Contents QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR POWER. Introduction. Qualifications Pack- Power Plant High Pressure Welder
|
|
|
- Marlene Tyler
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR POWER Contents 1. Introduction and Contacts Qualifications Pack OS Units Glossary of Key Terms.3 OS describe what individuals need to do, know and understand in order to carry out a particular job role or function OS are performance standards that individuals must achieve when carrying out functions in the workplace, together with specifications of the underpinning knowledge and understanding Power Sector Skill Council 2 nd Floor, CBIP Building, Malcha Marg, Chanakyapuri, New Delhi - pssc@cbip.org 5. Annexure: Nomenclature for QP & OS..57 Qualifications Pack- Power Plant High Pressure Welder SECTOR: POWER SUB-SECTOR: Generation OCCUPATION: Welding and Cutting REFERENCE ID: PSS / Q 0401 ALIGNED TO: NCO-2004/NIL Introduction Power Plant High Pressure Welders are responsible for welding of ferrous and nonferrous pressure products such as structures, frames, plate and sheet assemblies, pipework and vessels used for producing pressure vessels, boilers and high pressure pipework, as per given specifications. The welding will comply with very high quality standards. Brief Job Description: The welder will use different welding methods like Tungsten Inert gas welding, Manual metal arc welding, submerged arc welding, stud welding as well as Oxy-fuel gas cutting in all positions; apply welding principles to plan the weld; mark out the material; prepare and perform the weld that can clear various tests such as visual examination, tension tests, guided-bend tests, notch-toughness tests, studweld tests, micro tests radiographic or ultrasonic examination, liquid penetrant. Personal Attributes: Physically and mentally able to safely perform essential functions of the job. The candidate should be able to climb ladders, scaffolds, poles and towers of various heights. Also able to crawl and work in confined spaces such as attics, manholes and crawlspaces.the candidate should be able to read and understand instructions and warnings.
2 Qualifications Pack For Power Plant High Pressure Welder Job Details Qualifications Pack Code PSS / Q 0401 Job Role Power Plant High Pressure Welder Credits (NSQF) TBD Version number 1.0 Sector Power Drafted on 26/03/15 Sub-sector Generation Last reviewed on 26/03/15 Occupation Welding and Cutting Next review date 26/03/17 Job Role Power Plant High Pressure Welder Role Description NSQF level Minimum Educational Qualifications Maximum Educational Qualifications Training (Suggested but not mandatory) Experience Applicable National Occupational Standards (NOS) Performance Criteria Power Plant High Pressure Welders are responsible for welding of ferrous and non-ferrous pressure products such as structures, frames, plate and sheet assemblies, pipe-work and vessels used for producing pressure vessels, boilers and high pressure pipework, as per given specifications th NA ITI or Certificate in Basic MMAW, Gas cutting, Plasma arc cutting 1 year as MMAW, TIG or MIG welder Compulsory: 1. PSS/ N 0401 (Perform welding on pressure vessels, boilers and high pressure equipment in a power plant) 2. CSC/ N 0208 (Manually weld carbon steel/ low alloy steel and austenitic stainless steel using Metal Arc Welding / Shielded Metal Arc Welding ) 3. CSC/ N 0212 (Perform basic manual Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) Welding also known as Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW) welding) 4. CSC/ N 0210 (Weld stud joints using stud welding equipment/machines ) 5. PSS/ N 2001 (Use basic health and safety practices for power related work) 6. CSC/ N 1336 (Work effectively with others) Optional: N.A. As described in the relevant OS units 2
3 Qualifications Pack For Power Plant High Pressure Welder Definitions Keywords /Terms Core Skills/Generic Skills Function Job role Knowledge and Understanding National Occupational Standards (NOS) Occupation Organisational Context Performance Criteria Qualifications Pack(QP) Qualifications Pack Code Scope Sector Sub-Sector Sub-functions Technical Knowledge Unit Code Unit Title Vertical Description Core Skills or Generic Skills are a group of skills that are key to learning and working in today's world. These skills are typically needed in any work environment. In the context of the NOS, these include communication related skills that are applicable to most job roles. Function is an activity necessary for achieving the key purpose of the sector, occupation, or area of work, which can be carried out by a person or a group of persons. Functions are identified through functional analysis and form the basis of NOS. Job role defines a unique set of functions that together form a unique employment opportunity in an organization. Knowledge and Understanding are statements which together specify the technical, generic, professional and organizational specific knowledge that an individual needs in order to perform to the required standard. NOS are Occupational Standards which apply uniquely in the Indian context Occupation is a set of job roles, which perform similar/related set of functions in an industry. Organisational Context includes the way the organization is structured and how it operates, including the extent of operative knowledge managers have of their relevant areas of responsibility. Performance Criteria are statements that together specify the standard of performance required when carrying out a task. Qualifications Pack comprises the set of NOS, together with the educational, training and other criteria required to perform a job role. A Qualifications Pack is assigned a unique qualification pack code. Qualifications Pack Code is a unique reference code that identifies a qualifications pack. Scope is the set of statements specifying the range of variables that an individual may have to deal with in carrying out the function which have a critical impact on the quality of performance required. Sector is a conglomeration of different business operations having similar businesses and interests. It may also be defined as a distinct subset of the economy whose components share similar characteristics and interests. Sub-sector is derived from a further breakdown based on the characteristics and interests of its components. Sub-functions are sub-activities essential to fulfil the achieving the objectives of the function. Technical Knowledge is the specific knowledge needed to accomplish specific designated responsibilities. Unit Code is a unique identifier for a NOS unit, which can be denoted with an N Unit Title gives a clear overall statement about what the incumbent should be able to do Vertical may exist within a sub-sector representing different domain areas or the client industries served by the industry. 3
4 Qualifications Pack For Power Plant High Pressure Welder Acronyms Keywords /Terms MIG GMAW WPS NDT DT RT UT DPT MPT FPT IS EN ASME ISO MIG D.C. STT PQR CO2 CPR PPE Description Metal Inert Gas Welding Gas Metal Arc Welding Welding Procedure Speciation Non-Destructive Testing Destructive Testing Radiographic Testing Ultrasonic Testing Dye Penetrant Testing Magnetic Particle Testing Fluorescent Penetrant Testing Indian Standards European Standards American Society of Mechanical Engineers International Organization for Standardization Metal Inert Gas Welding Direct Current Surface Tension Transfer Process Qualification Record Carbon dioxide Cardiac Pulmonary Resuscitation Personal Protective Equipment 4
5 PSS/ N 0401: Perform welding for pressure vessels, boilers and high pressure pipes in power plants Overview This unit covers welding of ferrous and non-ferrous pressure products such as structures, frames, plate and sheet assemblies, pipe-work and vessels used for producing pressure vessels, boilers and high pressure pipework, as per given specifications. 5 P age
6 National Occupational Standard PSS/ N 0401: Perform welding for pressure vessels, boilers and high pressure pipes in power plants Unit Code PSS/ N 0401 Unit Title (Task) Description Scope Perform welding for pressure vessels, boilers and high pressure pipes in power plants This unit covers welding of ferrous and non-ferrous pressure products such as structures, frames, plate and sheet assemblies, pipe-work and vessels used for producing pressure vessels, boilers and high pressure pipework, as per given specifications. The candidate will be expected to use different welding methods like Tungsten Inert gas welding, Manual metal arc welding, submerged arc welding, stud welding as well as Oxy-fuel gas cutting in the following positions and comply with very high quality standards. Groove Welds (Plate positions: 1G,2G,3G,4G; Pipe Positions : 1G,2G,3G,4G,5G,6G) Fillet Welds(Plate position:1f,2f,3f,4f; Pipe Positions: 1F,2F,2FR,4F,5F) The candidate will apply welding principles to plan the weld, use appropriate tools and equipment to mark out the material for the features to be produced, prepare and perform the weld that can clear various tests such as visual examination, tension tests, guided-bend tests, notch-toughness tests, stud-weld tests, micro tests radiographic or ultrasonic examination, liquid penetrant, while coordinating with the fitters and other team members adhering to applicable regulations and safety standards. The candidate will work independently, whilst taking responsibility for their own actions as well as for the team outcomes in terms of productivity, quality and accuracy of the work being carried out. This unit/task covers the following: Work safely Plan and prepare for the welding operations Mark out the components Perform welding operations Performance Criteria(PC) w.r.t. the Scope Element Work safely Plan and Prepare for welding Performance Criteria The user/individual on the job should be able to: PC1. comply with health and safety, environmental and other relevant regulations and guidelines at work PC2. adhere to procedures and guidelines for personal protective equipment (PPE) and other relevant safety regulations while performing broaching operations PC3. ensure work area is clean and safe from hazards Hazards: use of power tools, trailing leads or hoses, damaged or badly maintained tools and equipment; using files with damaged or poor fitting handles; handling of chemicals like fluxes, oil, grease; misuses of tools; not following laid-down procedures, handling long pipe lengths, using damaged or badly maintained tools and equipment, working at heights, working in windy and moist environments, etc. PC4. ensure that all tools, equipment, power sources, power tool cables, extension leads are in a safe and usable condition PC5. ensure that all machines and machine tools are secured at all times The user/individual on the job should be able to: PC6. determine job requirement from job specification documents or WPS obtained from 6 P age
7 PSS/ N 0401: power plants operations Mark out the components Perform welding for pressure vessels, boilers and high pressure pipes in PC7. PC8. PC9. valid sources Job requirements: raw materials or components required (type, quality, quantity); dimensions; limits and tolerances; surface texture requirements; operations required (list, sequence and procedures where applicable); shape or profiles to be fabricated; cutting, bending and rolling allowances for fabricated forms; instruments and tools to be used; interdependencies; timelines Job specification documents: detailed component drawings; approved sketches/illustrations; national, international and organisational standards; reference tables and charts; fabrication/casting drawings Valid source: job instruction sheet/job card; work drawings and instructions; planning documentation; quality control documents; operation sheets; process specifications; instructions from supervisor recognize physically, the different equipment installed within the plant premises and identify function of the individual equipment interpret weld procedure data sheets specifications Interpreting the WPS: welding process (ISO Codes); parent metal; consumables; pre welding joint preparation (cleaning, edge preparation, assembly, pre-heat); welding parameters; welding positions; number and arrangement of runs to fully fill/weld joints; electrode (W); filler wire; electrical conditions required (type of current, alternating [A.C.] direct [D.C.], electrode polarity (negative), welding current ranges; methods of arc ignition (scratch, high frequency, lift start); shielding gas (type, flow rate, pre-weld gas flow, post-weld gas flow); techniques (including autogenous); control of heat input; interpass/run cleaning/back gouging methods; root pass with back purging of gases on the root side of the welding; post welding activities (wiring brushing, removal of excess weld metal where required); post-weld heat treatment (normalising, stress relief) select welding machines e.g. transformer, inverters (AC/DC), rectifiers and generators, according to the materials and task PC10. identify and evaluate properties and limitations of various thermal welding and mechanical jointing systems for the job PC11. establish the type of welding to be done and procedures to complete the pipe fitting or assembling operations PC12. perform trail weld and confirm that specifications are achieved by selected welding procedure PC13. plan the sequence of activities and resources required PC14. identify and obtain materials or components to be welded and the applicable parent metal group in accordance with applicable data PC15. identify and obtain welding equipment as per the weld type established PC16. inspect the equipment for serviceability and correctly set up in accordance with standard operating procedures PC17. prepare the material for welding Preparation of materials: e.g. preheating; setting up of jigs, fixtures, clamps, etc.; joint preparation such as beveling, hard facing, etc. The user/individual on the job should be able to: PC18. prepare/determine suitable datums from which to mark out (e.g. choosing a machine face or filing a flat face as a datum) PC19. apply a marking medium to enhance clarity of the marking out 7 P age
8 PSS/ N 0401: power plants Perform welding operations Knowledge and Understanding (K) A. Organizational Context (Knowledge of the company / organization and its processes) Perform welding for pressure vessels, boilers and high pressure pipes in PC20. use an appropriate method of marking out Marking out methods: e.g. direct marking using tapes and markers, set-outs of pipework using templates, producing set wires, set-outs of pipework onto floor PC21. use a range of marking out equipment (e.g. rules, squares, scribers, vernier instruments) Marking tools: rules/tapes, dividers/trammels, scribers, punches, scribing blocks, squares, protractor, permanent markers PC22. mark out a range of features required to perform the welding Features: datum lines; welding or cutting guidelines The user/individual on the job should be able to: PC23. perform various types of welding of cutting as per requirements Types of Welding: TIG welding, MMAW welding, stud welding, oxy-fuel gas cutting, plasma arc cutting(manual) PC24. produce joints from various materials in different forms Materials: carbon steel, low alloy steel, high alloy steel, stainless steel and aluminium Forms: structures, frames, plates and sheet assemblies, pipe-work and vessels PC25. perform groove and fillet weld in various positions Groove Welds: Plate positions (1G,2G,3G,4G); Pipe Positions (1G,2G,3G,4G,5G,6G) Fillet Welds: Plate position (1F,2F,3F,4F); Pipe Positions (1F,2F,2FR,4F,5F) PC26. ensure welds are deposited correctly as per specifications. PC27. select and apply appropriate distortion prevention measures for the weld type and material to ensure that distortions are rectified as required Distortion prevention measures: e.g. preheating, setting up of jigs, fixtures, clamps, etc. PC28. achieve joint quality, tolerances and acceptance levels that clears the following tests as laid out in ASME Pressure Vessel Code Sections I XI, BS EN ISO5817 Tests: Visual examination, Tension Tests, Guided-Bend Tests, Notch-Toughness Tests, Stud-Weld Tests, Radiographic or ultrasonic examination, Liquid Penetrant PC29. co-ordinate with the fitter while performing the weld PC30. prepare the welded assembly and welded surface for quality tests to be conducted PC31. shut down and make safe the welding equipment on completion of the welding activities PC32. make sure that the work area is maintained and left in a safe and tidy condition The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand: KA1. legislation, standards, policies, and procedures followed in the company relevant to own employment and performance conditions KA2. relevant health and safety requirements applicable in the work place KA3. Layout of a power plant and the various functions KA4. importance of working in clean and safe environment KA5. own job role and responsibilities and sources for information pertaining to employment terms, entitlements, job role and responsibilities KA6. reporting structure, inter-dependent functions, lines and procedures in the work area KA7. relevant people and their responsibilities within the work area KA8. escalation matrix and procedures for reporting work and employment related issues 8 P age
9 PSS/ N 0401: power plants B. Technical Knowledge Perform welding for pressure vessels, boilers and high pressure pipes in KA9. documentation and related procedures applicable in the context of employment and work KA10. importance and purpose of documentation in context of employment and work KA11. service request procedures, tools, and techniques KA12. company policy on repair/replacement of components during the maintenance process KA13. organizational procedure(s) to be adopted for the safe disposal of waste of all types of materials The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand: KB1. the hazards associated with the pressure products welding activities and precautions that can be taken to minimize the risk Safety precautions: protection from live and other electrical components, including insulation, proper earthing, etc.; proper handling and placement of hot metal(adequate ventilation, fume extraction, away from naked flames, avoiding skin contact); taking account of spatter and related safe distance; adequate lighting; appropriate personal protective equipment- suitable aprons, welding gloves, respirators, safety boots, correctly fitting overalls, suitable eye shields/goggles, hard hat/helmet; protection of self and others from the effects of the welding arc; fume extraction/control measures; safety measures for elevated and windy areas (eg. harness, etc.) KB2. effects of exposure to the electric arc KB3. types of fire extinguishers and their suitable uses KB4. effects of exposure to welding fume KB5. methods of managing welding fume hazards KB6. personal protective equipment (PPE) and clothing to be worn during welding KB7. Personal protective equipment (PPE): suitable aprons, welding gloves, respirators, safety boots, correctly fitting overalls, suitable eye shields/goggles, hard hat/helmet KB8. precautions to be taken when using gas torches to form the joint, and the effect of KB9. overheating the joint Relevant information about the power plant Information: different flow cycles/ systems, e.g. Water Flow (ACW, CCW, DM water ) System, Fuel Flow (Coal/Gas/Fuel Oil) System, Steam and Condensate Flow System, Air & Flue Gas Flow and Ash Handling System etc.; function of above flow cycles/systems, involved in power generation; raw materials/ resources used (including Hazardous materials) in above flow cycles/systems and waste/byproducts generated (including Hazardous waste) during electric power generation; basic function, construction and capacity of major equipment of power plant KB10. various possible work environments for a pressure product welder Possible work environments: e.g. at heights, in confined spaces, engineering construction sites, inside a plant, fabrication workshops, nuclear sites, onshore and offshore installations, potential explosive atmospheres, shafts, tunnels, on access structures (scaffold), etc. KB11. some high pressure equipment and their applications Some high pressure equipment: e.g. boilers, pressure vessels, compressors, engines, heat exchangers, HVAC systems, pumps, protection devices, rotating equipment and tools, turbines, etc. KB12. range of pipe fittings that can be used, and how to identify them KB13. methods used to prepare pipe ends and fittings for welding, and why it is necessary 9 P age
10 PSS/ N 0401: power plants Perform welding for pressure vessels, boilers and high pressure pipes in to ensure that these preparations are carried out KB14. various types of pipe connectors and joints used in pressure products KB15. the importance of quality welding for high pressure products KB16. welding symbols used and their correct interpretation KB17. power plant terminology KB18. various types of welding or thermal cutting used in pressure products, their respective equipment and uses Types of Welding: TIG welding, MIG/MAG welding, MMAW welding, flux cored welding, submerged arc welding, stud welding, oxy-fuel gas cutting, plasma arc cutting(manual and machine) KB19. various materials that need to be welded for pressure products and the relevant characteristics and identification Materials: carbon steel, low alloy steel, high alloy steel, stainless steel and aluminium KB20. type and thickness of base metals to be welded KB21. common use of carbon steel, stainless steel, mild steel, copper, bronze and aluminum in power plant KB22. ways in which a metal can fail KB23. how to conduct a spark test KB24. density, speed & velocity, acceleration, torque, flow and their relevance to welding and welding principles KB25. types of joint configurations Joints: fillet and groove (lap joints, tee fillet joints, corner joints, butt joints- square, single vee, double vee) KB26. various positions such as flat, horizontal, vertical and overhead Groove Welds: Plate positions (1G,2G,3G,4G); Pipe Positions (1G,2G,3G,4G,5G,6G) Fillet Welds: Plate position (1F,2F,3F,4F); Pipe Positions (1F,2F,2FR,4F,5F) KB27. main components and controls of welding equipment KB28. how to connect electrical components correctly KB29. type of current used and implication KB30. preparation of materials in readiness for the marking out activities, in order to enhance clarity, accuracy and safety KB31. how to prepare the pressure components and pipes in readiness for the marking out activities Preparation: e.g. visually checking for defects, cleaning the materials, removing burrs and sharp edges, pre-heating, hard facing, etc. KB32. selection and establishment of a suitable datum KB33. importance of ensuring that marking out is undertaken from the selected datum KB34. possible effects of working from an incorrect datum KB35. mark-out conventions when marking out the workpiece KB36. uses of various methods of deposition of welds and their relevant characteristics KB37. need for distortion prevention measures and their applicability as per weld type and material Distortion prevention measures: e.g. preheating, setting up of jigs, fixtures, clamps, etc. KB38. various defects associated with high pressure welding process Weld defects: lack of continuity of the weld; uneven and irregular ripple formation; excessive spatter; incorrect weld size or profile; burn through; undercutting; overlap; 10 P age
11 PSS/ N 0401: power plants Skills (S) [Optional] A. Core Skills/ Generic Skills Perform welding for pressure vessels, boilers and high pressure pipes in inclusions; distortion; porosity; internal cracks; surface cracks; lack of fusion or incomplete fusion; lack of penetration; excessive penetration; gouges; stray arc strikes; sharp edges; excessive convexity KB39. importance of maintaining welding standards specified for the job KB40. impact of a welding job done right, acceptable or non-acceptable KB41. how to determine the overall length of the pipework required, taking into account allowances for pipe fittings and (where appropriate) screwed connections KB42. achieve joint quality, tolerances and acceptance levels that clears the following tests as laid out in ASME Pressure Vessel Code Sections I XI, BS EN 287 ISO5817 Tests: visual examination, tension tests, guided-bend tests, notch-toughness tests, stud-weld tests, radiographic or ultrasonic examination, liquid penetrant, micro testing KB43. various codes applicable to welding of pressure products - ISO ASME EN & BS KB44. how to prepare the welded assembly and welded surface for quality tests to be conducted KB45. how to check the workpiece and the measuring equipment that is used Measuring equipment: external micrometers, vernier/digital/dial caliper, surface finish equipment (e.g. comparison plates, machines), rules, squares, protractors, depth micrometers, depth verniers, feeler gauges, bore/hole gauges, slip gauges, radius/profile gauges, thread gauges, height gauge, hardness tester, dial test indicators (DTI), surface roughness tester, coordinate measuring machine (CMM), profile projectors, form testers KB46. need to check that the measuring equipment is within current calibration dates, and that the instruments are correctly zeroed KB47. measuring internal and external dimensions KB48. measuring geometric features KB49. types of visual inspection indicators and methods Visual inspections: e.g. use of visual techniques, distance from workpiece, angle of observation, adequate lighting, low powered magnification, fillet weld gauges, etc. KB50. types of NDT and DT inspection methods KB51. procedure to conduct DP testing KB52. importance of shutting down and making safe the welding equipment on completion of the welding activities KB53. importance of keeping the work area in a safe and tidy condition Communication The user/ individual on the job needs to know and understand how to: SA1. read and interpret information correctly from various job specification documents, manuals, health and safety instructions, memos, etc. applicable to the job in English and/or local language SA2. fill up appropriate technical forms, process charts, activity logs as per organizational format in English and/or local language SA3. convey and share technical information clearly using appropriate language SA4. check and clarify task-related information SA5. liaise with appropriate authorities using correct protocol SA6. communicate with people in respectful form and manner in line with organizational protocol 11 P age
12 PSS/ N 0401: power plants B. Professional Skills Perform welding for pressure vessels, boilers and high pressure pipes in Numerical and computational skills The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to: SA7. undertake numerical operations, and calculations/ formulae Numerical computations: addition(with decimal digits and with carrying), subtraction(with decimal digits and with borrowing), multiplication(with decimal digits), division(with decimal digit), fractions and decimals, percentages and proportions, simple ratios and averages SA8. identify and draw various basic, compound and solid shapes as per dimensions given Basic shapes: square, rectangle, triangle, circle Compound shapes: involving squares, rectangles, triangles, circles, semi-circles, quadrants of a circle Solid shapes: cube, rectangular prism, cylinder SA9. demonstrate measurement and calculation of Angle, Perimeter, Area of a common geometrical shape and can co-relate with job area requirements SA10. use appropriate measuring techniques and units of measurement SA11. use British and metric system of measurement and make conversions between them SA12. describe the difference between Celsius & Fahrenheit Scale and relationship between them SA13. use appropriate units and number systems to express degree of accuracy Units and number systems representing degree of accuracy: decimals places, significant figures, fractions as a decimal quantity SA14. interpret and express tolerance in terms of limits on dimensions SA15. calculation of the value of angles in a triangle using trigonometry Angles in a triangle: right-angled, isosceles, equilateral Learning The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to: SA16. participate in on-the-job and other learning, training and development interventions and assessments SA17. clarify task related information with appropriate personnel or technical adviser SA18. seek to improve and modify own work practices SA19. maintain current knowledge of application standards, legislation, codes of practice and product/process developments Problem Solving The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to: SB1. identify problems with work planning, procedures, output and behavior and their implications SB2. prioritize and plan for problem solving SB3. communicate problems appropriately to others SB4. identify sources of information and support for problem solving SB5. seek assistance and support from other sources to solve problems SB6. identify effective resolution techniques SB7. select and apply resolution techniques SB8. seek evidence for problem resolution Plan and Organize The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to: SB9. plan, prioritize and sequence work operations as per job requirements 12 P age
13 PSS/ N 0401: power plants Perform welding for pressure vessels, boilers and high pressure pipes in SB10. organize and analyze information relevant to work SB11. basic concepts of shop-floor work productivity including waste reduction, efficient material usage and optimization of time Initiative and Enterprise The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to: SB12. undertake and express new ideas and initiatives to others SB13. modify work plan to overcome unforeseen difficulties or developments that occur as work progresses SB14. participate in improvement procedures including process, quality and internal/external customer/supplier relationships SB15. one s competencies in new and different situations and contexts to achieve more Self-Management The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to: SB16. exercise restraint while expressing dissent and during conflict situations SB17. avoid and manage distractions to be disciplined at work SB18. manage own time for achieving better results Teamwork The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to: SB19. work in a team in order to achieve better results SB20. identify and clarify work roles within a team SB21. communicate and cooperate with others in the team for better results SB22. seek assistance from fellow team members 13 P age
14 PSS/ N 0401: power plants Perform welding for pressure vessels, boilers and high pressure pipes in NOS Version Control NOS Code CSC/ N 0401 Credits (NSQF) TBD Version number 1.0 Industry Power Sector Drafted on 26/03/15 Industry Sub-sector Power Generation Last reviewed on 26/03/15 Next review date 26/03/17 14 P age
15 CSC/ N 0208: Manually weld carbon steel/ low alloy steel and austenitic stainless steel using Metal Arc Welding / Shielded Metal Arc Welding Overview This unit covers the performing of manual metal arc welding (MMAW) also known as shielded metal arc welding (SMAW) for producing a range of joints on various forms of metal and metal alloys including mild or low carbon steels and austenitic stainless steel as per welding specification procedures (WPS). 15 P age
16 CSC/ N 0208: Manually weld carbon steel/ low alloy steel and austenitic stainless steel using Metal Arc Welding / Shielded Metal Arc Welding National Occupational Standard Unit Code CSC/ N 0208 Unit Title (Task) Description Scope Manually weld carbon steel/ low alloy steel and austenitic stainless steel using Metal Arc Welding / Shielded Metal Arc Welding This OS unit is about performing manual metal arc welding (MMAW) welding also known as Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW) for a range of standard welding job requirements. This is for a skilled welder who can weld different materials (mild or low carbon steel and austenitic stainless steel) in 1G/1F, 2G/2F, 3G/3F, 4G/4F, 5G/5F and 6G positions. The welder can prepare various joints including various groove and fillet welds. The welder carries out these operations in a safe manner following practices that ensure safety for self, others and the work environment. This unit/task covers the following: Working safely Preparing for welding operations Carrying out welding operations Testing for quality Post-welding activities Dealing with contingencies Performance Criteria(PC) w.r.t. the Scope Element Working Safely Performance Criteria The user/individual on the job should be able to: PC1. work safely at all times, complying with health and safety legislation, regulations and other relevant guidelines PC2. adhere to procedures or systems in place for health and safety, personal protective equipment (PPE) and other relevant safety regulations Safety precautions (general): general workshop safety; fire prevention; general hazards; manual lifting; overhead lifting; shopfloor housekeeping including surface conditions; waste disposal; stability of surrounding structures, furniture etc. PC3. check the condition of, and correctly connect, welding leads, earthing arrangements and electrode holder PC4. deal with any faults or differential as per laid procedures PC5. follow fume extraction safety procedures Preparing for welding operations The user/individual on the job should be able to: PC6. read and interpret routine information on written job instructions, welding procedure specifications (WPS) and standard operating procedures WPS: e.g. welding process (ISO codes); parent metal; consumables; pre welding joint preparation (edge preparation, assembly, pre-heat); welding parameters; welding positions (ISO 6947 PA, PB, PC, PD, PE, PF, PG; ASME IX I-6 G/1-6 F); number and arrangement of runs to fully fill/weld joints; electrode sizes for joint thicknesses; electrode and covering; electrical 16 P age
17 CSC/ N 0208: Manually weld carbon steel/ low alloy steel and austenitic stainless steel using Metal Arc Welding / Shielded Metal Arc Welding conditions required (type of current, alternating [A.C.] direct [D.C.], electrode polarity (positive or negative), welding current ranges); welding techniques; sequence of welding; control of heat input; interpass/run cleaning/back gouging methods; post welding activities (wire brushing and grinding, removal of excess weld metal where required); post-weld heat treatment (normalising, stress relief), etc. PC7. select welding machines (e.g. transformers, rectifiers, inverters and generators, etc.) according to the task PC8. select type and size of electrodes according to classification and specifications PC9. re-dry electrodes as per electrode classification requirement PC10. prepare the work area for the welding activities PC11. perform measurements for joint preparation and routine MMAW PC12. prepare the materials and joint in readiness for welding Material and joint preparation: made rust free; cleaned free from scaling, paint, oil/grease; made dry and free from moisture; edges to be welded prepared as per job requirement - such as flat, square or bevelled; use various machines and techniques for the above (e.g. chamfering machine, grinding and stripping, gas or plasma cutting, etc.); correctly positioned- positioning: devices and techniques; jigs and fixtures; restraining devices such as clamps and weights/blocks; setting up the joint in the correct position and alignment PC13. tack weld the joint at appropriate intervals, and check the joint for accuracy before final welding PC14. use manual metal-arc welding and related equipment to include a. alternating current (AC) equipment b. direct current (DC) equipment MMAW equipment: e.g. transformers; rectifiers; generators; invertors; consumables electrodes, dyes; welding accessories - holders, cables and accessories; ancillary equipment - (power saw, angle, pedestal and straight grinders, tong tester, etc.); electrode drying oven, etc. PC15. connect equipment to power source PC16. connect cables, electrode holders, return leads and ground clamps to appropriate terminal PC17. set, read and adjust amperage controls PC18. verify set up by running test and appropriately handle weld specimen (scrap plate) Handling specimens: handling hot materials; using chemicals for cleaning and etching; using equipment to fracture welds 17 P age
18 CSC/ N 0208: Manually weld carbon steel/ low alloy steel and austenitic stainless steel using Metal Arc Welding / Shielded Metal Arc Welding Carrying out welding operations Testing for quality The user/individual on the job should be able to: PC19. strike and maintain a stable arc PC20. stop and properly re-start arc to avoid welding defects (scratch start, tapping techniques) PC21. manipulate electrode angle using various methods as per WPS PC22. maintain constant puddle by using appropriate travel speed PC23. remove slag in an appropriate manner (e.g. wire brush, hammer, etc.) PC24. weld the joint to the specified quality, dimensions and profile applicable to range of material from 1.5 mm 24 mm Materials: mild or low carbon steel, austenitic stainless, low alloy steel, Forms: plate, sheet (1.5mm), structural section, other forms (hollow tubes, sections, shapes, etc.) PC25. produce range of welded joints to within the mentioned standard using single or multi-run welds (as appropriate) Joints: fillet and groove PC26. produce joints of the required quality and of specified dimensional accuracy which achieve a weld quality equivalent to Level C of ISO 5817 Weld quality standards: required parameters for dimensional accuracy; weld finishes are built up to the full section of the weld; joins at stop/start positions merge smoothly; weld surface is: free from cracks, substantially free from porosity, free from any pronounced hump or crater, substantially free from shrinkage cavities, substantially free from trapped slag, substantially free from arcing or chipping marks; fillet welds are: equal in leg length, slightly convex in profile (where applicable), size of the fillet equivalent to the thickness of the material welded: weld contour is: of linear and of uniform profile; smooth and free from excessive undulations; regular and has an even ripple formation; welds are adequately fused, and there is minimal undercut, overlap and surface inclusions; tack welds are blended in to form part of the finished weld, without excessive hump; corner joints have minimal burn through to the underside of the joint or, where appropriate PC27. produce range of welded joints in various positions as per the WPS specified Positions: flat (PA) IG/1F, horizontal vertical (PB) 2F, horizontal (PC) 2G, vertical upwards (PF) 3F / 3G, vertical downwards (PG) 3F / 3G, 4G Plate (overhead) Plate to Pipe (Fixed) 5F, pipe welding 5G/5F and 6G PC28. shut down and make safe the welding equipment on completion of the welding activities The user/individual on the job should be able to: PC29. identify various weld defects, use appropriate methods and equipment to check the quality, and that all dimensional and geometrical aspects of the weld are to the specification Weld defects: lack of continuity of the weld; uneven and irregular ripple formation; excessive spatter; incorrect weld size or profile; burn through; undercutting; overlap; inclusions; distortion; porosity; internal cracks; surface cracks; lack of fusion or incomplete fusion; lack of penetration; excessive 18 P age
19 CSC/ N 0208: Manually weld carbon steel/ low alloy steel and austenitic stainless steel using Metal Arc Welding / Shielded Metal Arc Welding penetration; gouges; stray arc strikes; sharp edges; excessive convexity PC30. check that the welded joint conforms to the specification, by checking various quality parameters by visual inspection Quality parameters: dimensional accuracy; alignment/squareness; size and profile of weld; visual defects; NDT/DT tested defects Visual inspections: e.g. use of visual techniques, distance from workpiece, angle of observation, adequate lighting, low powered magnification, fillet weld gauges, etc. PC31. detect surface imperfections and deal with them appropriately PC32. carry out DPT tests to assess fine defect open to the surface not detected by visual inspection (VT) Post-welding activities Dealing with contingencies The user/individual on the job should be able to: PC33. assist in preparation for non-destructive testing of the welds, for a range of tests Non-destructive tests (NDT): Penetrant testing- dye penetrant (DPT), fluorescent penetrant (FPT); magnetic particle (MPT); radiographic (RT); ultrasonic (UT) PC34. prepare for destructive tests on weld specimens for fillet, butt and corner Destructive tests (DT): macro examination; fractured test- nick break test; bend tests (such as face, root or side, as appropriate); mechanical (tensile and shear, impact); chemical The user/individual on the job should be able to: PC35. deal promptly and effectively with problems within their control, and seek help and guidance from the relevant people if they have problems that they cannot resolve Knowledge and Understanding (K) A. Organizational Context (Knowledge of the company / organization and its processes) The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand: KA1. relevant legislation, standards, policies, and procedures followed in the company KA2. key purpose of the organization KA3. department structure and hierarchy protocols KA4. work flow and own role in the workflow KA5. dependencies and interdependencies in the workflow KA6. support functions and types of support available for incumbents in this role 19 P age
20 CSC/ N 0208: Manually weld carbon steel/ low alloy steel and austenitic stainless steel using Metal Arc Welding / Shielded Metal Arc Welding B. Technical Knowledge The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand: KB1. health and safety, hazards and precautions associated with MMAW/SMAW welding Safety precautions (MMAW/SMAW Welding): protection from live and other electrical components, including insulation, proper earthing, etc.; proper handling and placement of hot metal; taking account of spatter and related safe distance; adequate lighting; appropriate personal protective equipmentsuitable aprons, welding gloves, respirators, safety boots, correctly fitting overalls, suitable eye shields/goggles, hard hat/helmet; protection of self and others from the effects of the welding arc; fume extraction/control measures; safety measures for elevated and trench workings (e.g. harness, etc.) KB2. applications of manual metal arc welding KB3. effects of exposure to the electric arc KB4. types of fire extinguishers and their suitable uses KB5. effects of exposure to welding fume KB6. methods of managing welding fume hazards KB7. personal protective equipment (PPE) and clothing to be worn during MMAW/SMAW welding Personal protective equipment (PPE): (suitable aprons, welding gloves, respirators, safety boots, correctly fitting overalls, suitable eye shields/goggles, hard hat/helmet KB8. welding specific equipment requirements for MMAW/SMAW welding MMAW equipment: e.g. transformers; rectifiers; generators; invertors; consumables electrodes, dyes; welding accessories - holders, cables and accessories; ancillary equipment - (power saw, angle, pedestal and straight grinders, tong tester, etc.); electrode drying oven, etc. KB9. main components and controls of welding equipment KB10. how to connect electrical components correctly KB11. type of current used and implication KB12. welding symbols used and their correct interpretation KB13. consumables used for MMAW/SMAW welding KB14. various types of electrodes (classification) based on covering Electrodes: rutile, basic, cellulosic, acid KB15. function of covering KB16. various defects associated with the MMAW/SMAW welding process Weld defects: lack of continuity of the weld; uneven and irregular ripple formation; excessive spatter; incorrect weld size or profile; burn through; undercutting; overlap; inclusions; distortion; porosity; internal cracks; surface cracks; lack of fusion or incomplete fusion; lack of penetration; excessive penetration; gouges; stray arc strikes; sharp edges; excessive convexity KB17. types of joint configurations Joints: fillet and groove (lap joints, tee fillet joints, corner joints, butt jointssquare, single vee, double vee) KB18. factors that determine weld bead shape Factors: electrode angles and welding technique (push, perpendicular, drag); arc length; thickness of base metal; travel speed (slow, normal, fast) KB19. types of beads, their characteristics and uses (stringer, weave, weave 20 P age
21 CSC/ N 0208: Manually weld carbon steel/ low alloy steel and austenitic stainless steel using Metal Arc Welding / Shielded Metal Arc Welding patterns) Bead characteristics: spatter deposits, roughness, evenness, fill, crater, overlap KB20. factors that affect weld quality Quality standards: required parameters for dimensional accuracy; weld finishes are built up to the full section of the weld; joins at stop/start positions merge smoothly; weld surface is (free from cracks; substantially free from porosity; free from any pronounced hump or crater; substantially free from shrinkage cavities; substantially free from trapped slag; substantially free from arcing or chipping marks ); fillet welds are (equal in leg length, slightly convex in profile (where applicable), size of the fillet equivalent to the thickness of the material welded); weld contour is (of linear and of uniform profile; smooth and free from excessive undulations; regular and has an even ripple formations); welds are adequately fused, and there is minimal undercut, overlap and surface inclusions; tack welds are blended in to form part of the finished weld, without excessive hump; corner joints have minimal burn through to the underside of the joint or, where appropriate KB21. weld positions such as flat, horizontal, vertical and overhead KB22. types of equipment components such as electrode holders, work leads cables and ground clamps KB23. awareness and importance of cable size and length KB24. types of polarity such as AC and DC electrode negative and DC electrode positive for welding purposes KB25. various types of base metals used in welding and their implications KB26. type and thickness of base metals to be welded Base metals: e.g. mild or low carbon steel, austenitic stainless steel, etc. KB27. distortion and how to control distortion Distortion (causes and control methods): Causes: improper sequence of weld runs; direction of weld runs; heat input errors; lack of inaccuracy of jigs and fixture; Control Methods: sequence of welding as materials; proper direction; tacking and its frequency (where applicable; use clamping and jigs and fixtures (where applicable) KB28. magnetic arc blow or arc deflection, causes and methods to avoid or compensate KB29. storage requirements for consumable electrodes KB30. electrode classifications such as tensile strength, position and composition KB31. electrode types based on covering, their characteristics and uses KB32. purpose of re-drying and procedure for different classification of electrode KB33. welding process and method specification sheet, process qualification record (PQR) and related essential variables KB34. travel speed and heat inputs KB35. amperage requirements for different classification of electrodes and positions KB36. importance and implications of various diameters of electrodes KB37. gouging and back gouging principles, methods and procedures KB38. purpose and importance of pre-heating requirements for base metals KB39. purpose and importance of post-heating in welding KB40. methods to achieve pre-heat and post heat requirements 21 P age
22 CSC/ N 0208: Manually weld carbon steel/ low alloy steel and austenitic stainless steel using Metal Arc Welding / Shielded Metal Arc Welding Skills (S) [Optional] A. Core Skills/ Generic Skills KB41. tools and methods to measure temperature for pre-heat and post-heat requirements such as thermal chalk, thermocouple, etc. KB42. significance of diffusible hydrogen for welds KB43. importance of maintaining welding standards specified for the job KB44. impact of a welding job done right, acceptable or non-acceptable KB45. types of visual inspection indicators and methods Visual inspections: e.g. use of visual techniques, distance from workpiece, angle of observation, adequate lighting, low powered magnification, fillet weld gauges, etc. KB46. types of NDT and DT inspection methods KB47. procedure to conduct DP testing KB48. common welder testing codes and their purpose Testing codes: ASME section IX, EN 287, ISO 9606, IS 731 Communication The user/ individual on the job needs to know and understand how to: SA1. read and interpret information correctly from various job specification documents, manuals, health and safety instructions, memos, etc. applicable to the job in English and/or local language SA2. fill up appropriate technical forms, process charts, activity logs as per organizational format in English and/or local language SA3. convey and share technical information clearly using appropriate language SA4. check and clarify task-related information SA5. liaise with appropriate authorities using correct protocol SA6. communicate with people in respectful form and manner in line with organizational protocol Numerical and computational skills The user/individual on the job needs to know and understand how to: SA7. undertake numerical operations, geometry and calculations/ formulae (including addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, fractions and decimals, percentages and proportions, simple ratios and averages) SA8. use appropriate measuring techniques SA9. use and convert imperial and metric systems of measurements SA10. apply appropriate degree of accuracy to express numbers SA11. calculate tolerance in terms of limits of size SA12. check measurements, angles, orientation and slopes SA13. types of reference lines such as tangent lines, datum lines, centre lines and work points SA14. check square of material using corner-to-corner dimensions and triangulation (3-4-5) method SA15. select and use tools and equipment such as measuring tapes, levels, squares, protractors and dividers SA16. ability to check dimensions of components SA17. calculate the value of angles in a triangle 22 P age
WORD DEFINITION WORD (NATIONAL LANGUAGE)
 WELDING GLOSSARY The Glossary has been created as part of the Migration for Development in the Western Balkans (MIDWEB) project, which received financial assistance from the European Commission IPA 2009
WELDING GLOSSARY The Glossary has been created as part of the Migration for Development in the Western Balkans (MIDWEB) project, which received financial assistance from the European Commission IPA 2009
Chapter 5 - Aircraft Welding
 Chapter 5 - Aircraft Welding Chapter 5 Section A Study Aid Questions Fill in the Blanks 1. There are 3 types of welding:, and, welding. 2. The oxy acetylene flame, with a temperature of Fahrenheit is produced
Chapter 5 - Aircraft Welding Chapter 5 Section A Study Aid Questions Fill in the Blanks 1. There are 3 types of welding:, and, welding. 2. The oxy acetylene flame, with a temperature of Fahrenheit is produced
INDIAN STANDARDS (BIS) ON WELDING
 ** IS 82:957 Glossary of terms relating to welding and cutting of Sep 2008 metals 2 IS 83:986 Scheme of symbols for welding (revised) Sep 2008 3 IS 84:2004 Covered electrodes for manual metal arc welding
** IS 82:957 Glossary of terms relating to welding and cutting of Sep 2008 metals 2 IS 83:986 Scheme of symbols for welding (revised) Sep 2008 3 IS 84:2004 Covered electrodes for manual metal arc welding
SEMPEO2-54 - SQA Unit Code FP47 04 Carrying out heat treatment of engineering materials
 Overview This standard covers a broad range of basic competences that you need, to apply specified heat treatment processes to engineering materials/components. It will prepare you for entry into the engineering
Overview This standard covers a broad range of basic competences that you need, to apply specified heat treatment processes to engineering materials/components. It will prepare you for entry into the engineering
Job Ready Assessment Blueprint. Welding. Test Code: 4172 / Version: 01. Copyright 2013. All Rights Reserved.
 Job Ready Assessment Blueprint Welding Test Code: 4172 / Version: 01 Copyright 2013. All Rights Reserved. General Assessment Information Blueprint Contents General Assessment Information Written Assessment
Job Ready Assessment Blueprint Welding Test Code: 4172 / Version: 01 Copyright 2013. All Rights Reserved. General Assessment Information Blueprint Contents General Assessment Information Written Assessment
WELDING TECHNOLOGY DEGREES AND CERTIFICATES. Welding Technology Degree. Shielded Metal Arc Plate and Pipe (270 hours) Certificate
 Area: Technical Education Dean: Dr. Trish Caldwell Phone: (916) 484-8354 Counseling: (916) 484-8572 www.arc.losrios.edu/~welding/ The American Welding Society (AWS) nationally accredits American River
Area: Technical Education Dean: Dr. Trish Caldwell Phone: (916) 484-8354 Counseling: (916) 484-8572 www.arc.losrios.edu/~welding/ The American Welding Society (AWS) nationally accredits American River
Field Welding Inspection Guide
 Field Welding Inspection Guide Assistance in interpretation of any specification or questions concerning field welding issues can be obtained from the Office of Materials Management, Structural Welding
Field Welding Inspection Guide Assistance in interpretation of any specification or questions concerning field welding issues can be obtained from the Office of Materials Management, Structural Welding
www.klmtechgroup.com TABLE OF CONTENT
 Page : 1 of 45 Project Engineering Standard www.klmtechgroup.com KLM Technology #03-12 Block Aronia, Jalan Sri Perkasa 2 Taman Tampoi Utama 81200 Johor Bahru Malaysia TABLE OF CONTENT 1.0 SCOPE 2 2.0 CONFLICTS
Page : 1 of 45 Project Engineering Standard www.klmtechgroup.com KLM Technology #03-12 Block Aronia, Jalan Sri Perkasa 2 Taman Tampoi Utama 81200 Johor Bahru Malaysia TABLE OF CONTENT 1.0 SCOPE 2 2.0 CONFLICTS
North Carolina FFA Association Agricultural Mechanics Career Development Event
 North Carolina FFA Association Three (3) of the following Agricultural Mechanics Performance Skills will be selected for the state competition. North Carolina FFA Association Agricultural Mechanics Performance
North Carolina FFA Association Three (3) of the following Agricultural Mechanics Performance Skills will be selected for the state competition. North Carolina FFA Association Agricultural Mechanics Performance
SEMFWE232 SQA Unit Code H2BN 04 Cutting plate and sections using shearing machines
 Overview This standard identifies the competencies you need for cutting and shaping metal plate and sections (3 mm thickness and above) for fabrications using guillotines and section cropping machines,
Overview This standard identifies the competencies you need for cutting and shaping metal plate and sections (3 mm thickness and above) for fabrications using guillotines and section cropping machines,
QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR ELECTRONICS INDUSTRY SECTOR: ELECTRONICS SUB-SECTOR: STRATEGIC ELECTRONICS
 QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR ELECTRONICS INDUSTRY What are Occupational Standards(OS)? OS describe what individuals need to do, know and understand in order to carry out a particular
QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR ELECTRONICS INDUSTRY What are Occupational Standards(OS)? OS describe what individuals need to do, know and understand in order to carry out a particular
Application of Welding Standards in Hong Kong. S. K. Babu Laboratory Manager - Foundation Techniques Ltd
 Application of Welding Standards in Hong Kong S. K. Babu Laboratory Manager - Foundation Techniques Ltd Introduction: This paper summarizes the current welding standards practiced in Hong Kong & also outlines
Application of Welding Standards in Hong Kong S. K. Babu Laboratory Manager - Foundation Techniques Ltd Introduction: This paper summarizes the current welding standards practiced in Hong Kong & also outlines
QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR LIFE SCIENCES INDUSTRY OCCUPATION: RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT REFERENCE ID: LFS/Q0503
 h QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR LIFE SCIENCES INDUSTRY Contents OS describe what individuals need to do, know and understand in order to carry out a particular job role or function OS
h QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR LIFE SCIENCES INDUSTRY Contents OS describe what individuals need to do, know and understand in order to carry out a particular job role or function OS
11. NONDESTRUCTIVE TESTING
 11. NONDESTRUCTIVE TESTING Nondestructive testing includes magnetic particle testing (MT), Liquid Dye Penetrant testing (PT), Radiographic Testing (RT) and Ultrasonic Testing (UT). The purpose of nondestructive
11. NONDESTRUCTIVE TESTING Nondestructive testing includes magnetic particle testing (MT), Liquid Dye Penetrant testing (PT), Radiographic Testing (RT) and Ultrasonic Testing (UT). The purpose of nondestructive
Automotive Skills Development Council
 h Automotive Skills Development Council QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR AUTOMOTIVE INDUSTRY Contents What are ccupational tandards (OS)? OS describe what individuals need to do, know and
h Automotive Skills Development Council QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR AUTOMOTIVE INDUSTRY Contents What are ccupational tandards (OS)? OS describe what individuals need to do, know and
Forename: Surname: School / College/ Institution. Course date: / / RDTHSC:
 Specialist Extension Level S5HS Forename: Surname: School / College/ Institution Course date: / / RDTHSC: These Training and Accreditation Guidelines are based on the following essential publications:
Specialist Extension Level S5HS Forename: Surname: School / College/ Institution Course date: / / RDTHSC: These Training and Accreditation Guidelines are based on the following essential publications:
GMAW Aluminum Plate Annotated Instructor s Guide
 GMAW Aluminum Plate Annotated Instructor s Guide Module 29401-10 Module Overview This module covers the basics of aluminum metallurgy. It also explains how to make fillet and V-groove welds on aluminum
GMAW Aluminum Plate Annotated Instructor s Guide Module 29401-10 Module Overview This module covers the basics of aluminum metallurgy. It also explains how to make fillet and V-groove welds on aluminum
A Beginner s Guide to MIG Welding
 A Beginner s Guide to MIG Welding MIG Welding Names MIG welding, or MIG, is an acronym for Metal Inert Gas welding. MIG is a commonly used and accepted slang term that was appropriate when the process
A Beginner s Guide to MIG Welding MIG Welding Names MIG welding, or MIG, is an acronym for Metal Inert Gas welding. MIG is a commonly used and accepted slang term that was appropriate when the process
FIELD ACCEPTANCE OF FIELD WELDING GUIDE
 Page 1 of 17 Oklahoma DOT Materials & Testing January 14, 2004 Publication: GFA-FW (Updated to reference current Structural Materials Branch of the ODOT Materials Division URL 07/06/2016) FIELD ACCEPTANCE
Page 1 of 17 Oklahoma DOT Materials & Testing January 14, 2004 Publication: GFA-FW (Updated to reference current Structural Materials Branch of the ODOT Materials Division URL 07/06/2016) FIELD ACCEPTANCE
Structural welding is a process by which the parts that are to be connected are heated and
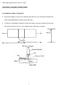 CHAPTER 6. WELDED CONNECTIONS 6.1 INTRODUCTORY CONCEPTS Structural welding is a process by which the parts that are to be connected are heated and fused, with supplementary molten metal at the joint. A
CHAPTER 6. WELDED CONNECTIONS 6.1 INTRODUCTORY CONCEPTS Structural welding is a process by which the parts that are to be connected are heated and fused, with supplementary molten metal at the joint. A
SMARTY 160 POWER page 4-5 SMARTY 180 / 220 XL page 4-6 SMARTY TX 250 page 4-7. SMARTY TX 160 Alu page 4-8 SMARTY TX 220 Alu page 4-9
 CHAPTER TIG welding Introduction pages - & - WELDING POWER SOURCES DC power sources SMARTY 60 POWER page -5 SMARTY 80 / 0 XL page -6 SMARTY TX 50 page -7 AC/DC power sources SMARTY TX 60 Alu page -8 SMARTY
CHAPTER TIG welding Introduction pages - & - WELDING POWER SOURCES DC power sources SMARTY 60 POWER page -5 SMARTY 80 / 0 XL page -6 SMARTY TX 50 page -7 AC/DC power sources SMARTY TX 60 Alu page -8 SMARTY
Duplex Stainless Steel Fabrication. Gary M. Carinci TMR Stainless Consultant for International Molybdenum Association
 Duplex Stainless Steel Fabrication Gary M. Carinci TMR Stainless Consultant for International Molybdenum Association 1 Promoting molybdenum - as a material with superior properties and performance in a
Duplex Stainless Steel Fabrication Gary M. Carinci TMR Stainless Consultant for International Molybdenum Association 1 Promoting molybdenum - as a material with superior properties and performance in a
Weld Cracking. An Excerpt from The Fabricators' and Erectors' Guide to Welded Steel Construction. The James F. Lincoln Arc Welding Foundation
 Weld Cracking An Excerpt from The Fabricators' and Erectors' Guide to Welded Steel Construction The James F. Lincoln Arc Welding Foundation Weld Cracking Several types of discontinuities may occur in welds
Weld Cracking An Excerpt from The Fabricators' and Erectors' Guide to Welded Steel Construction The James F. Lincoln Arc Welding Foundation Weld Cracking Several types of discontinuities may occur in welds
STANDARDS FOR THE MATERIALS
 STANDARDILUETTELO 1(15) Kpl Standardin numero STANDARDS FOR THE MATERIALS 1 EN 10204 2004-10 Metallic products.types of inspection documents 2 EN 10079 1992-10 Definition of steel products 3 EN 10027-1
STANDARDILUETTELO 1(15) Kpl Standardin numero STANDARDS FOR THE MATERIALS 1 EN 10204 2004-10 Metallic products.types of inspection documents 2 EN 10079 1992-10 Definition of steel products 3 EN 10027-1
Model Curriculum. CNC Programmer SECTOR: SUB-SECTOR:
 Model Curriculum CNC Programmer SECTOR: SUB-SECTOR: OCCUPATION: REF. ID: NSQF LEVEL: CGSC MACHINE TOOLS DIES,MOULDS AND PRESS TOOLS PLASTICS MANUFACTURING MACHINERY TEXTILE MANUFACTURING MACHINERY PROCESS
Model Curriculum CNC Programmer SECTOR: SUB-SECTOR: OCCUPATION: REF. ID: NSQF LEVEL: CGSC MACHINE TOOLS DIES,MOULDS AND PRESS TOOLS PLASTICS MANUFACTURING MACHINERY TEXTILE MANUFACTURING MACHINERY PROCESS
SEMPEO1-35 - SQA Unit Code H034 04 Applying heat treatment to engineering materials
 Overview This standard covers a range of basic competences that you need, to apply specified heat treatment processes to engineering materials/components. It will prepare you for entry into the engineering
Overview This standard covers a range of basic competences that you need, to apply specified heat treatment processes to engineering materials/components. It will prepare you for entry into the engineering
BASIC PRINCIPLES OF WELDING
 BASIC PRINCIPLES OF WELDING COURSE DESCRIPTION Basic Principles of Welding* is a course designed to follow Introduction to Welding, in which students will learn more advanced skills and knowledge related
BASIC PRINCIPLES OF WELDING COURSE DESCRIPTION Basic Principles of Welding* is a course designed to follow Introduction to Welding, in which students will learn more advanced skills and knowledge related
MARC5001A Employ tools, equipment and materials in a shipboard context
 MARC5001A Employ tools, equipment and materials in a shipboard context Release 1 MARC5001A Employ tools, equipment and materials in a shipboard context Modification History Release 1 This is the first
MARC5001A Employ tools, equipment and materials in a shipboard context Release 1 MARC5001A Employ tools, equipment and materials in a shipboard context Modification History Release 1 This is the first
QUALIFICATION PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARD FOR MINING INDUSTRY
 QUALIFICATION PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARD FOR MINING INDUSTRY OS describe what individuals need to do, know and understand in order to carry out a particular job role or function OS are performance standard
QUALIFICATION PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARD FOR MINING INDUSTRY OS describe what individuals need to do, know and understand in order to carry out a particular job role or function OS are performance standard
Gas Tungsten Arc Welding GTAW (40 Hours Course)
 Gas Tungsten Arc Welding GTAW (40 Hours Course) Table of Contents Gas Tungsten Arc Welding GTAW (40 Hours Course)...1 GENERAL SURVEY...1 1. SHORT DISCRIPTION OF THE MOST COMMON WELDING PROCESSES...3 1.1
Gas Tungsten Arc Welding GTAW (40 Hours Course) Table of Contents Gas Tungsten Arc Welding GTAW (40 Hours Course)...1 GENERAL SURVEY...1 1. SHORT DISCRIPTION OF THE MOST COMMON WELDING PROCESSES...3 1.1
APPLICATION COMPETENCY FIELD
 UNIT CODE UNIT TITLE APPLICATION COMPETENCY FIELD ELEMENTS Elements describe the essential outcomes. 1 Follow safe work practices MARC018 Employ tools, equipment and materials in a shipboard context This
UNIT CODE UNIT TITLE APPLICATION COMPETENCY FIELD ELEMENTS Elements describe the essential outcomes. 1 Follow safe work practices MARC018 Employ tools, equipment and materials in a shipboard context This
QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR ELECTRONICS INDUSTRY. SECTOR: ELECTRONICS SUB-SECTOR: Semiconductor Design and Active Components
 QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR ELECTRONICS INDUSTRY Contents 1. Introduction and Contacts..P1 2. Qualifications Pack....P2 What are Occupational Standards(OS)? OS describe what individuals
QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR ELECTRONICS INDUSTRY Contents 1. Introduction and Contacts..P1 2. Qualifications Pack....P2 What are Occupational Standards(OS)? OS describe what individuals
QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR ELECTRONICS INDUSTRY SUB-SECTOR: STRATEGIC ELECTRONICS OCCUPATION: PRODUCTION PLANNING AND CONTROL
 QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR ELECTRONICS INDUSTRY What are Occupational Standards(OS)? OS describe what individuals need to do, know and understand in order to carry out a particular
QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR ELECTRONICS INDUSTRY What are Occupational Standards(OS)? OS describe what individuals need to do, know and understand in order to carry out a particular
EML 2322L MAE Design and Manufacturing Laboratory. Welding
 EML 2322L MAE Design and Manufacturing Laboratory Welding Intro to Welding A weld is made when separate pieces of material to be joined combine and form one piece when heated to a temperature high enough
EML 2322L MAE Design and Manufacturing Laboratory Welding Intro to Welding A weld is made when separate pieces of material to be joined combine and form one piece when heated to a temperature high enough
A Beginner s Guide to TIG Welding
 A Beginner s Guide to TIG Welding TIG Welding Names TIG Welding, or TIG, is an acronym for Tungsten Inert Gas welding. TIG is a commonly used and accepted slag term. The proper terminology is Gas Tungsten
A Beginner s Guide to TIG Welding TIG Welding Names TIG Welding, or TIG, is an acronym for Tungsten Inert Gas welding. TIG is a commonly used and accepted slag term. The proper terminology is Gas Tungsten
TIG WELDING TIPS by Tom Bell
 (This is a two-part document, with general tig welding first followed by one aluminum-specific.) TIG WELDING TIPS by Tom Bell 1. The bigger the rod, the easier it is to feed. Use larger diameter rods (3/32
(This is a two-part document, with general tig welding first followed by one aluminum-specific.) TIG WELDING TIPS by Tom Bell 1. The bigger the rod, the easier it is to feed. Use larger diameter rods (3/32
Mandan Public Schools
 Mandan Public School District Career & Technical Education 2010 1 Table of Contents Table of Contents...2 Preface...4 Writing Committee Members...5 Vision, Mission, Slogan and Philosophy...5 Philosophy
Mandan Public School District Career & Technical Education 2010 1 Table of Contents Table of Contents...2 Preface...4 Writing Committee Members...5 Vision, Mission, Slogan and Philosophy...5 Philosophy
Structural Steel Welding
 PDH Course S150 Structural Steel Welding Semih Genculu, P.E. 2007 PDH Center 2410 Dakota Lakes Drive Herndon, VA 20171-2995 Phone: 703-478-6833 Fax: 703-481-9535 www.pdhcenter.com An Approved Continuing
PDH Course S150 Structural Steel Welding Semih Genculu, P.E. 2007 PDH Center 2410 Dakota Lakes Drive Herndon, VA 20171-2995 Phone: 703-478-6833 Fax: 703-481-9535 www.pdhcenter.com An Approved Continuing
ASTM A860/A860M-09 Standard Specification for Wrought High Strength. Ferritic Steel Butt Welding Fittings. 1. Scope :- 2. Reference Documents :-
 Standard Specification for Wrought High Strength Ferritic Steel Butt Welding Fittings 1. Scope :- 1.1 This specification covers wrought high strength ferritic steel butt-welding fitting of seamless and
Standard Specification for Wrought High Strength Ferritic Steel Butt Welding Fittings 1. Scope :- 1.1 This specification covers wrought high strength ferritic steel butt-welding fitting of seamless and
Apprenticeship and Industry Training
 Apprenticeship and Industry Training Welder Apprenticeship Course Outline 1214 (2014) ALBERTA INNOVATION AND ADVANCED EDUCATION Welder : apprenticeship course outline ISBN 978-1-4601-1633-3 ALL RIGHTS
Apprenticeship and Industry Training Welder Apprenticeship Course Outline 1214 (2014) ALBERTA INNOVATION AND ADVANCED EDUCATION Welder : apprenticeship course outline ISBN 978-1-4601-1633-3 ALL RIGHTS
Apprenticeship Training Standard. Welder. Trade Code: 456A. Development Date: October 2007
 Apprenticeship Training Standard Welder Trade Code: 456A Development Date: October 2007 This document is the property of the apprentice named inside and represents the official record of his/her training
Apprenticeship Training Standard Welder Trade Code: 456A Development Date: October 2007 This document is the property of the apprentice named inside and represents the official record of his/her training
SEMFEW226 - SQA Unit Code H2BJ 04 Cutting and shaping materials using NC/CNC laser profiling machines
 Cutting and shaping materials using NC/CNC laser profiling machines Overview This unit identifies the competencies you need to carry out cutting and profiling operations using NC/CNC laser profiling machines,
Cutting and shaping materials using NC/CNC laser profiling machines Overview This unit identifies the competencies you need to carry out cutting and profiling operations using NC/CNC laser profiling machines,
SEMMME2-20 - SQA Unit Code H2AB 04 Operating CNC Milling Machines
 Overview This unit identifies the competences you need to operate Computer Numerical Control (CNC) three-axis or multi-axis machines, or CNC machining centres, in accordance with approved procedures. You
Overview This unit identifies the competences you need to operate Computer Numerical Control (CNC) three-axis or multi-axis machines, or CNC machining centres, in accordance with approved procedures. You
Automotive Skills Development Council
 h Automotive Skills Development Council QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR AUTOMOTIVE INDUSTRY Contents What are ccupational tandards (OS)? OS describe what individuals need to do, know and
h Automotive Skills Development Council QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR AUTOMOTIVE INDUSTRY Contents What are ccupational tandards (OS)? OS describe what individuals need to do, know and
SEMAE3221 Machining aircraft components using CNC milling machines
 Machining aircraft components using CNC milling machines Overview This standard identifies the competences you need to operate Computer Numerical Control (CNC) three axis or five axis machines or CNC machining
Machining aircraft components using CNC milling machines Overview This standard identifies the competences you need to operate Computer Numerical Control (CNC) three axis or five axis machines or CNC machining
Contents. QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR IT-ITeS INDUSTRY. What are National Occupational Standards (NOS)?
 QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR IT-ITeS INDUSTRY What are National Occupational Standards (NOS)? NOS describe what individuals need to do, know and understand in order to carry out a particular
QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR IT-ITeS INDUSTRY What are National Occupational Standards (NOS)? NOS describe what individuals need to do, know and understand in order to carry out a particular
Welding of Boilers, Pressure Vessels and Pressure Piping
 WELDING OF BOILERS, PRESSURE VESSELS 1 Welding of Boilers, Pressure Vessels and Pressure Piping Repealed by Chapter B-5.1 Reg 1 (effective January 1, 2007) Formerly Saskatchewan Regulation 61/78 (effective
WELDING OF BOILERS, PRESSURE VESSELS 1 Welding of Boilers, Pressure Vessels and Pressure Piping Repealed by Chapter B-5.1 Reg 1 (effective January 1, 2007) Formerly Saskatchewan Regulation 61/78 (effective
A Beginners Guide to Flux Cored Arc Welding
 A Beginners Guide to Flux Cored Arc Welding When it comes to Flux cored arc welding or FCAW many people think it is a different welding process when in reality it is not! Even though there are books, classes
A Beginners Guide to Flux Cored Arc Welding When it comes to Flux cored arc welding or FCAW many people think it is a different welding process when in reality it is not! Even though there are books, classes
TARIFF CODE and updates standard
 TARIFF CODE and updates standard No HS CODE AHTN CODE PRODUCT DESCRIPTION PRODUCT TYPE STANDARDS IDENTIFIED 7207 Semi finished products of iron or non alloy steel Containing by weight less than 0.25% of
TARIFF CODE and updates standard No HS CODE AHTN CODE PRODUCT DESCRIPTION PRODUCT TYPE STANDARDS IDENTIFIED 7207 Semi finished products of iron or non alloy steel Containing by weight less than 0.25% of
QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR IT-ITeS INDUSTRY. SECTOR: IT-ITES ITES)ces Helpdesk Attendant SUB-SECTOR: Business Process Management
 QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR IT-ITeS INDUSTRY OS describe what individuals need to do, know and understand in order to carry out a particular job role or function OS are performance
QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR IT-ITeS INDUSTRY OS describe what individuals need to do, know and understand in order to carry out a particular job role or function OS are performance
GK Packing System Welding Instructions
 GK Packing System Welding Instructions Roxtec GmbH Neuer Höltigbaum 1-3, 22143 Hamburg GERMANY Tel +49 (040) 657398-0, Fax +49 (040) 657398-50 EMAIL info@de.roxtec.com, www.roxtec.de Welding instructions
GK Packing System Welding Instructions Roxtec GmbH Neuer Höltigbaum 1-3, 22143 Hamburg GERMANY Tel +49 (040) 657398-0, Fax +49 (040) 657398-50 EMAIL info@de.roxtec.com, www.roxtec.de Welding instructions
Reproduced with the permission of the American Welding Society (AWS), Miami, Florida - 09/15/2011. 7. Stud Welding
 7. Stud Welding 7.1 Scope Section 7 contains general requirements for welding steel studs to steel (see 7.2.7 and 1.2.2 for approved steels). In addition, it stipulates specific requirements for the following:
7. Stud Welding 7.1 Scope Section 7 contains general requirements for welding steel studs to steel (see 7.2.7 and 1.2.2 for approved steels). In addition, it stipulates specific requirements for the following:
PART QW WELDING ARTICLE I WELDING GENERAL REQUIREMENTS
 PART QW WELDING ARTICLE I WELDING GENERAL REQUIREMENTS QW-100 GENERAL Section IX of the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code relates to the qualification of welders, welding operators, brazers, and brazing
PART QW WELDING ARTICLE I WELDING GENERAL REQUIREMENTS QW-100 GENERAL Section IX of the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code relates to the qualification of welders, welding operators, brazers, and brazing
FACILITY ACCREDITATION CHECKLIST #001 APPRENTICESHIP. Rating Code: Y = Yes * N = No * R = Required * AUDIT AREA: DATE: / / HAND TOOLS Y N R
 FACILITY ACCREDITATION CHECKLIST #001 APPRENTICESHIP Designated Trade: Level 1 2 3 4 Institution: Evaluator(s) / / Rating Code: Y = Yes * N = No * R = Required * * Please use a CHECKMARK under the appropriate
FACILITY ACCREDITATION CHECKLIST #001 APPRENTICESHIP Designated Trade: Level 1 2 3 4 Institution: Evaluator(s) / / Rating Code: Y = Yes * N = No * R = Required * * Please use a CHECKMARK under the appropriate
European Welding Standards
 European Welding Standards John Dyson 15 th March 2004 European Standards Harmonised Standards Not all EN Standards are Harmonised, only those that are considered to satisfy relevant ESRs in product directives.
European Welding Standards John Dyson 15 th March 2004 European Standards Harmonised Standards Not all EN Standards are Harmonised, only those that are considered to satisfy relevant ESRs in product directives.
QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR IT-ITeS INDUSTRY. SECTOR: IT-ITES ITES)ces Helpdesk Attendant SUB-SECTOR: Business Process Management
 QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR IT-ITeS INDUSTRY Contents 1. Introduction and Contacts.......P.1 2. Qualifications Pack....P.2 3. Glossary of Key Terms.......P.3 4. NOS Units.. P.5 OS
QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR IT-ITeS INDUSTRY Contents 1. Introduction and Contacts.......P.1 2. Qualifications Pack....P.2 3. Glossary of Key Terms.......P.3 4. NOS Units.. P.5 OS
Gas tungsten arc welding, commonly called TIG (tungsten inert gas), produces an arc between a
 DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS FOR WELDING Apart from resistance spot welding (RSW), three processes are most commonly used for welding metal stampings and fabrications: gas metal arc welding (GMAW) or MIG; gas
DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS FOR WELDING Apart from resistance spot welding (RSW), three processes are most commonly used for welding metal stampings and fabrications: gas metal arc welding (GMAW) or MIG; gas
WELDING & CUTTING MAIN EQUIPMENT
 GASES DIVISION GAS WELDING & CUTTING EQUIPMENT WELDING & CUTTING MAIN EQUIPMENT GAS WELDING & CUTTING KIT The MARIGASES GAS WELDING AND CUTTING KIT is a high quality set containing all the tools and components
GASES DIVISION GAS WELDING & CUTTING EQUIPMENT WELDING & CUTTING MAIN EQUIPMENT GAS WELDING & CUTTING KIT The MARIGASES GAS WELDING AND CUTTING KIT is a high quality set containing all the tools and components
Welding. Module 19.2.1
 Welding Module 19.2.1 Hard Soldering Hard soldering is a general term for silver soldering and brazing. These are very similar thermal joining processes to soft soldering in as much that the parent metal
Welding Module 19.2.1 Hard Soldering Hard soldering is a general term for silver soldering and brazing. These are very similar thermal joining processes to soft soldering in as much that the parent metal
QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR MEDIA AND ENTERTAINMENT INDUSTRY. Qualifications Pack- Lighting Technician
 QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR MEDIA AND ENTERTAINMENT INDUSTRY Contents 1. Introduction and Contacts.. P.1 2. Qualifications Pack.. P.2 3. OS Units.....P.2 4. Glossary of Key Terms P.3
QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR MEDIA AND ENTERTAINMENT INDUSTRY Contents 1. Introduction and Contacts.. P.1 2. Qualifications Pack.. P.2 3. OS Units.....P.2 4. Glossary of Key Terms P.3
Contents QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR TELECOM INDUSTRY. Introduction. Qualifications Pack- Telecom Network Security Technician
 QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR TELECOM INDUSTRY Contents 1. Introduction and Contacts....1 W h a t a r e O c c u p a t i o n a l S t a n d a r d s ( O S )? OS describe what individuals
QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR TELECOM INDUSTRY Contents 1. Introduction and Contacts....1 W h a t a r e O c c u p a t i o n a l S t a n d a r d s ( O S )? OS describe what individuals
Summary of Changes in. ASME Section IX, 2000 Addenda
 Summary of Changes in ASME Section IX, 2000 Addenda Prepared by Walter J. Sperko, P.E. Sperko Engineering Services, Inc 4803 Archwood Drive Greensboro, NC 27406 USA Voice: 336-674-0600 FAX: 336-674-0600
Summary of Changes in ASME Section IX, 2000 Addenda Prepared by Walter J. Sperko, P.E. Sperko Engineering Services, Inc 4803 Archwood Drive Greensboro, NC 27406 USA Voice: 336-674-0600 FAX: 336-674-0600
QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR IT-ITeS INDUSTRY. SECTOR: IT-ITES ITES)ces Helpdesk Attendant SUB-SECTOR: Business Process Management
 QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR IT-ITeS INDUSTRY SSC/ N 3003 Deal remotely with customer queries What are Occupational Standards(OS)? OS describe what individuals need to do, know and
QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR IT-ITeS INDUSTRY SSC/ N 3003 Deal remotely with customer queries What are Occupational Standards(OS)? OS describe what individuals need to do, know and
QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FORa LIFE SCIENCES INDUSTRY Contents
 h QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FORa LIFE SCIENCES INDUSTRY Contents OS describe what individuals need to do, know and understand in order to carry out a particular job role or function
h QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FORa LIFE SCIENCES INDUSTRY Contents OS describe what individuals need to do, know and understand in order to carry out a particular job role or function
QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR IT-ITeS INDUSTRY. ITES)ces Helpdesk Attendant. OCCUPATION: IT Support Services/Helpdesk
 QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR IT-ITeS INDUSTRY What are Occupational Standards(OS)? OS describe what individuals need to do, know and understand in order to carry out a particular job
QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR IT-ITeS INDUSTRY What are Occupational Standards(OS)? OS describe what individuals need to do, know and understand in order to carry out a particular job
TERMS AND TERMINOLOGY FOR WELDING PROCESSES AND WELD CONFIGURATIONS
 ECCC ECCC RECOMMENDATIONS - VOLUME 2 Part IIa [Issue 2] TERMS AND TERMINOLOGY FOR WELDING PROCESSES AND WELD CONFIGURATIONS blank page blank page ABSTRACT ECCC Recommendations Volume 2 Part IIa presents
ECCC ECCC RECOMMENDATIONS - VOLUME 2 Part IIa [Issue 2] TERMS AND TERMINOLOGY FOR WELDING PROCESSES AND WELD CONFIGURATIONS blank page blank page ABSTRACT ECCC Recommendations Volume 2 Part IIa presents
Automotive Skills Development Council
 h Automotive Skills Development Council QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR AUTOMOTIVE INDUSTRY Contents OS describe what individuals need to do, know and understand in order to carry out
h Automotive Skills Development Council QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR AUTOMOTIVE INDUSTRY Contents OS describe what individuals need to do, know and understand in order to carry out
Apprenticeship Training Standard. Schedule of Training. Hydraulic/Pneumatic Mechanic. Trade Code: 277Z. Development Date: 2000
 Apprenticeship Training Standard Schedule of Training Hydraulic/Pneumatic Mechanic Trade Code: 277Z Development Date: 2000 This document is the property of the apprentice named inside and represents the
Apprenticeship Training Standard Schedule of Training Hydraulic/Pneumatic Mechanic Trade Code: 277Z Development Date: 2000 This document is the property of the apprentice named inside and represents the
SPECIFICATION FOR PIPEWORK WELDING, INSPECTION, SUPPORTING AND TESTING
 SPECIFICATION FOR PIPEWORK WELDING, INSPECTION, SUPPORTING AND TESTING CU11 Page 1 of 111 Contents SECTION 1: SPECIFICATION FOR PIPEWORK WELDING INSPECTION AND TESTING GENERAL CLASSIFICATION OF PIPEWORK
SPECIFICATION FOR PIPEWORK WELDING, INSPECTION, SUPPORTING AND TESTING CU11 Page 1 of 111 Contents SECTION 1: SPECIFICATION FOR PIPEWORK WELDING INSPECTION AND TESTING GENERAL CLASSIFICATION OF PIPEWORK
Automotive Skills Development Council
 h Automotive Skills Development Council QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR AUTOMOTIVE INDUSTRY Contents OS describe what individuals need to do, know and understand in order to carry out
h Automotive Skills Development Council QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR AUTOMOTIVE INDUSTRY Contents OS describe what individuals need to do, know and understand in order to carry out
SPECIFICATION Aluminum Module Frames. Allowed anodization before fabrication for clear frames.
 SPECIFICATION Allowed anodization before fabrication for clear frames. Page 2 of 9 1. SCOPE 1.1. This document provides general requirements for aluminum frames used in the assembly of photovoltaic modules.
SPECIFICATION Allowed anodization before fabrication for clear frames. Page 2 of 9 1. SCOPE 1.1. This document provides general requirements for aluminum frames used in the assembly of photovoltaic modules.
QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR IT-ITeS INDUSTRY. SUB-SECTOR: Software Products. OCCUPATION: Product Development and Delivery
 QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR IT-ITeS INDUSTRY Contents 1. Introduction and Contacts.......P.1 2. Qualifications Pack....P.2 3. Glossary of Key Terms.......P.3 4. NOS Units...P.5 OS
QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR IT-ITeS INDUSTRY Contents 1. Introduction and Contacts.......P.1 2. Qualifications Pack....P.2 3. Glossary of Key Terms.......P.3 4. NOS Units...P.5 OS
Contents. QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR IT-ITeS INDUSTRY. Introduction. Qualifications Pack-Software Developer
 QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR IT-ITeS INDUSTRY Contents 1. Introduction and Contacts.......P.1 2. Qualifications Pack....P.2 3. Glossary of Key Terms.......P.3 4. NOS Units...P.5 OS
QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR IT-ITeS INDUSTRY Contents 1. Introduction and Contacts.......P.1 2. Qualifications Pack....P.2 3. Glossary of Key Terms.......P.3 4. NOS Units...P.5 OS
Conceptual Design of Buildings (Course unit code 1C2)
 (Course unit code 1C2) Module C Design of Steel Members J.P. Jaspart (University of Liège) 520121-1-2011-1-CZ-ERA MUNDUS-EMMC Bolts are the main type of fasteners used in steel joints. The main geometrical
(Course unit code 1C2) Module C Design of Steel Members J.P. Jaspart (University of Liège) 520121-1-2011-1-CZ-ERA MUNDUS-EMMC Bolts are the main type of fasteners used in steel joints. The main geometrical
Welding & Fabrication Industry Certification Programs
 FALL 2013 Welding & Fabrication Industry Certification Programs Co-Sponsored by: Rochester Arc + Flame Center 125 Fedex Way, Rochester, NY 14624 www.rocafc.com Welding Industry Opportunities Welders are
FALL 2013 Welding & Fabrication Industry Certification Programs Co-Sponsored by: Rochester Arc + Flame Center 125 Fedex Way, Rochester, NY 14624 www.rocafc.com Welding Industry Opportunities Welders are
FIELD WELDER QUALIFICATION PROCESS
 FIELD WELDER QUALIFICATION PROCESS Office of Structures Metals Engineering Unit April 2007 Amended October 2008 Table of Contents Page Number Description 1 Introduction 2-6 Qualification Tests Requirements
FIELD WELDER QUALIFICATION PROCESS Office of Structures Metals Engineering Unit April 2007 Amended October 2008 Table of Contents Page Number Description 1 Introduction 2-6 Qualification Tests Requirements
Problems in Welding of High Strength Aluminium Alloys
 Singapore Welding Society Newsletter, September 1999 Problems in Welding of High Strength Aluminium Alloys Wei Zhou Nanyang Technological University, Singapore E-mail: WZhou@Cantab.Net Pure aluminium has
Singapore Welding Society Newsletter, September 1999 Problems in Welding of High Strength Aluminium Alloys Wei Zhou Nanyang Technological University, Singapore E-mail: WZhou@Cantab.Net Pure aluminium has
QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR IT-ITeS INDUSTRY. SUB-SECTOR: Business Process Management. ITES)ces Helpdesk Attendant
 QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR IT-ITeS INDUSTRY OS describe what individuals need to do, know and understand in order to carry out a particular job role or function OS are performance
QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR IT-ITeS INDUSTRY OS describe what individuals need to do, know and understand in order to carry out a particular job role or function OS are performance
Contents. QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR IT-ITeS INDUSTRY. Introduction. Qualifications Pack-Junior Data Associate
 QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR IT-ITeS INDUSTRY Contents 1. Introduction and Contacts.......P.1 2. Qualifications Pack....P.2 3. Glossary of Key Terms.......P.3 4. NOS Units...P.5 OS
QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR IT-ITeS INDUSTRY Contents 1. Introduction and Contacts.......P.1 2. Qualifications Pack....P.2 3. Glossary of Key Terms.......P.3 4. NOS Units...P.5 OS
Level 4 NVQ Extended Diploma in Engineering Leadership (9220-41)
 QUALIFICATION HANDBOOK Level 4 NVQ Extended Diploma in Engineering Leadership (9220-41) Performing Engineering Operations Units January 2013 Version 1.0 Contents 1 Units 5 Unit 202 Unit 203 Producing mechanical
QUALIFICATION HANDBOOK Level 4 NVQ Extended Diploma in Engineering Leadership (9220-41) Performing Engineering Operations Units January 2013 Version 1.0 Contents 1 Units 5 Unit 202 Unit 203 Producing mechanical
Ultrasonic Reference Blocks
 Ultrasonic Reference Blocks Custom and Standard Test Blocks for Nondestructive Testing Introduction 3 IIW Type 1 Calibration Block 4 Miniature Angle Beam (ROMPAS) Calibration Block 4 Distance Calibration
Ultrasonic Reference Blocks Custom and Standard Test Blocks for Nondestructive Testing Introduction 3 IIW Type 1 Calibration Block 4 Miniature Angle Beam (ROMPAS) Calibration Block 4 Distance Calibration
3.3 Welding and welded connections
 3.3 Welding and welded connections Welding is the process of joining two pieces of metal by creating a strong metallurgical bond between them by heating or pressure or both. It is distinguished from other
3.3 Welding and welded connections Welding is the process of joining two pieces of metal by creating a strong metallurgical bond between them by heating or pressure or both. It is distinguished from other
COASTAL BEND COLLEGE WELDING SYLLABUS (Revise 11/13) Intermediate Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW)
 COASTAL BEND COLLEGE WELDING SYLLABUS (Revise 11/13) WLDG 1457: Intermediate Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW) Semester Hours: 4 Textbook: Course Description: Course Learning Outcomes: Supplementary Materials:
COASTAL BEND COLLEGE WELDING SYLLABUS (Revise 11/13) WLDG 1457: Intermediate Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW) Semester Hours: 4 Textbook: Course Description: Course Learning Outcomes: Supplementary Materials:
NDT Procedure for Liquid Penetrant Inspection TRINITY NDT. An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Company
 NDT Procedure for Liquid Penetrant Inspection A Nondestructive testing (NDT) Procedure suitable for General Liquid/Dye Penetrant Inspections. This is a sample LPT procedure and may be required to be modified
NDT Procedure for Liquid Penetrant Inspection A Nondestructive testing (NDT) Procedure suitable for General Liquid/Dye Penetrant Inspections. This is a sample LPT procedure and may be required to be modified
Welding Procedure Guide
 Welding Procedure Guide An easy to follow guide covering the preparation of welding procedure data sheets Copyright 2008 CWB Group - Industry Services Copyright CWB Group - Industry Services Revised September
Welding Procedure Guide An easy to follow guide covering the preparation of welding procedure data sheets Copyright 2008 CWB Group - Industry Services Copyright CWB Group - Industry Services Revised September
BODY OF KNOWLEDGE API-653 ABOVEGROUND STORAGE TANK INSPECTOR CERTIFICATION EXAMINATION November 2015, March 2016 and July 2016 (Replaces October 2013)
 BODY OF KNOWLEDGE API-653 ABOVEGROUND STORAGE TANK INSPECTOR CERTIFICATION EXAMINATION November 2015, March 2016 and July 2016 (Replaces October 2013) API Authorized Aboveground Storage Tank Inspectors
BODY OF KNOWLEDGE API-653 ABOVEGROUND STORAGE TANK INSPECTOR CERTIFICATION EXAMINATION November 2015, March 2016 and July 2016 (Replaces October 2013) API Authorized Aboveground Storage Tank Inspectors
DOCUMENTATION FOR QUALIFICATION SYSTEM
 DOCUMENTATION FOR QUALIFICATION SYSTEM MATERIAL GROUP: PRESSURE EQUIPMENT MAINTENANCE, REPAIR INTERNAL CODE OF MATERIAL GROUP: MM10300 New code according the registration on myhome: MMGV03 CPV CODE: 45259000-7,
DOCUMENTATION FOR QUALIFICATION SYSTEM MATERIAL GROUP: PRESSURE EQUIPMENT MAINTENANCE, REPAIR INTERNAL CODE OF MATERIAL GROUP: MM10300 New code according the registration on myhome: MMGV03 CPV CODE: 45259000-7,
PSAC/SAIT Well Testing Training Program Learning Outcomes/Objectives Level B
 s/objectives Level B CHEM 6014: Properties and Characteristics of Natural Gases Discuss the pertinent properties and uses of natural gases as they occur in gas processing. 1. Describe the physical properties
s/objectives Level B CHEM 6014: Properties and Characteristics of Natural Gases Discuss the pertinent properties and uses of natural gases as they occur in gas processing. 1. Describe the physical properties
QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR LOGISTICS INDUSTRY. SUB-SECTOR: Land Transportation. OCCUPATION: Consignment Tracking Executive
 QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR LOGISTICS INDUSTRY Contents 1. Introduction and Contacts.. P.1 2. Qualifications Pack...P.2 3. OS Units... P.2 4. Glossary of Key Terms..P.3 OS describe
QUALIFICATIONS PACK - OCCUPATIONAL STANDARDS FOR LOGISTICS INDUSTRY Contents 1. Introduction and Contacts.. P.1 2. Qualifications Pack...P.2 3. OS Units... P.2 4. Glossary of Key Terms..P.3 OS describe
WHAT EVERY ENGINEER SHOULD KNOW ABOUT WELDING
 WHAT EVERY ENGINEER SHOULD KNOW ABOUT WELDING From amperage to preheat, there s more to welding procedures than meets the eye By Duane K. Miller, P.E. WITHIN THE WELDING INDUS- TRY, THE TERM WELDING PROCEDURE
WHAT EVERY ENGINEER SHOULD KNOW ABOUT WELDING From amperage to preheat, there s more to welding procedures than meets the eye By Duane K. Miller, P.E. WITHIN THE WELDING INDUS- TRY, THE TERM WELDING PROCEDURE
HOT WORK PERMIT PROCEDURES
 COLUMBIA UNIVERSITY ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH & SAFETY HOT WORK PERMIT PROCEDURES COLUMBIA UNIVERSITY MEDICAL CENTER February 2010 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS A. PURPOSE 3 B. SCOPE 3 C. POLICIES AND PROCEDURES 3-4
COLUMBIA UNIVERSITY ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH & SAFETY HOT WORK PERMIT PROCEDURES COLUMBIA UNIVERSITY MEDICAL CENTER February 2010 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS A. PURPOSE 3 B. SCOPE 3 C. POLICIES AND PROCEDURES 3-4
STATEMENT OF WORK (SOW) On-Call Certified Welding Inspections and Nondestructive Testing
 1.0 INTRODUCTION Colorado Springs Utilities (UTILITIES) is seeking qualified firms to provide verification welding inspection services, nondestructive testing services, and technical reporting to Colorado
1.0 INTRODUCTION Colorado Springs Utilities (UTILITIES) is seeking qualified firms to provide verification welding inspection services, nondestructive testing services, and technical reporting to Colorado
Experimental Study on Non Destructive Testing Techniques (NDTT)
 Experimental Study on Non Destructive Testing Techniques (NDTT) G.Lalitha 1, K.Bala Showry 2 1 G.Lalitha Assistant Prof, Civil Engineering, BVRIT, TS, India 2 Dr.K.Bala Showry Professor, Mechanical Engineering,
Experimental Study on Non Destructive Testing Techniques (NDTT) G.Lalitha 1, K.Bala Showry 2 1 G.Lalitha Assistant Prof, Civil Engineering, BVRIT, TS, India 2 Dr.K.Bala Showry Professor, Mechanical Engineering,
