Improving the Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Tract Infection in family medicine, Systemic review
|
|
|
- Erica Perkins
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Improving the Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Tract Infection in family medicine, Systemic review 1 Rehab Ismail Mohammed Abdullah, 2 Taghreed Ismail Mohammed Abdullah Abstract: Background: Recurrent uncomplicated urinary tract infection (UTI) is a common presentation to family doctors. Thus most improve their techniques of diagnosing and treating this condition in appropriate methods. Objective: to systematically review studies investigating the developed ways and how could be the diagnostic procedures and treatments approaches of Urinary tract infection in primary care more developed to reach the maximum effectiveness. Methodology: We conducting systematic review by searching Observational and experimental studies identified through Medline, Embase, and Cochrane published in any language between 1955 and July MeSH terms for these databases included primary health care, urinary tract infections, and diagnosis and managment. Conclusion: Guidelines regarding the diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up of urinary tract infections (UTIs) in population continue to evolve. Although a somewhat less aggressive approach to evaluation is now recommended, it is important for primary care physicians to appropriately diagnose and treat UTIs in all parts of population Keywords: Diagnosis and Treatment, diagnostic procedures, aggressive approach. 1. INTRODUCTION Acute urinary tract infection (UTI) is one of the most common acute bacterial infections in primary care especially among women. (1,2) The prevalence is highly dependent on age and gender (figure1). (3) Conventional diagnosis relies on identifying a potential urinary pathogen from culture of a midstream specimen of urine (MSU) in a symptomatic patient. The standard for reporting UTI in most previous research and clinical practice was 105 colony-forming units per ml (cfu/ml). (4) The gold standard for the diagnosis of a urinary tract infection is the detection of the pathogen in the presence of clinical symptoms. The pathogen is detected and identified by urine culture (using midstream urine). This also allows an estimate of the level of the bacteriuria. However, the minimum level of bacteriuria demonstrating an infection of the urinary tract has not been defined in scientific literature or standardized by microbiological laboratories. Many laboratories define 10 5 colony forming units (cfu)/ml urine as the threshold. However, this threshold misses many relevant infections. There are therefore other recommendations (5,6) that recommend the diagnosis of UTI from a count of 10 3 cfu/ml, depending on the types of bacteria detected. Dipsticks are the most widely used simple near patient tests in primary care. (7 10) Summary data are available from studies that assessed nitrite and leucocyte esterase separately, but primary data are needed to assess the independent predictive value of all dipstick results. (11) A systematic review suggested that the evidence base for dipstick use in primary care is poor, due to the paucity of studies and spectrum bias. (10,12) Evidence from emergency settings suggests that dipsticks may be particularly helpful where clinical assessment indicates a moderate probability of infection. (13) Other studies from primary care have not assessed the independent value of dipstick results (hence over-complicating clinical decision rules), and/or mixed clinical and dipstick variables, and/or had low power. (8,10,14,15) Page 394
2 Figure 1: Prevalence of infections of the urinary tract in primary care (authors illustration; data taken from (3) The guideline recommendations for the antibiotic treatment of infections of the urinary tract are often not implemented in practice. National and international recommendations warn against the broad and uncritical use of fluoroquinolones for uncomplicated infections. (5) The numbers of prescriptions show how widely these recommendations are ignored in practice. These prescription practices have led to increasing resistance and endanger the use of fluoroquinolones in severe infections (16). 2. OBJECTIVES Prevalence of resistance to commonly prescribed antibiotics in primary care for patients with urinary tract infections is high, particularly in some developing countries. This could render some antibiotics ineffective as first line treatments for urinary tract infection. Routine use of antibiotics in primary care contributes to antimicrobial resistance, which can persist for up to six months after treatment and due to the lack of diagnostic guidelines in some countries. therefore this study aimed to systematically review studies investigating the developed ways and how could be the diagnostic procedures and treatments approaches of Urinary tract infection in primary care more developed to reach the maximum effectiveness. Design: Systematic review study Data Sources: 3. METHODOLOGY We conducting systematic review by searching Observational and experimental studies identified through Medline, Embase, and Cochrane published in any language between 1955 and July MeSH terms for these databases included primary health care, urinary tract infections, and diagnosis and managment. MeSH terms were combined with text word searches that included antibiotic(s), primary care, family practice, ambulatory care, community, UTI, and urinary bacteria. We screened reference lists of selected key papers and contacted authors who appeared multiple times to request details of further published and unpublished work. Diagnosis UTI in General primary care: 4. RESULTS It is of concern that GPs diagnose UTIs in children without checking a urine sample at all, and alarming that almost two thirds do so at weekends; a trend reported previously. (17) It needs to be remembered that, in terms of routine laboratory services, a weekend constitutes nearly 40% of the week. Symptoms are often not diagnostic of UTI in children; febrile children may have a false-positive diagnosis because of dysuria from a concentrated urine and have unnecessary imaging investigations, while children with a UTI may have no dysuria, a false-negative diagnosis and develop avoidable scarring, hypertension or renal failure. a sin study by Vernon et al, 1997 (18), stated that Despite requiring more effort and more help from community and local paediatric staff, more GPs collect satisfactory urine samples from infants than from older children. This probably reflects their awareness of their greater risk of reflux nephropathy. It must be remembered that, even with satisfactory methods, there is a chance of contamination, which could appear as a false-positive result, except Page 395
3 perhaps from suprapubic puncture, which is impractical in general practice. approximately three quarters of GPs always use urine culture as their primary diagnostic test, and up to nearly 90% sometimes do; this figure falls by about half at weekends (Table 1). (18) as in the same study by Vernon et al, A small number of GPs examine urine under a microscope for bacteria to test for UTI and do so equally on weekdays and weekends; only infected samples were cultured. During the week, up to one third of GPs test urine samples with dipsticks, and % use this as their sole diagnostic test. At weekends, when fewer GPs culture urine routinely, between 9.2% and 19.1% use dipsticks as their sole diagnostic test. Table 1: Primary methods of urine analysis used by GPs to diagnose UTIs, from Vernon et al.1997 (18) Clinical variables: According to study by Little et al, 2006, (34) four variables independently predicted UTI (Table 2): cloudy urine, offensive smell, and dysuria and/or nocturia of moderate severity. Severity was an important aspect of prediction: symptoms rated as slight problems were much less predictive. A cut off of 2 or more of a score based on the sum of the rounded logistic coefficients (a clinical decision rule based on 2 out of 4 features) had sensitivity 65% and specificity 69% (see Tables 3). Each end of the score could be used to improve performance by varying the cut-off point. Thus the NPV was 71% for none of the four clinical features, and the PPV 84% for three or more features. (34) Table 2: Clinical predictors of laboratory diagnosis of urinary tract infection according to European guidelines. Urine cloudy on examination Urine has offensive smell on examination dysuria nocturia daytime urgency haematuria UTI (n = 254) n(%) No UTI (n = 154) n(%) Crude odds ratio (95% CI) Adjusted odds ratio b (95% CI) P- value 117 (46) 32 (21) 3.26 (2.05 to 5.16) 2.32 (1.40 to 3.85) (24) 16 (10) 2.79 (1.54 to 5.03) 2.02 (1.05 to 3.90) (70) 66 (43) 3.18 (2.10 to 4.83) 2.76 (1.78 to 4.28) < (54) 56 (36) 2.05 (1.36 to 3.09) 1.81 (1.16 to 2.80) (72) 94 (61) 1.71 (1.12 to 2.62) 1.37 (0.85 to 2.22) (62) 77 (50) 1.65 (1.10 to 2.47) 1.01 (0.63 to 1.61) (23) 18 (12) 2.29 (1.29 to 4.05) 1.71 (0.93 to 3.16) a 10 3 colony-forming units per ml. Page 396
4 b Mutually adjusted for all significant predictors. Other variables tested but not significant in either univariate or multivariate analysis: history of backache, fever, feeling unwell, abdominal pain, prior duration, daytime or nighttime frequency (number of times), renal angle tenderness, lower abdominal tenderness, previous history of UTI. UTI = urinary tract infection. Table3: Clinical rule performance in predicting laboratory diagnosis of urinary tract infection (34) Test Standard Clinical rule a Clinical rule + b Total UTI UTI Total a One or less of the following: moderately severe dysuria, moderately severe nocturia, urine smell offensive, urine cloudy or nitrite, or leucocyte and blood. b Two or more of the following: moderately severe dysuria, moderately severe nocturia, urine smell offensive, urine cloudy or nitrite, or leucocyte and blood. Treatment of UTI in primary care and some improving strategies: The decision to prescribe antibiotics is one of the most common treatment decisions faced by frontline primary care clinicians daily, and urinary tract infection (UTI) is one of the most common bacterial infections encountered. (19) Although antimicrobial treatment for UTI is accepted in clinical practice, antibiotic resistance in urinary bacteria is increasing, (20) with rates cited in the literature of between 20% and 40% to trimethoprim and amoxicillin respectively. (21) Bacteria are adept at side-stepping human intervention (for example, antibiotics and vaccines) and are developing resistance to antibiotics faster than the pharmaceutical industry is developing new ones: only two new classes of antibiotics have been developed in the last 30 years. (22) These problems highlight the need for high quality evidence to help primary care clinicians optimise the diagnosis and management of UTI. Fortunately, a plethora of high quality, clinically valuable, primary care research papers have been published in 2010, including four in the BMJ journal ( 23 26) and two in British Journal of General Practice (BJGP). (27,28) study by Vellinga and colleagues they found that a previous measure of resistance to co-amoxiclav, ampicillin, ciprofloxacin, and trimethoprim remains predictive of further resistance at 3 and 12 months. The long duration of effects, although not as strong as at 3 months, may surprise many clinicians, but is not an isolated finding. A recently published systematic review (29) reports a similar trend of effects in three studies (21,30,31) that, when pooled, show that the relationship between antibiotics prescribed over a 12-month period and bacterial resistance cannot be explained by chance (odds ratio = 1.33, 95% CI = 1.15 to 1.53). Two Cochrane systematic reviews, published in 2003 and 2004, summarised the evidence from randomised controlled trials for the efficacy and safety of different antibiotic regimens for the treatment of acute UTI in children. (32,33) The first (32) reviewed RCTs comparing 2 4 days of antibiotic treatment with 7 14 day courses in children without acute pyelonephritis (diagnosed on the basis of absence of fever of 38 C or above). The authors concluded that a 2 4 day course of oral antibiotics appears to be as effective as 7 14 days in eradicating acute lower UTI. The second review (33) identified 18 randomised controlled trials involving over 2600 children with pyelonephritis, treated either in inpatient or outpatient settings. Outcomes studied included clearance of bacteriuria, resolution of symptoms, abnormalities on DMSA scan, and adverse effects. 5. CONCLUSION Guidelines regarding the diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up of urinary tract infections (UTIs) in population continue to evolve. Although a somewhat less aggressive approach to evaluation is now recommended, it is important for primary care physicians to appropriately diagnose and treat UTIs in all parts of population. Some underlying etiologies, including renal scarring and renal disease, can lead to considerable morbidity later in life. Page 397
5 REFERENCES [1] Foxman B. Epidemiology of urinary tract infections: Incidence, morbidity, and economic costs. Am J Med. 2002;113(Suppl 1):5s 13s. [2] Office of Population Census and Survey. Morbidity statistics from general practice: Fourth national study London: HMSO; [3] Guido Schmiemann, Eberhardt Kniehl, Klaus Gebhardt, Martha M Matejczyk,Eva Hummers-Pradier. The Diagnosis of Urinary Tract Infection, A Systematic Review. Dtsch Arztebl Int May; 107(21): [4] Bent S, Nallamothu BK, Simel DL, et al. Does this woman have an acute uncomplicated urinary tract infection? JAMA. 2002;287(20): [5] Schmiemann G, Gebhardt K, Matejczyk M, Hummers-Pradier E. DEGAM-Leitlinie Nr 1: Brennen beim Wasserlassen - Update Düsseldorf: Omikron publishing; [6] EAU (European Association of Urology) Guidelines on Urological Infections. European Association of Urology. /guidelines/online/ [7] Bailey BL., Jr Urinalysis predictive of urine culture results. J Fam Pract. 1995;40(1): [8] Ditchburn RK, Ditchburn JS. A study of microscopical and chemical tests for the rapid diagnosis of urinary tract infections in general practice. Br J Gen Pract. 1990;40(339): [9] Schulz HJ, McCaffrey LA, Keys TF, Nobrega FT. Acute cystitis: a prospective study of laboratory tests and duration of therapy. Mayo Clin Proc. 1984;59(6): [10] Winkens RA, Leffers P, Trienekens TA, Stobberingh EE. The validity of urine examination for urinary tract infections in daily practice. Fam Pract. 1995;12(3): [11] Hurlburt TA, III, Littenberg B. The diagnostic accuracy of rapid dipstick tests to predict urinary tract infection. Am J Clin Pathol. 1991;96(5): [12] Hobbs FDR, Delaney BC, Fitzmaurice DA, et al. A review of near patient testing in primary care. Health Technol Assess (5): [13] Sultana RW, Zalstein S, Cameron P, Campbell D. Dipstick urinalysis and the accuracy of the clinical diagnosis of urinary tract infection. J Emerg Med. 2001;20(1): [14] Dobbs FF, Fleming DM. A simple scoring system for evaluating symptoms, history and urine dipstick testing in the diagnosis of urinary tract infection. J R Coll Gen Pract. 1987;37(296): [15] McIsaac WJ, Low DE, Biringer A, et al. The impact of empirical management of acute cystitis on unnecessary antibiotic use. Arch Intern Med. 2002;162(5): [16] Samenvattingskaart NHG-Standaard. URINEWEGINFECTIES NHG-STANDAARD. /104/standaarden/ M05/start.html. [17] Jadresic L, Cartwright K, Cowie N, et al. Investigation of urinary tract infection in childhood. BMJ 1993; 307: [18] S Vernon, C K Foo, and M G Coulthard. How general practitioners manage children with urinary tract infection: an audit in the former Northern Region. Br J Gen Pract May; 47(418): [19] McCormick A, Fleming D, Charlton J. Morbidity statistics from general practice fourth national study London: HMSO; [20] Department for Environment FaRA. Overview of antimicrobial usage and bacterial resistance in selected human and animal pathogens in the UK: Department of Health, [21] Hillier S, Roberts Z, Dunstan F, et al. Prior antibiotics and risk of antibiotic-resistant community-acquired urinary tract infection: a case-control study. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2007;60(1): Page 398
6 [22] Infectious Diseases Society of America. Bad bugs, no drugs: as antibiotic discovery stagnate and a public health crisis brews. Arlington, VA, US: Infectious Diseases Society of America; [23] Little P, Moore MV, Turner S, et al. Effectiveness of five different approaches in management of urinary tract infection: randomised controlled trial. BMJ. 2010;340:c199. [24] Turner D, Little P, Raftery J, et al. Cost effectiveness of management strategies for urinary tract infections: results from randomised controlled trial. BMJ. 2010;340:c346. [25] Leydon GM, Turner S, Smith H, Little P, on behalf of the UTIS team Women's views about management and cause of urinary tract infection: qualitative interview study. BMJ. 2010;340:c279. [26] Little P, Merriman R, Turner S, et al. Presentation, pattern, and natural course of severe symptoms, and role of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance among patients presenting with suspected uncomplicated urinary tract infection in primary care: observational study. BMJ. 2010;340 b5633. [27] Vellinga A, Cormican M, Hanahoe B, Murphy AW. Predictive value of antimicrobial susceptibility from previous urinary tract infection in the treatment of re-infection. Br J Gen Pract. 2010;60: [28] Little P, Turner S, Rumsby K, et al. Validating the prediction of lower urinary tract infection in primary care: sensitivity and specificity of urinary dipsticks and clinical scores in women. Br J Gen Pract.2010;60: [29] Costelloe C, Metcalfe C, Lovering A, et al. Effect of antibiotic prescribing in primary care on antimicrobial resistance in individual patients: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2010;340:c2096. [30] Donnan PT, Wei L, Steinke DT, et al. Presence of bacteriuria caused by trimethoprim resistant bacteria in patients prescribed antibiotics: multilevel model with practice and individual patient data. BMJ.2004;328(7451) [31] Hay AD, Thomas M, Montgomery A, et al. The relationship between primary care antibiotic prescribing and bacterial resistance in adults in the community: a controlled observational study using individual patient data. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2005;56(1): [32] Michael M, Hodson EM, Craig JC, et al. Short versus standard duration oral antibiotic therapy for acute urinary tract infection in children. The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2003, issue 1. [33] Bloomfield P, Hodson EM, Craig JC. Antibiotics for acute pyelonephritis in children. The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2005, issue 1. [34] Little P, Turner S, Rumsby K, Warner G, Moore M, Lowes A, et al. Developing clinical rules to predict urinary tract infection in primary care settings: sensitivity and specificity of near patient tests (dipsticks) and clinical scores. Br J Gen Pract 2006;529: Page 399
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections Overview A urine culture must ALWAYS be interpreted in the context of the urinalysis and patient symptoms. If a patient has no signs of infection on urinalysis, no symptoms of
Urinary Tract Infections Overview A urine culture must ALWAYS be interpreted in the context of the urinalysis and patient symptoms. If a patient has no signs of infection on urinalysis, no symptoms of
Protocol for Macroscopic and Microscopic Urinalysis and Investigation of Urinary Tract Infections
 Protocol for Macroscopic and Microscopic Urinalysis and Investigation of Urinary Tract Infections Reprinted 2004 Scope The purpose of this protocol is to avoid unnecessary testing in routine cases while
Protocol for Macroscopic and Microscopic Urinalysis and Investigation of Urinary Tract Infections Reprinted 2004 Scope The purpose of this protocol is to avoid unnecessary testing in routine cases while
UTI in children. Quick reference guide. Issue date: August 2007. Urinary tract infection in children: diagnosis, treatment and long-term management
 Issue date: August 2007 UTI in children Urinary tract infection in children: diagnosis, treatment and long-term management Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Women s and Children s Health
Issue date: August 2007 UTI in children Urinary tract infection in children: diagnosis, treatment and long-term management Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for Women s and Children s Health
Urinary Tract Infection Update Kim Gibson, MD Joseph Toscano, MD
 82 Urinary Tract Infection Update Kim Gibson, MD Joseph Toscano, MD Abstract Urinary tract infections are commonly treated in urgent care practice. Clinicians need to be aware of the advantages and limitations
82 Urinary Tract Infection Update Kim Gibson, MD Joseph Toscano, MD Abstract Urinary tract infections are commonly treated in urgent care practice. Clinicians need to be aware of the advantages and limitations
Antibiotic Prophylaxis for Short-term Catheter Bladder Drainage in adults. A Systematic Review (Cochrane database August 2013)
 Antibiotic Prophylaxis for Short-term Catheter Bladder Drainage in adults A Systematic Review (Cochrane database August 2013) Gail Lusardi, Senior Lecturer Dr Allyson Lipp, Principal Lecturer, Dr Chris
Antibiotic Prophylaxis for Short-term Catheter Bladder Drainage in adults A Systematic Review (Cochrane database August 2013) Gail Lusardi, Senior Lecturer Dr Allyson Lipp, Principal Lecturer, Dr Chris
A Practical Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment of Infection in the Outpatient Setting Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections
 A Practical Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment of Infection in the Outpatient Setting Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections By Gary R. Skankey, MD, FACP, Infectious Disease, Las Vegas, NV Sponsored
A Practical Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment of Infection in the Outpatient Setting Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections By Gary R. Skankey, MD, FACP, Infectious Disease, Las Vegas, NV Sponsored
The American Academy of Pediatrics
 Revised AAP Guideline on UTI in Febrile Infants and Young Children KENNETH B. ROBERTS, MD, University of rth Carolina School of Medicine, Chapel Hill, rth Carolina In 2011, the American Academy of Pediatrics
Revised AAP Guideline on UTI in Febrile Infants and Young Children KENNETH B. ROBERTS, MD, University of rth Carolina School of Medicine, Chapel Hill, rth Carolina In 2011, the American Academy of Pediatrics
PRIORITY RESEARCH TOPICS
 PRIORITY RESEARCH TOPICS Understanding all the issues associated with antimicrobial resistance is probably impossible, but it is clear that there are a number of key issues about which we need more information.
PRIORITY RESEARCH TOPICS Understanding all the issues associated with antimicrobial resistance is probably impossible, but it is clear that there are a number of key issues about which we need more information.
Do general practitioners prescribe more antimicrobials when the weekend comes?
 DOI 10.1186/s40064-015-1505-6 RESEARCH Open Access Do general practitioners prescribe more antimicrobials when the weekend comes? Meera Tandan 1*, Sinead Duane 1 and Akke Vellinga 1,2 Abstract Inappropriate
DOI 10.1186/s40064-015-1505-6 RESEARCH Open Access Do general practitioners prescribe more antimicrobials when the weekend comes? Meera Tandan 1*, Sinead Duane 1 and Akke Vellinga 1,2 Abstract Inappropriate
Etiology and treatment of chronic bacterial prostatitis the Croatian experience
 Etiology and treatment of chronic bacterial prostatitis the Croatian experience Višnja Škerk University Hospital for Infectious Diseases "Dr. Fran Mihaljevic" Zagreb Croatia Milano, Malpensa, 14 Nov 2008
Etiology and treatment of chronic bacterial prostatitis the Croatian experience Višnja Škerk University Hospital for Infectious Diseases "Dr. Fran Mihaljevic" Zagreb Croatia Milano, Malpensa, 14 Nov 2008
Could bacteriuria hold the key to understanding urgency/ urge incontinence
 Could bacteriuria hold the key to understanding urgency/ urge incontinence 8:15 to 8:20min: Prof Kate Moore, introduction and welcome 8:20-8:35: Dr Colin Walsh 8:35-8:45: Discussion 8:45-9.00: Dr Kylie
Could bacteriuria hold the key to understanding urgency/ urge incontinence 8:15 to 8:20min: Prof Kate Moore, introduction and welcome 8:20-8:35: Dr Colin Walsh 8:35-8:45: Discussion 8:45-9.00: Dr Kylie
Urinary Tract Infection among Clean-Room Workers
 J Occup Health 2002; 44: 329 333 Journal of Occupational Health Urinary Tract Infection among Clean-Room Workers Jian-Nan WANG 1, Shih-Bin SU 2, 3 and How-Ran GUO 3 1 Department of Family Medicine, Chie-Mei
J Occup Health 2002; 44: 329 333 Journal of Occupational Health Urinary Tract Infection among Clean-Room Workers Jian-Nan WANG 1, Shih-Bin SU 2, 3 and How-Ran GUO 3 1 Department of Family Medicine, Chie-Mei
NICE Pathways bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic.
 Initial assessment and investigation of urinary incontinence bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used
Initial assessment and investigation of urinary incontinence bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used
A PRINTED copy of this guideline may not be the most recent version. The OFFICIAL version is located on IHNET at the Policies & Procedures Home Page
 A PRINTED copy of this guideline may not be the most recent version. The OFFICIAL version is located on IHNET at the Policies & Procedures Home Page IX0200: Prevention & Control of Catheter Associated
A PRINTED copy of this guideline may not be the most recent version. The OFFICIAL version is located on IHNET at the Policies & Procedures Home Page IX0200: Prevention & Control of Catheter Associated
Drug Utilization and Evaluation of Cephalosporin s At Tertiary Care Teaching Hospital, Bangalore
 Research Article Drug Utilization and Evaluation of Cephalosporin s At Tertiary Care Teaching Hospital, Bangalore HS. Shekar 1*, HR. Chandrashekhar 2, M. Govindaraju 3, P. Venugopalreddy 1, Chikkalingiah
Research Article Drug Utilization and Evaluation of Cephalosporin s At Tertiary Care Teaching Hospital, Bangalore HS. Shekar 1*, HR. Chandrashekhar 2, M. Govindaraju 3, P. Venugopalreddy 1, Chikkalingiah
ANTIBIOTICS FROM HEAD TO TOE: PART 5 - URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS LAUREN HYNICKA, PHARM.D.
 ANTIBIOTICS FROM HEAD TO TOE: PART 5 - URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS LAUREN HYNICKA, PHARM.D. ANTIBIOTICS FROM HEAD TO TOE: PART 5 - URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS ACTIVITY DESCRIPTION Antibiotic use in the safest
ANTIBIOTICS FROM HEAD TO TOE: PART 5 - URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS LAUREN HYNICKA, PHARM.D. ANTIBIOTICS FROM HEAD TO TOE: PART 5 - URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS ACTIVITY DESCRIPTION Antibiotic use in the safest
Non-response bias in a lifestyle survey
 Journal of Public Health Medicine Vol. 19, No. 2, pp. 203-207 Printed in Great Britain Non-response bias in a lifestyle survey Anthony Hill, Julian Roberts, Paul Ewings and David Gunnell Summary Background
Journal of Public Health Medicine Vol. 19, No. 2, pp. 203-207 Printed in Great Britain Non-response bias in a lifestyle survey Anthony Hill, Julian Roberts, Paul Ewings and David Gunnell Summary Background
Childhood Urinary Tract Infections
 Childhood Urinary Tract Infections What is a UTI? Urinary tract infection (UTI) is one of the most common infections in childhood. It can cause distress to the child, concerns to the parents, and may
Childhood Urinary Tract Infections What is a UTI? Urinary tract infection (UTI) is one of the most common infections in childhood. It can cause distress to the child, concerns to the parents, and may
10. Treatment of peritoneal dialysis associated fungal peritonitis
 10. Treatment of peritoneal dialysis associated fungal peritonitis Date written: February 2003 Final submission: July 2004 Guidelines (Include recommendations based on level I or II evidence) The use of
10. Treatment of peritoneal dialysis associated fungal peritonitis Date written: February 2003 Final submission: July 2004 Guidelines (Include recommendations based on level I or II evidence) The use of
Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Event
 Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection () Event Introduction: Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are tied with pneumonia as the second most common type of healthcare-associated infection, second only
Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection () Event Introduction: Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are tied with pneumonia as the second most common type of healthcare-associated infection, second only
POAC CLINICAL GUIDELINE
 POAC CLINICAL GUIDELINE Acute Pylonephritis DIAGNOSIS COMPLICATED PYELONEPHRITIS EXCLUSION CRITERIA: Male Known or suspected renal impairment (egfr < 60) Abnormality of renal tract Known or suspected renal
POAC CLINICAL GUIDELINE Acute Pylonephritis DIAGNOSIS COMPLICATED PYELONEPHRITIS EXCLUSION CRITERIA: Male Known or suspected renal impairment (egfr < 60) Abnormality of renal tract Known or suspected renal
Don t Go With The Flow! Control and Management of UTIs in the Elderly
 Don t Go With The Flow! Control and Management of UTIs in the Elderly Acknowledgements Central West Infection Control Network Toronto Central Infection Control Network Erie St Clair Infection Control Network
Don t Go With The Flow! Control and Management of UTIs in the Elderly Acknowledgements Central West Infection Control Network Toronto Central Infection Control Network Erie St Clair Infection Control Network
A Summary of the Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of. Urinary Tract Infections in Long Term Care
 A Summary of the Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Urinary Tract Infections in Long Term Care Exclusions Community acquired UTIs UTIs in acute care Prevention Limit use of catheters Ensure
A Summary of the Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Urinary Tract Infections in Long Term Care Exclusions Community acquired UTIs UTIs in acute care Prevention Limit use of catheters Ensure
Ceftriaxone Therapy Vs. Ciprofloxacin In Treatment Of Typhoid Fever In Adult Patients.
 Dec QMJ VOL.5 No.8 Ceftriaxone Therapy Vs. Ciprofloxacin In Treatment Of Typhoid Fever In Adult Patients. Radhi F.Alshaibani* الخلاصھ لا زالت حمى التایفوید سببا مھما من اسباب الامراض وفقدان ساعات العمل
Dec QMJ VOL.5 No.8 Ceftriaxone Therapy Vs. Ciprofloxacin In Treatment Of Typhoid Fever In Adult Patients. Radhi F.Alshaibani* الخلاصھ لا زالت حمى التایفوید سببا مھما من اسباب الامراض وفقدان ساعات العمل
Title: Microbiology Urine Screening Effective date: 05/08/2013. Summary of Significant Changes at this Revision
 COPY Summary of Significant Changes at this Revision Add maintenance procedure and not doing dipstick from urine collected into boric acid Purpose and Scope Items Required The purpose of this process is
COPY Summary of Significant Changes at this Revision Add maintenance procedure and not doing dipstick from urine collected into boric acid Purpose and Scope Items Required The purpose of this process is
Does This Woman Have an Acute Uncomplicated Urinary Tract Infection?
 THE RATIONAL CLINICAL EXAMINATION CLINICIAN S CORNER Does This Woman Have an Acute Uncomplicated Urinary Tract Infection? Stephen Bent, MD Brahmajee K. Nallamothu, MD, MPH David L. Simel, MD, MHS Stephan
THE RATIONAL CLINICAL EXAMINATION CLINICIAN S CORNER Does This Woman Have an Acute Uncomplicated Urinary Tract Infection? Stephen Bent, MD Brahmajee K. Nallamothu, MD, MPH David L. Simel, MD, MHS Stephan
Beryl Navti SEPT Pharmacy Department. 24/06/2013 Beryl Navti, Clinical Pharmacist, SEPT
 URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS Beryl Navti SEPT Pharmacy Department The Genitourinary System The organs system of the reproductive organs and urinary system Grouped dtogether th because of their proximity it
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS Beryl Navti SEPT Pharmacy Department The Genitourinary System The organs system of the reproductive organs and urinary system Grouped dtogether th because of their proximity it
Urinary Tract Infection
 Guidelines for Clinical Care Ambulatory Urinary Tract Infection Guideline Team Team Leader Steven E Gradwohl, MD General Medicine Team Members Catherine M Bettcher, MD Family Medicine Carol E Chenoweth,
Guidelines for Clinical Care Ambulatory Urinary Tract Infection Guideline Team Team Leader Steven E Gradwohl, MD General Medicine Team Members Catherine M Bettcher, MD Family Medicine Carol E Chenoweth,
URINARY TRACT INFECTION IN CHILDREN. Yap Hui Kim, Belinda Murugasu
 URINARY TRACT INFECTION IN CHILDREN Yap Hui Kim, Belinda Murugasu Urinary tract infection (UTI) is a common problem in childhood and the primary health care practitioner is usually the frontline in diagnosis
URINARY TRACT INFECTION IN CHILDREN Yap Hui Kim, Belinda Murugasu Urinary tract infection (UTI) is a common problem in childhood and the primary health care practitioner is usually the frontline in diagnosis
Welcome and Instructions
 Welcome and Instructions For audio, join by telephone at 877-594-8353, participant code: 56350822 Your line is OPEN. Please do not use the hold feature on your phone but do mute your line by dialing *6.
Welcome and Instructions For audio, join by telephone at 877-594-8353, participant code: 56350822 Your line is OPEN. Please do not use the hold feature on your phone but do mute your line by dialing *6.
THE KIDNEY. Bulb of penis Abdominal aorta Scrotum Adrenal gland Inferior vena cava Urethra Corona glandis. Kidney. Glans penis Testicular vein
 29 THE KIDNEY 9. Recurrent urinary tract infections Recurrent urinary tract infections The urinary tract consists of the urethra, the bladder, the ureters, the kidneys and in men the prostate gland. An
29 THE KIDNEY 9. Recurrent urinary tract infections Recurrent urinary tract infections The urinary tract consists of the urethra, the bladder, the ureters, the kidneys and in men the prostate gland. An
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN YOUNG WOMEN
 URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN YOUNG WOMEN Reviewed by Finnish Centre for Health Promotion Publisher: Ylioppilaiden terveydenhoitosäätiö Töölönkatu 37 A 00260 Helsinki Orders: julkaisutilaukset@yths.fi Author:
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN YOUNG WOMEN Reviewed by Finnish Centre for Health Promotion Publisher: Ylioppilaiden terveydenhoitosäätiö Töölönkatu 37 A 00260 Helsinki Orders: julkaisutilaukset@yths.fi Author:
Patient with: 3 or more UTI in 6 months 4 or more UTI in 12 months
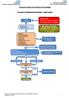 Recurrent UTI Management Pathway adult females Initial assessment Assessment questionnaire questionnaire bladder scan dipstick dipstick of of urine urine pregnancy neurological disease long - term catheters
Recurrent UTI Management Pathway adult females Initial assessment Assessment questionnaire questionnaire bladder scan dipstick dipstick of of urine urine pregnancy neurological disease long - term catheters
Original Research Paper
 Original Research Paper Sore throat diagnosis and management in a general practice after-hours service Marjan Kljakovic is a senior lecturer, department of general practice, Wellington School of Medicine
Original Research Paper Sore throat diagnosis and management in a general practice after-hours service Marjan Kljakovic is a senior lecturer, department of general practice, Wellington School of Medicine
Implementing the Long-Term Care UTI Toolkit Wisconsin Coalition on HealthCare Association Infection in Long Term Care
 Implementing the Long-Term Care UTI Toolkit Wisconsin Coalition on HealthCare Association Infection in Long Term Care MetaStar Health Care Quality Symposium: The Value of Better Health Paula Kock RN paulak@parkmanorwi.com
Implementing the Long-Term Care UTI Toolkit Wisconsin Coalition on HealthCare Association Infection in Long Term Care MetaStar Health Care Quality Symposium: The Value of Better Health Paula Kock RN paulak@parkmanorwi.com
CAGE. AUDIT-C and the Full AUDIT
 CAGE In the past have you ever: C tried to Cut down or Change your pattern of drinking or drug use? A been Annoyed or Angry because of others concern about your drinking or drug use? G felt Guilty about
CAGE In the past have you ever: C tried to Cut down or Change your pattern of drinking or drug use? A been Annoyed or Angry because of others concern about your drinking or drug use? G felt Guilty about
How To Find Out If A Diabetic Woman Has A Urinary Tract Infection
 Mindanao Journal of Science and Technology Vol. 12 (2014) 171-178 Difference on the Incidence of Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) between Diabetic and Non-diabetic Women Admitted in Metro Cebu, Philippines
Mindanao Journal of Science and Technology Vol. 12 (2014) 171-178 Difference on the Incidence of Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) between Diabetic and Non-diabetic Women Admitted in Metro Cebu, Philippines
Riesa Gusewelle, MNSc, RN, APRN, GNP-BC. OBJECTIVES Identify early warning signs of urinary tract
 Detection, Early Management & Prevention, of Urinary Tract Infections in Older Adults Riesa Gusewelle, MNSc, RN, APRN, GNP-BC OBJECTIVES Identify early warning signs of urinary tract infections (UTIs)
Detection, Early Management & Prevention, of Urinary Tract Infections in Older Adults Riesa Gusewelle, MNSc, RN, APRN, GNP-BC OBJECTIVES Identify early warning signs of urinary tract infections (UTIs)
"Statistical methods are objective methods by which group trends are abstracted from observations on many separate individuals." 1
 BASIC STATISTICAL THEORY / 3 CHAPTER ONE BASIC STATISTICAL THEORY "Statistical methods are objective methods by which group trends are abstracted from observations on many separate individuals." 1 Medicine
BASIC STATISTICAL THEORY / 3 CHAPTER ONE BASIC STATISTICAL THEORY "Statistical methods are objective methods by which group trends are abstracted from observations on many separate individuals." 1 Medicine
Diagnostic Studies Dr. Annette Plüddemann
 Diagnostic Studies Dr. Annette Plüddemann Department of Primary Care Health Sciences, University of Oxford Centre for Evidence Based Medicine What kinds of EBM questions have you asked? How should I treat
Diagnostic Studies Dr. Annette Plüddemann Department of Primary Care Health Sciences, University of Oxford Centre for Evidence Based Medicine What kinds of EBM questions have you asked? How should I treat
Urinary tract infection in children. Urinary tract infection in children: diagnosis, treatment and long-term management
 Issue date: August 2007 Urinary tract infection in children Urinary tract infection in children: diagnosis, treatment and long-term management NICE clinical guideline 54 Developed by the National Collaborating
Issue date: August 2007 Urinary tract infection in children Urinary tract infection in children: diagnosis, treatment and long-term management NICE clinical guideline 54 Developed by the National Collaborating
Root Cause Analysis following
 Root Cause Analysis following MRSA Bacteraemia: Reviewing the Patient s Journey Sharren Pells Senior Infection Control Nurse NHS Swindon Helen Forrest Infection Control Nurse Specialist NHS Swindon Aims
Root Cause Analysis following MRSA Bacteraemia: Reviewing the Patient s Journey Sharren Pells Senior Infection Control Nurse NHS Swindon Helen Forrest Infection Control Nurse Specialist NHS Swindon Aims
Urinary tract infection in children
 Urinary tract infection in children Diagnosis, treatment and long-term management Issued: August 2007 NICE clinical guideline 54 guidance.nice.org.uk/cg54 NICE 2007 Vad är Hypotoni? Contents Introduction...
Urinary tract infection in children Diagnosis, treatment and long-term management Issued: August 2007 NICE clinical guideline 54 guidance.nice.org.uk/cg54 NICE 2007 Vad är Hypotoni? Contents Introduction...
Antimicrobial Stewardship for Hospital Acquired Infection Prevention: Focus on C. difficile infection
 Antimicrobial Stewardship for Hospital Acquired Infection Prevention: Focus on C. difficile infection Emi Minejima, PharmD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pharmacy USC School of Pharmacy minejima@usc.edu
Antimicrobial Stewardship for Hospital Acquired Infection Prevention: Focus on C. difficile infection Emi Minejima, PharmD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pharmacy USC School of Pharmacy minejima@usc.edu
Eva Hummers-Pradier 1 Email: eva.hummers-pradier@med.uni-goettingen.de. Humboldtallee 38, Goettingen 37073, Germany
 Immediate versus conditional treatment of uncomplicated urinary tract infection - a randomized-controlled comparative effectiveness study in general practices Abstract Background Ildikó Gágyor 1* * Corresponding
Immediate versus conditional treatment of uncomplicated urinary tract infection - a randomized-controlled comparative effectiveness study in general practices Abstract Background Ildikó Gágyor 1* * Corresponding
The Minnesota Chlamydia Strategy: Action Plan to Reduce and Prevent Chlamydia in Minnesota Minnesota Chlamydia Partnership, April 2011
 The Minnesota Chlamydia Strategy: Action Plan to Reduce and Prevent Chlamydia in Minnesota Minnesota Chlamydia Partnership, April 2011 Section 5: Screening, Treating and Reporting Chlamydia While the information
The Minnesota Chlamydia Strategy: Action Plan to Reduce and Prevent Chlamydia in Minnesota Minnesota Chlamydia Partnership, April 2011 Section 5: Screening, Treating and Reporting Chlamydia While the information
Pyelonephritis: Kidney Infection
 Pyelonephritis: Kidney Infection National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is pyelonephritis? Pyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis: Kidney Infection National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is pyelonephritis? Pyelonephritis
healthcare associated infection 1.2
 healthcare associated infection A C T I O N G U I D E 1.2 AUSTRALIAN SAFETY AND QUALITY GOALS FOR HEALTH CARE What are the goals? The Australian Safety and Quality Goals for Health Care set out some important
healthcare associated infection A C T I O N G U I D E 1.2 AUSTRALIAN SAFETY AND QUALITY GOALS FOR HEALTH CARE What are the goals? The Australian Safety and Quality Goals for Health Care set out some important
PERTUSSIS SURVEILLANCE AND RESPONSE PROTOCOL
 PERTUSSIS SURVEILLANCE AND RESPONSE PROTOCOL Public Health Action 1. Educate the public, particularly parents of infants, about the dangers of whooping cough and the advantages of initiating immunization
PERTUSSIS SURVEILLANCE AND RESPONSE PROTOCOL Public Health Action 1. Educate the public, particularly parents of infants, about the dangers of whooping cough and the advantages of initiating immunization
Diabetic nephropathy is detected clinically by the presence of persistent microalbuminuria or proteinuria.
 Kidney Complications Diabetic Nephropathy Diabetic nephropathy is detected clinically by the presence of persistent microalbuminuria or proteinuria. The peak incidence of nephropathy is usually 15-25 years
Kidney Complications Diabetic Nephropathy Diabetic nephropathy is detected clinically by the presence of persistent microalbuminuria or proteinuria. The peak incidence of nephropathy is usually 15-25 years
Examination Content Blueprint
 Examination Content Blueprint Overview The material on NCCPA s certification and recertification exams can be organized in two dimensions: (1) organ systems and the diseases, disorders and medical assessments
Examination Content Blueprint Overview The material on NCCPA s certification and recertification exams can be organized in two dimensions: (1) organ systems and the diseases, disorders and medical assessments
PREVENTION OF CATHETER-ASSOCIATED URINARY TRACT INFECTION FOLLOWING GYNAECOLOGIC SURGERY: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
 PREVENTION OF CATHETER-ASSOCIATED URINARY TRACT INFECTION FOLLOWING GYNAECOLOGIC SURGERY: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW *Christine M. Chu, Lily A. Arya Division of Urogynecology, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
PREVENTION OF CATHETER-ASSOCIATED URINARY TRACT INFECTION FOLLOWING GYNAECOLOGIC SURGERY: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW *Christine M. Chu, Lily A. Arya Division of Urogynecology, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Prevention. Basics of Infection Prevention 2 Day Mini-Course 2013
 Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Prevention Basics of Infection Prevention 2 Day Mini-Course 2013 2 Objectives Define the scope of healthcare-associated urinary tract infections (UTI)
Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Prevention Basics of Infection Prevention 2 Day Mini-Course 2013 2 Objectives Define the scope of healthcare-associated urinary tract infections (UTI)
Diagnosis, Treatment and Prevention of Typhoid Fever in the Children of Bangladesh: A Microbiologist s View.
 Diagnosis, Treatment and Prevention of Typhoid Fever in the Children of Bangladesh: A Microbiologist s View. Samir K Saha, Ph.D. Department of Microbiology Dhaka Shishu Hospital Bangladesh Typhoid Fever:Salmonella
Diagnosis, Treatment and Prevention of Typhoid Fever in the Children of Bangladesh: A Microbiologist s View. Samir K Saha, Ph.D. Department of Microbiology Dhaka Shishu Hospital Bangladesh Typhoid Fever:Salmonella
Blood in the Urine (Haematuria)
 Kidney Health Information Blood in the Urine (Haematuria) What is blood in the urine? Sometimes blood in the urine can be seen, but at other times it is present in such small quantities that it is not
Kidney Health Information Blood in the Urine (Haematuria) What is blood in the urine? Sometimes blood in the urine can be seen, but at other times it is present in such small quantities that it is not
CARE PROCESS STEP EXPECTATIONS RATIONALE
 URINARY INCONTINENCE CARE PROCESS STEP EXPECTATIONS RATIONALE ASSESSMENT/PROBLEM RECOGNITION 1. Did the staff and physician seek and document risk factors for urinary incontinence and any history of urinary
URINARY INCONTINENCE CARE PROCESS STEP EXPECTATIONS RATIONALE ASSESSMENT/PROBLEM RECOGNITION 1. Did the staff and physician seek and document risk factors for urinary incontinence and any history of urinary
AWARENESS OF THE ORAL HEALTH OF PEDIATRIC PATIENTS AMONG THE PEDIATRICIANS IN AHMEDABAD CITY- AN EPIDEMIOLOGICAL RESEARCH
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE AWARENESS OF THE ORAL HEALTH OF PEDIATRIC PATIENTS AMONG THE PEDIATRICIANS IN AHMEDABAD CITY- AN EPIDEMIOLOGICAL RESEARCH Maithilee Jani 1, Anshul Shah 1, Ajay Pala 2 B.D.S, 1 Ahmedabad
ORIGINAL ARTICLE AWARENESS OF THE ORAL HEALTH OF PEDIATRIC PATIENTS AMONG THE PEDIATRICIANS IN AHMEDABAD CITY- AN EPIDEMIOLOGICAL RESEARCH Maithilee Jani 1, Anshul Shah 1, Ajay Pala 2 B.D.S, 1 Ahmedabad
Chapter 2 What is evidence and evidence-based practice?
 Chapter 2 What is evidence and evidence-based practice? AIMS When you have read this chapter, you should understand: What evidence is Where evidence comes from How we find the evidence and what we do with
Chapter 2 What is evidence and evidence-based practice? AIMS When you have read this chapter, you should understand: What evidence is Where evidence comes from How we find the evidence and what we do with
Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA
 Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA 4671 S. Congress Avenue, Lake Worth, FL 33461 561.434.0111 4631 N. Congress Avenue, Suite 102, West Palm Beach, FL 33407 Urinary Tract Infection About one of every
Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA 4671 S. Congress Avenue, Lake Worth, FL 33461 561.434.0111 4631 N. Congress Avenue, Suite 102, West Palm Beach, FL 33407 Urinary Tract Infection About one of every
Uterine Fibroid Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
 Fibroids and IR Uterine Fibroid Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment Interventional radiologists use MRIs to determine if fibroids can be embolised, detect alternate causes for the symptoms and rule out misdiagnosis,
Fibroids and IR Uterine Fibroid Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment Interventional radiologists use MRIs to determine if fibroids can be embolised, detect alternate causes for the symptoms and rule out misdiagnosis,
C-Difficile Infection Control and Prevention Strategies
 C-Difficile Infection Control and Prevention Strategies Adrienne Mims, MD MPH VP, Chief Medical Officer Adrienne.Mims@AlliantQuality.org 1/18/2016 1 Disclosure This educational activity does not have commercial
C-Difficile Infection Control and Prevention Strategies Adrienne Mims, MD MPH VP, Chief Medical Officer Adrienne.Mims@AlliantQuality.org 1/18/2016 1 Disclosure This educational activity does not have commercial
6. MEASURING EFFECTS OVERVIEW CHOOSE APPROPRIATE METRICS
 45 6. MEASURING EFFECTS OVERVIEW In Section 4, we provided an overview of how to select metrics for monitoring implementation progress. This section provides additional detail on metric selection and offers
45 6. MEASURING EFFECTS OVERVIEW In Section 4, we provided an overview of how to select metrics for monitoring implementation progress. This section provides additional detail on metric selection and offers
How To Determine The Prevalence Of Microalbuminuria
 Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences Prevalence of Microalbuminuria in relation to HbA1c among known Type2 Diabetic Patients in Puducherry population Muraliswaran P 1 *,
Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences Prevalence of Microalbuminuria in relation to HbA1c among known Type2 Diabetic Patients in Puducherry population Muraliswaran P 1 *,
SAMPLE ANTIMICROBIAL STEWARDSHIP POLICY
 SAMPLE ANTIMICROBIAL STEWARDSHIP POLICY FOR A LOCAL HEALTH DISTRICT OR NETWORK Purpose of this document The development of an official policy for Antimicrobial Stewardship (AMS) is a fundamental step towards
SAMPLE ANTIMICROBIAL STEWARDSHIP POLICY FOR A LOCAL HEALTH DISTRICT OR NETWORK Purpose of this document The development of an official policy for Antimicrobial Stewardship (AMS) is a fundamental step towards
1. What is the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test?
 1. What is the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test? Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) is a protein produced by the cells of the prostate gland. The PSA test measures the level of PSA in the blood. The doctor
1. What is the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test? Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) is a protein produced by the cells of the prostate gland. The PSA test measures the level of PSA in the blood. The doctor
This series of articles is designed to
 Research and diabetes nursing. Part 3: Quantitative designs Vivien Coates This article is the third in a series that aims to assist nurses working in diabetes to understand research from a broad perspective,
Research and diabetes nursing. Part 3: Quantitative designs Vivien Coates This article is the third in a series that aims to assist nurses working in diabetes to understand research from a broad perspective,
Urinary Tract Infections. Clinical Scenario #1. Urinary Tract Infections. Clinical Scenario #1 : Labs
 Clinical Scenario #1 : Labs Urinary Tract Infections Magdalena Sobieszczyk, MD Urinalysis: pyuria (WBC too numerous to count), RBC and bacteria present Urine dipstick: positive leukocyte esterase and nitrite
Clinical Scenario #1 : Labs Urinary Tract Infections Magdalena Sobieszczyk, MD Urinalysis: pyuria (WBC too numerous to count), RBC and bacteria present Urine dipstick: positive leukocyte esterase and nitrite
Avoiding Urinary Tract Infections in Patients practising Intermittent Catheterization
 Avoiding Urinary Tract Infections in Patients practising Intermittent Catheterization H.J. Mulder MANP 1-11-2011 Henk-Jan Mulder MANP Department of Urology Martini General Hospital Van Swietenplein 1 9700
Avoiding Urinary Tract Infections in Patients practising Intermittent Catheterization H.J. Mulder MANP 1-11-2011 Henk-Jan Mulder MANP Department of Urology Martini General Hospital Van Swietenplein 1 9700
Prevention of CAUTI is discussed in the CDC/HICPAC document, Guideline for Prevention of Catheter-associated Urinary Tract Infection 4.
 Urinary Tract Infection (Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection [] and Non-Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection [UTI]) and Other Urinary System Infection [USI]) Events Introduction: Urinary
Urinary Tract Infection (Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection [] and Non-Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection [UTI]) and Other Urinary System Infection [USI]) Events Introduction: Urinary
Health Benchmarks Program Clinical Quality Indicator Specification 2013
 Health Benchmarks Program Clinical Quality Indicator Specification 2013 Measure Title USE OF IMAGING STUDIES FOR LOW BACK PAIN Disease State Musculoskeletal Indicator Classification Utilization Strength
Health Benchmarks Program Clinical Quality Indicator Specification 2013 Measure Title USE OF IMAGING STUDIES FOR LOW BACK PAIN Disease State Musculoskeletal Indicator Classification Utilization Strength
PSA Testing for Prostate Cancer An information sheet for men considering a PSA Test
 PSA Testing for Prostate Cancer An information sheet for men considering a PSA Test What is the aim of this leaflet? Prostate cancer is a serious condition. The PSA test, which can give an early indication
PSA Testing for Prostate Cancer An information sheet for men considering a PSA Test What is the aim of this leaflet? Prostate cancer is a serious condition. The PSA test, which can give an early indication
Guidelines for Cancer Prevention, Early detection & Screening. Prostate Cancer
 Guidelines for Cancer Prevention, Early detection & Screening Prostate Cancer Intervention Comments & Recommendations For primary prevention, it has been suggested that diets low in meat & other fatty
Guidelines for Cancer Prevention, Early detection & Screening Prostate Cancer Intervention Comments & Recommendations For primary prevention, it has been suggested that diets low in meat & other fatty
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections Magdalena Sobieszczyk, MD MPH Division of Infectious Diseases Columbia University Clinical Scenario #1 23 y.o woman presents to her doctor complaining of 1 day of increased urinary
Urinary Tract Infections Magdalena Sobieszczyk, MD MPH Division of Infectious Diseases Columbia University Clinical Scenario #1 23 y.o woman presents to her doctor complaining of 1 day of increased urinary
Frequently Asked Questions
 Guidelines for Testing and Treatment of Gonorrhea in Ontario, 2013 Frequently Asked Questions Table of Contents Background... 1 Treatment Recommendations... 2 Treatment of Contacts... 4 Administration
Guidelines for Testing and Treatment of Gonorrhea in Ontario, 2013 Frequently Asked Questions Table of Contents Background... 1 Treatment Recommendations... 2 Treatment of Contacts... 4 Administration
Antibiotic Guidelines: Ear Nose and Throat (ENT) Infections. Contents
 Antibiotic Guidelines: Ear Nose and Throat (ENT) Infections. Classification: Clinical Guideline Lead Author: Antibiotic Steering Committee Additional author(s): Authors Division: DCSS & Tertiary Medicine
Antibiotic Guidelines: Ear Nose and Throat (ENT) Infections. Classification: Clinical Guideline Lead Author: Antibiotic Steering Committee Additional author(s): Authors Division: DCSS & Tertiary Medicine
Medication error is the most common
 Medication Reconciliation Transfer of medication information across settings keeping it free from error. By Jane H. Barnsteiner, PhD, RN, FAAN Medication error is the most common type of error affecting
Medication Reconciliation Transfer of medication information across settings keeping it free from error. By Jane H. Barnsteiner, PhD, RN, FAAN Medication error is the most common type of error affecting
Clinical pathway concept - a key to seamless care
 SECTION 5: PATIENT SAFETY AND QUALITY ASSURANCE 1 Clinical pathway concept - a key to seamless care Audrey Janoly-Dumenil, Hôpital Edouard Herriot, CHU Lyon Marie-Camille Chaumais, Hôpital Antoine Béclère,
SECTION 5: PATIENT SAFETY AND QUALITY ASSURANCE 1 Clinical pathway concept - a key to seamless care Audrey Janoly-Dumenil, Hôpital Edouard Herriot, CHU Lyon Marie-Camille Chaumais, Hôpital Antoine Béclère,
signs suggesting chlamydia:
 Chlamydia - uncomplicated genital - Management View full scenario When should I suspect and test for chlamydia? Women: o Test for chlamydia if they are sexually active with symptoms and signs suggesting
Chlamydia - uncomplicated genital - Management View full scenario When should I suspect and test for chlamydia? Women: o Test for chlamydia if they are sexually active with symptoms and signs suggesting
GUIDELINES FOR THE TREATMENT OF DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY*
 71 GUIDELINES FOR THE TREATMENT OF DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY* Ryuichi KIKKAWA** Asian Med. J. 44(2): 71 75, 2001 Abstract: Diabetic nephropathy is the most devastating complication of diabetes and is now the
71 GUIDELINES FOR THE TREATMENT OF DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY* Ryuichi KIKKAWA** Asian Med. J. 44(2): 71 75, 2001 Abstract: Diabetic nephropathy is the most devastating complication of diabetes and is now the
Have a shower, rather than a bath to avoid exposing your genitals to the chemicals in your cleaning products for too long. Always empty your bladder
 Cystitis, Avenue Medical Practice Neat Guideline Introduction Cystitis means 'inflammation of the bladder'. It causes: an urgent and frequent need to urinate, and Pain, or stinging, when passing urine.
Cystitis, Avenue Medical Practice Neat Guideline Introduction Cystitis means 'inflammation of the bladder'. It causes: an urgent and frequent need to urinate, and Pain, or stinging, when passing urine.
Recognizing Signs and Symptoms of a Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
 Use this checklist to help identify signs and symptoms of a or other illnesses. If the person you support has one or more of these signs and symptoms, call the doctor for advice and a medical appointment.
Use this checklist to help identify signs and symptoms of a or other illnesses. If the person you support has one or more of these signs and symptoms, call the doctor for advice and a medical appointment.
Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Definitions and Reporting
 AHRQ Safety Program for Long-term Care: HAIs/CAUTI Learning Objectives Upon completion of the webinar, core team members will be able to: Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Definitions
AHRQ Safety Program for Long-term Care: HAIs/CAUTI Learning Objectives Upon completion of the webinar, core team members will be able to: Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Definitions
Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute Uncomplicated Cystitis
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute Uncomplicated Cystitis RICHARD COLGAN, MD, and MOZELLA WILLIAMS, MD University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltime, Maryland Urinary tract infections are the most common
Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute Uncomplicated Cystitis RICHARD COLGAN, MD, and MOZELLA WILLIAMS, MD University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltime, Maryland Urinary tract infections are the most common
Three Versus Seven-Day Treatment of Asymptomatic Bacteriuria in Pregnant Women: A Pilot Investigation
 94 The Open Infectious Diseases Journal, 2009, 3, 94-98 Open Access Three Versus Seven-Day Treatment of Asymptomatic Bacteriuria in Pregnant Women: A Pilot Investigation Pooja Mittal, Vivien Pan and Deborah
94 The Open Infectious Diseases Journal, 2009, 3, 94-98 Open Access Three Versus Seven-Day Treatment of Asymptomatic Bacteriuria in Pregnant Women: A Pilot Investigation Pooja Mittal, Vivien Pan and Deborah
Physical therapy for patients dying at home of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease A Qualitative Study
 Physical therapy for patients dying at home of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease A Qualitative Study D.M. Keesenberg, Pt, student Science for physical therapy Physical therapy practice Zwanenzijde,
Physical therapy for patients dying at home of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease A Qualitative Study D.M. Keesenberg, Pt, student Science for physical therapy Physical therapy practice Zwanenzijde,
Urinary Tract Infections
 1 Infections in the urinary tract are relatively common. These infections are often referred to as bladder infections. They are also known as UTI s or urinary tract infections. When an infection is confined
1 Infections in the urinary tract are relatively common. These infections are often referred to as bladder infections. They are also known as UTI s or urinary tract infections. When an infection is confined
Improving access and reducing costs of care for overactive bladder through a multidisciplinary delivery model
 Improving access and reducing costs of care for overactive bladder through a multidisciplinary delivery model Trafford Crump, Ph.D. Department of Surgery, University of Calgary Presentation to: Canadian
Improving access and reducing costs of care for overactive bladder through a multidisciplinary delivery model Trafford Crump, Ph.D. Department of Surgery, University of Calgary Presentation to: Canadian
190.12 - Urine Culture, Bacterial Summary Information Highlighted items indicate most frequently used codes.
 Medicare National Coverage Determination (NCD) (Jan 2011) Source: CMS: Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services To view full document: www.cms.gov/coveragegeninfo. Select Lab NCDs, then select NCD Coding
Medicare National Coverage Determination (NCD) (Jan 2011) Source: CMS: Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services To view full document: www.cms.gov/coveragegeninfo. Select Lab NCDs, then select NCD Coding
THE INTERNET STROKE CENTER PRESENTATIONS AND DISCUSSIONS ON STROKE MANAGEMENT
 THE INTERNET STROKE CENTER PRESENTATIONS AND DISCUSSIONS ON STROKE MANAGEMENT Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation Gregory Albers, M.D. Director Stanford Stroke Center Professor of Neurology and Neurological
THE INTERNET STROKE CENTER PRESENTATIONS AND DISCUSSIONS ON STROKE MANAGEMENT Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation Gregory Albers, M.D. Director Stanford Stroke Center Professor of Neurology and Neurological
Expedited Partner Therapy (EPT) for Sexually Transmitted Diseases Protocol for Health Care Providers in Oregon
 Expedited Partner Therapy (EPT) for Sexually Transmitted Diseases Protocol for Health Care Providers in Oregon Oregon Health Authority Center for Public Health Practice HIV/STD/TB Section Principles of
Expedited Partner Therapy (EPT) for Sexually Transmitted Diseases Protocol for Health Care Providers in Oregon Oregon Health Authority Center for Public Health Practice HIV/STD/TB Section Principles of
Primary Care Management of Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms. Matthew B.K. Shaw Consultant Urological Surgeon
 Primary Care Management of Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Matthew B.K. Shaw Consultant Urological Surgeon NICE LUTS Guidelines Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) in men. NICE Clinical Guideline 97
Primary Care Management of Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Matthew B.K. Shaw Consultant Urological Surgeon NICE LUTS Guidelines Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) in men. NICE Clinical Guideline 97
Clinical Study Design and Methods Terminology
 Home College of Veterinary Medicine Washington State University WSU Faculty &Staff Page Page 1 of 5 John Gay, DVM PhD DACVPM AAHP FDIU VCS Clinical Epidemiology & Evidence-Based Medicine Glossary: Clinical
Home College of Veterinary Medicine Washington State University WSU Faculty &Staff Page Page 1 of 5 John Gay, DVM PhD DACVPM AAHP FDIU VCS Clinical Epidemiology & Evidence-Based Medicine Glossary: Clinical
If several different trials are mentioned in one publication, the data of each should be extracted in a separate data extraction form.
 General Remarks This template of a data extraction form is intended to help you to start developing your own data extraction form, it certainly has to be adapted to your specific question. Delete unnecessary
General Remarks This template of a data extraction form is intended to help you to start developing your own data extraction form, it certainly has to be adapted to your specific question. Delete unnecessary
echat: Screening & intervening for mental health & lifestyle issues
 echat: Screening & intervening for mental health & lifestyle issues Felicity Goodyear-Smith Professor & Academic Head Dept of General Practice & Primary Health Care Faculty of Medicine & Health Science
echat: Screening & intervening for mental health & lifestyle issues Felicity Goodyear-Smith Professor & Academic Head Dept of General Practice & Primary Health Care Faculty of Medicine & Health Science
How To Treat An Elderly Patient
 1. Introduction/ Getting to know our Seniors a. Identify common concepts and key terms used when discussing geriatrics b. Distinguish between different venues of senior residence c. Advocate the necessity
1. Introduction/ Getting to know our Seniors a. Identify common concepts and key terms used when discussing geriatrics b. Distinguish between different venues of senior residence c. Advocate the necessity
How To Test For Pneumonia In The Kandidat
 innovation Nationaal POCT symposium Antwerpen 23 okt 2014 POCT Pearls and Pitfalls in Primary care Progressing towards better patient care. The Dutch experience Rogier Hopstaken MD PhD Ron Kusters PhD
innovation Nationaal POCT symposium Antwerpen 23 okt 2014 POCT Pearls and Pitfalls in Primary care Progressing towards better patient care. The Dutch experience Rogier Hopstaken MD PhD Ron Kusters PhD
Prevention of CAUTI is discussed in the CDC/HICPAC document, Guideline for Prevention of Catheter-associated Urinary Tract Infection 4.
 Urinary Tract Infection (Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection [CA] and Non-Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection []) and Other Urinary System Infection [USI]) Events Introduction: Urinary
Urinary Tract Infection (Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection [CA] and Non-Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection []) and Other Urinary System Infection [USI]) Events Introduction: Urinary
Quantifying Medication Adherence: Practical Challenges and an Approach to Linking Alternative Measures
 Quantifying Medication Adherence: Practical Challenges and an Approach to Linking Alternative Measures Christine Poulos, PhD, RTI Health Solutions Jay P. Bae, PhD, Eli Lilly and Company Sean D. Candrilli,
Quantifying Medication Adherence: Practical Challenges and an Approach to Linking Alternative Measures Christine Poulos, PhD, RTI Health Solutions Jay P. Bae, PhD, Eli Lilly and Company Sean D. Candrilli,
GUIDELINES FOR TUBERCULOSIS PREVENTIVE THERAPY AMONG HIV INFECTED INDIVIDUALS IN SOUTH AFRICA
 GUIDELINES FOR TUBERCULOSIS PREVENTIVE THERAPY AMONG HIV INFECTED INDIVIDUALS IN SOUTH AFRICA 2010 1 TB prophylaxis GUIDELINES FOR TUBERCULOSIS PREVENTIVE THERAPY AMONG HIV INFECTED INDIVIDUALS Background
GUIDELINES FOR TUBERCULOSIS PREVENTIVE THERAPY AMONG HIV INFECTED INDIVIDUALS IN SOUTH AFRICA 2010 1 TB prophylaxis GUIDELINES FOR TUBERCULOSIS PREVENTIVE THERAPY AMONG HIV INFECTED INDIVIDUALS Background
Guideline for Microalbuminuria Screening
 East Lancashire Diabetes Network Guideline for Microalbuminuria Screening Produced by: Task and Finish Group, Clinical Standards Group Produced: August 2006 Approved by: East Lancashire Diabetes Network
East Lancashire Diabetes Network Guideline for Microalbuminuria Screening Produced by: Task and Finish Group, Clinical Standards Group Produced: August 2006 Approved by: East Lancashire Diabetes Network
