Relationship of anthropometric indicators with blood pressure levels in rural Wardha
|
|
|
- Everett Dennis
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Indian J Med Res 123, May 2006, pp Relationship of anthropometric indicators with blood pressure levels in rural Wardha P.R. Deshmukh, S.S. Gupta, A.R. Dongre, M.S. Bharambe, C. Maliye, S. Kaur & B.S. Garg Department of Community Medicine, Mahatma Gandhi Institute of Medical Sciences, Wardha, India Received November 18, 2004 Background & objectives: Overweight and obesity are important determinants of health leading to adverse metabolic changes, including increase in blood pressure. Being overweight is associated with two- to six-fold increase in the risk of developing hypertension. Studies in urban Indian population showed strong relationship between different anthropometric indicators and blood pressure levels. Surprisingly, little is known about these relationships in rural population of India. The present study was carried out to examine the relationship between different anthropometric indicators and blood pressure levels in rural population of Wardha district in central India. Methods: This cross-sectional study was carried out in the areas of two Rural Health Training Centres (RHTC) of Department of Community Medicine, Mahatma Gandhi Institute of Medical Sciences, Sewagram; namely Bhidi and Anji through house-to-house visits. Two stage sampling method (30 cluster followed by systematic random) was used to reach the respondents households. Partial correlation coefficients were used for continuous variables. Linear regression analysis was used to assess the influence of different anthropometric indicators on the systolic and diastolic blood pressure. ROC analysis was done to identify optimal cut-off values while likelihood ratios were calculated to identify the odds of having hypertension in comparison to those with lower values of anthropometric indicators. Results: The mean systolic blood pressures were and mmhg while the mean diastolic blood pressures were 77.7 and 76.3 mmhg in men and women respectively. There was a significant positive correlation of obesity indicators with both systolic and diastolic blood pressure. For SBP, the correlation coefficient was 0.23 with BMI, 0.23 with waist circumference, 0.11 with WHR and 0.22 with WHtR. For DBP, it was 0.13 with BMI, 0.12 with WC, 0.04 with WHR and 0.11 with WHtR. Step-wise linear regression suggested that BMI and WC were important predictors of hypertension. The suggested cut-off values for BMI were 21.7 for men and 21.2 for women; for waist circumference, the cut-offs were 72.5 for men and 65.5 for women. Interpretation & conclusion: BMI and WC had strong correlation with systolic and diastolic blood pressure. The suggested lower cut-off values of the anthropometric indicators will cover maximum of the population with higher odds of having hypertension and may help in reducing the mean population blood pressure levels. Key words Body mass index - hypertension - likelihood ratio - obesity - ROC - waist circumference - waist-height ratio - waist-hip ratio 657
2 658 INDIAN J MED RES, MAY 2006 Overweight and obesity are important determinants of health and lead to adverse metabolic changes, including increase in blood pressure, unfavourable cholesterol levels, hypertriglyceridaemia, increased resistance to insulin, low high density lipoprotein (HDL) and greater prevalence of metabolic syndrome 1. They raise the risk of coronary heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes mellitus and many forms of cancer. The prevalence of obesity is increasing in both developed and developing countries 2. Body mass index or BMI (weight in kilograms divided by the square of the height in meters) is promulgated by the World Health Organization as the most useful epidemiological measure of obesity. It is nevertheless a crude index that does not take into account the distribution of body fat, resulting in variability in different individuals and populations 2. Waist-hip circumference ratio (WHR), waist-height ratio (WHtR) and waist circumference are commonly used to predict the risk of obesity related morbidity and mortality as they account for regional abdominal adiposity 3-5. Being overweight is associated with two- to sixfold increase in the risk of developing hypertension. An increase of 2-3 mmhg in systolic and 1-3 mmhg in diastolic blood pressure has been shown for each 10 kg increase in weight in western population 6. Studies in urban Indian population also showed strong relationship between different anthropometric indicators and blood pressure levels 7-9. Little is known about these relationships in rural Indian population. The present study was therefore undertaken to examine the relationship between different anthropometric indicators and blood pressure levels in rural population of Wardha district in central India. Material & Methods Study design & setting: This cross-sectional study was carried out in the areas of two Rural Health Training Centres (RHTC) of Department of Community Medicine, Mahatma Gandhi Institute of Medical Sciences, Sewagram; namely Bhidi and Anji through house-to-house visits during May-June Sampling design: Two stage sampling method was used to reach the respondents households. In first stage, cluster sampling method 10 was used to identify 30 clusters in each RHTC area separately (Sampling interval was 644 for RHTC, Bhidi and 1383 for RHTC, Anji). In the second stage, systematic random sampling method was used to identify16 households per cluster in RHTC, Bhidi area and 32 households per cluster in RHTC, Anji area. As the population of RHTC, Anji area was almost double the population of RHTC, Bhidi area, we doubled the respondents from each cluster of RHTC, Anji area to get better representation from all the clusters. All households in the cluster were listed and number of households was divided by the required number of households (16 in Bhidi and 32 in Anji) to get the sampling interval. First household was selected randomly by using lottery method and then subsequent households were identified by adding sampling interval to the random number. All family members of 18 yr and above from the selected households were included in the study. The teams visited the households in morning and evening time only to get maximum number of family members at home. Two visits were made to ensure maximum participation in the study. The objective of the study and the method was explained to the formal and informal leaders of the clusters and eligible people were requested to stay at home on the scheduled date and time. Those who were absent were asked to be present at the second visit. Pregnant women and those who were unable to stand erect were excluded from the study. Measurement of blood pressure: After obtaining oral consent, blood pressure was measured on left arm by auscultatory method using mercury sphygmomanometer (Diamond Co., Industrial Electronics and Allied Products, Electronics Cooperative Estate, Pune, Maharashtra). The individual was made comfortable and seated at least for five minutes in the chair before measurement. Two readings were taken half an hour apart and the average of two was taken 11. Hypertension was defined as systolic blood pressure (SBP) >140 mmhg and/or diastolic blood pressure (DBP) >90 mmhg as per US Seventh Joint National Committee on Detection, Evaluation and Treatment of Hypertension (JNC VII) criteria 12.
3 DESHMUKH et al: OBESITY & HYPERTENSION IN RURAL POPULATION 659 Anthropometrical measurement: Body weight was measured (to the nearest 0.5 kg) with the subject standing motionless on the bathroom weighing scale 13. Each weighing scale was standardized every day with a weight of 50 kg. Height was measured (to the nearest 0.5 cm) with the subject standing in an erect position against a vertical scale of portable stadiometer and with the head positioned so that the top of the external auditory meatus was in level with the inferior margin of the bony orbit. BMI was calculated as weight in kilograms divided by squared height in meter. Waist circumference was measured at the level halfway between the iliac crest and the costal margin in the mid-axillary line after exhaling with the subject in standing position. Hip circumference was measured at the level of greater trochanters with the subject in standing position and both feet together. Two consecutive recordings were made for each site to the nearest 0.5 cm using a non stretchable fibre measuring tape on a horizontal plane without compression of skin. The mean of two sets of values was used 11. BMI >23.0 and >25.0 kg/m 2 was taken as cut-off for overweight and obesity respectively. Waist circumference (WC) cut-offs were taken as >90 for males and >80 for females to define overweight 14. The cut-off used for WHR were >0.9 for males and >0.8 for females 15. For WHtR, the cut-off used was 0.5 for both sexes 16. Data analysis: Data were analyzed using SPSS The population characteristics, anthropometric indicators, SBP and DBP are shown as mean and standard deviation. Standard error was analyzed by CSample program of epi_info 6.04 software as the data were collected by cluster sampling method. Means were compared by using t-test. Partial correlation coefficients were used for continuous variables. Linear regression analysis was used to assess the influence of different anthropometric indicators on the SBP and DBP. Receiver operating characteristics (ROC) analysis was done to identify the cut-off values of anthropometric indicators to identify the risk of hypertension. Sensitivity and specificity were calculated and point having highest sum was taken as cut-off value for the indicator. Software CIcalculator was used to calculate 95 per cent confidence interval (CI) of the sensitivity and specificity 17. Likelihood ratio (LR) was calculated as sensitivity/ (1-specificity) to estimate the odds of having hypertension in subjects with various cut-off values of the anthropometric indicators in comparison to those who have lower values of anthropometric indicators. All tests of significance were two tailed and level of significance was taken at P<0.05. Results Of the total 3514 individuals above 18 yr of age in the study area, 2746 individuals were included giving the coverage of per cent. Of these, 46 records were incomplete and hence here we present the analysis of 2700 individuals. The mean systolic blood pressures were 120.2±0.54 and 118.4±0.51 mmhg and mean diastolic blood pressures were 77.7±0.38 and 76.3±0.61 mmhg in men and women respectively (Table I). The prevalence of the hypertension was 21.8 per cent among males and 19.8 per cent among females. The prevalence of overweight and obesity defined as BMI >23.0 and >25.0 was found to be 6.5 and 5.1 per cent in males respectively and 5.4 and 5.2 per cent in females respectively; 7.6 per cent males and 8.7 per cent females had higher waist circumference than cut-off value; 21.5 per cent males and 30.5 per Table I. Baseline characteristics of study population Characteristics Men Women Number of subjects Number of hypertensives (%) 231(21.8%) 325 (19.8%) Age (yr) 38.2± ±18.2 Height (cm) 163.8± ±8.9 Weight (kg) 51.2± ±15.4 Body mass index (kg/m 2 ) 19.1± ±6.08 Waist-hip ratio 0.84± ±0.122 Waist circumference (cm) 72.5± ±16.6 Waist-height ratio 0.44± ±0.122 Systolic blood pressure (mmhg) 120.2± ±20.7 Diastolic blood pressure (mmhg) 77.7± ±24.7 Values are mean ± SD
4 660 INDIAN J MED RES, MAY 2006 cent females had WHR higher than the cut-off value (Table II). Mean values of body mass index, waisthip ratio, waist circumference and waist-height ratio was significantly higher among hypertensive than normotensive men and women (Table III). Results of partial correlation coefficients controlled for age and sex for all the anthropometric indicators (BMI, WHR, WC, WhtR) indicated a significant positive correlation with both systolic and diastolic blood pressure; except for WHR and diastolic blood pressure where the correlation was not statistically significant. For SBP, the correlation Table II. Prevalence of overweight/obesity as per different anthropometric indicators Anthropometric Males (n=1059) Females (n=1641) indicator number (%) number (%) Body mass index (kg/m 2 ) < (48.9) 873 (53.2) (39.5) 594 (36.2) (6.5) 89 (5.4) > (5.1) 85 (5.2) Waist circumference (cm)* <Cut-off 978 (92.4) 1498 (91.3) >Cut-off 81 (7.6) 143 (8.7) Waist-hip circumference ratio** <Cut-off 831 (78.5) 1141 (69.5) >Cut-off 228 (21.5) 500 (30.5) Waist-height ratio < (81.5) 1396 (85.1) > (18.5) 245 (14.9) *Cut-off value for waist circumference was 90 cm for males and 80 cm for females **Cut-off value for waist-hip circumference ratio was 0.9 for males and 0.8 for females coefficient was 0.23 with BMI, 0.23 with waist circumference, 0.11 with WHR and 0.22 with WHtR. For DBP, it was 0.13 with BMI, 0.12 with waist circumference, 0.04 with WHR and 0.11 with WHtR. Step-wise linear regression models were fitted for systolic and diastolic blood pressure as dependent variables and BMI, WHR, WC and WHtR as independent variables controlled for age and sex to determine their influence on the variance of these dependent variables. In this study, body mass index was correlated better with both systolic (beta 0.37, SE 0.17, P<0.05) and diastolic blood pressure (beta 0.50, SE 0.12, P<0.001) than waist circumference (beta 0.25, SE 0.09, P<0.01 and beta 0.26 SE 0.68, P<0.001 respectively). WHR and WHtR did not contribute significantly. The cut-off values for all the anthropometric indicators were worked out by ROC analysis separately for male and female population to identify the risk of hypertension. The BMI cut-off for the study population was 21.7 (sensitivity = and specificity = 0.325) and 21.2 (sensitivity = and specificity = 0.372) for males and females respectively. For waist circumference cut-off was 72.5 (sensitivity = and specificity = 0.632) and 65.5 (sensitivity = and specificity = 0.630) for males and females respectively (Table IV). Figs 1 and 2 show LR for hypertension in subjects with different values of anthropometric indicator for men and women respectively. At above mentioned cut-off values for all the indicators, the risk of hypertension increased significantly (for BMI, LR=2.5, for WC, LR=1.8, for WHR, LR=2.0 and for WHtR, LR=1.7 for men) and (for BMI, LR=2.2, for WC, LR=1.6, for WHR, LR=1.3 and for WHtR, LR=1.8 for women). Table III. Sex-wise (mean±sd) values of anthropometric indicators among normotensive and hypertensive individuals Characteristics Men Women Normotensive Hypertensive Normotensive Hypertensive (n = 828) (n = 231) (n = 1316) (n = 325) Body mass index (kg/m 2 ) 18.70± ±3.95* 18.49± ±5.77* Waist-hip circumference ratio 0.83± ±0.091* 0.77± ±0.020* Waist circumference (cm) 71.09± ±14.1* 64.38± ±14.6* Waist-height ratio 0.44± ±0.076* 0.43± ±0.090* *P< compared to normotensive in the respective group
5 DESHMUKH et al: OBESITY & HYPERTENSION IN RURAL POPULATION 661 Fig. 1. Likelihood ratios for hypertension at different levels of anthropometric indicators among men. Discussion Importance of BMI, WC, WHR, WHtR have been recognized for estimating cardiovascular disease risk factors, particularly due to their positive association with hypertension 18. In the present study, mean values of all these anthropometric indicators were significantly higher in hypertensive than in normotensive population in both the genders. The findings were similar to many studies We also found significant positive correlation between all these anthropometric indicators and systolic and diastolic blood pressure except for WHR and diastolic blood pressure. Many investigators have earlier reported significant positive correlation of body mass index with systolic and diastolic blood pressure Significant positive correlation between WHR and systolic and diastolic blood pressure have been reported earlier 24,26,28,29. However, in our study, the correlation between WHR and DBP was not statistically significant. Woo et al 30 reported that waist-hip ratio was not a useful predictor of health outcome while Dalton et al 5 found that BMI, WC and WHR were equally related with hypertension. Wang et al 31 reported better correlation of BMI and waist circumference with blood pressure than waisthip ratio. In contrast, Janssen et al 32 reported waist circumference and not BMI explains obesity related health risk including hypertension. In the present study, we found BMI and WC as the significant predictors of both systolic and diastolic blood pressure. Independent association between BMI and systolic/diastolic blood pressure and between waist-hip ratio and systolic/diastolic blood pressure have been reported earlier 24-26,28,29. Sayeed et al 33 reported that waist-height ratio was a better obesity index than body mass index and waisthip ratio for predicting hypertension. Lin et al 34 also reported that waist-height ratio may be better indicator for screening obesity related cardiovascular disease risk factors including blood pressure than BMI, waist circumference and waist-hip ratio. Zang 35 reported that BMI, WC, WHR and WHtR all were positively associated with risk of coronary heart disease in Chinese women. The differences in findings may be attributed to the fact that majority of the population in the present study was non obese. In Caucasian populations, the association between BMI and mortality is J-shaped and nadir of the curve between kg/m 2 is taken as healthy BMI 36. Cut-off values of 25.0 and 30.0 kg/m 2 are taken for overweight and obesity respectively and also for identifying the risk of associated morbidities 14. In an effort to map the epidemic of obesity and associated risk of co-morbidities, it has become common practice to use these cut-off values in different populations with the assumption that
6 662 INDIAN J MED RES, MAY 2006 Fig. 2. Likelihood ratios for hypertension at different levels of anthropometric indicators among women. different ethnic groups have similar morbidity/ mortality risk for the specific BMI level in absence of any such evidence 37. Same is true for other anthropometric indicators. As evidence emerged from many studies about the higher susceptibility of Asians at lower BMI, international task force suggested lower cut-off values for them (23 and 25 kg/m 2 for overweight and obesity respectively) 14. Studies from urban India suggested lower cut-off values of these anthropometric indicators. The present study also suggests further lower cut-off values for the rural population and odds of having hypertension at these lower cut-off values were significantly high. Dudeja et al 40 had shown a BMI of 21.5 kg/m 2 for men and 19.0 kg/m 2 for women. Snehalata et al 38 suggested healthy BMI for an Indian was less than 23 kg/m 2 and cut-offs for waist circumference were 85 cm for men and 80 cm for women, and for WHR they were 0.89 for men and 0.81 for women. Indian population has higher upper body and visceral adiposity for a given BMI when compared with the Western population 41. In our population, an interaction between upper body and visceral adiposity increased the risk of related morbidity such as hypertension at lower cut-off values of different anthropometric indicators 38. Table IV. Cut-off points for different anthropometric indicators along with their sensitivity and specificity Anthopometric Cut-off Sensitivity Specificity indicators (95% CI) (95% CI) Males: Body mass index (kg/m 2 ) ( ) ( ) Waist circumference (cm) ( ) ( ) Waist hip-circumference ratio ( ) ( ) Waist height ratio ( ) ( ) Females: Body mass index (kg/m 2 ) ( ) ( ) Waist circumference (cm) ( ) ( ) Waist hip-circumference ratio ( ) ( ) Waist height ratio ( ) ( )
7 DESHMUKH et al: OBESITY & HYPERTENSION IN RURAL POPULATION 663 To summarize, rural population of Wardha had high prevalence of hypertension and low prevalence of overweight. BMI and waist circumference had strong correlation with systolic and diastolic blood pressure. The suggested low cut-off values of the anthropometric indicators will cover maximum of the population with higher odds of having hypertension and may help in reducing the mean population blood pressure levels. Acknowledgment The authors thank World Health Organization (India Country Office) and Government of India for providing financial assistance. References 1. Mishra A. Central obesity: Origin and relevance. In: The metabolic syndrome, Seventh Annual Symposium, New Delhi, December New Delhi: Ranbaxy Science Foundation. 2. World Health Organization. Reducing risks, promoting healthy life - The World Health Report. Geneva: World Health Organization; Welborn TA, Dhaliwal SS, Bennett SA. Waist-hip ratio is the dominant risk factor predicting cardiovascular death in Australia. Med J Aust 2003; 179 : Ko GT, Chan JC, Cockram CS, Woo J. Prediction of hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidaemia or albuminuria using simple anthropometric indexes in Hong Kong Chinese. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1999; 23 : Dalton M, Cameron AJ, Zimmet PZ, Shaw JE, Jolley D, Dunstan DW, et al. Waist circumference, waist-hip ratio and body mass index and their correlation with cardiovascular disease risk factors in Australian adults. J Intern Med 2003; 254 : World Health Organization. Hypertension control. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 1996 (Tech Rep Ser. No. 862). 7. Bose K, Ghosh A, Roy S, Gangopadhyay S. Blood pressure and waist circumference: an empirical study of the effcts of waist circumference on blood pressure among Bengalee male jute workers of Belur, West Bengal, India. J Physiol Anthropol Appl Human Sci 2003; 22 : Shanthirani CS, Pradeepa R, Deepa R, Premalatha G, Saroja R, Mohan V. Prevalence and risk factors of hypertension in selected South Indian population - the Chennai Urban Population Study. J Assoc Physicians India 2003; 51 : Gupta R, Mehrishi S. Waist-hip ratio and blood pressure correlation in an urban Indian population. J Indian Med Assoc 1997; 95 : Bennet S. A simplified general method for cluster - sample surveys of health in developing countries. World Health Stat Q 1991; 44 : Luepker RV, Evans A, McKeigue P, Reddy KS. Cardiovascular survey methods. 3 rd ed. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2004 p JNC VII Express: Prevention, detection, evaluation and treatment of high blood pressure. Available at Accessed on November 15, Jellife DB, Jellife EF, editors. Community nutritional assessment with special reference to less technically developed countries, 1st ed. New York: Oxford Press; 1989 p World Health Organization. The Asia-Pacific perspective: Redefining obesity and its treatment. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; Webb GP. Nutrition: A health promotion approach. 2 nd ed. London: Arnold Publishers; 2002 p Hsieh SD, Muto T. A simple and practical index for assessing the risk of metabolic syndrome during routine health checkups. Nippon Rinsho 2004; 62 : Herbert R. Confidence Interval Calculator (v4, November 2002) CIcalculator.xls. Accessed on September 14, Pi-Sunyer FX. Medical hazards of obesity. Ann Intern Med 1993; 119 : Fang F, Nie J. Study of body mass index and waist circumference in association with blood pressure in adult Guangzhou residents. Di Yi Jun Yi Da Xue Xue Bao 2003; 23 : Wilsgaard T, Schirmer H, Arnesen E. Impact of body weight on blood pressure with a focus on sex differences: the Tromso Study, Arch Intern Med 2000; 160 : Gryglewska B, Grodzicki T, Kocemba J. Obesity and blood pressure in the elderly free-living population. J Hum Hypertens 1998; 12 : Zhao LC, Wu YF, Zhou BF, Li Y, Yang J. Mean level of blood pressure and rate of hypertension among people with different levels of body mass index and waist circumference. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi 2003; 24 : Doll S, Paccaud F, Bovet P, Burnier M, Wietlisbach V. Body mass index, abdominal adiposity and blood pressure: consistency of their association across developing and developed countries. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2002; 26 :
8 664 INDIAN J MED RES, MAY Shahbazpour N. Prevalence of overweight and obesity and their relation to hypertension in adult male university students in Kerman, Iran. Int J Endocrinol Metab 2003; 2 : Hsieh SD, Yoshinaga H, Muto T, Sakurai Y, Kosaka K. Health risks among Japanese men with moderate body mass index. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2000; 24 : Seidell JC, Cigolini M, Deslypere JP, Charzewska J, Ellsinger BM, Cruz A. Body fat distribution in relation to serum lipids and blood pressure in 38-year-old European men: the European fat distribution study. Atherosclerosis 1991; 86 : Gus M, Fuchs SC, Moreira LB, Moraes RS, Wiehe M, Silva AF, et al. Association between different measurements of obesity and the incidence of hypertension. Am J Hypertens 2004; 17 : Assmann G, editor. Lipid metabolism disorders and coronary heart disease: primary prevention, diagnosis, and therapy guidelines for general practice. 2 nd ed. Munich: MMV Medizin Verlag; 1993 p Bonorra E, Zenere M, Branzi P, Bagnani M, Maggiulli L, Tosi F, et al. Influence of body fat and its regional localization on risk factors for atherosclerosis in young men. Am J Epidemiol 1992; 135 : Woo J, Ho SC, Yu AL, Sham A. Is waist circumference a useful measure in predicting health outcomes in the elderly? Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2002; 26 : Wang W, Wang K, Li T, Xiang H, Ma L, Fu Z, et al. A discussion on utility and purposed value of obesity and abdomen obesity when body mass index, waist circumference, waist to hip ratio used as indexes predicting hypertension and hyper-blood glucose. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi 2002; 23 : Janssen I, Katzmarzyk PT, Ross R. Body mass index, waist circumference, and health risk: evidence in support of current National Institutes of Health guidelines. Arch Intern Med 2002; 162 : Sayeed MA, Mahtab H, Latif ZA, Khanam PA, Ahsan KA, Banu A, et al. Waist-to-height ratio is a better obesity index than body mass index and waist-to-hip ratio for predicting diabetes, hypertension and lipidemia. Bangladesh Med Res Counc Bull 2003; 29 : Lin WY, Lee LT, Chen CY, Lo H, Hsia HH, Liu IL, et al. Optimal cutoff values for obesity: using simple anthropometric indices to predict cardiovascular risk factors in Taiwan. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2002; 26 : Zhang X, Shu XO, Gao YT, Yang G, Matthews CE, Li Q, et al. Anthropometric predictors of coronary heart disease in Chinese women. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2004; 28 : Stevens J, Cai J, Pamuk ER, Williamson DF, Thun MJ, Wood JL. The effect of age on the association between body mass index and mortality. N Engl J Med 1998; 338 : de Onis M, Habicht JP. Anthropometric reference data for international use: Recommendations form World Health Organization Expert Committee. Am J Clin Nutr 1996; 64 : Snehalata C, Vishwanathan V, Ramachandran A. Cutoff values for normal anthropometric variables in Asian Indian Adults. Diabetes Care 2003; 26 : Ramachandran A, Snehalata C, Dharmaraj D, Vishwanathan M. Prevalence of glucose intolerance in Asian Indians: urban-rural difference and significance of upper body adiposity. Diabetes Care 1992; 15 : Dudeja V, Mishra A, Pandey RM, Devina G, Kumar G, Vikram NK. BMI does not accurately predict overweight in Asian Indians in Northern India. Br J Nutr 2001; 86 : Banerji MA, Faridi N, Atluri R, Chaiken RL, Lebovitz HE. Body composition, visceral fat, leptin and insulin resistance in Asian Indian men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1999; 84 : Reprint requests: Dr P.R. Deshmukh, Reader in Epidemiology, Department of Community Medicine Mahatma Gandhi Institute of Medical Sciences, Sewagram, Wardha , India prd_wda@sancharnet.in
The Prevalence and Determinants of Undiagnosed and Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes in Middle-Aged Irish Adults
 The Prevalence and Determinants of Undiagnosed and Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes in Middle-Aged Irish Adults Seán R. Millar, Jennifer M. O Connor, Claire M. Buckley, Patricia M. Kearney, Ivan J. Perry Email:
The Prevalence and Determinants of Undiagnosed and Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes in Middle-Aged Irish Adults Seán R. Millar, Jennifer M. O Connor, Claire M. Buckley, Patricia M. Kearney, Ivan J. Perry Email:
Ethnic Differences in the BMI-Hypertension Relation Bell et al. Ethnic Differences in the Association between Body Mass Index and Hypertension
 American Journal of Epidemiology Copyright 2002 by the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health All rights reserved Vol. 155, No. 4 Printed in U.S.A. Ethnic Differences in the BMI-Hypertension Relation
American Journal of Epidemiology Copyright 2002 by the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health All rights reserved Vol. 155, No. 4 Printed in U.S.A. Ethnic Differences in the BMI-Hypertension Relation
Examining the Validity of the Body Mass Index Cut-Off Score for Obesity of Different Ethnicities
 Volume 2, Issue 1, 2008 Examining the Validity of the Body Mass Index Cut-Off Score for Obesity of Different Ethnicities Liette B. Ocker, Assistant Professor, Texas A&M University-Corpus Christi, liette.ocker@tamucc.edu
Volume 2, Issue 1, 2008 Examining the Validity of the Body Mass Index Cut-Off Score for Obesity of Different Ethnicities Liette B. Ocker, Assistant Professor, Texas A&M University-Corpus Christi, liette.ocker@tamucc.edu
Clinical Research on Lifestyle Interventions to Treat Obesity and Asthma in Primary Care Jun Ma, M.D., Ph.D.
 Clinical Research on Lifestyle Interventions to Treat Obesity and Asthma in Primary Care Jun Ma, M.D., Ph.D. Associate Investigator Palo Alto Medical Foundation Research Institute Consulting Assistant
Clinical Research on Lifestyle Interventions to Treat Obesity and Asthma in Primary Care Jun Ma, M.D., Ph.D. Associate Investigator Palo Alto Medical Foundation Research Institute Consulting Assistant
Renal cell carcinoma and body composition:
 Renal cell carcinoma and body composition: Results from a case-control control study Ryan P. Theis, MPH Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics College of Public Health and Health Professions University
Renal cell carcinoma and body composition: Results from a case-control control study Ryan P. Theis, MPH Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics College of Public Health and Health Professions University
Improving cardiometabolic health in Major Mental Illness
 Improving cardiometabolic health in Major Mental Illness Dr. Adrian Heald Consultant in Endocrinology and Diabetes Leighton Hospital, Crewe and Macclesfield Research Fellow, Manchester University Metabolic
Improving cardiometabolic health in Major Mental Illness Dr. Adrian Heald Consultant in Endocrinology and Diabetes Leighton Hospital, Crewe and Macclesfield Research Fellow, Manchester University Metabolic
How To Know If You Have Microalbuminuria
 3 PREVALENCE AND PREDICTORS OF MICROALBUMINURIA IN PATIENTS WITH TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS: A CROSS-SECTIONAL OBSERVATIONAL STUDY Dr Ashok S Goswami *, Dr Janardan V Bhatt**; Dr Hitesh Patel *** *Associate
3 PREVALENCE AND PREDICTORS OF MICROALBUMINURIA IN PATIENTS WITH TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS: A CROSS-SECTIONAL OBSERVATIONAL STUDY Dr Ashok S Goswami *, Dr Janardan V Bhatt**; Dr Hitesh Patel *** *Associate
The Link Between Obesity and Diabetes The Rapid Evolution and Positive Results of Bariatric Surgery
 The Link Between Obesity and Diabetes The Rapid Evolution and Positive Results of Bariatric Surgery Michael E. Farkouh, MD, MSc Peter Munk Chair in Multinational Clinical Trials Director, Heart and Stroke
The Link Between Obesity and Diabetes The Rapid Evolution and Positive Results of Bariatric Surgery Michael E. Farkouh, MD, MSc Peter Munk Chair in Multinational Clinical Trials Director, Heart and Stroke
General and Abdominal Adiposity and Risk of Death in Europe
 Deutsches Institut für Ernährungsforschung Potsdam-Rehbrücke General and Abdominal Adiposity and Risk of Death in Europe Tobias Pischon Department of Epidemiology German Institute of Human Nutrition Potsdam-Rehbruecke
Deutsches Institut für Ernährungsforschung Potsdam-Rehbrücke General and Abdominal Adiposity and Risk of Death in Europe Tobias Pischon Department of Epidemiology German Institute of Human Nutrition Potsdam-Rehbruecke
Hypertension and Diabetes Status. 2011 Bangladesh Demographic and Health Survey
 Hypertension and Diabetes Status 2011 Bangladesh Demographic and Health Survey Methodology and Sampling Total 18,000 households were selected nationwide (207 in urban and 393 in rural areas) One-third
Hypertension and Diabetes Status 2011 Bangladesh Demographic and Health Survey Methodology and Sampling Total 18,000 households were selected nationwide (207 in urban and 393 in rural areas) One-third
Mortality Associated with Diabetes
 Mortality Associated with Diabetes A review paper prepared for the 7th Global Conference of Actuaries, New Delhi, 15-16 February, 2005 Dr. David Muiry, MB;BS, FIA, FASI David_Muiry@swissre.com Introduction
Mortality Associated with Diabetes A review paper prepared for the 7th Global Conference of Actuaries, New Delhi, 15-16 February, 2005 Dr. David Muiry, MB;BS, FIA, FASI David_Muiry@swissre.com Introduction
Role of Body Weight Reduction in Obesity-Associated Co-Morbidities
 Obesity Role of Body Weight Reduction in JMAJ 48(1): 47 1, 2 Hideaki BUJO Professor, Department of Genome Research and Clinical Application (M6) Graduate School of Medicine, Chiba University Abstract:
Obesity Role of Body Weight Reduction in JMAJ 48(1): 47 1, 2 Hideaki BUJO Professor, Department of Genome Research and Clinical Application (M6) Graduate School of Medicine, Chiba University Abstract:
The WHI 12 Years Later: What Have We Learned about Postmenopausal HRT?
 AACE 23 rd Annual Scientific and Clinical Congress (2014) Syllabus Materials: The WHI 12 Years Later: What Have We Learned about Postmenopausal HRT? JoAnn E. Manson, MD, DrPH, FACP, FACE Chief, Division
AACE 23 rd Annual Scientific and Clinical Congress (2014) Syllabus Materials: The WHI 12 Years Later: What Have We Learned about Postmenopausal HRT? JoAnn E. Manson, MD, DrPH, FACP, FACE Chief, Division
Appraisal of risk factors for diabetes mellitus type 2 in central Indian population: a case control study
 Physical Anthropology 103-110 Appraisal of risk factors for diabetes mellitus type 2 in central Indian population: a case control study Rama Lakshmi G. 1, Bandyopadhyay S.S. 1, Bhaskar L.V.K.S. 2, Sharma
Physical Anthropology 103-110 Appraisal of risk factors for diabetes mellitus type 2 in central Indian population: a case control study Rama Lakshmi G. 1, Bandyopadhyay S.S. 1, Bhaskar L.V.K.S. 2, Sharma
Metabolic Syndrome Overview: Easy Living, Bitter Harvest. Sabrina Gill MD MPH FRCPC Caroline Stigant MD FRCPC BC Nephrology Days, October 2007
 Metabolic Syndrome Overview: Easy Living, Bitter Harvest Sabrina Gill MD MPH FRCPC Caroline Stigant MD FRCPC BC Nephrology Days, October 2007 Evolution of Metabolic Syndrome 1923: Kylin describes clustering
Metabolic Syndrome Overview: Easy Living, Bitter Harvest Sabrina Gill MD MPH FRCPC Caroline Stigant MD FRCPC BC Nephrology Days, October 2007 Evolution of Metabolic Syndrome 1923: Kylin describes clustering
Sedentarity and Exercise in the Canadian Population. Angelo Tremblay Division of kinesiology
 Sedentarity and Exercise in the Canadian Population Angelo Tremblay Division of kinesiology Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest Évolution de la pratique d activité physique des adultes canadiens
Sedentarity and Exercise in the Canadian Population Angelo Tremblay Division of kinesiology Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest Évolution de la pratique d activité physique des adultes canadiens
BMJ Open. Secondary Subject Heading: Epidemiology, Public health, Cardiovascular medicine
 Waist circumference values equivalent to body mass index points for predicting absolute cardiovascular disease risks among adults in an Aboriginal Australian community: a prospective cohort study. Journal:
Waist circumference values equivalent to body mass index points for predicting absolute cardiovascular disease risks among adults in an Aboriginal Australian community: a prospective cohort study. Journal:
Adult obesity and overweight
 Adult obesity and overweight 9 Rachel Scantlebury and Alison Moody Summary This chapter presents measured height, weight, and waist circumference in participants aged 16 and over in 14. The main focus
Adult obesity and overweight 9 Rachel Scantlebury and Alison Moody Summary This chapter presents measured height, weight, and waist circumference in participants aged 16 and over in 14. The main focus
1. PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF METABOLIC SYNDROME
 1. PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF METABOLIC SYNDROME Izet Aganović, Tina Dušek Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Endocrinology, University Hospital Center Zagreb, Croatia 1 Introduction The metabolic syndrome
1. PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF METABOLIC SYNDROME Izet Aganović, Tina Dušek Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Endocrinology, University Hospital Center Zagreb, Croatia 1 Introduction The metabolic syndrome
Appendix: Description of the DIETRON model
 Appendix: Description of the DIETRON model Much of the description of the DIETRON model that appears in this appendix is taken from an earlier publication outlining the development of the model (Scarborough
Appendix: Description of the DIETRON model Much of the description of the DIETRON model that appears in this appendix is taken from an earlier publication outlining the development of the model (Scarborough
How Do You Recognize the BMI Diagnosis of Obesity?
 Virtual Mentor American Medical Association Journal of Ethics April 2010, Volume 12, Number 4: 292-298. CLINICAL PEARL Diagnosing Obesity: Beyond BMI Francisco Lopez-Jimenez, MD, MSc, and William R. Miranda,
Virtual Mentor American Medical Association Journal of Ethics April 2010, Volume 12, Number 4: 292-298. CLINICAL PEARL Diagnosing Obesity: Beyond BMI Francisco Lopez-Jimenez, MD, MSc, and William R. Miranda,
Family history of type 2 diabetes and prevalence of metabolic syndrome in adult Asian Indians
 JCDR Original Article Family history of type 2 diabetes and prevalence of metabolic syndrome in adult Asian Indians Mithun Das, Susil Pal 1, Arnab Ghosh 2 Department of Anthropology, Sree Chaitanya College,
JCDR Original Article Family history of type 2 diabetes and prevalence of metabolic syndrome in adult Asian Indians Mithun Das, Susil Pal 1, Arnab Ghosh 2 Department of Anthropology, Sree Chaitanya College,
Protein Intake in Potentially Insulin Resistant Adults: Impact on Glycemic and Lipoprotein Profiles - NPB #01-075
 Title: Protein Intake in Potentially Insulin Resistant Adults: Impact on Glycemic and Lipoprotein Profiles - NPB #01-075 Investigator: Institution: Gail Gates, PhD, RD/LD Oklahoma State University Date
Title: Protein Intake in Potentially Insulin Resistant Adults: Impact on Glycemic and Lipoprotein Profiles - NPB #01-075 Investigator: Institution: Gail Gates, PhD, RD/LD Oklahoma State University Date
Diabetes Prevention in Latinos
 Diabetes Prevention in Latinos Matthew O Brien, MD, MSc Assistant Professor of Medicine and Public Health Northwestern Feinberg School of Medicine Institute for Public Health and Medicine October 17, 2013
Diabetes Prevention in Latinos Matthew O Brien, MD, MSc Assistant Professor of Medicine and Public Health Northwestern Feinberg School of Medicine Institute for Public Health and Medicine October 17, 2013
Hôpitaux Universitaires de Genève Lipides, métabolisme des hydrates de carbonne et maladies cardio-vasculaires
 Hôpitaux Universitaires de Genève Lipides, métabolisme des hydrates de carbonne et maladies cardio-vasculaires Prof. J. Philippe Effect of estrogens on glucose metabolism : Fasting Glucose, HbA1c and C-Peptide
Hôpitaux Universitaires de Genève Lipides, métabolisme des hydrates de carbonne et maladies cardio-vasculaires Prof. J. Philippe Effect of estrogens on glucose metabolism : Fasting Glucose, HbA1c and C-Peptide
CHEM 1406 BSA/BMI Measurement Laboratory (revised 01/03//06) BSA, Body Surface Area
 CHEM 1406 BSA/BMI (revised 01/03//06) BSA, Body Surface Area See pages 105-110 of dosage text for equations, calculations and adult nomogram See pages 270-273 of dosage calculation text for pediatric nomogram
CHEM 1406 BSA/BMI (revised 01/03//06) BSA, Body Surface Area See pages 105-110 of dosage text for equations, calculations and adult nomogram See pages 270-273 of dosage calculation text for pediatric nomogram
How To Determine The Prevalence Of Microalbuminuria
 Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences Prevalence of Microalbuminuria in relation to HbA1c among known Type2 Diabetic Patients in Puducherry population Muraliswaran P 1 *,
Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences Prevalence of Microalbuminuria in relation to HbA1c among known Type2 Diabetic Patients in Puducherry population Muraliswaran P 1 *,
Obstructive sleep apnea and type 2 diabetes Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) may contribute to or exacerbate type 2 diabetes for some of your patients.
 Obstructive sleep apnea and type 2 diabetes Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) may contribute to or exacerbate type 2 diabetes for some of your patients. Prevalence of OSA and diabetes Prevalence of OSA Five
Obstructive sleep apnea and type 2 diabetes Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) may contribute to or exacerbate type 2 diabetes for some of your patients. Prevalence of OSA and diabetes Prevalence of OSA Five
AusDiab 2005. The Australian Diabetes, Obesity and Lifestyle Study. Tracking the Accelerating Epidemic: Its Causes and Outcomes
 AusDiab 2005 The Australian Diabetes, Obesity and Lifestyle Study Tracking the Accelerating Epidemic: Its Causes and Outcomes AusDiab 2005 The Australian Diabetes, Obesity and Lifestyle Study Tracking
AusDiab 2005 The Australian Diabetes, Obesity and Lifestyle Study Tracking the Accelerating Epidemic: Its Causes and Outcomes AusDiab 2005 The Australian Diabetes, Obesity and Lifestyle Study Tracking
DIET AND EXERCISE STRATEGIES FOR WEIGHT LOSS AND WEIGHT MAINTENANCE
 DIET AND EXERCISE STRATEGIES FOR WEIGHT LOSS AND WEIGHT MAINTENANCE 40 yo woman, BMI 36. Motivated to begin diet therapy. Which of the following is contraindicated: Robert B. Baron MD MS Professor and
DIET AND EXERCISE STRATEGIES FOR WEIGHT LOSS AND WEIGHT MAINTENANCE 40 yo woman, BMI 36. Motivated to begin diet therapy. Which of the following is contraindicated: Robert B. Baron MD MS Professor and
Multiple comorbidities: additive and predictive of cardiovascular risk. Peter M. Nilsson Lund University University Hospital Malmö, Sweden
 Multiple comorbidities: additive and predictive of cardiovascular risk Peter M. Nilsson Lund University University Hospital Malmö, Sweden Clinical outcomes: major complications of CVD Heart Attack/ACS
Multiple comorbidities: additive and predictive of cardiovascular risk Peter M. Nilsson Lund University University Hospital Malmö, Sweden Clinical outcomes: major complications of CVD Heart Attack/ACS
Epidemiology of hypertension and its risk factors in a village of west Bengal
 Original Research Paper IJRRMS 03;3(3) Epidemiology of hypertension and its risk factors in a village of west Bengal Basu G, Biswas S ABSTRACT Background: Hypertension is a leading public health problem
Original Research Paper IJRRMS 03;3(3) Epidemiology of hypertension and its risk factors in a village of west Bengal Basu G, Biswas S ABSTRACT Background: Hypertension is a leading public health problem
Body Mass Index as a measure of obesity
 Body Mass Index as a measure of obesity June 2009 Executive summary Body Mass Index (BMI) is a person s weight in kilograms divided by the square of their height in metres. It is one of the most commonly
Body Mass Index as a measure of obesity June 2009 Executive summary Body Mass Index (BMI) is a person s weight in kilograms divided by the square of their height in metres. It is one of the most commonly
Obesity in the United States Workforce. Findings from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (NHANES) III and 1999-2000
 P F I Z E R F A C T S Obesity in the United States Workforce Findings from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (NHANES) III and 1999-2000 p p Obesity in The United States Workforce One
P F I Z E R F A C T S Obesity in the United States Workforce Findings from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (NHANES) III and 1999-2000 p p Obesity in The United States Workforce One
Men Sexual Dysfunction Associated with Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome
 Men Sexual Dysfunction Associated with Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome By Aly A. Abbassy, MD, FACE Professor of Medicine (Endocrinology) Alexandria University My Talk will include: 1-Types of Men sexual
Men Sexual Dysfunction Associated with Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome By Aly A. Abbassy, MD, FACE Professor of Medicine (Endocrinology) Alexandria University My Talk will include: 1-Types of Men sexual
HEALTH MANAGEMENT PLAN PROGRAMME
 HEALTH MANAGEMENT PLAN PROGRAMME Medical Controls for Referees and Candidates The FIVB believes that Referees and Referees Candidates health is very important therefore in accordance with the Medical and
HEALTH MANAGEMENT PLAN PROGRAMME Medical Controls for Referees and Candidates The FIVB believes that Referees and Referees Candidates health is very important therefore in accordance with the Medical and
ADVANCE: a factorial randomised trial of blood pressure lowering and intensive glucose control in 11,140 patients with type 2 diabetes
 ADVANCE: a factorial randomised trial of blood pressure lowering and intensive glucose control in 11,140 patients with type 2 diabetes Effects of a fixed combination of the ACE inhibitor, perindopril,
ADVANCE: a factorial randomised trial of blood pressure lowering and intensive glucose control in 11,140 patients with type 2 diabetes Effects of a fixed combination of the ACE inhibitor, perindopril,
Life Style and Nutritional Profile of Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus (NIDDM) Patients
 Life Style and Nutritional Profile of Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus (NIDDM) Patients Kaur, I. P. and Kalra, R. Govt. College for Girls, Patiala-147001, Punjab, India Abstract The present investigation
Life Style and Nutritional Profile of Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus (NIDDM) Patients Kaur, I. P. and Kalra, R. Govt. College for Girls, Patiala-147001, Punjab, India Abstract The present investigation
The first endoscopically-delivered device therapy for obese patients with type 2 diabetes
 DIABETES WEIGHT ENDOBARRIER THERAPY The first endoscopically-delivered device therapy for obese patients with type 2 diabetes Restore the metabolic health of your patients with EndoBarrier Therapy. Dual
DIABETES WEIGHT ENDOBARRIER THERAPY The first endoscopically-delivered device therapy for obese patients with type 2 diabetes Restore the metabolic health of your patients with EndoBarrier Therapy. Dual
Boehringer Ingelheim- sponsored Satellite Symposium. HCV Beyond the Liver
 Boehringer Ingelheim- sponsored Satellite Symposium HCV Beyond the Liver HCV AS A METABOLIC MODIFIER: STEATOSIS AND INSULIN RESISTANCE Francesco Negro University Hospital of Geneva Switzerland Clinical
Boehringer Ingelheim- sponsored Satellite Symposium HCV Beyond the Liver HCV AS A METABOLIC MODIFIER: STEATOSIS AND INSULIN RESISTANCE Francesco Negro University Hospital of Geneva Switzerland Clinical
Mortality Assessment Technology: A New Tool for Life Insurance Underwriting
 Mortality Assessment Technology: A New Tool for Life Insurance Underwriting Guizhou Hu, MD, PhD BioSignia, Inc, Durham, North Carolina Abstract The ability to more accurately predict chronic disease morbidity
Mortality Assessment Technology: A New Tool for Life Insurance Underwriting Guizhou Hu, MD, PhD BioSignia, Inc, Durham, North Carolina Abstract The ability to more accurately predict chronic disease morbidity
Prevalence and determinants of diabetes among the elderly population in the Kathmandu Valley of Nepal
 Original Article Nepal Med Coll J 2009; 11(1): 34-38 Prevalence and determinants of diabetes among the elderly population in the Kathmandu Valley of Nepal MR Chhetri 1,2 and RS Chapman 1 1 College of Public
Original Article Nepal Med Coll J 2009; 11(1): 34-38 Prevalence and determinants of diabetes among the elderly population in the Kathmandu Valley of Nepal MR Chhetri 1,2 and RS Chapman 1 1 College of Public
Losing Weight in Singapore - Public Perception of Obesity
 Singapore Med J 2012; 53(2) : 104 Public perceptions of obesity and bariatric surgery in Singapore: a pilot study Teo EY 1, MBBS, MRCP, Lew PS 2, MBBS, Foo CS 2, FRCS, FAMS Introduction Obesity is a real
Singapore Med J 2012; 53(2) : 104 Public perceptions of obesity and bariatric surgery in Singapore: a pilot study Teo EY 1, MBBS, MRCP, Lew PS 2, MBBS, Foo CS 2, FRCS, FAMS Introduction Obesity is a real
Kansas Behavioral Health Risk Bulletin
 Kansas Behavioral Health Risk Bulletin Kansas Department of Health and Environment November 7, 1995 Bureau of Chronic Disease and Health Promotion Vol. 1 No. 12 Diabetes Mellitus in Kansas Diabetes mellitus
Kansas Behavioral Health Risk Bulletin Kansas Department of Health and Environment November 7, 1995 Bureau of Chronic Disease and Health Promotion Vol. 1 No. 12 Diabetes Mellitus in Kansas Diabetes mellitus
Body Mass Index and Calorie Intake
 The Science of Nutrition Laboratory Science 70 Body Mass Index and Calorie Intake One of the easiest ways to assess if you are healthy weight is to measure your body mass index (BMI). The BMI is a calculation
The Science of Nutrition Laboratory Science 70 Body Mass Index and Calorie Intake One of the easiest ways to assess if you are healthy weight is to measure your body mass index (BMI). The BMI is a calculation
DIABETES YOUR GUIDE TO
 YOUR GUIDE TO DIABETES b What is diabetes? b Type 2 diabetes prevention b Prevention checklist b Living with diabetes b Complications b Terms to know b Resources To promote and protect the health of Canadians
YOUR GUIDE TO DIABETES b What is diabetes? b Type 2 diabetes prevention b Prevention checklist b Living with diabetes b Complications b Terms to know b Resources To promote and protect the health of Canadians
NHS Diabetes Prevention Programme (NHS DPP) Non-diabetic hyperglycaemia. Produced by: National Cardiovascular Intelligence Network (NCVIN)
 NHS Diabetes Prevention Programme (NHS DPP) Non-diabetic hyperglycaemia Produced by: National Cardiovascular Intelligence Network (NCVIN) Date: August 2015 About Public Health England Public Health England
NHS Diabetes Prevention Programme (NHS DPP) Non-diabetic hyperglycaemia Produced by: National Cardiovascular Intelligence Network (NCVIN) Date: August 2015 About Public Health England Public Health England
A Fuzzy Logic Based Model for Life Insurance Underwriting When Insurer Is Diabetic
 European Journal of Applied Sciences 4 (5): 196-202, 2012 ISSN 2079-2077 IDOSI Publications, 2012 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.ejas.2012.4.5.2027 A Fuzzy Logic Based Model for Life Insurance Underwriting When Insurer
European Journal of Applied Sciences 4 (5): 196-202, 2012 ISSN 2079-2077 IDOSI Publications, 2012 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.ejas.2012.4.5.2027 A Fuzzy Logic Based Model for Life Insurance Underwriting When Insurer
HYPOTHESIS TESTING (ONE SAMPLE) - CHAPTER 7 1. used confidence intervals to answer questions such as...
 HYPOTHESIS TESTING (ONE SAMPLE) - CHAPTER 7 1 PREVIOUSLY used confidence intervals to answer questions such as... You know that 0.25% of women have red/green color blindness. You conduct a study of men
HYPOTHESIS TESTING (ONE SAMPLE) - CHAPTER 7 1 PREVIOUSLY used confidence intervals to answer questions such as... You know that 0.25% of women have red/green color blindness. You conduct a study of men
Barriers to Healthcare Services for People with Mental Disorders. Cardiovascular disorders and diabetes in people with severe mental illness
 Barriers to Healthcare Services for People with Mental Disorders Cardiovascular disorders and diabetes in people with severe mental illness Dr. med. J. Cordes LVR- Klinikum Düsseldorf Kliniken der Heinrich-Heine-Universität
Barriers to Healthcare Services for People with Mental Disorders Cardiovascular disorders and diabetes in people with severe mental illness Dr. med. J. Cordes LVR- Klinikum Düsseldorf Kliniken der Heinrich-Heine-Universität
EXPANDING THE EVIDENCE BASE IN OUTCOMES RESEARCH: USING LINKED ELECTRONIC MEDICAL RECORDS (EMR) AND CLAIMS DATA
 EXPANDING THE EVIDENCE BASE IN OUTCOMES RESEARCH: USING LINKED ELECTRONIC MEDICAL RECORDS (EMR) AND CLAIMS DATA A CASE STUDY EXAMINING RISK FACTORS AND COSTS OF UNCONTROLLED HYPERTENSION ISPOR 2013 WORKSHOP
EXPANDING THE EVIDENCE BASE IN OUTCOMES RESEARCH: USING LINKED ELECTRONIC MEDICAL RECORDS (EMR) AND CLAIMS DATA A CASE STUDY EXAMINING RISK FACTORS AND COSTS OF UNCONTROLLED HYPERTENSION ISPOR 2013 WORKSHOP
Absolute cardiovascular disease risk assessment
 Quick reference guide for health professionals Absolute cardiovascular disease risk assessment This quick reference guide is a summary of the key steps involved in assessing absolute cardiovascular risk
Quick reference guide for health professionals Absolute cardiovascular disease risk assessment This quick reference guide is a summary of the key steps involved in assessing absolute cardiovascular risk
Body Composition & Longevity. Ohan Karatoprak, MD, AAFP Clinical Assistant Professor, UMDNJ
 Body Composition & Longevity Ohan Karatoprak, MD, AAFP Clinical Assistant Professor, UMDNJ LONGEVITY Genetic 25% Environmental Lifestyle Stress 75% BMI >30 OBESE 25-30 OVERWEIGHT 18-25 NORMAL WEIGHT 18
Body Composition & Longevity Ohan Karatoprak, MD, AAFP Clinical Assistant Professor, UMDNJ LONGEVITY Genetic 25% Environmental Lifestyle Stress 75% BMI >30 OBESE 25-30 OVERWEIGHT 18-25 NORMAL WEIGHT 18
Original Research Paper
 1 of 6 Original Research Paper Age at diagnosis and family history in Type II diabetes: implications for office screening Ching-Ye Hong MBBS, MCGP, FAFP, FRACGP Kee-Seng Chia MBBS, MSc (OM), MD Ching-Ye
1 of 6 Original Research Paper Age at diagnosis and family history in Type II diabetes: implications for office screening Ching-Ye Hong MBBS, MCGP, FAFP, FRACGP Kee-Seng Chia MBBS, MSc (OM), MD Ching-Ye
Diabetes and Hypertension Care For Adults in Primary Care Settings
 and Hypertension Care For Adults in Primary Care Settings What is Type 2? The carbohydrates including sugar and starch which we take become glucose after digestion. It will then be absorbed by the small
and Hypertension Care For Adults in Primary Care Settings What is Type 2? The carbohydrates including sugar and starch which we take become glucose after digestion. It will then be absorbed by the small
Obesity and ethnicity
 Obesity and ethnicity January 2011 NOO Obesity and ethnicity 2 NOO is delivered by Solutions for Public Health Contents Executive summary...3 Introduction...3 Defining ethnicity...4 Population overview...4
Obesity and ethnicity January 2011 NOO Obesity and ethnicity 2 NOO is delivered by Solutions for Public Health Contents Executive summary...3 Introduction...3 Defining ethnicity...4 Population overview...4
Psoriasis Co-morbidities: Changing Clinical Practice. Theresa Schroeder Devere, MD Assistant Professor, OHSU Dermatology. Psoriatic Arthritis
 Psoriasis Co-morbidities: Changing Clinical Practice Theresa Schroeder Devere, MD Assistant Professor, OHSU Dermatology Psoriatic Arthritis Psoriatic Arthritis! 11-31% of patients with psoriasis have psoriatic
Psoriasis Co-morbidities: Changing Clinical Practice Theresa Schroeder Devere, MD Assistant Professor, OHSU Dermatology Psoriatic Arthritis Psoriatic Arthritis! 11-31% of patients with psoriasis have psoriatic
Client Sex Facility Birth Date Height Weight Measured Sample Client Male (not specified) 00/00/0000 72.0 in. 180.0 lbs. 02/20/2016
 SUMMARY RESULTS This table provides an overview of your total body composition, broken down into total body fat %, total mass, fat tissue, lean tissue, and bone mineral content. These metrics establish
SUMMARY RESULTS This table provides an overview of your total body composition, broken down into total body fat %, total mass, fat tissue, lean tissue, and bone mineral content. These metrics establish
Prescription Pattern of Anti Hypertensive Drugs used in Hypertensive Patients with Associated Type2 Diabetes Mellitus in A Tertiary Care Hospital
 Research Article Prescription Pattern of Anti Hypertensive Drugs used in Hypertensive Patients with Associated Type2 Diabetes Mellitus in A Tertiary Care Hospital *T. JANAGAN 1, R. KAVITHA 1, S. A. SRIDEVI
Research Article Prescription Pattern of Anti Hypertensive Drugs used in Hypertensive Patients with Associated Type2 Diabetes Mellitus in A Tertiary Care Hospital *T. JANAGAN 1, R. KAVITHA 1, S. A. SRIDEVI
Aggressive Lowering of Blood Pressure in type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: The Diastolic Cost
 Aggressive Lowering of Blood Pressure in type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: The Diastolic Cost Naftali Stern Institute of Endocrinology, Metabolism and Hypertension Tel Aviv -Sourasky Medical Center and Sackler
Aggressive Lowering of Blood Pressure in type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: The Diastolic Cost Naftali Stern Institute of Endocrinology, Metabolism and Hypertension Tel Aviv -Sourasky Medical Center and Sackler
Sanjeev Kumar 1 and Hemlata Jain 2
 IJFSRS: 5(1), June 2012, pp. 51-58, Life Insurance Serials Publications, Underwriting ISSN: when 0974-858 Insurer is Diabetic: A Fuzzy Approach 51 Sanjeev Kumar 1 and Hemlata Jain 2 1,2 Department of Mathematics,
IJFSRS: 5(1), June 2012, pp. 51-58, Life Insurance Serials Publications, Underwriting ISSN: when 0974-858 Insurer is Diabetic: A Fuzzy Approach 51 Sanjeev Kumar 1 and Hemlata Jain 2 1,2 Department of Mathematics,
Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial (SPRINT) Principal Results
 Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial (SPRINT) Principal Results Paul K. Whelton, MB, MD, MSc Chair, SPRINT Steering Committee Tulane University School of Public Health and Tropical Medicine, and
Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial (SPRINT) Principal Results Paul K. Whelton, MB, MD, MSc Chair, SPRINT Steering Committee Tulane University School of Public Health and Tropical Medicine, and
C-Reactive Protein and Diabetes: proving a negative, for a change?
 C-Reactive Protein and Diabetes: proving a negative, for a change? Eric Brunner PhD FFPH Reader in Epidemiology and Public Health MRC Centre for Causal Analyses in Translational Epidemiology 2 March 2009
C-Reactive Protein and Diabetes: proving a negative, for a change? Eric Brunner PhD FFPH Reader in Epidemiology and Public Health MRC Centre for Causal Analyses in Translational Epidemiology 2 March 2009
Plasma Testosterone Level in Male Patients with Metabolic Syndrome
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 77, No. 1, June: 351-357, 2009 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.com Plasma Testosterone Level in Male Patients with Metabolic Syndrome NASHWA EL-SARRAF, M.D. and AMR EL-HADIDY,
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 77, No. 1, June: 351-357, 2009 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.com Plasma Testosterone Level in Male Patients with Metabolic Syndrome NASHWA EL-SARRAF, M.D. and AMR EL-HADIDY,
Adult Weight Management Training Summary
 Adult Weight Management Training Summary The Commission on Dietetic Registration, the credentialing agency for the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics Marilyn Holmes, MS, RDN, LDN About This Presentation
Adult Weight Management Training Summary The Commission on Dietetic Registration, the credentialing agency for the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics Marilyn Holmes, MS, RDN, LDN About This Presentation
Antiretroviral treatment is Associated with increased Arterial Stiffness in Sub- Saharan African HIV-1 Infected Patients: A cross- Sectional Study
 Antiretroviral treatment is Associated with increased Arterial Stiffness in Sub- Saharan African HIV-1 Infected Patients: A cross- Sectional Study Titus F. Msoka Supervisors Marceline van Furth Yvo Smulders
Antiretroviral treatment is Associated with increased Arterial Stiffness in Sub- Saharan African HIV-1 Infected Patients: A cross- Sectional Study Titus F. Msoka Supervisors Marceline van Furth Yvo Smulders
EUROPEAN JOURNAL EPIDEMIOLOGY
 Eur. J. Epidemiol. 0392-2990 March 1993, p. 134-139 EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF EPIDEMIOLOGY Vol. 9, No. 2 HIGH BI~OOD PRESSURE AND THE INCIDENCE OF NON-INSULIN I)EPENDENT DIABETES MELI,ITUS: FINDINGS IN A 11.5
Eur. J. Epidemiol. 0392-2990 March 1993, p. 134-139 EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF EPIDEMIOLOGY Vol. 9, No. 2 HIGH BI~OOD PRESSURE AND THE INCIDENCE OF NON-INSULIN I)EPENDENT DIABETES MELI,ITUS: FINDINGS IN A 11.5
The South Asian Indian Women s s Weight Loss Study. Latha Palaniappan, MD, MS BIRCWH Scholar October 20, 2005
 The South Asian Indian Women s s Weight Loss Study Latha Palaniappan, MD, MS BIRCWH Scholar October 20, 2005 South Asian Emigrants and second generation from India Bhutan Bangladesh Maldives Nepal Pakistan
The South Asian Indian Women s s Weight Loss Study Latha Palaniappan, MD, MS BIRCWH Scholar October 20, 2005 South Asian Emigrants and second generation from India Bhutan Bangladesh Maldives Nepal Pakistan
Prevalence of Obesity among Type-2 Diabetics
 Kamla-Raj 2009 J Hum Ecol, 25(1): 31-35 (2009) Prevalence of Obesity among Type-2 Diabetics Shilpi Sharma and Shashi Jain College of Home Science, Department of Foods and Nutrition, MPUAT, Udaipur, Rajasthan,
Kamla-Raj 2009 J Hum Ecol, 25(1): 31-35 (2009) Prevalence of Obesity among Type-2 Diabetics Shilpi Sharma and Shashi Jain College of Home Science, Department of Foods and Nutrition, MPUAT, Udaipur, Rajasthan,
Session 89 WS, Around the Globe: China--Closing the Financial Gap for Cardiovascular Disease. Moderator: Audrey A. Chervansky, FSA, MAAA
 Session 89 WS, Around the Globe: China--Closing the Financial Gap for Cardiovascular Disease Moderator: Audrey A. Chervansky, FSA, MAAA Presenters: Daniel Garrett Ryan Xiaojie Wang, FSA, CERA Closing the
Session 89 WS, Around the Globe: China--Closing the Financial Gap for Cardiovascular Disease Moderator: Audrey A. Chervansky, FSA, MAAA Presenters: Daniel Garrett Ryan Xiaojie Wang, FSA, CERA Closing the
PRACTICE PROBLEMS FOR BIOSTATISTICS
 PRACTICE PROBLEMS FOR BIOSTATISTICS BIOSTATISTICS DESCRIBING DATA, THE NORMAL DISTRIBUTION 1. The duration of time from first exposure to HIV infection to AIDS diagnosis is called the incubation period.
PRACTICE PROBLEMS FOR BIOSTATISTICS BIOSTATISTICS DESCRIBING DATA, THE NORMAL DISTRIBUTION 1. The duration of time from first exposure to HIV infection to AIDS diagnosis is called the incubation period.
HYPOTHESIS TESTING (ONE SAMPLE) - CHAPTER 7 1. used confidence intervals to answer questions such as...
 HYPOTHESIS TESTING (ONE SAMPLE) - CHAPTER 7 1 PREVIOUSLY used confidence intervals to answer questions such as... You know that 0.25% of women have red/green color blindness. You conduct a study of men
HYPOTHESIS TESTING (ONE SAMPLE) - CHAPTER 7 1 PREVIOUSLY used confidence intervals to answer questions such as... You know that 0.25% of women have red/green color blindness. You conduct a study of men
Treating Patients with PRE-DIABETES David Doriguzzi, PA-C First Valley Medical Group. Learning Objectives. Background. CAPA 2015 Annual Conference
 Treating Patients with PRE-DIABETES David Doriguzzi, PA-C First Valley Medical Group Learning Objectives To accurately make the diagnosis of pre-diabetes/metabolic syndrome To understand the prevalence
Treating Patients with PRE-DIABETES David Doriguzzi, PA-C First Valley Medical Group Learning Objectives To accurately make the diagnosis of pre-diabetes/metabolic syndrome To understand the prevalence
Epidemiology of Hypertension 陈 奕 希 3120000591 李 禾 园 3120000050 王 卓 3120000613
 Epidemiology of Hypertension 陈 奕 希 3120000591 李 禾 园 3120000050 王 卓 3120000613 1 Definition Hypertension is a chronic medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is elevated. 2 Primary
Epidemiology of Hypertension 陈 奕 希 3120000591 李 禾 园 3120000050 王 卓 3120000613 1 Definition Hypertension is a chronic medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is elevated. 2 Primary
Why have new standards been developed?
 Why have new standards been developed? Fitnessgram is unique (and widely accepted) because the fitness assessments are evaluated using criterion-referenced standards. An advantage of criterion referenced
Why have new standards been developed? Fitnessgram is unique (and widely accepted) because the fitness assessments are evaluated using criterion-referenced standards. An advantage of criterion referenced
The Influence of Infant Health on Adult Chronic Disease
 The Influence of Infant Health on Adult Chronic Disease Womb to Tomb Dr Clare MacVicar Introduction Many diseases in adulthood are related to growth patterns during early life Maternal nutrition important
The Influence of Infant Health on Adult Chronic Disease Womb to Tomb Dr Clare MacVicar Introduction Many diseases in adulthood are related to growth patterns during early life Maternal nutrition important
Recommendations for Prescribing Exercise to Overweight and Obese Patients
 10 Recommendations for Prescribing Exercise to Overweight and Obese Patients 10 10 Recommendations for Prescribing Exercise to Overweight and Obese Patients Effects of Exercise The increasing prevalence
10 Recommendations for Prescribing Exercise to Overweight and Obese Patients 10 10 Recommendations for Prescribing Exercise to Overweight and Obese Patients Effects of Exercise The increasing prevalence
Original Article. Risk factors for diabetic retinopathy in selfreported rural population with diabetes
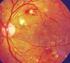 Original Article www.jpgmonline.com Risk factors for diabetic retinopathy in selfreported rural population with diabetes Rani PK, Raman R, Chandrakantan A, Pal SS, Perumal GM, Sharma T Vision Research
Original Article www.jpgmonline.com Risk factors for diabetic retinopathy in selfreported rural population with diabetes Rani PK, Raman R, Chandrakantan A, Pal SS, Perumal GM, Sharma T Vision Research
MY TYPE 2 DIABETES NUMBERS
 BLOOD SUGAR MANAGEMENT GUIDE MY TYPE 2 DIABETES NUMBERS Understanding and Tracking the ABCs of Type 2 Diabetes 1 BLOOD MY TYPE SUGAR 2 DIABETES MANAGEMENT ABC NUMBERS GUIDE When you have type 2 diabetes,
BLOOD SUGAR MANAGEMENT GUIDE MY TYPE 2 DIABETES NUMBERS Understanding and Tracking the ABCs of Type 2 Diabetes 1 BLOOD MY TYPE SUGAR 2 DIABETES MANAGEMENT ABC NUMBERS GUIDE When you have type 2 diabetes,
A prospective study on drug utilization pattern of anti-diabetic drugs in rural areas of Islampur, India
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2015, 7 (5):33-37 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2015, 7 (5):33-37 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Stand Up Australia Sedentary behaviour in workers
 Stand Up Australia behaviour in workers August 2009 Research into office-based, call centre and retail employee behaviours revealed that 77 percent of the working day is spent sitting. Individuals who
Stand Up Australia behaviour in workers August 2009 Research into office-based, call centre and retail employee behaviours revealed that 77 percent of the working day is spent sitting. Individuals who
Antipsychotic Medications and the Risk of Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease
 Antipsychotic Medications and the Risk of Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease Professional Tool #1: Screening and Monitoring in a High-Risk Population: Questions and Answers Overview of Cardiometabolic
Antipsychotic Medications and the Risk of Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease Professional Tool #1: Screening and Monitoring in a High-Risk Population: Questions and Answers Overview of Cardiometabolic
FACTORS ASSOCIATED WITH HEALTHCARE COSTS AMONG ELDERLY PATIENTS WITH DIABETIC NEUROPATHY
 FACTORS ASSOCIATED WITH HEALTHCARE COSTS AMONG ELDERLY PATIENTS WITH DIABETIC NEUROPATHY Luke Boulanger, MA, MBA 1, Yang Zhao, PhD 2, Yanjun Bao, PhD 1, Cassie Cai, MS, MSPH 1, Wenyu Ye, PhD 2, Mason W
FACTORS ASSOCIATED WITH HEALTHCARE COSTS AMONG ELDERLY PATIENTS WITH DIABETIC NEUROPATHY Luke Boulanger, MA, MBA 1, Yang Zhao, PhD 2, Yanjun Bao, PhD 1, Cassie Cai, MS, MSPH 1, Wenyu Ye, PhD 2, Mason W
HAWAI`I HEALTH SURVEY HHS INTRODUCTION 2002
 HAWAI`I HEALTH SURVEY HHS INTRODUCTION 2002 Hawai`i Department of Health Office of Health Status Monitoring Alvin T. Onaka, State Registrar, and Chief Brian Horiuchi, Supervisor Research & Statistics Honolulu,
HAWAI`I HEALTH SURVEY HHS INTRODUCTION 2002 Hawai`i Department of Health Office of Health Status Monitoring Alvin T. Onaka, State Registrar, and Chief Brian Horiuchi, Supervisor Research & Statistics Honolulu,
Karen Kovach M.S, R.D Chief Scientific Officer Weight Watchers International Inc.
 Waking up to real solutions to Chronic Disease: Tackling obesity can reduce the burden of chronic disease and deliver substantial cost savings to struggling European healthcare systems Karen Kovach M.S,
Waking up to real solutions to Chronic Disease: Tackling obesity can reduce the burden of chronic disease and deliver substantial cost savings to struggling European healthcare systems Karen Kovach M.S,
Underwriting Critical Illness Insurance: A model for coronary heart disease and stroke
 Underwriting Critical Illness Insurance: A model for coronary heart disease and stroke Presented to the 6th International Congress on Insurance: Mathematics and Economics. July 2002. Lisbon, Portugal.
Underwriting Critical Illness Insurance: A model for coronary heart disease and stroke Presented to the 6th International Congress on Insurance: Mathematics and Economics. July 2002. Lisbon, Portugal.
High Blood Cholesterol
 National Cholesterol Education Program ATP III Guidelines At-A-Glance Quick Desk Reference 1 Step 1 2 Step 2 3 Step 3 Determine lipoprotein levels obtain complete lipoprotein profile after 9- to 12-hour
National Cholesterol Education Program ATP III Guidelines At-A-Glance Quick Desk Reference 1 Step 1 2 Step 2 3 Step 3 Determine lipoprotein levels obtain complete lipoprotein profile after 9- to 12-hour
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition that occurs as a result of problems with the production and/or action of insulin in the body.
 International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Background Information Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition that occurs as a result of problems with the production and/or action of insulin in the body.
International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Background Information Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition that occurs as a result of problems with the production and/or action of insulin in the body.
THE STUDY OF NEWLY DISCOVERED CASES OF DIABETES MELLITUS IN BIHOR COUNTY
 Analele UniversităŃii din Oradea Fascicula:Ecotoxicologie, Zootehnie şi Tehnologii de Industrie Alimentară, 2012 THE STUDY OF NEWLY DISCOVERED CASES OF DIABETES MELLITUS IN BIHOR COUNTY *University of
Analele UniversităŃii din Oradea Fascicula:Ecotoxicologie, Zootehnie şi Tehnologii de Industrie Alimentară, 2012 THE STUDY OF NEWLY DISCOVERED CASES OF DIABETES MELLITUS IN BIHOR COUNTY *University of
Impact of Body Mass Index on the Incidence of Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Ambulatory Care Settings over 5 Years or Morevhe_649 265..
 Volume 13 Number 2 2010 VALUE IN HEALTH Impact of Body Mass Index on the Incidence of Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Ambulatory Care Settings over 5 Years or Morevhe_649 265..272 Qayyim Said, PhD, 1 Carrie
Volume 13 Number 2 2010 VALUE IN HEALTH Impact of Body Mass Index on the Incidence of Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Ambulatory Care Settings over 5 Years or Morevhe_649 265..272 Qayyim Said, PhD, 1 Carrie
Factors in Women Aged 35-57 Years in Khuzestan. Province of Iran
 Advanced Studies in Biology, Vol., 0, no., 7 6 Prevalence of Overweight, Obesity and the Related Factors in Women Aged -7 Years in Khuzestan Province of Iran S. Nouhjah*, M. Nadi-baghu, M. Salehi and H.
Advanced Studies in Biology, Vol., 0, no., 7 6 Prevalence of Overweight, Obesity and the Related Factors in Women Aged -7 Years in Khuzestan Province of Iran S. Nouhjah*, M. Nadi-baghu, M. Salehi and H.
Main Effect of Screening for Coronary Artery Disease Using CT
 Main Effect of Screening for Coronary Artery Disease Using CT Angiography on Mortality and Cardiac Events in High risk Patients with Diabetes: The FACTOR-64 Randomized Clinical Trial Joseph B. Muhlestein,
Main Effect of Screening for Coronary Artery Disease Using CT Angiography on Mortality and Cardiac Events in High risk Patients with Diabetes: The FACTOR-64 Randomized Clinical Trial Joseph B. Muhlestein,
BARIATRIC SURGERY. Prerequisites. Authorization, Notification and Referral
 BARIATRIC SURGERY Policy NHP reimburses participating providers for specific types of medically necessary bariatric surgery when needed to either alleviate or correct medical problems caused by severe
BARIATRIC SURGERY Policy NHP reimburses participating providers for specific types of medically necessary bariatric surgery when needed to either alleviate or correct medical problems caused by severe
Blood Pressure, Body Composition, and Fat Tissue Cellularity in Adults ROGER M. SIERVOGEL, PH.D., ALEX F. ROCHE, M.D., PH.D., D.
 Blood Pressure, Body Composition, and Fat Tissue Cellularity in Adults ROGER M. SIERVOGEL, PH.D., ALEX F. ROCHE, M.D., PH.D., D. SC, WILLIAM CAMERON CHUMLEA, PH.D., JAMES G. MORRIS, M. STAT., PAUL WEBB,
Blood Pressure, Body Composition, and Fat Tissue Cellularity in Adults ROGER M. SIERVOGEL, PH.D., ALEX F. ROCHE, M.D., PH.D., D. SC, WILLIAM CAMERON CHUMLEA, PH.D., JAMES G. MORRIS, M. STAT., PAUL WEBB,
It s just puppy fat Tackling obesity in children and adolescents
 It s just puppy fat Tackling obesity in children and adolescents Webinar, SPH, Usyd, September 2013 Louise A Baur University of Sydney: Discipline of Paediatrics & Child Health, Sydney Medical School,
It s just puppy fat Tackling obesity in children and adolescents Webinar, SPH, Usyd, September 2013 Louise A Baur University of Sydney: Discipline of Paediatrics & Child Health, Sydney Medical School,
Adherence to insulin therapy at a tertiary care diabetes center in South India
 Original Article: Adherence to insulin therapy at a tertiary care diabetes center in South India M.S. Raut, J. Balasubramanian, R.M. Anjana, R Unnikrishnan, *V. Mohan Abstract To assess patient adherence
Original Article: Adherence to insulin therapy at a tertiary care diabetes center in South India M.S. Raut, J. Balasubramanian, R.M. Anjana, R Unnikrishnan, *V. Mohan Abstract To assess patient adherence
Vascular Risk Reduction: Addressing Vascular Risk
 Vascular Risk Reduction: Addressing Vascular Risk Vascular Risk Reduction (VRR) Welcome! Presentation & Activities Focus: Managing known risk factors for vascular disease. Engage, collaborate and have
Vascular Risk Reduction: Addressing Vascular Risk Vascular Risk Reduction (VRR) Welcome! Presentation & Activities Focus: Managing known risk factors for vascular disease. Engage, collaborate and have
Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) Brief
 Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) Brief What is Coronary Heart Disease? Coronary Heart Disease (CHD), also called coronary artery disease 1, is the most common heart condition in the United States. It occurs
Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) Brief What is Coronary Heart Disease? Coronary Heart Disease (CHD), also called coronary artery disease 1, is the most common heart condition in the United States. It occurs
Control of hypertension in Nigerians with Diabetes Mellitus: A report of the Ibadan Diabetic / Kidney Disease Study Group.
 Int J Diabetes & Metabolism (2007) 15: 82-86 Control of hypertension in Nigerians with Diabetes Mellitus: A report of the Ibadan Diabetic / Kidney Disease Study Group. Ayodeji Arije, 1 Modupe Kuti, 2 Adesoji
Int J Diabetes & Metabolism (2007) 15: 82-86 Control of hypertension in Nigerians with Diabetes Mellitus: A report of the Ibadan Diabetic / Kidney Disease Study Group. Ayodeji Arije, 1 Modupe Kuti, 2 Adesoji
Connecticut Diabetes Statistics
 Connecticut Diabetes Statistics What is Diabetes? State Public Health Actions (1305, SHAPE) Grant March 2015 Page 1 of 16 Diabetes is a disease in which blood glucose levels are above normal. Blood glucose
Connecticut Diabetes Statistics What is Diabetes? State Public Health Actions (1305, SHAPE) Grant March 2015 Page 1 of 16 Diabetes is a disease in which blood glucose levels are above normal. Blood glucose
