The Oxford Shoulder Instability Score; validation in Dutch and first-time assessment of its smallest detectable change
|
|
|
- Barry Jordan
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 van der Linde et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2015) 10:146 DOI /s RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The Oxford Shoulder Instability Score; validation in Dutch and first-time assessment of its smallest detectable change Just A. van der Linde 1*, Derk A. van Kampen 2, Loes W. A. H. van Beers 1, Derek F. P. van Deurzen 1, Caroline B. Terwee 3 and W. Jaap Willems 4 Abstract Background: The Oxford Shoulder Instability Score (OSIS) is a short, self-reported outcome measurement for patients with shoulder instability. In this study, the OSIS was validated in Dutch by testing the internal consistency, reliability, measurement error, validity and the floor and ceiling effects, and its smallest detectable change (SDC) was calculated. Methods: A total of 138 patients were included. Internal consistency was calculated with Cronbach s α. Reliability (test-retest) was calculated with the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC). The measurement error was calculated (SEM), and the SDC was estimated in a subgroup of 99 patients that completed the re-test after a mean of 13 days (5 30 days). Construct validity was evaluated by comparing the OSIS with the Western Ontario Shoulder Instability index (WOSI), the Simple Shoulder Test (SST), the Oxford Shoulder Score (OSS), the Disability of the Arm, Shoulder, and Hand assessment (DASH), and the Short Form-36 (SF-36). Results: Internal consistency was good, with a Cronbach s α of The reliability was excellent, with an ICC of The SEM was 3.3 and the SDC was 9 points (on a scale of 0 48). Regarding the construct validity, 80 % of the results were in accordance with the hypotheses, including a high correlation (0.82) with the WOSI. No floor or ceiling effects were found. Conclusions: The Dutch version of the OSIS showed good reliability and validity in a cohort of patients with shoulder instability. Keywords: Validation, Oxford, Shoulder, Instability, Score, Dutch Background Shoulder instability is common in orthopedic practice; it generally affects young, active patients [1 3]. Research and evaluation of therapies for shoulder instability should focus both on objectively verifiable outcomes, such as the range of motion and re-dislocations, and on subjective functioning. A variety of patient-reported outcome measures (PROM) exist, some of which are specifically designed to reflect the patient s subjective assessment of function. They enable the practitioner to detect functional changes in a standardized format. Because * Correspondence: javdlinde@gmail.com 1 Department of Orthopedic Surgery and Traumatology, Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis, Postbus 95500, 1090 HM Amsterdam, The Netherlands Full list of author information is available at the end of the article patients and doctors do not always agree on functional outcome after therapeutic interventions [4], PROMs have become increasingly important in assessing patient health status [5]. They can focus on general health; a physical domain or body part, such as the shoulder; or a specific condition or disease, such as instability [5 7]. The Oxford Shoulder Instability Score (OSIS) is a comprehensive questionnaire including 12 questions to assess shoulder instability. With a Cronbach s α of 0.92, a Pearson correlation coefficient of 0.97 and measurement error of 5.7, the OSIS has proven to be valid and reliable, making it clinically important in patients with shoulder instability [8]. The OSIS was proven to be a useful outcome measure in several clinical studies [9 11], but 2015 van der Linde et al. Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
2 van der Linde et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2015) 10:146 Page 2 of 8 it has not been translated and validated in languages other than English. Translation and validation of internationally used PROMs will lead to culturally equivalent instruments and allow direct comparisons of national and international study results [12 14]. The aim of this study was to translate and validate the OSIS for the Dutch population and to evaluate its measurement properties according to the Consensusbased Standards for the selection of health Measurement Instruments (COSMIN) guidelines [15]. Methods Translation procedure After we obtained the official licence for the original English version, the OSIS was independently translated into Dutch by three native Dutch-speaking, medically educated translators. When they reached a consensus, a professional translator and a native English speaker (without a medical background) independently translated the version back into English; both were blinded to the first version and emphasized specifically on the linguistic aspects. Finally, the latter version was compared to the original text, composing a pre-final version. All items were agreed to be relevant for this patient population, and taken together, the items represented a comprehensive measurement of shoulder instability. The pre-final version was checked for cross-cultural differences. It was subsequently completed by 13 patients with shoulder instability that were asked independently to assess the comprehensibility of all questions. These patients were not included in our final analysis. Patients and procedures To assess the reliability and validity of the OSIS in the Dutch population, 154 patients with shoulder instability were recruited. Institutional approval was obtained by the local ethics committee; Institutional Review Board (IRB): METC, OLVG Hospital, Amsterdam, The Netherlands. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants. We planned to include at least 100 patients, which is considered excellent for assessing measurement properties [15, 16]. A total of 154 patients with shoulder instability were included; all were diagnosed by one of the doctors in the outpatient clinic or the emergency department. Patients were eligible to participate when they were 16 years or older and had been diagnosed with shoulder instability, based on their history and clinical examination. All patients were included on the ER or outpatient department of a hospital in Amsterdam. Exclusion criteria were an inability to master the Dutch language, a fracture in the glenoid, or a fracture in the humeral head. Hill-Sachs lesions and bony Bankart lesions were included. Tourists and temporary inhabitants of Amsterdam that were followed up in another clinic were also excluded, to avoid patient burden as a result of double follow-up. All patients were assigned a study number and received either a web-based questionnaire, or alternatively, an identical paper questionnaire to complete at home. The order of administration was fixed. The web-based version required answers to all questions prior to submission. Missing values in paper submissions were completed in an interview by telephone. Patients were asked to complete the questionnaire twice, without intervention. Both times, the questionnaire was either web-based or on paper. The repeated questionnaire was completed after a maximum interval of 5 to 30 days; this interval was considered long enough to forget prior answers, and short enough to assume an unchanged shoulder condition [17, 18]. Oxford Shoulder Instability Score The OSIS is a disease-specific PROM that was developed by Dawson et al. in 1999 in the UK for assessing the outcome of treatment for shoulder instability [8]. This 12-item questionnaire contained five response categories for each question. In the original scoring system, answers were scored from 1 to 5 points and summarized to a total score that ranged from 12 (least impaired) to 60 (most impaired). The scoring system was revised in 2009, in accordance with the revised scoring for the Oxford Shoulder Score (OSS), which originated in the same institute [19]. In the revised scoring system, answers were scored from 0 to 4, and the score was reversed; thus, the total score ranged from 0 (most impaired) to 48 (least impaired). We presented the results in terms of the new scoring system. The OSIS was originally validated in 92 patients with shoulder instability that against the Rowe and Constant scores, with correlations of 0.51 and 0.56, respectively. The internal consistency (Cronbach s α) was The reliability was 0.97, calculated with a Pearson correlation coefficient. The measurement error was 5.7 points, calculated with the Bland and Altman method. No intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) was calculated [8]. To date, no cross-cultural validation has been conducted. Validation instruments The following instruments were solely used to assess the construct validity of the OSIS. No other data is used from these additional questionnaires. All instruments have been validated in Dutch, with good to excellent reliability and internal consistency [17, 20 23]. Western Ontario Shoulder Instability index (WOSI) The WOSI is a disease-specific PROM for assessing the outcome of treatment for shoulder instability [24, 25].
3 van der Linde et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2015) 10:146 Page 3 of 8 Responses to the 21-item questionnaire were summarized in a total score, ranging from 0 or 0 % (no limitations) to 2100 or 100 % (extreme limitations). It has been validated in Italian, German, Swedish, Japanese and Dutch [20, 26 30]. The Dutch version was validated using the same dataset as was used for the OSIS validation. Simple Shoulder Test (SST) The SST is a body-part-specific PROM [31]. It was designed to measure functional limitations of patients with general shoulder complaints. A cumulative score is calculated based on 12 questions (yes/no) and ranges from 0 (poor) to 12 (excellent shoulder function). It was validated against the American Shoulder and Elbow Surgeons (ASES) survey with a correlation of 0.81 [31]. Oxford Shoulder Score (OSS) The OSS is a body-part-specific PROM. It was developed and validated for patients with general shoulder complaints [32]. Responses to the 12-item questionnaire were summarized to a total score that ranged from 12 (least impaired) to 60 (most impaired). This scoring system was revised in 2009 [19]. Currently, answers are scored from 0 to 4, and the summary is reversed; thus, the total score ranges from 0 (most impaired) to 48 (least impaired). The OSS was originally validated against the Constant shoulder score and the SF-36 subscales [32]. Since that validation, it has been validated in Danish, Korean, Turkish, Italian, German, and Dutch [22, 33 37]. Disability of the Arm, Shoulder, and Hand (DASH) assessment The DASH assessment is a body-part-specific PROM designed [38] to measure physical function and symptoms in patients with musculoskeletal disorders from any condition in any joint in the upper extremity. Responses to the 30-item questionnaire are used to calculatethetotalscorebyaveragingtheitemscores,subtracting 1, and multiplying the result by 25. The resulting score ranged from 0 (no disability) to 100 (extreme disability). The DASH was shown to be reliable, valid, and responsive for patients with shoulder disabilities [39, 40]. Short form 36 Health Survey, version 1 (SF-36) The SF-36 is a general health PROM that includes 36 questions for assessing the general health of patients with all kinds of disorders. It is the most widely used PROM for assessing general health [41]. It includes eight domains: physical function, social function, role limitations caused by physical problems (role physical), role limitations caused by emotional problems (role emotional), general mental health, vitality, bodily pain and perception of general health. Each domain has a total score of 0 (extremely poor) to 100 points (no complaint) [42]. The SF-36 was translated and validated in a Dutch general population, with a mean alpha coefficient across all scales and samples of Previous studies have also validated the SF-36 specifically for shoulder complaints [43, 44]. Assessments of measurement properties Internal consistency and factor analysis Internal consistency tells you to what extend different items within one questionnaire measure the same construct of interest (e.g. shoulder instability). Ideally, this score is high, indicating that all items measure the same construct. The internal consistency of the OSIS was assessed by calculating Cronbach s α. For acceptable internal consistency, the Cronbach s α should preferably be 0.7 [43]. Internal consistency can also be addressed using confirmatory factor analysis. See Additional file 1: Appendix 1. Measurement error Measurement error is the systematic, random error in the construct, which cannot be attributed to true changes in the patient s condition [6]. When a score changes within the range of measurement error, it is not clear whether the change is a true effect of therapy or whether it should be attributed to measurement error. Measurement error can be expressed as the standard deviation of repeated measurements in a single patient, referred to as the standard error of measurement (SEM). The SEM was calculated from the square root of the variance between the measurements and the error variance of the ICC. Subsequently, the SEM can be transformed into the smallest detectable change (SDC = 1.96* 2*SEM). The SDC represents the minimal change that a patient must show to ensure that the observed change is real, and not a measurement error [45]. The SDC is thus calculated; it is not derived from clinical observations following treatment. Reliability Since each instrument has a degree of uncertainty due to measurement error, reliability is defined as the degree to which the measurement is free from measurement error [6]. The reliability refers to the proportion of the total variance in the measurements that can be attributed to true differences between patients. Reliability was assessed by calculating the ICC, which was calculated with a two-way, mixed-effects model for absolute agreement. The mixed-effect model is used because a fixed value (all questions remained unchanged during the whole cohort) is compared to a random value (a cohort of patients was selected from all patients with shoulder instability). Scores 0.70 are considered adequate [45].
4 van der Linde et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2015) 10:146 Page 4 of 8 Construct validity Construct validity reflects whether the instrument measures what it was designed to measure. In case of shoulder instability, do questions actually measure the typical complaints following shoulder instability (e.g. How much pain do you experience in your shoulder with overhead activities?)? In the absence of a gold standard for comparison, hypotheses are formulated that state the expected correlation between the investigated instrument and similar PROMs. In this study, the condition-specific OSIS was compared with the condition-specific WOSI (instability) and with the body-part-specific SST, OSS and DASH (shoulder). Finally, it was compared with several subscales of the original version of the SF-36 for measuring general health status. Pre-determined a priori hypotheses are stated in Table 1. These six hypotheses lead to a total of 42 correlations (or comparisons between correlations). The hypotheses were based on clinical experience, knowledge about several PROMs, and a consensus among the study investigators. The highest correlation ( 0.7) was expected between the two disease-specific PROMs (OSIS and WOSI). High correlations ( 0.6) were expected between similar bodypart-specific PROMs (OSIS and SST, OSS, and DASH). These correlation coefficients were expected to be at least 0.1 higher than the correlations between the OSIS and the more general subscales of the SF-36. Finally, because the OSIS predominantly measured physical function, we expected the correlation between the OSIS and the SF-36 physical function to be at least 0.1 higher than the correlations between the OSIS and the other SF-36 subscales. Construct validity was considered good when at least 75 % of the results (correlations) were in accordance with our hypotheses [46]. Floor and ceiling effects Floor and ceiling effects occur when more than 15 % of patients achieve the lowest or highest possible score, respectively [47]. Moreover, when a patient scores close Table 1 Pre-determined hypotheses for testing the validity of the Dutch version of OSIS; expected correlations Expected correlations 1. OSIS and WOSI OSIS and SST OSIS and OSS OSIS and DASH Correlation between OSIS and body-part-specific PROMs (SST, OSS, and DASH) should be at least 0.1 higher than that between OSIS and the generic SF-36 subscales 6. Correlation between OSIS and SF-36 physical function scale should be at least 0.1 higher than the correlations between OSIS and the other SF-36 subscales to one of the extremes at baseline, a real change (defined as the SDC) could cross that extreme. Patients that score within the SDC-range from one of the extremes can thus be regarded as being at either their floor or ceiling too. Statistical analyses Statistical analyses were performed with SPSS software, version (SPSS, Gorinchem, The Netherlands). Results No major differences occurred between the OSIS translations into Dutch and back into English, no content- or linguistic-related difficulties were reported. The final version was considered free of cross-cultural inconsistencies; all questions are applicable to the Dutch population. Figure 1 presents the selection of participating patients. One hundred and thirty-eight patients with shoulder instabilities completed the first questionnaire; 99 patients were eligible for the second questionnaire. The shoulder function, presented as the mean and SD scores of the WOSI, SST, OSS and DASH, did not differ significantly between the two measurements. The demographic data and mean PROM scores are summarized in Table 2. Internal consistency and factor analysis For all 138 patients that completed the OSIS at baseline, the Cronbach s α was 0.88, indicating good internal consistency. Reliability The mean time between the completion of the first and second questionnaires was 13 days (5 30). Table 3 presents the scores of the tests and re-tests and the ICC with a 95 % confidence interval (ICC is 0.87 ( ). These results indicate excellent reliability. Measurement error The SEM was 3.3, which resulted in a SDC of 9.0 points, indicating that a patient has to show a change of 9.0 points to ensure the detection of a true change. This is 19 % of the total range. Construct validity The observed correlation results are summarized in Table 4. In total, 80 % of the results were in accordance with our hypotheses. The hypotheses were confirmed for the correlation between the OSIS and the other instabilityspecific WOSI (0.82; 0.7 expected) and the correlations between the OSIS and the shoulder-specific SST, OSS and DASH (0.69, 0.76, and 0.79, respectively; 0.6 expected). The hypothesis was partly confirmed for the strength of the correlation between the OSIS and the SF-36 subscales.
5 van der Linde et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2015) 10:146 Page 5 of 8 Fig. 1 Flowchart of selection of patients that participated in the study Table 2 Demographic data of patients completing baseline and the reliability cohort Baseline assessment Reliability cohort N (%) N (%) Mean age, year (SD) 32 (12) 32 (14) Gender (male) 98 (71 %) 66 (66 %) Dislocated shoulder Right 72 (53 %) 54 (55 %) Left 59 (43 %) 40 (40 %) Both 6 (4 %) 5 (5 %) Dominant side dislocated 73 (53 %) 53 (54 %) Time first dislocation to completion OSIS <1 month 8 (6 %) 8 (8 %) 1 6 months 21 (15 %) 17 (17 %) >6 months 2 years 40 (29 %) 25 (25 %) > 2 years 67 (49 %) 49 (50 %) Sports-related traumatic 71 (54 %) 47 (47 %) instability WOSI (100 0) a 46.0 (22.3) 45.7 (24.2) b SST (0 12) a 8.8 (3.1) 8.8 (3.2) b OSS (48 0) a 23.7 (7.8) 22.8 (8.3) b DASH (100 0) a 22.2 (16.7) 22.7 (18.3) b a Ranges reflect most impaired to least impaired function b No significant change in shoulder function (WOSI, SST, OSS, DASH) was observed at re-test compared to the baseline assessment Floor and ceiling effects No patients scored minimum or maximum scores. At most, 12 % of patients scored within the SDC-range for the lowest possible score. The results are presented in Table 5. Discussion There is a growing interest in PROMs for both clinical and research purposes to supplement clinical outcome measures. To our knowledge, this is the first study to validate the OSIS in a foreign language and the first to report the measurement error and evaluate floor and ceiling effects. The results show a high internal consistency (Cronbach s α = 0.88); it was only slightly lower than that described in the original article (Cronbach s α = 0.91 at pre treatment [n = 92] and 0.92 at follow-up [n = 64]). Compared to other Dutch-validated PROMs, our Cronbach s α for the OSIS was higher than that of the SST (0.78) and lower than that of the OSS (0.92) [17, 22]. Considering the content of the questions, it is clear that the OSIS measures several constructs, such as pain, physical-, social-, and role functioning, frequency of dislocation and worries. The reliability was addressed with a test-retest sample in 99 patients with a mean interval of 13 days (5 30) and showed an ICC of This was lower than the 0.97 that Dawson et al. described after a 24-h interval in 34 patients; nevertheless, 0.88 is considered a very good ICC. To our knowledge, the measurement error (SDC) of the OSIS has not been reported previously. Our SDC value showed that, to determine a treatment effect, one
6 van der Linde et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2015) 10:146 Page 6 of 8 Table 3 Test-retest reliability (ICC), standard error of measurement (SEM) and smallest detectable change (SDC) for the OSIS Baseline Re-test Change SEM SDC ICC (95 % CI) Mean (SD) Mean (SD) Mean (SD) New scoring system 27.2 (9.3) 27.6 (9.7) 0.4 (4.8) ( ) Scores are expressed according to the new scoring system. This analysis included 99 patients that completed the baseline and retest evaluations must find a difference of at least 9 points between two scores from an individual patient to ensure that the difference was not due to measurement error [48]. To assess the construct validity, Dawson et al. calculated correlations with the Rowe and Constant scores. However, the Rowe and Constant scores are not PROMs but observer-based measurement instruments. Moreover, the Constant score is not considered applicable to shoulder instability [49, 50]. Therefore, the construct validity was assessed by calculating correlations with the WOSI, the SST, the OSS, the DASH and the SF-36 subscales. With 80 % of the results in accordance with our hypotheses, the construct validity was considered good. The highest correlation (0.82) was observed between the two instabilityspecific PROMs (OSIS and the WOSI). A high correlation was observed with the DASH (0.79), which addresses daily activities more specifically than the OSIS. However, many questions overlapped such as putting on a pullover sweater (DASH) and during the last three months, have you had any trouble (or worry) dressing, because of your shoulder? (OSIS). This similarity might explain the high correlation between the two instruments. The OSIS was more closely correlated with the SF-36 subscales pain (0.78) and role physical (0.69) than with the subscale physical function (0.65). These correlations were comparable to those described by Dawson et al. This may indicate that, in addition to physical function, Table 4 Observed correlations for testing the validity of the Dutch version of OSIS Observed correlations 1. OSIS and WOSI OSIS and SST OSIS and OSS OSIS and DASH OSIS and SF-36 subscales: Physical function 0.65 General health 0.31 Social function 0.56 Vitality 0.39 Mental health 0.20 Role emotional 0.41 Role functional 0.69 Bodily Pain 0.78 the OSIS measures aspects of pain and role limitations due to physical problems. In previous studies, floor and ceiling effects were not addressed. In this study, no patient had the maximum or minimum score. The estimation of the smallest detectable change indicated that the baseline patient scores should ideally be at least 9 points different from the extremes. That margin would enable detection of improvements and deteriorations that are distinct from measurement errors at follow-up. At most, 12 % of patients scored within the SDC-margin; thus, these scores were less than the commonly used cut off of 15 % [47]. A strong aspect of this study was the large size of our patient population without missing values. Conversely, an unavoidable limitation of this study was the total number of questions posed to the patients. Completing six questionnaires at once requires considerable time and concentration, and patients might have digressed or lost focus. Also, although web-based versions have many advantages over paper versions such as an increased follow-up ratio and prevention of missing data, validation of digital formats should still be performed. Here, the results are expressed according to the new scoring system. It is important to be aware of the changed scoring system, and we recommend that future studies should specify the scoring system used. Finally, for future studies, it would be very interesting to determine responsiveness and the minimal important change (MIC) of the OSIS. This information can be used to determine whether the observed change is important to the patient and to calculate the percentage of patients that report changes greater than the MIC (responders) in each arm of a trial. Then, the percentage of responders can be compared between groups [51]. Conclusion This study found that the Dutch version of the OSIS was a reliable outcome measure in patients with shoulder Table 5 Floor and ceiling effects of the OSIS scoring system Scoring system Absolute floor Absolute ceiling SDC SDC-range from % of patients scoring within SDC range Floor Ceiling Floor Ceiling New (48 0) a No No % 4 % From left to right, the new scoring system with the ranges and the absolute floor and ceiling scores are presented. The smallest detectable change (SDC) and the percentage of scores that fell within the SDC-range for both extremes a Ranges reflect least impaired to most impaired function
7 van der Linde et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2015) 10:146 Page 7 of 8 instability, with a Cronbach s α of 0.87 and an ICC of In addition, the construct validity was considered good. Comprising 12 questions, the OSIS is user-friendly and can be easily administered. Furthermore, in the absence of floor or ceiling effects, it is a valuable PROM in clinical practice. Patients need to change at least 9 points to ensure that the difference is not due to measurement error. The Dutch version of the OSIS can be acquired by its managing institution, Isis Outcomes, Isis Innovation Ltd, holding its copyright ( Additional file Additional file 1: Appendix 1. Confirmatory factor analysis to assess internal consistency. (DOCX 19 kb) Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Authors contributions All authors have made substantial contributions to conception and design, or acquisition of data, or analysis and interpretation of data; have been involved in drafting the manuscript or revising it critically for important intellectual content; have given final approval of the version to be published; and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved. JvdL is the principal investigator for this study. He carried out the final inclusion of patients and data collection, and he is the author of the first and consecutive drafts of the manuscript. He is the corresponding author. DvK initiated the inclusion of patients and designed the study protocol. He contributed daily help in the analysis and obtained ethical approval for this study. LvB assisted significantly in the analysis and interpretation of the data. DvD supervised the inclusion of patients at the end of the study. He actively participated in the writing. CT designed the study protocol and kept an overview on the analysis, writing and completion of this study. WW was the initiator of this study and included a significant part of the patients; he supervised this study. Acknowledgements We thank Mr. R. Cohen for his help in the translation and Mrs. R. Pepping for her help in coordinating patients affairs. We thank the Department of Orthopedic Surgery and Traumatology at the Waterlandziekenhuis, the Netherlands for their financial contribution to publish this study. Author details 1 Department of Orthopedic Surgery and Traumatology, Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis, Postbus 95500, 1090 HM Amsterdam, The Netherlands. 2 Department of Orthopedic Surgery and Traumatology, Waterland Ziekenhuis, Purmerend, The Netherlands. 3 Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics and the EMGO Institute for Health and Care Research, VU Medical Center, Amsterdam, The Netherlands. 4 Department of Orthopedic Surgery and Traumatology, De Lairesse Kliniek, Amsterdam, The Netherlands. Received: 6 July 2015 Accepted: 2 September 2015 References 1. Leroux T, Wasserstein D, Veillette C, Khoshbin A, Henry P, Chahal J, et al. Epidemiology of primary anterior shoulder dislocation requiring closed reduction in Ontario, Canada. Am J Sports Med. 2014;42: Liavaag S, Svenningsen S, Reikeras O, Enger M, Fjalestad T, Pripp AH, et al. The epidemiology of shoulder dislocations in Oslo. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2011;21:e Zacchilli MA, Owens BD. Epidemiology of shoulder dislocations presenting to emergency departments in the United States. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92: Janse AJ, Gemke RJ, Uiterwaal CS, van dt I, Kimpen JL, Sinnema G. Quality of life: patients and doctors don t always agree: a meta-analysis. J Clin Epidemiol. 2004;57: Wright RW, Baumgarten KM. Shoulder outcomes measures. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2010;18: Irrgang JJ, Lubowitz JH. Measuring arthroscopic outcome. Arthroscopy. 2008;24: Poolman RW, Swiontkowski MF, Fairbank JC, Schemitsch EH, Sprague S, de Vet HC. Outcome instruments: rationale for their use. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91 Suppl 3: Dawson J, Fitzpatrick R, Carr A. The assessment of shoulder instability. The development and validation of a questionnaire. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1999;81: Steffen V, Hertel R. Rim reconstruction with autogenous iliac crest for anterior glenoid deficiency: forty-three instability cases followed for 5 19 years. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2013;22: Tan CK, Guisasola I, Machani B, Kemp G, Sinopidis C, Brownson P, et al. Arthroscopic stabilization of the shoulder: a prospective randomized study of absorbable versus nonabsorbable suture anchors. Arthroscopy. 2006;22: van der Linde JA, van Kampen DA, Terwee CB, Dijksman LM, Kleinjan G, Willems WJ. Long-term results after arthroscopic shoulder stabilization using suture anchors: an 8- to 10-year follow-up. Am J Sports Med. 2011;39: Beaton DE, Bombardier C, Guillemin F, Ferraz MB. Guidelines for the process of cross-cultural adaptation of self-report measures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000;15;25: Guillemin F, Bombardier C, Beaton D. Cross-cultural adaptation of health-related quality of life measures: literature review and proposed guidelines. J Clin Epidemiol. 1993;46: Wild D, Grove A, Martin M, Eremenco S, McElroy S, Verjee-Lorenz A, et al. Principles of good practice for the translation and cultural adaptation process for patient-reported outcomes (PRO) measures: report of the ISPOR task force for translation and cultural adaptation. Value Health. 2005;8: Mokkink LB, Terwee CB, Patrick DL, Alonso J, Stratford PW, Knol DL, et al. The COSMIN checklist for assessing the methodological quality of studies on measurement properties of health status measurement instruments: an international Delphi study. Qual Life Res. 2010;19: Terwee CB, Mokkink LB, Knol DL, Ostelo RW, Bouter LM, de Vet HC. Rating the methodological quality in systematic reviews of studies on measurement properties: a scoring system for the COSMIN checklist. Qual Life Res. 2012;21: van Kampen DA, van Beers LW, Scholtes VA, Terwee CB, Willems WJ. Validation of the Dutch version of the simple shoulder test. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2012;21: de Vet HC, Terwee CB, Mokkink LB, Knol DL. Design of simple reliability studies. Measurement in medicine. New York: Cambridge University Press; p Dawson J, Rogers K, Fitzpatrick R, Carr A. The Oxford shoulder score revisited. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2009;129: van der Linde JA, Willems WJ, van Kampen DA, van Beers LW, van Deurzen DF, Terwee CB. Measurement properties of the Western Ontario Shoulder Instability index in Dutch patients with shoulder instability. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2014;15: Godfrey J, Hamman R, Lowenstein S, Briggs K, Kocher M. Reliability, validity, and responsiveness of the simple shoulder test: psychometric properties by age and injury type. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2007;16: Berendes T, Pilot P, Willems J, Verburg H, te SR. Validation of the Dutch version of the Oxford Shoulder Score. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2010;19: Veehof MM, Sleegers EJ, van Veldhoven NH, Schuurman AH, van Meeteren NL. Psychometric qualities of the Dutch language version of the Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder, and Hand questionnaire (DASH-DLV). J Hand Ther. 2002;15: Kirkley A, Griffin S, McLintock H, Ng L. The development and evaluation of a disease-specific quality of life measurement tool for shoulder instability. The Western Ontario Shoulder Instability Index (WOSI). Am J Sports Med. 1998;26: Kirkley A, Griffin S, Dainty K. Scoring systems for the functional assessment of the shoulder. Arthroscopy. 2003;19:
8 van der Linde et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2015) 10:146 Page 8 of Cacchio A, Paoloni M, Griffin SH, Rosa F, Properzi G, Padua L, et al. Cross-cultural adaptation and measurement properties of an Italian version of the Western Ontario Shoulder Instability Index (WOSI). J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2012;42: Hatta T, Shinozaki N, Omi R, Sano H, Yamamoto N, Ando A, et al. Reliability and validity of the Western Ontario Shoulder Instability Index (WOSI) in the Japanese population. J Orthop Sci. 2011;16: Salomonsson B, Ahlstrom S, Dalen N, Lillkrona U. The Western Ontario Shoulder Instability Index (WOSI): validity, reliability, and responsiveness retested with a Swedish translation. Acta Orthop. 2009;80: Hofstaetter JG, Hanslik-Schnabel B, Hofstaetter SG, Wurnig C, Huber W. Cross-cultural adaptation and validation of the German version of the Western Ontario Shoulder Instability index. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2010;130: Drerup S, Angst F, Griffin S, Flury MP, Simmen BR, Goldhahn J. Western Ontario shoulder instability index (WOSI): translation and cross-cultural adaptation for use by German speakers. Orthopade. 2010;39: Lippitt SBHDIMFI. A practical tool for evaluating function: the Simple Shoulder Test. In: Matsen III FA, Fu FH, Hawkins RJ, editors. The shoulder: a balance of mobility and stability. Rosemont (IL): American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons; Dawson J, Fitzpatrick R, Carr A. Questionnaire on the perceptions of patients about shoulder surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1996;78: Frich LH, Noergaard PM, Brorson S. Validation of the Danish version of Oxford Shoulder Score. Dan Med Bull. 2011;58:A Huber W, Hofstaetter JG, Hanslik-Schnabel B, Posch M, Wurnig C. The German version of the Oxford Shoulder Score cross-cultural adaptation and validation. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2004;124: Murena L, Vulcano E, D'Angelo F, Monti M, Cherubino P. Italian cross-cultural adaptation and validation of the Oxford Shoulder Score. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2010;19: Roh YH, Noh JH, Kim W, Oh JH, Gong HS, Baek GH. Cross-cultural adaptation and validation of the Korean version of the Oxford shoulder score. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2012;132: Tugay U, Tugay N, Gelecek N, Ozkan M. Oxford Shoulder Score: cross-cultural adaptation and validation of the Turkish version. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2011;131: Hudak PL, Amadio PC, Bombardier C. Development of an upper extremity outcome measure: the DASH (disabilities of the arm, shoulder and hand) [corrected]. The Upper Extremity Collaborative Group (UECG). Am J Ind Med. 1996;29: Beaton DE, Katz JN, Fossel AH, Wright JG, Tarasuk V, Bombardier C. Measuring the whole or the parts? Validity, reliability, and responsiveness of the Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder and Hand outcome measure in different regions of the upper extremity. J Hand Ther. 2001;14: Desai AS, Dramis A, Hearnden AJ. Critical appraisal of subjective outcome measures used in the assessment of shoulder disability. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2010;92: Garratt A, Schmidt L, Mackintosh A, Fitzpatrick R. Quality of life measurement: bibliographic study of patient assessed health outcome measures. BMJ. 2002;15;324: Salaffi F, De Angelis R, Stancati A, Grassi W. Health-related quality of life in multiple musculoskeletal conditions: a cross-sectional population based epidemiological study. II. The MAPPING study. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2005;23: Gartsman GM, Brinker MR, Khan M, Karahan M. Self-assessment of general health status in patients with five common shoulder conditions. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1998;7: Ostor AJ, Richards CA, Prevost AT, Speed CA, Hazleman BL. Diagnosis and relation to general health of shoulder disorders presenting to primary care. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2005;44: Snyder CF, Aaronson NK, Choucair AK, Elliott TE, Greenhalgh J, Halyard MY, et al. Implementing patient-reported outcomes assessment in clinical practice: a review of the options and considerations. Qual Life Res. 2012;21: Terwee CB, Bot SD, de Boer MR, van der Windt DA, Knol DL, Dekker J, et al. Quality criteria were proposed for measurement properties of health status questionnaires. J Clin Epidemiol. 2007;60: McHorney CA, Tarlov AR. Individual-patient monitoring in clinical practice: are available health status surveys adequate? Qual Life Res. 1995;4: de Vet HC, Terwee CB, Knol DL, Bouter LM. When to use agreement versus reliability measures. J Clin Epidemiol. 2006;59: Jensen KU, Bongaerts G, Bruhn R, Schneider S. Not all Rowe scores are the same! Which Rowe score do you use? J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2009;18: Lillkrona U. How should we use the Constant Score? A commentary. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2008;17: Schunemann HJ, Akl EA, Guyatt GH. Interpreting the results of patient reported outcome measures in clinical trials: the clinician's perspective. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2006;4:62. Submit your next manuscript to BioMed Central and take full advantage of: Convenient online submission Thorough peer review No space constraints or color figure charges Immediate publication on acceptance Inclusion in PubMed, CAS, Scopus and Google Scholar Research which is freely available for redistribution Submit your manuscript at
Impact of adhesive capsulitis on quality of life in elderly subjects with diabetes: A cross sectional study
 Original Article Impact of adhesive capsulitis on quality of life in elderly subjects with diabetes: A cross sectional study Saumen Gupta, Kavitha Raja, Manikandan N Department of Physical Therapy, Manipal
Original Article Impact of adhesive capsulitis on quality of life in elderly subjects with diabetes: A cross sectional study Saumen Gupta, Kavitha Raja, Manikandan N Department of Physical Therapy, Manipal
Quality criteria were proposed for measurement properties of health status questionnaires
 Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 60 (2007) 34e42 Quality criteria were proposed for measurement properties of health status questionnaires Caroline B. Terwee a, *, Sandra D.M. Bot a, Michael R. de Boer
Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 60 (2007) 34e42 Quality criteria were proposed for measurement properties of health status questionnaires Caroline B. Terwee a, *, Sandra D.M. Bot a, Michael R. de Boer
A Manual Therapy and Exercise Approach to Breast Cancer Rehabilitation Course
 2014 Annual Breast Cancer Rehabilitation Healthcare Provider Event A Manual Therapy and Exercise Approach to Breast Cancer Rehabilitation Course November 7 th and 8 th, 2014 Mercer University, Atlanta,
2014 Annual Breast Cancer Rehabilitation Healthcare Provider Event A Manual Therapy and Exercise Approach to Breast Cancer Rehabilitation Course November 7 th and 8 th, 2014 Mercer University, Atlanta,
8 General discussion. Chapter 8: general discussion 95
 8 General discussion The major pathologic events characterizing temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis include synovitis and internal derangements, giving rise to pain and restricted mobility of the temporomandibular
8 General discussion The major pathologic events characterizing temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis include synovitis and internal derangements, giving rise to pain and restricted mobility of the temporomandibular
Summary chapter 1 chapter 2 147
 146 There is an increasing need for questionnaires to assess the health-related quality of life of Turkish and Moroccan cancer patients in the Netherlands (chapter 1). The first generation of Turkish and
146 There is an increasing need for questionnaires to assess the health-related quality of life of Turkish and Moroccan cancer patients in the Netherlands (chapter 1). The first generation of Turkish and
Developing a Tool to Assess Administrative Evidence-Based Practices in Local Health Departments
 Frontiers in Public Health Services and Systems Research Manuscript 1044 Developing a Tool to Assess Administrative Evidence-Based Practices in Local Health Departments Rodrigo S. Reis Kathleen Duggan
Frontiers in Public Health Services and Systems Research Manuscript 1044 Developing a Tool to Assess Administrative Evidence-Based Practices in Local Health Departments Rodrigo S. Reis Kathleen Duggan
Reproducibility of the Portuguese version of the PEDro Scale. Reprodutibilidade da Escala de Qualidade PEDro em português. Abstract RESEARCH NOTE
 NOTA RESEARCH NOTE 2063 Reproducibility of the Portuguese version of the PEDro Scale Reprodutibilidade da Escala de Qualidade PEDro em português Silvia Regina Shiwa 1 Leonardo Oliveira Pena Costa 1,2 Luciola
NOTA RESEARCH NOTE 2063 Reproducibility of the Portuguese version of the PEDro Scale Reprodutibilidade da Escala de Qualidade PEDro em português Silvia Regina Shiwa 1 Leonardo Oliveira Pena Costa 1,2 Luciola
Improving the Measurement Properties of Depressive Symptom Instruments for Use after SCI
 Improving the Measurement Properties of Depressive Symptom Instruments for Use after SCI Allen Heinemann, PhD Ryan Williams, PhD Charles Bombardier, PhD Martin Forchheimer, MPP Jesse Fann, MD Holly Neumann,
Improving the Measurement Properties of Depressive Symptom Instruments for Use after SCI Allen Heinemann, PhD Ryan Williams, PhD Charles Bombardier, PhD Martin Forchheimer, MPP Jesse Fann, MD Holly Neumann,
What factors determine poor functional outcome following Total Knee Replacement (TKR)?
 Specific Question: What factors determine poor functional outcome following Total Knee Replacement ()? Clinical bottom line All groups derived benefit from undergoing a, reviews suggests that the decision
Specific Question: What factors determine poor functional outcome following Total Knee Replacement ()? Clinical bottom line All groups derived benefit from undergoing a, reviews suggests that the decision
Second Look Arthroscopy Following Arthroscopic Shoulder Anterior Instability Reconstruction
 Second Look Arthroscopy Following Arthroscopic Shoulder Anterior Instability Reconstruction Emmanuel Antonogiannakis, Christos K. Yiannakopoulos, George Babalis, Dimitrios Kostopoulos, Gerasimos Gialas,
Second Look Arthroscopy Following Arthroscopic Shoulder Anterior Instability Reconstruction Emmanuel Antonogiannakis, Christos K. Yiannakopoulos, George Babalis, Dimitrios Kostopoulos, Gerasimos Gialas,
The Palliative care Outcome Scale (POS) Manual for cross-cultural adaptation and psychometric validation
 The Palliative care Outcome Scale (POS) Manual for cross-cultural adaptation and psychometric validation Author: Bárbara Antunes 1 Contributors: Barbara Daveson 1, Christina Ramsenthaler 1, Hamid Benalia
The Palliative care Outcome Scale (POS) Manual for cross-cultural adaptation and psychometric validation Author: Bárbara Antunes 1 Contributors: Barbara Daveson 1, Christina Ramsenthaler 1, Hamid Benalia
SHOULDER INSTABILITY. E. Edward Khalfayan, MD
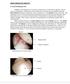 SHOULDER INSTABILITY E. Edward Khalfayan, MD Instability of the shoulder can occur from a single injury or as the result of repetitive activity such as overhead sports. Dislocations of the shoulder are
SHOULDER INSTABILITY E. Edward Khalfayan, MD Instability of the shoulder can occur from a single injury or as the result of repetitive activity such as overhead sports. Dislocations of the shoulder are
Health Benchmarks Program Clinical Quality Indicator Specification 2013
 Health Benchmarks Program Clinical Quality Indicator Specification 2013 Measure Title USE OF IMAGING STUDIES FOR LOW BACK PAIN Disease State Musculoskeletal Indicator Classification Utilization Strength
Health Benchmarks Program Clinical Quality Indicator Specification 2013 Measure Title USE OF IMAGING STUDIES FOR LOW BACK PAIN Disease State Musculoskeletal Indicator Classification Utilization Strength
The reproducibility of the Canadian Occupational Performance Measure
 Postprint Version 1.0 Journal website http://www.sagepub.co.uk/journalsproddesc.nav?prodid=journal201806 Pubmed link http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=retrieve&db=pubmed&dop t=a bstract&list_uids=16323388&query_hl=9&itool=pubmed_docsum
Postprint Version 1.0 Journal website http://www.sagepub.co.uk/journalsproddesc.nav?prodid=journal201806 Pubmed link http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=retrieve&db=pubmed&dop t=a bstract&list_uids=16323388&query_hl=9&itool=pubmed_docsum
The influence of applying insurance medicine guidelines for depression on disability assessments
 Schellart et al. BMC Research Notes 2013, 6:225 RESEARCH ARTICLE The influence of applying insurance medicine guidelines for depression on disability assessments Antonius JM Schellart 1,2,3, Feico Zwerver
Schellart et al. BMC Research Notes 2013, 6:225 RESEARCH ARTICLE The influence of applying insurance medicine guidelines for depression on disability assessments Antonius JM Schellart 1,2,3, Feico Zwerver
SHOULDER INSTABILITY IN PATIENTS WITH EDS
 EDNF 2012 CONFERENCE LIVING WITH EDS SHOULDER INSTABILITY IN PATIENTS WITH EDS Keith Kenter, MD Associate Professor Sports Medicine & Shoulder Reconstruction Director, Orthopaedic Residency Program Department
EDNF 2012 CONFERENCE LIVING WITH EDS SHOULDER INSTABILITY IN PATIENTS WITH EDS Keith Kenter, MD Associate Professor Sports Medicine & Shoulder Reconstruction Director, Orthopaedic Residency Program Department
Spinal cord injury and quality of life: a systematic review of outcome measures
 Systematic review Spinal cord injury and quality of life: a systematic review of outcome measures 37 37 44 Spinal cord injury and quality of life: a systematic review of outcome measures Authors Jefferson
Systematic review Spinal cord injury and quality of life: a systematic review of outcome measures 37 37 44 Spinal cord injury and quality of life: a systematic review of outcome measures Authors Jefferson
Mid-term follow up of whiplash with Bournemouth Questionnaire: The significance of the initial
 Mid-term follow up of whiplash with Bournemouth Questionnaire: The significance of the initial depression to pain outcome Introduction Symptoms from Whiplash Associated Disorder (WAD) impair patients quality
Mid-term follow up of whiplash with Bournemouth Questionnaire: The significance of the initial depression to pain outcome Introduction Symptoms from Whiplash Associated Disorder (WAD) impair patients quality
Patient Reported Outcomes
 Patient Reported Outcomes 16 December 2013, Nottingham Esther van Zuuren Dermatologist, Leiden University Medical Centre Netherlands Patient Reported Outcomes A Patient Reported Outcome (PRO): any aspect
Patient Reported Outcomes 16 December 2013, Nottingham Esther van Zuuren Dermatologist, Leiden University Medical Centre Netherlands Patient Reported Outcomes A Patient Reported Outcome (PRO): any aspect
Neck Pain & Cervicogenic Headache Integrating Research into Practice: San Luis Sports Therapy s Approach to Evidence-Based Practice
 Neck Pain & Cervicogenic Headache Integrating Research into Practice: San Luis Sports Therapy s Approach to Evidence-Based Practice PROBLEM: Neck Pain and Cervicogenic Headache 66% Proportion of individuals
Neck Pain & Cervicogenic Headache Integrating Research into Practice: San Luis Sports Therapy s Approach to Evidence-Based Practice PROBLEM: Neck Pain and Cervicogenic Headache 66% Proportion of individuals
Treatment Satisfaction among patients attending a private dental school in Vadodara, India
 J. Int Oral Health 2010 Case Report All right reserved Treatment Satisfaction among patients attending a private dental school in Vadodara, India Thanveer K* Ajith Krishnan** Sudheer Hongal*** *M.D.S,
J. Int Oral Health 2010 Case Report All right reserved Treatment Satisfaction among patients attending a private dental school in Vadodara, India Thanveer K* Ajith Krishnan** Sudheer Hongal*** *M.D.S,
Prevalence of self reported multimorbidity in the general population and in primary care practices: a cross sectional study
 DOI 10.1186/s13104-016-2121-4 BMC Research Notes RESEARCH ARTICLE Prevalence of self reported multimorbidity in the general population and in primary care practices: a cross sectional study Nadjib Mohamed
DOI 10.1186/s13104-016-2121-4 BMC Research Notes RESEARCH ARTICLE Prevalence of self reported multimorbidity in the general population and in primary care practices: a cross sectional study Nadjib Mohamed
If several different trials are mentioned in one publication, the data of each should be extracted in a separate data extraction form.
 General Remarks This template of a data extraction form is intended to help you to start developing your own data extraction form, it certainly has to be adapted to your specific question. Delete unnecessary
General Remarks This template of a data extraction form is intended to help you to start developing your own data extraction form, it certainly has to be adapted to your specific question. Delete unnecessary
Tara Stevermuer (MAppStat), Centre for Health Service Development, University of Wollongong.
 ENAR - PAIN RELIEF THAT S FAST AND LASTS Tara Stevermuer (MAppStat), Centre for Health Service Development, University of Wollongong. Introducing ENAR The ENAR (Electro-Neuro-Adaptive-Regulator) is a Russian
ENAR - PAIN RELIEF THAT S FAST AND LASTS Tara Stevermuer (MAppStat), Centre for Health Service Development, University of Wollongong. Introducing ENAR The ENAR (Electro-Neuro-Adaptive-Regulator) is a Russian
The Disabilities of the Arm Shoulder and Hand (DASH) Symptom Scale
 The Disabilities of the Arm Shoulder and Hand (DASH) Symptom Scale Overview: The Disabilities of the Arm Shoulder and Hand (DASH) symptom scale can be used to evaluate a patient with a disorder of the
The Disabilities of the Arm Shoulder and Hand (DASH) Symptom Scale Overview: The Disabilities of the Arm Shoulder and Hand (DASH) symptom scale can be used to evaluate a patient with a disorder of the
LIST OF PUBLICATIONS
 LIST OF PUBLICATIONS List of publications 166 List of publications Papers van der Lugt JC, Valstar ER, Witvoet-Braam SW, Nelissen, RG. Migration of the humeral component of the Souter-Strathclyde elbow
LIST OF PUBLICATIONS List of publications 166 List of publications Papers van der Lugt JC, Valstar ER, Witvoet-Braam SW, Nelissen, RG. Migration of the humeral component of the Souter-Strathclyde elbow
Evidence of Validity for the Foot and Ankle Ability Measure (FAAM)
 FOOT &ANKLE INTERNATIONAL Copyright 2005 by the American Orthopaedic Foot & Ankle Society, Inc. Evidence of Validity for the Foot and Ankle Ability Measure (FAAM) RobRoy L. Martin, P.T., Ph.D., C.S.C.S.
FOOT &ANKLE INTERNATIONAL Copyright 2005 by the American Orthopaedic Foot & Ankle Society, Inc. Evidence of Validity for the Foot and Ankle Ability Measure (FAAM) RobRoy L. Martin, P.T., Ph.D., C.S.C.S.
Is Test of Performance Strategies (TOPS) a Precise Tool for Iranian Adult Athletes?
 Middle-East Journal of Scientific Research 22 (8): 1219-1227, 2014 ISSN 1990-9233 IDOSI Publications, 2014 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.mejsr.2014.22.08.22030 Is Test of Performance Strategies (TOPS) a Precise Tool
Middle-East Journal of Scientific Research 22 (8): 1219-1227, 2014 ISSN 1990-9233 IDOSI Publications, 2014 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.mejsr.2014.22.08.22030 Is Test of Performance Strategies (TOPS) a Precise Tool
Handicap after acute whiplash injury A 1-year prospective study of risk factors
 1 Handicap after acute whiplash injury A 1-year prospective study of risk factors Neurology 2001;56:1637-1643 (June 26, 2001) Helge Kasch, MD, PhD; Flemming W Bach, MD, PhD; Troels S Jensen, MD, PhD From
1 Handicap after acute whiplash injury A 1-year prospective study of risk factors Neurology 2001;56:1637-1643 (June 26, 2001) Helge Kasch, MD, PhD; Flemming W Bach, MD, PhD; Troels S Jensen, MD, PhD From
Victims Compensation Claim Status of All Pending Claims and Claims Decided Within the Last Three Years
 Claim#:021914-174 Initials: J.T. Last4SSN: 6996 DOB: 5/3/1970 Crime Date: 4/30/2013 Status: Claim is currently under review. Decision expected within 7 days Claim#:041715-334 Initials: M.S. Last4SSN: 2957
Claim#:021914-174 Initials: J.T. Last4SSN: 6996 DOB: 5/3/1970 Crime Date: 4/30/2013 Status: Claim is currently under review. Decision expected within 7 days Claim#:041715-334 Initials: M.S. Last4SSN: 2957
WHIPLASH. Risk Factors - Prognostic Factors - Therapy. D. Verhulst,W. Jak Geneeskundige Dagen Antwerpen 11 september 2015
 WHIPLASH Risk Factors - Prognostic Factors - Therapy D. Verhulst,W. Jak Geneeskundige Dagen Antwerpen 11 september 2015 Definition 1995 Quebec Task Force on Whiplash Associated Disorders (WAD): Whiplash
WHIPLASH Risk Factors - Prognostic Factors - Therapy D. Verhulst,W. Jak Geneeskundige Dagen Antwerpen 11 september 2015 Definition 1995 Quebec Task Force on Whiplash Associated Disorders (WAD): Whiplash
Progress Report Phase I Study of North Carolina Evidence-based Transition to Practice Initiative Project Foundation for Nursing Excellence
 Progress Report Phase I Study of North Carolina Evidence-based Transition to Practice Initiative Project Foundation for Nursing Excellence Prepared by the NCSBN Research Department INTRODUCTION In 2006,
Progress Report Phase I Study of North Carolina Evidence-based Transition to Practice Initiative Project Foundation for Nursing Excellence Prepared by the NCSBN Research Department INTRODUCTION In 2006,
An evaluation of a tailored intervention on village doctors use of electronic health records
 He et al. BMC Health Services Research 2014, 14:217 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access An evaluation of a tailored intervention on village doctors use of electronic health records Peiyuan He 1, Zhaokang Yuan
He et al. BMC Health Services Research 2014, 14:217 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access An evaluation of a tailored intervention on village doctors use of electronic health records Peiyuan He 1, Zhaokang Yuan
Translating and normalising CORE system CORE System Trust (CST) position statement
 Translating/transferring the CORE-OM Translating and normalising CORE system CORE System Trust (CST) position statement If you want to translate any CORE measures into another language: translate this
Translating/transferring the CORE-OM Translating and normalising CORE system CORE System Trust (CST) position statement If you want to translate any CORE measures into another language: translate this
Validation of the Treatment Related Impact Measure for Diabetes Treatment and Device: TRIM-Diabetes and TRIM-Device
 Validation of the Treatment Related Impact Measure for Diabetes Treatment and Device: TRIM-Diabetes and TRIM-Device Authors Meryl Brod President, The Brod Group Mette Hammer Associate Director, Health
Validation of the Treatment Related Impact Measure for Diabetes Treatment and Device: TRIM-Diabetes and TRIM-Device Authors Meryl Brod President, The Brod Group Mette Hammer Associate Director, Health
.org. Shoulder Pain and Common Shoulder Problems. Anatomy. Cause
 Shoulder Pain and Common Shoulder Problems Page ( 1 ) What most people call the shoulder is really several joints that combine with tendons and muscles to allow a wide range of motion in the arm from scratching
Shoulder Pain and Common Shoulder Problems Page ( 1 ) What most people call the shoulder is really several joints that combine with tendons and muscles to allow a wide range of motion in the arm from scratching
Preoperative Health Status of Patients With Four Knee Conditions Treated With Arthroscopy
 CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 395 pp. 164 173 2002 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Preoperative Health Status of Patients With Four Knee Conditions Treated With Arthroscopy Daniel
CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 395 pp. 164 173 2002 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Preoperative Health Status of Patients With Four Knee Conditions Treated With Arthroscopy Daniel
How You Can Do Research in Your Practice: Case Studies
 How You Can Do Research in Your Practice: Case Studies SCCA Convention 2014 Luke Henry, D.C. 1 Introduction Why you should be interested in research Enhance chiropractic education Increases recognition
How You Can Do Research in Your Practice: Case Studies SCCA Convention 2014 Luke Henry, D.C. 1 Introduction Why you should be interested in research Enhance chiropractic education Increases recognition
Title:Online training course on critical appraisal for nurses: adaptation and assessment
 Author's response to reviews Title:Online training course on critical appraisal for nurses: adaptation and assessment Authors: Eva Reviriego (ereviriego@ej-gv.es) María Ángeles Cidoncha (mariaangeles.cidonchamoreno@osakidetza.net)
Author's response to reviews Title:Online training course on critical appraisal for nurses: adaptation and assessment Authors: Eva Reviriego (ereviriego@ej-gv.es) María Ángeles Cidoncha (mariaangeles.cidonchamoreno@osakidetza.net)
1 of 6 1/22/2015 10:06 AM
 1 of 6 1/22/2015 10:06 AM 2 of 6 1/22/2015 10:06 AM This cross-section view of the shoulder socket shows a typical SLAP tear. Injuries to the superior labrum can be caused by acute trauma or by repetitive
1 of 6 1/22/2015 10:06 AM 2 of 6 1/22/2015 10:06 AM This cross-section view of the shoulder socket shows a typical SLAP tear. Injuries to the superior labrum can be caused by acute trauma or by repetitive
1.0 Abstract. Title: Real Life Evaluation of Rheumatoid Arthritis in Canadians taking HUMIRA. Keywords. Rationale and Background:
 1.0 Abstract Title: Real Life Evaluation of Rheumatoid Arthritis in Canadians taking HUMIRA Keywords Rationale and Background: This abbreviated clinical study report is based on a clinical surveillance
1.0 Abstract Title: Real Life Evaluation of Rheumatoid Arthritis in Canadians taking HUMIRA Keywords Rationale and Background: This abbreviated clinical study report is based on a clinical surveillance
WHAT IS A JOURNAL CLUB?
 WHAT IS A JOURNAL CLUB? With its September 2002 issue, the American Journal of Critical Care debuts a new feature, the AJCC Journal Club. Each issue of the journal will now feature an AJCC Journal Club
WHAT IS A JOURNAL CLUB? With its September 2002 issue, the American Journal of Critical Care debuts a new feature, the AJCC Journal Club. Each issue of the journal will now feature an AJCC Journal Club
Prepared by:jane Healey (Email: janie_healey@yahoo.com) 4 th year undergraduate occupational therapy student, University of Western Sydney
 1 There is fair (2b) level evidence that living skills training is effective at improving independence in food preparation, money management, personal possessions, and efficacy, in adults with persistent
1 There is fair (2b) level evidence that living skills training is effective at improving independence in food preparation, money management, personal possessions, and efficacy, in adults with persistent
An Empirical Study on the Effects of Software Characteristics on Corporate Performance
 , pp.61-66 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2014.48.12 An Empirical Study on the Effects of Software Characteristics on Corporate Moon-Jong Choi 1, Won-Seok Kang 1 and Geun-A Kim 2 1 DGIST, 333 Techno Jungang
, pp.61-66 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2014.48.12 An Empirical Study on the Effects of Software Characteristics on Corporate Moon-Jong Choi 1, Won-Seok Kang 1 and Geun-A Kim 2 1 DGIST, 333 Techno Jungang
Curriculum Vitae Curtis R. Noel, MD
 Curriculum Vitae Curtis R. Noel, MD Education Fellowship: Steadman-Hawkins Clinic of the Carolinas 2005 2006 Spartanburg, SC Residency: Summa Health Systems 2000-2005 Akron, OH Medical School: University
Curriculum Vitae Curtis R. Noel, MD Education Fellowship: Steadman-Hawkins Clinic of the Carolinas 2005 2006 Spartanburg, SC Residency: Summa Health Systems 2000-2005 Akron, OH Medical School: University
Quality and critical appraisal of clinical practice guidelines a relevant topic for health care?
 Quality and critical appraisal of clinical practice guidelines a relevant topic for health care? Françoise Cluzeau, PhD St George s Hospital Medical School, London on behalf of the AGREE Collaboration
Quality and critical appraisal of clinical practice guidelines a relevant topic for health care? Françoise Cluzeau, PhD St George s Hospital Medical School, London on behalf of the AGREE Collaboration
The 2012 User's Guide to: Knee injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score KOOS
 KOOS User s Guide 1.1 Updated August 2012 1 The 2012 User's Guide to: Knee injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score KOOS This guide is intended to serve as an introduction for clinicians and researchers
KOOS User s Guide 1.1 Updated August 2012 1 The 2012 User's Guide to: Knee injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score KOOS This guide is intended to serve as an introduction for clinicians and researchers
The Application of Migraine Disability Assessment Questionnaire (MIDAS)
 Continuing Medical Education 43 The Application of Migraine Disability Assessment Questionnaire () Pei-Hua Hung, Jong-Ling Fuh, and Shuu-Jiun Wang Abstract- Migraine is a recurring and disabling pain disorder
Continuing Medical Education 43 The Application of Migraine Disability Assessment Questionnaire () Pei-Hua Hung, Jong-Ling Fuh, and Shuu-Jiun Wang Abstract- Migraine is a recurring and disabling pain disorder
Summary. Pediatric traffic injuries: consequences for the child and the parents
 Summary Pediatric traffic injuries: consequences for the child and the parents Injuries constitute an important health problem among children and adolescents, not only because they can be life threatening,
Summary Pediatric traffic injuries: consequences for the child and the parents Injuries constitute an important health problem among children and adolescents, not only because they can be life threatening,
CARE MANAGEMENT FOR LATE LIFE DEPRESSION IN URBAN CHINESE PRIMARY CARE CLINICS
 CARE MANAGEMENT FOR LATE LIFE DEPRESSION IN URBAN CHINESE PRIMARY CARE CLINICS Dept of Public Health Sciences February 6, 2015 Yeates Conwell, MD Dept of Psychiatry, University of Rochester Shulin Chen,
CARE MANAGEMENT FOR LATE LIFE DEPRESSION IN URBAN CHINESE PRIMARY CARE CLINICS Dept of Public Health Sciences February 6, 2015 Yeates Conwell, MD Dept of Psychiatry, University of Rochester Shulin Chen,
EMPLOYMENT: PEACHTREE ORTHOPAEDIC CLINIC ATLANTA- GA 2013- PRESENT Orthopaedic Surgeon Northside Hospital, Atlanta, GA
 GEORGE N. GUILD III, M.D. ORTHOPAEDIC SURGEON: ADULT HIP AND KNEE RECONSTRUCTION PEACHTREE ORTHOPAEDIC CLINIC 5505 PEACHTREE DUNWOODY ROAD SUITE 600 ATLANTA, GA 30342 TEL. (404)- 355-0743 FAX: 404-355-
GEORGE N. GUILD III, M.D. ORTHOPAEDIC SURGEON: ADULT HIP AND KNEE RECONSTRUCTION PEACHTREE ORTHOPAEDIC CLINIC 5505 PEACHTREE DUNWOODY ROAD SUITE 600 ATLANTA, GA 30342 TEL. (404)- 355-0743 FAX: 404-355-
Guidance for Peer Reviewers. The Journal of the American Osteopathic Association (JAOA)
 Guidance for Peer Reviewers The Journal of the American Osteopathic Association (JAOA) JAOA Editorial Staff This module is available online at http://jaoa.org/documentlibrary/prmodule.pdf Guidance for
Guidance for Peer Reviewers The Journal of the American Osteopathic Association (JAOA) JAOA Editorial Staff This module is available online at http://jaoa.org/documentlibrary/prmodule.pdf Guidance for
Administration of Emergency Medicine
 doi:10.1016/j.jemermed.2005.07.008 The Journal of Emergency Medicine, Vol. 30, No. 4, pp. 455 460, 2006 Copyright 2006 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0736-4679/06 $ see front matter
doi:10.1016/j.jemermed.2005.07.008 The Journal of Emergency Medicine, Vol. 30, No. 4, pp. 455 460, 2006 Copyright 2006 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0736-4679/06 $ see front matter
Arthroscopic Management of Superior Labral Anterior and Posterior (SLAP) and Associated Lesions: Clinical Features and Functional Outcome
 44 Original Article Arthroscopic Management of Superior Labral Anterior and Posterior (SLAP) and Associated Lesions: Clinical Features and Functional Outcome Mui Hong Lim, 1 MBBS, MRCS (Edin), MMed (Orth),
44 Original Article Arthroscopic Management of Superior Labral Anterior and Posterior (SLAP) and Associated Lesions: Clinical Features and Functional Outcome Mui Hong Lim, 1 MBBS, MRCS (Edin), MMed (Orth),
LEVEL ONE MODULE EXAM PART ONE [Clinical Questions Literature Searching Types of Research Levels of Evidence Appraisal Scales Statistic Terminology]
![LEVEL ONE MODULE EXAM PART ONE [Clinical Questions Literature Searching Types of Research Levels of Evidence Appraisal Scales Statistic Terminology] LEVEL ONE MODULE EXAM PART ONE [Clinical Questions Literature Searching Types of Research Levels of Evidence Appraisal Scales Statistic Terminology]](/thumbs/27/12305234.jpg) 1. What does the letter I correspond to in the PICO format? A. Interdisciplinary B. Interference C. Intersession D. Intervention 2. Which step of the evidence-based practice process incorporates clinical
1. What does the letter I correspond to in the PICO format? A. Interdisciplinary B. Interference C. Intersession D. Intervention 2. Which step of the evidence-based practice process incorporates clinical
Olga Golubnitschaja 1,2. Abstract
 EDITORIAL Open Access Time for new guidelines in advanced healthcare: the mission of The EPMA Journal to promote an integrative view in predictive, preventive and personalized medicine Olga Golubnitschaja
EDITORIAL Open Access Time for new guidelines in advanced healthcare: the mission of The EPMA Journal to promote an integrative view in predictive, preventive and personalized medicine Olga Golubnitschaja
Research should be undertaken to answer a question. The question asked
 Authors: Derick T. Wade Affiliations: Clinical Trials From the Department of Neurological Disability, Oxford Centre for Enablement, Oxford, UK. FIM is a trademark of the Uniform Data System for Medical
Authors: Derick T. Wade Affiliations: Clinical Trials From the Department of Neurological Disability, Oxford Centre for Enablement, Oxford, UK. FIM is a trademark of the Uniform Data System for Medical
Current reporting in published research
 Current reporting in published research Doug Altman Centre for Statistics in Medicine, Oxford, UK and EQUATOR Network Research article A published research article is a permanent record that will be used
Current reporting in published research Doug Altman Centre for Statistics in Medicine, Oxford, UK and EQUATOR Network Research article A published research article is a permanent record that will be used
Robert Okwemba, BSPHS, Pharm.D. 2015 Philadelphia College of Pharmacy
 Robert Okwemba, BSPHS, Pharm.D. 2015 Philadelphia College of Pharmacy Judith Long, MD,RWJCS Perelman School of Medicine Philadelphia Veteran Affairs Medical Center Background Objective Overview Methods
Robert Okwemba, BSPHS, Pharm.D. 2015 Philadelphia College of Pharmacy Judith Long, MD,RWJCS Perelman School of Medicine Philadelphia Veteran Affairs Medical Center Background Objective Overview Methods
Guide to Biostatistics
 MedPage Tools Guide to Biostatistics Study Designs Here is a compilation of important epidemiologic and common biostatistical terms used in medical research. You can use it as a reference guide when reading
MedPage Tools Guide to Biostatistics Study Designs Here is a compilation of important epidemiologic and common biostatistical terms used in medical research. You can use it as a reference guide when reading
DO PATIENT-REPORTED OUTCOME MEASURES IN HIP AND KNEE ARTHROPLASTY REHABILITATION HAVE ROBUST MEASUREMENT ATTRIBUTES? A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
 J Rehabil Med 2011; 43: 572 583 Review Article DO PATIENT-REPORTED OUTCOME MEASURES IN HIP AND KNEE ARTHROPLASTY REHABILITATION HAVE ROBUST MEASUREMENT ATTRIBUTES? A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW Maria Jenelyn Alviar,
J Rehabil Med 2011; 43: 572 583 Review Article DO PATIENT-REPORTED OUTCOME MEASURES IN HIP AND KNEE ARTHROPLASTY REHABILITATION HAVE ROBUST MEASUREMENT ATTRIBUTES? A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW Maria Jenelyn Alviar,
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP)
 CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) FOCUSED QUESTION Does a neurocognitive habilitation therapy service improve executive functioning and emotional and social problem-solving skills in children with fetal
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) FOCUSED QUESTION Does a neurocognitive habilitation therapy service improve executive functioning and emotional and social problem-solving skills in children with fetal
University of Hawai i Human Studies Program. Guidelines for Developing a Clinical Research Protocol
 University of Hawai i Human Studies Program Guidelines for Developing a Clinical Research Protocol Following are guidelines for writing a clinical research protocol for submission to the University of
University of Hawai i Human Studies Program Guidelines for Developing a Clinical Research Protocol Following are guidelines for writing a clinical research protocol for submission to the University of
Exercise therapy in the management of upper limb dysfunction in people with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Speaker declaration: no conflicts of interest
 Exercise therapy in the management of upper limb dysfunction in people with Rheumatoid Arthritis Speaker declaration: no conflicts of interest Exercise a planned, structured and repetitive bodily movement
Exercise therapy in the management of upper limb dysfunction in people with Rheumatoid Arthritis Speaker declaration: no conflicts of interest Exercise a planned, structured and repetitive bodily movement
John E. O Toole, Marjorie C. Wang, and Michael G. Kaiser
 Hypothermia and Human Spinal Cord Injury: Updated Position Statement and Evidence Based Recommendations from the AANS/CNS Joint Sections on Disorders of the Spine & Peripheral Nerves and Neurotrauma &
Hypothermia and Human Spinal Cord Injury: Updated Position Statement and Evidence Based Recommendations from the AANS/CNS Joint Sections on Disorders of the Spine & Peripheral Nerves and Neurotrauma &
Competency in musculoskeletal
 Competency in Musculoskeletal and Sports Medicine: Evaluating a PGY-1 Curriculum Steve A. Watts, MD; Zhen Zhang, PhD BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: The introduction of a prescribed curriculum and a clinical
Competency in Musculoskeletal and Sports Medicine: Evaluating a PGY-1 Curriculum Steve A. Watts, MD; Zhen Zhang, PhD BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: The introduction of a prescribed curriculum and a clinical
Do general practitioners prescribe more antimicrobials when the weekend comes?
 DOI 10.1186/s40064-015-1505-6 RESEARCH Open Access Do general practitioners prescribe more antimicrobials when the weekend comes? Meera Tandan 1*, Sinead Duane 1 and Akke Vellinga 1,2 Abstract Inappropriate
DOI 10.1186/s40064-015-1505-6 RESEARCH Open Access Do general practitioners prescribe more antimicrobials when the weekend comes? Meera Tandan 1*, Sinead Duane 1 and Akke Vellinga 1,2 Abstract Inappropriate
Basic research methods. Basic research methods. Question: BRM.2. Question: BRM.1
 BRM.1 The proportion of individuals with a particular disease who die from that condition is called... BRM.2 This study design examines factors that may contribute to a condition by comparing subjects
BRM.1 The proportion of individuals with a particular disease who die from that condition is called... BRM.2 This study design examines factors that may contribute to a condition by comparing subjects
Audit on treatment and recovery of ankle sprain
 Hong Kong Journal of Emergency Medicine Audit on treatment and recovery of ankle sprain WY Lee Study Objectives: The object of this study is to audit the care of ankle sprain of different severity and
Hong Kong Journal of Emergency Medicine Audit on treatment and recovery of ankle sprain WY Lee Study Objectives: The object of this study is to audit the care of ankle sprain of different severity and
PEER REVIEW HISTORY ARTICLE DETAILS VERSION 1 - REVIEW. Avinesh Pillai Department of Statistics University of Auckland New Zealand 16-Jul-2015
 PEER REVIEW HISTORY BMJ Open publishes all reviews undertaken for accepted manuscripts. Reviewers are asked to complete a checklist review form (http://bmjopen.bmj.com/site/about/resources/checklist.pdf)
PEER REVIEW HISTORY BMJ Open publishes all reviews undertaken for accepted manuscripts. Reviewers are asked to complete a checklist review form (http://bmjopen.bmj.com/site/about/resources/checklist.pdf)
Return to work a,er rotator cuff repair. Dr. Jean Stalder FB- Tag / Journée de perfec?onnement 17.01.2015
 Return to work a,er rotator cuff repair Dr. Jean Stalder FB- Tag / Journée de perfec?onnement 17.01.2015 CH 5 543 cases/year (average 2008-2012) Treatment 48.2 Mio /year Work compensa?on 157.2 Mio/year
Return to work a,er rotator cuff repair Dr. Jean Stalder FB- Tag / Journée de perfec?onnement 17.01.2015 CH 5 543 cases/year (average 2008-2012) Treatment 48.2 Mio /year Work compensa?on 157.2 Mio/year
Notice of Independent Review Decision DESCRIPTION OF THE SERVICE OR SERVICES IN DISPUTE:
 Notice of Independent Review Decision DATE OF REVIEW: 12/10/10 IRO CASE #: NAME: DESCRIPTION OF THE SERVICE OR SERVICES IN DISPUTE: Determine the appropriateness of the previously denied request for right
Notice of Independent Review Decision DATE OF REVIEW: 12/10/10 IRO CASE #: NAME: DESCRIPTION OF THE SERVICE OR SERVICES IN DISPUTE: Determine the appropriateness of the previously denied request for right
What are confidence intervals and p-values?
 What is...? series Second edition Statistics Supported by sanofi-aventis What are confidence intervals and p-values? Huw TO Davies PhD Professor of Health Care Policy and Management, University of St Andrews
What is...? series Second edition Statistics Supported by sanofi-aventis What are confidence intervals and p-values? Huw TO Davies PhD Professor of Health Care Policy and Management, University of St Andrews
Quality of care from the perspective of elderly people: the QUOTE-Elderly instrument
 Age and Ageing 2000; 29: 173 178 2000, British Geriatrics Society Quality of care from the perspective of elderly people: the QUOTE-Elderly instrument HERMAN J. SIXMA, CRÉTIEN VAN CAMPEN, JAN J. KERSSENS,
Age and Ageing 2000; 29: 173 178 2000, British Geriatrics Society Quality of care from the perspective of elderly people: the QUOTE-Elderly instrument HERMAN J. SIXMA, CRÉTIEN VAN CAMPEN, JAN J. KERSSENS,
Vectra DA Blood Test for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Original Policy Date January /2014
 MP 2.04.81 Vectra DA Blood Test for Rheumatoid Arthritis Medical Policy Section 2.0 Original Policy Date January /2014 Last Review Status/Date 1/2014 Disclaimer Our medical policies are designed for informational
MP 2.04.81 Vectra DA Blood Test for Rheumatoid Arthritis Medical Policy Section 2.0 Original Policy Date January /2014 Last Review Status/Date 1/2014 Disclaimer Our medical policies are designed for informational
Lost in Translation: The use of in-person interpretation vs. telephone interpretation services in the clinic setting with Spanish speaking patients
 Kellie Hawkins, MD, MPH CRC IRB Proposal November 2011 Lost in Translation: The use of in-person interpretation vs. telephone interpretation services in the clinic setting with Spanish speaking patients
Kellie Hawkins, MD, MPH CRC IRB Proposal November 2011 Lost in Translation: The use of in-person interpretation vs. telephone interpretation services in the clinic setting with Spanish speaking patients
Form B-1. Inclusion form for the effectiveness of different methods of toilet training for bowel and bladder control
 Form B-1. Inclusion form for the effectiveness of different methods of toilet training for bowel and bladder control Form B-2. Assessment of methodology for non-randomized controlled trials for the effectiveness
Form B-1. Inclusion form for the effectiveness of different methods of toilet training for bowel and bladder control Form B-2. Assessment of methodology for non-randomized controlled trials for the effectiveness
Title Older people s participation and engagement in falls prevention interventions: Comparing rates and settings
 Title Older people s participation and engagement in falls prevention interventions: Comparing rates and settings Keywords: patient adherence; falls, accidental; intervention studies; patient participation;
Title Older people s participation and engagement in falls prevention interventions: Comparing rates and settings Keywords: patient adherence; falls, accidental; intervention studies; patient participation;
Arthroscopic Shoulder Procedures. David C. Neuschwander MD. Shoulder Instability. Allegheny Health Network Orthopedic Associates of Pittsburgh
 Arthroscopic Shoulder Procedures David C. Neuschwander MD Allegheny Health Network Orthopedic Associates of Pittsburgh Shoulder Instability Anterior Instability Posterior Instability Glenohumeral Joint
Arthroscopic Shoulder Procedures David C. Neuschwander MD Allegheny Health Network Orthopedic Associates of Pittsburgh Shoulder Instability Anterior Instability Posterior Instability Glenohumeral Joint
Critical Appraisal of a Research Paper
 Critical Appraisal of a Research Paper Andrew MacInnes, BDS (Hons.) MFDS, RCPS (Glasgow), Senior House Officer 1 Thomas Lamont, BDS, MFDS, RCPS (Glasgow), Clinical Research Fellow/Honorary Restorative
Critical Appraisal of a Research Paper Andrew MacInnes, BDS (Hons.) MFDS, RCPS (Glasgow), Senior House Officer 1 Thomas Lamont, BDS, MFDS, RCPS (Glasgow), Clinical Research Fellow/Honorary Restorative
Summary of Clinical Outcome Measures for Sports-Related Knee Injuries
 Summary of Clinical Outcome Measures for Sports-Related Knee Injuries Final Report June 5, 2012 AOSSM Outcomes Task Force James Irrgang, PT, PhD, ATC, FAPTA Table of Contents AOSSM Outcomes Task Force....1
Summary of Clinical Outcome Measures for Sports-Related Knee Injuries Final Report June 5, 2012 AOSSM Outcomes Task Force James Irrgang, PT, PhD, ATC, FAPTA Table of Contents AOSSM Outcomes Task Force....1
Designing Clinical Addiction Research
 Designing Clinical Addiction Research Richard Saitz MD, MPH, FACP, FASAM Professor of Medicine & Epidemiology Boston University Schools of Medicine & Public Health Director, Clinical Addiction, Research
Designing Clinical Addiction Research Richard Saitz MD, MPH, FACP, FASAM Professor of Medicine & Epidemiology Boston University Schools of Medicine & Public Health Director, Clinical Addiction, Research
Patient Experiences with Acute Inpatient Hospital Care in British Columbia, 2011/12. Michael A. Murray PhD
 Patient Experiences with Acute Inpatient Hospital Care in British Columbia, 2011/12 Michael A. Murray PhD Dec 7, 2012 Table of Contents TABLE OF CONTENTS... 2 TABLE OF FIGURES... 4 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS...
Patient Experiences with Acute Inpatient Hospital Care in British Columbia, 2011/12 Michael A. Murray PhD Dec 7, 2012 Table of Contents TABLE OF CONTENTS... 2 TABLE OF FIGURES... 4 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS...
MEDICAL POLICY I. POLICY OCCUPATIONAL THERAPY (OUTPATIENT) MP-8.004 POLICY TITLE POLICY NUMBER
 Original Issue Date (Created): 7/1/2002 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): 3/24/2015 Effective Date: 11/2/2015 POLICY PRODUCT VARIATIONS DESCRIPTION/BACKGROUND RATIONALE DEFINITIONS BENEFIT VARIATIONS
Original Issue Date (Created): 7/1/2002 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): 3/24/2015 Effective Date: 11/2/2015 POLICY PRODUCT VARIATIONS DESCRIPTION/BACKGROUND RATIONALE DEFINITIONS BENEFIT VARIATIONS
Spine Vol. 30 No. 16; August 15, 2005, pp 1799-1807
 A Randomized Controlled Trial of an Educational Intervention to Prevent the Chronic Pain of Whiplash Associated Disorders Following Rear-End Motor Vehicle Collisions 1 Spine Vol. 30 No. 16; August 15,
A Randomized Controlled Trial of an Educational Intervention to Prevent the Chronic Pain of Whiplash Associated Disorders Following Rear-End Motor Vehicle Collisions 1 Spine Vol. 30 No. 16; August 15,
2011 Validity and Reliability Results Regarding the SIS
 2011 Validity and Reliability Results Regarding the SIS Jon Fortune, Ed.D., John, Agosta, Ph.D., March 14, 2011 and Julie Bershadsky, Ph.D. Face Validity. Developed to measure the construct of supports,
2011 Validity and Reliability Results Regarding the SIS Jon Fortune, Ed.D., John, Agosta, Ph.D., March 14, 2011 and Julie Bershadsky, Ph.D. Face Validity. Developed to measure the construct of supports,
Perception of Safety Attitude and Priority and Progress of Safe Practices of Nurses in Emergency Services Hospitals
 , pp.156-163 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2015.104.34 Perception of Safety Attitude and Priority and Progress of Safe Practices of Nurses in Emergency Services Hospitals Sung Jung Hong 1 1 Department
, pp.156-163 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2015.104.34 Perception of Safety Attitude and Priority and Progress of Safe Practices of Nurses in Emergency Services Hospitals Sung Jung Hong 1 1 Department
Depressive Disorders Inpatient Management v.1.1
 Depressive Disorders Inpatient Management v.1.1 Executive Summary Citation Information Explanation of Evidence Ratings Summary of Version Changes Intake Admission interview, physical exam, and review of
Depressive Disorders Inpatient Management v.1.1 Executive Summary Citation Information Explanation of Evidence Ratings Summary of Version Changes Intake Admission interview, physical exam, and review of
CHILDHOOD CANCER SURVIVOR STUDY Analysis Concept Proposal
 CHILDHOOD CANCER SURVIVOR STUDY Analysis Concept Proposal 1. STUDY TITLE: Longitudinal Assessment of Chronic Health Conditions: The Aging of Childhood Cancer Survivors 2. WORKING GROUP AND INVESTIGATORS:
CHILDHOOD CANCER SURVIVOR STUDY Analysis Concept Proposal 1. STUDY TITLE: Longitudinal Assessment of Chronic Health Conditions: The Aging of Childhood Cancer Survivors 2. WORKING GROUP AND INVESTIGATORS:
The Importance and Impact of Nursing Informatics Competencies for Baccalaureate Nursing Students and Registered Nurses
 IOSR Journal of Nursing and Health Science (IOSR-JNHS) e-issn: 2320 1959.p- ISSN: 2320 1940 Volume 5, Issue 1 Ver. IV (Jan. - Feb. 2016), PP 20-25 www.iosrjournals.org The Importance and Impact of Nursing
IOSR Journal of Nursing and Health Science (IOSR-JNHS) e-issn: 2320 1959.p- ISSN: 2320 1940 Volume 5, Issue 1 Ver. IV (Jan. - Feb. 2016), PP 20-25 www.iosrjournals.org The Importance and Impact of Nursing
Program Approved by AoA, NCOA. Website: www.homemeds.org
 MEDICATION MANAGEMENT IMPROVEMENT SYSTEM: HomeMeds SM The HomeMeds SM system is a collaborative approach to identifying, assessing, and resolving medication problems in community-dwelling older adults.
MEDICATION MANAGEMENT IMPROVEMENT SYSTEM: HomeMeds SM The HomeMeds SM system is a collaborative approach to identifying, assessing, and resolving medication problems in community-dwelling older adults.
Rotator Cuff Tears in Football
 Disclosures Rotator Cuff Tears in Football Roger Ostrander, MD Consultant: Mitek Consultant: On-Q Research Support: Arthrex Research Support: Breg Research Support: Arthrosurface 2 Anatomy 4 major muscles:
Disclosures Rotator Cuff Tears in Football Roger Ostrander, MD Consultant: Mitek Consultant: On-Q Research Support: Arthrex Research Support: Breg Research Support: Arthrosurface 2 Anatomy 4 major muscles:
Glossary of Methodologic Terms
 Glossary of Methodologic Terms Before-After Trial: Investigation of therapeutic alternatives in which individuals of 1 period and under a single treatment are compared with individuals at a subsequent
Glossary of Methodologic Terms Before-After Trial: Investigation of therapeutic alternatives in which individuals of 1 period and under a single treatment are compared with individuals at a subsequent
Clinical Research. Issues in Data Collection. James N. Weinstein, DO, MS, and Richard A. Deyo, MD, MPH
 SPINE Volume 25, Number 24, pp 3104 3109 2000, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Clinical Research Issues in Data Collection James N. Weinstein, DO, MS, and Richard A. Deyo, MD, MPH This focus issue
SPINE Volume 25, Number 24, pp 3104 3109 2000, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Clinical Research Issues in Data Collection James N. Weinstein, DO, MS, and Richard A. Deyo, MD, MPH This focus issue
Patient Reported Outcomes for Mental Health Services: Current Practice and Future Possibilities
 Patient Reported Outcomes for Mental Health Services: Current Practice and Future Possibilities Arne Beck, PhD Kaiser Permanente Colorado Institute for Health Research September 12, 2012 DRAFT For Discussion
Patient Reported Outcomes for Mental Health Services: Current Practice and Future Possibilities Arne Beck, PhD Kaiser Permanente Colorado Institute for Health Research September 12, 2012 DRAFT For Discussion
Saskatchewan Workers Compensation Act Committee of Review
 Submission to the Saskatchewan Workers Compensation Act Committee of Review Submitted by the 3420A Hill Avenue Regina, SK S4S 0W9 Phone: (306) 585-1411 - Fax: (306) 585-0685 E-mail: cas@saskchiropractic.ca
Submission to the Saskatchewan Workers Compensation Act Committee of Review Submitted by the 3420A Hill Avenue Regina, SK S4S 0W9 Phone: (306) 585-1411 - Fax: (306) 585-0685 E-mail: cas@saskchiropractic.ca
Analysis of the question answer service of the Emma Children s Hospital information centre
 Eur J Pediatr (2010) 169:853 860 DOI 10.1007/s00431-009-1129-3 ORIGINAL PAPER Analysis of the question answer service of the Emma Children s Hospital information centre Frea H. Kruisinga & Richard C. Heinen
Eur J Pediatr (2010) 169:853 860 DOI 10.1007/s00431-009-1129-3 ORIGINAL PAPER Analysis of the question answer service of the Emma Children s Hospital information centre Frea H. Kruisinga & Richard C. Heinen
The ACGME Resident Survey Aggregate Reports: An Analysis and Assessment of Overall Program Compliance
 The ACGME Resident Survey Aggregate Reports: An Analysis and Assessment of Overall Program Compliance Kathleen D. Holt, PhD Rebecca S. Miller, MS Abstract Background The Accreditation Council for Graduate
The ACGME Resident Survey Aggregate Reports: An Analysis and Assessment of Overall Program Compliance Kathleen D. Holt, PhD Rebecca S. Miller, MS Abstract Background The Accreditation Council for Graduate
Symptoms and Signs of Irritation of the Brachial Plexus in Whiplash Injuries
 1 Symptoms and Signs of Irritation of the Brachial Plexus in Whiplash Injuries J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 2001 Mar;83(2):226-9 Ide M, Ide J, Yamaga M, Takagi K Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kumamoto University
1 Symptoms and Signs of Irritation of the Brachial Plexus in Whiplash Injuries J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 2001 Mar;83(2):226-9 Ide M, Ide J, Yamaga M, Takagi K Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kumamoto University
