Microstructure evolution of tin-lead solder
|
|
|
- Colin Robinson
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Mirostruture evolution of tin-lead solder R.L.J.M Ubahs, P.J.G. Shreurs, and M.G.D. Geers Eindhoven University of Tehnology, Department of Mehanial Engineering, Setion of Materials Tehnology, PO Box 53, 56 MB Eindhoven, the Netherlands. Abstrat Mirostrutural length sales are relatively large in typial soldered onnetions. The mirostruture whih is ontinuously evolving is known to have a strong influene on damage initiation and propagation. In order to make aurate life-time preditions by numerial simulations, it is therefore neessary to take the mirostrutural evolution into aount. In this work this is aomplished by using a diffuse interfae model based on a strongly nonloal variable. It an be seen as an extension of the Cahn-Hilliard model, whih is weakly nonloal sine it depends on higher order gradients whih are by definition onfined to the infinitesimal neighbourhood of the onsidered material point. Next to introduing a truly nonloal measure in the free energy, this nonloal formulation has the advantage that it is numerially more effiient. Additionally the model is extended to inlude elastially stored energy as a driving fore for diffusion after whih the entire system is solved using the finite element approah. The model results in a omputational effiient algorithm whih is apable of simulating the phase separation and oarsening of a solder material aused by ombined thermal and mehanial loading. Introdution Solder joints serve two important purposes. Firstly, they form the eletrial onnetion between the omponent, e.g. a hip or resistor, and a substrate, e.g. a motherboard, and seondly, they onstitute the mehanial bond that holds the omponent to the substrate. The most ommonly used solder alloy up till now is the lead-tin system. When an eletroni devie is in use, solder onnetions will be subjeted to mehanial stresses and strains. These arise beause of the mismath between the oeffiients of thermal expansion (CTE) of the eletroni omponent and the board onto whih it is onneted. Beause solder materials are multiphase systems there are also differenes between CTEs of the phases within the solder leading to internal stresses. Note that these stresses an arise even in a single phase material if there are different CTEs for different lattie diretions. The on and off swithing of a system thus leads to yli thermomehanial loads, resulting in stresses and strains in the solder joint. The soldered onnetion an also be subjeted to external loads aused by e.g. bending of the substrate. Sine solder alloys are required to operate at high homologous temperatures their deformation is governed by high temperature mehanisms suh as reep, rerystallisation, oarsening, and reovery. An important mehanial property of solder joints is undoubtedly their resistane to fatigue under thermal yling. Sine failure of a solder joint will render a omplete devie useless, it is important to predit the lifetime of suh a onnetion. Beause of time limitations solder joints are often tested for their thermomehanial fatigue properties by subjeting them to aelerated tests methods. However, during these aelerated experiments damage mehanisms might be invoked whih do not our during normal usage. Preditions based on aelerated yling tests are therefore unreliable. Thermomehanial modelling an be used during the design proess to simulate the real life onditions of a solder joint, and thus give an aurate predition of its lifetime, with a signifiant redution in ost and time when ompared to prototype testing. The properties of a solder joint are highly dependent on its mirostruture, whih hanges onsiderably during its lifetime. The high homologous temperature at whih solder materials operate provokes mirostrutural oarsening, resulting in a markedly different mirostruture after only a short time after solidifiation, as an be seen in figure. During thermomehanial yling of a soldered onnetion the oarsening proess will not be homogeneous. Frear et al. [8] found that regions of high shear strain within an euteti tin-lead onnetion oarsened more. These regions of inhomogeneous oarsening are know to be rak nuleation sites during thermal yling [6; 7; 8]. It is also well-known that thermal yling leads to faster oarsening rates than stati thermal aging [], possibly due to the mehanial stresses whih arise within the material due to differenes in thermal expansion oeffiients. Another fator whih influenes the diffusion proess is the surfae tension between different phases. It ontrols the number, steepness, orientation, and the final shape of the interfaes within the oarsened struture. The magnitude of the surfae tension an vary in different diretions of the rystal lattie. 2 A truly nonloal diffuse interfae theory Beause the mirostruture has a large influene on the material properties and oarsening readily ours during the lifetime of a soldered onnetion, it is important to take the mirostrutural evolution into aount during numerial simulation of fatigue damage propagation. Speifially in tin-lead solder oarsening will our beause of the high solubility of tin in lead and vie versa. Various attempts have been made to inlude a mirostutural variable like the average grain size in the stress-strain relation [; 2; 2]. Viano et al. [3] and Frear et al. [7] also inlude grain size evolution in their models. In the literature
2 Free energy To omplete the diffusion equation the free energy funtion is needed. At any time there will be different kinds of energy available in a system. Firstly, eah phase will have different energy values for different ompositions, whih onstitutes the onfigurational energy F. Seondly, interfaes will ontribute to the surfae energy, denoted F γ, and thirdly, stresses and strains will ause elasti energy, indiated as Fε, to be stored in the system. So F = F + F γ + Fε J/mol (3) The onfigurational free energy denotes the ontribution of the pure phase. For a system where only binary interations take plae the funtion will have the following form: F = i g i + R T i ln i + i j χ ij (4) i i i j>i where g i and χ ij are oeffiients dependent on temperature. Spinodal points Figure : Optial mirographs illustrating the oarsening of the Pb-rih phase partiles in 63Sn-37Pb samples under stati aging onditions. Left: Quenhed in liquid nitrogen. Right: aged at 5 C for 5 hours. Free energy binodal points Composition several equations an be found that desribe the evolution of the grain size [4; 3]. No information about the distribution or shape of the grains is inorporated however. This information an be found by using of a diffuse interfae theory [3]. Diffuse interfae theories are based on the notion that the free energy is not only a funtion of a loal order parameter, but also depends on the value of this parameter in neighbouring points. In this setion first the diffusion equation will be introdued, after whih a diffuse interfae theory will be presented based on a truly nonloal order parameter. Diffusion equation The diffusion equation reads: ρ d i dt = [ˆρ i ( v i v)] = j i () where the j i is the diffusion mass flow per unit area per unit time. Using the phenomenologial approah of lassial irreversible thermodynamis [9], the following expression for the diffusion mass flow is found: ( ) j i = ρ M F (2) i where F is the speifi Helmholtz free energy and M the mobility tensor. This means that for a system to be in equilibrium the derivative of the Helmholtz free energy with respet to the omposition, also alled the hemial potential, has to be homogeneous throughout the system. Figure 2: Free energy urves for the α and β phase, and binodal and spinodal points. For a two-phase material (phases α and β), the onfigurational energy will be a double-well potential, see figure 2. It an be onstruted from the onfigurational energy urves of the individual phases by assuming that at a ertain omposition only the phase with the lowest energy will exist. Equilibrium is then found when the hemial potential is homogeneous throughout the system. Note that this does not mean that the mass fration has to be homogeneous. The onfiguration with the lowest possible free energy is found when, due to phase separation, all of the material has either one of two ompositions defined by the so-alled binodal points. These binodal points an be found by onstruting a double tangent to the free energy urve. If the binodal points are plotted at different temperatures the phase diagram will be obtained. The elastially stored energy is due to stresses and strains whih our in the material. Thus in order to alulate it, a onstitutive model needs to be hosen and the momentum equation, has to be solved. As a first approximation linear elastiity is assumed and inertia effets and body fores are left out of onsideration, yielding the momentum equation σ = C : ε = (5) where C is the fourth-order material tensor, σ denotes the stress tensor, and ε is the strain tensor defined as 2 { u +
3 ( u) } The elasti energy is then defined as Fε = 2 ε : C : ε (6) Note that the elastially stored energy term introdues a fourth-order gradient of the displaements into the diffusion equation. Beause the system will be solved by using a finite element method it is onvenient to eliminate these fourth-order gradient terms. This is aomplished by introduing a new independent variable, ψ, defined as the derivative of the elasti energy with respet to the loal mass fration. Thus an additional equation is added to the system: ψ = 2 ε : C : ε (7) The surfae free energy aounts for energy due to interfaes between phase regions. This means that it annot be only a funtion of the loal mass fration,. The omposition of the surroundings of a material point has to be taken into aount as well. In diffuse interfae theories this is done by taking the free energy to be dependent on both the loal omposition and its derivatives. These models an be onsidered to be weakly nonloal, sine the derivatives of the omposition are by definition onfined to the infinitesimal neighbourhood of the onsidered material point. In this work the free energy is taken to be a funtion of the loal mass fration and a weighted averaged value of this variable, denoted. This variable is alulated by solving an impliit Helmholtz equation: l 2 2 = (8) where l is an internal length parameter defined as l 2 = ξ 2 g(ξ) dω (9) 2 Ω Ω with g a normalised weighting funtion and ξ a loal oordinate vetor. The surfae energy is next related to the square of the differene between the nonloal and loal mass fration: F γ = 2 κ ( )2 () where κ is the surfae tension oeffiient tensor. Total system of equations The system of equations whih has to be solved, onsists of the diffusion equation for the loal mass fration, an impliit Helmholtz equation for the nonloal mass fration, the momentum equation for stresses and strains, and the equation for the derivative of the elastially stored energy with respet to the loal mass fration: [ ρ M ρ d dt = l 2 2 = σ = ψ = 2 ε : C : ε ( F )] κ ( ) + ψ () 3 Finite element implementation The system of equations is solved using the finite element method. The first step towards a finite element sheme is time disretisation of the diffusion equation. This is done by using the impliit or bakward Euler sheme, whih is unonditionally stable and first-order aurate. Next a linearised weighted residual form of the equations is onstruted in whih essential boundary onditions are taken are off. Finally all variables are disretised and interpolation funtions are hosen, linear for all variables. The total system is then divided into two systems of two equations whih are solved deoupled. The first set ontains the diffusion equation and the nonloality equation. The seond set momentum balane and the derivative of the elastially stored energy. In matrix form the systems then are: K int K δ = f (2) int K K δ f ext int K uu δũ u u = f f (3) int K ψu K ψψ ψ δψ f These systems are then solved with a onjugant gradient solver in order to redue the required amount of omputer memory ompared to using a diret solver. 4 Model parameters The euteti tin-lead system has been hosen fore these simulations, beause it has been most extensively studied in the literature. For this system the α phase is a lead-rih BCC rystal struture, whih for the euteti forms islands in a tin-rih matrix, the β phase. The neessary material data were obtained from literature, and are summarised in table. The internal length parameter l is taken to be in the order of magnitude of the real interfae width, and κ is hosen suh that surfae energy has the same order of magnitude as the onfigurational energy. The mobility of the α phase is supposed to be signifiantly lower than that of the β phase, hene it is assumed to be negligible. The mobility of the β is fitted using the omparison between a twodimensional simulation and an ageing experiment, whih will be disussed later. All the parameters are assumed to vary linearly with the mass fration. Configurational free energy Figure 3 shows the onfigurational part of the Helmholtz free energy urve for the tin-lead system at 5 C. Where it is assumed that at a ertain omposition the material will assume the phase whih has the lowest free energy at that omposition. The data used to alulate this urve is taken from MTDATA R [5; ]. Next the urve is fitted to the following funtion to failitate the finite element routine. F =g + g 2 ( ) + g 3 ln + +g 4 ( ) ln( ) + g 5 ( ) (4)
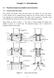
4 Table : Material data for the tin-lead solder system. mass density of tin ρ Sn [kg/m 3 ] 726 mass density of lead ρ P b [kg/m 3 ] 3 Young s modulus of tin E Sn [N/m 2 ] Young s modulus of lead E P b [N/m 2 ] 6. 9 Poisson s ratio of tin ν Sn [ ].36 Poisson s ratio of lead ν P b [ ].44 CTE of tin α Sn [/K].67 5 CTE of lead α P b [/K] surfae tension oeff. κ [J].6 mobility of α-phase M α [m 5 /(J s)] mobility of β-phase M β [m 5 /(J s)].2 2 internal length sale l [m] 25 9 onfigurational energy [J/m 3 ].35 x mass fration Figure 3: Configurational free energy F for the tin-lead system at 5 C. Resulting parameter values for T=5 C are: g =.36 9, g 2 =.52 9, g 3 =.36 9, g 4 =.6 9, and g 5 = One-dimensional simulations One-dimensional alulations have been performed to investigate the behaviour of the model. Two different initial onfigurations are used, see figure 4. First the initial ondition was taken to be a step funtion in the mass fration in the middle of the domain in order to investigate the influene of the internal length sale parameter l and the surfae tension oeffiient κ on the equilibrium interfae whih develops. The effet of external loading has been studied as well. Seondly, spinodal deomposition was investigated starting from a homogeneous, euteti, mass fration distribution with random imperfetions imposed. mass fration [ ] Figure 4: Initial onditions for one-dimensional analyses. Left: step funtion; Right: homogeneous distribution with random imperfetions imposed. Disontinuous interfae Calulations were performed to investigate the influene of the internal length sale parameter, l, and the surfae tension oeffiient, κ. When using the expliit formulation for alulating the nonloal field, whih is idential to the Cahn-Hilliard model, inreasing κ will have the same effet as inreasing l 2. Both these parameters serve as a multipliation fator for the Laplaian of the loal mass fration. However for the impliit formulation this is no longer the ase. For this ase, substituting the nonloality equation in the diffusion equation yields ρ d dt = [ ρ M ( F + κ l2 2 + ψ )] (5) However, even if the produt κ l 2 is kept onstant, interfae width still dereases with an inreasing value of l. see figure 5. This is due to the fat that hanging this parameter hanges the nonloal field whih in turn affets the loal mass fration. The internal length sale an be onsidered a measure for the distane at whih an interfae an affet the bulk material. The surfae tension remains a multipliation fator whih determines the amount of influene an interfae an exert. Figure 6 shows the influene of the internal length sale while the surfae tension oeffiient is kept onstant. The parameter influenes the interfae width linearly. The interfae width is defined as the distane over whih the mass fration deviates.5 or more from the bulk mass fration, either of the α or β phase. If another value for the deviation is hosen the results are affeted quantitatively but not qualitatively. In figure 7 the interfae width as a funtion of the square root of κ is shown. Similarly to the influene of l, here also a linear relationship an be seen. It should be noted that the model is more sensitive to variations of κ than of l. This effet an also be seen in figure 5. Under the influene of straining the shape of the interfae between the two phases also hanges. Interfaial width dereases under the influene of either ompression or tension, see figure 8. This an be explained by the fat that the interfae is determined by the ratio between the surfae energy and the total free energy. If this ratio dereases, as in the ase of external loading, interfaes beome steeper and onsequently thinner. The reason for the loss of symmetry of these results at larger deformations ould be aused by the small strain assumption used in the model. Homogeneous distribution One-dimensional simulations of the phase separation and onsequent oarsening proess have been performed. The initial ondition is a homogeneous distribution of the tin mass fration at the euteti omposition of the tin-lead system, =.63. To trigger spinodal deomposition random imperfetions on the mass fration are imposed (normal distribution with mean and variane.), see figure 4. The imperfetions are the same for all alulations. First a alulation is performed without external loading
5 interfaial width [µm] internal length sale [µm] Figure 5: Interfae width as a funtion of the internal length sale, keeping the produt κ l 2 onstant interfaial width [µm] internal length sale [µm] Figure 6: Interfae width as a funtion of the internal length sale l, keeping κ onstant. interfae width [µm] square root of surfae tension oeffiient x 5 Figure 7: Interfae width as a funtion of the square root of the surfae tension oeffiient κ, keeping l onstant. interfaial width [µm] Figure 8: strain strain [ ] Interfae width versus applied marosopi Figure 9: Development of one-dimensional tin-lead system starting from a homogeneous distribution with random imperfetions imposed. l = 25 nm and κ = 2 GJ (κ l 2 = 2.5 mj m 2 ). From top to bottom: t=.4,.9,.4, 4.8, and 5 hours. and l = 25 nm and κ = 2 GJ, see figure 9. The figure shows the apability of the model to desribe phase separation and oarsening. Next a alulation with external loading of % global tensile strain is also performed to demonstrate the effet of elastially stored energy on the system. The results are shown in figure. In this ase deomposition is faster and the final struture shows slightly more oarsening. The results show a shift of the binodal points, downward for the α phase and upward for the β phase, and steeper interfaes ompared to the referene alulation. 6 Two-dimensional simulations To validate the model an experiment has been performed of the ageing of euteti tin-lead solder. The speimen was rapidly ooled in liquid nitrogen and onsequently aged at 5 C. During the ageing proess photographs where made of the same area using an Sanning Eletron Mirosope. Some of the results are shown in figure. Next a simulation was performed taking the initial ondition from the SEM photograph made immediately after ooling. The results of the simulation are shown in figure next to SEM photographs of approximately the same area at the same time. The simulated mirostruture exhibits break-up and oalesene of phase regions, and phase regions growing and dissolving, similar to what an be observed experimentally. In order to make a omparison between the numerial simulations and the experimental data the results need to be
6 .5 t = hours t = 2 hours Figure : Development of one-dimensional tin-lead system starting from a homogeneous distribution, with an imposed global strain of %. l = 25 nm and κ = 2 GJ (κ l 2 = 2.5 mj m 2 ). From top to bottom: t=.4,.9,.4, 4.8, and 5 hours. t = 6 hours quantified. Sine minimization of surfae energy, and thus minimization of surfae area, is a driving fore for the diffusion proess, the total surfae area per unit volume is taken as a quantifiable number to be ompared. The results of this quantifiation is next used to fit the unknown mobility of the β phase. This parameter is found to be.2 2 m 5 /(J s). Figure 2 shows the surfae area development over time after fitting the mobility of the β phase. The agreement between experimental and numerial data is very good. 7 Conlusions In this paper an extension of the Cahn-Hilliard model is presented to desribe the mirostruture evolution of tinlead solder. The free energy density is taken to be a funtion of the loal and a strongly nonloal mass fration whih an be alulated by solving a Helmholtz equation. The differene between the nonloal and the loal mass fration is assoiated with the surfae energy. The derivative with respet to loal mass fration of this energy ats as a driving fore for the oarsening proess. Inorporation of additional driving fores into the free energy is straightforward. In this way the effet of stresses on diffusion is also aounted for through the elastially stored energy. The model inludes an internal length sale l and a surfae tension oeffiient κ as parameters. The produt κ l 2 appears as a multipliation fator for the derivative of the surfae energy with respet to the mass fration in the diffusion equation. One-dimensional simulations are used to investigate the influene of these parameters on interfae t = 9 hours t = 2 hours t = 5 hours Figure : Experimental and numerial thermal ageing of tinlead solder at 5 C, (size is µm).
7 fatigue of solder joints, Journal of Eletroni Materials 28(9), Interfae area per unit volume [ / µm ].2.8 experimental numerial, M=.2e time [hours] Figure 2: Interfae area per unit volume for experimental and numerial results, see figure. development and oarsening. It is found that inreasing either the internal length sale or the surfae tension oeffiient inreases the interfae. Inreasing l while hanging κ appropriately to keep the produt κ l 2 onstant leads to a steeper interfaes. The influene of external loading on the phase separation and oarsening proess is also investigated. It is found that elastially stored energy, either due to tensile or ompressive loading, auses a shift of the binodal points and dereases the interfae width. Furthermore, it inreases the deomposition rate and oarsening. The model is validated by omparing a two-dimensional simulation with experimental data. The model is able to predit break-up, oalesene, growth and dissolution of phase regions, similar to what an be observed experimentally. The total surfae area per unit volume is used to quantify the mirostruture. The results are in good agreement with experimental data. Aknowledgements This researh is supported by the Tehnology Foundation STW, applied siene division of NWO and the tehnology programme of the Ministry of Eonomi Affairs. We would like to thank M.A. Matin for providing the experimental data. Referenes [] Basaran, C. and Chanderoy, R. [998], Mehanis of Pb4/Sn6 near-euteti solder alloys subjeted to vibration, Applied Mathematial Modelling 22, [5] Dreyer, W. and Müller, W. [2], A study of the oarsening in tin/lead solders, International Journal of Solids and Strutures 37, [6] Frear, D. [989], Thermomehanial fatigue of solder joints: A new omprehensive test method, IEEE Transations on Composites, Hybrids, and Manufaturing Tehnology 2(4), [7] Frear, D., Burhet, S., Neilsen, M. and Stephens, J. [997], Mirostruturally based finite element simulation on solder joint behaviour, Soldering and Surfae Mount Tehnology 9(), [8] Frear, D., Grivas, D. and Morris, Jr., J. [988], A mirostrutural study of the thermal fatigue failures of 6Sn-4Pb solder joints, Journal of Eletroni Materials 7, 7 8. [9] Groot, S. d. and Mazur, P. [984], Non-equilibrium thermodynamis, Dover Publiations, In., New York. [] Hake, P., Spreher, A. and Conrad, H. [998], Mirostruture oarsening during thermo-mehanial fatigue of Pb-Sn solder joints, Journal of Eletroni Materials 26(7), [] MTData [998], Npl Databank for Materials Thermohemistry, Tehnial report, National Physial Laboratory, Queens Road, Tedington, Middlesex, TW LW. [2] Pan, T.-Y. [99], Thermal yling indued plasti deformation in solder joints - part ii: Aumulated deformation in through hole joints, IEEE Transations on Components, Hybrids, and Manufaturing Tehnology 4(4), [3] Viano, P., Burhet, S., Neilsen, M., Rejent, J. and Frear, D. [999], Coarsening of the sn-pb solder mirostruture in onstitutive model-based preditions of solder joint thermal mehanial fatigue, Journal of Eletroni Materials 28(), [2] Basaran, C. and Chanderoy, R. [2], Using finite element analysis for simulation of reliability tests on solder joints in miroeletroni pakaging, Computers and strutures 74, [3] Cahn, J. and Hilliard, J. [958], Free energy of a nonuniform system, I: Interfaial energy, The Journal of Chemial Physis 28(2), [4] Conrad, H., Guo, Z., Fahmy, Y. and Yang, D. [999], Influene of mirostruture on the plasti deformation kinetis, fatigue rak growth rate, and low-yle
Chapter 5 Single Phase Systems
 Chapter 5 Single Phase Systems Chemial engineering alulations rely heavily on the availability of physial properties of materials. There are three ommon methods used to find these properties. These inlude
Chapter 5 Single Phase Systems Chemial engineering alulations rely heavily on the availability of physial properties of materials. There are three ommon methods used to find these properties. These inlude
Impact Simulation of Extreme Wind Generated Missiles on Radioactive Waste Storage Facilities
 Impat Simulation of Extreme Wind Generated issiles on Radioative Waste Storage Failities G. Barbella Sogin S.p.A. Via Torino 6 00184 Rome (Italy), barbella@sogin.it Abstrat: The strutural design of temporary
Impat Simulation of Extreme Wind Generated issiles on Radioative Waste Storage Failities G. Barbella Sogin S.p.A. Via Torino 6 00184 Rome (Italy), barbella@sogin.it Abstrat: The strutural design of temporary
THE PERFORMANCE OF TRANSIT TIME FLOWMETERS IN HEATED GAS MIXTURES
 Proeedings of FEDSM 98 998 ASME Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting June 2-25, 998 Washington DC FEDSM98-529 THE PERFORMANCE OF TRANSIT TIME FLOWMETERS IN HEATED GAS MIXTURES John D. Wright Proess
Proeedings of FEDSM 98 998 ASME Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting June 2-25, 998 Washington DC FEDSM98-529 THE PERFORMANCE OF TRANSIT TIME FLOWMETERS IN HEATED GAS MIXTURES John D. Wright Proess
A Holistic Method for Selecting Web Services in Design of Composite Applications
 A Holisti Method for Seleting Web Servies in Design of Composite Appliations Mārtiņš Bonders, Jānis Grabis Institute of Information Tehnology, Riga Tehnial University, 1 Kalu Street, Riga, LV 1658, Latvia,
A Holisti Method for Seleting Web Servies in Design of Composite Appliations Mārtiņš Bonders, Jānis Grabis Institute of Information Tehnology, Riga Tehnial University, 1 Kalu Street, Riga, LV 1658, Latvia,
THE EFFECT OF WATER VAPOR ON COUNTERFLOW DIFFUSION FLAMES
 THE EFFECT OF WATER VAPOR ON COUNTERFLOW DIFFUSION FLAMES by Jaeil Suh and Arvind Atreya Combustion and Heat Tkansfer Laboratory Department of Mehanial Engineering and Applied Mehanis The University of
THE EFFECT OF WATER VAPOR ON COUNTERFLOW DIFFUSION FLAMES by Jaeil Suh and Arvind Atreya Combustion and Heat Tkansfer Laboratory Department of Mehanial Engineering and Applied Mehanis The University of
A novel active mass damper for vibration control of bridges
 IABMAS 08, International Conferene on Bridge Maintenane, Safety and Management, 3-7 July 008, Seoul, Korea A novel ative mass damper for vibration ontrol of bridges U. Starossek & J. Sheller Strutural
IABMAS 08, International Conferene on Bridge Maintenane, Safety and Management, 3-7 July 008, Seoul, Korea A novel ative mass damper for vibration ontrol of bridges U. Starossek & J. Sheller Strutural
HEAT CONDUCTION. q A q T
 HEAT CONDUCTION When a temperature gradient eist in a material, heat flows from the high temperature region to the low temperature region. The heat transfer mehanism is referred to as ondution and the
HEAT CONDUCTION When a temperature gradient eist in a material, heat flows from the high temperature region to the low temperature region. The heat transfer mehanism is referred to as ondution and the
Sebastián Bravo López
 Transfinite Turing mahines Sebastián Bravo López 1 Introdution With the rise of omputers with high omputational power the idea of developing more powerful models of omputation has appeared. Suppose that
Transfinite Turing mahines Sebastián Bravo López 1 Introdution With the rise of omputers with high omputational power the idea of developing more powerful models of omputation has appeared. Suppose that
Measurement of Powder Flow Properties that relate to Gravity Flow Behaviour through Industrial Processing Lines
 Measurement of Powder Flow Properties that relate to Gravity Flow ehaviour through Industrial Proessing Lines A typial industrial powder proessing line will inlude several storage vessels (e.g. bins, bunkers,
Measurement of Powder Flow Properties that relate to Gravity Flow ehaviour through Industrial Proessing Lines A typial industrial powder proessing line will inlude several storage vessels (e.g. bins, bunkers,
Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Review 6 (5) (2013) 143-148. Research Article
 Jestr Journal o Engineering Siene and Tehnology Review 6 (5) (13) 143-148 Researh Artile JOURNAL OF Engineering Siene and Tehnology Review www.jestr.org Numerial Analyses on Seismi Behaviour o Conrete-illed
Jestr Journal o Engineering Siene and Tehnology Review 6 (5) (13) 143-148 Researh Artile JOURNAL OF Engineering Siene and Tehnology Review www.jestr.org Numerial Analyses on Seismi Behaviour o Conrete-illed
Chapter 1: Introduction
 Chapter 1: Introdution 1.1 Pratial olumn base details in steel strutures 1.1.1 Pratial olumn base details Every struture must transfer vertial and lateral loads to the supports. In some ases, beams or
Chapter 1: Introdution 1.1 Pratial olumn base details in steel strutures 1.1.1 Pratial olumn base details Every struture must transfer vertial and lateral loads to the supports. In some ases, beams or
A Three-Hybrid Treatment Method of the Compressor's Characteristic Line in Performance Prediction of Power Systems
 A Three-Hybrid Treatment Method of the Compressor's Charateristi Line in Performane Predition of Power Systems A Three-Hybrid Treatment Method of the Compressor's Charateristi Line in Performane Predition
A Three-Hybrid Treatment Method of the Compressor's Charateristi Line in Performane Predition of Power Systems A Three-Hybrid Treatment Method of the Compressor's Charateristi Line in Performane Predition
Static Fairness Criteria in Telecommunications
 Teknillinen Korkeakoulu ERIKOISTYÖ Teknillisen fysiikan koulutusohjelma 92002 Mat-208 Sovelletun matematiikan erikoistyöt Stati Fairness Criteria in Teleommuniations Vesa Timonen, e-mail: vesatimonen@hutfi
Teknillinen Korkeakoulu ERIKOISTYÖ Teknillisen fysiikan koulutusohjelma 92002 Mat-208 Sovelletun matematiikan erikoistyöt Stati Fairness Criteria in Teleommuniations Vesa Timonen, e-mail: vesatimonen@hutfi
Earthquake Loss for Reinforced Concrete Building Structures Before and After Fire damage
 Earthquake Loss for Reinfored Conrete Building Strutures Before and After Fire damage Pai-Mei LIU, Yi-Hsuan Tu and Maw-Shyong SHEU 3 ABSTRACT The purpose of this paper is to propose a rational analytial
Earthquake Loss for Reinfored Conrete Building Strutures Before and After Fire damage Pai-Mei LIU, Yi-Hsuan Tu and Maw-Shyong SHEU 3 ABSTRACT The purpose of this paper is to propose a rational analytial
THERMAL TO MECHANICAL ENERGY CONVERSION: ENGINES AND REQUIREMENTS Vol. I - Thermodynamic Cycles of Reciprocating and Rotary Engines - R.S.
 THERMAL TO MECHANICAL ENERGY CONVERSION: ENGINES AND REQUIREMENTS Vol. I - Thermodynami Cyles of Reiproating and Rotary Engines - R.S.Kavtaradze THERMODYNAMIC CYCLES OF RECIPROCATING AND ROTARY ENGINES
THERMAL TO MECHANICAL ENERGY CONVERSION: ENGINES AND REQUIREMENTS Vol. I - Thermodynami Cyles of Reiproating and Rotary Engines - R.S.Kavtaradze THERMODYNAMIC CYCLES OF RECIPROCATING AND ROTARY ENGINES
Computational Analysis of Two Arrangements of a Central Ground-Source Heat Pump System for Residential Buildings
 Computational Analysis of Two Arrangements of a Central Ground-Soure Heat Pump System for Residential Buildings Abstrat Ehab Foda, Ala Hasan, Kai Sirén Helsinki University of Tehnology, HVAC Tehnology,
Computational Analysis of Two Arrangements of a Central Ground-Soure Heat Pump System for Residential Buildings Abstrat Ehab Foda, Ala Hasan, Kai Sirén Helsinki University of Tehnology, HVAC Tehnology,
Chapter 1 Microeconomics of Consumer Theory
 Chapter 1 Miroeonomis of Consumer Theory The two broad ategories of deision-makers in an eonomy are onsumers and firms. Eah individual in eah of these groups makes its deisions in order to ahieve some
Chapter 1 Miroeonomis of Consumer Theory The two broad ategories of deision-makers in an eonomy are onsumers and firms. Eah individual in eah of these groups makes its deisions in order to ahieve some
Effects of Inter-Coaching Spacing on Aerodynamic Noise Generation Inside High-speed Trains
 Effets of Inter-Coahing Spaing on Aerodynami Noise Generation Inside High-speed Trains 1 J. Ryu, 1 J. Park*, 2 C. Choi, 1 S. Song Hanyang University, Seoul, South Korea 1 ; Korea Railroad Researh Institute,
Effets of Inter-Coahing Spaing on Aerodynami Noise Generation Inside High-speed Trains 1 J. Ryu, 1 J. Park*, 2 C. Choi, 1 S. Song Hanyang University, Seoul, South Korea 1 ; Korea Railroad Researh Institute,
) ( )( ) ( ) ( )( ) ( ) ( ) (1)
 OPEN CHANNEL FLOW Open hannel flow is haraterized by a surfae in ontat with a gas phase, allowing the fluid to take on shapes and undergo behavior that is impossible in a pipe or other filled onduit. Examples
OPEN CHANNEL FLOW Open hannel flow is haraterized by a surfae in ontat with a gas phase, allowing the fluid to take on shapes and undergo behavior that is impossible in a pipe or other filled onduit. Examples
Electrician'sMathand BasicElectricalFormulas
 Eletriian'sMathand BasiEletrialFormulas MikeHoltEnterprises,In. 1.888.NEC.CODE www.mikeholt.om Introdution Introdution This PDF is a free resoure from Mike Holt Enterprises, In. It s Unit 1 from the Eletrial
Eletriian'sMathand BasiEletrialFormulas MikeHoltEnterprises,In. 1.888.NEC.CODE www.mikeholt.om Introdution Introdution This PDF is a free resoure from Mike Holt Enterprises, In. It s Unit 1 from the Eletrial
10.1 The Lorentz force law
 Sott Hughes 10 Marh 2005 Massahusetts Institute of Tehnology Department of Physis 8.022 Spring 2004 Leture 10: Magneti fore; Magneti fields; Ampere s law 10.1 The Lorentz fore law Until now, we have been
Sott Hughes 10 Marh 2005 Massahusetts Institute of Tehnology Department of Physis 8.022 Spring 2004 Leture 10: Magneti fore; Magneti fields; Ampere s law 10.1 The Lorentz fore law Until now, we have been
In order to be able to design beams, we need both moments and shears. 1. Moment a) From direct design method or equivalent frame method
 BEAM DESIGN In order to be able to design beams, we need both moments and shears. 1. Moment a) From diret design method or equivalent frame method b) From loads applied diretly to beams inluding beam weight
BEAM DESIGN In order to be able to design beams, we need both moments and shears. 1. Moment a) From diret design method or equivalent frame method b) From loads applied diretly to beams inluding beam weight
Weighting Methods in Survey Sampling
 Setion on Survey Researh Methods JSM 01 Weighting Methods in Survey Sampling Chiao-hih Chang Ferry Butar Butar Abstrat It is said that a well-designed survey an best prevent nonresponse. However, no matter
Setion on Survey Researh Methods JSM 01 Weighting Methods in Survey Sampling Chiao-hih Chang Ferry Butar Butar Abstrat It is said that a well-designed survey an best prevent nonresponse. However, no matter
protection p1ann1ng report
 f1re~~ protetion p1ann1ng report BUILDING CONSTRUCTION INFORMATION FROM THE CONCRETE AND MASONRY INDUSTRIES Signifiane of Fire Ratings for Building Constrution NO. 3 OF A SERIES The use of fire-resistive
f1re~~ protetion p1ann1ng report BUILDING CONSTRUCTION INFORMATION FROM THE CONCRETE AND MASONRY INDUSTRIES Signifiane of Fire Ratings for Building Constrution NO. 3 OF A SERIES The use of fire-resistive
Performance Analysis of IEEE 802.11 in Multi-hop Wireless Networks
 Performane Analysis of IEEE 80.11 in Multi-hop Wireless Networks Lan Tien Nguyen 1, Razvan Beuran,1, Yoihi Shinoda 1, 1 Japan Advaned Institute of Siene and Tehnology, 1-1 Asahidai, Nomi, Ishikawa, 93-19
Performane Analysis of IEEE 80.11 in Multi-hop Wireless Networks Lan Tien Nguyen 1, Razvan Beuran,1, Yoihi Shinoda 1, 1 Japan Advaned Institute of Siene and Tehnology, 1-1 Asahidai, Nomi, Ishikawa, 93-19
Lecture 24: Spinodal Decomposition: Part 3: kinetics of the
 Leture 4: Spinodal Deoposition: Part 3: kinetis of the oposition flutuation Today s topis Diffusion kinetis of spinodal deoposition in ters of the onentration (oposition) flutuation as a funtion of tie:
Leture 4: Spinodal Deoposition: Part 3: kinetis of the oposition flutuation Today s topis Diffusion kinetis of spinodal deoposition in ters of the onentration (oposition) flutuation as a funtion of tie:
SHAFTS: TORSION LOADING AND DEFORMATION
 ECURE hird Edition SHAFS: ORSION OADING AND DEFORMAION A. J. Clark Shool of Engineering Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering 6 Chapter 3.1-3.5 by Dr. Ibrahim A. Assakkaf SPRING 2003 ENES 220
ECURE hird Edition SHAFS: ORSION OADING AND DEFORMAION A. J. Clark Shool of Engineering Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering 6 Chapter 3.1-3.5 by Dr. Ibrahim A. Assakkaf SPRING 2003 ENES 220
Intelligent Measurement Processes in 3D Optical Metrology: Producing More Accurate Point Clouds
 Intelligent Measurement Proesses in 3D Optial Metrology: Produing More Aurate Point Clouds Charles Mony, Ph.D. 1 President Creaform in. mony@reaform3d.om Daniel Brown, Eng. 1 Produt Manager Creaform in.
Intelligent Measurement Proesses in 3D Optial Metrology: Produing More Aurate Point Clouds Charles Mony, Ph.D. 1 President Creaform in. mony@reaform3d.om Daniel Brown, Eng. 1 Produt Manager Creaform in.
An integrated optimization model of a Closed- Loop Supply Chain under uncertainty
 ISSN 1816-6075 (Print), 1818-0523 (Online) Journal of System and Management Sienes Vol. 2 (2012) No. 3, pp. 9-17 An integrated optimization model of a Closed- Loop Supply Chain under unertainty Xiaoxia
ISSN 1816-6075 (Print), 1818-0523 (Online) Journal of System and Management Sienes Vol. 2 (2012) No. 3, pp. 9-17 An integrated optimization model of a Closed- Loop Supply Chain under unertainty Xiaoxia
Customer Efficiency, Channel Usage and Firm Performance in Retail Banking
 Customer Effiieny, Channel Usage and Firm Performane in Retail Banking Mei Xue Operations and Strategi Management Department The Wallae E. Carroll Shool of Management Boston College 350 Fulton Hall, 140
Customer Effiieny, Channel Usage and Firm Performane in Retail Banking Mei Xue Operations and Strategi Management Department The Wallae E. Carroll Shool of Management Boston College 350 Fulton Hall, 140
Classical Electromagnetic Doppler Effect Redefined. Copyright 2014 Joseph A. Rybczyk
 Classial Eletromagneti Doppler Effet Redefined Copyright 04 Joseph A. Rybzyk Abstrat The lassial Doppler Effet formula for eletromagneti waves is redefined to agree with the fundamental sientifi priniples
Classial Eletromagneti Doppler Effet Redefined Copyright 04 Joseph A. Rybzyk Abstrat The lassial Doppler Effet formula for eletromagneti waves is redefined to agree with the fundamental sientifi priniples
Supply chain coordination; A Game Theory approach
 aepted for publiation in the journal "Engineering Appliations of Artifiial Intelligene" 2008 upply hain oordination; A Game Theory approah Jean-Claude Hennet x and Yasemin Arda xx x LI CNR-UMR 668 Université
aepted for publiation in the journal "Engineering Appliations of Artifiial Intelligene" 2008 upply hain oordination; A Game Theory approah Jean-Claude Hennet x and Yasemin Arda xx x LI CNR-UMR 668 Université
Relativity in the Global Positioning System
 Relativity in the Global Positioning System Neil Ashby Department of Physis,UCB 390 University of Colorado, Boulder, CO 80309-00390 NIST Affiliate Email: ashby@boulder.nist.gov July 0, 006 AAPT workshop
Relativity in the Global Positioning System Neil Ashby Department of Physis,UCB 390 University of Colorado, Boulder, CO 80309-00390 NIST Affiliate Email: ashby@boulder.nist.gov July 0, 006 AAPT workshop
Neural network-based Load Balancing and Reactive Power Control by Static VAR Compensator
 nternational Journal of Computer and Eletrial Engineering, Vol. 1, No. 1, April 2009 Neural network-based Load Balaning and Reative Power Control by Stati VAR Compensator smail K. Said and Marouf Pirouti
nternational Journal of Computer and Eletrial Engineering, Vol. 1, No. 1, April 2009 Neural network-based Load Balaning and Reative Power Control by Stati VAR Compensator smail K. Said and Marouf Pirouti
Conversion of short optical pulses to terahertz radiation in a nonlinear medium: Experiment and theory
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B 76, 35114 007 Conversion of short optial pulses to terahertz radiation in a nonlinear medium: Experiment and theory N. N. Zinov ev* Department of Physis, University of Durham, Durham
PHYSICAL REVIEW B 76, 35114 007 Conversion of short optial pulses to terahertz radiation in a nonlinear medium: Experiment and theory N. N. Zinov ev* Department of Physis, University of Durham, Durham
arxiv:astro-ph/0304006v2 10 Jun 2003 Theory Group, MS 50A-5101 Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory One Cyclotron Road Berkeley, CA 94720 USA
 LBNL-52402 Marh 2003 On the Speed of Gravity and the v/ Corretions to the Shapiro Time Delay Stuart Samuel 1 arxiv:astro-ph/0304006v2 10 Jun 2003 Theory Group, MS 50A-5101 Lawrene Berkeley National Laboratory
LBNL-52402 Marh 2003 On the Speed of Gravity and the v/ Corretions to the Shapiro Time Delay Stuart Samuel 1 arxiv:astro-ph/0304006v2 10 Jun 2003 Theory Group, MS 50A-5101 Lawrene Berkeley National Laboratory
Channel Assignment Strategies for Cellular Phone Systems
 Channel Assignment Strategies for Cellular Phone Systems Wei Liu Yiping Han Hang Yu Zhejiang University Hangzhou, P. R. China Contat: wliu5@ie.uhk.edu.hk 000 Mathematial Contest in Modeling (MCM) Meritorious
Channel Assignment Strategies for Cellular Phone Systems Wei Liu Yiping Han Hang Yu Zhejiang University Hangzhou, P. R. China Contat: wliu5@ie.uhk.edu.hk 000 Mathematial Contest in Modeling (MCM) Meritorious
 Chapter 6 A N ovel Solution Of Linear Congruenes Proeedings NCUR IX. (1995), Vol. II, pp. 708{712 Jerey F. Gold Department of Mathematis, Department of Physis University of Utah Salt Lake City, Utah 84112
Chapter 6 A N ovel Solution Of Linear Congruenes Proeedings NCUR IX. (1995), Vol. II, pp. 708{712 Jerey F. Gold Department of Mathematis, Department of Physis University of Utah Salt Lake City, Utah 84112
International Journal of Supply and Operations Management. Mathematical modeling for EOQ inventory system with advance payment and fuzzy Parameters
 nternational Journal of Supply and Operations Management JSOM November 0, Volume, ssue 3, pp. 60-78 SSN-Print: 383-359 SSN-Online: 383-55 www.ijsom.om Mathematial modeling for EOQ inventory system with
nternational Journal of Supply and Operations Management JSOM November 0, Volume, ssue 3, pp. 60-78 SSN-Print: 383-359 SSN-Online: 383-55 www.ijsom.om Mathematial modeling for EOQ inventory system with
Explanatory Examples on Indian Seismic Code IS 1893 (Part I)
 Doument No. :: IITK-GSDMA-EQ1-V.0 inal Report :: A - Earthquake Codes IITK-GSDMA Projet on Building Codes Explanatory Examples on Indian Seismi Code IS 1893 (Part I) by Dr. Sudhir K Jain Department of
Doument No. :: IITK-GSDMA-EQ1-V.0 inal Report :: A - Earthquake Codes IITK-GSDMA Projet on Building Codes Explanatory Examples on Indian Seismi Code IS 1893 (Part I) by Dr. Sudhir K Jain Department of
HEAT EXCHANGERS-2. Associate Professor. IIT Delhi E-mail: prabal@mech.iitd.ac.in. P.Talukdar/ Mech-IITD
 HEA EXHANGERS-2 Prabal alukdar Assoiate Professor Department of Mehanial Engineering II Delhi E-mail: prabal@meh.iitd.a.in Multipass and rossflow he subsripts 1 and 2 represent the inlet and outlet, respetively..
HEA EXHANGERS-2 Prabal alukdar Assoiate Professor Department of Mehanial Engineering II Delhi E-mail: prabal@meh.iitd.a.in Multipass and rossflow he subsripts 1 and 2 represent the inlet and outlet, respetively..
Derivation of Einstein s Equation, E = mc 2, from the Classical Force Laws
 Apeiron, Vol. 14, No. 4, Otober 7 435 Derivation of Einstein s Equation, E = m, from the Classial Fore Laws N. Hamdan, A.K. Hariri Department of Physis, University of Aleppo, Syria nhamdan59@hotmail.om,
Apeiron, Vol. 14, No. 4, Otober 7 435 Derivation of Einstein s Equation, E = m, from the Classial Fore Laws N. Hamdan, A.K. Hariri Department of Physis, University of Aleppo, Syria nhamdan59@hotmail.om,
VOLUME 13, ARTICLE 5, PAGES 117-142 PUBLISHED 05 OCTOBER 2005 DOI: 10.4054/DemRes.2005.13.
 Demographi Researh a free, expedited, online journal of peer-reviewed researh and ommentary in the population sienes published by the Max Plank Institute for Demographi Researh Konrad-Zuse Str. 1, D-157
Demographi Researh a free, expedited, online journal of peer-reviewed researh and ommentary in the population sienes published by the Max Plank Institute for Demographi Researh Konrad-Zuse Str. 1, D-157
Finite Element Modelling of Vibro-Acoustic Systems for Active Noise Reduction
 ECHNISCHE MECHANIK, Band 25, Heft 3-4, (25), 24-247 Manuskripteingang:. Dezember 25 Finite Element Modelling of Vibro-Aousti Systems for Ative Noise Redution J. Lefèvre, U. Gabbert Over the past years
ECHNISCHE MECHANIK, Band 25, Heft 3-4, (25), 24-247 Manuskripteingang:. Dezember 25 Finite Element Modelling of Vibro-Aousti Systems for Ative Noise Redution J. Lefèvre, U. Gabbert Over the past years
Recovering Articulated Motion with a Hierarchical Factorization Method
 Reovering Artiulated Motion with a Hierarhial Fatorization Method Hanning Zhou and Thomas S Huang University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 405 North Mathews Avenue, Urbana, IL 680, USA {hzhou, huang}@ifpuiuedu
Reovering Artiulated Motion with a Hierarhial Fatorization Method Hanning Zhou and Thomas S Huang University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 405 North Mathews Avenue, Urbana, IL 680, USA {hzhou, huang}@ifpuiuedu
Granular Problem Solving and Software Engineering
 Granular Problem Solving and Software Engineering Haibin Zhu, Senior Member, IEEE Department of Computer Siene and Mathematis, Nipissing University, 100 College Drive, North Bay, Ontario, P1B 8L7, Canada
Granular Problem Solving and Software Engineering Haibin Zhu, Senior Member, IEEE Department of Computer Siene and Mathematis, Nipissing University, 100 College Drive, North Bay, Ontario, P1B 8L7, Canada
Hierarchical Clustering and Sampling Techniques for Network Monitoring
 S. Sindhuja Hierarhial Clustering and Sampling Tehniques for etwork Monitoring S. Sindhuja ME ABSTRACT: etwork monitoring appliations are used to monitor network traffi flows. Clustering tehniques are
S. Sindhuja Hierarhial Clustering and Sampling Tehniques for etwork Monitoring S. Sindhuja ME ABSTRACT: etwork monitoring appliations are used to monitor network traffi flows. Clustering tehniques are
Computer Networks Framing
 Computer Networks Framing Saad Mneimneh Computer Siene Hunter College of CUNY New York Introdution Who framed Roger rabbit? A detetive, a woman, and a rabbit in a network of trouble We will skip the physial
Computer Networks Framing Saad Mneimneh Computer Siene Hunter College of CUNY New York Introdution Who framed Roger rabbit? A detetive, a woman, and a rabbit in a network of trouble We will skip the physial
Heat Generation and Removal in Solid State Lasers
 Chapter 1 Heat Generation and Removal in Solid State Lasers V. Ashoori, M. Shayganmanesh and S. Radmard Additional information is available at the end of the hapter http://dx.doi.org/10.577/63 1. Introdution
Chapter 1 Heat Generation and Removal in Solid State Lasers V. Ashoori, M. Shayganmanesh and S. Radmard Additional information is available at the end of the hapter http://dx.doi.org/10.577/63 1. Introdution
Previously Published Works UC Berkeley
 Previously Published Works UC Berkeley A University of California author or department has made this artile openly available. Thanks to the Aademi Senate s Open Aess Poliy, a great many UC-authored sholarly
Previously Published Works UC Berkeley A University of California author or department has made this artile openly available. Thanks to the Aademi Senate s Open Aess Poliy, a great many UC-authored sholarly
Procurement auctions are sometimes plagued with a chosen supplier s failing to accomplish a project successfully.
 Deision Analysis Vol. 7, No. 1, Marh 2010, pp. 23 39 issn 1545-8490 eissn 1545-8504 10 0701 0023 informs doi 10.1287/dea.1090.0155 2010 INFORMS Managing Projet Failure Risk Through Contingent Contrats
Deision Analysis Vol. 7, No. 1, Marh 2010, pp. 23 39 issn 1545-8490 eissn 1545-8504 10 0701 0023 informs doi 10.1287/dea.1090.0155 2010 INFORMS Managing Projet Failure Risk Through Contingent Contrats
Cement and Concrete Research
 Cement and Conrete Researh 39 (2009) 255 265 Contents lists available at SieneDiret Cement and Conrete Researh journal homepage: http://ees.elsevier.om/cemcon/default.asp Hydration kinetis modeling of
Cement and Conrete Researh 39 (2009) 255 265 Contents lists available at SieneDiret Cement and Conrete Researh journal homepage: http://ees.elsevier.om/cemcon/default.asp Hydration kinetis modeling of
cos t sin t sin t cos t
 Exerise 7 Suppose that t 0 0andthat os t sin t At sin t os t Compute Bt t As ds,andshowthata and B ommute 0 Exerise 8 Suppose A is the oeffiient matrix of the ompanion equation Y AY assoiated with the
Exerise 7 Suppose that t 0 0andthat os t sin t At sin t os t Compute Bt t As ds,andshowthata and B ommute 0 Exerise 8 Suppose A is the oeffiient matrix of the ompanion equation Y AY assoiated with the
Impedance Method for Leak Detection in Zigzag Pipelines
 10.478/v10048-010-0036-0 MEASUREMENT SCIENCE REVIEW, Volume 10, No. 6, 010 Impedane Method for Leak Detetion in igzag Pipelines A. Lay-Ekuakille 1, P. Vergallo 1, A. Trotta 1 Dipartimento d Ingegneria
10.478/v10048-010-0036-0 MEASUREMENT SCIENCE REVIEW, Volume 10, No. 6, 010 Impedane Method for Leak Detetion in igzag Pipelines A. Lay-Ekuakille 1, P. Vergallo 1, A. Trotta 1 Dipartimento d Ingegneria
Deadline-based Escalation in Process-Aware Information Systems
 Deadline-based Esalation in Proess-Aware Information Systems Wil M.P. van der Aalst 1,2, Mihael Rosemann 2, Marlon Dumas 2 1 Department of Tehnology Management Eindhoven University of Tehnology, The Netherlands
Deadline-based Esalation in Proess-Aware Information Systems Wil M.P. van der Aalst 1,2, Mihael Rosemann 2, Marlon Dumas 2 1 Department of Tehnology Management Eindhoven University of Tehnology, The Netherlands
Deduplication with Block-Level Content-Aware Chunking for Solid State Drives (SSDs)
 23 IEEE International Conferene on High Performane Computing and Communiations & 23 IEEE International Conferene on Embedded and Ubiquitous Computing Dedupliation with Blok-Level Content-Aware Chunking
23 IEEE International Conferene on High Performane Computing and Communiations & 23 IEEE International Conferene on Embedded and Ubiquitous Computing Dedupliation with Blok-Level Content-Aware Chunking
Price-based versus quantity-based approaches for stimulating the development of renewable electricity: new insights in an old debate
 Prie-based versus -based approahes for stimulating the development of renewable eletriity: new insights in an old debate uthors: Dominique FINON, Philippe MENNTEU, Marie-Laure LMY, Institut d Eonomie et
Prie-based versus -based approahes for stimulating the development of renewable eletriity: new insights in an old debate uthors: Dominique FINON, Philippe MENNTEU, Marie-Laure LMY, Institut d Eonomie et
Improved SOM-Based High-Dimensional Data Visualization Algorithm
 Computer and Information Siene; Vol. 5, No. 4; 2012 ISSN 1913-8989 E-ISSN 1913-8997 Published by Canadian Center of Siene and Eduation Improved SOM-Based High-Dimensional Data Visualization Algorithm Wang
Computer and Information Siene; Vol. 5, No. 4; 2012 ISSN 1913-8989 E-ISSN 1913-8997 Published by Canadian Center of Siene and Eduation Improved SOM-Based High-Dimensional Data Visualization Algorithm Wang
Learning Curves and Stochastic Models for Pricing and Provisioning Cloud Computing Services
 T Learning Curves and Stohasti Models for Priing and Provisioning Cloud Computing Servies Amit Gera, Cathy H. Xia Dept. of Integrated Systems Engineering Ohio State University, Columbus, OH 4310 {gera.,
T Learning Curves and Stohasti Models for Priing and Provisioning Cloud Computing Servies Amit Gera, Cathy H. Xia Dept. of Integrated Systems Engineering Ohio State University, Columbus, OH 4310 {gera.,
10 UNSTEADY FLOW IN OPEN CHANNELS
 0 UNTEY FLOW IN OEN CHNNEL 0. Introdution Unsteady flow in open hannels differs from that in losed onduits in that the eistene of a free surfae allows the flow ross-setion to freely hange, a fator whih
0 UNTEY FLOW IN OEN CHNNEL 0. Introdution Unsteady flow in open hannels differs from that in losed onduits in that the eistene of a free surfae allows the flow ross-setion to freely hange, a fator whih
Isaac Newton. Translated into English by
 THE MATHEMATICAL PRINCIPLES OF NATURAL PHILOSOPHY (BOOK 1, SECTION 1) By Isaa Newton Translated into English by Andrew Motte Edited by David R. Wilkins 2002 NOTE ON THE TEXT Setion I in Book I of Isaa
THE MATHEMATICAL PRINCIPLES OF NATURAL PHILOSOPHY (BOOK 1, SECTION 1) By Isaa Newton Translated into English by Andrew Motte Edited by David R. Wilkins 2002 NOTE ON THE TEXT Setion I in Book I of Isaa
Paid Placement Strategies for Internet Search Engines
 Paid Plaement Strategies for Internet Searh Engines Hemant K. Bhargava Smeal College of Business Penn State University 342 Beam Building University Park, PA 16802 bhargava@omputer.org Juan Feng Smeal College
Paid Plaement Strategies for Internet Searh Engines Hemant K. Bhargava Smeal College of Business Penn State University 342 Beam Building University Park, PA 16802 bhargava@omputer.org Juan Feng Smeal College
User s Guide VISFIT: a computer tool for the measurement of intrinsic viscosities
 File:UserVisfit_2.do User s Guide VISFIT: a omputer tool for the measurement of intrinsi visosities Version 2.a, September 2003 From: Multiple Linear Least-Squares Fits with a Common Interept: Determination
File:UserVisfit_2.do User s Guide VISFIT: a omputer tool for the measurement of intrinsi visosities Version 2.a, September 2003 From: Multiple Linear Least-Squares Fits with a Common Interept: Determination
Relativistic Kinematics -a project in Analytical mechanics Karlstad University
 Relativisti Kinematis -a projet in Analytial mehanis Karlstad University Carl Stigner 1th January 6 Abstrat The following text is a desription of some of the ontent in hapter 7 in the textbook Classial
Relativisti Kinematis -a projet in Analytial mehanis Karlstad University Carl Stigner 1th January 6 Abstrat The following text is a desription of some of the ontent in hapter 7 in the textbook Classial
1.3 Complex Numbers; Quadratic Equations in the Complex Number System*
 04 CHAPTER Equations and Inequalities Explaining Conepts: Disussion and Writing 7. Whih of the following pairs of equations are equivalent? Explain. x 2 9; x 3 (b) x 29; x 3 () x - 2x - 22 x - 2 2 ; x
04 CHAPTER Equations and Inequalities Explaining Conepts: Disussion and Writing 7. Whih of the following pairs of equations are equivalent? Explain. x 2 9; x 3 (b) x 29; x 3 () x - 2x - 22 x - 2 2 ; x
Algorithm of Removing Thin Cloud-fog Cover from Single Remote Sensing Image
 Journal of Information & Computational Siene 11:3 (2014 817 824 February 10, 2014 Available at http://www.jois.om Algorithm of Removing Thin Cloud-fog Cover from Single Remote Sensing Image Yinqi Xiong,
Journal of Information & Computational Siene 11:3 (2014 817 824 February 10, 2014 Available at http://www.jois.om Algorithm of Removing Thin Cloud-fog Cover from Single Remote Sensing Image Yinqi Xiong,
AUDITING COST OVERRUN CLAIMS *
 AUDITING COST OVERRUN CLAIMS * David Pérez-Castrillo # University of Copenhagen & Universitat Autònoma de Barelona Niolas Riedinger ENSAE, Paris Abstrat: We onsider a ost-reimbursement or a ost-sharing
AUDITING COST OVERRUN CLAIMS * David Pérez-Castrillo # University of Copenhagen & Universitat Autònoma de Barelona Niolas Riedinger ENSAE, Paris Abstrat: We onsider a ost-reimbursement or a ost-sharing
Capacity at Unsignalized Two-Stage Priority Intersections
 Capaity at Unsignalized Two-Stage Priority Intersetions by Werner Brilon and Ning Wu Abstrat The subjet of this paper is the apaity of minor-street traffi movements aross major divided four-lane roadways
Capaity at Unsignalized Two-Stage Priority Intersetions by Werner Brilon and Ning Wu Abstrat The subjet of this paper is the apaity of minor-street traffi movements aross major divided four-lane roadways
Soft-Edge Flip-flops for Improved Timing Yield: Design and Optimization
 Soft-Edge Flip-flops for Improved Timing Yield: Design and Optimization Abstrat Parameter variations ause high yield losses due to their large impat on iruit delay. In this paper, we propose the use of
Soft-Edge Flip-flops for Improved Timing Yield: Design and Optimization Abstrat Parameter variations ause high yield losses due to their large impat on iruit delay. In this paper, we propose the use of
How To Fator
 CHAPTER hapter 4 > Make the Connetion 4 INTRODUCTION Developing seret odes is big business beause of the widespread use of omputers and the Internet. Corporations all over the world sell enryption systems
CHAPTER hapter 4 > Make the Connetion 4 INTRODUCTION Developing seret odes is big business beause of the widespread use of omputers and the Internet. Corporations all over the world sell enryption systems
REDUCTION FACTOR OF FEEDING LINES THAT HAVE A CABLE AND AN OVERHEAD SECTION
 C I E 17 th International Conferene on Eletriity istriution Barelona, 1-15 May 003 EUCTION FACTO OF FEEING LINES THAT HAVE A CABLE AN AN OVEHEA SECTION Ljuivoje opovi J.. Elektrodistriuija - Belgrade -
C I E 17 th International Conferene on Eletriity istriution Barelona, 1-15 May 003 EUCTION FACTO OF FEEING LINES THAT HAVE A CABLE AN AN OVEHEA SECTION Ljuivoje opovi J.. Elektrodistriuija - Belgrade -
Availability, Reliability, Maintainability, and Capability
 Availability, Reliability, Maintainability, and Capability H. Paul Barringer, P.E. Barringer & Assoiates, In. Humble, TX Triplex Chapter Of The Vibrations Institute Hilton Hotel Beaumont, Texas February
Availability, Reliability, Maintainability, and Capability H. Paul Barringer, P.E. Barringer & Assoiates, In. Humble, TX Triplex Chapter Of The Vibrations Institute Hilton Hotel Beaumont, Texas February
Marker Tracking and HMD Calibration for a Video-based Augmented Reality Conferencing System
 Marker Traking and HMD Calibration for a Video-based Augmented Reality Conferening System Hirokazu Kato 1 and Mark Billinghurst 2 1 Faulty of Information Sienes, Hiroshima City University 2 Human Interfae
Marker Traking and HMD Calibration for a Video-based Augmented Reality Conferening System Hirokazu Kato 1 and Mark Billinghurst 2 1 Faulty of Information Sienes, Hiroshima City University 2 Human Interfae
From a strategic view to an engineering view in a digital enterprise
 Digital Enterprise Design & Management 2013 February 11-12, 2013 Paris From a strategi view to an engineering view in a digital enterprise The ase of a multi-ountry Telo Hervé Paault Orange Abstrat In
Digital Enterprise Design & Management 2013 February 11-12, 2013 Paris From a strategi view to an engineering view in a digital enterprise The ase of a multi-ountry Telo Hervé Paault Orange Abstrat In
The Optimal Deterrence of Tax Evasion: The Trade-off Between Information Reporting and Audits
 The Optimal Deterrene of Tax Evasion: The Trade-off Between Information Reporting and Audits Yulia Paramonova Department of Eonomis, University of Mihigan Otober 30, 2014 Abstrat Despite the widespread
The Optimal Deterrene of Tax Evasion: The Trade-off Between Information Reporting and Audits Yulia Paramonova Department of Eonomis, University of Mihigan Otober 30, 2014 Abstrat Despite the widespread
The following excerpt are pages from the North American Product Technical Guide, Volume 2: Anchor Fastening, Edition 16.
 The following exerpt are pages from the North Amerian Produt Tehnial Guide, Volume 2: Anhor Fastening, Edition 16. Please refer to the publiation in its entirety for omplete details on this produt inluding
The following exerpt are pages from the North Amerian Produt Tehnial Guide, Volume 2: Anhor Fastening, Edition 16. Please refer to the publiation in its entirety for omplete details on this produt inluding
Prices and Heterogeneous Search Costs
 Pries and Heterogeneous Searh Costs José L. Moraga-González Zsolt Sándor Matthijs R. Wildenbeest First draft: July 2014 Revised: June 2015 Abstrat We study prie formation in a model of onsumer searh for
Pries and Heterogeneous Searh Costs José L. Moraga-González Zsolt Sándor Matthijs R. Wildenbeest First draft: July 2014 Revised: June 2015 Abstrat We study prie formation in a model of onsumer searh for
Asimple analytic method for transistor
 A Simple Analyti Method for ransistor Osillator Design his straightforward mathematial tehnique helps optimize osillator designs By Andrei Grennikov Institute of Miroeletronis, Singapore Asimple analyti
A Simple Analyti Method for ransistor Osillator Design his straightforward mathematial tehnique helps optimize osillator designs By Andrei Grennikov Institute of Miroeletronis, Singapore Asimple analyti
Dataflow Features in Computer Networks
 Magyar Kutatók 1. Nemzetközi Szimpóziuma 1 th International Symposium of Hungarian Researhers on Computational Intelligene and Informatis Gyula Max Budapest University of Tehnology and Eonomis, Department
Magyar Kutatók 1. Nemzetközi Szimpóziuma 1 th International Symposium of Hungarian Researhers on Computational Intelligene and Informatis Gyula Max Budapest University of Tehnology and Eonomis, Department
State of Maryland Participation Agreement for Pre-Tax and Roth Retirement Savings Accounts
 State of Maryland Partiipation Agreement for Pre-Tax and Roth Retirement Savings Aounts DC-4531 (08/2015) For help, please all 1-800-966-6355 www.marylandd.om 1 Things to Remember Complete all of the setions
State of Maryland Partiipation Agreement for Pre-Tax and Roth Retirement Savings Aounts DC-4531 (08/2015) For help, please all 1-800-966-6355 www.marylandd.om 1 Things to Remember Complete all of the setions
To the Graduate Council:
 o the Graduate Counil: I am submitting herewith a dissertation written by Yan Xu entitled A Generalized Instantaneous Nonative Power heory for Parallel Nonative Power Compensation. I have examined the
o the Graduate Counil: I am submitting herewith a dissertation written by Yan Xu entitled A Generalized Instantaneous Nonative Power heory for Parallel Nonative Power Compensation. I have examined the
On the Notion of the Measure of Inertia in the Special Relativity Theory
 www.senet.org/apr Applied Physis Researh Vol. 4, No. ; 1 On the Notion of the Measure of Inertia in the Speial Relativity Theory Sergey A. Vasiliev 1 1 Sientifi Researh Institute of Exploration Geophysis
www.senet.org/apr Applied Physis Researh Vol. 4, No. ; 1 On the Notion of the Measure of Inertia in the Speial Relativity Theory Sergey A. Vasiliev 1 1 Sientifi Researh Institute of Exploration Geophysis
A Static Friction Model for Elastic-Plastic Contacting Rough Surfaces
 Lior Kogut 1 Mem. ASME e-mail: mekogut@tx.tehnion.a.il Izhak Etsion Fellow ASME e-mail: etsion@tx.tehnion.a.il Dept. of Mehanial Engineering, Tehnion, Haifa 32000, Israel A Stati Frition Model for Elasti-Plasti
Lior Kogut 1 Mem. ASME e-mail: mekogut@tx.tehnion.a.il Izhak Etsion Fellow ASME e-mail: etsion@tx.tehnion.a.il Dept. of Mehanial Engineering, Tehnion, Haifa 32000, Israel A Stati Frition Model for Elasti-Plasti
The analysis of brushing tool characteristics
 ARCHIVES OF CIVIL AND MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Vol. IV 004 No. 4 The analysis of rushing tool harateristis Kiele University of Tehnology, al. Tysiąleia P. P. 7, 5-34 Kiele In this paper, an analytial proedure
ARCHIVES OF CIVIL AND MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Vol. IV 004 No. 4 The analysis of rushing tool harateristis Kiele University of Tehnology, al. Tysiąleia P. P. 7, 5-34 Kiele In this paper, an analytial proedure
Findings and Recommendations
 Contrating Methods and Administration Findings and Reommendations Finding 9-1 ESD did not utilize a formal written pre-qualifiations proess for seleting experiened design onsultants. ESD hose onsultants
Contrating Methods and Administration Findings and Reommendations Finding 9-1 ESD did not utilize a formal written pre-qualifiations proess for seleting experiened design onsultants. ESD hose onsultants
FIRE DETECTION USING AUTONOMOUS AERIAL VEHICLES WITH INFRARED AND VISUAL CAMERAS. J. Ramiro Martínez-de Dios, Luis Merino and Aníbal Ollero
 FE DETECTION USING AUTONOMOUS AERIAL VEHICLES WITH INFRARED AND VISUAL CAMERAS. J. Ramiro Martínez-de Dios, Luis Merino and Aníbal Ollero Robotis, Computer Vision and Intelligent Control Group. University
FE DETECTION USING AUTONOMOUS AERIAL VEHICLES WITH INFRARED AND VISUAL CAMERAS. J. Ramiro Martínez-de Dios, Luis Merino and Aníbal Ollero Robotis, Computer Vision and Intelligent Control Group. University
Physical and mathematical postulates behind relativity
 Physial and mathematial postulates behind relativity Tuomo Suntola Physis Foundations Soiety, Finland, www.physisfoundations.org In this presentation we look for answers to questions: What was the problem
Physial and mathematial postulates behind relativity Tuomo Suntola Physis Foundations Soiety, Finland, www.physisfoundations.org In this presentation we look for answers to questions: What was the problem
BEARING CAPACITY OF SOIL
 BEARING CAPACITY OF SOIL Dr. S. K. Prasad Professor of Civil Engineering S. J. College of Engineering, Mysore 7.0 Syllabus. Definition of ultimate, net and safe bearing apaities, Allowable bearing pressure
BEARING CAPACITY OF SOIL Dr. S. K. Prasad Professor of Civil Engineering S. J. College of Engineering, Mysore 7.0 Syllabus. Definition of ultimate, net and safe bearing apaities, Allowable bearing pressure
Big Data Analysis and Reporting with Decision Tree Induction
 Big Data Analysis and Reporting with Deision Tree Indution PETRA PERNER Institute of Computer Vision and Applied Computer Sienes, IBaI Postbox 30 11 14, 04251 Leipzig GERMANY pperner@ibai-institut.de,
Big Data Analysis and Reporting with Deision Tree Indution PETRA PERNER Institute of Computer Vision and Applied Computer Sienes, IBaI Postbox 30 11 14, 04251 Leipzig GERMANY pperner@ibai-institut.de,
The Reduced van der Waals Equation of State
 The Redued van der Waals Equation of State The van der Waals equation of state is na + ( V nb) n (1) V where n is the mole number, a and b are onstants harateristi of a artiular gas, and R the gas onstant
The Redued van der Waals Equation of State The van der Waals equation of state is na + ( V nb) n (1) V where n is the mole number, a and b are onstants harateristi of a artiular gas, and R the gas onstant
Improved Vehicle Classification in Long Traffic Video by Cooperating Tracker and Classifier Modules
 Improved Vehile Classifiation in Long Traffi Video by Cooperating Traker and Classifier Modules Brendan Morris and Mohan Trivedi University of California, San Diego San Diego, CA 92093 {b1morris, trivedi}@usd.edu
Improved Vehile Classifiation in Long Traffi Video by Cooperating Traker and Classifier Modules Brendan Morris and Mohan Trivedi University of California, San Diego San Diego, CA 92093 {b1morris, trivedi}@usd.edu
protection p1ann1ng report
 ( f1re protetion p1ann1ng report I BUILDING CONSTRUCTION INFORMATION FROM THE CONCRETE AND MASONRY INDUSTRIES NO. 15 OF A SERIES A Comparison of Insurane and Constrution Costs for Low-Rise Multifamily
( f1re protetion p1ann1ng report I BUILDING CONSTRUCTION INFORMATION FROM THE CONCRETE AND MASONRY INDUSTRIES NO. 15 OF A SERIES A Comparison of Insurane and Constrution Costs for Low-Rise Multifamily
Suggested Answers, Problem Set 5 Health Economics
 Suggested Answers, Problem Set 5 Health Eonomis Bill Evans Spring 2013 1. The graph is at the end of the handout. Fluoridated water strengthens teeth and redues inidene of avities. As a result, at all
Suggested Answers, Problem Set 5 Health Eonomis Bill Evans Spring 2013 1. The graph is at the end of the handout. Fluoridated water strengthens teeth and redues inidene of avities. As a result, at all
Open and Extensible Business Process Simulator
 UNIVERSITY OF TARTU FACULTY OF MATHEMATICS AND COMPUTER SCIENCE Institute of Computer Siene Karl Blum Open and Extensible Business Proess Simulator Master Thesis (30 EAP) Supervisors: Luiano Garía-Bañuelos,
UNIVERSITY OF TARTU FACULTY OF MATHEMATICS AND COMPUTER SCIENCE Institute of Computer Siene Karl Blum Open and Extensible Business Proess Simulator Master Thesis (30 EAP) Supervisors: Luiano Garía-Bañuelos,
Draft Notes ME 608 Numerical Methods in Heat, Mass, and Momentum Transfer
 Draft Notes ME 608 Numerial Methods in Heat, Mass, and Momentum Transfer Instrutor: Jayathi Y. Murthy Shool of Mehanial Engineering Purdue University Spring 2002 1998 J.Y. Murthy and S.R. Mathur. All Rights
Draft Notes ME 608 Numerial Methods in Heat, Mass, and Momentum Transfer Instrutor: Jayathi Y. Murthy Shool of Mehanial Engineering Purdue University Spring 2002 1998 J.Y. Murthy and S.R. Mathur. All Rights
Tax-loss Selling and the Turn-of-the-Year Effect: New Evidence from Norway 1
 Tax-loss Selling and the Turn-of-the-Year Effet: New Evidene from Norway 1 Qinglei Dai Universidade Nova de Lisboa September 2005 1 Aknowledgement: I would like to thank Kristian Rydqvist at Binghamton
Tax-loss Selling and the Turn-of-the-Year Effet: New Evidene from Norway 1 Qinglei Dai Universidade Nova de Lisboa September 2005 1 Aknowledgement: I would like to thank Kristian Rydqvist at Binghamton
From the Invisible Handshake to the Invisible Hand? How Import Competition Changes the Employment Relationship
 From the Invisible Handshake to the Invisible Hand? How Import Competition Changes the Employment Relationship Marianne Bertrand, University of Chiago, Center for Eonomi Poliy Researh, and National Bureau
From the Invisible Handshake to the Invisible Hand? How Import Competition Changes the Employment Relationship Marianne Bertrand, University of Chiago, Center for Eonomi Poliy Researh, and National Bureau
Lemon Signaling in Cross-Listings Michal Barzuza*
 Lemon Signaling in Cross-Listings Mihal Barzuza* This paper analyzes the deision to ross-list by managers and ontrolling shareholders assuming that they have private information with respet to the amount
Lemon Signaling in Cross-Listings Mihal Barzuza* This paper analyzes the deision to ross-list by managers and ontrolling shareholders assuming that they have private information with respet to the amount
DSP-I DSP-I DSP-I DSP-I
 DSP-I DSP-I DSP-I DSP-I Digital Signal Proessing I (8-79) Fall Semester, 005 IIR FILER DESIG EXAMPLE hese notes summarize the design proedure for IIR filters as disussed in lass on ovember. Introdution:
DSP-I DSP-I DSP-I DSP-I Digital Signal Proessing I (8-79) Fall Semester, 005 IIR FILER DESIG EXAMPLE hese notes summarize the design proedure for IIR filters as disussed in lass on ovember. Introdution:
Recent Progress in Brillouin Scattering Based Fiber Sensors
 Sensors 011, 11, 415-4187; doi:10.3390/s11040415 OPEN ACCESS sensors ISSN 144-80 www.mdpi.om/journal/sensors Review Reent Progress in rillouin Sattering ased Fiber Sensors Xiaoyi ao * and Liang Chen Physis
Sensors 011, 11, 415-4187; doi:10.3390/s11040415 OPEN ACCESS sensors ISSN 144-80 www.mdpi.om/journal/sensors Review Reent Progress in rillouin Sattering ased Fiber Sensors Xiaoyi ao * and Liang Chen Physis
