Optimization of Soft Handover Parameters for UMTS Network in Indoor Environment
|
|
|
- Elisabeth Casey
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
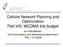
1 Optimization of Soft Handover Parameters for UMTS Network in Indoor Environment J. Łcki, J. Niemelä, J. Lempiäinen Institute of Communications Engineering Tampere University of Technology P.O. Box 533 FI Tampere, Finland Abstract The aim of this paper is to present the impact of different parameters on UMTS network performance in indoor environment. The measurement results of the impact of the most important parameters, i.e., the thresholds for add and drop events and their time to trigger values are presented on UMTS indoor network performance in terms of average downlink SIR target, downlink transmit power, probability, and observed BER values. Due to indoor propagation channel, which causes smaller delay spread and hence less multipath diversity, a UMTS signal becomes inherently narrowband. Therefore, the gain of against fast and slow fading would be crucial. Moreover, the characteristics of indoor radio channel enforce to apply different parameter settings than for outdoor network. In the frame of this paper, the analysis is based on the downlink as it is seen more crucial from point of view due to additional link required for s. The measurement results indicate that relatively large thresholds for add and drop events simultaneously with a long time to trigger for drop event are the most suitable for UMTS indoor environment due to the lack of multipath diversity, and to combat fast and deep fluctuations of the indoor radio channel. Key words: indoor, optimization, soft handover, UMTS. 1. Introduction WCDMA (wideband code division multiple access) technology introduces other kind of handovers, namely (soft handover) and SfHO (softer handover). A soft handover occurs, when two or more BSs serve a MS simultaneously. During a soft handover, MS is in the coverage area of two or more sectors belonging to different BSs. On the other hand, in softer handover, the MS is in the coverage of two or more sectors, which belong to the same base station. and SfHO are supported in UTRA FDD (UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Frequency Division Duplex) mode only. The performance and functionality of and SfHO is controlled through dedicated functionalities and their parameters (see Section II). So far, most of the research concerning (herein is understood as and SfHO as function does not separate these two) parameter optimization has been concentrated on outdoor UMTS networks (e.g., [1] and [2]). Moreover, other already accomplished simulations of in [3] shows that optimum static parameters, i.e., the thresholds for add and drop events and dynamic parameters, i.e., time to trigger values of add and drop events can improve the downlink performance, and therefore also the overall network performance, quality of service (QoS) and capacity. However, during the current evolution of the 3G radio networks, indoor UMTS networks are becoming more and more important and also more popular. Moreover, the indoor environment introduces different radio propagation characteristics than outdoor environment. Due to small delay spread in a typical indoor propagation channel, the resulting amount of multipath diversity is inherently small. Moreover, due to frequency non-selective channel, the fading of the signal is mostly characterized by large amplitude variations. In terms of function and parameters, small delay spread values and lack of multipath diversity should be taken into account when setting the different parameters for function. Due to the fact that diversity reception is typically not used in passive indoor antenna systems due to cost constrains, the possibility of using the diversity component of against fast and slow fading indoor radio channel should be studied. In this paper, the measurement results of thresholds for add and drop events together with their time to trigger values are shown for the indoor UMTS network in the downlink direction. 2. UTRA FDD soft handover 2.1. Soft handover procedure and algorithm The soft handover procedure is divided into three phases: measurements, decision, and execution. In the measurement phase, energy per chip over interference spectral density ratio (E c /N 0 ) is evaluated based on the measurements on the downlink primary common pilot channel (P-CPICH) and received signal strength indicator (RSSI) as shown in (1): E /N = RSCP (1) RSSI c o RSCP (received signal code power) is the power of decoded pilot channel. The performed measurements results are sent by the MS to the BS. All measurements parameters are contained in measurement report, and then passed to RNC (radio network controller), where the decision phase takes place. In this phase, the performed
2 Figure 1: The meaning of parameters. measurements are compared with predefined soft handover criteria. This process is carried out by RNC. After the decision phase, the execution of soft handover is accomplished, if the soft handover criteria are fulfilled. The effect of the execution phase is that the MS either enters or leaves area. The algorithm currently used in WCDMA systems and in measurements presented in this paper is adopted from [1]. In explanation of soft handover algorithm, the following terms are crucial, and have to be defined: Active set contains the list of cells, having the connection with MS, in other words, the cells, which are in soft handover connection. Monitored set contains the list of cells, which pilot channels power is not high enough to be added to the active set, or active set is already full. The RNC decides, which event is triggered based on continuous measurements performed by MS on P-CPICH channel. These events are radio link addition (event 1A), radio link removal (event 1B), and radio link replacement (event 1C). These events are executed depending on relative strengths the pilot signal from different cells as well as on the time to trigger value ( T). A cell is added or dropped from active set depending on the difference between its P-CPICH E c /N 0 level and the power level of the best pilot signal in active set. algorithm is illustrated in Figure 1 and more details can be found from [7] Soft handover performances Soft handovers provide many advantages to the WCDMA network. One of them is smaller amount of ping-pong event, which occurs, when a mobile moves closer and further from a cell boundary causing frequent handovers. Non-optimal parameters may cause unnecessary high power rise peaks, which result in high interference and reduce network capacity. This negative effect can be mitigated by providing a larger hysteresis margin for execution of. However, in turn, this solution may introduce longer handover delays and higher interference Figure 2: Antenna positions and orientations during the measurements. in neighbor cells. This ping-pong effect is strongly decreased by soft handovers. The other feature of soft handovers is smoother data transmission. During a soft handover, there is no break in data transmission like during hard handovers. Moreover, s eliminate possible data loss and decrease drop call rate. This feature is very essential, because high transmission data rates are utilized in UMTS networks, where even a short brake in the transmission can cause a loss of high amount of data. The s have also negative effects. There is more complexity in implementation of s than with, e.g., hard handovers (HHO), as well as additional consumption of downlink resources (transmit power and spreading codes) is caused by the mobile being in. advantages and disadvantages give the reason to consider its parameters, algorithms, etc. The soft handover function should be planned carefully and have to be compromise between power gain and possible losses. 3. Measurement environment and setup 3.1. General description UMTS indoor test nework The measurements were conducted in indoor UMTS test network implemented in a university building. In the measurements, two cells belonging to different BSs were used. Base stations were connected through Iub interface to RNC/Iub simulator. RNC/Iub was supporting soft handovers between BSs [8]-[9]. Coaxial cable (i.e., a passive distributed antenna system, DAS) was employed to connect transmitting antennas and radiating cables to BSs. Antennas used in measurements were two standard discrete UMTS antennas [10]. Used antennas are highlighted in Figure 2. Antennas gain was 7 dbi and the horizontal beam width was 90. The effective isotropic radiated power (EIRP) values for antennas were close to dbm Measurement equipment The equipment used to provide the result was two base stations, two discrete antennas, MS, RNC/Iub simulator [8] and WCDMA radio interface analyzer [11] RNC/Iub
3 simulator was used in this measurement campaign for setting parameters, and capturing the transmit powers of two BSs. The radio interface analyzer was used to measure and store the radio interface parameters during the measurements. The mobile equipment connected to a laptop was placed on small trolley. The height of the trolley was approximately 1 m. During the measurements the trolley was moved along a pre-defined route (see the black solid line in Figure 2), on which the measurements were performed. The speed of the trolley was approximately 2-3 km/h Measurement campaign Two antennas belonging to different BSs were symmetrically placed and their beams were partly overlapping in this area on each other. Measurements were partly conducted in corridors, where a clear area was obtained (Corridor C in Figure 2). Measurements were mostly conducted during weekends in order to minimize the impact of external interferences on the measurement results. During the measurements, the trolley with laptop and mobile was moved from corridor G to the corridor F, through the C corridor of the first floor (Figure 2). While the trolley was moved, the transmit powers from both base stations were recorded. Radio interface analyzer recorded the time, when the MS was in area, and when MS was connected to only one cell. Moreover, the radio interface analyzer stored also other parameters like BER (bit error rate) and downlink SIR (signal to interference) target values. The measurements were conducted for the combination of various static and dynamic parameters. During each measurement, the transmit powers of both base stations were recorded. Power levels were later averaged in such manner that first the power outside area was averaged and added to the sum of average power transmitted during from both base stations. Finally, the sum of these two values was averaged again. Hence, it impact of additional radio link and additional transmit power was taken into account in final transmit power values. In this paper, probability is the ratio of the time, when the mobile is in area to the total time of the connection. Only one mobile was used for making a call (12.2 kbps speech bearer), and this call was reflected from the RNC/Iub simulator. Reflection of the call means that the call was initiated and terminated by the same MS. 4. Measurement results Tables 1-4 presents the measurement results with all measured sets of considered parameters. The rows contain the list of thresholds for add and drop events (in db) in such a manner that add thresholds are in the left side of the brackets and the drop thresholds in the right side. The columns contain the time-to-trigger values for add and drop events expressed (in ms), respectively. Table 1 shows the required SIR target values for used radio bearer (12.2 kbps speech). SIR target is set per bearer basis in RNC, and corrected in outer loop power control. In practice, the lower the average SIR target is, the smaller is also the amount of required resources, i.e., downlink transmit power. If power control is able to compensate the changes in the radio channel, the average SIR (adjusted by closed-loop power control) should correspond to average SIR target. As indicated by the results, increasing the threshold for add event decreases slightly the required SIR target. However, increasing the time-to-trigger for add event increases the required SIR target. Hence, the results indicate that in indoor environment in order to achieve lower SIR target values, the threshold for add event should be high but the time-totrigger value short. In other words, a cell is easily and quickly included in the active set in order to provide as much diversity gain as possible. On the contrary, if the threshold for drop event is increased, the required SIR target decreases as well. However, this phenomenon is the most efficient with higher time-to-trigger values for drop event. Hence, the results indicate that also high threshold for drop event should be used but also with longer timeto-trigger values. In other words, a cell is not easily dropped from the active set, and if it is about to drop, the level of the signal should maintain for a longer time below the threshold for drop event. Nevertheless, the results clearly point out that in indoor environment, the used thresholds should be high with short time-to-trigger for add event and long for drop event. Table 2 presents the average downlink transmit power for different sets of parameters. The average downlink transmit powers are mostly inline with the required SIR target values. However, in some cases, the downlink transmit power is lower although the required SIR target has been higher. The reason for this might have been the different distribution of area and certain level of measurement inaccuracy. Nevertheless, the measured results show that the used thresholds should be high with short time-to-trigger for add event and long for drop event. Figure 3a shows the comparison of transmission powers between different time-to-trigger values for all measured combinations of the thresholds for add and drop events. With low thresholds, the difference between [160ms 1280ms] scenario and [100ms 640ms] is minimal. However, with higher thresholds the gain of longer timeto-trigger values is obvious. In addition, the trend of all time-to-trigger curves indicates that even higher thresholds than [6dB 9dB] should be used for indoor networks. For example, with [0dB 1dB] thresholds for add and drop events and with [100ms 240ms] time-to-trigger values, the resulting downlink transmit power was around 31 dbm where as with the highest measured add and drop thresholds [6dB 9dB] and with the longest time-to-trigger values [160ms 1280ms], the resulting average downlink transmit power was only 22.7 dbm. Hence, over the measurement route, the gain of more correct parameters is 8.3 db in the downlink transmit power. However, as a consequence of this, the resulting probability increases over the measurement route from 16% up to 51% (see Table 3). Meaning that instead of having 1/6 of the users in, there are half of the users
4 Table 1. Required SIR target values for kbps speech link [db]. threshold [0 1] [1 2] [1 4] [2 4] [1 5] [2 5] [3 4] [3 5] [3 6] [3 8] [4 7] [6 9] Table 2. Required DL transmit powers in [dbm]. [0 1] [1 2] [1 4] [2 4] [1 5] [2 5] [3 4] [3 5] [3 6] [3 8] [4 7] [6 9] Table 3. Resulting probabilities [%]. [0 1] [1 2] [1 4] [2 4] [1 5] [2 5] [3 4] [3 5] [3 6] [3 8] [4 7] [6 9] Table 4. BER values of P-CPICH [%]. [0 1] [1 2] [1 4] [2 4] [1 5] [2 5] [3 4] [3 5] [3 6] [3 8] [4 7] [6 9] continuously in. Note that the impact of additional radio links required for is already taken into account when calculating the average transmit powers of the base stations for a single user. However, in multi-user scenario, the gain in the downlink transmit power is not as huge as indicated by the results, but since the downlink power requirement for users in is considerably smaller than for mobiles not in, the overall gain of having large thresholds for add and drop events is expected to be significant. Hence, the only implication is the increased probability that causes a higher requirement of Iub capacity from the indoor base station. Table 3 gathers the BER values calculated at the mobile station on the P- CPICH. These results further verify the previous discussion about parameter settings for indoor environment. Figure 3a shows the comparison of transmission powers between different time-to-trigger values for all measured combinations of the thresholds for add and drop events. With low thresholds, the difference between [160ms 1280ms] scenario and [100ms 640ms] is minimal. However, with higher thresholds the gain of longer timeto-trigger values is obvious. In addition, the trend of all time-to-trigger curves indicates that even higher thresholds than [6dB 9dB] should be used for indoor networks. Figure 3b shows the cumulative distribution function (CDF) of the downlink transmit power with [160ms 1280ms] time-to-trigger values for [6dB 9dB] (solid) and for [0dB 1dB] (dashed) parameter setups. As clearly indicated by the figure, the fast fading dips with small thresholds for add and drop events requires larger dynamics for the downlink transmit power as the required power varies between 16 dbm and 36 dbm, whereas with higher thresholds, the required range is between 16 dbm and 22 dbm. The fundamental difference in the downlink transmit power comes directly from the possible area (i.e., from Corridor C in Figure 2) since in the non- areas (i.e., Corridors F and G) the required transmit power is the same (see Figure 3). Figure 4 shows the drop call rates for all measured timeto-trigger values with [3dB 4dB] thresholds for add and drop events. As indicated by the curve, the resulting drop call rate decreases tremendously from % down to 4% when time-to-trigger values are changed from [100ms 240ms] to [160ms 1280ms]. However, since the acceptable drop call rate is typically 1-2%, the results clearly indicate that in addition to long drop timer, higher thresholds for add and drop event are needed for indoor UMTS networks. The impact of different parameter values on the required downlink SIR target, downlink transmit power, probability and P-CPICH BER was analyzed in this paper. The analyzed parameters
5 DL transmission power [dbm] Best case [ ] Typical case [ ] Worst case [ ] Measurement point (a) CDF[%] Best case [6dB 9dB] Worst case [0dB 1dB] Transmit power [dbm] Figure 3: (a) An example of downlink transmit powers for three different sets of time-to-trigger values. Measurement points correspond to all measuremed combinations of the thresholds for add and drop event in order of appearance in the tables. (b) Cumulative distribution function of the transmit power with high [6 db 9 db] and low [0 db 1dB] add and drop window sizes. (b) were the threshold values for add and drop events together with their time-to-trigger values. Due to smaller delay spread values in indoor environment, UMTS signal is behaving inherently as a narrowband signal. Moreover, due to resulting lack of multipath diversity, the required SIR target for a radio bearer increases if is not utilized. Hence, the diversity gain provided by clearly reduces the required SIR target, and hence results in also smaller required TX power. This fundamentally increases the capacity of an indoor network. Drop call rate [%] Conclusions The smallest SIR target values and correspondingly the smallest downlink TX powers were observed with [6dB 9dB] thresholds for add and drop events and with [160ms 1280ms] time-to-trigger values, correspondingly. However, the measurement results and analysis indicate that even higher thresholds or longer time-to-trigger for drop event should be utilized. The required dynamic range for downlink TX power is considerably smaller with higher threshold for add and drop events. The future studies concentrate on providing the impact of diversity gain on the capacity of indoor network. Moreover, the impact of larger thresholds for add and drop events with longer time-to-trigger values is analyzed in uplink direction. Acknowledgement Authors would like to thank European Communications Engineering (ECE) Ltd for helpful comments, Elisa Mobile Finland for allocating the frequency for UMTS test network, Nemo Technologies for providing radio interface analyzer, and the National Technology Agency of Finland for funding the work. REFERENCES [1] I. Forkel1, M. Schinnenburg1, B. Wouters, Performance evaluation of soft handover in a realistic UMTS network, in Measurement point Figure 4: Drop call rates as a function of add and drop window sizes. Proc. IEEE 57 th Semiannual Vehicular Technology Conference, vol. 3, pp , April 03. [2] M. Schinnenburg1, I. Forkel1, B. Haverkamp, Realization and Optimization of Soft and Softer Handover in UMTS Networks, in Proc. IEEE 5 th Personal Mobile Communications Conference, pp , April 03. [3] D. Wong, T.J. Lim, Soft Handoffs in CDMA mobile systems, IEEE Transition on Personal Communications, vol. 4, issue 6, pp. 6-17, December [4] N. Binucci, K. Hiltunen, M. Caselli, Soft Handover gain in WCDMA, in Proc. IEEE 52 th Semiannual Vehicular Technology Conference, vol. 3, pp , September 00. [5] X. Yang, S. Ghaheri-Niri, R. Tafazolli, UTRA Soft Handover optimization, in Proc. IEE 3 rd International Conference on 3G Mobile Communication Technologies, pp , May 02. [6] 3GPP, TS , Radio resource control, Version 5.2.0, Release 5. [7] 3GPP, TR , Radio resource management strategies, Version 3.8.0, Release 6. [8] Web site, NetHawk Oyj, NetHawk RNC/Iub Simulator. [9] 3GPP, TS , UTRAN Iub interface NBAP signaling, Version 4.5.0, Release 4. [10] Web site, Indoor Directional Antenna MHz. [11] Web site, Nemo Technologies, Nemo outdoor, Radio Interface Analyzer.
CDMA Network Planning
 CDMA Network Planning by AWE Communications GmbH www.awe-com.com Contents Motivation Overview Network Planning Module Air Interface Cell Load Interference Network Simulation Simulation Results by AWE Communications
CDMA Network Planning by AWE Communications GmbH www.awe-com.com Contents Motivation Overview Network Planning Module Air Interface Cell Load Interference Network Simulation Simulation Results by AWE Communications
HSDPA Throughput Performances Using an Experimental HSDPA Transmission System
 NTT DoCoMo Technical Journal Vol. 6 No.4 HSDPA Throughput Performances Using an Experimental HSDPA Transmission System Shinya Tanaka, Hiroyuki Ishii, Tomoki Sao, Yousuke Iizuka and Takeshi Nakamori The
NTT DoCoMo Technical Journal Vol. 6 No.4 HSDPA Throughput Performances Using an Experimental HSDPA Transmission System Shinya Tanaka, Hiroyuki Ishii, Tomoki Sao, Yousuke Iizuka and Takeshi Nakamori The
192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking. Lecture 5: Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) [Schiller, Section 4.4]
![192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking. Lecture 5: Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) [Schiller, Section 4.4] 192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking. Lecture 5: Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) [Schiller, Section 4.4]](/thumbs/18/698539.jpg) 192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking Lecture 5: Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) [Schiller, Section 4.4] Geert Heijenk Outline of Lecture 5 Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) q Evolution of cellular
192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking Lecture 5: Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) [Schiller, Section 4.4] Geert Heijenk Outline of Lecture 5 Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) q Evolution of cellular
Inter-Cell Interference Coordination (ICIC) Technology
 Inter-Cell Interference Coordination (ICIC) Technology Dai Kimura Hiroyuki Seki Long Term Evolution (LTE) is a promising standard for next-generation cellular systems targeted to have a peak downlink bit
Inter-Cell Interference Coordination (ICIC) Technology Dai Kimura Hiroyuki Seki Long Term Evolution (LTE) is a promising standard for next-generation cellular systems targeted to have a peak downlink bit
COMPATIBILITY STUDY FOR UMTS OPERATING WITHIN THE GSM 900 AND GSM 1800 FREQUENCY BANDS
 Electronic Communications Committee (ECC) within the European Conference of Postal and Telecommunications Administrations (CEPT) COMPATIBILITY STUDY FOR UMTS OPERATING WITHIN THE GSM 900 AND GSM 1800 FREQUENCY
Electronic Communications Committee (ECC) within the European Conference of Postal and Telecommunications Administrations (CEPT) COMPATIBILITY STUDY FOR UMTS OPERATING WITHIN THE GSM 900 AND GSM 1800 FREQUENCY
International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering
 Volume 2, Issue 11, November 2012 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Automated
Volume 2, Issue 11, November 2012 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Automated
A Novel Decentralized Time Slot Allocation Algorithm in Dynamic TDD System
 A Novel Decentralized Time Slot Allocation Algorithm in Dynamic TDD System Young Sil Choi Email: choiys@mobile.snu.ac.kr Illsoo Sohn Email: sohnis@mobile.snu.ac.kr Kwang Bok Lee Email: klee@snu.ac.kr Abstract
A Novel Decentralized Time Slot Allocation Algorithm in Dynamic TDD System Young Sil Choi Email: choiys@mobile.snu.ac.kr Illsoo Sohn Email: sohnis@mobile.snu.ac.kr Kwang Bok Lee Email: klee@snu.ac.kr Abstract
An Interference Avoiding Wireless Network Architecture for Coexistence of CDMA 2000 1x EVDO and LTE Systems
 ICWMC 211 : The Seventh International Conference on Wireless and Mobile Communications An Interference Avoiding Wireless Network Architecture for Coexistence of CDMA 2 1x EVDO and LTE Systems Xinsheng
ICWMC 211 : The Seventh International Conference on Wireless and Mobile Communications An Interference Avoiding Wireless Network Architecture for Coexistence of CDMA 2 1x EVDO and LTE Systems Xinsheng
Evaluating the 3G Network Performance by Virtual Testing
 1 and 2 1 INTI International University, Malaysia, Faculty of Engineering and Information Technology 2 INTI International University, Malaysia, Faculty of Engineering and Information Technology Corresponding
1 and 2 1 INTI International University, Malaysia, Faculty of Engineering and Information Technology 2 INTI International University, Malaysia, Faculty of Engineering and Information Technology Corresponding
CDMA Performance under Fading Channel
 CDMA Performance under Fading Channel Ashwini Dyahadray 05307901 Under the guidance of: Prof Girish P Saraph Department of Electrical Engineering Overview Wireless channel fading characteristics Large
CDMA Performance under Fading Channel Ashwini Dyahadray 05307901 Under the guidance of: Prof Girish P Saraph Department of Electrical Engineering Overview Wireless channel fading characteristics Large
Performance Evaluation of Six-Sectored Configuration in Hexagonal WCDMA (UMTS) Cellular Network Layout
 LAPPEENRANTA UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Shyam Babu Mahato Performance Evaluation of Six-Sectored Configuration in Hexagonal WCDMA (UMTS) Cellular Network Layout Master
LAPPEENRANTA UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Shyam Babu Mahato Performance Evaluation of Six-Sectored Configuration in Hexagonal WCDMA (UMTS) Cellular Network Layout Master
Scanning with Sony Ericsson TEMS Phones. Technical Paper
 Scanning with Sony Ericsson TEMS Phones Technical Paper Scanning with Sony Ericsson TEMS Phones 2009-05-13 Ascom 2009. All rights reserved. TEMS is a trademark of Ascom. All other trademarks are the property
Scanning with Sony Ericsson TEMS Phones Technical Paper Scanning with Sony Ericsson TEMS Phones 2009-05-13 Ascom 2009. All rights reserved. TEMS is a trademark of Ascom. All other trademarks are the property
Cellular Network Planning and Optimization Part VIII: WCDMA link budget. Jyri Hämäläinen, Communications and Networking Department, TKK, 15.2.
 Cellular Network Planning and Optimization Part VIII: WCDMA link budget Jyri Hämäläinen, Communications and Networking Department, TKK, 15.2.2008 WCDMA Network planning High level objectives for the planning
Cellular Network Planning and Optimization Part VIII: WCDMA link budget Jyri Hämäläinen, Communications and Networking Department, TKK, 15.2.2008 WCDMA Network planning High level objectives for the planning
Location management Need Frequency Location updating
 Lecture-16 Mobility Management Location management Need Frequency Location updating Fig 3.10 Location management in cellular network Mobility Management Paging messages Different paging schemes Transmission
Lecture-16 Mobility Management Location management Need Frequency Location updating Fig 3.10 Location management in cellular network Mobility Management Paging messages Different paging schemes Transmission
ESG Engineering Services Group
 ESG Engineering Services Group WCDMA Network Planning and Optimization 80-W0853-1 Revision B May, 2006 QUALCOMM Incorporated 5775 Morehouse Drive San Diego, CA 92121-1714 U.S.A. This technology is controlled
ESG Engineering Services Group WCDMA Network Planning and Optimization 80-W0853-1 Revision B May, 2006 QUALCOMM Incorporated 5775 Morehouse Drive San Diego, CA 92121-1714 U.S.A. This technology is controlled
communication over wireless link handling mobile user who changes point of attachment to network
 Wireless Networks Background: # wireless (mobile) phone subscribers now exceeds # wired phone subscribers! computer nets: laptops, palmtops, PDAs, Internet-enabled phone promise anytime untethered Internet
Wireless Networks Background: # wireless (mobile) phone subscribers now exceeds # wired phone subscribers! computer nets: laptops, palmtops, PDAs, Internet-enabled phone promise anytime untethered Internet
Lecture 1. Introduction to Wireless Communications 1
 896960 Introduction to Algorithmic Wireless Communications Lecture 1. Introduction to Wireless Communications 1 David Amzallag 2 May 25, 2008 Introduction to cellular telephone systems. How a cellular
896960 Introduction to Algorithmic Wireless Communications Lecture 1. Introduction to Wireless Communications 1 David Amzallag 2 May 25, 2008 Introduction to cellular telephone systems. How a cellular
Efficient resource utilization improves the customer experience
 White paper Efficient resource utilization improves the customer experience Multiflow, aggregation and multi band load balancing for Long Term HSPA Evolution Executive summary Contents 2. Executive summary
White paper Efficient resource utilization improves the customer experience Multiflow, aggregation and multi band load balancing for Long Term HSPA Evolution Executive summary Contents 2. Executive summary
Planning of UMTS Cellular Networks for Data Services Based on HSDPA
 Planning of UMTS Cellular Networks for Data Services Based on HSDPA Diana Ladeira, Pedro Costa, Luís M. Correia 1, Luís Santo 2 1 IST/IT Technical University of Lisbon, Lisbon, Portugal 2 Optimus, Lisbon,
Planning of UMTS Cellular Networks for Data Services Based on HSDPA Diana Ladeira, Pedro Costa, Luís M. Correia 1, Luís Santo 2 1 IST/IT Technical University of Lisbon, Lisbon, Portugal 2 Optimus, Lisbon,
: Update of TS 25.225 concerning measurement definitions, ranges and mappings
 Agenda Item : adhoc 16 (Measurements) Source Title : Siemens : Update of TS 25.225 concerning measurement definitions, ranges and mappings Document for : approval 1.Introduction This Tdoc proposes changes
Agenda Item : adhoc 16 (Measurements) Source Title : Siemens : Update of TS 25.225 concerning measurement definitions, ranges and mappings Document for : approval 1.Introduction This Tdoc proposes changes
An Algorithm for Automatic Base Station Placement in Cellular Network Deployment
 An Algorithm for Automatic Base Station Placement in Cellular Network Deployment István Törős and Péter Fazekas High Speed Networks Laboratory Dept. of Telecommunications, Budapest University of Technology
An Algorithm for Automatic Base Station Placement in Cellular Network Deployment István Törős and Péter Fazekas High Speed Networks Laboratory Dept. of Telecommunications, Budapest University of Technology
3GPP Wireless Standard
 3GPP Wireless Standard Shishir Pandey School of Technology and Computer Science TIFR, Mumbai April 10, 2009 Shishir Pandey (TIFR) 3GPP Wireless Standard April 10, 2009 1 / 23 3GPP Overview 3GPP : 3rd Generation
3GPP Wireless Standard Shishir Pandey School of Technology and Computer Science TIFR, Mumbai April 10, 2009 Shishir Pandey (TIFR) 3GPP Wireless Standard April 10, 2009 1 / 23 3GPP Overview 3GPP : 3rd Generation
Analysis of Macro - Femtocell Interference and Implications for Spectrum Allocation
 Analysis of Macro - Femtocell Interference and Implications for Spectrum Allocation Juan Espino, Jan Markendahl, Aurelian Bria Wireless@KTH, The Royal institute of Technology, Electrum 48, SE-4 4 Kista,
Analysis of Macro - Femtocell Interference and Implications for Spectrum Allocation Juan Espino, Jan Markendahl, Aurelian Bria Wireless@KTH, The Royal institute of Technology, Electrum 48, SE-4 4 Kista,
LTE-Advanced Carrier Aggregation Optimization
 Nokia Networks LTE-Advanced Carrier Aggregation Optimization Nokia Networks white paper LTE-Advanced Carrier Aggregation Optimization Contents Introduction 3 Carrier Aggregation in live networks 4 Multi-band
Nokia Networks LTE-Advanced Carrier Aggregation Optimization Nokia Networks white paper LTE-Advanced Carrier Aggregation Optimization Contents Introduction 3 Carrier Aggregation in live networks 4 Multi-band
How To Understand And Understand The Power Of A Cdma/Ds System
 CDMA Technology : Pr. Dr. W. Skupin www.htwg-konstanz.de Pr. S. Flament www.greyc.fr/user/99 On line Course on CDMA Technology CDMA Technology : Introduction to Spread Spectrum Technology CDMA / DS : Principle
CDMA Technology : Pr. Dr. W. Skupin www.htwg-konstanz.de Pr. S. Flament www.greyc.fr/user/99 On line Course on CDMA Technology CDMA Technology : Introduction to Spread Spectrum Technology CDMA / DS : Principle
How To Know If You Are Safe To Use An Antenna (Wired) Or Wireless (Wireless)
 1 2 The range of RF spans 3 KHz (3000 Hz) to 300 GHz (300 million Hz) Frequencies of RF devices range from the low frequency AM broadcasts (80 MHz) to higher frequency mobile phones (1900 MHz) smart meters
1 2 The range of RF spans 3 KHz (3000 Hz) to 300 GHz (300 million Hz) Frequencies of RF devices range from the low frequency AM broadcasts (80 MHz) to higher frequency mobile phones (1900 MHz) smart meters
Fachgebiet für Kommunikationstechnik. Prof. Dr.-Ing. Klaus David. HSDPA for UMTS. Stephan Sigg 18.04.2005
 Fachgebiet für Kommunikationstechnik Prof. Dr.-Ing. Klaus David HSDPA for UMTS Stephan Sigg 18.04.2005 Gliederung HSDPA Concepts HSDPA Control Channels HSUPA Fast Scheduling in HSDPA Fachgebiet für Kommunikationstechnik
Fachgebiet für Kommunikationstechnik Prof. Dr.-Ing. Klaus David HSDPA for UMTS Stephan Sigg 18.04.2005 Gliederung HSDPA Concepts HSDPA Control Channels HSUPA Fast Scheduling in HSDPA Fachgebiet für Kommunikationstechnik
NSN White paper February 2014. Nokia Solutions and Networks Smart Scheduler
 NSN White paper February 2014 Nokia Solutions and Networks Smart Scheduler CONTENTS 1. Introduction 3 2. Smart Scheduler Features and Benefits 4 3. Smart Scheduler wit Explicit Multi-Cell Coordination
NSN White paper February 2014 Nokia Solutions and Networks Smart Scheduler CONTENTS 1. Introduction 3 2. Smart Scheduler Features and Benefits 4 3. Smart Scheduler wit Explicit Multi-Cell Coordination
Characteristics of terrestrial IMT-Advanced systems for frequency sharing/ interference analyses
 Report ITU-R M.2292-0 (12/2013) Characteristics of terrestrial IMT-Advanced systems for frequency sharing/ interference analyses M Series Mobile, radiodetermination, amateur and related satellite services
Report ITU-R M.2292-0 (12/2013) Characteristics of terrestrial IMT-Advanced systems for frequency sharing/ interference analyses M Series Mobile, radiodetermination, amateur and related satellite services
Customer Training Catalog Training Programs WCDMA RNP&RNO Technical Training
 Customer Training Catalog Training Programs Customer Training Catalog Training Programs WCDMA RNP&RNO Technical Training HUAWEI Learning Service 2015 COMMERCIAL IN CONFIDENCE 1 Customer Training Catalog
Customer Training Catalog Training Programs Customer Training Catalog Training Programs WCDMA RNP&RNO Technical Training HUAWEI Learning Service 2015 COMMERCIAL IN CONFIDENCE 1 Customer Training Catalog
GSM frequency planning
 GSM frequency planning Band : 890-915 and 935-960 MHz Channel spacing: 200 khz (but signal bandwidth = 400 khz) Absolute Radio Frequency Channel Number (ARFCN) lower band: upper band: F l (n) = 890.2 +
GSM frequency planning Band : 890-915 and 935-960 MHz Channel spacing: 200 khz (but signal bandwidth = 400 khz) Absolute Radio Frequency Channel Number (ARFCN) lower band: upper band: F l (n) = 890.2 +
ETSI TR 125 951 V10.0.0 (2011-05) Technical Report
 TR 125 951 V10.0.0 (2011-05) Technical Report Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); FDD Base Station (BS) classification (3GPP TR 25.951 version 10.0.0 Release 10) 1 TR 125 951 V10.0.0 (2011-05)
TR 125 951 V10.0.0 (2011-05) Technical Report Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); FDD Base Station (BS) classification (3GPP TR 25.951 version 10.0.0 Release 10) 1 TR 125 951 V10.0.0 (2011-05)
LTE Evolution for Cellular IoT Ericsson & NSN
 LTE Evolution for Cellular IoT Ericsson & NSN LTE Evolution for Cellular IoT Overview and introduction White Paper on M2M is geared towards low cost M2M applications Utility (electricity/gas/water) metering
LTE Evolution for Cellular IoT Ericsson & NSN LTE Evolution for Cellular IoT Overview and introduction White Paper on M2M is geared towards low cost M2M applications Utility (electricity/gas/water) metering
Omni Antenna vs. Directional Antenna
 Omni Antenna vs. Directional Antenna Document ID: 82068 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Basic Definitions and Antenna Concepts Indoor Effects Omni Antenna Pros
Omni Antenna vs. Directional Antenna Document ID: 82068 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Basic Definitions and Antenna Concepts Indoor Effects Omni Antenna Pros
Voice services over Adaptive Multi-user Orthogonal Sub channels An Insight
 TEC Voice services over Adaptive Multi-user Orthogonal Sub channels An Insight HP 4/15/2013 A powerful software upgrade leverages quaternary modulation and MIMO techniques to improve network efficiency
TEC Voice services over Adaptive Multi-user Orthogonal Sub channels An Insight HP 4/15/2013 A powerful software upgrade leverages quaternary modulation and MIMO techniques to improve network efficiency
How To Understand Power Consumption Of An Option Wireless Module
 Power Considerations for 2G & 3G Modules in MID Designs 1 Confidentiality All data and information contained or disclosed by this document is confidential and proprietary of Option NV, and all rights therein
Power Considerations for 2G & 3G Modules in MID Designs 1 Confidentiality All data and information contained or disclosed by this document is confidential and proprietary of Option NV, and all rights therein
PART 5D TECHNICAL AND OPERATING CHARACTERISTICS OF MOBILE-SATELLITE SERVICES RECOMMENDATION ITU-R M.1188
 Rec. ITU-R M.1188 1 PART 5D TECHNICAL AND OPERATING CHARACTERISTICS OF MOBILE-SATELLITE SERVICES Rec. ITU-R M.1188 RECOMMENDATION ITU-R M.1188 IMPACT OF PROPAGATION ON THE DESIGN OF NON-GSO MOBILE-SATELLITE
Rec. ITU-R M.1188 1 PART 5D TECHNICAL AND OPERATING CHARACTERISTICS OF MOBILE-SATELLITE SERVICES Rec. ITU-R M.1188 RECOMMENDATION ITU-R M.1188 IMPACT OF PROPAGATION ON THE DESIGN OF NON-GSO MOBILE-SATELLITE
How To Understand The Power Of A Cell Phone Network
 TS 25.225 V3.12.0 (2003-06) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio Access Network; Physical layer Measurements (TDD) (Release 1999) The present
TS 25.225 V3.12.0 (2003-06) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio Access Network; Physical layer Measurements (TDD) (Release 1999) The present
White Paper: Microcells A Solution to the Data Traffic Growth in 3G Networks?
 White Paper: Microcells A Solution to the Data Traffic Growth in 3G Networks? By Peter Gould, Consulting Services Director, Multiple Access Communications Limited www.macltd.com May 2010 Microcells were
White Paper: Microcells A Solution to the Data Traffic Growth in 3G Networks? By Peter Gould, Consulting Services Director, Multiple Access Communications Limited www.macltd.com May 2010 Microcells were
DVB-T and Wireless Microphone Exclusion Area Computation Through Interference Analysis
 SE43(11)Info 12 DVB-T and Wireless Microphone Exclusion Area Computation Through Interference Analysis Rogério Dionísio Instituto de Telecomunicações - Portugal 11th SE43 meeting, 19 September 2011 Page
SE43(11)Info 12 DVB-T and Wireless Microphone Exclusion Area Computation Through Interference Analysis Rogério Dionísio Instituto de Telecomunicações - Portugal 11th SE43 meeting, 19 September 2011 Page
GSM VOICE CAPACITY EVOLUTION WITH VAMOS Strategic White Paper
 GSM VOICE CAPACITY EVOLUTION WITH VAMOS Strategic White Paper Table of contents VAMOS increases your GSM voice capacity at minimum investment / 1 Take the full benefit of VAMOS / 1 Standard aspects / 1
GSM VOICE CAPACITY EVOLUTION WITH VAMOS Strategic White Paper Table of contents VAMOS increases your GSM voice capacity at minimum investment / 1 Take the full benefit of VAMOS / 1 Standard aspects / 1
2G/3G Mobile Communication Systems
 2G/3G Mobile Communication Systems Winter 2012/13 Integrated Communication Systems Group Ilmenau University of Technology Outline 2G Review: GSM Services Architecture Protocols Call setup Mobility management
2G/3G Mobile Communication Systems Winter 2012/13 Integrated Communication Systems Group Ilmenau University of Technology Outline 2G Review: GSM Services Architecture Protocols Call setup Mobility management
SURVEY OF LTE AND LTE ADVANCED SYSTEM
 IMPACT: International Journal of Research in Engineering & Technology (IMPACT: IJRET) ISSN(E): 2321-8843; ISSN(P): 2347-4599 Vol. 2, Issue 5, May 2014, 1-6 Impact Journals SURVEY OF LTE AND LTE ADVANCED
IMPACT: International Journal of Research in Engineering & Technology (IMPACT: IJRET) ISSN(E): 2321-8843; ISSN(P): 2347-4599 Vol. 2, Issue 5, May 2014, 1-6 Impact Journals SURVEY OF LTE AND LTE ADVANCED
EPL 657 Wireless Networks
 EPL 657 Wireless Networks Some fundamentals: Multiplexing / Multiple Access / Duplex Infrastructure vs Infrastructureless Panayiotis Kolios Recall: The big picture... Modulations: some basics 2 Multiplexing
EPL 657 Wireless Networks Some fundamentals: Multiplexing / Multiple Access / Duplex Infrastructure vs Infrastructureless Panayiotis Kolios Recall: The big picture... Modulations: some basics 2 Multiplexing
Performance Issues of TCP and MPEG-4 4 over UMTS
 Performance Issues of TCP and MPEG-4 4 over UMTS Anthony Lo A.Lo@ewi.tudelft.nl 1 Wiskunde end Informatica Outline UMTS Overview TCP and MPEG-4 Performance Summary 2 1 Universal Mobile Telecommunications
Performance Issues of TCP and MPEG-4 4 over UMTS Anthony Lo A.Lo@ewi.tudelft.nl 1 Wiskunde end Informatica Outline UMTS Overview TCP and MPEG-4 Performance Summary 2 1 Universal Mobile Telecommunications
Bluetooth voice and data performance in 802.11 DS WLAN environment
 1 (1) Bluetooth voice and data performance in 802.11 DS WLAN environment Abstract In this document, the impact of a 20dBm 802.11 Direct-Sequence WLAN system on a 0dBm Bluetooth link is studied. A typical
1 (1) Bluetooth voice and data performance in 802.11 DS WLAN environment Abstract In this document, the impact of a 20dBm 802.11 Direct-Sequence WLAN system on a 0dBm Bluetooth link is studied. A typical
Nokia Siemens Networks LTE 1800 MHz Introducing LTE with maximum reuse of GSM assets
 Nokia Siemens Networks LTE 1800 MHz Introducing LTE with maximum reuse of GSM assets White paper Table of contents 1. Overview... 3 2. 1800 MHz spectrum... 3 3. Traffic Migration... 5 4. Deploying LTE-GSM
Nokia Siemens Networks LTE 1800 MHz Introducing LTE with maximum reuse of GSM assets White paper Table of contents 1. Overview... 3 2. 1800 MHz spectrum... 3 3. Traffic Migration... 5 4. Deploying LTE-GSM
ENTERPRISE. Functionality chart
 ENTERPRISE Functionality chart Cellular Expert Enterprise module features Tasks Network data management Site, sector, construction, customer, repeater management: Add Edit Move Copy Delete Site re-use
ENTERPRISE Functionality chart Cellular Expert Enterprise module features Tasks Network data management Site, sector, construction, customer, repeater management: Add Edit Move Copy Delete Site re-use
A Framework for supporting VoIP Services over the Downlink of an OFDMA Network
 A Framework for supporting VoIP Services over the Downlink of an OFDMA Network Patrick Hosein Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 10180 Telesis Court, Suite 365, San Diego, CA 92121, US Tel: 858.882.0332, Fax:
A Framework for supporting VoIP Services over the Downlink of an OFDMA Network Patrick Hosein Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 10180 Telesis Court, Suite 365, San Diego, CA 92121, US Tel: 858.882.0332, Fax:
How To Understand The Gsm And Mts Mobile Network Evolution
 Mobile Network Evolution Part 1 GSM and UMTS GSM Cell layout Architecture Call setup Mobility management Security GPRS Architecture Protocols QoS EDGE UMTS Architecture Integrated Communication Systems
Mobile Network Evolution Part 1 GSM and UMTS GSM Cell layout Architecture Call setup Mobility management Security GPRS Architecture Protocols QoS EDGE UMTS Architecture Integrated Communication Systems
3GPP Technologies: Load Balancing Algorithm and InterNetworking
 2014 4th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence with Applications in Engineering and Technology 3GPP Technologies: Load Balancing Algorithm and InterNetworking Belal Abuhaija Faculty of Computers
2014 4th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence with Applications in Engineering and Technology 3GPP Technologies: Load Balancing Algorithm and InterNetworking Belal Abuhaija Faculty of Computers
MIMO Antenna Systems in WinProp
 MIMO Antenna Systems in WinProp AWE Communications GmbH Otto-Lilienthal-Str. 36 D-71034 Böblingen mail@awe-communications.com Issue Date Changes V1.0 Nov. 2010 First version of document V2.0 Feb. 2011
MIMO Antenna Systems in WinProp AWE Communications GmbH Otto-Lilienthal-Str. 36 D-71034 Böblingen mail@awe-communications.com Issue Date Changes V1.0 Nov. 2010 First version of document V2.0 Feb. 2011
Figure 1: cellular system architecture
 Question 1: (30 marks) Consider a FDM cellular system with 120 cites, a frequency reuse factor of N=12, and 900 overall two-way channels. Omni-directional antennas are used: Figure 1 shows some of the
Question 1: (30 marks) Consider a FDM cellular system with 120 cites, a frequency reuse factor of N=12, and 900 overall two-way channels. Omni-directional antennas are used: Figure 1 shows some of the
The Effect of Network Cabling on Bit Error Rate Performance. By Paul Kish NORDX/CDT
 The Effect of Network Cabling on Bit Error Rate Performance By Paul Kish NORDX/CDT Table of Contents Introduction... 2 Probability of Causing Errors... 3 Noise Sources Contributing to Errors... 4 Bit Error
The Effect of Network Cabling on Bit Error Rate Performance By Paul Kish NORDX/CDT Table of Contents Introduction... 2 Probability of Causing Errors... 3 Noise Sources Contributing to Errors... 4 Bit Error
is the power reference: Specifically, power in db is represented by the following equation, where P0 P db = 10 log 10
 RF Basics - Part 1 This is the first article in the multi-part series on RF Basics. We start the series by reviewing some basic RF concepts: Decibels (db), Antenna Gain, Free-space RF Propagation, RF Attenuation,
RF Basics - Part 1 This is the first article in the multi-part series on RF Basics. We start the series by reviewing some basic RF concepts: Decibels (db), Antenna Gain, Free-space RF Propagation, RF Attenuation,
Wideband Code Division Multiple Access (W CDMA) Tutorial
 Wideband Code Division Multiple Access (W CDMA) Tutorial Definition Wideband code division multiple access (W CDMA) is a CDMA channel that is four times wider than the current channels that are typically
Wideband Code Division Multiple Access (W CDMA) Tutorial Definition Wideband code division multiple access (W CDMA) is a CDMA channel that is four times wider than the current channels that are typically
Electronic Communications Committee (ECC) within the Conference of Postal and Telecommunications Administrations (CEPT)
 Page 1 Electronic Communications Committee (ECC) within the Conference of Postal and Telecommunications Administrations (CEPT) ECC RECOMMENDATION (05)08 (replacing recommendations T/R 20-08 and 22-07)
Page 1 Electronic Communications Committee (ECC) within the Conference of Postal and Telecommunications Administrations (CEPT) ECC RECOMMENDATION (05)08 (replacing recommendations T/R 20-08 and 22-07)
Maximizing Throughput and Coverage for Wi Fi and Cellular
 Maximizing Throughput and Coverage for Wi Fi and Cellular A White Paper Prepared by Sebastian Rowson, Ph.D. Chief Scientist, Ethertronics, Inc. www.ethertronics.com March 2012 Introduction Ask consumers
Maximizing Throughput and Coverage for Wi Fi and Cellular A White Paper Prepared by Sebastian Rowson, Ph.D. Chief Scientist, Ethertronics, Inc. www.ethertronics.com March 2012 Introduction Ask consumers
Multiple Access Techniques
 Chapter 8 Multiple Access Techniques Multiple access techniques are used to allow a large number of mobile users to share the allocated spectrum in the most efficient manner. As the spectrum is limited,
Chapter 8 Multiple Access Techniques Multiple access techniques are used to allow a large number of mobile users to share the allocated spectrum in the most efficient manner. As the spectrum is limited,
CNR Requirements for DVB-T2 Fixed Reception Based on Field Trial Results
 CNR Requirements for DVB-T2 Fixed Reception Based on Field Trial Results Iñaki Eizmendi, Gorka Berjon-Eriz, Manuel Vélez, Gorka Prieto, Amaia Arrinda This letter presents the C/N requirements for DVB-T2
CNR Requirements for DVB-T2 Fixed Reception Based on Field Trial Results Iñaki Eizmendi, Gorka Berjon-Eriz, Manuel Vélez, Gorka Prieto, Amaia Arrinda This letter presents the C/N requirements for DVB-T2
Long-Term Evolution. Mobile Telecommunications Networks WMNet Lab
 Long-Term Evolution Mobile Telecommunications Networks WMNet Lab Background Long-Term Evolution Define a new packet-only wideband radio with flat architecture as part of 3GPP radio technology family 2004:
Long-Term Evolution Mobile Telecommunications Networks WMNet Lab Background Long-Term Evolution Define a new packet-only wideband radio with flat architecture as part of 3GPP radio technology family 2004:
HandoffHandoverMechanismforMobilityImprovementinWirelessCommunication. Handoff / Handover Mechanism for Mobility Improvement in Wireless Communication
 Global Journal of Researches in Engineering Electrical and Electronics Engineering Volume 13 Issue 16 Version 1.0 Year 2013 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global
Global Journal of Researches in Engineering Electrical and Electronics Engineering Volume 13 Issue 16 Version 1.0 Year 2013 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global
Spectrum and Power Measurements Using the E6474A Wireless Network Optimization Platform
 Application Note Spectrum and Power Measurements Using the E6474A Wireless Network Optimization Platform By: Richard Komar Introduction With the rapid development of wireless technologies, it has become
Application Note Spectrum and Power Measurements Using the E6474A Wireless Network Optimization Platform By: Richard Komar Introduction With the rapid development of wireless technologies, it has become
What is going on in Mobile Broadband Networks?
 Nokia Networks What is going on in Mobile Broadband Networks? Smartphone Traffic Analysis and Solutions White Paper Nokia Networks white paper What is going on in Mobile Broadband Networks? Contents Executive
Nokia Networks What is going on in Mobile Broadband Networks? Smartphone Traffic Analysis and Solutions White Paper Nokia Networks white paper What is going on in Mobile Broadband Networks? Contents Executive
Dynamic Reconfiguration & Efficient Resource Allocation for Indoor Broadband Wireless Networks
 Dynamic Reconfiguration & Efficient Resource Allocation for Indoor Broadband Wireless Networks Tim Farnham, Brian Foxon* Home Communications Department HP Laboratories Bristol HPL-98-123 June, 1998 broadband,
Dynamic Reconfiguration & Efficient Resource Allocation for Indoor Broadband Wireless Networks Tim Farnham, Brian Foxon* Home Communications Department HP Laboratories Bristol HPL-98-123 June, 1998 broadband,
Assessment of Cellular Planning Methods for GSM
 Assessment of Cellular Planning Methods for GSM Pedro Assunção, Rui Estevinho and Luis M. Correia Instituto das Telecomunicações/Instituto Superior Técnico, Technical University of Lisbon Av. Rovisco Pais,
Assessment of Cellular Planning Methods for GSM Pedro Assunção, Rui Estevinho and Luis M. Correia Instituto das Telecomunicações/Instituto Superior Técnico, Technical University of Lisbon Av. Rovisco Pais,
Smart Mobility Management for D2D Communications in 5G Networks
 Smart Mobility Management for D2D Communications in 5G Networks Osman N. C. Yilmaz, Zexian Li, Kimmo Valkealahti, Mikko A. Uusitalo, Martti Moisio, Petteri Lundén, Carl Wijting Nokia Research Center Nokia
Smart Mobility Management for D2D Communications in 5G Networks Osman N. C. Yilmaz, Zexian Li, Kimmo Valkealahti, Mikko A. Uusitalo, Martti Moisio, Petteri Lundén, Carl Wijting Nokia Research Center Nokia
LTE in Unlicensed Spectrum: European Regulation and Co-existence Considerations
 3GPP workshop on LTE in unlicensed spectrum Sophia Antipolis, France, June 13, 2014 RWS-140002 LTE in Unlicensed Spectrum: European Regulation and Co-existence Considerations Sari Nielsen & Antti Toskala
3GPP workshop on LTE in unlicensed spectrum Sophia Antipolis, France, June 13, 2014 RWS-140002 LTE in Unlicensed Spectrum: European Regulation and Co-existence Considerations Sari Nielsen & Antti Toskala
REPORT ITU-R M.2134. Requirements related to technical performance for IMT-Advanced radio interface(s)
 Rep. ITU-R M.2134 1 REPORT ITU-R M.2134 Requirements related to technical performance for IMT-Advanced radio interface(s) (2008) TABLE OF CONTENTS... Page 1 Introduction... 2 2 Scope and purpose... 2 3
Rep. ITU-R M.2134 1 REPORT ITU-R M.2134 Requirements related to technical performance for IMT-Advanced radio interface(s) (2008) TABLE OF CONTENTS... Page 1 Introduction... 2 2 Scope and purpose... 2 3
Customer Training Catalog Course Descriptions WCDMA RNP&RNO Technical Training
 Customer Training Catalog Course Descriptions Customer Training Catalog Course Descriptions WCDMA RNP&RNO Technical Training HUAWEI Learning Service 2015 COMMERCIAL IN CONFIDENCE 1 Customer Training Catalog
Customer Training Catalog Course Descriptions Customer Training Catalog Course Descriptions WCDMA RNP&RNO Technical Training HUAWEI Learning Service 2015 COMMERCIAL IN CONFIDENCE 1 Customer Training Catalog
Evolution of GSM in to 2.5G and 3G
 CMPE 477 Wireless and Mobile Networks Evolution of GSM in to 2.5G and 3G New Data Services for GSM CMPE 477 HSCSD GPRS 3G UMTS IMT2000 UMTS Architecture UTRAN Architecture Data services in GSM I Data transmission
CMPE 477 Wireless and Mobile Networks Evolution of GSM in to 2.5G and 3G New Data Services for GSM CMPE 477 HSCSD GPRS 3G UMTS IMT2000 UMTS Architecture UTRAN Architecture Data services in GSM I Data transmission
COMMISSION OF THE EUROPEAN COMMUNITIES. Draft COMMISSION DECISION
 COMMISSION OF THE EUROPEAN COMMUNITIES Brussels, C (2008) Draft COMMISSION DECISION of [ ] on harmonised conditions of spectrum use for the operation of mobile communication services on aircraft (MCA services)
COMMISSION OF THE EUROPEAN COMMUNITIES Brussels, C (2008) Draft COMMISSION DECISION of [ ] on harmonised conditions of spectrum use for the operation of mobile communication services on aircraft (MCA services)
CHAPTER - 4 CHANNEL ALLOCATION BASED WIMAX TOPOLOGY
 CHAPTER - 4 CHANNEL ALLOCATION BASED WIMAX TOPOLOGY 4.1. INTRODUCTION In recent years, the rapid growth of wireless communication technology has improved the transmission data rate and communication distance.
CHAPTER - 4 CHANNEL ALLOCATION BASED WIMAX TOPOLOGY 4.1. INTRODUCTION In recent years, the rapid growth of wireless communication technology has improved the transmission data rate and communication distance.
Antenna Deployment Technical Brief
 ProCurve Networking Antenna Deployment Technical Brief Introduction... 2 Antenna types... 2 Omni directional antennas... 2 Directional antennas... 2 Diversity antennas... 3 High gain directional antennas...
ProCurve Networking Antenna Deployment Technical Brief Introduction... 2 Antenna types... 2 Omni directional antennas... 2 Directional antennas... 2 Diversity antennas... 3 High gain directional antennas...
How To Make A Cell Phone Network More Efficient
 Cellular Network Planning and Optimization Part V: GSM Jyri Hämäläinen, Communications and Networking Department, TKK, 18.1.2008 GSM Briefly 2 General GSM was the first digital cellular system. GSM was
Cellular Network Planning and Optimization Part V: GSM Jyri Hämäläinen, Communications and Networking Department, TKK, 18.1.2008 GSM Briefly 2 General GSM was the first digital cellular system. GSM was
LTE Performance and Analysis using Atoll Simulation
 IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 2320-3331, Volume 9, Issue 6 Ver. III (Nov Dec. 2014), PP 68-72 LTE Performance and Analysis using Atoll Simulation
IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 2320-3331, Volume 9, Issue 6 Ver. III (Nov Dec. 2014), PP 68-72 LTE Performance and Analysis using Atoll Simulation
Interference from future mobile network services in frequency band 790 862 MHz to digital TV in frequencies below 790 MHz.
 2009-02-05 Interference from future mobile network services in frequency band 790 862 MHz to digital TV in frequencies below 790 MHz. TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 SUMMARY...3 2 BACKGROUND /INTRODUCTION...3 3 APPROACH,
2009-02-05 Interference from future mobile network services in frequency band 790 862 MHz to digital TV in frequencies below 790 MHz. TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 SUMMARY...3 2 BACKGROUND /INTRODUCTION...3 3 APPROACH,
HSDPA Mobile Broadband Data A Smarter Approach to UMTS Downlink Data
 HSDPA Mobile Broadband Data A Smarter Approach to UMTS Downlink Data UMTS mobile wireless systems have enjoyed widespread uptake of high-quality circuit-switched applications like voice and video telephony.
HSDPA Mobile Broadband Data A Smarter Approach to UMTS Downlink Data UMTS mobile wireless systems have enjoyed widespread uptake of high-quality circuit-switched applications like voice and video telephony.
Measurement based Analysis and Modelling of UMTS DCH Error Characteristics for Static Scenarios
 8th International Symposium on DSP and Communication Systems, DSPCS'25" & "4th Workshop on the Internet, Telecommunications and Signal Processing, WITSP'25", Noosa Heads (Sunshine Coast, Australia), 9
8th International Symposium on DSP and Communication Systems, DSPCS'25" & "4th Workshop on the Internet, Telecommunications and Signal Processing, WITSP'25", Noosa Heads (Sunshine Coast, Australia), 9
Pradipta Biswas Roll No. 04IT6007 M. Tech. (IT) School of Information Technology Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Pradipta Biswas Roll No. 04IT6007 M. Tech. (IT) School of Information Technology Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur ABSTRACT W-CDMA (Wideband Code-Division Multiple Access), an ITU standard derived
Pradipta Biswas Roll No. 04IT6007 M. Tech. (IT) School of Information Technology Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur ABSTRACT W-CDMA (Wideband Code-Division Multiple Access), an ITU standard derived
Mobile Communications TCS 455
 Mobile Communications TCS 455 Dr. Prapun Suksompong prapun@siit.tu.ac.th Lecture 26 1 Office Hours: BKD 3601-7 Tuesday 14:00-16:00 Thursday 9:30-11:30 Announcements Read the following from the SIIT online
Mobile Communications TCS 455 Dr. Prapun Suksompong prapun@siit.tu.ac.th Lecture 26 1 Office Hours: BKD 3601-7 Tuesday 14:00-16:00 Thursday 9:30-11:30 Announcements Read the following from the SIIT online
Cooperative Techniques in LTE- Advanced Networks. Md Shamsul Alam
 Cooperative Techniques in LTE- Advanced Networks Md Shamsul Alam Person-to-person communications Rich voice Video telephony, video conferencing SMS/MMS Content delivery Mobile TV High quality video streaming
Cooperative Techniques in LTE- Advanced Networks Md Shamsul Alam Person-to-person communications Rich voice Video telephony, video conferencing SMS/MMS Content delivery Mobile TV High quality video streaming
GSM Network and Services
 GSM Network and Services Cellular networks GSM Network and Services 2G1723 Johan Montelius 1 The name of the game The number one priority for mobile/cellular networks is to implement full-duplex voice
GSM Network and Services Cellular networks GSM Network and Services 2G1723 Johan Montelius 1 The name of the game The number one priority for mobile/cellular networks is to implement full-duplex voice
Revision of Lecture Eighteen
 Revision of Lecture Eighteen Previous lecture has discussed equalisation using Viterbi algorithm: Note similarity with channel decoding using maximum likelihood sequence estimation principle It also discusses
Revision of Lecture Eighteen Previous lecture has discussed equalisation using Viterbi algorithm: Note similarity with channel decoding using maximum likelihood sequence estimation principle It also discusses
Log-Likelihood Ratio-based Relay Selection Algorithm in Wireless Network
 Recent Advances in Electrical Engineering and Electronic Devices Log-Likelihood Ratio-based Relay Selection Algorithm in Wireless Network Ahmed El-Mahdy and Ahmed Walid Faculty of Information Engineering
Recent Advances in Electrical Engineering and Electronic Devices Log-Likelihood Ratio-based Relay Selection Algorithm in Wireless Network Ahmed El-Mahdy and Ahmed Walid Faculty of Information Engineering
Solution for cell edge performance improvement and dynamic load balancing. Qualcomm Technologies, Inc.
 HSPA+ Multiflow Solution for cell edge performance improvement and dynamic load balancing Feburary 1, 2014 Qualcomm Technologies, Inc. Not to be used, copied, reproduced, or modified in whole or in part,
HSPA+ Multiflow Solution for cell edge performance improvement and dynamic load balancing Feburary 1, 2014 Qualcomm Technologies, Inc. Not to be used, copied, reproduced, or modified in whole or in part,
REPORT ITU-R M.2045. Rep. ITU-R M.2045 1 (2004)
 Rep. ITU-R M.2045 1 REPORT ITU-R M.2045 Mitigating techniques to address coexistence between IMT-2000 time division duplex and frequency division duplex radio interface technologies within the frequency
Rep. ITU-R M.2045 1 REPORT ITU-R M.2045 Mitigating techniques to address coexistence between IMT-2000 time division duplex and frequency division duplex radio interface technologies within the frequency
GSM Frequency Planning with Band Segregation for the Broadcast Channel Carriers
 GSM Frequency Planning with Band Segregation for the Broadcast Channel Carriers F. Galliano (1), N.P. Magnani (1), G. Minerva (1), A. Rolando (2), P. Zanini (3) (1) CSELT - Via G. Reiss Romoli, 274 - Torino
GSM Frequency Planning with Band Segregation for the Broadcast Channel Carriers F. Galliano (1), N.P. Magnani (1), G. Minerva (1), A. Rolando (2), P. Zanini (3) (1) CSELT - Via G. Reiss Romoli, 274 - Torino
How To Understand The Theory Of Time Division Duplexing
 Multiple Access Techniques Dr. Francis LAU Dr. Francis CM Lau, Associate Professor, EIE, PolyU Content Introduction Frequency Division Multiple Access Time Division Multiple Access Code Division Multiple
Multiple Access Techniques Dr. Francis LAU Dr. Francis CM Lau, Associate Professor, EIE, PolyU Content Introduction Frequency Division Multiple Access Time Division Multiple Access Code Division Multiple
CABLES CABLES. Application note. Link Budget
 CABLES CABLES radiating Link Budget 3. 1. LINK BUDGET The basic elements to calculate a link budget can be illustrated by considering the example shown in Figure 4. It involves a GSM 900 radio coverage
CABLES CABLES radiating Link Budget 3. 1. LINK BUDGET The basic elements to calculate a link budget can be illustrated by considering the example shown in Figure 4. It involves a GSM 900 radio coverage
Dynamic Frequency Selection (DFS) and the 5GHz Unlicensed Band
 Dynamic Frequency Selection (DFS) and the 5GHz Unlicensed Band by Mark Briggs, Principal Engineer, Elliott Laboratories- An NTS Company Note: This article combines the content from several papers released
Dynamic Frequency Selection (DFS) and the 5GHz Unlicensed Band by Mark Briggs, Principal Engineer, Elliott Laboratories- An NTS Company Note: This article combines the content from several papers released
ETSI EN 302 774 V1.2.1 (2012-02)
 EN 302 774 V1.2.1 (2012-02) Harmonized European Standard Broadband Wireless Access Systems (BWA) in the 3 400 MHz to 3 800 MHz frequency band; Base Stations; Harmonized EN covering the essential requirements
EN 302 774 V1.2.1 (2012-02) Harmonized European Standard Broadband Wireless Access Systems (BWA) in the 3 400 MHz to 3 800 MHz frequency band; Base Stations; Harmonized EN covering the essential requirements
Cellular Network Planning and Optimization Part XI: HSDPA. Jyri Hämäläinen, Communications and Networking Department, TKK, 25.1.
 Cellular Network Planning and Optimization Part XI: HSDPA Jyri Hämäläinen, Communications and Networking Department, TKK, 25.1.2008 HSDPA HSDPA = High Speed Downlink Packet Access. Release 5 was the first
Cellular Network Planning and Optimization Part XI: HSDPA Jyri Hämäläinen, Communications and Networking Department, TKK, 25.1.2008 HSDPA HSDPA = High Speed Downlink Packet Access. Release 5 was the first
Module 5. Broadcast Communication Networks. Version 2 CSE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 5 Broadcast Communication Networks Lesson 9 Cellular Telephone Networks Specific Instructional Objectives At the end of this lesson, the student will be able to: Explain the operation of Cellular
Module 5 Broadcast Communication Networks Lesson 9 Cellular Telephone Networks Specific Instructional Objectives At the end of this lesson, the student will be able to: Explain the operation of Cellular
AN1200.04. Application Note: FCC Regulations for ISM Band Devices: 902-928 MHz. FCC Regulations for ISM Band Devices: 902-928 MHz
 AN1200.04 Application Note: FCC Regulations for ISM Band Devices: Copyright Semtech 2006 1 of 15 www.semtech.com 1 Table of Contents 1 Table of Contents...2 1.1 Index of Figures...2 1.2 Index of Tables...2
AN1200.04 Application Note: FCC Regulations for ISM Band Devices: Copyright Semtech 2006 1 of 15 www.semtech.com 1 Table of Contents 1 Table of Contents...2 1.1 Index of Figures...2 1.2 Index of Tables...2
Antenna Based Self Optimizing Networks for Coverage and Capacity Optimization
 Antenna Based Self Optimizing Networks for Coverage and Capacity Optimization Abstract Antenna tilt is a powerful parameter for optimization of a cellular network as it has the most direct impact on shaping
Antenna Based Self Optimizing Networks for Coverage and Capacity Optimization Abstract Antenna tilt is a powerful parameter for optimization of a cellular network as it has the most direct impact on shaping
Mobile Phone Antenna Performance 2013
 Mobile Phone Antenna 2013 Version 2.2, 28 November 2013 Gert Frølund Pedersen Professor, PhD Aalborg University Introduction This study investigates the radio coverage capabilities of mobile phones. The
Mobile Phone Antenna 2013 Version 2.2, 28 November 2013 Gert Frølund Pedersen Professor, PhD Aalborg University Introduction This study investigates the radio coverage capabilities of mobile phones. The
ETSI TS 102 735 V7.1.0 (2010-01) Technical Specification
 TS 102 735 V7.1.0 (2010-01) Technical Specification Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); Band-specific requirements for UMTS Frequency Division Duplex (FDD) operation in the bands 1 900 to
TS 102 735 V7.1.0 (2010-01) Technical Specification Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); Band-specific requirements for UMTS Frequency Division Duplex (FDD) operation in the bands 1 900 to
The future of mobile networking. David Kessens <david.kessens@nsn.com>
 The future of mobile networking David Kessens Introduction Current technologies Some real world measurements LTE New wireless technologies Conclusion 2 The future of mobile networking
The future of mobile networking David Kessens Introduction Current technologies Some real world measurements LTE New wireless technologies Conclusion 2 The future of mobile networking
Handover parameter optimization in LTE selforganizing
 FP7 ICT-SOCRATES Handover parameter optimization in LTE selforganizing networks TD (1)168 COST 1, 1 th MCM Athens, Greece February 3 rd 5 th TUBS, Braunschweig, Germany IBBT, Ghent, Belgium VOD, Newbury,
FP7 ICT-SOCRATES Handover parameter optimization in LTE selforganizing networks TD (1)168 COST 1, 1 th MCM Athens, Greece February 3 rd 5 th TUBS, Braunschweig, Germany IBBT, Ghent, Belgium VOD, Newbury,
