Osteoporosis Fracture Prevention Guideline September 2011
|
|
|
- Edwin Newton
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Osteoporosis Fracture Prevention Guideline September 2011 Rationale for Guideline This is a consensus-based guideline. Although many studies have been published about osteoporosis treatment in postmenopausal women, only 1 trial in early postmenopausal women has evaluated the effectiveness of osteoporosis screening on fracture outcome (Barr RJ Osteoporos Int (2010) 21: ). Therefore, direct evidence that screening improves outcomes is limited. Recommendation for screening is based on the following three points: 1) The risk of osteoporosis increases with advancing age particularly for postmenopausal women 2) Accurate screening tests for osteoporosis exist and decreased BMD does strongly predict fracture risk 3) High quality trials have demonstrated the efficacy of bisphosphonates in preventing hip fractures and selective estrogen-receptor modulator medications in preventing vertebral fractures in women with osteoporosis. The average mortality rate in the first year following a hip fracture is approximately 25% and ~25% of previously ambulatory hip fracture survivors require subsequent long-term care. Despite this impact on premature morbidity and mortality and recommendations by many organizations including the USPSTF, assessment of fracture risk and screening for osteoporosis is not routine. Definition Osteoporosis is defined as a skeletal disorder characterized by compromised bone strength predisposing to an increased risk of fracture. Bone strength reflects both bone density and bone quality. Target Population Women over age 65 years and women age 50 and over with risk factors for osteoporosis. Men over age 70 with risk factors or men age 50 and over at high risk due to other conditions (e.g., chronic glucocorticoid use). Source of Evidence See National Osteoporosis Guideline Nov 2008 for problem formulations, evidence discussion and evidence tables. This guideline has been modified to align with formulary and operational issues in KPCO. See also Nelson HD, Haney EM, Dana T, Bougatsos C, Chou R. Screening for osteoporosis: an update for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Ann Intern Med 2010; 153(2): Screening for osteoporosis: U.S. preventive services task force recommendation statement. Ann Intern Med 2011; 154(5): Settings for Application Internal Medicine, Family Practice, Ob/Gyn, Radiology, Endocrinology, Nephrology, Rheumatology and other specialties as appropriate
2 Methods for Measuring Compliance Osteoporosis Screening HEDIS rates, hip fracture rates and cost, number of average women over age 65 screened or treated, medication compliance. 1. Screening Bone Mineral Density (Average Risk) Postmenopausal women: 1A. A bone mineral density (BMD) test by dual energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) is recommended for postmenopausal women age 65 and older who are not on drug treatment for osteoporosis. (Evidence based: B) Please note that those with clinically diagnosed osteoporosis(i.e., prior fragility fracture of the hip or spine) and those at very high risk of fracture (i.e., oral glucocorticoid users and other secondary causes of low BMD) are excluded from this problem formulation. 1B. A bone mineral density (BMD) test by dual energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) is recommended for postmenopausal women under the age of 65 whose fracture risk is equal to that of a 65 year-old white woman with no additional risk factors (i.e., 10-yr hip fracture risk of 1.2% or a 10-yr major osteoporotic fracture risk of 9.3%). This risk can be assessed by calculating a FRAX score prior to obtaining a BMD ( (Consensus based) Risk Factors for osteoporosis include: Evidence-based: A Fragility fracture after age 50 History of frequent falling in the past year Smoking Weight <127 lbs, or BMI <21 1st degree relative with hip fracture Consensus-based: 15 years of menopause or estrogen deficiency for women Note that 60% of fracture risk can be accounted for by bone density and the remaining 40% is due to other factors (i.e., bone strength). Men: 1C. Screening is an option for men over age 70 with risk factors.(consensus based) Optimal screening frequency: 1D. Because evidence is lacking, consensus based recommendations for repeating a screening DXA scan vary widely - from no recommendation to intervals as long as 10 years. Thus, consider a 5 year retesting interval in untreated persons at high risk for
3 fracture. (Consensus based) *For a healthy 65 yo. woman with a T-score of -1.0, it will take ~8 yrs for her to reach even a 20% chance of developing either a T-score of -2.5 or a fragility fracture. (SA Frost J Bone Miner Res 2009;24: ) 2. Testing for Women and Men at Very High Risk of Fracture Women and Men with prior fragility fracture* after the age of 50: 2A. For women and men with a fragility fracture of the hip or spine (i.e., clinical osteoporosis) after the age of 50: Initiating treatment directly without undergoing testing with BMD is recommended. (Consensus based) For women and men with other fragility fractures (e.g., wrist or humerus) after the age of 50: Initiating treatment directly without undergoing testing with BMD is an option. (Consensus based) *A fragility fracture is a low-trauma fracture resulting from a fall from standing height or less. Women and Men on oral glucocorticoid therapy*: 2B For women and men on oral glucocorticoid therapy: Initiating treatment with bisphosphonates directly without undergoing testing with BMD is an option (Evidence based: B) *>5 mg/day prednisone or equivalent for >3 months duration 3. Bone Mineral Density Screening Measurement Sites 3A. The hip and lumbar spine are recommended measurement sites for BMD to predict risk of osteoporotic fracture in women and men. (Evidence-based: B) 3B. BMD of the forearm is an option for patients in whom hip and spine BMD cannot be measured or interpreted. (Evidence-based: B) 4. Lifestyle Changes 4A. The following lifestyle changes are recommended for all women and men to reduce the risk of osteoporosis: Exercise regular weight-bearing and muscle-building exercise Smoking cessation (Consensus-based) 4B. Home safety proofing is recommended for postmenopausal women and men at risk of falling.* (Consensus-based)
4 4C. The routine use of hip protectors is not recommended as an intervention for reducing the risk of hip fractures in postmenopausal women and men aged 50 and older. (Evidence-based D) NOTE: WITH THE RECENT SCANDAL REGARDING THE NEGATIVE HIP PROTECTOR TRIAL, THIS REC MAY NOT HOLD: *Home safety proofing includes removing rugs, adding grab bars, establishing adequate lighting (i.e. nightlights), and securing electrical cord placement. Preventive measures for women or men with and without osteoporosis 5A. Total daily intake of calcium is recommended for all pre- or post-menopausal women and older men (1,000 mg/day for premenopausal women; 1,200 mg/day for postmenopausal women and men over age 50). (Consensus-based) 5B. Total daily intake of at least 1000 IU/day vitamin D is recommended for all pre- or postmenopausal women and men over age 50. (Evidence based: B) Preventive measures for women and men without osteoporosis 5C. Hormone therapy solely for the prevention of osteoporosis is not recommended. (Consensus-based) Preventive measures for postmenopausal women diagnosed with osteoporosis by: Postmenopausal women with a prior fragility fracture. (Evidence based: A) Women aged 65 or older with a diagnosis of osteoporosis (T score 2.5). Evidence based: A Osteopenia with 10 year risk of hip fracture 3% or a 10 year major osteoporotic fx risk 20% per FRAX calculation First-line drug therapies Note: Test for Vitamin D deficiency (25-OH Vitamin D level) when therapy is initiated. 5D. Bisphosphonates. Current preferred formulary agent: Alendronate 70 mg once weekly If alendronate is NOT tolerated, risedronate (Actonel) 35 mg weekly is an option (requires NF review per medical necessity) NOTE: Bisphosphonates should be used in caution with chronic kidney disease and reduced GFR and consider decreasing dose of oral bisphosphonates to every other week if CrCl < 30 ml/min Zoledronic acid (Reclast) IV can be considered for pts with contraindications or intolerances to two oral bisphosphonates Second-line drug therapies (The following medications are for use only when bisphosphonates are contraindicated or not tolerated in postmenopausal women. It is recommended treatment be discussed with endocrinology before ordering any of the below agents). 5E. Raloxifene is an option for postmenopausal women with prior vertebral fracture and low risk for thrombotic complications. Evidence has NOT demonstrated a statistically significant decrease in the incidence of hip fractures with this agent. (Evidence based: B). 5F. Calcitonin is an option for postmenopausal women over the age of 65 with a prior vertebral fracture or T-score at or below Evidence has NOT demonstrated a
5 statistically significant decrease in the incidence of hip fractures with this agent. (Evidence based: B) 5G. Teriparatide (Forteo): Part D formulary only (non-formulary review required for commercial members). 5H. Denosumab (Prolia): Non-formulary agent (requires NF review per medical necessity). Preventive measures for premenopausal women with a T-score at or below H. There is insufficient evidence to recommend for or against treatment with any prescribed pharmacological therapy for premenopausal women.* (Evidence based: I) *Bisphosphonates are not recommended in women of childbearing age without adequate contraception. Preventive measures for women and men taking corticosteroid therapy 5I. Bisphosphonates: Alendronate 70 mg once weekly is recommended as first-line therapy for women and men taking oral corticosteroid medication (>5 mg/day prednisone or equivalent, for >3 months duration). If alendronate is not tolerated, consider risedronate (Actonel) 35 mg once weekly (Non-Formulary). * (Evidence based: B) *Bisphosphonates are not recommended in women of childbearing age without adequate contraception. Bisphosphonates should be used with caution in patients with chronic kidney disease and reduced GFR. Treatment Durations 5J. There is insufficient evidence on optimal treatment durations for the pharmacologic management of osteoporosis. (Evidence based: I) 6. Monitoring Treatment 6A. Routine BMD testing is not recommended for monitoring the rate of bone loss after initiation of treatment in women or men. (Consensus based) 6B. There is insufficient evidence on routine bone turnover testing with biochemical markers [N-telopeptide (NTx) and C-telopeptide (CTx)] for monitoring women and men taking antiresorptive therapy for osteoporosis. (Evidence based: I) 6C. There is insufficient evidence for routine bone turnover testing with biochemical markers [N-telopeptide (NTx) or C-telopeptide (CTx)] to assess a patient s risk for developing osteonecrosis of the jaw (ONJ) while on bisphopshonate therapy. (Consensus-based) 7. Evaluation of secondary causes 7A. History and physical are critical in evaluation of secondary causes 7B. The following lab tests may also be considered (consensus based): CBC Comprehensive metabolic profile TSH with reflex T4 PTH panel 25 hydroxy Vit D level
6 For males- testosterone level Consider 24 hr urine calcium For all patients with secondary causes, consider endocrinology/other appropriate consult using p advice endo. 8. Supplemental Information on Secondary Causes of Bone Loss Data from The North American Menopause Society, Position Statement 2010 (Menopause: The Journal of The North American Menopause Society Vol. 17, No. 1, pp. 25/54) (note that these are not listed in order of frequency or clinical importance) Medications Oral or intramuscular use of glucocorticoids for > 3 months Aromatase inhibitors: anastrozole (Arimidex), letrozole (Femara), exemestane (Aromasin) Long-term use of certain anticonvulsants (carbamazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin, primidone, valproic acid) Heparin Cytotoxic agents Gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists or analogues Intramuscular medroxyprogesterone contraceptive Immunosuppressives (eg, cyclosporine, tacrolimus) Excessive thyroxine doses Genetic Disorders Osteogenesis imperfecta Thalassemia Hypophosphatasia Hemochromatosis Disorders of calcium balance Hypercalciuria Vitamin D deficiency Endocrinopathies Cortisol excess Cushing s syndrome Gonadal insufficiency (primary and secondary) Hyperthyroidism Type 1 diabetes mellitus Primary hyperparathyroidism Gastrointestinal disease Chronic liver disease (eg,primary biliary cirrhosis)
7 Malabsorption syndromes (eg, celiac disease, Crohn s disease) Total gastrectomy Billroth I gastroenterostomy Other disorders and conditions Multiple myeloma Lymphoma and leukemia Systemic mastocytosis Nutritional disorders (eg, anorexia nervosa) Rheumatoid arthritis Chronic renal disease For all patients with secondary causes, consider endocrinology/other appropriate consult using p advice endo. These procedures are informational only and are not intended or designed to substitute the reasonable exercise of independent clinical judgment by the practitioner in any particular set of circumstances for each patient encounter. The guidelines are flexible and are intended for use as a resource for integration with a sound exercise of clinical judgment. They can be used to create an approach to care that is unique to the needs of each individual patient.
Clinical Practice Guideline for Osteoporosis Screening and Treatment
 Clinical Practice Guideline for Osteoporosis Screening and Treatment Osteoporosis is a condition of decreased bone mass, leading to bone fragility and an increased susceptibility to fractures. While osteoporosis
Clinical Practice Guideline for Osteoporosis Screening and Treatment Osteoporosis is a condition of decreased bone mass, leading to bone fragility and an increased susceptibility to fractures. While osteoporosis
PROTOCOL FOR PATIENTS WITH ABNORMAL LAB AND X-RAY VALUES
 PROTOCOL FOR PATIENTS WITH ABNORMAL LAB AND X-RAY VALUES Patients newly diagnosed as osteopenic or osteoporotic on a radiology report or patients receiving abnormal lab values on the following lab tests
PROTOCOL FOR PATIENTS WITH ABNORMAL LAB AND X-RAY VALUES Patients newly diagnosed as osteopenic or osteoporotic on a radiology report or patients receiving abnormal lab values on the following lab tests
DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) OSTEOPOROSIS GUIDELINE
 DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) OSTEOPOROSIS GUIDELINE This is an updated guideline It incorporates the latest NICE guidance There are strong recommendations for calcium + vitamin D
DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) OSTEOPOROSIS GUIDELINE This is an updated guideline It incorporates the latest NICE guidance There are strong recommendations for calcium + vitamin D
BULLETIN. Slovak Republic Ministry of Health
 BULLETIN Slovak Republic Ministry of Health Part 51-53 November 13, 2009 No. 57 CONTENTS: 52. Slovak Republic Ministry of Health Guidelines for the Diagnosis of Glucocorticoidinduced Osteoporosis 52. Slovak
BULLETIN Slovak Republic Ministry of Health Part 51-53 November 13, 2009 No. 57 CONTENTS: 52. Slovak Republic Ministry of Health Guidelines for the Diagnosis of Glucocorticoidinduced Osteoporosis 52. Slovak
Bone Basics National Osteoporosis Foundation 2013
 When you have osteoporosis, your bones become weak and are more likely to break (fracture). You can have osteoporosis without any symptoms. Because it can be prevented and treated, an early diagnosis is
When you have osteoporosis, your bones become weak and are more likely to break (fracture). You can have osteoporosis without any symptoms. Because it can be prevented and treated, an early diagnosis is
Osteoporosis has been identified by the US Surgeon General
 New Guidelines for the Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis E. Michael Lewiecki, MD, and Nelson B. Watts, MD Abstract: The World Health Organization Fracture Risk Assessment Tool (FRAX ) and the National
New Guidelines for the Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis E. Michael Lewiecki, MD, and Nelson B. Watts, MD Abstract: The World Health Organization Fracture Risk Assessment Tool (FRAX ) and the National
Osteoporosis Diagnosis: BMD, FRAX and Assessment of Secondary Osteoporosis. Disclosure and Conflicts of Interest Steven T Harris MD 2014-2015
 Osteoporosis Diagnosis: BMD, FRAX and Assessment of Secondary Osteoporosis Steven T Harris MD FACP Clinical Professor of Medicine University of California, San Francisco steve.harris@ucsf.edu Disclosure
Osteoporosis Diagnosis: BMD, FRAX and Assessment of Secondary Osteoporosis Steven T Harris MD FACP Clinical Professor of Medicine University of California, San Francisco steve.harris@ucsf.edu Disclosure
Fast Facts on Osteoporosis
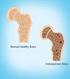 Fast Facts on Osteoporosis Definition Prevalence Osteoporosis, or porous bone, is a disease characterized by low bone mass and structural deterioration of bone tissue, leading to bone fragility and an
Fast Facts on Osteoporosis Definition Prevalence Osteoporosis, or porous bone, is a disease characterized by low bone mass and structural deterioration of bone tissue, leading to bone fragility and an
How To Choose A Biologic Drug
 North Carolina Rheumatology Association Position Statements I. Biologic Agents A. Appropriate delivery, handling, storage and administration of biologic agents B. Indications for biologic agents II. III.
North Carolina Rheumatology Association Position Statements I. Biologic Agents A. Appropriate delivery, handling, storage and administration of biologic agents B. Indications for biologic agents II. III.
Module 5 - Speaking of Bones Osteoporosis For Health Professionals: Fracture Risk Assessment. William D. Leslie, MD MSc FRCPC
 Module 5 - Speaking of Bones Osteoporosis For Health Professionals: Fracture Risk Assessment William D. Leslie, MD MSc FRCPC Case #1 Age 53: 3 years post-menopause Has always enjoyed excellent health with
Module 5 - Speaking of Bones Osteoporosis For Health Professionals: Fracture Risk Assessment William D. Leslie, MD MSc FRCPC Case #1 Age 53: 3 years post-menopause Has always enjoyed excellent health with
Clinical Policy Guideline
 Clinical Policy Guideline Policy Title: Bone Density Testing Policy No: B0215A.00 Effective Date: 01/01/15 Date Reviewed: 03/25/15 I. DEFINITION/BACKGROUND Bone density testing is used to estimate the
Clinical Policy Guideline Policy Title: Bone Density Testing Policy No: B0215A.00 Effective Date: 01/01/15 Date Reviewed: 03/25/15 I. DEFINITION/BACKGROUND Bone density testing is used to estimate the
Osteoporosis Assessment Using DXA and Instant Vertebral Assessment. Working Together For A Healthier Community
 Osteoporosis Assessment Using DXA and Instant Vertebral Assessment Working Together For A Healthier Community Osteoporosis The Silent Thief The Facts About Osteoporosis 1 in 2 women will develop osteoporosis
Osteoporosis Assessment Using DXA and Instant Vertebral Assessment Working Together For A Healthier Community Osteoporosis The Silent Thief The Facts About Osteoporosis 1 in 2 women will develop osteoporosis
Drug treatment pathway for Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women
 Drug treatment pathway for Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women Version 1.0 Ratified by: East Sussex HEMC Date ratified: 26.01.2011 Job title of originator/author Gillian Ells, East Sussex HEMC Pharmacist
Drug treatment pathway for Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women Version 1.0 Ratified by: East Sussex HEMC Date ratified: 26.01.2011 Job title of originator/author Gillian Ells, East Sussex HEMC Pharmacist
Osteoporosis Treatment Guide
 Osteoporosis Treatment Guide An estimated 10 million Americans have osteoporosis. Another 34 million have low bone mass. If left untreated, osteoporosis can be both debilitating and painful. Fortunately,
Osteoporosis Treatment Guide An estimated 10 million Americans have osteoporosis. Another 34 million have low bone mass. If left untreated, osteoporosis can be both debilitating and painful. Fortunately,
Go to Table of Contents. The Man s Guide. to Osteoporosis. National Osteoporosis Foundation
 Go to Table of Contents The Man s Guide to Osteoporosis National Osteoporosis Foundation Contents Introduction... 2 Chapter 1: Start with bone healthy behaviors... 3 Get the calcium and vitamin D you need
Go to Table of Contents The Man s Guide to Osteoporosis National Osteoporosis Foundation Contents Introduction... 2 Chapter 1: Start with bone healthy behaviors... 3 Get the calcium and vitamin D you need
Bone Basics National Osteoporosis Foundation 2013
 Certain people are more likely to develop osteoporosis than others. While you have no control over some risk factors for osteoporosis, there are others you can change. By making healthier choices you can
Certain people are more likely to develop osteoporosis than others. While you have no control over some risk factors for osteoporosis, there are others you can change. By making healthier choices you can
Osteoporosis Medications
 Osteoporosis Medications When does a doctor prescribe osteoporosis medications? Healthcare providers look at several pieces of information before prescribing a bone- preserving or bone- building medication.
Osteoporosis Medications When does a doctor prescribe osteoporosis medications? Healthcare providers look at several pieces of information before prescribing a bone- preserving or bone- building medication.
Cystic fibrosis and bone health
 Cystic fibrosis and bone health Factsheet March 2013 Cystic fibrosis and bone health Introduction As we get older our bones become thinner and weaker, and may become more susceptible to fracture. However
Cystic fibrosis and bone health Factsheet March 2013 Cystic fibrosis and bone health Introduction As we get older our bones become thinner and weaker, and may become more susceptible to fracture. However
Osteoporosis. Drugs to prevent bone fractures in people with: Contents. 2: Our Recommendations. 3: Welcome. 6: Who Needs Drugs to Prevent Fractures?
 Drugs to prevent bone fractures in people with: Osteoporosis Comparing Effectiveness, Safety, and Price Contents 2: Our Recommendations 3: Welcome 6: Who Needs Drugs to Prevent Fractures? 8: Choosing a
Drugs to prevent bone fractures in people with: Osteoporosis Comparing Effectiveness, Safety, and Price Contents 2: Our Recommendations 3: Welcome 6: Who Needs Drugs to Prevent Fractures? 8: Choosing a
Scans and tests and osteoporosis
 Scans and tests and osteoporosis What is osteoporosis? Osteoporosis occurs when the struts which make up the mesh-like structure within bones become thin causing them to become fragile and break easily,
Scans and tests and osteoporosis What is osteoporosis? Osteoporosis occurs when the struts which make up the mesh-like structure within bones become thin causing them to become fragile and break easily,
Osteoporosis Update. Laura E. Ryan, MD
 Osteoporosis Update Laura E. Ryan, MD Assistant Director for Special Programs Center for Women s Health Clinical Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism The Ohio
Osteoporosis Update Laura E. Ryan, MD Assistant Director for Special Programs Center for Women s Health Clinical Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism The Ohio
Medications for Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis
 1 Medications for Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis Osteoporosis is a disease where the strength of bones is less than normal, making them more susceptible to fracture, or breaking, than normal
1 Medications for Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis Osteoporosis is a disease where the strength of bones is less than normal, making them more susceptible to fracture, or breaking, than normal
Objectives. Osteoporosis a major public health threat. Bone-Up on Osteoporosis Update 2011
 Bone-Up on Osteoporosis Update 2011 3/30/11 Kristine Olson, MS, APN, FNP-BC Nurse Practitioner Mercer Bucks Hematology Oncology 1 Objectives Review risk factors and screening for osteoporosis. Describe
Bone-Up on Osteoporosis Update 2011 3/30/11 Kristine Olson, MS, APN, FNP-BC Nurse Practitioner Mercer Bucks Hematology Oncology 1 Objectives Review risk factors and screening for osteoporosis. Describe
What You Need to Know for Better Bone Health
 What You Need to Know for Better Bone Health A quick lesson about bones: Why healthy bones matter The healthier your bones The more active you can be Bone health has a major effect on your quality of life
What You Need to Know for Better Bone Health A quick lesson about bones: Why healthy bones matter The healthier your bones The more active you can be Bone health has a major effect on your quality of life
Osteoporosis Clinical guideline for prevention and treatment
 Osteoporosis Clinical guideline for prevention and treatment Executive Summary Updated November 2014 National Osteoporosis Guideline Group on behalf of the Bone Research Society, British Geriatrics Society,
Osteoporosis Clinical guideline for prevention and treatment Executive Summary Updated November 2014 National Osteoporosis Guideline Group on behalf of the Bone Research Society, British Geriatrics Society,
Osteoporosis. Am I at Risk?
 Osteoporosis Am I at Risk? TABLE OF CONTENTS What is osteoporosis?...1 Who gets osteoporosis?...2 How can I prevent osteoporosis?...3 How do I know if I have osteoporosis?...4 What is a bone mineral density
Osteoporosis Am I at Risk? TABLE OF CONTENTS What is osteoporosis?...1 Who gets osteoporosis?...2 How can I prevent osteoporosis?...3 How do I know if I have osteoporosis?...4 What is a bone mineral density
How To Take A Bone Marrow Transplant
 Drug treatments to protect your bones This information is an extract from the booklet, Bone health. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page 5. Contents Bisphosphonates
Drug treatments to protect your bones This information is an extract from the booklet, Bone health. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page 5. Contents Bisphosphonates
Osteoporosis: key concepts. Azeez Farooki, MD Endocrinologist
 Osteoporosis: key concepts Azeez Farooki, MD Endocrinologist Outline I) Composition of bone II) Definition & pathophysiology of osteoporosis III) Peak bone mass IV) Secondary osteoporosis V) Vitamin D
Osteoporosis: key concepts Azeez Farooki, MD Endocrinologist Outline I) Composition of bone II) Definition & pathophysiology of osteoporosis III) Peak bone mass IV) Secondary osteoporosis V) Vitamin D
NATIONAL OSTEOPOROSIS FOUNDATION OSTEOPOROSIS CLINICAL UPDATES Bariatric Surgery And Skeletal Health CE APPLICATION FORM
 NATIONAL OSTEOPOROSIS FOUNDATION OSTEOPOROSIS CLINICAL UPDATES Bariatric Surgery And Skeletal Health CE APPLICATION FORM First Name: Last Name: Mailing Address: City: State: Zip/Postal Code: Country: Phone
NATIONAL OSTEOPOROSIS FOUNDATION OSTEOPOROSIS CLINICAL UPDATES Bariatric Surgery And Skeletal Health CE APPLICATION FORM First Name: Last Name: Mailing Address: City: State: Zip/Postal Code: Country: Phone
Recent Topics in Treatment of Osteoporosis
 Review Article Recent Topics in Treatment of Osteoporosis JMAJ 49(9 10): 309 314, 2006 Satoshi Soen* 1 Abstract It has come to light that osteoporosis-related fractures are more critical than previously
Review Article Recent Topics in Treatment of Osteoporosis JMAJ 49(9 10): 309 314, 2006 Satoshi Soen* 1 Abstract It has come to light that osteoporosis-related fractures are more critical than previously
POSITION STATEMENT Management of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women: 2006 position statement of The North American Menopause Society
 Menopause: The Journal of The North American Menopause Society Vol. 13, No. 3, pp. 340-367 DOI: 10.1097/01.gme.0000222475.93345.b3 * 2006 by The North American Menopause Society 5 Text printed on acid-free
Menopause: The Journal of The North American Menopause Society Vol. 13, No. 3, pp. 340-367 DOI: 10.1097/01.gme.0000222475.93345.b3 * 2006 by The North American Menopause Society 5 Text printed on acid-free
Drug treatments for osteoporosis
 Drug treatments for osteoporosis What is osteoporosis? Osteoporosis occurs when the struts which make up the mesh-like structure within bones become thin causing them to become fragile and break easily,
Drug treatments for osteoporosis What is osteoporosis? Osteoporosis occurs when the struts which make up the mesh-like structure within bones become thin causing them to become fragile and break easily,
Bone Markers in Osteoporosis: Prediction of Fractures & Treatment Monitoring
 Bone Markers in Osteoporosis: Prediction of Fractures & Treatment Monitoring Richard Eastell, MD FRCP FRCPath FMedSci, Professor of Bone Metabolism, University of Sheffield, Sheffield, UK Usefulness of
Bone Markers in Osteoporosis: Prediction of Fractures & Treatment Monitoring Richard Eastell, MD FRCP FRCPath FMedSci, Professor of Bone Metabolism, University of Sheffield, Sheffield, UK Usefulness of
Osteoporosis. Dr Gordon MacDonald BSc MB BChir MRCP Consultant Rheumatologist. Rheumatology and Arthritis Seminar Tuesday 5 th February 2013
 Osteoporosis Dr Gordon MacDonald BSc MB BChir MRCP Consultant Rheumatologist Rheumatology and Arthritis Seminar Tuesday 5 th February 2013 Plan What is osteoporosis? Consequences of osteoporosis Risk factors
Osteoporosis Dr Gordon MacDonald BSc MB BChir MRCP Consultant Rheumatologist Rheumatology and Arthritis Seminar Tuesday 5 th February 2013 Plan What is osteoporosis? Consequences of osteoporosis Risk factors
Falls and Fracture Risk assessment and management
 Falls and Fracture Risk assessment and management Disclosures: Although various guidelines and studies were reviewed, this represents my own personal bias and conclusions. What do we know? 1) Fractures
Falls and Fracture Risk assessment and management Disclosures: Although various guidelines and studies were reviewed, this represents my own personal bias and conclusions. What do we know? 1) Fractures
A Treatment Algorithm for Indian Patients of Osteoporosis
 Indian Medical Gazette FEBRUARY 2012 67 Symposia Update A Treatment Algorithm for Indian Patients of Osteoporosis Shailendra Mohan Lakhotia, Senior Consultant Orthopedic Surgeon, Kolkata 700 045. Prashant
Indian Medical Gazette FEBRUARY 2012 67 Symposia Update A Treatment Algorithm for Indian Patients of Osteoporosis Shailendra Mohan Lakhotia, Senior Consultant Orthopedic Surgeon, Kolkata 700 045. Prashant
Osteoporosis and you. Find out about the implications of osteoporosis and what you can do for your bone health
 Osteoporosis and you Find out about the implications of osteoporosis and what you can do for your bone health 2 What is osteoporosis? Osteoporosis, which literally means porous bone, is a disease in which
Osteoporosis and you Find out about the implications of osteoporosis and what you can do for your bone health 2 What is osteoporosis? Osteoporosis, which literally means porous bone, is a disease in which
OSTEOPOROSIS REHABILITATION PROGRAM
 OSTEOPOROSIS REHABILITATION PROGRAM Tricia Orme, R.N. BSc(N) Mary Pack Arthritis Program Victoria i Arthritis i Centre Objectives Participants will gain an understanding of what Osteoporosis is and how
OSTEOPOROSIS REHABILITATION PROGRAM Tricia Orme, R.N. BSc(N) Mary Pack Arthritis Program Victoria i Arthritis i Centre Objectives Participants will gain an understanding of what Osteoporosis is and how
Bone Densitometry. What is a Bone Density Scan (DXA)?
 Scan for mobile link. Bone Densitometry Bone densitometry, also called dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry or DEXA, uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of the inside of the body
Scan for mobile link. Bone Densitometry Bone densitometry, also called dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry or DEXA, uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of the inside of the body
Treatment of osteoporosis in fragility fractures
 Orthogeriatrics Clinical Summary Document Treatment of osteoporosis in fragility fractures Fragility fractures are extremely prevalent in older adults with a staggering cost of treatment. As the population
Orthogeriatrics Clinical Summary Document Treatment of osteoporosis in fragility fractures Fragility fractures are extremely prevalent in older adults with a staggering cost of treatment. As the population
 BISPHOSPHONATE RELATED OSTEONECROSIS OF THE JAW (BRONJ) BISPHOSPHONATES AND WHAT HAPPENS TO BONE VINCENT E. DIFABIO, DDS, MS MEMBER OF THE COMMITTEE ON HEALTHCARE AND ADVOCACY FROM THE AMERICAN ASSOCIATION
BISPHOSPHONATE RELATED OSTEONECROSIS OF THE JAW (BRONJ) BISPHOSPHONATES AND WHAT HAPPENS TO BONE VINCENT E. DIFABIO, DDS, MS MEMBER OF THE COMMITTEE ON HEALTHCARE AND ADVOCACY FROM THE AMERICAN ASSOCIATION
CMAJ JAMC. 2002 clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of osteoporosis in Canada
 CANADIAN M EDICAL A SSOCIATION J OURNAL J OURNAL DE L ASSOCIATION MÉDICALE CANADIENNE CMAJ JAMC 2002 clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of osteoporosis in Canada CMAJ 2002;167(10
CANADIAN M EDICAL A SSOCIATION J OURNAL J OURNAL DE L ASSOCIATION MÉDICALE CANADIENNE CMAJ JAMC 2002 clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of osteoporosis in Canada CMAJ 2002;167(10
2-1. Osteoporose. Dr. P. Van Wettere Radiologie en medische beeldvorming
 2-1 Osteoporose Dr. P. Van Wettere Radiologie en medische beeldvorming 2-2 Osteoporose Definitie Incidentie, mortaliteit, morbiditeit, kost Diagnose Radiologie Botdensitometrie FRAX FractureCascade History
2-1 Osteoporose Dr. P. Van Wettere Radiologie en medische beeldvorming 2-2 Osteoporose Definitie Incidentie, mortaliteit, morbiditeit, kost Diagnose Radiologie Botdensitometrie FRAX FractureCascade History
Medications to Prevent and Treat Osteoporosis
 Medications to Prevent and Treat Osteoporosis National Institutes of Health Osteoporosis and Related Bone Diseases ~ National Resource Center 2 AMS Circle Bethesda, MD 20892-3676 Tel: (800) 624-BONE or
Medications to Prevent and Treat Osteoporosis National Institutes of Health Osteoporosis and Related Bone Diseases ~ National Resource Center 2 AMS Circle Bethesda, MD 20892-3676 Tel: (800) 624-BONE or
OSTEOPOROSIS -Medical Management of Men and Women who have (or are at risk of ) Osteoporosis
 Basingstoke, Southampton and Winchester District Prescribing Committee OSTEOPOROSIS -Medical Management of Men and Women who have (or are at risk of ) Osteoporosis Frail, increased fall risk + housebound
Basingstoke, Southampton and Winchester District Prescribing Committee OSTEOPOROSIS -Medical Management of Men and Women who have (or are at risk of ) Osteoporosis Frail, increased fall risk + housebound
Osteoporosis Medicines and Jaw Problems
 Osteoporosis Medicines and Jaw Problems J. Michael Digney, D.D.S. Osteoporosis is a condition that affects over 10 million patients in this country, with the majority of those being post-menopausal women.
Osteoporosis Medicines and Jaw Problems J. Michael Digney, D.D.S. Osteoporosis is a condition that affects over 10 million patients in this country, with the majority of those being post-menopausal women.
Osteoporosis Treatments That Help Prevent Broken Bones. A Guide for Women After Menopause
 Osteoporosis Treatments That Help Prevent Broken Bones A Guide for Women After Menopause June 2008 fast facts Medicines for osteoporosis (OSS-tee-oh-puh-ROW-sis) can lower your chance of breaking a bone.
Osteoporosis Treatments That Help Prevent Broken Bones A Guide for Women After Menopause June 2008 fast facts Medicines for osteoporosis (OSS-tee-oh-puh-ROW-sis) can lower your chance of breaking a bone.
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: testing_serum_vitamin_d_levels 9/2015 2/2016 2/2017 2/2016 Description of Procedure or Service Vitamin D,
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: testing_serum_vitamin_d_levels 9/2015 2/2016 2/2017 2/2016 Description of Procedure or Service Vitamin D,
The Diagnosis and Workup of Patients for Osteoporosis or Osteopenia (Low Bone Mass)
 The Diagnosis and Workup of Patients for Osteoporosis or Osteopenia (Low Bone Mass) 6 Frank Bonura St. Catherine of Siena Medical Center, Smithtown, NY USA 1. Introduction The rate of screening and treatment
The Diagnosis and Workup of Patients for Osteoporosis or Osteopenia (Low Bone Mass) 6 Frank Bonura St. Catherine of Siena Medical Center, Smithtown, NY USA 1. Introduction The rate of screening and treatment
Osteoporosis/Bone Health in Adults as a National Public Health Priority
 Position Statement Osteoporosis/Bone Health in Adults as a National Public Health Priority This Position Statement was developed as an educational tool based on the opinion of the authors. It is not a
Position Statement Osteoporosis/Bone Health in Adults as a National Public Health Priority This Position Statement was developed as an educational tool based on the opinion of the authors. It is not a
PRACTICAL DENSITOMETRY
 PRACTICAL DENSITOMETRY The Challenge of Osteoporosis Osteoporosis is a silent disease that develops over decades Goal: identify patients with osteoporosis before fractures occur Means: measure bone density
PRACTICAL DENSITOMETRY The Challenge of Osteoporosis Osteoporosis is a silent disease that develops over decades Goal: identify patients with osteoporosis before fractures occur Means: measure bone density
Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Osteoporosis in Canada: Background and Technical Report
 Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Osteoporosis in Canada: Background and Technical Report Authors: Alexandra Papaioannou MD MSc 1, Suzanne Morin MD MSc 2, Angela M. Cheung
Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Osteoporosis in Canada: Background and Technical Report Authors: Alexandra Papaioannou MD MSc 1, Suzanne Morin MD MSc 2, Angela M. Cheung
Drug-Induced Osteoporosis
 Drug-Induced Osteoporosis By Susan K. Bowles, Pharm.D., MSc, FCCP Reviewed by Mary Beth O Connell, Pharm.D., FCCP, FASHP, BCPS; and Michelle M. Richardson, Pharm.D., FCCP, BCPS Learning Objectives 1. Apply
Drug-Induced Osteoporosis By Susan K. Bowles, Pharm.D., MSc, FCCP Reviewed by Mary Beth O Connell, Pharm.D., FCCP, FASHP, BCPS; and Michelle M. Richardson, Pharm.D., FCCP, BCPS Learning Objectives 1. Apply
SIGMA sums it up: Answers to questions about osteoporosis and denosumab therapy
 SIGMA sums it up: Answers to questions about osteoporosis and denosumab therapy Table of contents Who is SIGMA? Frequently asked questions we will address: 1. What is osteoporosis? 2. Why is it important
SIGMA sums it up: Answers to questions about osteoporosis and denosumab therapy Table of contents Who is SIGMA? Frequently asked questions we will address: 1. What is osteoporosis? 2. Why is it important
Osteoporosis. The inside looks like honeycomb, with blood vessels and bone marrow in the spaces between bone.
 Osteoporosis The bones in our skeleton are made of a thick outer shell and a strong inner mesh filled with collagen (protein), calcium salts and other minerals. Osteoporosis The inside looks like honeycomb,
Osteoporosis The bones in our skeleton are made of a thick outer shell and a strong inner mesh filled with collagen (protein), calcium salts and other minerals. Osteoporosis The inside looks like honeycomb,
Bone Mineral Density Studies
 Bone Mineral Density Studies Policy Number: 6.01.01 Last Review: 5/2015 Origination: 10/1988 Next Review: 5/2016 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will provide coverage for bone
Bone Mineral Density Studies Policy Number: 6.01.01 Last Review: 5/2015 Origination: 10/1988 Next Review: 5/2016 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will provide coverage for bone
Clinician s Guide. to Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis. Developed by the National Osteoporosis Foundation
 Clinician s Guide to Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis Developed by the National Osteoporosis Foundation Clinician s Guide to Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis Developed by the National Osteoporosis
Clinician s Guide to Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis Developed by the National Osteoporosis Foundation Clinician s Guide to Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis Developed by the National Osteoporosis
Table 2. Clinical Risk Categories for Osteoporosis and Osteoporotic Fractures
 5 Osteoporosis Guideline Team Team Lead Robert W. Lash, MD Endocrinology Team Members R. Van Harrison, PhD Medical Education Jane T. McCort, MD General Medicine Jane M. Nicholson, MD Obstetrics/Gynecology
5 Osteoporosis Guideline Team Team Lead Robert W. Lash, MD Endocrinology Team Members R. Van Harrison, PhD Medical Education Jane T. McCort, MD General Medicine Jane M. Nicholson, MD Obstetrics/Gynecology
AACE Guidelines. Copyright 2010 AACE.
 AACE Guidelines Nelson B. Watts, MD, FACP, MACE; John P. Bilezikian, MD, MACE; Pauline M. Camacho, MD, FACE; Susan L. Greenspan, MD, FACP, FACE; Steven T. Harris, MD, FACE; Stephen F. Hodgson, MD, FACP,
AACE Guidelines Nelson B. Watts, MD, FACP, MACE; John P. Bilezikian, MD, MACE; Pauline M. Camacho, MD, FACE; Susan L. Greenspan, MD, FACP, FACE; Steven T. Harris, MD, FACE; Stephen F. Hodgson, MD, FACP,
American College of Rheumatology 2010 Recommendations for the Prevention and Treatment of
 merican ollege of Rheumatology 2 Recommendations for the Prevention and Treatment of G L U O O R T I O I D - I N D U E D O S T E O P O R O S I S L I N I I N S G U I D E The objective of this guide is to
merican ollege of Rheumatology 2 Recommendations for the Prevention and Treatment of G L U O O R T I O I D - I N D U E D O S T E O P O R O S I S L I N I I N S G U I D E The objective of this guide is to
Secondary Causes of Osteoporosis The female athlete triad secondary osteoporosis Chronic Conditions Chronic digestive tract conditions
 Spring 2009 Newsletter # 23 Biannual Newsletter The Creighton University Osteoporosis Research Center Secondary Causes of Osteoporosis (Much of this content has been adapted from materials provided by
Spring 2009 Newsletter # 23 Biannual Newsletter The Creighton University Osteoporosis Research Center Secondary Causes of Osteoporosis (Much of this content has been adapted from materials provided by
Clinical guideline for the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women and older men
 Clinical guideline for the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women and older men February 2010 Approved by NHMRC on 5 February 2010 The Royal Australian College of General Practitioners,
Clinical guideline for the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women and older men February 2010 Approved by NHMRC on 5 February 2010 The Royal Australian College of General Practitioners,
Measure #41: Osteoporosis: Pharmacologic Therapy for Men and Women Aged 50 Years and Older National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care
 Measure #41: Osteoporosis: Pharmacologic Therapy for Men and Women Aged 50 Years and Older National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: CLAIMS, REGISTRY
Measure #41: Osteoporosis: Pharmacologic Therapy for Men and Women Aged 50 Years and Older National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: CLAIMS, REGISTRY
DEFINITION OF OSTEOPOROSIS
 CHAPTER 27 OSTEOPOROSIS AND OSTEOMALACIA DEFINITION OF OSTEOPOROSIS THE EPIDEMIOLOGY AND CONSEQUENCES OF OSTEOPOROSIS REVIEW OF BONE REMODELING BONE LOSS PATHOGENESIS OF OSTEOPOROSIS DIAGNOSIS OF OSTEOPOROSIS
CHAPTER 27 OSTEOPOROSIS AND OSTEOMALACIA DEFINITION OF OSTEOPOROSIS THE EPIDEMIOLOGY AND CONSEQUENCES OF OSTEOPOROSIS REVIEW OF BONE REMODELING BONE LOSS PATHOGENESIS OF OSTEOPOROSIS DIAGNOSIS OF OSTEOPOROSIS
Proposed Changes to Existing Measure for HEDIS 1 2015: Osteoporosis Management in Women Who Had a Fracture (OMW)
 Draft Document for HEDIS 2015 Public Comment Obsolete After March 19, 2014 1 Proposed Changes to Existing Measure for HEDIS 1 2015: Osteoporosis Management in Women Who Had a Fracture (OMW) NCQA seeks
Draft Document for HEDIS 2015 Public Comment Obsolete After March 19, 2014 1 Proposed Changes to Existing Measure for HEDIS 1 2015: Osteoporosis Management in Women Who Had a Fracture (OMW) NCQA seeks
Osteoporosis and Arthritis: Two Common but Different Conditions
 and : Two Common but Different Conditions National Institutes of Health and Related Bone Diseases ~ National Resource Center 2 AMS Circle Bethesda, MD 20892 3676 Tel: 800 624 BONE or 202 223 0344 Fax:
and : Two Common but Different Conditions National Institutes of Health and Related Bone Diseases ~ National Resource Center 2 AMS Circle Bethesda, MD 20892 3676 Tel: 800 624 BONE or 202 223 0344 Fax:
How To Treat Osteoporosis
 Treatment Guidelines for Osteoporosis in Adults. Background Osteoporosis is a condition characterised by a reduction in bone mass density increasing the risk of fracture. Fractures occur most commonly
Treatment Guidelines for Osteoporosis in Adults. Background Osteoporosis is a condition characterised by a reduction in bone mass density increasing the risk of fracture. Fractures occur most commonly
COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP) GUIDELINE ON THE EVALUATION OF MEDICINAL PRODUCTS IN THE TREATMENT OF PRIMARY OSTEOPOROSIS
 European Medicines Agency London, 16 November 2006 Doc. Ref. CPMP/EWP/552/95 Rev. 2 COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP) GUIDELINE ON THE EVALUATION OF MEDICINAL PRODUCTS IN THE TREATMENT
European Medicines Agency London, 16 November 2006 Doc. Ref. CPMP/EWP/552/95 Rev. 2 COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP) GUIDELINE ON THE EVALUATION OF MEDICINAL PRODUCTS IN THE TREATMENT
NATIONAL OSTEOPOROSIS FOUNDATION OSTEOPOROSIS CLINICAL UPDATES Rehabilitation of Patients With Fragility-Related Fractures CE APPLICATION FORM
 NATIONAL OSTEOPOROSIS FOUNDATION OSTEOPOROSIS CLINICAL UPDATES Rehabilitation of Patients With Fragility-Related Fractures CE APPLICATION FORM First Name: Last Name: Mailing Address: City: State: Zip/Postal
NATIONAL OSTEOPOROSIS FOUNDATION OSTEOPOROSIS CLINICAL UPDATES Rehabilitation of Patients With Fragility-Related Fractures CE APPLICATION FORM First Name: Last Name: Mailing Address: City: State: Zip/Postal
Bone Disease in Myeloma
 Bone Disease in Myeloma Washington, DC August 8, 2009 Brian G.M. Durie, M.D. Bone Disease in Myeloma Lytic Lesions Spike Bone Marrow Plasma Cells Collapse of Vertebrae Biology of Myeloma Vascular Cytokines
Bone Disease in Myeloma Washington, DC August 8, 2009 Brian G.M. Durie, M.D. Bone Disease in Myeloma Lytic Lesions Spike Bone Marrow Plasma Cells Collapse of Vertebrae Biology of Myeloma Vascular Cytokines
NAMS continuing medical education activity
 Menopause: The Journal of The North American Menopause Society Vol. 17, No. 1, pp. 23/24 DOI: 10.1097/gme.0b013e3181cdd4a7 * 2010 by The North American Menopause Society 5 Text printed on acid-free paper
Menopause: The Journal of The North American Menopause Society Vol. 17, No. 1, pp. 23/24 DOI: 10.1097/gme.0b013e3181cdd4a7 * 2010 by The North American Menopause Society 5 Text printed on acid-free paper
SUMMARY OF THE RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (by medicinal product)
 PART VI SUMMARY OF THE RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (by medicinal product) Format and content of the summary of the RMP The summary of the RMP part VI contains information based on RMP modules SI, SVIII and RMP
PART VI SUMMARY OF THE RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (by medicinal product) Format and content of the summary of the RMP The summary of the RMP part VI contains information based on RMP modules SI, SVIII and RMP
Anti-epileptic drugs and osteoporosis
 Anti-epileptic drugs and osteoporosis What is osteoporosis? Osteoporosis occurs when the struts which make up the mesh-like structure within bones become thin causing them to become fragile and break easily
Anti-epileptic drugs and osteoporosis What is osteoporosis? Osteoporosis occurs when the struts which make up the mesh-like structure within bones become thin causing them to become fragile and break easily
Bone Disease in Myeloma. St. Petersburg, Russia September 16, 2009
 Bone Disease in Myeloma St. Petersburg, Russia September 16, 2009 Bi Brian G.M. GMDurie, M.D. MD Bone Disease in Myeloma Lytic Lesions Spike Bone Marrow Plasma Cells Collapse of Vertebrae Biology of Myeloma
Bone Disease in Myeloma St. Petersburg, Russia September 16, 2009 Bi Brian G.M. GMDurie, M.D. MD Bone Disease in Myeloma Lytic Lesions Spike Bone Marrow Plasma Cells Collapse of Vertebrae Biology of Myeloma
BONE MINERAL DENSITOMETRY REPORTING
 CAR TECHNICAL STANDARDS FOR BONE MINERAL DENSITOMETRY REPORTING APPROVED: JANUARY 25, 2013 KERRY SIMINOSKI, MD, FRCPC; MARGARET O'KEEFFE, MD, FRCPC; JACQUES P. BROWN, MD, FRCPC; STEVEN BURRELL, MD, FRCPC;
CAR TECHNICAL STANDARDS FOR BONE MINERAL DENSITOMETRY REPORTING APPROVED: JANUARY 25, 2013 KERRY SIMINOSKI, MD, FRCPC; MARGARET O'KEEFFE, MD, FRCPC; JACQUES P. BROWN, MD, FRCPC; STEVEN BURRELL, MD, FRCPC;
CPT 76977, 77078, 77079, 77080, 77081, 77083, or HCPCS G0130:
 Bone Mass Measurements Coverage Information Noridian Administrative Services (NAS), LLC, is providing coverage information regarding Bone Mass Measurements (BMM) in response to multiple provider inquiries.
Bone Mass Measurements Coverage Information Noridian Administrative Services (NAS), LLC, is providing coverage information regarding Bone Mass Measurements (BMM) in response to multiple provider inquiries.
Closing Performance Gaps in the Diagnosis and Management of Osteoporosis
 Closing Performance Gaps in the Diagnosis and Management of Osteoporosis Andrea J. Singer. MD, FACP, CCD Associate Professor of Medicine and Obstetrics and Gynecology Director, Bone Densitometry Medstar
Closing Performance Gaps in the Diagnosis and Management of Osteoporosis Andrea J. Singer. MD, FACP, CCD Associate Professor of Medicine and Obstetrics and Gynecology Director, Bone Densitometry Medstar
Bone Disease in Myeloma
 Bone Disease in Myeloma Boston, Massachusetts Saturday, July 26, 2008 Brian G.M. Durie, M.D. Bone Disease in Myeloma Lytic Lesions Spike Bone Marrow Plasma Cells Collapse of Vertebrae Biology of Myeloma
Bone Disease in Myeloma Boston, Massachusetts Saturday, July 26, 2008 Brian G.M. Durie, M.D. Bone Disease in Myeloma Lytic Lesions Spike Bone Marrow Plasma Cells Collapse of Vertebrae Biology of Myeloma
Easy-to-Read Information for Patients and Families. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services National Institutes of Health
 BONE HEALTH FOR LIFE Easy-to-Read Information for Patients and Families U.S. Department of Health and Human Services National Institutes of Health National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and
BONE HEALTH FOR LIFE Easy-to-Read Information for Patients and Families U.S. Department of Health and Human Services National Institutes of Health National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and
X-Plain Vertebral Compression Fractures Reference Summary
 X-Plain Vertebral Compression Fractures Reference Summary Introduction Back pain caused by a vertebral compression fracture, or VCF, is a common condition that affects thousands of people every year. A
X-Plain Vertebral Compression Fractures Reference Summary Introduction Back pain caused by a vertebral compression fracture, or VCF, is a common condition that affects thousands of people every year. A
Osteoarthritis and osteoporosis
 Osteoarthritis and osteoporosis What is osteoporosis? Osteoporosis occurs when the struts which make up the mesh-like structure within bones become thin causing them to become fragile and break easily,
Osteoarthritis and osteoporosis What is osteoporosis? Osteoporosis occurs when the struts which make up the mesh-like structure within bones become thin causing them to become fragile and break easily,
Guidance for the Management of Breast Cancer Treatment-Induced Bone Loss
 Guidance for the Management of Breast Cancer Treatment-Induced Bone Loss A consensus position statement from a UK Expert Group Reviewed and supported by the National Osteoporosis Society (NOS), the National
Guidance for the Management of Breast Cancer Treatment-Induced Bone Loss A consensus position statement from a UK Expert Group Reviewed and supported by the National Osteoporosis Society (NOS), the National
Osteoporosis. CME Objective: To review current evidence for the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of osteoporosis.
 Section Editors Deborah Cotton, MD, MPH Darren Taichman, MD, PhD Sankey Williams, MD Physician Writer E. Michael Lewiecki, MD Osteoporosis Screening and Prevention Diagnosis and Evaluation Treatment Patient
Section Editors Deborah Cotton, MD, MPH Darren Taichman, MD, PhD Sankey Williams, MD Physician Writer E. Michael Lewiecki, MD Osteoporosis Screening and Prevention Diagnosis and Evaluation Treatment Patient
Florida Breast Health Specialists Hormone Therapy Information and Questions to Ask Your Doctor
 What is Hormone Therapy? Hormonal therapy medicines are whole-body (systemic) treatment for hormone-receptorpositive breast cancers. Hormone receptors are like ears on breast cells that listen to signals
What is Hormone Therapy? Hormonal therapy medicines are whole-body (systemic) treatment for hormone-receptorpositive breast cancers. Hormone receptors are like ears on breast cells that listen to signals
Consumer and Family Sciences
 Purdue Extension Consumer and Family Sciences Department of Foods and Nutrition CFS-150-W Osteoporosis: What You Should Know April C. Mason, Ph.D. William D. Evers, Ph.D., RD Erin E. Hanley, RD Osteoporosis,
Purdue Extension Consumer and Family Sciences Department of Foods and Nutrition CFS-150-W Osteoporosis: What You Should Know April C. Mason, Ph.D. William D. Evers, Ph.D., RD Erin E. Hanley, RD Osteoporosis,
Prolia 2 shots a year proven to help strengthen bones.
 Ask your doctor if Prolia (denosumab) is right for you and visit us at www.prolia.com For women with postmenopausal osteoporosis at high risk for fracture: there s Prolia. Prolia 2 shots a year proven
Ask your doctor if Prolia (denosumab) is right for you and visit us at www.prolia.com For women with postmenopausal osteoporosis at high risk for fracture: there s Prolia. Prolia 2 shots a year proven
Vibration Therapy and Osteoporosis
 Vibration Therapy and Osteoporosis What is osteoporosis? Osteoporosis literally means porous bones. It occurs when the struts which make up the mesh like structure within bones become thin, causing bones
Vibration Therapy and Osteoporosis What is osteoporosis? Osteoporosis literally means porous bones. It occurs when the struts which make up the mesh like structure within bones become thin, causing bones
Osteoporosis in elderly: prevention and treatment
 Clin Geriatr Med 18 (2002) 529 555 Osteoporosis in elderly: prevention and treatment Manish Srivastava, MD a, Chad Deal, MD b, * a Section of Geriatric Medicine, A91 Cleveland Clinic Foundation, 9500 Euclid
Clin Geriatr Med 18 (2002) 529 555 Osteoporosis in elderly: prevention and treatment Manish Srivastava, MD a, Chad Deal, MD b, * a Section of Geriatric Medicine, A91 Cleveland Clinic Foundation, 9500 Euclid
Prevention of Osteoporosis
 www.bpac.org.nz keyword: osteoporosis Prevention of Osteoporosis Key reviewers: Professor Ian Reid, Faculty of Medical and Health Sciences, University of Auckland Dr Rebecca Grainger, Rheumatologist and
www.bpac.org.nz keyword: osteoporosis Prevention of Osteoporosis Key reviewers: Professor Ian Reid, Faculty of Medical and Health Sciences, University of Auckland Dr Rebecca Grainger, Rheumatologist and
Osteoporosis Update: Adding New Tools and Treatments to Disease Management
 Osteoporosis Update: Adding New Tools and Treatments to Disease Management Release Date: 11/22/2011 Expiration Date: 11/22/2014 FACULTY: Nicole Van Hoey, PharmD FACULTY AND ACCREDITOR DISCLOSURE STATEMENTS:
Osteoporosis Update: Adding New Tools and Treatments to Disease Management Release Date: 11/22/2011 Expiration Date: 11/22/2014 FACULTY: Nicole Van Hoey, PharmD FACULTY AND ACCREDITOR DISCLOSURE STATEMENTS:
Denosumab (Prolia) for postmenopausal osteoporosis
 Denosumab (Prolia) for postmenopausal osteoporosis This Medicine Update is for women who are using, or thinking about using, denosumab. Summary Denosumab is a new medicine for women with osteoporosis.
Denosumab (Prolia) for postmenopausal osteoporosis This Medicine Update is for women who are using, or thinking about using, denosumab. Summary Denosumab is a new medicine for women with osteoporosis.
Contractor Information. LCD Information. Contractor Name First Coast Service Options, Inc. Document Information LCD ID L32100
 Local Coverage Determination (LCD): Bisphosphonates (Intravenous [IV]) and Monoclonal Antibodies in the Treatment of Osteoporosis and Their Other Indications (L32100) Contractor Information Contractor
Local Coverage Determination (LCD): Bisphosphonates (Intravenous [IV]) and Monoclonal Antibodies in the Treatment of Osteoporosis and Their Other Indications (L32100) Contractor Information Contractor
Presented by: Nicole Nisly, MD
 Presented by: Nicole Nisly, MD About Today s Presentation I will discuss osteoporosis and focus on causes, treatment op;ons and preven;on I will discuss medica;ons and life style choices that can be of
Presented by: Nicole Nisly, MD About Today s Presentation I will discuss osteoporosis and focus on causes, treatment op;ons and preven;on I will discuss medica;ons and life style choices that can be of
NATIONAL OSTEOPOROSIS FOUNDATION OSTEOPOROSIS CLINICAL UPDATES Vitamin D and Bone Health CE APPLICATION FORM
 NATIONAL OSTEOPOROSIS FOUNDATION OSTEOPOROSIS CLINICAL UPDATES Vitamin D and Bone Health CE APPLICATION FORM First Name: Last Name: Mailing Address: City: State: Zip/Postal Code: Country: Phone Number:
NATIONAL OSTEOPOROSIS FOUNDATION OSTEOPOROSIS CLINICAL UPDATES Vitamin D and Bone Health CE APPLICATION FORM First Name: Last Name: Mailing Address: City: State: Zip/Postal Code: Country: Phone Number:
BONE HEALTH AND DISEASE. Bone Health and Disease Goals & Objectives
 Bone Health and Disease Goals & Objectives Course Description Bone Health and Disease is an online continuing education course for physical therapists and physical therapist assistants. This course presents
Bone Health and Disease Goals & Objectives Course Description Bone Health and Disease is an online continuing education course for physical therapists and physical therapist assistants. This course presents
Treating Osteoporosis WITH BISPHOSPHONATES
 Treating Osteoporosis WITH BISPHOSPHONATES Who is SIGMA? SIGMA is the Canadian Menopause Society. We are professionals specialized in different areas of post-menopausal women s health care, including family
Treating Osteoporosis WITH BISPHOSPHONATES Who is SIGMA? SIGMA is the Canadian Menopause Society. We are professionals specialized in different areas of post-menopausal women s health care, including family
MOH/P/PAK/240.12(GU) June 2012. Clinical Guidance on Management. Osteoporosis 2 0 12. Malaysian Osteoporosis Society
 MOH/P/PAK/240.12(GU) June 2012 Clinical Guidance on Management of Osteoporosis 2 0 12 Malaysian Osteoporosis Society Academy of Medicine Ministry of Health Malaysia Published by: Malaysian Osteoporosis
MOH/P/PAK/240.12(GU) June 2012 Clinical Guidance on Management of Osteoporosis 2 0 12 Malaysian Osteoporosis Society Academy of Medicine Ministry of Health Malaysia Published by: Malaysian Osteoporosis
RISK EVALUATION AND MITIGATION STRATEGY (REMS)
 Page 1 Initial REMS Approval: July 2009 Most Recent Modification: August 2013 NDA 21-318 FORTEO (teriparatide) (rdna origin) Injection RISK EVALUATION AND MITIGATION STRATEGY (REMS) Eli Lilly and Company
Page 1 Initial REMS Approval: July 2009 Most Recent Modification: August 2013 NDA 21-318 FORTEO (teriparatide) (rdna origin) Injection RISK EVALUATION AND MITIGATION STRATEGY (REMS) Eli Lilly and Company
16. ARTHRITIS, OSTEOPOROSIS, AND CHRONIC BACK CONDITIONS
 16. ARTHRITIS, OSTEOPOROSIS, AND CHRONIC BACK CONDITIONS Goal Reduce the impact of several major musculoskeletal conditions by reducing the occurrence, impairment, functional limitations, and limitation
16. ARTHRITIS, OSTEOPOROSIS, AND CHRONIC BACK CONDITIONS Goal Reduce the impact of several major musculoskeletal conditions by reducing the occurrence, impairment, functional limitations, and limitation
NHS GGC Vitamin D Supplementation Frequently asked Questions
 Pharmacy & Prescribing Support Unit NHS GGC Vitamin D Supplementation Frequently asked Questions In February 2012 the Scottish Government issued advice on supplements for groups at risk of vitamin D deficiency.
Pharmacy & Prescribing Support Unit NHS GGC Vitamin D Supplementation Frequently asked Questions In February 2012 the Scottish Government issued advice on supplements for groups at risk of vitamin D deficiency.
