COMP 347: Computer Networks Cisco Laboratory 1 Introduction to Cisco IOS
|
|
|
- Isaac Mason
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 COMP 347: Computer Networks Cisco Laboratory 1 Introduction to Cisco IOS Objective Log into a router and go to the user and privileged modes and get familiar with these modes. Get familiar with basic IOS commands. Use the router HELP facility. Assign a name to the router. Set and manage passwords. Use several basic router commands to determine how the router is configured. Note: Please read and thoroughly understand the Theory section before proceeding to the lab exercises. Theory Most Cisco routers run on an operating system referred to as IOS. Cisco IOS (originally Internetwork Operating System) is the software used on the vast majority of Cisco Systems routers and all current Cisco network switches. IOS is a package of routing, switching, internetworking and telecommunications functions tightly integrated with a multitasking operating system. The first IOS was written by William Yeager. In all versions of Cisco IOS, packet routing and forwarding (switching) are distinct functions. Routing and other protocols run as Cisco IOS processes and contribute to the Routing Information Base (RIB). This is processed to generate the final IP forwarding table (FIB - - Forwarding Information Base), which is used by the forwarding function of the router. Cisco IOS has a characteristic command line interface (CLI), whose style has been widely copied by other networking products. The IOS CLI provides a fixed set of multiple-word commands -- the set available is determined by the "mode" and the privilege level of the current user. "Global configuration mode" provides commands to change the system's configuration, and "interface configuration mode" provides commands to change the configuration of a specific interface. A typical command may be "show interface fa0/48" or "no ip cef traffic-statistics". All commands are assigned a privilege level, from 0 to 15, and can only be accessed by users with the necessary privilege. Through the CLI, the commands available to each privilege level can be defined. Background and Preparation Cisco IOS is a text based command line interface that allows you to type in the various commands and set device parameters. This lab exercise will be focusing on using the IOS to help shorten your learning curve. This lab exercise contains two sections A and B. In section A there are three exercises. Exercise 1 gets you familiar with basic IOS commands, the router HELP facility and also
2 identifies basic router modes of operation. Exercise 2 and 3 deal with setting hostnames and passwords respectively. In Section B, the focus is on router line configuration. In particular, it introduces you to basic LAN and WAN interface configuration commands. Any router that meets the interface requirements may be used. Possible routers include 800, 1600, 1700, 2500, 2600 routers, or a combination. The configuration output used in this lab is produced from 1721 series routers. Any other router used may produce slightly different output. Note: You must thoroughly know this material before proceeding to attempt exercises in subsequent weeks. Please do not hesitate to seek lab assistant s help. Equipment required for each group If your class has 10 or less students you may work in pairs, otherwise work in groups of three. Two additional straight through network cables per group. Two serial cables per group (for console connections). One DTE/smart serial cable and one DCE/smart serial cable per group. Two Cisco switches per group. Two Cisco routers per group. Procedure Section A: Get familiar with Cisco IOS modes and Basic IOS commands Configure a simple network as shown below. Host Router Procedure Start a HyperTerminal session. Reset the routers: Erasing and reloading the router Note: You must perform these steps on all routers in this lab exercise before continuing. Since many of the labs require a clean router configuration, it is always advised to run this procedure through before performing the relevant exercise. Step 1: Enter into the global configuration mode (privileged EXEC mode) by typing the following: Router>enable Step 2: At the privileged EXEC mode, enter the following command: Router#erase startup-config
3 The responding prompt will be: Erasing the nvram filesystem will remove all files! Continue? [confirm] Press Enter to confirm The response should be: Erase of nvram: complete Step 3: Now at the privileged EXEC mode, enter the following command: Router#reload The responding prompt line will be: System configuration has been modified. Save? [yes/no]: n Proceed with reload? [confirm] Press Enter to confirm The Corresponding line prompt will be: Proceed with reload? [confirm] Press Enter to confirm. In the first line of the response will be: Reload requested by the console. After the router has reloaded, the line prompt will be: Would you like to enter the initial configuration dialog? [yes/no]: n If you are asked... Would you like to terminate autoinstall? [yes]: y The responding line prompt will be: Press Return to get started! Press Enter. Now the router is ready for the assigned lab exercise to be performed.
4 Exercise 1: IOS modes, Help, basic commands By pressing enter, you should see a prompt ending with >. This indicates that you are in user mode. The user mode is used for viewing the user configuration. Step 1: Enter into the privileged mode. Router>enable or en Privileged Exec Mode is simply the administration mode for the router. This mode by itself allows you to view router settings that are considered private. Privileged mode has a few sub modes as well such as global configuration mode, interface configuration mode, and routing configuration mode, which are described below. Step 2: Exit the privileged mode. Router>#disable This changes the prompt to Router> Step 3: Enter into the global configuration mode. To enter into the global configuration mode, give the following commands: Router>enable Router#configure terminal or conf t This mode allows you to make changes to the router settings that are currently in memory. The configuration that is currently in memory is referred to as the running configuration. Cisco Modes User Exec Mode Privleged Mode (en) Global Configuration (conf t) Interface (int...) Routing (route..) Step 4: Exit the global configuration mode. Exit the global configuration mode by using the command: Router(config)#exit or press ctrl+z This changes the prompt to Router# indicating you are in privileged mode. Step 5: Exit the privileged mode.
5 Router#exit This changes the prompt to Router> indicating you are back in user mode. Step 6: System Help Commands. Type? in user mode. Press enter at more prompt. List eight available commands from the router response: In any mode of IOS (see below) you can query for help. Just by entering a? by itself, a list of available commands will be displayed corresponding to the mode you are currently in. This displays the list of available commands in the current mode. At the more prompt, repeatedly press enter to scroll by line. Note: You can type? in any mode to view list of available commands. Step 7: Enter into privileged mode and type?. Press spacebar at more prompt. List 10 commands from the router response: Step 8: List all the show commands by entering show? At the router privileged mode. Router#show? Observation: Is running config one of the available commands from this mode? Ans. Step 9: Examine the running configuration. Display the running router configuration by using the command show running-config at the privileged mode prompt. Router#show running-config
6 List six key pieces of information shown with this command: Note: Running-Config vs. Startup-Config The router keeps two different sets of configurations. When you first turn it on the router loads the startup configuration into memory. Now that it is loaded it is now called the running configuration, the startup configuration is the original copy. When you make a change, it happens on the fly and is applied to the running configuration. Suppose you totally screw up and cannot even telnet to the router anymore, just unplug it and plug it back in and it will boot up off the startup configuration again. This is a good feature in this case, but what if you made a bunch of changes, forgot to update the startup configuration and then the power goes out? You guessed it, all your work is lost. So keep in mind what you are doing and keep track of when you want to save. Saving the running configuration is easily done with the command (Do not type these commands): copy running-config startup-config copy run start And of course if you ever screw anything up but still have access to the router, you can always copy the startup configuration to the running configuration. And you do not even have to reboot. Step 10: Use? to view the options to a command. The? is a powerful help utility. You can type any command followed by? to view supported command options. Give the command: Router#configure? You can use this option to view available options for all supported commands. Note that there is a space the command and question mark. Step 11: Exit the privileged exec mode. Router#exit Step 12: Type in the following commands:
7 Router>show version or sh version Router>show clock or sh clock Router>show users or sh users Show version: Displays the IOS version number and its internal name. The IOS internal name tells you about its capabilities and options. Show users: Displays users who are connected to the Cisco router Show clock: Displays the clock settings Step 13: Press up arrow to recall an old command and press down arrow to recall a new command. Exercise 2: Setting Hostname In this exercise you will set the hostname for the router. This changes the router prompt. The default hostname is router. Step 1: Enter the privileged mode and then the global configuration mode. Router>enable or en Router#configure terminal or conf t Step 2: Change the hostname to semsim. Router(config)#hostname semsim You can keep a hostname of your preference. This changes the prompt to the new hostname e.g. semsim (Config). The text in our instructions assumes the default hostname Router. Step 3: Exit the global configuration mode. Router(config)#exit This changes the prompt to semsim#. Step 4: View the running-config to ensure the new hostname is set. Type the following command: Semsim#show running-config or sh run You should see the hostname specified in running-config. Exercise 3: Managing Passwords In this lab you will enable, view, encrypt and disable the password to the privileged mode of the router. Access to the privileged mode permits modification of the router configuration, it is important to have an access constraint to this mode.
8 Step 1: Enter the global configuration mode. Semsim>enable or en Semsim#configure terminal or conf t Step 2: Password protect the privileged mode. Type the following command: Semsim(config)#enable password mypwd Step 3: Exit the global configuration mode. Semsim(config)#exit or press Ctrl + z Step 4: View the running-config. Type the following command: Semsim# show running-config or sh run Observation: Is the password encrypted?.. You should see the unencrypted password specified in the running-config. Step 5: Enter global configuration mode. Semsim#conf t Step 6: Protect the privileged mode with encrypted password. Type the following command: Semsim(config)#enable secret myencryptedpwd Step 7: Exit the global configuration mode. Semsim(config)#exit Step 8: View the running-config. Is the password encrypted? Semsim#show running-config or sh run You should see encrypted password specified in the running-config. Step 9: Exit the privileged mode. To exit the privileged mode type the command: Semsim#disable
9 This changes the prompt to Semsim>. Step 10: Enter the privileged mode. Which password do you enter? Type: Semsim>enable or en You will be prompted to enter the password. Enter the enable secret password as it takes precedence when both unencrypted and encrypted passwords are set. Step11: Enter global configuration mode. Semsim#conf t Step 12: Disable enable secret password. Type the following command: Semsim(Config)#no enable secret Step 13: Disable enable password. Type the following command: Semsim(config)#no enable password Step 14: Exit the global configuration mode. Semsim(config)#exit Step 15: Ext the privileged mode Semsim#disable This changes the prompt to Semsim> Step 16: Enter the privileged mode. Do you still need to specify a password? Use the command: Semsim>enable or en This changes the prompt to Semsim# indicating that you have entered the privileged mode. You were not prompted for password since you disabled them. Step 17: Reboot the router. Use the following command: Semsim#reload
10 You will be prepared for reboot. Press y or Y: Proceed with reload? [confirm] Y
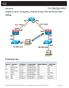
11 Section B: Router Line Configuration To bring up an Ethernet/Serial interface, all that is necessary is to assign it an IP address, associate a netmask with that address, and turn up the interface. There is also a need to enable the routing protocol for packet forwarding. In this exercise we will learn how to configure Router Ethernet and serial interfaces and learn to enable Routing Information Protocol (RIP) for packet forwarding. Configure the network as shown below. Before configuring routers, reset them using the instructions below. Router 1 Router 2 Switch Straight through RJ45 cable DCE/DTE cable Console serial cable Crossover-cable Note: Do not enter the no shutdown command for the serial interface of router 2-- leave that interface down at the start of the exercise. This means that the network will not be properly connected. Name the two routers with different names (Router1 and Router 2) Use the network (i.e x) for the local network side of router 1. Use the network for the local network side of router 2. Use the network for the serial connection between the two routers. Procedure Start a HyperTerminal session. Reset the routers: Erasing and reloading the router Note: You must perform these steps on all routers in this lab exercise before continuing. Note: Please refer to the meaning and structure of the command syntax provided at the end of the exercise.
12 Step 1: Enter into the global configuration mode (privileged EXEC mode) by typing the following: Router> enable Step 2: At the privileged EXEC mode, enter the following command: Router# erase startup-config The responding prompt will be: Erasing the nvram filesystem will remove all files! Continue? [confirm] Press Enter to confirm The response should be: Erase of nvram: complete Step 3: Now at the privileged EXEC mode, enter the following command: Router# reload The responding prompt line will be: System configuration has been modified. Save? [yes/no]: n Proceed with reload? [confirm] Press Enter to confirm The Corresponding line prompt will be: Proceed with reload? [confirm] Press Enter to confirm. In the first line of the response will be: Reload requested by the console. After the router has reloaded, the line prompt will be: Would you like to enter the initial configuration dialog? [yes/no]: n If you are asked... Would you like to terminate autoinstall? [yes]: y The responding line prompt will be: Press Return to get started! Press Enter. Now the router is ready for the assigned lab exercise to be performed.
13 Exercise 4: Configuring Router Ethernet and Serial Interfaces. Configure Router 1 Step 1: Enter into the privileged mode and the global configuration mode. Router1>enable Router1#config t Step 2: Configuring the serial interface of router Router1(config)#host router1 Router1(config)#interface serial 0/0 This changes the prompt to Router1(config-if)#. This mode is entered by already being in global configuration mode (see the diagram above) and then entering interface mode for serial. Step 3: Set the IP address and the mask for the serial interface. Type in the following command: Router1(config-if)#ip address Assigning IP address and mask to the serial interface of router 1. Step 4: Set the clock rate for Serial interface. Type in the following command: Router1(config-if)#clock rate This command sets the clock rate for a router with a DCE cable to 56K Step 5: Enable the serial interface. Type in the following command: Router1(config-if)#no shutdown This command enables the interface. Step 6: Exit the router serial configuration mode. Type in the following command: Router1(config-if)#exit Step 7: Enter the router Ethernet interface configuration mode. Type in the following command: Router1(config)#interface fast 0/0 This mode is entered by already being in global configuration mode (see the diagram above) and then entering interface mode for fast Ethernet.
14 Step 8: Set the IP address and the mask for the Ethernet interface. Type in the following command: Router1(config-if)#ip address Assigning IP address and mask to the fast Ethernet interface of router 1. Step 9: Enable the Ethernet interface. Type in the following command: Router1(config-if)#no shutdown This command enables the interface. Step 10: Exit the router Ethernet configuration mode. Type in the following command: Router1(config-if)#exit This changes the prompt to Router1(config#). Step 11: Enable Routing Information Protocol (RIP) in the router. Router1(config#)router rip This command enables Routing Information Protocol (RIP) on all router interfaces to forward packets. Step 12: Enable the interfaces for RIP forwarding. Type in the following command: Router1(config-if)# network Router1(config-if)# network RIP routing for packet forwarding is now enabled on Ethernet and Serial interfaces. Step 13: Exit the router RIP configuration mode and router configuration mode. Type in the following command: Router1(config-if)#exit Router1(config)#exit Then exit the global configuration mode. Configure Router 2: Repeat the same steps for Router2. Router2>enable Router2#config t Router2(config)#host router2 Router2(config)#interface serial 0/0
15 Router2(config-if)#ip address Router2(config-if)#exit Router2(config)#interface fast 0/0 Router2(config-if)#ip address Router2(config-if)#no shutdown Router2(config-if)#exit Router2(config)#router rip Router2(config-if)#network Router2(config-if)#network Router2(config-if)#exit Router2(config)# exit Configure the hosts Use a static IP address matching the local area network of the connected router. (e.g for router 1; for router 2) Use the router s fast Ethernet interface IP address as the gateway address for the PC. (e.g for router 1; for router 2) Use the network mask Disable the wireless network. Connect the network Connect the network cables. Power-up the switches. Reset the switches Reset the switches Wait until the switch has finished booting. Press and hold the mode button on the front of the switch until 4 lights in a row come on. Release the mode button. Press and hold the mode button. After a little while, the four lights should start flashing. Hold the mode button down until the four lights stop flashing. Ping the hosts and routers to test connectivity.
Lab 1.2.3 Review of Basic Router Configuration with RIP. Objective. Background / Preparation. General Configuration Tips
 Lab 1.2.3 Review of Basic Router Configuration with RIP Objective Cable and configure workstations and routers Setup IP addressing scheme using Class B networks Configure Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
Lab 1.2.3 Review of Basic Router Configuration with RIP Objective Cable and configure workstations and routers Setup IP addressing scheme using Class B networks Configure Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
3.1 Connecting to a Router and Basic Configuration
 3.1 Connecting to a Router and Basic Configuration Objective This lab will focus on the ability to connect a PC to a router in order to establish a console session and observe the user interface. A console
3.1 Connecting to a Router and Basic Configuration Objective This lab will focus on the ability to connect a PC to a router in order to establish a console session and observe the user interface. A console
Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths
 Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths Objective Configure Load balance across multiple paths. Observe the load balancing process. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in the
Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths Objective Configure Load balance across multiple paths. Observe the load balancing process. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in the
Configuring a Router
 CHAPTER 3 Configuring a Router This chapter provides information and commands concerning the following topics: Configuring a router, specifically: Names Passwords Interfaces MOTD banners IP host tables
CHAPTER 3 Configuring a Router This chapter provides information and commands concerning the following topics: Configuring a router, specifically: Names Passwords Interfaces MOTD banners IP host tables
Lab 4.2.4 Advanced Telnet Operations
 Lab 4.2.4 Advanced Telnet Operations Objective Use the telnet command to remotely access other routers. Verify that the application layer between the source and the destination is working properly. Suspend
Lab 4.2.4 Advanced Telnet Operations Objective Use the telnet command to remotely access other routers. Verify that the application layer between the source and the destination is working properly. Suspend
Lab 1.4.1 Introductory Lab 1 - Getting Started and Building Start.txt
 Lab 1.4.1 Introductory Lab 1 - Getting Started and Building Start.txt Objective This lab may introduce new CCNP lab equipment and certain IOS features. This introductory activity also describes how to
Lab 1.4.1 Introductory Lab 1 - Getting Started and Building Start.txt Objective This lab may introduce new CCNP lab equipment and certain IOS features. This introductory activity also describes how to
Applicazioni Telematiche
 Angelo Coiro Laboratorio Applicazioni Telematiche L emulatore Packet Tracer Packet Tracer Cisco Packet Tracer is an academic software that allows to emulate Cisco devices Packet Tracer can be used for
Angelo Coiro Laboratorio Applicazioni Telematiche L emulatore Packet Tracer Packet Tracer Cisco Packet Tracer is an academic software that allows to emulate Cisco devices Packet Tracer can be used for
Lab 5.3.9b Managing Router Configuration Files Using TFTP
 Lab 5.3.9b Managing Router Configuration Files Using TFTP Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Download and install TFTP server software.
Lab 5.3.9b Managing Router Configuration Files Using TFTP Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Download and install TFTP server software.
Lab 1.5.1 Introductory Lab 1 Getting Started and Building Start.txt
 Lab 1.5.1 Introductory Lab 1 Getting Started and Building Start.txt Objective This lab will introduce to the student the CCNP lab equipment and certain IOS features that might be new. This introductory
Lab 1.5.1 Introductory Lab 1 Getting Started and Building Start.txt Objective This lab will introduce to the student the CCNP lab equipment and certain IOS features that might be new. This introductory
Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI
 Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP address Subnet mask R1 R1 Serial 0/0/0 (DCE) 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 FastEthernet 0/0 172.16.0.1 255.255.0.0
Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP address Subnet mask R1 R1 Serial 0/0/0 (DCE) 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 FastEthernet 0/0 172.16.0.1 255.255.0.0
Connect the Host to attach to Fast Ethernet switch port Fa0/2. Configure the host as shown in the topology diagram above.
 Lab 1.2.2 Capturing and Analyzing Network Traffic Host Name IP Address Fa0/0 Subnet Mask IP Address S0/0/0 Subnet Mask Default Gateway RouterA 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 192.168.1.1 (DCE) 255.255.255.0 N/A
Lab 1.2.2 Capturing and Analyzing Network Traffic Host Name IP Address Fa0/0 Subnet Mask IP Address S0/0/0 Subnet Mask Default Gateway RouterA 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 192.168.1.1 (DCE) 255.255.255.0 N/A
Lab 2 - Basic Router Configuration
 CS326 Fall 2001 Room: PAI 5.48 Name: Lab 2 - Basic Router Configuration In this lab you will learn: the various configuration modes of Cisco 2621 routers how to set up IP addresses for such routers how
CS326 Fall 2001 Room: PAI 5.48 Name: Lab 2 - Basic Router Configuration In this lab you will learn: the various configuration modes of Cisco 2621 routers how to set up IP addresses for such routers how
Lab 3 Routing Information Protocol (RIPv1) on a Cisco Router Network
 Lab 3 Routing Information Protocol (RIPv1) on a Cisco Router Network CMPE 150 Fall 2005 Introduction Today you are going to be thrown into using Cisco s Internetwork Operating System (IOS) to configure
Lab 3 Routing Information Protocol (RIPv1) on a Cisco Router Network CMPE 150 Fall 2005 Introduction Today you are going to be thrown into using Cisco s Internetwork Operating System (IOS) to configure
Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths Instructor Version 2500 Objective onfigure Load balance across multiple paths. Observe the load balancing process. Background/Preparation able a network similar
Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths Instructor Version 2500 Objective onfigure Load balance across multiple paths. Observe the load balancing process. Background/Preparation able a network similar
Lab: Basic Router Configuration
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Def. Gateway R1 Fa0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R2 Fa0/0 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Def. Gateway R1 Fa0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R2 Fa0/0 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Lab 5.3.8 Configuring PAT with SDM and Static NAT using Cisco IOS Commands
 Lab 5.3.8 Configuring PAT with SDM and Static NAT using Cisco IOS Commands Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 CustomerRouter Serial 0/0/0 (DTE) 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 Fast Ethernet
Lab 5.3.8 Configuring PAT with SDM and Static NAT using Cisco IOS Commands Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 CustomerRouter Serial 0/0/0 (DTE) 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 Fast Ethernet
Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI
 Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Serial 0/0/0 (DCE) 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 FastEthernet 0/0 172.16.0.1 255.255.0.0
Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Serial 0/0/0 (DCE) 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 FastEthernet 0/0 172.16.0.1 255.255.0.0
Objectives. Router as a Computer. Router components and their functions. Router components and their functions
 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public Objectives Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1 Identify a router as a computer with an OS and
2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public Objectives Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1 Identify a router as a computer with an OS and
Router Lab Reference Guide
 Router Lab Reference Guide 1 PURPOSE AND GOALS The routing lab allows testing different IP-related protocols and solutions in a close to live environment. You can learn how to configure Cisco routers and
Router Lab Reference Guide 1 PURPOSE AND GOALS The routing lab allows testing different IP-related protocols and solutions in a close to live environment. You can learn how to configure Cisco routers and
Lab 4.1.4 Creating a Network Map using CDP Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 4.1.4 Creating a Network Map using CDP Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) commands to get information about neighboring network devices. Background/Preparation CDP
Lab 4.1.4 Creating a Network Map using CDP Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) commands to get information about neighboring network devices. Background/Preparation CDP
LAB Configuring NAT. Objective. Background/Preparation
 LAB Configuring NAT Objective Configure a router to use network address translation (NAT) to convert internal IP addresses, typically private addresses, into outside public addresses. Configure static
LAB Configuring NAT Objective Configure a router to use network address translation (NAT) to convert internal IP addresses, typically private addresses, into outside public addresses. Configure static
Lab 2.3.2 Configuring OSPF with Loopback Addresses
 Lab 2.3.2 Configuring OSPF with Loopback Addresses Objective Configure routers with a Class C IP addressing scheme. Observe the election process for designated routers (DR) and backup designated routers
Lab 2.3.2 Configuring OSPF with Loopback Addresses Objective Configure routers with a Class C IP addressing scheme. Observe the election process for designated routers (DR) and backup designated routers
LAB MANUAL for Computer Network
 LAB MANUAL for Computer Network CSE-310 F Computer Network Lab L T P - - 3 Class Work : 25 Marks Exam : 25 MARKS Total : 50 Marks This course provides students with hands on training regarding the design,
LAB MANUAL for Computer Network CSE-310 F Computer Network Lab L T P - - 3 Class Work : 25 Marks Exam : 25 MARKS Total : 50 Marks This course provides students with hands on training regarding the design,
Lab 8.3.3b Configuring a Remote Router Using SSH
 Lab 8.3.3b Configuring a Remote Router Using SSH Objectives Use SDM to configure a router to accept SSH connections. Configure SSH client software on a PC. Establish a connection to a Cisco ISR using SSH
Lab 8.3.3b Configuring a Remote Router Using SSH Objectives Use SDM to configure a router to accept SSH connections. Configure SSH client software on a PC. Establish a connection to a Cisco ISR using SSH
CCNA Exploration 4.0.5.0 Routing Protocols and Concepts Student Lab Manual
 4.0.5.0 Routing Protocols and Concepts Student Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution
4.0.5.0 Routing Protocols and Concepts Student Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution
Lab 3.1.2 Creating a Logical Network Diagram
 Lab 3.1.2 Creating a Logical Network Diagram Objectives Use router and switch commands to obtain information about an existing network. Use Cisco Network Assistant to obtain information about an existing
Lab 3.1.2 Creating a Logical Network Diagram Objectives Use router and switch commands to obtain information about an existing network. Use Cisco Network Assistant to obtain information about an existing
Cisco Router Configuration Tutorial
 Cisco Router Configuration Tutorial Cisco Inter-network Operating System: Cisco IOS Modes of Operation The Cisco IOS software provides access to several different command modes. Each command mode provides
Cisco Router Configuration Tutorial Cisco Inter-network Operating System: Cisco IOS Modes of Operation The Cisco IOS software provides access to several different command modes. Each command mode provides
Lab 5.3.7 Configuring DHCP with SDM and the Cisco IOS CLI
 Lab 5.3.7 Configuring DHCP with SDM and the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 Customer Serial 0/0/1 (DTE) 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 Fast Ethernet 0/0 192.168.1.1
Lab 5.3.7 Configuring DHCP with SDM and the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 Customer Serial 0/0/1 (DTE) 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 Fast Ethernet 0/0 192.168.1.1
Angelos Stavrou. OF COURSE there is no Magic so lets see show things work in practice...
 Cisco Inter-network Operating System (IOS) A short guide for the NetAdmin Angelos Stavrou Let's start out at the very beginning with the question: "What is a Command?" The most important thing to understand
Cisco Inter-network Operating System (IOS) A short guide for the NetAdmin Angelos Stavrou Let's start out at the very beginning with the question: "What is a Command?" The most important thing to understand
Procedure: You can find the problem sheet on Drive D: of the lab PCs. Part 1: Router & Switch
 University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Computer Engineering Department Computer Networks Laboratory 907528 Lab. 2 Network Devices & Packet Tracer Objectives 1. To become familiar with
University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Computer Engineering Department Computer Networks Laboratory 907528 Lab. 2 Network Devices & Packet Tracer Objectives 1. To become familiar with
Cisco Router Configuration Basics. Scalable Infrastructure Workshop
 Cisco Router Configuration Basics Scalable Infrastructure Workshop Router Components p RAM n Holds operating system, data structures, packet buffers, ARP cache, and routing tables n Reset on reload n Router
Cisco Router Configuration Basics Scalable Infrastructure Workshop Router Components p RAM n Holds operating system, data structures, packet buffers, ARP cache, and routing tables n Reset on reload n Router
Configuring the Switch with the CLI-Based Setup Program
 APPENDIX D Configuring the Switch with the CLI-Based Setup Program This appendix provides a command-line interface (CLI)-based setup procedure for a standalone switch. For product overview information,
APPENDIX D Configuring the Switch with the CLI-Based Setup Program This appendix provides a command-line interface (CLI)-based setup procedure for a standalone switch. For product overview information,
Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 3600 and 3800 Series Routers
 Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 3600 and 3800 Series Routers Document ID: 22189 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions Step by Step Procedure
Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 3600 and 3800 Series Routers Document ID: 22189 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions Step by Step Procedure
How to Configure Cisco 2600 Routers
 Helsinki University of Technology Department of Communications and Networking How to Configure Cisco 2600 Routers Juha Järvinen 10.6.2004 [email protected] Modified by Zhong Yunqiu 7.8.2008 Table
Helsinki University of Technology Department of Communications and Networking How to Configure Cisco 2600 Routers Juha Järvinen 10.6.2004 [email protected] Modified by Zhong Yunqiu 7.8.2008 Table
ICND1 Lab Guide. 100-101 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 Version 2.0. Labs powered by
 ICND1 Lab Guide 100-101 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 Version 2.0 ii Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 100-101 Lab Guide LM20130929/BV2.01 iii 25 Century Blvd. Ste. 500
ICND1 Lab Guide 100-101 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 Version 2.0 ii Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 100-101 Lab Guide LM20130929/BV2.01 iii 25 Century Blvd. Ste. 500
Note: This case study utilizes Packet Tracer. Please see the Chapter 5 Packet Tracer file located in Supplemental Materials.
 Note: This case study utilizes Packet Tracer. Please see the Chapter 5 Packet Tracer file located in Supplemental Materials. CHAPTER 5 OBJECTIVES Configure a router with an initial configuration. Use the
Note: This case study utilizes Packet Tracer. Please see the Chapter 5 Packet Tracer file located in Supplemental Materials. CHAPTER 5 OBJECTIVES Configure a router with an initial configuration. Use the
Lab 8.4.3a Managing Cisco IOS Images with TFTP
 Lab 8.4.3a Managing Cisco IOS Images with TFTP Host Device Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Analyze the Cisco IOS image and router flash memory.
Lab 8.4.3a Managing Cisco IOS Images with TFTP Host Device Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Analyze the Cisco IOS image and router flash memory.
USB Disable for Cisco ISRs Feature Module
 USB Disable for Cisco ISRs Feature Module First Published: March 28, 2011 Part Number: This guide describes the USB Disable feature in the following major sections: Feature Introduction, page 1 Restrictions,
USB Disable for Cisco ISRs Feature Module First Published: March 28, 2011 Part Number: This guide describes the USB Disable feature in the following major sections: Feature Introduction, page 1 Restrictions,
Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 806, 826, 827, 828, 831, 836, 837 and 881 Series Routers
 Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 806, 826, 827, 828, 831, 836, 837 and 881 Series Routers Document ID: 12065 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions
Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 806, 826, 827, 828, 831, 836, 837 and 881 Series Routers Document ID: 12065 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions
ENetwork Basic Configuration PT Practice SBA
 ENetwork Basic Configuration PT Practice SBA A few things to keep in mind while completing this activity: 1. Do not use the browser Back button or close or reload any exam windows during the exam. 2. Do
ENetwork Basic Configuration PT Practice SBA A few things to keep in mind while completing this activity: 1. Do not use the browser Back button or close or reload any exam windows during the exam. 2. Do
Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding. Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1
 Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1 1 1 Objectives Identify a router as a computer with an OS and hardware designed for the routing process. Demonstrate
Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1 1 1 Objectives Identify a router as a computer with an OS and hardware designed for the routing process. Demonstrate
Configuring the Switch with the CLI Setup Program
 APPENDIXC Configuring the Switch with the CLI Setup Program This appendix provides a command-line interface (CLI) setup procedure for a standalone switch. To set up the switch by using Express Setup, see
APPENDIXC Configuring the Switch with the CLI Setup Program This appendix provides a command-line interface (CLI) setup procedure for a standalone switch. To set up the switch by using Express Setup, see
Lab 6.2.3 Managing the MAC Address Table
 Lab 6.2.3 Managing the MAC Address Table Objective Create a basic switch configuration. Manage the switch MAC table. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in the diagram. The configuration
Lab 6.2.3 Managing the MAC Address Table Objective Create a basic switch configuration. Manage the switch MAC table. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in the diagram. The configuration
Basic Configuration of the Cisco 12000 Series Internet Router
 CHAPTER 2 Basic Configuration of the Cisco 12000 Series Internet Router This chapter describes how to boot and configure the Cisco 12000 Series Internet Router. It discusses the following subjects: Cisco
CHAPTER 2 Basic Configuration of the Cisco 12000 Series Internet Router This chapter describes how to boot and configure the Cisco 12000 Series Internet Router. It discusses the following subjects: Cisco
Cisco Configuration Professional Quick Start Guide
 Cisco Configuration Professional Quick Start Guide April 29, 2011 This document explains how to start using Cisco Configuration Professional Express (Cisco CP Express) and Cisco Configuration Professional
Cisco Configuration Professional Quick Start Guide April 29, 2011 This document explains how to start using Cisco Configuration Professional Express (Cisco CP Express) and Cisco Configuration Professional
Objectives Understand Cisco IOS system architecture components. Work with the Cisco IOS Command Line Interface (CLI) and common commands.
 Objectives Understand Cisco IOS system architecture components. Work with the Cisco IOS Command Line Interface (CLI) and common commands. Learn about Cisco IOS troubleshooting techniques. Understand upgrading
Objectives Understand Cisco IOS system architecture components. Work with the Cisco IOS Command Line Interface (CLI) and common commands. Learn about Cisco IOS troubleshooting techniques. Understand upgrading
Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco Catalyst 2948G L3, 4840G, and 4908G L3 Switch Routers
 Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco Catalyst 2948G L3, 4840G, and 4908G L3 Switch Routers Document ID: 12738 Contents Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Step by Step Procedure
Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco Catalyst 2948G L3, 4840G, and 4908G L3 Switch Routers Document ID: 12738 Contents Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Step by Step Procedure
Connecting to the Firewall Services Module and Managing the Configuration
 CHAPTER 3 Connecting to the Firewall Services Module and This chapter describes how to access the command-line interface and work with the configuration. This chapter includes the following sections: Connecting
CHAPTER 3 Connecting to the Firewall Services Module and This chapter describes how to access the command-line interface and work with the configuration. This chapter includes the following sections: Connecting
Lab 8.4.3b Managing Cisco IOS images with ROMMON and TFTP
 Lab 8.4.3b Managing Cisco IOS images with ROMMON and TFTP Host Device Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Analyze the Cisco IOS image and router
Lab 8.4.3b Managing Cisco IOS images with ROMMON and TFTP Host Device Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Analyze the Cisco IOS image and router
Skills Assessment Student Training Exam
 Skills Assessment Student Training Exam Topology Assessment Objectives Part 1: Initialize Devices (8 points, 5 minutes) Part 2: Configure Device Basic Settings (28 points, 30 minutes) Part 3: Configure
Skills Assessment Student Training Exam Topology Assessment Objectives Part 1: Initialize Devices (8 points, 5 minutes) Part 2: Configure Device Basic Settings (28 points, 30 minutes) Part 3: Configure
Lab 8.3.1.2 Configure Basic AP Security through IOS CLI
 Lab 8.3.1.2 Configure Basic AP Security through IOS CLI Estimated Time: 30 minutes Number of Team Members: Students will work in teams of two. Objective In this lab, the student will learn the following
Lab 8.3.1.2 Configure Basic AP Security through IOS CLI Estimated Time: 30 minutes Number of Team Members: Students will work in teams of two. Objective In this lab, the student will learn the following
HOW TO CONFIGURE CISCO FIREWALL PART I
 HOW TO CONFIGURE CISCO FIREWALL PART I Cisco Abstract: Please find below a step by step process to configure the PIX Firewall from scratch. A simple scenario is given here where you have a corporate network
HOW TO CONFIGURE CISCO FIREWALL PART I Cisco Abstract: Please find below a step by step process to configure the PIX Firewall from scratch. A simple scenario is given here where you have a corporate network
Basic Router and Switch Instructions (Cisco Devices)
 Basic Router and Switch Instructions (Cisco Devices) Basic Device Connection 1. Connect to the device via the console cable (light blue cable) and the use of a terminal program (Windows Hyperterminal,
Basic Router and Switch Instructions (Cisco Devices) Basic Device Connection 1. Connect to the device via the console cable (light blue cable) and the use of a terminal program (Windows Hyperterminal,
Configuring a Cisco 2509-RJ Terminal Router
 created by: Rainer Bemsel Version 1.0 Dated: Dec/08/2012 For my Cisco LAB, I ve purchased a used Cisco 2509-RJ with RJ45-RJ45 roll-over cables. This TechTip shows my configuration setup, so you can easily
created by: Rainer Bemsel Version 1.0 Dated: Dec/08/2012 For my Cisco LAB, I ve purchased a used Cisco 2509-RJ with RJ45-RJ45 roll-over cables. This TechTip shows my configuration setup, so you can easily
- Advanced IOS Functions -
 1 The Configuration Register - Advanced IOS Functions - The configuration register (config-register) is a hexadecimal value that controls various aspects of how a router boots, including: Baud Rate Boot
1 The Configuration Register - Advanced IOS Functions - The configuration register (config-register) is a hexadecimal value that controls various aspects of how a router boots, including: Baud Rate Boot
ROLE-BASED COMMAND-LINE INTERFACE ACCESS
 ROLE-BASED COMMAND-LINE INTERFACE ACCESS DENISE HELFRICH MARCH 2004 1 Agenda Role-Based Command-Line Interface (CLI) Access Overview Configuration Tasks CLI Views Lawful Intercept View How to access and
ROLE-BASED COMMAND-LINE INTERFACE ACCESS DENISE HELFRICH MARCH 2004 1 Agenda Role-Based Command-Line Interface (CLI) Access Overview Configuration Tasks CLI Views Lawful Intercept View How to access and
IST 220 Honors Project. Subnets with Variable Length Subnet Masks
 IST 220 Honors Project Subnets with Variable Length Subnet Masks Project Objectives: In this project, you will subnet the IP address 193.170.10.0 according to needs of the organization. Overview a) Perform
IST 220 Honors Project Subnets with Variable Length Subnet Masks Project Objectives: In this project, you will subnet the IP address 193.170.10.0 according to needs of the organization. Overview a) Perform
Basic Software Configuration Using the Cisco IOS Command-Line Interface
 Basic Software Configuration Using the Cisco IOS Command-Line Interface This document describes how to use the Cisco IOS command-line interface (CLI) to perform a basic software configuration for your
Basic Software Configuration Using the Cisco IOS Command-Line Interface This document describes how to use the Cisco IOS command-line interface (CLI) to perform a basic software configuration for your
Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 2900 Series Integrated Services Router
 Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 2900 Series Integrated Services Router Document ID: 112033 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions Step by
Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 2900 Series Integrated Services Router Document ID: 112033 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions Step by
Lab - Using IOS CLI with Switch MAC Address Tables
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12
APNIC Members Training Course Security workshop. 2-4 July, 2008. Port Vila Vanuatu. In conjunction with PACNOG 4
 APNIC Members Training Course Security workshop 2-4 July, 2008 Port Vila Vanuatu In conjunction with PACNOG 4 Router device security lab 1. APNIC s remote lab In these exercises you will be remotely accessing
APNIC Members Training Course Security workshop 2-4 July, 2008 Port Vila Vanuatu In conjunction with PACNOG 4 Router device security lab 1. APNIC s remote lab In these exercises you will be remotely accessing
Building a Network in GNS3
 Building a Network in GNS3 In this tutorial, you will create a network in GNS3 between two routers, and each router will have one host connected to it. The ultimate goal is to route data between network
Building a Network in GNS3 In this tutorial, you will create a network in GNS3 between two routers, and each router will have one host connected to it. The ultimate goal is to route data between network
During this lab time you will configure the routing protocol OSPF with IPv4 addresses.
 Lab 2: OSPF During this lab time you will configure the routing protocol OSPF with IPv4 addresses. It is your responsibility to create an appropriate IPv4 subnet plan and address plan. To ensure a timely
Lab 2: OSPF During this lab time you will configure the routing protocol OSPF with IPv4 addresses. It is your responsibility to create an appropriate IPv4 subnet plan and address plan. To ensure a timely
Using Cisco IOS Software
 Using Cisco IOS Software This chapter provides helpful tips for understanding and configuring Cisco IOS software using the command-line interface (CLI). It contains the following sections: Understanding
Using Cisco IOS Software This chapter provides helpful tips for understanding and configuring Cisco IOS software using the command-line interface (CLI). It contains the following sections: Understanding
PT Activity: Configure Cisco Routers for Syslog, NTP, and SSH Operations
 PT Activity: Configure Cisco Routers for Syslog, NTP, and SSH Operations Instructor Version Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 FA0/1
PT Activity: Configure Cisco Routers for Syslog, NTP, and SSH Operations Instructor Version Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 FA0/1
Chapter 8 Lab B: Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client
 Chapter 8 Lab B: Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client Topology Note: ISR G2 devices have Gigabit Ethernet interfaces instead of FastEthernet Interfaces. All contents are Copyright 1992 2012
Chapter 8 Lab B: Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client Topology Note: ISR G2 devices have Gigabit Ethernet interfaces instead of FastEthernet Interfaces. All contents are Copyright 1992 2012
Course "Netzwerke" LAB 2 Basic Router Configuration
 Course "Netzwerke" LAB 2 Basic Router Configuration Learning Objectives Review of previously learned skills. Basic IOS Command Line Interface operation. Basic Router configuration. Verification and testing
Course "Netzwerke" LAB 2 Basic Router Configuration Learning Objectives Review of previously learned skills. Basic IOS Command Line Interface operation. Basic Router configuration. Verification and testing
CHAPTER 3 STATIC ROUTING
 CHAPTER 3 STATIC ROUTING This chapter addresses the end-to-end delivery service of IP and explains how IP routers and hosts handle IP datagrams. The first section discusses how datagrams are forwarded
CHAPTER 3 STATIC ROUTING This chapter addresses the end-to-end delivery service of IP and explains how IP routers and hosts handle IP datagrams. The first section discusses how datagrams are forwarded
The Purpose and Use of the Configuration Register on All Cisco Routers
 The Purpose and Use of the Configuration Register on All Cisco Routers Document ID: 50421 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions The Purpose of the Configuration Register
The Purpose and Use of the Configuration Register on All Cisco Routers Document ID: 50421 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions The Purpose of the Configuration Register
Lab assignment #2 IPSec and VPN Tunnels (Document version 1.1)
 University of Pittsburgh School of Information Science IS2820/TEL2813 - Security Management Lab assignment #2 IPSec and VPN Tunnels (Document version 1.1) Lab GSA: Carlos Caicedo Page I. Lab resources
University of Pittsburgh School of Information Science IS2820/TEL2813 - Security Management Lab assignment #2 IPSec and VPN Tunnels (Document version 1.1) Lab GSA: Carlos Caicedo Page I. Lab resources
Telnet, Console and AUX Port Passwords on Cisco Routers Configuration Example
 Telnet, Console and AUX Port Passwords on Cisco Routers Configuration Example Document ID: 45843 Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Configure Passwords
Telnet, Console and AUX Port Passwords on Cisco Routers Configuration Example Document ID: 45843 Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Configure Passwords
This techno knowledge paper can help you if: You need to setup a WAN connection between a Patton Router and a NetGuardian.
 Problem: Patton / 240T WAN Setup Platform: NetGuardian 240T This TKP is a guide to setting up a PPP to T1 WAN connection between a Patton Model 2603 Router and a NetGuardian 240T. The example in this guide
Problem: Patton / 240T WAN Setup Platform: NetGuardian 240T This TKP is a guide to setting up a PPP to T1 WAN connection between a Patton Model 2603 Router and a NetGuardian 240T. The example in this guide
Lab 4.5.4 Diagramming External Traffic Flows
 Lab 4.5.4 Diagramming External Traffic Flows Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Business Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 R2 R3 FC-CPE-1 FC-CPE-2 ISP Fa0/1 172.17.0.1
Lab 4.5.4 Diagramming External Traffic Flows Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Business Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 R2 R3 FC-CPE-1 FC-CPE-2 ISP Fa0/1 172.17.0.1
- The PIX OS Command-Line Interface -
 1 PIX OS Versions - The PIX OS Command-Line Interface - The operating system for Cisco PIX/ASA firewalls is known as the PIX OS. Because the PIX product line was acquired and not originally developed by
1 PIX OS Versions - The PIX OS Command-Line Interface - The operating system for Cisco PIX/ASA firewalls is known as the PIX OS. Because the PIX product line was acquired and not originally developed by
LAB THREE STATIC ROUTING
 LAB THREE STATIC ROUTING In this lab you will work with four different network topologies. The topology for Parts 1-4 is shown in Figure 3.1. These parts address router configuration on Linux PCs and a
LAB THREE STATIC ROUTING In this lab you will work with four different network topologies. The topology for Parts 1-4 is shown in Figure 3.1. These parts address router configuration on Linux PCs and a
Configuring Voice over IP
 CHAPTER 4 This chapter explains how to configure voice interfaces and ports, which convert telephone voice signals for transmission over an IP network. This chapter presents the following major topics:
CHAPTER 4 This chapter explains how to configure voice interfaces and ports, which convert telephone voice signals for transmission over an IP network. This chapter presents the following major topics:
Packet Tracer 3 Lab VLSM 2 Solution
 Packet Tracer 3 Lab VLSM 2 Solution Objective Create a simulated network topology using Packet Tracer Design an IP addressing scheme using a Class B subnetwork address and VLSM Apply IP addresses to the
Packet Tracer 3 Lab VLSM 2 Solution Objective Create a simulated network topology using Packet Tracer Design an IP addressing scheme using a Class B subnetwork address and VLSM Apply IP addresses to the
Connecting the DG-102S VoIP Gateway to your network
 Contents of Package: DG-102S VoIP Station Gateway Power adapter CD-ROM, including User s Manual Quick Install Guide Requirements: RS-232 Console Cable Two RJ-45 CAT-5 Straight-Through Cables For more information
Contents of Package: DG-102S VoIP Station Gateway Power adapter CD-ROM, including User s Manual Quick Install Guide Requirements: RS-232 Console Cable Two RJ-45 CAT-5 Straight-Through Cables For more information
Comware versus Cisco IOS Command Guide
 Technical Marketing Engineering Routing and Switching Technology Routing and Switching Comware versus Cisco IOS Command Guide Technical Marketing Brief Revision v5 March 23, 2009 http://www.3com.com 3Com
Technical Marketing Engineering Routing and Switching Technology Routing and Switching Comware versus Cisco IOS Command Guide Technical Marketing Brief Revision v5 March 23, 2009 http://www.3com.com 3Com
Configuring the PIX Firewall with PDM
 Configuring the PIX Firewall with PDM Objectives In this lab exercise you will complete the following tasks: Install PDM Configure inside to outside access through your PIX Firewall using PDM Configure
Configuring the PIX Firewall with PDM Objectives In this lab exercise you will complete the following tasks: Install PDM Configure inside to outside access through your PIX Firewall using PDM Configure
Understanding Interface Numbering and Cisco IOS Software Basics
 CHAPTER 1 and Cisco IOS Software Basics This chapter provides an overview of the interface numbering in the Cisco 2600 series, Cisco 3600 series, and Cisco 3700 series routers. It also describes how to
CHAPTER 1 and Cisco IOS Software Basics This chapter provides an overview of the interface numbering in the Cisco 2600 series, Cisco 3600 series, and Cisco 3700 series routers. It also describes how to
Objectives. Background. Required Resources. CCNA Security
 Chapter 8 Lab B, Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client Topology IP Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 FA0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Chapter 8 Lab B, Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client Topology IP Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 FA0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Lab 5.5.4 Configuring the Cisco 2960 Switch
 Lab 5.5.4 Configuring the Cisco 2960 Switch Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port S1 CustomerSwitch VLAN 1 192.168.1.5 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 N/A R1 CustomerRouter
Lab 5.5.4 Configuring the Cisco 2960 Switch Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port S1 CustomerSwitch VLAN 1 192.168.1.5 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 N/A R1 CustomerRouter
RIPv2 with Variable Length Subnet Masks (VLSMs)
 RIPv2 with Variable Length Subnet Masks (VLSMs) This chapter will discuss the RIPv2 routing process. This is an important subject to understand as it pertains to all routers and configurations that use
RIPv2 with Variable Length Subnet Masks (VLSMs) This chapter will discuss the RIPv2 routing process. This is an important subject to understand as it pertains to all routers and configurations that use
Cisco CCNA Optional Semester 4 Labs Wide Area Networking LAB 1 T1 TSU WAN LINK OVERVIEW - Instructor Guide (Estimated time: 30 minutes)
 CNAP @ VCC 1 of 8 LAB 1 T1 TSU WAN LINK OVERVIEW - Instructor Guide (Estimated time: 30 minutes) Objectives: Understand the function of a T1 Service Unit (TSU) in network telecommunications Connect routers
CNAP @ VCC 1 of 8 LAB 1 T1 TSU WAN LINK OVERVIEW - Instructor Guide (Estimated time: 30 minutes) Objectives: Understand the function of a T1 Service Unit (TSU) in network telecommunications Connect routers
Chapter 6 Updating Software Images and Configuration Files
 Chapter 6 Updating Software Images and Configuration Files This chapter describes how to copy and save configuration files and software image files. Downloading and Uploading a Software Image on a TFTP
Chapter 6 Updating Software Images and Configuration Files This chapter describes how to copy and save configuration files and software image files. Downloading and Uploading a Software Image on a TFTP
School of Information Technology and Engineering (SITE) CEG 4395: Computer Network Management. Lab 4: Remote Monitoring (RMON) Operations
 School of Information Technology and Engineering (SITE) CEG 4395: Computer Network Management Lab 4: Remote Monitoring (RMON) Operations Objective To become familiar with basic RMON operations, alarms,
School of Information Technology and Engineering (SITE) CEG 4395: Computer Network Management Lab 4: Remote Monitoring (RMON) Operations Objective To become familiar with basic RMON operations, alarms,
- Basic Router Security -
 1 Enable Passwords - Basic Router Security - The enable password protects a router s Privileged mode. This password can be set or changed from Global Configuration mode: Router(config)# enable password
1 Enable Passwords - Basic Router Security - The enable password protects a router s Privileged mode. This password can be set or changed from Global Configuration mode: Router(config)# enable password
1 Basic Configuration of Cisco 2600 Router. Basic Configuration Cisco 2600 Router
 1 Basic Configuration of Cisco 2600 Router Basic Configuration Cisco 2600 Router I decided to incorporate the Cisco 2600 into my previously designed network. This would give me two seperate broadcast domains
1 Basic Configuration of Cisco 2600 Router Basic Configuration Cisco 2600 Router I decided to incorporate the Cisco 2600 into my previously designed network. This would give me two seperate broadcast domains
Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 2 Conceitos de protocolos de Encaminhamento Cap 2
 Static Routing Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 2 1 1 Objectives Define the general role a router plays in networks. Describe the directly connected networks, different router interfaces Examine
Static Routing Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 2 1 1 Objectives Define the general role a router plays in networks. Describe the directly connected networks, different router interfaces Examine
DVQ-2, DMR8RT, DMR16RT QUICK-START GUIDE
 DVQ-2, DMR8RT, DMR16RT QUICK-START GUIDE IMPORTANT!!! PLEASE READ BEFORE OPERATING YOUR DVR Ready to go, right out of the box! This digital video recorder is designed to function right out of the box.
DVQ-2, DMR8RT, DMR16RT QUICK-START GUIDE IMPORTANT!!! PLEASE READ BEFORE OPERATING YOUR DVR Ready to go, right out of the box! This digital video recorder is designed to function right out of the box.
Experts in Networking. CCNA Cheat Sheet. This CCNA command cheat sheet covers both ICND parts 1 & 2 and covers the current CCNA exam (640-802).
 CCNA Cheat Sheet This CCNA command cheat sheet covers both ICND parts 1 & 2 and covers the current CCNA exam (640-802). Whilst not an exhaustive IOS command list it covers the majority of commands found
CCNA Cheat Sheet This CCNA command cheat sheet covers both ICND parts 1 & 2 and covers the current CCNA exam (640-802). Whilst not an exhaustive IOS command list it covers the majority of commands found
AN ANALYTICAL STUDY OF INTERNET AND INTRANET CONNECTIONS AND CONFIGURATIONS IN ISP
 AN ANALYTICAL STUDY OF INTERNET AND INTRANET CONNECTIONS AND CONFIGURATIONS IN ISP Mst. Najnin Sultana, Abu Jafar Md. Masud Karim Daffodil International University, Dhaka, Bangladesh E-mail: [email protected]
AN ANALYTICAL STUDY OF INTERNET AND INTRANET CONNECTIONS AND CONFIGURATIONS IN ISP Mst. Najnin Sultana, Abu Jafar Md. Masud Karim Daffodil International University, Dhaka, Bangladesh E-mail: [email protected]
Configuring a Leased Line
 CHAPTER 4 Configuring a Leased Line The configuration in this chapter describes how to configure a Cisco 1700 router for IP and IPX over a synchronous serial line. Before You Begin The configuration in
CHAPTER 4 Configuring a Leased Line The configuration in this chapter describes how to configure a Cisco 1700 router for IP and IPX over a synchronous serial line. Before You Begin The configuration in
Using the Command Line Interface (CLI)
 4 Using the Command Line Interface (CLI) Contents Overview...................................................... 4-2 Accessing the CLI............................................... 4-2...................................................
4 Using the Command Line Interface (CLI) Contents Overview...................................................... 4-2 Accessing the CLI............................................... 4-2...................................................
Lab Exercise Configure the PIX Firewall and a Cisco Router
 Lab Exercise Configure the PIX Firewall and a Cisco Router Scenario Having worked at Isis Network Consulting for two years now as an entry-level analyst, it has been your hope to move up the corporate
Lab Exercise Configure the PIX Firewall and a Cisco Router Scenario Having worked at Isis Network Consulting for two years now as an entry-level analyst, it has been your hope to move up the corporate
Deploying Secure Internet Connectivity
 C H A P T E R 5 Deploying Secure Internet Connectivity This chapter is a step-by-step procedure explaining how to use the ASDM Startup Wizard to set up the initial configuration for your ASA/PIX Security
C H A P T E R 5 Deploying Secure Internet Connectivity This chapter is a step-by-step procedure explaining how to use the ASDM Startup Wizard to set up the initial configuration for your ASA/PIX Security
Using the Cisco IOS Command Line Interface
 CHAPTER 3 Using the Cisco IOS Line Interface 3.1 Using the CLI Cisco IOS software provides a command line interface (CLI) that allows you to configure and manage the Cisco 6200 advanced digital subscriber
CHAPTER 3 Using the Cisco IOS Line Interface 3.1 Using the CLI Cisco IOS software provides a command line interface (CLI) that allows you to configure and manage the Cisco 6200 advanced digital subscriber
Lab 4.1.2 Characterizing Network Applications
 Lab 4.1.2 Characterizing Network Applications Objective Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Business Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 FC-CPE-1 Fa0/1 172.17.0.1 Fa0/0 10.0.0.1
Lab 4.1.2 Characterizing Network Applications Objective Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Business Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 FC-CPE-1 Fa0/1 172.17.0.1 Fa0/0 10.0.0.1
