 (see legend for Figures 1 and 2 below).
9 China-Finland e-health Partnership 9 (56) China national level CDC Ministry of Health Public Health Insurance (national level) Shanghai Health Administration (Municipal level) MCH Shanghai Municipal Health Bureau SMHB CDC Districts; n=19 Pudong New Area (District level) Shanghai Shen Kang Hospital Authority (managing 23 big hospitals) managing some teaching hospitals Level 3 hospitals Specialist Specialist Hospital Hospital Y1...Yn Y1...Yn Teaching Hospital Y1...Yn University Cooperation Shanghai Public Health Insurance (municipal level) Pudong Social Development Bureau Health Sector of Social Development Bureau Birth Controll Office Mental Health Health Supervision CDC: Centre for Disease Control Pudong Hospital Authority n=29 MCH: Maternity & Child Health Centre HS: Health station HS n=29 Level 1 hospitals CHC: CHC Community Health Centre Specialist Hospital Y2 HS HS CHC Will be managing in next 2 years CHC HS HS Level 2 hospitals General General General Hospital Hospital Hospital X1...Xn X1...Xn X1...Xn Figure 1. Healthcare organizations in Shanghai
10 China-Finland e-health Partnership 10 (56) 2.2. Managerial and statistical information flows between organizations The Health Information Web/Portal is established in the Pudong Region, and the Regional Data Centre is set up in the Zhangjiang Area, and they are remotely controlled at the Pudong CDC. Moreover, the Pudong government has invested a huge amount of money to complete the network for all the health organization in the whole Pudong region, all of which can connect with the Health Information Web/Portal. The Data Centre collects mainly public health data.the Web portal is not used in every hospital, and most information for different reports is still collected manually from different sources, both digital and paper based. The reports are sent either by post (paper-based collection) or by (see Figure 2). Reporting diseases (for disease control and prevention): In the Pudong area, the CHCs and hospitals send reports about diseases to the Pudong CDC, which summarizes the data and reports further to the CDC in Shanghai. The reporting frequency depends on the disease: reports can be sent daily, weekly, monthly or quarterly. Reporting patient volumes (for healthcare quality management and decision making): In the Pudong area, the CHCs and hospitals send reports about patient volumes, numbers of laboratory tests taken etc. to the Health Sector of the Social Development Bureau in Pudong. Reporting maternity issues: In the Pudong area, the CHCs and hospitals send reports concerning maternity issues, e.g number of pregnant women and babies delivered in the community, to the Pudong Maternity and Child Healthcare Centre, which collects the data and reports further to the Health Sector of the Social Development Bureau in Pudong and the MCH in Shanghai. Insurance information: Hospitals of all levels send summaries of payment information to the insurance office. The insurance offices return a small percentage of hospital payments to the citizens, except in the case of pregnant women. The amount returned to them depends on the size of the pregnant woman's salary. Information about salaries is obtained from the tax authority. Within the maternity pathway, pregnant women pay for their healthcare services all along the pathway, collect all the receipts and send them to the insurance organization all at once only after delivery.
11 China-Finland e-health Partnership 11 (56) Information flows upwards China national level CDC Ministry of Health Public Health Insurance (national level) Shanghai Health Administration (Municipal level) Summary of reports MCH Shanghai Municipal Health Bureau SMHB CDC Pudong New Area (District level) Summary of reports Summary of disease information Shanghai Shen Kang Hospital Authority (managing 23 big hospitals) Level 3 hospitals Specialist Specialist Hospital Hospital Y1...Yn Y1...Yn Teaching Hospital Y1...Yn Shanghai Public Health Insurance (municipal level) Pudong Social Development Bureau Health Sector of Social Development Bureau Summary of disease information Number of patient visits, labtests, etc. Birth Controll Office Summary of payments: client and payment information, Summary of maternity information, e.g. number of pregnancies and child births MCH: Maternity & Child Health Centre Maternity information CDC: Center for Disease Control Disease information Specialist Hospital Y2 Pudong Hospital n=29 Authority Level 1 hospitals CHC: Community Health Centre Disease information Maternity information Level 2 hospitals General General General Hospital Hospital Hospital X1...Xn X1...Xn X1...Xn Money citizen Health station Figure 2. Information flows upwards between healthcare organizations
12 China-Finland e-health Partnership 12 (56) Clinical healthcare information is not shared between different healthcare-providing organizations in Pudong: the clinical data are still isolated at each hospital. To explain the need for sharing clinical information within the maternity healthcare chain, we describe the maternity pathway through different organizations in Chapter Standards In recent years, under the Centre for Health Statistics Information (CHSI) of the MOH, health information standardization work has achieved a great deal in China. In 2002, the 'Basic function norm of the hospital information system (HIS) was issued by the MOH, which was regarded as the admission rule and annual appraisal regulation of setting up HIS for the local organizations, hospitals (users), and companies (suppliers). In 2003, the 'National Health Information Development Plan ( )' was published, which contains the general healthcare information development plan for China. The MOH asked national experts to make a standard for PACS in 2003, called 'CPACS'. They selected DICOM3 as the reference to establish a set of standards such as image architecture, data repository, workflow, quality control and communication. In addition, the MOH appointed the Chinese Hospital Information Management Association (CHIMA) to set up a 'Hospital information Basic Data Set Standard (HIBDSS)', and CHIMA planned to use the HL7 as the reference to fulfill the information exchange between hospitals and other health organizations. Structure and Standard of Electronic Patient Record (EPR)' and 'Structure and Standard of Electronic Health Record (EHR)' are being planned by the MOH, to be developed in these years; drafts of the Basic Data Set in Public Health Information and Community Health Information have been made available for discussion. The MOH assigned the Centre of Disease Prevention and Control (CDC) and the China health information institute (public health) to study and build the BDSS for public health information. The aim of the project was to ensure that the public health information systems at different levels are interoperable, and that data can be exchanged across the public health information systems. The China Public Health Information Classification and Basic Data Set Standard version 1 was released in Maternity pathway By the maternity pathway we mean a path through which a pregnant woman contacts different healthcare organizations for maternity healthcare and to deliver the baby. The maternity pathway takes place in the time slot beginning when a woman who thinks that she might be pregnant makes the first contact with a healthcare organization, and ending when all follow-ups with the new mother and her new-born baby have been completed. In this section we identify and describe the actors, workflows and information flows, as well as the information systems used in the Weifang CHC and East Hospital in the maternity case. What information and data are used within the maternity pathway? Who is using the information and for what purpose? Where are the data recorded and in what form? What information tools are used, both paper based and digital? Possible bottlenecks and development points in the maternity pathway are identified. The description provides detailed information for an implementation plan concerning the maternity case. The information needs can be further studied in relation to the core dataset and centralized database. The impact of new systems and changes in the work flows can be identified. The basic flow of the maternity pathway is described in three levels. 1. The maternity pathway overview provides a roadmap to show the care chain as a whole. 2. The Maternity processes of early pregnancy, late pregnancy, and after delivery relate information used and needed within the processes and information sharing between the facilities. 3. Detailed information about workflows connects actors, information, information tools and information systems. The levels are traceable with each other. The maternity pathway is described in sections 3.1 and 3.2 and in Figures The relationship between the Figures is shown in the map in Appendix 1.
13 China-Finland e-health Partnership 13 (56) 3.1. Maternity pathway overview Overview: Maternity care services are given in CHCs and hospitals. Women are advised to visit a CHC (level 1 hospital) in the community where they live, but they can freely choose.higher level hospitals Women visit hospital mostly to confirm that they are pregnant, but pregnancy can also be confirmed in a CHC. Floating women are advised to register pregnancy at the Birth Control Office. Women often visit a CHC during the first 16 weeks of pregnancy, then level 2 or 3 hospitals after 16 weeks. If the woman has a high risk of hypertension or diabetes, the health provider of the CHC will recommend that she visits a special hospital. Delivery takes place in level 2 or 3 hospitals, in the maternity department. The CHC takes care of follow-ups after delivery. Public health providers of the CHC visit homes twice 3-7 days after delivery. When the baby is 1 month old, the mother must bring the baby to the maternity and child health centre for examination. The mother goes for a check up in the delivery hospital 42 days after delivery. Figure 3 shows an example of the maternity pathway. Hospitals are depicted with rectangles, activities with ovals, and the actors involved are named inside the ovals. Under the hospitals there is a timeline depicting the duration of the pregnancy. Example of maternity pathway: Mrs. Yang visits East Hospital to confirm her pregnancy. Because she has no regular residence in Shanghai, she registers her pregnancy in the Birth Control Office. She visits the Weifang CHC for the first four months for regular examinations, including lab tests and medication when necessary. The GP sets up a Maternity Card for her (to keep with her during the pregnancy), and a paper-based maternity health record to be kept in the Weifang CHC. From week 16 Mrs. Yang visits East Hospital for regular examinations, including laboratory tests and medication when necessary. A new paper-based maternity health record is set up and kept in East Hospital. She delivers her baby in East Hospital and stays for a few days in the maternity department as an inpatient. She goes home with her baby and the Weifang CHC's public health providers take care of follow-ups: two or three home visits and checks on the baby (immunization etc.) in the CHC. After all that is necessary has been done, the GP 'closes the case', writes a summary in the electronic maternity IS and archives the paper-based maternity health record. After 42 days from delivery, Mrs. Yang goes to East Hospital for a physical check up. Figure 3. Activities related to maternity care in the CHC and East Hospital
14 China-Finland e-health Partnership 14 (56) 3.2. Maternity processes and related information in Weifang CHC and East Hospital The maternity pathway is divided here into three processes: Early pregnancy in the Weifang CHC (sub-section 3.2.1), Late pregnancy and delivery in East Hospital (sub-section 3.2.2), and Followups in the Weifang CHC and Mrs.Yang's home and East Hospital (sub-section 3.2.3). Activities, information, information tools, and information systems are described; and development points in information sharing are identified. Each process description has three parts: firstly, the processes are described with narrative texts (parts of the maternity story) and a summary of paper-based maternity information, digital information systems and development points in the process is provided after the story. Then the processes are illustrated with swim line diagrams at the end of each description. Basic workflows of outpatient-visit in both hospitals are described in more details in sub-sections and , and work flows for arranging follow-ups, home visit and case closing in subsection This chapter focuses on information within the maternity pathway and information sharing points, and information sharing needs from the healthcare actors' viewpoint Early pregnancy: Weifang CHC Mrs. Yang visits the Weifang Community Health Centre (Weifang CHC) regularly for first four months of the pregnancy. In the first visit, the maternity health provider, a general practitioner (GP), sets up the Maternity Card for her. Mrs. Yang s personal information, clinical information and results of regular tests will be written in the card during the CHC and hospital visits. The card also contains guidelines for nutrition and healthy habits, etc. The GP creates a paper-based maternity health record, kept in CHC. If Mrs. Yang has a high risk of hypertension or diabetes, the health provider recommends that she go to a special hospital, and writes three copies of referral letters. If there is a need for special tests that cannot be done in the Weifang CHC, the samples will be collected and then sent to another hospital by mailing service staff at CHC. Samples are sent weekly or every two or three days, and the test results are sent back by mail or phone call. After the first 4 months of pregnancy, Mrs. Yang chooses a hospital to visit for the rest of the pregnancy including delivery of her baby. She can tell the CHC the name of the delivery hospital, to help contacting. Figure 4 shows the process for the early part of the pregnancy. Yellow boxes depict development points in information sharing. Regular examinations are described in more detail in the outpatient workflow description in subsection Digital information systems: HIS with basic functions: outpatient registration and payment (invoice), admission and discharging management, pharmacy management, hospital manager inquiry system; EHR system; doctor and nurse work stations; LIS; RIS and Mini PACS; other systems related to Public Health field. Paper-based maternity information: Confirmation note of the pregnancy, given in East Hospital Registration note from the Birth Control Office Patient Card which is used to record clinical information such as test results, kept by mother Maternity Card created in the CHC, kept by mother Maternity health record, kept in the CHC Referral letter, sent to a higher level hospital when necessary Manually written or printed prescription for the patient Laboratory test order to higher level hospital and test results, when needed Development points in information sharing:
15 China-Finland e-health Partnership 15 (56) No information transfer between facilities, e.g. between East Hospital and the Weifang CHC (pregnancy confirmation), or between the Birth Control office and Weifang CHC (pregnancy registration). EHR, LIS, etc should be integrated with each other Paper-based maternity health record is used in the Weifang CHC, and no information is shared with other facilities Laboratory test results from higher level hospitals come by mail or by phone call, so information can be delayed Legend for swim line diagrams
16 China-Finland e-health Partnership 16 (56) Legend Institution, formal organization E-card Paper-based document Action Actor Computer-based information system Telephone Development point Information flow Missing information flow
17 China-Finland e-health Partnership 17 (56) Home Weifang CHC East Hospital Birth Controll Office Maternity and Child Healthcare Center Early pregnancy start insurance e-card WeifangCHC e-card Patient Card Confir mation Pregnancy test & confirmation Receipt of payment Confir mation Floating people: pregnancy registration Registration note No information transfer insurance e-card WeifangCHC e-card Receipt of payment Patient Card Registration note First visit: Creating Maternity Card Maternity Card Creating paperbased maternal health record Maternity Card Patient Maternity Card Card Weifang CHC e-card insurance e-card Receipt of payment Receipt of payment Receipt of payment Patient Card EHR,LIS, dr.workstation etc. in use. integration? Regular visits See diagrams 5-11 for more details Maternity health record Maternity health record Info can be used only in Weifang CHC Specialist Consultation by phone Consultation by spcialists visits Lab test orders & results by post Specialized hospital ~week 16 of pregnancy Record the name of the delivery hospital Maternity health record Not always known Figure 4. Early pregnancy process
18 China-Finland e-health Partnership 18 (56) Basic workflow in regular visits to Weifang CHC The activities identified in the basic outpatient workflow in regular visits are: Entering the CHC, GP examination, Laboratory tests and Medication (Figure 5). Each activity is described in this section with a short narrative text (part of the maternity story) including location of activity, actors, information tools, information and information systems in use. Activities are also described in one or several diagrams (Figures 6-11). Figure 5. Activities in Outpatient workflow in regular visits in Weifang CHC Legend for diagrams Legend Action Card reader Wall screen Actor E-card Paper-based document Workstation and application Telephone Electronic card reader Wall screen for announcements Information entity, different groups can be marked with different colors Computer-based information system Information flow Missing information flow Information kept with mother/patient Development point Printer Printer
19 China-Finland e-health Partnership 19 (56) Registration desk: Making an appointment Waiting hall: Waiting for one s turn Mrs. Yang goes to the CHC, and first she goes to the reception desk. The reception nurse asks her what she wants. Then she chooses an available GP, or the nurse chooses a GP for her if she is visiting for the first time. The reception nurse collects her data using the card reader (health insurance card) or types the basic information into the system when she visits for the first time. The registration fee and other fees during the visit are collected in the electronic system, and she can pay everything when she is leaving the CHC (at the end of the visit). She waits outside the doctor s room for her turn. There is a screen on the wall, which lists the patient s name, the GP s name and the number of the room. The GP can see the list of his/her patients at the doctor s workstation system and the GP will call Mrs. Yang when it is her turn (Figure 6). Information tools: insurance card, hospital card which can be reused only at the Weifang CHC (given to Mrs. Yang if she has no insurance card), paper-based Patient Card, big screen Information: personal data (name, sex, age, address, telephone and other contact information etc.), insurance data (type of insurance), appointment number, doctor s name, clinic room Information systems: card reader, outpatient registration system, wall screen connected to the GP s doctor s workstation system and outpatient registration system (the nurse operates the screen).
20 China-Finland e-health Partnership 20 (56) Mrs. Yang visits Weifang CHC: making appointment Actors: Reception nurse Mrs. Yang GP Information tools: insurance e-card Weifang CHC e-card Card reader Nurse s workstation Appointment wall screen Payment wall screen Doctor s workstation Information Insurance data Personal data Appointment data Invoice data Information systems: HIS: outpatient registration and payment; pharmacy management; admission and discharge management; hospital management inquiry Doctor s Workstation system Own database Figure 6. Making an appointment
Principles of integrating added-value applications to health information management and sharing
 China-Finland e-health Partnership 1 (60) China-Finland e-health Partnership Research Project Report 3 Principles of integrating added-value applications to health information management and sharing Hannu
China-Finland e-health Partnership 1 (60) China-Finland e-health Partnership Research Project Report 3 Principles of integrating added-value applications to health information management and sharing Hannu
The agenda of the Shanghai healthcare delegations meeting on September 5 th morning at Tekes
 The agenda of the Shanghai healthcare delegations meeting on September 5 th morning at Tekes Place: Tekes Address: Kyllikinportti 2, Länsi Pasila Room: No.3 Date and Time: Sep 5th, 09.00 11.00, Chair:
The agenda of the Shanghai healthcare delegations meeting on September 5 th morning at Tekes Place: Tekes Address: Kyllikinportti 2, Länsi Pasila Room: No.3 Date and Time: Sep 5th, 09.00 11.00, Chair:
ehealth Interoperability State of the Art in Serbia
 ehealth Interoperability State of the Art in Serbia Nada Teodosijević ProRec Serbia Western Balkan Summit on ehealth interoperability Ljubljana, 3 rd April 2014 Topics 1. ehealth State of the art in the
ehealth Interoperability State of the Art in Serbia Nada Teodosijević ProRec Serbia Western Balkan Summit on ehealth interoperability Ljubljana, 3 rd April 2014 Topics 1. ehealth State of the art in the
Health Information Technology & Management Chapter 2 HEALTH INFORMATION SYSTEMS
 Health Information Technology & Management Chapter 2 HEALTH INFORMATION SYSTEMS INFORMATION SYSTEM *Use of computer hardware and software to process data into information. *Healthcare information system
Health Information Technology & Management Chapter 2 HEALTH INFORMATION SYSTEMS INFORMATION SYSTEM *Use of computer hardware and software to process data into information. *Healthcare information system
Overview of the national laws on electronic health records in the EU Member States National Report for Lithuania
 Overview of the national laws on electronic health records in the EU Member States and their interaction with the provision of cross-border ehealth services Contract 2013 63 02 Overview of the national
Overview of the national laws on electronic health records in the EU Member States and their interaction with the provision of cross-border ehealth services Contract 2013 63 02 Overview of the national
Siemens Roadmap to ehealth
 Siemens Roadmap to ehealth 4. th. ehealth national conference, Sofia Michael Gorgi June 26 th., 2007 Siemens Bulgaria Agenda ehealth? Evolution of ehealth Systems Siemens & ehealth Page 2 June 2007 Siemens
Siemens Roadmap to ehealth 4. th. ehealth national conference, Sofia Michael Gorgi June 26 th., 2007 Siemens Bulgaria Agenda ehealth? Evolution of ehealth Systems Siemens & ehealth Page 2 June 2007 Siemens
EHR Software Requirements Specification
 Hospital Health Information System EU HIS Contract No. IPA/2012/283-805 Final version July 2015 Visibility: Public Target Audience: EU-IHIS Stakeholders EHR System Architects EHR Developers EPR Systems
Hospital Health Information System EU HIS Contract No. IPA/2012/283-805 Final version July 2015 Visibility: Public Target Audience: EU-IHIS Stakeholders EHR System Architects EHR Developers EPR Systems
Healthcare Information Technology Infrastructures in Turkey
 Healthcare Information Technology Infrastructures in Turkey G O KC E B. L A L EC I E RTURKMEN S R D C LT D BASED O N IMIA 2 0 1 4 YEA R B O O K E D I T I ON A RTICLE BY A. D O G AC 1, M. YUKSEL 1, G. L.
Healthcare Information Technology Infrastructures in Turkey G O KC E B. L A L EC I E RTURKMEN S R D C LT D BASED O N IMIA 2 0 1 4 YEA R B O O K E D I T I ON A RTICLE BY A. D O G AC 1, M. YUKSEL 1, G. L.
EHR STRATEGY FINLAND. Kari Harno Helsinki University Central Hospital
 EHR STRATEGY FINLAND Kari Harno Helsinki University Central Hospital The Nordic Welfare Model In Finland this model includes: universal coverage of services universal social security scheme health insurance
EHR STRATEGY FINLAND Kari Harno Helsinki University Central Hospital The Nordic Welfare Model In Finland this model includes: universal coverage of services universal social security scheme health insurance
HEALTH PROFESSIONALS IN EUROPE: NEW ROLES, NEW SKILLS
 HEALTH PROFESSIONALS IN EUROPE: NEW ROLES, NEW SKILLS "HEALTH PROFESSIONALS IN EUROPE: NEW ROLES, NEW SKILLS" HOPE EXCHANGE PROGRAMME 2009 HOPE, the European Hospital and Healthcare Federation, is a non-profit
HEALTH PROFESSIONALS IN EUROPE: NEW ROLES, NEW SKILLS "HEALTH PROFESSIONALS IN EUROPE: NEW ROLES, NEW SKILLS" HOPE EXCHANGE PROGRAMME 2009 HOPE, the European Hospital and Healthcare Federation, is a non-profit
Introduction to Information and Computer Science: Information Systems
 Introduction to Information and Computer Science: Information Systems Lecture 1 Audio Transcript Slide 1 Welcome to Introduction to Information and Computer Science: Information Systems. The component,
Introduction to Information and Computer Science: Information Systems Lecture 1 Audio Transcript Slide 1 Welcome to Introduction to Information and Computer Science: Information Systems. The component,
Approaching Harmonised Medication Information Management through Process and Information Modelling
 Medical Informatics in a United and Healthy Europe K.-P. Adlassnig et al. (Eds.) IOS Press, 2009 2009 European Federation for Medical Informatics. All rights reserved. doi:10.3233/978-1-60750-044-5-557
Medical Informatics in a United and Healthy Europe K.-P. Adlassnig et al. (Eds.) IOS Press, 2009 2009 European Federation for Medical Informatics. All rights reserved. doi:10.3233/978-1-60750-044-5-557
DEMYSTIFYING ELECTRONIC HEALTH Presented to Central East LHIN Board of Directors. January 22, 2014
 DEMYSTIFYING ELECTRONIC HEALTH Presented to Central East LHIN Board of Directors January 22, 2014 What is ehealth? What is an Electronic Health System? EHR, EMR and PHR / CIS/HIS Where does the electronic
DEMYSTIFYING ELECTRONIC HEALTH Presented to Central East LHIN Board of Directors January 22, 2014 What is ehealth? What is an Electronic Health System? EHR, EMR and PHR / CIS/HIS Where does the electronic
The Healthy Michigan Plan Handbook
 The Healthy Michigan Plan Handbook Introduction The Healthy Michigan Plan is a health care program through the Michigan Department of Community Health (MDCH). Eligibility for this program will be determined
The Healthy Michigan Plan Handbook Introduction The Healthy Michigan Plan is a health care program through the Michigan Department of Community Health (MDCH). Eligibility for this program will be determined
Task Analysis and Application Services for Cross-Organizational Scheduling and Citizen ebooking
 332 Medical Informatics in a United and Healthy Europe K.-P. Adlassnig et al. (Eds.) IOS Press, 2009 2009 European Federation for Medical Informatics. All rights reserved. doi:10.3233/978-1-60750-044-5-332
332 Medical Informatics in a United and Healthy Europe K.-P. Adlassnig et al. (Eds.) IOS Press, 2009 2009 European Federation for Medical Informatics. All rights reserved. doi:10.3233/978-1-60750-044-5-332
E-health croatia: National healthcare information system
 E-health croatia: National healthcare information system Andrea Budin, M.Sc.C.S. (andrea.budin@ericsson.com) Karlo Guštin, MBA (karlo.gustin@ericsson.com) ICT for Industry & Society Ericsson Nikola Tesla,
E-health croatia: National healthcare information system Andrea Budin, M.Sc.C.S. (andrea.budin@ericsson.com) Karlo Guštin, MBA (karlo.gustin@ericsson.com) ICT for Industry & Society Ericsson Nikola Tesla,
The White Paper on China s Hospital Information System
 Robert W. Ball China Hospital Information Management Association Prof Li Baoluo The White Paper on China s Hospital Information System Agenda Prof Li Baoluo 1. White Paper Overview (10 mins) 2. China HIT
Robert W. Ball China Hospital Information Management Association Prof Li Baoluo The White Paper on China s Hospital Information System Agenda Prof Li Baoluo 1. White Paper Overview (10 mins) 2. China HIT
The Third Party Consultancy Company helps hospital
 The Third Party Consultancy Company helps hospital optimize its IT management Cui Yong Dr. MA Jun, the president of Shanghai Changning Maternity & Infant Health Institute (SCMI) began her career of clinical
The Third Party Consultancy Company helps hospital optimize its IT management Cui Yong Dr. MA Jun, the president of Shanghai Changning Maternity & Infant Health Institute (SCMI) began her career of clinical
how to choose the health plan that s right for you
 how to choose the health plan that s right for you It s easy to feel a little confused about where to start when choosing a health plan. Some people ask their friends, family, or co-workers for advice.
how to choose the health plan that s right for you It s easy to feel a little confused about where to start when choosing a health plan. Some people ask their friends, family, or co-workers for advice.
AHE 232 Introduction to Clinical Software. Week ten:
 AHE 232 Introduction to Clinical Software Week ten: Note: I have set up the entire curriculum for this class with weekly lesson plans. This will allow the Instructor to determine how to incorporate the
AHE 232 Introduction to Clinical Software Week ten: Note: I have set up the entire curriculum for this class with weekly lesson plans. This will allow the Instructor to determine how to incorporate the
EHR System MojTermin: Implementation and Initial Data Analysis
 872 Digital Healthcare Empowering Europeans R. Cornet et al. (Eds.) 2015 European Federation for Medical Informatics (EFMI). This article is published online with Open Access by IOS Press and distributed
872 Digital Healthcare Empowering Europeans R. Cornet et al. (Eds.) 2015 European Federation for Medical Informatics (EFMI). This article is published online with Open Access by IOS Press and distributed
An integrated approach to HIS strengthening Ministry of Health, Belize
 An integrated approach to HIS strengthening Ministry of Health, Belize Institutional readiness Understanding the Universal Health Problem System development methodology How mature is our HIS Best practices
An integrated approach to HIS strengthening Ministry of Health, Belize Institutional readiness Understanding the Universal Health Problem System development methodology How mature is our HIS Best practices
The Healthy Michigan Plan Handbook
 The Healthy Michigan Plan Handbook Introduction The Healthy Michigan Plan is a health care program through the Michigan Department of Community Health (MDCH). The Healthy Michigan Plan provides health
The Healthy Michigan Plan Handbook Introduction The Healthy Michigan Plan is a health care program through the Michigan Department of Community Health (MDCH). The Healthy Michigan Plan provides health
Healthy Michigan MEMBER HANDBOOK
 Healthy Michigan MEMBER HANDBOOK 2014 The new name for Healthy 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS WELCOME TO HARBOR HEALTH PLAN.... 2 Who Is Harbor Health Plan?...3 How Do I Reach Member Services?...3 Is There A Website?....
Healthy Michigan MEMBER HANDBOOK 2014 The new name for Healthy 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS WELCOME TO HARBOR HEALTH PLAN.... 2 Who Is Harbor Health Plan?...3 How Do I Reach Member Services?...3 Is There A Website?....
Health Care in Estonia. Kadri Eisenschmidt Health Care and Communications Department Estonian Health Insurance Fund 01.02.2016
 Health Care in Estonia Kadri Eisenschmidt Health Care and Communications Department Estonian Health Insurance Fund 01.02.2016 Health insurance in Estonia Estonian health insurance is a social insurance
Health Care in Estonia Kadri Eisenschmidt Health Care and Communications Department Estonian Health Insurance Fund 01.02.2016 Health insurance in Estonia Estonian health insurance is a social insurance
Fujitsu Healthcare Business Overview
 ITU Workshop on E-health services in low-resource settings: Requirements and ITU role (Tokyo, Japan, 4-5 February 2013) Fujitsu Healthcare Business Overview Yoshiyuki Takahashi, Director, Global / New
ITU Workshop on E-health services in low-resource settings: Requirements and ITU role (Tokyo, Japan, 4-5 February 2013) Fujitsu Healthcare Business Overview Yoshiyuki Takahashi, Director, Global / New
Sample Assignment 1: Workflow Analysis Directions
 Sample Assignment 1: Workflow Analysis Directions Purpose The Purpose of this assignment is to: 1. Understand the benefits of nurse workflow analysis in improving clinical and administrative performance
Sample Assignment 1: Workflow Analysis Directions Purpose The Purpose of this assignment is to: 1. Understand the benefits of nurse workflow analysis in improving clinical and administrative performance
Medicaid Health Plans: Adding Value for Beneficiaries and States
 Medicaid Health Plans: Adding Value for Beneficiaries and States Medicaid is a program with numerous challenges, both for its beneficiaries and the state and federal government. In comparison to the general
Medicaid Health Plans: Adding Value for Beneficiaries and States Medicaid is a program with numerous challenges, both for its beneficiaries and the state and federal government. In comparison to the general
ehealth, HIS, etc ehealth All information about health HMIS mhealth HIS Statistical IS Credited: Karl Brown, Rockefeller Foundation
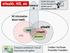 ehealth, HIS, etc Statistical IS Health Informatics: Formal discipline that studies use of information in health All information about health HIS HMIS ehealth mhealth Tele-medicine Enterprise architecture:
ehealth, HIS, etc Statistical IS Health Informatics: Formal discipline that studies use of information in health All information about health HIS HMIS ehealth mhealth Tele-medicine Enterprise architecture:
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGIES FOR PATIENT CARE MANAGEMENT
 SUMMARY Features INTERIN Technology, a complex of software tools and techniques for building health care information systems, was developed in the Program Systems Institute, Russian Academy of Sciences.
SUMMARY Features INTERIN Technology, a complex of software tools and techniques for building health care information systems, was developed in the Program Systems Institute, Russian Academy of Sciences.
Who Is Involved in Your Care?
 Patient Education Page 3 Pregnancy and Giving Birth Who Is Involved in Your Care? Our goal is to surround you and your family with a safe environment for the birth of your baby. We look forward to providing
Patient Education Page 3 Pregnancy and Giving Birth Who Is Involved in Your Care? Our goal is to surround you and your family with a safe environment for the birth of your baby. We look forward to providing
Welcome to Our Practice Welcome to Patriot Pediatrics!
 Welcome to Our Practice Welcome to Patriot Pediatrics! Thank you for choosing Patriot Pediatrics to care for your child s health. You are your child s most important caregiver, and we look forward to working
Welcome to Our Practice Welcome to Patriot Pediatrics! Thank you for choosing Patriot Pediatrics to care for your child s health. You are your child s most important caregiver, and we look forward to working
Creating a national electronic health record: The Canada Health Infoway experience
 Creating a national electronic health record: The Canada Health Infoway experience Presentation by Dennis Giokas Chief Technology Officer, Canada Health Infoway October 11, 2007 Overview The need for EHR
Creating a national electronic health record: The Canada Health Infoway experience Presentation by Dennis Giokas Chief Technology Officer, Canada Health Infoway October 11, 2007 Overview The need for EHR
What you should know about Data Quality. A guide for health and social care staff
 What you should know about Data Quality A guide for health and social care staff Please note the scope of this document is to provide a broad overview of data quality issues around personal health information
What you should know about Data Quality A guide for health and social care staff Please note the scope of this document is to provide a broad overview of data quality issues around personal health information
The ecosystem of the OpenClinic GA open source hospital information management software
 The ecosystem of the OpenClinic GA open source hospital information management software HEALTH FACILITY INFORMATION SYSTEMS AND INTEROPERABILITY FRANK VERBEKE, VRIJE UNIVERSITEIT BRUSSEL OpenClinic login
The ecosystem of the OpenClinic GA open source hospital information management software HEALTH FACILITY INFORMATION SYSTEMS AND INTEROPERABILITY FRANK VERBEKE, VRIJE UNIVERSITEIT BRUSSEL OpenClinic login
Care4u his Hospital information system. Commercial presentation
 Care4u his Hospital information system Commercial presentation content HealthCare provider challenges Ericsson OFFERING Care4u-his functionalities Ericsson healthcare portfolio Healthcare provider challenges
Care4u his Hospital information system Commercial presentation content HealthCare provider challenges Ericsson OFFERING Care4u-his functionalities Ericsson healthcare portfolio Healthcare provider challenges
8th Medical Open Source Software Symposium
 8th Medical Open Source Software Symposium openehr as A New Approach to Electronic Health Record System in Cambodia Maternity Care Program Kakada Hok 2009.10.31 1 Objectives of the Research Study To identify
8th Medical Open Source Software Symposium openehr as A New Approach to Electronic Health Record System in Cambodia Maternity Care Program Kakada Hok 2009.10.31 1 Objectives of the Research Study To identify
Implementation of ehealth in Croatia
 Implementation of ehealth in Croatia Hrvoje Belani, MSc EE Director s Adviser for Information Security Croatian Health Insurance Fund 11.5.2015 1 Content Croatian Health Network ehealth in Croatia Major
Implementation of ehealth in Croatia Hrvoje Belani, MSc EE Director s Adviser for Information Security Croatian Health Insurance Fund 11.5.2015 1 Content Croatian Health Network ehealth in Croatia Major
Increasing Capability for EHDI-EHR Interoperability A Self-Assessment Tool. Photo credit: Dawn Arlotta
 Increasing Capability for EHDI-EHR Interoperability A Self-Assessment Tool Photo credit: Dawn Arlotta Version 5, October 29, 2014 Introduction The National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities
Increasing Capability for EHDI-EHR Interoperability A Self-Assessment Tool Photo credit: Dawn Arlotta Version 5, October 29, 2014 Introduction The National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities
Introducing Care Connect
 Introducing Care Connect Our NEW Electronic Medical Record System Rochester General Health System (RGHS) is working hard to achieve its vision to become this community s healthcare provider of choice,
Introducing Care Connect Our NEW Electronic Medical Record System Rochester General Health System (RGHS) is working hard to achieve its vision to become this community s healthcare provider of choice,
Medical Information Systems
 Medical Information Systems Introduction The introduction of information systems in hospitals and other medical facilities is not only driven by the wish to improve management of patient-related data for
Medical Information Systems Introduction The introduction of information systems in hospitals and other medical facilities is not only driven by the wish to improve management of patient-related data for
NATIONAL EHEALTH ARCHITECTURE - FROM STRATEGY TO PRACTICE. Ministry of Social Affairs and Health, Finland
 NATIONAL EHEALTH ARCHITECTURE - FROM STRATEGY TO PRACTICE Ministry of Social Affairs and Health, Finland Agenda Finnish healthcare system on-going & upcoming reforms National ehealth architecture and implementation
NATIONAL EHEALTH ARCHITECTURE - FROM STRATEGY TO PRACTICE Ministry of Social Affairs and Health, Finland Agenda Finnish healthcare system on-going & upcoming reforms National ehealth architecture and implementation
THE ORGANISATION AND FINANCING OF HEALTH CARE SYSTEM IN LATVIA
 THE ORGANISATION AND FINANCING OF HEALTH CARE SYSTEM IN LATVIA Eriks Mikitis Ministry of Health of the Republic of Latvia Department of Health Care Director General facts, financial resources Ministry
THE ORGANISATION AND FINANCING OF HEALTH CARE SYSTEM IN LATVIA Eriks Mikitis Ministry of Health of the Republic of Latvia Department of Health Care Director General facts, financial resources Ministry
CHAPTER 6. Discussion and Conclusion. patient health information, such as diagnosis, medicine orders, managing patient
 CHAPTER 6 Discussion and Conclusion 6.1 Introduction Health care information system is a computer application to represent patient information in a friendly user interface and allowing users to review
CHAPTER 6 Discussion and Conclusion 6.1 Introduction Health care information system is a computer application to represent patient information in a friendly user interface and allowing users to review
On the Requirements for Cooperative Assistance in the Medical Domain
 On the Requirements for Cooperative Assistance in the Medical Domain L. Ardissono, A. Di Leva, G. Petrone, M. Segnan and M. Sonnessa Dipartimento di Informatica, Università di Torino, corso Svizzera 185,
On the Requirements for Cooperative Assistance in the Medical Domain L. Ardissono, A. Di Leva, G. Petrone, M. Segnan and M. Sonnessa Dipartimento di Informatica, Università di Torino, corso Svizzera 185,
Workflow Redesign Templates
 Workflow Redesign Templates Provided By: The National Learning Consortium (NLC) Developed By: Health Information Technology Research Center (HITRC) Practice and Workflow Redesign Community of Practice
Workflow Redesign Templates Provided By: The National Learning Consortium (NLC) Developed By: Health Information Technology Research Center (HITRC) Practice and Workflow Redesign Community of Practice
EHR vs CCR: What is the difference between the electronic health record and the continuity of care record?
 Health IT Library EHR vs CCR: What is the difference between the electronic health record and the continuity of care record? Written by C. Peter Waegemann The idea of the electronic health record was born
Health IT Library EHR vs CCR: What is the difference between the electronic health record and the continuity of care record? Written by C. Peter Waegemann The idea of the electronic health record was born
Eng. Ismail Torky Chief Information Technology Officer istorky@mohp.gov.eg www.mohp.gov.eg
 Ministry of Health and Population Egypt Eng. Ismail Torky Chief Information Technology Officer istorky@mohp.gov.eg www.mohp.gov.eg Without planning Disease Surv. Health Unit HIS, EIS GIS Apps. Data Center
Ministry of Health and Population Egypt Eng. Ismail Torky Chief Information Technology Officer istorky@mohp.gov.eg www.mohp.gov.eg Without planning Disease Surv. Health Unit HIS, EIS GIS Apps. Data Center
A Roadmap to Better Care and a Healthier You
 FROM COVERAGE TO CARE A Roadmap to Better Care and a Healthier You Step 2 Understand your health coverage Your ROADMAP to health 2 Understand your health coverage Check with your insurance plan or state
FROM COVERAGE TO CARE A Roadmap to Better Care and a Healthier You Step 2 Understand your health coverage Your ROADMAP to health 2 Understand your health coverage Check with your insurance plan or state
State Health Plan: Savings Plan Coverage Period: 01/01/2015-12/31/2015
 This is only a summary. If you want more detail about your coverage and costs, you can get the complete terms in the policy or plan document at www.eip.sc.gov or by calling 1-888-260-9430. Important Questions
This is only a summary. If you want more detail about your coverage and costs, you can get the complete terms in the policy or plan document at www.eip.sc.gov or by calling 1-888-260-9430. Important Questions
Health Informatics Development in the Hospital Authority
 Health Informatics Development in the Hospital Authority Dr CP Wong Chairman, Clinical Informatics Program Executive Group Co-Chairman, Clinical Informatics Program Steering Group Begin to take off in
Health Informatics Development in the Hospital Authority Dr CP Wong Chairman, Clinical Informatics Program Executive Group Co-Chairman, Clinical Informatics Program Steering Group Begin to take off in
CMS & ehr - An Update
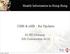 Health Informatics in Hong Kong CMS & ehr - An Update Dr NT Cheung HA Convention 2010 CMS / epr is essential in the HA Each Day... 12,000 users 90,000 patients 8M CMS transactions 700,000 epr views In
Health Informatics in Hong Kong CMS & ehr - An Update Dr NT Cheung HA Convention 2010 CMS / epr is essential in the HA Each Day... 12,000 users 90,000 patients 8M CMS transactions 700,000 epr views In
HEAL NY Phase 5 Health IT RGA Section 7.1: HEAL NY Phase 5 Health IT Candidate Use Cases Interoperable EHR Use Case for Medicaid
 HEAL NY Phase 5 Health IT RGA Section 7.1: HEAL NY Phase 5 Health IT Candidate Use Cases Interoperable EHR Use Case for Medicaid Interoperable Electronic Health Records (EHRs) Use Case for Medicaid (Medication
HEAL NY Phase 5 Health IT RGA Section 7.1: HEAL NY Phase 5 Health IT Candidate Use Cases Interoperable EHR Use Case for Medicaid Interoperable Electronic Health Records (EHRs) Use Case for Medicaid (Medication
i-care Integrated Hospital Information System
 i-care Integrated Hospital Information Empowering Healthcare Through Integrated Information and Intelligence Iterum TM i-care Hospital Information (HIS) provides a comprehensive and integrated solution
i-care Integrated Hospital Information Empowering Healthcare Through Integrated Information and Intelligence Iterum TM i-care Hospital Information (HIS) provides a comprehensive and integrated solution
Working Together HEALTH SERVICES FOR CHILDREN IN FOSTER CARE
 Chapter Eight Maintaining Health Records Maintaining the health records of children in foster care is critical to providing and monitoring health care on an ongoing basis. When health records are maintained
Chapter Eight Maintaining Health Records Maintaining the health records of children in foster care is critical to providing and monitoring health care on an ongoing basis. When health records are maintained
Health Information Systems: Scaling up solutions to transform healthcare delivery in Africa
 7th HELINA Conference Yaoundé, Cameroon, 29 November 2011 Systems: Scaling up solutions to transform healthcare delivery in Africa Mikko Korpela, DTech, Docent Research Director, UEF, School of Computing,
7th HELINA Conference Yaoundé, Cameroon, 29 November 2011 Systems: Scaling up solutions to transform healthcare delivery in Africa Mikko Korpela, DTech, Docent Research Director, UEF, School of Computing,
Meaningful Use. Goals and Principles
 Meaningful Use Goals and Principles 1 HISTORY OF MEANINGFUL USE American Recovery and Reinvestment Act, 2009 Two Programs Medicare Medicaid 3 Stages 2 ULTIMATE GOAL Enhance the quality of patient care
Meaningful Use Goals and Principles 1 HISTORY OF MEANINGFUL USE American Recovery and Reinvestment Act, 2009 Two Programs Medicare Medicaid 3 Stages 2 ULTIMATE GOAL Enhance the quality of patient care
The ELGA initiative: A plan for implementing a nationwide electronic health records system in Austria
 The ELGA initiative: A plan for implementing a nationwide electronic health records system in Austria Georg Duftschmid, Wolfgang Dorda, Walter Gall Core Unit of Medical Statistics and Informatics Section
The ELGA initiative: A plan for implementing a nationwide electronic health records system in Austria Georg Duftschmid, Wolfgang Dorda, Walter Gall Core Unit of Medical Statistics and Informatics Section
Information for Our Patients
 Information for Our Patients Locations Artemis Health 2561 Lac De Ville Boulevard, Suite 202 Rochester, NY 14618 585-244-7330 Greece Health Center 470 Long Pond Road Rochester, NY 14612 585-227-7600 Irondequoit
Information for Our Patients Locations Artemis Health 2561 Lac De Ville Boulevard, Suite 202 Rochester, NY 14618 585-244-7330 Greece Health Center 470 Long Pond Road Rochester, NY 14612 585-227-7600 Irondequoit
32 MILLION PEOPLE SHARE OUR SOLUTIONS
 THE HEALTHCARE IT SOLUTIONS 32 MILLION PEOPLE SHARE OUR SOLUTIONS 4 continents already use our healthcare solutions indracompany.com THE HEALTHCARE IT SOLUTIONS 32 MILLION PEOPLE SHARE OUR SOLUTIONS Our
THE HEALTHCARE IT SOLUTIONS 32 MILLION PEOPLE SHARE OUR SOLUTIONS 4 continents already use our healthcare solutions indracompany.com THE HEALTHCARE IT SOLUTIONS 32 MILLION PEOPLE SHARE OUR SOLUTIONS Our
ELECTRONIC MEDICAL RECORDS (EMR)
 ELECTRONIC MEDICAL RECORDS (EMR) SAUDI BOARD FOR COMMUNITY MEDICINE FIRST PART - FIRST SEMESTER (FALL 2010) COURSE SBCM 002: MEDICAL INFORMATICS Osama Alswailem MD MA Medical Record function 1. It s a
ELECTRONIC MEDICAL RECORDS (EMR) SAUDI BOARD FOR COMMUNITY MEDICINE FIRST PART - FIRST SEMESTER (FALL 2010) COURSE SBCM 002: MEDICAL INFORMATICS Osama Alswailem MD MA Medical Record function 1. It s a
Physician Practice Connections Patient Centered Medical Home
 Physician Practice Connections Patient Centered Medical Home Getting Started Any practice assessing its ability to achieve NCQA Physician Recognition in PPC- PCMH is taking a bold step toward aligning
Physician Practice Connections Patient Centered Medical Home Getting Started Any practice assessing its ability to achieve NCQA Physician Recognition in PPC- PCMH is taking a bold step toward aligning
How To Prepare For A Patient Care System
 Preparing for Online Communication with Your Patients A Guide for Providers This easy-to-use, time-saving guide is designed to help medical practices and community clinics prepare for communicating with
Preparing for Online Communication with Your Patients A Guide for Providers This easy-to-use, time-saving guide is designed to help medical practices and community clinics prepare for communicating with
Healthcare Associates Caring for You
 Healthcare Associates Caring for You Welcome to Healthcare Associates Dedicated to You At Healthcare Associates (HCA), patients come first, and caring for you is what we do best. We are pleased to offer
Healthcare Associates Caring for You Welcome to Healthcare Associates Dedicated to You At Healthcare Associates (HCA), patients come first, and caring for you is what we do best. We are pleased to offer
China s 12th Five-Year Plan: Healthcare sector
 China s 12th Five-Year Plan: Healthcare sector May 2011 KPMG CHINA One of the guiding principles of the 12th Five-Year Plan (5YP) is inclusive growth : helping ensure that the benefits of the country s
China s 12th Five-Year Plan: Healthcare sector May 2011 KPMG CHINA One of the guiding principles of the 12th Five-Year Plan (5YP) is inclusive growth : helping ensure that the benefits of the country s
How To Improve The Finnish Public Sector Information Resources
 Memorandum VM040:00/2013 885/00.01.00.01/2013 1 (11) 19.10.2015 Public Sector ICT Ministry of Finance Anne Kauhanen-Simanainen Margit Suurhasko Mikael Vakkari Open Data Policy in the Finnish Government
Memorandum VM040:00/2013 885/00.01.00.01/2013 1 (11) 19.10.2015 Public Sector ICT Ministry of Finance Anne Kauhanen-Simanainen Margit Suurhasko Mikael Vakkari Open Data Policy in the Finnish Government
E-HEALTH PLATFORMS AND ARCHITECTURES
 E-HEALTH PLATFORMS AND ARCHITECTURES E-Government Andreas Meier Nicolas Werro University of Fribourg Alfredo Santa Cruz 19.01.2007 Contents 1. Introduction 2. Existing Capabilities and Strategic Approach
E-HEALTH PLATFORMS AND ARCHITECTURES E-Government Andreas Meier Nicolas Werro University of Fribourg Alfredo Santa Cruz 19.01.2007 Contents 1. Introduction 2. Existing Capabilities and Strategic Approach
What s happening with 2014 EHR Incentive Program Attestations?
 In this issue: 2014 EHR Incentive Program Attestations Stage 2 MU & DIRECT Messaging MU & Clinical Decision Rules MU Time lines New Provider Registration & Current Provider Re- Qualification And, the Survey
In this issue: 2014 EHR Incentive Program Attestations Stage 2 MU & DIRECT Messaging MU & Clinical Decision Rules MU Time lines New Provider Registration & Current Provider Re- Qualification And, the Survey
Finland: country update. IHE Symposium 2016 in Bochum Konstantin Hyppönen, Kanta services, Kela, Finland
 Finland: country update IHE Symposium 2016 in Bochum Konstantin Hyppönen, Kanta services, Kela, Finland Content National Archive of Health Information = Kanta The timeline of interoperability In Finland
Finland: country update IHE Symposium 2016 in Bochum Konstantin Hyppönen, Kanta services, Kela, Finland Content National Archive of Health Information = Kanta The timeline of interoperability In Finland
The application of information technology in health care can be seen as follows:
 This article has appeared in 10 th anniversary bulletin, Norwegian Centre for Telemedicine Health Informatics and Telemedicine in Norway by Jacob Hygen, Managing Director, Norwegian Centre for Informatics
This article has appeared in 10 th anniversary bulletin, Norwegian Centre for Telemedicine Health Informatics and Telemedicine in Norway by Jacob Hygen, Managing Director, Norwegian Centre for Informatics
MyMoney s guide to medical insurance
 The best deals from leading insurers MyMoney s guide to medical insurance Public versus Private Medical Coverage Reasons why people buy Private Medical Insurance What are the different options available
The best deals from leading insurers MyMoney s guide to medical insurance Public versus Private Medical Coverage Reasons why people buy Private Medical Insurance What are the different options available
Streamline Your Radiology Workflow. With Radiology Information Systems (RIS) and EHR
 Streamline Your Radiology Workflow With Radiology Information Systems (RIS) and EHR 2 Practicing medicine effectively requires transferring large amounts of information quickly, accurately, and securely.
Streamline Your Radiology Workflow With Radiology Information Systems (RIS) and EHR 2 Practicing medicine effectively requires transferring large amounts of information quickly, accurately, and securely.
Land of Lincoln Health : Family Health Network LLH 3-Tier Bronze PPO Coverage Period: 01/01/2016 12/31/2016
 This is only a summary. If you want more detail about your coverage and costs, you can get the complete terms in the policy or plan document at www.landoflincolnhealth.org or by calling 1-844-FHN-4YOU.
This is only a summary. If you want more detail about your coverage and costs, you can get the complete terms in the policy or plan document at www.landoflincolnhealth.org or by calling 1-844-FHN-4YOU.
ehealth in Spain: A Strategy for a Decentralised National Health Service
 ehealth in Spain: A Strategy for a Decentralised National Health Service Juan Fernando Muñoz Chief Information Officer (CIO) Ministry of Health, Social Services and Equality ICT as an Element for Transformation
ehealth in Spain: A Strategy for a Decentralised National Health Service Juan Fernando Muñoz Chief Information Officer (CIO) Ministry of Health, Social Services and Equality ICT as an Element for Transformation
HEALTHNET HEALTHNET Regional Chain of Care in North Karelia Hospital District
 Heading Description Short name of case Long name of case HEALTHNET HEALTHNET Regional Chain of Care in North Karelia Hospital District Type of e-health application e.g. Regional network (no. of family
Heading Description Short name of case Long name of case HEALTHNET HEALTHNET Regional Chain of Care in North Karelia Hospital District Type of e-health application e.g. Regional network (no. of family
Greek ehealth Strategy under public consultation
 Greek ehealth Strategy under public consultation Mina Boubaki Ministry of Health, IT Department ehealth Network, ehealth Forum Recent relevant Reforms Law 3892/2010 Electronic Recording of Prescription
Greek ehealth Strategy under public consultation Mina Boubaki Ministry of Health, IT Department ehealth Network, ehealth Forum Recent relevant Reforms Law 3892/2010 Electronic Recording of Prescription
Priorities and strategies for successful EHR adoption
 HIQA Electronic Health Records Workshop Priorities and strategies for successful EHR adoption Dr Dipak Kalra Centre for Health Informatics and Multiprofessional Education (CHIME) University College London
HIQA Electronic Health Records Workshop Priorities and strategies for successful EHR adoption Dr Dipak Kalra Centre for Health Informatics and Multiprofessional Education (CHIME) University College London
HIS Implementation Guide
 Introduction The main goal of the Integrated Health Information System (EU-IHIS) Project is to implement and integrate hospital information systems (HIS) in 19 beneficiary hospitals and link these systems
Introduction The main goal of the Integrated Health Information System (EU-IHIS) Project is to implement and integrate hospital information systems (HIS) in 19 beneficiary hospitals and link these systems
Survey on Attitudes toward Sharing and Managing Medical Records
 Survey on Attitudes toward Sharing and Managing Medical Records Yasuharu Ukai, Director The Research Institute for Socionetwork Strategies (RISS) at Kansai University This survey was conducted as part
Survey on Attitudes toward Sharing and Managing Medical Records Yasuharu Ukai, Director The Research Institute for Socionetwork Strategies (RISS) at Kansai University This survey was conducted as part
PPO Hospital Care I DRAFT 18973
 This is only a summary. If you want more detail about your coverage and costs, you can get the complete terms in the policy or plan document at www.ibx.com or by calling 1-800-ASK-BLUE. Important Questions
This is only a summary. If you want more detail about your coverage and costs, you can get the complete terms in the policy or plan document at www.ibx.com or by calling 1-800-ASK-BLUE. Important Questions
ICT in HSE Where are we now. Fran Thompson
 ICT in HSE Where are we now Fran Thompson HSE Overview The HSE is responsible for managing and delivering health and personal social services in Ireland. Employs in excess of 108,000 staff - largest employer
ICT in HSE Where are we now Fran Thompson HSE Overview The HSE is responsible for managing and delivering health and personal social services in Ireland. Employs in excess of 108,000 staff - largest employer
HL7 and Meaningful Use
 HL7 and Meaningful Use Grant M. Wood HL7 Ambassador HIMSS14 2012 Health Level Seven International. All Rights Reserved. HL7 and Health Level Seven are registered trademarks of Health Level Seven International.
HL7 and Meaningful Use Grant M. Wood HL7 Ambassador HIMSS14 2012 Health Level Seven International. All Rights Reserved. HL7 and Health Level Seven are registered trademarks of Health Level Seven International.
Conference Paper A successful model of regional healthcare information exchange in Japan: Case Study in Kagawa Prefecture
 econstor www.econstor.eu Der Open-Access-Publikationsserver der ZBW Leibniz-Informationszentrum Wirtschaft The Open Access Publication Server of the ZBW Leibniz Information Centre for Economics Yamakata,
econstor www.econstor.eu Der Open-Access-Publikationsserver der ZBW Leibniz-Informationszentrum Wirtschaft The Open Access Publication Server of the ZBW Leibniz Information Centre for Economics Yamakata,
NOVA SCOTIA DRUG INFORMATION SYSTEM
 1 NOVA SCOTIA DRUG INFORMATION SYSTEM Private Healthcare Organization Toolkit Department of Health and Wellness [Type text] Page 0 Version 1.0 (Jul. 1, 2015) 2 Intentionally left blank 3 The Nova Scotia
1 NOVA SCOTIA DRUG INFORMATION SYSTEM Private Healthcare Organization Toolkit Department of Health and Wellness [Type text] Page 0 Version 1.0 (Jul. 1, 2015) 2 Intentionally left blank 3 The Nova Scotia
HOSPITAL MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
 HOSPITAL MANAGEMENT SYSTEM PURPOSE The basic design of healthcare management system on a web application is that the application sits on a web server, and all users will access it via web browser over
HOSPITAL MANAGEMENT SYSTEM PURPOSE The basic design of healthcare management system on a web application is that the application sits on a web server, and all users will access it via web browser over
HL7 and Meaningful Use
 HL7 and Meaningful Use HIMSS Las Vegas February 23, 2012 Grant M. Wood Intermountain Healthcare Clinical Genetics Institute Meaningful Use What Does It Mean? HITECH rewards the Meaningful Use of health
HL7 and Meaningful Use HIMSS Las Vegas February 23, 2012 Grant M. Wood Intermountain Healthcare Clinical Genetics Institute Meaningful Use What Does It Mean? HITECH rewards the Meaningful Use of health
United States Fire Insurance Company: International Technological University Coverage Period: beginning on or after 9/7/2014
 or after 9/7/2014 Summary of Benefits and Coverage: What this Plan Covers & What it Costs Coverage for: Individual Plan Type: PPO This is only a summary. If you want more detail about your coverage and
or after 9/7/2014 Summary of Benefits and Coverage: What this Plan Covers & What it Costs Coverage for: Individual Plan Type: PPO This is only a summary. If you want more detail about your coverage and
Addressing the State of the Electronic Health Record (EHR)
 Addressing the State of the Electronic Health Record (EHR) Agenda Definitions Attributes Differences Adoption Model Current State Challenges Implementation considerations What is it? EMR CMR EHR EPR PHR
Addressing the State of the Electronic Health Record (EHR) Agenda Definitions Attributes Differences Adoption Model Current State Challenges Implementation considerations What is it? EMR CMR EHR EPR PHR
Hospital Information Systems HIS
 Hospital Information Systems HIS What Does Patient Mean? People s bad situation by means of social, physical and spiritual condition What does Healthcare Organization Mean? Public or private institutions
Hospital Information Systems HIS What Does Patient Mean? People s bad situation by means of social, physical and spiritual condition What does Healthcare Organization Mean? Public or private institutions
Answers to Your Questions about All Kids
 State of Illinois Department of Healthcare and Family Services Answers to Your Questions about All Kids 1-866-ALL-KIDS www.allkids.com All Kids is Illinois program for children who need comprehensive,
State of Illinois Department of Healthcare and Family Services Answers to Your Questions about All Kids 1-866-ALL-KIDS www.allkids.com All Kids is Illinois program for children who need comprehensive,
A document oriented approach to building a national EHR - applying CDA R2 in Finland
 International HL7 Interoperability Conference IHIC 2006 A document oriented approach to building a national EHR - applying CDA R2 in Finland Jari Porrasmaa & Vesa Pakarinen (VTT ) University of Kuopio,
International HL7 Interoperability Conference IHIC 2006 A document oriented approach to building a national EHR - applying CDA R2 in Finland Jari Porrasmaa & Vesa Pakarinen (VTT ) University of Kuopio,
Heath Shield Heath Care Management System
 Heath Shield Heath Care Management System Introduction Heath Shield will be an integrated, modular client server based system which can be extended to a web based solution also. The programs will have
Heath Shield Heath Care Management System Introduction Heath Shield will be an integrated, modular client server based system which can be extended to a web based solution also. The programs will have
MDH Scope Statement: Public Health Informatics Profile
 Project Name: Date: Project Managers: Project Sponsors: Version No: Public Health Informatics Profile Current Situation: The MDH Common Ground grant, focused on chronic disease surveillance, and the MN
Project Name: Date: Project Managers: Project Sponsors: Version No: Public Health Informatics Profile Current Situation: The MDH Common Ground grant, focused on chronic disease surveillance, and the MN
An integrated IT approach to Chronic Disease Management
 An integrated IT approach to Chronic Disease Management Presented by: Steve Courtney Chief Executive Officer Health Information Systems (UK) Ltd March 2011 Who are Health Information Systems (UK) Ltd Company
An integrated IT approach to Chronic Disease Management Presented by: Steve Courtney Chief Executive Officer Health Information Systems (UK) Ltd March 2011 Who are Health Information Systems (UK) Ltd Company
Make sure you have health cover for your family. Allianz Global Assistance OSHC offers three types of policies:
 Overseas Student Health Cover Pregnancy Fact Sheet This fact sheet aims to help you understand the Australian healthcare system when having a baby. During your pregnancy Make sure you have health cover
Overseas Student Health Cover Pregnancy Fact Sheet This fact sheet aims to help you understand the Australian healthcare system when having a baby. During your pregnancy Make sure you have health cover
Introducing. MEDITECH's Electronic Health Record. Here are the components comprising. MEDITECH's Electronic Health Record...
 Introducing MEDITECH's Electronic Health Record MEDITECH s Electronic Health Record is a well-crafted suite of integrated applications including EPR and PAS designed to support the delivery of safe, cost-effective
Introducing MEDITECH's Electronic Health Record MEDITECH s Electronic Health Record is a well-crafted suite of integrated applications including EPR and PAS designed to support the delivery of safe, cost-effective
Existing concepts and experiences with interoperability initiatives
 Existing concepts and experiences with interoperability initiatives Geert Claeys, M. Sc. Co-Chairman Europe Technology Manager, Agfa Healthcare/R&D Topics Interoperability problems in healthcare process
Existing concepts and experiences with interoperability initiatives Geert Claeys, M. Sc. Co-Chairman Europe Technology Manager, Agfa Healthcare/R&D Topics Interoperability problems in healthcare process
empowersystemstm empowerhis Advanced Core Hospital Information System Technology Comprehensive Solutions for Facilities of Any Size
 empowersystemstm empowerhis TM Advanced Core Hospital Information System Technology Comprehensive Solutions for Facilities of Any Size ADT / Patient Registration System + Fully Integrated Patient Registration
empowersystemstm empowerhis TM Advanced Core Hospital Information System Technology Comprehensive Solutions for Facilities of Any Size ADT / Patient Registration System + Fully Integrated Patient Registration
Introduction of ehr Application. Ellen TONG, Dep SHI(eHR & SCP) Hospital Authority of Hong Kong
 Introduction of ehr Application Ellen TONG, Dep SHI(eHR & SCP) Hospital Authority of Hong Kong Background Public consultation done on health-care system reform in 2008 & proposed to develop ehr sharing
Introduction of ehr Application Ellen TONG, Dep SHI(eHR & SCP) Hospital Authority of Hong Kong Background Public consultation done on health-care system reform in 2008 & proposed to develop ehr sharing
Public Health Reporting Initiative Functional Requirements Description
 Public Health Reporting Initiative Functional Requirements Description 9/25/2012 1 Table of Contents 1.0 Preface and Introduction... 2 2.0 Initiative Overview... 3 2.1 Initiative Challenge Statement...
Public Health Reporting Initiative Functional Requirements Description 9/25/2012 1 Table of Contents 1.0 Preface and Introduction... 2 2.0 Initiative Overview... 3 2.1 Initiative Challenge Statement...
