Venepuncture and Cannulation Study Day
|
|
|
- Liliana Powell
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Venepuncture and Cannulation Study Day
2 Objectives To understand Trust policies on venepuncture, cannulation & flushing To understand professional responsibilities relating to these skills To understand venous anatomy & physiology To understand infection control issues relating to the skills To understand potential complications & how to minimise the risks To understand the importance of documentation & aftercare To demonstrate safe & correct procedure on a training arm
3 Timetable Registration Guidelines for professional practice Venous anatomy and physiology Infection control issues Laboratory perspective Coffee Venepuncture equipment, technique & Practice Lunch Cannulation equipment, technique & practice Flushing peripheral venous cannula Coffee Complications, reflection & evaluation Close
4 Professional Responsibilities All staff who practise venepuncture must have received approved training and documented, supervised practice. The onus is also on individuals to ensure their knowledge and skills are maintained, both from a theoretical and practical perspective. All practitioners must operate within the protocols/guidelines of their particular organisation
5 Who can carry out the procedures? An Accountable practitioner! To include; Medical Staff Registered Nurse Midwives Radiographers Other non-registered staff who have undergone Trust approved training and have proved to be competent RUH Venepuncture Policy
6 Guidelines for Professional Practice Duty of Care : Health and Safety Act Employment Law Civilly Liable to patients (you can be held liable for adverse effects to patients if procedures are not followed correctly ) Your safety, consider the risks
7 Guidelines for Professional Practice IGNORANCE IS NOT A DEFENCE It is your responsibility to keep up to date with current practices Extended Roles Where do your responsibilities lie?
8 Professional Responsibility Summary Never carry out a procedure that you have not been trained to do, signed as competent to do or do not feel confident to do. Registered and non-registered staff have responsibilities to act lawfully Keep up to date with current practices Remember these skills are extended roles and should not take priority over basic nursing care
9 Venous Anatomy and Physiology Objectives Differentiate between an artery and a vein Identify and name the commonly used veins for venepuncture and cannulation Be aware of nerves in the arm Understand how to choose an appropriate vein for venepuncture and cannulation avoiding hazardous anatomical structures
10 Anatomy and Physiology The most common site for venepuncture is the Antecubital Fossa where the Median Cubital, Cephalic and Basilic veins lie close to the skins surface making them easily accessible. They are the most prominent, there are numerous of them and they have been shown to minimise discomfort (Weinstein, 1997). Always use veins in the upper extremities before using lower extremity sites for VENEPUNCTURE. Veins of the lower limbs are usually only used in exceptional circumstances in adults. However! For CANNULATION you should start distally and work proximally
11
12 Nerves of the Arm to consider.. Three main nerves run past the elbow and wrist to the hand. Median nerve. This nerve passes down the inside of the arm and crosses the front of the elbow.the median nerve supplies muscles that help bend the wrist and fingers. It is a main nerve for the muscles that bend the thumb. The median nerve also gives feeling to the skin on much of the hand around the palm, the thumb, and the index and middle fingers. When the median nerve is compressed over a long period, it can cause carpal tunnel syndrome.
13 Nerves Ulnar nerve. This nerve passes down the inside of the arm. It then passes behind the elbow, where it lies in a groove between two bony points on the back and inner side of the elbow. The ulnar nerve supplies muscles that help bend the wrist and fingers, and that help move the fingers from side to side. It also gives feeling to the skin of the outer part of the hand, including the little finger and the outer half of the back of the hand, palm, and ring finger. When the elbow is bumped over the ulnar nerve, it's often called hitting the "funny bone."
14 Nerves continued Radial nerve. This nerve passes down the back and outside of the upper arm. The radial nerve supplies muscles that straighten the elbow, and lift and straighten the wrist, thumb, and fingers. The radial nerve gives feeling to the skin on the outside of the thumb and on the back of the hand and the index finger, middle finger, and half of the ring finger.
15 Main nerves of the Arm
16 Differences between arteries and veins ARTERIES Take oxygenated blood from the heart to tissues Have thick walls Small Lumen Elastic No valves Deep seated (Usually) Do not collapse High pressure VEINS Take deoxygenated blood from the tissues to the heart Thin walls Large lumen Less elastic Have valves to prevent any backflow of blood Lie closer to the skin Tendency to collapse Low blood pressure
17 Vein Structure Anatomy The structure of a vein is as follows; The walls (outer structure) of veins consist of three layers of tissues that are thinner and less elastic than the corresponding layers of arteries. Veins include valves that aid the return of blood to the heart by preventing blood from flowing in the reverse direction.
18
19 Vein and Artery Structure Tunica Intima (inner lining) ; has a smooth lining, is fragile and sensitive. Valves are present here in veins. Tunica Media (Middle lining) ; Smooth muscle, elastic tissue which can constrict and dilate. Less thick in veins Tunica Externa or Adventitia; thick layer of connective tissue
20 Suitable Veins Visible Palpable Bouncy Soft Well supported Refills when depressed Straight and non-toruous
21 Sites to avoid Evidence of venous fibrosis; Evidence of haematoma/oedema formation; Evidence of localised infection/inflammation; Any vascular access device; Fistulae or vascular grafts. Limbs with fractures Small, visible but impalpable veins The affected side in patients postmastectomy or postcardiovascular accident.
22 Anatomy and Physiology Summary Only perform venepuncture and cannulation on healthy tissue Be aware of the artery at the Antecubital Fossa Be aware of the nerves at the Antecubital Fossa In some individuals the artery lies over the vein so remember to check if there is a pulse! If your ever not sure, then always ask.
23 Infection Control Issues Why do you think Infection Control is a relevant issues with regards to venepuncture and cannulation??
24 Sharps Safety (RUH Sharps Policy) Take sharps bin to patient Sharps must be disposed of immediately Fill to line only Never re-sheath needles Report sharps injuries as per RUH policy
25 Key Principles for sharps 1. Never attempt to use a sharp without preparation for its disposal 2. Never re-sheath a needle (Even a clean one) 3. Never carry loose sharps in your hand- always use a plastic tray 4. Never expect someone else to dispose of your sharps 5. Never leave sharps to dispose of later 6. Never underestimate the implications of a sharps injury
26 Key Principles Sharps ALWAYS 1. Wear appropriate personal protective equipment 2. Assemble devices with care 3. Be especially vigilant during emergency situations and procedures 4. Ask for assistance when taking blood from uncooperative patients 5. Dispose of sharps as soon as possible 6. Report all incidents involing contaminated sharps 7. Report all near misses and examples of bad practice 8. Prohibit hand to hand passing of sharps devices.
27 Infection control key points and summary Always use ANTT when performing venepuncture and cannulation as will reduce the risk of patients developing bacteraemias Tourniquets should be single use Remember the correct disposal of equipment as per RUH policy Sharps injuries do happen!! Think personal protective equipment and your safety
28 Venepuncture Equipment, Technique and Practice 4 stage techniques 1. Visual picture of skill demonstrated in real time 2. Explanation of demonstration 3. Student talk through whilst performed by trainer 4. Student talks through and demonstrates the skill BUT FIRST A FEW KEY POINTS
29 Patient Consent How do we gain consent from our patients? How do we correctly identify our patients? What about confused or unconscious patients?
30 Venepuncture Checklist Have you checked and confirmed the identity of the patient? Have you obtained verbal informed consent? Has the use of local anaesthesia been considered? Have you selected all equipment required? Does the patient have any IV infusion in progress in the limb you propose to use? ANTT If the tourniquet is non-disposable, is it socially clean and has it been laundered at 60 c within the last 7 days? Have you disposed of any waste including sharps, in accordance with trust policies? Have you documented the procedure?
31 Venepuncture key points How many attempts will you have at any one given time for a single patient? What will you do if you have been unsuccessful? Where do you document the procedure?
32 Order of Collection Blood Cultures, then Blue Top (Clotting screen) Orange/ beige top (Chemistry profile) Lavender top ( Full Blood Count (FBC))
33 Labelling of blood bottles How to label 1. Use a ball point pen 2. Include full name, D.O.B, Ward, date and time 3. Write the time of collection on the request form and initial the form 4. Place the tubes in the bag and attach the blood form and seal THINK IS THIS BLOOD NEEDED URGENTLY? WHAT ARRANGMENTS WILL YOU NEED TO MAKE?
34 Any Questions?
35 Venepuncture summary and key points Always gain consent Always wear gloves when carrying out venepuncture and cannulation Always use vacutainer equipment when taking blood, never a needle and syringe Always label blood bottles immediately after taken Always follow trust policy and guidelines Always perform the skill under direct supervision by a trained member of staff competent in the skill and who uses them regularly, until such time that you are signed off as competent
36 Venepuncture. LETS PRACTICE!
37 Peripheral Cannulation
38 Aim and Objectives AIM To provide a guide to peripheral intravenous cannulation and advice on the continuing care of patients with such devices in place. Objectives Each practitioner will be able to: Ensure that a short peripheral cannula is the appropriate device for intended need Decide the size/type of device to be used Choose an appropriate insertion site Prepare the appropriate equipment Complete the procedure safely Conclude the care episode
39 Cannulation Why is cannulation necessary for some patients?
40 What size cannula? Before beginning it is important to choose the correct size of cannula. The options, in order of decreasing bore size are; 16 gauge (grey) for surgical emergencies (170mls/min); 18 gauge (green) for blood transfusions or larger volumes (80mls/min); 20 gauge (pink) for maintenance of intravenous fluids; and 22 gauge (blue) for difficult veins, slow intravenous fluids, or intravenous drugs in a patient who can take oral fluids (31mls/min)
41 Cannula selection The cannula chosen should be the smallest to meet the clinical need. Clearly the larger the lumen of the catheter the faster the flow rate. The indication for cannulation should be considered and the cannula gauge chosen accordingly. For example emergency colloid or blood replacement after a post partum haemorrhage will require a grey cannula whereas a line for intermittent intravenous bolus injections of antibiotics could be green or pink. Think; purpose of infusion, type of infusate, length of treatment
42 Insertion site Commonly chosen sites include: Veins in the back of the hand or forearm. In an emergency any available large peripheral vein may be used e.g. median cubital vein in the anti-cubital fossa. If the cannula has to be positioned over a joint a splint may be required to ensure continuing satisfactory flow.
43 Cannulation documentation What needs to be considered with regards to the documentation of cannula? What aftercare considerations are there?
44 Any Questions?
45 Cannulation. LETS PRACTICE!!
46 Potential Complication Objectives To understand the potential complications of Venepuncture and Cannulation To understand how to deal with such complications if they should occur
47 Potential complications Syncope / fainting Haematoma / bruising Petechiae / broken capillary blood vessels Haemolysis Infection Infiltration Extravasation Occlusion Embolus
48 Complications continued Haematoma If a haematoma begins to form, release the tourniquet, remove the needle from the vein and apply firm pressure to the site. The incidence of haematoma after venepuncture can be decreased by applying pressure to the site after the needle is removed. Carefull technique should reduce the risk of developing a haematoma.
49 Complications continued Petechiae A petechiae is a small (1-2mm) red or purple spot on the body, caused by a minor haemorrhage (broken capillary blood vessel) This often occurs in patients with a coagulopathy but can also occur if the tourniquet is left tightened for prolonged periods of time
50 Complications continued Haemolysis Haemolysis can affect some results (e.g. potassium), although it may be a result of the patients disease process it is most often the result of poor technique. Remember to invert the blood tubes gently to mix the blood.
51 Complications continued Infection Local cellulitis or septicaemia are uncommon complications of venepuncture- remember strict asceptic technique during venepuncture and cannulation will reduce the risk of patients developing a bacteraemia. REMEMBER ANTT!! All patient with an intravenous access device in place must have the cannula site checked daily for signs of infusion phlebitis. Two of the most common causes of infusion phlebitis are chemical and mechanical; therefore the correct choice of a suitable access device for a particular patient is vital (Freytes 2000).
52 Cannulation and Infusion Complications INFILTRATION Inadvertent administration of a non-vesicant solution or drug into the tissues (Weinstein 1997). Venous access devices must be secured in away that does not impede fluid/blood flow and allows the insertion site to be monitored. EXTRAVASATION Inadvertent administration of a vesicant solution or drug into the tissues (Weinstein 1997)). Tissue necrosis may follow, therefore it is vital that cannulae are assessed as patent prior to use and monitored closely.
53 Infiltration and extravasation How will you tell if this occurs? 1. Pain when flushing 2. Possible swelling distally to the cannula 3. Pressure when attempting to flush Prevention 1. Close observation 2. Regular flushing 3. Careful fixation REMEMBER VIP SCORE EVERY SHIFT!!
54 Complications continued OCCLUSION Cannulae may become occluded when infusion containers run dry or flush solutions are not administered appropriately (Dougherty and Lamb 1999). Cannula s must never be forcibly flushed. Remember VIP SCORES!!
55 Complications continued Embolus, air or blood Ensure all connections are tight. Never reintroduce stylet If clotted then remove Careful when drawing up the flush to prevent air bubbles.
56 Questions What action should you take in the event of an injury to a nerve? 1. Remove the needle immediately and apply pressure 2. Seek medical help 3. Give an explanation to the patient 4. Make sure the incident is documented and fill out an incident form
57 Questions What action should you take in the event of puncturing an artery? 1. Remove device immediately and apply pressure until bleeding stops and then apply an appropriate dressing 2. Seek medical help 3. Document in the notes 4. Give an explanation to the patient
58 Complications summary Remember never to rush Careful technique will reduce incidents of complications Document all attempts as per trust policy Only two attempts for the same patient episode. Always ask someone if you are not sure.
59 Any Questions?
60 Key points You need to be signed of by a competent practitioner before you are able to practice the skills alone, that includes competencies for; Venepuncture Cannulation Flushing There is also a competency for sending blood for cross match or group and save. Speak to a competent staff member in your ward areas.
61 Objectives To understand Trust policies on venepuncture, cannulation & flushing To understand professional responsibilities relating to these skills To understand venous anatomy & physiology To understand infection control issues relating to the skills To understand potential complications & how to minimise the risks To understand the importance of documentation & aftercare To demonstrate safe & correct procedure on a training arm
62 References and further reading Campbell, H et al (1999) A practical guide to venepuncture and management of complications, British Journal of Nursing 8 (7) Heywood Jones, I (1994) Venepuncture using vacuum tubes, Community Outlook 7, Griffths, E. (1999) Venepuncture. Practice Nursing 10 (1) Scales, K (2008) A practical guide to venepuncture and blood sampling. Nursing standard, 22 (29) Witt, B (2004) The Royal Marsden Hospital Manual of Clinical Nursing Procedures. 6 th ed. Oxford, Blackwell pp RUH Venepuncture Policy (2009) accessed via intranet Lavery, I (2003) Peripheral venous cannulation and patient consent. 17 (28) 40-42
63 References continued NHS National Patient Safety Agency (2007) right patient, right blood BDS 19 Preparing to administer blood/ blood components to patient and administering a transfusion of blood DoH (2006) Saving Lives: High Impact Interventions No. 1 Preventing the risk of microbial contamination The Royal Marsden (2006) Clinical Nursing Procedures 6 th Ed, Blackwell Publishing LTD Clinical Governance 17, Collection of Blood Samples Campbell, L (1998) IVrelated phlebitis, complications and length of hospital stay
64 References continued Jackson, A (1997) Performing peripheral intravenous cannulation. Professional Nurse. 13 (1) Jackson, A (2003) reflecting on the nursing contribution to vascular access. British journal of nursing 12(11) Scales, K. (2005) vascular access. A guide to peripheral venous cannulation. Nursing standard 19 (49) 48-52
VENEPUNCTURE. Eileen Whitehead 2010 East Lancashire HC NHS Trust
 Eileen Whitehead 2010 East Lancashire HC NHS Trust 1 Definition The term venepuncture describes the procedure of inserting a needle into a vein, usually for the purpose of withdrawing blood for haematological,
Eileen Whitehead 2010 East Lancashire HC NHS Trust 1 Definition The term venepuncture describes the procedure of inserting a needle into a vein, usually for the purpose of withdrawing blood for haematological,
Certificate for the Administration of Intravenous Radiopharmaceuticals by Healthcare Professionals Working in Nuclear Medicine
 Certificate for the Administration of Intravenous Radiopharmaceuticals by Healthcare Professionals Working in Nuclear Medicine A collaboration between the British Nuclear Medicine Society Nurses and Technology
Certificate for the Administration of Intravenous Radiopharmaceuticals by Healthcare Professionals Working in Nuclear Medicine A collaboration between the British Nuclear Medicine Society Nurses and Technology
Obtaining a venous blood sample
 Obtaining a venous blood sample About this workforce competence This workforce competence covers the issue of obtaining a venous blood sample from a patient. The key tasks include correctly identifying
Obtaining a venous blood sample About this workforce competence This workforce competence covers the issue of obtaining a venous blood sample from a patient. The key tasks include correctly identifying
Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) for Outpatient
 Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) for Outpatient Introduction A Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter, or PICC line, is a thin, long, soft plastic tube inserted into a vein of the arm. It
Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) for Outpatient Introduction A Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter, or PICC line, is a thin, long, soft plastic tube inserted into a vein of the arm. It
Venepuncture Year 2 Dental Students Practical Skill Session
 Venepuncture Year 2 Dental Students Practical Skill Session Page 1 of 13 Contents Anatomy And Physiology 3 Structure Of Veins 4 Superficial Veins 5 Antecubital Fossa 7 Veins 7 Arteries 7 Patient Assessment
Venepuncture Year 2 Dental Students Practical Skill Session Page 1 of 13 Contents Anatomy And Physiology 3 Structure Of Veins 4 Superficial Veins 5 Antecubital Fossa 7 Veins 7 Arteries 7 Patient Assessment
Renal Vascular Access Having a Fistula For Haemodialysis
 Renal Vascular Access Having a Fistula For Haemodialysis Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Renal Vascular Access Having a Fistula For Haemodialysis Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Arterio-Venous Fistula or Arterio-Venous Graft for Haemodialysis
 Department of Nephrology Care of your Fistula Nephrology Department Lower Lane Liverpool L9 7AL Tel:0151-525-5980 Arterio-Venous Fistula or Arterio-Venous Graft for Haemodialysis Haemodialysis access In
Department of Nephrology Care of your Fistula Nephrology Department Lower Lane Liverpool L9 7AL Tel:0151-525-5980 Arterio-Venous Fistula or Arterio-Venous Graft for Haemodialysis Haemodialysis access In
PICC & Midline Catheters Patient Information Guide
 PICC & Midline Catheters Patient Information Guide medcompnet.com 1 table of contents Introduction 4 What is a PICC or Midline Catheter? 4 How is the PICC or Midline Catheter Inserted? 6 Catheter Care
PICC & Midline Catheters Patient Information Guide medcompnet.com 1 table of contents Introduction 4 What is a PICC or Midline Catheter? 4 How is the PICC or Midline Catheter Inserted? 6 Catheter Care
Ward 29 guide to the safe preparation and administration of intravenous (IV) antibiotics at home
 Ward 29 guide to the safe preparation and administration of intravenous (IV) antibiotics at home Contents Page Important contact numbers 1 General information on preparing and administering IV antibiotics
Ward 29 guide to the safe preparation and administration of intravenous (IV) antibiotics at home Contents Page Important contact numbers 1 General information on preparing and administering IV antibiotics
Section 4: Your Vascular Access. What is vascular access?
 Section 4: Your Vascular Access What is vascular access? What is a fistula? Taking care of a new fistula What is a graft? Taking care of a new graft What is a hemodialysis catheter? Taking care of a hemodialysis
Section 4: Your Vascular Access What is vascular access? What is a fistula? Taking care of a new fistula What is a graft? Taking care of a new graft What is a hemodialysis catheter? Taking care of a hemodialysis
Vaxcel PICCs Valved and Non-Valved. A Patient s Guide
 Vaxcel PICCs Valved and Non-Valved A Patient s Guide Information about your Vaxcel PICC is available by calling the Navilyst Medical Vascular Access Information Line 800.513.6876 Vaxcel Peripherally Inserted
Vaxcel PICCs Valved and Non-Valved A Patient s Guide Information about your Vaxcel PICC is available by calling the Navilyst Medical Vascular Access Information Line 800.513.6876 Vaxcel Peripherally Inserted
A4.7 Management of a totally occluded central catheter and persistent withdrawal occlusion (PWO)
 A4.7 Management of a totally occluded central catheter and persistent withdrawal occlusion (PWO) Types of Catheter Related Thrombotic A catheter-related thrombus may be intraluminal (inside the catheter)
A4.7 Management of a totally occluded central catheter and persistent withdrawal occlusion (PWO) Types of Catheter Related Thrombotic A catheter-related thrombus may be intraluminal (inside the catheter)
376 OBTAIN VENOUS BLOOD SAMPLES
 Unit overview Elements of competence 376a 376b Obtain venous blood from individuals Label and prepare blood for transportation About this unit For this unit you need to use venepuncture/phlebotomy techniques
Unit overview Elements of competence 376a 376b Obtain venous blood from individuals Label and prepare blood for transportation About this unit For this unit you need to use venepuncture/phlebotomy techniques
Administration of Medications & Fluids via a Peripheral Intravenous Cannula
 Administration of Medications & Fluids via a Peripheral Intravenous Cannula Clinical S.O.P. No.: 22.0 Compiled by: Approved by: Review date: November 2016 Administration of Medications & Fluids via S.O.P.
Administration of Medications & Fluids via a Peripheral Intravenous Cannula Clinical S.O.P. No.: 22.0 Compiled by: Approved by: Review date: November 2016 Administration of Medications & Fluids via S.O.P.
Understanding your Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) Patient Information
 Understanding your Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) Patient Information The Purpose of this Information Sheet This information sheet has been written by patients, members of the public and
Understanding your Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) Patient Information The Purpose of this Information Sheet This information sheet has been written by patients, members of the public and
Peripheral Venous Cannula (PVC) Insertion and Management Guidelines
 Peripheral Venous Cannula (PVC) Insertion and Management Guidelines This procedural document supersedes: PAT/T 45 v.1 - Policy for the Insertion and Management of Peripheral Venous Cannula (PVC). Did you
Peripheral Venous Cannula (PVC) Insertion and Management Guidelines This procedural document supersedes: PAT/T 45 v.1 - Policy for the Insertion and Management of Peripheral Venous Cannula (PVC). Did you
Flushing and Dressing a Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC Line): a Guide for Nurses
 Flushing and Dressing a Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC Line): a Guide for Nurses Information for Nurses Introduction This information is for community nursing staffs who have been asked to
Flushing and Dressing a Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC Line): a Guide for Nurses Information for Nurses Introduction This information is for community nursing staffs who have been asked to
Hand & Plastics Physiotherapy Department Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Hand & Plastics Physiotherapy Department Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients page 2 What is the Carpal Tunnel? The carpal tunnel is made up of the bones
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Hand & Plastics Physiotherapy Department Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients page 2 What is the Carpal Tunnel? The carpal tunnel is made up of the bones
Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter
 Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) by Patricia Griffin Kellicker, BSN En Español (Spanish Version) Definition A peripherally inserted central catheter is a long, thin tube that is inserted through
Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) by Patricia Griffin Kellicker, BSN En Español (Spanish Version) Definition A peripherally inserted central catheter is a long, thin tube that is inserted through
Lifecath Midline. A Nurses Guide to Lifecath Midline
 Lifecath Midline A Nurses Guide to Lifecath Midline [email protected] www.vygon.co.uk Lifecath Midline A Nurses Guide to Lifecath Midline This booklet provides guidance in the care and maintenance of Midline
Lifecath Midline A Nurses Guide to Lifecath Midline [email protected] www.vygon.co.uk Lifecath Midline A Nurses Guide to Lifecath Midline This booklet provides guidance in the care and maintenance of Midline
X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary
 X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary Introduction A Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter, or subclavian line, is a long thin hollow tube inserted in a vein under the
X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary Introduction A Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter, or subclavian line, is a long thin hollow tube inserted in a vein under the
PERIPHERALLY INSERTED CENTRAL CATHETERS (PICC) Fong So Kwan APN, Haematology unit Medical Department, QMH
 PERIPHERALLY INSERTED CENTRAL CATHETERS (PICC) Fong So Kwan APN, Haematology unit Medical Department, QMH 1 What is a PICC catheter? Primary vascular access device since their introduction in the mid-1970s,
PERIPHERALLY INSERTED CENTRAL CATHETERS (PICC) Fong So Kwan APN, Haematology unit Medical Department, QMH 1 What is a PICC catheter? Primary vascular access device since their introduction in the mid-1970s,
Intravenous Therapy Principles of Care. Breege Smithers Practice Educator
 Intravenous Therapy Principles of Care Breege Smithers Practice Educator Objectives State indications for intravenous therapy List the advantages and disadvantages of intravenous therapy Identify the principles
Intravenous Therapy Principles of Care Breege Smithers Practice Educator Objectives State indications for intravenous therapy List the advantages and disadvantages of intravenous therapy Identify the principles
Within the Scope of Practice/Role of APRN RN _ X_LPN CNA
 Wyoming State Board of Nursing 130 Hobbs Avenue, Suite B Cheyenne, WY 82002 Phone (307) 777-7601 Fax (307) 777-3519 E-Mail: [email protected] Home Page: https://nursing-online.state.wy.us/ OPINION:
Wyoming State Board of Nursing 130 Hobbs Avenue, Suite B Cheyenne, WY 82002 Phone (307) 777-7601 Fax (307) 777-3519 E-Mail: [email protected] Home Page: https://nursing-online.state.wy.us/ OPINION:
Patient Information. PORT-A-CATH Implantable Venous Access Systems
 Patient Information PORT-A-CATH Implantable Venous Access Systems Your doctor has prescribed treatment that requires the frequent administration of medications or other fluids directly into your bloodstream
Patient Information PORT-A-CATH Implantable Venous Access Systems Your doctor has prescribed treatment that requires the frequent administration of medications or other fluids directly into your bloodstream
Medications or therapeutic solutions may be injected directly into the bloodstream
 Intravenous Therapy Medications or therapeutic solutions may be injected directly into the bloodstream for immediate circulation and use by the body. State practice acts designate which health care professionals
Intravenous Therapy Medications or therapeutic solutions may be injected directly into the bloodstream for immediate circulation and use by the body. State practice acts designate which health care professionals
Adult Forearm Fractures
 Adult Forearm Fractures Your forearm is made up of two bones, the radius and ulna. In most cases of adult forearm fractures, both bones are broken. Fractures of the forearm can occur near the wrist at
Adult Forearm Fractures Your forearm is made up of two bones, the radius and ulna. In most cases of adult forearm fractures, both bones are broken. Fractures of the forearm can occur near the wrist at
Epidural Continuous Infusion. Patient information Leaflet
 Epidural Continuous Infusion Patient information Leaflet April 2015 Introduction You may already know that epidural s are often used to treat pain during childbirth. This same technique can also used as
Epidural Continuous Infusion Patient information Leaflet April 2015 Introduction You may already know that epidural s are often used to treat pain during childbirth. This same technique can also used as
An introduction to the principles and practice of safe and effective administration of injections
 An introduction to the principles and practice of safe and effective administration of injections Introduction Giving an injection safely is considered to be a routine nursing activity. However it requires
An introduction to the principles and practice of safe and effective administration of injections Introduction Giving an injection safely is considered to be a routine nursing activity. However it requires
Guy s, King s and St Thomas Cancer Centre The Cancer Outpatient Clinic Central venous catheter: Peripherally inserted central catheter
 Guy s, King s and St Thomas Cancer Centre The Cancer Outpatient Clinic Central venous catheter: Peripherally inserted central catheter This information leaflet aims to help answer some of the questions
Guy s, King s and St Thomas Cancer Centre The Cancer Outpatient Clinic Central venous catheter: Peripherally inserted central catheter This information leaflet aims to help answer some of the questions
Hand & Plastics Physiotherapy Department Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Hand & Plastics Physiotherapy Department Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients This leaflet has been developed to answer any questions you may have regarding
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Hand & Plastics Physiotherapy Department Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients This leaflet has been developed to answer any questions you may have regarding
CATHETER for Hemodialysis
 CATHETER for Hemodialysis What You Need to Know to Stay Healthy with a Catheter One treatment choice for kidney failure is hemodialysis (HD). HD removes wastes and excess fluid from your blood. Your lifeline
CATHETER for Hemodialysis What You Need to Know to Stay Healthy with a Catheter One treatment choice for kidney failure is hemodialysis (HD). HD removes wastes and excess fluid from your blood. Your lifeline
Hemodialysis Access: What You Need to Know
 Hemodialysis Access: What You Need to Know Hemodialysis Access: What You Need To Know Whether you already get hemodialysis treatment, or you will need to start dialysis soon, this booklet will help you
Hemodialysis Access: What You Need to Know Hemodialysis Access: What You Need To Know Whether you already get hemodialysis treatment, or you will need to start dialysis soon, this booklet will help you
MISSISSIPPI BOARD OF NURSING IV THERAPY COURSE FOR THE EXPANDED ROLE LICENSED PRACTICAL NURSE COURSE OUTLINE
 THEORY MINIMUM 40 HOURS COURSE OUTLINE UNIT TOPIC HOURS* I LEGAL ASPECTS AND PRACTICE OF IV THERAPY 1 II REVIEW OF ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY 6 III FLUID AND ELECTROLYTE BALANCE 10 IV EQUIPMENT AND PROCEDURES
THEORY MINIMUM 40 HOURS COURSE OUTLINE UNIT TOPIC HOURS* I LEGAL ASPECTS AND PRACTICE OF IV THERAPY 1 II REVIEW OF ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY 6 III FLUID AND ELECTROLYTE BALANCE 10 IV EQUIPMENT AND PROCEDURES
A PROCEDURAL GUIDE TO MIDLINE CATHETER INSERTION
 A PROCEDURAL GUIDE TO MIDLINE CATHETER INSERTION See Also CPG midline catheters for indications, contraindications and post insertion management What is a midline A midline catheter is an 8-12 cm catheter
A PROCEDURAL GUIDE TO MIDLINE CATHETER INSERTION See Also CPG midline catheters for indications, contraindications and post insertion management What is a midline A midline catheter is an 8-12 cm catheter
Care of your peripherally inserted central catheter
 Care of your peripherally inserted central catheter A guide for patients and their carers We care, we discover, we teach Contents What is a PICC?.... 1 How is it put in?.... 1 What are the benefits of
Care of your peripherally inserted central catheter A guide for patients and their carers We care, we discover, we teach Contents What is a PICC?.... 1 How is it put in?.... 1 What are the benefits of
Wrist Fracture. Please stick addressograph here
 ORTHOPAEDIC UNIT: 01-293 8687 /01-293 6602 UPMC BEACON CENTRE FOR ORTHOPAEDICS: 01-2937575 PHYSIOTHERAPY DEPARTMENT: 01-2936692 GUIDELINES FOR PATIENTS FOLLOWING WRIST FRACTURE Please stick addressograph
ORTHOPAEDIC UNIT: 01-293 8687 /01-293 6602 UPMC BEACON CENTRE FOR ORTHOPAEDICS: 01-2937575 PHYSIOTHERAPY DEPARTMENT: 01-2936692 GUIDELINES FOR PATIENTS FOLLOWING WRIST FRACTURE Please stick addressograph
I-140 Venipuncture for Blood Specimen Collection
 I-140 Venipuncture for Blood Specimen Collection Purpose Obtain a blood specimen by venipuncture for laboratory analysis using aseptic technique. Applies To Registered Nurses Licensed Practical/Vocational
I-140 Venipuncture for Blood Specimen Collection Purpose Obtain a blood specimen by venipuncture for laboratory analysis using aseptic technique. Applies To Registered Nurses Licensed Practical/Vocational
Provided by the American Venous Forum: veinforum.org
 CHAPTER 1 NORMAL VENOUS CIRCULATION Original author: Frank Padberg Abstracted by Teresa L.Carman Introduction The circulatory system is responsible for circulating (moving) blood throughout the body. The
CHAPTER 1 NORMAL VENOUS CIRCULATION Original author: Frank Padberg Abstracted by Teresa L.Carman Introduction The circulatory system is responsible for circulating (moving) blood throughout the body. The
INTERDISCIPLINARY CLINICAL MANUAL Policy and Procedure
 INTERDISCIPLINARY CLINICAL MANUAL Policy and Procedure TITLE: Venipuncture for Blood Specimen NUMBER: Collection Effective Date : October 2013 Page 1 of 10 Applies To: Holders of Interdisciplinary Clinical
INTERDISCIPLINARY CLINICAL MANUAL Policy and Procedure TITLE: Venipuncture for Blood Specimen NUMBER: Collection Effective Date : October 2013 Page 1 of 10 Applies To: Holders of Interdisciplinary Clinical
The temporary haemodialysis catheter
 The temporary haemodialysis catheter Department of Renal Medicine Patient Information Leaflet Introduction The information in this booklet is for: People have renal failure and who require urgent haemodialysis.
The temporary haemodialysis catheter Department of Renal Medicine Patient Information Leaflet Introduction The information in this booklet is for: People have renal failure and who require urgent haemodialysis.
Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC)
 Patient information leaflet Royal Surrey County Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) Intravenous Therapy What is a PICC? A PICC is a very fine flexible tube measuring
Patient information leaflet Royal Surrey County Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) Intravenous Therapy What is a PICC? A PICC is a very fine flexible tube measuring
9.Pediatric Procedures
 9.Pediatric Procedures A. Introduction 1. Pediatric blood collection may be by skin puncture or venipuncture. 2. Skill in pediatric phlebotomy is gained by knowledge of special collection equipment, observation
9.Pediatric Procedures A. Introduction 1. Pediatric blood collection may be by skin puncture or venipuncture. 2. Skill in pediatric phlebotomy is gained by knowledge of special collection equipment, observation
Hand Injuries and Disorders
 Hand Injuries and Disorders Introduction Each of your hands has 27 bones, 15 joints and approximately 20 muscles. There are many common problems that can affect your hands. Hand problems can be caused
Hand Injuries and Disorders Introduction Each of your hands has 27 bones, 15 joints and approximately 20 muscles. There are many common problems that can affect your hands. Hand problems can be caused
Having denervation of the renal arteries for treatment of high blood pressure
 Having denervation of the renal arteries for treatment of high blood pressure The aim of this information sheet is to help answer some of the questions you may have about having denervation of the renal
Having denervation of the renal arteries for treatment of high blood pressure The aim of this information sheet is to help answer some of the questions you may have about having denervation of the renal
2. (U4C2L3:F2) If your friend received a deep cut on her wrist, what would you do?
 Cadet Name: Date: 1. (U4C2L3:F1) Your friend receives a deep cut on her wrist while washing dishes. She asks for your help. How confident are you that you could provide appropriate aid? A) My friend is
Cadet Name: Date: 1. (U4C2L3:F1) Your friend receives a deep cut on her wrist while washing dishes. She asks for your help. How confident are you that you could provide appropriate aid? A) My friend is
Epidurals for pain relief after surgery
 Epidurals for pain relief after surgery This information leaflet is for anyone who may benefit from an epidural for pain relief after surgery. We hope it will help you to ask questions and direct you to
Epidurals for pain relief after surgery This information leaflet is for anyone who may benefit from an epidural for pain relief after surgery. We hope it will help you to ask questions and direct you to
Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) Patient Instructions
 Patient Care Services 300 Pasteur Drive Stanford, CA 94305 Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) Patient Instructions A Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) is a soft flexible tube inserted
Patient Care Services 300 Pasteur Drive Stanford, CA 94305 Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) Patient Instructions A Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) is a soft flexible tube inserted
REMOVAL OF A PICC. Possible Cause Nursing Actions Prevention
 REMOVAL OF A PICC PICC lines are removed following a physician order, when therapy is completed or complications such as line sepsis, thrombosis or phlebitis, require removal. The removal of a PICC line
REMOVAL OF A PICC PICC lines are removed following a physician order, when therapy is completed or complications such as line sepsis, thrombosis or phlebitis, require removal. The removal of a PICC line
How To Treat A Heart Attack
 13 Resuscitation and preparation for anaesthesia and surgery Key Points 13.1 MANAGEMENT OF EMERGENCIES AND CARDIOPULMONARY RESUSCITATION ESSENTIAL HEALTH TECHNOLOGIES The emergency measures that are familiar
13 Resuscitation and preparation for anaesthesia and surgery Key Points 13.1 MANAGEMENT OF EMERGENCIES AND CARDIOPULMONARY RESUSCITATION ESSENTIAL HEALTH TECHNOLOGIES The emergency measures that are familiar
PICC/Midclavicular/Midline Catheter
 47 PICC/Midclavicular/Midline Catheter Introduction- PICC/ MCV/ Midline You have a PICC/Midclavicular/Midline (peripherally inserted) catheter. This catheter should make receiving I.V. medicines or solutions
47 PICC/Midclavicular/Midline Catheter Introduction- PICC/ MCV/ Midline You have a PICC/Midclavicular/Midline (peripherally inserted) catheter. This catheter should make receiving I.V. medicines or solutions
Oxford Centre for Respiratory Medicine Bronchial-Artery Embolisation Information for patients
 Oxford Centre for Respiratory Medicine Bronchial-Artery Embolisation Information for patients This leaflet tells you about the bronchial-artery embolisation procedure. It explains what is involved and
Oxford Centre for Respiratory Medicine Bronchial-Artery Embolisation Information for patients This leaflet tells you about the bronchial-artery embolisation procedure. It explains what is involved and
BD Saf-T-Intima. Hidden talents of BD Saf-T-Intima. BD SAF-T-Intima and SUBCUTANEOUS THERAPY REHYDRATION PALLIATIVE CARE. POST OPERATIVe PAIN RELIEF
 Hidden talents of BD Saf-T-Intima BD Saf-T-Intima SUBCUTANEOUS INFUSION REHYDRATION PALLIATIVE CARE BD SAF-T-Intima and SUBCUTANEOUS THERAPY PAEDIATRIC CARE POST OPERATIVe PAIN RELIEF BD Saf-T-Intima First
Hidden talents of BD Saf-T-Intima BD Saf-T-Intima SUBCUTANEOUS INFUSION REHYDRATION PALLIATIVE CARE BD SAF-T-Intima and SUBCUTANEOUS THERAPY PAEDIATRIC CARE POST OPERATIVe PAIN RELIEF BD Saf-T-Intima First
Section 10. Guidelines for the Safe Handling and Disposal of Needles and Sharps
 Section 10 Guidelines for the Safe Handling and Disposal of Needles and Sharps On behalf of Infection Control Policy Review Group NHS Ayrshire and Arran Warning - this document is uncontrolled when printed
Section 10 Guidelines for the Safe Handling and Disposal of Needles and Sharps On behalf of Infection Control Policy Review Group NHS Ayrshire and Arran Warning - this document is uncontrolled when printed
The Golden Rule of Specimen Collection: The Patient Test Result is Only as Good as the Sample We Get
 The Golden Rule of Specimen Collection: The Patient Test Result is Only as Good as the Sample We Get Jan Frerichs, MLS (ASCP) The University of Iowa [email protected] Importance of Phlebotomist
The Golden Rule of Specimen Collection: The Patient Test Result is Only as Good as the Sample We Get Jan Frerichs, MLS (ASCP) The University of Iowa [email protected] Importance of Phlebotomist
Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC Line)
 Feedback We appreciate and encourage feedback. If you need advice or are concerned about any aspect of care or treatment please speak to a member of staff or contact the Patient Advice and Liaison Service
Feedback We appreciate and encourage feedback. If you need advice or are concerned about any aspect of care or treatment please speak to a member of staff or contact the Patient Advice and Liaison Service
OPERATION:... Proximal tibial osteotomy Distal femoral osteotomy
 AFFIX PATIENT DETAIL STICKER HERE Forename.. Surname NHS Organisation. Responsible surgeon. Job Title Hospital Number... D.O.B.././ No special requirements OPERATION:..... Proximal tibial osteotomy Distal
AFFIX PATIENT DETAIL STICKER HERE Forename.. Surname NHS Organisation. Responsible surgeon. Job Title Hospital Number... D.O.B.././ No special requirements OPERATION:..... Proximal tibial osteotomy Distal
Chapter 33. Nerve Physiology
 Chapter 33 NERVE AND VASCULAR INJURIES OF THE HAND KEY FIGURES: Digital nerve location on finger Epineurial repair Nerves and blood vessels of the hand and fingers usually are quite delicate, and some
Chapter 33 NERVE AND VASCULAR INJURIES OF THE HAND KEY FIGURES: Digital nerve location on finger Epineurial repair Nerves and blood vessels of the hand and fingers usually are quite delicate, and some
Liau DW : Injuries and Liability Related to Peripheral Catheters: A Closed Claims Analysis. ASA Newsletter 70(6): 11-13 & 16, 2006.
 Citation Liau DW : Injuries and Liability Related to Peripheral Catheters: A Closed Claims Analysis. ASA Newsletter 70(6): 11-13 & 16, 2006. Full Text An anesthesiologist inserted a 14-gauge peripheral
Citation Liau DW : Injuries and Liability Related to Peripheral Catheters: A Closed Claims Analysis. ASA Newsletter 70(6): 11-13 & 16, 2006. Full Text An anesthesiologist inserted a 14-gauge peripheral
Blood sampling and transportation Standard Operating Procedure
 Blood sampling and transportation Standard Operating Procedure 1. Rationale for test 2. Requirements 3. Equipment 4. Method for blood taking 5. Instructions for Safe Box and transportation of samples 6.
Blood sampling and transportation Standard Operating Procedure 1. Rationale for test 2. Requirements 3. Equipment 4. Method for blood taking 5. Instructions for Safe Box and transportation of samples 6.
PRACTICE GUIDELINE TITLE: INTRAVENOUS LINE INSERTION: PERIPHERAL AND CENTRAL
 PRACTICE GUIDELINE Effective Date: 9-17-04 Manual Reference: Deaconess Trauma Services TITLE: INTRAVENOUS LINE INSERTION: PERIPHERAL AND CENTRAL PURPOSE: To outline the indications and options for intravenous
PRACTICE GUIDELINE Effective Date: 9-17-04 Manual Reference: Deaconess Trauma Services TITLE: INTRAVENOUS LINE INSERTION: PERIPHERAL AND CENTRAL PURPOSE: To outline the indications and options for intravenous
Page 1. Introduction The blood vessels of the body form a closed delivery system that begins and ends at the heart.
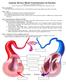 Anatomy Review: Blood Vessel Structure & Function Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction The blood vessels
Anatomy Review: Blood Vessel Structure & Function Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction The blood vessels
Clinical Guideline for: Aseptic Technique
 Clinical Guideline for: Technique Summary This guideline provides the principles of, Non Touch, and Clean Techniques to be implemented in the hospital environment. Key Points The essential elements of
Clinical Guideline for: Technique Summary This guideline provides the principles of, Non Touch, and Clean Techniques to be implemented in the hospital environment. Key Points The essential elements of
www.ghadialisurgery.com
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
Cytotoxic and Biotherapies Credentialing Programme Module 6
 Cytotoxic and Biotherapies Credentialing Programme Module 6 1. Safe Handling and Administration of Cytotoxic and Biotherapies 2. Waste and Spill Management At the completion of this module the RN will
Cytotoxic and Biotherapies Credentialing Programme Module 6 1. Safe Handling and Administration of Cytotoxic and Biotherapies 2. Waste and Spill Management At the completion of this module the RN will
Peripherally Inserted Central Venous Catheter (PICC) Invasive Devices Clinical Nurse Specialist Chief Nurse
 Peripherally Inserted Central Venous Catheter (PICC) Invasive Devices Clinical Nurse Specialist Chief Nurse This leaflet has been designed to give you important information about your condition / procedure,
Peripherally Inserted Central Venous Catheter (PICC) Invasive Devices Clinical Nurse Specialist Chief Nurse This leaflet has been designed to give you important information about your condition / procedure,
V: Infusion Therapy. Alberta Licensed Practical Nurses Competency Profile 217
 V: Infusion Therapy Alberta Licensed Practical Nurses Competency Profile 217 Competency: V-1 Knowledge of Intravenous Therapy V-1-1 V-1-2 V-1-3 V-1-4 V-1-5 Demonstrate knowledge and ability to apply critical
V: Infusion Therapy Alberta Licensed Practical Nurses Competency Profile 217 Competency: V-1 Knowledge of Intravenous Therapy V-1-1 V-1-2 V-1-3 V-1-4 V-1-5 Demonstrate knowledge and ability to apply critical
PERIPHERAL INTRAVENOUS CATHETER MANAGEMENT Adult & Paed
 Auckland District BOARD Clinical Practice Health Board (Section 1) Manual Overview This Document This document covers recommended best practices relating to the selection, insertion, care and management
Auckland District BOARD Clinical Practice Health Board (Section 1) Manual Overview This Document This document covers recommended best practices relating to the selection, insertion, care and management
Going home with your Tunneled Catheter
 Going home with your Tunneled Catheter Your Tunneled Catheter was put in by on Interventional Radiologist Date Your Tunneled Catheter was put in at: McMaster University Medical Centre Hamilton General
Going home with your Tunneled Catheter Your Tunneled Catheter was put in by on Interventional Radiologist Date Your Tunneled Catheter was put in at: McMaster University Medical Centre Hamilton General
Total hip replacement
 Patient Information to be retained by patient What is a total hip replacement? In a total hip replacement both the ball (femoral or thigh bone) side of the hip joint and the socket (acetabular or pelvic
Patient Information to be retained by patient What is a total hip replacement? In a total hip replacement both the ball (femoral or thigh bone) side of the hip joint and the socket (acetabular or pelvic
Care for your child s Central Venous Catheter (CVC)
 Care for your child s Central Venous Catheter (CVC) This booklet is intended for general informational purposes only. You should consult your doctor for medical advice. Please call the clinic or your home
Care for your child s Central Venous Catheter (CVC) This booklet is intended for general informational purposes only. You should consult your doctor for medical advice. Please call the clinic or your home
Human Anatomy and Physiology II Laboratory
 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Laboratory The Circulation (Two Weeks) 1 This lab involves two weeks work studying the vasculature of the human body. Both weeks involve the exercise in the lab manual entitled
Human Anatomy and Physiology II Laboratory The Circulation (Two Weeks) 1 This lab involves two weeks work studying the vasculature of the human body. Both weeks involve the exercise in the lab manual entitled
Section Two: Arterial Pressure Monitoring
 Section Two: Arterial Pressure Monitoring Indications An arterial line is indicated for blood pressure monitoring for the patient with any medical or surgical condition that compromises cardiac output,
Section Two: Arterial Pressure Monitoring Indications An arterial line is indicated for blood pressure monitoring for the patient with any medical or surgical condition that compromises cardiac output,
How to care for a Midline Catheter
 How to care for a Midline Catheter Developed by the health care professionals of the IV Program with assistance from the Department of Learning and Development. All rights reserved. No part of this book
How to care for a Midline Catheter Developed by the health care professionals of the IV Program with assistance from the Department of Learning and Development. All rights reserved. No part of this book
The risk assessment confirms that these materials are fit for the purpose as stated above. Further information can be obtained from:
 Introduction to Blood Transfusion Competencies Blood transfusion is a complex multi-step process involving personnel from diverse background with different levels of knowledge and understanding. In order
Introduction to Blood Transfusion Competencies Blood transfusion is a complex multi-step process involving personnel from diverse background with different levels of knowledge and understanding. In order
Flushing and Dressing a Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC Line)
 Flushing and Dressing a Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC Line) Patient Information Introduction This booklet has been written to provide information to patients with a Peripherally Inserted
Flushing and Dressing a Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC Line) Patient Information Introduction This booklet has been written to provide information to patients with a Peripherally Inserted
Venefit treatment for varicose veins
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Venefit treatment for varicose veins Information for patients Your consultant has recommended that we treat your varicose veins with a procedure known as Venefit radio
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Venefit treatment for varicose veins Information for patients Your consultant has recommended that we treat your varicose veins with a procedure known as Venefit radio
Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal
 Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal What is Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal? An inferior vena cava filter placement procedure involves an interventional radiologist (a specialist doctor)
Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal What is Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal? An inferior vena cava filter placement procedure involves an interventional radiologist (a specialist doctor)
PATIENT GUIDE. Understand and care for your peripherally inserted central venous catheter (PICC). MEDICAL
 PATIENT GUIDE Understand and care for your peripherally inserted central venous catheter (PICC). MEDICAL Introduction The following information is presented as a guideline for your reference. The best
PATIENT GUIDE Understand and care for your peripherally inserted central venous catheter (PICC). MEDICAL Introduction The following information is presented as a guideline for your reference. The best
Ulnar nerve decompression
 Patient information Ulnar nerve decompression This information has been produced to help you gain the maximum benefit and understanding of your condition and its treatment. It includes the following information:
Patient information Ulnar nerve decompression This information has been produced to help you gain the maximum benefit and understanding of your condition and its treatment. It includes the following information:
Informed Patient Tutorial Copyright 2012 by the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
 Informed Patient Tutorial Copyright 2012 by the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Informed Patient - Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery Introduction Welcome to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons'
Informed Patient Tutorial Copyright 2012 by the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Informed Patient - Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery Introduction Welcome to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons'
PERIPHERAL STEM CELL TRANSPLANT INTRODUCTION
 PERIPHERAL STEM CELL TRANSPLANT INTRODUCTION This booklet was designed to help you and the important people in your life understand the treatment of high dose chemotherapy with stem cell support: a procedure
PERIPHERAL STEM CELL TRANSPLANT INTRODUCTION This booklet was designed to help you and the important people in your life understand the treatment of high dose chemotherapy with stem cell support: a procedure
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) in pregnancy
 Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) in pregnancy Information and advice for women and families Maternity What is a deep vein thrombosis (DVT)? A deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot that forms in a deep leg
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) in pregnancy Information and advice for women and families Maternity What is a deep vein thrombosis (DVT)? A deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot that forms in a deep leg
NIH Clinical Center Patient Education Materials Giving a subcutaneous injection
 NIH Clinical Center Patient Education Materials What is a subcutaenous injection? A subcutaneous injection is given in the fatty layer of tissue just under the skin. A subcutaneous injection into the fatty
NIH Clinical Center Patient Education Materials What is a subcutaenous injection? A subcutaneous injection is given in the fatty layer of tissue just under the skin. A subcutaneous injection into the fatty
Information for you Treatment of venous thrombosis in pregnancy and after birth. What are the symptoms of a DVT during pregnancy?
 Information for you Treatment of venous thrombosis in pregnancy and after birth Published in September 2011 What is venous thrombosis? Thrombosis is a blood clot in a blood vessel (a vein or an artery).
Information for you Treatment of venous thrombosis in pregnancy and after birth Published in September 2011 What is venous thrombosis? Thrombosis is a blood clot in a blood vessel (a vein or an artery).
Significant nerve damage is uncommonly associated with a general anaesthetic
 Risks associated with your anaesthetic Section 10: Nerve damage associated with an operation under general anaesthetic Section 10: Significant nerve damage is uncommonly associated with a general anaesthetic
Risks associated with your anaesthetic Section 10: Nerve damage associated with an operation under general anaesthetic Section 10: Significant nerve damage is uncommonly associated with a general anaesthetic
Total knee replacement
 Patient Information to be retained by patient What is a total knee replacement? In a total knee replacement the cartilage surfaces of the thigh bone (femur) and leg bone (tibia) are replaced. The cartilage
Patient Information to be retained by patient What is a total knee replacement? In a total knee replacement the cartilage surfaces of the thigh bone (femur) and leg bone (tibia) are replaced. The cartilage
VENOUS BLOOD COLLECTION
 Venous Blood Collection p. 1 of 5 Johns Hopkins Medical Laboratories Department of Pathology Core Lab Clinical Services Zd7: Word: JHH Venous Blood Collection Procedure Signature Date Signature Date Written
Venous Blood Collection p. 1 of 5 Johns Hopkins Medical Laboratories Department of Pathology Core Lab Clinical Services Zd7: Word: JHH Venous Blood Collection Procedure Signature Date Signature Date Written
Inguinal Hernia (Female)
 Inguinal Hernia (Female) WHAT IS AN INGUINAL HERNIA? 2 WHAT CAUSES AN INGUINAL HERNIA? 2 WHAT DOES TREATMENT / MANAGEMENT INVOLVE? 3 DAY SURGERY MANAGEMENT 3 SURGICAL REPAIR 4 WHAT ARE THE RISKS/COMPLICATIONS
Inguinal Hernia (Female) WHAT IS AN INGUINAL HERNIA? 2 WHAT CAUSES AN INGUINAL HERNIA? 2 WHAT DOES TREATMENT / MANAGEMENT INVOLVE? 3 DAY SURGERY MANAGEMENT 3 SURGICAL REPAIR 4 WHAT ARE THE RISKS/COMPLICATIONS
X-Plain Hip Replacement Surgery - Preventing Post Op Complications Reference Summary
 X-Plain Hip Replacement Surgery - Preventing Post Op Complications Reference Summary Introduction Severe arthritis in the hip can lead to severe pain and inability to walk. To relieve the pain and improve
X-Plain Hip Replacement Surgery - Preventing Post Op Complications Reference Summary Introduction Severe arthritis in the hip can lead to severe pain and inability to walk. To relieve the pain and improve
Module 2 Peripheral Intravenous Insertion Learning Package August 2007 Revised November 2011 & January 2013
 Module 2 Peripheral Intravenous Insertion Learning Package August 2007 Revised November 2011 & January 2013 Table of Contents Introduction and Competency 3 Objectives 4 Indications for IV therapy 5 Professional
Module 2 Peripheral Intravenous Insertion Learning Package August 2007 Revised November 2011 & January 2013 Table of Contents Introduction and Competency 3 Objectives 4 Indications for IV therapy 5 Professional
NHS FORTH VALLEY. Venepuncture Policy
 NHS FORTH VALLEY Venepuncture Policy Date of First Issue 21/12/2011 Approved 07/08/2015 Current Issue Date August 2015 Review Date August 2017 Version 1.2 EQIA Yes 05/01/2012 Author / Contact Sharon Faulds
NHS FORTH VALLEY Venepuncture Policy Date of First Issue 21/12/2011 Approved 07/08/2015 Current Issue Date August 2015 Review Date August 2017 Version 1.2 EQIA Yes 05/01/2012 Author / Contact Sharon Faulds
CLINICAL GUIDELINES/NURSING Guideline for Venepuncture Using the Vacutainer System Reference 1438 Date approved
 CLINICAL GUIDELINES/NURSING Guideline for Venepuncture Using the Vacutainer System Reference 1438 Date approved Approving Body Matron s Forum Supporting Policy/ Working in Venepuncture using vacutainer
CLINICAL GUIDELINES/NURSING Guideline for Venepuncture Using the Vacutainer System Reference 1438 Date approved Approving Body Matron s Forum Supporting Policy/ Working in Venepuncture using vacutainer
Measuring central venous pressure
 Elaine Cole Senior lecturer ED/Trauma, City University Barts and the London NHS Trust 1 Learning outcomes That the clinician can: Describe the sites of central venous catheterisation Understand why central
Elaine Cole Senior lecturer ED/Trauma, City University Barts and the London NHS Trust 1 Learning outcomes That the clinician can: Describe the sites of central venous catheterisation Understand why central
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO CARDIAC CATHETERIZATION
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO CARDIAC CATHETERIZATION The science of medicine. The compassion to heal. This teaching booklet is designed to introduce you to cardiac catheterization. In the following pages, we will
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO CARDIAC CATHETERIZATION The science of medicine. The compassion to heal. This teaching booklet is designed to introduce you to cardiac catheterization. In the following pages, we will
Catheter Embolization and YOU
 Catheter Embolization and YOU What is catheter embolization? Embolization therapy is a minimally invasive (non-surgical) treatment that occludes or blocks one or more blood vessels or vascular channels
Catheter Embolization and YOU What is catheter embolization? Embolization therapy is a minimally invasive (non-surgical) treatment that occludes or blocks one or more blood vessels or vascular channels
Headache after an epidural or spinal injection What you need to know. Patient information Leaflet
 Headache after an epidural or spinal injection What you need to know Patient information Leaflet April 2015 We have produced this leaflet to give you general information about the headache that may develop
Headache after an epidural or spinal injection What you need to know Patient information Leaflet April 2015 We have produced this leaflet to give you general information about the headache that may develop
Modern Varicose Vein Treatments: What Every Patient Should Know
 The Skin and Vein Center Oneonta Laser Derm & Day Spa Natural Good Looks and Leg Veins Our Specialty Dr Eric Dohner, MD 41-45 Dietz St Oneonta, NY 13820 607/431-2525 www.oneontalaserderm.com Modern Varicose
The Skin and Vein Center Oneonta Laser Derm & Day Spa Natural Good Looks and Leg Veins Our Specialty Dr Eric Dohner, MD 41-45 Dietz St Oneonta, NY 13820 607/431-2525 www.oneontalaserderm.com Modern Varicose
CLINICAL GUIDELINE HOW TO PERFORM A VENESECTION, DETAILING VEIN SELECTION AND PATIENT CARE 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline
 CLINICAL GUIDELINE HOW TO PERFORM A VENESECTION, DETAILING VEIN SELECTION AND PATIENT CARE 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1. Venesection is a clinical procedure commonly performed in the Haematology
CLINICAL GUIDELINE HOW TO PERFORM A VENESECTION, DETAILING VEIN SELECTION AND PATIENT CARE 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1. Venesection is a clinical procedure commonly performed in the Haematology
Elbow Examination. Haroon Majeed
 Elbow Examination Haroon Majeed Key Points Inspection Palpation Movements Neurological Examination Special tests Joints above and below Before Starting Introduce yourself Explain to the patient what the
Elbow Examination Haroon Majeed Key Points Inspection Palpation Movements Neurological Examination Special tests Joints above and below Before Starting Introduce yourself Explain to the patient what the
